3Com 3CDSG10PWR - OfficeConnect Managed Gigabit PoE Switch User Manual
Summary of 3CDSG10PWR - OfficeConnect Managed Gigabit PoE Switch
Page 1
3com ® officeconnect managed gigabit poe switch user guide 3cdsg10pwr www.3com.Com part number 10016182 rev. Aa published july 2007.
Page 2
3com corporation 350 campus drive marlborough, ma 01752-3064 copyright © 2007, 3com corporation. All rights reserved. No part of this documentation may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to make any derivative work (such as translation, transformation, or adaptation) without written p...
Page 3: Bout
A bout t his g uide this guide provides information about the web user interface for the 3com® officeconnect managed gigabit poe switch. The web interface is a network management system that allows you to configure, monitor, and troubleshoot your switch from a remote web browser. The web interface w...
Page 4
4 a bout t his g uide ■ aggregating ports — provides information for configuring link aggregation which optimizes port usage by linking a group of ports together to form a single lag. ■ configuring vlans — provides information for configuring vlans. Vlans are logical subgroups with a local area netw...
Page 5
Intended audience 5 intended audience this guide is intended for network administrators familiar with it concepts and terminology. If release notes are shipped with your product and the information there differs from the information in this guide, follow the instructions in the release notes. Most u...
Page 6: Ontents
C ontents a bout t his g uide user guide overview ................................................................................. 3 intended audience..................................................................................... 5 conventions ....................................................
Page 7
2 u sing the 3c om w eb i nterface starting the 3com web interface .............................................................31 multi-session web connections ..................................................... 31 accessing the 3com web interface ................................................ ...
Page 8: Vlan
Viewing acl binding ..................................................................... 83 configuring acl binding ............................................................... 84 removing acl binding .................................................................. 85 enabling broadcast storm ...
Page 9: Mac A
9 c onfiguring ip and mac a ddress i nformation defining ip addressing ................................................................. 126 configuring arp settings .......................................................................127 viewing arp settings .........................................
Page 10
Configuring trust settings ........................................................... 169 viewing bandwidth settings ........................................................ 170 defining bandwidth settings ........................................................ 172 defining voice vlan................
Page 11: Cli R
A 3c om n etwork m anagement 3com network supervisor......................................................................212 3com network director .........................................................................213 3com network access manager ..................................................
Page 12
Upgrade ...................................................................................... 233 initialize ....................................................................................... 234 reboot ........................................................................................ 23...
Page 13: Etting
1 g etting s tarted this chapter contains introductory information about the 3com ® officeconnect managed gigabit poe switch (hereafter called the switch) and how they can be used in your network. It covers summaries of hardware and software features and also the following topics: ■ about the office...
Page 14
14 c hapter 1: g etting s tarted about the officeconnect managed gigabit poe switch the officeconnect managed gigabit poe switch is a gigabit ethernet switching products that delivers flexible three-speed performance (10/100/1000), power over ethernet (poe) and advanced voice-optimized features such...
Page 15
Front panel detail 15 front panel detail figure 1 shows the front panel of the officeconnect managed gigabit poe switch 10-port unit figure 1 officeconnect managed gigabit poe switch 10-port—front panel. Traffic prioritization supported (using the ieee std 802.Id, 1998 edition): eight traffic queues...
Page 16
16 c hapter 1: g etting s tarted led status indicators the officeconnect managed gigabit poe 10-port ethernet switch provides led indicators on the front panel for your convenience to monitor the switch. Table 2 describes the meanings of the leds. Table 2 description on the leds of the officeconnect...
Page 17
System specifications 17 system specifications table 3 contains the system specifications of the officeconnect managed gigabit poe series switch. Additional specifications can be found in appendix b “device specifications and features”. Table 3 system specifications of the switch officeconnect manag...
Page 18
18 c hapter 1: g etting s tarted installing the switch this section contains information that you need to install and set up your 3com switch. Warning: safety information. Before you install or remove any components from the switch or carry out any maintenance procedures, you must read the 3com swit...
Page 19
Setting up for management 19 setting up for management to make full use of the features offered by your switch, and to change and monitor the way it works, you have to access the management software that resides on the switch. This is known as managing the switch. Managing the switch can help you to...
Page 20
20 c hapter 1: g etting s tarted figure 2 web interface management over the network refer to “setting up web interface management” on page 27. Snmp management you can manage a switch using any network management workstation running the simple network management protocol (snmp) as shown in figure 3. ...
Page 21
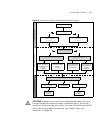
Switch setup overview 21 figure 4 initial switch setup and management flow diagram caution to protect your switch from unauthorized access, you must change the default password as soon as possible, even if you do not intend to actively manage your switch. For more information on default users and ch...
Page 22
22 c hapter 1: g etting s tarted ip configuration the switch’s ip configuration is determined automatically using dhcp, or manually using values you assign. Automatic ip configuration using dhcp by default the switch tries to configure its ip information without requesting user intervention. It trie...
Page 23
Using the command line interface (cli) 23 ■ your dhcp server does not allow you to allocate static ip addresses. (static ip addresses are necessary to ensure that the switch is always allocated the same ip information.) for most installations, 3com recommends that you configure the switch ip informa...
Page 24
24 c hapter 1: g etting s tarted connecting the workstation to the switch 1 connect the workstation to the console port using the console cable as shown in figure 5. Figure 5 connecting a workstation to the switch using the console port to connect the cable: a attach the cable’s rj-45 connector to t...
Page 25
Using the command line interface (cli) 25 1 connect to the switch console port as described in “connecting to the console port” page 23. 2 the command line interface login sequence begins as soon as the switch detects a connection to its console port. When the process completes, the login prompt dis...
Page 26
26 c hapter 1: g etting s tarted 5 enter summary to view a summary of allocated ip addresses. The following is an example of the display from the summary command. Select menu option# summary ip method: default ip address: 169.254.99.51 subnet mask: 255.255.0.0 runtime version: 00_00_38 (date 01-apr-...
Page 27
Setting up web interface management 27 setting up web interface management this section describes how you can set up web interface management over the network. Prerequisites ■ ensure you have already set up the switch with ip information as described in “methods of managing a switch” on page 19. ■ e...
Page 28
28 c hapter 1: g etting s tarted web management over the network to manage a switch using the web interface over an ip network: 1 be sure that you know your switch’s ip address. See “ip configuration” on page 22, and “viewing ip information using the console port” on page 25. 2 check that your manag...
Page 29
Default users and passwords 29 default users and passwords if you intend to manage the switch or to change the default passwords, you must log in with a valid user name and password. The switch has one default user name. The default user is listed in table 5. Use the admin default user name (no pass...
Page 30: Sing
2 u sing the 3c om w eb i nterface this section provides an introduction to the user interface, and includes the following topics: ■ starting the 3com web interface ■ understanding the 3com web interface ■ saving the configuration ■ resetting the device ■ restoring factory defaults ■ logging off the...
Page 31
Starting the 3com web interface 31 starting the 3com web interface this section includes the following topics: ■ multi-session web connections ■ accessing the 3com web interface multi-session web connections the multi-session web connections feature enables 10 users to be created and access the swit...
Page 32
32 c hapter 2: u sing the 3c om w eb i nterface accessing the 3com web interface this section contains information on starting the 3com web interface. To access the 3com user interface: 1 open an internet browser. 2 enter the device ip address in the address bar and press enter. The enter network pa...
Page 33
Understanding the 3com web interface 33 figure 7 3com web interface home page understanding the 3com web interface the 3com web interface home page contains the following views: ■ tab view — provides the device summaryconfiguration located at the top of the home page. ■ tree view — provides easy nav...
