- DL manuals
- 3Com
- Switch
- 9100
- User Manual
3Com 9100 User Manual
Summary of 9100
Page 1
® http://www.3com.Com/ superstack ® ii switch 9100 user guide part no. Dua1770-5aaa01 published january 2000
Page 2
3com corporation 5400 bayfront plaza santa clara, california 95052-8145 copyright © 1999, 3com technologies. All rights reserved. No part of this documentation may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to make any derivative work (such as translation, transformation, or adaptation) witho...
Page 3: Ontents
C ontents a bout t his g uide terminology 11 conventions 12 related documentation 13 year 2000 compliance 13 product registration 13 1 s witch 9100 o verview about the switch 9100 15 summary of features 15 port connections 16 full-duplex 17 load sharing 17 switch operation 17 virtual lans (vlans) 17...
Page 4
2 i nstallation and s etup determining the switch 9100 location 25 configuration rules for ethernet 26 installing the switch 9100 26 rack mounting 26 free-standing 27 stacking the switch and other devices 28 connecting equipment to the console port 28 powering-up the switch 30 checking the installat...
Page 5: Lan
Connecting to another host using telnet 46 configuring switch ip parameters 46 using a bootp server 46 manually configuring the ip settings 47 disconnecting a telnet session 49 disabling telnet access 49 ip host configuration commands 50 using the web interface 50 disabling web access 51 using snmp ...
Page 6: (Fdb)
Spanning switches with port-based vlans 67 tagged vlans 69 uses of tagged vlans 70 assigning a vlan tag 70 mixing port-based and tagged vlans 72 protocol-based vlans 72 predefined protocol filters 73 defining protocol filters 74 deleting a protocol filter 75 precedence of tagged packets over protoco...
Page 7
Configuring stp on the switch 94 stp configuration example 96 displaying stp settings 96 disabling and resetting stp 97 7 q uality of s ervice (q o s) overview of quality of service 99 building blocks 99 qos profiles 100 modifying a qos profile 101 the blackhole qos profile 102 traffic groupings and...
Page 8
Real-time display 117 remote logging 117 logging commands 118 rmon 119 about rmon 119 about the rmon groups 120 statistics 120 history 120 alarms 120 events 121 benefits of rmon 121 improving efficiency 121 allowing proactive management 121 reducing the traffic load 121 rmon and the switch 122 rmon ...
Page 9
Upgrading bootrom 133 accessing the bootrom menu 133 boot option commands 135 a s afety i nformation important safety information 138 lithium battery 140 l’information de sécurité importante 141 batterie au lithium 143 wichtige sicherheitsinformationen 144 europe 144 lithiumbatterie 145 b t echnical...
Page 10: Emc S
G lossary i ndex i ndex of c ommands 3c om c orporation l imited w arranty emc s tatements.
Page 11: Bout
A bout t his g uide this guide describes the required information to install and configure the superstack ® ii switch 9100 (3c17705). This guide is intended for use by network administrators who are responsible for installing and setting up network equipment. It assumes a basic working knowledge of:...
Page 12
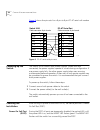
12 a bout t his g uide conventions table 1 and table 2 list conventions that are used throughout this guide. Table 1 notice icons icon notice type description information note information that describes important features or instructions caution information that alerts you to potential loss of data ...
Page 13
Related documentation 13 related documentation the switch 9100 documentation set includes the following documents. To order additional copies, contact your sales representative. ■ superstack ii switch 9100 quick reference guide this guide describes the commands used to configure your superstack ii s...
Page 14
14 a bout t his g uide.
Page 15: Witch
1 s witch 9100 o verview this chapter describes the following: ■ switch 9100 features ■ how to use the switch 9100 in your network configuration ■ switch 9100 front view ■ switch 9100 rear view ■ factory default settings about the switch 9100 network managers are currently faced with the challenge o...
Page 16
16 c hapter 1: s witch 9100 o verview ■ controls traffic (including broadcasts) ■ provides extra security ■ protocol-sensitive filtering for vlans ■ responds to 802.3x flow-control messages ■ autonegotiation to ieee 802.3z for gigabit ethernet ■ load sharing on multiple ports ■ spanning tree protoco...
Page 17
Summary of features 17 100/1000base-tx ports are configured as mdix (crossover). A crossover cable will typically be needed to connect these ports to another switch. Full-duplex the switch 9100 provides full-duplex support for all ports. Full-duplex allows frames to be transmitted and received simul...
Page 18
18 c hapter 1: s witch 9100 o verview spanning tree protocol (stp) the switch 9100 supports the ieee 802.1d spanning tree protocol (stp), which is a bridge-based mechanism for providing fault tolerance on networks. Stp allows you to implement parallel paths for network traffic, and ensure the follow...
Page 19
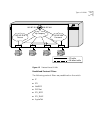
Network configuration example 19 figure 1 switch 9100 used in a backbone configuration the switch 3300 on each floor has a 1000mbps full-duplex link to the switch 9100. Two servers on one floor of the building are connected to the switch 9100 by way of two gigabit ethernet links. The two gigabit eth...
Page 20
20 c hapter 1: s witch 9100 o verview in addition to providing a gigabit backbone between fast ethernet workgroups, gigabit ethernet equipped file servers and services may be directly attached to the switch 9100 providing improved performance to the fast ethernet desktop. Switch 9100 front view figu...
Page 21
Switch 9100 front view 21 warnhinweis : rj-45 ports. Rj-45-anschlüsse. Dies sind abgeschirmte rj-45-datenbuchsen. Sie können nicht als telefonanschlußbuchsen verwendet werden. An diesen buchsen dürfen nur rj-45-datenstecker angeschlossen werden. Diese datenstecker können entweder mit abgeschirmten o...
