- DL manuals
- ABB
- Controller
- ACS800-37-0060-3
- Hardware manual
ABB ACS800-37-0060-3 Hardware manual
Summary of ACS800-37-0060-3
Page 1
Acs800 hardware manual acs800-37 drives (55 to 2700 kw / 75 to 3000 hp).
Page 3: Hardware Manual
Acs800-37 drives 55 to 2700 kw (75 to 3000 hp) hardware manual 3afe68557925 rev b en effective: 01.11.2005 © 2005 abb oy. All rights reserved..
Page 5: Safety Instructions
Safety instructions 5 safety instructions what this chapter contains this chapter contains safety instructions you must follow when installing, operating and servicing the drive. If ignored, physical injury or death may follow, or damage may occur to the drive, the motor or driven equipment. Read th...
Page 6: •
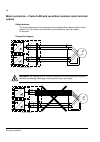
Safety instructions 6 installation andmaintenance work these warnings are intended for all who work on the drive, motor cable or motor. Ignoring the instructions can cause physical injury or death, or damage the equipment. Warning! • only qualified electricians are allowed to install and maintain th...
Page 7: •
Safety instructions 7 warning! • during the installation procedure, supply, filter or inverter modules may have to be temporarily extracted from the cabinet. The modules have a high centre of gravity. In order to minimise the danger of toppling over, keep the support legs (if provided) of the module...
Page 8: •
Safety instructions 8 grounding these instructions are intended for all who are responsible for the grounding of the drive. Incorrect grounding can cause physical injury, death or equipment malfunction and increase electromagnetic interference. Fibre optic cables warning! • ground the drive, the mot...
Page 9: Operation
Safety instructions 9 operation these warnings are intended for all who plan the operation of the drive or operate the drive. Ignoring the instructions can cause physical injury or death or damage the equipment. Warning! • before adjusting the drive and putting it into service, make sure that the mo...
Page 10
Safety instructions 10 permanent magnet motor drives these are additional warnings concerning permanent magnet motor drives. Warning! Do not work on the drive when the permanent magnet motor is rotating. Also when the supply power is switched off, a rotating permanent magnet motor feeds power to the...
Page 11: Table Of Contents
Table of contents 11 table of contents safety instructions what this chapter contains . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 usage of warnings and notes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 12
Table of contents 12 door switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36 main switch-disconnector (q1 in frame size r6 to r8i) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36 air circuit breaker (q1 in frame si...
Page 13
Table of contents 13 permanent magnet synchronous motor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64 thermal overload and short-circuit protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64 supply (ac line) cab...
Page 14
Table of contents 14 connection procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .81 motor connection – frame r7i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .82 connectio...
Page 15
Table of contents 15 installation checklist . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101 start-up procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ....
Page 16
Table of contents 16 technical data what this chapter contains . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .123 iec ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 17
Table of contents 17 frame size 6×r8i . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 207 resistor braking what this chapter contains . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 18
Table of contents 18.
Page 19: About This Manual
About this manual 19 about this manual what this chapter contains this chapter describes the intended audience and contents of the manual. It contains a flowchart of steps in checking the delivery, installing and commissioning the drive. The flowchart refers to chapters/sections in this manual and o...
Page 20
About this manual 20 motor control and i/o board (rmio) shows external control connections to the motor control and i/o board and its specifications. Installation checklist and start-up helps in checking the mechanical and electrical installation of the drive. Maintenance contains preventive mainten...
Page 21: Inquiries
About this manual 21 inquiries address any inquiries about the product to the local abb representative, quoting the type code and serial number of the unit. If the local abb representative cannot be contacted, address inquiries to abb oy, ac drives, po box 184, 00381 helsinki, finland. Connect the p...
Page 22: Terms And Abbreviations
About this manual 22 terms and abbreviations term/abbreviation explanation agps gate driver power supply board. An optional board within drives, used to implement the prevention of unexpected start function. Apbu type of optical branching unit used for connecting parallel-connected converter modules...
Page 23: The Acs800-37
The acs800-37 23 the acs800-37 what this chapter contains this chapter describes the construction of the drive in short. The acs800-37 the acs800-37 is a cabinet-built, low-harmonic drive for controlling ac motors. Cabinet line-up the drive consists of one or more cubicles that contain the supply an...
Page 24
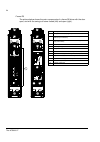
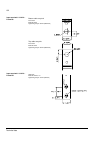
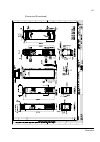
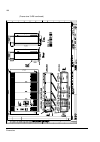
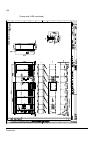
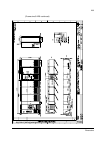
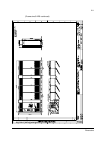
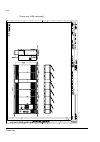
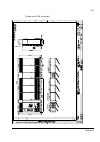
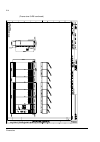
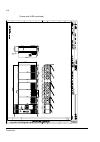
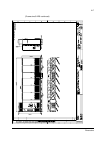
The acs800-37 24 frame r6 the picture below shows the main components of a frame r6 drive with the door open, and with the swing-out frame closed (left) and open (right). No. Description 1 swing-out frame (see page 27 ) 2 cable entries for power and control cables (bottom cable entry/exit models) 3 ...
Page 25
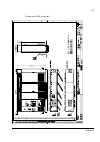
The acs800-37 25 frame r7i the picture below shows the main components of a frame r7i drive with the door and the swing-out frame open. 10 9 7 8 5 4 3 2 no. Description 1 swing-out frame (see page 27 ) (not shown). The drive control units for both converter modules are installed on the swing-out fra...
Page 26
The acs800-37 26 frame r8i the picture below shows the main components of a frame r8i drive with the doors open. 5 14 no. Description 1 swing-out frame (see picture on page 27 ) 2 supply unit controller (rdcu) 3 inverter unit controller (rdcu) 4 switch-disconnector* 5 input contactor* 6 lcl filter 7...
