- DL manuals
- WavePhore Networks
- Receiver
- IDR V1000
- User Manual
WavePhore Networks IDR V1000 User Manual
Summary of IDR V1000
Page 1
Idr v1000 user’s guide installing and operating the intelligent data receiver v1000 ms-4900, rev. A january 1998.
Page 2
This equipment complies with the requirements in part 15 of the fcc rules for a class computing device. Operation of this equipment in a residential area may cause unacceptable interference to radio and tv reception, requiring the operator to take whatever steps are necessary to correct the interfer...
Page 3: Table of Contents
Ms-4900, rev. A iii table of contents section 1. Using this guide about this guide ......................................................................................................... 1-1 audience .....................................................................................................
Page 4
Table of contents iv ms-4900, rev. A section 4. Interpreting screen displays identifying problem indications .................................................................................. 4-1 check signal quality.......................................................................................
Page 5
Table of contents ms-4900, rev. A v supplementary information appendix a. Technical specifications ............................................................................ A-1 appendix b. Pin-outs ......................................................................................................
Page 6: About This
Ms-4900, rev. A 1-1 section 1. Using this guide this guide describes how to install and use a wavephore intelligent data receiver™ v1000 (idr v1000). The idr v1000s comprise a family of satellite receivers that receive, demodulate, and process data streams over high-speed carriers. These data stream...
Page 7
Using this guide ms-4900, rev. A 1–2 audience two types of audiences are assumed to be users of this guide: the primary audience is the technical user who is assumed to have a working knowledge of satellite and telecommunications equipment. These users include installation technicians, network opera...
Page 8: Customer
Using this guide ms-4900, rev. A 1–3 • terms • abbreviations and acronyms glossary terminology the terms “idr,” “idr v1000,” or “the receiver,” used in this manual, refer to all of the idr v1000 models. A specific model is noted where the information applies only to that model. Terms that are unique...
Page 9: Safety
Using this guide ms-4900, rev. A 1–4 safety issues following some basic, common-sense procedures will protect you and will help keep the idr v1000 operating without disruption. Do: • unplug power before changing external cables. This reduces the chance of electrical shorts that could damage the rece...
Page 10: Before You
Ms-4900, rev. A 2–1 section 2. Installing the idr v1000 the installation process covers the following steps: 1. Ensuring all cables are properly connected. 2. Tuning the idr v1000 to its maximum achievable levels for that site 3. Notifying the network operator that installation is complete and to do...
Page 11: Step 1:
Installing the idr v1000 2–2 ms-4900, rev. A step 1: connect the cables 1. Connect the coaxial cable to the rf input connector 2. Connect data cables between the serial or ethernet outputs on the idr v1000 and the external devices. See figures 2-1 and 2-2. 3. Connect the power module to the idr v100...
Page 12: Step 2:
Installing the idr v1000 ms-4900, rev. A 2-3 step 2: verify initial lock on carrier as soon as power is supplied to the idr v1000, an automatic self-test runs. The idr v1000 then locates and “locks” onto the preset frequency. When this completes successfully, the following identification screen appe...
Page 13: Step 4:
Installing the idr v1000 2–4 ms-4900, rev. A step 4: call the network operator once the e b /n 0 and agc readings are at the expected levels and the e b /n 0 has been maximized by adjusting the dish alignment, notify the network operator that the receiver has been installed and is ready to be downlo...
Page 14: Viewing
Ms-4900, rev. A 3–1 section 3. Using the front panel this section describes how to use the front panel of the idr v1000 to view or modify receiver settings. This information includes the following: • displaying and deleting messages • viewing and modifying configuration parameters • changing screen ...
Page 15
Using the front panel 3–2 ms-4900, rev. A figure 3-2. Idr v1000 front panel understanding the identification screen the first screen that appears after the self-test is the identification screen. It displays the idr v1000 model number, locally set time of day, main serial number, and current lock st...
Page 16
Using the front panel ms-4900, rev. A 3–3 choose operation: show status press select from the show status main topic to access the following displays: • logical receiver activity • “summary” screen of active stat mux sessions and memory utilization • “superscreen” data (stat mux status, data errors,...
