- DL manuals
- 3Com
- Switch
- LANPLEX 2500 EXTENDEDPLEX®2500 EXTENDED
- User Manual
3Com LANPLEX 2500 EXTENDEDPLEX®2500 EXTENDED User Manual
Summary of LANPLEX 2500 EXTENDEDPLEX®2500 EXTENDED
Page 1
® lan plex ® 2500 e xtended s witching u ser g uide part no. 801-00343-000 published november 1996 revision 02.
Page 2
3com corporation ■ 5400 bayfront plaza ■ santa clara, california ■ 95052-8145 © 3com corporation, 1996. All rights reserved. No part of this documentation may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to make any derivative work (such as translation, transformation, or adaptation) without pe...
Page 3: Ontents
C ontents a bout t his g uide introduction 1 how to use this guide 1 conventions 2 lanplex 2500 documentation 3 documentation comments 5 p art i g etting s tarted 1 lan plex ® e xtended s witching f eatures about lanplex extended switching 1-1 using menus 1-2 bridge menu 1-3 ip menu 1-4 ipx menu 1-5...
Page 4: III
Modifying the default vlan 2-5 how the lanplex® system makes flooding decisions 2-5 vlan exception flooding 2-6 overlapped ip vlans 2-7 routing between vlans 2-8 vlan examples 2-10 example 1 2-10 example 2 2-11 p art iii a bout r outing p rotocols 3 b ridging and r outing in the lan plex ® s ystem w...
Page 5
5 r outing with ip m ulticast about ip multicast routing 5-1 igmp 5-1 dvmrp 5-2 the mbone 5-2 multicast routing algorithms 5-3 flooding 5-3 spanning trees 5-3 reverse path forwarding 5-4 pruning 5-5 multicast interfaces 5-5 dvmrp metric value 5-5 time-to-live (ttl) threshold 5-5 rate limit 5-6 multi...
Page 6
7 r outing in an a pple t alk ® e nvironment about appletalk® 7-1 appletalk® network elements 7-1 appletalk® networks 7-2 appletalk® nodes 7-2 named entities 7-2 appletalk® zones 7-3 seed routers 7-4 appletalk protocols 7-4 physical connectivity 7-5 the datagram delivery protocol (ddp) 7-6 end-to-en...
Page 7
Defining a static route 9-11 removing a route 9-12 flushing a route 9-12 setting the default route 9-12 removing the default route 9-13 administering the arp cache 9-13 displaying the arp cache 9-14 removing an arp cache entry 9-14 flushing the arp cache 9-15 administering atm arp servers 9-15 displ...
Page 8
Displaying routes 10-8 displaying the multicast cache 10-9 11 a dministering ipx r outing administering interfaces 11-2 displaying ipx interfaces 11-3 defining an ipx interface 11-3 modifying an interface 11-4 removing an interface 11-4 administering routes 11-5 displaying the routing table 11-6 def...
Page 9: (Rmon)
Configuring forwarding 12-11 configuring checksum 12-12 pinging an appletalk node 12-12 viewing appletalk statistics 12-13 displaying ddp statistics 12-13 displaying rtmp information 12-14 displaying zip information 12-15 displaying nbp information 12-17 p art v r emote m onitoring (rmon) and the la...
Page 10
Support from 3com a-4 returning products for repair a-4 i ndex.
Page 11: Bout
A bout t his g uide introduction the lanplex® 2500 extended switching user guide provides information about the features included with the lanplex extended switching software. These features include ip, ip multicast, classical ip over atm, ipx, and appletalk routing, virtual lan (vlan) configuration...
Page 12
2 a bout t his g uide conventions table 1 and table 2 list conventions that are used throughout this guide. Ipx routing and its protocols chapter 6 appletalk routing, network elements, and protocols chapter 7 how to administer vlans chapter 8 how to administer ip routing chapter 9 how to administer ...
Page 13
Lanplex 2500 documentation 3 lanplex 2500 documentation the following documents comprise the lanplex 2500 documentation set. If you want to order a document that you do not have or order additional documents, contact your sales representative for assistance. ■ lanplex® 2500 unpacking instructions de...
Page 14
4 a bout t his g uide ■ lanplex® 2500 software release notes provide information about the software release, including new features and bug fixes. It also provides information about any changes to the lanplex system’s documentation. (shipped with system) ■ lanplex® 2500 getting started describes all...
Page 15
Documentation comments 5 ■ module installation guides provide an overview, installation instructions, led status information, and pin-out information for the particular option module. (shipped with individ- ual modules) documentation comments your suggestions are very important to us and will help m...
Page 16
6 a bout t his g uide.
Page 17: Lan
1 lan plex ® e xtended s witching f eatures this chapter provides an overview of the extended switching software, and describes the enhanced administration console menus. About lanplex extended switching the lanplex extended switching software replaces your existing lanplex software and adds new fun...
Page 18
1-2 c hapter 1: lan plex ® e xtended s witching f eatures using menus when you gain access to the administration console, the top-level menu appears. The extended switching software contains top-level menus and additions to the bridge and ip menu options not available with intelligent switching soft...
Page 19
Using menus 1-3 bridge menu from the bridge menu, you can view information about and configure ethernet lans, including vlans. Figure 1-1 shows the bridge menu. Figure 1-1 bridge menu hierarchy top-level menu bridge menu interface menu system display summary ethernet mode detail fddi ipfragmentation...
Page 20
1-4 c hapter 1: lan plex ® e xtended s witching f eatures ip menu from the ip menu, you can view information about and configure internet protocol (ip) interfaces and routes as well as ip multicast routing. You can administer the address resolution protocol (arp), the routing information protocol (r...
Page 21
Using menus 1-5 ipx menu from the ipx menu, you can view information about and configure internet packet exchange (ipx) interfaces, routes, and servers. You can also administer the routing information protocol (rip), enhanced rip mode, service advertising protocol (sap), and statistics. Figure 1-3 s...
