- DL manuals
- 3Com
- Switch
- 3C63311 - SuperStack II PathBuilder S310 Bridge/router
- Reference Manual
3Com 3C63311 - SuperStack II PathBuilder S310 Bridge/router Reference Manual
Summary of 3C63311 - SuperStack II PathBuilder S310 Bridge/router
Page 1
Http://www.3com.Com/ ¨ superstack ® ii pathbuilder ® s330/s310 wan access switches reference guide release 2.03 part no. 010-11941-0004 published december 1998.
Page 2
3com corporation 5400 bayfront plaza santa clara, california 95052-8145 copyright © 1998, 3com corporation. All rights reserved. No part of this documentation may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to make any derivative work (such as translation, transformation, or adaptation) withou...
Page 3: Ontents
C ontents w arning i nformation servicing ix rack mounting ix power and power cords x emi x safety classification of ports for connection to telecommunications networks x s upplementary r egulatory i nformation fcc part 68 statement xi canadian cs-03 approval information xi ce notice xii a bout t hi...
Page 4
Step 4: connect i/o cabling 40 connecting to the t1/e1 uni interface 42 connecting to the serial port 42 connecting to the ethernet port 51 connecting to the oc3/stm-1 port 52 connecting to the cbr module 53 connecting to the voice compression module 55 connecting to the ds3/e3 module 56 step 5: con...
Page 5
Configuring ctx buffers 86 setting congestion thresholds 88 configuring ports 88 configuring the t1/e1 interface 89 configuring the t1/e1 ports 89 activation/deactivation bit error rates 91 configuring uni and ima groups 92 adding uni groups 92 adding ima groups 94 viewing and modifying ima and uni ...
Page 6
Virtual circuit parameters 151 common virtual circuit parameters 151 mcpu virtual circuit parameters 151 t1/e1 uni port virtual circuit parameters 151 oc3/stm-1 port virtual circuit parameters 151 serial port virtual circuit parameters 151 ethernet port virtual circuit parameters 154 cbr module virt...
Page 7
Viewing t1/e1 uni card statistics 186 t1/e1 port/link statistics 187 t1/e1 group statistics 188 viewing oc3/stm-1 card statistics 189 viewing oc3/stm-1 performance statistics 189 viewing oc3/stm-1 atm statistics 191 viewing ds3 card statistics 192 viewing ds3 uni performance statistics 192 viewing d...
Page 8
B p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odule and a pplication o verview management cpu 209 ctx switch 209 ctx output queues and memory partition 210 setting up a virtual circuit 211 vpi and vci ranges 212 early and partial packet discard 212 t1/e1 uni interface 212 oc3/stm-1 port 213 ds3/e3 uni modules 213 se...
Page 9: Arning
W arning i nformation this section contains warning information for ac-powered systems. Caution: use of controls or adjustments of performance or procedures other than those specified herein may result in hazardous radiation exposure. Caution: danger of explosion if battery is incorrectly replaced. ...
Page 10
X c hapter : w arning i nformation power and power cords this equipment is not intended for use with it power distribution systems whose line to line voltage exceeds 250 vac rms defined by en 60950 as having no direct connection to earth. The pathbuilder s330/s310 will auto-configure for 115 vac or ...
Page 11: Upplementary
S upplementary r egulatory i nformation this section describes the compliance of the superstack ® ii pathbuilder ® s330 and the superstack ® ii pathbuilder ® s310 wan access switches (pathbuilder s330/s310) with fcc, industry canada, and ce regulations. Fcc part 68 statement this equipment complies ...
Page 12
Xii c hapter : s upplementary r egulatory i nformation repairs to certified equipment should be made by an authorized canadian maintenance facility designated by the supplier. Any repairs or alterations you make to this equipment, or equipment malfunctions, may give the telecommunications company ca...
Page 13: Bout
A bout t his g uide about this guide provides an overview of this guide, tells you where to look for specific information, and describes guide conventions. Introduction this guide describes how to install and configure the superstack ® ii pathbuilder ® s330 and superstack ® ii pathbuilder ® s310 wan...
Page 14
2 a bout t his g uide conventions table 2 and table 3 list conventions that are used throughout this guide. Related documentation in addition to this guide, the following documentation may help you use the pathbuilder s330/s310: pathbuilder s330/s310 release notes—provides configuration help and inf...
Page 15: Ystem
1 s ystem d escription this chapter describes the superstack ® ii pathbuilder ® s330 and superstack ® ii pathbuilder ® s310 wan access switches (pathbuilder s330/s310), and lists pathbuilder s330 and pathbuilder s310 system specifications. It includes the following sections: n pathbuilder s330/s310 ...
Page 16
4 c hapter 1: s ystem d escription n choice of either single-mode or multi-mode oc3/stm-1 (separate units), through the oc3/stm-1 module. Single-mode enables higher-speed trunking if you have access to fiber wan, while multi-mode is ideal for connecting high-speed servers, switches, or hubs equipped...
Page 17
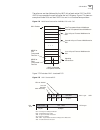
Pathbuilder s330/s310 overview 5 figure 1 pathbuilder s330 wan access switch pathbuilder s310 features the pathbuilder s310 is a feature-restricted version of the pathbuilder s330 providing remote site cpe access. Its physical appearance is the same as that of the pathbuilder s330 but its software d...
Page 18
6 c hapter 1: s ystem d escription the following optional modules are available for use with the pathbuilder s310: n the two-port cbr module services traffic generated by your existing pbxs, channels, t1/e1 multiplexers, csu/dsus, and video conferencing devices. The cbr module consists of one v.35/r...
Page 19
Pathbuilder s330/s310 overview 7 application support the pathbuilder s330/s310 supports the following applications: s330 only n 4 x t1/e1 ima function on the trunk, up to four trunk groups (individual t1s/e1s) n single t1/e1 for pathbuilder s310 s330 only n oc3/stm-1 uni port interface (multi-mode o...
Page 20
8 c hapter 1: s ystem d escription n easily upgradable; no additional hardware required to move from the pathbuilder s310 to the pathbuilder s330; update your system simply by purchasing a software upgrade. N a sophisticated traffic management system allows management of a mix of applications simult...
Page 21
Specifications 9 regulatory compliance safety emissions ul listed (1950, 3rd edition) csa 22.2 en60950 fcc part 68 fcc part 15, class a standards atm forum uni 3.X, t1/e1 ces 2.0, ima, atm dxi 1.0 ansi t1.403, t1.617 annex d tia/eia eia232, 574, 449/422/423, 366 at&t pubs 62411 and 54016 frame relay...
Page 22
10 c hapter 1: s ystem d escription ethernet interface number of ports interface type connector type connector pinouts data support atm support shaping forwarding rate 1 vc level, dual leaky bucket, 56kbps to 6mbps rj48 pin 1 - tx+ pin 2 - tx- pin 3 - rx+ pin 4 - pin 5 - pin 6 - rx- pin 7 - pin 8 - ...
Page 23
Specifications 11 oc3/stm-1 interface number of ports interface type connector type line code fiber type wavelength receiver input power transmit output power clock application support atm support 1 sr or ir duplex sc sonet scrambled, nrz multi-mode or single-mode 1300nm -30.0 dbm minimum (sr), -31 ...
Page 24
12 c hapter 1: s ystem d escription connector type at end of rs-422 cable connector pinouts db-37 subminiature, female for dce, male for dte a side b side chassis ground 1 send data 4 22 send timing 5 23 receive data 6 24 req to send 7 25 receive timing 8 26 clear to send 9 27 terminal ready 12 30 r...
Page 25
Specifications 13 connector type at end of x.21 cable x.21 dte cable pinouts (60-pin connector) to db-15 male db-15 subminiature, female for dce, male for dte signal pin # on pin # on direction (for name 60-pin db-15 serial port) frame gnd 46 1 circuit gnd 15 8 rts 9,10 3,10 out cts 1,2 5,12 in dsr ...
Page 26
14 c hapter 1: s ystem d escription x.21 dce cable pinouts (60-pin connector) to db-15 female signal pin # on pin # on direction name 60-pin db-15 (for qsim) frame gnd 46 1 circuit gnd 15 8 rts 1,2 3,10 in cts 9,10 5,12 out dsr out dcd (not used; tristate when in dte mode) dtr in ll (not used) in sd...
Page 27
Specifications 15 cbr module specifications number of ports interface type(s) t1-dsx/e1 physical impedance framing line coding lbo serial clock front panel leds (1-3) data rates atm support timing cell delay variation tolerance class of service t1-dsx/e1connector type t1-dsx/e1 connector pinouts 4 3...