Page 17
Using the front panel 3–4 ms-4900, rev. A choose operation: specify setup press select from the specify setup main topic. Then use the buttons to access screens for the following purposes: • change output port configuration settings • enable or disable a screen login • enter a password to restrict a...
Page 18
Using the front panel ms-4900, rev. A 3–5 to specify a password: this set of screens enables you to enter the password that restricts access to many screens. Caution: before you enter and activate the password protection, be sure the site requires that level of security. The password/login function ...
Page 19
Using the front panel 3–6 ms-4900, rev. A choose operation: set features set local time the first screen within the set features topic allows you to set the time that this receiver will use to log messages and events. Press select once to display this screen: press select again to display this scree...
Page 20
Using the front panel ms-4900, rev. A 3–7 choose operation: logoff press select from the logoff main topic to disable stat mux or transparent asynchronous mode output. (the “enable login” option in the specify setup screens must first be enabled.) the password entry screen appears. Enter the passwor...
Page 21
Using the front panel 3–8 ms-4900, rev. A.
Page 22: Identifying
Ms-4900, rev. A 4–1 section 4. Interpreting screen displays the idr v1000 screens provide detailed information on the status of the receiver, the satellite signal, the received data, and the output ports. This section describes how to interpret the screen information to troubleshoot problems or to m...
Page 23
Interpreting screen displays 4–2 ms-4900, rev. A check signal quality the “superscreen” under the show status topic provides a quick summary of signal status, but most of the fields relate to stat mux operation (*): figure 4-1. Superscreen note: in general, any incrementing number field of the super...
Page 24
Interpreting screen displays ms-4900, rev. A 4–3 table 4-3. Superscreen fields, transparent asynchronous data field: should be: meaning: character counter incrementing asynchronous data is being received carrier lock status l = locked on signal if lock is not established (l), or if the receiver keep...
Page 25
Interpreting screen displays 4–4 ms-4900, rev. A tdd screen fields the time-division de-multiplexer screen reflects control channel information logged by the tdd. This screen is meaningful with all data modes. Figure 4-3. Tdd screen table 4-5. Tdd screen fields field should be: meaning: cluster id a...
Page 26
Interpreting screen displays ms-4900, rev. A 4–5 active sessions screen fields this summary screen lists the total number of active sessions for all logical receivers, and is meaningful only in terms of stat mux processing. An active session means the receiver currently has data addressed to it and ...
Page 27
Interpreting screen displays 4–6 ms-4900, rev. A check output ports evaluate the output error indications based on whether output was being displayed successfully: output data has been displaying successfully and has suddenly stopped: check flow control and logical receiver memory utilization, as in...
Page 28
Interpreting screen displays ms-4900, rev. A 4–7 table 4-7. Logical receiver status fields field should be: meaning: logical receiver r0 through r3 status only note: logical receivers are assigned in stat mux operation only serial port r0 = serial 1 r1 = serial 2 r2 = serial 3 r3 = serial 4 port bei...
Page 29
Interpreting screen displays 4–8 ms-4900, rev. A table 4-8. Setup of serial ports field should be: meaning: port mode • pad or node • df • pd/nd • mode • default destination; data addressed to df ports will go to this receiver • data addressed to pad ports will go to this receiver; data addressed to...
Page 30
Interpreting screen displays ms-4900, rev. A 4–9 check output ports (cont’d) the diagnostics screens provide a serial port test through which you can send a repeating test pattern to the designated port. The test pattern continues through that port until you press the cancel button. Any network data...
Page 31: Verifying
Interpreting screen displays 4–10 ms-4900, rev. A verifying ethernet screens additional screens within the view setup and specify setup main topics provide information relevant to the ethernet model of the idr v1000. This section describes the contents of those screens. Note: the following screens d...
Page 32
Interpreting screen displays ms-4900, rev. A 4–11 snmp trap ip address this is the address of the computer running the snmp manager software and to which the idr v1000 can report its status events (such as acquiring or losing carrier lock). Assuming both the snmp server and the idr v1000 are connect...