Page 27
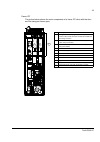
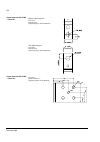
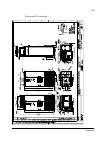
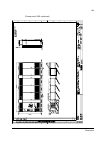
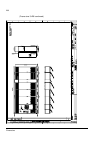
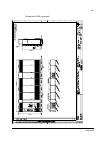
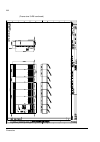
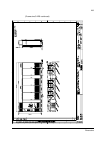
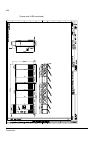
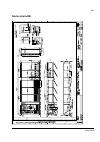
The acs800-37 27 swing-out frame the swing-out frame provides space for the control circuitry of the drive as well as optional electrical equipment. The frame can be opened by removing the two locking screws (arrowed in the picture below) and moving the swing-out frame aside. Depending on the frame ...
Page 28
The acs800-37 28 the following is a generic device layout diagram for the swing-out frame (drive frame size r8i). The diagram is also attached to the inside of the cubicle door, with installed devices marked. Refer to the circuit diagrams delivered with the drive for device designations..
Page 29
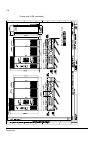
The acs800-37 29 cabling direction the drawing below shows the available power cabling directions of the drive. Description 1 input/motor output – bottom entry 2 input/motor output – top entry (ip21-42) 3 input/motor output – top entry (ip54) 4 signal cable input/output – bottom entry 5 signal cable...
Page 30
The acs800-37 30 10 1 a c description a input/output cubicle b supply and inverter unit cubicle c common motor terminal cubicle (optional)* 1 standard input (bottom entry) 2 standard input (top entry) 3 standard output (bottom exit) 4 standard output (top exit) 5 optional output (bottom exit, 1st en...
Page 31
The acs800-37 31 single-line circuit diagram of the drive note: this diagram represents a frame 2×r8i drive without a common motor terminal cubicle. M g rou nd faul t s uper v is ion moto r fa n s u ppl y 400 v a c m 230/1 1 5 v a c dc b u s m 3~ 40 0 v a c 400 v a c ma in s upp ly m m 400 v a c 4 0...
Page 32: Operation Principle
The acs800-37 32 operation principle the line-side and motor-side converters have their own rdcu control units and control programs. The parameters of each program can be viewed and changed using one control panel. The converter to be controlled can be selected using the control panel; see the secti...
Page 33
The acs800-37 33 ac voltage and current waveforms the ac current is sinusoidal at a unity power factor. The igbt supply unit does not generate characteristic current or voltage overtones like a traditional 6- or 12-pulse bridge does. The total harmonic distortion (thd) in voltage depends slightly on...
Page 34
The acs800-37 34 motor-side converter the motor control is based on the direct torque control (dtc) method. Two phase currents and dc link voltage are measured and used for the control. The third phase control is measured for earth fault (ground fault) protection. The motor-side converter is control...
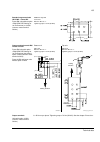
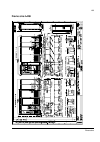
Page 35: Controls
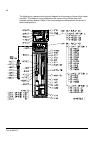
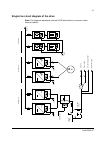
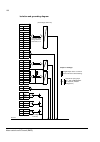
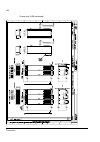
The acs800-37 35 controls control interfaces of the drive the following diagram shows the control interfaces and i/o options of the drive. ~ = e x te rn al c o nt ro l v ia ana lo g ue/ di g it a l input s a nd out put s inpu t power to m o to r sup p ly u n it in v e rt er uni t ~ = m o to r c o n ...
Page 36: Er Enc
The acs800-37 36 door switches main switch-disconnector (q1 in frame size r6 to r8i) the switch-disconnector handle switches the main and auxiliary voltages to the drive on and off. Air circuit breaker (q1 in frame size 2×r8i and up) the air circuit breaker controls the main supply voltage (phases l...
Page 37
The acs800-37 37 control panel a control panel (type cdp-312r) is installed on the door of the drive. The cdp-312r is the user interface of the supply unit (line-side converter) and the inverter unit (motor-side converter) of the drive, providing the essential controls such as start/ stop/direction/...
Page 38
The acs800-37 38 fieldbus control of the line-side converter fieldbus control of the line-side converter is performed via the motor-side converter rmio board as shown in the block diagram below. Block diagram: reference select the figure below shows the parameters for dc and reactive power reference...
Page 39: Type Code
The acs800-37 39 type code the type code of the drive is indicated on the type designation label, attached on the cabinet door. The type code contains information on the specifications and configuration of the drive. The first digits from left express the basic configuration (e.G. Acs800-37-0490-3)....
Page 40
The acs800-37 40 frame sizes 2×r8i to 6×r8i cabling h351 = top entry h353 = top exit h358 = us/uk gland/conduit plate h359 = common motor terminal cubicle – frame r8i with +e202 only auxiliary voltage g304 = 115 v ac – standard with +c129 and +c134 cabinet options g300 = cabinet heaters (external su...
Page 41
The acs800-37 41 construction c121 = marine construction (reinforced mechanical parts and fastening, marking of conductors [a1], door handles, self-extinctive materials) c129 = ul listed – includes +h358 c134 = csa approved – includes +h358 resistor braking d150 = brake chopper(s). D151 = brake resi...
Page 42
The acs800-37 42.
Page 43: Mechanical Installation
Mechanical installation 43 mechanical installation what this chapter contains this chapter describes the mechanical installation procedure of the drive. General see chapter technical data for allowable operating conditions and requirements for free space around the unit. The unit should be installed...
