- DL manuals
- 3Com
- Switch
- 9000 SX
- User Manual
3Com 9000 SX User Manual
Summary of 9000 SX
Page 1
® http://www.3com.Com/ superstack ® ii switch 9000 sx user guide part no. Dua1699-0aaa02 100001-00 rev. 02 published april 1998 sw9000.Bk page i wednesday, april 1, 1998 11:00 am.
Page 2
Ii 3com corporation 5400 bayfront plaza santa clara, california 95052-8145 copyright © 3com corporation, 1998. All rights reserved. No part of this documentation may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to make any derivative work (such as translation, transformation, or adaptation) wit...
Page 3
Iii vcci statement information to the user if this equipment does cause interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures: ■ reorient the recei...
Page 4
Iv sw9000.Bk page iv wednesday, april 1, 1998 11:00 am.
Page 5: Ontents
V c ontents a bout t his g uide introduction 1 terminology 1 finding information in this guide 2 conventions 3 command syntax symbols 4 line-editing commands 5 related publications 5 1 s witch 9000 o verview about the switch 9000 1-1 summary of features 1-1 port connections 1-2 full duplex 1-3 switc...
Page 6
Vi 2 i nstallation and s etup following safety information 2-1 determining the switch 9000 location 2-1 configuration rules for gigabit ethernet 2-2 installing the switch 9000 2-2 rack mounting 2-2 free-standing 2-3 stacking the switch and other devices 2-4 connecting equipment to the console port 2...
Page 7
Vii configuring snmp settings 3-10 displaying snmp settings 3-11 resetting and disabling snmp 3-12 checking basic connectivity 3-12 ping 3-12 traceroute 3-13 configuring ports 3-13 enabing and disabling ports 3-13 configuring autonegotiation 3-13 port commands 3-14 load sharing 3-14 configuring load...
Page 8
Viii basic ip commands 4-15 ip arp commands 4-16 ip route table commands 4-17 icmp commands 4-17 4-18 rip commands 4-19 4-20 logging commands 4-21 4-22 configuration and image commands 4-23 5 v irtual lan s (vlan s ) overview of virtual lans 5-1 benefits 5-1 types of vlans 5-2 port-based vlans 5-2 e...
Page 9
Ix configuring fdb entries 6-3 fdb configuration example 6-3 displaying fdb entries 6-3 removing fdb entries 6-4 7 s panning t ree p rotocol (stp) overview of the spanning tree protocol 7-1 how stp works 7-3 initialization 7-3 stabilization 7-4 reconfiguration 7-4 spanning tree domains 7-4 defaults ...
Page 10
X 9 s tatus m onitoring and s tatistics status monitoring 9-1 port statistics 9-4 port errors 9-6 switch logging 9-7 local logging 9-8 real-time display 9-8 remote logging 9-9 logging commands 9-10 rmon 9-11 about rmon 9-11 about the rmon groups 9-12 statistics 9-12 history 9-12 alarms 9-13 events 9...
Page 11
Xi fiber optic ports a-3 lithium battery a-4 l’information de sécurité importante a-4 power a-5 cordon électrique a-6 fuse a-6 ports pour fibres optiques a-7 batterie au lithium a-7 wichtige sicherheitsinformationen a-8 power a-8 power cord a-9 fuse a-9 faseroptikanschlüsse - optische sicherheit a-1...
Page 12
Xii g lossary i ndex 3c om c orporation l imited w arranty sw9000.Bk page xii wednesday, april 1, 1998 11:00 am.
Page 13: Bout
A bout t his g uide about this guide provides an overview of this guide, describes guide conventions, tells you where to look for specific information and lists other publications that may be useful. Introduction this guide provides the required information to install and configure the superstack ® ...
Page 14
2 a bout t his g uide finding information in this guide this table shows where to find specific information in this guide. Task location learning concepts chapter 1, “switch 9000 overview” installing the switch 9000 chapter 2, “installation and setup” appendix a, “safety information” setting up user...
Page 15
Conventions 3 conventions table 1 and table 2 list conventions that are used throughout this guide. Table 1 notice icons icon notice type alerts you to... Note important features or instructions caution risk of personal injury, system damage, or loss of data warning risk of severe personal injury ta...
Page 16
4 a bout t his g uide command syntax symbols you may see a variety of symbols shown as part of the command syntax. These symbols explain how to enter the command, and you do not type them as part of the command itself. Table 3 summarizes command syntax symbols. Table 3 command syntax symbols symbol ...
Page 17
Line-editing commands 5 line-editing commands table 4 describes the line-editing commands available using the command-line interface. The command syntax is explained in chapter 4. Related publications the switch 9000 documentation set includes the following: ■ superstack ii switch 9000 sx quick refe...
Page 18
6 a bout t his g uide sw9000.Bk page 6 wednesday, april 1, 1998 11:00 am.
Page 19: Witch
1 s witch 9000 o verview this chapter describes the following: ■ switch 9000 features ■ how to use the switch 9000 in your network configuration ■ switch 9000 front view ■ switch 9000 rear view ■ factory default settings about the switch 9000 network managers are currently faced with the challenge o...
Page 20
1-2 c hapter 1: s witch 9000 o verview ■ virtual lans (vlans) ■ support for 64 vlans on a single switch 9000 ■ support for ieee 802.1q tagging ■ controls traffic (including broadcasts) ■ provides extra security ■ protocol-sensitive filtering for vlans ■ recognition of the priority access control ena...
