- DL manuals
- 3Com
- Switch
- SuperStack II
- Manual
3Com SuperStack II Manual
Summary of SuperStack II
Page 1
® http://www.3com.Com/ superstack ® ii switch management guide for units in the superstack ii switch 1100/3300 and 610/630 family management software version 2.50 part no. Dua1695-0baa04 published may 2000
Page 2
3com corporation 5400 bayfront plaza santa clara, california 95052-8145 copyright © 2000, 3com technologies. All rights reserved. No part of this documentation may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to make any derivative work (such as translation, transformation, or adaptation) witho...
Page 3: Ontents
C ontents a bout t his g uide conventions 13 related documentation 15 year 2000 compliance 15 documentation comments 16 product registration 16 i getting started with management 1 s uper s tack ii s witch m anagement s oftware what is management software? 20 summary of software features 20 software ...
Page 4: The Management Interfaces
2 s etting u p for m anagement methods of managing a switch 32 setting up web interface management 33 setting up through the console port 33 setting up over the network 34 installing online help and documentation 34 choosing a browser 35 configuring the browser 35 setting up command line interface m...
Page 5
Setting up ip information 58 configuring a port 59 configuring the console port 66 changing the management settings for the stack 67 specifying a descriptive name 67 changing your password 68 specifying a physical location 69 accessing the getting started pages 69 specifying the location of the onli...
Page 6
Defining monitor ports and analysis ports 87 enabling the roving analysis system 88 resetting all the units in the stack 88 what happens during a reset? 88 initializing all the units in the stack 88 what happens during an initialization? 88 upgrading management software 89 displaying statistics for ...
Page 7
Displaying port summary information 113 enabling and disabling vlt tagging on a port 114 setting the bridge spanning tree forward delay 114 setting the bridge spanning tree hello timer 115 setting the bridge spanning tree maximum age 115 setting the spanning tree bridge priority 115 enabling and dis...
Page 8
Specifying ip and slip information 133 displaying ip and slip information 135 enabling and disabling bootp 135 pinging other devices 136 resetting the ip configuration 136 displaying and changing snmp-related information 137 specifying snmp community strings 137 specifying trap destination details 1...
Page 9: III
Iii management reference 5 p ort t runks what are port trunks? 158 port trunks and your switch 158 placing ports in a port trunk 159 port trunk example 160 6 v irtual lan s (vlan s ) what are vlans? 164 benefits of vlans 164 vlans and your switch 165 the default vlan 165 defining new vlans 166 untag...
Page 10: Rmon
8 m ulticast f iltering what is a multicast? 190 what is multicast filtering? 190 multicast filtering and your switch 191 ieee 802.1p multicast filtering 191 enabling 802.1p multicast learning 191 igmp multicast filtering 192 enabling igmp multicast learning 192 manual filtering 192 9 s panning t re...
Page 11: Problem Solving
Iv problem solving 11 p roblem s olving solving web interface problems 214 solving command line interface problems 216 solving snmp management software problems 218 solving serial web utility problems 219 solving management software upgrade utility problems 220 solving other problems 221 v appendice...
Page 13: Bout
A bout t his g uide this guide provides all the information you need to manage units in the superstack ® ii switch 1100/3300 and 610/630 family with management software version 2.50. The guide is intended for use by network administrators who are responsible for installing and setting up network equ...
Page 14
14 a bout t his g uide table 2 text conventions convention description screen displays this typeface represents information as it appears on the screen. Syntax the word “syntax” means that you must evaluate the syntax provided and then supply the appropriate values for the placeholders that appear i...
Page 15
Related documentation 15 related documentation in addition to this guide, each document set in the switch 1100/3300 and 610/630 family includes the following: ■ user guide this guide contains all the hardware and installation information for the switch. ■ quick reference guide this guide contains a ...
Page 16
16 a bout t his g uide documentation comments your suggestions are very important to us. They will help make our documentation more useful to you. Please e-mail comments about this document to 3com at: pddtechpubs_comments@3com.Com please include the following information when commenting: ■ document...
Page 17: Etting
I g etting s tarted with m anagement chapter 1 superstack ii switch management software chapter 2 setting up for management.
Page 19: Uper
1 s uper s tack ii s witch m anagement s oftware this chapter contains introductory information about the superstack ® ii switch management software and how it can be used in your network. It covers the following topics: ■ what is management software? ■ summary of software features ■ software featur...
Page 20
20 c hapter 1: s uper s tack ii s witch m anagement s oftware what is management software? Your switch contains software that allows you to change and monitor the way it works. This management software is not required to get the switch working, but if you do use it, you may improve the efficiency of...
Page 21
Software features explained 21 software features explained stack management units in the switch 1100/3300 family can be interconnected so that they form a stack, that is, a group of devices that are managed as a single device. Stackability is not supported by the switch 610/630 units. You can interc...
Page 22
22 c hapter 1: s uper s tack ii s witch m anagement s oftware units in the switch 1100/610 family support three forwarding modes in addition to store and forward: ■ fast forward — packets are forwarded as soon as the destination address is received and processed. With fast forward, packets take less...
Page 23
Software features explained 23 flow control all the ports on your switch support flow control, which is a congestion control mechanism. Congestion is caused by one or more devices sending traffic to an already overloaded port on the switch. Flow control prevents packet loss and inhibits the devices ...
Page 24
24 c hapter 1: s uper s tack ii s witch m anagement s oftware if you use ieee 802.1p traffic prioritization, we recommend that all relevant ports on your switch are placed in one or more virtual lans (vlans) using 802.1q tagging. For a brief explanation of vlans, see “virtual lans” on page 26 . For ...
Page 25
Software features explained 25 ■ no other address can be learned until security is disabled or the address is manually removed from the database. ■ the address cannot be learned on another port until security is disabled or the address is manually removed from the database. For more information abou...
Page 26
26 c hapter 1: s uper s tack ii s witch m anagement s oftware broadcast storm control your switch supports broadcast storm control, a system that automatically creates an alarm for each port to monitor the level of broadcast traffic on that port. If the broadcast traffic level rises to 2976 frames p...
Page 27
Software features explained 27 multicast filtering your switch supports two multicast filtering systems: ■ ieee 802.1p, which uses the garp multicast registration protocol (gmrp) ■ igmp (internet group management protocol) these systems allow the switch to forward multicast traffic to the endstation...
Page 28
28 c hapter 1: s uper s tack ii s witch m anagement s oftware roving analysis your switch supports roving analysis, a system that allows you to attach a network analyzer to one port and use it to monitor the traffic of other ports on the switch. The system works by enabling you to define an analysis...
Page 29
Default settings 29 default settings table 4 shows the default settings of units in the switch 1100/3300 and 610/630 family. If you initialize one of these switch units, it is returned to these defaults. Table 4 default settings switch 1100/610 family switch 3300/630 family port status enabled enabl...
Page 30
30 c hapter 1: s uper s tack ii s witch m anagement s oftware rmon alarm (errors over 1 min) enabled: high threshold: 20 errors per second — notify low threshold: 1 error per second — no action enabled: high threshold: 20 errors per second — notify low threshold: 1 error per second — no action table...
Page 31: Etting
2 s etting u p for m anagement this chapter explains the various ways of managing a switch, and details the steps required before you can configure a switch to suit the needs of your network. It covers the following topics: ■ methods of managing a switch ■ setting up web interface management ■ setti...