Page 28
16 c hapter 1: s ystem d escription connector type at end of v.35/rs-366 cable connector pinouts db-25 subminiature, female for dce from to frame ground j1-46 j2-a circuit ground j1-45 j2-b rts j1-35 j2-c cts j1-42 j2-d dsr j1-43 j2-e dcd j1-44 j2-f dtr j1-34 j2-h ll j1-33 j2-k sd+ j1-28 j2-p sd- j1...
Page 29
Specifications 17 voice compression module specifications number of ports interface type(s) t1-dsx/e1 physical impedance framing line coding lbo clock front panel leds (1-7) data rates atm support timing class of service t1-dsx/e1connector type t1-dsx/e1 connector pinouts frame relay support compres...
Page 30
18 c hapter 1: s ystem d escription table 5 pathbuilder s310 system specifications system specifications ethernet 10 base t 1 v.35/rs422 1 t1/e1 uni 1 mechanical: shelf dimensions 19” rack mountable rack mount spacing cooling unit weight (approx.) shipping weight (approx.) 3.5” x 17” x 15.25” (h x w...
Page 31
Specifications 19 front panel leds: common ethernet serial t1 power, status, alert tx, rx, link td, rd alert, active management interface interface type connector type connector pinouts rs-232c female db-9 pin 1 - carrier detect pin 2 - rx data pin 3 - tx data pin 4 - dtr pin 5 - signal ground pin 6...
Page 32
20 c hapter 1: s ystem d escription t1/e1 uni interface number of ports type of interface connector type connector pinouts framing line coding atm framing atm support lbo electrical interface attenuation payload scrambling 1 t1/e1 (with integral csu and dsx) rj48c or g703 coax with e1 balun adapter ...
Page 33
Specifications 21 serial interface number of ports interface type data support atm support clock shaping data rates: minimum maximum maximum cable length clock outputs connector type on unit 1 hd 60-pin (dce or dte), female; v.35/rs-449/eia530 (through cable converters) transparent hdlc/sdlc, frame ...
Page 34
22 c hapter 1: s ystem d escription connector type at end of eia530 cable connector pinouts db-25 subminiature, female for dce, male for dte a side b side chassis ground 1 send data 2 14 send timing 15 12 receive data 3 16 req to send 4 19 receive timing 17 9 clear to send 5 13 terminal ready 20 23 ...
Page 35
Specifications 23 x.21 dce cable pinouts (60-pin connector) to db-15 female signal pin # on pin # on direction name 60-pin db-15 (for qsim) frame gnd 46 1 circuit gnd 15 8 rts 1,2 3,10 in cts 9,10 5,12 out dsr out dcd (not used; tristate when in dte mode) dtr in ll (not used) in sd+ 28 2 in sd- 27 9...
Page 36
24 c hapter 1: s ystem d escription cbr module specifications number of ports interface type(s) t1-dsx/e1 physical impedance framing line coding lbo serial clock front panel leds (1-3) data rates atm support timing cell delay variation tolerance class of service t1-dsx/e1 connector type t1-dsx/e1 co...
Page 37
Specifications 25 connector type at end of v.35/rs-366 cable connector pinouts db-25 subminiature, female for dce from to frame ground j1-46 j2-a circuit ground j1-45 j2-b rts j1-35 j2-c cts j1-42 j2-d dsr j1-43 j2-e dcd j1-44 j2-f dtr j1-34 j2-h ll j1-33 j2-k sd+ j1-28 j2-p sd- j1-27 j2-s rd+ j1-18...
Page 38
26 c hapter 1: s ystem d escription voice compression module specifications number of ports interface type(s) t1-dsx/e1 physical impedance framing line coding lbo clock front panel leds (1-7) data rates atm support timing class of service t1-dsx/e1connector type t1-dsx/e1 connector pinouts frame rel...
Page 39
Options and parts list 27 options and parts list the tables below list available pathbuilder s330/s310 options. Contact 3com or your var with the appropriate part number for ordering and pricing information. Table 6 pathbuilder s330 part numbers part number description 3c63300a-ac-nc superstack ii p...
Page 40
28 c hapter 1: s ystem d escription 3c63504 optional two-port cbr module with one t1-dsx port and one v.35/rs-449 port 3c63504 optional two-port cbr module with one e1 port and one v.35/rs-449 port 3c63311 optional ds1 voice compression module + 1 simm 3c63314 optional e1 voice compression module + ...
Page 41: Nstallation
2 i nstallation this chapter tells you how to mechanically and electrically install superstack ® ii pathbuilder ® s330 and superstack ® ii pathbuilder ® s310 wan access switches (pathbuilder s330/s310) in your network and describes the pathbuilder s330/s310 ports and modules. It contains the followi...
Page 42
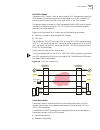
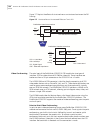
30 c hapter 2: i nstallation installation overview figure 3 summarizes the overall installation procedure for the pathbuilder s330/s310. Figure 3 general installation procedure prepare the site: verify clearance around the shelf site step 1 install the optional modules install the unit in the rack s...
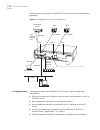
Page 43
Installation overview 31 figure 4 shows an example of a pathbuilder s330 configuration with all of the associated cabling connected. Figure 4 pathbuilder s330 full system configuration lan nms console rs-232 router pbx pbx t1-dsx/e1 t1-dsx/e1 oc3/stm-1 n x t1/e1 ima 10base-t v.35/ rs-449/ rs-530/ x....
Page 44
32 c hapter 2: i nstallation figure 5 shows an example of a pathbuilder s310 with all of the associated cabling connected. Figure 5 pathbuilder s310 full system configuration site requirements the operating site for the pathbuilder s330/s310 must meet the following requirements: n be within the maxi...
Page 45
Installation procedures 33 installation procedures this section provides detailed instructions for completing the steps in the installation procedure illustrated earlier in figure 3. Step 1 (optional): install the optional modules in the unit this section tells you how to install the optional module...
Page 46
34 c hapter 2: i nstallation n voice compression module—a board consisting of one t1-dsx or e1 interface. It services traffic generated by your existing pbxs, channels, t1/e1 multiplexers, csu/dsus, and video conferencing devices. Install the voice compression module in slot 7 or slot 8. Figure 7 sh...
Page 47
Installation procedures 35 installing the optional modules in the unit to install an option module in the unit, follow these steps: caution: many of the integrated circuits on the modules are sensitive to static electricity. When installing plug-in modules, always wear a properly-grounded anti-stati...
Page 48
36 c hapter 2: i nstallation 3 remove the cover plate from the slot into which you want to install the optional module by unscrewing the two retaining screws. Figure 11 shows the retaining screws being removed from slot 7. Figure 11 removing the cover plate from slot 7 4 insert the optional card int...
Page 49
Installation procedures 37 5 replace the unit’s cover. A slide the cover back into place so that the five tabs go under the lip of the front panel (arrow 1) and push it down at the rear (arrow 2), as shown in figure 13. Figure 13 replacing the pathbuilder s330/s310 cover b secure the cover with the ...
Page 50
38 c hapter 2: i nstallation figure 14 rack mounting ear configuration 3 support the shelf in its mounting place and attach the mounting hardware. Step 3: connect ac or dc power and (optionally) the rps system you connect the ac/dc power at the rear of the pathbuilder s330/s310 shelf. Table 10 outli...
Page 51
Installation procedures 39 caution: centralized 48vdc units -to be installed only in restricted access areas (dedicated equipment rooms, equipment closets, etc.) in accordance with articles 110-16 or 110-17, and 110-18 of the national electrical code, ansi/nfpa no.70. 1 turn off the ac/dc power sour...
Page 52
40 c hapter 2: i nstallation figure 16 illustrates the power supply socket and fuse. Figure 16 superstack ii rps power supply socket and fuse the pathbuilder s330/s310 automatically adjusts to the supply voltage. The fuse is suitable for both 110v ac and 220-240v ac operations. To change the fuse, f...
Page 53
Installation procedures 41 figure 17 pathbuilder s330/s310 common leds figure 18 shows the port configuration of a pathbuilder s330/s310. Figure 18 pathbuilder s330/s310 ports and cbr module the following sections tell you how to make connections to the ports of the pathbuilder s330/s310. Alert stat...
Page 54
42 c hapter 2: i nstallation connecting to the t1/e1 uni interface as shown above in figure 18, the pathbuilder s330 t1/e1 uni with ima interface provides four t1/e1 ports. You can connect a single t1/e1 line to this interface, or connect up to four t1/e1 lines and combine them to form a logical, in...
Page 55
Installation procedures 43 the following tables describe the serial port connector pinouts. Note that pathbuilder s330/s310 cables are compatible with cisco cables, except for the dce eia530 which cisco does not manufacture. Table 11 connector pinouts for v.35 dte cable (60-pin connector) to v.35 ma...
