- DL manuals
- 3Com
- Switch
- SuperStack 4
- Configuration Manual
3Com SuperStack 4 Configuration Manual
Summary of SuperStack 4
Page 1
Superstack ® 4 switch 5500g-ei family configuration guide http://www.3com.Com/ part number: dua1725-0baa02 published: august 2005.
Page 2
3com corporation 350 campus drive marlborough, ma usa 01752-3064 copyright © 2005, 3com corporation. All rights reserved. No part of this documentation may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to make any derivative work (such as translation, transformation, or adaptation) without writt...
Page 3: Bout
A bout t his g uide this guide provides information about configuring your network using the commands supported on the 3com ® superstack ® 4 switch 5500g-ei. Organization of the manual the switch 5500g-ei configuration guide consists of the following chapters: ■ getting started — details the main fe...
Page 4
16 a bout t his g uide conventions this manual uses the following conventions: table 1 icons icon notice type description information note information that describes important features or instructions. Caution information that alerts you to potential loss of data or potential damage to an applicatio...
Page 5
Related manuals 17 related manuals the 3com superstack 4 switch 5500g-ei getting started guide provides information about installation. The 3com superstack 4 switch 5500g-ei command reference guide provides all the information you need to use the configuration commands..
Page 6
18 a bout t his g uide.
Page 7: Etting
1 g etting s tarted this chapter covers the following topics: ■ product overview ■ xrn overview ■ product features ■ logging in to the switch ■ command line interface ■ user interface configuration product overview the switch 5500g-ei family are wire speed layer 3 switching products supporting expan...
Page 8
20 c hapter 1: g etting s tarted ■ 8 port 1000 mbps sfp module ■ 1 port 10 gbps xenpak module the front panel has 48 x 10/100/1000base-t auto-negotiation ethernet ports with rj-45 connectors and 4 sfp combo ports. Each combo port corresponds to an ethernet port, so there are 4 port pairs. Only 1 por...
Page 9
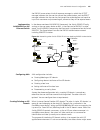
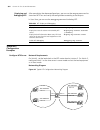
Xrn overview 21 xrn overview brief introduction with the xrn (expandable resilient networking) feature, you can connect several devices into a combined device and manage them as a single unit. The combined device is called the fabric, while the member devices are units. With xrn you can: ■ manage mu...
Page 10
22 c hapter 1: g etting s tarted figure 1 networking topology with xrn product features table 4 lists the function features: unit 2 unit 1 unit3 unit 4 fabric server core switches workgroup switches desktop pcs table 4 function features features description vlan vlan compliant with ieee 802.1q stand...
Page 11
Product features 23 security features multi-level user management and password protect 802.1x authentication packet filtering quality of service (qos) traffic classification bandwidth control priority queues of different priority on the port queue scheduling: supports strict priority queuing (sp), w...
Page 12
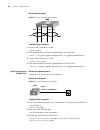
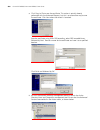
24 c hapter 1: g etting s tarted logging in to the switch setting up configuration environment through the console port 1 to set up the local configuration environment, connect the serial port of a pc (or a terminal) to the console port of the switch with the console cable (see figure 2 ). Figure 2 ...
Page 13
Logging in to the switch 25 figure 3 setting up a new connection figure 4 configuring the port for connection.
Page 14
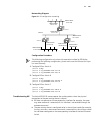
26 c hapter 1: g etting s tarted figure 5 setting communication parameters 3 the switch is powered on and it displays self-test information. Press to show the command line prompt such as . 4 enter a command to configure the switch or view the operation state. Enter a ? To view online help. For detai...
Page 15
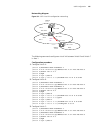
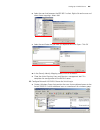
Logging in to the switch 27 figure 6 setting up the configuration environment through telnet 3 run telnet on the pc and enter the ip address of the vlan connected to the network port on the pc. Figure 7 running telnet 4 the terminal displays login authentication and prompts the user to enter the log...
Page 16
28 c hapter 1: g etting s tarted figure 8 providing telnet client service 1 authenticate the telnet user through the console port on the telnet server (a switch) before login. By default, the password is required to authenticate telnet users and to enable them to log on to the switch. If a user logs...
Page 17
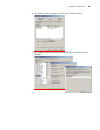
Logging in to the switch 29 [sw5500-ui-aux0]set authentication password simple xxxx (xxxx is the preset login password of the modem user.) 2 perform the following configurations on the modem that is directly connected to the switch. (you are not required to configure the modem connected to the termi...
Page 18
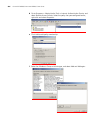
30 c hapter 1: g etting s tarted figure 10 setting the dialed number figure 11 dialing on the remote pc 5 enter the preset login password on the remote terminal emulator and wait for the prompt . Then you can configure and manage the switch. Enter ? To view online help. For details of specific comma...
Page 19
Command line interface 31 command line interface command line interface the switch 5500g-ei family provide a series of configuration commands and command line interfaces for configuring and managing the switch. The command line interface has the following characteristics: ■ local configuration throu...
Page 20
32 c hapter 1: g etting s tarted login users are also classified into four levels that correspond to the four command levels respectively. After users of different levels log in, they can only use commands at the levels that are equal to or lower than their own level. To prevent unauthorized users f...
Page 21
Command line interface 33 table 5 describes the features of different views and the ways to enter or quit. Table 5 features of command views command view function prompt command to enter command to exit user view show the basic information about operation and statistics this is the view you are in a...
Page 22
34 c hapter 1: g etting s tarted rip view configure rip parameters [sw5500-rip] enter rip in system view quit returns to system view return returns to user view ospf view configure ospf parameters [sw5500-ospf] enter ospf in system view quit returns to system view return returns to user view ospf ar...
Page 23
Command line interface 35 features and functions of command line command line help the command line interface provides full and partial online help. You can get help information through the online help commands, which are described below: 1 enter ? In any view to get all the commands in that view. 2...
Page 24
36 c hapter 1: g etting s tarted command buffer is defaulted as 10. That is, the command line interface stores 10 history commands for each user. The operations are shown in table 7 . Cursor keys can be used to retrieve the history commands in windows 3.X terminal and telnet. However, in windows 9x ...
Page 25
User interface configuration 37 user interface configuration user interface overview user interface configuration is another way provided by the switch to configure and manage the port data. Switch 5500 family supports the following configuration methods: ■ local configuration through the console po...
Page 26
38 c hapter 1: g etting s tarted user interface configuration tasks for configuring the user interface are described in the following sections: ■ entering user interface view ■ configuring the user interface-supported protocol ■ configuring the attributes of aux (console) port ■ configuring the term...
Page 27
User interface configuration 39 perform the following configurations in user interface (aux user interface only) view. Configuring the transmission speed on the aux (console) port by default, the transmission speed on the aux (console) port is 9600bps. Configuring the flow control on the aux (consol...
Page 28
40 c hapter 1: g etting s tarted configuring the terminal attributes the following commands can be used for configuring the terminal attributes, including enabling/disabling terminal service, disconnection upon timeout, lockable user interface, configuring terminal screen length, and history command...
Page 29
User interface configuration 41 setting the screen length if a command displays more than one screen of information, you can use the following command to set how many lines to be displayed in a screen, so that the information can be separated in different screens and you can view it more convenientl...
Page 30
42 c hapter 1: g etting s tarted perform the following configuration in user interface view. Configure for password authentication when a user logs in through a vty 0 user interface and set the password to 3com. [sw5500]user-interface vty 0 [sw5500-ui-vty0]authentication-mode password [sw5500-ui-vty...
Page 31
User interface configuration 43 by default, the specified logged-in user can access the commands at level 1. Setting the command level used after a user logs in from a user interface you can use the following command to set the command level after a user logs in from a specific user interface, so th...
Page 32
44 c hapter 1: g etting s tarted configuring redirection send command the following command can be used for sending messages between user interfaces. Perform the following configuration in user view. Auto-execute command the following command is used to automatically run a command after you log in. ...
Page 34
46 c hapter 1: g etting s tarted.
Page 35: Ort
2 p ort o peration this chapter covers the following topics: ■ ethernet port configuration ■ link aggregation configuration ethernet port configuration ethernet port overview the switch 5500g-ei 24 port provides 24 fixed 10/100/1000base-t ethernet ports, 4 combo sfp ports, 2 fixed stack ports and on...
Page 36
48 c hapter 2: p ort o peration ■ setting the description character string for the ethernet port ■ setting the duplex attribute of the ethernet port ■ setting speed on the ethernet port ■ setting the cable type for the ethernet port ■ enabling/disabling flow control for the ethernet port ■ permittin...
Page 37
Ethernet port configuration 49 by default, the port description is a null character string. The cascade ports do not support the undo description command. Setting the duplex attribute of the ethernet port to configure a port to send and receive data packets at the same time, set it to full-duplex. T...
Page 38
50 c hapter 2: p ort o peration setting the cable type for the ethernet port ethernet ports support straight-through and cross-over network cables. Use the following command to configure the cable type. Perform the following configuration in ethernet port view. By default, the cable type is auto (au...
Page 39
Ethernet port configuration 51 perform the following configuration in ethernet port view. By default, all traffic is allowed to pass through, that is, no suppression is performed. Setting the link type for an ethernet port an ethernet port can operate in three different link types: access, hybrid, a...
Page 40
52 c hapter 2: p ort o peration adding an ethernet port to specified vlans use the following commands to add an ethernet port to a specified vlan. An access port can only be added to one vlan, while hybrid and trunk ports can be added to multiple vlans. Perform the following configuration in etherne...
Page 41
Ethernet port configuration 53 by default, the vlan of a hybrid port and a trunk port is vlan 1 and that of the access port is the vlan to which it belongs. Note that to guarantee the proper packet transmission, the default vlan id of the local hybrid port or trunk port should be identical with that...
Page 42
54 c hapter 2: p ort o peration perform the following configuration in system view. Note that if the copy source is an aggregation group, take the port with minimum id as the source; if the copy destination is an aggregation group, make the configurations of all group member ports identical with tha...
Page 43
Link aggregation configuration 55 ■ when receiving packets without a vlan tag, the port can forward them to the member ports belonging to the default vlan ■ when it is sending the packets with vlan tag and the packet vlan id is the default vlan id, the trunk port will remove the packet vlan tag and ...
Page 44
56 c hapter 2: p ort o peration for the member ports in an aggregation group, their basic configurations must be the same. That is, if one is a trunk port, the others must also be; when it turns into access port, then others must change to access port. The basic configuration includes stp setting, q...
Page 45
Link aggregation configuration 57 with the minimum port number serves as the master port, while others as sub-ports. In a manual aggregation group, the system sets the ports to active or inactive state by using these rules: ■ the system sets the port with the highest priority to active state, and ot...
Page 46
58 c hapter 2: p ort o peration systems as well as under manual control through direct manipulation of the state variables of link aggregation (for example, keys) by a network manager. Dynamic lacp aggregation can be established even for a single port, as is called single port aggregation. Lacp is e...
Page 47
Link aggregation configuration 59 a load sharing aggregation group may contain several selected ports, but a non-load sharing aggregation group can only have one selected port, while others are unselected ports. Selection criteria of selected ports vary for different types of aggregation groups. Lin...
Page 48
60 c hapter 2: p ort o peration aggregation group: when you delete a manual aggregation group, all its member ports are disaggregated; when you delete a static or dynamic lacp aggregation group, its member ports form one or several dynamic lacp aggregation groups. Perform the following configuration...
Page 49
Link aggregation configuration 61 ■ port with 802.1x enabled. ■ you must delete the aggregation group, instead of the port, if the manual or static lacp aggregation group contains only one port. Setting/deleting the aggregation group descriptor perform the following configuration in system view. By ...
Page 50
62 c hapter 2: p ort o peration perform the following configuration in ethernet port view. By default, port priority is 32768. Displaying and debugging link aggregation after the above configuration, enter the display command in any view to display the running of the link aggregation configuration, ...
Page 51
Link aggregation configuration 63 networking diagram figure 13 networking for link aggregation configuration procedure the following only lists the configuration for switch a; configure switch b similarly. 1 manual link aggregation a create manual aggregation group 1. [sw5500]link-aggregation group ...
Page 52
64 c hapter 2: p ort o peration only when the three ports are configured with identical basic configuration, rate and duplex mode, can they be added into a same dynamic aggregation group after lacp is enabled on them, for load sharing..
Page 53: Vlan O
3 vlan o peration this chapter covers the following topics: ■ vlan configuration ■ voice vlan configuration vlan configuration vlan overview a virtual local area network (vlan) creates logical groups of lan devices into segments to implement virtual workgroups. Ieee issued the ieee 802.1q in 1999, w...
Page 54
66 c hapter 3: vlan o peration note that the default vlan, namely vlan 1, cannot be deleted. Adding ethernet ports to a vlan use the following command to add ethernet ports to a vlan. Perform the following configuration in vlan view. By default, the system adds all the ports to a default vlan, whose...
Page 55
Vlan configuration 67 create a vlan first before creating an interface for it. For this configuration task, vlan_id takes the vlan id. Shutting down/enabling the vlan interface use the following command to shut down/enable a vlan interface. Perform the following configuration in vlan interface view....