Page 44: Moving The Unit
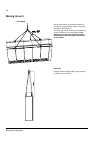
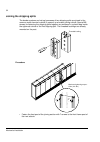
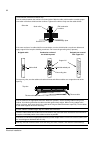
Mechanical installation 44 moving the unit …by crane use the steel lifting lugs attached to the top of the cabinet. Insert the lifting ropes or slings into the holes of the lifting lugs. The lifting lugs can be removed (not mandatory) once the cabinet is in its final position. If the lifting lugs ar...
Page 45
Mechanical installation 45 …by fork-lift or pallet truck …on rollers (not allowed with marine versions) laying the unit on its back the centre of gravity may be quite high. Be therefore careful when transporting the unit. Tilting the cabinets must be avoided. The units are to be moved only in the up...
Page 46
Mechanical installation 46 final placement of the unit the cabinet can be moved into its final position with an iron bar and a wooden piece at the bottom edge of the cabinet. Care is to be taken to properly place the wooden piece so as not to damage the cabinet frame..
Page 47: Before Installation
Mechanical installation 47 before installation delivery check the drive delivery contains: • drive cabinet line-up • optional modules (if ordered) installed into the control rack at the factory • ramp for extracting supply and inverter modules from the cabinet • hardware manual • appropriate firmwar...
Page 48: Installation Procedure
Mechanical installation 48 installation procedure see detailed instructions in the following few pages. (1) the cabinet can be installed with its back against a wall, or back-to-back with another unit. Fasten the unit (or first shipping split) to the floor with fastening clamps or through the holes ...
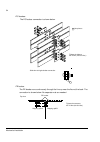
Page 49
Mechanical installation 49 fastening the cabinet to the floor (non-marine units) the cabinet is to be fastened to the floor by using clamps along the edge of the cabinet bottom, or by bolting the cabinet to the floor through the holes inside. Clamping insert the clamps into the twin slots along the ...
Page 50
Mechanical installation 50 holes inside the cabinet the cabinet can be fastened to the floor using the fastening holes inside the cabinet, if they are accessible. The recommended maximum distance between the fastening points is 800 mm (31.5”). If there is not enough working space behind the cabinet ...
Page 51
Mechanical installation 51 fastening the unit to the floor and wall (marine units) the unit must be fastened to the floor and roof (wall) as follows: use m10 or m12 screws; welding not recommended (see section electric welding below). 1 2 3 1 2 3 bolt the unit to the floor through the holes in each ...
Page 52
Mechanical installation 52 joining the shipping splits the busbar systems and wiring harnesses of two shipping splits are joined in the common motor terminal cubicle (if present) or a busbar joining cubicle. Special m6 screws for fastening the shipping splits together are enclosed in a plastic bag i...
Page 53
Mechanical installation 53 • remove any intermediate or partitioning plates covering the rear posts of the joining cubicle. • fasten the rear post of the joining section with seven screws (below the busbar joining part) to the rear post of the next cubicle. • replace all partitioning plates in the u...
Page 54
Mechanical installation 54 dc busbars the dc busbar connection is shown below. Pe busbar the pe busbar runs continuously through the line-up near the floor at the back. The connection is shown below. No separate nuts are needed. Tighten the bolts to 55–70 nm (40–50 ft.-lbs.) side view of single busb...
Page 55: Miscellaneous
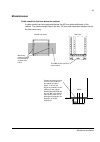
Mechanical installation 55 miscellaneous cable conduit in the floor below the cabinet a cable conduit can be constructed below the 400 mm wide middle part of the cabinet. The cabinet weight lies on the two 100 mm wide transverse sections which the floor must carry. Viewed from above side view this a...
Page 56
Mechanical installation 56 cooling air intake through bottom of cabinet units with air intake through the bottom of the cabinet (optional feature) are intended for installation on an air duct in the floor. The required air inlets in the floor are as listed below. Refer also to the dimensional drawin...
Page 57
Mechanical installation 57 electric welding it is not recommended to fasten the cabinet by welding. Cabinets without flat bars at the base • connect the return conductor of the welding equipment to the cabinet frame at the bottom within 0.5 metres of the welding point. Cabinets with flat bars at the...
Page 58
Mechanical installation 58.
Page 59
Planning the electrical installation 59 planning the electrical installation what this chapter contains this chapter contains the instructions that you must follow when selecting the motor, the cables, the protections, the cable routing and the way of operation for the drive system. Note: the instal...
Page 60
Planning the electrical installation 60 3. Check that the motor voltage rating meets the application requirements: see notes 6 and 7 below the requirements table. 4. Consult the motor manufacturer before using a motor in a drive system where the motor nominal voltage differs from the ac power source...
Page 61
Planning the electrical installation 61 the stress on motor insulation can be avoided by using optional abb du/dt filters. Du/dt filters also reduce bearing currents. To avoid damage to motor bearings, the cables must be selected and installed according to the instructions given in this manual. In a...
Page 62
Planning the electrical installation 62 * manufactured before 1.1.1998 ** for motors manufactured before 1.1.1998, check for additional instructions with the motor manufacturer. *** if the intermediate dc circuit voltage of the drive will be increased from the nominal level by resistor braking or by...
Page 63
Planning the electrical installation 63 given below. For other motor types, see the requirements table above. Apply the requirements of range “100 kw p n p n p n > 350 kw to motors within the range “100 kw p n manufacturer. Note 4: hxr and ama motors all ama machines (manufactured in helsinki) for d...
Page 64
Planning the electrical installation 64 note 9: sine filters sine filters protect the motor insulation system. Therefore, a du/dt filter can be replaced with a sine filter. The peak phase-to-phase voltage with a sine filter is approximately 1.5 × u n . Permanent magnet synchronous motor only one per...
Page 65: Emergency Stop Devices
Planning the electrical installation 65 supply (ac line) cable short-circuit protection always protect the input cable with fuses. In networks with a short-circuit withstand of 65 ka or less, standard gg fuses can be used. No fuses need be installed at the drive input. If the drive is supplied throu...
Page 66
Planning the electrical installation 66 prevention of unexpected start the drive can be equipped with an optional prevention of unexpected start function according to standards iec/en 60204-1: 1997; iso/dis 14118: 1996 and en 1037: 1996. The circuit conforms to en954-1, category 3. The function is a...
