- DL manuals
- 3Com
- Switch
- 4210 PWR
- Configuration Manual
3Com 4210 PWR Configuration Manual
Summary of 4210 PWR
Page 1
3com ® switch 4210 family configuration guide switch 4210 pwr 9-port switch 4210 pwr 18-port switch 4210 pwr 26-port switch 4210 9-port switch 4210 18-port switch 4210 26-port www.3com.Com part number: 10016117 rev. Aa published: august, 2007.
Page 2
3com corporation 350 campus drive marlborough, ma usa 01752-3064 copyright © 2006-2007, 3com corporation. All rights reserved. No part of this documentation may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to make any derivative work (such as translation, transformation, or adaptation) without ...
Page 3: Ontents
C ontents a bout t his g uide conventions 9 related documentation 10 1 cli c onfiguration introduction to the cli 11 command hierarchy 11 cli views 14 cli features 16 2 l ogging into an e thernet s witch supported user interfaces 21 logging in through the console port 23 logging in through telnet 37...
Page 4
7 ip a ddressing c onfiguration ip addressing overview 87 configuring ip addresses 89 displaying ip addressing configuration 90 ip address configuration examples 90 8 ip p erformance c onfiguration ip performance overview 91 configuring ip performance 91 displaying and maintaining ip performance con...
Page 5
Configuration example 137 14 mstp c onfiguration stp overview 139 mstp overview 147 configuring root bridge 153 configuring leaf nodes 167 performing mcheck operation 172 configuring guard functions 173 configuring digest snooping 177 configuring rapid transition 178 stp maintenance configuration 18...
Page 6
19 s ystem -g uard c onfiguration system-guard configuration 235 displaying and maintaining the system-guard function 236 20 aaa o verview introduction to aaa 237 introduction to aaa services 238 21 aaa c onfiguration aaa configuration task list 245 radius configuration task list 251 displaying and ...
Page 7
Configuring a dhcp/bootp client 287 displaying dhcp/bootp client configuration 288 dhcp client configuration example 288 27 acl c onfiguration acl overview 291 acl configuration 293 example for upper-layer software referencing acls 297 28 q o s c onfiguration overview 299 qos supported by switch 421...
Page 8
34 rmon c onfiguration introduction to rmon 361 rmon configuration 363 displaying rmon 364 rmon configuration examples 364 35 ntp c onfiguration introduction to ntp 367 ntp configuration tasks 371 configuring ntp implementation modes 372 configuring access control right 375 configuring ntp authentic...
Page 9
41 b oot rom and h ost s oftware l oading introduction to loading approaches 469 local boot rom and software loading 469 remote boot rom and software loading 478 42 b asic s ystem c onfiguration and d ebugging basic system configuration 483 displaying the system status 484 debugging the system 484 4...
Page 10
Password control configuration 556 displaying password control 563 password control configuration example 564.
Page 11: Bout
A bout t his g uide this guide describes the 3com ® switch 4210 and how to install hardware, configure and boot software, and maintain software and hardware. This guide also provides troubleshooting and support information for your switch. This guide is intended for qualified service personnel who a...
Page 12
10 a bout t his g uide related documentation the following manuals offer additional information necessary for managing your switch 4210: ■ switch 4210 command reference guide — provides detailed descriptions of command line interface (cli) commands, that you require to manage your switch 4210. ■ swi...
Page 13: Cli C
1 cli c onfiguration introduction to the cli a command line interface (cli) is a user interface to interact with a switch. Through the cli on a switch, you can enter commands to configure the switch and check output information to verify the configuration. Each switch 4210 provides an easy-to-use cl...
Page 14
12 c hapter 1: cli c onfiguration support for services. Commands concerning file system, ftp/tftp/xmodem downloading, user management, and level setting are at this level. By default, the console user (a user who logs into the switch through the console port) is a level-3 user and telnet users are l...
Page 15
Command hierarchy 13 super 3 password: user privilege level is 3, and only those commands can be used whose level is equal or less than this. Privilege note: 0-visit, 1-monitor, 2-system, 3-manage # after configuring the switch, the general user switches back to user level 0. Super 0 user privilege ...
Page 16
14 c hapter 1: cli c onfiguration this allows general telnet users to use the tftp get command to download file bootrom.Btm and other files from tftp server 192.168.0.1 and other tftp servers. Cli views cli views are designed for different configuration tasks. When you first log into the switch, you...
Page 17
Cli views 15 ethernet port view configure ethernet port parameters 100 mbps ethernet port view: [4210-ethernet1/0/1] execute the interface ethernet command in system view. Execute the quit command to return to system view. Execute the return command to return to user view. 1000 mbps ethernet port vi...
Page 18
16 c hapter 1: cli c onfiguration n the shortcut key is equivalent to the return command. Cli features online help when configuring the switch, you can use the online help to get related help information. The cli provides two types of online help: complete and partial. Complete online help 1 enter a...
Page 19
Cli features 17 clock ? Datetime specify the time and date summer-time configure summer time timezone configure time zone if the question mark “?” is at an argument position in the command, the description of the argument displays: [4210] interface vlan-interface ? Vlan interface number if only is d...
Page 20
18 c hapter 1: cli c onfiguration commands and execute them again. By default, the cli stores up to 10 most recently executed commands for each user. You can view the command history by performing the operations listed in table 6. N ■ the windows 9x hyperterminal defines the up and down arrow keys i...
Page 21
Cli features 19 right arrow key or move the cursor one character to the right. Up arrow key or down arrow key or display history commands. Use the partial online help. That is, when you input an incomplete keyword and press , if the input parameter uniquely identifies a complete keyword, the system ...
Page 22
20 c hapter 1: cli c onfiguration.
Page 23: Ogging
2 l ogging into an e thernet s witch you can log into a switch 4210 in one of the following ways: ■ logging in locally through the console port ■ logging in locally or remotely through an ethernet port by means of telnet or ssh ■ using telnet to access the console port using a modem ■ logging into t...
Page 24
22 c hapter 2: l ogging into an e thernet s witch 2 a relative user interface index can be obtained by appending a number to the identifier of a user interface type. It is generated by user interface type. The relative user interface indexes are as follows: ■ aux user interface is numbered 0. ■ vty ...
Page 25
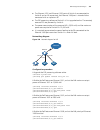
Logging in through the console port 23 logging in through the console port logging in through the console port is the most common way to log into a switch. If you do not know the ip address of the switch, it is the only way to log-in to the switch.It is also the prerequisite to configure other login...
Page 26
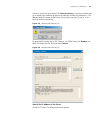
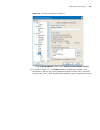
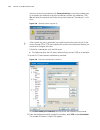
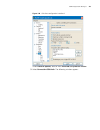
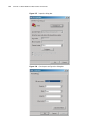
24 c hapter 2: l ogging into an e thernet s witch figure 2 create a connection figure 3 specify the port used to establish the connection.
Page 27
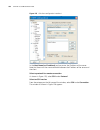
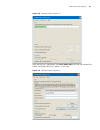
Logging in through the console port 25 figure 4 set port parameters 3 plug in the switch so it has power. You will be prompted to press the enter key if the switch successfully completes post (power-on self test). The prompt (such as ) appears after you press the enter key, as shown in figure 5. Fig...
Page 28
26 c hapter 2: l ogging into an e thernet s witch common configurations table 12 lists the common configurations of console port login. C caution: the change to console port configuration takes effect immediately, so the connection may be disconnected when you log in through a console port and then ...
Page 29
Logging in through the console port 27 n changes made to the authentication mode for console port login takes effect after you quit the command-line interface and then log in again. Configuring console port login with no authentication password configure the password configure the password for local...
Page 31
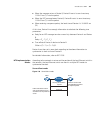
Logging in through the console port 29 configuration example network requirements assume that the switch is configured to allow users to log in through telnet, and the user level is set to the administrator level (level 3). Perform the following configurations for users logging in through the consol...
Page 32
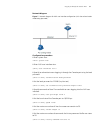
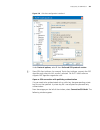
30 c hapter 2: l ogging into an e thernet s witch network diagram figure 6 network diagram for aux user interface configuration (with the authentication mode being none) configuration procedure # enter system view. System-view # enter aux user interface view. [4210] user-interface aux 0 # specify no...
Page 33
Logging in through the console port 31 [4210-ui-aux0] idle-timeout 6 after the above configuration, you need to modify the configuration of the terminal emulation utility running on the pc accordingly in the dialog box shown in figure 4 to log into the switch successfully. Configuring console port l...
Page 34
32 c hapter 2: l ogging into an e thernet s witch configuration example network requirements assume the switch is configured to allow users to log in through telnet, and the user level is set to the administrator level (level 3). Perform the following configurations for users logging in through the ...
Page 35
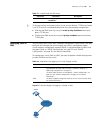
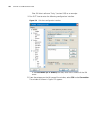
Logging in through the console port 33 network diagram figure 7 network diagram for aux user interface configuration (with the authentication mode being password) configuration procedure # enter system view. System-view # enter aux user interface view. [4210] user-interface aux 0 # specify to authen...
Page 36
34 c hapter 2: l ogging into an e thernet s witch # set the timeout time of the aux user interface to 6 minutes. [4210-ui-aux0] idle-timeout 6 after the above configuration, you need to modify the configuration of the terminal emulation utility running on the pc accordingly in the dialog box shown i...
Page 37
Logging in through the console port 35 note that if you configure to authenticate the users in the scheme mode, the command level available to users logging into a switch depends on the command level specified in the service-type terminal [ level level ] command. Configure the console port set the b...
Page 38
36 c hapter 2: l ogging into an e thernet s witch configuration example network requirements assume the switch is configured to allow users to log in through telnet, and the user level is set to the administrator level (level 3). Perform the following configurations for users logging in through the ...
Page 39
Logging in through telnet 37 [4210-luser-guest] service-type terminal level 2 [4210-luser-guest] quit # enter aux user interface view. [4210] user-interface aux 0 # configure to authenticate users logging in through the console port in the scheme mode. [4210-ui-aux0] authentication-mode scheme # set...
Page 40
38 c hapter 2: l ogging into an e thernet s witch n telnetting to a switch using ipv6 protocols is similar to telnetting to a switch using ipv4 protocols. Refer to “ipv6 mangement configuration” on page 525 for related information. Common configuration table 18 lists the common telnet configuration....
Page 41
Logging in through telnet 39 n to improve security and prevent attacks to the unused sockets, tcp 23 and tcp 22, ports for telnet and ssh services respectively, will be enabled or disabled after corresponding configurations. ■ if the authentication mode is none, tcp 23 will be enabled, and tcp 22 wi...
Page 42
40 c hapter 2: l ogging into an e thernet s witch note that if you configure not to authenticate the users, the command level available to users logging into a switch depends on the user privilege level level command configuration example network requirements assume current user logins through the c...
Page 43
Logging in through telnet 41 ■ telnet protocol is supported. ■ the screen can contain up to 30 lines. ■ the history command buffer can contain up to 20 commands. ■ the timeout time of vty 0 is 6 minutes. Network diagram figure 9 network diagram for telnet configuration (with the authentication mode ...
Page 44
42 c hapter 2: l ogging into an e thernet s witch telnet configuration with authentication requiring a password configuration procedure table 21 telnet configuration with the authentication mode being password operation command description enter system view system-view - enter one or more vty user i...
Page 45
Logging in through telnet 43 when the authentication mode is password, the command level available to users logging into the user interface is determined by the user privilege level command. Configuration example network requirements the current user logs in through the console port and the user lev...
Page 46
44 c hapter 2: l ogging into an e thernet s witch # enter vty 0 user interface view. [4210] user-interface vty 0 # configure to authenticate users logging into vty 0 using the password. [4210-ui-vty0] authentication-mode password # set the local password to 123456 (in plain text). [4210-ui-vty0] set...
Page 47
Telnet configuration with authentication mode being scheme 45 configure the authenticati on scheme enter the default isp domain view domain domain-name optional by default, the local aaa scheme is applied. If you specify to apply the local aaa scheme, you need to perform the configuration concerning...
Page 49
Telnet configuration with authentication mode being scheme 47 n refer to “aaa configuration” on page 245 and “ssh configuration” on page 387 for information about aaa, radius, and ssh. Table 23 determine the command level when users logging into switches are authenticated in the scheme mode scenario...
Page 50
48 c hapter 2: l ogging into an e thernet s witch configuration example network requirements assume current user logins through the console port and the user level is set to the administrator level (level 3). Perform the following configurations for users logging into vty 0 using telnet. ■ configure...
Page 51
Telnet configuration with authentication mode being scheme 49 # configure telnet protocol is supported. [4210-ui-vty0] protocol inbound telnet # set the maximum number of lines the screen can contain to 30. [4210-ui-vty0] screen-length 30 # set the maximum number of commands the history command buff...
Page 52
50 c hapter 2: l ogging into an e thernet s witch figure 13 the terminal window ■ perform the following operations in the terminal window to assign ip address 202.38.160.92/24 to vlan-interface 1 of the switch. System-view [4210] interface vlan-interface 1 [4210-vlan-interface1] ip address 202.38.16...
Page 53
Telnet configuration with authentication mode being scheme 51 figure 15 launch telnet 5 if the password authentication mode is specified, enter the password when the telnet window displays "login authentication" and prompts for login password. The cli prompt (such as ) appears if the password is cor...
Page 54
52 c hapter 2: l ogging into an e thernet s witch note that xxxx is the ip address or the host name of the switch operating as the telnet server. You can use the ip host to assign a host name to a switch. 4 after successful login, the cli prompt (such as ) appears. If all the vty user interfaces of ...
Page 55
Logging in using a modem 53 switch configuration n after logging into a switch through its console port by using a modem, you will enter the aux user interface. The corresponding configuration on the switch is the same as those when logging into the switch locally through its console port except tha...
Page 56
54 c hapter 2: l ogging into an e thernet s witch figure 17 establish the connection by using modems 4 launch a terminal emulation utility on the pc and set the telephone number to call the modem directly connected to the switch, as shown in figure 18 through figure 20. Note that you need to set the...
Page 57
Logging in using a modem 55 figure 19 set the telephone number figure 20 call the modem 5 if the password authentication mode is specified, enter the password when prompted. If the password is correct, the prompt (such as ) appears. You can then configure or manage the switch. You can also enter the...
Page 58
56 c hapter 2: l ogging into an e thernet s witch logging in through the web-based network management system a switch 4210 has a web server built in. It enables you to log into a switch 4210 through a web browser and then manage and maintain the switch intuitively by interacting with the built-in we...
Page 59
Logging in through the web-based network management system 57 figure 21 establish an http connection between your pc and the switch 4 log into the switch through ie. Launch ie on the web-based network management terminal (your pc) and enter the ip address of the management vlan interface of the swit...
Page 60
58 c hapter 2: l ogging into an e thernet s witch network diagram figure 23 network diagram for login banner configuration configuration procedure # enter system view. System-view # configure the banner "welcome" to be displayed when a user logs into the switch through web. [4210] header login %welc...
Page 61
Managing from an nms 59 n to improve security and prevent attack to the unused sockets, tcp 80 port (which is for http service) is enabled/disabled after the corresponding configuration. ■ enabling the web server (by using the undo ip http shutdown command) opens tcp 80 port. ■ disabling the web ser...
Page 62
60 c hapter 2: l ogging into an e thernet s witch user control n refer to“password control configuration operations” on page 555 for information about the acl. A switch provides ways to control different types of login users, as listed in table 29. Controlling telnet users prerequisites the controll...
Page 63
User control 61 controlling telnet users by source and destination ip addresses controlling telnet users by source and destination ip addresses is achieved by applying advanced acls, which are numbered from 3000 to 3999. Controlling telnet users by source mac addresses controlling telnet users by so...
Page 64
62 c hapter 2: l ogging into an e thernet s witch configuration example network requirements only the telnet users sourced from the ip address of 10.110.100.52 are permitted to access the switch. Network diagram figure 26 network diagram for controlling telnet users using acls configuration procedur...
Page 65
User control 63 prerequisites the controlling policy against network management users is determined, including the source ip addresses to be controlled and the controlling actions (permitting or denying). Controlling network management users by source ip addresses controlling network management user...
Page 66
64 c hapter 2: l ogging into an e thernet s witch acls in the commands, the network management users are filtered by the snmp group name and snmp user name. Configuration example network requirements only snmp users sourced from the ip addresses of 10.110.100.52 are permitted to log into the switch....
Page 67
User control 65 disconnecting a web user by force the administrator can disconnect a web user by force using the related commands. Configuration example network requirements only the web users sourced from the ip address of 10.110.100.52 are permitted to access the switch. Network diagram figure 28 ...
Page 68
66 c hapter 2: l ogging into an e thernet s witch # apply acl 2030 to only permit the web users sourced from the ip address of 10.110.100.52 to access the switch. [4210] ip http acl 2030
Page 69: Onfiguration
3 c onfiguration f ile m anagement introduction to configuration file a configuration file records and stores the user settings for a switch. It also enables users to check switch configurations easily. Types of configuration the configuration of a device falls into two types: ■ saved configuration,...
Page 70
68 c hapter 3: c onfiguration f ile m anagement the following three situations are concerned with the main/backup attributes: ■ when saving the current configuration, you can specify the file to be a main or backup or normal configuration file. ■ when removing a configuration file from a device, you...
Page 71
Management of configuration file 69 configuration file in the device even if the device reboots or the power fails during the process. C caution: the configuration file to be used for next startup may be lost if the device reboots or the power fails during the configuration file saving process. In t...