Page 22
1-6 c hapter 1: lan plex ® e xtended s witching f eatures appletalk menu from the appletalk menu, you can view information about and configure appletalk interfaces, routes, and zones. You can also administer the appletalk address resolution protocol (aarp), appletalk forwarding, and statistics. Figu...
Page 23: Vlan
2 vlan s on the lan plex ® s ystem this chapter contains: ■ a description of virtual lan (vlan) concepts and their operational aspects in the lanplex® 2500 system ■ examples of vlan configurations about vlans the vlan concept in lan technology helps minimize broadcast and multicast traffic. It also ...
Page 24
2-2 c hapter 2: vlan s on the lan plex ® s ystem the data contained in the frames. Port groups are useful when traffic patterns are known to be directly associated with particular ports. They can benefit the user by restricting traffic based on a set of simple rules. Mac address group vlans vlans al...
Page 25
About vlans 2-3 layer 3 subnet address information. Protocol-sensitive vlans allow the restriction of flood traffic for both routable and nonroutable protocols. They have a relatively simple configuration comprising one or more protocols and groups of switch ports. These protocol-sensitive vlans ope...
Page 26
2-4 c hapter 2: vlan s on the lan plex ® s ystem switch ports a group of switch ports is any combination of switch ports on the lanplex system. Included are switch ports created as atm lan emulation clients (atm lecs). Vlans do not support media implementations that do not run over switch (bridge) p...
Page 27
About vlans 2-5 default vlan when you start up the lanplex system, the system automatically creates a vlan interface called the default vlan. Initially, the default vlan includes all of the switch ports in the system. In the lanplex system, the default vlan serves to define: ■ the flood domain for p...
Page 28
2-6 c hapter 2: vlan s on the lan plex ® s ystem this example shows how flooding decisions are made according to vlans set up by protocol (assuming an 18-port switch): vlan exception flooding if data arrives on a switch port for a certain protocol and vlans for that protocol are defined in the syste...
Page 29
About vlans 2-7 overlapped ip vlans the lanplex system also gives you the ability to assign network layer information to ip vlans. This capability allows network administrators to manage their vlans by subnet. Flooding decisions are made by first matching the incoming frame using the protocol (ip) a...
Page 30
2-8 c hapter 2: vlan s on the lan plex ® s ystem as shown in this example, when the subnet address of an ip packet does not match any subnet address of any defined ip vlan in the system, it is flooded to all of the ip vlans that share the source switch port, in this case, port 6. Routing between vla...
Page 31
About vlans 2-9 if layer 3 information is provided in the ip vlan for which you are configuring an ip interface, the subnet portion of both addresses must be compatible. For example: ip vlan subnet 157.103.54.0 with subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 ip host interface address 157.103.54.254 with subnet ma...
Page 32
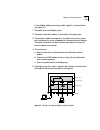
2-10 c hapter 2: vlan s on the lan plex ® s ystem vlan examples example 1 figure 2-1 is an example of a simple configuration that contains three protocol-sensitive vlans (2 ip and 1 ipx) that share a high-speed fddi link. The end-stations and servers are on 10mbps ports with traffic segregated by pr...
Page 33
About vlans 2-11 example 2 figure 2-2 is an example of a configuration that contains two different protocol-sensitive vlans (ip and ipx) with servers on separate high-speed 100base-t ports. The end-station clients share the same switch ports, yet the ip and ipx traffic stays separate. See figure 2-2...
Page 34
2-12 c hapter 2: vlan s on the lan plex ® s ystem.
Page 35: Ridging
3 b ridging and r outing in the lan plex ® s ystem this chapter shows how the lanplex® system operates in a subnetworked routing environment and describes the lanplex routing methodology — specifically, how the lanplex bridging and routing model compares with traditional models. What is routing? Rou...
Page 36
3-2 c hapter 3: b ridging and r outing in the lan plex ® s ystem figure 3-1 traditional architecture of a routed network lanplex in a subnetworked environment the lanplex system allows you to fit ethernet switching capability into highly subnetworked environments. When you put the lanplex system int...
Page 37
What is routing? 3-3 integrating bridging and routing the lanplex system integrates bridging and routing. Multiple switch ports can be assigned to each subnet. See figure 3-3. Traffic between ports assigned to the same subnet is switched transparently using transparent bridging or express switching ...
Page 38
3-4 c hapter 3: b ridging and r outing in the lan plex ® s ystem in the traditional model, if you want to increase the level of segmentation in your network, you must create additional subnets and assign new network addresses to your existing hosts. Bridging and routing models the way routing is imp...
Page 39
Bridging and routing models 3-5 figure 3-4 bridging in the traditional bridging and routing model in the traditional bridging and routing model, a packet is routed as follows (see figure 3-5): 1 the packet enters the bridge or router. 2 the bridge or router determines that the packet belongs to a re...
Page 40
3-6 c hapter 3: b ridging and r outing in the lan plex ® s ystem lanplex bridging and routing model the lanplex 2500 system uses the destination mac address to determine whether it will bridge or route a packet. Before a host system sends a packet to another host, it compares its own network address...
Page 41
Bridging and routing models 3-7 in the lanplex bridging and routing model, a packet is routed as follows (see figure 3-7): 1 the packet enters the lanplex system. 2 the packet’s destination address is examined by the bridging layer. 3 the destination address corresponds to the address of one of the ...
Page 42
3-8 c hapter 3: b ridging and r outing in the lan plex ® s ystem.
Page 43: Outing
4 r outing with ip t echnology this chapter gives an overview of ip routing technology, specifically defining: ■ what ip routing involves ■ what elements are necessary for ip routers to effectively transmit packets ■ how ip routing transmission errors are detected and resolved ■ routing with classic...
Page 44
4-2 c hapter 4: r outing with ip t echnology when an ip router sends a packet, it does not know the complete path to a destination — only the next hop. Each hop involves three steps: ■ the ip routing algorithm computes the next hop ip address, and next router interface, using the routing table entri...