Page 21
Summary of features 1-3 full duplex the switch 9000 provides full-duplex support for all ports. Full-duplex allows frames to be transmitted and received simultaneously and, in effect, doubles the bandwidth available on a link. The switch 9000 will refuse a half duplex connection on any port. Switch ...
Page 22
1-4 c hapter 1: s witch 9000 o verview ■ redundant paths are disabled when the main paths are operational. ■ redundant paths are enabled if the main traffic paths fail. For more information on stp, refer to chapter 7. Ip unicast routing the switch 9000 can route ip traffic between the vlans configur...
Page 23
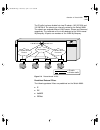
Network configuration example 1-5 figure 1-1 switch 9000 used in a backbone configuration the switch 3000 on each floor is provided with a gigabit ethernet full-duplex link to the switch 9000. Using gigabit ethernet as a backbone technology removes bottlenecks by providing scalable bandwidth, low-la...
Page 24
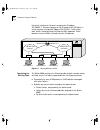
1-6 c hapter 1: s witch 9000 o verview attached to the switch 9000 providing improved performance to the ethernet desktop. Switch 9000 front view figure 1-2 shows the switch 9000 front view. Figure 1-2 switch 9000 front view the front panel has the following features: ports the switch 9000 has eight...
Page 25
Switch 9000 front view 1-7 leds table 1-2 describes the led behavior on the switch 9000. Table 1-2 switch 9000 leds led color indicates port status leds packet yellow off frames are being transmitted/received on this port. No activity on this port. Status green green flashing off link is present; po...
Page 26
1-8 c hapter 1: s witch 9000 o verview switch 9000 rear view figure 1-3 shows the switch 9000 rear view. Figure 1-3 switch 9000 rear view the rear panel has the following features: power socket the switch 9000 automatically adjusts to the supply voltage. The power supply operates down to 90 v. The f...
Page 27
Factory defaults 1-9 factory defaults table 1-3 shows the factory defaults for the switch 9000 features. Table 1-3 switch 9000 factory defaults item default setting port status enabled on all ports default user account admin with no password and user with no password console port configuration 9600 ...
Page 28
1-10 c hapter 1: s witch 9000 o verview sw9000.Bk page 10 wednesday, april 1, 1998 11:00 am.
Page 29: Nstallation
2 i nstallation and s etup this chapter describes the following: ■ how to decide where to install the switch 9000 ■ gigabit ethernet configuration rules ■ how to install the switch in a rack or free-standing ■ how to connect equipment to the console port ■ how to check the installation using the pow...
Page 30
2-2 c hapter 2: i nstallation and s etup ■ water or moisture cannot enter the case of the unit. ■ temperature must be within the range of 0 to 40 degrees celsius. ■ air-flow around the unit and through the vents in the side of the case is not restricted. You should provide a minimum of 25mm (1-inch)...
Page 31
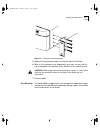
Installing the switch 9000 2-3 figure 2-1 fitting the mounting bracket 5 repeat the three previous steps for the other side of the switch. 6 refer to the instructions that shipped with your rack, runners, shelf or tray to complete the installation of the switch into the mounting rack. Caution: when ...
Page 32
2-4 c hapter 2: i nstallation and s etup stacking the switch and other devices up to four units can be placed on top of one another. If mixing switch 9000, switch 3000 fx, switch 1000, switch 1200, and other superstack ® ii hubs, the smaller units must be positioned at the top using rubber feet. Thi...
Page 33
Connecting equipment to the console port 2-5 figure 2-2 shows the pin-outs for a 9-pin to rs-232 25-pin null modem cable. Figure 2-2 null modem cable pin-outs figure 2-3 shows the pin-outs for a 9-pin to 9-pin pc-at serial null modem cable. Figure 2-3 pc-at serial cable pin-outs screen txd rxd groun...
Page 34
2-6 c hapter 2: i nstallation and s etup powering-up the switch to power-up the switch, follow these steps: 1 connect the power cable to the switch. 2 connect the power cable to the wall outlet 3 turn the on/off switch to the on position. Checking the installation after turning on power to the switc...
Page 35
Logging on for the first time 2-7 5 assign an ip address and subnetwork mask for vlan default. The example below assigns an ip address of 123.45.67.8 and a subnetwork mask of 255.255.255.0. Config vlan default ipaddress 123.45.67.8 255.255.255.0 your changes take effect immediately. 6 save your conf...
Page 36
2-8 c hapter 2: i nstallation and s etup sw9000.Bk page 8 wednesday, april 1, 1998 11:00 am.
Page 37: Ccessing
3 a ccessing t he s witch this chapter describes the following information that you can use to begin managing the switch 9000: ■ security access level overview ■ configuring the switch for management ■ switch management methods ■ configuring snmp caution: in order for configuration changes to be ret...
Page 38
3-2 c hapter 3: a ccessing t he s witch administrator access level an administrator-level account can view and change all switch parameters, add and delete users, and change the password associated with any account name. The administrator can disconnect a telnet management session. If this happens, ...
Page 39
Security access levels 3-3 4 enter the new password at the prompt. 5 re-enter the new password at the prompt. 6 save your changes by typing save creating a management account the switch can have a total of three management accounts. You can use the default names (admin and user), or you can create n...
Page 40
3-4 c hapter 3: a ccessing t he s witch 3 enter the new password at the prompt. 4 re-enter the new password at the prompt. 5 save your changes by typing save if you forget your password contact your local technical support representative, who will advise on your next course of action. Viewing switch...