Page 22
22 c hapter 1: s witch 9100 o verview switch 9100 rear view figure 3 shows the switch 9100 rear view. Figure 3 switch 9100 rear view 100/1000base-tx port status leds link/activity green yellow green flashing off link is present; port is enabled. Frames are being transmitted/received on this port. Li...
Page 23
Factory defaults 23 the rear panel has the following features: power sockets the switch 9100 has two, fully redundant, load-sharing power supplies. Both automatically adjust to the supply voltage. The power supplies operate down to 90 v. The fuse is suitable for both 110 v ac and 220–240 v ac operat...
Page 24
24 c hapter 1: s witch 9100 o verview spanning tree protocol disabled for the switch; enabled for each port in the stpd 802.1p priority recognition enabled 802.3x flow control enabled on gigabit ethernet ports 802.1q tagging all packets are untagged on the default vlan ( default) forwarding database...
Page 25: Nstallation
2 i nstallation and s etup this chapter describes the following: ■ how to decide where to install the switch 9100 ■ ethernet configuration rules ■ how to install the switch in a rack or free-standing ■ how to connect equipment to the console port ■ how to check the installation using the power on se...
Page 26
26 c hapter 2: i nstallation and s etup caution: when using a rack mounting system, the switch must be mounted on a shelf or runners. The rack mounting brackets alone are not sufficient to support the weight of the switch. The rack mounting brackets are provided to ensure stability across the horizo...
Page 27
Installing the switch 9100 27 to install the mounting brackets on the switch, follow these steps: 1 place the switch the right way up on a hard flat surface, with the front facing toward you. 2 remove the existing screws from the sides of the chassis. 3 locate a mounting bracket over the mounting ho...
Page 28
28 c hapter 2: i nstallation and s etup stacking the switch and other devices up to four units can be placed on top of one another. If mixing superstack ii devices, the smaller units must be positioned at the top using rubber pads. This section relates only to physically placing the devices on top o...
Page 29
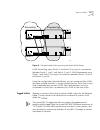
Connecting equipment to the console port 29 figure 5 shows the pin-outs for a 9-pin to rs-232 25-pin null modem cable. Figure 5 null modem cable pin-outs gnd (ground) 5 - dsr (data set ready) 6 in rts (request to send) 7 out cts (clear to send 8 in table 6 console connector pinouts (continued) funct...
Page 30
30 c hapter 2: i nstallation and s etup figure 6 shows the pin-outs for a 9-pin to 9-pin pc-at serial null modem cable. Figure 6 pc-at serial cable pin-outs powering-up the switch the switch 9100 contains two power supplies. When both are connected, the power supplies operate in a load-sharing confi...
Page 31
Logging on for the first time 31 if the switch passes the post, the mgmt led stops blinking and remains green. If the switch fails the post, the mgmt led shows a solid yellow light. Logging on for the first time after the switch has completed the post, it is operational. Once operational, you can lo...
Page 32
32 c hapter 2: i nstallation and s etup.
Page 33: Ccessing
3 a ccessing the s witch this chapter provides the following required information to begin managing the switch 9100: ■ understanding the command syntax ■ line-editing commands ■ command history substitution ■ configuring the switch for management ■ switch management methods ■ configuring snmp ■ chec...
Page 34
34 c hapter 3: a ccessing the s witch understanding the command syntax this section describes the steps to take when entering a command. Refer to the sections that follow for detailed information on using the command-line interface. To use the command-line interface (cli), follow these steps: 1 when...
Page 35
Understanding the command syntax 35 abbreviated syntax abbreviated syntax is the shortest, most unambiguous, allowable abbreviation of a command or parameter. Typically, this is the first three letters of the command. When using abbreviated syntax, you must enter enough characters to make the comman...
Page 36
36 c hapter 3: a ccessing the s witch symbols you may see a variety of symbols shown as part of the command syntax. These symbols explain how to enter the command, and you do not type them as part of the command itself. Table 7 summarizes command syntax symbols. Table 7 command syntax symbols symbol...
Page 37
Line-editing keys 37 line-editing keys table 8 describes the line-editing keys available using the cli. Command history the switch “remembers” the last 49 commands you have entered. You can display a list of these commands by using the following command: history common commands table 9 describes com...
Page 38
38 c hapter 3: a ccessing the s witch create vlan creates a vlan. Config account {encrypted} {} configures a user account password. Passwords must have a minimum of four characters and can have a maximum of 12 characters. User names and passwords are case-sensitive. Config banner configures the bann...
Page 40
40 c hapter 3: a ccessing the s witch configuring management access the switch 9100 supports the following two level levels of management: ■ user ■ administrator a user-level account has viewing access to all manageable parameters, with the exception of the following: ■ user account database ■ snmp ...
Page 41
Configuring management access 41 if an asterisk (*) appears in front of the command-line prompt, it indicates that you have outstanding configuration changes that have not been saved. For example: *3c17705:19# for more information on saving configuration changes, refer to chapter 10 . Default accoun...
Page 42
42 c hapter 3: a ccessing the s witch to add a password to the default user account, follow these steps: 1 log in to the switch using the name admin . 2 at the password prompt, press [return], or enter the password that you have configured for the admin account. 3 add a default user password by typi...
Page 43
Methods of managing the switch 9100 43 deleting an account to delete an account, you must have administrator privileges. Use the following command to delete an account: delete account the account name admin cannot be deleted. Methods of managing the switch 9100 you can manage the switch using the fo...
Page 44
44 c hapter 3: a ccessing the s witch the most common applications that use access profiles allow you to remotely manage the switch across the network, for example: ■ snmp read access ■ snmp read and write access ■ telnet ■ web access creating an access profile access profiles are created to specifi...
