- DL manuals
- 3Com
- Switch
- 3C780 - LinkBuilder FDDI Base Unit
- User Manual
3Com 3C780 - LinkBuilder FDDI Base Unit User Manual
Summary of 3C780 - LinkBuilder FDDI Base Unit
Page 1
I linkbuilder ® fddi workgroup hub user guide a member of the linkbuilder fddi family for 3com user group information 1-800-net-3com or your local 3com office manual part no. 09-0447-000 published july 1993. Printed in the u.S.A..
Page 2
Ii 3com corporation 5400 bayfront plaza santa clara california, usa 95052-8145 © 3com corporation, 1993. All rights reserved. No part of this manual may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to make any derivative work (such as translation, transformation, or adaptation) without permissi...
Page 3
Iii limited warranty hardware: 3com warrants its hardware products to be free from defects in workmanship and materials, under normal use and service, for the following lengths of time from the date of purchase from 3com or its authorized reseller: bridge, gateway, and other internetworking products...
Page 4
Iv warranties exclusive: if a 3com product does not operate as warranted above, customer’s sole remedy shall be repair, replacement, or refund of the purchase price paid, at 3com’s option. The foregoing warranties and remedies are exclusive and are in lieu of all other warranties, express or implied...
Page 5
V warning: this equipment (3c781, 3c782, 3c783) has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a class b digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the fcc rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipmen...
Page 6
Vi vde class b compliance hiermit wird bescheinigt, dass die 3c781, 3c782, 3c783 in Übereinstimmung mit den bestimmungen der vfg 1046/1984 funk-entstört sind. Der deutschen bundespost wurde das inverkehrbringen dieses gërates angezeigt und die berechtigung zur Überprüfung der serie auf einhaltung de...
Page 7: Contents
Vii contents quick start road map to hub operations 1 unpacking the hub 2 unpacking the modules 3 installing the modules 4 connecting to the ring 6 chapter 1 overview fddi technology 1-2 physical medium dependent (pmd) protocol 1-4 fiber-optic 1-4 shielded twisted pair (stp) 1-4 unshielded twisted p...
Page 8
Viii chapter 2 installing the hub unpacking the hub 2-1 mounting the hub in a rack 2-2 equipping the hub 2-5 basic contents 2-5 hub chassis 2-6 media port modules 2-6 installing the battery 2-7 keys for fiber port modules 2-9 stp cascade connector 2-11 installing modules 2-12 removing modules 2-14 a...
Page 9
Ix port connections 3-11 configuring modules 3-15 using the stp cascade connector 3-18 chapter 4 setting up the hub commands 4-1 command descriptions 4-2 display of command results 4-2 setting addresses 4-3 ip address 4-3 netmask 4-4 broadcast address 4-4 default gateway address 4-4 setting the pass...
Page 10
X chapter 5 using the hub getting hub information 5-1 show hub configuration 5-1 show mac frame statistics 5-1 show ip addresses 5-3 show mib counters 5-3 show neighbor stations 5-4 show station identification 5-4 show ports information 5-5 module designation 5-6 pmd class 5-6 phy type 5-7 neighbor ...
Page 11
Xi appendix a system messages error messages a-1 download messages a-4 fault log error code messages a-6 appendix b technical specifications appendix c commands management console commands c-1 set commands c-1 set attach c-1 set baud c-2 set boot c-3 set gateway c-4 set help c-4 set ip c-4 set ler c...
Page 12
Xii show sid c-14 show tmax c-14 show tneg c-15 show tnotify c-15 show treq c-15 show tvx c-15 diagnostic and connectivity commands c-16 arp c-16 clear c-16 connect c-17 disconnect c-17 help c-17 logout c-17 ping c-18 reset c-18 route c-18 primitive console commands c-19 set commands c-20 set attach...
Page 14: Figures
Xiv figures 1-1. Ring wrap 1-3 1-2. The linkbuilder fddi workgroup hub 1-8 1-3. Physical topology for typical fddi ring 1-9 1-4. Fddi ring of trees 1-10 1-5. Management module, front panel 1-11 1-6. Fiber media port module, front panel 1-13 1-7. Removing a dust plug from a fiber transceiver 1-13 1-8...
Page 15
Xv 3-1. Dual attachment hub (dac) 3-2 3-2. Dual attachment hubs (dacs) in wrap state 3-3 3-3. Single attachment hub (sac) 3-4 3-4. Null attachment hub (nac) and connected stations (sas and das) 3-5 3-5. Dual homing connections 3-6 3-6. Upstream and downstream neighbors 3-13 3-7. Using two stp cascad...
Page 16: Tables
Xvi tables 2-1. Db-9 stp connector pin assignments 2-21 2-2. Rj-45 utp connector pin assignments 2-22 2-3. Fddi port types 2-23 3-1. Linkbuilder fddi workgroup hub default configuration 3-7 3-2. Selecting port configurations for attachment types 3-12 3-3. Port connection rules 3-14 3-4. Definitions ...
Page 17: 3Com’S Fddi Training and
® 3 2 1 0 linkbuilder ® fddi workgroup hub ® fiber port module utp port module management module optical bypass serial port m/m attach b/a s/m status token wrap fan fail hi temp low batt pwr ® grn grn yel = signal detect = port state = link error pwr ® grn grn yel = signal detect = port state = link...
Page 18: Additional 3Com Data
® 3 2 1 0 linkbuilder ® fddi workgroup hub ® fiber port module utp port module management module optical bypass serial port m/m attach b/a s/m status token wrap fan fail hi temp low batt pwr ® grn grn yel = signal detect = port state = link error pwr ® grn grn yel = signal detect = port state = link...
Page 19: Wants to Hear From You!
1-1 chapter title ® wants to hear from you! To ensure the very best 3com service and support, take advantage of our one-year warranty on 3com‘s linkbuilder ® fddi workgroup hub. Please fill out and return the enclosed registration card to start your one-year warranty period..