Page 41
Using telnet 3-5 using the console interface the command-line interface built into the switch is accessible by way of the 9-pin, rs-232 console port located on the rear of the unit. For more information on the console port pin-outs, refer to chapter 2. Once the connection is established, you will se...
Page 43
Using telnet 3-7 4 at the password prompt, enter the password and press [return]. When you have successfully logged on to the switch, the command-line prompt displays the name of the switch in its prompt. 5 assign an ip address and subnetwork mask for the default vlan by using the following command ...
Page 44
3-8 c hapter 3: a ccessing t he s witch sample output from the show session command is as follows: 3c16990:2 # sh sess # login time user type location ============================================================ 0 tue mar 10 11:10:53 1998 admin console serial 4 tue mar 10 13:11:13 1998 user telnet 1...
Page 45
Using snmp 3-9 accessing switch agents in order to have access to the snmp agent residing in the switch, at least one vlan on the switch must have an ip address assigned to it. For more information on assigning an ip address, refer to “manually configuring the ip settings,” on page 3-6. Saving confi...
Page 46
3-10 c hapter 3: a ccessing t he s witch configuring snmp settings the following snmp parameters can be configured on the switch: ■ authorized trap receivers — an authorized trap receiver can be one or more network management stations on your network. The switch sends snmp traps to the trap receiver...
Page 47
Using snmp 3-11 displaying snmp settings to display the snmp settings configured on the switch 9000, use the following command: show management this command displays the following information: ■ enable/disable state for telnet, snmp, and web access ■ snmp community strings table 3-4 snmp configurati...
Page 48
3-12 c hapter 3: a ccessing t he s witch ■ authorized snmp station list ■ snmp trap receiver list ■ logon statistics resetting and disabling snmp to reset or disable snmp settings, use the commands in table 3-5. Checking basic connectivity the switch 9000 has the following two facilities for checkin...
Page 49
Configuring ports 3-13 options for the ping command are described in table 3-6. Traceroute the traceroute command allows you to trace the routed path between the switch and a destination endstation. The traceroute command syntax is as follows: traceroute where ip_address is the ip address of the des...
Page 50
3-14 c hapter 3: a ccessing t he s witch to configure the switch to autonegotiate, use the following command: config port auto on port commands table 3-7 describes port commands. Load sharing load sharing with switch 9000 switches allows you to increase bandwidth and resilience by using a group of p...
Page 51
Load sharing 3-15 load sharing is most useful in cases where the traffic transmitted from the switch to the load-sharing group is sourced from an equal or greater number of ports on the switch. For example, traffic transmitted to a 2-port load-sharing group should originate from a minimum of two oth...
Page 52
3-16 c hapter 3: a ccessing t he s witch the following example defines a load-sharing group that contains ports 4 through 7, and uses the first port in the group as the master logical port 4: enable sharing 4 grouping 4-7 in this example, logical port 4 represents physical ports 4 through 7. When us...
Page 53: Ommands
4 c ommands this chapter contains a description of each command-line interface command for the switch 9000. It also provides the following information related to switch 9000 commands: ■ command syntax ■ line editing commands ■ command history substitution if an asterisk (*) appears in front of the c...
Page 54
4-2 c hapter 4: c ommands if the command does not include a parameter, skip to step 3. If the command requires more information, or if you want to include optional parameters, continue to step 2a. A if the command has additional parameters include them after the command name. B if the command includ...
Page 55
Understanding the command syntax 4-3 config vlan engineering add port 1-3,6 could use the following shortcut: config engineering add port 1-3, 6 numerical ranges commands that require you to enter one or more port numbers use the parameter, , in the syntax. A portlist can be a range of numbers, for ...
Page 57
Command history substitution 4-5 command history substitution the switch 9000 “remembers” the last 50 commands you enter. You can display a list of these commands by using the following command: history common commands table 4-3 describes common commands used to manage the switch. Commands specific ...
Page 58
4-6 c hapter 4: c ommands switch 9000 commands the tables in this section list all of the commands used on the switch 9000. The commands are organized by the following categories: ■ general switch commands ■ user account commands ■ switch management commands ■ vlan commands ■ protocol commands ■ fdb...
Page 59
Switch 9000 commands 4-7 general switch commands table 4-4 describes general switch commands. Table 4-4 general switch commands command description show switch displays the current switch information, including: ■ sysname, syslocation, syscontact ■ mac address ■ current date and time, and system upt...
Page 61
Switch 9000 commands 4-9 switch management commands table 4-6 describes switch management commands table 4-6 switch management commands command description show management displays network management configuration and statics including enable/disable states for telnet and snmp, snmp community string...
Page 62
4-10 c hapter 4: c ommands vlan commands table 4-7 describes vlan commands. Config snmp syscontact allows you to configure the name of the system contact. A maximum of 32 characters is allowed config snmp sysname allows you to configure the name of the switch. The sysname appears in the command line...
Page 64
4-12 c hapter 4: c ommands port commands table 4-10 describes port commands. Create fdbentry vlan allows you to create a permanent fdb entry. Specify the following: ■ mac_address — device mac address, using colon separated bytes ■ name — vlan associated with mac address ■ portlist — port number asso...
Page 65
Port commands 4-13 pace commands table 4-11 describes pace commands. Stp commands table 4-12 describes stp commands. Enable port allows you to enable one or more ports. Disable port allows you to disable one or more ports. Table 4-10 port commands command description table 4-11 pace commands command...