Page 45
Elements of ip routing 4-3 address classes the boundary of the network part and the host part depends on the class that the central agency assigns to your network. The primary classes of ip addresses are class a, class b, and class c. ■ class a addresses — have 8 bits for the network part and 24 bit...
Page 46
4-4 c hapter 4: r outing with ip t echnology figure 4-3 how a subnet mask is applied to the ip address an example of an ip address that includes network, subnet, and host parts is 158.101.230.52 with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 . This address is divided as follows: ■ 158.101 is the network part ■...
Page 47
Elements of ip routing 4-5 figure 4-4 router interfaces in the lanplex system routing table a routing table allows a router or host to determine how to send a packet toward the packet’s ultimate destination. The routing table contains an entry for every destination network, subnet, or host to which ...
Page 48
4-6 c hapter 4: r outing with ip t echnology figure 4-5 example of a routing table in the lanplex routing model routing table information is generated and updated in either of the following ways: ■ statically — you manually enter routes, which do not change until you change them (that is, they will ...
Page 49
Elements of ip routing 4-7 an active router sends a rip message every 30 seconds. This message contains both the ip address and a metric (the distance to the destination from that router) for each destination. In rip, each router that a packet must travel through to reach a destination equals one ho...
Page 50
4-8 c hapter 4: r outing with ip t echnology protocol. The two key elements of the arp request are the target and source addresses for both the hardware (mac addresses) and the protocol (ip addresses). See figure 4-7. Figure 4-7 example of an arp request packet when the devices on the network receiv...
Page 51
Ip routing transmission errors 4-9 ip routing transmission errors because each router only knows about the next hop, it is not aware of problems that might be further “down the road” toward the destination. Destinations can be unreachable if: ■ hardware is temporarily out of service ■ you inadverten...
Page 52
4-10 c hapter 4: r outing with ip t echnology routing with classical ip over atm lanplex extended switching software supports classical ip routing over atm arp in an atm network. Classical ip over atm uses logical ip subnets (liss) to forward packets within the network environment. See the lanplex® ...
Page 53
Ip routing references 4-11 forwarding to nodes within an lis nodes can forward packets directly to other nodes in the same lis. To forward a packet within the same lis, the sending node requests a translation from the destination ip address to the corresponding atm address from the atm arp server. ■...
Page 54
4-12 c hapter 4: r outing with ip t echnology.
Page 55: Outing
5 r outing with ip m ulticast this chapter describes the ip multicast routing implementation on the lanplex® system. About ip multicast routing ip multicast routing is an extension of the internet protocol. Multicast routing allows a router or switch to send packets to a specific group of hosts with...
Page 56
5-2 c hapter 5: r outing with ip m ulticast dvmrp the distance vector multicast routing protocol (dvmrp) establishes the multicast delivery path over a series of routing devices. Dvmrp is a simple distance vector routing protocol, similar to the ip routing information protocol (rip). Multicast route...
Page 57
Multicast routing algorithms 5-3 multicast routing algorithms the lanplex system uses three algorithms that support multicast routing: ■ flooding ■ spanning trees ■ reverse path forwarding flooding several types of flooding algorithms exist, but they all share the same general principles: a node in ...
Page 58
5-4 c hapter 5: r outing with ip m ulticast figure 5-1 shows a simple network with five links. Figure 5-1 simple network implemented without using spanning tree a spanning tree for this network consists of links 1, 2, 3, and 4. See figure 5-2. Figure 5-2 spanning tree algorithm implemented to block ...
Page 59
Multicast interfaces 5-5 pruning pruning is a method used in the rpf algorithm to forward packets to a spanning tree only if group members exist in the tree. This method results in fewer spanning trees, but it requires dynamic updates to the routing table. Nodes that are at the border of the network...
Page 60
5-6 c hapter 5: r outing with ip m ulticast rate limit the rate limit determines how many multicast packets can travel over the interface in kilobytes-per-second. The lanplex system drops multicast traffic that travels faster than this rate. The default is set to 0, which implies no rate limit is se...
Page 61: Outing
This chapter provides an overview of ipx routing, including: ■ what part ipx plays in the netware environment ■ how ipx works ■ what elements are necessary for ipx routers to transmit packets effectively ipx routing in the netware ® environment the netware® network operating system was developed and...
Page 62
6-2 c hapter 6: r outing with ipx figure 6-1 netware protocols and the osi reference model the lanplex system uses the following protocols for routing in a netware environment: ■ internet packet exchange (ipx) ■ routing information protocol (rip) ■ service advertisement protocol (sap) internet packe...
Page 63
Ipx routing in the netware® environment 6-3 routing information protocol (rip) rip allows the exchange of routing information on a netware network. Ipx routers use rip to dynamically create and maintain their routing tables. Rip allows one router to exchange routing information with a neighboring ro...
Page 64
6-4 c hapter 6: r outing with ipx how ipx routing works a router operates at the network layer of the osi reference model. This means that it receives its instructions to route packets from one segment to another from a network-layer protocol. Ipx, with the help of rip, performs these network layer ...
Page 65
How ipx routing works 6-5 the packet format consists of the following elements: ■ checksum — the ipx packet begins with a 16-bit checksum field that is set to 1 s. ■ packet length — this 16-bit field contains the length, in bytes, of the complete network packet. This field includes both the ipx head...
Page 66
6-6 c hapter 6: r outing with ipx ipx packet delivery on a netware network, the successful delivery of a packet depends both on the proper addressing of the packet and on the internetwork configuration. Packet addressing is handled in the packet’s media access control (mac) protocol header and ipx h...
Page 67
How ipx routing works 6-7 to find this router, the sending node broadcasts a rip packet requesting the best route to the destination node’s network number. The router residing on the sending node’s segment with the shortest path to the destination segment responds to the rip request. The router’s re...
Page 68
6-8 c hapter 6: r outing with ipx the elements of ipx routing ipx routers use the following elements to transmit packets over an intranetwork: ■ router interfaces ■ routing tables ■ service advertising protocol (sap) router interfaces a router interface is the connection between the router and the n...