Page 34
34 c hapter 2: u sing the 3c om w eb i nterface figure 8 web interface components the following table lists the user interface components with their corresponding numbers: this section provides the following additional information: ■ device representation — provides an explanation of the user interf...
Page 35
Understanding the 3com web interface 35 device representation the 3com web interface home page contains a graphical panel representation of the device that appears within the device view tab. To access the device representation: 1 click device summary > device view. Figure 9 device representation 2 ...
Page 36
36 c hapter 2: u sing the 3c om w eb i nterface using screen and table options 3com contains screens and tables for configuring devices. This section contains the following topics: ■ viewing configuration information ■ adding configuration information ■ modifying configuration information ■ removing...
Page 37
Using screen and table options 37 adding configuration information user-defined information can be added to specific 3com web interface pages, by opening the ip setup page. To configure ip setup: 1 click administration > ip setup.The ip setup page opens: figure 11 ip setup page 2 enter requisite inf...
Page 38
38 c hapter 2: u sing the 3c om w eb i nterface modifying configuration information 1 click administration > system access > modify. The system access modify page opens: figure 12 system access modify page 2 modify the fields. 3 click . The access fields are modified..
Page 39
Using screen and table options 39 removing configuration information 1 click administration > system access > remove.The system access remove page opens: figure 13 system access remove page 2 select the user account to be deleted. 3 click . The user account is deleted, and the device is updated..
Page 40
40 c hapter 2: u sing the 3c om w eb i nterface saving the configuration configuration changes are only saved to the device once the user saves the changes to the flash memory. The save configuration tab allows the latest configuration to be saved to the flash memory. To save the device configuratio...
Page 41
Resetting the device 41 resetting the device the reset page enables resetting the device from a remote location. To prevent the current configuration from being lost, use the save configuration page to save all user-defined changes to the flash memory before resetting the device. To reset the device...
Page 42
42 c hapter 2: u sing the 3c om w eb i nterface 3 click . The device is reset, and a prompt for a user name and password is displayed. Figure 16 user name and password page 4 enter a user name and password to reconnect to the web interface..
Page 43
Restoring factory defaults 43 restoring factory defaults the restore option appears on the reset page. The restore option restores device factory defaults. To restore the device: 1 click administration > reset. The reset page opens: figure 17 reset page the reset page contains the following fields: ...
Page 44
44 c hapter 2: u sing the 3c om w eb i nterface logging off the device to log off the device: 1 click . The logout page opens. 2 the following message appears: 3 click . The 3com web interface home page closes..
Page 45: Iewing
3 v iewing b asic s ettings this section contains information for viewing basic settings. The 3com web interface home page presents a device summary section that provides the system administrator with the option to view essential information required for setting up and maintaining device settings. T...
Page 46
46 c hapter 3: v iewing b asic s ettings viewing device settings the device summary page displays parameters for viewing general device information, including the system name, location, and contact, the system mac address, system object id, system up time, and mac addresses, and both software, boot,...
Page 47
47 ■ system object id — displays the vendor’s authoritative identification of the network management subsystem contained in the entity. ■ mac address — displays the device mac address. ■ system up time — displays the amount of time since the most recent device reset. The system time is displayed in ...
Page 48
48 c hapter 3: v iewing b asic s ettings viewing color keys the color key page provides information regarding the rj45 or sfp port status on the device. The various colors key indicate the port status, speed and link of a selected port. To view color keys: 1 click device summary > color key. The col...
Page 49: Anaging
4 m anaging d evice s ecurity the management security section provides information for configuring system access, defining radius authentication, port-based authentication and defining access control lists. This section includes the following topics: ■ configuring system access ■ defining radius cli...
Page 50
50 c hapter 4: m anaging d evice s ecurity configuring system access network administrators can define users, passwords, and access levels for users using the system access interface. The multi-session web feature is enabled on device and allows 10 users to be created and access the switch concurren...
Page 51
Configuring system access 51 viewing system access settings the system access summary page displays the current users and access levels defined on the device. To view system access settings: 1 click administration > system access > summary. The system access summary page opens: figure 20 system acce...
Page 52
52 c hapter 4: m anaging d evice s ecurity defining system access the system access setup page allows network administrators to define users, passwords, and access levels for users using the system access interface. Monitor users have no access to this page. To define system access: 1 click administ...
Page 53
Configuring system access 53 modifying system access the system access modify page allows network administrators to modify users, passwords, and access levels for users using the system access interface. Monitor users have no access to this page. To modify system access: 1 click administration > sys...
Page 54
54 c hapter 4: m anaging d evice s ecurity removing system access thesystem access remove pageallows network administrators to remove users from the system access interface. Monitor users have no access to this page. To remove users: 1 click administration > system access > remove. The system access...
Page 55
Defining radius clients 55 defining radius clients remote authorization dial-in user service (radius) servers provide additional security for networks. Radius servers provide a centralized authentication method for 802.1x. The default parameters are user-defined, and are applied to newly defined rad...
Page 56
56 c hapter 4: m anaging d evice s ecurity ■ authentication port — defines the authentication port. The authentication port is used to verify the radius server authentication. The authentication port default is 1812. ■ number of retries — defines the number of transmitted requests sent to the radius...
Page 57
Defining port-based authentication (802.1x) 57 defining port-based authentication (802.1x) port-based authentication authenticates users on a per-port basis via an external server. Only authenticated and approved system users can transmit and receive data. Ports are authenticated via the radius serv...
Page 58
58 c hapter 4: m anaging d evice s ecurity viewing 802.1x authentication the 802.1x summary page allows the network administrator to view port-based authentication settings. To view port-based authentication: 1 click security > 802.1x > summary.The 802.1x summary page opens: figure 25 802.1x summary...
Page 59
Defining port-based authentication (802.1x) 59 ■ current port control — displays the current port authorization state. ■ guest vlan — indicates whether an unauthorized port is allowed to join the guest vlan. The possible field values are: ■ enable — enables an unauthorized port to join the guest vla...
Page 60
60 c hapter 4: m anaging d evice s ecurity defining 802.1x authentication the 802.1x setup page contains information for configuring 802.1x global settings on the device and defining specific 802.1x setting for each port individually. Monitor users have no access to this page. To configure 802.1x se...
Page 61
Defining port-based authentication (802.1x) 61 ■ enable guest vlan — provides limited network access to authorized ports. If a port is denied network access via port-based authorization, but the guest vlan is enabled, the port receives limited network access. For example, a network administrator can...
Page 62
62 c hapter 4: m anaging d evice s ecurity defining access control lists access control lists (acls) allow network managers to define classification actions and rules for specific ingress ports. Packets entering an ingress port, with an active acl are either admitted or denied entry. If they are den...
Page 63
Defining access control lists 63 viewing mac based acls the mac based acl summary page displays information regarding mac based acls configured on the device. Ports are reactivated from the port administration setup page. To view mac based acls: 1 click device > acl > mac based acl > summary. The ma...
Page 64
64 c hapter 4: m anaging d evice s ecurity ■ ethertype — provides an identifier that differentiates between various types of protocols. ■ action — indicates the acl forwarding action. In addition, the port can be shut down, a trap can be sent to the network administrator, or packet is assigned rate ...
Page 65
Defining access control lists 65 ■ selection acl — selects an existing mac-based acl to which rules are to be added. ■ create acl — defines a new user-defined mac-based access control list. Add rules to acl ■ priority — sets the rule priority, which determines which rule is matched to a packet on a ...
Page 66
66 c hapter 4: m anaging d evice s ecurity ■ ethertype — provides an identifier that differentiates between various types of protocols. ■ action — specifies the acl forwarding action. In addition, the port can be shut down, a trap can be sent to the network administrator, or packet is assigned rate ...