Page 32
32 c hapter 2: s etting u p for m anagement methods of managing a switch you can manage a switch using one of the following methods: ■ web interface management — each switch has an internal set of web pages that allow you to manage the switch using a java ® -enabled web browser. ■ command line inter...
Page 33
Setting up web interface management 33 setting up web interface management you can access the web interface using: ■ a management workstation connected to the console port of a switch, running the serial line internet protocol (slip). ■ a management workstation connected to a switch over an ip netwo...
Page 34
34 c hapter 2: s etting u p for m anagement setting up over the network to manage a switch using the web interface over an ip network: 1 you must set up the switch with ip information. To do this: a access the web interface of the switch through the console port. See “setting up through the console ...
Page 35
Setting up web interface management 35 ■ on the cd-rom, inserted into the cd-rom drive of a networked cd-rom server ■ on a web server if several users are using the web interface, we recommend that you copy the files onto a server, or insert the cd-rom into a networked cd-rom server. 2 if the files ...
Page 36
36 c hapter 2: s etting u p for m anagement setting up command line interface management you can access the command line interface using: ■ a terminal or terminal emulator connected to the console port of a switch directly, or through a modem ■ a terminal or terminal emulator connected to a switch o...
Page 37
Setting up snmp management 37 setting up over the network to manage a switch using the command line interface over a network using telnet: 1 you must set up the switch with ip information. To do this: a access the command line interface of the switch through the console port. See “setting up through...
Page 38
38 c hapter 2: s etting u p for m anagement managing a switch over the network when managing a switch over the network, the switch must be correctly configured with the following ip information: ■ an ip address — for more information, see “ip addresses” on page 38 . ■ a subnet mask — for more inform...
Page 39
Logging in as a default user 39 world wide web site: http://www.Internic.Net subnets and using a subnet mask you can divide your ip network into sub-networks or subnets. Support for subnets is important because the number of bits assigned to the device part of an ip address limits the number of devi...
Page 40
40 c hapter 2: s etting u p for m anagement caution: to protect your switch from unauthorized access, you must change all default passwords as soon as possible. Security security security — the user can access and change all manageable parameters admin (no password) security — the user can access an...
Page 41: Anagement
Ii t he m anagement i nterfaces chapter 3 working with the web interface chapter 4 working with the command line interface.
Page 43: Orking
3 w orking w ith the w eb i nterface this chapter describes how to access and use the web interface. It covers the following topics: ■ accessing the web interface ■ the getting started pages ■ the main web interface ■ configuring the current switch ■ changing the management settings for the stack ■ ...
Page 44
44 c hapter 3: w orking w ith the w eb i nterface accessing the web interface you can access the web interface through the console port or over the network. To access the web interface through the console port, you must install, configure and run the serial web utility described in “serial web utili...
Page 45
Accessing the web interface 45 4 enter your user name and password: ■ if you have been assigned a user name and password, enter those details. ■ if you are accessing the web interface for the first time, enter a default user name and password to match your access requirements. The defaults are descr...
Page 46
46 c hapter 3: w orking w ith the w eb i nterface the getting started pages when you access the web interface for the first time or after a power-off/on cycle, a set of getting started pages are displayed. The first getting started page, getting started - introduction is shown in figure 3 . Figure 3...
Page 47
The getting started pages 47 3 the url or file path of the online help and online documentation for the stack. ■ if the files are installed on your management workstation, on the cd-rom, or on a network server, you must begin the file path with file:// ■ if the files are stored on a web server, you ...
Page 48
48 c hapter 3: w orking w ith the w eb i nterface the main web interface the main web interface is made up of three areas: ■ the banner this is always displayed at the top of the browser window. It displays the name of the current switch in the stack, and contains several external link icons that al...
Page 49
The main web interface 49 the external link icons the banner of the main web interface contains several external link icons that allow you to access information outside of the interface; these are shown in table 6 . Table 6 external link icons and their actions external link icon action if your mana...
Page 50
50 c hapter 3: w orking w ith the w eb i nterface the management icons the side-bar of the main web interface contains several management icons that allow you to display web pages in the page area; these are shown in table 7 . For an overview of the pages accessed using these icons, see “the page ar...
Page 51
The main web interface 51 ■ unit status — this page allows you to display the general administration details of the switch. ■ ip setup — this page allows you to set up ip information for the switch. ■ port setup — this page allows you to configure individual ports on the switch. ■ console port confi...
Page 52
52 c hapter 3: w orking w ith the w eb i nterface ■ roving analysis setup — this page allows you to set up roving analysis ports for the stack. ■ resilient links — this page allows you to set up resilient links for the stack. ■ reset — this page allows you to reset the switch units in the stack. ■ p...
Page 53
The main web interface 53 figure 5 web interface map making changes in the page area if you change any setting on a page in the page area, you must click the apply button at the bottom right of the page to make the change to the stack. The change is only made when you click the apply button. If you ...
Page 54
54 c hapter 3: w orking w ith the w eb i nterface configuring the current switch you can configure the current switch and the ports on that switch using the unit pages. These pages allow you to: ■ display the status of the ports on the switch ■ display the general administration details of the switc...
Page 55
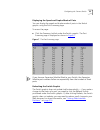
Configuring the current switch 55 displaying the speed and duplex mode of ports you can display the speed and duplex mode of ports in the switch graphic using the port summary page. To access the page: ■ click the summary hotlink under the switch graphic. The port summary page is displayed as shown ...
Page 56
56 c hapter 3: w orking w ith the w eb i nterface displaying administration details you can display general administration details about the switch using the unit status page. To access the page: ■ click the unit icon on the side-bar. The unit status page is displayed as shown in figure 8 . Some fie...
Page 57
Configuring the current switch 57 hardware rev displays the version number of the switch hardware. Mac address displays the mac (ethernet) address assigned to the switch. Software version displays the version number of the management software currently installed on the switch. For information about ...
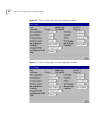
Page 58
58 c hapter 3: w orking w ith the w eb i nterface setting up ip information you can set up the ip information for the switch using the ip setup page. To access the page: 1 click the unit icon on the side-bar. The unit status page is displayed. 2 click the ip setup hotlink on the unit status page. Th...
Page 59
Configuring the current switch 59 default router if your network contains one or more routers, this field allows you to enter the ip address of the default router. For more information about ip addresses, see “managing a switch over the network” on page 38 . Bootp on / off if you have a bootp server...
Page 60
60 c hapter 3: w orking w ith the w eb i nterface figure 10 the port setup page with auto-negotiation enabled figure 11 the port setup page with auto-negotiation disabled.
Page 61
Configuring the current switch 61 the port setup page contains the following elements: port displays the number of the selected port. Link state enabled / disabled displays the state of the link connected to the port. Media type displays the media type of the link connected to the port. Port speed d...
Page 62
62 c hapter 3: w orking w ith the w eb i nterface switch 610 and switch 1100 only. The 10base-t/100base-tx ports on the switch 1100 cannot auto-negotiate ieee802.3x flow control. Follow the instructions below to enable flow control on the switch 1100 10base-t/100basetx ports. To enable flow control ...
Page 63
Configuring the current switch 63 hd flow control enabled / disabled allows you to enable or disable the intelligent flow management flow control that can be used when the port is operating in half duplex. Flow control prevents any packet loss that may occur on congested ports. The half duplex flow ...