Page 69
The elements of ipx routing 6-9 ■ hops to network — provides the number of routers that must be crossed to reach the network segment. ■ ticks to network — provides an estimate of the time necessary to reach the destination segment. ■ node — the node address of the router that can forward packets to ...
Page 70
6-10 c hapter 6: r outing with ipx system uses rip (one of the most widely used igps), to dynamically build its routing tables. Rip operates in terms of active and passive devices. The active devices , usually routers, broadcast their rip messages to all devices in a network; they update their own r...
Page 71
The elements of ipx routing 6-11 a workstation must first know a server’s network address before it can initiate a session with a file server. Sap packet structure sap uses ipx and the medium-access protocols for its transport. The packet structure allows the following functions: ■ a workstation req...
Page 72
6-12 c hapter 6: r outing with ipx a sap packet consists of the following fields: ■ operation — this field indicates the type of operation the sap packet performs. It can be set to one of the following values: 1=request 2=response 3=get nearest server request 4=get nearest server response ■ server e...
Page 73
The elements of ipx routing 6-13 the sap broadcasts that servers and routers send are local and, therefore, only received by sap agents on their connected segments. However, sap agents periodically broadcast their server information so that all sap agents on the internetwork have information about a...
Page 74
6-14 c hapter 6: r outing with ipx static servers. A static server is one you manually configure in the server information table. Static servers are useful in environments where no routing protocol is used or where you want to override some of the servers generated with a routing/server protocol. Be...
Page 75
The elements of ipx routing 6-15 elapsed since information was received concerning a particular table entry. Since this information is either new or changed, the sap agent that receives this information immediately passes it on, and the change is quickly learned throughout the internetwork. Sap requ...
Page 76
6-16 c hapter 6: r outing with ipx.
Page 77: Outing
This chapter provides an overview of appletalk® routing, and includes these topics: ■ appletalk network elements ■ appletalk protocols ■ about aarp about appletalk® appletalk is a suite of protocols defined by apple computer, inc., for connecting computers, peripherals devices, and other equipment o...
Page 78
7-2 c hapter 7: r outing in an a pple t alk ® e nvironment appletalk® networks a network in an appletalk internet is a cable segment attached to a router. Each network is identified by a network number or range of network numbers. The network administrator assigns these numbers from a range of valid...
Page 79
Appletalk® network elements 7-3 appletalk® zones an appletalk zone is a logical collection of nodes on an appletalk internet. A zone can include all nodes in a single network or a collection of nodes in different networks. You assign a unique name to each zone to identify it in the internet. Figure ...
Page 80
7-4 c hapter 7: r outing in an a pple t alk ® e nvironment quickly within the zone because the zone includes fewer devices than the entire internet does. Seed routers a seed router initializes the internet with appletalk configuration information, including network numbers and zone names. The seed r...
Page 81
Appletalk protocols 7-5 figure 7-2 appletalk protocols and the osi reference model the appletalk six-layer protocol suite is not fully compliant with the osi seven-layer reference model. However, appletalk provides many of the functions and services provided by osi. Note that appletalk has no specif...
Page 82
7-6 c hapter 7: r outing in an a pple t alk ® e nvironment because it is closely related to the ethernet and token ring laps. This protocol is usually included in the definition of each lap, so it does not appear in the reference model. See the section “about aarp” later in this chapter for more inf...
Page 83
Appletalk protocols 7-7 each router builds a routing table that is the basis of dynamic routing operations in an appletalk internet. Every 10 seconds, each router sends an rtmp data packet to the network. Routers use the information that they receive in the rtmp broadcasts to build their routing tab...
Page 84
7-8 c hapter 7: r outing in an a pple t alk ® e nvironment figure 7-3 a simple appletalk network you can view the appletalk routing tables in your network through the administration console. Appletalk echo protocol (aep). Appletalk nodes use the aep to send datagrams to other nodes in the network. I...
Page 85
Appletalk protocols 7-9 appletalk transaction protocol (atp). This protocol, along with the appletalk data stream protocol (adsp), ensures that ddp packets are delivered to a destination without any losses or corruption. Name binding protocol (nbp). This protocol translates alphanumeric entity names...
Page 86
7-10 c hapter 7: r outing in an a pple t alk ® e nvironment appletalk data stream protocol (adsp). The adsp works with the atp to ensure reliable data transmission. Unlike atp, however, adsp provides full-duplex byte-stream delivery. This means that two nodes can communicate simultaneously. Asdp als...
Page 87
About aarp 7-11 the aarp maintains an address mapping table (amt) with the most recently used hardware addresses and their corresponding aarp addresses. If an address is not in this table, aarp sends a request to the protocol address and adds the hardware address to the table when the destination no...
Page 88
7-12 c hapter 7: r outing in an a pple t alk ® e nvironment.
Page 89: Dministering
8 a dministering vlan s this chapter describes how to display information about vlans and how to configure vlans. Through the administration console, you can: ■ display summary or detailed information on vlans ■ define or modify a vlan definition ■ delete a vlan definition displaying vlan informatio...
Page 90
8-2 c hapter 8: a dministering vlan s index name layer 3 1 none 2 eastgroup 158.101.111.16 255.255.255.0 3 westgroup none 4 northgroup 158.101.112.14 255.255.255.0 example of a detailed display for the vlans: select menu option (bridge/vlan): detail index protocol identifier ports 1 default 0 1-17 2...
Page 91
Defining vlan information 8-3 defining vlan information follow these steps to create a vlan definition: 1 from the top level of the administration console, enter: bridge vlan define 2 enter the appropriate protocol suite: (ip, ipx, appletalk, xns, decnet, sna, banyan, x.25, netbios, netbeui, default...
Page 93
Removing vlan information 8-5 example: select menu option (bridge/vlan): modify select vlan interface [1-2]: 2 protocol suite (ip,ipx,appletalk,xns,decnet,sna, banyan,x.25,netbios,netbeui,default) [appletalk]: ip vlan identifier [1]: 2 vlan name [sales]: ports 1=fddi, 2-17=ethernet enter port(s) (1-...