Page 66
4-14 c hapter 4: c ommands config stpd forwarddelay allows you to specify the time (in seconds) that the ports on this stpd spend in the listening and learning states when the switch is the root bridge. The range is 4 through 30. The default setting is 15 seconds. Config stpd maxage allows you to sp...
Page 70
4-18 c hapter 4: c ommands enable icmp useredirects allows you to enable the modification of route table information when an icmp redirect message is received. The default setting is disabled. Disable icmp useredirects allows you to disable the changing of routing table information when an icmp redi...
Page 72
4-20 c hapter 4: c ommands enable rip exportstatic allows you to enable the advertisement of static routes using rip. The default setting is enabled. Disable rip exportstatic allows you to disable the filtering of static routes. Config rip updatetime {} allows you to change the periodic rip update t...
Page 73
Port commands 4-21 logging commands table 4-18 describes switch logging commands. Table 4-18 logging commands command description show log config displays the log configuration, including the syslog host ip address, the priority level of messages being logged locally, and the priority level of messa...
Page 74
4-22 c hapter 4: c ommands config syslog {} {} allows you to configure the syslog host address and filter messages sent to the syslog host. Options include: ■ ipaddress — the ip address of the syslog host. ■ facility — the syslog facility level for local use. ■ priority — filters the log to display ...
Page 76
4-24 c hapter 4: c ommands sw9000.Bk page 24 wednesday, april 1, 1998 11:00 am.
Page 77: Irtual
5 v irtual lan s (vlan s ) setting up virtual local area networks (vlans) on the switch 9000 eases many time-consuming tasks of network administration while increasing efficiency in network operations. This chapter describes the vlan concepts and explains how to implement vlans on the switch 9000. O...
Page 78
5-2 c hapter 5: v irtual lan s (vlan s ) ■ it helps to control traffic. With traditional networks, congestion can be caused by broadcast traffic that is directed to all network devices, regardless of whether they require it. Vlans increase the efficiency of your network because each vlan can be set ...
Page 79
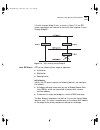
Overview of virtual lans 5-3 for example, in figure 5-1, the vlans are configured as followings: ■ ports 1, 2, and 5 are part of vlan marketing ■ ports 3, 4, and 6 are part of vlan sales ■ ports 7 and 8 are part of vlan finance figure 5-1 example of a port-based vlan even though they are physically ...
Page 80
5-4 c hapter 5: v irtual lan s (vlan s ) expanding port-based vlans across switches to create a port-based vlan that spans two switches you must do two things: ■ assign the port on each switch to the vlan. ■ cable the two switches together using one port on each switch per vlan. Figure 5-2 illustrat...
Page 81
Overview of virtual lans 5-5 figure 5-3 illustrates two vlans spanning two switches. On switch 1, ports 1–4 are part of vlan accounting ; ports 5–8 are part of vlan engineering . On switch 2, ports 1–4 are part of vlan accounting ; ports 5–8 are part of vlan engineering . Vlan accounting spans switc...
Page 82
5-6 c hapter 5: v irtual lan s (vlan s ) tagged vlans the switch 9000 uses the ieee 802.1q d4 draft standard for rules associated with vlan tagging. Tagging is a process that inserts a marker (called a tag ) into the ethernet frame. The tag contains the identification number of a specific vlan, call...
Page 83
Overview of virtual lans 5-7 figure 5-4 illustrates the physical view of a network that uses tagged and untagged traffic. Figure 5-4 physical diagram of tagged and untagged traffic figure 5-5 shows a logical diagram of the same network. Figure 5-5 logical view of tagged and untagged traffic switch 1...
Page 84
5-8 c hapter 5: v irtual lan s (vlan s ) in figure 5-4 and figure 5-5: ■ the trunk port on each switch carries traffic for both vlan marketing and vlan sales . ■ the trunk port on each switch is tagged. ■ the server connected to port 1 on switch 1 has a nic that supports 802.1q tagging. ■ the server...
Page 85
Overview of virtual lans 5-9 the ip traffic has been divided into two ip subnets, 192.207.35.0 and 192.207.36.0. The subnets are internally routed by the switch 9000. The subnets are assigned different vlan names, finance and personnel , respectively. The remainder of the traffic belongs to the vlan...
Page 86
5-10 c hapter 5: v irtual lan s (vlan s ) defining protocol filters if necessary, you can define a customized protocol filter based on ethertype, llc, and/or snap. Up to six filters may be part of a protocol filter. To define a protocol filter, do the following: ■ create a protocol using the followi...
Page 87
Configuring vlans on the switch 9000 5-11 the default vlan the switch 9000 ships with one default vlan that has the following properties: ■ the vlan name is default. ■ it contains all the ports on a new or initialized switch. ■ the default vlan is untagged, and has no vlanid or protocol filter assig...
Page 88
5-12 c hapter 5: v irtual lan s (vlan s ) table 5-1 describes the commands used to configure a vlan. Vlan configuration examples the following example creates a port-based vlan named accounting , assigns the ip address 132.15.121.1, and assigns ports 1, 2, 3, and 6 to it: create vlan accounting conf...
Page 89
Displaying vlan settings 5-13 the following example creates a tag-based vlan named video . It assigns the vlanid 1000. Ports 4–8 are added as tagged ports to the vlan. Create vlan video config video tag 1000 config video add port 4-8 tagged the following example creates a vlan named sales , with the...