Page 67
Defining access control lists 67 modifying mac based acls the mac based acl modify page allows the network administrator to modify an existing mac-based acl rule. Monitor users have no access to this page. To modify a mac-based acl rule: 1 click device > acl > mac based acl > modify. The mac based a...
Page 68
68 c hapter 4: m anaging d evice s ecurity for example, if the source mac address is e0:3b:4a:c2:ca:e2 and the wildcard mask is 00:00:00:00:00:ff, the first five bytes of the mac are used, while the last byte is ignored. For the source mac address e0:3b:4a:c2:ca:e2, this wildcard mask matches all ma...
Page 69
Defining access control lists 69 removing mac based acls the mac based acl remove page allows the user to remove mac-based acls or mac-based acl rules. Monitor users have no access to this page. Click device > acl > mac based acl > remove. The mac based acl remove page opens: figure 30 mac based acl...
Page 70
70 c hapter 4: m anaging d evice s ecurity ■ cos mask — displays the wildcard mask bits to be applied to the cos. ■ ethertype — provides an identifier that differentiates between various types of protocols. ■ action — indicates the acl forwarding action. In addition, the port can be shut down, a tra...
Page 71
Defining access control lists 71 viewing ip based acls the ip based acl summary page displays information regarding ip-based acls configured on the device. To view ip-based acls: 1 click device > acl > ip based acl > summary. The ip based acl summary page opens: figure 31 ip based acl summary page t...
Page 72
72 c hapter 4: m anaging d evice s ecurity ■ icmp code — indicates the icmp message code for filtering icmp packets. Icmp packets that are filtered by icmp message type can also be filtered by the icmp message code. ■ igmp type — indicates the igmp message type filter. ■ source address — matches the...
Page 73
Defining access control lists 73 monitor users have no access to this page. To configure ip-based acls: click device > acl > ip based acl > setup. The ip based acl setup page opens: figure 32 ip based acl setup page the ip based acl setup page contains the following fields: ■ selection acl — selects...
Page 74
74 c hapter 4: m anaging d evice s ecurity ■ source port — defines the source port that is used for matched packets. Enabled only when tcp or udp are selected in the protocol list. The field value is either user defined or any. If any is selected the ip based acl is applied to any source port. ■ des...
Page 75
Defining access control lists 75 ■ icmp code — if checked, enables specifying an icmp message code for filtering icmp packets. Icmp packets that are filtered by icmp message type can also be filtered by the icmp message code. ■ igmp — if checked, enables filtering igmp packets for an igmp message ty...
Page 76
76 c hapter 4: m anaging d evice s ecurity wildcard mask matches all ip addresses in the range 149.36.184.0 to 149.36.184.255. A wildcard mask must not contain leading zeroes. For example, a wildcard mask of 010.010.011.010 is invalid, but a wildcard mask of 10.10.11.10 is valid. ■ match dscp— match...
Page 77
Defining access control lists 77 modifying ip based acls the ip based acl modify page allows the network administrator to modify ip based acl rules. To modify an ip-based acl rule: 1 click device > acl > ip based acl > modify. The ip based acl modify page opens: monitor users have no access to this ...
Page 78
78 c hapter 4: m anaging d evice s ecurity ■ select from list — selects a protocol from a list by which packets are matched to the rule. ■ protocol id — adds user-defined protocols by which packets are matched to the rule. Each protocol has a specific protocol number which is unique. The possible fi...
Page 79
Defining access control lists 79 ■ icmp — if checked, enables filtering icmp packets for an icmp message type. The possible values are: ■ select from list — selects an icmp message type from a list. ■ icmp type — specifies an icmp message type. ■ any — does not filter for an icmp message type. ■ icm...
Page 80
80 c hapter 4: m anaging d evice s ecurity ■ match ip precedence— matches the packet ip precedence value to the rule. Either the dscp value or the ip precedence value is used to match packets to the rule. ■ action — selects the acl forwarding action. In addition, the port can be shut down, a trap ca...
Page 81
Defining access control lists 81 figure 34 ip based acl remove page the ip based acl remove page contains the following fields: ■ acl name — selects an acl name from a list of the ip-based acls. ■ remove acl — enables the acl to be removed. ■ checkbox (unnamed) — when checked, selects the rule for r...
Page 82
82 c hapter 4: m anaging d evice s ecurity ■ source address — indicates the source ip address. ■ source mask — indicates the source ip address mask. ■ destination address — indicates the destination ip address. ■ destination mask — indicates the destination ip address mask. ■ dscp — matches the pack...
Page 83
Defining access control lists 83 viewing acl binding the acl binding summary page displays the user-defined acls mapped to the interfaces. To view acl binding: 1 click device > acl > acl binding > summary. The acl binding summary page opens: figure 35 acl binding summary page the acl binding summary...
Page 84
84 c hapter 4: m anaging d evice s ecurity configuring acl binding the acl binding setup page allows the network administrator to bind specific ports to mac- or ip-based acls. The monitor user has no access to this page. To define acl binding: 1 click device > acl > acl binding > setup. The acl bind...
Page 85
Defining access control lists 85 removing acl binding the acl binding remove page allows the network administrator to remove user-defined acls from a selected interface. Monitor users have no access to this page. To remove acl binding: 1 click device > acl > acl binding > remove. The acl binding rem...
Page 86
86 c hapter 4: m anaging d evice s ecurity enabling broadcast storm broadcast storm limits the amount of multicast and broadcast frames accepted and forwarded by the device. When layer 2 frames are forwarded, broadcast and multicast frames are flooded to all ports on the relevant vlan. This occupies...
Page 87
Enabling broadcast storm 87 monitor users have no access to this page. To define broadcast storm traffic: 1 click device > broadcast storm > setup. The broadcast storm setup page opens: figure 38 broadcast storm setup page the broadcast storm setup page contains the following fields: ■ broadcast sto...
Page 88: Anaging
5 m anaging s ystem i nformation this section contains information for configuring general system information, and includes the following: ■ viewing system description ■ defining system settings ■ saving the device configuration ■ resetting the device.
Page 89
89 viewing system description the device view page displays parameters for configuring general device information, including the system name, location, and contact, the system mac address, system object id, system up time, and mac addresses, and both software, boot, and hardware versions. To view de...
Page 90
90 c hapter 5: m anaging s ystem i nformation ■ mac address — displays the device mac address. ■ system up time — displays the amount of time since the most recent device reset. The system time is displayed in the following format: days, hours, minutes, and seconds. For example, 41 days, 2 hours, 22...
Page 91
91 defining system settings the following section allows system administrators to configure advanced system settings. The section includes the following topics: ■ configuring system name ■ configuring system time.
Page 92
92 c hapter 5: m anaging s ystem i nformation configuring system name the system name page allows the network administrator to provide a user-defined system name, location, and contact information for the device. Monitor users have read-only permissions on this page. To configure the system name: 1 ...
Page 93
93 configuring system time the system time setup page contains fields for defining system time parameters for the local hardware clock. Daylight savings time can be enabled on the device. Monitor users have limited permissions on this page. To configure the system time: 1 click administration > syst...
Page 94
94 c hapter 5: m anaging s ystem i nformation ■ daylight saving — enables setting automatic daylight savings time (dst) on the device, either on a non-recurring or recurring basis. In the non-recurring case, dst is configured to apply to one specific period of time only, defined by specifying the be...