Page 94
8-6 c hapter 8: a dministering vlan s.
Page 95: Dministering
9 a dministering ip r outing this chapter describes how to set up your lanplex® system to use the internet protocol (ip). For more information about how ip works, see part iii of this guide. You can display or configure the following ip characteristics on your lanplex system: ■ ip interfaces ■ route...
Page 96
9-2 c hapter 9: a dministering ip r outing lis interfaces a logical ip subnet (lis) interface supports logical ip over atm. You define lis interfaces for the ports on atm modules only. See the chapter 11 of the lanplex® 2500 operation guide for more information about the atm protocol. See the lanple...
Page 97
Administering interfaces 9-3 this option, the system displays a list of available vlan indexes and the bridge ports associated with them. ■ lis interface — when you select lis as the interface type, the administration console prompts you for lis interface information. The information you enter depen...
Page 98
9-4 c hapter 9: a dministering ip r outing example summary display: example detail display: defining an ip lis interface when you define an ip lis interface, you specify several general ip interface characteristics and ip lis characteristics. Before you define an ip lis interface with svcs, be sure ...
Page 99
Administering interfaces 9-5 the console prompts you for the interface’s parameters. To use the value in brackets, press [return] at the prompt. 2 enter the ip address of the interface. 3 enter the subnet mask of the network to which the interface is to be connected. 4 enter the cost value of the in...
Page 100
9-6 c hapter 9: a dministering ip r outing defining an ip vlan interface when you define an ip vlan interface, you specify several interface characteristics, as well as the index of the vlan associated with the interface. You must first define a vlan, as described in chapter 8, administering vlans, ...
Page 101
Administering interfaces 9-7 modifying an interface you might want to change the configuration of an interface you have already defined. You can add one or more advertisement addresses or pvcs to an interface through the addadvertisement and addpvc commands as well as through the ip interface modify...
Page 102
9-8 c hapter 9: a dministering ip r outing adding an advertisement address this command adds an advertisement address to the advertisement address list associated with the interface. To add an advertisement address: 1 from the top level of the administration console, enter: ip interface addadvertise...
Page 103
Administering routes 9-9 adding a permanent virtual circuit (pvc) this command adds a pvc to an lis interface. To add a pvc: 1 from the top level of the administration console, enter: ip interface addpvc 2 enter the index interface number that you want to associate with the pvc. 3 enter the virtual ...
Page 104
9-10 c hapter 9: a dministering ip r outing more than one routing table entry matching an address, it uses the most specific route, which is the route with the most bits set in its subnet mask. For example, the route to a subnet within a destination network is more specific than the route to the des...
Page 105
Administering routes 9-11 displaying the routing table you can display a switching module’s routing table to determine which routes are configured and whether the routes are operational. To display the contents of the routing table, enter the following command string from the top level of the admini...
Page 106
9-12 c hapter 9: a dministering ip r outing example: enter destination ip address: 158.101.4.0 enter subnet mask [255.255.0.0]: 255.255.255.0 enter gateway ip address: 158.101.2.8 removing a route to remove a route: 1 from the top level of the administration console, enter: ip route remove 2 enter t...
Page 107
Administering the arp cache 9-13 to statically configure the default route: 1 from the top level of the administration console, enter: ip route default 2 enter the gateway ip address of the route. The default route is immediately added to the routing table. Removing the default route to remove a def...
Page 108
9-14 c hapter 9: a dministering ip r outing displaying the arp cache you can display the contents of the arp cache for your system. To display the contents of the arp cache, enter the following command string from the top level of the administration console: ip arp display example display of the con...
Page 109
Administering atm arp servers 9-15 flushing the arp cache you might want to delete all entries from the arp cache if the mac address has changed. To remove all entries from the arp cache, from the top level of the administration console, enter: ip arp flush the arp cache entries are immediately remo...
Page 110
9-16 c hapter 9: a dministering ip r outing defining an atm arp server determine the location of the atm arp server you want to use. You can define the atm arp server externally on another lanplex system or on an atm switch, such as 3com’s cellplex™ 7000 system. 1 to define an atm arp server, from t...
Page 111
Administering atm arp servers 9-17 displaying the atm arp cache to display the contents of the atm arp cache, from the top level of the administration console, enter: ip atmarpserver arp display example: removing an atm arp cache entry to remove an entry from the atm arp cache, from the top level of...
Page 112
9-18 c hapter 9: a dministering ip r outing flushing the atm arp cache to remove all entries from the atm arp cache, from the top level of the administration console, enter: ip atmarpserver arp flush the atm arp cache entries are immediately removed from the table. Administering udp helper udp helpe...
Page 113
Administering udp helper 9-19 displaying udp helper information you can display the hop count and threshold configuration and list the ports with their ip forwarding addresses that are defined for your lanplex system. To display udp helper information, enter the following command string from the top...
Page 114
9-20 c hapter 9: a dministering ip r outing setting the bootp hop count limit you can set the maximum hop count for a packet to be forwarded through the router. The range is 0 through 16. The default is 4. To set the hop count limit: 1 from the top level of the administration console, enter: ip udph...
Page 115
Enabling and disabling icmp router discovery 9-21 enabling and disabling icmp router discovery the internet control message protocol (icmp) router discovery protocol (rfc 1256) allows an appropriately configured end station to locate one or more routers on the lan to which it is attached. The end st...
Page 116
9-22 c hapter 9: a dministering ip r outing rip default mode by default, rip operates in passive mode. To set the rip operating mode: 1 from the top level of the administration console, enter: ip rip 2 enter the rip mode ( off , passive , or active ). To use the value in brackets, press [return] at ...
Page 117
Displaying ip statistics 9-23 displaying ip statistics to display ip statistics, enter the following from the top level of the administration console: ip statistics example: ip routing is enabled, rip is active, icmp router discovery is disabled. Inreceives forwdatagrams indelivers outrequests 51213...
Page 118
9-24 c hapter 9: a dministering ip r outing.