Page 45
Using access profiles 45 the subnet mask specified in the access profile command is interpreted as a reverse mask . A reverse mask indicates the bits that are significant in the ip address. In other words, a reverse mask specifies the part of the address that must match the ip address to which the p...
Page 46
46 c hapter 3: a ccessing the s witch to view the telnet configuration, type: show management using telnet any workstation with a telnet facility should be able to communicate with the switch over a tcp/ip network. Up to eight active telnet sessions can access the switch concurrently. If idle timeou...
Page 47
Using telnet 47 ■ subnet address mask (optional) the switch mac address is found on the rear label of the switch. Once this is done, the ip address and subnetwork mask for the switch will be downloaded automatically. You can then start managing the switch without further configuration. You can enabl...
Page 48
48 c hapter 3: a ccessing the s witch to manually configure the ip settings, perform the following steps: 1 connect a terminal or workstation running terminal-emulation software to the console port. 2 at your terminal, press [return] one or more times until you see the login prompt. 3 at the login p...
Page 49
Using telnet 49 for example: config iproute add default 123.45.67.1 7 save your configuration changes so that they will be in effect after the next switch reboot, by typing save for more information on saving configuration changes, refer to chapter 10 . 8 when you are finished using the facility, lo...
Page 50
50 c hapter 3: a ccessing the s witch ip host configuration commands table 12 describes the commands that are used to configure ip settings on the switch. Using the web interface the web interface is device-management software running in the switch that enables you to access the switch over a tcp/ip...
Page 51
Using snmp 51 the default home page of the switch can be accessed using the following command: http:// when you access the home page of the switch, you are presented with the logon screen. For more information on using the web interface, refer to chapter 9 . Disabling web access by default, web acce...
Page 52
52 c hapter 3: a ccessing the s witch configuring snmp settings the following snmp parameters can be configured on the switch: ■ authorized trap receivers — an authorized trap receiver can be one or more network management stations on your network. The switch sends snmp traps to all trap receivers. ...
Page 53
Using snmp 53 displaying snmp settings to display the snmp settings configured on the switch, enter the following command: show management this command displays the following information: ■ enable/disable state for telnet, snmp, and web access ■ snmp community strings ■ authorized snmp station list ...
Page 54
54 c hapter 3: a ccessing the s witch ■ login statistics ■ access profile assignments resetting and disabling snmp to reset and disable snmp settings, use the commands in table 14 . Checking basic connectivity the switch offers the ping command for checking basic connectivity. The ping command enabl...
Page 56
56 c hapter 3: a ccessing the s witch flow control flow control is supported on gigabit ethernet ports. It is enabled or disabled as part of autonegotiation. If autonegotiation is set to off, flow control is disabled. When autonegotiation is turned on, flow control is enabled. Switch 9100 port comma...
Page 57
Switch 9100 port commands 57 disable learning ports disables mac address learning on one or more ports for security purposes. If mac address learning is disabled, only broadcast traffic and packets destined to a permanent mac address matching that port number, are forwarded. The default setting is e...
Page 58
58 c hapter 3: a ccessing the s witch load sharing on the switch 9100 load sharing with switch 9100 devices allows you to increase bandwidth and resilience between switches by using a group of ports to carry traffic in parallel between switches. The sharing algorithm allows the switch to use multipl...
Page 59
Load sharing on the switch 9100 59 ■ all other packets — uses the source and destination mac address. ■ round-robin — when the switch receives a stream of packets, it forwards one packet out of each physical port in the load-sharing group using a round-robin scheme. Using the round-robin algorithm, ...
Page 60
60 c hapter 3: a ccessing the s witch it is recommended that you configure the same duplex and speed settings for all ports in a load-sharing group. Do not disable a port that is part of a load-sharing group. Disabling the port prevents it from forwarding traffic, but still allows the link to initia...
Page 61
Switch 9100 port-mirroring 61 port-mirroring commands switch 9100 port-mirroring commands are described in table 17 . Switch 9100 port-mirroring example the following example selects port 3 as the mirror port, and sends all traffic coming into or out of the switch on port 1 to the mirror port: enabl...
Page 62
62 c hapter 3: a ccessing the s witch.
Page 63: Irtual
4 v irtual lan s (vlan s ) setting up virtual local area networks (vlans) on the switch eases many time-consuming tasks of network administration while increasing efficiency in network operations. This chapter describes the concept of vlans and explains how to implement vlans on the switch. Overview...
Page 64
64 c hapter 4: v irtual lan s (vlan s ) ■ vlans ease the change and movement of devices. With traditional networks, network administrators spend much of their time dealing with moves and changes. If users move to a different subnetwork, the addresses of each endstation must be updated manually. For ...
Page 65
Igmp overview 65 the switch is configured to perform igmp snooping and there is no other reliable querier on the network. Igmp configuration commands are described in table 18 . Table 18 igmp configuration commands command description enable igmp {vlan } enables igmp. If no vlan is specified, igmp i...
Page 66
66 c hapter 4: v irtual lan s (vlan s ) types of vlans the switch supports a maximum of 256 vlans. Vlans can be created according to the following criteria: ■ physical port ■ 802.1q tag ■ ethernet, llc sap, or llc/snap ethernet protocol type ■ a combination of these criteria port-based vlans in a po...
Page 67
Types of vlans 67 for example, in figure 7, the vlans are configured as follows: ■ ports 1 and 3 are part of vlan sales ■ ports 2 and 5 are part of vlan marketing ■ ports 4 and 6 are part of vlan finance figure 7 example of a port-based vlan on the switch 9100 even though they are physically connect...
Page 68
68 c hapter 4: v irtual lan s (vlan s ) figure 8 illustrates a single vlan that spans two switch 9100 devices. All ports on both switches belong to vlan sales . The two switches are connected using port 1 on switch 1, and port 6 on switch 2. Figure 8 single port-based vlan spanning two switches to c...
