- DL manuals
- NCT Group
- Lathe
- 100T
- Operator's Manual
NCT Group 100T Operator's Manual
Summary of 100T
Page 1
Nct® 100t nct® 990t nct® 2000t controls for lathes operator`s manual valid from software version x.057.
Page 2
Produced and developed by nct automation kft. H1148 budapest fogarasi út 7 : letters: h1631 bp. Pf.: 26 f phone: (+36 1) 467 63 00 f fax:(+36 1) 363 6605 e-mail: nct@nct.Hu home page: www.Nct.Hu.
Page 3
Contents introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 1 operator’s panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8 1.1 the nc control panel:...
Page 4
4.1 structure of part program . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56 4.2 division of edit screen during editing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57 4.3 basic editing functions: typing, cursor moving, delete, inser...
Page 5
12.1 single block execution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99 12.2 dry run (all feedrates at high speed) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99 12.3 machine lock function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 6
© copyright nct march 18, 2003 the publisher reserves all rights for the con- tents of this manual. No reprinting, even in extracts, is permissible unless our written consent is obtained. The text of this manual has been compiled and checked with utmost care, yet we assume no liability for possible ...
Page 7
Introduction 7 introduction dear user, thank you for having opted for one of our nct100t, nct990t, or nct2000t control systems.It is hoped sincerely that you will be always satisfied in your work with its facilities. It should be remembered that the skill of operating the machine can only be learnt ...
Page 8
1 operator’s panel 8 operator’s panel with 9" monochrome monitor and with optional machine control board 1 operator’s panel 1.1 the nc control panel: display unit and data input keyboard the nc control panel employs the display unit (monitor), the softkeys beneath, and the data input keyboard. The n...
Page 9
1 operator’s panel 9 operator’s panel with 15" color monitor and with optional machine control board.
Page 10
1 operator’s panel 10 1.1.1 data input keyboard in case of a 9" monitor directly beneath the screen are five softkeys, in case of a 15" monitor ten softkeys built together with the screen. In both cases the meaning of these softkeys can be read in the menu bars found in the bottom line of screen, th...
Page 11
1 operator’s panel 11 keys pgup and pgdn are used for turning pages within the text. Keys ins and del serve for inserting and deleting characters. The above listed units (monitor and keyboard) constitute the permanent part of nc and are transported together with the control in any case of configurat...
Page 12
1 operator’s panel 12 3 functional state of automatic and manual data input – nsch: block search – intd: automatic execution interrupted – strt: start state – stop: stop state 4 program manipulation state – load: loading program from external device – save: saving program to external device – sort: ...
Page 13
1 operator’s panel 13 the operator’s messages of plc are displayed. The date and time display can also be found in this line. In the third line the name of the active general displaying area and behind the number of programs indicated for running can be read. In case of manual data input mode, the n...
Page 14
1 operator’s panel 14 optional machine control board bel ow the operating items of machine control board delivered by nct are described. The lighting state of led in the top left corner of buttons shows, that the function indicated by the key is active. Emergency stop. By its depressing the nc regis...
Page 15
1 operator’s panel 15 automatic manual data input increment selectors: selecting 1, 10, 100, 1000 increment size. Override switches: feedrate override switch. By affecting it the programmed feedrate can be changed in the 0-120% range. Rapid traverse override value can be influenced by four optionall...
Page 16
1 operator’s panel 16 block restart block return function lock movement, start and stop buttons start button. Details of its functioning are discussed in the forthcoming chapters of the manual. Stop button. Details of its functioning are discussed in the forthcoming chapters of the manual. Jog butto...
Page 17
2 general operating knowledge 17 2 general operating knowledge 2.1 screen menu after turning the power on among the captions interpreting the softkeys the screen menu is active. On a color screen the default background color of the menu bar of the screen menu is light grey. In order to switch over f...
Page 18
2 general operating knowledge 18 further items after service screen menu, those would be shown by pressing the screen menu key , until the first part of screen menu is returned. The number seen in the bottom right corner of menu field indicates the softkey number of the appropriate menu field and no...
Page 19
2 general operating knowledge 19 setting #1- #33 1 #100- #199 2 #500- #599 3 timer / counter4 tool pot 5 plc ta- ble 6 user’s params7 security 8 9 0 service param 1 plc 2 test i/o 3 logic anal 4 test mes 5 scope 6 errors 7 version 8 9 0 summary: the screen menus are in two levels. The first level ha...