Page 72
70 c hapter 3: c onfiguration f ile m anagement ■ while the reset saved-configuration [ main ] command erases the configuration file with main attribute, it only erases the main attribute of a configuration file having both main and backup attribute. ■ while the reset saved-configuration backup comm...
Page 73
Management of configuration file 71 table 40 display device configuration operation command description display the initial configuration file saved in the storage device display saved-configuration [ unit unit-id ] [ by-linenum ] you can execute the display command in any view. Display the configur...
Page 74
72 c hapter 3: c onfiguration f ile m anagement.
Page 75: Vlan O
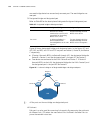
4 vlan o verview vlan overview introduction to vlan the traditional ethernet is a broadcast network, where all hosts are in the same broadcast domain and connected with each other through hubs or switches. Hubs and switches, which are the basic network connection devices, have limited forwarding fun...
Page 76
74 c hapter 4: vlan o verview figure 29 a vlan implementation advantages of vlans compared with the traditional ethernet, vlan enjoys the following advantages. ■ broadcasts are confined to vlans. This decreases bandwidth consumption and improves network performance. ■ network security is improved. B...
Page 77
Vlan overview 75 in figure 30 da refers to the destination mac address, sa refers to the source mac address, and type refers to the upper layer protocol type of the packet. Ieee 802.1q protocol defines that a 4-byte vlan tag is encapsulated after the destination mac address and source mac address to...
Page 78
76 c hapter 4: vlan o verview currently, the 3com switch 4210 family adopts the ivl mode only. For more information about the mac address forwarding table, refer to “mac address table management” on page 131. Vlan classification depending on how vlans are established, vlans fall into the following s...
Page 79: Vlan C
5 vlan c onfiguration vlan configuration vlan configuration tasks basic vlan configuration c caution: ■ vlan 1 is the system default vlan, which needs not to be created and cannot be removed, either. Table 41 vlan configuration tasks configuration tasks description related section basic vlan configu...
Page 80
78 c hapter 5: vlan c onfiguration basic vlan interface configuration configuration prerequisites before configuring a vlan interface, create the corresponding vlan. Configuration procedure n ■ the operation of enabling/disabling a vlan’s vlan interface does not influence the physical status of the ...
Page 81
Configuring a port-based vlan 79 configuring a port-based vlan configuring a port-based vlan configuration prerequisites create a vlan before configuring a port-based vlan. Configuration procedure c caution: the commands above are effective for access ports only. If you want to add trunk ports or hy...
Page 82
80 c hapter 5: vlan c onfiguration configuration procedure ■ configure switch a. # create vlan 101, specify its descriptive string as "dmz", and add ethernet1/0/1 to vlan 101. System-view [switcha] vlan 101 [switcha-vlan101] description dmz [switcha-vlan101] port ethernet 1/0/1 [switcha-vlan101] qui...
Page 83
Configuring a port-based vlan 81 n for the command of configuring a port link type (port link-type) and the command of allowing packets of certain vlans to pass through a port (port trunk permit), refer to “ethernet port configuration” on page 96 ..
Page 84
82 c hapter 5: vlan c onfiguration.
Page 85: Anaging
6 m anaging the vlan vlan overview to manage an ethernet switch remotely through telnet or the built-in web server, the switch need to be assigned an ip address, and make sure that a route exists between the user and the switch. For the switch 4210, only the management vlan interface can be assigned...
Page 86
84 c hapter 6: m anaging the vlan configuring vlan management before configuring the management vlan, make sure the vlan operating as the management vlan exists. If vlan 1 (the default vlan) is the management vlan, just go ahead. Overviw c caution: to create the vlan interface for the management vla...
Page 87
Configuring vlan management 85 network diagram figure 33 network diagram for management vlan configuration configuration procedure n perform the following configurations after the current user logs in to switch a through the console port. # enter system view. System-view # create vlan 10 and configu...
Page 88
86 c hapter 6: m anaging the vlan displaying and maintaining management vlan configuration table 1-2 displaying and maintaining management vlan configuration table 47 operation command remarks display the ip-related information about a management vlan interface display ip interface [ vlan-interface ...
Page 89: Ip A
7 ip a ddressing c onfiguration ip addressing overview ip address classes ip addressing uses a 32-bit address to identify each host on a network. An example is 01010000100000001000000010000000 in binary. To make ip addresses in 32-bit form easier to read, they are written in dotted decimal notation,...
Page 90
88 c hapter 7: ip a ddressing c onfiguration special case ip addresses the following ip addresses are for special use, and they cannot be used as host ip addresses: ■ ip address with an all-zeros net id: identifies a host on the local network. For example, ip address 0.0.0.16 indicates the host with...
Page 91
Configuring ip addresses 89 while allowing you to create multiple logical networks within a single class a, b, or c network, subnetting is transparent to the rest of the internet. All these networks still appear as one. As subnetting adds an additional level, subnet id, to the two-level hierarchy wi...
Page 92
90 c hapter 7: ip a ddressing c onfiguration displaying ip addressing configuration after the above configuration, you can execute the display command in any view to display the operating status and configuration on the interface to verify your configuration. Ip address configuration examples ip add...
Page 93: Ip P
8 ip p erformance c onfiguration ip performance overview introduction to ip performance configuration in some network environments, you need to adjust the ip parameters to achieve best network performance. The ip performance configuration supported by switch 4210 family includes: ■ configuring tcp a...
Page 94
92 c hapter 8: ip p erformance c onfiguration the system restarts the timer from receiving the last non-fin packet. The connection is broken after the timer expires. ■ size of tcp receive/send buffer disabling icmp to send error packets sending error packets is a major function of icmp protocol. In ...
Page 95
Displaying and maintaining ip performance configuration 93 displaying and maintaining ip performance configuration after the above configurations, you can execute the display command in any view to display the running status to verify your ip performance configuration. Use the reset command in user ...
Page 96
94 c hapter 8: ip p erformance c onfiguration.
Page 97: Ort
9 p ort b asic c onfiguration ethernet port overview link types of ethernet ports an ethernet port on an switch 4210 can be of the following three link types. ■ access. An access port can belong to only one vlan. It is used to provide network access for terminal users. ■ trunk: a trunk port can belo...
Page 98
96 c hapter 9: p ort b asic c onfiguration c caution: you are recommended to set the default vlan id of the local hybrid or trunk ports to the same value as that of the hybrid or trunk ports on the peer switch. Otherwise, packet forwarding may fail on the ports. Adding an ethernet port to specified ...
Page 99
Ethernet port configuration 97 configuring port auto-negotiation speed you can configure an auto-negotiation speed for a port by using the speed auto command. Take a 10/100/1000 mbps port as an example. ■ if you expect that 10 mbps is the only available auto-negotiation speed of the port, you just n...
Page 100
98 c hapter 9: p ort b asic c onfiguration n ■ only ports on the front panel of the device support the auto-negotiation speed configuration feature. And ports on the extended interface card do not support this feature currently. ■ after you configure auto-negotiation speed(s) for a port, if you exec...
Page 101
Ethernet port configuration 99 ■ the local switch sends a message to notify the peer switch of stopping sending packets to itself or reducing the sending rate temporarily. ■ the peer switch will stop sending packets to the local switch or reduce the sending rate temporarily when it receives the mess...
Page 102
100 c hapter 9: p ort b asic c onfiguration configuring a trunk port duplicating the configuration of a port to other ports to make other ports have the same configuration as that of a specific port, you can duplicate the configuration of a port to specific ports. Specifically, the following types o...
Page 103
Ethernet port configuration 101 ■ if loopback is found on an access port, the system disables the port, sends a trap message to the client and removes the corresponding mac forwarding entry. ■ if loopback is found on a trunk or hybrid port, the system sends a trap message to the client. When the loo...
Page 104
102 c hapter 9: p ort b asic c onfiguration n ■ external: performs external loop test. In the external loop test, self-loop headers must be used on the port of the switch ( for 100m port, the self-loop headers are made from four cores of the 8-core cables, for 1000m port, the self-loop header are ma...
Page 105
Disabling up/down log output on a port 103 disabling up/down log output on a port an ethernet port has two physical link statuses: up and down. When the physical link status of an ethernet port changes, the switch will send log to the log server, which in turn acts accordingly. If the status of ethe...
Page 106
104 c hapter 9: p ort b asic c onfiguration # after you disable ethernet 1/0/1 from outputting up/down log information and execute the shutdown command or the undo shutdown command on ethernet 1/0/1, no up/down log information is output for ethernet 1/0/1. [4210-ethernet1/0/1] undo enable log updown...
Page 107
Troubleshooting ethernet port configuration 105 configuration procedure n ■ only the configuration for switch a is listed below. The configuration for switch b is similar to that of switch a. ■ this example supposes that vlan 2, vlan 6 through vlan 50 and vlan 100 have been created. # enter ethernet...
Page 108
106 c hapter 9: p ort b asic c onfiguration.
Page 109: Ink
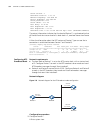
10 l ink a ggregation c onfiguration overview introduction to link aggregation link aggregation can aggregate multiple ethernet ports together to form a logical aggregation group. To upper layer entities, all the physical links in an aggregation group are a single logical link. Link aggregation is d...
Page 110
108 c hapter 10: l ink a ggregation c onfiguration link aggregation classification depending on different aggregation modes, the following three types of link aggregation exist: ■ manual aggregation ■ static lacp aggregation ■ dynamic lacp aggregation manual aggregation group introduction to manual ...
Page 111
Link aggregation classification 109 must contain at least one port. When a static aggregation group contains only one port, you cannot remove the port unless you remove the whole aggregation group. Lacp is enabled on the member ports of static aggregation groups. When you remove a static aggregation...
Page 112
110 c hapter 10: l ink a ggregation c onfiguration port status of dynamic aggregation group a port in a dynamic aggregation group can be in one of the two states: selected and unselected. ■ both the selected and the unselected ports can receive/transmit lacp protocol packets; ■ the selected ports ca...
Page 113
Link aggregation configuration 111 load-sharing aggregation resources are allocated to aggregation groups in the following order: ■ an aggregation group containing special ports which require hardware aggregation resources has higher priority than any aggregation group containing no special port. ■ ...
Page 114
112 c hapter 10: l ink a ggregation c onfiguration configuring a manual aggregation group you can create a manual aggregation group, or remove an existing manual aggregation group (after that, all the member ports will be removed from the group). For a manual aggregation group, a port can only be ma...
Page 115
Link aggregation configuration 113 n for a static lacp aggregation group or a manual aggregation group, you are recommended not to cross cables between the two devices at the two ends of the aggregation group. For example, suppose port 1 of the local device is connected to port 2 of the peer device....
Page 116
114 c hapter 10: l ink a ggregation c onfiguration c caution: if you have saved the current configuration with the save command, after system reboot, the configuration concerning manual and static aggregation groups and their descriptions still exists, but that of dynamic aggregation groups and thei...
Page 117
Link aggregation configuration example 115 network diagram figure 38 network diagram for link aggregation configuration configuration procedure n the following example only lists the configuration required on switch a; you must perform the same configuration proceedure on switch b to implement link ...
Page 118
116 c hapter 10: l ink a ggregation c onfiguration [4210-ethernet1/0/3] port link-aggregation group 1 3 adopting dynamic lacp aggregation mode # enable lacp on ethernet1/0/1 through ethernet1/0/3. System-view [4210] interface ethernet1/0/1 [4210-ethernet1/0/1] lacp enable [4210-ethernet1/0/1] quit [...
Page 119: Ort
11 p ort i solation c onfiguration port isolation overview through the port isolation feature, you can add the ports to be controlled into an isolation group to isolate the layer 2 and layer 3 data between each port in the isolation group. Thus, you can construct your network in a more flexible way ...
Page 120
118 c hapter 11: p ort i solation c onfiguration displaying port isolation configuration after the above configuration, you can execute the display command in any view to display the result of your port isolation configuration, thus verifying your configuration. Port isolation configuration example ...
Page 121
Port isolation configuration example 119 [4210] interface ethernet1/0/4 [4210-ethernet1/0/4] port isolate [4210-ethernet1/0/4] quit [4210] quit # display information about the ports in the isolation group. Display isolate port isolated port(s) on unit 1: ethernet1/0/2, ethernet1/0/3, ethernet1/0/4.
Page 122
120 c hapter 11: p ort i solation c onfiguration.
Page 123: Ort
12 p ort s ecurity c onfiguration port security overview introduction port security is a security mechanism for network access control. It brings together both 802.1x access control and mac address authentication and allows for combinations of these technologies. Port security allows you to define v...
Page 124
122 c hapter 12: p ort s ecurity c onfiguration table 77 description of port security modes security mode description feature norestriction in this mode, access to the port is not restricted. In this mode, neither the ntk nor the intrusion protection feature is triggered. Autolearn in this mode, the...
Page 125
Port security overview 123 userloginsecure mac-based 802.1x authentication is performed on the access user. The port is enabled only after the authentication succeeds. When the port is enabled, only the packets of the successfully authenticated user can pass through the port. In this mode, only one ...
Page 126
124 c hapter 12: p ort s ecurity c onfiguration n ■ when the port operates in the userlogin-withoui mode, intrusion protection will not be triggered even if the oui address does not match. ■ in the macaddresselseuserloginsecure or macaddresselseuserloginsecureext security mode, the mac address of a ...
Page 127
Port security configuration 125 enabling port security before enabling port security, you need to disable 802.1x and mac authentication globally. C caution: enabling port security resets the following configurations on the ports to the defaults (shown in parentheses below): ■ 802.1x (disabled), port...
Page 128
126 c hapter 12: p ort s ecurity c onfiguration n ■ assume that, in the macaddressoruserloginsecureext port security mode, you have configured to allow up to n authenticated users to access the network. When all of these n authenticated users are connected to the network and one or more of them are ...
Page 129
Port security configuration 127 ■ after you set the port security mode to autolearn, you cannot configure any static or blackhole mac addresses on the port. ■ if the port is in a security mode other than norestriction, before you can change the port security mode, you need to restore the port securi...
Page 130
128 c hapter 12: p ort s ecurity c onfiguration configuring the trap feature ignoring the authorization information from the radius server after an 802.1x user or mac-authenticated user passes remote authentication dial-in user service (radius) authentication, the radius server delivers the authoriz...
Page 131
Displaying port security configuration 129 before continuing, make sure that: ■ port security is enabled. ■ the maximum number of security mac addresses allowed on the port is set. ■ the security mode of the port is set to autolearn. Displaying port security configuration after the above configurati...
Page 132
130 c hapter 12: p ort s ecurity c onfiguration network diagram figure 40 network diagram for port security configuration configuration procedure # enter system view. System-view # enable port security. [4210] port-security enable # enter ethernet1/0/1 port view. [4210] interface ethernet1/0/1 # set...
Page 133: Mac A
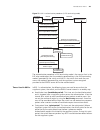
13 mac a ddress t able m anagement n this chapter describes the management of static, dynamic, and blackhole mac address entries. For information about the management of multicast mac address entries, refer to “multicast overview” on page 185. Introduction to the mac address table an ethernet switch...
Page 134
132 c hapter 13: mac a ddress t able m anagement packet, that is, the address "mac-a" of user a to the mac address table of the switch, forming an entry shown in figure 42. Figure 41 mac address learning diagram (1) figure 42 mac address table entry of the switch (1) 2 after learning the mac address...
Page 135
Managing mac address table 133 switch records the association between the mac address of user b and the corresponding port to the mac address table of the switch. Figure 44 mac address learning diagram (3) 4 at this time, the mac address table of the switch includes two forwarding entries shown in f...
Page 136
134 c hapter 13: mac a ddress t able m anagement n aging timer only takes effect on dynamic mac address entries. Entries in a mac address table entries in a mac address table fall into the following categories according to their characteristics and configuration methods: ■ static mac address entry: ...
Page 137
Configuring mac address table management 135 configuring a mac address entry you can add, modify, or remove a mac address entry, remove all mac address entries concerning a specific port, or remove specific type of mac address entries (dynamic or static mac address entries). You can add a mac addres...
Page 138
136 c hapter 13: mac a ddress t able m anagement normally, you are recommended to use the default aging time, namely, 300 seconds. The no-aging keyword specifies that mac address entries do not age out. N mac address aging configuration applies to all ports, but only takes effect on dynamic mac addr...
Page 139
Configuration example 137 configuration example adding a static mac address entry manually network requirements the server connects to the switch through ethernet 1/0/2. To prevent the switch from broadcasting packets destined for the server, it is required to add the mac address of the server to th...
Page 140
138 c hapter 13: mac a ddress t able m anagement.
Page 141: Mstp C
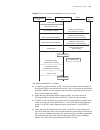
14 mstp c onfiguration stp overview functions of stp spanning tree protocol (stp) is a protocol conforming to ieee 802.1d. It aims to eliminate loops on data link layer in a local area network (lan). Devices running this protocol detect loops in the network by exchanging packets with one another and...
Page 142
140 c hapter 14: mstp c onfiguration non-root-bridge device has one and only one root port. The root bridge has no root port. 3 designated bridge and designated port refer to table 95 for the description of designated bridge and designated port. Figure 46 shows designated bridges and designated port...
Page 143
Stp overview 141 how stp works stp identifies the network topology by transmitting configuration bpdus between network devices. Configuration bpdus contain sufficient information for network devices to complete the spanning tree calculation. Important fields in a configuration bpdu include: ■ root b...
Page 144
142 c hapter 14: mstp c onfiguration n principle for configuration bpdu comparison: ■ the configuration bpdu that has the lowest root bridge id has the highest priority. ■ if all the configuration bpdus have the same root bridge id, they will be compared for their root path costs. If the root path c...
