- DL manuals
- ABB
- DC Drives
- DCS 400
- Manual
ABB DCS 400 Manual - Planned For 2000
II K 2-2
Planned for 2000
under preparation
2.1
Environmental conditions
Mains supply - power part
Voltage, 3-phase:
230 to 500 V in acc. with IEC 38
Voltage deviation:
±10% permanent
Rated frequency:
50 Hz or 60 Hz
Static frequency deviation:
50 Hz ±2 %; 60 Hz ±2 %
Dynamic:
frequency range:
50 Hz: ±5 Hz; 60 Hz: ± 5 Hz
df/dt:
17 % / s
Mains supply - Electronics supply
Voltage, 1-phase:
115 to 230 V in acc. with IEC 38
Voltage deviation:
-15% / +10%
Frequency range:
45 Hz to 65 Hz
Degree of protection
Power converter module:
IP 00
Paint finish
Power converter module, cover:
RAL 9002 light-grey
housing:
RAL 7012 dark-grey
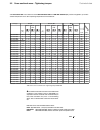
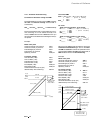
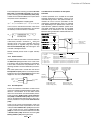
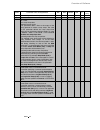
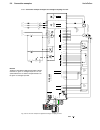
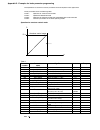
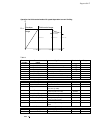
Fig. 2.1/1: Effect of the site elevation above sea level on the
power converter's load capacity
Current reduction to (%) for armature circuit and field supply
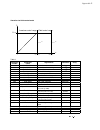
Fig. 2.1/2: Effect of the ambient temperature on the converter
module load capacity.
Current reduction to (%) for armature circuit and field supply
Environmental limit values
Permissible ambient temp. with rated current I
DC
: +5 to +40°C
Ambient temp., power conv. module:+40°C to 55°C; s. Fig. 2.1/2
Alteration in the ambient temp.:
< 0,5°C / minute
Storage temperature:
-40 to +55°C
Transport temperature:
-40 to +70°C
Relative humidity:
5 to 95%,
no condensation
Pollution degree:
Grade 2
Site elevation:
<1000 m above M.S.L.:
100%, without current reduction
>1000 m above M.S.L.:
with current reduct., s. Fig. 2.1/1
Vibration converter module: 0,5 g; 5 Hz to 55 Hz
Noises:
Size
as module
(1 m distance)
A1
55 dBA
A2
55 dBA
A3
60 dBA
A4
66...70 dBA, dependent on fan
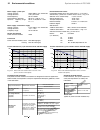
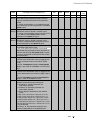
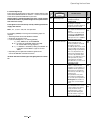
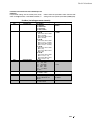
Compliance with standards
The power converter modules and cubicles are designed for industrial applications.
Within the EU, the components satisfy the requirements European guidelines, shown
in the table below.
Standards in North America
In North America, the system components
satisfy the requirements as listed in the
table below.
70
80
90
100
110
30
35
40
45
50
55°C
Please note:
applies for power converter modules only.
50
60
70
80
90
100
1000
2000
3000
4000
5000 m
European Union Directive
Manufacturer’s Assurance
Harmonized Standards
Converter module
Machinery Directive
89/392/EEC
93/68/EEC
Declaration of
Incorporation
EN 60204-1
[IEC 204-1]
Low Voltage Directive
73/23/EEC
93/68/EEC
Declaration of Conformity
EN 60146-1-1
[IEC 146-1-1]
EN 50178 [IEC --]
see additional
IEC 664
EMC Directive
89/336/EEC
93/68/EEC
Declaration of Conformity.
Provided that all installation
instructions concerning
cable selection, cabling and
EMC filters or dedicated
transformer are followed.
EN 61800-3
¥
[IEC 1800-3]
where limits are under consideration
EN 50081-2 / EN 50082-2 has been supplied
¥
in accordance with 3ADW 000 032
’Installation in accordance with EMC’
The Technical Construction File to which this
Declaration relates has been assessed by
Report and Certificate from ABB EMC
Certification AB being the Competent Body
according to the EMC Directive.