Page 64
64 c hapter 3: w orking w ith the w eb i nterface fwd unknown vlan tags enabled / disabled / auto allows you to specify whether the port forwards traffic that uses unknown ieee 802.1q tags. If 802.1q vlan learning is disabled, you can specify: ■ enabled — use this setting if the port is connected to...
Page 65
Configuring the current switch 65 you cannot enable security on a port that is part of a resilient link, or a port that is part of a port trunk. For more information, see “setting up resilient links” on page 79 and “port trunks” on page 157 . Pace stack default / enabled / disabled allows you to spe...
Page 66
66 c hapter 3: w orking w ith the w eb i nterface 802.1q vlan learning stack default / disabled allows you to specify whether the port uses ieee 802.1q learning (gvrp) to place ports in vlans automatically: ■ stack default — the port takes the 802.1q vlan learning setting from the advanced stack set...
Page 67
Changing the management settings for the stack 67 the console port configuration page contains the following elements: console connection terminal / modem allows you to specify the device that you are connecting to the console port. Port speed autoconfig / 1200 / 2400 / 4800 / 9600 / 19200 allows yo...
Page 68
68 c hapter 3: w orking w ith the w eb i nterface figure 13 the system name page the name field allows you to enter a descriptive name for the stack. The name can be up to 20 characters long. Changing your password you can change the password for your user using the password setting page. To access ...
Page 69
Changing the management settings for the stack 69 the password setting page contains the following elements: new password allows you to enter a new password for your user. The password can be up to 10 characters long. Passwords must only contain alpha-numeric characters. Confirm password allows you ...
Page 70
70 c hapter 3: w orking w ith the w eb i nterface specifying the location of the online help and documentation you can specify the location of the online help and documentation for the stack using the documentation page. To access the page: 1 click the management settings icon on the side-bar. 2 cli...
Page 71
Configuring the stack 71 specifying contact details you can specify the details of a person to contact about the stack using the contact page. To access the contact page: 1 click the management settings icon on the side-bar. 2 click the contact hotlink. The contact page is displayed as shown in figu...
Page 72
72 c hapter 3: w orking w ith the w eb i nterface configuring the switch database you can configure the switch database of the stack using the switch database page. To access the page: 1 click the configuration icon on the side-bar. 2 click the switch database hotlink. The switch database page is di...
Page 73
Configuring the stack 73 databases entries can have three states: ■ learned — the stack has placed the entry into the switch database when a packet was received from an endstation: ■ learned entries are removed (aged out) from the switch database if the stack does not receive packets from that endst...
Page 74
74 c hapter 3: w orking w ith the w eb i nterface to display a subset of the entries for the current unit: 1 from the port filter listbox, select a port that has submitted the relevant entries or all ports. 2 from the vlan filter listbox, select the local id of a vlan associated with the relevant en...
Page 75
Configuring the stack 75 the display database entries table is not automatically updated with the new entry. To update the table: a from the select action type listbox, select display all. B click the apply button. When inserting a permanent entry, two error messages can be displayed in the status c...
Page 76
76 c hapter 3: w orking w ith the w eb i nterface configuring the advanced stack settings you can configure the advanced settings of the stack using the advanced stack setup page. To access the page: 1 click the configuration icon on the side-bar. 2 click the advanced stack setup hotlink. The advanc...
Page 77
Configuring the stack 77 short time to be forwarded, but all error packets except fragments are propagated. ■ store and forward — received packets are buffered entirely before they are forwarded, which ensures that only good packets are forwarded to their destination. With store and forward, packets...
Page 78
78 c hapter 3: w orking w ith the w eb i nterface ageing time (secs) 0 / 60 ... 1000000 allows you to specify the ageing time (in seconds) for all learned entries in the switch database of the stack; the default time is 1800 seconds (30 minutes). If you specify an ageing time of 0, the ageing proces...
Page 79
Configuring the stack 79 setting up resilient links you can set up resilient links for the stack using the resilient links page. To access the page: 1 click the configuration icon on the side-bar. 2 click the resilient links hotlink. The resilient links page is displayed as shown in figure 20 . Figu...
Page 80
80 c hapter 3: w orking w ith the w eb i nterface ■ resilient link pairs can only be set up using fiber or twisted pair ports. The main and standby ports in the same pair, however, can use any combination of these media. ■ a resilient link pair must only be defined at one end of the link. ■ a resili...
Page 81
Configuring the stack 81 3 click the next... Button. 4 from the main link field, select the main port of the resilient link pair. 5 click the next... Button. 6 from the standby link field, select the standby port of the resilient link pair. 7 click the next... Button. The resilient links page is dis...
Page 82
82 c hapter 3: w orking w ith the w eb i nterface figure 21 the port trunk setup page what are port trunks? Port trunks are connections that allow devices to communicate using up to four links in parallel. Port trunks provide two benefits: ■ they can potentially double, triple or quadruple the bandw...
Page 83
Configuring the stack 83 3 click a port in the available ports listbox. 4 click the add >> button. The port is assigned to the port trunk, and the port is displayed in the trunk members listbox. There are several conditions that need to be satisfied before a port can be placed in a port trunk. See “...
Page 84
84 c hapter 3: w orking w ith the w eb i nterface what are vlans? A vlan is a flexible group of devices that can be located anywhere in a network, but they communicate as if they are on the same physical segment. With vlans, you can segment your network without being restricted by physical connectio...
Page 85
Configuring the stack 85 you cannot edit the 802.1q vlan id if ports are already assigned to the vlan. Deleting vlan information the vlan setup page allows you to delete any vlan information that you define in the create vlan page. To do this: 1 from the vlans available listbox, select a vlan. 2 cli...
Page 86
86 c hapter 3: w orking w ith the w eb i nterface 5 to place the port in another vlan, repeat steps 1 to 4 with that vlan. To place a port back in the available ports listbox, click the port in the vlan members listbox and click the button. The vlan members listbox displays two types of port that do...
Page 87
Configuring the stack 87 what is roving analysis? Roving analysis is a system that allows you to attach a network analyzer to one port and use it to monitor the traffic of other ports in the stack. The system works by enabling you to define an analysis port (the port that is connected to the analyze...
Page 88
88 c hapter 3: w orking w ith the w eb i nterface enabling the roving analysis system the roving analysis setup page allows you to enable the roving analysis system. To do this: 1 from the roving analysis state listbox, select enabled. 2 click apply. Resetting all the units in the stack you can rese...
Page 89
Configuring the stack 89 setting is the ip and slip information, which is retained to ensure that you can continue managing the stack. You may want to initialize the stack if it has previously been used in a different part of your network, and its settings are incorrect for the new environment. Caut...
Page 90
90 c hapter 3: w orking w ith the w eb i nterface to upgrade the management software: 1 copy the software upgrade file into an appropriate directory on a tftp server. For information on using a tftp server, see the documentation that accompanies it. Caution: you must ensure that the port connected t...
Page 91
Displaying statistics for the current switch 91 displaying statistics for the current switch you can display statistics for the current switch in the stack using the health pages. These pages allow you to: ■ display a range of statistics for all the ports on the switch ■ display a range of statistic...
Page 92
92 c hapter 3: w orking w ith the w eb i nterface to display the total errors graph: 1 from the listbox, choose total errors. 2 click apply. If you click a port on the bandwidth utilization or total errors graph, the graph for that port is displayed. Interpreting the statistics ■ the bandwidth utili...