Page 145
Stp overview 143 the following is an example of how the stp algorithm works. The specific network diagram is shown in figure 47. The priority of device a is 0, the priority of device b is 1, the priority of device c is 2, and the path costs of these links are 5, 10 and 4 respectively. Figure 47 netw...
Page 146
144 c hapter 14: mstp c onfiguration table 99 comparison process and result on each device device comparison process bpdu of port after comparison device a ■ port ap1 receives the configuration bpdu of device b {1, 0, 1, bp1}. Device a finds that the configuration bpdu of the local port {0, 0, 0, ap...
Page 147
Stp overview 145 after the comparison processes described in the table above, a spanning tree with device a as the root bridge is stabilized, as shown in figure 48. Device c ■ port cp1 receives the configuration bpdu of device a {0, 0, 0, ap2}. Device c finds that the received configuration bpdu is ...
Page 148
146 c hapter 14: mstp c onfiguration figure 48 the final calculated spanning tree n to facilitate description, the spanning tree calculation process in this example is simplified, while the actual process is more complicated. 2 the bpdu forwarding mechanism in stp ■ upon network initiation, every sw...
Page 149
Mstp overview 147 designated port begin to forward data as soon as they are elected, loops may temporarily occur. For this reason, the protocol uses a state transition mechanism. Namely, a newly elected root port and the designated ports must go through a period, which is twice the forward delay tim...
Page 150
148 c hapter 14: mstp c onfiguration ■ mstp supports mapping vlans to mst instances by means of a vlan-to-instance mapping table. Mstp introduces "instance" (integrates multiple vlans into a set) and can bind multiple vlans to an instance, thus saving communication overhead and improving resource ut...
Page 151
Mstp overview 149 a switched network can contain multiple mst regions. You can group multiple switches into one mst region by using the corresponding mstp configuration commands. As shown in figure 49, all the switches in region a0 are of the same mst region-related configuration, including: ■ regio...
Page 152
150 c hapter 14: mstp c onfiguration region root a region root is the root of the ist or an msti in an mst region. Different spanning trees in an mst region may have different topologies and thus have different region roots. In region d0 shown in figure 49, the region root of msti 1 is switch b, and...
Page 153
Mstp overview 151 figure 50 port roles port state in mstp, a port can be in one of the following three states: ■ forwarding state. Ports in this state can forward user packets and receive/send bpdu packets. ■ learning state. Ports in this state can receive/send bpdu packets. ■ discarding state. Port...
Page 154
152 c hapter 14: mstp c onfiguration calculate an msti in an mst region, different mstis are generated for different vlans based on the vlan-to-msti mappings. Each spanning tree is calculated independently, in the same way as how stp/rstp is calculated. Implement stp algorithm in the beginning, each...
Page 155
Configuring root bridge 153 ■ determining the root port for each switch in a network, the port on which the configuration bpdu with the highest priority is received is chosen as the root port of the switch. ■ determining the designated port first, the switch calculates a designated port configuratio...
Page 156
154 c hapter 14: mstp c onfiguration n in a network containing switches with both gvrp and mstp enabled, gvrp packets are forwarded along the cist. If you want to advertise packets of a specific vlan through gvrp, be sure to map the vlan to the cist when configuring the mstp vlan mapping table (the ...
Page 157
Configuring root bridge 155 configuring an mst region configuration procedure n ntdp packets sent by devices in a cluster can only be transmitted within the instance where the management vlan of the cluster resides. Configuring mst region-related parameters (especially the vlan mapping table) result...
Page 158
156 c hapter 14: mstp c onfiguration [4210-mst-region] instance 2 vlan 20 to 30 [4210-mst-region] revision-level 1 [4210-mst-region] active region-configuration # verify the above configuration. [4210-mst-region] check region-configuration admin configuration format selector :0 region name :info rev...
Page 159
Configuring root bridge 157 when the root bridge fails or is turned off, the secondary root bridge becomes the root bridge if no new root bridge is configured. If you configure multiple secondary root bridges for a spanning tree instance, the one with the smallest mac address replaces the root bridg...
Page 160
158 c hapter 14: mstp c onfiguration ■ during the selection of the root bridge, if multiple switches have the same bridge priority, the one with the smallest mac address becomes the root bridge. Configuration example # set the bridge priority of the current switch to 4,096 in spanning tree instance ...
Page 161
Configuring root bridge 159 configuration example # configure ethernet 1/0/1 to recognize and send packets in dot1s format. System-view [4210] interface ethernet1/0/1 [4210-ethernet1/0/1] stp compliance dot1s # restore the default mode for ethernet 1/0/1 to recognize/send mstp packets. [4210-etherne...
Page 162
160 c hapter 14: mstp c onfiguration configuration procedure configuration example # specify the mstp operation mode as stp-compatible. System-view [4210] stp mode stp configuring the maximum hop count of an mst region the maximum hop count configured on the region root is also the maximum hops of t...
Page 163
Configuring root bridge 161 configuring the network diameter of the switched network in a switched network, any two switches can communicate with each other through a specific path made up of multiple switches. The network diameter of a network is measured by the number of switches; it equals the nu...
Page 164
162 c hapter 14: mstp c onfiguration all switches in a switched network adopt the three time-related parameters configured on the cist root bridge. C caution: ■ the forward delay parameter and the network diameter are correlated. Normally, a large network diameter corresponds to a large forward dela...
Page 165
Configuring root bridge 163 number to avoid such cases. Normally, the timeout time can be four or more times of the hello time. For a steady network, the timeout time can be five to seven times of the hello time. Configuration procedure for a steady network, the timeout time can be five to seven tim...
Page 166
164 c hapter 14: mstp c onfiguration prevent mstp from occupying too many network resources. The default value is recommended. Configuration example # set the maximum transmitting speed of ethernet 1/0/1 to 15. 1 configure the maximum transmitting speed in system view system-view [4210] stp interfac...
Page 167
Configuring root bridge 165 configuration example # configure ethernet 1/0/1 as an edge port. 1 configure ethernet1/0/1 as an edge port in system view system-view [4210] stp interface ethernet1/0/1 edged-port enable 2 configure ethernet 1/0/1 as an edge port in ethernet port view system-view [4210] ...
Page 168
166 c hapter 14: mstp c onfiguration link of a port is not a point-to-point link and you forcibly configure the link as a point-to-point link, loops may occur temporarily. Configuration example # configure the link connected to ethernet 1/0/1 as a point-to-point link. 1 perform this configuration in...
Page 169
Configuring leaf nodes 167 other mstp-related settings can take effect only after mstp is enabled on the switch. Configuration example # enable mstp on the switch and disable mstp on ethernet 1/0/1. 1 perform this configuration in system view system-view [4210] stp enable [4210] stp interface ethern...
Page 170
168 c hapter 14: mstp c onfiguration n in a network containing switches with both gvrp and mstp enabled, gvrp packets are forwarded along the cist. In this case, if you want to broadcast packets of a specific vlan through gvrp, be sure to map the vlan to the cist when configuring the mstp vlan mappi...
Page 171
Configuring leaf nodes 169 standards for calculating path costs of ports currently, a switch can calculate the path costs of ports based on one of the following standards: ■ dot1d-1998: adopts the ieee 802.1d-1998 standard to calculate the default path costs of ports. ■ dot1t: adopts the ieee 802.1t...
Page 172
170 c hapter 14: mstp c onfiguration whereas the 802.1t standard does. The following formula is used to calculate the path cost of an aggregated link: path cost = 200,000/ link transmission speed, where ‘link transmission speed" is the sum of the speeds of all the unblocked ports on the aggregated l...
Page 173
Configuring leaf nodes 171 system-view [4210] interface ethernet1/0/1 [4210-ethernet1/0/1] stp instance 1 cost 2000 configuration example (b) # configure the path cost of ethernet 1/0/1 in spanning tree instance 1 to be calculated by the mstp-enabled switch according to the ieee 802.1d-1998 standard...
Page 174
172 c hapter 14: mstp c onfiguration a smaller port priority value indicates a higher possibility for the port to become the root port. If all the ports of a switch have the same port priority value, the port priorities are determined by the port indexes. Changing the priority of a port will cause s...
Page 175
Configuring guard functions 173 perform the mcheck operation in system view perform the mcheck operation in ethernet port view configuration example # perform the mcheck operation on ethernet 1/0/1. 1 perform this configuration in system view system-view [4210] stp interface ethernet1/0/1 mcheck 2 p...
Page 176
174 c hapter 14: mstp c onfiguration root guard a root bridge and its secondary root bridges must reside in the same region. The root bridge of the cist and its secondary root bridges are usually located in the high-bandwidth core region. Configuration errors or attacks may result in configuration b...
Page 177
Configuring guard functions 175 the maximum times for a switch to remove the mac address table and arp entries to 100 and the switch receives 200 tc-bpdus in the period, the switch removes the mac address table and arp entries for only 100 times within the period. Configuration prerequisites mstp ru...
Page 178
176 c hapter 14: mstp c onfiguration system-view [4210] interface ethernet1/0/1 [4210-ethernet1/0/1] stp root-protection configuring loop guard configuration procedure configuration example # enable the loop guard function on ethernet 1/0/1. System-view [4210] interface ethernet1/0/1 [4210-ethernet1...
Page 179
Configuring digest snooping 177 configuring digest snooping introduction according to ieee802.1s, two interconnected switches can communicate with each other through mstis in an mst region only when the two switches have the same mst region-related configuration. Interconnected mstp-enabled switches...
Page 180
178 c hapter 14: mstp c onfiguration n ■ when the digest snooping feature is enabled on a port, the port state turns to the discarding state. That is, the port will not send bpdu packets. The port is not involved in the stp calculation until it receives bpdu packets from the peer port. ■ the digest ...
Page 181
Configuring rapid transition 179 figure 51 and figure 52 illustrate the rapid transition mechanisms on designated ports in rstp and mstp. Figure 51 the rstp rapid transition mechanism figure 52 the mstp rapid transition mechanism the cooperation between mstp and rstp is limited in the process of rap...
Page 182
180 c hapter 14: mstp c onfiguration manufacturer’s switch running proprietary spanning tree protocols, you can enable the rapid transition feature on the ports of the 3com series switch operating as the downstream switch. Among these ports, those operating as the root ports will then send agreement...
Page 183
Stp maintenance configuration 181 n ■ the rapid transition feature can be enabled on only root ports or alternate ports. ■ if you configure the rapid transition feature on a designated port, the feature does not take effect on the port. Stp maintenance configuration introduction in a large-scale net...
Page 184
182 c hapter 14: mstp c onfiguration ■ network topology changes are detected. Configuration procedure configuration example # enable a switch to send trap messages conforming to 802.1d standard to the network management device when the switch becomes the root bridge of instance 1. System-view [4210]...
Page 185
Mstp configuration example 183 switch b are configured as the root bridges of spanning tree instance 1 and spanning tree instance 3 respectively. Switch c is configured as the root bridge of spanning tree instance 4. Network diagram figure 54 network diagram for mstp configuration n the word "permit...
Page 186
184 c hapter 14: mstp c onfiguration [4210-mst-region] active region-configuration # specify switch b as the root bridge of spanning tree instance 3. [4210] stp instance 3 root primary 3 configure switch c. # enter mst region view. System-view [4210] stp region-configuration # configure the mst regi...
Page 187: Ulticast
15 m ulticast o verview multicast overview with development of networks on the internet, more and more interaction services such as data, voice, and video services are running on the networks. In addition, highly bandwidth- and time-critical services, such as e-commerce, web conference, online aucti...
Page 188
186 c hapter 15: m ulticast o verview the server must send many pieces of information with the same content to the users. Therefore, the limited bandwidth becomes the bottleneck in information transmission. This shows that unicast is not good for the transmission of a great deal of information. Info...
Page 189
Multicast overview 187 the information only once. With multicast distribution trees established for multicast data packets through multicast routing protocols, the packets are duplicated and distributed at the nearest nodes, as shown in figure 57: figure 57 information transmission in the multicast ...
Page 190
188 c hapter 15: m ulticast o verview ■ all receivers interested in the same information form a multicast group. Multicast groups are not subject to geographic restrictions. ■ a router that supports layer 3 multicast is called multicast router or layer 3 multicast device. In addition to providing mu...
Page 191
Multicast models 189 multicast models based on the multicast source processing modes, there are three multicast models: ■ any-source multicast (asm) ■ source-filtered multicast (sfm) ■ source-specific multicast (ssm) asm model in the asm model, any sender can become a multicast source and send infor...
Page 192
190 c hapter 15: m ulticast o verview ■ host registration: a receiving host joins and leaves a multicast group dynamically using the membership registration mechanism. ■ multicast routing: a router or switch transports packets from a multicast source to receivers by building a multicast distribution...
Page 193
Multicast architecture 191 class d ip addresses range from 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255. For details, see table 142. As specified by iana, the ip addresses ranging from 224.0.0.0 to 224.0.0.255 are reserved for network protocols on local networks. Table 143 lists commonly used reserved ip multicast ...
Page 194
192 c hapter 15: m ulticast o verview ethernet multicast mac address when a unicast ip packet is transported in an ethernet network, the destination mac address is the mac address of the receiver. When a multicast packet is transported in an ethernet network, a multicast mac address is used as the d...
Page 195
Multicast architecture 193 figure 59 positions of layer 2 multicast protocols running on layer 2 devices, internet group management protocol snooping (igmp snooping) are multicast constraining mechanisms that manage and control multicast groups by listening to and analyzing igmp messages exchanged b...
Page 196
194 c hapter 15: m ulticast o verview figure 60 positions of layer 3 multicast protocol ■ multicast management protocols typically, the internet group management protocol (igmp) is used between hosts and layer 3 multicast devices directly connected with the hosts. These protocols define the mechanis...
Page 197
Multicast packet forwarding mechanism 195 multicast packet forwarding mechanism in a multicast model, a multicast source sends information to the host group identified by the multicast group address in the destination address field of the ip packets. Therefore, to deliver multicast packets to receiv...
Page 198
196 c hapter 15: m ulticast o verview rpf check the basis for an rpf check is a unicast route. A unicast routing table contains the shortest path to each destination subnet. A multicast routing protocol does not independently maintain any type of unicast route; instead, it relies on the existing uni...
Page 199: Igmp S
16 igmp s nooping c onfiguration igmp snooping overview internet group management protocol snooping (igmp snooping) is a multicast constraining mechanism that runs on layer 2 devices to manage and control multicast groups. Principle of igmp snooping by analyzing received igmp messages, a layer 2 dev...
Page 200
198 c hapter 16: igmp s nooping c onfiguration figure 63 igmp snooping related ports ports involved in igmp snooping, as shown in figure 63, are described as follows: ■ router port: a router port is a port on the layer 3 multicast device (dr or igmp querier) side of the ethernet switch. In figure 63...
Page 201
Igmp snooping overview 199 upon receiving an igmp general query, the switch forwards it through all ports in the vlan except the receiving port and performs the following to the receiving port: ■ if the receiving port is a router port existing in its router port list, the switch resets the aging tim...
Page 202
200 c hapter 16: igmp s nooping c onfiguration the forwarding entry corresponding to that port from the forwarding table; instead, it resets the aging timer of the member port. Upon receiving the igmp leave message from a host, the igmp querier resolves from the message the address of the multicast ...
Page 203
Igmp snooping configuration 201 c caution: ■ before enabling igmp snooping in a vlan, be sure to enable igmp snooping globally in system view; otherwise the igmp snooping settings will not take effect. ■ if igmp snooping and vlan vpn are enabled on a vlan at the same time, igmp queries are likely to...
Page 204
202 c hapter 16: igmp s nooping c onfiguration configuring fast leave processing with fast leave processing enabled, when the switch receives an igmp leave message on a port, the switch directly removes that port from the forwarding table entry for the specific group. If only one host is attached to...
Page 205
Igmp snooping configuration 203 configuring a multicast group filter on an igmp snooping-enabled switch, the configuration of a multicast group allows the service provider to define restrictions on multicast programs available to different users. In an actual application, when a user requests a mult...
Page 206
204 c hapter 16: igmp s nooping c onfiguration configuring the maximum number of multicast groups on a port by configuring the maximum number of multicast groups that can be joined on a port, you can limit the number of multicast programs on-demand available to users, thus to regulate traffic on the...
Page 207
Igmp snooping configuration 205 in ethernet port view in vlan interface view configuring a static router port in a network where the topology is unlikely to change, you can configure a port on the switch as a static router port, so that the switch has a static connection to a multicast router and re...
Page 208
206 c hapter 16: igmp s nooping c onfiguration in ethernet port view in vlan view configuring a port as a simulated group member generally, hosts running igmp respond to the igmp query messages of the multicast switch. If hosts fail to respond for some reason, the multicast switch may consider that ...
Page 209
Displaying and maintaining igmp snooping 207 c caution: ■ before configuring a simulated host, enable igmp snooping in vlan view first. ■ the port to be configured must belong to the specified vlan; otherwise the configuration does not take effect. ■ you can use the source-ip source-address command ...
Page 210
208 c hapter 16: igmp s nooping c onfiguration igmp snooping configuration examples configuring igmp snooping network requirements to prevent multicast traffic from being flooded at layer 2, enable igmp snooping on layer 2 switches. ■ as shown in figure 64, router a connects to a multicast source (s...
Page 211
Igmp snooping configuration examples 209 # enable ip multicast routing, enable pim-dm on each interface, and enable igmp on ethernet1/0/1. System-view [routera] multicast routing-enable [routera] interface ethernet 1/0/1 [routera-ethernet1/0/1] igmp enable [routera-ethernet1/0/1] pim dm [routera-eth...