Page 69
Types of vlans 69 figure 9 two port-based vlans spanning two switch 9100 devices vlan accounting spans switch 1 and switch 2 by way of a connection between switch 1, port 1 and switch 2, port 3. Vlan engineering spans switch 1 and switch 2 by way of a connection between switch 1, port 5, and switch ...
Page 70
70 c hapter 4: v irtual lan s (vlan s ) uses of tagged vlans tagging is most commonly used to allow vlans to span switches. The switch-to-switch connections are typically called trunks . Using tags, multiple vlans can span multiple switches using one or more trunks. In a port-based vlan, each vlan r...
Page 71
Types of vlans 71 figure 10 physical diagram of tagged and untagged traffic figure 11 shows a logical diagram of the same network. Figure 11 logical diagram of tagged and untagged traffic switch 1 switch 2 = marketing = sales m s = tagged port 802.1q tagged server 91_006 7 8 4 5 6 1 2 3 s s m 7 8 4 ...
Page 72
72 c hapter 4: v irtual lan s (vlan s ) in figure 10 and figure 11 : ■ the trunk port on each switch carries traffic for both vlan marketing and vlan sales . ■ the trunk port on each switch is tagged. ■ the server connected to port 1 on switch 1 has a nic that supports 802.1q tagging. ■ the server c...
Page 73
Types of vlans 73 figure 12 protocol-based vlans predefined protocol filters the following protocol filters are predefined on the switch: ■ ip ■ ipx ■ netbios ■ decnet ■ ipx_8022 ■ ipx_snap ■ appletalk 91_008 = ip traffic = all other traffic 1 finance personnel my company 192.207.36.0 192.207.35.0 1...
Page 74
74 c hapter 4: v irtual lan s (vlan s ) defining protocol filters if necessary, you can define a customized protocol filter based on ethertype, logical link control (llc), and/or subnetwork access protocol (snap). Up to six protocols may be part of a protocol filter. To define a protocol filter, do ...
Page 75
Vlan names 75 for more information on snap for ethernet protocol types, see tr 11802-5:1997 (iso/iec) [ansi/ieee std. 802.1h, 1997 edition]. Deleting a protocol filter if a protocol filter is deleted from a vlan, the vlan is assigned a protocol filter of none . You can continue to configure the vlan...
Page 76
76 c hapter 4: v irtual lan s (vlan s ) configuring vlans on the switch this section describes the commands associated with setting up vlans on the switch. Configuring a vlan involves the following steps: 1 create and name the vlan. 2 assign an ip address and mask (if applicable) to the vlan, if nee...
Page 77
Configuring vlans on the switch 77 vlan configuration examples the following switch 9100 example creates a port-based vlan named accounting , assigns the ip address 132.15.121.1, and assigns ports 1, 2, 3, and 6 to it: create vlan accounting config accounting ipaddress 132.15.121.1 config default de...
Page 78
78 c hapter 4: v irtual lan s (vlan s ) the following switch 9100 example creates a vlan named sales , with the vlanid 120. The vlan uses both tagged and untagged ports. Ports 1 through 3 are tagged, and ports 4 and 7 are untagged. Note that when not explicitly specified, ports are added as untagged...
Page 79
Deleting vlans 79 ■ ports assigned ■ tagged/untagged status for each port ■ how the ports were added to the vlan (manually or by gvrp) to display protocol information, use the following command: show protocol {} this show command displays protocol information, including the following: ■ protocol nam...
Page 80
80 c hapter 4: v irtual lan s (vlan s ).
Page 81: Orwarding
5 f orwarding d atabase (fdb) this chapter describes the contents of the forwarding database (fdb), how the fdb works, and how to configure the fdb. Overview of the fdb the switch maintains a database of all media access control (mac) addresses received on all of its ports. It uses the information i...
Page 82
82 c hapter 5: f orwarding d atabase (fdb) way of the command-line interface are stored as permanent. The switch can support a maximum of 64 permanent entries. Once created, permanent entries stay the same as when they were created. For example. The permanent entry store is not updated when any of t...
Page 83
Configuring fdb entries 83 configuring fdb entries to configure entries in the fdb, use the commands listed in table 21 . Fdb configuration examples the following example adds a permanent entry to the fdb: create fdbentry 00:d0:96:bf:31:50 vlan marketing port 4 the permanent entry has the following ...
Page 84
84 c hapter 5: f orwarding d atabase (fdb) ■ port number for this device is 4. This example associates the qos profile qp2 with a dynamic entry that will be learned by the fdb: create fdbentry 00:d0:96:bf:31:50 vlan net34 dynamic qosprofile qp2 this entry has the following characteristics: ■ mac add...
Page 85
Removing fdb entries 85 removing fdb entries you can remove one or more specific entries from the fdb, or you can clear the entire fdb of all entries by using the commands listed in table 22 . Table 22 removing fdb entry commands command description delete fdbentry vlan deletes a permanent fdb entry...
Page 86
86 c hapter 5: f orwarding d atabase (fdb).
Page 87: Panning
6 s panning t ree p rotocol (stp) using the spanning tree protocol (stp) functionality of the switch makes your network more fault tolerant. The following sections explain more about stp and the stp features supported by the switch 9100. Stp is a part of the 802.1d bridge specification defined by th...
Page 88
88 c hapter 6: s panning t ree p rotocol (stp) figure 13 network with an illegal topology this configuration is illegal because it creates loops that cause the network to overload. However, stp allows you to use this configuration because stp detects duplicate paths and immediately prevents (or bloc...