Page 90
5-14 c hapter 5: v irtual lan s (vlan s ) ■ status for each port ■ enabled/disabled ■ tagged/untagged ■ protocol information ■ ip address ■ stpd information sample output from this command is as follows: 3c16990:7 # sh vlan all vlan "default" created by user tagging: 802.1q tag 1 ip: 192.207.37.214/...
Page 91
Deleting and resetting vlans 5-15 sample output from this command is as follows: show protocol all protocol name type value ----------------- ---- ----- ip etype 0x0806 etype 0x0800 ipx etype 0x8137 netbios 11c 0xf0f0 decnet etype 0x6004 etype 0x6003 this show command displays protocol information, ...
Page 92
5-16 c hapter 5: v irtual lan s (vlan s ) sw9000.Bk page 16 wednesday, april 1, 1998 11:00 am.
Page 93: Witch
6 s witch f orwarding d atabase (fdb) this chapter describes the contents of the switch forwarding database (fdb), how the fdb works, and how to configure the fdb. Overview of the fdb the switch 9000 maintains a database of all addresses received on all of its ports. It uses the information in this ...
Page 94
6-2 c hapter 6: s witch f orwarding d atabase (fdb) ■ permanent entries — permanent entries are retained in the database if the switch is reset or a power off/on cycle occurs. The system administrator must make entries permanent. A permanent entry can either be a unicast or multicast mac address. Al...
Page 95
Configuring fdb entries 6-3 configuring fdb entries to configure entries in the fdb, use the commands listed in table 6-1. Fdb configuration example this example adds a permanent entry to the fdb: create fdbentry 02:60:8c:12:34:56 vlan marketing port 4 the permanent entry has the following character...
Page 96
6-4 c hapter 6: s witch f orwarding d atabase (fdb) ■ portlist — displays the entries for one or more ports ■ permanent — displays all permanent entries the following sample output shows the information displayed when you request output for all fdb entries: show fdb hash num mac vlan flags ptag port...
Page 97: Panning
7 s panning t ree p rotocol (stp) using the spanning tree protocol (stp) functionality of the switch 9000 makes your network more fault tolerant. The following sections describe stp concepts, and how stp features are supported by the switch. Stp is a part of the 802.1d bridge specification defined b...
Page 98
7-2 c hapter 7: s panning t ree p rotocol (stp) figure 7-1 network with an illegal topology this configuration is illegal because it creates loops that cause the network to overload. However, stp allows you to use this configuration because stp detects duplicate paths and immediately prevents (or bl...
Page 99
Overview of the spanning tree protocol 7-3 if the link through bridge c fails, as shown in figure 7-3, the stp system reconfigures the network so that traffic from segment 2 flows through bridge b. Figure 7-3 traffic flowing through bridge b how stp works stp has the following three stages of operat...
Page 100
7-4 c hapter 7: s panning t ree p rotocol (stp) the root bridge generates bpdus on all ports at a regular interval known as the hello time. All other bridges in the network have a root port. This is the port that costs the least in getting to the root bridge, and it is used for receiving the bpdus i...
Page 101
Spanning tree domains 7-5 ■ within any given stpd, all vlans belonging to it use the same spanning tree. Care must be taken to ensure that stpd instances within a single switch do not see each other in the same broadcast domain. This could happen if, for example, another external bridge is used to c...
Page 102
7-6 c hapter 7: s panning t ree p rotocol (stp) stp configurations when you assign vlans to an stpd, pay careful attention to the stp configuration and its effect on the forwarding of vlan traffic. Figure 7-4 illustrates a network that uses vlan tagging for trunk connections. The following four vlan...
Page 103
Stp configurations 7-7 when the switches in this configuration start up, stp configures each stp domain such that there are no active loops in the topology. Stp could configure the topology in a number of ways to make it loop-free. In figure 7-4, the connection between switch a and switch b is put i...
Page 104
7-8 c hapter 7: s panning t ree p rotocol (stp) stp configurations to avoid within a single stpd, you must be careful when configuing your vlans. The following figures illustrate networks that have been incorrectly set up so that the stp configuration disables the ability of the switches to forward ...
Page 105
Creating stp domains 7-9 figure 7-6 shows a similar configuration in which the vlans are all port-based. The trunk connections between the switches require one trunk port per switch for each vlan. Figure 7-6 port-based stp configuration to remove all the bridging loops, stp may block traffic on the ...
Page 108
7-12 c hapter 7: s panning t ree p rotocol (stp) configuration example the following example creates and enables an stpd named backbone_st . It assigns the manufacturing vlan to the stpd. It disables stp on ports 1 through 3, and port 4. Create stpd backbone_st config stpd backbone_st add vlan manuf...
Page 109
Displaying stp settings 7-13 sample output from the command is as follows: 3c16990:28 # sh stpd s0 po 5-8 stpd: s0 port: 8 portid: 8008 stp: enabled path cost: 4 port state: forwarding topology change ack: false port priority: 128 designated root: 80:00:08:00:4e:2c:13:00 designated cost: 0 designate...
Page 110
7-14 c hapter 7: s panning t ree p rotocol (stp) disabling and resetting stp to disable stp or return stp settings to their defaults, use the commands listed in table 7-2. Caution: if you ignore warnings and delete an stpd without removing all of its vlan members first, those vlans will also be dele...
Page 111: Ip U
8 ip u nicast r outing this chapter describes how to configure ip routing on the switch 9000. It assumes that you are already familiar with ip unicast routing. If not, refer to the following publications for additional information: rfc 1058 — routing information protocol rfc 1256 — icmp router disco...
