- DL manuals
- Quidway
- Network Hardware
- WB2011
- User Manual
Quidway WB2011 User Manual
Summary of WB2011
Page 1
User guide.
Page 2
Command line interface 6-20 6 sntp-server ip this command sets the ip address of the servers to which sntp time requests are issued. Use the this command with no arguments to clear all time servers from the current list. Syntax sntp-server ip 1
Page 3
User guide guide outdoor 5 ghz wireless bridge ieee 802.11a wireless bridge.
Page 4
Wb2011 f1.1.1.0 e102004-r01.
Page 5: Compliances
I compliances federal communication commission interference statement this equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause interference to radio communications. It has been tested and found to compl...
Page 6
Ii safety compliance power cord safety please read the following safety information carefully before installing the wireless bridge: warning: installation and removal of the unit must be carried out by qualified personnel only. • the unit must be connected to an earthed (grounded) outlet to comply w...
Page 7
Iii veuillez lire à fond l'information de la sécurité suivante avant d'installer le wireless bridge: avertissement: l’installation et la dépose de ce groupe doivent être confiés à un personnel qualifié. • ne branchez pas votre appareil sur une prise secteur (alimentation électrique) lorsqu'il n'y a ...
Page 8
Iv bitte unbedingt vor dem einbauen des wireless bridges die folgenden sicherheitsanweisungen durchlesen: warnung: die installation und der ausbau des geräts darf nur durch fachpersonal erfolgen. • das gerät sollte nicht an eine ungeerdete wechselstromsteckdose angeschlossen werden. • das gerät muß ...
Page 9: Contents
V contents chapter 1: introduction 1-1 package checklist 1-1 hardware description 1-2 component description 1-2 system configuration 1-5 system components 1-5 point-to-point configuration 1-5 point-to-multipoint configuration 1-5 features and benefits 1-6 system defaults 1-7 chapter 2: bridge link p...
Page 10
Contents vi snmp 5-7 administration 5-10 system log 5-13 wireless distribution system (wds) 5-17 bridge 5-18 spanning tree protocol (stp) 5-21 radio interface 5-25 radio settings (802.11a) 5-25 security 5-28 status information 5-33 wireless bridge status 5-33 station status 5-35 event logs 5-36 chap...
Page 11
Contents vii password 6-13 ip http port 6-14 ip http server 6-14 show system 6-15 show version 6-15 system logging commands 6-16 logging on 6-16 logging host 6-17 logging console 6-17 logging level 6-18 logging facility-type 6-18 show logging 6-19 system clock commands 6-19 sntp-server ip 6-20 sntp-...
Page 12
Contents viii bridge stp-port spanning-disabled 6-39 show bridge 6-39 filtering commands 6-40 filter ap-manage 6-40 filter ethernet-type enable 6-41 filter ethernet-type protocol 6-41 show filters 6-42 ethernet interface commands 6-43 interface ethernet 6-43 dns server 6-43 ip address 6-44 ip dhcp 6...
Page 13
Contents ix appendix c: cables and pinouts c-1 twisted-pair cable assignments c-1 10/100base-tx pin assignments c-1 straight-through wiring c-2 crossover wiring c-2 8-pin din connector pinout c-3 8-pin din to rj-45 cable wiring c-4 glossary index.
Page 14
Contents x.
Page 15: Chapter 1: Introduction
1-1 chapter 1: introduction • wb2011– provides only external antenna options and is designed to operate as the “master” bridge in point-to-multipoint configurations, supporting wireless connections to as many as 16 wb2011 slave units. Each wireless bridge model is housed in a weatherproof enclosure ...
Page 16: Hardware Description
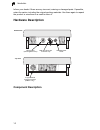
Introduction 1-2 1 inform your dealer if there are any incorrect, missing or damaged parts. If possible, retain the carton, including the original packing materials. Use them again to repack the product in case there is a need to return it. Hardware description component description ethernet port (a...
Page 17
Hardware description 1-3 1 external antenna options ( wb2011 only) the wb2011 master bridge unit does not include an integrated antenna, but provides various external antenna options. In a point-to-multipoint configuration an external high-gain omnidirectional, or panel antenna can be used to commun...
Page 18
Introduction 1-4 1 however, when connecting the access point to a workstation or other device that does not have mdi-x ports, you must use crossover twisted-pair cable. The wireless bridge does not have a power switch. It is powered on when its ethernet port is connected to the power injector module...
Page 19: System Configuration
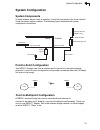
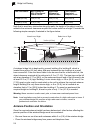
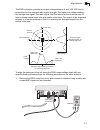
System configuration 1-5 1 system configuration system components at each location where a unit is installed, it must be connected to the local network using the power injector module. The following figure illustrates the system component connections. Point-to-point configuration two wb2011 bridges ...
Page 20: Features And Benefits
Introduction 1-6 1 features and benefits data rate using integrated high-gain 17 dbi antennas • maximum data rate up to 108 mbps • outdoor weatherproof design • ieee 802.11a compliant • local network connection via 10/100 mbps ethernet port • powered through its ethernet cable connection to the powe...
Page 21: System Defaults
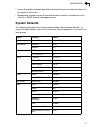
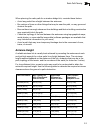
System defaults 1-7 1 • scans all available channels and selects the best channel and data rate based on the signal-to-noise ratio • manageable through an easy-to-use web-browser interface, command line (via telnet), or snmp network management tools system defaults the following table lists some of ...
Page 22
Introduction 1-8 1 system logging syslog disabled logging host disabled logging console disabled ip address / host name 0.0.0.0 logging level informational logging facility type 16 spanning tree status enabled ethernet interface speed and duplex auto wireless interface 802.11a status enabled turbo m...
Page 23: Data Rates
2-1 chapter 2: bridge link planning the outdoor 5 ghz wireless bridge supports fixed point-to-point or point-to-multipoint wireless links. A single link between two points can be used to connect a remote site to larger core network. Multiple bridge links can provide a way to connect widespread ether...
Page 24: Radio Path Planning
Bridge link planning 2-2 2 radio path planning although the wireless bridge uses ieee 802.11a radio technology, which is capable of reducing the effect of multipath signals due to obstructions, the wireless bridge link requires a “radio line-of-sight” between the two antennas for optimum performance...
Page 25: Antenna Height
Radio path planning 2-3 2 when planning the radio path for a wireless bridge link, consider these factors: • avoid any partial line-of-sight between the antennas. • be cautious of trees or other foliage that may be near the path, or may grow and obstruct the path. • be sure there is enough clearance...
Page 26
Bridge link planning 2-4 2 note that to avoid any obstruction along the path, the height of the object must be added to the minimum clearance required for a clear radio line-of-sight. Consider the following simple example, illustrated in the figure below. A wireless bridge link is deployed to connec...
Page 27: Radio Interference
Radio path planning 2-5 2 • avoid placing the wireless bridge too close to any metallic, reflective surfaces, such as roof-installed air-conditioning equipment, tinted windows, wire fences, or water pipes • the wireless bridge antennas at both ends of the link must be positioned with the same polari...
Page 28: Ethernet Cabling
Bridge link planning 2-6 2 maximum wind velocity and direction at the site and be sure that any supporting structure, such as a pole, mast, or tower, is built to withstand this force. • lightning — the wireless bridge includes its own built-in lightning protection. However, you should make sure that...
Page 29: Mount The Unit
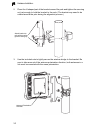
3-1 chapter 3: hardware installation before mounting antennas to set up your wireless bridge links, be sure you have selected appropriate locations for each antenna. Follow the guidance and information in chapter 2, “wireless link planning.” also, before mounting units in their intended locations, y...
Page 30
Hardware installation 3-2 3 2. Place the u-shaped part of the bracket around the pole and tighten the securing nut just enough to hold the bracket to the pole. (the bracket may need to be rotated around the pole during the alignment process.) 3. Use the included nuts to tightly secure the wireless b...
Page 31
Mount the unit 3-3 3 mounting on larger diameter poles in addition, there is a method for attaching the pole-mounting bracket to a pole that is 2 to 5 inches in diameter using an adjustable steel band clamp (not included in the kit). A steel band clamp up to 0.5 inch (1.27 cm) wide can be threaded t...
Page 32: Connect The External Antenna
Hardware installation 3-4 3 2. Position the bracket in the intended location and mark the position of the three mounting screw holes. 3. Drill three holes in the wall that match the screws and wall plugs included in the bracket kit, then secure the bracket to the wall. 4. Use the included nuts to ti...
Page 33: Connect Cables To The Unit
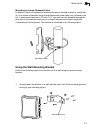
Connect cables to the unit 3-5 3 connect cables to the unit 1. Attach the ethernet cable to the ethernet port on the wireless bridge. Note: the ethernet cable included with the package is 30 m (100 ft) long. To wire a longer cable (maximum 100 m, 325 ft), follow the connector pinout information in a...
Page 34: Align Antennas
Hardware installation 3-6 3 3. Insert the power cable plug directly into the standard ac receptacle on the power injector. 4. Plug the other end of the power cable into a grounded, 3-pin socket, ac power source. Note: for international use, you may need to change the ac line cord. You must use a lin...
Page 35
Align antennas 3-7 3 the rssi connector provides an output voltage between 0 and 3.28 vdc that is proportional to the received radio signal strength. The higher the voltage reading, the stronger the signal. The radio signal from the remote antenna can be seen to have a strong central main lobe and s...
Page 36
Hardware installation 3-8 3 2. Pan the antenna horizontally back and forth by rotating the mounting bracket around the pole while checking the rssi voltage. 3. Find the point where the signal is strongest (highest voltage) and secure the mounting bracket firmly to the pole. Note: sometimes there may...
Page 37
4-1 chapter 4: initial configuration the wireless bridge offers a variety of management options, including a web-based interface, a command line interface (cli), or using snmp management software. Most initial configuration steps can be made through the web browser interface using the setup wizard (...
Page 38: Initial Configuration Steps
Initial configuration 4-2 4 initial configuration steps setting the country code – regulations for wireless products differ from country to country. Setting the country code restricts the wireless bridge to use only the radio channels and power settings permitted in the specified country of operatio...
Page 39
Using the web-based management setup wizard 4-3 4 using the web-based management setup wizard there are only a few basic steps you need to complete to set up the wireless bridge for your network. The setup wizard takes you through configuration procedures for the radio channel selection, ip configur...
Page 40
Initial configuration 4-4 4 launching the setup wizard – to perform initial configuration, click setup wizard on the home page, then click on the [next] button to start the process..
Page 41
Using the web-based management setup wizard 4-5 4 1. Radio channel – you must enable radio communications for the 802.11a radio and set the operating channel. • 802.11a turbo mode – if you select enable, the wireless bridge will operate in turbo mode with a data rate of up to 108 mbps. Normal mode s...
Page 42
Initial configuration 4-6 4 2. Ip configuration – either enable or disable (dynamic host configuration protocol (dhcp) for automatic ip configuration. If you disable dhcp, then manually enter the ip address and subnet mask. If a management station exists on another network segment, then you must ent...
Page 43
Using the web-based management setup wizard 4-7 4 3. Security – enable wired equivalent privacy (wep) encryption and set an encryption key. 4. Click finish. 5. Click the ok button to restart the access point..
Page 44
Initial configuration 4-8 4.
Page 45: Advanced Configuration
5-1 chapter 5: system configuration before continuing with advanced configuration, first complete the initial configuration steps described in chapter 4 to set up an ip address for the wireless bridge. The wireless bridge can be managed by any computer using a web browser (internet explorer 5.0 or a...
Page 46: System Identification
System configuration 5-2 5 system identification the system information parameters for the wireless bridge can be left at their default settings. However, modifying these parameters can help you to more easily distinguish different devices in your network. Filter control enables vlan support and fil...
Page 47: Tcp / Ip Settings
Advanced configuration 5-3 5 system name – an alias for the wireless bridge, enabling the device to be uniquely identified on the network. (default: outdoor bridge; range: 1-22 characters) location – a text string that describes the system location. (maximum length: 20 characters) contact – a text s...
Page 48
System configuration 5-4 5 by default, the wireless bridge will be automatically configured with ip settings from a dynamic host configuration protocol (dhcp) server. However, if you are not using a dhcp server to configure ip addressing, use the cli to manually configure the initial ip values (page...
Page 49
Advanced configuration 5-5 5 if you have management stations, dns, or other network servers located on another subnet, type the ip address of the default gateway router in the text field provided. Otherwise, leave the address as all zeros (0.0.0.0). • primary and secondary dns address: the ip addres...
Page 50: Filter Control
System configuration 5-6 5 filter control the wireless bridge can employ vlan tagging support and network traffic frame filtering to control access to network resources and increase security. Native vlan id – the vlan id used to tag traffic passing from the wireless interface to the wired network. (...
Page 51: Snmp
Advanced configuration 5-7 5 cli commands for vlan support– from the global configuration mode use the native-vlanid command to set the default vlan id for the ethernet interface, then enable vlans using the vlan enable command. When you change the access point’s vlan support setting, you must reboo...
Page 52
System configuration 5-8 5 snmp – enables or disables snmp management access and also enables the wireless bridge to send snmp traps (notifications). Snmp management is enabled by default. Community name (read only) – defines the snmp community access string that has read-only access. Authorized man...
Page 53
Advanced configuration 5-9 5 cli commands for snmp – use the snmp-server enable server command from the global configuration mode to enable snmp. To set read/write and read-only community names, use the snmp-server community command. The snmp-server host command defines a trap receiver host. To view...
Page 54: Administration
System configuration 5-10 5 administration changing the password management access to the web and cli interface on the wireless bridge is controlled through a single user name and password. You can also gain additional access security by using control filters (see “filter control” on page 5-6). To p...
Page 55
Advanced configuration 5-11 5 upgrading firmware you can upgrade new wireless bridge software from a local file on the management workstation, or from an ftp or tftp server. After upgrading new software, you must reboot the wireless bridge to implement the new code. Until a reboot occurs, the wirele...
Page 56
System configuration 5-12 5 firmware upgrade local – downloads an operation code image file from the web management station to the wireless bridge using http. Use the browse button to locate the image file locally on the management station and click start upgrade to proceed. • new firmware file: spe...
Page 57: System Log
Advanced configuration 5-13 5 be used to check that the new file is present in the wireless bridge file system. To run the new software, use the reset board command to reboot the wireless bridge. System log the wireless bridge can be configured to send event and error messages to a system log server...
Page 58
System configuration 5-14 5 enabling system logging the wireless bridge supports a logging process that can control error messages saved to memory or sent to a syslog server. The logged messages serve as a valuable tool for isolating wireless bridge and network problems. System log setup – enables t...
Page 59
Advanced configuration 5-15 5 command to set the facility-type number to use on the syslog server. To view the current logging settings, use the show logging command. Configuring sntp simple network time protocol (sntp) allows the wireless bridge to set its internal clock based on periodic updates f...
Page 60
System configuration 5-16 5 indicate the number of hours your time zone is located before (east) or after (west) utc. Enable daylight saving – the wireless bridge provides a way to automatically adjust the system clock for daylight savings time changes. To use this feature you must define the month ...
Page 61
Advanced configuration 5-17 5 wireless distribution system (wds) the ieee 802.11a standard defines a wireless distribution system (wds) for connections between wireless bridges. The outdoor wireless bridge uses wds to forward traffic on links between units. When using wds, only wireless bridge units...
Page 62: Bridge
System configuration 5-18 5 mac address – the physical layer address of the wireless bridge unit at the other end of the wireless link. (12 hexadecimal digits in the form “xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx”) port status – enables or disables the wireless bridge link. Note: the wireless mac address for each bridge u...
Page 63
Advanced configuration 5-19 5 bridge aging time – changes the aging time for entries in the dynamic address table: • ethernet: the time after which a learned ethernet port entry is discarded. (range: 60-1800 seconds; default: 100 seconds) • wireless 802.11a: the time after which a learned wireless e...
Page 64
System configuration 5-20 5 cli commands for bridging– the following example shows how to set the mac address aging time for the wireless bridge. Outdoor bridge(config)#bridge timeout 0 300 6-33 outdoor bridge(config)#bridge timeout 2 1000 6-33 outdoor bridge(config)#exit outdoor bridge#show bridge ...
Page 65: Spanning Tree Protocol (Stp)
Advanced configuration 5-21 5 spanning tree protocol (stp) the spanning tree protocol (stp) can be used to detect and disable network loops, and to provide backup links between switches, bridges or routers. This allows the wireless bridge to interact with other bridging devices (that is, an stp-comp...
Page 66
System configuration 5-22 5 forward delay – the maximum time (in seconds) this device waits before changing states (i.E., discarding to learning to forwarding). This delay is required because every device must receive information about topology changes before it starts to forward frames. In addition...
Page 67
Advanced configuration 5-23 5 priority – defines the priority used for this port in the spanning tree protocol. If the path cost for all ports on a switch are the same, the port with the highest priority (i.E., lowest value) will be configured as an active link in the spanning tree. This makes a por...
Page 68
System configuration 5-24 5 cli commands for stp– the following example configures spanning tree paramters for the bridge and wireless port 5. Outdoor bridge(config)#bridge stp-bridge priority 40000 6-36 outdoor bridge(config)#bridge stp-bridge hello-time 5 6-35 outdoor bridge(config)#bridge stp-bri...
Page 69: Radio Interface
Radio interface 5-25 5 radio interface the ieee 802.11a radio interface includes configuration options for radio signal characteristics and wireless security features. Note: the radio channel settings for the wireless bridge are limited by local regulations, which determine the number of channels th...
Page 70
System configuration 5-26 5 note: in normal mode, the wireless bridge provides a channel bandwidth of 20 mhz, and supports the maximum number of channels permitted by local regulations (e.G., 11 channels for the united states). In turbo mode, the channel bandwidth is increased to 40 mhz to support t...
Page 71
Radio interface 5-27 5 the wireless bridge will save all broadcast/multicast frames for the basic service set (bss) and forward them after every second beacon. Using smaller dtim intervals delivers broadcast/multicast frames in a more timely manner, causing stations in power save mode to wake up mor...
Page 72: Security
System configuration 5-28 5 security wired equivalent privacy (wep) and advanced encryption standard (aes) are implemented in the wireless bridge to prevent unauthorized access to network data. For more secure data transmissions, enable wep or aes encryption for the wireless bridge and set at least ...
Page 73
Radio interface 5-29 5 setting up ieee 802.11 wired equivalent privacy (wep) shared keys enables the wireless bridge to prevent unauthorized access to the network. Be sure to define at least one static wep key for data encryption. Also, be sure that the wep keys are the same for all bridge units in ...
Page 74
System configuration 5-30 5 advanced encryption standard (aes) aes has been designated by the national institute of standards and technology as the successor to the data encryption standard (des) encryption algorithm, and will be used by the u.S. Government for encrypting all sensitive, nonclassifie...
Page 75
Radio interface 5-31 5 • alphanumeric: enter keys as an alphanumeric string using between 8 and 31 characters. Note: for each wireless port link (1 to 16), the aes keys must match on the corresponding bridge unit. Cli commands for wep security – from the 802.11a interface configuration mode, use the...
Page 76
System configuration 5-32 5 cli commands for aes security – from the 802.11a interface configuration mode, use the encryption command to enable aes encryption. To enter aes keys, use the key command. To view the current security settings, use the show interface wireless a command. Note: the key type...
Page 77: Status Information
Status information 5-33 5 status information the status page includes information on the following items: wireless bridge status the ap status window displays basic system configuration settings, as well as the settings for the wireless interface. Ap system configuration – the ap system configuratio...
Page 78
System configuration 5-34 5 • ip default gateway: ip address of the gateway router between this device and management stations that exist on other network segments. • http server: shows if management access via http is enabled. • http server port: shows the tcp port used by the http interface. • ver...
Page 79: Station Status
Status information 5-35 5 station status the station status window shows remote wireless bridges currently associated with the local wireless bridge. The station status page displays basic connection information for each wireless bridge link. Note that this page is automatically refreshed every five...
Page 80: Event Logs
System configuration 5-36 5 event logs the event logs window shows the log messages generated by the wireless bridge and stored in memory. The event logs table displays the following information: • log time: the time the log message was generated. • event level: the logging level associated with thi...
Page 81: Accessing The Cli
6-1 chapter 6: command line interface using the command line interface accessing the cli when accessing the management interface for the wireless bridge via a telnet connection, the wireless bridge can be managed by entering command keywords and parameters at the prompt. Using the wireless bridge’s ...
Page 82: Entering Commands
Command line interface 6-2 6 entering commands this section describes how to enter cli commands. Keywords and arguments a cli command is a series of keywords and arguments. Keywords identify a command, and arguments specify configuration parameters. For example, in the command “show interface ethern...
Page 83: Partial Keyword Lookup
Entering commands 6-3 6 interface). You can also display a list of valid keywords for a specific command. For example, the command “show ?” displays a list of possible show commands: the command “show interface ?” will display the following information: partial keyword lookup if you terminate a part...
Page 84: Understanding Command Modes
Command line interface 6-4 6 understanding command modes the command set is divided into exec and configuration classes. Exec commands generally display information on system status or clear statistical counters. Configuration commands, on the other hand, modify interface parameters or enable certai...
Page 85: Command Line Processing
Entering commands 6-5 6 change to “outdoor bridge(if-ethernet)#,” or “outdoor bridge(if-wireless a)” indicating that you have access privileges to the associated commands. You can use the end command to return to the exec mode. Command line processing commands are not case sensitive. You can abbrevi...
Page 86: Command Groups
Command line interface 6-6 6 command groups the system commands can be broken down into the functional groups shown below. The access mode shown in the following tables is indicated by these abbreviations: gc (global configuration), and ic (interface configuration. General commands command group des...
Page 87: Configure
General commands 6-7 6 configure this command activates global configuration mode. You must enter this mode to modify most of the settings on the wireless bridge. You must also enter global configuration mode prior to enabling the context modes for interface configuration. See “using the command lin...
Page 90: Show Line
Command line interface 6-10 6 show line this command displays the console port’s configuration settings. Command mode exec example the console port settings are fixed at the values shown below. System management commands these commands are used to configure the user name, password, browser managemen...
Page 91: Country
System management commands 6-11 6 country this command configures the wireless bridge’s country code, which identifies the country of operation and sets the authorized radio channels. Syntax country country_code> country_code - a two character code that identifies the country of operation. See the f...
Page 92: Prompt
Command line interface 6-12 6 default setting us - for units sold in the united states 99 (no country set) - for units sold in other countries command mode exec command usage • if you purchased an wireless bridge outside of the united states, the country code must be set before radio functions are e...
Page 93: Username
System management commands 6-13 6 default setting outdoor bridge command mode global configuration example username this command configures the user name for management access. Syntax username name name - the name of the user. (length: 3-16 characters, case sensitive) default setting admin command m...
Page 94: Ip Http Port
Command line interface 6-14 6 example ip http port this command specifies the tcp port number used by the web browser interface. Use the no form to use the default port. Syntax ip http port port-number no ip http port port-number - the tcp port to be used by the browser interface. (range: 1024-65535...
Page 95: Show System
System management commands 6-15 6 related commands ip http port (6-14) show system this command displays basic system configuration settings. Default setting none command mode exec example show version this command displays the software version for the system. Default setting none command mode exec ...
Page 96: System Logging Commands
Command line interface 6-16 6 system logging commands these commands are used to configure system logging on the wireless bridge. Logging on this command controls logging of error messages; i.E., sending debug or error messages to memory. The no form disables the logging process. Syntax logging on n...
Page 99: Show Logging
System clock commands 6-19 6 command usage the command specifies the facility type tag sent in syslog messages. (see rfc 3164.) this type has no effect on the kind of messages reported by the wireless bridge. However, it may be used by the syslog server to sort messages or to store messages in the c...
Page 101: Sntp-Server Date-Time
System clock commands 6-21 6 command usage the time acquired from time servers is used to record accurate dates and times for log events. Without sntp, the wireless bridge only records the time starting from the factory default set at the last bootup (i.E., 00:14:00, january 1, 1970). Example relate...
Page 102: Sntp-Server Timezone
Command line interface 6-22 6 command mode global configuration command usage the command sets the system clock back one hour during the specified period. Example this sets daylight savings time to be used from july 1st to september 1st. Sntp-server timezone this command sets the time zone for the w...
Page 103: Snmp Commands
Snmp commands 6-23 6 example snmp commands controls access to this wireless bridge from management stations using the simple network management protocol (snmp), as well as the hosts that will receive trap messages. Snmp-server community this command defines the community access string for the simple...
Page 104: Snmp-Server Contact
Command line interface 6-24 6 default setting • public - read-only access. Authorized management stations are only able to retrieve mib objects. • private - read/write access. Authorized management stations are able to both retrieve and modify mib objects. Command mode global configuration command u...
Page 105: Snmp-Server Enable Server
Snmp commands 6-25 6 snmp-server enable server this command enables snmp management access and also enables this device to send snmp traps (i.E., notifications). Use the no form to disable snmp service and trap messages. Syntax snmp-server enable server no snmp-server enable server default setting e...
Page 106: Snmp-Server Location
Command line interface 6-26 6 command mode global configuration command usage the snmp-server host command is used in conjunction with the snmp-server enable server command to enable snmp notifications. Example related commands snmp-server enable server (6-25) snmp-server location this command sets ...
Page 107: Flash/file Commands
Flash/file commands 6-27 6 example flash/file commands these commands are used to manage the system code or configuration files. Bootfile this command specifies the image used to start up the system. Syntax bootfile filename> filename - name of the image file. Default setting none command mode exec ...
Page 108: Copy
Command line interface 6-28 6 example copy this command copies a boot file, code image, or configuration file between the wireless bridge’s flash memory and a ftp/tftp server. When you save the configuration settings to a file on a ftp/tftp server, that file can later be downloaded to the wireless b...
Page 109: Delete
Flash/file commands 6-29 6 example the following example shows how to upload the configuration settings to a file on the tftp server: the following example shows how to download a configuration file: delete this command deletes a file or image. Syntax delete filename filename - name of the configura...
Page 110: Dir
Command line interface 6-30 6 dir this command displays a list of files in flash memory. Command mode exec command usage file information is shown below: example the following example shows how to display all file information: wds commands the commands described in this section are used to configure...
Page 111: Wds Mac-Address
Wds commands 6-31 6 wds mac-address this command enters wireless mac addresses in the wds forwarding table for each node in the wireless bridge network. Syntax wds mac-address port-id> mac-address> • port-id - the wireless port number for the bridge link. (1 for slave units; 1-16 for master units) •...
Page 113: Bridge Commands
Bridge commands 6-33 6 bridge commands the commands described in this section are used to set the mac address table aging time and spanning tree parameters for both the ethernet and wireless interfaces. Bridge timeout this command sets the aging time for both the ethernet port and the wireless inter...
Page 114
Command line interface 6-34 6 bridge stp-bridge spanning-tree use this command to enable the spanning tree protocol globally for the wireless bridge. Use the no form to disable it. Syntax bridge stp-bridge spanning-tree no bridge stp-bridge spanning-tree default setting spanning tree is enabled. Com...
Page 115: Bridge Stp-Bridge Hello-Time
Bridge commands 6-35 6 command usage this command sets the maximum time (in seconds) the root device will wait before changing states (i.E., discarding to learning to forwarding). This delay is required because every device must receive information about topology changes before it starts to forward ...
Page 116: Bridge Stp-Bridge Priority
Command line interface 6-36 6 default setting 20 seconds command mode global configuration command usage this command sets the maximum time (in seconds) a device can wait without receiving a configuration message before attempting to reconfigure. All device ports (except for designated ports) should...
Page 117: Bridge Stp-Port Path-Cost
Bridge commands 6-37 6 bridge stp-port path-cost use this command to configure the spanning tree path cost for the specified port. Use the no form to restore the default for the specified port. Syntax bridge stp-port path-cost port> cost no bridge stp-port path-cost port> • port - specifies the port...
Page 118: Bridge Stp-Port Portfast
Command line interface 6-38 6 command usage • this command defines the priority for the use of a port in the spanning tree protocol. If the path cost for all ports on a wireless bridge are the same, the port with the highest priority (that is, lowest value) will be configured as an active link in th...
Page 119: Show Bridge
Bridge commands 6-39 6 bridge stp-port spanning-disabled this command disables the spanning tree protocol for the specified interface. Use the no form to reenable the spanning tree protocol for the specified interface. Syntax bridge stp-port spanning-disabled port> no bridge stp-port spanning-disabl...
Page 120: Filtering Commands
Command line interface 6-40 6 example filtering commands the commands described in this section are used to control access to the management interface from the wireless interface and filter traffic using specific ethernet protocol types. Filter ap-manage this command prevents access to wireless brid...
Page 121
Filtering commands 6-41 6 command mode global configuration example filter ethernet-type enable this command checks the ethernet type on all incoming and outgoing ethernet packets against the protocol filtering table. Use the no form to disable this feature. Syntax filter ethernet-type enable no fil...
Page 122: Show Filters
Command line interface 6-42 6 command mode global configuration command usage use the filter ethernet-type enable command to enable filtering for ethernet types specified in the filtering table, or the no filter ethernet-type enable command to disable all filtering based on the filtering table. Exam...
Page 123: Ethernet Interface Commands
Ethernet interface commands 6-43 6 ethernet interface commands the commands described in this section configure connection parameters for the ethernet interface. Interface ethernet this command enters ethernet interface configuration mode. Syntax interface ethernet default setting none command mode ...
Page 124: Ip Address
Command line interface 6-44 6 command mode global configuration command usage the primary and secondary name servers are queried in sequence. Example this example specifies two domain-name servers. Related commands show interface ethernet (6-46) ip address this command sets the ip address for the (1...
Page 125: Ip Dhcp
Ethernet interface commands 6-45 6 example related commands ip dhcp (6-45) ip dhcp this command sets the ip address for the currently selected vlan interface. Use the no form to restore the default ip address. Syntax ip dhcp no ip dhcp default setting enabled command mode interface configuration (et...
Page 126: Shutdown
Command line interface 6-46 6 shutdown this command disables the ethernet interface. To restart a disabled interface, use the no form. Syntax shutdown no shutdown default setting interface enabled command mode interface configuration (ethernet) command usage this command allows you to disable the et...
Page 127: Wireless Interface Commands
Wireless interface commands 6-47 6 example wireless interface commands the commands described in this section configure connection parameters for the wireless interface. Outdoor bridge#show interface ethernet ethernet interface information ======================================== ip address : 192.16...
Page 128: Interface Wireless
Command line interface 6-48 6 interface wireless this command enters wireless interface configuration mode. Syntax interface wireless a a - 802.11a radio interface. Default setting none command mode global configuration example to specify the wireless interface, enter the following command: descript...
Page 129: Speed
Wireless interface commands 6-49 6 speed this command configures the maximum data rate at which remote bridges can connect to the local bridge. Syntax speed speed> speed - maximum access speed allowed for remote bridges. (options: 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, 54 mbps) default setting 54 mbps command mo...
Page 130: Turbo
Command line interface 6-50 6 example turbo this command sets the wireless bridge to an enhanced mode (not regulated in ieee 802.11a) that provides a higher data rate of up to 108 mbps. Default setting disabled command mode interface configuration (wireless - 802.11a) command usage • the normal 802....
Page 131: Dtim-Period
Wireless interface commands 6-51 6 command usage the beacon signals allow remote bridges to maintain contact with the local wireless bridge. They may also carry power-management information. Example dtim-period this command configures the rate at which remote bridges in sleep mode must wake up to re...
Page 132: Fragmentation-Length
Command line interface 6-52 6 fragmentation-length this command configures the minimum packet size that can be fragmented when passing through the wireless bridge. Syntax fragmentation-length length> length - minimum packet size for which fragmentation is allowed. (range: 256-2346 bytes) default set...
Page 133: Encryption
Wireless interface commands 6-53 6 command usage • if the threshold is set to 0, the wireless bridge never sends rts signals. If set to 2347, the wireless bridge always sends rts signals. If set to any other value, and the packet size equals or exceeds the rts threshold, the rts/cts (request to send...
Page 134: Key
Command line interface 6-54 6 encrypting all sensitive, nonclassified information. Because of its strength, and resistance to attack, aes is also being incorporated as part of the 802.11 standard. • the wep settings must be the same on all bridges in your wireless network. • the wep encryption lengt...
Page 135: Transmit-Key
Wireless interface commands 6-55 6 command usage • to enable wep encryption, use the encryption command to specify the key type and length, and use the key command to configure at least one key. • to enable aes encryption, use the encryption command to specify the key type, and use the key command t...
Page 136: Transmit-Power
Command line interface 6-56 6 example transmit-power this command adjusts the power of the radio signals transmitted from the wireless bridge. Syntax transmit-power signal-strength> signal-strength - signal strength transmitted from the wireless bridge. (options: full, half, quarter, eighth, min) ac...
Page 137: Show Interface Wireless
Wireless interface commands 6-57 6 example show interface wireless this command displays the status for the wireless interface. Syntax show interface wireless a • a - 802.11a radio interface. Command mode exec example outdoor bridge(if-wireless a)#shutdown outdoor bridge(if-wireless a)# outdoor brid...
Page 138: Vlan Commands
Command line interface 6-58 6 vlan commands the wireless bridge can enable the support of vlan-tagged traffic passing between the wireless interface and the wired network. When vlan support is enabled, the wireless bridge tags traffic passing to the wired network with the assigned native vlan id (a ...
Page 139: Native-Vlanid
Vlan commands 6-59 6 example related commands native-vlanid (6-59) native-vlanid this command configures the native vlan id for the wireless bridge. Syntax native-vlanid vlan-id> vlan-id - native vlan id. (range: 1-64) default setting 1 command mode global configuration command usage when vlans are ...
Page 140
Command line interface 6-60 6.
Page 141: Appendix A: Troubleshooting
A-1 appendix a: troubleshooting check the following items before you contact local technical support. 1. If wireless bridge units do not associate with each other, check the following: • check the power injector led for each bridge unit to be sure that power is being supplied • be sure that antennas...
Page 142
Troubleshooting a-2 a 5. If you forgot or lost the password: • contact technical support..
Page 143: Appendix B: Specifications
B-1 appendix b: specifications general specifications maximum channels 802.11a: us & canada: 8 (normal mode), 3 (turbo mode) japan: 4 (normal mode), 1 (turbo mode) etsi: 11 channels (normal mode), 4 (turbo mode) china: 5 (normal mode), 2(turbo mode) data rate 802.11a: normal mode: 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, ...
Page 144
Specifications b-2 b humidity 15% to 95% (non-condensing) emc compliance (class a) fcc class a (us) radio signal certification fcc part 15 15.407(b) safety csa/ntrl (csa 22.2 no. 950 & ul 1950) standards ieee 802.3 10base-t, ieee 802.3u 100base-tx, ieee 802.11a.
Page 145: Appendix
C-1 appendix c: cables and pinouts twisted-pair cable assignments for 10/100base-tx connections, a twisted-pair cable must have two pairs of wires. Each wire pair is identified by two different colors. For example, one wire might be green and the other, green with white stripes. Also, an rj-45 conne...
Page 146: Straight-Through Wiring
Cables and pinouts c-2 c connecting to devices that support automatic mdi/mdi-x pinout configuration, you can use either straight-through or crossover cable. Straight-through wiring because the 10/100 mbps input port on the power injector uses an mdi pin configuration, you must use “straight-through...
Page 147: 8-Pin Din Connector Pinout
8-pin din connector pinout c-3 c connecting supports automatic mdi/mdi-x operation, you can use either “straight-through” or “crossover” cable. 8-pin din connector pinout the ethernet cable from the power injector connects to an 8-pin din connector on the wireless bridge. This connector is described...
Page 148
Cables and pinouts c-4 c 8-pin din to rj-45 cable wiring to construct an extended ethernet cable to connect from the power injector’s rj-45 output port to the wireless bridge’s 8-pin din connector, follow the wiring diagram below. Use category 5 or better utp or stp cable, maximum length 100 m (328 ...
Page 149: Glossary
Glossary-1 glossary 10base-t ieee 802.3 specification for 10 mbps ethernet over two pairs of category 3 or better utp cable. 100base-tx ieee 802.3u specification for 100 mbps fast ethernet over two pairs of category 5 or better utp cable. Access point an internetworking device that seamlessly connec...
Page 150
Glossary glossary-2 encryption data passing between the access point and clients can use encryption to protect from interception and evesdropping. Ethernet a popular local area data communications network, which accepts transmission from computers and terminals. File transfer protocol (ftp) a tcp/ip...
Page 151
Glossary-3 glossary service set identifier (ssid) an identifier that is attached to packets sent over the wireless lan and functions as a password for joining a particular radio cell; i.E., basic service set (bss). Session key session keys are unique to each client, and are used to authenticate a cl...
Page 152: Index
Index-1 a aes, configuring 5-28, 5-30, 6-53 b beacon interval 5-26, 6-50 rate 5-26, 6-51 bpdu 5-21 c cable assignments c-1 crossover c-2 straight-through c-2 channel 5-26, 6-49 channels, maximum b-1 clear to send see cts cli 6-1 command modes 6-4 command line interface see cli community name, config...
Page 153
Index-2 index m maximum data rate 5-26, 6-49 802.11a interface 5-26, 6-49 mdi, rj-45 pin configuration 1-3 o ofdm 1-1 operating frequency b-1 p package checklist 1-1 password configuring 5-10, 6-13 management 5-10, 6-13 poe 1-3, 3-5 specifications b-1 port priority, stp 6-37 power over ethernet see ...
Page 154
Index-3 index w wep 5-28, 6-53 configuring 5-28, 6-53 shared key 5-29, 6-54 wired equivalent protection see wep.
Page 155
Index-4 index.
Page 157
Wb2011 e102004-r01.