Page 67: Selecting The Power Cables
Planning the electrical installation 67 selecting the power cables general rules dimension the supply (input power) and motor cables according to local regulations: • the cable must be able to carry the drive load current. See chapter technical data for the rated currents. • the cable must be rated ...
Page 68
Planning the electrical installation 68 alternative power cable types power cable types that can be used with the drive are represented below. Motor cable shield to effectively suppress radiated and conducted radio-frequency emissions, the shield conductivity must be at least 1/10 of the phase condu...
Page 69
Planning the electrical installation 69 additional us requirements type mc continuous corrugated aluminum armor cable with symmetrical grounds or shielded power cable must be used for the motor cables if metallic conduit is not used. For the north american market, 600 vac cable is accepted for up to...
Page 70
Planning the electrical installation 70 power factor compensation capacitors power factor compensation is not needed with ac drives. However, if a drive is to be connected in a system with compensation capacitors installed, note the following restrictions. Warning! Do not connect power factor compen...
Page 71
Planning the electrical installation 71 before opening an output contactor (in dtc motor control mode) stop the drive and wait for the motor to stop before opening a contactor between the output of the drive and the motor when the dtc control mode is selected. (see the firmware manual of the drive f...
Page 72
Planning the electrical installation 72 selecting the control cables all control cables must be shielded. Use a double-shielded twisted pair cable (see figure a) for analogue signals. This type of cable is recommended for the pulse encoder signals also. Employ one individually shielded pair for each...
Page 73: Routing The Cables
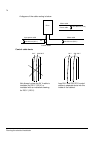
Planning the electrical installation 73 connection of a motor temperature sensor to the drive i/o warning! Iec 60664 requires double or reinforced insulation between live parts and the surface of accessible parts of electrical equipment which are either non- conductive or conductive but not connecte...
Page 74
Planning the electrical installation 74 a diagram of the cable routing is below. Control cable ducts 90 ° min 500 mm (20 in.) motor cable input power cable control cables min 200 mm (8 in.) min 300 mm (12 in.) motor cable power cable drive 230/120 v 24 v 24 v 230/120 v lead 24 v and 230/120 v contro...
Page 75: Electrical Installation
Electrical installation 75 electrical installation what this chapter contains this chapter describes the electrical installation procedure of the drive. Warning! Only qualified electricians are allowed to carry out the work described in this chapter. Follow the safety instructions on the first pages...
Page 76: Before Installation
Electrical installation 76 before installation checking the insulation of the assembly every drive has been tested for insulation between the main circuit and the chassis (2500 v rms 50 hz for 1 second) at the factory. Therefore, do not make any voltage tolerance or insulation resistance tests (e.G....
Page 77
Electrical installation 77 input power connection – frame r6 connection diagram connection procedure note: before making the cable connections, check that the input of the auxiliary voltage transformer (t10) is selected correctly according to the supply voltage. 1. Open the door of the cabinet. 2. R...
Page 78
Electrical installation 78 input power connection – frame r7i connection diagram connection procedure note: before making the cable connections, check that the input of the auxiliary voltage transformer (t10) is selected correctly according to the supply voltage. 1. Open the door of the cabinet. 2. ...
Page 79
Electrical installation 79 input power connection – frame size r8i connection diagram connection procedure note: before making the cable connections, check that the tap settings of the auxiliary voltage transformer (t10, located in the input/output cubicle) are correct in regard to the supply voltag...
Page 80
Electrical installation 80 input power connection – frame size 2×r8i and up connection diagram connection procedure 1. Open the door of the incoming cubicle (see section cabling direction starting on page 29 ). 2. Remove any shrouds that protect the input busbars and cable entries. 3. Lead the cable...
Page 81
Electrical installation 81 motor connection – frame r6 connection diagram connection procedure 1. Open the cabinet door. 2. Remove any shrouds that protect the output busbars and cable entries. 3. Lead the cables into the inside of the cubicle. It is recommended to apply 360° grounding of the cable ...
Page 82
Electrical installation 82 motor connection – frame r7i connection diagram connection procedure 1. Open the cabinet door. 2. Remove any shrouds that protect the output busbars and cable entries. 3. Lead the cables into the inside of the cubicle. It is recommended to apply 360° grounding of the cable...
Page 83
Electrical installation 83 motor connection – frame r8i units without option +e202 or +h359 connection diagram connection procedure note: before making the cable connections, consider checking the tap settings of the auxiliary voltage transformer located in the input/output cubicle. See instructions...
Page 84
Electrical installation 84 motor connection – frame r8i with option +e202 but without +h359 output busbars the motor cables are to be connected to the output busbars behind the inverter module. For the location and dimensions of the busbars, see the chapter dimensions . Connection diagram connection...
Page 85
Electrical installation 85 5 4 7 8 9a 9b 6a 3 6b 6c.
Page 86
Electrical installation 86 lead the cables into the cabinet at the inverter module. Make the 360° earthing arrangement at the cable entry as shown. Cut the cables to suitable length. Strip the cables and conductors. Twist the cable screens into bundles and connect to cabinet pe (ground) busbar. Conn...
Page 87
Electrical installation 87 motor connection – units with common motor terminal cubicle (+h359) connection diagram connection procedure 1. Open the door of the common motor terminal cubicle (see section cabling direction starting on page 29 ). 2. Remove any shrouds that protect the output busbars and...
Page 88: Cubicle
Electrical installation 88 motor connection – frame 2×r8i and up without common motor terminal cubicle output busbars the motor cables are to be connected to the output busbars behind each inverter module. For the location and dimensions of the busbars, see the chapter dimensions . Connection diagra...
Page 89
Electrical installation 89 connection procedure warning! The inverter modules are heavy and have a high centre of gravity. Be careful when manoeuvring the modules. In order to minimise the danger of toppling over, keep the support legs of the modules extended whenever manoeuvring the modules outside...