Page 95
95 ■ minutes — the minute of the hour at which dst ends. The field range is 0-59. ■ month — the month of the year in which dst ends. The field range is 1-12. ■ day — the day of the month at which dst ends. The field range is 1-31. ■ year — the year in which dst ends. The field range is 2000-2037. ■ ...
Page 96
96 c hapter 5: m anaging s ystem i nformation saving the device configuration the save configuration page allows the latest device configuration to be saved to the flash memory. Monitor users have no access to this page. To save the device configuration: 1 click save configuration. The save configur...
Page 97
97 resetting the device the reset page enables resetting the device from a remote location. To prevent the current configuration from being lost, save the current device configuration before resetting the device. Monitor users have no access to this page. To reset the device configuration: 1 click a...
Page 98: Onfiguring
6 c onfiguring p orts this section contains information for configuring port settings, and includes the following sections: ■ viewing port settings ■ defining port settings ■ viewing port details.
Page 99
99 viewing port settings the port administration summary page permits the network manager to view the current ports configuration. When configuring the port speed and port duplex mode, please note the following: ■ setting the port speed to 10/100/1000 and the duplex mode to half = admin speed is = 1...
Page 100
100 c hapter 6: c onfiguring p orts to view port settings: 1 click port > administration > summary. The port administration summary page opens: figure 44 port administration summary page the port administration summary page contains the following fields: ■ port — indicates the selected port number. ...
Page 101
101 ■ 10m — indicates the port is currently operating at 10 mbps. ■ 100m — indicates the port is currently operating at 100 mbps. ■ 1000m — indicates the port is currently operating at 1000 mbps. ■ duplex mode — displays the port duplex mode. This field is configurable only when auto negotiation is ...
Page 102
102 c hapter 6: c onfiguring p orts defining port settings the port administration setup page allows network managers to configure port parameters for specific ports. Monitor users have no access to this page. To configure port settings: 1 click port > administration > setup. The port administration...
Page 103
103 ■ 10 — indicates the port is currently operating at 10 mbps. ■ 100 — indicates the port is currently operating at 100 mbps. ■ 1000 — indicates the port is currently operating at 1000 mbps. ■ auto — use to automatically configure the port. ■ no change — retains the current port speed. ■ duplex — ...
Page 104
104 c hapter 6: c onfiguring p orts viewing port details the port detail page displays the current port parameters for specific ports. Monitor users have no access to this page. To view port details: 1 click port > administration > detail. The port detail page opens: figure 46 port detail page the p...
Page 105
105 ■ speed — displays the configured rate for the port. The port type determines what speed setting options are available. Port speeds can only be configured when auto negotiation is disabled. The possible field values are: ■ 10 — indicates the port is currently operating at 10 mbps. ■ 100 — indica...
Page 106: Ggregating
7 a ggregating p orts this section contains information for configuring link aggregation, which optimizes port usage by linking a group of ports together to form a single lag. A link aggregation group (lag) aggregates ports or vlans into a single virtual port or vlan . Aggregating ports multiplies t...
Page 107
107 viewing link aggregation the link aggregation summary page displays port usage by linking a group of ports together to form a single lag. Aggregating ports multiplies the bandwidth between the devices, increases port flexibility, and provides link redundancy. To view link aggregation: 1 click po...
Page 108
108 c hapter 7: a ggregating p orts monitor users have no access to this page. To create link aggregation: 1 click ports > link aggregation > create.The link aggregation create page opens: figure 48 link aggregation create page the link aggregation create page includes the following fields: ■ enter ...
Page 109
109 summary ■ group id — displays the link aggregated group id. The field range is 1-4. ■ type — displays the type of link aggregation. The possible field values are static or lacp. ■ member ports — displays the ports configured to the link aggregation. 2 define the fields. 3 click . The link aggreg...
Page 110
110 c hapter 7: a ggregating p orts modifying link aggregation the link aggregation modify page optimizes port usage by linking a group of ports together to form a single lag. Aggregating ports multiplies the bandwidth between the devices, increases port flexibility, and provides link redundancy. Mo...
Page 111
111 deselected ports ■ white — not a member of any aggregation. ■ grey — displays a member of an existing aggregation or vlan. Summary ■ group id — displays the link aggregated group id. The field range is 1-4. ■ type — displays the link aggregation type. The possible field values are static or lacp...
Page 112
112 c hapter 7: a ggregating p orts removing link aggregation the link aggregation remove page allows the network manager to remove group ids containing member ports. Monitor users have no access to this page. To remove link aggregation: 1 click ports > link aggregation > remove.The link aggregation...
Page 113
113 viewing lacp lag ports can contain different media types if the ports are operating at the same speed. Aggregated links can be set up manually or automatically established by enabling lacp on the relevant links. Aggregate ports can be linked into link-aggregation port-groups. The lacp summary pa...
Page 114
114 c hapter 7: a ggregating p orts modifying lacp lag ports can contain different media types if the ports are operating at the same speed. Aggregated links can be set up manually or automatically established by enabling lacp on the relevant links. Aggregate ports can be linked into link-aggregatio...
Page 115
115 2 define the fields. 3 click . The lacp link aggregation is modified, and the application is updated..
Page 116: Onfiguring
8 c onfiguring vlan s vlans are logical subgroups with a local area network (lan) which combine user stations and network devices into a single unit, regardless of the physical lan segment to which they are attached. Vlans allow network traffic to flow more efficiently within subgroups. Vlans use so...
Page 117
117 viewing vlan details the vlan detail page provides information and global parameters on vlans configured on the system. To view vlan details: 1 click device > vlan > vlan detail. The vlan detail page opens: figure 53 vlan detail page the vlan detail page contains the following information: ■ sel...
Page 118
118 c hapter 8: c onfiguring vlan s viewing vlan port details the vlan port detail page provides information on vlan configured ports. To view vlan port details: 1 click device > vlan > port detail. The vlan port detail page opens: figure 54 vlan port detail page the vlan port detail page contains t...
Page 119
119 creating vlans the vlan setup page allows the network administrator to create or rename vlans. The monitor users have no access to this page. To create vlans: 1 click device > vlan > setup. The vlan setup page opens: figure 55 vlan setup page the vlan setup page contains the following fields: cr...
Page 120
120 c hapter 8: c onfiguring vlan s rename vlan ■ id — displays the vlan id selected from the above list. ■ name — defines the new vlan name. ■ rename — renames the user-defined vlan name. 2 enter the vlan id number(s). 3 click . The vlan(s) are created, and the device is updated. To rename a vlan: ...
Page 121
121 modifying vlan settings the modify vlan page allows the network manager to rename vlans and change vlan membership. The monitor users have no access to this page. To edit vlan settings: click device > vlan > modify vlan. The modify vlan page opens: figure 56 modify vlan page the modify vlan page...
Page 122
122 c hapter 8: c onfiguring vlan s ■ not a member — indicates the interface is not a member of the vlan. ■ not available for selection — indicates the interface is not available for selection. ■ select port to add to this vlan — adds a selected port to the vlan. ■ select all — allows the user to se...
Page 123
123 modifying port vlan settings the modify vlan port page allows the network manager to modify port vlan settings. The monitor users have no access to this page. To modify port vlan settings: 1 click device > vlan > modify port. The modify vlan port page opens: figure 57 modify vlan port page the m...
Page 124
124 c hapter 8: c onfiguring vlan s 2 select a port. 3 select the port’s membership type. 4 enter the vlan id to be assigned to the port. 5 click . The vlans are configured, and the device is updated. Removing vlans the vlan remove page allows the network administrator to remove vlans. The monitor u...
Page 125: Onfiguring
9 c onfiguring ip and mac a ddress i nformation this section contains information for defining ip interfaces, and includes the following sections: ■ defining ip addressing ■ configuring arp settings ■ configuring address tables.