Page 20
1-2 chapter title customers in the countries shown below should send the completed registration card to the appropriate address. ■ france, spain, portugal, greece 3com france, marketing department za de courtaboeuf 25, ave de la baltique b.P. 609 91945 les ulis cedex france ■ italy 3com mediterraneo...
Page 21: Quick Start
1 quick start quick start use this quick start procedure if: ■ you are experienced in installing and operating linkbuilder fddi hubs. ■ you have an fddi segment running with other network devices attached to it. Road map to hub operations the steps listed below summarize the procedures needed to mak...
Page 22: Unpacking The Hub
2 quick start 7. Configuring attachment ports – chapter 3: “configuring modules” 8. Setting up the hub for network operations – chapter 4: “setting addresses”; “using station management parameters”; “downloading new images” 9. Monitoring hub operations – chapter 5: “getting hub information”; “interp...
Page 23: Unpacking The Modules
3 quick start the linkbuilder fddi system software diskette, version 1.0, contains a readme file and a backup image for the flash eprom. A 3-volt lithium battery is shipped with the management module. The battery is in a small bag inside the management module shipping container. If you ordered an st...
Page 24: Installing The Modules
4 quick start 2. Keep all packing and shipping materials. If a module must be returned, ship it in its original shipping container (or one providing equivalent protection), or the warranty will be voided. 3. One at a time, remove each module from its antistatic bag. 4. Check the modules for any visi...
Page 25
5 quick start to install the modules, follow these steps: 1. Remove all jewelry from your hands and wrists. 2. If necessary, remove blanking plates from the module slots. Keep the removed blanking plates in a safe place for possible future use. 3. Remove the module from its antistatic bag. Prepare a...
Page 26: Connecting to The Ring
6 quick start connecting to the ring after installing the modules and plugging in the power cord, you are ready to connect the hub to the ring by attaching the appropriate cables to the attachment ports, which are the two leftmost ports on the module installed in slot 1. To complete the connection t...
Page 27: Chapter 1
1-1 overview chapter 1 overview the 3com ® linkbuilder ® fddi workgroup hub brings fiber distributed data interface (fddi) high-speed lan technology to the desktop. (throughout this guide, the linkbuilder fddi workgroup hub will be referred to as “the hub.”) the hub supports remote management via st...
Page 28: Fddi Technology
1-2 overview the management module is based on the motorola ® 68ec020 processor, which provides the following: ■ 256 kb of nonvolatile ram ■ 1 mb of local ram ■ 512 kb of eprom ■ 1 mb of flash memory ■ 128 kb of ram for frame buffer and descriptors this guide is intended for network installers and o...
Page 29
1-3 overview primary ring secondary ring ring wrap ring wrap break in ring or station failure figure 1-1. Ring wrap the fddi standard developed by the american national standards institute (ansi) defines four protocols: ■ physical medium dependent (pmd) ■ physical (phy) ■ media access control (mac) ...
Page 30
1-4 overview physical medium dependent (pmd) protocol the physical medium dependent protocol provides all of the services necessary to exchange data across the cable medium. Pmd also specifies an optional optical bypass facility that enhances reliability. This bypass capability is invoked when an fd...
Page 31
1-5 overview unshielded twisted pair (utp) the ansi tp-pmd standard provides these services for utp: ■ cable requirements for category 5 utp as defined by eia/tia-568 ■ electrical requirements for utp transceivers ■ fddi-utp cable connector physical (phy) protocol the physical protocol is responsibl...
Page 32: Features and Functions
1-6 overview note: in contrast to the pmd protocol, the phy and mac protocols are media-independent; that is, the same protocols function regardless of the medium being used (fiber, stp, or utp). Station management (smt) protocol the station management protocol is involved in network management and ...
Page 33
1-7 overview the hub provides the following features: ■ media flexibility. You can use any mix of one, two, or three of these port modules in the hub: – fddi media port module supporting 62.5/125 µm fiber-optic cable per the ansi fddi standard – stp media port module supporting shielded twisted-pair...
Page 34: Site Selection
1-8 overview figure 1-2 shows the linkbuilder fddi hub with the management module and all three types of media modules installed. Pwr ® fiber port module grn grn yel = signal detect = port state = link error pwr ® utp port module grn grn yel = signal detect = port state = link error pwr ® management...
Page 35: Typical Fddi Ring Setups
1-9 overview typical fddi ring setups the hub can be used singly or in groups to bring fddi to the desktop. Figure 1-3 shows a typical ring setup, in which: ■ two dual attachment stations (das) are connected to the trunk ring. ■ two dual attachment hubs (dac) are connected to the trunk ring. ■ two s...
Page 36
1-10 overview the most common “fddi to the desktop” configuration is the ring of trees topology, shown in figure 1-4. This figure illustrates the connecting of stations using a hub to form a tree-like structure that branches off the main trunk ring. Das dac sac das sas sas sac sas sas sas sas figure...
Page 37: Management and Media Modules
1-11 overview management and media modules the hub chassis provides slots for one management module (required) and three media modules, which can be mixed or matched. This section briefly describes each of these modules. (for information about the operation of the management and media modules, see c...
Page 38
1-12 overview by interpreting the leds on the management module, you can: ■ monitor network activity ■ determine chassis environmental factors ■ discover ring attachment configuration refer to “interpreting the leds” in chapter 5 for detailed information about the leds on all hub modules. Media modu...
Page 39
1-13 overview pwr ® fiber port module grn grn yel = signal detect = port state = link error figure 1-6. Fiber media port module, front panel if you insert the module in slots 2 or 3, all ports are automatically configured as m ports. With three fiber modules installed in the hub, 12 fiber mic ports ...
Page 40
1-14 overview stp media port module figure 1-8 shows the front panel of the six-port stp media port module. All of its ports are configured as m ports by default. You can specify any port configuration for the attachment ports, but you must use a special connector called the stp cascade connector to...