Page 90
Electrical installation 90 lead the cables into the cabinet at the inverter module. Make the 360° earthing arrangement at the cable entry as shown. Cut the cables to suitable length. Strip the cables and conductors. Twist the cable screens into bundles and connect to cabinet pe (ground) busbar. Conn...
Page 91: Control Connections
Electrical installation 91 control connections drive control connections the control connections are made on the terminal blocks provided in the swing-out frame of the drive. Refer to the circuit diagrams delivered with the drive, and to the chapter motor control and i/o board (rmio) . Supply unit c...
Page 92
Electrical installation 92 units with emi conductive cushions only: run the cables between the cushions as shown below. Strip the cable at this location to enable proper connection of the bare shield and the cushions. Tighten the cushions firmly onto the cable shields. If the outer surface of a cabl...
Page 93
Electrical installation 93 installation of optional modules and pc optional modules (such as fieldbus adapters, i/o extension modules and pulse encoder interfaces) are inserted into the optional module slot of the rmio boards (built in the rdcu drive control units) and secured with two screws . The ...
Page 94
Electrical installation 94 tap settings of the auxiliary voltage transformer (frame r8i and up) installation of brake resistors see the chapter resistor braking . 3~ input pr im a ry se conda ry 3~ input 1~ output 3~ output supply voltage terminals tap settings supply voltage 230 v 115 v 400 v (50 h...
Page 95: Note On Terminal Labelling
Motor control and i/o board (rmio) 95 motor control and i/o board (rmio) what this chapter contains this chapter shows • external control connections to the rmio board for the the acs 800 standard application program (factory macro) • specifications of the inputs and outputs of the board. To which p...
Page 96
Motor control and i/o board (rmio) 96 external control connections (non-us) external control cable connections to the rmio board for the acs 800 standard application program (factory macro) are shown below. For external control connections of other application macros and programs, see the appropriat...
Page 97
Motor control and i/o board (rmio) 97 external control connections (us) external control cable connections to the rmio board for the acs 800 standard application program (factory macro us version) are shown below. For external control connections of other application macros and programs, see the app...
Page 98: Rmio Board Specifications
Motor control and i/o board (rmio) 98 rmio board specifications analogue inputs with standard application program two programmable differential current inputs (0 ma / 4 ma ... 20 ma, r in = 100 ohm) and one programmable differential voltage input (-10 v / 0 v / 2 v ... +10 v, r in > 200 kohm). The a...
Page 99
Motor control and i/o board (rmio) 99 relay outputs three programmable relay outputs switching capacity 8 a at 24 vdc or 250 vac, 0.4 a at 120 vdc minimum continuous current 5 ma rms at 24 vdc maximum continuous current 2 a rms isolation test voltage 4 kvac, 1 minute ddcs fibre optic link with optio...
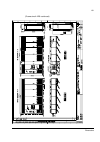
Page 100
Motor control and i/o board (rmio) 100 isolation and grounding diagram x20 1 vref- 2 agnd x21 1 vref+ 2 agnd 3 ai1+ 4 ai1- 5 ai2+ 6 ai2- 7 ai3+ 8 ai3- 9 ao1+ 10 ao1- 11 ao2+ 12 ao2- x22 1 di1 2 di2 3 di3 4 di4 9 dgnd1 5 di5 6 di6 7 +24vd 8 +24vd 11 diil 10 dgnd2 x23 1 +24 v 2 gnd x25 1 ro1 2 ro1 3 r...
Page 101: Installation Checklist
Installation checklist and start-up 101 installation checklist and start-up what this chapter contains this chapter contains an installation checklist, a start-up procedure for the drive, and listings of parameters specific to the acs800-37. Installation checklist check the mechanical and electrical...
Page 102: Start-Up Procedure
Installation checklist and start-up 102 start-up procedure for drives with category 1 emergency stop function: the time relay has been set to a suitable value (e.G. Somewhat longer than the stop ramp of the inverter units). All shrouds are in place. Action additional information warning! Ensure that...
Page 103
Installation checklist and start-up 103 close the auxiliary circuit on/off switch (q100) if present. Starting the supply unit close the main switch/disconnector (q1). Units with emergency stop: turn the start switch on the cabinet door from 0 into start position for 2 seconds, then release the switc...
Page 104
Installation checklist and start-up 104 acs800-37-specific parameters in the igbt supply control program the signals and parameters described in the tables below are included in the igbt supply control program. Terms and abbreviations parameters term definition b boolean c character string def. Defa...
Page 105
Installation checklist and start-up 105 fixed parameters with the acs800-37 when the igbt supply control program is loaded into the acs800-37, the following parameters receive the default values given in the table below. 31.02 trial time defines the time for the automatic fault reset function. See p...
Page 106
Installation checklist and start-up 106 acs800-37-specific parameters in the application program the actual signals and parameters described in this section are included in the acs800 standard application program. Terms and abbreviations term definition actual signal signal measured or calculated by...
Page 107
Installation checklist and start-up 107 actual signals and parameters of line-side converter in motor-side converter program no. Name/value description fbeq def. 09 actual signals signals from the line converter. 09.12 lcu act signal 1 line converter signal selected by par. 95.08 lcu par1 sel. 1 = 1...
Page 108
Installation checklist and start-up 108.
Page 109: Maintenance
Maintenance 109 maintenance what this chapter contains this chapter contains preventive maintenance instructions. Safety instructions only a qualified electrician is allowed to perform the maintenance. Before starting work inside the cabinet, • isolate the drive from the supply (note that any switch...
Page 110: Reduced Run Capability
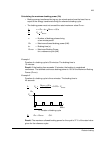
Maintenance 110 reduced run capability if one of the parallel-connected supply or inverter modules must be taken out of the cabinet for service, it is possible to continue operation at reduced power using the remaining modules. Note: this function is only available if the drive is equipped with a pp...
Page 111
Maintenance 111 quick connectors (frame r8i and up) 1. Read and repeat the steps in section safety instructions above. 2. Open the cabinet doors. 3. Extract one supply or inverter module from the cabinet as described in the connection procedures in the chapter electrical installation . 4. Check the ...