Page 93
Displaying statistics for the current switch 93 figure 26 the graphs displayed by the port graph page you can choose to display graphs for utilization, total errors or packet size distribution: to display the utilization graph: 1 from the first listbox, choose a port. 2 from the second listbox, choo...
Page 94
94 c hapter 3: w orking w ith the w eb i nterface to display the packet size distribution graph: 1 from the first listbox, choose a port. 2 from the second listbox, choose packet size distribution. 3 click apply. Interpreting the statistics ■ the utilization graph scales automatically to display the...
Page 95: Orking
4 w orking w ith the c ommand l ine i nterface this chapter describes how to access and use the command line interface. It covers the following topics: ■ accessing the interface ■ about the interface menus ■ a quick guide to the commands ■ displaying and changing bridging/vlans information ■ display...
Page 96
96 c hapter 4: w orking w ith the c ommand l ine i nterface accessing the interface to access the command line interface, take the following steps: 1 set up your network for command line interface management; for more information, see “setting up command line interface management” on page 36 . The l...
Page 97
About the interface menus 97 how many users can access the interface? The command line interface can be accessed by several users at the same time: ■ if the stack contains multiple switch units, the command line interface can be accessed through each console port in the stack at the same time. ■ if ...
Page 98
98 c hapter 4: w orking w ith the c ommand l ine i nterface ■ feature menu this menu contains commands that allow you to configure roving analysis port, enable or disable broadcast storm control, set up or remove resilient links, and configure trunks on the switch. ■ ip menu this menu contains comma...
Page 99
About the interface menus 99 figure 28 command line interface menu structure entering commands the command area of the command line interface contains a select menu option prompt that allows you to enter the commands in the menu area commands are not case-sensitive. ■ to enter a simple command: at t...
Page 100
100 c hapter 4: w orking w ith the c ommand l ine i nterface ■ to enter multiple commands: at the prompt, enter each command in succession. For example, to display the system menu and reset the switch units in the stack, enter: system reset ■ to enter commands that require values: append the values ...
Page 101
A quick guide to the commands 101 a quick guide to the commands table 8 describes the commands that are available in the command line interface. Table 8 command line interface commands command what does it do? Logout exits the current user from the command line interface. Bridge agingtime specifies ...
Page 102
102 c hapter 4: w orking w ith the c ommand l ine i nterface bridge port vltmode enables or disables vlt tagging on a port on the current switch unit. Bridge stpforwarddelay sets the bridge forward delay spanning tree parameter. Bridge stphellotime sets the bridge hello timer spanning tree parameter...
Page 103
A quick guide to the commands 103 feature analyzer display displays information about the roving analysis port configured in the stack. Feature analyzer remove removes the designated roving analysis port from the current port. Feature analyzer start specifies the roving analysis monitor port (that i...
Page 104
104 c hapter 4: w orking w ith the c ommand l ine i nterface snmp get performs an snmp get command, that allows you to retrieve values of snmp objects from the stack. Snmp next performs an snmp getnext command, that allows you to specify an snmp object and then retrieve the next few snmp objects fro...
Page 105
Displaying and changing bridging/vlans information 105 displaying and changing bridging/vlans information you can display and change the bridging functions of the switch, such as stp, multicast filtering, and also vlans using the commands in the bridge menu. These commands allow you to: ■ specify th...
Page 106
106 c hapter 4: w orking w ith the c ommand l ine i nterface to display the statistical information: 1 at the top-level menu, enter: bridge display 2 the bridge information for the switch is displayed as shown in the following example. The following bridge information is displayed: ■ stpstate — disp...
Page 107
Displaying and changing bridging/vlans information 107 ■ maxage — displays the maximum age in seconds at which the stored configuration message information is judged to be too old and is discarded. This value is determined by the root bridge. ■ bridgehellotime — displays the hello time value, used w...
Page 108
108 c hapter 4: w orking w ith the c ommand l ine i nterface enabling and disabling router port auto-discovery you can enable or disable router port auto-discovery for all switch units in the stack using the autodiscovery command on the router port menu. The default setting for the switch is router ...
Page 109
Displaying and changing bridging/vlans information 109 2 the router port information for all switch units in the stack is displayed in ascending unit and port number order. An example of the router port information is shown below: removing a router port you can remove a router port from any switch u...
Page 110
110 c hapter 4: w orking w ith the c ommand l ine i nterface adding a statically configured address to a switch database you can add a statically configured address to a switch database using the add command on the address menu. To add an address to a port: 1 at the top-level menu, enter: bridge por...
Page 111
Displaying and changing bridging/vlans information 111 displaying mac addresses for a port you can display a list of mac addresses associated with a selected port using the list command on the address menu. To display a list of mac addresses: 1 at the top-level menu, enter: bridge port address list ...
Page 112
112 c hapter 4: w orking w ith the c ommand l ine i nterface 2 enter the number of a port on the switch unit. If the port selected is working in vlt mode the display will show the port as being a member of all current vlans with tagging shown as vlt . The port information for the switch is displayed...
Page 113
Displaying and changing bridging/vlans information 113 2 enter the number of the port to be enabled or disabled. The following prompt is displayed: enter new value (disable, enable) [disable]: 3 enter enable or disable . Displaying port summary information you can display summary information about a...
Page 114
114 c hapter 4: w orking w ith the c ommand l ine i nterface ■ blocking - equivalent to stp blocking state ■ listening - equivalent to stp listening state ■ learning - equivalent to stp learning state ■ forwarding - equivalent to stp forwarding state ■ broken - port is broken ■ fwdtransitions — disp...
Page 115
Displaying and changing bridging/vlans information 115 setting the bridge spanning tree hello timer you can set the bridge hello timer spanning tree parameter of the current switch using the stphellotime command on the bridge menu. To set the bridge spanning tree hello timer: 1 at the top-level menu...
Page 116
116 c hapter 4: w orking w ith the c ommand l ine i nterface enabling and disabling spanning tree on a bridge you can enable or disable spanning tree on a bridge of the current switch unit using the stpstate command on the bridge menu. To enable or disable spanning tree on a bridge: 1 at the top-lev...
Page 117
Displaying and changing bridging/vlans information 117 the following prompt is displayed: enter vlan id (2-4094) [3]: 2 enter the number of the vlan id that you wish to create. The default option is the lowest value within the vlan id range not currently used in the stack. The following prompt is di...
Page 118
118 c hapter 4: w orking w ith the c ommand l ine i nterface the following prompt is displayed: select vlan id (1-4094) [1]: 2 enter the vlan id that you wish to display. The detailed vlan information for the selected vlan id is displayed as shown in the example below. Immediately after creating a v...
Page 119
Displaying and changing bridging/vlans information 119 removing a port from a vlan you can remove a single port from a vlan, or remove all ports on the current switch unit from the selected vlan using the removeport command on the vlan menu. To remove a port from a vlan: 1 at the top-level menu, ent...
Page 120
120 c hapter 4: w orking w ith the c ommand l ine i nterface displaying and changing port information you can display and change information about the ports on the current switch unit in the stack using the commands on the ethernet menu. These commands allow you to: ■ enable and disable ethernet por...
Page 121
Displaying and changing port information 121 specifying the speed and duplex mode you can specify the speed and duplex mode of ethernet ports on the switch using the portmode command on the ethernet menu. To specify the speed and duplex mode of a port: 1 at the top-level menu, enter: ethernet portmo...