Page 20
2 general operating knowledge 20 – the digit entered is interpreted as an integer or as a decimal digit before or after the decimal point has been pressed, respectively. – it is not necessary to enter the right-hand insignificant zeros behind the decimal point or the decimal point (in the case of an...
Page 21
3 general displaying areas and actions executed on them 21 3 general displaying areas and actions executed on them each general displaying area is accessible any time, independent of the current operation mode or other states of control. However actions belonging to the given display cannot be execu...
Page 22
3.1 position screens 22 3.1 position screens there can be five types of position screens. The first four screens displays the selected position with big-size characters, meanwhile on the fifth screen all position displays as well as in case of six or fewer axes the feed and revolution values are als...
Page 23
3.1 position screens 23 cartesian position screen: in the state of polar coordinate interpolation on (g12.1) it indicates the tool position in the programmed cartesian coordinate system. In the state of polar coordinate interpolation off (g13.1) positions indicated here are the same as on the screen...
Page 24
3.2 check screens 24 3.2 check screens this screen serves for displaying running programs and their states. 3.2.1 program text screen, listing of running program in the lower part of general dis- playing area the list of the run- ning program can be seen. One block on the list is highlighted; this i...
Page 25
3.2 check screens 25 3.2.3 last and active screens. G codes and compensations. On the last and active screens the active g codes and compensations under block display (last) and program execution (active) can be seen. The last screen corresponds to the values of #4000..., #4100... Macro variables, w...
Page 26
3.2 check screens 26 action i can be used for input of incremental operator. Action block delete clears the whole block in buffer. 3.2.4 operator’s panel screen the general display area of op- erator’s panel shows a view on the state of the most essential machine control items. The controllability o...
Page 27
3.2 check screens 27 operation modes actions (modes) the following modes can be selected: edit 1 auto 2 mdi 3 jog 4 incr 5 handle 6 ref 7 8 9 0 axes actions in the menu bar all axes of the machine tool are listed. Here the axis, with which an action must be done, can be selected. This action is nece...
Page 28
3.2 check screens 28 clear relative position actions (clear relpnt) the relative coordinate displays can be zeroed by means of action keys. Relative position setting by axes is discussed in the chapter 3.4.5 . 3.2.5 messages screen in this general displaying area the momentary messages in waiting st...
Page 29
3.3 program screens 29 3.3 program screens screens of actions executed on part programs. 3.3.1 directory screen in the top line of general displaying area the number of programs in memory and the free memory in bytes can be seen. The programs in memory are listed in the middle part. The control reco...
Page 30
3.3 program screens 30 new action: when pressing the softkey a window opens in the bottom left part of general displaying area, where the program num- ber can be typed in. The input can be terminated by any arrow key. In this case a new program oc- curs with the number entered, or an error mes- sage...
Page 31
3.3 program screens 31 dnc contact working on the basis of dnc protocol can be implemented. The chart action is only effective in edit mode. By pressing it, provided program no. T (tool pot table) or p (plc table) is highlighted, the file containing the selected chart is loaded to the appropriate ch...
Page 32
3.3 program screens 32 last action: when pressing the key the highlighting bar goes to the last block of the program. Check action: when pressing the key control brings the highlighting bar to the last block of the program, meanwhile it reads the entire program and examines its check sum. This way i...
Page 33
3.3 program screens 33 3.3.4 block input screen in the upper part of general displaying area the current posi- tion can be seen. It is possible to enter single block as well as to re-execute or to modify a block entered earlier on by pressing action menu key . A sing- le block is to be entered simil...
Page 34
3.4 offsets screens 34 3.4 offsets screens screens of actions executed on zero point and offset registers. 3.4.1 work offsets screen in the general displaying area are offset values of g54, ..., g58, common zero point offsets, as well as of offsets programmed by means of commands g52 and g92. The co...
Page 35
3.4 offsets screens 35 activated by pressing action menu key : clear group 1 clear all 2 i 3 /2 4 save 5 6 7 8 9 0 clear group action menu: when pressing the key the question clear g5x? (g5x according to current coordinate system) appears in the bottom left part of general displaying area, together ...
Page 36
3.4 offsets screens 36 keys and . This bar selects the offset register to be modified. Actions of tool offsets screen actions executed on tool offsets screen overwrite offset registers instantly, however it is registered by the program under execution only if the program has been started from the be...
Page 37
3.4 offsets screens 37 on the figures below the interpretation of the imaginary tool nose number (q) can be seen..