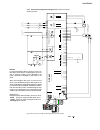
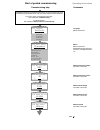
System overview of DCS 400
Safety for Power
conversion Equipment
≤ 600 V
Standard for module
UL 508 C
Industrial control
Equipment: industrial
products
≤ 600 V
CSA C 22.2. No.1495
Summary of DCS 400
Page 1
Ii k 1-1 dcs thyristor power converter for dc drive systems 20 to 1000 a 9 to 522 kw manual dcs 400
Page 2
Ii k 1-2 list of contents m anual 1 dcs 400 - the compact-size dc drive ........ Ii k 1-3 2 system overview of dcs 400 .................... Ii k 2-1 2.1 environmental conditions ............................................. Ii k 2-2 2.2 dcs 400 power converter modules ............................ Ii...
Page 3
Ii k 1-3 1 dcs 400 - the compact-size dc drive dcs 400 is a new generation of dc drives, which is rated from 9 to 522 kw and for use on all line supply voltages from 230 to 500 v. Total ease of use was the brief given to the drive`s designers. The result is a dc drive that meets the needs of machine...
Page 4
Ii k 1-4 activation and operator-control analogue and digital inputs and outputs fieldbusses mmc (man-machine communication) via: drive window light (start-up and maintenance program) pc pro- grams can be run under all commonly used windows ® environments (3.1x, 95,98, nt): parameter programming ...
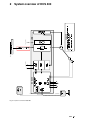
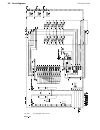
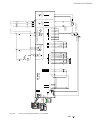
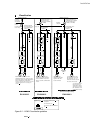
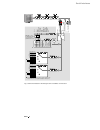
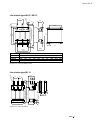
Page 5: System Overview of Dcs 400
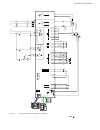
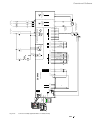
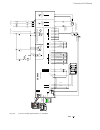
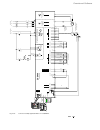
Ii k 2-1 2 system overview of dcs 400 fig. 2/1: system overview of dcs 400 l1 k1 q1 0 t t 6 ' & 6 & 2 1 $ 4 2 f1 23 0. .. 5 0 0 v µ p m '& 6 11 5. ..2 3 0 v a c 1 1 5 / 2 3 0 v ac 82 1 rs232 6 ' & 6 3 ,1 $ ( 0 & il owh u )l ho g ex v wr wk h 3 /& /h jh qg 3 rz hu 6 xs so \ 7k \u lv wr u fr qw ur o 3...
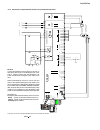
Page 6: Planned For 2000
Ii k 2-2 planned for 2000 under preparation 2.1 environmental conditions mains supply - power part voltage, 3-phase: 230 to 500 v in acc. With iec 38 voltage deviation: ±10% permanent rated frequency: 50 hz or 60 hz static frequency deviation: 50 hz ±2 %; 60 hz ±2 % dynamic: frequency range: 50 hz: ...
Page 7
Ii k 2-3 2.2 dcs 400 power converter modules size a2 size a1 size a3 size a4 sizes ➀ fan with 115 v/1 ph available as option system overview dcs 400 converter type line voltage 400 v 500 v i dc [a] i ac [a] i f [a] p [kw] p [kw] dcs402.0025 25 20 4 10 13 dcs402.0050 50 41 6 21 26 dcs402.0075 75 61 6...
Page 8
Ii k 2-4 2.3 dcs 400 overload withstand capability system overview of dcs 400 to match a drive systems components as efficiently as possible to the driven machines load profile, the power converters can be dimensioned by means of the load cycle. Load cycles for driven machines have been defined in...
Page 9
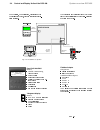
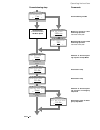
Ii k 2-5 system overview dcs 400 2.4 control and display units of the dcs 400 fig. 2.4/1: possibilities of operation for operation, commissioning, diagnosis and for controlling the drive, there are different possibil- ities available. Panel dcs 400 pan features guided commissioning (panel wizard) ...
Page 10
Ii k 2-6 operation by pc components : rs232 standard cable, 9-pin sub-d connector, male-female, non-crossing functionality: software package "drive window light" system requirements/recommendation: pc with 386 processor or higher hard disk with 5 mb free memory vga monitor windows 3.1, 3...