Page 89
Overview of the spanning tree protocol 89 if the link through bridge c fails, as shown in figure 15 , the stp system reconfigures the network so that traffic from segment 2 flows through bridge b. Figure 15 traffic flowing through bridge b how stp works stp has the following three stages of operatio...
Page 90
90 c hapter 6: s panning t ree p rotocol (stp) the root bridge generates bpdus on all ports at a regular interval known as the hello time. All other bridges in the network have a root port. This is the port that costs the least in getting to the root bridge, and it is used for receiving the bpdus in...
Page 91
Stp configurations 91 care must be taken to ensure that multiple stpd instances within a single switch do not see each other in the same broadcast domain. This could happen if, for example, another external bridge is used to connect vlans belonging to separate stpds. If you delete an stpd, the vlans...
Page 92
92 c hapter 6: s panning t ree p rotocol (stp) figure 16 multiple spanning tree domains when the switches in this configuration start up, stp configures each stpd such that there are no active loops in the topology. Stp could configure the topology in a number of ways to make it loop-free. In figure...
Page 93
Stp configurations 93 figure 17 tag-based stp configuration the tag-based network in figure 17 has the following configuration: ■ switch 1 contains vlan marketing and vlan sales . ■ switch 2 contains vlan engineering and vlan sales . ■ switch 3 contains vlan marketing , vlan engineering , and vlan s...
Page 94
94 c hapter 6: s panning t ree p rotocol (stp) configuring stp on the switch stp configuration involves the following actions: ■ create one or more stp domains using the following command: create stpd stpd, vlan, and qos profile names must all be unique. For example, a name used to identify a vlan c...
Page 95
Configuring stp on the switch 95 table 23 shows the commands used to configure stp. Table 23 stp configuration commands command description create stpd creates an stpd. When created, an stpd has the following default parameters: ■ bridge priority — 32,768 ■ hello time — two seconds ■ forward delay —...
Page 96
96 c hapter 6: s panning t ree p rotocol (stp) stp configuration example the following example creates and enables an stpd named backbone_st . It assigns the manufacturing vlan to the stpd. It disables stp on ports 1 through 3, and port 6. Create stpd backbone_st config stpd backbone_st add vlan man...
Page 97
Disabling and resetting stp 97 to display the stp state of a port, use the following command: show stpd port this command displays the following: ■ stpd port configuration ■ stpd state (root bridge, and so on) ■ stpd port state (forwarding, blocking, and so on) disabling and resetting stp to disable...
Page 98
98 c hapter 6: s panning t ree p rotocol (stp).
Page 99: Uality
7 q uality of s ervice (q o s) this chapter describes the concept of quality of service (qos) and explains how to configure qos on the switch. Overview of quality of service qos is a feature of the switch 9100 that allows you to specify different service levels for traffic traversing the switch. Qos...
Page 100
100 c hapter 7: q uality of s ervice (q o s) the next sections describe how qos profiles are used and modified. After this, various traffic groupings are explained and qos profiles are assigned to the traffic groupings. Qos profiles eight default qos profiles are provided that can be modified, but n...
Page 101
Qos profiles 101 a qos profile does not alter the behavior of the switch until it is assigned to a traffic grouping. The settings of the default profiles are shown in table 25 . Modifying a qos profile you can modify the profile defaults as desired. To modify the parameters of an existing qos profil...
Page 102
102 c hapter 7: q uality of s ervice (q o s) the blackhole qos profile in the description of various options for configuring policy-based qos, there is an option to specify blackhole in place of a named qos profile. As its name implies, a traffic grouping assigned to the “blackhole” goes nowhere, an...
Page 103
Traffic groupings and creating a qos policy 103 mac-based traffic groupings qos profiles can be assigned to destination mac addresses. The various options that fall into this category are as follows: ■ permanent ■ dynamic ■ blackhole ■ broadcast/unknown rate limiting mac-based traffic groupings are ...
Page 104
104 c hapter 7: q uality of s ervice (q o s) the command to clear the fdb is as follows: clear fdb blackhole using the blackhole option configures the switch to not forward any packets to the destination mac address on any ports for the vlan specified. The blackhole option is configured using the fo...
Page 105
Traffic groupings and creating a qos policy 105 802.1p packets when traffic that contains 802.1p prioritization bits is seen, the traffic is mapped to the eight default qos profiles. No user configuration is required for this type of traffic grouping. Table 27 describes 802.1p values and their assoc...
Page 106
106 c hapter 7: q uality of s ervice (q o s) source port a source port traffic grouping implies that any traffic sourced from this physical port uses the indicated qos profile when the traffic is transmitted out any other port. To configure a source port traffic grouping, use the following command: ...
Page 107
Verifying configuration and performance 107 verifying configuration and performance the following information is used to verify the qos configuration and monitor the use of the qos policies that are in place. Displaying qos information to display qos information on the switch, use the following comm...
Page 108
108 c hapter 7: q uality of s ervice (q o s) qos monitor sampling is configured as follows: ■ the port is monitored for 20 seconds before the switch moves on to the next port in the list. ■ a port is sampled for five seconds before the packets per second (pps) value is displayed on the screen. Monit...
Page 109
Configuring qos 109 ■ for physical and logical groupings of a source port or vlan, re-apply the qos profile to the source port or vlan. You can also save and reboot the switch. Configuring qos table 29 describes the commands used to configure qos. Table 29 qos configuration commands command descript...
Page 110
110 c hapter 7: q uality of s ervice (q o s).
Page 111: Tatus
8 s tatus m onitoring and s tatistics this chapter describes how to view the current operating status of the switch, how to display information in the log, and how to take advantage of available remote monitoring (rmon) capabilities. Viewing statistics on a regular basis allows you to see how well y...