Page 38
3.4 offsets screens 38 3.4.3 work offset measure screen in the upper part of general displaying area the current tool position can be seen. The first column always shows the machine position, the middle column the position in the selected coordinate system, while the last one the distance to go posi...
Page 39
3.4 offsets screens 39 for detailed description of work offset measure see the chapter 7.2.1 “work offset mea- sure” on the page 76 . 3.4.4 tool length offset measure screen in the upper part of general displaying area the position dis- play can be seen. The following information can be seen in the ...
Page 40
3.4 offsets screens 40 for detailed description of work offset measure see the chapter 7.2.2 “tool length offset measure inside the machine” on the page 79 . 3.4.5 relative position offsets screen in the general displaying area below the current tool position are the values of relative position offs...
Page 41
3.5 graphic position screens 41 3.5 graphic position screens in automatic operation mode the graphic position display shows the path of the imaginary tool nose. In the case of graphic position display the tool nose path stored in a buffer is drawn on the screen. As the buffer (which is a part of the...
Page 42
3.5 graphic position screens 42 in case the value of the auto erase is other than zero, when starting the automatic program execution both the drawing area and the buffer are cleared. If the value of the path color is 0 rapid traverse is drawn with red, feed with green, while thread cutting with yel...
Page 43
3.5 graphic position screens 43 3.5.2 draw screen in the drawing area in the middle of screen the current tool center is shown by a cross. The following information can be read in the top right corner of the screen: current feed, spindle revolution and the number of the current tool. Fur- ther on in...
Page 44
3.5 graphic position screens 44 down (pgdn). By means of softkeys, as well as the page keys the drawing area can be halved or doubled. As the effect of full sceen action the centre of the screen automatically adjusted to the middle of the tool path and scaling is set that the tool path covers the wh...
Page 45
3.6 setting screens 45 3.6 setting screens the following screens can be found in this menu; local macro variables #1–#33, common macro variables #100–#199 and #500–#599, timer and counter, tool position table, plc table, tool wear table, user’s parameters and security settings. Contents of variables...
Page 46
3.6 setting screens 46 3.6.2 screen of common macro variables #100–#199 in the general displaying area common macro variables #100–#199 and their values can be seen. Variables #120–#199 are vacated upon power-off and when resetting automatic mode (reset) variables #100–#119 are also vacated in case ...
Page 47
3.6 setting screens 47 3.6.3 screen of common macro variables #500–#599 in the general displaying area common macro variables #500–#599 and their values can be seen. These variables are not vacated upon power-off or when restoring automatic mode (reset), on the other hand by switching to parameters,...
Page 48
3.6 setting screens 48 3.6.4 timer and counter screen in the general displaying area the different timers and counters can be seen. The highlighting bar can be moved to the timer or counter to be modified by means of arrow keys. Apart from the operating time the values are free to overwrite. Actions...
Page 49
3.6 setting screens 49 the length of the tool pot table can be set in parameter magazine no. 0061. In parameter magazine the number of tool pots in the magazine is to be entered. Line 0 of table shows the code of the tool in spindle, i.E., the spindle is pot no. 0. In the first column of the table t...
Page 50
3.6 setting screens 50 actions in the menu bar, the meaning of which is the usual. With exec in effect the selected line is cleared. Save action: when pressing the key the program number can be entered into the bottom data input line. In case the input is terminated by any of the keys or , the progr...
Page 51
3.6 setting screens 51 program can also be named there. As the effect of keys and values are saved in the appropriate macro variable. It is registered in the directory not under program number o, but under address t. Restoring values of the table is discussed in the chapter 3.3.1 on the page 30 “dir...
Page 52
3.6 setting screens 52 3.6.8 security panel screen the control provides wide-range data security service. The picture shows the security panel screen. When the general security gate is open the other security gates have no significant role, thus all actions listed on the screen can be executed even ...
Page 53
3.6 setting screens 53 the below table contains the codes of the appropriate functions: function code function code general security gate generated work offsets 15962 open new program 95148 relative position 15962 delete program 95148 tool offsets 15962 edit program 95148 tool pot table 15962 load p...
Page 54
3.6 setting screens 54 is entered the data input can be closed by means of button and the function is enabled. Close action: if a function is to be locked move symbol = (cursor) to the function. Press close button. The selected function is locked independent of the state of the general security gate...
Page 55
4 editing part programs 55 4 editing part programs 4.1 structure of part program the part program is made up of blocks. A block consists of words. Word: address and data a word is formed by two components: address and data (e.G., x127.064 or z#103). The address may comprise one or more characters (x...