Page 112: Cooling Fans
Maintenance 112 cooling fans supply/inverter module cooling fan replacement (frame r6) 1. Read and repeat the steps in section safety instructions above. 2. Loosen the fastening screws of the top plate. 3. Lift the top plate upwards and pull it out. 4. Disconnect the fan supply wires (detachable con...
Page 113
Maintenance 113 supply/inverter module cooling fan replacement (frame r7i) 1. Disconnect the wire plug. 2. Remove the two screws holding the fan unit. 3. Pull the fan unit slightly towards the front of the cubicle, then downwards to free it. 4. Install new fan in reverse order. 3 2 1.
Page 114
Maintenance 114 lcl filter module cooling fan replacement (frame r7i) 1. Disconnect the wire plug (1). 2. Remove the two screws holding the fan unit (2). 3. Pull the fan unit out (3). 4. Install new fan in reverse order. 2 2 3 1.
Page 115
Maintenance 115 supply and inverter module cooling fan replacement (frame r8i and up) the lifespan of the cooling fans of the supply and inverter modules is about 50 000 hours. The actual lifespan depends on the running time of the fan, ambient temperature and dust concentration. Each supply and inv...
Page 116
Maintenance 116 lcl filter cooling fan replacement (frame r8i and up) the lifespan of the cooling fans of the lcl filter modules is about 60 000 hours. The actual lifespan depends on the running time of the fan, ambient temperature and dust concentration. Replacements are available from abb. Do not ...
Page 117
Maintenance 117 cabinet fan replacement (frame r6) 1. Read and repeat the steps in section safety instructions above. 2. Open the cubicle door. 3. Remove the shroud covering the top of the cubicle. 4. Disconnect the fan wiring. Make note of the connections at the terminal block. 5. Undo the two fast...
Page 118
Maintenance 118 cabinet fan replacement (frame r8i and up with ip54) 1. Remove the front and back gratings of the fan cubicle by lifting them upwards. 2. Remove the shrouds by undoing the fastening screws. 3. Undo the fastening screws of the side/top cover of the fan. 4. Lift the side/top cover of t...
Page 119: Heatsinks
Maintenance 119 heatsinks the heatsink fins of the power modules pick up dust from the cooling air. The module runs into overtemperature warnings and faults if the heatsinks are not clean. In a “normal” environment (not especially dusty nor clean) the heatsinks should be checked annually, in a dusty...
Page 120: Other Maintenance Actions
Maintenance 120 other maintenance actions power module replacement (frame r8i and up) to replace power modules (i.E. Supply and inverter modules), follow the instructions on module removal and refitting given in the chapter electrical installation ..
Page 121: Fault Tracing
Fault tracing 121 fault tracing faults and warnings displayed by the cdp-312r control panel the control panel will display the warnings and faults of the unit (i.E. Supply unit or inverter unit) the panel is currently controlling. The warnings and faults concerning the inverter unit (motor-side conv...
Page 122: Leds Of The Drive
Fault tracing 122 leds of the drive location led indication rmio board (rdcu drive control unit) red fault state. Green the power supply on the board is ok. Control panel mounting platform (with the control panel removed) red fault state. Green the main + 24 v power supply for the control panel and ...
Page 123: Technical Data
Technical data 123 technical data what this chapter contains this chapter contains the technical specifications of the drive, e.G. Ratings, frame sizes and technical requirements, provisions for fulfilling the requirements for ce and other markings, and warranty information. Iec ratings the ratings ...
Page 124
Technical data 124 symbols acs800-37-1820-5 2037 2956 1400 1956 1300 1524 1000 67 10240 78 acs800-37-2200-5 2529 3670 1800 2428 1700 1892 1350 81 12800 79 three-phase supply voltage 525 v, 550 v, 575 v, 600 v, 660 v, or 690 v acs800-37-0170-7 139 202 132 133 110 104 90 8 1300 74 acs800-37-0210-7 162...
Page 125
Technical data 125 derating the load capacity (current and power) decreases if the installation site altitude exceeds 1000 metres (3281 ft), or if the ambient temperature exceeds 40 °c (104 °f). Temperature derating in the temperature range +40 °c (+104 °f) to +50 °c (+122 °f), the rated output curr...
Page 126: Nema Ratings
Technical data 126 nema ratings the ratings for the acs800-37 with a 60 hz supply are given below. The symbols are described below the table. Acs800-37 type nominal ratings normal use heavy-duty use heat dis- sipation air flow noise level i max a p cont.Max hp i 2n a p n hp i 2hd a p hd hp btu/h ft ...
Page 127
Technical data 127 symbols note: the ratings apply in an ambient temperature of 40 °c (104 °f). In lower temperatures, the ratings are higher. Nominal ratings i max maximum output current. Allowable for 10 seconds at start, otherwise as long as allowed by drive temperature. P cont.Max typical motor ...
Page 128
Technical data 128 acs800-37 frame sizes and power module types acs800-37 type frame size supply module(s) used lcl filter(s) used inverter modules used qty type qty type qty type three-phase supply voltage 380 v, 400 v or 415 v acs800-37-0060-3 r6 1 acs800-11-0060-3* n/a n/a acs800-37-0070-3 r6 1 a...
Page 129: Ac Fuses
Technical data 129 ac fuses notes: • larger fuses must not be used. • fuses from other manufacturers can be used if they meet the ratings. • the recommended fuses are for branch circuit protection per nec as required for ul approval. Drive type ac fuse information qty i n ar, iec ar, ul recognized b...
Page 130: Dc Fuses
Technical data 130 dc fuses notes: • larger fuses must not be used. • fuses from other manufacturers can be used if they meet the ratings. • the recommended fuses are for branch circuit protection per nec as required for ul approval. Drive type dc fuse information qty iec ul recognized bussmann ferr...
Page 131: Input Power Connection
Technical data 131 input power connection voltage (u 1 ) 380/400/415 vac 3-phase± 10% for 400 vac units 380/400/415/440/460/480/500 vac 3-phase± 10% for 500 vac units 525/550/575/600/660/690 vac 3-phase± 10% for 690 vac units prospective short-circuit current (iec 60439-1, ul508c) 65 ka (i cf ) for ...