Page 56
68 c hapter 3: vlan o peration networking diagram figure 14 vlan configuration example 1 configuration procedure 1 create vlan 2 and enter its view. [sw5500]vlan 2 2 add gigabitethernet1/0/1 and gigabitethernet1/0/2 to vlan2. [sw5500-vlan2]port gigabitethernet1/0/1 to gigabitethernet1/0/2 3 create v...
Page 57
Voice vlan configuration 69 voice vlan configuration voice vlan overview voice vlan is specially designed for users’ voice flow, and it distributes different port precedence in different cases. The system uses the source mac of the traffic traveling through the port to identify the ip phone data flo...
Page 58
70 c hapter 3: vlan o peration ■ setting/removing the oui address learned by voice vlan ■ enabling/disabling voice vlan security mode ■ enabling/disabling voice vlan auto mode ■ setting the aging time of voice vlan if you change the status of voice vlan security mode, you must first enable voice vla...
Page 59
Voice vlan configuration 71 there are four default oui addresses after the system starts. Enabling/disabling voice vlan security mode in security mode, the system can filter out the traffic whose source mac is not oui within the voice vlan, while the other vlans are not influenced. If security mode ...
Page 60
72 c hapter 3: vlan o peration perform the following configuration in system view. The default aging time is 1440 minutes. Displaying and debugging of voice vlan after completing the above configuration, enter the display command in any view to view the configuration and running state of voice vlan....
Page 61
Voice vlan configuration 73 [sw5500-gigabitethernet1/0/2]quit [sw5500]undo voice vlan mode auto [sw5500]voice vlan mac_address 0011-2200-0000 mask ffff-ff00-0000 description private [sw5500]voice vlan 2 enable [sw5500]voice vlan aging 100
Page 62
74 c hapter 3: vlan o peration.
Page 63: Ower
4 p ower over e thernet (p o e) c onfiguration this chapter covers the following topics: ■ poe overview ■ poe configuration poe overview the switch 5500g-ei 24 port pwr and switch 5500g-ei 48 port pwr support power over ethernet (poe). This feature uses twisted pairs to provide -44 through -62 vdc p...
Page 64
76 c hapter 4: p ower over e thernet (p o e) c onfiguration ■ when using the pwr switches to supply power to remote pds, the pds need not have any external power supply. ■ if a remote pd has an external power supply, the pwr switches and the external power supply will be redundant with each other fo...
Page 65
Poe configuration 77 setting the maximum power output on a port the maximum power that can be supplied by an ethernet port of the s5624p-pwr/s5648p-pwr to its pd is 15400 mw. In practice, you can set the maximum power on a port depending on the actual power of the pd, with a range from 1000 to 15400...
Page 66
78 c hapter 4: p ower over e thernet (p o e) c onfiguration table 70 setting the power supply management mode on the switch by default, the power supply management mode on the switch is auto . Setting the port priority set the priority of the current port in ethernet port view. Table 71 setting the ...
Page 67
Poe configuration 79 upgrading the pse processing software online the online upgrading of pse processing software can update the processing software or repair the software if it is damaged. After upgrading files are downloaded, you can use the following command to perform online upgrading on the pse...
Page 68
80 c hapter 4: p ower over e thernet (p o e) c onfiguration 12000 mw. This is required to guarantee the power feeding to the pd that will be connected to the gigabitethernet1/0/24 even when the switch 5500 pwr is in full load. Network diagram figure 17 poe remote power supply configuration procedure...
Page 69
Poe configuration 81.
Page 70
82 c hapter 4: p ower over e thernet (p o e) c onfiguration.
Page 71: Etwork
5 n etwork p rotocol o peration this chapter covers the following topics: ■ ip address configuration ■ arp configuration ■ resilient arp configuration ■ bootp client configuration ■ dhcp configuration ■ access management configuration ■ udp helper configuration ■ ip performance configuration ip addr...
Page 72
84 c hapter 5: n etwork p rotocol o peration the ip address is in dotted decimal format. Each ip address contains 4 integers in dotted decimal notation. Each integer corresponds to one byte, for example, 10.110.50.101. When using ip addresses, note that some of them are reserved for special uses, an...
Page 73
Ip address configuration 85 a mask is a 32-bit number corresponding to an ip address. The number consists of 1s and 0s. Principally, these 1s and 0s can be combined randomly. However, the first consecutive bits are set to 1s when designing the mask. The mask divides the ip address into two parts: su...
Page 74
86 c hapter 5: n etwork p rotocol o peration the ip address configuration is described in the following sections: ■ configuring the hostname and host ip address ■ configuring the ip address of the vlan interface configuring the hostname and host ip address perform the following configuration in syst...
Page 75
Arp configuration 87 ip address configuration example networking requirements configure the ip address as 129.2.2.1 and subnet mask as 255.255.255.0 for vlan interface 1 of the ethernet switch. Networking diagram figure 20 ip address configuration networking configuration procedure 1 enter vlan inte...
Page 76
88 c hapter 5: n etwork p rotocol o peration dynamic arp mapping entry is not in use for a specified period of time, the host will remove it from the arp mapping table so as to save the memory space and shorten the interval for switch to search arp mapping table. Suppose there are two hosts on the s...
Page 77
Arp configuration 89 by default, the arp mapping table is empty and the address mapping is obtained through dynamic arp. Note that: ■ static arp map entry will be always valid as long as the ethernet switch works normally. But if the vlan corresponding to the arp mapping entry is deleted, the arp ma...
Page 78
90 c hapter 5: n etwork p rotocol o peration by default, this feature is enabled. Displaying and debugging arp after the above configuration, enter the display command in any view to display the running of the arp configuration, and to verify the effect of the configuration. Enter the debugging comm...
Page 79
Resilient arp configuration 91 perform the following configuration in system view. By default, resilient arp function is enabled. If you are attempting to stop the switch from transmitting packets, you need to disable all features which may generate packets. By default these are: ■ dhcp ■ resilient ...
Page 80
92 c hapter 5: n etwork p rotocol o peration you can also enter the debugging command in user view to debug the resilient arp function. Resilient arp configuration example networking requirement there are four units, numbered respectively unit 1 through unit 4, in the xrn network. Unit 1 and unit 3 ...
Page 81
Bootp client configuration 93 bootp client configuration overview of bootp client a bootp client can request the server to allocate an ip address to it using bootp (bootstrap protocol). These two major processes are included on the bootp client: ■ sending bootp request message to the server ■ proces...
Page 82
94 c hapter 5: n etwork p rotocol o peration dhcp configuration overview of dhcp dynamic host configuration protocol (dhcp) offers dynamic ip address assignment. Dhcp works in client-server mode. With this protocol, the dhcp client can dynamically request configuration information and the dhcp serve...
Page 83
Dhcp configuration 95 dhcp server sends the dhcp_ack message containing the allocated ip address and other settings back to the client. Then the dhcp client binds its tcp/ip components to the nic (network interface card). Other dhcp servers not selected still can allocate their ip addresses to other...
Page 84
96 c hapter 5: n etwork p rotocol o peration figure 23 typical dhcp relay application dhcp relay works on the following principle: ■ when the dhcp client starts and initializes dhcp, it broadcasts the request message to the local network. ■ if there is a dhcp server on the local network, it can begi...
Page 85
Dhcp configuration 97 dhcp relay configuration dhcp relay configuration is described in the followng sections: ■ configuring the ip address for the dhcp server ■ configuring the dhcp server group for the vlan interfaces ■ configuring the user address entry for the dhcp server group ■ enabling/disabl...
Page 86
98 c hapter 5: n etwork p rotocol o peration configuring the user address entry for the dhcp server group to ensure that a valid user with a fixed ip address in a vlan configured with dhcp relay passes the address validity check of the dhcp security feature, you must add a static address entry which...
Page 87
Dhcp configuration 99 dhcp relay configuration example one networking requirements there are two vlans (1 and 10) and they both need to use the same dhcp server. Networking diagram figure 24 configuring dhcp relay configuration procedure 1 create a dhcp server group that will use two dhcp servers (a...
Page 88
100 c hapter 5: n etwork p rotocol o peration networking diagram figure 25 networking diagram of configuration dhcp relay configuration procedure 1 configure the group number of dhcp server as 1 and the ip address as 202.38.1.2. [sw5500]dhcp-server 1 ip 202.38.1.2 2 associate the vlan interface 2 wi...
Page 89
Access management configuration 101 enable the debugging dhcp-relay in user view and then use the terminal debugging command to output the debugging information to the console. In this way, you can view the detailed information of all dhcp packets on the console as they apply for the ip address, and...
Page 90
102 c hapter 5: n etwork p rotocol o peration by default, the ip address pools for access control on the port are null and all the packets are permitted. Note that if the ip address pool to be configured contains the ip addresses configured in the static arp at other ports, then the system prompts y...
Page 91
Access management configuration 103 perform the following configuration in system view. By default, the access management trap is disabled. Displaying and debugging access management after the above configuration, enter the display command in any view to display the current configurations of access ...
Page 92
104 c hapter 5: n etwork p rotocol o peration 4 configure the ip address pool for access management on port 2 [sw5500-gigabitethernet1/0/1]interface gigabitethernt1/0/2 [sw5500-gigabitethernet1/0/2]am ip-pool 202.10.20.21 30 5 add port 2 into isolation group. [sw5500-gigabitethernet1/0/2]port isolat...
Page 93
Udp helper configuration 105 note: ■ after you have configured dhcp relay, the switch automatically configure udp-helper whether the switch is a single unit or in a fabric. The udp-helper configuration remains when you remove the dhcp relay configuration. ■ if you remove udp-helper configuration whe...
Page 94
106 c hapter 5: n etwork p rotocol o peration note that : ■ you must first enable the udp helper function and then configure the udp port with the relay function. Otherwise, error information will appear. ■ the parameters dns , netbios-ds, netbios-ns, tacacs , tftp and time respectively refer to the...
Page 95
Ip performance configuration 107 udp helper configuration example networking requirement the ip address of vlan interface 2 on the switch is 10.110.1.1, which is connected with network segment 10.110.0.0. Set to relay-forward the broadcast packets with destination ip of all 1s and destination udp po...
Page 96
108 c hapter 5: n etwork p rotocol o peration perform the following configuration in system view. By default, the tcp finwait timer is 675 seconds, the synwait timer is 75 seconds, and the receiving/sending buffer size of connection-oriented socket is 8k bytes. Displaying and debugging ip performanc...
Page 97
Ip performance configuration 109 troubleshooting ip performance fault: ip layer protocol works normally but tcp and udp cannot work normally. In the event of such a fault, you can enable the corresponding debugging information output to view the debugging information. ■ use the terminal debugging co...
Page 98
110 c hapter 5: n etwork p rotocol o peration.
Page 99: Ip R
6 ip r outing p rotocol o peration ip routing protocol overview routers select an appropriate path through a network for an ip packet according to the destination address of the packet. Each router on the path receives the packet and forwards it to the next router. The last router in the path submit...
Page 100
112 c hapter 6: ip r outing p rotocol o peration if a router in a network is regarded as a node and a route segment in the internet is regarded as a link, message routing in the internet works in a similar way as the message routing in a conventional network. The shortest route may not always be the...
Page 101
Ip routing protocol overview 113 to limit the size of the routing table, an option is available to set a default route. All the packets that fail to find a suitable table entry are forwarded through this default route. In a complicated internet configuration, as shown in figure 29 , the number in ea...
Page 102
114 c hapter 6: ip r outing p rotocol o peration in table 107 , 0 indicates a direct route, and 255 indicates any route from an unreliable source. Except for direct routing and bgp (ibgp and ebgp), the preferences of various dynamic routing protocols can be manually configured to meet the user requi...
Page 103
Static routes 115 import routes of other protocols” on page 125 , “configuring ospf to import the default route” on page 146 and “importing routing information discovered by other routing protocols” on page 158 . Static routes a static route is a route that is manually configured by the network admi...
Page 104
116 c hapter 6: ip r outing p rotocol o peration configuring static routes static route configuration tasks are described in the following sections: ■ configuring a static route ■ configuring a default route ■ deleting all the static routes ■ displaying and debugging static routes configuring a stat...
Page 105
Static routes 117 configuring a default route perform the following configurations in system view. The parameters for the default route are the same as those for the static route. Deleting all the static routes you can use the undo ip route-static command to delete a static route. The switch 5500g-e...
Page 106
118 c hapter 6: ip r outing p rotocol o peration example: typical static route configuration networking requirements the masks of all the ip addresses shown in figure 30 are 255.255.255.0. All the hosts or switches must be interconnected in pairs by configuring static routes. Networking diagram figu...
Page 107
Rip 119 ■ use the display ip routing-table command to view whether the corresponding route is valid. Rip routing information protocol (rip) is a simple dynamic routing protocol, that is distance-vector (d-v) algorithm based. It uses hop counts to measure the distance to the destination host. This is...
Page 108
120 c hapter 6: ip r outing p rotocol o peration timeout mechanism to handle timed out routes to ensure the timeliness and validity of the routes. With these mechanisms, rip, an interior routing protocol, enables the router to learn the routing information of the entire network. Rip has become one o...
Page 109
Rip 121 by default, rip is not enabled. Enabling rip on a specified network for flexible control of rip operation, you can specify the interface and configure the network on which the interface is located to the rip network, so that these interfaces can send and receive rip packets. Perform the foll...