Page 126
126 c hapter 9: c onfiguring ip and mac a ddress i nformation defining ip addressing the ip setup page contains fields for assigning an ip address. The default gateway is erased when the ip address is modified and changed. Packets are forwarded to the default gateway when sent to a remote network. T...
Page 127
Configuring arp settings 127 configuring arp settings the address resolution protocol (arp) converts ip addresses into physical addresses, and maps the ip address to a mac address. Arp allows a host to communicate with other hosts when only the ip address of its neighbors is known. This section incl...
Page 128
128 c hapter 9: c onfiguring ip and mac a ddress i nformation viewing arp settings the arp settings summary page displays the current arp settings. To view arp settings: 1 click administration > arp settings > summary. The arp settings summary page opens: figure 60 arp settings summary page the arp ...
Page 129
Configuring arp settings 129 defining arp settings the arp settings setup page allows network managers to define arp parameters for specific interfaces. The monitor users have no access to this page. To configure arp entries: 1 click administration > arp settings > setup. The arp settings setup page...
Page 130
130 c hapter 9: c onfiguring ip and mac a ddress i nformation removing arp entries thearp settings remove page provides parameters for removing arp entries from the arp table. The monitor user has no access to this page. To remove arp entries: 1 click administration > arp settings > remove. The arp ...
Page 131
Configuring arp settings 131 ■ mac address — displays the station mac address, which is associated in the arp table with the ip address. ■ status — displays the arp tableentry type. Possible field values are: ■ dynamic — indicates the arp entry is learned dynamically. ■ static — indicates the arp en...
Page 132
132 c hapter 9: c onfiguring ip and mac a ddress i nformation configuring address tables mac addresses are stored in either the static address or the dynamic address databases. A packet addressed to a destination stored in one of the databases is forwarded immediately to the port. The dynamic addres...
Page 133
Configuring address tables 133 viewing address table settings the address table summary page displays the current mac address table configuration. To view address table settings: 1 click monitoring > address table > summary. The address table summary page opens: figure 63 address table summary page ...
Page 134
134 c hapter 9: c onfiguring ip and mac a ddress i nformation ■ state — displays the mac address configuration method. Possible values are: ■ config static — indicates the mac address is statically configured. ■ config dynamic — indicates the mac address is dynamically configured. ■ port index — ind...
Page 135
Configuring address tables 135 ■ state — filters the list of mac addresses displayed according to the type of mac address configuration. Possible values are: ■ all — displays all mac addresses assigned to the port. ■ static — displays static mac addresses assigned to the port. ■ dynamic — displays d...
Page 136
136 c hapter 9: c onfiguring ip and mac a ddress i nformation adding mac addresses to the address table the address table add page allows the network manager to assign mac addresses to ports with vlans. The monitor users have no access to this page. To add mac addresses to the address table: 1 click...
Page 137
Configuring address tables 137 ■ mac address — displays the current mac addresses listed in the mac address table. ■ vlan id — displays the vlan id associated with the port and mac address. ■ state — displays the current mac address configuration method. Possible values are: ■ config static — indica...
Page 138
138 c hapter 9: c onfiguring ip and mac a ddress i nformation defining aging time the address table setup page allows the network manager to define the address table aging time. The aging time is the amount of time the mac addresses remain in the dynamic address table before they are timed out if no...
Page 139
Configuring address tables 139 removing address table ports the port remove page allows the network manager to remove ports from the address table. The monitor users have no access to this page. To remove ports: 1 click monitoring > address table > port remove. The port remove page opens: figure 67 ...
Page 140
140 c hapter 9: c onfiguring ip and mac a ddress i nformation ■ state — displays the mac address configuration method. Possible values are: ■ config static — indicates the mac address is statically configured. ■ port index — indicates the port through which the address was learned. ■ aging time — in...
Page 141
Configuring address tables 141 removing mac addresses from the address table the address table remove page allows the network manager to remove current mac addresses from the address table. The monitor users have no access to this page. To remove mac addresses from the address table: 1 click monitor...
Page 142
142 c hapter 9: c onfiguring ip and mac a ddress i nformation ■ port index — indicates the port through which the address was learned. ■ aging time — indicates the amount of time the mac address remains in the dynamic address table before it is timed out if no traffic from the source is detected. Th...
Page 143: Onfiguring
10 c onfiguring igmp s nooping this section contains information for configuring igmp snooping. When igmp snooping is enabled globally, all igmp packets are forwarded to the cpu. The cpu analyzes the incoming packets and determines: ■ which ports want to join which multicast groups. ■ which ports ha...
Page 144
144 c hapter 10: c onfiguring igmp s nooping defining igmp snooping the igmp snooping setup page allows network managers to define igmp snooping parameters for vlans. The monitor users have read-only access to this page. To configure igmp snooping: click device > igmp snooping > setup. The igmp snoo...
Page 145
145 ■ enable — enables igmp snooping on the vlan. ■ vlan — displays the vlan id. ■ status — displays the igmp snooping status for the vlan. The possible field values are enable and disable. To enable or disable igmp snooping on the device: 1 select enable or disable from the igmp snooping status lis...
Page 146: Onfiguring
11 c onfiguring s panning t ree this section contains information for configuring stp. The spanning tree protocol (stp) provides tree topography for any arrangement of bridges. Stp also provides a single path between end stations on a network, eliminating loops. Loops occur when alternate routes exi...
Page 147
147 viewing spanning tree the spanning tree summary page displays the current spanning tree parameters for all ports. To view spanning tree summary: 1 click device > spanning tree > summary.The spanning tree summary page opens: figure 70 spanning tree summary page the spanning tree summary page cont...
Page 148
148 c hapter 11: c onfiguring s panning t ree ■ root guard — indicates if the interface is acting as the root port of the switch. The possible field values are: ■ enable — indicates root guard is enabled on the port ■ disable — indicates root guard is disabled on the port. ■ port state — displays th...
Page 149
149 ■ path cost — indicates the port contribution to the root path cost. The path cost is adjusted to a higher or lower value, and is used to forward traffic when a path is re-routed. ■ priority — indicates the priority value of the port. The priority value influences the port choice when a bridge h...
Page 150
150 c hapter 11: c onfiguring s panning t ree defining spanning tree network administrators can assign stp settings to specific interfaces using the spanning tree setup page. The monitor user has no access to this page. To configure spanning tree setup: 1 click device > spanning tree > setup.The spa...
Page 151
151 ■ bpdu handling — determines how bpdu packets are managed when stp is disabled on the port or device. Bpdus are used to transmit spanning tree information. The possible field values are: ■ filtering — filters bpdu packets when spanning tree is disabled on an interface. This is the default value....
Page 152
152 c hapter 11: c onfiguring s panning t ree designated root ■ bridge id — identifies the bridge priority and mac address. ■ root bridge id — identifies the root bridge priority and mac address. ■ root port — indicates the port number that offers the lowest cost path from this bridge to the root br...
Page 153
153 modifying spanning tree thespanning tree modify page contains information for modifying spanning tree parameters. Monitor users have no access to this page. To modify spanning tree: 1 click device > spanning tree > modify.The spanning tree modify page opens: figure 72 spanning tree modify page t...
Page 154
154 c hapter 11: c onfiguring s panning t ree ■ enabled — indicates fast link is enabled on the port. ■ auto — enables the device to automatically establish a fast link. ■ disabled — indicates fast link is disabled on the port. ■ root guard — restricts the interface from acting as the root port of t...