Page 112
112 c hapter 8: s tatus m onitoring and s tatistics table 30 describes show commands that are used to monitor the status of the switch. Table 30 status monitoring commands command description show log {} displays the current snapshot of the log. The priority option filters the log to display message...
Page 113
Port statistics 113 port statistics the switch 9100 provides a facility for viewing port statistic information. The summary information lists values for the current counter against each port on each operational module in the system, and it is refreshed approximately every two seconds. Values are dis...
Page 114
114 c hapter 8: s tatus m onitoring and s tatistics port errors the switch keeps track of errors for each port. To view port transmit errors, use the following command: show ports txerrors the following port transmit error information is collected by the system: ■ link status — the current status of...
Page 115
Port monitoring display keys 115 ■ receive alignment errors (rx align) — the total number of frames received by the port that occurs if a frame has a crc error and does not contain an integral number of octets. ■ receive frames lost (rx lost) — the total number of frames received by the port that we...
Page 116
116 c hapter 8: s tatus m onitoring and s tatistics by default, log entries that are assigned a critical or warning level remain in the log after a switch reboot. Issuing a clear log command does not remove these static entries. To remove log entries of all levels (including warning or critical), us...
Page 117
Logging 117 real-time display in addition to viewing a snapshot of the log, you can configure the system to maintain a running real-time display of log messages on the console. To turn on the log display, enter the following command: enable log display to configure the log display, use the following...
Page 118
118 c hapter 8: s tatus m onitoring and s tatistics logging commands the commands described in table 34 allow you to configure logging options, reset logging options, display the log, and clear the log. Table 34 logging commands command description enable cli-config-logging enables logging cli confi...
Page 119
Rmon 119 rmon using the remote monitoring (rmon) capabilities of the switch allows network administrators to improve system efficiency and reduce the load on the network. The following sections explain more about the rmon concept and the rmon features supported by the switch. You can only use the rm...
Page 120
120 c hapter 8: s tatus m onitoring and s tatistics about the rmon groups the ietf defines nine groups of ethernet rmon statistics. The switch supports the following four of these groups: ■ statistics ■ history ■ alarms ■ events this section describes these groups, and discusses how they can be used...
Page 121
Rmon 121 events the events group creates entries in an event log and/or sends snmp traps to the management workstation. An event is triggered by an rmon alarm. The action taken can be configured to ignore it, to log the event, to send an snmp trap to the receivers listed in the trap receiver table, ...
Page 122
122 c hapter 8: s tatus m onitoring and s tatistics an rmon probe, however, autonomously looks at the network on behalf of the management workstation without affecting the characteristics and performance of the network. The probe reports by exception, which means that it only informs the management ...
Page 123
Rmon 123 when using the rmon features of the switch, you should note the following: ■ after the default sessions are created, they have no special status. You can delete or change them as required. ■ the greater the number of rmon sessions, the greater the burden on the management resources of the s...
Page 124
124 c hapter 8: s tatus m onitoring and s tatistics.
Page 125: Sing
9 u sing the w eb i nterface the web interface is device-management software running in the switch that allows you to access the switch over a tcp/ip network, using a standard web browser. Any properly configured standard web browser that supports frames and javascript (such as netscape navigator 3....
Page 126
126 c hapter 9: u sing the w eb i nterface setting up your browser in general, the default settings that come configured on your browser work well with the web interface. The following are recommended settings that you can use to improve the display features and functionality of the web interface: ■...
Page 127
Navigating the web interface 127 if you have entered the name and password of an administrator-level account, you have access to all web interface pages. If you have used a user-level account name and password, you only have access to the statistics and support information. For more information on a...
Page 128
128 c hapter 9: u sing the w eb i nterface content frame the content frame contains the main body of information in the web interface. For example, if you select an option from the configuration task button, enter configuration parameters in the content frame. If you select the statistics task butto...
Page 129
Saving changes 129 saving changes there are two ways to save your changes to non-volatile storage using the web interface: ■ select save configuration from the configuration task button, switch option. This field contains a drop-down list box that allows you to select either the primary or secondary...
Page 130
130 c hapter 9: u sing the w eb i nterface.
Page 131: Oftware
10 s oftware u pgrade and b oot o ptions this chapter describes the procedure for upgrading the switch software image. This chapter also discusses how to save and load a primary and secondary image and configuration file on the switch. Downloading a new image the image file contains the executable c...
Page 132
132 c hapter 10: s oftware u pgrade and b oot o ptions the switch can store up to two images; a primary and a secondary. When you download a new image, you must select into which image space (primary or secondary) you want the new image to be placed. You can select which image the switch will load o...
Page 134
134 c hapter 10: s oftware u pgrade and b oot o ptions to access the bootrom menu, follow these steps: 1 attach to the console port of the switch, as described in chapter 2 . 2 with the serial port connected to a properly configured terminal or terminal emulator, power cycle the switch while depress...
Page 135
Boot option commands 135 boot option commands table 38 lists the commands associated with switch boot options. Table 38 boot option commands command description show configuration displays the current configuration to the terminal. You can then capture the output and store it as a file. Download boo...
Page 136
136 c hapter 10: s oftware u pgrade and b oot o ptions.
Page 137: Afety
A s afety i nformation you must read the following safety information before carrying out any installation or removal of components, or any maintenance procedures on the switch 9100. Warning: warnings contain directions that you must follow for your personal safety. Follow all directions carefully. ...
Page 138
138 a ppendix a: s afety i nformation important safety information ■ installation and removal of the unit must be carried out by qualified personnel only. ■ if installing the switch 9100 in a stack with superstack ii units that are narrower than the 9100, the switch 9100 unit must be installed below...
Page 139
Important safety information 139 ■ this unit operates under selv (safety extra low voltage) conditions according to iec 950. The conditions are only maintained if the equipment to which it is connected also operates under selv conditions. ■ france and peru only: this unit cannot be powered from it †...