Page 110
122 c hapter 6: ip r outing p rotocol o peration multicast mode is that the hosts in the same network that do not run rip, do not receive rip broadcast packets. In addition, this mode prevents the hosts that are running rip-1 from incorrectly receiving and processing the routes with subnet masks in ...
Page 111
Rip 123 before rip completely deletes an unreachable route from the routing table, it advertises the route by sending four update packets with a route metric of 16, to let all the neighbors know that the route is unreachable. Routes do not always become unreachable when a new period starts so the ac...
Page 112
124 c hapter 6: ip r outing p rotocol o peration disabling host route in some cases, the router can receive many host routes from the same segment, and these routes are of little help in route addressing but consume a lot of network resources. Routers can be configured to reject host routes by using...
Page 113
Rip 125 perform the following configuration in interface view: the usual packet format follows rfc1723 and nonstandard follows rfc2082. Configuring split horizon split horizon means that the route received through an interface will not be sent through this interface again. The split horizon algorith...
Page 114
126 c hapter 6: ip r outing p rotocol o peration route, rip will set the cost to the default cost, specified by the default cost parameter. Perform the following configurations in rip view. By default, the cost value for the rip imported route is 1. Setting the rip preference each routing protocol h...
Page 115
Rip 127 configuring route filtering the router provides a route filtering function. You can configure the filter policy rules by specifying the acl and ip-prefix for route redistribution and distribution. To import a route, the rip packet of a specific router can also be received by designating a ne...
Page 116
128 c hapter 6: ip r outing p rotocol o peration enabled, then traffic can be distributed equally among interfaces by employing equivalent routes. Table 129 configuring rip to filter the distributed routes displaying and debugging rip after configuring rip, enter the display command in any view to d...
Page 117
Rip 129 networking diagram figure 31 rip configuration networking configuration procedure the following configuration only shows the operations related to rip. Before performing the following configuration, please make sure the ethernet link layer can work normally. 1 configure rip on switch a [swit...
Page 118
130 c hapter 6: ip r outing p rotocol o peration ospf configuration open shortest path first (ospf) is an interior gateway protocol based on the link state developed by ietf. The switch 5500g-ei uses ospf version 2 (rfc2328), which has the following features: ■ scope — supports networks of various s...
Page 119
Ospf configuration 131 the hello packet is the most common packet sent by the ospf protocol. A router periodically sends it to its neighbor. It contains the values of some timers, dr, bdr and the known neighbor. ■ database description (dd) packet. When two routers synchronize their databases, they u...
Page 120
132 c hapter 6: ip r outing p rotocol o peration the segment, and routing information is also exchanged between them. After the existing dr fails, the bdr will immediately becomes a dr. ■ area if all routers on a large network are running ospf, the large number of routers results in an enormous lsd,...
Page 121
Ospf configuration 133 ■ setting a dead timer for the neighboring routers ■ configuring an interval required for sending lsu packets ■ setting an interval for lsa retransmission between neighboring routers ■ setting a shortest path first (spf) calculation interval for ospf ■ configuring stub area of...
Page 122
134 c hapter 6: ip r outing p rotocol o peration entering ospf area view perform the following configurations in ospf view. Area_id is the id of the ospf area, which can be a decimal integer or in ip address format. Specifying the interface ospf divides the as into different areas. You must configur...
Page 123
Ospf configuration 135 to ensure the stability of ospf, you must determine the division of router ids and manually configure them when implementing network planning. Configuring the network type on the ospf interface the route calculation of ospf is based upon the topology of the adjacent network of...
Page 124
136 c hapter 6: ip r outing p rotocol o peration perform the following configuration in interface view: after the interface has been configured with a new network type, the original network type of the interface is removed automatically. Configuring the cost for sending packets on an interface you c...
Page 125
Ospf configuration 137 note that: ■ the dr on the network is not necessarily the router with the highest priority. Likewise, the bdr is not necessarily the router with the second highest priority. If a new router is added after dr and bdr election, it is impossible for the router to become the dr ev...
Page 126
138 c hapter 6: ip r outing p rotocol o peration perform the following configuration in interface view by default, p2p and broadcast interfaces send hello packets every 10 seconds, and p2mp and nbma interfaces send hello packets every 30 seconds. Setting a dead timer for the neighboring routers if h...
Page 127
Ospf configuration 139 setting an interval for lsa retransmission between neighboring routers if a router transmits an lsa (link state advertisements) to the peer, it requires an acknowledgement packet from the peer. If it does not receive the acknowledgement packet within the retransmit time, it re...
Page 128
140 c hapter 6: ip r outing p rotocol o peration note the following items when you configure a stub area: ■ the backbone area cannot be configured as a stub area, and virtual links cannot pass through the stub area. ■ if you want to configure an area as a stub area, all the routers in this area shou...
Page 129
Ospf configuration 141 figure 32 nssa area perform the following configuration in ospf area view. All the routers connected to the nssa should use the nssa command to configure the area with the nssa attributes. The default-route-advertise parameter is used to generate the default type-7 lsas. When ...
Page 130
142 c hapter 6: ip r outing p rotocol o peration once the aggregate segment of a certain network is added to the area, all the internal routes of the ip addresses in the range of the aggregate segment will no longer be separately advertised to other areas. Only the route summary of the whole aggrega...
Page 131
Ospf configuration 143 virtual link refers to a logic channel set up through the area of a non-backbone internal route between two abrs. Both ends of the logic channel should be abrs and the connection can take effect only when both ends are configured. The virtual link is identified by the id of th...
Page 132
144 c hapter 6: ip r outing p rotocol o peration configuring ospf packet authentication ospf supports simple authentication or md5 authentication between neighboring routers. Perform the following configuration in interface view: by default, the interface is not configured with either simple authent...
Page 133
Ospf configuration 145 router to the asbr and the cost from the asbr to the destination are of the same size, then the cost of the router to the asbr will also be included. Perform the following configuration in ospf view. By default, ospf does not import the routing information of other protocols. ...
Page 134
146 c hapter 6: ip r outing p rotocol o peration by default, when importing external routes, the type of imported route is type-2, the cost is 1 and the tag is 1. The interval of importing the external route is 1 second. The upper limit to the external routes imported is 1000 per second. Configuring...
Page 135
Ospf configuration 147 configuring ospf to filter the received routes configuring ospf to filter the distributed routes by default, ospf will not filter the imported and distributed routing information. ■ the filter-policy import command only filters the ospf routes of this process received from the...
Page 136
148 c hapter 6: ip r outing p rotocol o peration by default, the interface does not fill in the mtu field when transmitting dd packets, and the mtu in the dd packets is 0. Disabling the interface to send ospf packets use the silent-interface command to prevent the interface from transmitting ospf pa...
Page 137
Ospf configuration 149 perform the following configuration in system view. By default, ospf trap function is disabled, so the switch does not send trap packets when any ospf process is abnormal. The configuration is valid to all ospf processes if you do not specify a process id. For detailed configu...
Page 138
150 c hapter 6: ip r outing p rotocol o peration configuration. Execute the debugging command in user view to debug the ospf module. Example: configuring dr election based on ospf priority networking requirements in this example, four switch 5500g-eis, switch a, switch b, switch c and switch d, whic...
Page 139
Ospf configuration 151 networking diagram figure 33 networking for configuring dr election based on ospf priority the commands listed in the following examples enable switch a and switch c to be dr and bdr, respectively. The priority of switch a is 100, which is the highest on the network, so it is ...
Page 140
152 c hapter 6: ip r outing p rotocol o peration [switch d-ospf-1]area 0 [switch d-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0]network 196.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 on switch a, run the display ospf peer command to show the switch’s ospf neighbors. Note that switch a has three neighbors. The status of each neighbor is full, which me...
Page 141
Ospf configuration 153 networking diagram figure 34 ospf virtual link configuration networking the following commands configure a virtual link between switch b and switch c in area 1. Configuration procedure 1 configure switch a: [switch a]interface vlan-interface 1 [switch a-vlan-interface1]ip addr...
Page 142
154 c hapter 6: ip r outing p rotocol o peration [switch c-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1]network 197.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [switch c-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1]vlink-peer 2.2.2.2 [switch c-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1]quit [switch c-ospf-1]area 2 [switch c-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.2]network 152.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 troubleshooting ospf ospf h...
Page 143
Ip routing policy 155 ■ if more than two areas are configured on a router, at least one area should be configured as the backbone area. As shown in figure 35 , rta and rtd are each configured to belong to only one area, whereas rtb and rtc are both configured to belong to two areas. Rtb belongs to a...
Page 144
156 c hapter 6: ip r outing p rotocol o peration actions that are performed after the node match test concerning the attribute settings of the route information. The comparisons of different nodes in a route policy uses a boolean “or” statement. The system examines the nodes in the route policy in s...
Page 145
Ip routing policy 157 perform the following configurations in system view. The permit parameter specifies that if a route satisfies all the if-match clauses of a node, the route passes the filtering of the node, and the apply clauses for the node are executed without taking the test of the next node...
Page 146
158 c hapter 6: ip r outing p rotocol o peration by default, no matching is performed. The if-match clauses for a node in the route policy require that the route satisfy all the clauses to match the node before the actions specified by the apply clauses can be executed. If no if-match clauses are sp...
Page 147
Ip routing policy 159 perform the following configuration in routing protocol view. By default, the routes discovered by other protocols will not be distributed. In different routing protocol views, the parameter options are different. For details, refer to the description of the import-route comman...
Page 148
160 c hapter 6: ip r outing p rotocol o peration filter-policy gateway command specifies that only the update packets from a specific neighboring router will be received. By default, the filtering of received routes is not performed. Configuring the filtering of distributed routes define a policy co...
Page 149
Ip routing policy 161 displaying and debugging the routing policy enter the display command in any view to display the operation of the routing policy configuration, and to verify the effect of the configuration. Typical ip routing policy configuration example configuring the filtering of the receiv...
Page 150
162 c hapter 6: ip r outing p rotocol o peration 2 configure switch b: a configure the ip address of vlan interface. [switch b]interface vlan-interface 100 [switch b-vlan-interface100]ip address 10.0.0.2 255.0.0.0 b configure the access control list. [switch b]acl number 2000 [switch b-acl-basic-200...
Page 151
Route capacity configuration 163 limiting route capacity the size of the routing table is determined by ospf routes. Therefore, the route capacity limitation of the switch 5500g-ei is only effective for these two types of routes and has no impact on static routes and other dynamic routing protocols....
Page 152
164 c hapter 6: ip r outing p rotocol o peration displaying and debugging route capacity enter the display command in any view to display the operation of the route capacity configuration. Table 173 displaying and debugging route capacity operation command display the route capacity memory informati...
Page 153: Ulticast
7 m ulticast p rotocol this chapter includes information on the following: ■ ip multicast overview ■ igmp snooping ■ common multicast configuration ■ internet group management protocol (igmp) ■ pim-dm overview ■ pim-sm overview ip multicast overview many transmission methods can be used when the des...
Page 154
166 c hapter 7: m ulticast p rotocol figure 37 comparison between the unicast and multicast transmission a multicast source does not necessarily belong to a multicast group. It only sends data to the multicast group and it is not necessarily a receiver. Multiple sources can send packets to a multica...
Page 155
Ip multicast overview 167 members in the group can change. The number of members in a permanent multicast group can be random or even 0. Those ip multicast addresses that are not reserved for permanent multicast groups can be used by temporary groups. Ranges and meanings of class d addresses are sho...
Page 156
168 c hapter 7: m ulticast p rotocol assigned number authority) stipulates that the higher 24 bits of the multicast mac address is 0x01005e and the lower 23 bits of the mac address is the lower 23 bits of the multicast ip address. Figure 38 mapping between the multicast ip address and the ethernet m...
Page 157
Ip multicast overview 169 a distribution tree architecture. A multicast router can use multiple methods to build up a path for data transmission, i.E., the distribution tree. Pim-dm (protocol-independent multicast dense mode, pim-dm) pim dense mode is suitable for small networks. It assumes that eac...
Page 158
170 c hapter 7: m ulticast p rotocol shortest path from the receiver to the source address. If a source tree is used, the source address is the address of the source host sending the multicast packet. If a shared tree is used, the source address is the address of the root of the shared tree. When a ...
Page 159
Igmp snooping 171 figure 39 multicast packet transmission without igmp snooping when igmp snooping operates, packets are not forwarded to all ports, see figure 40 . Figure 40 multicast packet transmission when igmp snooping runs igmp snooping terminology table 176 explains switching terminology rele...
Page 160
172 c hapter 7: m ulticast p rotocol the switch 5500g-ei runs igmp snooping to listen to the igmp messages and map the host and its ports to the corresponding multicast group address. To implement igmp snooping, the switch processes different igmp messages as shown in figure 41 . Figure 41 implement...
Page 161
Igmp snooping 173 table 177 explains igmp snooping terminology. Configuring igmp snooping igmp snooping configuration includes: ■ enabling/disabling igmp snooping ■ configuring router port aging time ■ configuring maximum response time ■ configuring aging time of multicast group member of the above ...