Page 155: Onfiguring
12 c onfiguring snmp simple network management protocol (snmp) provides a method for managing network devices. The device supports the following snmp versions: ■ snmp version 1 ■ snmp version 2c snmp v1 and v2c the snmp agents maintain a list of variables, which are used to manage the device. The va...
Page 156
156 c hapter 12: c onfiguring snmp defining snmp communities access rights are managed by defining communities in the snmp communities setup page. When the community names are changed, access rights are also changed. Snmp communities are defined only for snmp v1 and snmp v2c. Monitor users have no a...
Page 157
157 ■ insert new community — enables adding an snmp community. Snmp management ■ management station— defines the management station ip address for which the snmp community is to be defined. ■ open access (0.0.0.0) — provides snmp access to all the stations. Community string ■ standard — selects pre-...
Page 158
158 c hapter 12: c onfiguring snmp removing snmp communities the snmp communities remove page allows the system manager to remove snmp communities. Monitor users have no access to this page. To remove snmp communities: 1 click administration > snmp > communities > remove. The snmp communities remove...
Page 159
159 ■ access mode — displays the access rights of the community. The possible field values are: ■ read only — management access is restricted to read-only, and changes cannot be made to the community. ■ read write — management access is read-write and changes can be made to the device configuration,...
Page 160
160 c hapter 12: c onfiguring snmp the snmp traps setup page contains the following fields: ■ recipients ip address — defines the ip address to which the traps are sent. ■ community string — defines the community string of the trap manager. ■ trap version — specifies the trap type. The possible fiel...
Page 161
161 the snmp traps remove page contains the following fields: ■ checkbox (unnamed) — when checked, selects an snmp trap for removal. The top checkbox is used to select all snmp traps for removal ■ recipients ip — displays the ip address to which the traps are sent. ■ trap — displays the trap type. T...
Page 162: Onfiguring
13 c onfiguring q uality of s ervice quality of service (qos) provides the ability to implement qos and priority queuing within a network. For example, certain types of traffic that require minimal delay, such as voice, video, and real-time traffic can be assigned a high priority queue, while other ...
Page 163
163 viewing cos settings the cos summary page displays cos default settings assigned to ports. To view cos settings: 1 click device > qos > cos > summary. The cos summary page opens: figure 77 cos summary page the cos summary page contains the following fields: ■ interface — displays the interface f...
Page 164
164 c hapter 13: c onfiguring q uality of s ervice defining cos the cos setup page contains information for enabling qos globally. Monitor users have no access to this page. To configure cos settings: 1 click device > qos > cos setup. The cos setup page opens: figure 78 cos setup page the cos setup ...
Page 165
165 viewing cos to queue the cos to queue summary page contains a table that displays the cos values mapped to traffic queues. To view cos values to queues: 1 click device > qos > cos to queue > summary. The cos to queue summary page opens: figure 79 cos to queue summary page the cos to queue summar...
Page 166
166 c hapter 13: c onfiguring q uality of s ervice to configure cos values to queues: 1 click device > qos > cos to queue > setup. The cos to queue setup page opens: figure 80 cos to queue setup page the cos to queue setup page contains the following fields: ■ restore defaults — restores the device ...
Page 167
167 viewing dscp to queue the dscp to queue summary page contains fields for mapping dscp settings to traffic queues. For example, a packet with a dscp tag value of 3 can be assigned to queue 4. To view the dscp queue: 1 click device > qos > dscp to queue > summary. The dscp to queue summary page op...
Page 168
168 c hapter 13: c onfiguring q uality of s ervice configuring dscp queue the dscp to queue setup page contains fields for mapping dscp settings to traffic queues. For example, a packet with a dscp tag value of 3 can be assigned to queue 1. The monitor user has no access to this page. To map cos to ...
Page 169
169 configuring trust settings the trust setup page contains information for enabling trust on the device. To enable trust: 1 click device > qos > trust > setup. The trust setup page opens: figure 83 trust setup page the trust setup page contains the following fields: ■ trust mode — specifies which ...
Page 170
170 c hapter 13: c onfiguring q uality of s ervice viewing bandwidth settings the bandwidth summary page displays bandwidth settings for a specified interface. To view bandwidth settings: 1 click device > qos > bandwidth > summary. The bandwidth summary page opens: figure 84 bandwidth summary page t...
Page 171
171 egress shaping rates ■ status — indicates the egress traffic shaping status for the interface. The possible field values are: ■ enable — egress traffic shaping is enabled for the interface. ■ disable — egress traffic shaping is disabled for the interface. This is the default. ■ cir— indicates th...
Page 172
172 c hapter 13: c onfiguring q uality of s ervice defining bandwidth settings the bandwidth setup page allows network managers to define the bandwidth settings for a specified interface. Interface shaping can be based on an interface. Shaping is determined by the lower specified value. The interfac...
Page 173
173 egress shaping rate ■ enable egress shaping rate— enables setting egress shaping rates. ■ committed information rate (cir)— defines the cir for the interface. The field range is 64-1,000,000,000 kbits per second. ■ committed burst size (cbs)— defines the cbs for the interface. The field range is...
Page 174
174 c hapter 13: c onfiguring q uality of s ervice defining voice vlan voice vlan allows network administrators to enhance voip service by configuring ports to carry ip voice traffic from ip phones on a specific vlan. Voip traffic has a preconfigured oui prefix in the source mac address. Network adm...
Page 175
Defining voice vlan 175 viewing voice vlans the voice vlan summary page contains information about the voice vlan currently enabled on the device, including the ports enabled and included in the voice vlan. To view voice vlan settings: 1 click device > qos > voip traffic setting > summary. The voice...
Page 176
176 c hapter 13: c onfiguring q uality of s ervice ■ ports in the voice vlan — displays the ports which are included in the voice vlan. The possible values are: ■ dynamic members — displays dynamic ports added to the voice vlan in auto mode. ■ static members — displays static ports that were manuall...
Page 177
Defining voice vlan 177 ■ voice vlan aging time — defines the amount of time after the last ip phone's oui is aged out for a specific port. The voice vlan aging time starts after the mac address is aged out from the dynamic mac address table. The port will age out after the bridge and voice aging ti...
Page 178
178 c hapter 13: c onfiguring q uality of s ervice the voice vlan port setup page contains the following fields: ■ voice vlan port mode — specifies the voice vlan mode. The possible field values are: ■ no changes — maintains the current voice vlan port/lag settings. This is the default value. ■ none...
Page 179
Defining voice vlan 179 viewing voice vlan port definitions the voice vlan port details page displays the voice vlan port settings for specific ports. The voice vlan port details page contains the following fields: ■ select port — selects specific ports to display their voice vlan port definitions. ...
Page 180
180 c hapter 13: c onfiguring q uality of s ervice to view voice vlan port detail settings: 1 click device > qos > voip traffic setting > port detail. The voice vlan port details page opens: figure 89 voice vlan port details page 2 select a port to view its settings. The port is highlighted blue, an...
Page 181
Defining voice vlan 181 to view voice vlan oui settings: 1 click device > qos > voip traffic setting > oui summary. The voice vlan oui summary page opens: figure 90 voice vlan oui summary page the voice vlan oui summary page contains the following fields: oui list ■ telephony oui(s) — lists the ouis...
Page 182
182 c hapter 13: c onfiguring q uality of s ervice modifying oui definitions the voice vlan oui modify page allows network administrators to add new ouis or to remove previously defined ouis from the voice vlan. The oui is the first half (three most significant bytes) of the mac address and is manuf...
Page 183
Defining voice vlan 183 2 enter an oui in the telephony oui field. 3 enter an oui description in the description field. 4 click to define a new oui, or click to delete an existing oui. The voice vlan table is modified, and the device is updated..