Page 122
122 c hapter 4: w orking w ith the c ommand l ine i nterface ■ if auto-negotiation is enabled on a 10base-t port, the duplex mode of the link is automatically detected and set accordingly. Caution: the duplex mode of a link is not detected if the port on the other end of the link is not auto-negotia...
Page 123
Displaying and changing port information 123 enabling and disabling flow control ieee 802.3x flow control prevents any packet loss that may occur on congested ports that are operating in full duplex. You can enable or disable ieee 802.3x flow control for ethernet ports on the switch using the flowco...
Page 124
124 c hapter 4: w orking w ith the c ommand l ine i nterface figure 29 ethernet statistics the following statistical information is displayed: received stats ■ unicast packets — displays the number of packets with a single destination address that have been successfully received by the port. ■ non u...
Page 125
Displaying and changing port information 125 transmitted stats ■ unicast packets — displays the number of packets with a single destination address that have been transmitted by the port. ■ non unicast packets — displays the number of packets with a multicast or broadcast destination address that ha...
Page 126
126 c hapter 4: w orking w ith the c ommand l ine i nterface packet size analysis displays the number of packets seen by the port that had a length which was in one of six ranges between 64 and 1518 octets. This information may help you to analyze the efficiency of your network layer protocol. Displ...
Page 127
Displaying and changing system feature information 127 displaying and changing system feature information you can display and change system feature information for the switch units in the stack using the commands on the feature menu. These commands allow you to: ■ set up roving port analysis. ■ enab...
Page 128
128 c hapter 4: w orking w ith the c ommand l ine i nterface the roving analysis port information is displayed as shown in the example below. Removing a roving analysis port you can remove the roving analysis port using the remove command on the analyzer menu. To remove a roving analysis port: at th...
Page 129
Displaying and changing system feature information 129 stopping data monitoring you can stop data monitoring by the roving analysis port and remove the monitor port from the roving analysis set up by using the stop command on the analyzer menu. To stop data monitoring by the roving analysis port and...
Page 130
130 c hapter 4: w orking w ith the c ommand l ine i nterface setting up a resilient link you can set up resilient links on the switch units within the stack using the define command on the resilience menu. To set up a resilient link: 1 at the top-level menu, enter: feature resilience define the foll...
Page 131
Displaying and changing system feature information 131 removing a resilient link you can remove resilient links from the switch units within the stack using the remove command on the resilience menu. To remove a resilient link: 1 at the top-level menu, enter: feature resilience remove the following ...
Page 132
132 c hapter 4: w orking w ith the c ommand l ine i nterface 3 enter the port number that you wish to add to the trunk. (the choice of port numbers reflects suitable candidate ports.) you can not add a port to a trunk that is already a member of a trunk, is part of a resilient link, is in vlt mode, ...
Page 133
Displaying and changing ip-related information 133 displaying summary trunk information you can display summary trunk information about all trunks supported by the stack using the summary command on the trunk menu. To display summary trunk information: 1 at the top-level menu, enter: feature trunk s...
Page 134
134 c hapter 4: w orking w ith the c ommand l ine i nterface to specify the ip and slip information: 1 at the top-level menu, enter: ip interface define the following prompt is displayed, allowing you to enter an ip address for the switch: enter ip address [0.0.0.0]: for more information about ip ad...
Page 135
Displaying and changing ip-related information 135 displaying ip and slip information you can display ip and slip information for the current switch unit in the stack using the display command on the ip/interface menu. For more information about ip and slip, see “managing a switch over the network” ...
Page 136
136 c hapter 4: w orking w ith the c ommand l ine i nterface pinging other devices the ping feature allows you to send out a ping request to test whether devices on an ip network are accessible and functioning correctly. This feature is useful for testing that the stack is installed and set up corre...
Page 137
Displaying and changing snmp-related information 137 displaying and changing snmp-related information you can display and change snmp-related information for the stack using the commands on the snmp menu. These commands allow you to: ■ specify snmp community strings for the stack ■ specify the trap ...
Page 138
138 c hapter 4: w orking w ith the c ommand l ine i nterface 2 enter the community string of the trap destination device. The following prompt is displayed: enter the trap destination address: 3 enter the ip address of the trap destination device. Displaying trap destination details you can display ...
Page 139
Displaying and changing snmp-related information 139 removing trap destination details you can remove the details of a current trap destination device using the remove command on the snmp/trap menu. To remove trap destination details: 1 at the top-level menu, enter: snmp trap remove the following pr...
Page 140
140 c hapter 4: w orking w ith the c ommand l ine i nterface the following prompt is displayed: enter object-identifier: 2 enter the identifier of an snmp object. The following prompt is displayed: enter count: 3 enter the number of snmp objects after the object specified for which you want to retri...
Page 141
Displaying and changing stack information 141 displaying and changing stack information you can display and change information about the switch units in the stack or the stack as a whole using the commands on the system menu. These commands allow you to: ■ move the focus of the command line interfac...
Page 142
142 c hapter 4: w orking w ith the c ommand l ine i nterface you can have up to four switch units in a stack: ■ if the stack contains one unit, that unit is unit 1. ■ if the stack contains two units connected using a matrix cable, the unit with the lowest mac address is unit 1 and the other unit is ...
Page 143
Displaying and changing stack information 143 displaying switch administration details you can display the administration details for the current switch unit in the stack using the display command on the system menu. This information may be useful for your technical support representative if you hav...
Page 144
144 c hapter 4: w orking w ith the c ommand l ine i nterface information about assigning new contact details, see “specifying stack administration details” on page 142 . Time since reset displays the time that has elapsed since the unit was last reset, initialized or powered-up. Operational version ...
Page 145
Displaying and changing stack information 145 to display the information: ■ from the top-level menu, enter: system inventory the summary information is displayed. An example of the summary information is shown below: the following read-only fields are displayed: position displays the number of the u...
Page 146
146 c hapter 4: w orking w ith the c ommand l ine i nterface configuring intelligent modules you can configure intelligent modules such as the switch layer 3 module and the switch atm expansion module. Setting module configuration you can set the ip configuration for an intelligent module using the ...
Page 147
Displaying and changing stack information 147 2 enter enable or disable . Changing your password you can change the password for the current user using the password command on the system menu. To change the password: 1 at the top-level menu, enter: system password the following prompt appears, allow...
Page 148
148 c hapter 4: w orking w ith the c ommand l ine i nterface enter the access level (monitor,manager,security) [security]: 3 enter an access level for the new user. The following prompt is displayed: enter the password: 4 enter a password for the new user. The following prompt is displayed: re-enter...
Page 149
Displaying and changing stack information 149 2 enter the name of the user to be modified. The following prompt is displayed: enter the password: 3 enter a password for the user. The following prompt is displayed: re-enter the password: 4 enter the password for the user again. The following prompt i...
Page 150
150 c hapter 4: w orking w ith the c ommand l ine i nterface modifying access rights you can modify access rights for the access levels in the stack using the modify command on the system/security/access menu. To modify the access rights for the stack: 1 from the top-level menu, enter: system securi...
Page 151
Displaying and changing stack information 151 ■ users cannot access the stack over the network using the web interface. ■ users cannot access the switch using an snmp network manager. ■ users can only access the command line interface or web interface using a direct connection to the console port of...
Page 152
152 c hapter 4: w orking w ith the c ommand l ine i nterface the stack takes about 10 seconds to reset. While the stack is resetting, you cannot communicate with it. Initializing all the units in the stack you can initialize all the switch units in the stack using the initialize command on the syste...