Page 212
210 c hapter 16: igmp s nooping c onfiguration troubleshooting igmp snooping symptom: multicast function does not work on the switch. Solution: possible reasons are: ■ igmp snooping is not enabled. ■ use the display current-configuration command to check the status of igmp snooping. ■ if igmp snoopi...
Page 213: 802.1
17 802.1 x c onfiguration n ■ the online user handshaking function is added. See “configuring basic 802.1x functions”. ■ the configuration of 802.1x re-authentication is added. See “configuring 802.1x re-authentication”. ■ the configuration of the 802.1x re-authentication interval is added. See “con...
Page 214
212 c hapter 17: 802.1 x c onfiguration supplicant system. Note that the client program must support extensible authentication protocol over lan (eapol). ■ the authenticator system is another entity residing at one end of a lan segment. It authenticates the connected supplicant systems. The authenti...
Page 215
Introduction to 802.1x 213 the way a port is controlled a port of a 3com series switch can be controlled in the following two ways. ■ port-based authentication. When a port is controlled in this way, all the supplicant systems connected to the port can access the network without being authenticated ...
Page 216
214 c hapter 17: 802.1 x c onfiguration in an eapol packet: ■ the pae ethernet type field holds the protocol identifier. The identifier for 802.1x is 0x888e. ■ the protocol version field holds the version of the protocol supported by the sender of the eapol packet. ■ the type field can be one of the...
Page 217
Introduction to 802.1x 215 ■ the length field indicates the size of an eap packet, which includes the code, identifier, length, and data fields. ■ the data field contains information about an eap packet. Its format is different than the code field. A success or failure packet does not contain the da...
Page 218
216 c hapter 17: 802.1 x c onfiguration 802.1x authentication procedure the switch 4210 can authenticate supplicant systems in eap terminating mode or eap relay mode. Eap relay mode this mode is defined in 802.1x. In this mode, eap-packets are encapsulated in higher level protocol (such as eapor) pa...
Page 219
Introduction to 802.1x 217 figure 72 802.1x authentication procedure (in eap relay mode) the detailed procedure is as follows. ■ a supplicant system launches an 802.1x client to initiate an access request by sending an eapol-start packet to the switch, with its user name and password provided. The 8...
Page 220
218 c hapter 17: 802.1 x c onfiguration ■ upon receiving the key (encapsulated in an eap-request/md5 challenge packet) from the switch, the client program encrypts the password of the supplicant system with the key and sends the encrypted password (contained in an eap-response/md5 challenge packet) ...
Page 221
Introduction to 802.1x 219 figure 73 802.1x authentication procedure (in eap terminating mode) the authentication procedure in eap terminating mode is the same as that in the eap relay mode except that the randomly-generated key in the eap terminating mode is generated by the switch, and that it is ...
Page 222
220 c hapter 17: 802.1 x c onfiguration ■ re-authentication timer (reauth-period): the switch will initiate 802.1x re-authentication at the interval set by the re-authentication timer. ■ radius server timer (server-timeout). This timer sets the server-timeout period. After sending an authentication ...
Page 223
Introduction to 802.1x 221 ■ only disconnects the supplicant system but sends no trap packets; ■ sends trap packets without disconnecting the supplicant system. This function needs the cooperation of 802.1x client and a cams server. ■ the 802.1x client needs to capable of detecting multiple network ...
Page 224
222 c hapter 17: 802.1 x c onfiguration ■ users belonging to the guest vlan can access the resources of the guest vlan without being authenticated. But they need to be authenticated when accessing external resources. Normally, the guest vlan function is coupled with the dynamic vlan delivery functio...
Page 225
802.1x configuration 223 802.1x configuration 802.1x provides a solution for authenticating users. To implement this solution, you need to execute 802.1x-related commands. You also need to configure aaa schemes on switches and specify the authentication scheme (radius, hwtacacs or local authenticati...
Page 226
224 c hapter 17: 802.1 x c onfiguration c caution: ■ 802.1x configurations take effect only after you enable 802.1x both globally and for specified ports. ■ if you enable 802.1x for a port, you cannot set the maximum number of mac addresses that can be learnt for the port. Meanwhile, if you set the ...
Page 227
Basic 802.1x configuration 225 from them in handshaking periods. To prevent users being falsely considered offline, you need to disable the online user handshaking function in this case. ■ for the handshaking packet secure function to take effect, the clients that enable the function need to coopera...
Page 228
226 c hapter 17: 802.1 x c onfiguration ■ as for the configuration of 802.1x timers, the default values are recommended. Advanced 802.1x configuration advanced 802.1x configurations, as listed below, are all optional. ■ configuration concerning cams, including multiple network adapters detecting, pr...
Page 229
Advanced 802.1x configuration 227 n as for the dot1x version-user command, if you execute it in system view without specifying the interface-list argument, the command applies to all ports. You can also execute this command in port view. In this case, this command applies to the current port only an...
Page 230
228 c hapter 17: 802.1 x c onfiguration c caution: ■ the guest vlan function is available only when the switch operates in the port-based authentication mode. ■ only one guest vlan can be configured for each switch. ■ the guest vlan function cannot be implemented when the switch executes the dot1x d...
Page 231
Displaying and debugging 802.1x 229 displaying and debugging 802.1x after performing the above configurations, you can display and verify the 802.1x-related configuration by executing the display command in any view. You can clear 802.1x-related statistics information by executing the reset command ...
Page 232
230 c hapter 17: 802.1 x c onfiguration network diagram figure 76 network diagram for aaa configuration with 802.1x and radius enabled configuration procedure n following configuration covers the major aaa/radius configuration commands. Refer to “aaa configuration” on page 245 for the information ab...
Page 233
Configuration example 231 [4210-radius-radius1] key authentication name # set the password for the switch and the accounting radius servers to exchange messages. [4210-radius-radius1] key accounting money # set the interval and the number of the retries for the switch to send packets to the radius s...
Page 234
232 c hapter 17: 802.1 x c onfiguration.
Page 235: Habp C
18 habp c onfiguration introduction to habp with 802.1x enabled, a switch authenticates and then authorizes 802.1x-enabled ports. Packets can be forwarded only by authorized ports. Received packets are, therefore, filtered for ports connected to a switch that is not authenticated and authorized by 8...
Page 236
234 c hapter 18: habp c onfiguration habp client configuration habp clients reside on switches attached to habp servers. After you enable habp for a switch, the switch operates as an habp client by default. So you only need to enable habp on a switch to make it an habp client. Displaying habp after ...
Page 237: Ystem
19 s ystem -g uard c onfiguration the system-guard function checks system-guard-enabled ports regularly to determine if the ports are under attack. With this function enabled, if the number of the packets received by a system-guard-enabled port exceeds the set threshold, the port is regarded to be u...
Page 238
236 c hapter 19: s ystem -g uard c onfiguration enabling system-guard on ports table 176 lists the operations to enable system-guard on ports. N after system-guard is enabled on a port, if the number of packets the port received and sent to the cpu in a specified interval exceeds the specified thres...
Page 239: Aaa O
20 aaa o verview introduction to aaa aaa is the acronym for the three security functions: authentication, authorization and accounting. It provides a uniform framework for you to configure these three functions to implement network security management. ■ authentication: defines what users can access...
Page 240
238 c hapter 20: aaa o verview accounting aaa supports the following accounting methods: ■ none accounting: no accounting is performed for users. ■ remote accounting: user accounting is performed on a remote radius server. Introduction to isp domain an internet service provider (isp) domain is a gro...
Page 241
Introduction to aaa services 239 ■ users: this database stores information about users (such as user name, password, protocol adopted and ip address). ■ clients: this database stores information about radius clients (such as shared key). ■ dictionary: the information stored in this database is used ...
Page 242
240 c hapter 20: aaa o verview the basic message exchange procedure of radius is as follows: 1 the user enters the user name and password. 2 the radius client receives the user name and password, and then sends an authentication request (access-request) to the radius server. 3 the radius server comp...
Page 243
Introduction to aaa services 241 figure 79 radius message format 1 the code field (one byte) decides the type of radius message, as shown in table 178. 2 the identifier field (one byte) is used to match requests and responses. It changes whenever the content of the attributes field changes, and when...
Page 244
242 c hapter 20: aaa o verview 3 the length field (two bytes) specifies the total length of the message (including the code, identifier, length, authenticator and attributes fields). The bytes beyond the length are regarded as padding and are ignored upon reception. If a received message is shorter ...
Page 245
Introduction to aaa services 243 figure 80 depicts the format of attribute 26. The vendor-id field used to identify a vendor occupies four bytes, where the first byte is 0, and the other three bytes are defined in rfc 1700. Here, the vendor can encapsulate multiple customized sub-attributes (contain...
Page 246
244 c hapter 20: aaa o verview.
Page 247: Aaa C
21 aaa c onfiguration aaa configuration task list you need to configure aaa to provide network access services for legal users while protecting network devices and preventing unauthorized access and repudiation behavior. Table 180 aaa configuration tasks (configuring a combined aaa scheme for an isp...
Page 248
246 c hapter 21: aaa c onfiguration creating an isp domain and configuring its attributes n note that: ■ on the switch 4210, each access user belongs to an isp domain. You can configure up to 16 isp domains on the switch. When a user logs in, if no isp domain name is carried in the user name, the sw...
Page 249
Aaa configuration task list 247 command has been executed, though it cannot perform accounting for the user in this case. ■ the self-service server location function needs the cooperation of a radius server that supports self-service, such as comprehensive access management server (cams). Through se...
Page 250
248 c hapter 21: aaa c onfiguration configuring separate aaa schemes you can use the authentication, authorization, and accounting commands to specify a scheme for each of the three aaa functions (authentication, authorization and accounting) respectively. The following gives the implementations of ...
Page 251
Aaa configuration task list 249 ■ integer: if the radius authentication server assigns integer type of vlan ids, you can set the vlan assignment mode to integer on the switch (this is also the default mode on the switch). Then, upon receiving an integer id assigned by the radius authentication serve...
Page 252
250 c hapter 21: aaa c onfiguration c caution: ■ the following characters are not allowed in the user-name string: /:*?. And you cannot input more than one "@" in the string. ■ after the local-user password-display-mode cipher-force command is executed, any password will be displayed in cipher mode ...
Page 253
Radius configuration task list 251 can access after login is determined by the privilege level of the user. For ssh users using rsa shared key for authentication, the commands they can access are determined by the levels set on their user interfaces. ■ if the configured authentication method is none...
Page 254
252 c hapter 21: aaa c onfiguration table 188 radius configuration tasks (the switch functions as a radius client) task remarks configuring the radius client “creating a radius scheme” required “configuring radius authentication/authorizati on servers” required “configuring radius accounting servers...
Page 255
Radius configuration task list 253 the radius service configuration is performed on a radius scheme basis. In an actual network environment, you can either use a single radius server or two radius servers (primary and secondary servers with the same configuration but different ip addresses) in a rad...
Page 256
254 c hapter 21: aaa c onfiguration n actually, the radius service configuration only defines the parameters for information exchange between switch and radius server. To make these parameters take effect, you must reference the radius scheme configured with these parameters in an isp domain view (r...
Page 257
Radius configuration task list 255 ■ in an actual network environment, you can specify one server as both the primary and secondary authentication/authorization servers, as well as specifying two radius servers as the primary and secondary authentication/authorization servers respectively. ■ the ip ...
Page 258
256 c hapter 21: aaa c onfiguration ■ with stop-accounting request buffering enabled, the switch first buffers the stop-accounting request that gets no response from the radius accounting server, and then retransmits the request to the radius accounting server until it gets a response, or the maximu...
Page 259
Radius configuration task list 257 configuring the type of radius servers to be supported n when the third party radius server is used, you can select standard or extended as the server-type in a radius scheme; when the cams server is used, you can select extended as the server-type in a radius sche...
Page 260
258 c hapter 21: aaa c onfiguration configuring the attributes of data to be sent to radius servers n ■ generally, the access users are named in the userid@isp-name format. Here, isp-name after the "@" character represents the isp domain name, by which the device determines which isp domain a user b...
Page 261
Radius configuration task list 259 radius servers cannot accept the user names that carry isp domain names. In this case, it is necessary to remove domain names from user names before sending the user names to radius server. For this reason, the user-name-format command is designed for you to specif...
Page 262
260 c hapter 21: aaa c onfiguration the switch can provide authentication service to up to 16 network access servers (including the switch itself) at the same time. ■ when acting as the local radius authentication server, the switch does not support eap authentication. Configuring timers for radius ...
Page 263
Radius configuration task list 261 enabling sending trap message when a radius server goes down n ■ this configuration takes effect on all radius schemes. ■ the switch considers a radius server as being down if it has tried the configured maximum times to send a message to the radius server but does...
Page 264
262 c hapter 21: aaa c onfiguration you choose to manually configure the attribute, be sure to configure an appropriate valid ip address. If this attribute is not configured, the switch will automatically choose the ip address of a vlan interface as the nas-ip-address. Displaying and maintaining aaa...
Page 265
Aaa configuration examples 263 aaa configuration examples remote radius authentication of telnet/ssh users n the configuration procedure for remote authentication of ssh users by radius server is similar to that for telnet users. The following text only takes telnet users as example to describe the ...
Page 266
264 c hapter 21: aaa c onfiguration ■ on the radius server, set the shared key it uses to exchange messages with the switch to "aabbcc," set the authentication port number, and add telnet user names and login passwords. The telnet user names added to the radius server must be in the format of userid...
Page 267
Aaa configuration examples 265 a telnet user logging into the switch by a name in the format of userid @cams belongs to the cams domain and will be authenticated according to the configuration of the cams domain. Local authentication of ftp/telnet users n the configuration procedure for local authen...
Page 268
266 c hapter 21: aaa c onfiguration this method is similar to the remote authentication method described in “remote radius authentication of telnet/ssh users”. However, you need to ■ change the server ip address, and the udp port number of the authentication server to 127.0.0.1, and 1645 respectivel...
Page 269
Troubleshooting aaa 267 ■ the switch requests that both the authentication/authorization server and the accounting server use the same device (with the same ip address), but in fact they are not resident on the same device - be sure to configure the radius servers on the switch according to the actu...
Page 270
268 c hapter 21: aaa c onfiguration.
Page 271: Mac A
22 mac a uthentication c onfiguration mac authentication overview mac authentication provides a way for authenticating users based on ports and mac addresses, without requiring any client software to be installed on the hosts. Once detecting a new mac address, it initiates the authentication process...
Page 272
270 c hapter 22: mac a uthentication c onfiguration ■ the service type of a local user needs to be configured as lan-access. Related concepts mac authentication timers the following timers function in the process of mac authentication: ■ offline detect timer: at this interval, the switch checks to s...
Page 273
Mac address authentication enhanced function configuration 271 c caution: ■ if mac authentication is enabled on a port, you cannot configure the maximum number of dynamic mac address entries for that port (through the mac-address max-mac-count command), and vice versa. ■ if mac authentication is ena...
Page 274
272 c hapter 22: mac a uthentication c onfiguration configuring a guest vlan n different from guest vlans described in the 802.1x and system-guard chapters, guest vlans mentioned in this section refer to guest vlans dedicated to mac address authentication. After completing configuration tasks in “co...
Page 275
Mac address authentication enhanced function configuration 273 c caution: ■ if more than one client are connected to a port, you cannot configure a guest vlan for this port. ■ when a guest vlan is configured for a port, only one mac address authentication user can access the port. Even if you set th...
Page 276
274 c hapter 22: mac a uthentication c onfiguration c caution: ■ if both the limit on the number of mac address authentication users and the limit on the number of users configured in the port security function are configured for a port, the smaller value of the two configured limits is adopted as t...
Page 277
Mac authentication configuration example 275 mac authentication configuration example network requirements as illustrated in figure 83, a supplicant is connected to the switch through port ethernet 1/0/2. ■ mac authentication is required on port ethernet 1/0/2 to control user access to the internet....
Page 278
276 c hapter 22: mac a uthentication c onfiguration # enable mac authentication globally (this is usually the last step in configuring access control related features. Otherwise, a user may be denied of access to the networks because of incomplete configuaration.) [4210] mac-authentication after doi...
Page 279: Arp C
23 arp c onfiguration introduction to arp arp function address resolution protocol (arp) is used to resolve an ip address into a data link layer address. An ip address is the address of a host at the network layer. To send a network layer packet to a destination host, the device must know the data l...
Page 280
278 c hapter 23: arp c onfiguration arp table in an ethernet, the mac addresses of two hosts must be available for the two hosts to communicate with each other. Each host in an ethernet maintains an arp table, where the latest used ip address-to-mac address mapping entries are stored. The switch 421...
Page 281
Arp configuration 279 arp process suppose that host a and host b are on the same subnet and that host a sends a message to host b. The resolution process is as follows: 1 host a looks in its arp mapping table to see whether there is an arp entry for host b. If host a finds it, host a uses the mac ad...
Page 282
280 c hapter 23: arp c onfiguration arp configuration example network requirement ■ disable arp entry check on the switch. ■ set the aging time for dynamic arp entries to 10 minutes. ■ add a static arp entry, with the ip address being 192.168.1.1, the mac address being 000f-e201-0000, and the outbou...
Page 283: Dhcp O
24 dhcp o verview introduction to dhcp with networks getting larger in size and more complicated in structure, lack of available ip addresses becomes the common situation the network administrators have to face, and network configuration becomes a tough task for the network administrators. With the ...