Page 132
Technical data 132 input terminals l1/l2/l3 – frame r6 input terminals l1/l2/l3 – frame r7i bottom cable entry/exit front view bolt size: m10 tightening torque: 40 nm (29.5 lbf.Ft) top cable entry/exit front view bolt size: m10 tightening torque: 40 nm (29.5 lbf.Ft) side view bolt size: m12 or ½” ti...
Page 133: Motor Connection
Technical data 133 input terminals l1/l2/l3 – frame r8i input terminals l1/l2/l3 – frame 2×r8i and up motor connection voltage (u 2 ) 0 to u 1 ,3-phase symmetrical, u max at the field weakening point frequency dtc mode: 0 to 3.2 × f fwp . Maximum frequency 300 hz. F fwp = where f fwp = frequency at ...
Page 134
Technical data 134 output terminals u2/v2/w2 – frame r6 output terminals u2/v2/w2 – frame r7i bottom cable entry/exit front view bolt size: m10 tightening torque: 40 nm (29.5 lbf.Ft) top cable entry/exit front view bolt size: m10 tightening torque: 40 nm (29.5 lbf.Ft) front view bolt size: m12 or ½”...
Page 135
Technical data 135 standard output terminals u2/v2/w2 – frame r8i frame r8i units without option +e202 (emc/rfi filtering for 1st environment) or +h359 (common motor terminal cubicle) output terminals at each r8i inverter module frame r8i units with option +e202 (emc/rfi filtering for 1st environmen...
Page 136: Efficiency
Technical data 136 maximum recommended motor cable length 100 m (328 ft). Motor cables up to 500 m (1640 ft) long are allowed but emc filtering within the specified limits will not be realised. Efficiency > 97% (at rated current and nominal supply voltage) cooling method internal fans, flow directio...
Page 137: Materials
Technical data 137 shock (iec 60068-2-29) not allowed max. 100 m/s 2 (330 ft./s 2 ), 11 ms max. 100 m/s 2 (330 ft./s 2 ), 11 ms free fall not allowed 100 mm (4 in.) for weight over 100 kg (220 lb) 100 mm (4 in.) for weight over 100 kg (220 lb) materials cabinet hot-dip zinc-coated (thickness approx....
Page 138
Technical data 138 • en 61800-3 (2004) adjustable speed electrical power drive systems. Part 3: emc requirements and specific test methods • ul 508c ul standard for safety, power conversion equipment, second edition • csa c22.2 no. 14-95 industrial control equipment.
Page 139: Ce Marking
Technical data 139 ce marking a ce mark is attached to the drive to verify that the unit follows the provisions of the european low voltage and emc directives (directive 73/23/eec, as amended by 93/68/eec and directive 89/336/ eec, as amended by 93/68/eec). Definitions emc stands for electromagnetic...
Page 140
Technical data 140 second environment (drive of category c3) the drive complies with the standard with the following provisions: 1. The drive is equipped with emc filter +e200. The filter is suitable for tn (earthed) and it (unearthed) networks. 2. The motor and control cables are selected as specif...
Page 141: “C-Tick” Marking
Technical data 141 “c-tick” marking “c-tick” marking is required in australia and new zealand. A “c-tick” mark is attached to each drive in order to verify compliance with the relevant standard (iec 61800-3 (2004) – adjustable speed electrical power drive systems. Part 3: emc product standard includ...
Page 142
Technical data 142 second environment (drive of category c3) the drive complies with the standard with the following provisions: 1. The drive is equipped with emc filter +e200. The filter is suitable for tn (earthed) and it (unearthed) networks. 2. The motor and control cables are selected as specif...
Page 143
Technical data 143 equipment warranty and liability the manufacturer warrants the equipment supplied against defects in design, materials and workmanship for a period of twelve (12) months after installation or twenty-four (24) months from date of manufacturing, whichever first occurs. The local abb...
Page 144
Technical data 144.
Page 145: Dimensions
Dimensions 145 dimensions what this chapter contains this chapter contains a table of weights as well as dimensional drawings of the different frame sizes of the acs800-37. Weights the following table shows the approximate weights of all acs800-37 types (without options). Acs800-37-… weight kg lb 00...
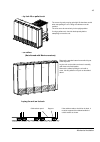
Page 146: Frame R6
Dimensions 146 frame r6.
Page 147
Dimensions 147 [frame size r6 continued].
Page 148
Dimensions 148 [frame size r6 continued].
Page 149
Dimensions 149 [frame size r6 continued].
Page 150: Frame R7I
Dimensions 150 frame r7i.
Page 151
Dimensions 151 [frame size r7i continued].
Page 152
Dimensions 152 [frame size r7i continued].
Page 153
Dimensions 153 [frame size r7i continued].
Page 154
Dimensions 154 [frame size r7i continued].
Page 155
Dimensions 155 [frame size r7i continued].
Page 156
Dimensions 156 [frame size r7i continued].
Page 157
Dimensions 157 frame r8i (without option +e202).
Page 158
Dimensions 158 [frame size r8i (without option +e202) continued].
Page 159
Dimensions 159 [frame size r8i (without option +e202) continued].
Page 160
Dimensions 160 [frame size r8i (without option +e202) continued].
Page 161
Dimensions 161 [frame size r8i (without option +e202) continued].
Page 162
Dimensions 162 [frame size r8i (without option +e202) continued].
Page 163
Dimensions 163 [frame size r8i (without option +e202) continued].
Page 164
Dimensions 164 [frame size r8i (without option +e202) continued].
Page 165
Dimensions 165 frame size r8i (with option +e202).
Page 166
Dimensions 166 [frame size r8i (with option +e202) continued].
Page 167
Dimensions 167 [frame size r8i (with option +e202) continued].
Page 168
Dimensions 168 [frame size r8i (with option +e202) continued].