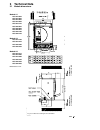
Page 11: Technical Data
Ii k 3-1 technical data 3 technical data 3.1 module dimensions module a1 dcs 401.0020 dcs 401.0045 dcs 401.0065 dcs 401.0090 dcs 401.0125 dcs 402.0025 dcs 402.0050 dcs 402.0075 dcs 402.0100 dcs 402.0140 module a2 dcs 401.0180 dcs 401.0230 dcs 402.0200 dcs 402.0260 module a3 dcs 401.0315 dcs 401.0405...
Page 12
Ii k 3-2 technical data module a4 dcs 401.0610 dcs 401.0740 dcs 401.0900 dcs 402.0680 dcs 402.0820 dcs 402.1000 dimensions in mm fig. 3.1/2: dimension drawing a4-module for m12 for m6.
Page 13
Ii k 3-3 technical data 3.2 cross-sectional areas - tightening torques ❶ you will find instructions on how to calculate the pe conductor’s cross-sectional area in vde 0100 or in equivalent national standards. We would remind you that power converters may have a current-limiting effect. This can lead...
Page 14: Under Preparation
Ii k 3-4 technical data • the dcs 400 should be installed in an enclosure that is minimum 150% of the dimensions of con- verter. • the dcs 400 is suitable for use in a circuit capable of delivering not more than 18 ka rms symetrical amperes, 500 v ac maximum. Recommended fuses must be used to provid...
Page 15
Ii k 3-5 technical data 3.3 power losses converter type power losses p l [w] load i dc [a] 25% 50% 75% 100% dcs401.0020 20 10 22 35 49 dcs401.0045 45 25 57 95 145 dcs401.0065 65 38 80 128 181 dcs401.0090 90 48 103 166 236 dcs401.0125 125 65 138 220 311 dcs401.0180 180 96 210 341 490 dcs401.0230 230 ...
Page 16
Ii k 3-6 technical data 3.4 power section cooling fan assignment for dcs 400 fan data for dcs 400 (data per fan) fan connection for dcs 400 configuration 3 configuration 2 configuration 1 table 3.4/2: fan data for dcs 400 table 3.4/1: fan assignment for dcs 400 monitoring the dcs 400 power section t...
Page 17
Ii k 3-7 technical data 3.5 control board sdcs-con-3a control functions (watchdog) the control board has an internal watchdog. The watchdog trip has the following effects: - thyristor firing control is reset and disabled. - digital outputs are forced to '0 v'. Fig. 3.5/1 layout of the control board ...
Page 18
Ii k 3-8 technical data fig. 3.5/3 terminal connection of the sdcs-con-3a board digital and analogue i/o connection of the sdcs-con-3a reso- input/output scaling load common remarks lution values by mode [bit] hardware range ±90...270 v 11 + sign ±30...90 v r 115/ ±20 v ➀ ➁ ±8...30 v software 11 + s...
Page 19
Ii k 3-9 technical data 3.6 power interface board sdcs-pin-3a the power interface board sdcs-pin-3a is used for all converter modules model a1...A4. Functions: - firing pulse circuits - measurement of the armature current - snubber circuit - ac and dc voltage measurement - heat sink temperature meas...
Page 20
Ii k 3-10 technical data the dcs 400 converter has an build-in three-phase field exciter with the following features: • smoothed field voltage - better commutation of the motor - increased brush life • less heat generation in the motor • less effort of cabling fig. 3.7/1 layout of the sdcs-fis-3a fi...
Page 21
Ii k 3-11 technical data 20 0,1 1 10 100 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 i f u f [a] [v] 220 1.5 0.3 16 important note: nominal field voltage and field current of the motor has to be within the field controller operating range. For application with constant field it is easy to check: transfer v...
Page 22
Ii k 3-12 technical data 3.8 ciruit diagrams fig. 3.8/1 circuit diagram 4-q converter 3 ,1 $ & 2 1 $ $ 9 9 ; & 5 2 9 . * 9 . * ) ) ) 9 . * . * 9 ' 9 * . . 9 * * . 9 ; * . . 9 * * . 9 9 . 6 / 6 . 6 / 6 7 7 * . $ 3 ( : / 8 9 / / ; ; ; ; ; ; / 6 . 6 7 ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; 9 ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; : 9 8 ' &...