Page 153
Displaying and changing stack information 153 upgrading management software you can upgrade the management software of all switch units in the stack using the softwareupgrade command on the system menu. To upgrade the management software: 1 copy the software upgrade file into an appropriate director...
Page 154
154 c hapter 4: w orking w ith the c ommand l ine i nterface.
Page 155: III
Iii m anagement r eference chapter 5 port trunks chapter 6 virtual lans (vlans) chapter 7 fastip chapter 8 multicast filtering chapter 9 spanning tree protocol chapter 10 rmon.
Page 157: Ort
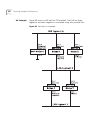
5 p ort t runks port trunks are connections that allow devices to communicate using up to four links in parallel. This chapter explains more about port trunks and how to set them up on your network. It covers the following topics: ■ what are port trunks? ■ port trunks and your switch ■ placing ports...
Page 158
158 c hapter 5: p ort t runks what are port trunks? Port trunks are connections that allow devices to communicate using up to four links in parallel. These parallel links provide two benefits: ■ they can potentially double, triple or quadruple the bandwidth of a connection. ■ they can provide a redu...
Page 159
Placing ports in a port trunk 159 when setting up a port trunk, note that: ■ the ports at both ends of a connection must be configured as trunk ports. ■ the trunk ports can only belong to one port trunk. ■ the trunk ports must be fiber or twisted pair ports. ■ the trunk ports must be from the same s...
Page 160
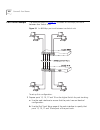
160 c hapter 5: p ort t runks port trunk example the example shown in figure 31 illustrates an 800mbps port trunk between two switch units. Figure 31 an 800mbps port trunk between two switch units to set up this configuration: 1 prepare ports 13, 15, 17 and 19 on the higher switch for port trunking:...
Page 161
Port trunk example 161 2 prepare ports 1, 3, 5 and 7 on the lower switch for port trunking: a use the web interface to ensure that the ports have an identical configuration: b use the port trunk setup page of the web interface to specify that ports 1, 3, 5 and 7 are ports of the port trunk. 3 connec...
Page 162
162 c hapter 5: p ort t runks.
Page 163: Irtual
6 v irtual lan s (vlan s ) setting up virtual local area networks (vlans) on your switch reduces the time and effort required by many network administration tasks, and increases the efficiency of your network. This chapter explains more about the concept of vlans and explains how they can be impleme...
Page 164
164 c hapter 6: v irtual lan s (vlan s ) what are vlans? A vlan is a flexible group of devices that can be located anywhere in a network, but they communicate as if they are on the same physical segment. With vlans, you can segment your network without being restricted by physical connections — a dr...
Page 165
Vlans and your switch 165 vlans and your switch your switch provides the following vlan features: ■ support for up to 16 vlans using the ieee 802.1q standard the ieee 802.1q standard allows each port on your switch to: ■ be placed in any single vlan defined on the switch. ■ be placed in several vlan...
Page 166
166 c hapter 6: v irtual lan s (vlan s ) defining new vlans if you want to move a port from the default vlan to another vlan, you must first define information about the new vlan on your switch. To do this, you use the vlan setup page of the web interface; see “defining vlan information” on page 84 ...
Page 167
Vlans and your switch 167 to create an 802.1q tagged link: 1 ensure that the device at the other end of the link uses the same 802.1q tags as your switch. 2 place the switch port in the required vlans using the vlan setup page of the web interface; see “placing ports in multiple vlans using 802.1q t...
Page 168
168 c hapter 6: v irtual lan s (vlan s ) the system works as follows: 1 the configured 802.1q endstation sends out a packet with a known multicast address to the whole network — this packet declares that the endstation is to receive traffic for specific vlans. 2 when the packet arrives at a port on ...
Page 169
Vlans and your switch 169 figure 32 forwarding unknown 802.1q tags.
Page 170
170 c hapter 6: v irtual lan s (vlan s ) connecting vlans to other vlans if the devices placed in a vlan need to talk to devices in a different vlan, each vlan requires a connection to a routing or layer 3 switching device. Communication between vlans can only take place if they are all connected to...
Page 171
Vlan configuration for beginners 171 vlan configuration for beginners this section contains examples of simple vlan configurations. It describes how to set up your switch to support simple untagged and tagged connections. For more advanced configuration examples, see “vlan configuration - advanced e...
Page 172
172 c hapter 6: v irtual lan s (vlan s ) to set up the configuration shown in figure 33 : 1 configure the vlans use the vlan setup page of the web interface to define vlan 2 on the switch. Vlan 1 is the default vlan and already exists. Do not add the ports to the vlan using this screen. For more inf...
Page 173
Vlan configuration for beginners 173 figure 34 simple example: untagged connections using hubs.
Page 174
174 c hapter 6: v irtual lan s (vlan s ) to set up the configuration shown in figure 34 : 1 configure the vlans use the vlan setup page of the web interface to define vlan 2 on the switch 3300. Vlan 1 is the default vlan and already exists. Do not add the ports to the vlan using this screen. For mor...
Page 175
Vlan configuration for beginners 175 figure 35 simple example: 802.1q tagged connections to set up the configuration shown in figure 35 : 1 configure the vlans on switch 1 use the vlan setup page of the web interface to define vlan 2. Vlan 1 is the default vlan and already exists. Do not add the por...
Page 176
176 c hapter 6: v irtual lan s (vlan s ) 3 add tagged port 26 on switch 1 use the vlan setup page of the web interface to assign port 26 on switch 1 to both vlans 1 and 2 so that all vlan traffic is passed over the link. 4 configure the vlans on switch 2 use the vlan setup page of the web interface ...
Page 177
Vlan configuration - advanced examples 177 vlan configuration - advanced examples the examples below describe how you can extend the functionality of simple vlans to provide more features and functionality within your network. Using 802.1q tagged connections and 802.1q learning the example shown in ...
Page 178
178 c hapter 6: v irtual lan s (vlan s ) to set up the configuration shown in figure 36 : 1 configure the endstations attached to the left switch 1100 so that they belong to vlans 1, 2 and 3. 2 configure the endstations attached to the right switch 1100 so that they belong to vlans 4, 5 and 6. 3 ena...
Page 179
Vlan configuration - advanced examples 179 b use the vlan setup page of the web interface to place ports 4 and 7 in vlans 1 and 2 using 802.1q tagging. C use the port setup page of the web interface to specify that port 26 uses vlt tagging. 2 connect port 26 on the switch 1100 to port 1 on the switc...
Page 180
180 c hapter 6: v irtual lan s (vlan s ).
Page 181: Ast
7 f ast ip fastip reduces the load on routing devices when vlans are implemented on your network. This chapter explains more about the concept of fastip and how it is enabled on your switch. It covers the following topics: ■ what is fastip? ■ how fastip works ■ an example ■ fastip and the switch dat...
Page 182
182 c hapter 7: f ast ip what is fastip? Fastip is a system that allows you to use the ieee 802.1q vlan standard to reduce the load on routing devices when vlans are implemented on your network. Endstations within different vlans can only communicate using a routing device; if there is a large amoun...
Page 183
An example 183 5 endstation b sends an nhrp packet with its own details back to endstation a. This packet, however, is sent directly through the switch units and not through the routing device. To do this, endstation b specifies that: ■ the packet is sent to the vlans that endstation a can receive. ...