Page 56
44 c hapter 2: i nstallation table 12 connector pinouts for v.35 dce cable (60-pin connector) to v.35 female signal name pin # on 60- pin connector pin # on v.35 connector direction (for serial port) frame gnd 46 a circuit gnd 45 b rts 35 c in cts 42 d out dsr 43 e out dcd 44 f out dtr 34 h in ll (n...
Page 57
Installation procedures 45 table 13 connector pinouts for rs-449 dte cable (60-pin connector) to db-37 male signal name pin # on 60-pin connector pin # on db-37 connector direction (for serial port) frame gnd 46 1 circuit gnd 15, 16, 45 19, 20, 37 rts 9, 10 7, 25 out cts 1, 2 9, 27 in dsr 3, 4 11, 2...
Page 58
46 c hapter 2: i nstallation table 14 connector pinouts for rs-449 dce cable (60-pin connector) to db-37 female signal name pin # on 60-pin connector pin # on db-37 connector direction (for serial port) frame gnd 46 1 circuit gnd 15, 16, 30 19, 20, 37 rts 1, 2 7, 25 in cts 9, 10 9, 27 out dsr 7, 8 1...
Page 59
Installation procedures 47 table 15 connector pinouts for eia530 dte cable (60-pin connector) to db-25 male signal name pin # on 60-pin connector pin # on db-25 connector direction (for serial port) frame gnd 46 1 circuit gnd 45 7 rts 9, 10 4, 19 out cts 1, 2 5, 13 in dsr 3, 4 6, 22 in dcd (not used...
Page 60
48 c hapter 2: i nstallation table 16 connector pinouts for eia530 dce cable (60-pin connector) to db-25 female signal name pin # on 60-pin connector pin # on db-25 connector direction (for serial port) frame gnd 46 1 circuit gnd 45 7 rts 1, 2 4, 19 in cts 9, 10 5, 13 out dsr 7, 8 6, 22 out dcd (not...
Page 61
Installation procedures 49 table 17 connector pinouts for x.21 dte cable (60-pin connector) to db-15 male signal name pin # on 60-pin connector pin # on db-25 connector direction (for serial port) frame gnd 46 1 circuit gnd 15 8 rts 9, 10 3, 10 out cts 1, 2 5, 12 in dsr in dcd (not used, see dce cab...
Page 62
50 c hapter 2: i nstallation serial port leds in addition to the common leds described earlier in this chapter, the following leds indicate the status of the serial port. See figure 20. Rd active (green)—flashes with receiving signals. Td active (green)—flashes with transmitting signals. Figure 20 p...
Page 63
Installation procedures 51 connecting to the ethernet port to connect to the ethernet port, run a cable from the port to the lan. The link led illuminates if you make the connection properly. The cable run from the pathbuilder s330/s310 ethernet port to the ethernet lan connection must be no longer ...
Page 64
52 c hapter 2: i nstallation connecting to the oc3/stm-1 port s330 only the oc3/stm-1 uni port is equipped with an internal sc-type connector supporting the use of multi-mode or single-mode fiber optic cable, as shown in figure 22 and figure 23. Figure 22 oc3/stm-1 uni (multi-mode fiber optic cable)...
Page 65
Installation procedures 53 oc3/stm-1 leds in addition to the common leds described earlier in this chapter, the following leds indicate the status of the oc3/stm-1 port. (see figure 24.) oc3/stm-1 alert (red)—powers up in the “off” state and illuminates when a loss of signal (los), loss of frame (lo...
Page 66
54 c hapter 2: i nstallation table 20 lists the cbr v.35/rs-366 y cable pinouts. Table 20 cbr v.35/rs-366 connector pinouts connector type at end of v.35/rs-366 cable connector pinouts db-25 subminiature, female for dce from to frame ground j1-46 j2-a circuit ground j1-45 j2-b rts j1-35 j2-c cts j1-...
Page 67
Installation procedures 55 cbr module leds the cbr module features the following front panel indicators: inservice (green)—powers up in the “off” state and illuminates when you set the administrative status of the t1-dsx/e1 or serial port to in service. See “configuring the cbr module” in chapter 4 ...
Page 68
56 c hapter 2: i nstallation the voice compression module features the following front panel indicators, as illustrated in figure 26: pwr—illuminates when the vcm is receiving power. Fail—illuminates when the vcm card fails. Test—illuminates during powerup, as internal diagnostics are being performe...
Page 69
Installation procedures 57 lof (red)—powers up in the “off” state and illuminates when a lof (loss of frame) condition is detected on the incoming ds3. The lof led is off when the signal is in frame. It reflects the lof state of the ds3 in real time (no integration of the state is needed). Locd (red...
Page 70
58 c hapter 2: i nstallation figure 28 illustrates the network management station terminal connection options. Figure 28 network management station terminal connection options lan vt-100 nms terminal rs-232 10base-t.
Page 71: Etting
3 g etting s tarted this chapter tells you how to initialize and prepare superstack ® ii pathbuilder ® s330 and superstack ® ii pathbuilder ® s310 wan access switches (pathbuilder s330/s310) for operation and how to use the pathbuilder s330/s310 menus. It contains the following sections: n logging o...
Page 72
60 c hapter 3: g etting s tarted when the pathbuilder s330/s310 is powered up and operating, and your terminal is connected, operating, and properly configured, the title screen shown in figure 30 appears on your terminal. Figure 30 nms pathbuilder s330/s310 title screen the title screen identifies ...
Page 73
Using the menus 61 use the options on the main menu as follows: n select [1] system administration to access common parameters. N select [2] configuration management to view or set configuration parameters for cards, ports, pvcs, video dialup, and other hardware and software features. N select [3] f...
Page 74
62 c hapter 3: g etting s tarted using the menus to change settings settings are displayed in prompts at the bottom of the menus. For example, if you select [2] configuration management [1] manage card [4] oc3/stm-1 uni [3] set atm payload scramble the following prompt appears at the bottom of the s...
Page 75
Performing initial system configuration 63 performing initial system configuration after you install the pathbuilder s330/s310 hardware, you must complete the following three steps in order to put the unit into operation: 1 configure the system clock 2 set up communication parameters 3 set the time ...
Page 76
64 c hapter 3: g etting s tarted to set system clocks, follow these steps: 1 from the system administration menu, select [4] manage system clock to display the system clock configuration menu, shown in figure 34. Figure 34 system clock configuration menu 2 select [3] set priorityclock 1 to specify t...
Page 77
Performing initial system configuration 65 figure 35 manage ip network configuration menu configuring the local host ip address in order for the pathbuilder s330/s310 to communicate on the network, you must use the vt100 terminal to assign an ip address to the device. Once you have entered the ip ad...
Page 78
66 c hapter 3: g etting s tarted 2 select [1] ethernet port ip configuration to display the ethernet port ip configuration menu, shown in figure 37. Figure 37 ethernet port ip configuration menu 3 enter the following information (by selecting the appropriate options and responding to the prompts tha...
Page 79
Performing initial system configuration 67 the ip address does not take effect until you apply your changes by selecting [2] apply ip configuration changes from the local host ip configuration menu (step 5 above). Configuring trap clients trap clients are the network management stations to which you...
Page 80
68 c hapter 3: g etting s tarted 3 enter the following information (by selecting the appropriate options and responding to the prompts that appear at the bottom of the screen) to configure the trap client: ip address—the ip address of the network management station to which you want the pathbuilder ...
Page 81
Performing initial system configuration 69 setting the time and date to set the time and date, follow these steps: it is important to set the time and date accurately because these settings provide the timestamp for alarms. 1 from the system administration menu, select [2] manage time and date to di...
Page 82
70 c hapter 3: g etting s tarted this section tells you how to set passwords. For details about how to take over read-write sessions and how to erase the system database, see “performing additional super user functions” later in this chapter. The default password for all three access levels is passw...
Page 83
Performing additional super user functions 71 3 select [1] set super user password, [2] set read-write password, or [3] set read-only password to set the desired password. The following prompt appears at the bottom of the screen: enter new password: 4 enter the new password. The password appears as ...
Page 84
72 c hapter 3: g etting s tarted to erase the system database, follow these steps: caution: before you erase the system database, make a record of all configuration settings; these settings will be lost when you erase the database. Also keep in mind that erasing the database is an action that cannot...
Page 85
Configuring in-band management 73 figure 45 add virtual circuit menu 3 build a pvc on the far-end pathbuilder s330/s310, using the mcpu as side a of the circuit. Set the following parameters on the add virtual circuit screen: n shaper number—choose the number corresponding to the desired shaper valu...
Page 86
74 c hapter 3: g etting s tarted.
Page 87: Onfiguring
4 c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications this chapter tells you how to configure the superstack ® ii pathbuilder ® s330 and superstack ® ii pathbuilder ® s310 wan access switches’ (pathbuilder s330/s310) cpu, modules, ports, and related applications so that the d...