Page 41: Chapter 2
2-1 installing the hub chapter 2 installing the hub this chapter describes installation of the linkbuilder fddi workgroup hub. It includes the following topics: ■ unpacking the hub ■ rack mounting the hub ■ equipping the hub ■ installing and removing modules ■ accessing the hub ■ understanding data ...
Page 42: Mounting The Hub In A Rack
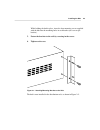
2-2 installing the hub mounting the hub in a rack mounting the hub in a rack involves installing mounting brackets onto the hub and mounting the hub in the rack. To mount the hub in a 19-inch distribution rack, follow these instructions: 1. Lift the hub from its packing container and place it on a t...
Page 43
2-3 installing the hub while holding the hub in place, insert the four mounting screws supplied with the hub into the mounting holes in each bracket (two screws per bracket). 5. Fasten the brackets to the rails by screwing in the screws. 6. Tighten each screw. Figure 2-1. Attaching mounting brackets...
Page 44
2-4 installing the hub pwr ® fiber port module grn grn yel = signal detect = port state = link error management module m/m attach b/a s/m status token wrap fan fail hi temp low batt serial port pwr ® reset optical bypass grn grn yel = signal detect = port state = link error pwr ® grn grn yel = signa...
Page 45: Equipping The Hub
2-5 installing the hub equipping the hub this section discusses the following hub equipment: ■ hub chassis ■ management module ■ lithium battery ■ media port modules ■ fiber port keys (optional) ■ cascade connector (optional) basic contents the basic package includes the following items: ■ linkbuild...
Page 46
2-6 installing the hub if you ordered a fiber media module, four small packets of fiber port module keys will be included with the module. For information on installing these keys, see the section “keys for fiber port modules” later in this chapter. If you ordered an stp media port module, one casca...
Page 47
2-7 installing the hub installing the battery a lithium battery, which powers the nonvolatile memory bank, is supplied with the management module. The hub’s nonvolatile memory preserves the following: ■ boot parameters ■ last download status ■ set command parameters ■ fault log entries the lithium b...
Page 48
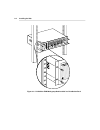
2-8 installing the hub you must insert the battery on the management module before installing the module in the hub. To install the battery in the management module, follow these steps: 1. Remove the battery from its container. Each management module is shipped with its battery in a small bag inside...
Page 49
2-9 installing the hub 4. Carefully slide the battery into its circular holder. Ensure that the “+” sign on the battery faces up and makes contact with the positive clip that holds the battery in place. The management module is now ready to be installed in slot 0. Follow the instructions given in th...
Page 50
2-10 installing the hub use of media module keys is optional. They can be used to ensure that the correct cable is inserted into each fiber transceiver. Once a key is in place, you can only insert the cable connector specified by that key into the transceiver. However, if the cable connector is univ...
Page 51
2-11 installing the hub 4. Push the back of the key down until it snaps into place. The key sits flush with the top of the transceiver. If you decide to change the configuration of a fiber module attachment port, you must change the key in the transceiver receptacle. To remove a key from the recepta...
Page 52: Installing Modules
2-12 installing the hub one cascade connector is supplied with each stp media port module. You can purchase additional cascade connectors by contacting your 3com sales representative. Figure 2-6 shows a cascade connector attached to the first port of an stp module installed in slot 1. ® stp port car...
Page 53
2-13 installing the hub to install the management module and the media modules for the first time, follow these steps: 1. Remove all jewelry from your hands and wrists. 2. If you are installing modules in slots 2 or 3, remove the blanking plates from those slots. Keep the removed blanking plates in ...
Page 54: Removing Modules
2-14 installing the hub there is no power switch on the hub. Power to the hub is provided by connecting the power cord to the hub and to an ac outlet. Note: the hub allows “power-on insertion,” which means that you do not have to unplug the power cord for module insertion or removal. When you replac...
Page 55
2-15 installing the hub 4. Turn the thumb screws on each end of the module counterclockwise to loosen them. 5. Holding a thumb screw in each hand, slowly pull the module from its slot. 6. Place the module on a clean surface, or replace the module in its original antistatic bag. 7. Place a blanking p...
Page 56: Accessing The Hub
2-16 installing the hub accessing the hub to monitor hub activity and (optionally) configure the hub to suit your particular network environment, you must set up an interface with the hub. You can access the hub in several ways: ■ connect a terminal such as a vt100 or similar dumb terminal to the rs...
Page 57
2-17 installing the hub to change the hub’s baud rate to match the baud rate of a terminal or modem, follow these steps: 1. Enter the set baud command. Type: set baud this selection prompt appears: select one of the following: 1. 1200 2. 2400 3. 4800 4. 9600 baudrate? 2. Type a number to select a ba...
Page 58
2-18 installing the hub installing an optional modem if you want to access the hub via a hayes modem, you must prepare the modem correctly for use with the hub. Follow these steps: 1. If necessary, change the hub’s baud rate to match the modem’s baud rate. Refer to the preceding section, “changing t...
Page 59: Planning Connections
2-19 installing the hub using telnet to access the hub to use the telnet protocol to access the hub, the hub must be connected to the network and must be running. You must also have the telnet protocol running on some device on your network. Follow these steps: 1. Enter the telnet command followed b...
Page 60
2-20 installing the hub fddi cabling rules the type of cabling you use depends on the media modules that you ordered. When installing the hub and the modules, observe these fddi cabling rules: fiber-optic cable ■ all cabling media must conform to the american national standard fddi physical layer me...
Page 61
2-21 installing the hub table 2-1. Db-9 stp connector pin assignments pin no. Function 1 transmit (+) 2 not used 3 not used 4 not used 5 receive (+) 6 transmit (–) 7 not used 8 not used 9 receive (–) unshielded twisted-pair cable ■ the standard utp cabling type supported by the linkbuilder fddi work...
Page 62
2-22 installing the hub table 2-2. Rj-45 utp connector pin assignments pin no. Function 1 transmit (+) 2 transmit (–) 3 not used 4 not used 5 not used 6 not used 7 receive (+) 8 receive (–) note: to minimize rf emissions, the connector shell must be connected to hub ground. Also, the connector shell...
Page 63
2-23 installing the hub data flow specifications the fddi standard specifies that data travels on the primary ring in a counterclockwise direction, and that data traveling on the secondary ring rotates clockwise. (refer to figure 3-1.) as you attach the hub to the ring and network devices to the hub...
Page 64
2-24 installing the hub p i s o s i p o a b mac das p i s o s i p o a b dac mac s mac s mac m sas sas p i p o m p i p o p o p i p o p i figure 2-9. Direction of data flow through a hub and stations the acronyms used in figure 2-9 are defined below and described in chapter 3: ■ das dual attachment st...
Page 65
2-25 installing the hub the default configuration of the attachment ports (the two leftmost ports on the module installed in slot 1) is b/a. If the attachment ports have been configured differently (as shown by the attach leds on the management module), you must reconfigure them, as detailed below: ...
Page 66
2-26 installing the hub installing an optical bypass switch in many network environments, mission-critical devices such as bridges, routers, and hubs should be connected to the primary dual ring only if they are equipped with an optical bypass switch (obs). An optical bypass switch is a device that ...
Page 67
2-27 installing the hub to detect the presence of an optical bypass switch on your system, enter the show obs command. To install an optical bypass switch with the configuration shown in figure 2-11, follow these steps: 1. Plug the a and b media interface connectors (mic connectors) from a network d...
Page 68
2-28 installing the hub 3. Plug the optical bypass switch’s power connector (a 6-pin mini-din plug) into the optical bypass interface receptacle on the management module. If you are installing the hub in a rack, you can purchase a cable tray to support the optical bypass switch unit, as shown in fig...
Page 69: Chapter 3
3-1 configuring the hub chapter 3 configuring the hub after you have installed the hub and its modules and physically connected it to the ring, you can configure the hub to operate in your network environment. This chapter discusses the following topics: ■ attachment options supported by the hub ■ d...
Page 70
3-2 configuring the hub dual attachment hub a dual attachment hub (dac) attaches to both the primary and the secondary rings. Figure 3-1 shows a hub functioning as a dual attachment hub. B a dac primary ring (trunk ring) secondary ring primary ring secondary ring legend figure 3-1. Dual attachment h...
Page 71
3-3 configuring the hub you can place a dual attachment hub directly on the trunk ring. This allows it to participate in ring wrapping if a segment of the trunk fails. Figure 3-2 shows dual attachment hubs in wrap state. B a dac dac das fault occurred in dual attached station b a figure 3-2. Dual at...
Page 72
3-4 configuring the hub single attachment hub a single attachment hub (sac) is never attached directly to the dual trunk ring. Instead, it is attached to another hub, which is connected to the main ring. Figure 3-3 shows a single attachment hub connected to the network via a dual attachment hub. The...
Page 73
3-5 configuring the hub null attachment hub a null attachment hub (nac) functions as a self-contained fddi network. It is an fddi backbone but is not connected to a dual ring backbone. The network is concentrated in the hub, and all of the attached devices communicate through it using fddi. Null att...
Page 74
3-6 configuring the hub dual homing dual homing (dh) configuration provides two attachments to the fddi network. One of them functions as a backup link if the primary link fails. This type of attachment is especially useful for connecting to mission-critical devices. Figure 3-5 illustrates valid con...
Page 75: Default Configuration
3-7 configuring the hub default configuration table 3-1 shows the hub’s factory default configuration on start-up. Table 3-1. Linkbuilder fddi workgroup hub default configuration description factory-set default t-notify 30 seconds tvx 2.6214 milliseconds* t-req 165 milliseconds ler cutoff 10.E-07 le...
Page 76
3-8 configuring the hub you can operate the hub using its default configuration without making any changes whatsoever. However, you may want to change various parameters to suit your particular network environment. Refer to chapters 4 and 5 and appendix c for information about making changes to the ...
Page 77
3-9 configuring the hub primitive console commands the “primitive” console commands, which are a subset of the management console commands, are accessible in case of unusual system situations. For example, you can access the primitive console command mode if: ■ you forget the password. (you do not n...
Page 78
3-10 configuring the hub if you do not press the reset button during the 10 seconds that the status led is flashing amber/green, you are denied access to the primitive console command mode, and this message appears: primitive console entry has timed out. 3. Press reset again. This message appears: p...
Page 79: Port Connections
3-11 configuring the hub returning to the management console command mode to return to the management console command mode without reattempting to enter the primitive console command mode, follow these steps: 1. Press [enter]. This message appears: 3com linkbuilder ® fddi workgroup hub the password ...
Page 80
3-12 configuring the hub table 3-2. Selecting port configurations for attachment types attachment type attachment ports configuration dual attachment b/a* dual homing attachment b/a* single attachment s/m null attachment m/m *the b/a configuration supports both dual attachment and dual homing. The b...
Page 81
3-13 configuring the hub the concept of neighbor is shown in figure 3-6. Upstream neighbor from b downstream neighbor from b c b a direction of data flow: a to b to c figure 3-6. Upstream and downstream neighbors to display the addresses of the hub’s upstream and downstream neighbors, enter the show...
Page 82
3-14 configuring the hub table 3-3. Port connection rules attachment neighbor ports ports a b m s a v, u, t v v, p, w v, u, w b v v, u, t v, p, w v, u, w m v, w v, w x v s v, u, w v, u, w v v table 3-4. Definitions for the port connection rules condition port connection definition of port indicator ...
Page 83: Configuring Modules
3-15 configuring the hub table 3-4. Definitions for the port connection rules (continued) condition port connection definition of port indicator condition condition w wrap state exists when a break in the primary ring occurs and the stations on either side of the break join the primary and secondary...
Page 84
3-16 configuring the hub all three types of port modules can be installed in slot 1. The type of module you install depends on the medium you are using to connect the hub to the next node. Table 3-5 shows how to configure each module for the type of attachment desired and what additional equipment o...
Page 85
3-17 configuring the hub table 3-5. Configuring modules (continued) attachment additional attachment port equipment module type configuration required utp dual b/a cross-over cable dual homing b/a cross-over cable single s/m cross-over cable null m/m cross-over cable to change the configuration of t...
Page 86
3-18 configuring the hub using the stp cascade connector by default, all ports on an stp media module are physically configured as m ports. If you want to configure the module for a b/a or s/m connection, you must use one or two stp cascade connectors to allow the new configuration. (the stp cascade...
Page 87
3-19 configuring the hub to use an stp module in a dual attachment configuration, for example, follow these steps: 1. If the attachment ports are not currently configured as b/a, configure the attachment ports to be b/a by invoking the set attach command. 2. Reset the hub. This step is unnecessary i...
Page 88: Chapter 4
4-1 setting up the hub chapter 4 setting up the hub the linkbuilder fddi workgroup hub is shipped ready to plug in and use without the need to change any parameters. In all probability, however, you will want to make a number of changes to adapt the hub to your network environment. This chapter disc...
Page 89
4-2 setting up the hub command descriptions for a complete listing and detailed description of all the commands, refer to appendix c, “commands.” ■ for a list of the set commands with brief definitions, type: set ? Or set help ■ for a list of the show commands with brief definitions, type: show ? Or...
Page 90: Setting Addresses
4-3 setting up the hub setting addresses the hub management module uses the tcp/ip network environment for downloading images and managing the hub. Refer to the section “downloading new images” later in this chapter for a discussion of downloading procedures. The console command set provides for set...
Page 91
4-4 setting up the hub note: in this manual, the address format used (three digits in each octet) is assumed to be decimal representation. If you prefer hexadecimal representation, the address format would be 0x12.0x34.0x56.0x78. The “0x” indicates that the subsequent digits represent hexadecimal va...
Page 92: Setting The Password
4-5 setting up the hub setting the password access to the hub is password-protected. To display the password prompt when the hub is first powered up, press any key. The modem init string (at&f) appears briefly. You are then prompted for the password. The hub is shipped with no password installed. At...
Page 93
4-6 setting up the hub setting attachment port configurations to configure the attachment ports, use the set attach command. 1. Type the command: set attach this selection prompt appears: select one of the following: 1. B/a 2. S/m 3. M/m attachment port configuration? 2. Enter the configuration you ...
Page 94
4-7 setting up the hub using station management parameters the hub supports a number of station management (smt) parameters to help you understand and manage the processes occurring in the fddi ring. You can set and display three of these parameters. You can display three other parameters, but you c...
Page 95
4-8 setting up the hub target token rotation time (t-req) the fddi ring is initialized every time a station joins or leaves the ring. During the initialization process, all stations on the ring agree on a “token rotation time.” this is the maximum amount of time that any station has to wait for a to...
Page 96
4-9 setting up the hub set this value higher if the link between stations must handle higher error levels. This can be necessary if you are waiting for minor unit or cable repairs but the ring is still operational. Set this value lower if you are confident of the quality of the link. To change the l...
Page 97
4-10 setting up the hub ler_cutoff. This threshold is the link error rate at which a faulty or poor link connection will be broken. The factory-set default is 10.E-07 (10 -7 ). If the ler exceeds the limits set by this option, the hub will automatically reestablish the connection to this port. If th...
Page 98
4-11 setting up the hub displaying smt parameters these three smt parameters, which you can display but cannot change, provide additional information about ring timer functions: ■ maximum token rotation time (t-max) ■ negotiated time (t-neg) ■ valid transmission timer (tvx) maximum token rotation ti...
Page 99: Downloading New Images
4-12 setting up the hub downloading new images when you power up the hub, it runs a series of self-tests and then executes the software image stored in the flash eprom. Whenever you receive a software upgrade from 3com, you will store the new image in an accessible network server that supports tftp ...
Page 100
4-13 setting up the hub 3. Set the tftp server’s ip address. Type: set boot server [enter] this prompt appears: enter server ip address in dot notation? 4. Type the server’s ip address. For example, type: 123.44.55.66 [enter] this confirmation appears: boot parameters method : tftp server : 123.44.5...
Page 101
4-14 setting up the hub 7. Enter the default gateway’s ip address. For example, type: set gateway 123.44.66.88 [enter] your local administrator should provide the gateway address you need. 8. Reset the hub. Press the reset button. The new image is now downloaded and stored in the flash eprom. If no ...
Page 102
4-15 setting up the hub table 4-1 summarizes the available boot methods. Table 4-1. Definition of boot methods boot method definition local runs flash eprom (default) tftp uses the tftp protocol and local configuration parameters to load a new image across the network.
Page 103: Chapter 5
5-1 using the hub chapter 5 using the hub this chapter discusses how to use the available commands and led indicators to operate the linkbuilder fddi workgroup hub. This includes: ■ getting information about hub operation ■ interpreting led behavior ■ using miscellaneous commands getting hub informa...
Page 104
5-2 using the hub >sh fstats raw frame statistics for primary mac: total transmit frames = 632 total received frames = 1561 total transmit smt frames = 550 total received smt frames = 1513 total transmit llc frames = 83 total received llc frames = 48 total received short frames = 0 total received in...
Page 105
5-3 using the hub show ip addresses to display the current ip address, ip netmask, and the internet broadcast address of the hub, enter the show ip command. An example of the resulting display is shown in figure 5-3. >sh ip ip address : 128.56.87.25 netmask : 255.255.0.0 broadcast : 128.56.255.255 f...
Page 106
5-4 using the hub the mib counters shown in figure 5-4 are defined in table 5-2. Table 5-2. Definition of mib counters mib counter definition fddimacframe-ct number of frames received fddimaccopied-ct number of frames copied fddimactransmit-ct total number of frames transmitted fddimactoken-ct numbe...