Page 162
174 c hapter 7: m ulticast p rotocol enabling/disabling igmp snooping use the commands in table 178 to enable/disable igmp snooping on layer 2. First enable igmp snooping globally in system view, and then enable igmp snooping of the corresponding vlan in vlan view. Perform the following configuratio...
Page 163
Igmp snooping 175 configuring aging time of multicast group member use the commands in table 181 to manually set the aging time of the multicast group member port. If the switch receives no multicast group report message during the member port aging time, it will transmit the specific query message ...
Page 164
176 c hapter 7: m ulticast p rotocol networking diagram figure 42 igmp snooping configuration network configuration procedure enable igmp snooping globally. [sw5500]igmp-snooping enable enable igmp snooping on vlan 10. [sw5500]vlan 10 [sw5500-vlan10]igmp-snooping enable igmp snooping fault diagnosis...
Page 165
Common multicast configuration 177 diagnosis 3: multicast forwarding table set up on the bottom layer is wrong. 1 enable igmp snooping group in user view and then input the command display igmp-snooping group to check if mac multicast forwarding table in the bottom layer and that created by igmp sno...
Page 166
178 c hapter 7: m ulticast p rotocol clearing mfc forwarding entries or statistics information use the command in table 185 to clear the multicast forwarding cache (mfc) forward entries or statistics information. Perform the following configuration in user view. Clearing route entries from the core ...
Page 167
Common multicast configuration 179 there are three types of multicast routing tables: individual multicast routing tables of each multicast routing protocol; a multicast kernel routing table integrating the routing information of those individual routing tables; and a multicast forwarding table in c...
Page 168
180 c hapter 7: m ulticast p rotocol internet group management protocol (igmp) igmp is a protocol in the tcp/ip suite, responsible for management of ip multicast members. It is used to establish and maintain multicast membership among ip hosts and their directly connected neighboring routers. Igmp e...
Page 169
Internet group management protocol (igmp) 181 specific group query in igmp version 1, a query of multicast routers is targeted at all the multicast groups on the network segment. This is known as general query. In addition to general query, igmp version 2 also supports group-specific query. The dest...
Page 170
182 c hapter 7: m ulticast p rotocol configuring the igmp version perform the following configuration in interface view. By default, igmp version 2 is used. All routers on a subnet must support the same version of igmp. After detecting the presence of igmp version 1 system, a router cannot automatic...
Page 171
Internet group management protocol (igmp) 183 5 if the igmp querier does not receive a report message from any other host within this period, then it takes it as timeout and ends membership maintenance for this group. This command can be used only when the querier runs igmp version 2, since a host r...
Page 172
184 c hapter 7: m ulticast p rotocol setting the maximum response time reasonably can enable the host to respond to query messages quickly. In this case, the router can fast master the existing status of the members of the multicast group. Perform the following configuration in interface view. The s...
Page 173
Internet group management protocol (igmp) 185 perform the following configuration in the corresponding view. By default, a router joins no multicast group. Limiting multicast groups an interface can access a multicast router learns whether there are members of a multicast group on the network via th...
Page 174
186 c hapter 7: m ulticast p rotocol perform the following configuration in interface view. When there are multiple multicast routers on a network segment, the querier is responsible for sending igmp query messages to all hosts on the lan. By default, the interval is 60 seconds. Deleting igmp groups...
Page 175
Pim-dm overview 187 neighbor discovery the pim-dm router uses hello messages to perform neighbor discovery when it is started. All network nodes running pim-dm stay in touch with one another by periodically sending hello messages. Flood&prune pim-dm assumes that all hosts on the network are ready to...
Page 176
188 c hapter 7: m ulticast p rotocol figure 43 assert mechanism diagram when they detect such a case, routers need to select a unique sender by using the assert mechanism. Routers will send assert packets to select the best path. If two or more than two paths have the same priority and metric, the p...
Page 177
Pim-dm overview 189 after pim-dm is enabled on an interface, it will send pim hello messages periodically and process protocol packets sent by pim neighbors. Perform the following configuration in interface view. 3com recommends that you configure pim-dm on all interfaces in non-special cases. This ...
Page 178
190 c hapter 7: m ulticast p rotocol configuring the filtering of multicast source/group you can set to filter the source (and group) address of multicast data packets via this command. When this feature is configured, the router filters not only multicast data, but the multicast data encapsulated i...
Page 179
Pim-dm overview 191 by default, the pim neighbors on the interface are limited to 128. If the number of pim neighbors of an interface has exceeded the configured value by the time of configuration, the existing pim neighbors will not be deleted. Clearing multicast route entries from pim routing tabl...
Page 180
192 c hapter 7: m ulticast p rotocol execute the debugging command in user view for the debugging of pim-dm. Pim-dm configuration example networking requirements switch_a has a port carrying vlan 10 to connect the multicast source, a port carrying vlan11 to connect switch_b and a port carrying vlan1...
Page 181
Pim-sm overview 193 networking diagram figure 44 pim-dm configuration networking configuration procedure this section only describes the configuration procedure for switch_a. Follow a similar configuration procedure for switch_b and switch_c. 1 enable the multicast routing protocol. [sw5500]multicas...
Page 182
194 c hapter 7: m ulticast p rotocol and the bsr (bootstrap router) to advertise multicast information to all pim-sm routers, and uses the join/prune information of the router to build the rp-rooted shared tree (rpt). This reduces the bandwidth occupied by data packets and control packets, and reduc...
Page 183
Pim-sm overview 195 figure 45 rpt schematic diagram multicast source registration when multicast source s sends a multicast packet to the multicast group g, the pim-sm multicast router directly connected to s will encapsulate the received packet into a registration packet and send it to the correspo...
Page 184
196 c hapter 7: m ulticast p rotocol configuring static rp the router that serves as the rp is the core router of multicast routes. If the dynamic rp elected by bsr mechanism is invalid for some reason, the static rp can be configured to specify rp. As the backup of dynamic rp, static rp improves ne...
Page 185
Pim-sm overview 197 repeat this configuration to enable pim-sm on other interfaces. Only one multicast routing protocol can be enabled on an interface at a time. Once enabled pim-sm on an interface, pim-dm cannot be enabled on the same interface and vice versa. Configuring the pim-sm domain border a...
Page 186
198 c hapter 7: m ulticast p rotocol address is considered better when the priority is the same. If the new bsr address is better, the candidate bsr will replace its bsr address and stop regarding itself as the bsr. Otherwise, the candidate bsr will keep its bsr address and continue to regard itself...
Page 187
Pim-sm overview 199 basic acl can control the range of multicast group served by static rp. If static rp is in use, all routers in the pim domain must adopt the same configuration. If the configured static rp address is the interface address of the local router whose state is up, the router will fun...
Page 188
200 c hapter 7: m ulticast p rotocol only the register messages matching the acl permit clause can be accepted by the rp. Specifying an undefined acl will make the rp to deny all register messages. Limiting the range of legal bsr in the pim sm network using bsr (bootstrap router) mechanism, every ro...
Page 189
Pim-sm overview 201 perform the following configuration in pim view. For detailed information of crp-policy , please refer to the command manual. Clearing multicast route entries from pim routing table refer to “pim-dm overview” on page 186 . Clearing pim neighbors refer to “pim-dm overview” on page...
Page 190
202 c hapter 7: m ulticast p rotocol networking diagram figure 46 pim-sm configuration networking configuration procedure 1 on switch_a: a enable pim-sm. [sw5500]multicast routing-enable [sw5500]vlan 10 [sw5500-vlan10]port gigabitethernet 1/0/2 to gigabitethernet 1/0/3 [sw5500-vlan10]quit [sw5500]in...
Page 191
Pim-sm overview 203 [sw5500-vlan-interface10]igmp enable [sw5500-vlan-interface10]pim sm [sw5500-vlan-interface10]quit [sw5500]vlan 11 [sw5500-vlan11]port gigabitethernet 1/0/4 to gigabitethernet 1/0/5 [sw5500-vlan11]quit [sw5500]interface vlan-interface 11 [sw5500-vlan-interface11]igmp enable [sw55...
Page 192
204 c hapter 7: m ulticast p rotocol [sw5500-vlan-interface12]igmp enable [sw5500-vlan-interface12]pim sm [sw5500-vlan-interface12]quit.
Page 193: Acl C
8 acl c onfiguration this chapter covers the following topics: ■ brief introduction to acl ■ qos configuration ■ qos profile configuration ■ acl control configuration brief introduction to acl a series of matching rules are required for the network devices to identify the packets to be filtered. Aft...
Page 194
206 c hapter 8: acl c onfiguration specifies the match-order of an access control rule, it cannot be modified later, unless all the content is deleted and the match-order specified again. The case includes: acl cited by route policy function, acl used for control logon user, and so on. The depth-fir...
Page 195
Brief introduction to acl 207 you can use the following command to set the time range by performing the following configuration in the system view. Table 224 set the absolute time range when the start-time and end-time are not configured, it will be all the time for one day. The end time shall be la...
Page 196
208 c hapter 8: acl c onfiguration table 225 define basic acl define advanced acl the rules of the classification for advanced acl are defined on the basis of the attributes such as source and destination ip address, the tcp or udp port number in use and packet priority to process the data packets. ...
Page 197
Brief introduction to acl 209 you can use the following command to define the numbered layer-2 acl. Perform the following configuration in corresponding view. Table 227 define layer-2 acl activating acl the defined acl can be active after being activated globally on the switch. This function is used...
Page 198
210 c hapter 8: acl c onfiguration advanced acl configuration example networking requirements the interconnection between different departments on a company network is implemented through the 1000 mbps ports of the switch. The ip address of the payment query server of the financial dept. Is 129.110....
Page 199
Brief introduction to acl 211 basic acl configuration example networking requirements using basic acl, filter the packet whose source ip address is 10.1.1.1 during the time range 8:00 ~ 18:00 every day. The host connects port gigabitethernet1/0/1 of the switch. Networking diagram figure 48 access co...
Page 200
212 c hapter 8: acl c onfiguration networking diagram figure 49 access control configuration example configuration procedure in the following configurations, only the commands related to acl configurations are listed. 1 define the time range define time range from 8:00 to 18:00. [sw5500]time-range 3...
Page 201
Qos configuration 213 packet filter packet filter is used to filter traffic. For example, the operation “deny” discards the traffic that is matched with a traffic classification rule, while allowing other traffic to pass through. With the complex traffic classification rules, the switche enables the...
Page 202
214 c hapter 8: acl c onfiguration figure 50 sp the sp is designed for the key service application. A significant feature of the key service is the need for priority to enjoy the service to reduce the responding delay when congestion occurs. Take 8 egress queues for each port as an example, sp divid...
Page 203
Qos configuration 215 qos configuration the process of qos based traffic: 1 identify the traffic by acl 2 perform the qos operation to the traffic. The configuration steps of qos based traffic: 1 define the acl 2 configure the qos operation if qos is not based on traffic, you need not define acl fir...
Page 204
216 c hapter 8: acl c onfiguration setting port mirroring port mirroring means duplicating data on the monitored port to the designated mirror port, for purpose of data analysis and supervision. The switch supports one monitor port and multi mirroring port. If several switches form a fabric, only on...
Page 205
Qos configuration 217 only one monitor port can be configured on one switch. If a group of switches form a fabric, only one monitor port can be configured on one fabric. 2 configure traffic mirroring perform the following configuration in the ethernet port view. Table 237 configuring traffic mirrori...
Page 206
218 c hapter 8: acl c onfiguration table 241 configure the queue scheduling algorithm by default, the switch uses the wrr algorithm. For details about the command, refer to the command reference manual. Setting traffic limit traffic limit refers to rate limit based on traffic. If the traffic thresho...
Page 207
Qos configuration 219 perform the following configurations in the ethernet port view. Table 244 relabeling priority level configuring packet redirection packet redirection is to redirect the packets to be forwarded to cpu or other output port. You can use the following command in ethernet port view ...
Page 208
220 c hapter 8: acl c onfiguration for details about the command, refer to the command reference manual. Displaying and debugging qos configuration you can use the display command in any view to see the qos operation and to check the status of the configuration. You can also clear the statistic info...
Page 209
Qos configuration 221 networking diagram figure 51 qos configuration example configuration procedure only the commands concerning qos/acl configuration are listed here. 1 define outbound traffic for the wage server. A enter numbered advanced acl view. [sw5500]acl number 3000 b define the traffic-of-...
Page 210
222 c hapter 8: acl c onfiguration networking diagram figure 52 qos configuration example configuration procedure define port mirroring, with monitoring port being ethernet3/0/8. [sw5500-ethernet3/0/8]monitor-port [sw5500-ethernet3/0/1]mirroring-port both priority relabeling configuration example ne...
Page 211
Qos profile configuration 223 3 relabel ef priority for pc1 packets. [sw5500-ethernet1/0/1]traffic-priority inbound ip-group 2000 dscp ef qos profile configuration when used together with the 802.1x authentication function, the qos profile function can offer preconfigured qos settings for a qualifie...
Page 212
224 c hapter 8: acl c onfiguration configuring qos profile you must first define acls for the traffic actions before adding the actions to the qos profile. Entering qos profile view to configure the qos profile, you must first enter qos profile view. Perform the following configuration in system vie...