Page 23
Ii k 3-13 technical data fig. 3.8/2 circuit diagram 2-q converter 3 ,1 $ & 2 1 $ $ ; & 5 2 ) ) ) ' ; . 6 / 6 . 6 / 6 7 7 $ 3 ( : / 8 9 / / ; ; ; ; ; ; / 6 . 6 7 ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; 9 ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; : 9 8 ' & ; ; ; 7 ; ; 7 ; 7 ; 7 ; 7 ; 7 ; 7 ; 7 ; 7 ; 7 ; 7 ; 7 * . * . . * . * * . . * . * * . *...
Page 24
Ii k 3-14 technical data.
Page 25: Overview of Software
Ii k 4-1 overview of software 4 overview of software (the software delivered may contain minor changes to the product described here.) parameter the parameters of the converter are subdivided into functional groups. These groups are listed in the table below. Parameter group functions 1 - motor sett...
Page 26
Ii k 4-2 overview of software selector remark motpotminspeed (9.12) motor potentiometer minimum speed ref. Ext field rev (9.13) external field reversal via external field reversing switch alternativparam (9.14) switch over between standard parame- ter set and alternative parameter set ext speed lim ...
Page 27
Ii k 4-3 overview of software overview of factory settings of macro-dependent parameters: macro Í 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Ï parameter standard man/const sp hand/auto hand/motpot jogging motor pot ext field rev torque ctrl cmd location (2.02) terminals terminals terminals terminals terminals terminals termin...
Page 28
Ii k 4-4 overview of software 4.2 application macros the following application macros are available: macro 1: standard drive switch-on/switch-off and enable via 2 digital inputs. Speed reference via analog input. External torque limiting via analog input. Jogging via 2 digital inputs. 2 digital inpu...
Page 29
Ii k 4-5 overview of software.
Page 30
Ii k 4-6 overview of software 4.2.1 macro 1 - standard description of i/o’s functionality i/o param function di1 jog speed 1. Speed can be defined in parameter 5.13. Accel/decel ramp for jogging can be defined in parameter 5.19/5.20. Di2 jog speed 2. Speed can be defined in parameter 5.14. Accel/dec...
Page 31
Ii k 4-7 overview of software fig. 4.2/1: connection example application-macro 1 - standard _ + in ou t d c s 40 0 p a n c 1 d 1 x9 8 : do 5 12 34 4 5 x9 9 : 1 2 3 u1 w 1 v1 pe x1 0 : 1 2 ai t a c a i1 ai 2 + 1 0 v -1 0 v ao1 a o2 di 1 d i2 di 3 d i4 di 5 d i6 di 7 d i8 + 2 4 v do1 d o2 do3 d o4 __ ...
Page 32
Ii k 4-8 overview of software 4.2.2 macro 2 - man/const sp description of i/o’s functionality i/o param function di1 drive is started by closing digital input di1 (di=1). Switches the drive on and start di2 drive is stopped by opening digital input di2 (di2=0). Di2 has a higher priority than di1, i....
Page 33
Ii k 4-9 overview of software fig. 4.2/2: connection example application-macro 2 - man/const sp _ + in ou t c 1 d 1 x9 8 : do 5 12 34 4 5 x9 9 : 1 2 3 u1 w 1 v1 pe x1 0 : 1 2 ai t a c a i1 ai 2 + 1 0 v -1 0 v ao1 a o2 di 1 d i2 di 3 d i4 di 5 d i6 di 7 d i8 + 2 4 v do1 d o2 do3 d o4 __ ++ t t k1 98 ...
Page 34
Ii k 4-10 overview of software 4.2.3 macro 3 - hand/auto description of i/o’s functionality i/o param function di1 start / stop hand. Start and stop the drive. Di1=0=stop , di1=1=start start switches the drive on and start. Stop the drive in according to parameter stop-mode and afterwards switch the...
Page 35
Ii k 4-11 overview of software fig. 4.2/3: connection example application-macro 3 - hand/auto _ + in ou t c 1 d 1 x9 8 : do 5 12 34 4 5 x9 9 : 1 2 3 u1 w 1 v1 pe x1 0 : 1 2 ai t a c a i1 ai 2 + 1 0 v -1 0 v ao1 a o2 di 1 d i2 di 3 d i4 di 5 d i6 di 7 d i8 + 2 4 v do1 d o2 do3 d o4 __ ++ t t k1 98 :1...