Page 119: Dministering
10 a dministering ip m ulticast r outing this chapter describes how to set up your lanplex® system to use ip multicast routing. You should have previously defined ip interfaces and routes as described in chapter 9: administering ip routing, before you define any ip multicast interfaces. This appendi...
Page 120
10-2 c hapter 10: a dministering ip m ulticast r outing enabling and disabling dvmrp dvmrp is the simple distance vector multicast routing protocol, similar to the ip routing information protocol. Multicast routers exchange distance vector updates that contain lists of destinations and the distance ...
Page 121
Administering ip multicast interfaces 10-3 when you select the igmp option, the interface prompts you to enable or disable igmp snooping mode and igmp query mode. Both are enabled by default. Under most conditions, igmp snooping mode and igmp query mode should remain enabled. To enable or disable ig...
Page 122
10-4 c hapter 10: a dministering ip m ulticast r outing rate limit the rate limit determines how fast multicast traffic can travel over the interface in kilobytes per second. Multicast traffic may not exceed this rate limit or the lanplex system will drop packets in order to maintain the set rate. T...
Page 123
Administering ip multicast interfaces 10-5 disabling multicast interfaces to disable multicast routing on an interface: 1 from the top level of the administration console, enter: ip multicast interface disable 2 enter the index number of the interface you want to disable. The interface is disabled. ...
Page 124
10-6 c hapter 10: a dministering ip m ulticast r outing administering multicast tunnels a multicast tunnel allows multicast packets to cross several unicast routers to a destination router that supports multicast. A tunnel has two end points. The local end point is associated with an interface on th...
Page 125
Administering multicast tunnels 10-7 defining a multicast tunnel to define an ip multicast tunnel: 1 from the top level of the administration console, enter: ip multicast tunnel define 2 enter the index number(s) of the interface(s) with which you want to associate a multicast tunnel. 3 enter the ip...
Page 126
10-8 c hapter 10: a dministering ip m ulticast r outing displaying routes to display all available routes in the ip multicast routing table: 1 from top level of the administration console, enter: ip multicast routedisplay the dvmrp status and igmp status appear on the screen. The following display s...
Page 127
Displaying the multicast cache 10-9 displaying the multicast cache the ip multicast cache contains the ip source address and destination address for packets observed on the system. The multicast cache shows you how information is routed over interfaces and ports in your system. To display all learne...
Page 128
10-10 c hapter 10: a dministering ip m ulticast r outing example: enter multicast source address [131.188.0.0] enter multicast group address [244.2.0.2] dvmrp is enabled, igmp snooping is enabled the following display shows the multicast cache configuration: multicast routing cache table (125 entrie...
Page 129
Displaying the multicast cache 10-11 table 10-2 describes the fields in the cache display. Table 10-2 information in the cache display field description origin the source of the incoming packets. Entries preceded by an angle bracket (>) indicate a multicast subnetwork. Entries without an angle brack...
Page 130
10-12 c hapter 10: a dministering ip m ulticast r outing.
Page 131: Dministering
11 a dministering ipx r outing this chapter describes how to set up your lanplex® system to use the internet packet exchange (ipx) protocol to route packets. For more information about how ipx works, see part iii of this guide. You can display and configure the following on your lanplex system: ■ ip...
Page 132
11-2 c hapter 11: a dministering ipx r outing administering interfaces an ipx interface defines the relationship between an ipx virtual lan (vlan) and the ipx network. Every ipx interface has one ipx vlan associated with it. Each switching module has one ipx interface defined for each subnet directl...
Page 133
Administering interfaces 11-3 displaying ipx interfaces you can display a table that shows all ipx interfaces and their parameter settings configured for the system. To display ipx interface information: from the administration console top-level menu, enter: ipx interface display as shown in the fol...
Page 134
11-4 c hapter 11: a dministering ipx r outing example: modifying an interface you might want to change the configuration of an interface that you have already defined. To modify an ipx interface: 1 from the administration console top-level menu, enter: ipx interface modify you are prompted for the i...
Page 135
Administering routes 11-5 administering routes your system maintains a table of routes to other ipx networks. You can either use the routing information protocol (rip) to exchange routing information automatically or make static entries in this table using the administration console. Each routing ta...
Page 136
11-6 c hapter 11: a dministering ipx r outing displaying the routing table you can display the routing tables for the system to determine which routes are configured and if they are operational. To display the contents of the routing table, from the administration console top-level menu, enter: ipx ...
Page 137
Administering routes 11-7 5 enter the node address of the route. A static route is defined in the following example: removing a route to remove a route: 1 from the administration console top-level menu, enter: ipx route remove 2 enter the 4-byte ipx network address. The route is immediately deleted ...
Page 138
11-8 c hapter 11: a dministering ipx r outing administering servers your system maintains a table of servers that reside on other ipx networks. You can either use the service advertising protocol (sap) to exchange server information automatically or make static entries in this server table using the...
Page 139
Administering servers 11-9 displaying the server table you can display the server table for the system to determine which servers are learned and if they are operational. To display the contents of the server table, from the administration console top-level menu, enter: ipx server display defining a...
Page 140
11-10 c hapter 11: a dministering ipx r outing 8 enter the number of hops to the server. Example: removing a server to remove a server: 1 from the administration console top-level menu, enter: ipx server remove 2 enter the service type of the server. 3 enter the service name of the server. The serve...
Page 141
Setting ipx forwarding 11-11 setting ipx forwarding you can control whether the system forwards or discards ipx packets addressed to other routers. When you enable ipx forwarding, the system acts as a normal ipx router, forwarding ipx packets from one network to another when required. When you disab...
Page 142
11-12 c hapter 11: a dministering ipx r outing rip default mode by default, rip is off . To set the rip operating mode: 1 from the administration console top-level menu, enter: ipx rip 2 enter the rip mode ( off , passive , or active ). To use the value in brackets, press [return] at the prompt. Set...