Page 88
76 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications figure 46 system administration menu specifying general system information general system information includes the following: n shelf name n customer name n phone number n maintenance contact n location n auto...
Page 89
Viewing and configuring system information 77 figure 47 specifying general system information viewing rs-232 port configuration information you enter initial configuration information using the vt100 terminal connected to the pathbuilder s330/s310’s rs-232 port. See “logging on” in chapter 3, for de...
Page 90
78 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications the report firmware version screen displays the following information about the management processor active firmware (the upgradeable firmware currently being used by the mcpu): version—the released firmware v...
Page 91
Viewing and configuring system information 79 downloading via the ethernet port to download new firmware using tftp, via the ethernet port, follow these steps: be sure to log in via telnet. If you log in at a serial port, the download sequence will attempt an xmodem rather than a tftp download. 1 ob...
Page 92
80 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications updating the flash file system the flash file system contains system configuration information which is automatically saved in flash memory at a predetermined interval. To update the flash file system immediat...
Page 93
Using the configuration management menu 81 the equipment list displays the following information for each installed module: slot—slot number. This is a reference number for the ports on the motherboard. This number corresponds to the number on the list card menu. (see figure 51, later in this chapte...
Page 94
82 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications using the list card menu the list card menu, shown in figure 51, lists the shelf and all installed interfaces. To display the list card menu follow these steps: 1 from the main menu select [2] configuration ma...
Page 95
Configuring the management cpu 83 figure 52 mcpu configuration menu viewing mcpu configuration information to view configuration information for the management cpu: from the mcpu configuration menu, select [1] card configuration to open the management processor configuration screen. This screen disp...
Page 96
84 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications caution: when assigning shapers for vcm circuits, be sure that the shapers are wider than the bandwidth used for the voice traffic. To configure the mcpu shapers, follow these steps: 1 from the mcpu card menu,...
Page 97
Configuring the ctx 85 configuring the ctx ctx configuration involves managing buffers and managing shapers. To display the ctx menu, follow these steps: 1 from the configuration management menu, in figure 50, select [1] manage card to display the list card menu, shown earlier in figure 51. 2 select...
Page 98
86 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications you can assign shapers for these queue-trunks based on peak rate (or bulk shaping) towards the wan. To do this, follow these steps: 1 from the configuration management menu, select [1] manage card to display t...
Page 99
Configuring the ctx 87 figure 56 ctx buffers menu 4 select the number corresponding to the queue for which you want to change the buffer size. The ctx queue buffer configuration menu, shown in figure 57, appears. This menu lists the current buffer configuration for the selected queue and provides op...
Page 100
88 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications when you select one of these options, a prompt appears at the bottom of the screen, allowing you to enter a new threshold in the range 0% to 100%. When the buffer reaches the congestion on threshold, the conge...
Page 101
Configuring the t1/e1 interface 89 configuring the t1/e1 interface configuring the t1/e1 interface involves the following tasks: n configuring the four individual t1/e1 ports n setting up and configuring uni and/or ima groups (if desired) n viewing ima link and group status n configuring the t1/e1 c...
Page 102
90 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications figure 59 t1 (ds1) uni port selection menu 4 select the number corresponding to the t1/e1port you want to configure to open the port configuration menu. Figure 60 shows a t1 (ds1) uni port configuration menu. ...
Page 103
Configuring the t1/e1 interface 91 lbo (t1 only)—line build out. The setting for the transmit signal level: 0, 7.5, 15, or 22 db. The lbo compensates for the distance between the card and the csu/repeater. It is a setting for the transmit signal level. Framing—the type of frame organization configur...
Page 104
92 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications the t1 (ds1)/e1 uni configuration menu lists the following additional read-only parameters: group—the number of the group to which the ports belong. Tx lid—transmit link identification. This should match the r...
Page 105
Configuring the t1/e1 interface 93 figure 61 group menu 4 select [2] add group to display the add group menu, shown in figure 62. Figure 62 add group menu (selecting group type) 5 select [1] uni. The add group menu appears as shown in figure 63..
Page 106
94 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications figure 63 add group menu (adding uni group) 6 select [1] set admin. Port(s). The following prompt appears at the bottom of the screen: enter admin port(s): 7 enter the port numbers for the t1/e1 port you want ...
Page 107
Configuring the t1/e1 interface 95 figure 64 group menu 4 select [2] add group to display the add group menu, shown in figure 65. Figure 65 add group menu (selecting group type) 5 select [2] ima. The add group menu appears as shown in figure 66..
Page 108
96 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications figure 66 add group menu (adding ima group) 6 select [1] set admin. Port(s). The following prompt appears at the bottom of the screen: enter admin port(s) (1..4): 7 enter the port numbers for the t1/e1 ports y...
Page 109
Configuring the t1/e1 interface 97 viewing and modifying ima and uni groups once you have added a group, you use the list/modify group menu to view and modify group configuration parameters. To view and/or modify an existing group, follow these steps: 1 from the group menu, shown in figure 61, selec...
Page 110
98 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications figure 68 delete group menu 3 enter y in response to the confirmation prompt to delete the group. When you delete an ima group, all the vcs using that group are also deleted. Viewing ima link status to view im...
Page 111
Configuring the t1/e1 interface 99 figure 70 ima link status screen the ima link status screen lists the following information pertaining to the ima status of an individual link in an ima group. Ne tx state—the near-end transmit state in the interworking link state machine. Table 23 lists the possib...
Page 112
100 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications tx lid—transmit logical link id: 0-31. This number reflects the local ima id. Rx lid—receive logical link id: 0-31. This number reflects the remote ima id. Operation link delay—the differential link delay ref...
Page 113
Configuring the t1/e1 interface 101 figure 71 group status selection menu 4 enter the number corresponding to the group for which you want to view ima status. The ima group status screen for that group appears, as shown in figure 72. Figure 72 ima group status screen the ima group status screen list...
Page 114
102 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications failure—failure status: near end asymmetric—near end rejected asymmetrical configuration or operation chosen by the far end. Far end invalid m—far end rejected the m value chosen by the user on the near end. ...
Page 115
Configuring the t1/e1 interface 103 # rx configured links—the number of configured receive links. #tx active links—the number of active transmit links. #rx active links—the number of active receive links. Configuring the t1/ e1 card the only type of configuration you can perform on the t1/e1 uni car...
Page 116
104 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications configuring the oc3/stm-1 port to configure the oc3/stm-1 port, follow these steps: the pathbuilder s310 does not support oc3/stm-1; the oc3/stm-1 port is disabled on that device. 1 from the configuration man...
Page 117
Configuring the ds3/e3 uni module 105 configuring the ds3/e3 uni module to configure the ds3 uni or e3 uni module, follow these steps: 1 from the list card menu, select [9] ds3 uni to open the ds3 uni configuration menu. Figure 75 shows the ds3 uni configuration menu. The e3 uni configuration menu i...
Page 118
106 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications feac loopback (ds3 only)—enables or disables the system from responding to feac (far-end alarm condition) loopback commands (loopback activate and deactivate feac codes) from the central office. Feac is a ds3...
Page 119
Configuring the serial interface 107 configuring the serial port to configure the serial port, follow these steps: 1 from the configuration management menu, select [1] manage card to display the list card menu, shown earlier in figure 51. 2 from the list card menu, select [5] sim to display the sim ...
Page 120
108 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications figure 78 configuring the serial port 5 change the following parameters, as desired: link type—the input/output protocol for encapsulation and sar to aal5 conversion. Dxi —atm forum mode 1a sdlc—itu standard ...
Page 121
Configuring the serial interface 109 data rate—the data rate supported by the port: 48k, 97k, 195k, 390k, 781k, 1.5m, 3.1m, or 6.2m. This parameter applies only when the attached cable is dce type cable. It is a very important parameter, as it allows you to direct the sim to shape particular data ap...
Page 122
110 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications configuring the serial card the only type of configuration you can perform on the serial card is to put it in service or out of service. To set the administrative status of the serial card, follow these steps...
Page 123
Configuring the ethernet interface 111 figure 81 ethernet configuration port/card selection menu 3 select [1] port 1 to display the ethernet port configuration menu, shown in figure 82. This menu displays the current ethernet port configuration and provides an option that allows you to set the admin...
Page 124
112 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications 3 select [2] card information to display the ethernet card configuration menu, shown in figure 83. This menu displays the current ethernet card configuration and provides an option that allows you to set the ...
Page 125
Configuring the ethernet interface 113 figure 84 manage bridge menu 2 from the manage bridge menu, select [1] bridge configuration to display the bridge configuration menu, shown in figure 85. The current aging timer setting is displayed below the menu title (3 minutes in the sample menu shown in th...
Page 126
114 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications figure 86 bridge menu from the bridge menu, you can: n configure source protocol filtering, source address filtering, and destination address filtering. N display the forwarding table for the bridge. N constr...
Page 127
Configuring the ethernet interface 115 to configure source protocol filtering, follow these steps: 1 from the bridge configuration menu, select [2] source protocol filtering to display the source protocol filter menu, shown in figure 87. Figure 87 source protocol filter menu the current statuses of ...
Page 128
116 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications figure 88 bridge setup menu 5 select [1] set source protocol filter. The following prompt appears at the bottom of the screen: enter source protocol filter (1=disable, 2=enable) 6 enter 2 to enable the source...
Page 129
Configuring the ethernet interface 117 to configure source address filtering, follow these steps: 1 from the bridge menu, select [3] source address filtering to display the source address filter menu, shown in figure 89. Figure 89 source address filter menu 2 select [2] add source filter address. Th...
Page 130
118 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications configuring destination address filtering destination address filtering prevents lan packets with destination addresses specified in the filter from being sent to the wan. You can use destination address filt...
Page 131
Configuring the ethernet interface 119 7 select [3] set destination address filter. The following prompt appears at the bottom of the screen: enter destination address filter (1=disable, 2=enable) 8 enter 2 to enable the destination address filter. Viewing the list forwarding table the list forwardi...
Page 132
120 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications age—the age of the station address entry in the list forwarding table: permanent (indicating that the entry is on the bridge static table) or a specified number of seconds. To specify the age, change the agin...
Page 133
Configuring the cbr module 121 enabling and disabling the spanning tree spanning tree (ieee 802.1d) is a technique that detects loops in a network and logically blocks the redundant paths, ensuring that only one route exists between any two lans. It eliminates the duplication of packets and provides...
Page 134
122 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications figure 93 cbr e1 configuration menu 3 select the option corresponding to the port you want to configure ([1] port 1, [2] port 2, or [3] port 3). The cbr t1-dsx/e1port configuration menu for the selected port ...
Page 135
Configuring the cbr module 123 as shown in figure 95, if you set the port mode to structured voice, you can set additional trunk conditioning (tc) parameters on the cbr port configuration menu. Figure 95 cbr e1 port configuration menu (structured voice mode) 4 set the following port configuration pa...
Page 136
124 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications structured voice — structured service provides n x 64 kbit/second capability, where n ranges between 1 and the maximum number of available ds0 channels. Structured voice service passes traffic with signaling ...
Page 137
Configuring the cbr module 125 figure 96 illustrates the srts and adaptive timing options. Figure 96 cbr t1-dsx timing options idle timer—this parameter applies to the video dial feature. Use it to set the length of time, in seconds (6-60) after which the cbr software shuts off cell transmission and...
Page 138
126 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications crc-4 (e1 only)—enables (yes) or disables (no) cyclic redundancy check 4 (crc-4) information. Crc-4 is a framing option that checks for errors in data. It is a communication check for parity/framing and is us...
Page 139
Configuring the cbr module 127 figure 97 configuring the cbr serial port 4 set the following port configuration parameters as desired: sct clock source—the type of input clock service configured for the port interface. Recovered—a non-required network-wide synchronization technique used to regenerat...
Page 140
128 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications dial timer—the amount of time, in seconds, after which dialing is assumed to be ended if no further digits have been received: 6-60. This parameter applies to the video dial feature. The rs-366 specification ...
Page 141
Configuring the voice compression module 129 figure 98 cbr card configuration menu 4 select [1] set admin status and enter 2 to put the cbr card in service or 1 to take it out of service. Configuring the voice compression module the optional voice compression module (vcm) consists of one t1/e1 inter...
Page 142
130 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications figure 99 vcm channel configuration menu 3 set the following channel configuration parameters: encoding—encoding scheme: a-law (united states) or mu-law (international). Voice coding—voice compression algorit...
Page 143
Configuring the voice compression module 131 3 from the list card menu, enter the number corresponding to the slot in which the vcm you want to configure is installed (7 or 8) to open the vcm configuration menu. Figure 100 shows the vcm t1-dsx configuration menu. The vcm e1 configuration menu is the...
Page 144
132 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications line code—the zero code suppression technique configured to the vcm t1/e1port. Set this parameter to match the service provider or device connection line coding. The line code must match at local and remote p...
Page 145
Configuring virtual circuits 133 configuring the vcm card to configure the vcm card, follow these steps: 1 from the vcm configuration menu, shown earlier in figure 100, select [3] card configuration to open the vcm card configuration menu. This menu lists information about the vcm card and allows yo...
Page 146
134 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications the port vpi/vci atm circuit designators must match the application being supported. For example, if an oc3/stm-1 multi-mode fiber module is installed in the side b slot of the pathbuilder wan access switch a...
Page 147
Configuring virtual circuits 135 2 select [2] add virtual circuit. The add virtual circuit screen appears as shown in figure 104. Figure 104 initial add virtual circuit screen 3 enter a description for the virtual circuit you are defining. We recommend that you do not use the description . This is t...
Page 148
136 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications 4 enter the number corresponding to the class of virtual circuit you want to define. N if you want to create a standard vpc/vcc permanent virtual circuit to connect data ports, select [1] pvc and follow the i...
Page 149
Configuring virtual circuits 137 figure 107 selecting a slot for side a of the virtual circuit 3 enter the slot number for the module that you want to define as side a of the virtual circuit. For example, to assign the sim card as side a, you would enter 5. The default slot number is indicated by an...
Page 150
138 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications figure 108 add virtual circuit screen with side a completed some parameters that appear on the add virtual circuit screen may not apply to the particular circuit you are configuring. The system skips any non-...
Page 151
Configuring virtual circuits 139 figure 109 completed data port vcc virtual circuit 9 press any key to return to the virtual circuit menu. Configuring cbr circuits for dba this section provides guidelines for configuring cbr circuits for various types of dynamic bandwidth allocation (dba)—both for c...
Page 152
140 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications configuring cbr circuits for structured voice dba (cas) in structured voice dba, the cbr software reads the stored signaling bits and releases bandwidth when it detects an on-hook (idle) condition. Use struct...
Page 153
Configuring virtual circuits 141 setting up a pri pbx tie line pri signaling is a type of ccs in which one channel (24) is used to signal for the other channels (1-23). This is in contrast to cas in which signaling is done on all channels. To set up a pri pbx tie line, follow these basic steps: 1 co...
Page 154
142 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications to define an rs366 (video) virtual circuit template, follow these steps: 1 when you are prompted to select the virtual circuit type, as shown earlier in figure 105, select [2] rs366 template. As shown in figu...
Page 155
Configuring virtual circuits 143 3 enter the desired port number. N if you are setting up point-to-point video conferencing (between remote pathbuilder s330/s310 switches). N enter 4 to select the serial (v.35) port. N if you are setting up multi-point video conferencing (both between remote pathbui...
Page 156
144 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications figure 113 side a completed for video virtual circuit using cbr t1-dsx/e1 port 5 select the slot number corresponding to the module by which you are connected to the network for side b of the circuit template...
Page 157
Configuring virtual circuits 145 adding voice compression module vcc circuits to configure a vpc/vcc virtual circuit to connect data ports, follow these steps: you must configure at least one vcm vcc circuit before you can configure any vcm subchannel circuits. 1 when you are prompted to select the ...
Page 158
146 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications figure 116 configuring side a of a vcm vcc virtual circuit when you have entered a setting for each parameter, the add virtual screen again displays the list of pathbuilder s330/s310 modules and ports by slot...
Page 159
Configuring virtual circuits 147 figure 118 completed vcm vcc virtual circuit 7 press any key to return to the virtual circuit menu. Adding vcm subchannel circuits to configure a vcm subchannel circuit, follow these steps: you must configure at least one vcm vcc circuit before you can configure any ...
Page 160
148 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications 2 enter the number corresponding to the vcm vcc circuit upon which you want to base the subchannel circuit to open the vcm subchannel add virtual circuit screen, shown in figure 120. Figure 120 configuring a ...
Page 161
Configuring virtual circuits 149 figure 121 completed vcm subchannel circuit 5 press any key to return to the virtual circuit menu. Vcm subchannel virtual circuit example the following example shows how you can set up a three-node vcm network by creating all required vcm vcc circuits and vcm subchan...
Page 162
150 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications for the purposes of this example, assume you want to make the following connections: n connect subchannels 1-4 on pbx-1 to subchannels 1-4 on pbx-2 n connect subchannels 5-8 on pbx-1 to subchannels 1-4 on pbx...
Page 163
Configuring virtual circuits 151 virtual circuit parameters the following subsections describe parameters you must enter when you configure virtual circuits for different port types. Common virtual circuit parameters the following parameters are common to most port types: slot/port or group/card—the...
Page 164
152 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications frame relay virtual circuit parameters if the serial port is configured as a frame relay port, you must set the following virtual circuit parameters in addition to the common shaper number, priority, and earl...
Page 165
Configuring virtual circuits 153 figure 124 translation encapsulation mode de-clp / clp-de—de to clp / clp to de mapping. De to clp defines the value to which clp will be set in outgoing atm cells. Clp to de mapping defines the value to which de will be set from incoming atm cells in outgoing frame ...
Page 166
154 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications fecn to efci mapping—defines the mapping of fecn incoming on frame relay to the outgoing atm cell pti congestion indicator. Direct—mode 1 mapping; matches fecn to the pti cn bit. When the serial port is in th...
Page 167
Configuring virtual circuits 155 cdv buffer size—the cell delay variation buffer size: 1-24 ms. Cell delay variation refers to the spacing between cells. The pathbuilder s330/s310 provides a buffer to account for cell delay variation and thereby prevent cell loss. If the cell delay variation exceeds...
Page 168
156 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications ds0 channels—(t1-dsx/e1 ports only) telco channels: the associated ds0s which have been assigned to the specified atm vc connection. All available ds0 channels are automatically allocated in unstructured mode...
Page 169
Configuring virtual circuits 157 figure 125 list virtual circuit summary screen the list virtual circuit summary screen shows a summary of all virtual circuits, with a virtual circuit number (vc#) assigned to each. It displays the following information: card—card type. S/p—slot and port numbers (for...
Page 170
158 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications figure 126 list virtual circuit detail screen viewing virtual circuits by port or group to view a summary of existing virtual circuits for a selected port or group, follow these steps: 1 from the configuratio...
Page 171
Configuring virtual circuits 159 figure 128 access virtual circuits by port/group screen the access virtual circuits by port/group screen provides the same information as the list virtual circuit screen. See “viewing virtual circuits for the entire chassis” earlier in this section for details. To vi...
Page 172
160 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications deleting virtual circuits to delete an existing virtual circuit, follow these steps: 1 from the virtual circuit menu, select [4] delete virtual circuit. The delete virtual circuit screen appears. This screen ...
Page 173
Managing the video dial feature 161 managing video dial-up sessions to set up, activate, and end a video dial-up session, follow these basic steps: 1 create virtual circuits between the appropriate pathbuilder s330/s310 units. This effectively builds a call routing table. For detailed instructions, ...
Page 174
162 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications 3 select [1] set destination pone # and enter the phone number of the site to which you want to connect. 4 select [2] set connection. The session begins as soon as the software matches the phone number you en...
Page 175
Managing the video dial feature 163 to view the video call routing table, follow these steps: 1 from the configuration management menu, select [4] manage video dial to display the manage video dial menu, shown earlier in figure 129. 2 from the manage video dial menu, select [1] display video call ro...
Page 176
164 c hapter 4: c onfiguring p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odules , p orts , and a pplications.
Page 177: Ath
5 p ath b uilder s330 d iagnostics and p erformance s tatistics this chapter tells you how to access and manage superstack ii pathbuilder s330 and s310 wan access switch (pathbuilder s330/s310) system alarms, how to use available loopbacks, and how to view performance statistics for the pathbuilder ...
Page 178
166 c hapter 5: p ath b uilder s330 d iagnostics and p erformance s tatistics 2 select [1] display current alarms to view a list of current alarms, as shown in figure 134. Figure 134 sample current alarm display to determine whether or not an alarm-generating condition has been resolved, clear the c...
Page 179
Managing system alarms 167 mcpu and ctx module (system) alarms table 26 describes the critical and major alarms associated with the cpu module. Table 26 mcpu and ctx module (system) alarms alarm meaning troubleshooting steps alarms cleared current alarms have been cleared by user. Information only. ...
Page 180
168 c hapter 5: p ath b uilder s330 d iagnostics and p erformance s tatistics queue 1 over threshold the congestion threshold for queue 1was exceeded. Check and correct vc connections. Check and adjust vi shaper values. Check and adjust incoming traffic volume. Check for faulty ima links which may r...
Page 181
Managing system alarms 169 alarms common to several interfaces table 27 describes major alarms common to several pathbuilder s330/s310 interfaces. Table 27 alarms common to several modules alarm meaning troubleshooting steps alarm indication signal(ais) an incoming alarm indication signal (ais) indi...
Page 182
170 c hapter 5: p ath b uilder s330 d iagnostics and p erformance s tatistics loss of signal(los) cannot detect a signal at a configured port. This alarm is applicable to ds3 uni, e3 uni, oc3/stm-1 uni, ds1 ima uni, and e1 ima uni ports. Check the cable between the interface port and the service pro...
Page 183
Managing system alarms 171 ds1/e1 uni module alarms table 28 describes the alarms specific to the ds1 uni and e1 uni modules. Atm forum required alarms are indicated by the notation atm forum (r-xxx), where xxx is the required alarm number. Table 28 ds1/e1 uni module alarms alarm meaning troubleshoo...
Page 184
172 c hapter 5: p ath b uilder s330 d iagnostics and p erformance s tatistics bad scci (3com patent pending) status and change control indication – the content of the icp cells has changed. The far end icp cell scci in this link does not agree with the scci of the other links in the group. Check the...
Page 185
Managing system alarms 173 group [n] dup. Ima id the same group ima id has been received on links belonging to different ima groups in the same card. Correct link or group configuration. Group [n] fe abort symmetry the far end rejects the symmetry sent by the near end. Check and correct near end sym...
Page 186
174 c hapter 5: p ath b uilder s330 d iagnostics and p erformance s tatistics group [n] multi ima id different group ima id received on different links in an ima group. Correct link connections and/or ima group configuration. Group [n] multi test atm forum (r-138) different test procedure request fr...
Page 187
Managing system alarms 175 port missing icp cells two consecutive icp cells missing from the ima frame. See also loss of ima frame (lif). This is a specific cause of that alarm and will also be reported. Rfi ima atm forum (r-121) remote failure indication: far end ima rx networking link state machin...
Page 188
176 c hapter 5: p ath b uilder s330 d iagnostics and p erformance s tatistics dsx-1/e1 cbr module alarms table 29 describes the alarms specific to dsx-1 and e1 cbr modules. . Table 29 dsx-1/e1 cbr module alarms alarm meaning troubleshooting steps cellbus parity parity error on cells received from ce...
Page 189
Managing system alarms 177 sim alarms table 30 describes the alarms specific to qsims and fams voice compression module alarms table 29 describes the major alarms specific to the voice compression module. . Transmit fifo overflow the cell bus is congested, and cells are backed up on the cbr. Traffic...
Page 190
178 c hapter 5: p ath b uilder s330 d iagnostics and p erformance s tatistics working with history alarms all alarms and information events are captured and kept in an alarm history file in the pathbuilder s330/s310. This file can hold up to 300 events; it fills on a first-in/first-out basis. We rec...
Page 191
Using loopbacks 179 using loopbacks loopbacks allow you to check circuit continuity between one point and another. You should use the pathbuilder s330/s310 loopback feature to check continuity to the nearest point first, and if the circuit is valid to that point, then loop to the next point. If a ci...
Page 192
180 c hapter 5: p ath b uilder s330 d iagnostics and p erformance s tatistics figure 137 oc3/stm-1 loopback menu 4 select [1] set loopback. A prompt listing the loopback choices for the selected port appears at the bottom of the screen. 5 enter the number corresponding to the type of loopback you wa...
Page 193
Using loopbacks 181 oc3/stm-1 loopbacks the following loopbacks are available for the oc3/stm-1 interface: network line—loops the oc3/stm-1 received data back on the output side after the digital data has been recovered. Local card—loops the transmit oc3/stm-1 output on the receive side; the transmi...
Page 194
182 c hapter 5: p ath b uilder s330 d iagnostics and p erformance s tatistics e3 loopbacks the e3 module supports the following loopbacks: local card—loops the transmit e3output on the receive side. All cells coming from the e3 port card are looped through the backplane and back to the e3 port card....
Page 195
Using loopbacks 183 setting vcm loopbacks for the voice compression module, you can set both card/line and channel loopbacks. When you set a vcm loopback, the mcpu sends a message to the vcm card to perform a maintenance function, and the vcm replies with an acknowledgment. When the vcm enters maint...
Page 196
184 c hapter 5: p ath b uilder s330 d iagnostics and p erformance s tatistics the following prompt appears: enter channel (1-8): 3 enter the number of the channel for which you want to set a loopback to open the vcm channel loopback menu for that channel. Figure 144 shows the vcm t1-dsx channel loop...
Page 197
Viewing performance and atm statistics 185 viewing performance and atm statistics this section tells you how to display the following types of pathbuilder s330/s310 statistics: n card statistics n performance monitoring screens lists statistics that reflect the physical monitoring of the line. These...
Page 198
186 c hapter 5: p ath b uilder s330 d iagnostics and p erformance s tatistics figure 146 card statistics menu 3 enter the number corresponding to the card for which you want to view statistics. The following sections describe the card statistics provided for each type of card. Viewing t1/e1 uni card...
Page 199
Viewing performance and atm statistics 187 t1/e1 port/link statistics this section describes the t1/e1 port/link statistics. T1/e1 port/link physical performance statistics the t1 (ds1)/e1 uni physical performance monitoring screen displays the following statistics. You can view the statistics as cu...
Page 200
188 c hapter 5: p ath b uilder s330 d iagnostics and p erformance s tatistics rx-uus-ima-fe—far end receive unusable seconds; the number of unusable seconds at the far end interworking rx link state machine. Tx-fc—number of near-end transmit failures. Rx-fc—number of near-end receive failures. Tx-fc...
Page 201
Viewing performance and atm statistics 189 rx icp cell errors—the number of cells received in a port/group since the counter was cleared. Tx cell rate—current transmitted data cells rate. Rx cell rate—current received data cells rate. Rx icp cell error rate—current icp received cell error rate. Avg....
Page 202
190 c hapter 5: p ath b uilder s330 d iagnostics and p erformance s tatistics oc3/stm-1 section performance statistics the oc3/stm-1 section performance monitoring screen displays the following statistics: es—the number of errored seconds (ess) encountered by the oc3/stm-1 section. Ses—the number of...
Page 203
Viewing performance and atm statistics 191 uas—the number of unavailable seconds (uass) encountered by the oc3/stm-1 path interface. Cvs—the number of coding violations (cvs) encountered by the oc3/stm-1 path interface. Lop—indicates whether or not a loss of pointer (lop) condition has been encounte...
Page 204
192 c hapter 5: p ath b uilder s330 d iagnostics and p erformance s tatistics viewing ds3 card statistics you can view both performance statistics and atm statistics for the ds3 uni module. Viewing ds3 uni performance statistics to view ds3 uni performance statistics, follow these steps: 1 from the ...
Page 205
Viewing performance and atm statistics 193 cells dropped—the number of idle/unassigned cells encountered and dropped on the interface. Cells with hcs errors—the number of header check sequence (hcs) errored cells encountered on the atm interface. Viewing e3 card statistics you can view both performa...
Page 206
194 c hapter 5: p ath b uilder s330 d iagnostics and p erformance s tatistics sim hdlc statistics sim hdlc statistics include: received frames—the total number of received frames with good fcs at this port. Transmitted frames—the total number of successfully-transmitted frames at this port. Discarde...
Page 207
Viewing performance and atm statistics 195 viewing ethernet card statistics ethernet statistics are collected according to the ethernet bridge mib on the ethernet port and on every atm connection tied to this port. You can view bridge, filtering, and ethernet statistics, and you can also view atm vc...
Page 208
196 c hapter 5: p ath b uilder s330 d iagnostics and p erformance s tatistics ethernet statistics transmitted frames—the total number of frames transmitted at this port. Transmitted bytes—the total number of bytes transmitted at this port. Received frames—the total number of frames received at this ...
Page 209
Viewing performance and atm statistics 197 forward delay—the amount of time in the “learning” and “listening” states; half the amount of time that must elapse between the time when it is decided that a port should become part of the spanning tree and the time when data traffic is allowed to be forwa...
Page 210
198 c hapter 5: p ath b uilder s330 d iagnostics and p erformance s tatistics cbr atm statistics atm cell statistics are cell counts since the last counter reset. On the atm statistics window, you can reset the counter by entering c. Atm statistics are displayed as a list rather than a table. The cb...
Page 211
Viewing performance and atm statistics 199 viewing voice compression module statistics you can view performance monitoring, virtual circuit, and port activity statistics for the voice compression module. To view vcm statistics, follow these steps: 1 from the card statistics menu, shown earlier in fi...
Page 212
200 c hapter 5: p ath b uilder s330 d iagnostics and p erformance s tatistics bes—the number of bursty errored seconds (bess) encountered by the vcm t1-dsx/e1 interface. Dm—the number of degraded minutes (dms) encountered by the vcm t1-dsx/e1 interface. Lcv—the number of line coding violations (lcvs...
Page 213
Viewing virtual circuit statistics 201 viewing virtual circuit statistics by circuit to display virtual circuit statistics by circuit, follow these steps: 1 from the configuration management menu, select [2] manage circuits to display the virtual circuit menu. 2 from the virtual circuit menu, select...
Page 214
202 c hapter 5: p ath b uilder s330 d iagnostics and p erformance s tatistics row 2 (left to right) n cells received on side a n cells dropped on side a n cells received on side b n cells dropped on side b to view additional information about a particular circuit, enter the desired virtual circuit n...
Page 215
Viewing virtual circuit statistics 203 figure 150 virtual circuit statistics by shaper summary screen 4 to view statistics for a single shaper, enter the desired shaper number. As shown in figure 151, the virtual statistics by shaper detail screen lists the number of cells received, dropped, and sen...
Page 216
204 c hapter 5: p ath b uilder s330 d iagnostics and p erformance s tatistics 6 to view virtual circuit statistics by port/group for the selected shaper, enter p from the virtual circuit statistics by shaper detail screen. The screen that appears displays the same information as the show virtual sta...
Page 217: Echnical
A t echnical s upport 3com provides easy access to technical support information through a variety of services. This appendix describes these services. Information contained in this appendix is correct at time of publication. For the very latest, 3com recommends that you access the 3com corporation ...
Page 218
206 a ppendix a: t echnical s upport 3com bulletin board service the 3com bbs contains patches, software, and drivers for 3com products. This service is available through analog modem or digital modem (isdn) 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. Access by analog modem to reach the service by modem, set you...
Page 219
Support from 3com 207 support from 3com if you are unable to obtain assistance from the 3com online technical resources or from your network supplier, 3com offers technical telephone support services. To find out more about your support options, please call the 3com technical telephone support phone...
Page 220
208 a ppendix a: t echnical s upport returning products for repair before you send a product directly to 3com for repair, you must first obtain a return materials authorization (rma) number. Products sent to 3com without rma numbers will be returned to the sender unopened, at the sender’s expense. T...
Page 221: Ath
B p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odule and a pplication o verview this chapter describes the operation and data flow for each of the superstack ® ii pathbuilder ® s330 and s310 wan access switch (pathbuilder s330/s310) modules and supported applications. It contains the following sections: n management ...
Page 222
210 a ppendix b: p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odule and a pplication o verview enabled, an early packet discard operation is performed to check if the cell needs to be discarded. Counters for cells received and cells dropped are also updated, depending on the operation. Ctx output queues and memory pa...
Page 223
Ctx switch 211 the default memory configuration uses all available memory. In order to reallocate memory to a given queue, you must first deallocate it from one of the other queues. Since the ctx is output-buffered, and if the wan trunk has the lowest speed (for nxt1/e1), the wan trunk should take u...
Page 224
212 a ppendix b: p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odule and a pplication o verview vpi and vci ranges as explained earlier in this chapter, address translation is performed in the ctx. For vp connections, the full 8 bits of the vpi is looked up, so up to 256 vp connections are supported per port. For vc c...
Page 225
Oc3/stm-1 port 213 n the cells are passed to a line hec framer to synchronize to the line speed. N the t1/e1 chip adds the t1/e1 overhead and converts the digital data into a bipolar format suitable for transmission. An 8 khz clock is extracted from the t1/e1 clock (on all t1’s/e1s) and is used for ...
Page 226
214 a ppendix b: p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odule and a pplication o verview serial interface the serial interface is designed to interconnect frame-based devices/networks and cell-based atm devices/networks. The pathbuilder s330/s310 provides a single serial interface that can be configured as dte ...
Page 227
Serial interface 215 when connecting the pathbuilder s330/s310 to an atm network, verify that the pvc mapping for in and out ports is defined for proper operation. (see figure 153.) figure 153 pathbuilder s330/s310 to atm pvc it is also important to select the proper traffic contract from the atm sw...
Page 228
216 a ppendix b: p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odule and a pplication o verview dxi protocol defines an open interface between the router and the data service unit. The data service unit off-loads cell encapsulation services from the brouter. This will allow your current brouter to support atm, simply ...
Page 229
Serial interface 217 through atm dxi, the dce allows the dte to participate in an atm network. (see figure 157.) figure 157 dce allows dte to participate in atm network through atm dxi dxi mode 1a is designed to allow legacy routers to utilize frame-based transmission to transmit an atm network to t...
Page 230
218 a ppendix b: p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odule and a pplication o verview dxi protocol frame is an hdlc llc1 frame similar to ppp protocol. Mode 1a supports an aal5 transit encapsulation. In terms of the brouter, it is easier to implement dxi protocol, since it only requires the brouter to encaps...