Page 213
Qos profile configuration 225 ■ user-based mode: if the source station information (source mac address, source ip address or source mac address + ip address) has been defined in the acl which is referenced in the traffic actions, the switch cannot deliver the qos profile; if no source station inform...
Page 214
226 c hapter 8: acl c onfiguration table 254 displaying qos profile configuration qos profile configuration example networking requirement the switch implements the qos profile function for the accessed user. The user (with user name someone and authentication password hello ) is accessed from the g...
Page 215
Acl control configuration 227 [sw5500-radius-radius1]quit e create the user domain 3com163.Net and specify radius1 as the radius server group for the user. [sw5500]domain 3com163.Net [sw5500-isp-3com163.Net]radius-scheme radius1 [sw5500-isp-3com163.Net]quit f define the acl [sw5500]acl number 3000 [...
Page 216
228 c hapter 8: acl c onfiguration table 255 defining basic acl you can define multiple rules for an acl by using the rule command several times. Importing acl you can import a defined acl in user interface view to achieve acl control. Perform the following configurations respectively in system view...
Page 217
Acl control configuration 229 2 import the acl. [sw5500]user-interface vty 0 4 [sw5500-ui-vty0-4]acl 2000 inbound configuring acl for snmp users the switch 5500g-ei family supports remote network management (nm) and the user can use snmp to access them. Proper acl configuration can prevent illegal u...
Page 218
230 c hapter 8: acl c onfiguration see the command manual for details about these commands. Uou can import only the basic acls with digit ids. Configuration example networking requirement only snmp users from 10.110.100.52 and 10.110.100.46 can access the switch. Networking diagram figure 57 acl con...
Page 219
Acl control configuration 231 perform the following configuration in system view. Table 258 calling acl to control http users for more about the commands, refer to the command reference manual. Only the numbered basic acl can be called for web nm user control. Configuration example networking requir...
Page 220
232 c hapter 8: acl c onfiguration.
Page 221: Xrn F
9 xrn f abric this chapter covers the following topics: ■ introduction to xrn ■ configuring an xrn fabric ■ fabric configuration example introduction to xrn several xrn switches of the same model can be interconnected to create a “fabric”, in which each switch is a unit. The ports used to interconne...
Page 222
234 c hapter 9: xrn f abric configuring an xrn fabric ftm provides user interfaces. You can configure vlan unit ids, fabric name, and the authentication mode between units by using the command. Table 259 configuring ftm setting unit ids for switches you can use the command in the following table to ...
Page 223
Fabric configuration example 235 displaying and debugging a fabric following completion of the above configuration, you can execute the display command in any view to view device management and verify the settings. Table 263 displaying and debugging ftm fabric configuration example networking requir...
Page 224
236 c hapter 9: xrn f abric [sw5500}set unit 1 name unit3 [sw5500]sysname hello configure switch d : [sw5500]change unit-id 1 to auto-numbering [sw5500}set unit 1 name unit [[sw5500]sysname hello in the example, it is assumed that the system will automatically change the unit ids of switch b, switch...
Page 225: Rstp C
10 rstp c onfiguration this chapter covers the following topics: ■ stp overview ■ rstp configuration ■ rstp configuration example stp overview spanning tree protocol (stp) is applied in loop networks to block some undesirable redundant paths with certain algorithms and prune the network into a loop-...
Page 226
238 c hapter 10: rstp c onfiguration what are the designated bridge and designated port? Figure 61 designated bridge and designated port for a switch, the designated bridge is a switch in charge of forwarding bpdu to the local switch via a port called the designated port. For a lan, the designated b...
Page 227
Stp overview 239 figure above, the priorities of switch a, b and c are 0, 1 and 2 and the path costs of their links are 5, 10 and 4 respectively. 1 initial state when initialized, each port of the switches will generate the configuration bpdu taking itself as the root with a root path cost as 0, des...
Page 228
240 c hapter 10: rstp c onfiguration the comparison process of each switch is as follows. ■ switch a: ap1 receives the configuration bpdu from switch b and finds out that the local configuration bpdu priority is higher than that of the received one, so it discards the received configuration bpdu. Th...
Page 229
Stp overview 241 cp2 will receive the updated configuration bpdu, {0, 5, 1, bp2 }, from switch b. Since this configuration bpdu is better then the old one, the old bpdu will be updated to {0, 5, 1, bp2 }. Meanwhile, cp1 receives the configuration bpdu from switch a but its configuration bpdu will no...
Page 230
242 c hapter 10: rstp c onfiguration designated port begin to send data again. That is, the root port and designated port should undergo a transitional state for a period of forward delay before they enter the forwarding state. Implement rstp on the switch the switch implements the rapid spanning tr...
Page 231
Rstp configuration 243 rstp configuration the configuration of rstp changes with the position of the switch in the network, as discussed below. Figure 64 configuring stp table 264 rstp configuration switch a and switch b: root bridge and backup root bridge switch c and switch d: intermediate switche...
Page 232
244 c hapter 10: rstp c onfiguration specify forward delay, hello time, and max age forward delay fixes on 15 seconds, hello times on 2 seconds, and max age on 20 seconds. The other switches copies the configuration on the root bridge with respect to these time parameters. You can therefore only con...
Page 233
Rstp configuration 245 specify the maximum transmission rate of stp packets on a port no ethernet port can send more than 3 stp packets within one hello time. The more stp packets a port sends within one hello time, the more resources are consumed. It is therefore recommended to limit the transmissi...
Page 234
246 c hapter 10: rstp c onfiguration after the stp protocol is enabled, the modification of any parameter will result in the re-calculation of the spanning tree on the switch. It is therefore recommended to configure all the rstp parameters before enabling the stp feature on the switch and the port....
Page 235
Rstp configuration 247 table 266 enable/disable rstp on a port note that the redundancy route may be generated after rstp is disabled on the ethernet port. By default, rstp on all the ports will be enabled after it is enabled on the switch. Configure rstp operating mode rstp is executable in rstp mo...
Page 236
248 c hapter 10: rstp c onfiguration by default, no vlan is stp-ignored if stp is enabled on the switch. Set priority of a specified bridge whether a bridge can be selected as the “root” of the spanning tree depends on its priority. By assigning a lower priority, a bridge can be artificially specifi...
Page 237
Rstp configuration 249 to configure a switch as the root of the spanning tree instance, you can specify its priority as 0 or simply set it as the root, using the command. It is not necessary to specify two or more roots for an sti — do not specify the root for an sti on two or more switches. You can...
Page 238
250 c hapter 10: rstp c onfiguration table 272 set hello time of the specified bridge an appropriate hello time can ensure that the bridge can detect certain link failures in the network in a timely manner. It is strongly recommended that default value of 2 seconds is retained. By default, the hello...
Page 239
Rstp configuration 251 by default, the multiple value of hello time of the bridge is 3. Specifying the maximum transmission rate of stp packets on a port the maximum transmission rate of stp packets on an ethernet port is dependent on the physical status of the port and the network architecture. You...
Page 240
252 c hapter 10: rstp c onfiguration by default, all the ethernet ports are configured as non-edgeport. Specifying the path cost on a port path cost is a parameter related with the link rate. Specify the path cost on a port you can specify the path cost on a port by using the following commands. Per...
Page 241
Rstp configuration 253 table 279 set the priority of a specified port by setting the priority of an ethernet port, you can put a specified ethernet port into the final spanning tree. Generally, the lower the value is set, the higher priority the port has and the more likely it is for this ethernet p...
Page 242
254 c hapter 10: rstp c onfiguration switch running rstp is still working in stp-compatible mode. You can use the following command to manually configure the port to work in rstp mode. This command can only be issued if the bridge runs rstp in rstp mode and has no effect in the stp-compatible mode. ...
Page 243
Rstp configuration 255 table 282 configure the switch security function after being configured with bpdu protection, the switch will disable the edge port through rstp, which receives a bpdu, and notify the network manager at the same time. Only the network manager can resume these ports. The port c...
Page 244
256 c hapter 10: rstp c onfiguration rstp configuration example networking requirements in the following scenario, switch c serves as a standby of switch b and forwards data when a fault occurs on switch b. They are connected to each other with two links, so that, in case one of the links fails, the...
Page 245
Rstp configuration example 257 e enable the root protection function on every designated port. [sw5500]interface gigabitethernet 2/0/1 [sw5500-gigabitethernet2/0/1]stp root-protection [sw5500]interface gigabitethernet 2/0/2 [sw5500-gigabitethernet2/0/2]stp root-protection 2 configure switch b a enab...
Page 246
258 c hapter 10: rstp c onfiguration rstp operating mode, time parameters, and port parameters take default values. 4 configure switch d a enable rstp globally. [sw5500]stp enable b the port rstp defaults are enabled after global rstp is enabled. You can disable rstp on those ports that are not invo...
Page 247: 802.1
11 802.1 x c onfiguration this chapter covers the following topics: ■ ieee 802.1x overview ■ configuring 802.1x ■ centralized mac address authentication configuration ■ aaa and radius protocol configuration for information on setting up a radius server and radius client refer to appendix b . For det...
Page 248
260 c hapter 11: 802.1 x c onfiguration the lan access control device needs to provide the authenticator system of 802.1x. The devices at the user side such as the computers need to be installed with the 802.1x client supplicant (user) software, for example, the 802.1x client provided by 3com (or by...
Page 249
Configuring 802.1x 261 the eapol-start, eapol-logoff and eapol-key only exist between the user and the authenticator. The eap-packet information is re-encapsulated by the authenticator system and then transmitted to the authentication server system. The eapol-encapsulated-asf-alert is related to the...
Page 250
262 c hapter 11: 802.1 x c onfiguration enabling/disabling 802.1x the following command can be used to enable/disable the 802.1x on the specified port or globally. When it is used in system view ,if the parameter interface-list is not specified, 802.1x will be globally enabled. If the parameter inte...
Page 251
Configuring 802.1x 263 by default, 802.1x authentication method on the port is macbased . That is, authentication is performed based on mac addresses. Checking the users that log on the switch via proxy the following commands are used for checking the users that log on the switch via proxy. Perform ...
Page 252
264 c hapter 11: 802.1 x c onfiguration by default, the switch can trigger the user id authentication over the users who configure static ip addresses in dhcp environment. Configuring the authentication method for 802.1x user the following commands can be used to configure the authentication method ...
Page 253
Configuring 802.1x 265 handshake-period: this timer begins after the user has passed the authentication. After setting handshake-period, system will send the handshake packet by the period. Suppose the dot1x retry time is configured as n, the system will consider the user having logged off and set t...
Page 254
266 c hapter 11: 802.1 x c onfiguration again. During the quiet period, the authenticator does not do anything related to 802.1x authentication. Perform the following configuration in system view. Table 293 enabling/disabling a quiet-period timer by default, the quiet-period timer is disabled. Displ...
Page 255
Configuring 802.1x 267 primary-authentication/second-accounting server. The latter one acts as the secondary-authentication/primary-accounting server. Set the encryption key as “name” when the system exchanges packets with the authentication radius server and “money” when the system exchanges packet...
Page 256
268 c hapter 11: 802.1 x c onfiguration 5 set the ip address of the secondary authentication/accounting radius servers. [sw5500-radius-radius1]secondary authentication 10.11.1.2 [sw5500-radius-radius1]secondary accounting 10.11.1.1 6 set the encryption key when the system exchanges packets with the ...
Page 257
Centralized mac address authentication configuration 269 user name and password. The authentication to the user initiates after the switch detects the user’s mac address for the first time. The switch 5500g-ei supports local and radius mac address authentication. When it functions as the radius clie...
Page 258
270 c hapter 11: 802.1 x c onfiguration table 297 configuring the isp domain used by the centralized mac address authentication user by default, the domain used by the centralized mac address authentication user is null, that is, not configured. Configuring centralized mac address authentication tim...
Page 259
Centralized mac address authentication configuration 271 table 300 auto vlan before the vlan is correctly received by the switch 5500g-ei, you need to execute the following command on the switch 5500g-ei to use standard private-group-id: [5500-xx]private-group-id mode standard configuration example ...
Page 260
272 c hapter 11: 802.1 x c onfiguration aaa and radius protocol configuration authentication, authorization and accounting (aaa) provide a uniform framework used for configuring these three security functions to implement the network security management. The network security mentioned here refers to...
Page 261
Aaa and radius protocol configuration 273 the radius server various kinds of response messages in which the accept message indicates that the user has passed the authentication, and the reject message indicates that the user has not passed the authentication and needs to input their username and pas...
Page 262
274 c hapter 11: 802.1 x c onfiguration users of different isp. Because the attributes of isp users, such as username and password formats, and so on, may be different, it is necessary to differentiate them through setting isp domain. In the switch 5500g-ei units, isp domain view, you can configure ...
Page 263
Aaa and radius protocol configuration 275 when using scheme radius-scheme radius-scheme-name local in the configuraton command, the local refers to the alternative authentication scheme if the radius server does not respond normally. Therefore, when radius server operates normally, the local scheme ...
Page 264
276 c hapter 11: 802.1 x c onfiguration perform the following configurations in isp domain view. Table 306 enabling the selection of the radius accounting option by default, the selection of radius accounting option is disabled. The accounting optional command can also be configured in the radius sc...