Page 140
140 a ppendix a: s afety i nformation if service personnel disregard the instructions and attempt to replace the bq4830/ds1644, replace the lithium battery with the same or equivalent type, as recommended by the manufacturer. Warning: there is danger of personal injury and explosion if battery is im...
Page 141
L’information de sécurité importante 141 l’information de sécurité importante ■ l'installation et la dépose de ce groupe doivent être confiés à un personnel qualifié. ■ si vous entassez l'unité switch avec les unités superstack ii hub, l'unité switch 9100 doit être installée en dessous des unités hu...
Page 142
142 a ppendix a: s afety i nformation ■ la prise secteur doit se trouver à proximité de l’appareil et son accès doit être facile. Vous ne pouvez mettre l’appareil hors circuit qu'en débranchant son cordon électrique au niveau de cette prise. ■ l’appareil fonctionne à une tension extrêmement basse de...
Page 143
L’information de sécurité importante 143 batterie au lithium les batteries du dispositif bq4830/ds1644 est hermétiquement scellé et ne peut donc pas être remplacé par l'utilisateur. Si les techniciens de maintenance outrepassent ces instructions et tentent de remplacer la bq4830/ds1644, la batterie ...
Page 144
144 a ppendix a: s afety i nformation wichtige sicherheitsinformat ionen ■ die installation und der ausbau des geräts darf nur durch fachpersonal erfolgen. ■ wenn die switch 9100 einheit in einer stapel mit anderen superstack ii hub einheiten eingebaut werden soll, muß die switch 9100 einheit unter ...
Page 145
Wichtige sicherheitsinformationen 145 warnhinweis : rj-45 ports. Rj-45-anschlüsse. Dies sind abgeschirmte rj-45-datenbuchsen. Sie können nicht als telefonanschlußbuchsen verwendet werden. An diesen buchsen dürfen nur rj-45-datenstecker angeschlossen werden. Diese datenstecker können entweder mit abg...
Page 146
146 a ppendix a: s afety i nformation ■ lithiumbatterien sind kein von der epa aufgelisteter sondermüll und können daher in der regel mit dem normalen müll entsorgt werden. ■ bei der entsorgung größerer mengen ist die örtliche müllverwaltungsstelle zu rate zu ziehen. ■ das batteriemodul enthält kein...
Page 147: Echnical
B t echnical s pecifications *category 5 screened or unscreened cables must be used to ensure compliance with the class a requirements of this standard. Physical dimensions height: 89mm (3.5 in.) x width: 440mm (17.3 in.) x depth: 472mm (18.6 in.) weight: 9.53kg (21 lb.) environmental requirements o...
Page 148
148 a ppendix b: t echnical s pecifications the following is a list of software standards supported by the switch 9100. For more information on drafts of the 802.3 mau mib + gigabit and the ether-like mib + gigabit, refer to: http://www.Ietf.Org/html.Charters/hubmib-charter.Html the ieee bridge mib ...
Page 149: Roubleshooting
C t roubleshooting if you encounter problems when using the switch, this appendix may be helpful. If you have a problem not listed here or in the “release notes,” contact your supplier. Leds power led does not light: check that the power cable is firmly connected to the device and to the supply outl...
Page 150
150 a ppendix c: t roubleshooting switch does not power up: the switch 9100 uses a digital power supply with surge protection. In the event of a power surge, the protection circuits shut down the power supply. To reset, unplug the switch for 1 minute, plug it back in, and attempt to power up the swi...
Page 151
Using the command-line interface 151 attempt to log in and the maximum number of telnet sessions are being used, you should receive an error message indicating so. Traps are not received by the snmp network manager: check that the snmp network manager's ip address and community string are correctly ...
Page 152
152 a ppendix c: t roubleshooting you forget your password and cannot log in: if you are not an administrator, another user having administrator access level can log in, delete your user name, and create a new user name for you, with a new password. Alternatively, another user having administrator a...
Page 153
Using the command-line interface 153 a mismatch of duplex mode between the switch 9100 and the network device will cause poor network performance. Viewing using the show port rx command on the switch 9100 may display a constant increment of crc errors. This is characteristic of a duplex mismatch bet...
Page 154
154 a ppendix c: t roubleshooting which should now allow you to re-enter the previous command without error as follows: localhost:26 # config vlan red add port 1,2 vlan names: there are restrictions on vlan names. They cannot contain whitespaces and cannot start with a numeric value unless you use q...
Page 155
Using the command-line interface 155 stp you have connected an endstation directly to the switch and the endstation fails to boot correctly: the switch 9100 has stp enabled, and the endstation is booting before the stp initialization process is complete. Specify that stp has been disabled for that v...
Page 156
156 a ppendix c: t roubleshooting.
Page 157: Echnical
D t echnical s upport 3com provides easy access to technical support information through a variety of services. This appendix describes these services. Information contained in this appendix is correct at time of publication. For the most recent information, 3com recommends that you access the 3com ...
Page 158
158 a ppendix d: t echnical s upport 3com ftp site download drivers, patches, software, and mibs across the internet from the 3com public ftp site. This service is available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. To connect to the 3com ftp site, enter the following information into your ftp client: ■ hostna...
Page 159
Support from your network supplier 159 access by digital modem isdn users can dial in to the 3com bbs using a digital modem for fast access up to 64 kbps. To access the 3com bbs using isdn, call the following number: 1 847 262 6000 3com facts automated fax service the 3com facts automated fax servic...
Page 160
160 a ppendix d: t echnical s upport when you contact 3com for assistance, have the following information ready: ■ product model name, part number, and serial number ■ a list of system hardware and software, including revision levels ■ diagnostic error messages ■ details about recent configuration c...