Page 143
Setting the sap mode 11-13 setting the sap mode you can select a sap mode that is appropriate for your network. Sap can operate in any of three modes: ■ off — the system ignores all incoming sap packets and does not generate any sap packets of its own. ■ passive — the system processes all incoming s...
Page 144
11-14 c hapter 11: a dministering ipx r outing displaying statistics the administration console allows you to display four types of ipx-related statistics: ■ ipx summary statistics ■ ipx rip statistics ■ ipx sap statistics ■ ipx forwarding statistics displaying ipx summary statistics to display ipx ...
Page 145
Displaying statistics 11-15 displaying ipx rip statistics to display ipx rip statistics, from the administration console top-level menu, enter: ipx statistics rip example below: table 11-2 describers the ipx rip statistics. Top-level menu system ethernet fddi atm bridge ip ➧ ipx appletalk snmp analy...
Page 146
11-16 c hapter 11: a dministering ipx r outing displaying ipx sap statistics to display ipx sap statistics, from the administration console top-level menu, enter: ipx statistics sap example: table 11-1 describes the ipx sap statistics. Top-level menu system ethernet fddi atm bridge ip ➧ ipx appletal...
Page 147
Displaying statistics 11-17 displaying ipx forwarding statistics to display ipx forwarding statistics, from the administration console top-level menu, enter: ipx statistics forwarding example: table 11-4 describes the ipx forwarding statistics. Top-level menu system ethernet fddi atm bridge ip ➧ ipx...
Page 148
11-18 c hapter 11: a dministering ipx r outing table 11-4 ipx forwarding statistics field description received number of ipx forwarding packets received transmitted number of ipx forwarding packets transmitted forwarded number of ipx packets forwarded by the ipx router hdr errors number of ipx packe...
Page 149: Dministering
12 a dministering a pple t alk ® r outing this chapter describes how to set up your lanplex® system to use the appletalk protocol to route packets. For more information on how appletalk routing works, see chapter 7: routing with appletalk. You can display and configure the following: ■ appletalk int...
Page 150
12-2 c hapter 12: a dministering a pple t alk ® r outing administering interfaces an appletalk interface defines the relationship between an appletalk virtual lan (vlan) and the appletalk network. Every appletalk interface has one appletalk vlan associated with it. Each switching module has one appl...
Page 151
Administering interfaces 12-3 displaying appletalk interfaces you can display a table that shows all appletalk interfaces and their parameter settings configured for the system. To display the appletalk interfaces defined on the router, from the administration console top-level menu, enter: appletal...
Page 152
12-4 c hapter 12: a dministering a pple t alk ® r outing 6 enter the zone name. You can enter up to 16 zone names per interface. 7 type q after entering all the zone names. 8 enter the index of the appletalk vlan associated with this interface. Example: removing an interface you might want to remove...
Page 153
Administering routes 12-5 administering routes your system maintains a table of routes to other appletalk networks. The routing table is generated automatically by the routing table maintenance protocol (rtmp). Rtmp defines 1) the rules for exchanging information between routers so that the routers ...
Page 154
12-6 c hapter 12: a dministering a pple t alk ® r outing the following example shows a routing table display: flushing all routes flushing deletes all dynamically learned routes from the routing table. To flush all learned routes: 1 at the administration console’s top-level menu, enter: appletalk ro...
Page 155
Administering the aarp cache 12-7 administering the aarp cache aarp allows hardware addresses to be mapped to an appletalk protocol address. Appletalk uses dynamically assigned 24-bit addresses, unlike the statically-assigned 48-bit addresses used by ethernet and token ring. To make the address mapp...
Page 156
12-8 c hapter 12: a dministering a pple t alk ® r outing displaying the aarp cache you can display the aarp cache for the system to determine which routes are configured and if they are operational. To display the contents of the aarp cache: from the administration console top-level menu, enter: app...
Page 157
Administering the aarp cache 12-9 removing an entry in the cache to remove an aarp cache entry: 1 at the administration console’s top-level menu, enter: appletalk aarp remove 2 enter the aarp address at the prompt. The entry is removed. Flushing all cache entries to flush all aarp cache entries: 1 a...
Page 158
12-10 c hapter 12: a dministering a pple t alk ® r outing displaying the zone table appletalk allows for the logical grouping of nodes into zones to make navigation through the network easier. This is done with the zone information protocol (zip). Zip helps routers maintain a mapping of network numb...
Page 159
Configuring forwarding 12-11 depending on the command entered, the zone table is displayed by network or zone. An example of each type of display is shown below: configuring forwarding you can control whether the router forwards or discards appletalk packets addressed to other hosts. When you enable...
Page 160
12-12 c hapter 12: a dministering a pple t alk ® r outing configuring checksum checksum is a simple method used for detecting errors in the transmission of data. Checksum generation totals the bytes comprising the data and adds this sum to the end of the data packet. Checksum verification allows you...
Page 161
Viewing appletalk statistics 12-13 viewing appletalk statistics you can view statistics specific to the following appletalk protocols: ■ datagram delivery protocol (ddp) ■ routing table maintenance protocol (rtmp) ■ zone information protocol (zip) ■ name binding protocol (nbp) displaying ddp statist...
Page 162
12-14 c hapter 12: a dministering a pple t alk ® r outing displaying rtmp information to display rtmp statistics: from the administration console top-level menu, enter: appletalk statistics rtmp an example of summary statistics is shown below: table 12-2 describes the rtmp statistics you can view. I...
Page 163
Viewing appletalk statistics 12-15 displaying zip information to display zip statistics: from the administration console top-level menu, enter: appletalk statistics zip table 12-2 rtmp statistics field description indatas number of good rtmp data packets received inrequests number of good rtmp reque...
Page 164
12-16 c hapter 12: a dministering a pple t alk ® r outing an example of summary statistics is shown below: table 12-3 describes the zip statistics you can view: ddp forwarding is enabled. Inqueries inreplies inexreplies ingnirequests 248 14 0 182 ingnireplies inlocalzones inzonelists 22 30 0 inobsol...