Page 266
278 c hapter 11: 802.1 x c onfiguration setting the attributes of local user s perform the following configurations in local user view. Table 311 setting/removing the attributes concerned with a specified user note the following two items when you configure these service types: ssh, telnet or termin...
Page 267
Aaa and radius protocol configuration 279 table 312 disconnecting a user by force by default, no online user will be disconnected by force. Configuring the radius protocol for the switch 5500g-ei, the radius protocol is configured on the per radius scheme basis. In a real networking environment, a r...
Page 268
280 c hapter 11: 802.1 x c onfiguration perform the following configurations in system view. Table 313 creating/deleting a radius server group by default, the system has a radius scheme named as default system whose attributes are all default values. The default attribute values will be introduced i...
Page 269
Aaa and radius protocol configuration 281 in real networking environments, you may specify two radius servers as primary and secondary authentication/authorization servers respectively, or specify one server to function as both. The radius service port settings on the switch 5500g-ei should be consi...
Page 270
282 c hapter 11: 802.1 x c onfiguration while, it will consider that there is device failure and stop accounting. It is necessary to disconnect the user at the nas end and on the radius server synchronously when some unpredictable failure occurs. The switch allows you to set the maximum number of ti...
Page 271
Aaa and radius protocol configuration 283 table 318 setting the maximum retransmitting times of stopping accounting reques t by default, the stopping accounting request can be retransmitted up to 500 times. Enabling the selection of the radius accounting option perform the following configurations i...
Page 272
284 c hapter 11: 802.1 x c onfiguration table 321 setting retransmission times of radius request packet by default, radius request packet will be retransmitted up to three times. Setting the supported type of the radius server the switch 5500g-ei supports the standard radius protocol and the extende...
Page 273
Aaa and radius protocol configuration 285 setting the username format transmitted to the radius server as mentioned above, the users are generally named in userid@isp-name format. The part following “@” is the isp domain name. The switch will put the users into different isp domains according to the...
Page 274
286 c hapter 11: 802.1 x c onfiguration by default, the ip address of the local radius authentication server is 127.0.0.1 and the password is 3com. 1) when using local radius authentication server function of 3com, remember the number of the udp port used for authentication is 1645 and that for acco...
Page 275
Aaa and radius protocol configuration 287 you can use the following command to set a real-time accounting interval. Perform the following configurations in radius scheme view. Table 329 setting a real-time accounting interval minute specifies the real-time accounting interval in minutes. The value s...
Page 276
288 c hapter 11: 802.1 x c onfiguration table 332 displaying and debugging aaa and radius protocol aaa and radius protocol configuration example for the hybrid configuration example of aaa/radius protocol and 802.1x protocol, refer to “802.1x configuration example” on page 266 . Configuring the ftp/...
Page 277
Aaa and radius protocol configuration 289 networking requirements in figure 69 , it is required to configure the remote radius authentication of telnet users. One radius server (as authentication server) is connected to the switch and the server ip address is 10.110.91.146. The password for exchangi...
Page 278
290 c hapter 11: 802.1 x c onfiguration configuring the ftp/telnet user local authentication configuring local authentication for ftp users is similar to that for telnet users. The following example is based on telnet users. Networking requirements configure the router to authenticate the login teln...
Page 279
Aaa and radius protocol configuration 291 information about the local domain can be seen by typing "display domain". For example: display domain 0 domain = default system state = active scheme = local access-limit = disable domain user template: idle-cut = disable self-service = disable messenger ti...
Page 280
292 c hapter 11: 802.1 x c onfiguration once enabled globally, the network login needs to be enabled on a per port basis. This can be done in one of two ways: ■ to enable dot1x on one port, enter the interface of the port and enable dot1x on the port. For example: [5500-xx]interface ethernet 1/0/7 [...
Page 281
Aaa and radius protocol configuration 293 the end of the username. This states the user is a member of the local domain, and as a result uses the local radius server. Based on the steps in section domain and radius scheme creation to login using the external radius server defined, you need to login ...
Page 282
294 c hapter 11: 802.1 x c onfiguration ■ the accounting service and authentication/authorization service are provided on different servers, but nas requires the services to be provided on one server (by specifying the same ip address). So make sure the settings of the servers are consistent with th...
Page 283: Ile
12 f ile s ystem m anagement this chapter covers the following topics: ■ file system overview ■ configuring file management ■ ftp overview ■ tftp overview ■ mac address table management ■ device management ■ system maintenance and debugging ■ displaying the state and information of the system ■ test...
Page 284
296 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement directory operation you can use the file system to create or delete a directory, display the current working directory, and display the information about the files or directories under a specified directory. You can use the following commands to perform dir...
Page 285
Configuring file management 297 perform the following configuration in system view. Table 335 execute the specified batch file storage device operation the file system can be used to format a specified memory device. You can use the following commands to format a specified memory device. Perform the...
Page 286
298 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement displaying the current-configuration and saved-configuration of the switch after being powered on, the system reads the configuration files from flash for the initialization of the device. (such configuration files are called saved-configuration files.) if ...
Page 287
Ftp overview 299 you may erase the configuration files from the flash in the following cases: ■ after being upgraded, the software does not match with the configuration files. ■ the configuration files in flash are damaged. (a common case is that a wrong configuration file has been downloaded.) conf...
Page 288
300 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement table 343 configuration of the switch as ftp client table 344 configuration of the switch as ftp server the prerequisite for normal ftp function is that the switch and pc are reachable. Enabling/disabling ftp server you can use the following commands to ena...
Page 289
Ftp overview 301 only the clients who have passed the authentication and authorization successfully can access the ftp server. Configuring the running parameters of ftp server you can use the following commands to configure the connection timeout of the ftp server. If the ftp server receives no serv...
Page 290
302 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement password hello and with read and write authority over the switch root directory on the pc. The ip address of a vlan interface on the switch is 1.1.1.1, and that of the pc is 2.2.2.2. The switch and pc are reachable. The switch application switch.App is stor...
Page 291
Ftp overview 303 6 use the quit command to release ftp connection and return to user view. [ftp]quit 7 use the boot boot-loader command to specify the downloaded program as the application at the next login and reboot the switch. Boot boot-loader switch.App reboot ftp server configuration example ne...
Page 292
304 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement use the boot boot-loader command to specify the downloaded program as the application at the next login and reboot the switch. Boot boot-loader switch.App reboot tftp overview trivial file transfer protocol (tftp) is a simple protocol for file transmission....
Page 293
Tftp overview 305 table 350 download files by means of tftp uploading files by means of tftp to upload a file, the client sends a request to the tftp server and then transmits data to it and receives the acknowledgement from it. You can use the following commands to upload files. Perform the followi...
Page 294
306 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement [sw5500] 4 configure ip address 1.1.1.1 for the vlan interface, ensure the port connecting the pc is also in this valn (vlan 1 in this example). [sw5500]interface vlan 1 [sw5500-vlan-interface1]ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 [sw5500-vlan-interface1]quit 5...
Page 295
Mac address table management 307 figure 76 the switch forwards packets with mac address table the switch also provides the function of mac address aging. If the switch receives no packet for a period of time, it will delete the related entry from the mac address table. However, this function takes n...
Page 296
308 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement when deleting the dynamic address table entries, the learned entries will be deleted simultaneously. Setting mac address aging time setting an appropriate aging time implements mac address aging. Too long or too short an aging time set by subscribers will c...
Page 297
Mac address table management 309 table 354 set the max count of mac address learned by a port by default, there is no limit to the mac addresses learned via the ethernet port. Displaying mac address table after the above configuration, execute the display command in all views to display the running ...
Page 298
310 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement networking diagram figure 77 display mac address table configuration procedure the display command shows a stack wide view of the mac address table. [sw5500]display mac-address mac addr vlan id state port index aging time(s) 00e0-fc00-3943 1 learned gigabit...
Page 299
Device management 311 networking diagram figure 78 typical configuration of address table management configuration procedure 1 enter the system view of the switch. System-view system view: return to user view with ctrl+z 2 add a mac address (specify the native vlan, port and state). [sw5500]mac-addr...
Page 300
312 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement perform the following configuration in user view. Table 356 reboot the switch enabling the timing reboot function after enabling the timing reboot function on the switch, the switch will be rebooted at the specified time. Perform the following configuration...
Page 301
Device management 313 table 360 display and debug device management device management configuration example networking requirement the user logs into the switch using telnet, downloads the application from the ftp server to the flash memory of the switch, and implements remote upgrade using the righ...
Page 302
314 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement caution: if the flash memory of the switch is not enough, you need to first delete the existing programs in the flash memory and then upload the new ones. 3 type in the correct command in user view to establish ftp connection, then enter the correct usernam...
Page 303
Displaying the state and information of the system 315 setting the system clock perform the operationof clock datetime command in the user view. Table 362 set the system clock setting the time zone you can configure the name of the local time zone and the time difference between the local time and t...
Page 304
316 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement configuration agent is one of the xrn features. You can log into one switch of the fabric to configure and manage the fabric. The functions of the configuration agent include: ■ distributing configuration commands to the right destination switches or proces...
Page 305
Displaying the state and information of the system 317 figure 80 debug output you can use the following commands to control the above-mentioned debugging. Perform the following operations in user view. Table 366 enable/disable the debugging for more about the usage and format of the debugging comman...
Page 306
318 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement after the synchronization of the whole fabric, a great deal of terminal display is generated. You are recommended not to enable the information synchronization switch of the whole fabric. If you enabled the information synchronization switch, after the sync...
Page 307
Hwping 319 table 369 test periodically if the ip address is reachable the switch can ping an ip address every one minute to test if it is reachable. Three ping packets can be sent at most for every ip address in every testing with a time interval of five seconds. If the switch cannot successfully pi...
Page 308
320 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement ■ configure the test parameter enable hwping client by enabling hwping client, various types of tests can be set and carried out. Perform the following configurations in system view. Table 370 enable hwping client by default, hwping client is disabled. Crea...
Page 309
Hwping 321 configuring a test type you can test various connections by using the hwping function. You can only configure one test type at a time. Currently, the system only supports icmp test. Perform the following configuration in hwping test group view. Table 373 configure a test type by default, ...
Page 310
322 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement regard the destination unreachable. The parameter discussed in this subsection is equal to the parameter -t in a ping command, except in a different time unit. Perform the following configurations in hwping test group view. Table 376 configure a test timeou...
Page 311
Hwping 323 typical hwping configuration example like ping test, icmp test in hwping determines the roundtrip delay of a packet by making use of icmp. Network diagram figure 82 hwping configuration procedure steps 1 to 3 and 6 are required for an icmp test and the remaining three steps are optional. ...
Page 312
324 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement logging function introduction to info-center the info-center serves as an information center of the system software modules. The logging system is responsible for most of the information outputs, and it also makes detailed classification to filter the infor...
Page 313
Logging function 325 if changed to boot format, it represents the milliseconds from system booting. Generally, the data are so large that two 32 bits integers are used, and separated with a dot '.'. For example: 0.166970 sw5500 ifnet/6/updown:line protocol on interface ethernet1/0/2, changed state t...
Page 314
326 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement note that there is a slash ('/') between module name and severity. 5 severity switch information falls into three categories: log information, debugging information and trap information. The info-center classifies every kind of information into 8 severity o...
Page 315
Logging function 327 definition of severity in logging information is as follows. Table 380 info-center-defined severity note that there is a slash between severity and digest. 6 digest the digest is abbreviation, it represent the abstract of contents. Note that there is a colon between digest and c...
Page 316
328 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement ■ the output language can be selected between chinese and english. 1 sending the information to loghost. Table 382 sending the information to loghos t 2 sending the information to the control terminal. Table 383 sending the information to the control termin...
Page 317
Logging function 329 table 384 sending the information to monitor terminal 4 sending the information to log buffer. Table 385 sending the information to log buffer 5 sending the information to trap buffer. Table 386 sending the information to trap buffer 6 sending the information to snmp device conf...
Page 318
330 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement table 387 sending the information to snmp 7 turn on/off the information synchronization switch in fabric figure 83 turn on/off the information synchronization switch in fabric sending the information to loghost to send information to the loghost, follow the...
Page 319
Logging function 331 table 389 configuring to output information to loghost ensure to enter the correct ip address using the info-center loghost command to configure loghost ip address. If you enter a loopback address, the system prompts of invalid address appears. 3 configuring the information sour...
Page 320
332 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement 4 configuring loghost the configuration on the loghost must be the same with that on the switch. For related configuration, see the configuration examples in the latter part of this chapter. Sending the information to control terminal to send information to...
Page 321
Logging function 333 when defining the information sent to the control terminal, channel-number or channel-name must be set to the channel that corresponds to the console direction. Every channel has been set with a default record, whose module name is default and the module number is 0xffff0000. Ho...
Page 322
334 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement table 396 enable/disable info-center info-center is enabled by default. After info-center is enabled, system performances are affected when the system processes much information because of information classification and outputting. 2 configuring to output i...
Page 323
Logging function 335 if you want to view the debugging information of some modules on the switch, you must select debugging as the information type when configuring information source, meantime using the debugging command to turn on the debugging switch of those modules. You can use the following co...
Page 324
336 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement info-center is enabled by default. After info-center is enabled, system performances are affected when the system processes much information because of information classification and outputting. 2 configuring to output information to the log buffer perform ...