Page 184: Anaging
14 m anaging s ystem f iles the configuration file structure consists of the following configuration files: ■ startup configuration file — contains the commands required to reconfigure the device to the same settings as when the device is powered down or rebooted. The startup file is created by copy...
Page 185
185 this section contains information for defining file maintenance and includes both configuration file management as well as device access. This section contains the following topics: ■ backing up system files ■ restoring files ■ restore the software image ■ activating image files.
Page 186
186 c hapter 14: m anaging s ystem f iles backing up system files the backup page permits network managers to backup the system configuration to a tftp or http server. The monitor users have no access to this page. To backup system files: 1 click administration > backup & restore > backup. The backu...
Page 187
187 restoring files the restore page restores files from the tftp or http server. The monitor users have no access to this page. To restore system files: 1 click administration > backup & restore > restore. The restore page opens: figure 93 restore page the restore page contains the following fields...
Page 188
188 c hapter 14: m anaging s ystem f iles restore the software image the restore image page permits network managers to retrieve the device software. The monitor user has no access to this page to download the software image: 1 click administration > firmware upgrade > restore image. The restore ima...
Page 189
189 activating image files the active image page allows network managers to select and reset the image files. The device boot is downloaded onto the device through the cli. To upload system files: 1 click administration > firmware upgrade > active image. The active image page opens: figure 95 active...
Page 190: Anaging
15 m anaging p ower over e thernet d evices power over ethernet (poe) provides power to devices over existing lan cabling, without updating or modifying the network infrastructure. Power over ethernet removes the necessity of placing network devices next to power sources. Power over ethernet can be ...
Page 191
191 viewing poe settings the port poe summary page displays system poe information on the device and attached ports, monitoring the current power usage and operational status. To view poe settings: 1 click port > poe > summary. The port poe summary page opens: figure 96 port poe summary page the por...
Page 192
192 c hapter 15: m anaging p ower over e thernet d evices ■ power used(watts) — indicates the actual amount of power currently used by the device. The field value is displayed in watts. ■ power free(watts) — displays the amount of additional power currently available to the device. The field value i...
Page 193
193 defining poe settings the port poe setup page allows users to configure ports for poe. To configure port poe settings: 1 click port > poe > setup. The port poe setup page opens: figure 97 port poe setup page the port poe setup page contains the following fields: ■ select ports — selects the port...
Page 194
194 c hapter 15: m anaging p ower over e thernet d evices ■ selected ports — displays the poe configuration for the selected ports. The fields displayed are: ■ port — indicates the port number. ■ state — indicates if the port is enabled to deliver power to powered devices. The possible field values ...
Page 195: Anaging
16 m anaging s ystem l ogs this section provides information for managing system logs. The system logs enable viewing device events in real time, and recording the events for later usage. System logs record and manage events and report errors and informational messages. Event messages have a unique ...
Page 196
196 c hapter 16: m anaging s ystem l ogs viewing logs the logging display page contains all system logs in a chronological order that are saved in ram (cache). The monitor user has read-only access to this feature. To view logging: 1 click administration > logging > display. The logging display page...
Page 197
197 configuring logging the logging setup page contains fields for defining which events are recorded to which logs. It contains fields for enabling logs globally, and parameters for defining logs. Log messages are listed from the highest severity to the lowest severity level. The monitor users have...
Page 198
198 c hapter 16: m anaging s ystem l ogs the logging setup page contains the following fields: ■ enable local logging — specifies if device local logs for cache and servers are enabled. Console logs are enabled by default. ■ severity level — specifies the minimum severity level for which a message w...
Page 199
199 ■ enable syslogging — specifies if device syslogs for cache and servers are enabled. ■ severity level — specifies the minimum severity level for which a message will be logged. When a severity level is selected, all severity level choices above the selection are selected automatically. The possi...
Page 200: Iewing
17 v iewing s tatistics this section contains information for viewing port statistics, and contains the following topics: ■ viewing port statistics.
Page 201
201 viewing port statistics the port statistics summary page contains fields for viewing information about device utilization and errors that occurred on the device. To view rmon statistics: 1 click ports > statistics > summary. The port statistics summary page opens: figure 100 port statistics summ...
Page 202
202 c hapter 17: v iewing s tatistics ■ received bytes (octets) — displays the number of octets received on the interface since the device was last refreshed. This number includes bad packets and fcs octets, but excludes framing bits. ■ received packets — displays the number of packets received on t...
Page 203
203 ■ frames of 128 to 255 bytes — displays the number of 128 to 255 byte frames received on the interface since the device was last refreshed. ■ frames of 256 to 511 bytes — displays the number of 256 to 511 byte frames received on the interface since the device was last refreshed. ■ frames of 512 ...
Page 204: Anaging
18 m anaging d evice d iagnostics this section contains information for viewing and configuring port and cable diagnostics, and includes the following topics: ■ configuring port mirroring ■ viewing cable diagnostics.
Page 205
Configuring port mirroring 205 configuring port mirroring port mirroring monitors and mirrors network traffic by forwarding copies of incoming and outgoing packets from one port to a monitoring port. Port mirroring can be used as a diagnostic tool as well as a debugging feature. Port mirroring also ...
Page 206
206 c hapter 18: m anaging d evice d iagnostics defining port mirroring the port mirroring setup page contains parameters for configuring port mirroring. The monitor user has limited access to this page. To enable port mirroring: 1 click monitoring > port mirroring > setup. The port mirroring setup ...
Page 207
Configuring port mirroring 207 ■ select port— selects the port for mirroring or monitoring. A port unavailable for mirroring is colored grey. ■ summary — displays the current monitor and mirror ports. The fields displayed are: ■ monitor — displays the monitor port. ■ mirror in — displays ports that ...
Page 208
208 c hapter 18: m anaging d evice d iagnostics removing port mirroring the port mirroring remove page permits the network manager to terminate port mirroring or monitoring. The monitor users have no access to this page. To remove port mirroring: 1 click monitoring > port mirroring > remove. The por...
Page 209
Viewing cable diagnostics 209 viewing cable diagnostics the cable diagnostics summary page contains fields for viewing tests on copper cables. Cable testing provides information about where errors occurred in the cable, the last time a cable test was performed, and the type of cable error which occu...
Page 210
210 c hapter 18: m anaging d evice d iagnostics ■ cable fault distance — indicates the distance in meters from the port where the cable error occurred. ■ last update — indicates the last time the port was tested. Configuring cable diagnostics the diagnostics page contains fields for performing tests...
Page 211
Viewing cable diagnostics 211 to test cables: 1 click monitoring > cable diagnostics > diagnostics. The diagnostics page opens: figure 104 diagnostics page the diagnostics page contains the following fields: ■ select a port — selects the port to be tested. ■ test result — displays the cable test res...
Page 212: Etwork
A 3c om n etwork m anagement 3com has a range of network management applications to address networks of all sizes and complexity, from small and medium businesses through large enterprises. The applications include: ■ 3com network supervisor ■ 3com network director ■ 3com network access manager ■ 3c...
Page 213
3com network director 213 3com network director 3com network director (3nd) is a standalone application that allows you to carry out key management and administrative tasks on midsized networks. By using 3nd you can discover, map, and monitor all your 3com devices on the network. It simplifies tasks...
Page 214
214 a ppendix a: 3c om n etwork m anagement 3com enterprise management suite 3com enterprise management suite (ems) delivers comprehensive management that is flexible and scalable enough to meet the needs of the largest enterprises and advanced networks. This solution provides particularly powerful ...