Page 284
282 c hapter 24: dhcp o verview ■ dynamic assignment. The dhcp server assigns ip addresses to dhcp clients for predetermined period of time. In this case, a dhcp client must apply for an ip address again at the expiration of the period. This policy applies to most clients. Obtaining ip addresses dyn...
Page 285
Dhcp packet format 283 if the dhcp client fails to update its ip address lease when half of the lease time elapses, it will update its ip address lease by broadcasting a dhcp-request packet to the dhcp servers again when seven-eighths of the lease time elapses. The dhcp server performs the same oper...
Page 286
284 c hapter 24: dhcp o verview ■ sname: name of the dhcp server. ■ file: path and name of the boot configuration file that the dhcp server specifies for the dhcp client. ■ option: optional variable-length fields, including packet type, valid lease time, ip address of a dns server, and ip address of...
Page 287: Dhcp S
25 dhcp s nooping c onfiguration introduction to dhcp snooping for the sake of security, the ip addresses used by online dhcp clients need to be tracked for the administrator to verify the corresponding relationship between the ip addresses the dhcp clients obtained from dhcp servers and the mac add...
Page 288
286 c hapter 25: dhcp s nooping c onfiguration dhcp snooping configuration n after dhcp snooping is enabled on an ethernet switch, clients connected with this switch cannot obtain ip addresses dynamically through bootp. Dhcp snooping configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 88, ...
Page 289: Dhcp/bootp C
26 dhcp/bootp c lient c onfiguration introduction to dhcp client after you specify a vlan interface as a dhcp client, the device can use dhcp to obtain parameters such as ip address dynamically from the dhcp server, which facilitates user configuration and management. “obtaining ip addresses dynamic...
Page 290
288 c hapter 26: dhcp/bootp c lient c onfiguration n currently, the switch 4210 functioning as the dhcp client can use an ip address for 24 days at most. That is, the dhcp client can obtain an address lease for no more than 24 days even though the dhcp server offers a longer lease period. N to impro...
Page 291
Dhcp client configuration example 289 network diagram figure 89 a dhcp network configuration procedure the following describes only the configuration on switch a serving as a dhcp client. # configure vlan-interface 1 to dynamically obtain an ip address by using dhcp. System-view [4210] interface vla...
Page 292
290 c hapter 26: dhcp/bootp c lient c onfiguration.
Page 293: Acl C
27 acl c onfiguration acl overview the switch 4210 supports software-based acls for the purpose of controlling management access into the switch 4210 from telnet and snmp management stations. As the network scale and network traffic are increasingly growing, security control and bandwidth assignment...
Page 294
292 c hapter 27: acl c onfiguration for depth-first rule, there are two cases: depth-first match order for rules of a basic acl 1 range of source ip address: the smaller the source ip address range (that is, the more the number of zeros in the wildcard mask), the higher the match priority. 2 fragmen...
Page 295
Acl configuration 293 ■ auto, where the rules in an acl are matched in the order determined by the system, namely the "depth-first" order. When applying an acl in this way, you can specify the order in which the rules in the acl are matched. The match order cannot be modified once it is determined, ...
Page 296
294 c hapter 27: acl c onfiguration note that: ■ if only a periodic time section is defined in a time range, the time range is active only when the system time is within the defined periodic time section. If multiple periodic time sections are defined in a time range, the time range is active only w...
Page 297
Acl configuration 295 configuration procedure note that: ■ with the config match order specified for the basic acl, you can modify any existent rule. The unmodified part of the rule remains. With the auto match order specified for the basic acl, you cannot modify any existent rule; otherwise the sys...
Page 298
296 c hapter 27: acl c onfiguration an advanced acl can be numbered from 3000 to 3999. Note that acl 3998 and acl 3999 cannot be configured because they are reserved for cluster management. Advanced acls support analysis and processing of three packet priority levels: type of service (tos) priority,...
Page 299
Example for upper-layer software referencing acls 297 configuration example # configure acl 3000 to permit the tcp packets sourced from the network 129.9.0.0/16 and destined for the network 202.38.160.0/24 and with the destination port number being 80. System-view [4210] acl number 3000 [4210-acl-ad...
Page 300
298 c hapter 27: acl c onfiguration configuration procedure # define acl 2000. System-view [4210] acl number 2000 [4210-acl-basic-2000] rule 1 permit source 10.110.100.52 0 [4210-acl-basic-2000] quit # reference acl 2000 on vty user interface to control telnet login users. [4210] user-interface vty ...
Page 301: S C
28 q o s c onfiguration overview introduction to qos quality of service (qos) is a concept generally existing in occasions with service supply and demand. It evaluates the ability to meet the need of the customers in service. Generally, the evaluation is not to grade precisely. Its purpose is to ana...
Page 302
300 c hapter 28: q o s c onfiguration delay may cause unexpected results. That is, they need to get serviced in time even if congestion occurs. Newly emerging applications demand higher service performance from ip networks. In addition to simply delivering packets to their destinations, better netwo...
Page 303
Qos supported by switch 4210 family 301 consisting of source address, source port number, protocol number, destination address, and destination port number. It can also be simply a network segment. Precedence ip precedence, tos precedence, and dscp precedence figure 92 ds field and tos byte the tos ...
Page 304
302 c hapter 28: q o s c onfiguration ■ class selector (cs) class: this class comes from the ip tos field and includes eight subclasses; ■ best effort (be) class: this class is a special class without any assurance in the cs class. The af class can be degraded to the be class if it exceeds the limit...
Page 305
Qos supported by switch 4210 family 303 the 4-byte 802.1q tag header consists of the tag protocol identifier (tpid, two bytes in length), whose value is 0x8100, and the tag control information (tci, two bytes in length). Figure 94 describes the detailed contents of an 802.1q tag header. Figure 94 80...
Page 306
304 c hapter 28: q o s c onfiguration you can also configure to trust packet priority. In this case, a received packet is processed in one of the following three ways: ■ with the 802.1p precedence of a packet trusted, the switch obtains the corresponding local precedence by looking up the 802.1p pre...
Page 307
Qos supported by switch 4210 family 305 port rate limiting port rate limiting refers to limiting the total rate of inbound or outbound packets on a port. Port rate limiting can be implemented through token buckets. The token bucket can be considered as a container with a certain capacity to hold tok...
Page 308
306 c hapter 28: q o s c onfiguration in the following section, weighted round robin (wrr), and hq-wrr (high queue-wrr) queues are introduced. Wrr queuing figure 96 diagram for wrr queuing wrr queue-scheduling algorithm schedules all the queues in turn and every queue can be assured of a certain ser...
Page 309
Qos configuration 307 although the burst function helps reduce the packet loss ratio and improve packet processing capability in the networks mentioned above, it may affect qos performance. So, use this function with caution. Qos configuration configuring port priority by default, for a packet with ...
Page 310
308 c hapter 28: q o s c onfiguration configuring to trust the 802.1p precedence of the received packets you can configure the switch to trust the 802.1p precedence of the received packets. In this case, the priority of the receiving port is not used as the 802.1p precedence of the received packet. ...
Page 311
Qos configuration 309 configuring priority mapping you can modify the cos-precedence-to-local-precedence, dscp-precedence-to-local-precedence and ip-precedence-to-local-precedence mapping tables as required to mark packets with different priorities. Configuration prerequisites the target cos-precede...
Page 312
310 c hapter 28: q o s c onfiguration cos(802.1p) : 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 ----------------------------------------------------------------------- local precedence(queue) : 0 0 1 1 2 2 3 3 configuring port rate limiting refer to “port rate limiting” on page 305 for information about port rate limiting. Con...
Page 313
Qos configuration 311 configuration procedure configuration example # adopt the wrr queue scheduling algorithm, with the weight for queue 0, queue 1, queue 2, and queue 3 as 12, 8, 4, and 1. Display the configuration information after configuration. Configuration procedure: system-view [4210] queue-...
Page 314
312 c hapter 28: q o s c onfiguration displaying qos after the above configuration, you can execute the display command in any view to view the running status of qos and verify the configuration. Table 236 display qos operation command description display the cos-precedence-to-local-preced ence mapp...
Page 315: Irroring
29 m irroring c onfiguration mirroring overview mirroring refers to the process of copying packets of one or more ports (source ports) to a destination port which is connected to a data detection device. Users can then use the data detection device to analyze the mirrored packets on the destination ...
Page 316
314 c hapter 29: m irroring c onfiguration when configuring local port mirroring, note that: ■ you need to configure the source and destination ports for the local port mirroring to take effect. ■ the destination port cannot be a member port of an aggregation group or a port enabled with lacp or stp...
Page 317
Mirroring configuration example 315 use the local port mirroring function to meet the requirement. Perform the following configurations on switch c. ■ configure ethernet 1/0/1 and ethernet 1/0/2 as mirroring source ports. ■ configure ethernet 1/0/3 as the mirroring destination port. Network diagram ...
Page 318
316 c hapter 29: m irroring c onfiguration.
Page 319: Luster
30 c luster cluster overview introduction to switch clustering a cluster contains a group of switches. Through cluster management, you can manage multiple geographically dispersed in a centralized way. Cluster management is implemented through 3com group management protocol (switch clustering). Swit...
Page 320
318 c hapter 30: c luster figure 99 a cluster implementation switch clustering v2 has the following advantages: ■ it eases the configuration and management of multiple switches: you just need to configure a public ip address for the management device instead of for all the devices in the cluster; an...
Page 321
Cluster overview 319 figure 100 illustrates the state machine of cluster role. Table 239 description of cluster roles role configuration function management device configured with a external ip address ■ provides an interface for managing all the switches in a cluster ■ manages member devices throug...
Page 322
320 c hapter 30: c luster figure 100 state machine of cluster role ■ a candidate device becomes a management device when you create a cluster on it. Note that a cluster must have one (and only one) management device. On becoming a management device, the device collects network topology information a...
Page 323
Cluster overview 321 ■ all devices use ndp to collect the information about their neighbors, including software version, host name, mac address, and port name. ■ the management device uses ntdp to collect the information about the devices within specific hops and the topology information about the d...
Page 324
322 c hapter 30: c luster ■ the management device sends ntdp topology collection requests periodically through its ntdp-enabled ports. ■ upon receiving an ntdp topology collection request, the device returns a ntdp topology collection response to the management device and forwards the request to its...
Page 325
Cluster overview 323 n on the management device, you need to enable the cluster function and configure cluster parameters. On the member/candidate devices, however, you only need to enable the cluster function so that they can be managed by the management device. Cluster maintenance 1 adding a candi...
Page 326
324 c hapter 30: c luster which case the management device considers the member device disconnected. Likewise, if this member device, which is in connect state, receives a handshake packet or management packet from the management device within the information holdtime, it changes its state to active...
Page 327
Cluster configuration tasks 325 cluster configuration tasks before configuring a cluster, you need to determine the roles and functions the switches play. You also need to configure the related functions, preparing for the communication between devices within the cluster. Configuring the management ...
Page 328
326 c hapter 30: c luster configuring ndp-related parameters enabling ntdp globally and on a specific port configuring ntdp-related parameters enable ndp globally ndp enable required by default, ndp is enabled globally. Enable ndp on specified ethernet ports in system view ndp enable interface port-...
Page 329
Cluster configuration tasks 327 enabling the cluster function configuring cluster parameters the establishment of a cluster and the related configuration can be accomplished in manual mode or automatic mode, as described below. 1 establishing a cluster and configuring cluster parameters in manual mo...
Page 330
328 c hapter 30: c luster 2 establish a cluster in automatic mode n ■ after a cluster is established automatically, acl 3998 and acl 3999 will be generated automatically. ■ after a cluster is established automatically, acl 3998 and acl 3999 can neither be modified nor removed. Configuring member dev...
Page 331
Cluster configuration tasks 329 ■ when you execute the add-member command on the management device to add a candidate device to a cluster, the candidate device changes to a member device and its udp port 40000 is opened at the same time. ■ when you execute the auto-build command on the management de...
Page 332
330 c hapter 30: c luster accessing the shared ftp/tftp server from a member device perform the following operations in user view on a member device. Managing a cluster through the management device you can manage the member devices through the management device, for example, adding/removing a clust...
Page 333
Cluster configuration tasks 331 n ■ when using the tracemac command to locate a device by its ip address, the switch will query the corresponding arp entry of the ip address, and then query the mac address based on the arp entry to locate the specified device finally. ■ if the ip address has its cor...
Page 334
332 c hapter 30: c luster configure cluster topology management function 1 configuration prerequisites before configuring the cluster topology management function, make sure that: ■ the basic cluster configuration is completed. ■ devices in the cluster work normally. 2 configuration procedure perfor...
Page 335
Displaying and maintaining cluster configuration 333 displaying and maintaining cluster configuration after the above configuration, you can execute the display commands in any view to display the configuration and running status of cluster, so as to verify your configuration. Cluster configuration ...
Page 336
334 c hapter 30: c luster serving as the management device, the switch 4210 manages the two member devices. The configuration for the cluster is as follows: ■ the two member devices connect to the management device through ethernet 1/0/2 and ethernet 1/0/3. ■ the management device connects to the in...
Page 337
Cluster configuration example 335 [4210] ntdp enable [4210] interface ethernet 1/1 [4210-ethernet1/1] ntdp enable [4210-ethernet1/1] quit # enable the cluster function. [4210] cluster enable 2 configure the management device # enable ndp globally and on ethernet 1/0/2 and ethernet 1/0/3. System-view...
Page 338
336 c hapter 30: c luster # name and build the cluster. [4210-cluster] build aaa [aaa_0.3com-cluster] # add the attached two switches to the cluster. [aaa_0.3com-cluster] add-member 1 mac-address 000f-e20f-0011 [aaa_0.3com-cluster] add-member 17 mac-address 000f-e20f-0012 # set the holdtime of membe...
Page 339
Cluster configuration example 337 ■ add the device with the mac address 0001-2034-a0e5 to the cluster blacklist, that is, prevent the device from being managed and maintained by the cluster. ■ save the current cluster topology as the base topology and save it in the flash of the local management dev...
Page 340
338 c hapter 30: c luster.
Page 341: E C
31 p o e c onfiguration poe overview introduction to poe power over ethernet (poe)-enabled devices use twisted pairs through electrical ports to supply power to the remote powered devices (pd) in the network and implement power supply and data transmission simultaneously. Advantages of poe ■ reliabi...
Page 342
340 c hapter 31: p o e c onfiguration a poe-enabled switch 4210 has the following features: ■ as the pse, it supports the ieee802.3af standard. It can also supply power to some pds that do not support the 802.3af standard. ■ it can deliver data and current simultaneously through data wires (1,2,3,6)...
Page 343
Poe configuration 341 enabling the poe feature on a port c caution: ■ by default, the poe function on a port is enabled by the default configuration file 3comoscfg-xxport.Def when the device is delivered. ■ if you delete the default configuration file without specifying another one, the poe function...
Page 344
342 c hapter 31: p o e c onfiguration priority. For example: port a has the priority of critical. When the switch poe is close to its full load and a new pd is now added to port a, the switch will power down the pd connected to the port with the lowest priority and turn to supply power to this new p...
Page 345
Poe configuration 343 after the poe feature is enabled, perform the following configuration to enable the pd compatibility detection function. Configuring a pd disconnection detection mode to detect the pd connection with pse, poe provides two detection modes: ac detection and dc detection. The ac d...
Page 346
344 c hapter 31: p o e c onfiguration n ■ in the case that the pse processing software is damaged (that is, no poe command can be executed successfully), use the full update mode to upgrade and thus restore the software. ■ the refresh update mode is to upgrade the original processing software in the...
Page 347
Poe configuration example 345 ■ the ethernet 1/0/1 and ethernet 1/0/2 ports of switch a are connected to switch b and an ap respectively; the ethernet 1/0/8 port is intended to be connected with an important ap. ■ the pse processing software of switch a is first upgraded online. The remotely accesse...
Page 348
346 c hapter 31: p o e c onfiguration [switcha-ethernet1/0/8] poe priority critical [switcha-ethernet1/0/8] quit # set the poe management mode on the switch to auto (it is the default mode, so this step can be omitted). [switcha] poe power-management auto # enable the pd compatibility detect of the ...
Page 349: E P
32 p o e p rofile c onfiguration introduction to poe profile on a large-sized network or a network with mobile users, to help network administrators monitor the switch’s poe features , the switch 4210 provides the poe profile features. A poe profile is a set of poe configurations, including multiple...
Page 350
348 c hapter 32: p o e p rofile c onfiguration note the following during the configuration: 1 when the apply poe-profile command is used to apply a poe profile to a port, some poe features in the poe profile can be applied successfully while some cannot. Poe profiles are applied to the switch 4210 a...
Page 351
Poe profile configuration example 349 poe profile configuration example poe profile application example network requirements switch a is a switch 4210 that supports poe. Ethernet 1/0/1 through ethernet 1/0/10 of switch a are used by users of group a, who have the following requirements: ■ the poe fu...
Page 352
350 c hapter 32: p o e p rofile c onfiguration configuration procedure # create profile1, and enter poe profile view. System-view [switcha] poe-profile profile1 # in profile1, add the poe policy configuration applicable to ethernet 1/0/1 through ethernet 1/0/5 ports for users of group a. [switcha-po...
Page 353: Snmp C
33 snmp c onfiguration snmp overview the simple network management protocol (snmp) is used for ensuring the transmission of the management information between any two network nodes. In this way, network administrators can easily retrieve and modify the information about any node on the network. In t...
Page 354
352 c hapter 33: snmp c onfiguration information, while those with read-write permission can configure the switch as well. ■ set the basic acl specified by the community name. Supported mibs an snmp packet carries management variables with it. Management variable is used to describe the management o...