Page 325
Logging function 337 table 404 configuring the output format of time-stamp sending the information to the trap buffer to send information to the trap buffer, follow the steps below: 1 enabling info-center perform the following operation in system view. Table 405 enabling/disabling info-center info-c...
Page 326
338 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement when defining the information sent to the trap buffer, channel-number or channel-name must be set to the channel that corresponds to the console direction. Every channel has been set with a default record, whose module name is default and the module number ...
Page 327
Logging function 339 with this configuration, you can define the information that is sent to snmp nm: generated by which modules, information type, information level, and so on. Perform the following operation in system view. Table 411 defining information source modu-name specifies the module name;...
Page 328
340 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement the switch provides a command to turn on/off the synchronization switch in every switch. If the synchronization switch of a switch is turned off, it does not send information to other switches but still receives information from others. 1 enable info-center...
Page 329
Logging function 341 ■ the information with the severitylevel above informational will be sent to the loghost ■ the output language is english ■ the modules that allowed to output information are arp and ip networking diagram figure 86 schematic diagram of configuration configuration procedure 1 con...
Page 330
342 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement (3) no redundant space after file name. (4) the device name and the acceptant log information level specified in /etc/syslog.Conf must be consistent with info-center loghost and info-center loghost a.B.C.D facility configured on the switch. Otherwise, the l...
Page 331
Logging function 343 [sw5500]info-center loghost 202.38.1.10 facility local7 language english [sw5500]info-center source default channel loghost log level informational 2 configuration on the loghost this configuration is performed on the loghost. A perform the following command as the super user (r...
Page 332
344 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement ■ the modules that allowed to output information are arp and ip networking diagram figure 88 schematic diagram of configuration configuration procedure 1 configuration on the switch enabling info-center [sw5500]info-center enable 2 configure control termina...
Page 333
Snmp configuration 345 to report the events whenever the device encounters any abnormalities such as new device found and restart. Snmp versions and supported mib to uniquely identify the management variables of a device in snmp messages, snmp adopts the hierarchical naming scheme to identify the ma...
Page 334
346 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement configure snmp the main configuration of snmp includes: ■ set community name ■ set the method of identifying and contacting the administrator ■ enable/disable snmp agent to send trap ■ set the destination address of trap ■ set snmp system information ■ set ...
Page 335
Snmp configuration 347 table 417 enable/disable snmp agent to send trap setting the destination address of trap you can use the following commands to set or delete the destination address of the trap. Perform the following configuration in system view. Table 418 set the destination address of trap s...
Page 336
348 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement by default, the syslocation is specified as a blank string, that is, “”. Setting the engine id of a local or remote device you can use the following commands to set the engine id of a local or remote device. Perform the following configuration in system vie...
Page 337
Snmp configuration 349 table 424 add/delete a user to/from an snmp group creating/updating view information or deleting a view you can use the following commands to create, update the information of views or delete a view. Perform the following configuration in system view. Table 425 create/update v...
Page 338
350 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement if user disable nmp agent, it will be enabled whatever snmp-agent command is configured thereafter. Displaying and debugging snmp after the above configuration, execute the display command in all views to display the running of the snmp configuration, and t...
Page 339
Snmp configuration 351 networking diagram figure 90 snmp configuration example configuration procedure 1 enter the system view. System-view 2 set the community name , group name and user. [sw5500]snmp-agent sys-info version all [sw5500]snmp-agent community write public [sw5500]snmp-agent mib include...
Page 340
352 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement reading usmusr table configuration example networking requirements viewdefault view should be reconfigured if you use snmp v3 to read the usmusr table. The snmpvacmmib and snmpusmmib should be included in viewdefault view. Networking diagram figure 91 snmp ...
Page 341
Rmon configuration 353 view name:viewdefault mib subtree:snmpmodules.18 subtree mask: storage-type: nonvolatile view type:excluded view status:active rmon configuration remote network monitoring (rmon) is a type of ietf-defined mib. It is the most important enhancement to the mib ii standard. It is ...
Page 342
354 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement ■ add/delete an entry to/from the statistics table adding/deleting an entry to/from the alarm table rmon alarm management can monitor the specified alarm variables such as the statistics on a port. When a value of the monitored data exceeds the defined thre...
Page 343
Rmon configuration 355 table 432 add/delete an entry to/from the history control termina l adding/deleting an entry to/from the extended rmon alarm table you can use the command to add/delete an entry to/from the extended rmon alarm table. Perform the following configuration in system view. Table 43...
Page 344
356 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement rmon configuration example networking requirements set an entry in rmon ethernet statistics table for the ethernet port performance, which is convenient for network administrators’ query. Networking diagram figure 92 rmon configuration networking configurat...
Page 345
Ntp overview 357 ntp overview as the network topology gets more and more complex, it becomes important to synchronize the clocks of the equipment on the whole network. Network time protocol (ntp) is the tcp/ip that advertises the accurate time throughout the network. Ntp ensures the consistency of t...
Page 346
358 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement ■ switch a sends an ntp packet to switch b. The packet carries the timestamp 10:00:00am (t 1 ) that tells when it left switch a. ■ when the ntp packet arrives at switch b, switch b adds a local timestamp 11:00:01am (t 2 ) to it. ■ when the ntp packet leaves...
Page 347
Ntp configuration 359 ■ configure ntp server mode ■ configure ntp peer mode ■ configure ntp broadcast server mode ■ configure ntp broadcast client mode ■ configure ntp multicast server mode ■ configure ntp multicast client mode configuring ntp server mode set a remote server whose ip address is ip-a...
Page 348
360 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement which the source ip address of the ntp packets sent from the local switch to the peer will be taken; priority indicates the peer will be the first choice for the time server. Configuring ntp broadcast server mode designate an interface on the local switch t...
Page 349
Ntp configuration 361 table 440 configure ntp multicast server mode ntp version number number ranges from 1 to 3 and defaults to 3; the authentication key id keyid ranges from 0 to 4294967295; ttl-number of the multicast packets ranges from 1 to 255; and the multicast ip address defaults to 224.0.1....
Page 350
362 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement table 443 configure ntp authentication key key number number ranges from 1 to 4294967295; the key value contains 1 to 32 ascii characters. Setting specified key as reliable this configuration task is to set the specified key as reliable. Perform the followi...
Page 351
Ntp configuration 363 table 446 enable/disable an interface to receive ntp message this configuration task must be performed on the interface to be disabled to receive ntp message. Setting authority to access a local switch set authority to access the ntp services on a local switch. This is a basic ...
Page 352
364 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement displaying and debugging ntp after completing the above configurations, you can use the display command to show how ntp runs and verify the configurations according to the outputs. In user view, you can use the debugging command to debug ntp. Table 449 ntp ...
Page 353
Typical ntp configuration examples 365 configuration procedure configure switch 1: 1 enter system view. System-view 2 set the local clock as the ntp master clock at stratum 2. [switch1]ntp-service refclock-master 2 configure switch 2: 1 enter system view. System-view 2 set sw5500 1 as the ntp server...
Page 354
366 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement ******************************************************************** [12345]1.0.1.11 local(0) 3 377 64 16 -0.4 0.0 0.9 note: 1 source(master),2 source(peer),3 selected,4 candidate,5 configured ntp peer configuration network requirements on switch 3, set loc...
Page 355
Typical ntp configuration examples 367 by this time, switch 4 has been synchronized by switch 5 and it is at stratum 2, or higher than switch 5 by 1. Display the sessions of switch 4 and you will see switch 4 has been connected with switch 5. [switch4]display ntp-service sessions source reference st...
Page 356
368 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement in the above examples switch 4 and switch 1 are configured to listen to the broadcast via vlan-interface2, switch 3 to broadcast packets from vlan-interface2. As switch 1 and switch 3 are not located on the same segment, they cannot receive any broadcast pa...
Page 357
Typical ntp configuration examples 369 [switch3-vlan-interface2]ntp-service multicast-server configure switch 4: 1 enter system view. System-view 2 enter vlan-interface2 view. [switch4]interface vlan-interface 2 3 enable multicast client mode. [switch4-vlan-interface2]ntp-service multicast-client co...
Page 358
370 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement [switch2]ntp-service authentication enable 4 set the key. [switch2]ntp-service authentication-keyid 42 authentication-mode md5 anicekey set the key as reliable. 5 [switch2]ntp-service reliable authentication-keyid 42 [switch2]ntp-service unicast-server 1.0....
Page 359
Ssh terminal services 371 the communication process between the server and client include these five stages: version negotiation stage, key negotiation stage, authentication stage, session request stage, interactive session stage. ■ version negotiation stage: the client sends tcp connection requirem...
Page 360
372 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement ■ setting system protocol and link maximum ■ configuring and deleting local rsa key pair ■ configuring authentication type ■ defining update interval of server key ■ defining ssh authentication timeout value ■ defining ssh authentication retry value ■ enter...
Page 361
Ssh terminal services 373 table 452 configuring authentication type if the configuration is rsa authentication type, then the rsa public key of the client user must be configured on the switch, that is to perform the 7 and 8 serial number marked configuration. By default, no authentication type is s...
Page 362
374 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement this operation is only available for the ssh users using rsa authentication. At the switch, you configure the rsa public key of the client, while at the client, you specify the rsa private key which corresponds to the rsa public key. This operation will fai...
Page 363
Ssh terminal services 375 ■ specifying rsa private key file. If you specify rsa authentication for the ssh user, you must specify rsa private key file. The rsa key, which includes the public key and private key, are generated by the client software. The former is configured in the server (switch) an...
Page 364
376 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement figure 99 ssh key convert. Use the save button to save this converted key to a file. Open the public key file in notepad and the following lines of text before the existing text: rsa peer-public-key mykey public-key-code begin where mykey is a name used to ...
Page 365
Ssh terminal services 377 figure 100 text file of mykey save this to a file ending with a ".Bat" extension e.G "keys.Bat". This file can be transferred to the switch using ftp or tftp. The key is installed using the execute command in the system view [sw5500]execute keys.Bat specifying server ip add...
Page 366
378 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement figure 101 ssh client configuration interface (1) in the host name (or ip address) text box key in the ip address of the switch, for example, 10.110.28.10. You can also input the ip address of an interface in up state, but its route to ssh client pc must be...
Page 367
Ssh terminal services 379 figure 102 ssh client configuration interface (2) you can select 1, as shown in the above figure. Specifying rsa private key file if you want to enable rsa authentication, you must specify rsa private key file, which is not required for password authentication. Click [ssh/a...
Page 368
380 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement figure 103 ssh client configuration interface (3) click browse to enter the file select interface. Choose a desired file and click ok. Opening ssh connection click open to enter ssh client interface. If it runs normally, you are prompted to enter username a...
Page 369
Ssh terminal services 381 log out of ssh connection with the logout command. Displaying and debugging ssh run the display command in any view to view the running of ssh and further to check configuration result. Run the debugging command to debug the ssh. Perform the following configurations in any ...
Page 370
382 c hapter 12: f ile s ystem m anagement connected to the switch and access the switch using username “client001” and password “3com”. 3 for rsa authentication mode: create local user client002 [sw5500]local-user client002 [sw5500-luser-client002]service-type ssh 4 specify aaa authentication on th...
Page 371: Assword
A p assword r ecovery p rocess introduction the switch 5500g-ei has two separate password systems: ■ passwords which are used by the web user inteface and the cli and are stored in the 3comoscfg.Cfg file. For more information on this, refer to the getting started guide which accompanies your switch....
Page 372
384 c hapter a: p assword r ecovery p rocess bootrom interface during the intitial boot phase of the switch (when directly connected via the console), various messages are displayed and the following prompt is shown with a five second countdown timer: press ctrl-b to enter boot menu... 4 before the ...
Page 373
Bootrom interface 385 skipping the current configuration file enter boot menu option 7 to enable the switch to boot from the factory default configuration file 3comoscfg.Def . When the switch has booted from the factory default it can be configured with an ip address and default gateway if needed. T...
Page 374
386 c hapter a: p assword r ecovery p rocess bootrom password recovery select option 8 to set the bootrom password discovery. The following is displayed: warning: if disable the bootrom password recovery, the super password based on switch mac address is invalid! The current mode is enable bootrom p...
Page 375: Radius S
B radius s erver and radius c lient s etup this appendix covers the following topics: ■ setting up a radius server ■ setting up the radius client setting up a radius server there are many third party applications available to configure a radius server. 3com has successfully installed and tested the ...
Page 376
388 c hapter b: radius s erver and radius c lient s etup and computers window, right-click domain and choose properties, select change mode. C add a user that is allowed to use the network. Go to active directory users and computers, from the left hand window right-click the users folder and choose ...
Page 377
Setting up a radius server 389 e the password for the user must be set to be stored in reversible encryption. Right-click the user account and select properties. Select the account tab, check the box labelled store password using reversible encryption. F now re-enter the password for the account, ri...
Page 378
390 c hapter b: radius s erver and radius c lient s etup in the certificate authority type window select enterprise root ca enter information to identify the certificate authority on the ca identifying information window. Enter the storage location on the data storage location window. To complete th...
Page 379
Setting up a radius server 391 5 configure a certificate authority a go to programs > administrative tools > certification authority and right-click policy settings under your certificate authority server. B select new > certificate to issue c select authenticated session and select ok. D go to prog...