Page 215: Evice
B d evice s pecifications and f eatures related standards the 3com ® officeconnect managed gigabit poe switch has been designed to the following standards: environmental physical function 8802-3, ieee 802.3 (ethernet), ieee 802.3u (fast ethernet), ieee 802.3ab (gigabit ethernet), ieee 802.1d (bridgi...
Page 216
216 a ppendix b: d evice s pecifications and f eatures electrical switch features this section describes the device features. The system supports the following features: line frequency 50/60 hz input voltage 100–240 vac (auto range) current rating 2 amp (max) maximum power consumption 358.4 btu/hr (...
Page 217
Switch features 217 command line interface the command line interface (cli) is an interface using a serial connection that allows basic features to be configured, including ip address management and firmware upgrading. The cli is not intended as the main interface for the switch. Configuration file ...
Page 218
218 a ppendix b: d evice s pecifications and f eatures lacp lacp uses peer exchanges across links to determine, on an ongoing basis, the aggregation capability of various links, and continuously provides the maximum level of aggregation capability achievable between a given pair of systems. Lacp aut...
Page 219
Switch features 219 power over ethernet provides power to devices over lan connection. Radius clients radius is a client/server-based protocol. A radius server maintains a user database, which contains per-user authentication information, such as user name, password and accounting information. Rapid...
Page 220
220 a ppendix b: d evice s pecifications and f eatures vlan support vlans are collections of switching ports that comprise a single broadcast domain. Packets are classified as belonging to a vlan based on either the vlan tag or based on a combination of the ingress port and packet contents. Packets ...
Page 221: Uts
C p in -o uts null modem cable rj-45 to rs-232 25-pin pc-at serial cable rj-45 to 9-pin screen txd rxd ground rts cts dsr dcd dtr screen rxd txd ground rts dtr cts dsr dcd shell 3 2 5 7 8 6 1 4 1 3 2 7 4 20 5 6 8 switch 5500 cable connector: rj-45 female pc/terminal cable connector: 25-pin male/fema...
Page 222
222 a ppendix c: p in -o uts modem cable rj-45 to rs-232 25-pin ethernet port rj-45 pin assignments 10/100 and 1000base-t rj-45 connections. Table 10 pin assignments screen txd rxd rts cts dsr ground dcd dtr screen txd rxd rts cts dsr ground dcd dtr shell 3 2 7 8 6 5 1 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 20 switch 55...
Page 223
Ethernet port rj-45 pin assignments 223 table 11 pin assignments pin number 10/100 1000 ports configured as mdix 1 receive data + bidirectional data b+ 2 receive data − bidirectional data b − 3 transmit data + bidirectional data a+ 4 not assigned bidirectional data a − 5 not assigned bidirectional d...
Page 224: Roubleshooting
D t roubleshooting this section describes problems that may arise when installing the and how to resolve these issue. This section includes the following topics: ■ problem management — provides information about problem management. ■ troubleshooting solutions — provides a list of troubleshooting iss...
Page 225
Troubleshooting solutions 225 problems possible cause solution cannot connect to management using rs-232 serial connection be sure the terminal emulator program is set to vt-100 compatible, 38400 baud rate, no parity, 8 data bits and one stop bit use the included cable, or be sure that the pin-out c...
Page 226
226 a ppendix d: t roubleshooting no connection and the port led is off incorrect ethernet cable, e.G., crossed rather than straight cable, or vice versa, split pair (incorrect twisting of pairs) fiber optical cable connection is reversed bad cable wrong cable type check pinout and replace if necess...
Page 227: Cli R
E 3c om cli r eference g uide this section describes using the command line interface (cli) to manage the device. The device is managed through the cli from a direct connection to the device console port getting started with the command line interface using the cli, network managers enter configurat...
Page 228
228 a ppendix e: 3c om cli r eference g uide 3 press enter. The password prompt displays: the login information is verified, and displays the following cli menu: if the password is invalid, the following message appears and login process restarts. Automatic logout the user session is automatically t...
Page 229
Cli commands 229 ? The ? Command displays a list of cli commands on the device. Syntax ? Default configuration this command has no default configuration. User guidelines there are no user guidelines for this command. Example the following displays the list presented for the ? Command: select menu op...
Page 231
Cli commands 231 summary the summary command displays the current ip configuration and software versions running on the device. It is intended for devices that support separate runtime and bootcode images. Syntax summary default configuration this command has no default configuration. User guideline...
Page 234
234 a ppendix e: 3c om cli r eference g uide initialize the initialize command resets the device configuration to factory defaults, including the ip configuration. Syntax initialize default configuration this command has no default configuration. User guidelines the system prompts for confirmation o...
Page 235
Cli commands 235 reboot the reboot command simulates a power cycle of the device. Syntax reboot default configuration this command has no default configuration. User guidelines there are no user guidelines for this command. Example select menu option: reboot are you sure you want to reboot the syste...
Page 236
236 a ppendix e: 3c om cli r eference g uide logout the logout command terminates the cli session. Syntax logout default configuration this command has no default configuration. User guidelines there are no user guidelines for this command. Example select menu option: logout exiting session... Usern...
Page 237
Cli commands 237 password the password command changes the user’s password. Syntax password default configuration this command has no default configuration. User guidelines the user needs to login to the session in order to change the password. Example select menu option: password change password fo...
Page 238: Lossary
F g lossary access control list (acl) acls can limit network traffic and restrict access to certain users or devices by checking each packet for certain ip or mac (i.E., layer 2) information. Address resolution protocol (arp) arp converts between ip addresses and mac (i.E., hardware) addresses. Arp ...
Page 239
239 extensible authentication protocol over lan (eapol) eapol is a client authentication protocol used by this switch to verify the network access rights for any device that is plugged into the switch. A user name and password is requested by the switch, and then passed to an authentication server (...
Page 240
240 a ppendix f: g lossary internet control message protocol (icmp) a network layer protocol that reports errors in processing ip packets. Icmp is also used by routers to feed back information about better routing choices. Internet group management protocol (igmp) a protocol through which hosts can ...
Page 241
241 multicast switching a process whereby the switch filters incoming multicast frames for services for which no attached host has registered, or forwards them to all ports contained within the designated multicast vlan group. Out-of-band management management of the network from a station not attac...
Page 242
242 a ppendix f: g lossary remote authentication dial-in user service (radius) radius is a logon authentication protocol that uses software running on a central server to control access to radius-compliant devices on the network. Remote monitoring (rmon) rmon provides comprehensive network monitorin...
Page 243
243 ip-like services. Udp packets are delivered just like ip packets – connection-less datagrams that may be discarded before reaching their targets. Udp is useful when tcp would be too complex, too slow, or just unnecessary. Virtual lan (vlan) a virtual lan is a collection of network nodes that sha...
Page 244: Btaining
G o btaining s upport for y our 3c om p roducts 3com offers product registration, case management, and repair services through esupport.3com.Com. You must have a user name and password to access these services, which are described in this appendix. Register your product to gain service benefits to t...
Page 245
Access software downloads 245 contact your authorized 3com reseller or 3com for additional product and support information. See the table of access numbers later in this appendix. Access software downloads you are entitled to bug fix / maintenance releases for the version of software that you initia...
Page 246
246 a ppendix g: o btaining s upport for y our 3c om p roducts to send a product directly to 3com for repair, you must first obtain a return materials authorization number (rma). Products sent to 3com without authorization numbers clearly marked on the outside of the package will be returned to the ...
Page 247
Contact us 247 you can also obtain support in this region using this url: http://emea.3com.Com/support/email.Html you can also obtain non-urgent support in this region at these email addresses: technical support and general requests: customer_support@3com.Com return material authorization: warranty_...
Page 248
R egulatory n otices fcc s tatement this equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a class a digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the fcc rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a comme...