Page 355
Configuring basic snmp functions 353 configuring basic snmp functions snmpv3 configuration is quite different from that of snmpv1 and snmpv2c. Therefore, the configuration of basic snmp functions is described by snmp versions, as listed in table 273 and table 274. Private mib dhcp mib qacl mib mstp ...
Page 357
Configuring trap parameters 355 n a switch 4210 provides the following functions to prevent attacks through unused udp ports. ■ executing the snmp-agent command or any of the commands used to configure snmp agent enables the snmp agent, and at the same opens udp port 161 and udp port 1024 used by sn...
Page 358
356 c hapter 33: snmp c onfiguration configuring extended trap the extended trap includes the following. ■ interface description" and "interface type" are added into the linkup/linkdown trap message. When receiving this extended trap message, nms can immediately determine which interface on the devi...
Page 359
Enabling logging for network management 357 enabling logging for network management n iuse the display logbuffer command to view the log of the get and set operations requested by the nms. Displaying snmp after the above configuration, you can execute the display command in any view to view the runn...
Page 360
358 c hapter 33: snmp c onfiguration thus, the nms is able to access switch a and receive the trap messages sent by switch a. Network diagram figure 107 network diagram for snmp configuration network procedure # enable snmp agent, and set the snmpv1 and snmpv2c community names. System-view [4210] sn...
Page 361
Snmp configuration examples 359 [4210] snmp-agent trap enable standard authentication [4210] snmp-agent trap enable standard coldstart [4210] snmp-agent trap enable standard linkup [4210] snmp-agent trap enable standard linkdown [4210] snmp-agent target-host trap address udp-domain 10.10.10.1 udp -p...
Page 362
360 c hapter 33: snmp c onfiguration.
Page 363: Rmon C
34 rmon c onfiguration introduction to rmon remote monitoring (rmon) is a kind of management information base (mib) defined by internet engineering task force (ietf). It is an important enhancement made to mib ii standards. Rmon is mainly used to monitor the data traffic across a network segment or ...
Page 364
362 c hapter 34: rmon c onfiguration managed network devices are connected. Thus, the nms can further manage the networks. Commonly used rmon groups event group event group is used to define the indexes of events and the processing methods of the events. The events defined in an event group are main...
Page 365
Rmon configuration 363 with the history data management function, you can configure network devices to collect history data, sample and store data of a specific port periodically. Statistics group statistics group contains the statistics of each monitored port on a switch. An entry in a statistics g...
Page 366
364 c hapter 34: rmon c onfiguration n ■ the rmon alarm and rmon prialarm commands take effect on existing nodes only. ■ for each port, only one rmon statistics entry can be created. That is, if an rmon statistics entry is already created for a given port, you will fail to create another statistics ...
Page 367
Rmon configuration examples 365 [4210-ethernet1/0/1] rmon statistics 1 [4210-ethernet1/0/1] quit # add the event entries numbered 1 and 2 to the event table, which will be trigg ered by the following extended alarm. [4210] rmon event 1 log [4210] rmon event 2 trap 10.21.30.55 # add an entry numbered...
Page 368
366 c hapter 34: rmon c onfiguration.
Page 369: Ntp C
35 ntp c onfiguration introduction to ntp network time protocol (ntp) is a time synchronization protocol defined in rfc 1305. It is used for time synchronization between a set of distributed time servers and clients. Carried over udp, ntp transmits packets through udp port 123. Ntp is intended for t...
Page 370
368 c hapter 35: ntp c onfiguration as the stratum number increases. A stratum 16 clock is in the unsynchronized state and cannot serve as a reference clock. ■ the local clock of a switch 4210 cannot be set as a reference clock. It can serve as a reference clock source to synchronize the clock of ot...
Page 371
Introduction to ntp 369 ■ when the message arrives at device b, device b inserts its own timestamp 11:00:01 am (t 2 ) into the packet. ■ when the ntp message leaves device b, device b inserts its own timestamp 11:00:02 am (t 3 ) into the packet. ■ when receiving a response packet, the local time of ...
Page 372
370 c hapter 35: ntp c onfiguration symmetric peer mode figure 111 symmetric peer mode in the symmetric peer mode, the local switch 4210 serves as the symmetric-active peer and sends clock synchronization request first, while the remote server serves as the symmetric-passive peer automatically. If b...
Page 373
Ntp configuration tasks 371 table 281 describes how the above mentioned ntp modes are implemented on the 3com switch 4210 family. C caution: ■ when the switch 4210 is in server mode or symmetric passive mode, you need not perform related configurations on this switch, but on the client or the symmet...
Page 374
372 c hapter 35: ntp c onfiguration configuring ntp implementation modes a switch 4210 can work in one of the following ntp modes: ■ “configuring ntp server/client mode” ■ “configuring the ntp symmetric peer mode” ■ “configuring ntp broadcast mode” ■ “configuring ntp multicast mode” n to protect unu...
Page 375
Configuring ntp implementation modes 373 configuring the ntp symmetric peer mode for switches working in the symmetric peer mode, you need to specify a symmetric-passive peer on the symmetric-active peer. N ■ in the symmetric peer mode, you need to execute the related ntp configuration commands (ref...
Page 376
374 c hapter 35: ntp c onfiguration configuring a switch to work in the ntp broadcast server mode configuring a switch to work in the ntp broadcast client mode configuring ntp multicast mode for switches working in the multicast mode, you need to configure both the server and clients. The multicast ...
Page 377
Configuring access control right 375 configuring a switch to work in the multicast client mode configuring access control right with the following command, you can configure the ntp service access-control right to the local switch for a peer device. There are four access-control rights, as follows: ...
Page 378
376 c hapter 35: ntp c onfiguration n the access-control right mechanism provides only a minimum degree of security protection for the local switch. A more secure method is identity authentication. Configuring ntp authentication in networks with higher security requirements, the ntp authentication f...
Page 379
Configuring ntp authentication 377 configuration procedure configuring ntp authentication on the client n ntp authentication requires that the authentication keys configured for the server and the client be the same. Besides, the authentication keys must be trusted keys. Otherwise, the clock of the ...
Page 380
378 c hapter 35: ntp c onfiguration n the procedure for configuring ntp authentication on the server is the same as that on the client. Besides, the client and the server must be configured with the same authentication key. Configuring optional ntp parameters configuring an interface on the local sw...
Page 381
Displaying ntp configuration 379 upon the receipt of a message, rather than creating an association (static or dynamic). In the symmetric mode, static associations will be created at the symmetric-active peer side, and dynamic associations will be created at the symmetric-passive peer side; in the b...
Page 382
380 c hapter 35: ntp c onfiguration ■ configure device b to work in the client mode, and then device a will automatically work in the server mode. Network diagram figure 114 network diagram for the ntp server/client mode configuration configuration procedure perform the following configurations on d...
Page 383
Configuration example 381 [deviceb] display ntp-service sessions source reference stra reach poll now offset delay disper ************************************************************************** [12345]1.0.1.11 127.127.1.0 2 1 64 1 350.1 15.1 0.0 note: 1 source(master),2 source(peer),3 selected,4 ...
Page 384
382 c hapter 35: ntp c onfiguration clock stratum: 2 reference clock id: 3.0.1.32 nominal frequency: 100.0000 hz actual frequency: 100.0000 hz clock precision: 2^18 clock offset: 0.66 ms root delay: 27.47 ms root dispersion: 208.39 ms peer dispersion: 9.63 ms reference time: 17:03:32.022 utc thu apr...
Page 385
Configuration example 383 system-view # set device c as the broadcast server, which sends broadcast messages through vlan-interface2. [devicec] interface vlan-interface 2 [devicec-vlan-interface2] ntp-service broadcast-server 2 configure device a. (perform the same configuration on device d) # enter...
Page 386
384 c hapter 35: ntp c onfiguration network diagram figure 117 network diagram for ntp multicast mode configuration configuration procedure 1 configure device c. # enter system view. System-view # set device c as a multicast server to send multicast messages through vlan-interface2. [devicec] interf...
Page 387
Configuration example 385 root dispersion: 208.39 ms peer dispersion: 9.63 ms reference time: 17:03:32.022 utc thu apr 2 2007 (bf422ae4.05aea86c) the output information indicates that device d is synchronized to device c, with a clock stratum level of 3, one stratum level lower than that device c. #...
Page 388
386 c hapter 35: ntp c onfiguration 2 to synchronize device b, you need to perform the following configurations on device a. # enable the ntp authentication function. [devicea] system-view [devicea] ntp-service authentication enable # configure an md5 authentication key, with the key id being 42 and...
Page 389: Ssh C
36 ssh c onfiguration ssh overview introduction to ssh secure shell (ssh) is a protocol that provides secure remote login and other security services in insecure network environments. In an ssh connection, data are encrypted before being sent out and decrypted after they reach the destination. This ...
Page 390
388 c hapter 36: ssh c onfiguration while the private key is effective only for the local end. Normally you cannot use the private key through the public key. Asymmetric key algorithm encrypts data using the public key and decrypts the data using the private key, thus ensuring data security. You can...
Page 391
Ssh overview 389 n ■ all the packets above are transferred in plain text. Key negotiation ■ the server and the client send algorithm negotiation packets to each other, which contain public key algorithm lists supported by the server and the client, encrypted algorithm list, message authentication co...
Page 392
390 c hapter 36: ssh c onfiguration and goes on to the interactive session stage with the client. Otherwise, the server sends back to the client an ssh_smsg_failure packet, indicating that the processing fails or it cannot resolve the request. The client sends a session request to the server, which ...
Page 393
Configuring the ssh server 391 c caution: ■ if you have configured a user interface to support ssh protocol, you must configure aaa authentication for the user interface by using the authentication-mode scheme command to ensure successful login. ■ on a user interface, if the authentication-mode pass...
Page 394
392 c hapter 36: ssh c onfiguration exporting the rsa or dsa public key you can display the generated rsa or dsa key pair on the screen in a specified format, or export it to a specified file for configuring the key at a remote end. N the dsa public key format can be ssh2 and openssh, while the rsa ...
Page 395
Configuring the ssh server 393 remote server. And the user can use its username and password configured on the remote server to access the network. ■ both publickey and rsa indicate public key authentication. They are implemented with the same method. ■ under the publickey authentication mode, the l...
Page 396
394 c hapter 36: ssh c onfiguration ■ for details of the header command, see the corresponding section in login command. Configuring the client public key on the server n this configuration is not necessary if the password authentication mode is configured for ssh users. With the publickey authentic...
Page 397
Configuring the ssh server 395 n the result of the display rsa local-key-pair public command or the public key converted with the sshkey tool contains no information such as the authentication type, so they cannot be directly used as parameters in the public-key peer command. For the same reason, ne...
Page 398
396 c hapter 36: ssh c onfiguration configuring the ssh client an ssh client software or ssh2-capable switch can serve as an ssh client to access the ssh server. Ssh client configuration tasks configuring the ssh client using an ssh client software a variety of ssh client software are available, suc...
Page 399
Configuring the ssh client 397 figure 120 generate a client key (1) note that while generating the key pair, you must move the mouse continuously and keep the mouse off the green process bar in the blue box of shown in figure 121. Otherwise, the process bar stops moving and the key pair generating p...
Page 400
398 c hapter 36: ssh c onfiguration figure 121 generate the client keys (2) after the key pair is generated, click save public key and enter the name of the file for saving the public key (public in this case) to save the public key. Figure 122 generate the client keys (3).
Page 401
Configuring the ssh client 399 likewise, to save the private key, click save private key. A warning window pops up to prompt you whether to save the private key without any precaution. Click yes and enter the name of the file for saving the private key ("private" in this case) to save the private ke...
Page 402
400 c hapter 36: ssh c onfiguration figure 125 ssh client configuration interface 1 in the host name (or ip address) text box, enter the ip address of the server. Note that there must be a route available between the ip address of the server and the client. Select a protocol for remote connection as...
Page 403
Configuring the ssh client 401 figure 126 ssh client configuration interface 2 under protocol options, select 2 from preferred ssh protocol version. N some ssh client software, for example, tectia client software, supports the des algorithm only when the ssh1 version is selected. The putty client so...
Page 404
402 c hapter 36: ssh c onfiguration figure 127 ssh client configuration interface 3 click browse... To bring up the file selection window, navigate to the private key file and click open to enter the following ssh client interface. If the connection is normal, a user will be prompted for a username....
Page 405
Configuring the ssh client 403 figure 128 ssh client interface (1) open an ssh connection with password authentication from the window shown in figure 127, click open. The following ssh client interface appears. If the connection is normal, you will be prompted to enter the username and password, as...
Page 406
404 c hapter 36: ssh c onfiguration figure 129 ssh client interface (2) enter the username and password to establish an ssh connection. To log out, enter the quit command. Configuring the ssh client on an ssh2-capable switch configure whether first-time authentication is supported when the device co...
Page 407
Configuring the ssh client 405 establish the connection between the ssh client and server the client’s method of establishing an ssh connection to the ssh server varies with authentication types. See table 316 for details. N when logging into the ssh server using public key authentication, an ssh cl...
Page 408
406 c hapter 36: ssh c onfiguration displaying ssh configuration after the above configuration, you can execute the display command in any view to display the configuration information and running status of ssh, so as to verify your configuration. Ssh configuration examples when the switch acts as t...
Page 409
Ssh configuration examples 407 # generate rsa and dsa key pairs. [4210] public-key local create rsa [4210] public-key local create dsa # set the authentication mode for the user interfaces to aaa. [4210] user-interface vty 0 4 [4210-ui-vty0-4] authentication-mode scheme # enable the user interfaces ...
Page 410
408 c hapter 36: ssh c onfiguration take ssh client software "putty" (version 0.58) as an example: 1 run putty.Exe to enter the following configuration interface. Figure 131 ssh client configuration interface in the host name (or ip address) text box, enter the ip address of the ssh server. 2 from t...
Page 411
Ssh configuration examples 409 figure 132 ssh client configuration interface 2 under protocol options, select 2 from preferred ssh protocol version. 3 as shown in figure 131, click open to enter the following interface. If the connection is normal, you will be prompted to enter the user name "client...
Page 412
410 c hapter 36: ssh c onfiguration figure 133 ssh client interface when the switch acts as an ssh server and the authentication type is publickey network requirements as shown in figure 134, establish an ssh connection between the host (ssh client) and the switch (ssh server) for secure data exchan...
Page 413
Ssh configuration examples 411 # generate rsa and dsa key pairs. [4210] public-key local create rsa [4210] public-key local create dsa # set the authentication mode for the user interfaces to aaa. [4210] user-interface vty 0 4 [4210-ui-vty0-4] authentication-mode scheme # enable the user interfaces ...
Page 414
412 c hapter 36: ssh c onfiguration # generate an rsa key pair, taking puttygen as an example. 1 run puttygen.Exe, choose ssh2(rsa) and click generate. Figure 135 generate a client key pair (1) n while generating the key pair, you must move the mouse continuously and keep the mouse off the green pro...
Page 415
Ssh configuration examples 413 figure 136 generate a client key pair (2) after the key pair is generated, click save public key and enter the name of the file for saving the public key ("public" in this case). Figure 137 generate a client key pair (3).
Page 416
414 c hapter 36: ssh c onfiguration likewise, to save the private key, click save private key. A warning window pops up to prompt you whether to save the private key without any protection. Click yes and enter the name of the file for saving the private key ("private.Ppk" in this case). Figure 138 g...
Page 417
Ssh configuration examples 415 figure 140 ssh client configuration interface 2 under protocol options, select 2 from preferred ssh protocol version. 3 select connection/ssh/auth. The following window appears..
Page 418
416 c hapter 36: ssh c onfiguration figure 141 ssh client configuration interface (2) click browse... To bring up the file selection window, navigate to the private key file and click ok. 4 from the window shown in figure 141, click open. The following ssh client interface appears. If the connection...
Page 419
Ssh configuration examples 417 figure 142 ssh client interface - when the switch acts as an ssh client and the authentication type is password network requirements as shown in figure 143, establish an ssh connection between switch a (ssh client) and switch b (ssh server) for secure data exchange. Th...
Page 420
418 c hapter 36: ssh c onfiguration # generate rsa and dsa key pairs. [4210] public-key local create rsa [4210] public-key local create dsa # set the authentication mode for the user interfaces to aaa. [4210] user-interface vty 0 4 [4210-ui-vty0-4] authentication-mode scheme # enable the user interf...
Page 421
Ssh configuration examples 419 network diagram figure 144 network diagram of ssh client configuration when using publickey authentication configuration procedure n in public key authentication, you can use either rsa or dsa public key. Here takes the dsa public key as an example. ■ configure switch ...
Page 422
420 c hapter 36: ssh c onfiguration # create a vlan interface on the switch and assign an ip address, which serves as the ssh client’s address in an ssh connection. System-view [4210] interface vlan-interface 1 [4210-vlan-interface1] ip address 10.165.87.137 255.255.255.0 [4210-vlan-interface1] quit...
Page 423
Ssh configuration examples 421 system-view [4210] interface vlan-interface 1 [4210-vlan-interface1] ip address 10.165.87.136 255.255.255.0 [4210-vlan-interface1] quit c generating the rsa and dsa key pairs on the server is prerequisite to ssh login. # generate rsa and dsa key pairs. [4210] public-ke...
Page 424
422 c hapter 36: ssh c onfiguration n after generating the public key, you need to upload the key pair file to the server through ftp or tftp and complete the server end configuration before you continue to configure the client. # disable first-time authentication on the device. [4210] undo ssh clie...