Page 380
392 c hapter b: radius s erver and radius c lient s etup e select the group policy tab, and ensure that the default domain policy is highlighted. Click edit to launch the group policy editor. F go to computer configuration > windows settings > security settings > public key policies, and right-click...
Page 381
Setting up a radius server 393 i open up a command prompt (start > run, enter cmd ). Enter secedit /refreshpolicy machine_policy . The command may take a few minutes to take effect. 6 setup the internet authentication service (ias) radius server a go to programs > administrative tools > internet aut...
Page 382
394 c hapter b: radius s erver and radius c lient s etup h select grant remote access permission, and select next i click on edit profile... And select the authentication tab. Ensure extensible authentication protocol is selected, and smart card or other certificate is set. Deselect any other authen...
Page 383
Setting up a radius server 395 b select the dial-in tab from the client properties window. Select allow access. Click ok. C click ok to confirm. 8 configure the switch 5500g-ei for raduis access and client authentication see chapter 11 “802.1x configuration” . 9 generate a certificate by requesting ...
Page 384
396 c hapter b: radius s erver and radius c lient s etup d select advanced request and click next > e select the first option and click next > f either copy the settings from the screenshot below or choose different key options. Click save to save the pkcs #10 file. The pkcs #10 file is used to gene...
Page 385
Setting up a radius server 397 followed by this warning message, select yes and then ok the pkcs #10 file is now saved to the local drive. H to generate a portable certificate using pkcs #10, click the home hyperlink at the top right of the ca webpage. I select request a certificate > next > advance...
Page 386
398 c hapter b: radius s erver and radius c lient s etup l paste the copied information into the saved request field as shown below. Select authenticated session from the certificate template selector and click submit > m download the certificate and certification path. Click on the download ca cert...
Page 387
Setting up a radius server 399 o click install certificate to launch the certificate import wizard p leave the settings on the next screen as is, click next > followed by finish and ok. This will install the certificate, q launch the certification authority management tool on the server and expand t...
Page 388
400 c hapter b: radius s erver and radius c lient s etup s click copy to file to save the certificate. This action is actually already performed with the advanced request, but this is an alternative way to save the certificate. Click next when the wizard is launched. Save the certificate using der x...
Page 389
Setting up a radius server 401 u select the user that becomes the ieee 802.1x client. Right-click on the user and select name mappings. Select add v select the certificate that you have just exported and click open. Click ok w in the security identity mapping screen, click ok to close it. X close th...
Page 390
402 c hapter b: radius s erver and radius c lient s etup b create a new remote access policy under ias and name it switch login. Select next>.. C specify switch login to match the users in the switch access group, select next > d allow switch login to grant access to these users, select next >.
Page 391
Setting up a radius server 403 e use the edit button to change the service-type to administrative. F add a vendor specific attribute to indicate the access level that should be provided:.
Page 392
404 c hapter b: radius s erver and radius c lient s etup the value 010600000003 indicates admin privileges for the switch. 01 at the end indicates monitor and 02 indicates manager access. On the switch 5500g-ei, 00 indicates visitor level. 11 configure the radius client. Refer to section setting up ...
Page 393
Setting up a radius server 405 follow these steps to set up auto vlan and qos for use by microsoft ias: 1 define the vlan groups on the active directory server and assign the user accounts to each vlan group. Go to programs > administrative tools > active directory users and computers a for example,...
Page 394
406 c hapter b: radius s erver and radius c lient s etup d go to programs > administrative tools > internet authentication service. And select remote access policies. Select the policy that you configured earlier, right-click and select properties. E click add to add policy membership. F select the ...
Page 395
Setting up a radius server 407 g select the vlan group that you have just created and click add and then ok to confirm. H click ok again to return you to the security policy properties. I click edit profile... And select the advanced tab. Click add. Refer to table 459 and table 460 for the radius at...
Page 396
408 c hapter b: radius s erver and radius c lient s etup table 459 summary of auto vlan attributes table 460 summary of qos attributes j select tunnel-medium-type and click add. K ensure that the attribute value is set to 802 and click ok. L click ok again on the multivalued attribute information sc...
Page 397
Setting up a radius server 409 m select the tunnel-pvt-group-id entry and click add. N click add, ensure that the attribute value is set to 4 (attribute value in string format), and click ok. This value represents the vlan id. O click ok again on the multivalued attribute information screen to retur...
Page 398
410 c hapter b: radius s erver and radius c lient s etup p click add again. In the pull down menu, select virtual lans and click ok. Q click ok again and to return to the add attributes screen. Click close. You will now see the added attributes r click ok to close the profile screen and ok again to ...
Page 399
Setting up a radius server 411 to configure funk radius as a radius server for networks with the switch 5500g-ei, follow these steps: 1 open file eap.Ini in \radius\service and remove the ";" before the md5-challenge line. This enables the md5-challenge 2 open file radius.Ini in \radius\service and ...
Page 400
412 c hapter b: radius s erver and radius c lient s etup 3 either re-boot the server or stop then restart the radius service. To stop and restart the steel-belted radius service, go to control panel > administrative tools > services. Scroll down to the steel-belted service, stop and restart it. Funk...
Page 401
Setting up a radius server 413 passwords are case sensitive. 6 enter the shared secret to encrypt the authentication data. The shared secret must be identical on the switch 5500g-ei and the radius server a select ras clients from the left hand list, enter a client name , the ip address and the share...
Page 402
414 c hapter b: radius s erver and radius c lient s etup configuring auto vlan and qos for funk radius to set up auto vlan and qos using funk radius, follow these steps: 1 edit the dictionary file radius.Dct so that return list attributes from the funk radius server are returned to the switch 5500g-...
Page 403
Setting up a radius server 415 the following example shows the user name homer with the correct return list attributes inserted, the vlans and qos profiles must also be created on the 3com switch 5500g-ei. Configuring freeradius 3com has successfully installed and tested freeradius running on solari...
Page 404
416 c hapter b: radius s erver and radius c lient s etup b edit the existing file dictionary in /usr/local/etc/raddb to add the following line: $include dictionary.3com the new file dictionary.3com will be used in configuring the freeradius server 3 locate the existing file users in /usr/local/etc/r...
Page 405
Setting up the radius client 417 windows 2000 built-in client windows 2000 requires service pack 3 and the ieee 802.1x client patch for windows 2000. 1 downloaded the patches if required from: http://www.Microsoft.Com/downloads/details.Aspx?Displaylang=en&famil yid=6b78edbe-d3ca-4880-929f-453c695b96...
Page 406
418 c hapter b: radius s erver and radius c lient s etup follow these steps to install the aegis client: 1 registering the aegis client. When using the aegis client for the first time, a license key will be requested. To obtain a valid license key, complete an online form on the meetinghouse website...
Page 407
Setting up the radius client 419 d click ok to finish the configuration. E restart the client either by rebooting, or stopping and re-starting the service. F click the ok button, then return tothe aegis client main interface. To restart the client, press the button with the red-cross. If authenticat...
Page 408
420 c hapter b: radius s erver and radius c lient s etup.
Page 409: Uthenticating
C a uthenticating the s witch 5500g-ei with c isco s ecure acs this appendix covers the following topics: ■ cisco secure acs (tacacs+) and the 3com switch 5500g-ei ■ setting up the cisco secure acs (tacacs+) server cisco secure acs (tacacs+) and the 3com switch 5500g-ei cisco secure acs and tacacs+ ...
Page 410
422 c hapter c: a uthenticating the s witch 5500g-ei with c isco s ecure acs adding a 3com switch 5500g-ei as a radius client once logged into the cisco secure acs interface, follow these steps: 1 select network configuration from the left hand side 2 select add entry from under aaa clients. 3 enter...
Page 411
Setting up the cisco secure acs (tacacs+) server 423 5 select interface configuration from the left hand side. 6 select radius (ietf) from the list under interface configuration. 7 check the radius attributes that you wish to install. If you want to use auto vlan and qos, ensure that you have the fo...
Page 412
424 c hapter c: a uthenticating the s witch 5500g-ei with c isco s ecure acs 8 select submit. 9 repeat steps 1 to 8 for each switch 5500g-ei on your network. When all of the switch 5500g-eis have been added as clients to the cisco secure acs server, restart the secure acs server by selecting system ...
Page 413
Setting up the cisco secure acs (tacacs+) server 425 the screen below shows specific radius attributes having been selected for the user. The user has the student profile selected and is assigned to vlan 10 untagged. The radius attributes need to have already been selected, see step 7 in adding a 3c...
Page 414
426 c hapter c: a uthenticating the s witch 5500g-ei with c isco s ecure acs 3=administrator b locate the application csutil.Exe . In the utils directory of the install path (eg. C:\program files\cisco secure acs\utils\). C copy the 3com.Ini file into the utils directory d at the command prompt ente...
Page 415
Setting up the cisco secure acs (tacacs+) server 427 3 select submit+restart the ietf attributes will still be available to the device, the 3com attributes are simply appended to them. 4 select interface configuration, followed by radius (3com) a ensure that the 3com-user-access-level option is sele...
Page 416
428 c hapter c: a uthenticating the s witch 5500g-ei with c isco s ecure acs by scrolling to the bottom of the user profile where there should be the option for configuring the access level as shown below: 6 in the radius (3com) attribute box , check 3com-user-access-level and select administrator f...
Page 417: Xrn
D 3c om xrn this section explains what 3com xrn™ (expandable resilient networking) is and how you can use it to benefit your network. It also explains how to implement xrn on your network. This chapter contains the following sections: ■ what is xrn? ■ xrn terminology ■ benefits of xrn ■ xrn features...
Page 418
430 a ppendix d: 3c om xrn what is xrn? Xrn (expandable resilient network) is a 3com lan technology built into the software and hardware of your switch that offers high availability, scalability, and connectivity. Supported switches xrn is supported by the 3com operating system on the following swit...
Page 419
Xrn features 431 ■ switching capacity that increases as you add a switch to the fabric. So network performance and resilience expand as the fabric grows. ■ link aggregation supported across the distributed fabric. ■ flexibility provided by: ■ support across any of the switches within an individual s...
Page 420
432 a ppendix d: 3c om xrn drr is an xrn-specific implementation that only operates on xrn within the distributed fabric. However it will interoperate with other routers outside of the xrn distributed fabric. Figure 106 network example illustrating distributed resilient routing distributed link aggr...
Page 421
How to implement xrn — overview 433 figure 107 distributed link aggregation at the network backbone how to implement xrn — overview this section provides an overview on how to implement xrn in your network. Following the steps below will ensure that your xrn network operates correctly. 1 design your...
Page 422
434 a ppendix d: 3c om xrn the command guide supplied in pdf format on the cd-rom that accompanies your switch or on the 3com web site. Important considerations and recommendations this section contains important points and recommendations that you need to consider or be aware of when designing a ne...
Page 423
Unit id numbering mechanism 435 if you are unable to use link aggregation on multihomed links, then stp/rstp should be used as the second option, and the last option would be to use resilient links. This implementation increases the level of fault tolerance as it also protects against loss of the ph...
Page 424
436 a ppendix d: 3c om xrn the unit leds will display the unit number in the fabric, from 1 to 8. Network example using xrn the following example explains how to set up xrn in a network to gain maximum resilence using two distributed fabrics. The same process scales for larger networks if you are us...
Page 425
Recovering your xrn network 437 3 connect up your ports. As lacp was enabled in step 1 the aggregated links will now automatically configure themselves. 4 configure the router ip interfaces. 5 ensure that rstp is enabled across the network. Legacy aggregated links are not resilient to an interconnec...
Page 426
438 a ppendix d: 3c om xrn how xrn interacts with other features this section provides supplementary information on how xrn interacts with other software features supported by your switch. Vlans figure 109 shows a single aggregated link, created automatically via lacp, connecting the switch 5500g-ei...
Page 427
How xrn interacts with other features 439 figure 109 how xrn interacts with vlans — example 1 the distributed resilient routing (drr) feature also requires that all units can communicate with each other on all vlans. This ensures that on an interconnect failure all units can communicate with each ot...
Page 428
440 a ppendix d: 3c om xrn however, in figure 111 , if the interconnect fails, the aggregation is still a single logical entity at the legacy switch end, but it is now split over both units within the distributed fabric. The legacy switch is not aware that the aggregation has split and will continue...
Page 429
How a failure affects the distributed fabric 441 for example, if the resilient links were configured on switches a and b, if the interconnect fails, both switches will detect a failed link to switch 3300 and both a and b will activate their links to switch 3300. So both links in the resilient link w...
Page 430
442 a ppendix d: 3c om xrn legacy stp (ieee802.1d) and rstp (ieee 802.1w) the switch 4200 is using legacy stp. Stp will reconfigure the network to open the previously blocked link to switch b. The stp reconfiguration will cause all switch forwarding databases (mac address tables) to be fast aged (if...
Page 431
How a failure affects the distributed fabric 443 lacp (ieee 802.3ad) and legacy aggregated links the switch 4400 automatically configured aggregated link (lacp) will reconfigure itself to create two separate aggregated links. The switch 4300 legacy aggregated link will be split between the two switc...
Page 432
444 a ppendix d: 3c om xrn.