Page 169
Dimensions 169 [frame size r8i (with option +e202) continued].
Page 170: Frame Size 2×R8I
Dimensions 170 frame size 2×r8i.
Page 171
Dimensions 171 (frame size 2×r8i continued).
Page 172
Dimensions 172 (frame size 2×r8i continued).
Page 173
Dimensions 173 (frame size 2×r8i continued).
Page 174
Dimensions 174 (frame size 2×r8i continued).
Page 175
Dimensions 175 (frame size 2×r8i continued).
Page 176
Dimensions 176 (frame size 2×r8i continued).
Page 177
Dimensions 177 (frame size 2×r8i continued).
Page 178
Dimensions 178 (frame size 2×r8i continued).
Page 179
Dimensions 179 (frame size 2×r8i continued).
Page 180
Dimensions 180 (frame size 2×r8i continued).
Page 181
Dimensions 181 (frame size 2×r8i continued).
Page 182
Dimensions 182 (frame size 2×r8i continued).
Page 183: Frame Size 3×R8I
Dimensions 183 frame size 3×r8i.
Page 184
Dimensions 184 (frame size 3×r8i continued).
Page 185
Dimensions 185 (frame size 3×r8i continued).
Page 186
Dimensions 186 (frame size 3×r8i continued).
Page 187
Dimensions 187 (frame size 3×r8i continued).
Page 188
Dimensions 188 (frame size 3×r8i continued).
Page 189: Frame Size 4×R8I
Dimensions 189 frame size 4×r8i.
Page 190
Dimensions 190 (frame size 4×r8i continued).
Page 191
Dimensions 191 (frame size 4×r8i continued).
Page 192
Dimensions 192 (frame size 4×r8i continued).
Page 193
Dimensions 193 (frame size 4×r8i continued).
Page 194
Dimensions 194 (frame size 4×r8i continued).
Page 195: Frame Size 5×R8I
Dimensions 195 frame size 5×r8i.
Page 196
Dimensions 196 (frame size 5×r8i continued).
Page 197
Dimensions 197 (frame size 5×r8i continued).
Page 198
Dimensions 198 (frame size 5×r8i continued).
Page 199
Dimensions 199 (frame size 5×r8i continued).
Page 200
Dimensions 200 (frame size 5×r8i continued).
Page 201
Dimensions 201 (frame size 5×r8i continued).
Page 202
Dimensions 202 (frame size 5×r8i continued).
Page 203
Dimensions 203 (frame size 5×r8i continued).
Page 204
Dimensions 204 (frame size 5×r8i continued).
Page 205
Dimensions 205 (frame size 5×r8i continued).
Page 206
Dimensions 206 (frame size 5×r8i continued).
Page 207: Frame Size 6×R8I
Dimensions 207 frame size 6×r8i.
Page 208
Dimensions 208 (frame size 6×r8i continued).
Page 209
Dimensions 209 (frame size 6×r8i continued).
Page 210
Dimensions 210 (frame size 6×r8i continued).
Page 211
Dimensions 211 (frame size 6×r8i continued).
Page 212
Dimensions 212 (frame size 6×r8i continued).
Page 213
Dimensions 213 (frame size 6×r8i continued).
Page 214
Dimensions 214 (frame size 6×r8i continued).
Page 215
Dimensions 215 (frame size 6×r8i continued).
Page 216
Dimensions 216 (frame size 6×r8i continued).
Page 217
Dimensions 217 (frame size 6×r8i continued).
Page 218
Dimensions 218 (frame size 6×r8i continued).
Page 219: Resistor Braking
Resistor braking 219 resistor braking what this chapter contains this chapter describes the resistor braking options of the acs800-37. Resistor braking options the following acs800-37 drives are available with brake choppers and resistors. For information on braking equipment for other acs800-37 typ...
Page 220
Resistor braking 220 chopper/resistor combinations – technical data the following table contains the technical data of selected chopper/resistor combinations. U n chopper(s) resistors r (ohm) p brmax (kw) p cont (kw) i max (a) duty cycle (10/60 s) duty cycle (1/5 min) airflow (m 3 /h) p br (kw) i rm...
Page 221
Resistor braking 221 brake choppers – technical data the following table contains the technical data for the nbra-6xx brake choppers. Brake resistors – technical data the following table contains the technical data for the resistors supplied by abb. U n chopper type p brmax (kw) p cont (kw) i max (a...
Page 222
Resistor braking 222 verifying the capacity of the braking equipment 1. Calculate the maximum power (p max ) generated by the motor during braking. 2. Ensure the following condition is met: the p brmax values specified in the technical data table above are for the reference braking cycle (1 minute o...
Page 223
Resistor braking 223 calculating the maximum braking power (p br ) • braking energy transferred during any ten minute period must be less than or equal to the energy transferred during the reference braking cycle. • the braking power must not exceed the rated maximum value p brmax . Example 1 durati...
Page 224
Resistor braking 224 example 3 duration of a braking cycle is three minutes. The braking time is 10 seconds. Result: the maximum allowed braking power for the cycle is equal to the maximum braking power (p brmax ) given for the reference cycle. T = duration of the braking cycle t br p brmax t p br 6...
Page 225
Resistor braking 225 custom resistor installation and wiring effective cooling of the resistors must be ensured. Warning! All materials near the brake resistors must be non-flammable. The surface temperature of the resistors is high. The temperature of the air rising from the resistors is hundreds o...
Page 226: Brake Circuit Commissioning
Resistor braking 226 the following is a wiring diagram example of the resistor connection. Brake circuit commissioning in the drive application program, overvoltage control of the drive must be disabled for correct operation of the brake chopper. This has been done at the factory for units with brak...
Page 228
3a f e 68557 925 re v b e n e f f e ct iv e : 01. 1 1 .2005 abb oy ac drives p.O. Box 184 fi-00381 helsinki finland telephone +358 10 22 11 fax +358 10 22 22681 internet http://www.Abb.Com abb inc. Automation technologies drives & motors 16250 west glendale drive new berlin, wi 53151 usa telephone 2...