Page 33: Examining
Interpreting screen displays 4–12 ms-4900, rev. A examining system messages you can examine system messages to get an indication of receiver activity over a span of time. The idr v1000 stores up to three user messages and three system messages in memory, each of which reflects an event in the receiv...
Page 34: Network
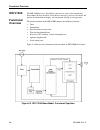
Ms-4900, rev. A 5– 1 section 5. Functional overview this section describes the function of the idr v1000 within a wavephore network: • “network overview” gives the “big picture” from point of origin to display on • “modes of moving data” describes some of the fundamental terms and concepts you need ...
Page 35
Functional overview 5– 2 ms-4900, rev. A the ncc: input and output input to the ncc consists of data feeds arriving through the access network. This can be data originating from a remote or local computer. Some of this data is processed in the statistical multiplexer, commonly called a stat mux. The...
Page 36
Functional overview ms-4900, rev. A 5– 3 figure 5-1. A sample wavephore network and the flow of data.
Page 37: Modes of
Functional overview 5– 4 ms-4900, rev. A the receiver: input and output input to the idr v1000 comes from the satellite dish. The downlinked data stream is amplified and shifted to a lower frequency by the lnb on the satellite dish and passed through the coaxial cable to the idr v1000. The receiver ...
Page 38
Functional overview ms-4900, rev. A 5– 5 stat mux data statistically-multiplexed data contains the message itself—a part of a news story or weather report—along with overhead information about the message, such as its length, its origin, and its destination. Destination information directs data to a...
Page 39
Functional overview 5– 6 ms-4900, rev. A table 5-1 reflects the availability and usage of the five possible serial ports, depending on the nature of the received data: transparent asynchronous, statistically- multiplexed, or transparent synchronous, or combinations thereof. Note: the functionality o...
Page 40
Functional overview ms-4900, rev. A 5– 7 pad mode and pvc sessions pad mode ports output original news stories directly. For pvc sessions, the output is straightforward: for any pvc session (of which only one is deliverable to any pad logical receiver), incoming stories are delivered to the logical ...
Page 41: Idr V1000:
Functional overview 5– 8 ms-4900, rev. A idr v1000: functional overview the idr v1000 receives, demodulates, and corrects errors in the transmission, disassembles the data stream to extract discrete messages, processes the blocks and packets of information for display, and can monitor and log its ow...
Page 42
Functional overview ms-4900, rev. A 5– 9 signal input: lnb and tuner the idr v1000 connects to the lnb on the satellite dish through the coaxial cable attached to the rear panel rf connector. The lnb (low noise block converter) receives power from the receiver, maps satellite signals to a pre-determ...
Page 43
Functional overview 5– 10 ms-4900, rev. A figure 5-4. Reed-solomon model, functional depiction time-division demultiplexer (tdd) after the signal has been demodulated and passed through error-correction, the aggregate data stream moves into the time-division demultiplexer, or the tdd. The tdd separa...
Page 44
Functional overview ms-4900, rev. A 5– 11 demultiplexing capability. As shown in figure 5-3, the processor connects to the tuner, controlling its frequency setting and the bit rate used by the demodulator. The processor programs the tdd at start-up to match the frame image stored in memory. The tdd ...
Page 45
Functional overview 5– 12 ms-4900, rev. A buffering and flow control buffering and flow control are important concepts related to moving the data through the output ports. The buffer is the area of ram in the idr v1000 allocated to temporarily store processed data when the external computer is unrea...
Page 46
Functional overview ms-4900, rev. A 5– 13 figure 5-5. Four-port daughtercard model.
Page 47
Functional overview 5– 14 ms-4900, rev. A figure 5-6. Ethernet model, functional depiction the ethernet model contains two independent logical receivers: • serial 1 asynchronous • ethernet high-speed synchronous sync/ethernet logical receiver status can be checked in two ways: 1. Leds on the rear pa...
Page 48
Functional overview ms-4900, rev. A 5– 15.