Page 184
184 c hapter 7: f ast ip figure 38 network without fastip figure 39 endstation a sends an nhrp packet to endstation b.
Page 185
An example 185 figure 40 endstation b sends an nhrp packet to endstation a figure 41 endstation a sends data packets to endstation b.
Page 186
186 c hapter 7: f ast ip fastip and the switch database by default, the switch database of a switch is divided by vlan — each vlan has an independent area of the database. With this system, the switch database can store an entry for a device in several vlans at the same time, and the entry for a par...
Page 187
Enabling fastip 187 when fastip is used by the switch, the switch database can no longer be divided by vlan — it must be shared by all the vlans. Although the vlans are still operational, this creates two limitations: ■ the switch database can store an entry for a device in several vlans at the same...
Page 188
188 c hapter 7: f ast ip.
Page 189: Ulticast
8 m ulticast f iltering setting up multicast filtering improves the performance of networks that carry multicast traffic. This chapter explains multicasts, multicast filtering, and how multicast filtering can be implemented on your switch. It covers the following topics: ■ what is a multicast? ■ wha...
Page 190
190 c hapter 8: m ulticast f iltering what is a multicast? A multicast is a packet that is sent to a subset of endstations in a lan, or vlan, that belong to a multicast group. If the network is set up correctly, a multicast can only be sent to an endstation if it has joined the relevant group. A typ...
Page 191
Multicast filtering and your switch 191 multicast filtering and your switch your switch provides automatic filtering support for two multicast systems: ■ ieee 802.1p, which uses the garp multicast registration protocol (gmrp) ■ igmp (internet group management protocol) in addition, you can manually ...
Page 192
192 c hapter 8: m ulticast f iltering igmp multicast filtering igmp is the system that all ip-supporting network devices use to register endstations with multicast groups. It can be used on all lans and vlans that contain an ip router and other network devices which support ip. Igmp multicast filter...
Page 193: Panning
9 s panning t ree p rotocol using the spanning tree protocol makes your network more resilient to link failure and also provides a protection from loops — one of the major causes of broadcast storms. This chapter explains more about the protocol and the protocol features supported by your switch. It...
Page 194
194 c hapter 9: s panning t ree p rotocol what is stp? Using the spanning tree protocol (stp) makes your network more resilient to link failure and also provides a protection from loops — one of the major causes of broadcast storms. Stp is a bridge-based system that allows you to implement parallel ...
Page 195
What is stp? 195 figure 46 traffic flowing through bridges c and a figure 47 traffic flowing through bridge b stp determines which is the most efficient path between each bridged segment and a specifically assigned reference point on the network. Once the most efficient path has been determined, all...
Page 196
196 c hapter 9: s panning t ree p rotocol how stp works stp requirements before it can configure the network, the stp system requires the following: ■ communication between all the bridges. This communication is carried out using bridge protocol data units (bpdus), which are transmitted in packets w...
Page 197
How stp works 197 stp calculation the first stage in the stp process is the calculation stage. During this stage, each bridge on the network transmits bpdus that allow the system to work out: ■ the identity of the bridge that is to be the root bridge — the central reference point from which the netw...
Page 198
198 c hapter 9: s panning t ree p rotocol an example figure 48 shows a lan that has stp enabled. The lan has three segments, and each segment is connected using two possible links. Figure 48 port costs in a network.
Page 199
How stp works 199 ■ bridge a has the lowest bridge identifier in the network, and has therefore been selected as the root bridge. ■ because bridge a is the root bridge, it is also the designated bridge for lan segment a. Port 1 on bridge a is therefore selected as the designated bridge port for segm...
Page 200
200 c hapter 9: s panning t ree p rotocol figure 49 stp configurations.
Page 201
Using stp on a network with multiple vlans 201 using stp on a network with multiple vlans your switch does not take into account vlans when it calculates stp information — the calculations are only performed on the basis of duplicate connections. For this reason, some network configurations can resu...
Page 202
202 c hapter 9: s panning t ree p rotocol connecting to stp systems on legacy switch units if you are connecting your switch to legacy units that support stp, note the following: ■ your switch supports one stp system; however legacy switch units (for example, the superstack ii switch 1000) may suppo...
Page 203: Rmon
10 rmon using the rmon (remote monitoring) capabilities of a switch allows network administrators to improve their efficiency and reduce the load on their network. This chapter explains more about the rmon concept and the rmon features supported by the switch. It covers the following topics: ■ what ...
Page 204
204 c hapter 10: rmon what is rmon? Rmon is the common abbreviation for remote monitoring, a system defined by the ietf that allows you to monitor the traffic of lans or vlans remotely. A typical rmon setup consists of two components: ■ the rmon probe — an intelligent, remotely-controlled device or ...
Page 205
What is rmon? 205 hosts the hosts group specifies a table of traffic and error statistics for each host (endstation) on a lan segment or vlan. Statistics include packets sent and received, octets sent and received, as well as broadcasts, multicasts, and error packets sent. The group supplies a list ...
Page 206
206 c hapter 10: rmon benefits of rmon using the rmon features of your switch has three main advantages: ■ it improves your efficiency using rmon probes allows you to remain at one workstation and collect information from widely dispersed lan segments or vlans. This means that the time taken to reac...
Page 207
Rmon and your switch 207 rmon and your switch your switch contains an rmon probe in its management software. Table 10 details the rmon support provided by this probe. When using the rmon features of the switch, you should note the following: ■ after the default sessions are created, they have no spe...
Page 208
208 c hapter 10: rmon sessions, the forwarding performance of the switch is not affected but you may experience slow response times from the web interface. The alarm events you can define up to 200 alarms for the switch. The events that you can define for each alarm are shown in table 11. The defaul...
Page 209
Rmon and your switch 209 the audit log the switch keeps an audit log of all management user sessions, providing a record of a variety of changes, including ones relating to rmon. The log can only be read by users at the security access level using an snmp network management application. Each entry i...
Page 210
210 c hapter 10: rmon.
Page 211: Roblem
Iv p roblem s olving chapter 11 problem solving.
Page 213: Roblem
11 p roblem s olving this chapter contains a list of known problems and suggested solutions. It covers the following topics: ■ solving web interface problems ■ solving command line interface problems ■ solving snmp management software problems ■ solving serial web utility problems ■ solving manageme...
Page 214
214 c hapter 11: p roblem s olving solving web interface problems the web browser cannot access the switch over the network. Check that: ■ the ip information for the switch is correctly configured. See “setting up ip information” on page 58 or “specifying ip and slip information” on page 133 for mor...
Page 215
Solving web interface problems 215 the web interface takes time to respond to commands, and "document contains no data" messages are displayed. Too many users are accessing the web interface at the same time. We recommend that you allow only three users to access the interface. "url not found" messa...
Page 216
216 c hapter 11: p roblem s olving to do this for microsoft internet explorer version 3.0: 1 start microsoft internet explorer. 2 from the view menu, select options. 3 the options dialog box appears. 4 select the advanced tab, and in the advanced property sheet click settings. 5 check the every visi...
Page 217
Solving command line interface problems 217 ■ the settings on your terminal or terminal emulator are correct: ■ 8 data bits ■ no parity ■ 1 stop bit the auto-configuration feature of the switch only works with line speeds from 1200 to 19,200 baud. ■ if you are managing the switch over the network: ■...
Page 218
218 c hapter 11: p roblem s olving you forget your password and cannot log in. Ask another user with security access level to log in and initialize the switch. This returns the switch to its default (factory) settings, including any password information. For more information, see “initializing all t...