Page 161
Returning products for repair 161 returning products for repair before you send a product directly to 3com for repair, you must first obtain an authorization number. Products sent to 3com without authorization numbers will be returned to the sender unopened, at the sender’s expense. To obtain an aut...
Page 163: Lossary
G lossary 10base-t the ieee specification for 10mbps ethernet over category 3, 4 or 5 twisted pair cable. 100base-fx the ieee specification for 100mbps fast ethernet over fiber-optic cable. 100base-tx the ieee specification for 100mbps fast ethernet over category 5 twisted-pair cable. 1000base-t the...
Page 164
164 g lossary bootp the bootp protocol allows you to automatically map an ip address to a given mac address each time a device is started. In addition, the protocol can assign the subnet mask and default gateway to a device. Bridge a device that interconnects two lans of a different type to form a s...
Page 165
G lossary 165 forwarding database a database that is stored by a switch to determine if a packet should be forwarded, and which port should forward the packet if it is to be forwarded. Also known as switch database. Filtering the process of screening a packet for certain characteristics, such as sou...
Page 166
166 g lossary ip internet protocol. Ip is a layer 3 network protocol that is the standard for sending data through a network. Ip is part of the tcp/ip set of protocols that describe the routing of packets to addressed devices. Ipx internetwork packet exchange. Ipx is a layer 3 and 4 network protocol...
Page 167
G lossary 167 mac address media access control address; also called hardware or physical address. A layer 2 address associated with a particular network device. Most devices that connect to a lan have a mac address assigned to them as they are used to identify other devices in a network. Mac address...
Page 168
168 g lossary repeater a simple device that regenerates lan traffic so that the transmission distance of that signal can be extended. Repeaters are used to connect two lans of the same network type. Resilient link a pair of ports that can be configured so that one takes over data transmission should...
Page 169
G lossary 169 standby port the port in a resilient link that takes over data transmission if the main port in the link fails. Stp see spanning tree protocol (stp) . Switch a device that interconnects several lans to form a single logical lan that comprises of several lan segments. Switches are simil...
Page 170
170 g lossary vlt virtual lan trunk. A switch-to-switch link that carries traffic for all the vlans on each switch. Wan wide area network. A communications network that covers a wide area. A wan can cover a large geographic area, and may contain several lans within it..
Page 171: Ndex
I ndex numbers 1000base-sx port 16 3com bulletin board service (3com bbs) 158 3com knowledgebase web services 157 3com url 157 3comfacts 159 a access levels 40 access profiles configuration commands (table) 44 creating 44 example 45 reverse mask 45 rules 45 use 43 accounts, creating 42 admin account...
Page 172
172 i ndex e enabling a port 55 errors, port 114 events, rmon 121, 122 f factory defaults 23 fax service (3comfacts) 159 fdb adding an entry 82 aging entries 81 blackhole entries 82 clear and delete commands (table) 85 configuration commands (table) 83 configuring 83 contents 81 creating a permanent...
Page 173
I ndex 173 o online technical services 157 p passwords default 41 forgetting 42 permanent entries, fdb 81 ping command 54 port commands (table) 56 enabling and disabling 55 errors,viewing 114 master port 59 monitoring display keys 115 priority, stp 94 receive errors 114 statistics, viewing 113 stp s...
Page 174
174 i ndex shortcuts, command 35 simple network management protocol. See snmp snap protocol 75 snmp authorized managers 52 community strings 52 configuration commands (table) 52 configuring 52 reset and disable commands (table) 54 settings, displaying 53 supported mibs 51 trap receivers 52 using 51 ...
Page 175
I ndex 175 configuring 76 default 75 delete and reset commands (table) 79 description 17 displaying settings 78 mixing port-based and tagged 72 names 75 port-based 66 protocol filters 73 protocol-based 72 restoring default values 79 tagged 69 trunks 70 types 66 w web interface accessing 126 browser ...
Page 176
176 i ndex.
Page 177: Ndex
I ndex of c ommands c clear counters 119 clear fdb 85 , 104 clear igmp snooping 66 clear iparp 50 clear log 116 , 119 clear session 39 , 49 config access-profile 44 config access-profile add 44 config access-profile delete 44 config account 38 config banner 38 config dot1p type 105 config dot1q ethe...
Page 178
178 i ndex of c ommands disable log display 118 disable mirroring 61 disable ports 55 , 57 disable qosmonitor 108 disable rmon 123 disable sharing 57 , 59 disable snmp access 54 disable snmp traps 54 disable stpd 97 disable stpd port 97 disable syslog 118 disable telnet 39 , 49 disable web 39 , 51 ,...
Page 179
I ndex of c ommands 179 u unconfig management 54 unconfig ports display-string 56 unconfig stpd 97 unconfig switch 40 , 133 unconfig vlan ipaddress 79 use configuration 133 , 135 use image 132 , 135.
Page 180
180 i ndex of c ommands.
Page 181
3com corporation l imited w arranty this warranty applies to customers located in the united states, australia, canada (except quebec), ireland, new zealand, u.K., and other english language countries, and countries for which a translation into the local language is not provided. Superstack ii switc...
Page 182
3com shall not be responsible for any software, firmware, information, or memory data of customer contained in, stored in, or integrated with any products returned to 3com for repair, whether under warranty or not. Dead- or defective-on-arrival . In the event a product completely fails to function o...
Page 183
G overning l aw this limited warranty shall be governed by the laws of the state of california, u.S.A. Excluding its conflicts of laws principles and excluding the united nations convention on contracts for the international sale of goods. 3com corporation 5400 bayfront plaza p.O. Box 58145 santa cl...
Page 184
Emc s tatements fcc s tatement this equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a class a digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the fcc rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial...