- DL manuals
- 3Com
- Software
- CommWorks 5210
- User Manual
3Com CommWorks 5210 User Manual
Summary of CommWorks 5210
Page 1
Commworks 5210 ip telephony manager user guide release 2.3 part number 10044879.
Page 3: Commworks 5210
Commworks 5210 ip telephony manager user guide release 2.3 part number 10044879.
Page 4
Copyright © 2001, 3com corporation. All rights reserved. No part of this documentation may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to make any derivative work (such as translation, transformation, or adaptation) without written permission from 3com corporation. 3com corporation reserves th...
Page 5: Ontents
C ontents c ontents a bout t his g uide finding information............................................................................................................Xiii conventions........................................................................................................................
Page 6
Vi auto response .................................................................................................................. 31 autoresponse configuration ........................................................................................ 31 setting authorized stations......................
Page 7
Vii 4 m aintenance upgrading software ...........................................................................................................69 software upgrade methods ..........................................................................................70 upgrading the software ..............
Page 8
Viii b c ommand l ine i nterface general syntax................................................................................................................. 101 ip telephony manager console ........................................................................................ 104 configuration...
Page 9: Ist
Ix l ist of t ables table 1 content description............................................................................................ Xiii table 2 notice icon description ....................................................................................... Xiv table 3 text convention descrip...
Page 10: Ist
X l ist of f igures figure 1 performance window ........................................................................................23 figure 2 media gateway network time protocol window ...............................................29 figure 3 server network time protocol window .................
Page 11
Xi figure 54 community string warning message .................................................................79 figure 55 device details dialog box ...................................................................................79 figure 56 inventory window ........................................
Page 13: Bout
A bout t his g uide about this guide contains an overview of the ip telephony manager user guide, describes where to find specific information, lists conventions and related documentation, and explains how to contact commworks corporation. This guide describes how to install, configure, and operate ...
Page 14
Xiv a bout t his g uide conventions the following tables list conventions in this guide. Related documentation the following documents contain information about the components of the commworks ip telephony platform: ■ commworks ip telephony system software installation guide ■ commworks ip telephony...
Page 15
Contacting commworks xv ■ commworks ip telephony parameter (mib) reference guide ■ commworks ip telephony trap (alarm) reference guide ■ commworks 4007 ss7 signaling gateway operation and maintenance guide contacting commworks for information about customer service, including support, training, code...
Page 17: Nstallation
1 i nstallation this chapter contains an overview of ip telephony manager and installation procedures for unix. This chapter contains the following topics: ■ overview ■ management workstation ■ prerequisites ■ before you begin ■ removing previous versions ■ installing ip telephony manager ■ starting...
Page 18
18 c hapter 1: i nstallation the management station uses management information bases (mibs), defined for each card in the hub, to issue commands to the nmc. The nmc executes the commands and obtains the results using a proprietary commworks protocol. The nmc uses snmp to send these results to the m...
Page 19
Before you begin 19 table 6 lists the software requirements needed to achieve the best performance from ip telephony manager. If you are installing hp openview for the first time, temporarily disable autodiscovery. Do not allow openview to discover the devices on your network automatically. This eas...
Page 20
20 c hapter 1: i nstallation if you are using hp openview, you must install it before you install ip telephony manager. If not, hp openview does not integrate correctly. Make sure ip telephony manager and hp openview are installed on the same system. Remember to disable hp openview autodiscovery bef...
Page 21
Installing ip telephony manager 21 8 from the command line prompt, type the following commands and press return after each: tcmhome= (for example, /opt/tcm) export tcmhome mkdir -p $tcmhome cd cdrom/cdrom0/tcm_sol (for hp, tcm_ux) ./install a message appears: the script will make adjustments, only a...
Page 22
22 c hapter 1: i nstallation starting ip telephony manager after you complete the installation and modify the path statement, you can start ip telephony manager. To start the ip telephony manager, from the command line prompt, type one of these commands: # xtcmvfpd or # xtcmvfpd target chassis ip ad...
Page 23
Connecting to entities 23 to view the entity after the it is connected using ip telephony manager: 1 start ip telephony manager. 2 click file and then click open from the ip telephony manger console window. 3 select the entity from the list. 4 click ok. The entity appears in graphical form. When sel...
Page 24
24 c hapter 1: i nstallation integrating with hp openview the ip telephony manager installation script installs openview integration files to the appropriate openview network node manager subdirectories. Openview integration occurs as part of the ip telephony manager installation, when the openview ...
Page 25
Integrating with hp openview 25 if commworks devices were populated in openview before ip telephony manager was installed, the network map will not display the commworks bitmaps correctly after ip telephony manager integration. This occurs even if the commworks menu options are not enabled and the i...
Page 26
26 c hapter 1: i nstallation linking commworks objects if you choose to install hp openview, you must install it before ip telephony manager. This lets you start ip telephony manager directly from hp openview. To link commworks objects in hp openview to ip telephony manager, use the following proced...
Page 27: Onfiguration
2 c onfiguration this chapter describes how to configure commworks ip telephony manager. This chapter contains the following topics: ■ management station configuration ■ component configuration ■ synchronizing network time ■ auto response ■ setting authorized stations ■ defining a range of ip addres...
Page 28
28 c hapter 2: c onfiguration component configuration the ip telephony manager console window is used to select target components whenever you are performing configuration, sending commands, or upgrading components through software download. Launching the configuration tool there are two ways to lau...
Page 29
Synchronizing network time 29 selecting public ntp servers 1 from any computer with internet access, access the following website: http://www.Eecis.Udel.Edu/~mills/ntp/clock1.Htm 2 from the website, record the ip addresses for two separate active servers. One is used as the primary ntp server, and t...
Page 30
30 c hapter 2: c onfiguration 5 enter the primary and secondary ntp ip addresses (refer to recording the ntp ip addresses ). 6 set the operational mode to unicast. 7 click set. Setting the ntp parameters for the other entities for each gatekeeper, sip proxy server, and back-end server: 1 using ip te...
Page 31
Auto response 31 auto response autoresponse lets network managers define a set of actions (auto response script) to be taken automatically when a specified event occurs in the chassis. The event may be specific to a particular module (nac or nmc) in a given slot of the chassis, or specific to a part...
Page 32
32 c hapter 2: c onfiguration 3 select the event from the event drop-down list. 4 select what you want the system to do when the selected event occurs from the available responses list and click add. The response is added to the responses configured list box. 5 click ok. The response scripts are loa...
Page 33
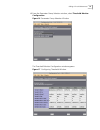
Setting authorized stations 33 figure 6 authorized stations add window 4 in the add dialog box, enter the ip address for the workstation you are currently working from and click ok. The authorized stations completion window appears with the newly added ip addresses listed. Figure 7 authorized statio...
Page 34
34 c hapter 2: c onfiguration defining a range of ip addresses for authorized access you can define a range of ip addresses for authorized access by using the network mask field in the authorized access list. The network mask that you type in this field masks the ip address for that entry to define ...
Page 35
Threshold monitoring configuration 35 figure 9 parameter group selection window the threshold monitor configuration window appears. Figure 10 configuring thresholds window.
Page 36
36 c hapter 2: c onfiguration the following table contains the fields and the values of the configuring threshold window. Table 8 threshold monitor configuration fields field name description possible selections threshold object object id which is to be monitored. This has 4294967294 at the end if a...
Page 37
Adding a threshold parameter 37 5 after you have set the trap thresholds on the gatekeeper, sip proxy server, or any of the back-end servers, you must restart the snmp agent. Refer to restarting other entities in chapter 4 for more information. Adding a threshold parameter to add a parameter to moni...
Page 38
38 c hapter 2: c onfiguration figure 11 selecting an entity window 4 from the parameter group selection window, select threshold monitor configuration. Figure 12 parameter group selection window the threshold monitor configuration window appears..
Page 39
Adding a threshold parameter 39 figure 13 configuring thresholds window 5 configure the fields in the configuring threshold window as needed. Refer to table 8 . Click set. 6 set threshold row status to createandgo. As shown in the following figure..
Page 40
40 c hapter 2: c onfiguration figure 14 adding threshold parameters window 7 click set. 8 if you changed the threshold parameters on the gatekeeper, sip proxy server, or any of the back-end servers, you must restart the snmp agent. Refer to restarting other entities in chapter 4 for more information...
Page 41
Editing a threshold parameter 41 4 from the parameter group selection window, select threshold monitor configuration. Figure 16 parameter group selection window the threshold monitor configuration window appears. Figure 17 configuring thresholds window.
Page 42
42 c hapter 2: c onfiguration 5 set threshold row status to notinsservice. 6 change the configuration as you need, refer to table 8 , and click set. 7 set the threshold row status to active. The following figure shows the threshold parameter drop-down list. Figure 18 editing threshold parameters win...
Page 43
Saving and restoring configurations 43 saving and restoring configurations the save configuration utility performs a discovery of the configuration of a device and saves it to a file. After it is saved to a file, the restore configuration utility is used to restore the configuration to that device, ...
Page 44
44 c hapter 2: c onfiguration figure 19 save chassis nvram dialog box 2 enter or select the .Nvr file you are saving to and click ok. The default directory for .Nvr files is: $tcmhome/data/nvram/. If you are saving or restoring from the command line and you are not using the x prefix option, progres...
Page 45
Saving and restoring configurations 45 figure 20 restore chassis nvram dialog box 2 enter or select the .Whb file you are restoring from and click ok. The default directory for .Nvr files is: $tcmhome/data/nvram/. If you are saving or restoring from the command line and you are not using the x prefi...
Page 46
46 c hapter 2: c onfiguration not all components support the save to nvram feature. For those that support this feature, the hiper dsp and nmc cards, you must select the right command type and group. For example, the modem software command group is available only when you select modems at the channe...
Page 47
Saving and restoring configurations 47 figure 21 save chassis cfm dialog box 3 enter or select the .Cfm file you are saving to and click ok. The default directory for .Nvr files is: $tcmhome/data/nvram/. If you are saving or restoring from the command line and you are not using the x prefix option, ...
Page 48
48 c hapter 2: c onfiguration figure 22 restore chassis cfm dialog box 2 enter or select the .Cfm file you are restoring from and click ok. The default directory for .Cfm files is: opt/tcm/data/cfm/tch. If you are saving or restoring from the command line and you are not using the x prefix option, p...
Page 49: Avigating
3 n avigating and u sing the s ystem this chapter describes the menus in the ip telephony manager. The function of the menus can vary depending on the component, if that is the case, then you are referred to that individual component’s user manual. This chapter contains the following topics: ■ acces...
Page 50
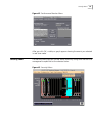
50 c hapter 3: n avigating and u sing the s ystem figure 23 ip telephony manager console window the ip telephony manager console window contains a graphical representation of the total control chassis. The view can be changed by the view menu to see the front or back of the chassis. Select the area ...
Page 51
Accessing ip telephony manager window 51 figure 24 ip telephony manager server window to perform a function on the gatekeeper, sip proxy server, or back-end server, click on the server icon and simply choose the command from the main menu. The remainder of this section describes the functions locate...
Page 52
52 c hapter 3: n avigating and u sing the s ystem file menu the file menu is used to open devices on the system, save and restore configurations, and to import software download files. Figure 25 shows an example of the file menu from the media gateway. Figure 25 file menu open submenu the open subme...
Page 53
File menu 53 save chassis nvram submenu the save chassis nvram submenu saves the media gateway chassis configuration to a specific file on nvram. Refer to chapter 2 for more information on saving the chassis to nvram (ip telephony manager chassis console only). Restore chassis nvram submenu the rest...
Page 54
54 c hapter 3: n avigating and u sing the s ystem view menu the view menu lets you adjust the way ip telephony manager displays the console or server window. Figure 28 view menu other side submenu the other side submenu displays the reverse side of the chassis. This guide shows the front panel of th...
Page 55
View menu 55 figure 30 icon view window the first icon displays the command tool dialog box for the chosen entity. The second icon displays the configuration menus. The third icon displays the software download dialog box for the selected entity. The forth icon displays diagnostics information for t...
Page 56
56 c hapter 3: n avigating and u sing the s ystem configuration menu the configuration menu is used to set the voip chassis to your environment requirements. Figure 31 configuration menu programmed settings submenu the programmed settings submenu displays the configuration tool window for the select...
Page 57
Configuration menu 57 figure 32 edgeserver pro card parameter group window the configuration tool menu contains the following fields: ■ selected targets—the name of the target to be configured from this menu that was selected from the ip telephony manager chassis or server. Displays the slot and cha...
Page 58
58 c hapter 3: n avigating and u sing the s ystem figure 33 example of hiper dsp modem identification configuration table click on the cell with the setting you want to edit. If a value is read-only, the cursor changes to the “no” sign when placed over the cell. If the value can be modified, an arro...
Page 59
Configuration menu 59 ■ exit—closes the window and displays the previous window. ■ adjusting column width—you can adjust the column width using the mouse. Place the cursor over the column divisor line until it changes to a bar and arrow, then click and drag the line left or right. Action/commands su...
Page 60
60 c hapter 3: n avigating and u sing the s ystem ■ execute—executes the selected command for the selected targets. ■ close—closes the command tool window. Software download submenu the software download submenu displays the files to be downloaded for the specified entity. You then select the files ...
Page 61
Configuration menu 61 for example, 0000000010010000 means that dip switches 8 and 5 are on and all others are off. ■ software version—version of software currently installed in the component's flash ram. You can perform the following tasks from this window: ■ save—saves the inventory data table to a...
Page 62
62 c hapter 3: n avigating and u sing the s ystem figure 37 auto response window the autoresponse dialog box contains the following fields and buttons: ■ selected targets—this box shows the slot(s) or channel(s) selected in the chassis display. ■ event—click this box to select an event. If you selec...
Page 63
Fault menu 63 fault menu the fault menu lets you enable/disable traps and define the trap’s destination. Figure 38 fault menu trap settings submenu the trap setting submenu defines the traps for the specified entity. Refer to the individual component user guide for information about setting this for...
Page 64
64 c hapter 3: n avigating and u sing the s ystem trap destination submenu the trap destination submenu defines and modifies where the traps are sent. Refer to the individual component user guide for information about setting this for your voip component. Figure 40 trap destination window performanc...
Page 65
Security menu 65 figure 42 performance monitor menu after you click ok, a table, or graph appears showing the events you selected in real time mode. Security menu the security menus lets you set the snmp community strings and maintain the management capabilities at the selected station. Figure 43 se...
Page 66
66 c hapter 3: n avigating and u sing the s ystem community names submenu the community names submenu lets you set the snmp community strings. The ip telephony manager default value for snmp community string is public for read only and private for read-write. To change the default values, you must f...
Page 67
Security menu 67 ■ modify— brings up a dialog box for changing the network mask or comment for the selected device. (you must select an entry from the list before using this button.) ■ delete—deletes the selected entry. When you click add, the authorized stations add dialog box appears. Figure 45 au...
Page 69: Aintenance
4 m aintenance this chapter describes how to use ip telephony manager to upgrade software and perform general maintenance tasks on commworks ip telephony platform cards. This chapter contains the following topics: ■ upgrading software ■ command tool ■ restarting other entities ■ setting manual switc...
Page 70
70 c hapter 4: m aintenance back-end servers: ■ commworks snmp subagent ■ oobman ■ provisioning server ■ directory mapping server ■ accounting server ■ billing support server remote upgrades of the above listed firmware cards are also accomplished through the use of sdl-2. Sms is no longer used for ...
Page 71
Upgrading software 71 ■ extracts the cab file from the dmf file. ■ extracts the installation files from the cab file. ■ runs the setup. Table 9 lists a comparison of the installation methods. Upgrading the software after you have decided what method you want to install the upgrades, you are ready to...
Page 72
72 c hapter 4: m aintenance if you do not have unzip capabilities on your unix system, you can download the freeware from the internet and install it on your system. 3 select the component to which you want to download software. The media gateway, gatekeeper, sip proxy server or select the back-end ...
Page 73
Command tool 73 when the software downloadis complete, a green box appears under the command status. 9 click ok when finished. Command tool the command tool is used to perform hardware and software commands on a selected component, such as busy-out, disconnect, reset, or save to nvram. As an example...
Page 74
74 c hapter 4: m aintenance figure 48 example hiper dsp hardware commands figure 49 shows the software commands that can be executed for the hiper dsp card. Figure 49 example hiper dsp software commands 1 select the type of command you want to perform from the command to execute or category drop-dow...
Page 75
Restarting other entities 75 figure 50 example media gateway command status color codes restarting other entities you can restart the gatekeepers, back-end servers, and sip proxy servers gracefully or by a hard restart. A graceful restart closes all open applications on the server, closes the operat...
Page 76
76 c hapter 4: m aintenance the entity has been successfully restarted. Restarting after parameter changes there are various parameters located under the configuration menu that can be set to meet your requirements. The parameters that are prefixed with an asterisks (*) require that the entity be re...
Page 77
Setting manual switchovers 77 for the back-end servers: ■ accounting server—restart 3com accounting service on ip telephony manager, or stop and start 3com voip accounting data service applet on the windows nt machine. ■ directory mapping server—restart 3com directory service on ip telephony manager...
Page 78
78 c hapter 4: m aintenance changing the snmp community strings the ip telephony manager default value for snmp community string is public for read only and private for read-write. To change the default values you must first change the community string on the devices and then on ip telephony manager...
Page 79
Changing the snmp community strings 79 a warning message appears verifying that you are about to change the community string and that this change will impact any user who tries to connect to the ip telephony manager chassis. Figure 54 community string warning message after you make this change, the ...
Page 80
80 c hapter 4: m aintenance 6 click ok. 7 if you changed the 3com snmp community strings on the gatekeeper, sip proxy server, or any of the back-end servers, you must restart the snmp agent. Refer to restarting other entities for more information. To change the ip telephony manager community string ...
Page 81
Displaying inventory information 81 displaying inventory information the ip telephony manager can display the installed components on your voip system; such as the serial numbers, hardware and software version, dip switch settings, and memory for each card. To display inventory information from the ...
Page 83: Rror
A e rror m essages overview error messages are divided into two types: ■ invocation errors —result from missing or invalid use of command syntax, and are reported immediately to stderr. They include: ■ command line target selection ■ chassis restore ■ chassis save ■ command tool ■ configuration tool...
Page 84
84 a ppendix : e rror m essages invocation errors this topic describes the error messages that can occur from a command syntax error. The invocation errors categories listed here are: ■ command line target selection ■ chassis restore ■ chassis save ■ command tool ■ configuration tool ■ software down...
Page 85
Invocation errors 85 channel range contains zero: target specification> a channel range includes 0 (e.G., s1c0-2). Time slot range contains zero: target specification> a time slot range contains zero. Expected slot-level target: target specification> the target specification began with a slot-level ...
Page 86
86 a ppendix : e rror m essages error, unexpected command line format the user did not supply an ip address, or (non-gui only) did not provide a filename. Command tool the following are the command tool error messages and what they indicate. Missing -e option the user did not choose a command to exe...
Page 87
Invocation errors 87 error: too many targets specified the user specified more than one ip address/slot-channel combination. (there is more than one white space-separated word in the target list.) invalid target name the target does not specify a valid ip address or host name. Software download the ...
Page 88
88 a ppendix : e rror m essages extension is not ’sdl ’fatal error (tcmsdl). Nonfatal error (xtcmsdl). This error occurs if the specified sdl file does not have the correct extension (*.Sdl). For tcmsdl, an error message is displayed on the screen or output to the log file, and then the utility term...
Page 89
Invocation errors 89 error: too many targets specified the user specified more than one ip address/slot-channel combination. (there is more than one white space-separated word in the target list.) invalid target format the target does not specify a valid ip address or host name. Missing -t option th...
Page 90
90 a ppendix : e rror m essages error: insufficient arguments a "-a", "-m", or "-d" directive ended unexpectedly. Error: no target supplied the user did not supply an ip address or host name on the command line. Error: invalid target format the target is not a valid ip address or host name, or conta...
Page 91
Execution errors 91 error constructing target specification...Hostname no longer valid? The user was prompted for target slot/channels using the chassis selection dialog. After targets were selected, the construction of a target failed, probably because an ip host name could not be found in the host...
Page 92
92 a ppendix : e rror m essages missing or invalid device.Dat file! Ip telephony manager has a corrupt device configuration schema, or other internal error. Missing or invalid software.Dat file! Ip telephony manager has a corrupt device configuration schema, or other internal error. Ip telephony man...
Page 93
Execution errors 93 the selected configuration file was saved from a chassis of a different size. Continue? Select either yes or no. .Whb file does not match chassis size fatal error unless -f (force mismatch) is specified. The selected configuration file is from a chassis with a different card conf...
Page 94
94 a ppendix : e rror m essages there are no commands for this type of device. The device configuration files do not list any commands for the target device. Invalid group name: name> the device configuration files do not list name> as a valid group. Invalid command: name> the device configuration f...
Page 95
Execution errors 95 cannot load between channel and card levels the "load from" source is at channel level while the target devices are at card level, or vice versa. Missing device configuration file there is no configuration schema file for the target devices. There are no configurable parameters f...
Page 96
96 a ppendix : e rror m essages cancel execution and exit program? Issued in a "yes/no" dialog when user quits from window frame while command/test is in progress. (gui, warning only) program exit during execution the command or test program was terminated (e.G., by a signal) while a command or test...
Page 97
Execution errors 97 selected device is not a modem the target slot is not a modem. Channel number out of range: number> the target channel number is invalid for the particular type of card. No ds0 assigned to modem. Test aborted. The modem does not have a time slot assignment and tone test is theref...
Page 98
98 a ppendix : e rror m essages community string and comment too long. Truncate? Issued in an "ok/cancel" dialog when a community string and/or comment is entered that is too long. (gui, warning only) trap query overrides -a/-m/-d the user specified both -q (query) and -a/-m/-d (table manipulation) ...
Page 99
Execution errors 99 filename> does not exist fatal error (tcmsdl). Nonfatal error (xtcmsdl). This error occurs if you selected a filename that does not exist. For tcmsdl, an error message is displayed on the screen or output to the log file, and then the utility terminates. For xtcmsdl, click ok to ...
Page 100
100 a ppendix : e rror m essages snmp set failed fatal error. This error occurs if the target card is communicating with the software download utility, but does not respond correctly to a snmp set command. The exact snmp error is displayed. For tcmsdl, an error message is displayed on the screen or ...
Page 101: Ommand
B c ommand l ine i nterface the command line interface consists of a number of non-interactive commands or utilities. These utilities are run at the command line from a shell prompt or a shell script. This appendix contains the following catatorgies of commands: ■ general syntax ■ ip telephony manag...
Page 102
102 a ppendix : c ommand l ine i nterface an "x" placed at the beginning of any ip telephony manager command omits command parameters and the target slot and channel designation-only the target ip address or hostname is required. Graphic user interfaces (guis), such as the ip telephony manager devic...
Page 103
General syntax 103 for instance, to display help for the software download utility, type the following command: tcmsdl -h [-c readcomm][-c writecomm] readcomm—read only community string writecomm—read/write community string used to specify the snmp community strings that have been assigned to the de...
Page 104
104 a ppendix : c ommand l ine i nterface s sets target slots in the specified range c sets target channels in the specified range. If omitted, execution at the card level is assumed. T sets target timeslots in the specified range. If omitted, execution at the channel (span line) level is assumed. W...
Page 105
Configuration 105 configuration the configuration command line interface (cli) uses the following syntax: tcmget command: tcmget [-h] [-l logfile] [-c readcomm] [-c writecomm] [-z] [-l] [-a] [-f file] [-f] [-g group [ parameter]...]... Target tcmset command: tcmset [-c readcomm] [-c writecomm] [-h] ...
Page 106
106 a ppendix : c ommand l ine i nterface -f ( filename) ■ tcmget: place the result output of the get operation in a file given by filename> (stdout can be designated using a filename of ’-’). ■ tcmset: read the output of the get operation from the file given by filename> and use it to set the value...
Page 107
Configuration 107 ( parameter) parameter whose value is to be printed (for tcmget) or set (for tcmset). (for example, ’serial number’.) each parameter should be separated by a space and requires proper shell quoting. At least one parameter should be supplied per group, unless -l (list parameters by ...
Page 108
108 a ppendix : c ommand l ine i nterface specifies slots or channels to be issued commands. Target has the following format: ip-host>:ss-range>[,cc-range>][,ss-range> [,c c-range>]...] where ip-host can be ip-dot notation, or a host name that is defined in the host database or /etc/hosts file. ■ :s...
Page 109
Actions/commands 109 actions/commands the command utility uses the following syntax: tcmcmd [-q] -e command -g group [-p parameter][-f][-p seconds]target query current command status (-q) where: [-q] displays the result of the last issued command the selected targets example: tcmcmd [-q] target -e c...
Page 110
110 a ppendix : c ommand l ine i nterface [-p seconds] sets amount of time, in seconds, between polls. Target follows general syntax. Note that if you omit a channel range, the command is assumed to be targeted at the slot level. This applies as well to timeslot designations for commands sent to t1 ...
Page 111
Snmp commands 111 snmp commands this describes how to set snmp community strings and how to monitor the snmp parameters. For security reasons, you can not view the community strings through ip telephony manager. Setting snmp community strings this section describes how to set the snmp community stri...
Page 112
112 a ppendix : c ommand l ine i nterface where: -l ( logfile) log file for system diagnostic messages. Gui default: log to unix syslog; cli default: stderr. Specify ’-’ (hyphen) to reverse these two behaviors. -h displays this help message. -c (readcomm) snmp read community string. -c (writecomm) s...
Page 113
Snmp commands 113 -g (bi) selects a group, followed by a list of parameters within that group which are to be retrieved. (for example, ’nmc identification’.) group specifications must appear after all other command arguments, and before the target. Group names are matched using substring comparison ...
Page 114
114 a ppendix : c ommand l ine i nterface tone test this section describes how to send and receive a tone test. Send tone test (-s) the following command causes the modem to send a tone of the specified frequency, duration, and amplitude. Tcmtone -s[-t][-s num][-p num] [freq[hz][ level[db]]]target w...
Page 115
Modem tests 115 receive tone test (-r) use the following command to receive a tone test: tcmtone -r [-t] [-s num] [-p num] target modem tests tcmtest -t test [-s num] target query current test status to query a modem to determine whether a test is already in progress, send the following command: tcm...
Page 116
116 a ppendix : c ommand l ine i nterface device save and restore the following commands are used to save and restore the configuration on the specified device. Save configuration tcmsave -f filenametarget where: filename the .Whb output file to which the configuration is stored. Target the ip addre...
Page 117
Software download 117 software download to run tcmsdl, issue the following command: tcmsdl [-s sdlfile] [-n nacfile] [-f] [-v] target where: sdlfile the sdl file name (if omitted, uses latest version available for card type). Nacfile the nac file name (if omitted, uses latest version available for c...
Page 118
118 a ppendix : c ommand l ine i nterface filename prefixes filename prefixes indicate which component type uses a given sdl or nac file. In most cases, the nac and sdl files for a given component have the same prefix. There are some exceptions, such as the single t1 card, as shown in the table belo...
Page 119
Feature enable 119 feature enable the following command line launches the feature enable option: tcminv [-l logfile] [-h] [-c readcomm] [-c writecomm] [ target] where: -l logfile the log file for system diagnostic messages. The gui log file default is the unix syslog file. The cli default is stderr....
Page 120
120 a ppendix : c ommand l ine i nterface where: ip-host can be in ip-dot notation, or a host name that is defined in the host database or \etc\hosts file. :s slot> the decimal number representing the location of the card in the chassis. Inventory use the following syntax to launch the inventory uti...
Page 121
Authorized station tool 121 -f filename the file to save inventory to (for cli only). Target specifies chassis host(s) to be displayed. The format for target is as follows: ip-host> can be in ip-dot notation, or a host name that is defined in the host database or /etc/hosts file. Authorized station ...
Page 122
122 a ppendix : c ommand l ine i nterface target an optional parameter that specifies the ip address or hostname of the nmc in which stations are being configured if no target is specified, the gui behaves as if -h was the only parameter passed. The format for target is as follows: ip-host> ip-hostc...
Page 123
Autoresponse 123 autoresponse the autoresponse can be invoked by the following syntax: tcmarsp [-e event] [-h] [target] where: -e event specifies which event to use as the default. The specified parameter must be a substring of one of the event descriptive strings described below. Substrings that ma...
Page 124
124 a ppendix : c ommand l ine i nterface slot level events and responses the following are the events and the responses to the events from the autoresponse command events: ■ module inserted ■ module re-initialized ■ module removed ■ module non-operational ■ module watchdog time-out responses (the "...
Page 125
Autoresponse 125 ■ reset by dte ■ dte transmit idle ■ block error count at threshold ■ fallback count at threshold ■ dial out login failure ■ dial out restricted number ■ dial in login failure ■ dial back restricted number ■ dial back using restricted modem ■ login attempt limit exceeded ■ user blac...
Page 126
126 a ppendix : c ommand l ine i nterface ■ test modem ■ test analog nic ■ test analog phone line ■ restore analog phone line ■ busy out ds0 - t1 slot (n) span (n) channel (n) ■ restore ds0 - t1 slot (n) span (n) channel (n) ■ modem software reset ■ terminate connection ■ busy out analog phone line ...
Page 127
Autoresponse 127 :s s-range> a decimal number of a range s1-s2 (where s1 and s2 are decimal numbers separated by a literal hyphen) representing the location of the card(s) in the chassis. :c c-range> a decimal number or a range c1-c2 (where c1 and c2 are decimal numbers separated by a literal hyphen...
Page 128
128 a ppendix : c ommand l ine i nterface.
Page 129: Lossary
C g lossary this appendix lists acronyms and terminology used in the commworks voip application. A-link access link. Ss7 signaling link used to connect the signaling transfer point (stp) and signaling switch point (ssp). Acf admission confirm—this is a call flow message. Ami alternate mark inversion...
Page 130
130 a ppendix : g lossary cd collision detection—a process where a simultaneous transmission has taken place. Workstations can determine if this has happened if they do not receive an acknowledgement from the receiving station within a certain amount of time. When this occurs, the workstation will t...
Page 131
Appendix : glossary 131 csma carrier sense multiple access—media-access mechanism wherein devices ready to transmit data first check the channel for a carrier. If no carrier is sensed for a specific period of time, a device can transmit. If two devices transmit at once, a collision occurs and is det...
Page 132
132 a ppendix : g lossary dram dynamic random access memory—the readable/writable memory used to store data in pcs. Dram stores each bit of information in a "cell" composed of a capacitor and a transistor. Drj disengage reject—this is a call flow message. Drq disengage request—this is a call flow me...
Page 133
Appendix : glossary 133 esd electrostatic discharge—discharge of stored static electricity that can damage electronic equipment and impair electrical circuitry, resulting in complete or intermittent failures. Esf extended super frame—framing type used on t1 circuits that consists of 24 frames of 192...
Page 134
134 a ppendix : g lossary ide integrated drive electronics—standard interface to the hard disk drive on the pc. Iec international electrotechnical commission—the international standards body for electrotechnology. Iis internet information server—microsoft windows nt web based server. It allows you t...
Page 135
Appendix : glossary 135 lrj location reject—this is a call flow message. Lrq location request—this is a call flow message. Mbp management bus protocol—this protocol was developed by 3com and is used in the nmc to communicate to the other cards in the total control chassis. Mfc multifrequency compell...
Page 136
136 a ppendix : g lossary oobman out-of-band manager—oobman is an application that runs on 3com windows nt components of the commworks ip telephony platform. It is designed to allow a user to dial into an nt device, using a terminal emulation program such as hyperterminal, and view or modify various...
Page 137
Appendix : glossary 137 rcf registration confirm—this is a call flow message. Risc reduced instruction set computer— central processing unit architecture that greatly reduces processing time by having fewer, simpler instructions programmed into rom, but allowing for complex processing by combining t...
Page 138
138 a ppendix : g lossary ss7 signaling system 7—a global standard for telecommunications as defined by the international telecommunication union (itu). The ss7 standard defines the procedure protocol by which network elements in the pstn exchange information over a digital signaling network. Sms sy...
Page 139
Appendix : glossary 139 tdma time division multiplexing adapter—a device that allows analog voice and data devices to work through an isdn connection. The terminal adapter is a protocol converter that adapts equipment not designed for isdn, such as phones, faxes, and modems. Tftp trivial file transf...
Page 140
140 a ppendix : g lossary zcs zero code suppression—used primarily with t1. The insertion of a one bit to prevent the transmission of eight consecutive zeros on an active line. When eight or more consecutive zeros are detected on the line, the system considers the line inactive, and releases the lin...
Page 141: Ndex
I ndex symbols .Cfm files 48 .Dmf 69 .Nvr files 44 , 47 a accessing ip telephony manager 49 acronyms 129 action/commands menu 59 adjusting column width 59 authorized access 66 authorized access list clearing 80 authorized station tool command 121 authorized stations configuring 32 authorized station...
Page 142
142 l led poll info menu 54 led status 54 linking objects in hp openview 26 m making changes 73 management functions 66 management station clearing 80 configuration 27 manual gatekeeper switchover 77 menu action/commands 59 authorized stations 66 autoresponse 61 chassis save all 52 community names 6...
Page 144
Commworks corporation 3800 golf road rolling meadows, il 60008 ©2001 3com corporation all rights reserved printed in the u.S.A. Part number 10044879.