Page 56
4 editing part programs 56 beginning and end of program the program begins and ends with character %. As a new program is loaded with the help of new action on directory screen string %onnnns% is formed automatically. In the course of editing a part program on the cnc the opening and closing % chara...
Page 57
4 editing part programs 57 4.2 division of edit screen during editing 19 lines are kept for editing in the middle of screen. The division of these is as follows: lines ranging from no. 1 to no. 16: program list and edit field. In the first column only character > representing a new block, i.E., code...
Page 58
4 editing part programs 58 4.3 basic editing functions: typing, cursor moving, delete, insert, select the editing gets started as the effect of action menu key . Basic editing functions are implemented with the help of the following keys: – characters: , , ... . By their use capital letters can be t...
Page 59
4 editing part programs 59 if value of parameter 0567 n step is other than 0, the block number is increased by the value given at the parameter for each push of the key and this is automatically inserted to the beginning of the new block at address n. If for example the value of parameter is 10 the ...
Page 60
4 editing part programs 60 as the effect of backspace key the character before the cursor is deleted and the characters behind step forward. Regarding logic lines (blocks) the same rearrangements are in force as those referring to delete key . Insert when opening, the editor accepts insert mode indi...
Page 61
4 editing part programs 61 4.4 editor action menu the following actions as well as action groups are available for editing, when action menu key is pressed: file 1 edit 2 insert misc 3 insert cond 4 insert operat 5 insert funct 6 window 7 change wind 8 help 9 0 4.5 file actions: save, save as file 1...
Page 62
4 editing part programs 62 copy action: by pressing the key the text selected earlier on is put to the clipboard and the original text remains at its position. Paste action: by pressing the key the content of the clipboard is inserted starting from the position next to the cursor. In case the clipbo...
Page 63
4 editing part programs 63 found string. If no text is given after the caption replace, replace action is equivalent to the deleting of the found text. Undo action can also be applied after replace action. 4.7 insert actions file 1 edit 2 insert misc 3 insert cond 4 insert operat 5 insert funct 6 wi...
Page 64
4 editing part programs 64 screen. By returning to the edit screen the other program can be seen in the window active when exiting. The active window as well as the program numbers shown in the windows are indicated in the 18 th status line. The cursor is seen in the active window, and this is also ...
Page 65
5 switching over operation modes 65 5 switching over operation modes with the help of the data input keyboard the state of operation modes, switches, etc., displayed on the operator’s panel screen can be changed by means of softkeys after action menu key has been pressed. The above switches are avai...
Page 66
6.1 manual reference point return mode 66 6 manual operation modes the manual operation modes are as follows: manual reference point return manual handle feed incremental jog jog 6.1 manual reference point return mode reference point can be returned only upon power-on state of the machine, i.E. When...
Page 67
6.1 manual reference point return mode 67 happened yet, symbol !! Can be seen beside the position. In case the reference point has been returned on all axes ref, i.E., the caption indicating lack of reference position is cleared from the general nc state field. L note: by different machine tools ret...
Page 68
6.2 jog mode 68 6.2 jog mode jogging can only be done upon power-on state of the machine, i.E. When there is no emg (emergency stop) state in the rightmost field (general nc state) of status bar. After selecting the operation mode in the 2 nd field of status bar caption jog appears. If the machine i...
Page 69
6.2 jog mode 69 l note: the above discussed cases are the basic cases of jog mode. By different machines functions contrary to these may be created by the machine tool builder. It is common, for example, if pressing of a jog button is followed by the pressing of the start button, than the jog button...
Page 70
6.3 incremental jog mode 70 6.3 incremental jog mode incremental jogging can only be done upon power-on state of the machine, i.E. When there is no emg (emergency stop) state in the rightmost field (general nc state) of status bar. After selecting the operation mode in the 2 nd field of status bar c...
Page 71
6.3 incremental jog mode 71 l warning! If in case of greater increment sizes the jog button is left hold for a short time, the movement stops and the desired distance is not stepped by the control, this way preventing it from possible collisions!.
Page 72
6.4 manual handle mode 72 6.4 manual handle mode moving by the use of manual handle can only be done upon power-on state of the machine, i.E. When there is no emg (emergency stop) state in the rightmost field (general nc state) of status bar. After selecting the operation mode in the 2 nd field of s...
Page 73
6.4 manual handle mode 73 speed in case of moving by the use of the manual handle the speed of the axis depends upon the selected increment size and upon the speed of the rotation of the handle. The movement is started by acceleration and finished by deceleration. The pulse number rotated is always ...
Page 74
7 actions executed in manual operation modes 74 7 actions executed in manual operation modes 7.1 single block operation a single block can be entered by selecting block input screen of the program screen menu and pressing the action menu key. This action can be used only in jog, incremental jog and ...
Page 75
7.2.1 work zero point offset measurement 75 7.2.1 work zero point offset measurement if work offset is to be measured inside the machine, select f3 w. Offs measure (work offset measurement) screen of off- sets screen menu and press the action menu key. The coordinate system to be measured can be sel...
Page 76
7.2.1 work zero point offset measurement 76 work zero point offset measurement, if tool length equals to tool overhang if tool length equals to the x- and z-direction tool overhang (because for example tool offset measuring was executed on an external measuring device) the work offset (work zero poi...
Page 77
7.2.1 work zero point offset measurement 77 work zero point offset measurement, if tool length equals to coordinate shift if tool lengths are measured so that they also contain the offsets of the work zero point (see tool length measurement) work off- sets do not have to be measured. An exception to...
Page 78
7.2.2 tool length offset measurement inside the machine 78 7.2.2 tool length offset measurement inside the machine tool length can be measured also inside the machine. For this softkey f4 t. Leng meas- ur (tool length measurement) of f5 offsets action menu must be selected. Select the tool length of...
Page 79
7.2.2 tool length offset measurement inside the machine 79 if no work zero point offset measurement had taken place previously if no work zero point offset had taken place previously, the ap- propriate work offset of the se- lected coordinate system is zero (m x =0, m z =0). The coordinate values me...
Page 80
7.2.3 automatic tool length offset measurement 80 7.2.3 automatic tool length offset measurement tool length offsets can also be measured automatically, provided the machine is mounted with a tool offset sensor. Select screen f4 t leng measure (tool length measurement) in screen menuof f5 offsets. S...
Page 81
7.2.4 calibrating tool offset sensor 81 7.2.4 calibrating tool offset sensor the tool offset sensor calibration means the definition and storage of button positions at para- meters contact. The sensor can be calibrated in two ways. The first possibility is that the button positions of the sensor are...
Page 82
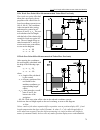
7.2.4 calibrating tool offset sensor 82 calibrating the sensor to the coordinate system of chuck the enclosed diagram beside shows the in- terpretation of contact parameters. Calibrating in x direction turn an optional workpiece, leave the workpiece in z direction and read the ma- chine position of ...
Page 83
7.2.4 calibrating tool offset sensor 83 calibrating the sensor to reference point the figure beside shows the interpretation of contact parameters. Let us examine the following example. Place a tool, the overhang of which is known in the tool holder. The tool overhang is indicated with x t , z t on ...
Page 84
8.1 automatic mode 84 8 modes of automatic operation the modes of automatic operation are: automatic edit manual data input 8.1 automatic mode program execution in automatic mode can only be done upon power-on state of the machine, i.E. When there is no emg (emergency stop) state in the rightmost fi...
Page 85
8.1 automatic mode 85 executed on the transmitter side. Program dnc-plus.Exe can be executed on ibm pc or on a compatible computer. It ensures connection between transmitter and receiver with protocol. Its advantage over simple dnc connection is that it calculates the checksum by each program block ...
Page 86
8.2 edit mode 86 8.2 edit mode in case there is no plc program or plc program or parameter area is damaged in control, edit mode is activated after turning the power on. . Edit mode is indicated by caption edit in the leftmost field of the status bar. The following actions can only be executed in ed...
Page 87
8.3 manual data input mode 87 8.3 manual data input mode program execution in manual data input mode can only be done upon power-on state of the machine, i.E. When there is no emg (emergency stop) state in the rightmost field (general nc state) of status bar. If the machine is mounted with nct machi...
Page 88
8.3 manual data input mode 88 in manual data input mode, during program execution, the operation of the following functions corresponds to that in automatic mode: – single block execution – conditional stop – conditional block – dry run – locking possibilities..
Page 89
9 override switches 89 switch state % 1 0 2 1 3 2 4 5 5 10 6 20 7 30 8 40 9 50 10 60 11 70 12 80 13 90 14 100 15 110 16 120 9 override switches the control can operate three override switches: – the feedrate, – the rapid traverse, and – the spindle speed override switches. 9.1 feedrate override swit...
Page 90
9 override switches 90 switch state % 1 f0 2 25 3 50 4 100 switch state % 1 50 2 60 3 70 4 80 5 90 6 100 7 110 8 120 9 130 10 140 9.2 rapid traverse override switch the rapid traverse override switch determines, by how many percent of the rapid traverse rate defined in the parameter should the axes ...
Page 91
9 override switches 91 pressing the button the control restores the programmed 100% rate. During thread cutting g33, g34, g76, g78 and tapping cycles g84.1, g84 the spindle speed override switch is ineffective. The control registers 100% independent of the switch position..
Page 92
10 program execution start and stop 92 10 program execution start and stop the program execution is started by the use of the start button. The program execution can be stopped by means of the following functions and keys: – with the stop button, – with the reset key, – at the end of block execution...
Page 93
10 program execution start and stop 93 at the same time some global messages are also cleared from the message field of the status bar. The plc program (generally) stops spindle rotation and suspends operation under execution. Besides reset key has other effects in the different modes as well. In au...
Page 94
10 program execution start and stop 94 executes block containing code m01 if switch cond. Stop is on, than stop state is assumed and the machining stops. With start button the machining is continued. Nothing happens if switch cond. Stop is off. 10.6 end of program: m02, m30 codes m02, m30 indicate t...
Page 95
11 intervention in the course of program execution 95 11 intervention in the course of program execution 11.1 conditional block skip if at the beginning of block con- ditional block skip /n is pro- grammed (n means the number of the conditional block switch), than – if switch no. N is on, it skips b...
Page 96
11 intervention in the course of program execution 96 11.3 intervention by means of manual handle in automatic operation the manual handle operation can also be turned on parallel to the automatic operation. In this case in the leftmost field of status bar caption autm or autd indicating automatic o...
Page 97
11 intervention in the course of program execution 97 effect of intervention to coordinate system – the manual handle pulses are also added to the offset on the appropriate axis in the common work zero point offset registers. This way all the works and local coordinate sys- tems are being shifted. –...
Page 98
12 debugging part program 98 12 debugging the part program the following functions help the testing, debugging of the part program: – single block execution, – dry run, – locking possibilities and – test run. These functions are not operation modes, but conditions influencing the program execution i...
Page 99
12 debugging part program 99 12.3 machine lock function switch machine lock can be reached on operator’s panel or position screens. After pressing the action menu key f5 conditions action menu must be selected, than softkey machine lock needs to be pressed. If nct machine control board is used selec...
Page 100
12 debugging part program 100 the different function and axis locking possibilities can be combined optionally. An axis, e.G. Z axis and the functions can be locked simultaneously. L note: about the different locking possibilities turn to the machine tool builder for an information material. 12.5 te...
Page 101
13 interruption and restart of automatic operation 101 13 interruption and restart of automatic operation in many cases the automatic operation needs to be interrupted, than later on the machining to be continued. Cases like this for example when: – the errors must be repaired, than the machining co...
Page 102
13 interruption and restart of automatic operation 102 if machining is started in intd state of automatic mode and start button is pressed, control registers stop state and message restore modal functions? Y is displayed (y=yes). By pressing key question restore modal functions? N is asked (n=no). T...
Page 103
13.3 unconditional restart of automatic operation 103 13.3 unconditional restart of automatic operation if automatic operation is started from interrupted state (intd) unconditionally after start the control goes to the end position of the interrupted block and carries on machining from there. The t...
Page 104
13.3 unconditional restart of automatic operation 104 2 nd case: in state g40 interrupting oblique linear interpolation let us examine fragments of the following sample programs: program no. 1: ... N40 g90 g0 x20 z–10 n50 x80 z–60 n60 z–85 ... Program no. 2: ... N40 g90 g0 x20 z–10 n50 g91 x60 z–50 ...
Page 105
13.3 unconditional restart of automatic operation 105 if in the selected plane the address of one of the axes has not been programmed (e.G., y) and movement has been made also in this direction, or in z direction, the movement may be led back to the 1 st case, i.E., the axes will move after pressing...
Page 106
13.3 unconditional restart of automatic operation 106 the cases below refer to the axes in the selected plane in when offset mode is on. To interrup- tion of axis movements outside the selected plane refer to interruption cases in state g40. 6 th case: in state g41 or g42 interrupting linear interpo...
Page 107
13.3 unconditional restart of automatic operation 107 when manual movement is done to a posi- tion, which is left from the end position of the circle, according to the diagram, the con- trol proceeds also as discussed above. How- ever this time the arc of the variable radius circle is close to 360° ...
Page 108
13.4 automatic operation restart with block restart condition 108 13.4 automatic operation restart with block restart condition if the condition block restart is switched on after returning to automatic mode and than start button is pressed, the control goes to the start position of the inter- rupte...
Page 109
13.4 automatic operation restart with block restart condition 109 13.4.3 cases of return by means of block restart condition return to block start position after interrupting simple movement block 1 st case: in state g40 interrupting and restarting linear interpolation the diagram shows the case, wh...
Page 110
13.4 automatic operation restart with block restart condition 110 x=100, y=70, z=10. 3 rd part block: hole machining and retraction to start position (g98) or to r-point (g99). In this part block the start position is coordinate x=100, y=70, z=2. At the end of all three part blocks the control stops...
Page 111
13.4 automatic operation restart with block restart condition 111 5 th case: return to block start position after interrupting machining in offset mode at outside corner by the use of block re- start condition it is set out from the offset vector on the start position of the interrupted block, the l...
Page 112
13.5 automatic mode restart with block return condition 112 13.5 automatic mode restart with block return condition if automatic operation has been interrupted, manual operation was used to move away from the workpiece and return is to be made to the interruption point, the block return condition ne...
Page 113
13.5 automatic mode restart with block return condition 113 13.5.3 cases of return by means of condition block return cases of return by means of block return condition correspond to that of block restart condition, except for return is made not to start position of block, but to the interruption po...
Page 114
13.5 automatic mode restart with block return condition 114 the canned cycle restarted by means of condition block return consists of 3 part blocks: 1 st part block: positioning in the selected plane (go x100 y70) 2 nd part block: positioning to point r (g0 z2) 3 rd part block: hole machining and re...
Page 115
13.5 automatic mode restart with block return condition 115 5 th case: return to interruption point machining in offset mode at outside corner by the use of the block return condition it states a perpendicular vector on the interruption point, the length of which corresponds to that of the new tool ...
Page 116
13.6 automatic operation start after block search 116 13.6 automatic operation start after block search in the course of machining there may be a need for executing the program selected for auto- matic mode not from the first block, but from a block within the program. For this, the appropriate bloc...
Page 117
13.6 automatic operation start after block search 117 pressing key . If the number of the subprogram is not numeric, but is an arithmetic expression it will not open the subprogram. If the subprogram is called by means of repetition count (l) the cycle number from which the program is to be executed...
Page 118
13.6 automatic operation start after block search 118 spindle rotation code: m3 the command referring to the last spindle rotation is gathered, in this case m3. Coolant code: m8 the command referring to coolant handling is gathered, in this case m8. Other functions: m other m functions in the progra...
Page 119
13.6 automatic operation start after block search 119 other intervention possibilities before start it is possible to change the order of execution, as well as to cancel the execution of other m codes before starting the execution of data gathered in automatic mode. The cursor can be moved along the...
Page 120
13.6 automatic operation start after block search 120 key has been pressed, block search action must be pressed on view screen. By the use of interrupted softkey the control starts searching for the block, the execution of which has been interrupted. Afterwards the process corresponds to that of com...
Page 121
14 listing of messages and their codes 121 14 listing of messages and their codes there may be two types of messages: local and global. 14.1 local message local messages are the ones connected to an action executed on a certain screen, and are not available on any other screen. These are for example...
Page 122
14 listing of messages and their codes 122 messages of custom macros: – error messages programmed by the user and waiting for to be canceled, or – messages programmed by the user waiting for start. In the case of global messages the different messages are needed to be answered differently, i.E., to ...
Page 123
14.3 listing of global messages 123 14.3 listing of global messages error code message description canceling and re- pairing method 0 servo 1 if the position deviation value exceeds the value specified at the appropriate parame- ter, servo alarm occurs. In message servon n=1...8 refers to the nth ax...
Page 124
14.3 listing of global messages error code message description canceling and re- pairing method 124 60 plc timeout 1 if either module :001 or module :002 of plc program does not expire in the time slice reserved for it, message plc time- out 1 or 2 is displayed. This message is generated in emg stat...
Page 125
14.3 listing of global messages error code message description canceling and re- pairing method 125 999 short mon this message is displayed, if mon (ma- chine on) output of control is short-cir- cuited or overloaded. This message is generated in emg state. This message causes emg state and loss of r...
Page 126
14.3 listing of global messages error code message description canceling and re- pairing method 126 1102 reference point t3 this message is displayed, if the zero pulse has not been found after leaving the reference switch within the distance spec- ified at parameter swshift + : zerod- is. Value of ...
Page 127
14.3 listing of global messages error code message description canceling and re- pairing method 127 1105 reference point t6 this message is displayed, if during refer- ence point return in case of distance-coded measuring system the distance between two zero pulses is not in accordance with the valu...
Page 128
14.3 listing of global messages error code message description canceling and re- pairing method 128 1340 limit t+ this message is displayed, if one of the axes has run on limit switch or on overtra- vel position specified at a parameter in direction –. Value of t is the name of the axis: x, y, z, u,...
Page 129
14.3 listing of global messages error code message description canceling and re- pairing method 129 2000 plc error 001 at most 152 different messages can be sent by plc. The message texts are optional. In case no text is added by the programmer of plc, message plc error ijk is displayed. For the lis...
Page 130
14.3 listing of global messages error code message description canceling and re- pairing method 130 3006 value excess h, d, p if in tool offset selection (h) or (d) the number entered under the address exceeds the range permitted. The same error occurs in case of value p of command g10 l(10, 11, 12,...
Page 131
14.3 listing of global messages error code message description canceling and re- pairing method 131 3018 ,a in g2, g3 if in circular interpolation block (g2, g3) angle (,a) has been programmed. The message is can- celed by reset key. 3019 d o m i n a t o r c o n - stant=0 if in 3d radius compensatio...
Page 132
14.3 listing of global messages error code message description canceling and re- pairing method 132 3029 group number is too high if in block g10 l3 (filling up life time ta- ble) the number of tool groups exceeds the maximum value registered on parameter 1181 groupnum. The message is can- celed by ...
Page 133
14.3 listing of global messages error code message description canceling and re- pairing method 133 3040 g38 not in g0, g1 if vector hold block g38 was programmed and the interpolation code is not g0 or g1. The message is can- celed by reset key. 3041 after g2, g3 illeg. Block if in offset mode (g41...
Page 134
14.3 listing of global messages error code message description canceling and re- pairing method 134 3051 g22, g28, ... G31, g37 if in block g22 incorrect address is found, if in block g22 p is not 0 or 1, if in block g22 relation between the value of addresses x y z and i j k is incorrect, if in blo...
Page 135
14.3 listing of global messages error code message description canceling and re- pairing method 135 3059 3060 3061 3062 3063 3064 bad macro state- ment if the macro expression is syntactically incorrect. The message is can- celed by reset key. 3065 too long block if the programmed block does not hav...
Page 136
14.3 listing of global messages error code message description canceling and re- pairing method 136 3073 not existing pro- gram no. If, in case of subprogram call (m98 p) or macro call (g65 or g66 or g66.1 p), the program number specified at address p is not in the memory, subprogram or macro call h...
Page 137
14.3 listing of global messages error code message description canceling and re- pairing method 137 3086 definition error g51 if scaling axis by axis is programmed (g51 x y z i j k) and x and u, or y and v, or z and w are in one block. The message is can- celed by reset key. 3087 illegal plane selec...
Page 138
14.3 listing of global messages error code message description canceling and re- pairing method 138 3100 3101 block not found if the block searched for is not found and the end of program is reached (m2, m30 or %). The message is can- celed by reset key. 3102 incorrect position g12.1 if polar coordi...
Page 139
14.3 listing of global messages error code message description canceling and re- pairing method 139 3123 3124 3125 3126 3127 3500 program edited this message is displayed, if program se- lected for automatic execution is edited in automatic mode, or if program selected for manual data input executio...
Page 140
14.3 listing of global messages error code message description canceling and re- pairing method 140 3508 nc status table bad if the check sum of the memory area con- taining the general nc state, preserved upon power-off is false. These data are as follows: g20/g21: inch/metric input; the number of ...
Page 141
14.3 listing of global messages error code message description canceling and re- pairing method 141 3518 directory full at most 254 programs can be stored, for the file manager built in control enables the registration of 254 programs in the di- rectory. This message is displayed, if more programs a...
Page 142
14.3 listing of global messages error code message description canceling and re- pairing method 142 3549 restore modal func- tions? Y if automatic operation is started from intd status by means of start, the control registers stop status and question restore modal functions? Y is displayed (y=yes). ...
Page 143
Notes 143 notes.
Page 144
144 alphabetical index: access forbidden . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12 address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56 alphabetical keys . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 arrow keys . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 beginning of program . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57 bl...