Page 112
8-2 c hapter 8: ip u nicast r outing the router interface for finance is assigned the ip address 192.206.35.1. Personnel belongs to the ip network 192.207.36.0; its router interface is assigned ip address 192.207.36.1. Traffic within each vlan is switched using the ethernet mac addresses. Traffic be...
Page 113
Overview of ip unicast routing 8-3 dynamic routes dynamic routes are typically learned by way of rip. Routers using rip exchange information in their routing tables in the form of rip advertisements. Using dynamic routes, the routing table contains only networks that are reachable. Dynamic routes ar...
Page 114
8-4 c hapter 8: ip u nicast r outing configuring ip unicast routing this section describes the commands associated with configuring ip unicast routing on the switch 9000. Configuring routing involves the following steps: ■ verify the switch operating mode is set to iprouting , by using the following...
Page 115
Verifying the ip unicast routing configuration 8-5 verifying the ip unicast routing configuration use the show iproute command to display the current configuration of ip unicast routing for the switch, and for each vlan. The show iproute command displays the currently configured routes, including ho...
Page 118
8-8 c hapter 8: ip u nicast r outing enable rip splithorizon enables the split horizon algorithm for rip. Default setting is enabled. Enable rip triggerupdate enables triggered updates. Triggered update s are a mechanism for immediately notifying a router’s neighbors when the router adds or deletes ...
Page 119
Configuring dhcp/bootp relay 8-9 table 8-4 describes the commands used to configure the icmp protocol. Disable rip splithorizon disables split horizon. Disable rip poisonreverse disables poison reverse. Disable rip triggerupdate disables triggered updates disable rip exportstatic disables the filter...
Page 120
8-10 c hapter 8: ip u nicast r outing routing configuration example figure 8-2 illustrates a switch that has three vlans defined as follows: ■ finance ■ protocol-sensitive vlan using the ip protocol ■ ports 1 and 3 have been assigned ■ ip address 192.207.35.1 ■ personnel ■ protocol-sensitive vlan us...
Page 121
Routing configuration example 8-11 figure 8-2 unicast routing configuration example in this configuration, all ip traffic from stations connected to ports 1 and 3 have access to the router by way of the vlan finance . Ports 2 and 4 reach the router by way of the vlan personnel . All other traffic (n...
Page 125: Tatus
9 s tatus m onitoring and s tatistics this chapter describes how to view the current operating status of the switch, how to display information in the switch log, and how to take advantage of the rmon capabilities available in the switch. Viewing statistics on a regular basis allows you to: ■ monito...
Page 127
Status monitoring 9-3 show port collisions displays collision statistics for each port. Show port config displays state, link status, speed, and autonegotiation setting for each port. Show port errors displays error information for one or more ports. Show port packet displays a histogram of packet s...
Page 128
9-4 c hapter 9: s tatus m onitoring and s tatistics port statistics the switch 9000 provides a facility for viewing port statistic information. The summary information lists values for the current counter against every port on the switch and it is refreshed approximately every 2 seconds. Values are ...
Page 129
Port statistics 9-5 the following port statistic information is collected by the switch: link status — the current status of the link. Options are: ■ ready — the port is ready to accept a link. ■ active — the link is present at this port. Transmit packet count (tx pkt count) — the number of packets ...
Page 130
9-6 c hapter 9: s tatus m onitoring and s tatistics port errors the switch 9000 keeps track of errors for each port. To view port error, type show port errors the following port error information is collected by the switch: link status — the current status of the link. Options are: ■ ready — the por...
Page 131
Switch logging 9-7 receive jabber frames (rx jab) — the total number of frames received by the port that were of longer than the support maximum length and had a cyclic redundancy check (crc) error. Receive alignment errors (rx align) — the total number of frames received by the port that occurs if ...
Page 132
9-8 c hapter 9: s tatus m onitoring and s tatistics ■ message — the message contains the log information with text that is specific to the problem. Local logging the switch maintains 1,000 messages in its internal log. You can display a snapshot of the log at any given point in time by using the fol...
Page 133
Switch logging 9-9 if priority is not specified, only messages of critical priority are displayed. If the subsystem is not specified, all subsystems are displayed. If you enable the log display on a terminal connected to the console port, your settings will remain in effect even after your console s...
Page 134
9-10 c hapter 9: s tatus m onitoring and s tatistics logging commands the commands described in table 9-4 allow you to do the following: ■ configure logging options ■ reset logging options ■ display the log ■ clear the log table 9-4 logging commands command description config log display {} {} allow...
Page 135
Rmon 9-11 rmon using the remote monitoring (rmon) capabilities of the switch allows network administrators to make decisions about improving switch efficiency and reducing the load on the network. The following sections explain more about the rmon concept and the rmon features supported by the switc...
Page 136
9-12 c hapter 9: s tatus m onitoring and s tatistics a typical rmon setup consists of the following two components: ■ the rmon probe — an intelligent, remotely controlled device or software agent that continually collects statistics about a lan segment or vlan. The probe transfers the information to...
Page 137
Rmon 9-13 alarms the alarms group provides a versatile, general mechanism for setting threshold and sampling intervals to generate events on any mib variable. Alarms inform you of a network performance problem and they can trigger automated action responses through the events group. Events effective...
Page 138
9-14 c hapter 9: s tatus m onitoring and s tatistics an rmon probe, however, autonomously looks at the network on behalf of the management workstation without affecting the characteristics and performance of the network. The probe reports by exception, which means that it only informs the management...