Page 107
5-5 using the hub note: the canonical form is a hexadecimal string, written from left to right, with hyphens separating the individual octets. The noncanonical form uses colons instead of hyphens as separators. Show ports information to view the details of a port module, enter the show ports command...
Page 108
5-6 using the hub the station management (smt) acronyms and other line items used in the show ports display are defined below along with the values that may appear. Module designation the first line in the show ports display gives the slot number of the module represented by the display and the numb...
Page 109
5-7 using the hub phy type the phy (physical layer) protocol specifies the rules for encoding data for transmission from one fddi station to another. Table 5-4 lists and defines the physical port types for the phy type line in figure 5-7. Table 5-4. Physical layer port types physical port type defin...
Page 110
5-8 using the hub table 5-5. Physical connection management states physical connection management states definition active the port is incorporated into the token ring path. Break a port connection has been broken and a restart process has begun. Connect both ends of the port’s requested connection ...
Page 111
5-9 using the hub connect state the connect state indicates the state of each ports’ connection. Table 5-6 lists the values and defines the connect states for the connect state line in figure 5-7. Table 5-6. Connect states connect state value definition active the port is incorporated into the token...
Page 112
5-10 using the hub lem rejects this parameter lists the number of times a link is removed because the error rate has exceeded the threshold test, as determined by the link error monitor (lem). Lem count this parameter provides the aggregate link error count, which is set to zero only on station init...
Page 113: Interpreting The Leds
5-11 using the hub table 5-7. Ring management states ring management state definition isolated the initial rmt state. Non_op the mac is participating in ring recovery, and the ring is not operational. Ring_op the mac is part of an operational fddi ring. Detect the ring has not been operational for a...
Page 114
5-12 using the hub table 5-8. Interpreting management module leds led color indicators meaning pwr green hub is on. Attach only one attachment exists at any one time. Configuration refers only to module in slot 1: b/a green port 1= b, port 2 = a, other ports = m s/m green port 1= s, other ports = m ...
Page 115
5-13 using the hub additional information about the last four leds in table 5-8 is provided below. Wrap led if the wrap led is on, a ring wrap condition exists on the hub. To determine where the wrap has occurred, enter the show cfm command. This command displays the configuration management (cfm) s...
Page 116
5-14 using the hub fan fail led if the fan fail led shows amber, the fan has failed and must be replaced. You must send the hub base unit back to 3com to replace the fan. Contact your 3com representative for a return materials authorization (rma). Hi temp led if the hi temp led shows amber, it means...
Page 117
5-15 using the hub if a high temperature condition existed but no longer does, this message appears: hardware: (high temp seen) to remove this message, enter the clear alarm command, as shown below: clear alarm [enter] this is the only environmental condition that requires you to invoke the clear al...
Page 118
5-16 using the hub reinitialize. If you press the reset button only briefly, the hub reinitializes and performs the power-on self-tests (post). The tests take several seconds to complete. Led check. If you hold down the reset button, all functioning leds on all installed modules light. This allows y...
Page 119: Using Miscellaneous Commands
5-17 using the hub table 5-10. Interpreting media module leds led color indicators meaning signal detect green the signal is detected. Off no signal exists. Port state green port is in active connection state. Flashing green/off port is in standby connection state. Off port is in disabled or connect...
Page 120
5-18 using the hub ping command the ping command sends echo frames to a host and expects to receive a like number of echo frames in return. Use the ping command to find out whether or not a host on the network is operational. For example, type: ping 128.45.87.20 where128.45.87.20 is the host address...
Page 121
5-19 using the hub if you type the count option with the ping command, the resulting display contains the ping statistics, which include the number of packets sent, the number of packets received, and the percentage of packets lost. For example, if you type this string, in which 64 is the size optio...
Page 122
5-20 using the hub by including a metric option, you can indicate the number of hops (number of gateways separating the source and destination) to the designated destination network. For example, to indicate five hops in the above command line, type: route add 128.87.45.12 128.87.45.33 5 ■ to delete...
Page 123
5-21 using the hub show log and clear log commands the fault log keeps a limited history of recent faults that have occurred in the system. ■ to display the fault log, type: show log a typical fault log is shown below: fault log: 1. 10000001 0# 0 2. 10000002 0# 0 the first column shows the order of ...
Page 124
5-22 using the hub using connectivity commands three connectivity commands deal with connecting the hub to the fddi ring, disconnecting the hub from the ring, and logging out of a console session. Connect and disconnect commands once you have installed the hub and attached it to the ring and to othe...
Page 125: Appendix A
A-1 system messages appendix a system messages this appendix lists the error and information messages that may be displayed on the terminal attached to the hub. The messages are listed alphabetically. Each message includes a brief explanation and suggested action. Error messages bad route command me...
Page 126
A-2 system messages invalid ip address xxxxxx meaning: you entered an ip address using an incorrect format. Action: reenter the address using the dotted decimal notation format xxx.Xxx.Xxx.Xxx where xxx.Xxx.Xxx.Xxx is the syntactic representation for a 32-bit integer consisting of four 8-bit numbers...
Page 127
A-3 system messages route already exists meaning: the route you attempted to add with the route command duplicates a route that already exists in the routing table. Action: reenter the route command with a different route specification. Route does not exist meaning: the route you attempted to delete...
Page 128: Download Messages
A-4 system messages the xx exponent must be >= the current cutoff exponent meaning: the ler alarm exponent must be greater than the ler cutoff exponent. Action: set the alarm exponent to be greater than the cutoff value. There are no ports in the management module slot meaning: you entered the slot ...
Page 129
A-5 system messages download image unusable — corrupted! Meaning: a serious error occurred during download. You no longer have an executable image in flash memory. Action: reissue the download request. Download image unusable — not executable! Meaning: a serious error occurred during download, or yo...
Page 130
A-6 system messages tftp abort - invalid nvram parameters. Meaning: the tftp download request could not be completed because the requested ip address, server ip address, or image filename was incorrect. The existing image will not be changed. Action: make sure that you have entered the correct the i...
Page 131
A-7 system messages 01xxxxxx meaning: flash memory error on the management module. Action: c ontact 3com support. 0xxxxxxx meaning: management module failure. Action: replace the module. 1pxxxxxx meaning: media module failure in slot 1. Action: if p is 0 or a value greater than the maximum number of...
Page 132
A-8 system messages 3pxxxxxx meaning: media module failure in slot 3. Action: if p is 0 or a value greater than the maximum number of ports on this module, replace this module. If p is a value between 1 and the maximum number of ports on the module, an error exists on the port number indicated by p....
Page 133: Appendix B
B-1 technical specifications appendix b technical specifications this appendix provides the physical, electrical, and environmental specifications for the linkbuilder fddi workgroup hub. Physical characteristics width 16.8 in (42.6 cm) depth 11.6 in (29.4 cm) height 5.2 in (13.3 cm) weight (empty) 1...
Page 134
B-2 technical specifications standards compliance fcc approval: fcc/vde class b (for linkbuilder fddi management module, fiber-optic module, and stp [sddi] module) fcc approval: fcc class a (for linkbuilder fddi utp module) if no utp modules are installed in the hub, the hub complies with the limits...
Page 135: Appendix C
C-1 commands appendix c commands this appendix describes the commands in the two command sets used to manage and configure the hub. The two command sets are: ■ management console commands ■ primitive console commands the commands in each set are grouped into categories and arranged alphabetically wi...
Page 136
C-2 commands example when you enter the set attach command, you are prompted to select an attachment configuration, as shown below: select one of the following: 1. B/a 2. S/m 3. M/m attachment port configuration? The possible selections are defined below: ■ b/a sets ports as b and a for dual attachm...
Page 138
C-4 commands ■ when you enter the set boot filename command, you are prompted to enter a filename for the software image, as shown below: enter filename? ■ when you enter the set boot server command, you are prompted to select a boot server, as shown below: enter servers ip address in dot notation? ...
Page 140
C-6 commands set pwd syntax set pwd description the set pwd command allows you to set and change the password: ■ you are prompted for the old password. ■ you are then prompted for a new password. ■ you are prompted for the new password again. Passwords can be one to eight alphanumeric characters and...
Page 141
C-7 commands show commands show attach syntax show attach description the show attach command displays the configuration of the attachment ports (the two leftmost ports) on the module in slot 1. The configuration is not restricted regardless of the slot 1 module type. If the module type physically c...
Page 142
C-8 commands the boot method can be one of the following: ■ local runs flash eprom (default) ■ tftp uses the tftp protocol and local configuration parameters to load a new image across the network the show boot load command displays the parameters used and the status of the last download to the flas...
Page 143
C-9 commands show fstats syntax show fstats description the show fstats command displays the following raw frame statistics for the hub’s mac: ■ total transmit frames ■ total received frames ■ total transmit smt frames ■ total received smt frames ■ total transmit llc frames ■ total received llc fram...
Page 145
C-11 commands ■ total number of frames received (fddimacframe-ct) ■ number of frames copied (fddimaccopied-ct) ■ number of frames transmitted (fddimactransmit-ct) ■ number of tokens (fddimactoken-ct) ■ number of error frames (fddimacerror-ct) ■ number of frames with format errors (fddimaclost-ct) ■ ...
Page 146
C-12 commands show ports syntax show ports # description the show ports command displays information about the ports on the media port module specified by the slot number. After entering show ports, specify the slot number of the module.If you do not specify a slot number, you will be prompted for o...
Page 147
C-13 commands ■ port pcm state (fddiportpcmstate) – active – break – connect – join – next – off – signal – trace – verify – maintenance (abbreviated as “maint”) ■ port status (fddiportconnectstate) – active – connecting (abbreviated as “connect”) – disabled (abbreviated as “disable”) – standby ■ le...
Page 148
C-14 commands show ring syntax show ring description the show ring command displays the ring management (rmt) state (fddimacrmtstate) for the mac on the primary ring. The possible rmt states are listed below: ■ isolated ■ non_op ■ ring_op ■ detect ■ non_op_dup ■ ring_op_dup ■ directed ■ trace show s...
Page 149
C-15 commands description the show tmax command displays the value of t-max (fddimact-max), the maximum length of time allowed for the token to move around the ring. Show tneg syntax show tneg description the show tneg command displays the current value of t-neg (fddimact-neg), the ring’s operationa...
Page 152
C-18 commands ping syntax ping host_address [size] [cnt] simplified syntax ping host_address the host address in internet dot notation. Ping host_address size (optional). Specifies the number of data bytes (defaults to 56 bytes). Ping host_address cnt (optional). Specifies the number of echo frames ...
Page 153: Primitive Console Commands
C-19 commands simplified syntax route add destination route add destination gateway route add destination gateway metric route delete destination route delete destination gateway route delete destination gateway metric routedump description the route command adds or deletes a path to a particular de...
Page 154
C-20 commands set commands set attach sets the configuration of the first two ports of the module in slot 1. Set baud sets the console (serial) port baud rate. Set boot sets the boot method, filename of the software image, or server ip address. Set defaults sets the factory defaults. Set gateway set...
Page 155
C-21 commands set treq sets the target token rotation time (t-req). Display commands show attach displays the configuration of the attachment ports on the module in slot 1 of the hub. Show baud displays the baud rate setting for the serial port. Show boot displays the boot method, filename of the so...
Page 156
C-22 commands show obs detects the presence or absence of an optical bypass switch. Show rev displays the revision number of the eprom and software. Show sid displays the 64-bit station id and the 48-bit mac address. Show tnotify displays the value of t-notify. Show treq displays the value of t-req....
Page 157: Appendix D
D-1 technical support appendix d technical support this appendix explains how to obtain worldwide support for 3com products. On-line product support 3com offers worldwide product support 24 hours a day, seven days a week, through automated on-line systems. Cardboard sm bulletin board service cardboa...
Page 158
D-2 technical support u.K. (44) 442 278278 up to 14400 baud, 8 data bits, no parity, 1 stop bit u.S. (1) (408) 980-8204 up to 19200 baud, 8 data bits, no parity, 1 stop bit for information on international cardboard access numbers added since this manual was published, contact your local 3com office...
Page 159
D-3 technical support 3com documentation on cd-rom an extensive library of 3com product documentation is available in cd-rom format through support on site for networks subscription service. This multivendor cd-rom service, offered by computer library, a division of ziff communication, contains tech...
Page 160
D-4 technical support nordic (46) 8 703 4870 singapore (65) 321 8929 taiwan (886) 2 775 4352 u.K. (44) 628 890 670 when you contact a 3com authorized service partner for assistance, have the following information ready: ■ diagnostic error messages ■ a list of system hardware and software, including ...
Page 161
D-5 technical support returning products for repair a product sent directly to 3com for repair must first be assigned a return materials authorization number (rma). A product sent to 3com without an rma number will be returned to the sender unopened, at the sender’s expense. When you call for an rma...
Page 162: Glossary
1 glossary glossary attachment the capability of a station or concentrator (or fddi hub) for connection into an fddi network. Stations and concentrators are classified as dual attachment, single attachment, or null attachment. Beacon a special type of frame transmitted when a station detects a logic...
Page 163
2 glossary concentrator a sophisticated multiplexer or hub device that has additional ports beyond those required for its own attachment to the main ring of an fddi network. These additional ports are for attaching other fddi nodes (including single attachment stations [sass] and other concentrators...
Page 164
3 glossary dual ring of trees one of the fddi-supported topologies in which only one ring is permitted to have multiple trees of any depth (consisting of single-attached concentrators and stations), which are cascaded off the main ring. Fddi fiber distributed data interface. The local area networkin...
Page 165
4 glossary mac media access control. Mac, the osi access layer, specifies the access mechanism used by fddi nodes for transmitting and receiving data on the ring. The mac is responsible for receiving frames and transmitting frames according to the rules of a timed token rotation protocol, a dynamic ...
Page 166
5 glossary phy physical layer protocol. The sublayer that describes the medium-independent portion of the osi physical layer and specifies the rules for encoding digital data for transmission from one fddi station to another. It also provides the link between the pmd and the mac layer. Ping packet i...
Page 167
6 glossary primary path the segment(s) of the primary ring that pass through a station. Conditions may exist in parts of the network that may cause the path to be in a different ring (that is, secondary instead of primary). Primary ring in thedual counter-rotating token ring architecture, the ring t...
Page 168
7 glossary station an addressable node on an fddi network capable of transmitting, repeating, and receiving information. A station has exactly one smt, at least one mac, at least one phy, and at least one pmd. Stp shielded twisted-pair. Shielded four-conductor electrical cable that can be used as th...
Page 169
8 glossary upstream the direction on a token ring network that is contrary to the normal direction of data flow (that is, downstream). Utp unshielded twisted-pair. A cable consisting of two twisted- pair conductors that are not insulated. Wrap a ring recovery condition that is automatically activate...
Page 170: Index
1 index index ? Command, c-17, c-22 3com sales offices, d-3 3comfacts, d-2 a a port, 2-23 accessing the hub, 2-16 via a modem, 2-16, 2-18 via a pc with terminal emulation, 2-16 via a terminal, 2-16 via telnet, 2-16, 2-19 accessing the primitive console command mode, 3-9 address resolution protocol (...
Page 171
Index 2 c (continued) cardfacts, d-2 cascade connector, 2-11, 3-18 cfm, 5-13 clear alarm command, 5-15, c-17 clear command, c-16, c-22 clear log command, 5-21, c-16 commands. See under individual command names. Computer library, d-3 configuration attachment ports, 3-11, 3-12, 4-6 hub, 3-1, 3-7 modul...
Page 172
3 index h (continued) change the baud rate, 2-16 clear the fault log, 5-21 configure attachment ports, 3-11, 4-6 configure modules, 3-15 connect a terminal to the hub, 2-16 detect the presence of dangerous conditions, 5-14 disconnect from the ring, 5-22 display port information, 5-5 display status o...
Page 173
Index 4 k keys, fiber port module, 2-9 l leds, 5-11 attach, 3-16, 5-12 fan fail, 5-12, 5-14 hi temp, 5-12, 5-14 link error, 5-17 low batt, 5-12, 5-14 management module, 5-11 media modules, 5-16 port state, 5-17 pwr, 5-12 signal detect, 5-17 status, 5-12 token, 5-12, 5-22 wrap, 5-12, 5-13 lem count, ...
Page 174
5 index p password, setting, 4-5 pcm neighbor fields, 5-7 state, 5-8 peer-mode connection, 5-13 phy layer functions, 1-5 port types, 5-7 protocol, 1-5 physical specifications, b-1 physical connection management (pcm), 5-7 states, 5-8 physical medium dependent (pmd) protocol, 1-3 physical (phy) layer...
Page 175
Index 6 s (continued) set ler alarm command, 4-9, c-5 set ler cutoff command, 4-10, c-5 set pwd command, 4-5, c-6, c-20 set tnotify command, c-6, c-20 set treq command, c-6, c-21 setup. See installation. Shielded twisted pair. See stp. Show ? Command, c-10, c-21 show attach command, 5-1, c-7, c-21 s...
Page 176
7 index u unshielded twisted pair. See utp. Utp cabling rules, 2-21 media port module, 1-14 pin assignments, 2-22 v valid transmission timer (tvx), 4-11 w wrap led, 5-12, 5-13 wrap state, 3-15, 5-13.