Page 425: Ile
37 f ile s ystem m anagement c onfiguration file system configuration to facilitate management on the switch’s memory, the switch 4210 provides the file system function, allowing you to access and manage the files and directories. You can create, remove, copy or delete a file through command lines, ...
Page 426
424 c hapter 37: f ile s ystem m anagement c onfiguration n ■ only empty directories can be deleted by using the rmdir command. ■ in the output information of the dir /all command, deleted files (that is, those stored in the recycle bin) are embraced in brackets. File operations the file system also...
Page 427
File system configuration 425 flash memory operations perform the following flash memory operations using commands listed in table 321. Perform the following configuration in user view. C caution: the format operation leads to the loss of all files, including the configuration files, on the flash me...
Page 428
426 c hapter 37: f ile s ystem m anagement c onfiguration dir /all directory of unit1>flash:/ 1 (*) -rw- 3579326 mar 28 2007 10:51:22 s3100.Bin 2 (*) -rw- 1235 apr 03 2000 16:04:52 config.Cfg 3 -rwh 151 apr 03 2000 16:04:55 private-data.Txt 4 -rwh 716 apr 04 2000 17:27:35 hostkey 5 -rwh 572 apr 04 2...
Page 429
File attribute configuration 427 n a file can have both the main and backup attributes. Files of this kind are labeled *b. Note that, there can be only one app file, one configuration file and one web file with the main attribute in the flash memory. If a newly created file is configured to be with ...
Page 430
428 c hapter 37: f ile s ystem m anagement c onfiguration c caution: ■ the configuration of the main or backup attribute of a web file takes effect immediately without restarting the switch. ■ after upgrading a web file, you need to specify the new web file in the boot menu after restarting the swit...
Page 431: Ftp
38 ftp and sftp c onfiguration introduction to ftp and sftp introduction to ftp ftp (file transfer protocol) is commonly used in ip-based networks to transmit files. Before world wide web comes into being, files are transferred through command lines, and the most popular application is ftp. At prese...
Page 432
430 c hapter 38: ftp and sftp c onfiguration introduction to sftp secure ftp (sftp) is established based on an ssh2 connection. It allows a remote user to log in to a switch to manage and transmit files, providing a securer guarantee for data transmission. In addition, since the switch can be used a...
Page 433
Ftp configuration 431 ■ operating as an ftp server, the switch 4210 cannot receive a file whose size exceeds its storage space. The clients that attempt to upload such a file will be disconnected with the ftp server due to lack of storage space on the ftp server. N to protect unused sockets against ...
Page 434
432 c hapter 38: ftp and sftp c onfiguration figure 147 process of displaying a shell banner n for details about the header command, refer to “logging into an ethernet switch” on page 21. Displaying ftp server information after the above configurations, you can execute the display commands in any vi...
Page 435
Ftp configuration 433 specify to transfer files in ascii characters ascii use either command by default, files are transferred in ascii characters. Specify to transfer files in binary streams binary set the data transfer mode to passive passive optional passive by default. Change the working directo...
Page 436
434 c hapter 38: ftp and sftp c onfiguration configuration example: a switch operating as an ftp server network requirements a switch operates as an ftp server and a remote pc as an ftp client. The application switch.Bin of the switch is stored on the pc. Upload the application to the remote switch ...
Page 437
Ftp configuration 435 # access the ethernet switch through ftp. Input the user name "switch" and password "hello" to log in and enter ftp view. C:\> ftp 1.1.1.1 connected to 1.1.1.1. 220 ftp service ready. User (1.1.1.1:(none)): switch 331 password required for switch. Password: 230 user logged in. ...
Page 438
436 c hapter 38: ftp and sftp c onfiguration ftp banner display configuration example network requirements configure the ethernet switch as an ftp server and the remote pc as an ftp client. After a connection between the ftp client and the ftp server is established and login succeeds, the banner is ...
Page 439
Ftp configuration 437 ftp configuration: a switch operating as an ftp client network requirements a switch operates as an ftp client and a remote pc as an ftp server. The switch application named switch.Bin is stored on the pc. Download it to the switch through ftp and use the boot boot-loader comma...
Page 440
438 c hapter 38: ftp and sftp c onfiguration password: 230 user logged in. [ftp] # enter the authorized directory on the ftp server. [ftp] cd switch # execute the put command to upload the configuration file named config.Cfg to the ftp server. [ftp] put config.Cfg # execute the get command to downlo...
Page 441
Sftp configuration 439 configuring connection idle time after the idle time is configured, if the server does not receive service requests from a client within a specified time period, it terminates the connection with the client, thus preventing a user from occupying the connection for a long time ...
Page 443
Sftp configuration 441 n if you specify to authenticate a client through public key on the server, the client needs to read the local private key when logging in to the sftp server. Since both rsa and dsa are available for public key authentication, you need to use the identity-key key word to speci...
Page 444
442 c hapter 38: ftp and sftp c onfiguration # configure the authentication mode as password. Authentication timeout time, retry number, and update time of the server key adopt the default values. [4210] ssh user client001 authentication-type password # specify the service type as sftp. [4210] ssh u...
Page 445
Sftp configuration 443 -rwxrwxrwx 1 noone nogroup 1759 aug 23 06:52 config.Cfg -rwxrwxrwx 1 noone nogroup 225 aug 24 08:01 pubkey2 -rwxrwxrwx 1 noone nogroup 283 aug 24 07:39 pubkey1 drwxrwxrwx 1 noone nogroup 0 sep 01 06:22 new -rwxrwxrwx 1 noone nogroup 225 sep 01 06:55 pub received status: end of...
Page 446
444 c hapter 38: ftp and sftp c onfiguration -rwxrwxrwx 1 noone nogroup 283 aug 24 07:39 pubkey1 drwxrwxrwx 1 noone nogroup 0 sep 01 06:22 new drwxrwxrwx 1 noone nogroup 0 sep 02 06:33 new2 -rwxrwxrwx 1 noone nogroup 283 sep 02 06:35 pub -rwxrwxrwx 1 noone nogroup 283 sep 02 06:36 puk received statu...
Page 447: Tftp C
39 tftp c onfiguration introduction to tftp compared with ftp, tftp (trivial file transfer protocol) features simple interactive access interface and no authentication control. Therefore, tftp is applicable in the networks where client-server interactions are relatively simple. Tftp is implemented b...
Page 448
446 c hapter 39: tftp c onfiguration tftp configuration basic configurations on a tftp client by default a switch can operate as a tftp client. In this case you can connect the switch to the tftp server to perform tftp-related operations (such as creating/removing a directory) by executing commands ...
Page 449
Tftp configuration 447 # log in to the switch. (you can log in to a switch through the console port or by telnetting the switch. See the "login" module for detailed information.) c caution: if available space on the flash memory of the switch is not enough to hold the file to be uploaded, you need t...
Page 450
448 c hapter 39: tftp c onfiguration.
Page 452
450 c hapter 39: tftp c onfiguration.
Page 453: Nformation
40 i nformation c enter information center overview introduction to information center acting as the system information hub, information center classifies and manages system information. Together with the debugging function (the debugging command), information center offers a powerful support for ne...
Page 454
452 c hapter 40: i nformation c enter ■ if the threshold is set to 1, only information with the severity being emergencies will be output; ■ if the threshold is set to 8, information of all severities will be output. Ten channels and six output directions of system information the system supports si...
Page 455
Information center overview 453 outputting system information by source module the system information can be classified by source module and then filtered. Some module names and description are shown in table 340. Table 340 source module name list module name description 8021x 802.1x module acl acce...
Page 456
454 c hapter 40: i nformation c enter to sum up, the major task of the information center is to output the three types of information of the modules onto the ten channels in terms of the eight severity levels and according to the user’s settings, and then redirect the system information from the ten...
Page 458
456 c hapter 40: i nformation c enter between "module" and "level" is a "/". Level (severity) system information can be divided into eight levels based on its severity, from 1 to 8. Refer to table 338 for definition and description of these severity levels. Note that there is a forward slash "/" bet...
Page 459
Information center configuration 457 n ■ if the system information is output before you input any information following the current command line prompt, the system does not echo any command line prompt after the system information output. ■ in the interaction mode, you are prompted for some informat...
Page 460
458 c hapter 40: i nformation c enter n to view the debugging information of some modules on the switch, you need to set the type of the output information to debug when configuring the system information output rules, and use the debugging command to enable debugging for the corresponding modules. ...
Page 461
Information center configuration 459 n make sure that the debugging/log/trap information terminal display function is enabled (use the terminal monitor command) before you enable the corresponding terminal display function by using the terminal debugging, terminal logging, or terminal trapping comma...
Page 462
460 c hapter 40: i nformation c enter and enable debugging for corresponding modules through the debugging command. Enabling system information display on a monitor terminal after setting to output system information to a monitor terminal, you need to enable the associated display function in order ...
Page 463
Information center configuration 461 n be sure to set the correct ip address when using the info-center loghost command. A loopback ip address will cause an error message prompting that this address is invalid. Setting to output system information to the trap buffer setting to output system informat...
Page 464
462 c hapter 40: i nformation c enter setting to output system information to the snmp nms n to send information to a remote snmp nms properly, related configurations are required on both the switch and the snmp nms. Displaying and maintaining information center after the above configurations, you c...
Page 465
Information center configuration examples 463 information center configuration examples log output to a unix log host network requirements the switch sends the following log information to the unix log host whose ip address is 202.38.1.10: the log information of the two modules arp and ip, with seve...
Page 466
464 c hapter 40: i nformation c enter # configure the host whose ip address is 202.38.1.10 as the log host. Permit arp and ip modules to output information with severity level higher than informational to the log host. [switch] info-center loghost 202.38.1.10 facility local4 [switch] info-center sou...
Page 467
Information center configuration examples 465 network diagram figure 154 network diagram for log output to a linux log host configuration procedure 1 configure the switch: # enable the information center. System-view [switch] info-center enable # configure the host whose ip address is 202.38.1.10 as...
Page 468
466 c hapter 40: i nformation c enter after all the above operations, the switch can record information in the corresponding log file. N through combined configuration of the device name (facility), information severity level threshold (severity), module name (filter) and the file "syslog.Conf", you...
Page 469
Information center configuration examples 467 configuration procedure # name the local time zone z8 and configure it to be eight hours ahead of utc time. Clock timezone z8 add 08:00:00 # set the time stamp format of the log information to be output to the log host to date. System-view system view: r...
Page 470
468 c hapter 40: i nformation c enter.
Page 471: Oot
41 b oot rom and h ost s oftware l oading traditionally, switch software is loaded through a serial port. This approach is slow, time-consuming and cannot be used for remote loading. To resolve these problems, the tftp and ftp modules are introduced into the switch. With these modules, you can load/...
Page 472
470 c hapter 41: b oot rom and h ost s oftware l oading copyright (c) 2004-2007 3com corporation creation date : apr 17 2007, 10:12:36 cpu clock speed : 200mhz bus clock speed : 33mhz memory size : 64mb mac address : 000fe2123456 press ctrl-b to enter boot menu... Press . The system displays: passwo...
Page 473
Local boot rom and software loading 471 loading boot rom follow these steps to load the boot rom: step 1: at the prompt "enter your choice(0-9):" in the boot menu, press or , and then press to enter the boot rom update menu shown below: bootrom update menu: 1. Set tftp protocol parameter 2. Set ftp ...
Page 474
472 c hapter 41: b oot rom and h ost s oftware l oading figure 157 properties dialog box figure 158 console port configuration dialog box.
Page 475
Local boot rom and software loading 473 step 5: click the button to disconnect the hyperterminal from the switch and then click the button to reconnect the hyperterminal to the switch, as shown in figure 159. Figure 159 connect and disconnect buttons n the new baudrate takes effect after you disconn...
Page 476
474 c hapter 41: b oot rom and h ost s oftware l oading figure 161 sending file page step 9: after the sending process completes, the system displays the following information: loading ...Cccccccccc done! Step 10: reset hyperterminal’s baudrate to 9600 bps (refer to step 4 and 5). Then, press any ke...
Page 477
Local boot rom and software loading 475 the subsequent steps are the same as those for loading the boot rom, except that the system gives the prompt for host software loading instead of boot rom loading. N you can also use the xmodem get command to load host software through the console port (of aux...
Page 478
476 c hapter 41: b oot rom and h ost s oftware l oading 0. Return to boot menu enter your choice(0-3): step 4: enter 1 in the above menu to download the boot rom using tftp. Then set the following tftp-related parameters as required: load file name : switch_02.Btm switch ip address :1.1.1.2 server i...
Page 479
Local boot rom and software loading 477 figure 163 local loading using ftp client 1 as shown in figure 163, connect the switch through an ethernet port to the ftp server, and connect the switch through the console port to the configuration pc. N you can use one computer as both configuration device ...
Page 480
478 c hapter 41: b oot rom and h ost s oftware l oading 0. Return to boot menu enter your choice(0-3): 2 enter 2 in the above menu to download the host software using ftp. The subsequent steps are the same as those for loading the boot rom, except for that the system gives the prompt for host softwa...
Page 481
Remote boot rom and software loading 479 step 3: restart the switch. Reboot n before restarting the switch, make sure you have saved all other configurations that you want, so as to avoid losing configuration information. 2 loading host software loading the host software is the same as loading the b...
Page 482
480 c hapter 41: b oot rom and h ost s oftware l oading c enable ftp service on the switch, and configure the ftp user name to test and password to pass. [4210-vlan-interface1] quit [4210] ftp server enable [4210] local-user test new local user added. [4210-luser-test] password simple pass [4210-lus...
Page 483
Remote boot rom and software loading 481 figure 167 enter boot rom directory f enter ftp 192.168.0.28 and enter the user name test, password pass, as shown in figure 168, to log on to the ftp server. Figure 168 log on to the ftp server g use the put command to upload the file switch.Btm to the switc...
Page 484
482 c hapter 41: b oot rom and h ost s oftware l oading figure 169 upload file switch.Btm to the switch h configure switch.Btm to be the boot rom at next startup, and then restart the switch. Boot bootrom switch.Btm this will update bootrom on unit 1. Continue? [y/n] y upgrading bootrom, please wait...
Page 486
484 c hapter 42: b asic s ystem c onfiguration and d ebugging displaying the system status you can use the following display commands to check the status and configuration information about the system. For information about protocols and ports, and the associated display commands, refer to relevant ...
Page 487
Debugging the system 485 figure 170 the relationship between the protocol and screen debugging switch n displaying debugging information on the terminal is the most commonly used way to output debugging information. You can also output debugging information to other directions. For details, refer to...
Page 488
486 c hapter 42: b asic s ystem c onfiguration and d ebugging displaying operating information about modules in system when an ethernet switch is in trouble, you may need to view a lot of operating information to locate the problem. Each functional module has its corresponding operating information ...
Page 489: Etwork
43 n etwork c onnectivity t est network connectivity test ping you can use the ping command to check the network connectivity and the reachability of a host. This command can output the following results: ■ response status for each ping packet. If no response packet is received within the timeout ti...
Page 490
488 c hapter 43: n etwork c onnectivity t est table 360 the tracert command operation command description view the gateways that a packet passes from the source host to the destination tracert [ -a source-ip ] [ -f first-ttl ] [ -m max-ttl ] [ -p port ] [ -q num-packet ] [ -w timeout ] string you ca...
Page 491: Evice
44 d evice m anagement device management configuration device management configuration tasks rebooting the ethernet switch you can perform the following operation in user view when the switch is faulty or needs to be rebooted. N before rebooting, the system checks whether there is any configuration ...
Page 492
490 c hapter 44: d evice m anagement n the switch timer can be set to precision of one minute, that is, the switch will reboot within one minute after the specified reboot date and time. Configuring real-time monitoring of the running status of the system this function enables you to dynamically rec...
Page 493
Displaying the device management configuration 491 displaying the device management configuration after the above configurations, you can execute the display command in any view to display the operating status of the device management to verify the configuration effects. Remote switch app upgrade co...
Page 494
492 c hapter 44: d evice m anagement network diagram figure 171 network diagram for ftp configuration configuration procedure 1 configure the following ftp server-related parameters on the pc: an ftp user with the username as switch and password as hello, who is authorized with the read-write right ...
Page 495
Remote switch app upgrade configuration example 493 upgrading bootrom, please wait... Upgrade bootrom succeeded! 9 specify the downloaded program as the host software to be adopted when the switch starts next time. Boot boot-loader switch.Bin the specified file will be booted next time on unit 1! Di...
Page 496
494 c hapter 44: d evice m anagement.
Page 497: Emote
45 r emote -p ing c onfiguration remote-ping overview introduction to remote-ping remote-ping (pronounced hua’wei ping) is a network diagnostic tool. It is used to test the performance of various protocols running in networks. Remote-ping provides more functions than the ping command. ■ the ping com...
Page 498
496 c hapter 45: r emote -p ing c onfiguration test types supported by remote-ping c caution: the switch 4210 does not support remote-ping dns tests. Remote-ping test parameters you need to configure corresponding test parameters for each type of remote-ping test. Remote-ping test parameters can be ...
Page 499
Remote-ping overview 497 source address (source-ip) for remote-ping tests other than dhcp test, you can specify a source ip address for test packets, which will be used by the server as the destination address of response packets. Source port (source-port) for remote-ping tests other than icmp, dhcp...
Page 500
498 c hapter 45: r emote -p ing c onfiguration remote-ping configuration the tcp/udp/jitter tests need the cooperation of remote-ping client and remote-ping server, other types of tests need to configure remote-ping client and corresponding different servers. Configuration on a remote-ping server yo...