Page 36
Ii k 4-12 overview of software 4.2.4 macro 4 - hand/motpot description of i/o’s functionality i/o param function di1 start / stop. Start and stop the drive. Di1=0=stop , di1=1=start. Start switches the drive on and start. Stop the drive in according to parameter stop-mode and afterwards switch the d...
Page 37
Ii k 4-13 overview of software fig. 4.2/4: connection example application-macro 4 - hand/motpot _ + in ou t c 1 d 1 x9 8 : do 5 12 34 4 5 x9 9 : 1 2 3 u1 w 1 v1 pe x1 0 : 1 2 ai t a c a i1 ai 2 + 1 0 v -1 0 v ao1 a o2 di 1 d i2 di 3 d i4 di 5 d i6 di 7 d i8 + 2 4 v do1 d o2 do3 d o4 __ ++ t t k1 98 ...
Page 38
Ii k 4-14 overview of software 4.2.5 macro 5 - jogging description of i/o’s functionality i/o param function di1 direction of rotation. Di1=0=forward , di1=1=reverse di2 jog speed 1. Speed can be defined in parameter 5.13. Accel/decel ramp for jogging can be defined in parameter 5.19/5.20. Di3 jog s...
Page 39
Ii k 4-15 overview of software fig. 4.2/5: connection example application-macro 5 - jogging _ + in ou t c 1 d 1 x9 8 : do 5 12 34 4 5 x9 9 : 1 2 3 u1 w 1 v1 pe x1 0 : 1 2 ai t a c a i1 ai 2 + 1 0 v -1 0 v ao1 a o2 di 1 d i2 di 3 d i4 di 5 d i6 di 7 d i8 + 2 4 v do1 d o2 do3 d o4 __ ++ t t k1 98 :1 9...
Page 40
Ii k 4-16 overview of software 4.2.6 macro 6 - motor pot description of i/o’s functionality i/o param function di1 direction of rotation. Di1=0=forward , di1=1=reverse di2 motor pot function „faster“.Accel ramp 5.09 di3 motor pot function „slower“. Decel ramp 5.10. Slower has precedence above faster...
Page 41
Ii k 4-17 overview of software fig. 4.2/6: connection example application-macro 6 - motor pot _ + in ou t c 1 d 1 x9 8 : do 5 12 34 4 5 x9 9 : 1 2 3 u1 w 1 v1 pe x1 0 : 1 2 ai t a c a i1 ai 2 + 1 0 v -1 0 v ao1 a o2 di 1 d i2 di 3 d i4 di 5 d i6 di 7 d i8 + 2 4 v do1 d o2 do3 d o4 __ ++ t t k1 98 :1...
Page 42
Ii k 4-18 overview of software 4.2.7 macro 7 - ext field rev with remanence contactor description of i/o’s functionality i/o param function di1 external field reversal with external field reversing switch. Only for 2q application. Di1=0=no field reversal di1=1=field reversal depend on field reversal...
Page 43
Ii k 4-19 overview of software fig. 4.2/7: connection example application-macro 7 - ext field rev _ + in ou t c 1 d 1 x9 8 : do 5 12 34 4 5 x9 9 : 1 2 3 u1 w 1 v1 pe x1 0 : 1 2 ai t a c a i1 ai 2 + 1 0 v -1 0 v ao1 a o2 di 1 d i2 di 3 d i4 di 5 d i6 di 7 d i8 + 2 4 v do1 d o2 do3 d o4 __ ++ t t k1 9...
Page 44
Ii k 4-20 overview of software 4.2.8 macro 8 - torque ctrl description of i/o’s functionality i/o param funktion di1 coast. Closed-circuit principle, must be closed for operation. Coast is the fastest way to stop the current controller. The current controller will decrease the armature current to ze...
Page 45
Ii k 4-21 overview of software fig. 4.2/8: connection example application-macro 8 - torque ctrl in ou t c 1 d 1 x9 8 : do 5 12 34 4 5 x9 9 : 1 2 3 u1 w 1 v1 pe x1 0 : 1 2 ai t a c a i1 ai 2 + 1 0 v -1 0 v ao1 a o2 di 1 d i2 di 3 d i4 di 5 d i6 di 7 d i8 + 2 4 v do1 d o2 do3 d o4 __ _ ++ + t t k1 98 ...