Page 165
Viewing appletalk statistics 12-17 displaying nbp information the nbp handles the translations between the numeric internet address and the alphanumeric entity names used by appletalk. To display nbp statistics: from the administration console top-level menu, enter: appletalk statistics nbp an examp...
Page 166
12-18 c hapter 12: a dministering a pple t alk ® r outing table 12-4 describes the nbp statistics you can view. Table 12-4 nbp statistics field description inlkupreqs number of nbp lookup requests received inbcastsreqs number of nbp broadcast requests received infwdreqs number of nbp forward request...
Page 167: Emote
V chapter 13 remote monitoring (rmon) technology r emote m onitoring (rmon) and the lan plex ® s ystem.
Page 168: Emote
13 r emote m onitoring (rmon) t echnology this chapter provides an overview of rmon and describes the specific lanplex® rmon implementation. What is rmon? The remote monitoring (rmon) management information base (mib) provides a way to monitor and analyze a local area network lan from a remote locat...
Page 169
13-2 c hapter 13: r emote m onitoring (rmon) t echnology benefits of rmon traditional network management applications poll network devices such as switches, bridges, and routers at regular intervals from a network management console. The console gathers statistics, identifies trends, and can highlig...
Page 170
Lanplex rmon implementation 13-3 3com transcend rmon agents rmon requires one probe per lan segment. Because a segment is a portion of the lan separated by a bridge or router, the cost of implementing many probes in a large network can be high. To solve this problem, 3com has built an inexpensive rm...
Page 171
13-4 c hapter 13: r emote m onitoring (rmon) t echnology figure 13-1 embedded rmon implemented on the lanplex system management information base (mib) a mib is a structured set of data that describes the way the network is functioning. The management software, known as the agent , gains access to th...
Page 172
Management information base (mib) 13-5 figure 13-2 example of an rmon mib counter object the displayed information includes these items: ■ the formal name of the counter is etherstatspkts. (ethernet, statistics, packets) ■ the access is read-only ■ the number of the counter’s column in the table: 5 ...
Page 173
13-6 c hapter 13: r emote m onitoring (rmon) t echnology alarms the lanplex system supports the following syntax for alarms: counters, gauges, integers and timeticks. These mechanisms report information about the network to the network administrator. Counters, for example, hold and update the number...
Page 174
Alarms 13-7 setting alarm thresholds thresholds determine when an alarm reports that a counter has exceeded a certain value. You can set alarm thresholds through the network manually, and choose any value for them that is appropriate for your application. The network management software monitors the...
Page 175
13-8 c hapter 13: r emote m onitoring (rmon) t echnology rmon hysteresis mechanism the rmon hysteresis mechanism provides a way to prevent small fluctuations in counter values from causing alarms. This mechanism generates an alarm only under the following conditions: ■ the counter value exceeds the ...
Page 176: Ppendix
Vi appendix a technical support a ppendix.
Page 177: Echnical
A t echnical s upport 3com provides easy access to technical support information through a variety of services. This appendix describes these services. On-line technical services 3com offers worldwide product support 24 hours a day, seven days a week, through the following on-line systems: ■ 3com bu...
Page 178
A-2 a ppendix a: t echnical s upport access by digital modem isdn users can dial in to 3combbs using a digital modem for fast access up to 56 kbps. To access 3combbs using isdn, dial the following number: (408) 654-2703 world wide web site access the latest networking information on 3com’s world wid...
Page 179
Support from your network supplier a-3 3comfacts ™ automated fax service 3com corporation’s interactive fax service, 3comfacts, provides data sheets, technical articles, diagrams, and troubleshooting instructions on 3com products 24 hours a day, seven days a week. Call 3comfacts using your touch-ton...
Page 180
A-4 a ppendix a: t echnical s upport support from 3com if you are unable to receive support from your network supplier, technical support contracts are available from 3com. In the u.S. And canada, call (800) 876-3266 for customer service. If you are outside the u.S. And canada, contact your local 3c...
Page 181: Ndex
I ndex numerics 3com bulletin board service (3combbs) a-1 3com sales offices a-4 3comfacts a-3 a aarp 7-10 aarp cache administering 12-7 displaying 12-8 removing an entry from 12-9 address classes 4-3 ip to mac, translating 9-13 mac 3-3 network 3-3 address resolution protocol. See arp administration...
Page 182
2 i ndex bridging/routing lanplex model 3-4 traditional model 3-4 bulletin board service a-1 c cache displaying the ip multicast 10-9 checksum configuring appletalk 12-12 chooser, macintosh 7-2 compuserve a-2 conventions notice icons 2 d datagram delivery protocol 7-6 datagrams, statistics 9-23 data...
Page 183
I ndex 3 displaying an 11-3 modifying an 11-4 removing an 11-4 interior gateway protocols (igp) 4-6, 6-9 internet address. See ip address internet control message protocol. See icmp internet protocol. See references with ip address intranetwork routing diagram 3-2 ip address translation 9-13 arp cac...
Page 184
4 i ndex lis interfaces characteristics of 9-3 defining 9-4 m mac (media access control). See fddi mac mac address 3-3 arp and 9-13 bridging in switching modules, and 3-6 compared to ip address 4-2 in arp request 4-8 located with arp 4-7 use in ip routing 4-8 macintosh, chooser 7-2 management ip int...
Page 185
I ndex 5 management console 13-1 mib 13-1, 13-2, 13-4 probe 13-1, 13-2 route, ip default 9-10 defining static 9-11 removing default 9-13 removing from table 9-12 status 9-10 route, ipx removing a 11-7 router interface, ip described 4-4 diagram 4-5 routing table, and the 4-5 router interface, ipx des...
Page 186
6 i ndex timing out, ip route status 9-10 t-notify configuring 8-4 transmission errors icmp redirect 4-9 reasons for 4-9 ttl threshold 5-5 ip multicast 10-3 tunnels ip multicast 5-6, 10-6 v vlan information defining 8-3 displaying 8-1 modifying 8-4 removing 8-5 vlan interfaces about 9-1 characterist...