Page 49: Idr V1000
Ms-4900, rev. A a-1 appendix a. Technical specifications idr v1000 the following specifications relate to the receiver’s functional characteristics and its external and environmental characteristics. Rf input level -85 dbm to -40 dbm rf input frequency 950 mhz to 1,525 mhz rf tuning synthesized, fro...
Page 50: Optional Daughtercards
Appendix a. Technical specifications a-2 ms-4900, rev. A remote control functions • carrier bit rate and modulation type • tdm channel selection • tune to new carrier frequency • statmux service selection (optional) • output port baud rate • permission/depermission output port remote receiver contro...
Page 51
Ms-4900, rev. A b-1 appendix b. Pin-out tables the pin-out tables describe the signal functions of the pin sockets for the asynchronous and synchronous serial output ports on the basic, reed-solomon, and the 4-port models, and the synchronous and 10base t output connections on the ethernet model. As...
Page 52: Ethernet
Appendix b pin-out tables b-2 ms-4900, rev. A ethernet the ethernet daughtercard contains three connectors: rs-422 (synchronous), aui (attachment unit interface, synchronous), and the 10base t. Synchronous rs-422 pin function signal direction (db-15 connector) 1 optional signal ground (set by intern...
Page 53
Appendix b pin-out tables ms-4900, rev. A b-3 10base t pin function signal direction 1 twisted pair + output 2 twisted pair - output 3 twisted pair + input 4 no connect n/a 5 no connect n/a 6 twisted pair - input 7 no connect n/a 8 no connect n/a.
Page 54
Appendix b pin-out tables b-4 ms-4900, rev. A.
Page 55: Screen Displays
Ms-4900, rev. A c-1 section1 . Appendix c. Idr v1000 screen displays the following fold-out pages depict the structure of the idr v1000 screen displays. The main topics are shown at the top of the pages. (the shaded-out topics are included on a different page.)to move from one screen to another on t...
Page 56: Glossary
Ms-4900, rev. A g-1 glossary access network the various routes by which data feeds originating in diverse locations come into the network control center for uplinking to wavephore networks acquisition the process by which the demodulator adjusts frequency, phase, gain, and code-word synchronization ...
Page 57
Glossary g-2 ms-4900, rev. A downlink information transmitted to an earth station from a satellite. Download control information transmitted from a network control center to a receiver eeprom electronic eraseable programmable read-only memory. Ethernet a popular local area network (lan) implementati...
Page 58
Glossary ms-4900, rev. A g-3 node mode of operation using a transport protocol that enables packets to be individually read, error-checked, reassembled, and output as integral blocks of information. The output blocks are packets of type “extract protocol.” used only with wavephore proprietary softwa...
Page 59
Glossary g-4 ms-4900, rev. A session a communication circuit selected for use by the idr v1000 when configured for stat demux operation. Active sessions in the screen display describe current stat mux activity statistical multiplexer also stat mux. A technique of time-sharing on a data stream that a...
Page 60
Glossary ms-4900, rev. A g-5 volatile memory segment of processor memory that is lost when power is turned off or interrupted. In the idr v1000, certain commands or settings, such as those used to perform a real-time function or enter a test mode, are temporarily stored in volatile memory. (configur...
Page 61
Glossary g-6 ms-4900, rev. A.
Page 62: Section1 . Index
Ms-4900, rev. A i-1 section1 . Index a agc troubleshooting signal strength, 4-3 verifying after installation, 2-3 active sessions fields, 4-5 automatic gain control see agc b buffering described, 5-11 c cables coaxial cable specifications, 5-9 connecting, 2-2 troubleshooting, 4-2, 4-3 checking agc. ...
Page 63
Index i-2 ms-4900, rev. A m main topics illustrated, 3-1 device restart, 3-6 diagnostics, 4-9 logoff, 3-7 messages, 3-2 set features, 3-6, 4-12 show status, 3-3, 4-2, 4-6 specify setup, 3-4 view setup, 3-3, 4-7, 4-8 viewing, 3-1 maintaining the equipment check alignment, 2-4 remove snow, 2-4 memory ...