Page 46
Ii k 4-22 overview of software 4.3 digital and analogue inputs/outputs digital inputs di1…di8 the drive is controlled via the digital inputs di1…di8. The significance of the inputs are defined by a macro. When you select a macro in the macro select (2.01) parameter the functions are assigned to the ...
Page 47
Ii k 4-23 overview of software dcs400 accuracy analog values will be converted to digital values via anlog digital converter (adc). The accuracy of res- olution depends on how much bits are used and is related to 100%. Bipolar values are marked at most significant bit (sign bit). Resolution of dcs40...
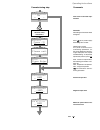
Page 48
Ii k 4-24 overview of software 4.4 drive logic the drive logic controls the switching on and off of the converter and the motor and protects both in excep- tional situations, in case of fault or emergency stop. This logic switches on the main contactor, the fans and the field supply. The drive logic...
Page 49
Ii k 4-25 overview of software neither the on nor the run command is active in this phase. Only upon reaching the minimum speed, can the drive be restarted with the rising edges of the on and the run command. If eme stop mode (2.04) = coast is set the pulses will be blocked, the main contactor, the ...
Page 50
Ii k 4-26 overview of software fig. 4.4/2: switch-off sequence of dcs 400 minimal circuitry for the drive logic all digital inputs of the drive logic are edge-sensitive, i.E. The function concerned will be executed only if there is a signal change from 0 ÿé 1 or 1ÿéÿ0. Drive is controlled using two ...
Page 51
Ii k 4-27 overview of software 4.5 regulator functions software functions are described in the context of the individual parameters (see parameter list). Special functions which require an comprehensive parame- terization or no parameterization and the service procedures are described below. 4.5.1 m...
Page 52
Ii k 4-28 overview of software 5% above this tripping threshold, an alarm signal a02-mains voltage low will be generated. The alarm range shifts when the net underv trip (1.10) parameter is altered. The alarm does not impair the drive in terms of its function. This message indicates that • in regene...
Page 53
Ii k 4-29 overview of software monitoring the mains voltage: e.G. Mains supply voltage = 400 v application = 4-q armature voltage nominal = 420 v …with maximum negative settings: net underv trip (1.10) = -10% 2-q - application u net (v) f09-fault level (v) a02-alarm level (v) u dc (v) u dc max (v) 2...
Page 54
Ii k 4-30 overview of software 4.5.3 automatic field weakening correlation of armature voltage and emf the dcs 400 drive calculates the true emf and does not take the armature voltage instead. Emf is calculated by emf nom = arm volt nom - (arm cur nom x arm resistance) the armature resistance is mea...
Page 55
Ii k 4-31 overview of software without speed-dependent current limiting the field weakening mode is selected or not selected as a function of the parameter values base speed (1.05) and max speed (1.06): no field weakening: if the contents of base speed (1.05) is identical with max speed (1.06) field...
Page 56
Ii k 4-32 overview of software 4.5.5 armature current controller the arm cur nom (1.01), arm cur max (3.04), torque lim pos (3.07) and torque lim neg (3.08) parameters are the ones relevant to the current limi- tation functions. Arm cur nom (1.01) scales the power converter to motor rated current. A...
Page 57
Ii k 4-33 overview of software armature current controller operating modes the speed of a dc motor is altered with the armature voltage. The range up to the point where the rated armature voltage is reached is referred to as the armature operating range. To enable the motor’s speed to be increased a...
Page 58
Ii k 4-34 overview of software 1 = speed contr / 2 = torque contr depending on the application involved, however, a constant torque is also required in the field weakening range (torque-controlled mode (3.14) = torque contr). For this purpose, the armature current has to be increased in this range, ...
Page 59
Ii k 4-35 overview of software 6 = lim trq ctr (window control mode) the idea of window control mode is to deactivate the speed control as long as the speed deviation remains within the window. This allows the torque reference to affect the process directly. In master / follower drives, where the fo...
Page 60
Ii k 4-36 overview of software speed act torque act > 3.17 time > 3.18 motor stalled (f19) the overload phase is set using parameters arm cur max (3.04) and overload time (3.05). The recovery phase is set using parameter recovery time (3.06). In order not to overload the motor, the i 2 t-plane of th...