Page 219
Solving serial web utility problems 219 ■ the port through which you are trying to manage the switch belongs to the default vlan (vlan 1). This is the only vlan that can be used to access the management software of the switch. Traps are not received by the snmp network management software. Check tha...
Page 220
220 c hapter 11: p roblem s olving you can change some of the settings for the management workstation using the advanced configuration parameters dialog box. To display this, select the serial web setup program item in the serial web program group. Solving management software upgrade utility problem...
Page 221
Solving other problems 221 an error occurs when the utility attempts to transfer the file. There could be a number of reasons for this: ■ the null modem cable has become disconnected from the switch or the pc during the file transfer. Reconnect the cable and start again. ■ power to the switch has be...
Page 222
222 c hapter 11: p roblem s olving you have specified that an endstation generates traffic that has a high priority, but when it passes through the network this priority information is lost. The endstation is attached to a switch port using an untagged vlan connection, and the switch is removing the...
Page 223
Solving other problems 223 you have attempted to upgrade several switch units in a stack using tftp, and one unit fails to upgrade. Take the following steps: 1 ensure that the unit has: ■ the ip address 0.0.0.0, or ■ a valid ip address that is in the same subnet as the tftp server 2 if the unit has ...
Page 224
224 c hapter 11: p roblem s olving.
Page 225: Ppendices
V a ppendices and i ndex chapter a serial web utility chapter b management software upgrade utility.
Page 227: Erial
A s erial w eb u tility introduction if you are using a management workstation running microsoft windows ® 95/98 and you want to access the web interface through the console port of your switch, you must use the 3com serial web utility (slip driver) on the cd-rom supplied with the switch. You can fi...
Page 228
228 a ppendix a: s erial w eb u tility 4 in the run dialog box, type drive:\win95\drivers\slip\setup (where drive is the letter of your cd-rom drive) and click ok. The installation program starts and checks your system configuration; enter any information that is requested. If the setup program cann...
Page 229
Using the serial web utility 229 6 when you have finished, the final installation dialog box is displayed informing you that the serial web utility has been installed on your management workstation. Click finish to close the dialog box. 7 you are asked if you want to restart windows so that it can u...
Page 230
230 a ppendix a: s erial w eb u tility the connection is complete if the password panel of the web interface is displayed. You are now ready to manage the switch or stack; see “working with the web interface” on page 43 ..
Page 231: Anagement
B m anagement s oftware u pgrade u tility the cd-rom supplied with your switch includes a management software upgrade utility that can be used to upgrade the management software of the switch. The utility should only be used if a previous upgrade has failed, and you are unable to communicate with th...
Page 232
232 a ppendix b: m anagement s oftware u pgrade u tility c copy the management software file to the upgrade directory on the hard drive. D change your directory to the upgrade directory on the hard drive. 5 at the ms-dos prompt, enter the upgrade command: update is the name of the management softwar...
Page 233: Lossary
G lossary 10base-t the ieee specification for 10mbps ethernet over category 3, 4 or 5 twisted pair cable. 100base-fx the ieee specification for 100mbps fast ethernet over fiber-optic cable. 100base-tx the ieee specification for 100mbps fast ethernet over category 5 twisted-pair cable. 1000base-t the...
Page 234
234 g lossary bridge a device that interconnects two lans of a different type to form a single logical network that comprises of two network segments. Bridges learn which endstations are on which network segment by examining the source addresses of packets. They then use this information to forward ...
Page 235
G lossary 235 filtering the process of screening a packet for certain characteristics, such as source address, destination address, or protocol. Filtering is used to determine whether traffic is to be forwarded, and can also prevent unauthorized access to a network or network devices. Flow control a...
Page 236
236 g lossary ietf internet engineering task force. An organization responsible for providing engineering solutions for tcp/ip networks. In the network management area, this group is responsible for the development of the snmp protocol. Ifm see intelligent flow management. Igmp internet group manage...
Page 237
G lossary 237 loop an event that occurs when two network devices are connected by more than one path, thereby causing packets to repeatedly cycle around the network and not reach their destination. Mac media access control. A protocol specified by the ieee for determining which devices have access t...
Page 238
238 g lossary post power on self test. An internal test that a switch carries out when it is powered-up. Protocol a set of rules for communication between devices on a network. The rules dictate format, timing, sequencing and error control. Repeater a simple device that regenerates lan traffic so th...
Page 239
G lossary 239 stack a group of network devices that are integrated to form a single logical device. Standby port the port in a resilient link that takes over data transmission if the main port in the link fails. Stp see spanning tree protocol (stp). Switch a device that interconnects several lans to...
Page 240
240 g lossary vlan tagging a system that allows traffic for multiple vlans to be carried on a single link. Vlt virtual lan trunk. A switch-to-switch link that carries traffic for all the vlans on each switch. Wan wide area network. A communications network that covers a wide area. A wan can cover a ...
Page 241: Ndex
I ndex symbols ? Command 100 numbers 3com contacts icon 49 3com icon 49 3com library icon 49 3com support icon 49 3com world wide web site, accessing 49 802.1p multicast learning listbox (advanced stack setup page) 78 802.1p multicast learning listbox (port setup page) 63 802.1q tagging 166 802.1q t...
Page 242
242 i ndex c capture (rmon group) 207 cd-rom 34, 227, 231 collisions field (ethernet/statistics menu) 125 color key page 54 color-coding of ports, displaying 54 command area of the command line interface 97 command line interface accessing 96 bridge menu 97 command summary 101 ethernet menu 97 exiti...
Page 243
I ndex 243 f factory defaults 29 fast forward forwarding mode 22 fastip 26, 181 effect on the switch database 186 enabling 187 example 183 fastip listbox (advanced stack setup page) 78 fd flow control listbox (port setup page) 62 feature menu 98 filter (rmon group) 205, 207 find command (bridge/port...
Page 244
244 i ndex j jabbers field (ethernet/statistics menu) 125 l learned sdb entries 73 link state field (port setup page) 61 list command (bridge/multicastfiltering/routerport menu) 108 list command (bridge/port/address menu) 111 local id listbox (create vlan page) 84 location field (system/display menu...
Page 245
I ndex 245 page area of the web interface 48, 50 making changes in 53 navigating 52 pair state column (resilient links page) 80 password command (system menu) 147 password dialog 44 password setting page 68 passwords changing 68, 147 default 39 entering 45, 47 of default users 39 path costs. See por...
Page 246
246 i ndex roving analysis 28, 87 displaying information via cli 127 enabling 88 ports, defining 87 removing via cli 128 setting up via cli 127 start data monitoring via cli 128 stop data monitoring via cli 129 roving analysis setup page 86 roving analysis state listbox (roving analysis setup page) ...
Page 247
I ndex 247 subnet mask 39 subnet mask field (ip setup page) 58 subnets 39 sub-networks. See subnets summary command (bridge/port menu) 113 summary command (bridge/vlan menu) 119 summary command (ethernet menu) 126 summary command (feature/trunk menu) 133 summary information, displaying for the curre...
Page 248
248 i ndex vlans (continued) ieee 802.1q learning 167 modifying a vlan name via cli 118 placing ports in multiple 85, 166 placing ports in single 85, 166 removing port(s) via cli 119 vlt tagging 167 vlans available listbox (vlan setup page) 84, 85 vlt tagging 167 vlt tagging listbox (port setup page...