Page 501
Remote-ping configuration 499 remote-ping server configuration tasks remote-ping server configuration table 371 describes the configuration on remote-ping server, which is the same for remote-ping test types that need to configure remote-ping server. Remote-ping client configuration remote-ping clie...
Page 502
500 c hapter 45: r emote -p ing c onfiguration n for a remote-ping icmp test, if no ip address is configured for the source interface configured through the source-interface command, the test cannot be performed; if a source ip address has already been configured through the source-ip command, the s...
Page 503
Remote-ping configuration 501 3 configuring ftp test on remote-ping client enable the remote-ping client function remote-ping-agent enable required by default, the remote-ping client function is disabled. Create a remote-ping test group and enter its view remote-ping administrator-name operation-tag...
Page 504
502 c hapter 45: r emote -p ing c onfiguration 4 configuring http test on remote-ping client configure the source port source-port port-number optional by default, no source port is configured. Configure the test type test-type ftp required by default, the test type is icmp. Configure the number of ...
Page 505
Remote-ping configuration 503 enable the remote-ping client function remote-ping-agent enable required by default, the remote-ping client function is disabled. Create a remote-ping test group and enter its view remote-ping administrator-name operation-tag required by default, no test group is config...
Page 507
Remote-ping configuration 505 6 configuring snmp test on remote-ping client configure the number of probes per test count times optional by default, each test makes one probe. Configure the maximum number of history records that can be saved history-records number figure 175 optional by default, the...
Page 508
506 c hapter 45: r emote -p ing c onfiguration 7 configuring tcp test on remote-ping client configure the source ip address source-ip ip-address optional by default, no source ip address is configured. Configure the source port source-port port-number optional by default, no source port is configure...
Page 509
Remote-ping configuration 507 configure the destination address destination-ip ip-address required this ip address and the one configured on the remote-ping server for listening services must be the same. By default, no destination address is configured. Configure the destination port destination-po...
Page 510
508 c hapter 45: r emote -p ing c onfiguration 8 configuring udp test on remote-ping client display test results display remote-ping results [ admin-name operation-tag ] required the display command can be executed in any view. Table 378 configure tcp test on remote-ping client operation command des...
Page 511
Remote-ping configuration 509 9 configuring dns test on remote-ping client configure the number of probes per test count times optional by default, one probe is made per test. Configure the maximum number of history records that can be saved history-records number figure 178 optional by default, the...
Page 512
510 c hapter 45: r emote -p ing c onfiguration configuring remote-ping client to send trap messages trap messages are generated regardless of whether the remote-ping test succeeds or fails. You can specify whether to output trap messages by enabling/disabling trap sending. Configure the maximum numb...
Page 513
Remote-ping configuration example 511 displaying remote-ping configuration after the above-mentioned configuration, you can use the display commands to view the results of the latest test and history information. Remote-ping configuration example icmp test network requirements the switch 4210 serves...
Page 514
512 c hapter 45: r emote -p ing c onfiguration [4210-remote-ping-administrator-icmp] test-type icmp # configure the destination ip address as 10.2.2.2. [4210-remote-ping-administrator-icmp] destination-ip 10.2.2.2 # configure to make 10 probes per test. [4210-remote-ping-administrator-icmp] count 10...
Page 515
Remote-ping configuration example 513 configuration procedure ■ configure dhcp server(switch b): ■ configure remote-ping client (switch a): # enable the remote-ping client. System-view [4210] remote-ping-agent enable # create a remote-ping test group, setting the administrator name to "administrator...
Page 516
514 c hapter 45: r emote -p ing c onfiguration ftp test network requirements both the remote-ping client and the ftp server are switch 4210s. Perform a remote-ping ftp test between the two switches to test the connectivity to the specified ftp server and the time required to upload a file to the ser...
Page 517
Remote-ping configuration example 515 # set the probe timeout time to 30 seconds. [4210-remote-ping-administrator-ftp] timeout 30 # configure the source ip address [4210-remote-ping-administrator-ftp] source-ip 10.1.1.1 # start the test. [4210-remote-ping-administrator-ftp] test-enable # display tes...
Page 518
516 c hapter 45: r emote -p ing c onfiguration network diagram figure 183 network diagram for the http test configuration procedure ■ configure the http server. Use a windows 2003 server as the http server and follow the instructions in your windows 2003 server documentation. ■ configure remote-ping...
Page 519
Remote-ping configuration example 517 tcp connect time: 73 http operation min time: 27 tcp connect min time: 5 http operation max time: 80 tcp connect max time: 20 tcp connect timeout times: 0 [4210-remote-ping-administrator-http] display remote-ping history administrator h ttp remote-ping entry(adm...
Page 520
518 c hapter 45: r emote -p ing c onfiguration # configure the test type as jitter [4210-remote-ping-administrator-jitter] test-type jitter # configure the ip address of the remote-ping server as 10.2.2.2. [4210-remote-ping-administrator-jitter] destination-ip 10.2.2.2 # configure the destination po...
Page 521
Remote-ping configuration example 519 for detailed output description, see the corresponding command manual. Snmp test network requirements both the remote-ping client and the snmp agent are switch 4210s. Perform remote-ping snmp tests between the two switches to test the time required from switch a...
Page 522
520 c hapter 45: r emote -p ing c onfiguration [4210-remote-ping-administrator-snmp] timeout 30 # start the test. [4210-remote-ping-administrator-snmp] test-enable # display test results [4210-remote-ping-administrator-snmp] display remote-ping results administrator s nmp remote-ping entry(admin adm...
Page 523
Remote-ping configuration example 521 system-view [4210] remote-ping-server enable [4210] remote-ping-server tcpconnect 10.2.2.2 8000 ■ configure remote-ping client (switch a): # enable the remote-ping client. System-view [4210] remote-ping-agent enable # create a remote-ping test group, setting the...
Page 524
522 c hapter 45: r emote -p ing c onfiguration for detailed output description, see the corresponding command manual. Udp test (udpprivate test) on the specified ports network requirements both the remote-ping client and the remote-ping server are switch 4210s. Perform a remote-ping udpprivate test ...
Page 525
Remote-ping configuration example 523 [4210-remote-ping-administrator-udpprivate] display remote-ping results administr ator udpprivate remote-ping entry(admin administrator, tag udpprivate) test result: destination ip address:10.2.2.2 send operation times: 10 receive response times: 10 min/max/aver...
Page 526
524 c hapter 45: r emote -p ing c onfiguration # configure the test type as dns. [4210-remote-ping-administrator-dns] test-type dns # configure the ip address of the dns server as 10.2.2.2. [4210-remote-ping-administrator-dns] dns-server 10.2.2.2 # configure to resolve the domain name www.Test.Com. ...
Page 527: 6 M
46 ip v 6 m angement c onfiguration n ■ the term "router" in this document refers to a router in a generic sense or an ethernet switch running a routing protocol. ■ 3com switch 4210 family supports ipv6 management features, but does not support ipv6 forwarding and related features. Ipv6 overview int...
Page 528
526 c hapter 46: ip v 6 m angement c onfiguration hierarchical address structure ipv6 adopts the hierarchical address structure to quicken route search and reduce the system source occupied by the ipv6 routing table by means of route aggregation. Automatic address configuration to simplify the host ...
Page 529
Ipv6 overview 527 ■ leading zeros in each group can be removed. For example, the above-mentioned address can be represented in shorter format as 2001:0:130f:0:0:9c0:876a:130b. ■ if an ipv6 address contains two or more consecutive groups of zeros, they can be replaced by the double-colon :: option. F...
Page 530
528 c hapter 46: ip v 6 m angement c onfiguration unicast address there are several forms of unicast address assignment in ipv6, including global unicast address, link-local address, and site-local address. ■ the global unicast address, equivalent to an ipv4 public address, is used for aggregatable ...
Page 531
Ipv6 overview 529 where, ff02:0:0:0:0:1:ff is permanent and consists of 104 bits, and xx:xxxx is the last 24 bits of an ipv6 address. Interface identifier in ieee eui-64 format interface identifiers in ipv6 unicast addresses are used to identify interfaces on a link and they are required to be uniqu...
Page 532
530 c hapter 46: ip v 6 m angement c onfiguration n ■ 3com switch 4210 family do not support rs, ra, or redirect message. ■ of the above mentioned ipv6 ndp functions, 3com switch 4210 family support the following three functions: address resolution, neighbor unreachability detection, and duplicate a...
Page 533
Ipv6 overview 531 solicited-node multicast address of node b. The ns message contains the link-layer address of node a. 2 after receiving the ns message, node b judges whether the destination address of the packet is the corresponding solicited-node multicast address of its own ipv6 address. If yes,...
Page 534
532 c hapter 46: ip v 6 m angement c onfiguration introduction to ipv6 dns in the ipv6 network, a domain name system (dns) supporting ipv6 converts domain names into ipv6 addresses. Different from an ipv4 dns, an ipv6 dns converts domain names into ipv6 addresses, instead of ipv4 addresses. However,...
Page 535
Ipv6 configuration task list 533 ■ to enable a host to access a public ipv6 network, you need to assign an ipv6 global unicast address to it. Ipv6 site-local addresses and global unicast addresses can be configured in either of the following ways: ■ eui-64 format: when the eui-64 format is adopted t...
Page 536
534 c hapter 46: ip v 6 m angement c onfiguration manually assigned link-local address is deleted, the automatically generated link-local address takes effect. ■ the manual assignment takes precedence over the automatic generation. That is, if you first adopt the automatic generation and then the ma...
Page 537
Ipv6 configuration task list 535 configure the attempts to send an ns message for duplicate address detection the device sends a neighbor solicitation (ns) message for duplicate address detection. If the device does not receive a response within a specified time (set by the ipv6 nd ns retrans-timer ...
Page 538
536 c hapter 46: ip v 6 m angement c onfiguration configure the neighbor reachable timeout time on an interface after a neighbor passed the reachability detection, the device considers the neighbor to be reachable in a specific period. However, the device will examine whether the neighbor is reachab...
Page 539
Ipv6 configuration task list 537 configuring the maximum number of ipv6 icmp error packets sent within a specified time if too many ipv6 icmp error packets are sent within a short time in a network, network congestion may occur. To avoid network congestion, you can control the maximum number of ipv6...
Page 540
538 c hapter 46: ip v 6 m angement c onfiguration configure dynamic dns resolution if you want to use the dynamic domain name function, you can use the following command to enable the dynamic domain name resolution function. In addition, you should configure a dns server so that a query request mess...
Page 541
Ipv6 configuration task list 539 displaying and maintaining ipv6 n the display dns domain and display dns server commands are the same as those of ipv4 dns. For details about the commands, refer to “dns configuration” on page 549. Table 399 display and maintain ipv6 to do... Use the command... Remar...
Page 542
540 c hapter 46: ip v 6 m angement c onfiguration ipv6 configuration example ipv6 unicast address configuration network requirements two switches are directly connected through two ethernet ports. The ethernet ports belong to vlan 2. Ipv6 addresses are configured for the interface vlan-interface2 on...
Page 543
Ipv6 configuration example 541 joined group address(es): ff02::1:ff00:1 ff02::1:ff47:4ca3 ff02::1 mtu is 1500 bytes nd dad is enabled, number of dad attempts: 1 nd reachable time is 30000 milliseconds nd retransmit interval is 1000 milliseconds hosts use stateless autoconfig for addresses # display ...
Page 544
542 c hapter 46: ip v 6 m angement c onfiguration bytes=56 sequence=3 hop limit=64 time = 6 ms reply from 3001::2 bytes=56 sequence=4 hop limit=64 time = 5 ms reply from 3001::2 bytes=56 sequence=5 hop limit=64 time = 6 ms --- 3001::2 ping statistics --- 5 packet(s) transmitted 5 packet(s) received ...
Page 545: 6 A
47 ip v 6 a pplication c onfiguration introduction to ipv6 application ipv6 are supporting more and more applications. Most of ipv6 applications are the same as those of ipv4. The applications supported on 3com switch 4210 family are: ■ ping ■ traceroute ■ tftp ■ telnet ipv6 application configuratio...
Page 546
544 c hapter 47: ip v 6 a pplication c onfiguration figure 194 traceroute process as figure 194 shows, the traceroute process is as follows: ■ the source sends an ip datagram with the hop limit of 1. ■ if the first hop device receiving the datagram reads the hop limit of 1, it will discard the packe...
Page 547
Ipv6 application configuration 545 c caution: when you use the tftp ipv6 command to connect to the tftp server, you must specify the "-i" keyword if the destination address is a link-local address. Ipv6 telnet telnet protocol belongs to application layer protocols of the tcp/ip protocol suite, and i...
Page 548
546 c hapter 47: ip v 6 a pplication c onfiguration ipv6 application configuration example ipv6 applications network requirements in figure 196, swa, swb, and swc are three switches, among which swa is an switch 4210, swb and swc are two switches supporting ipv6 forwarding. In a lan, there is a teln...
Page 549
Troubleshooting ipv6 application 547 5 packet(s) transmitted 5 packet(s) received 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 31/46/110 ms # on swa, configure static routes to swc, the telnet server, and the tftp server. System-view [swa] ipv6 route-static 3002:: 64 3003::1 [swa] ipv6 route-static 30...
Page 550
548 c hapter 47: ip v 6 a pplication c onfiguration unable to run traceroute symptom unable to trace the route by performing traceroute operations. Solution ■ check that the destination host can be pinged. ■ if the host can be pinged through, check whether the udp port that was included in the trace...
Page 551: Dns C
48 dns c onfiguration n this chapter covers only ipv4 dns configuration. For details about ipv6 dns, refer to “ipv6 mangement configuration” on page 525. Dns overview domain name system (dns) is a mechanism used for tcp/ip applications to provide domain name-to-ip address translation. With dns, you ...
Page 552
550 c hapter 48: dns c onfiguration figure 197 dynamic domain name resolution figure 197 shows the relationship between user program, dns client, and dns server. The resolver and cache comprise the dns client. The user program and dns client run on the same device, while the dns server and the dns c...
Page 553
Configuring domain name resolution 551 configuring domain name resolution configuring static domain name resolution n the ip address you assign to a host name last time will overwrite the previous one if there is any. You may create up to 50 static mappings between domain names and ip addresses. Con...
Page 554
552 c hapter 48: dns c onfiguration dns configuration example static domain name resolution configuration example network requirements the switch uses static domain name resolution to access host 10.1.1.2 through domain name host.Com. Network diagram figure 198 network diagram for static dns configu...
Page 555
Dns configuration example 553 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 2/3/5 ms dynamic domain name resolution configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 199, the switch serving as a dns client uses dynamic domain name resolution to access the host at 3.1.1.1/16 through its doma...
Page 556
554 c hapter 48: dns c onfiguration reply from 3.1.1.1: bytes=56 sequence=2 ttl=255 time=1 ms reply from 3.1.1.1: bytes=56 sequence=3 ttl=255 time=1 ms reply from 3.1.1.1: bytes=56 sequence=4 ttl=255 time=1 ms reply from 3.1.1.1: bytes=56 sequence=5 ttl=255 time=1 ms --- 3.1.1.1 ping statistics --- ...
Page 557: Assword
49 p assword c ontrol c onfiguration o perations introduction to password control configuration the password control feature is designed to manage the following passwords: ■ telnet passwords: passwords for logging into the switch through telnet. ■ ssh passwords: passwords for logging into the switch...
Page 558
556 c hapter 49: p assword c ontrol c onfiguration o perations password control configuration configuration prerequisites a user pc is connected to the switch to be configured; both devices are operating normally. Configuration tasks the following sections describe the configuration tasks for passwo...
Page 559
Password control configuration 557 ■ “configuring history password recording” ■ “configuring a user login password in interactive mode” ■ “configuring login attempt times limitation and failure processing mode” ■ “configuring the password authentication timeout time” ■ “configuring password composit...
Page 560
558 c hapter 49: p assword c ontrol c onfiguration o perations ■ settings in the local user view apply to the local user password only. ■ settings on the parameters of the super passwords apply to super passwords only. The priority of these settings is as follows: ■ for local user passwords, the set...
Page 561
Password control configuration 559 n in this section, you must note the effective range of the same commands when executed in different views or to different types of passwords: ■ global settings in system view apply to all local user passwords and super passwords. ■ settings in the local user view ...
Page 562
560 c hapter 49: p assword c ontrol c onfiguration o perations c caution: ■ when the system adds a new record but the number of the recorded history passwords has reached the configured maximum number, the system replaces the oldest record with the new one. ■ when you configure the maximum number of...
Page 563
Password control configuration 561 configuring login attempt times limitation and failure processing mode when the maximum number of attempts is exceeded, the system operates in one of the following processing mode: ■ lock-time: in this mode, the system inhibits the user from re-logging in within a ...
Page 564
562 c hapter 49: p assword c ontrol c onfiguration o perations configuring the password authentication timeout time when the local/remote server receives the user name, the authentication starts; when the user authentication is completed, the authentication ends. Whether the user is authenticated on...
Page 565
Displaying password control 563 n in this section, you must note the effective range of the same commands when executed in different views or to different types of passwords: ■ global settings in system view apply to all local user passwords and super passwords. ■ settings in the local user view app...
Page 566
564 c hapter 49: p assword c ontrol c onfiguration o perations password control configuration example network requirements the following password control functions should be implemented: ■ globally, the password aging time is 30 days. ■ for the super password, the minimum number of password composit...
Page 567
Password control configuration example 565 # set the aging time for the local user password to 20 days. [4210-luser-test] password-control aging 20 # configure the password of local user. [4210-luser-test] password simple 11111#####.