Page 231
Serial interface 219 hdlc/sdlc mode transparent hdlc mode is used for point-to-point hdlc connections across the atm network. No service-based encapsulation other than aal5 is needed. All packets are terminated and sar’d to a single vp/vc in the atm network. Transparent mode functionality is best im...
Page 232
220 a ppendix b: p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odule and a pplication o verview these interworking features are described in frf.8 and frf.5 respectively. The major difference between these two features is that there is no fr-sscs function required for service interworking. The following sections descr...
Page 233
Serial interface 221 n the pathbuilder s330/s310 sitting in the middle performs all the required translation and management functions between these two networks, implementing the stacks as indicated in figure 162 and performing the following key functions: n translating from q.922 frame to atm aal5 ...
Page 234
222 a ppendix b: p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odule and a pplication o verview n the pathbuilder s330/s310 performs all the required translation and management functions between these two networks, implementing the stacks as indicated in figure 162 and performing the following key functions: n transla...
Page 235
Ethernet interface 223 n the sar will then assemble the cells belonging to the connections specified for it. N when the cells are assembled, the cpu is given confirmation, and the bridge function of the cpu examines the packet header, removes the encapsulation, and—after learning the address and upd...
Page 236
224 a ppendix b: p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odule and a pplication o verview spanning tree spanning tree (ieee 802.1d) is a technique that detects loops in a network and logically blocks the redundant paths, ensuring that only one route exists between any two lans. It eliminates the duplication of p...
Page 237
Ethernet interface 225 spanning tree instances the spanning tree logic supports a maximum of 255 physical and virtual ports, thereby allowing a maximum of 254 atm vcs. (one ethernet port is required be set aside for other purposes.) for the purpose of spanning tree operation, each set of one etherne...
Page 238
226 a ppendix b: p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odule and a pplication o verview figure 163 virtual circuit scheme figure 164 illustrates this on a network using pathbuilder s330s. Suppose workstation 1 on lan aa wants to send data to workstation 2 on lan bb. It transmits ethernet packets which include ...
Page 239
Ethernet interface 227 the aggregate of vpis/vcis assigned to the ethernet connection of the pathbuilder s330/s310 is referred to as a bridge. Since the pathbuilder s330/s310 reads and stores mac addresses and associated vpis/vcis as described above, the bridge is called a learning bridge. Each lear...
Page 240
228 a ppendix b: p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odule and a pplication o verview segmentation once it is determined that a packet should go across the bridge, the packet is encapsulated per rfc 1483 and a pad and trailer conforming to aal5 (atm adaption layer 5) is added at the end of the packet. See fi...
Page 241
Ethernet interface 229 figure 167 pathbuilder s330/s310 application lan 2 lan 3 pathbuilder s330/s310 #1 n x t1 pathbuilder s330/s310 #2 pathbuilder s330/s310 #3 atm switched network port p2 port p3 port p1 n x t1 n x t1 unstructured input pbx 3 csu #3 pbx 2 structured input ds0 drop and insert csu ...
Page 242
230 a ppendix b: p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odule and a pplication o verview figure 168 shows three pathbuilder s330s connected through a carrier atm network or a private switch. The atm switch or network should be configured with permanent virtual circuits (pvcs) connecting one lan or ethernet port...
Page 243
Cbr module 231 each pvc represents the logical circuit being used to connect one pathbuilder s330/s310 port to a remote pathbuilder s330/s310 port. Once you have entered all pvcs, the bridge will learn the network addresses for the local and remote sites and start bridging packets to the correct des...
Page 244
232 a ppendix b: p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odule and a pplication o verview the t1-dsx/e1 inputs can be either esf, sf, or no-framing using b8zs or ami. In accordance with the atm forum’s circuit emulation service (ces) specifications, the received frame can be broken up into its dso and abcd signa...
Page 245
Cbr module 233 structured ds1 implement the structured service if you require ds0 midspan drop-and-insert. (see figure 170.) figure 170 cbr structured ds1 - drop and insert midspan drop and insert allows services such as public switched telephone service to be inserted into the atm link. Combining t...
Page 246
234 a ppendix b: p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odule and a pplication o verview drop-and-insert ds0 channels can be allowed to transit the entire path, providing ds0 to ds0 connectivity between end locations. Structured ds0s can also be groomed to be combined through an atm network, thereby allowing en...
Page 247
Cbr module 235 these frames are then followed by the abcd bits of each active ds0. Two ds0’s abcd bits are provided in each byte after the last ds0 group. Figure 174 shows an example of three ds0s and their abcd bits sent in a structured encapsulation. Figure 174 multiframe structure for 3x64kbit/s ...
Page 248
236 a ppendix b: p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odule and a pplication o verview structured data ds0s allow for clear channel signaling (ccs). As opposed to cas, in which signaling is done on all channels, in clear channel signaling (ccs) one channel is used to signal for the other channels. The pathbui...
Page 249
Cbr module 237 unstructured ds1 implement unstructured ds1 service when you want ds1 tunneling through an atm system. Ds1 tunneling allows an entire ds1 frame, including framing bits, to travel across an atm network. See figure 176. Figure 176 ds1 unstructured tunneling use unstructured services whe...
Page 250
238 a ppendix b: p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odule and a pplication o verview figure 177 depicts the effects of structured versus unstructured service on the ds1 framing. Figure 177 structured versus unstructured effects on transit ds1 video conferencing the serial port of the pathbuilder s330/s310 c...
Page 251
Cbr module 239 figure 178 illustrates point-to-point video conferencing between three pathbuilder s330 switches (#1111, #2222, and #3333). Table 33, table 34, and table 35 list possible routing tables for the three units. Figure 178 point-to-point video conferencing v.35/ rs-449/ rs-530/ x.21 video/...
Page 252
240 a ppendix b: p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odule and a pplication o verview multi-point video conferencing in multi-point video conferencing an mcu (multi conference unit) device is connected to one t1-dsx/e1 cbr port of a pathbuilder s600 or pathbuilder s330/s310 at the central site. The remote pa...
Page 253
Voice compression module 241 to set up multi-point video conferencing, you build virtual circuits (defined by transmit and receive vpi/vci combinations) between the remote units and between the remote units and the central unit. The remote units can use the same vpi/vci to communicate with the centr...
Page 254
242 a ppendix b: p ath b uilder s330/s310 m odule and a pplication o verview supported voice compression features the vcm supports the following features: n g.729a, g.726, and g.711 compression algorithms—you must configure the voice coding (compression) for each ds0 channel. The decompression runs ...
Page 255: Ndex
I ndex symbols # rx configured links 103 # tx configured links 102 #rx active links 103 #tx active links 103 (dfa) vci 154 (dfa) vci range 154 (dfa) vpi 154 numbers 3com bulletin board service (3com bbs) 206 3com url 205 3comfacts 206 56k/64k mode 127 a aal5 pad 228 ac or dc power, connecting 38 act...
Page 256
244 i ndex system clock 63 system information 75, 76 t1/e1 card 103 t1/e1 ports 89, 90 t1/e1 uni interface 89 time and date 69 trap clients 67 uni groups 92 vcm card 133 vcm channels 129 vcm t1/e1 ports 130 viewing rs-232 port settings 77 viewing shelf information 82 virtual circuits 133 voice compr...
Page 257
245 deletion of group 1 when ds3/e3 module installed 57, 92 modifying 97 selecting type (ima or uni) 94, 96 h hdlc/sdlc applications 219 hdlc/sdlc mode 219 hello time 197 i i/o cabling, connecting 40 icons, notice 2 idle timer 125 ima see also inverse multiplexing. Group queues 211 ima group status,...
Page 258
246 i ndex pathbuilder 330/310 external connections 31 integrated application 233 port configuration 41 receiving and inspecting 29 pathbuilder s310 upgrading to pathbuilder s330 8 pathbuilder s330/s310 applications 229 key benefits 7 overview 3 pathbuilder s330/s310. See also pathbuilder s330/s310....
Page 259
247 virtual circuit (by buffer) 204 virtual circuit (by circuit) 201 virtual circuit (by port/group) 202 virtual circuit (by shaper) 202 status 163 structured mode 123, 232, 233 structured service as opposed to unstructured 237 effects on transit ds1 238 subnet mask setting for ethernet port 66 sett...
Page 260
248 i ndex.
Page 261
3com corporation l imited w arranty h ardware 3com warrants its hardware products to be free from defects in workmanship and materials, under normal use and service, for the following lengths of time from the date of purchase from 3com or its authorized reseller: if a product does not operate as war...
Page 262
Use, performance, failure, or interruption of its products, even if 3com or its authorized reseller has been advised of the possibility of such damages, and limits its liability to repair, replacement, or refund of the purchase price paid, at 3com’s option. This disclaimer of liability for damages w...