Page 139
Rmon 9-15 when using the rmon features of the switch, you should note the following: ■ after the default sessions are created, they have no special status. You can delete or change them as required. ■ the greater the number of rmon sessions, the greater the burden on the management resources of the ...
Page 140
9-16 c hapter 9: s tatus m onitoring and s tatistics sw9000.Bk page 16 wednesday, april 1, 1998 11:00 am.
Page 141: Oftware
10 s oftware u pgrade and b oot o ptions this chapter describes the procedure for upgrading the switch software image. It also covers how to save and load a primary and secondary configuration file on the switch. Upgrading the software the image file contains the executable code that runs on the swi...
Page 143
Boot option commands 10-3 returning to factory defaults to return the switch configuration to factory defaults, use the following command: unconfig switch this command resets the entire configuration, with the exception of user accounts and passwords that have been configured. To reset all parameter...
Page 144
10-4 c hapter 10: s oftware u pgrade and b oot o ptions sw9000.Bk page 4 wednesday, april 1, 1998 11:00 am.
Page 145: Afety
A s afety i nformation you must read the following safety information before carrying out any installation or removal of components, or any maintenance procedures on the switch 9000. Important safety information warning: warnings contain directions that you must follow for your personal safety. Foll...
Page 146
A-2 a ppendix a: s afety i nformation ■ this unit operates under selv (safety extra low voltage) conditions according to iec 950. The conditions are only maintained if the equipment to which it is connected also operates under selv conditions. ■ the appliance coupler (the connector to the unit and n...
Page 147
Important safety information a-3 ■ if the power cord plug is unsuitable and must be replaced, you may find other codings for the respective connections. Connect the power supply wires for the unit according to the following scheme: ■ brown wire to the live (line) plug terminal which may be marked wi...
Page 148
A-4 a ppendix a: s afety i nformation lithium battery ■ replace the lithium battery with the same or equivalent type, as recommended by the manufacturer. Warning: there is a danger of explosion if the battery is incorrectly replaced. ■ dispose of used batteries according to the manufacturers instruc...
Page 149
L’information de sécurité importante a-5 ■ pour réduire les risques d'incendie ou de choc électrique, installez ce groupe sous abri dans une zone dont la température et l'humidité sont régulées et qui ne contient pas de produits contaminateurs conductifs. Power ■ pour garantir le respect des normes ...
Page 150
A-6 a ppendix a: s afety i nformation cordon électrique ■ il doit être agréé dans le pays d'utilisation : ■ si la prise mâle du cordon électrique est défectueuse, vous devez la remplacer en identifiant d'autres codages pour assurer les différentes connexions nécessaires. Branchez les fils d'alimenta...
Page 151
L’information de sécurité importante a-7 porte-fusibles. Pour ce groupe, vous devez uniquement utiliser des fusibles réalisés par le même constructeur et offrant le même pouvoir de coupure et respectant le même type que le fusible d'origine. Refermez le porte-fusibles. ■ pour respecter les normes eu...
Page 152
A-8 a ppendix a: s afety i nformation ■ les batteries au lithium ne figurent pas sur la liste epa des déchets dangereux. Par conséquent, vous pouvez en général vous en débarrasser comme s'il s'agissait d'un déchet normal. ■ si vous souhaitez vous débarrasser de quantités importantes, contactez un se...
Page 153
Wichtige sicherheitsinformationen a-9 ■ das gerät muß an eine geerdete steckdose angeschlossen werden, die die europäischen sicherheitsnormen erfüllt. ■ das gerät nicht an eine wechselstromsteckdose anschließen, die nicht geerdet ist. ■ die netzsteckdose muß in der nähe des geräts und leicht zugängl...
Page 154
A-10 a ppendix a: s afety i nformation ■ zur erfüllung europäischer sicherheitsnormen darf keine ersatzsicherung am geräteeingang angebracht werden. Es dürfen nur sicherungen vom gleichen hersteller, der gleichen marke und art mit dem gerät verwendet werden. Faseroptikanschlüsse - optische sicherhei...
Page 155
Wichtige sicherheitsinformationen a-11 lithiumbatterie ■ die lithiumbatterie nach den empfehlungen des herstellers durch eine batterie des gleichen oder eines gleichwertigen typs ersetzen. Warnhinweis: wird die batterie falsch ersetzt, besteht explosionsgefahr. ■ verbrauchte batterien nach den angab...
Page 156
A-12 a ppendix a: s afety i nformation sw9000.Bk page 12 wednesday, april 1, 1998 11:00 am.
Page 157: Echnical
B t echnical s pecifications physical dimensions height: 3.5 inches x width: 17.32 inches x depth: 17.32 inches weight: 22 pounds environmental requirements operating temperature 0 to 40˚ c storage temperature -10 to 70 ˚ c operating humidity 10% to 95% relative humidity, noncondensing standards en6...
Page 158
B-2 a ppendix b: t echnical s pecifications standards supported snmp snmp protocol (rfc 1157) mib-ii (rfc 1213) bridge mib (rfc 1493) vlan mib (rfc 1573) rmon mib (rfc 1757) terminal emulation telnet (rfc 854) protocols used for administration udp (rfc 768) ip (rfc 791) icmp (rfc 792) tcp (rfc 793) ...
Page 159: Roubleshooting
C t roubleshooting if you encounter problems when using the switch, this appendix may be helpful. If you have a problem which is not listed here or in the release notes, please contact your local technical support representative. Leds power led does not light: check that the power cable is firmly co...
Page 160
C-2 a ppendix c: t roubleshooting both sides if the gigabit link must be enabled or disabled. It the two are different, typically the side with auto-negotiation disabled will have the link led list, and the side with auto-negotiation enabled will not list. The default configuration for a gigabit por...
Page 161
Using the command-line interface c-3 traps are not received by the snmp network manager: check that the snmp network manager's ip address and community string are correctly configured and that the ip address of the trap receiver is configured properly on the switch. The snmp network manager or telne...
Page 162
C-4 a ppendix c: t roubleshooting you forget your password and cannot log on: if you are not an administrator, another user having administrator access level can log on, delete your user name, and create a new user name for you, with a new password. Alternatively, another user having administrator a...
Page 163
Using the command-line interface c-5 vlan names: there are restrictions on vlan names. They cannot contain white spaces and cannot start with a numeric value unless you use quotation marks around the name. If a name contains white spaces or starts with a numeric, you must use quotation marks wheneve...
Page 164
C-6 a ppendix c: t roubleshooting the switch keeps aging out endstation entries in the switch forwarding database (fdb): reduce the number of topology changes by disabling stp on those switches that do not use redundant paths. Specify that the endstation entries are static or permanent. Routing the ...
Page 165: Echnical
D t echnical s upport 3com provides easy access to technical support information through a variety of services. This appendix describes these services. Information contained in this appendix is correct at time of publication. For the very latest, we recommend that you access 3com corporation’s world...
Page 166
D-2 a ppendix d: t echnical s upport access by digital modem isdn users can dial in to 3combbs using a digital modem for fast access up to 56 kbps. To access 3combbs using isdn, use the following number: 408 654 2703 3comfacts sm automated fax service 3com corporation’s interactive fax service, 3com...
Page 167
Support from your network supplier d-3 3comforum on compuserve ® online service 3comforum is a compuserve-based service containing patches, software, drivers, and technical articles about all 3com products, as well as a messaging section for peer support. To use 3comforum, you need a compuserve acco...
Page 168
D-4 a ppendix d: t echnical s upport support from 3com if you are unable to receive support from your network supplier, technical support contracts are available from 3com. Contact your local 3com sales office to find your authorized service provider using one of these numbers: regional sales office...
Page 169
Returning products for repair d-5 returning products for repair before you send a product directly to 3com for repair, you must first be obtain a return materials authorization (rma) number. Products sent to 3com without rma numbers will be returned to the sender unopened, at the sender’s expense. T...
Page 170
D-6 a ppendix d: t echnical s upport sw9000.Bk page 6 wednesday, april 1, 1998 11:00 am.
Page 171: Lossary
G lossary ageing the automatic removal of dynamic entries from the switch database that have timed-out and are no longer valid. Arp address resolution protocol. The protocol used to dynamically bind high-level ip addresses to low-level hardware addresses. Arp is used only across a single physical ne...
Page 172
2 g lossary csma/cd carrier sense multiple access/collision detection that is a channel access method used by ethernet and ieee 802.3 standards in which devices transmit only after finding the data channel clear for some period of time. When two devices transmit simultaneously, a collision occurs an...
Page 173
3 lan local area network that consists of connected computing resources (such as pcs, printers, and servers) covering a relatively small geographic area (usually not larger than a floor or building). Characterized by high data rates and low error rates. Latency the delay between the time a device re...
Page 174
4 g lossary on a wide range of computers and networking equipment and may be used to manage many aspects of network and endstation operation. Spanning tree protocol (stp) a bridge-based mechanism for providing fault tolerance on networks. Stp works by allowing the implementation of parallel paths fo...
Page 175: Ndex
I ndex 1 i ndex numerics 3com bulletin board service (3combbs) d-1 3com sales offices d-4 3com url d-1 3comfacts d-2 3comforum d-3 a accounts, creating 3-3 alarms 9-15 alarms (rmon group) 9-13 , 9-14 autonegotiation 3-13 b bootp 3-5 bridge identifier 7-3 bridge priority, configuring 4-14 , 7-11 bull...
Page 176
2 i ndex dynamic routes 8-3 populating 8-2 static routes 8-3 settings, displaying 8-12 l leds 1-7 load sharing 3-14 load sharing, configuring 3-15 log display 9-8 logging and telnet 9-9 commands 9-10 fault level 9-7 local 9-8 real-time display 9-8 remote 9-9 subsystem 9-7 timestamp 9-7 logging on 3-...
Page 177
I ndex 3 max age configuring 4-14 , 7-11 overview 7-1 path costs 4-14 , 7-11 port priority 4-14 , 7-11 switch 9000 configuration examples 1-4 dimensions b-1 factory defaults 1-9 features 1-1 free-standing installation 2-3 front view 1-6 gigabit ethernet ports 1-6 installing 2-2 leds 1-7 positioning ...
Page 178
4 i ndex sw9000.Bk page 4 wednesday, april 1, 1998 11:00 am.
Page 179
3com corporation l imited w arranty h ardware 3com warrants its hardware products to be free from defects in workmanship and materials, under normal use and service, for the following lengths of time from the date of purchase from 3com or its authorized reseller: if a product does not operate as war...
Page 180
3com shall not be liable under this warranty if its testing and examination disclose that the alleged defect in the product does not exist or was caused by customer’s or any third person’s misuse, neglect, improper installation or testing, unauthorized attempts to repair or modify, or any other caus...