Page 61
Ii k 4-37 overview of software 4.5.9 service procedures, contr service (7.02) armature current controller (motor does not turn) autotuning • on the panel press button loc; loc is dis- played in the panel status row. • select parameter contr service (7.02) = arm autotun and confirm with enter. • with...
Page 62
Ii k 4-38 overview of software speed controller attention: motor will accelerate twice to 80% of base speed now autotuning • on the panel press button loc; loc is dis- played in the panel status row. • select parameter contr service (7.02) = sp autotun and confirm with enter. • within the next 30 se...
Page 63
Ii k 4-39 overview of software 4.5.10 internal scaling you can display all parameters of the dcs400 in their physical quantities by means of operating panel or the pc tool, in the way they are specified in the column "unit" at the parameter list: a, v, rpm, hz, %, s, ms, text, integer, mh, mohm, %/ ...
Page 64
Ii k 4-40 overview of software 4.5.11 signal definitions signal "at set point" speed reference reached. Speed actual value speed act (5.05) correspondes to speed reference value before ramp generator ramp in act (5.33). The deviation between both is less than ±1,56% (1/64) of parameter maximum speed...
Page 65
Ii k 4-41 overview of software 4.5.12 user events adaptation of digital inputs for user events first four digital inputs di1…di4 are re-configurable in parameter group 9-macro adaptation for macro 1, 5, 6, 7 and 8. This functionality is not available for macro 2, 3 and 4. For some user specific appl...
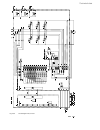
Page 66
Ii k 4-42 overview of software 4.6 software structure 6.27 1 x4: 2 9 +24 v 2.01 di1 di2 di3 di4 di5 di6 di7 di8 3 4 5 6 7 8 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.09 2.07 2.08 5.00s 2.10 1 2.11 4 mbaud 2.12 1 x5: 2 do1 do3 do5 do2 do4 3 4 x98:1 6.11 6.12 6.13 6.14 6.15 6.22 6.23 6.24 6.25 5 x98:2 8.01 6.28 2.05 ds1.1 ds1...
Page 67
Ii k 4-43 overview of software 6.06 6.07 10.00v 3.14 0.550 4.11 160ms 4.12 29% 4.07 53% 4.08 79% 4.09 0% 4.10 min Σ 3.02 100% 3.07 -100% 3.08 10%/ms 3.16 100% 3.04 0s 3.05 0s 3.06 100% 3.17 0.0s 3.18 0.100 3.09 50ms 3.10 50% 3.11 0mh 3.12 0m Ω 3.13 3.20 x2:8 6.05 6.09 6.10 10.00v x2:9 6.08 6.20 6.21...
Page 68
Ii k 4-44 overview of software 4.7 parameter list parameter overview 1 - motor settings 2 - operation mode 3 - armature 4 - field 1.01 arm cur nom * 2.01 macro select * 3.01 arm cur ref 4.01 field cur ref 1.02 arm volt nom * 2.02 cmd location 3.02 arm cur act 4.02 field cur act 1.03 field cur nom * ...
Page 69
Ii k 4-45 overview of software parno. Parameter name and significance min max default unit (1) custom setting grp 1 motor settings 1.01 wizard arm cur nom nominal motor current in amperes (indicated on the motor’s rating plate). 4 1000 (2) 4 a x 1.02 wizard arm volt nom nominal motor voltage in volt...
Page 70
Ii k 4-46 overview of software parno. Parameter name and significance min max default unit (1) custom setting grp 1 motor settings (continued) 1.11 net fail time during this time the supply voltage must return to a value higher than net underv trip (1.10). Otherwise an undervoltage trip will be gene...
Page 71
Ii k 4-47 overview of software parno. Parameter name and significance min max default unit (1) custom. Setting grp 2 operation mode 2.01 wizard macro select selection of desired macro: 0 = standard 1 = man/const sp 2 = hand/auto 3 = hand/motpot 4 = jogging 5 = motor pot 6 = ext fieldrev 7 = torque c...
Page 72
Ii k 4-48 overview of software parno. Parameter name and significance min max default unit (1) custom. Setting grp 2 operation mode (continued) 2.04 wizard eme stop mode selection of the desired operating response to an eme stop command (controller blocking) 0 = ramp motor decelerates in acc. To eme...
Page 73
Ii k 4-49 overview of software parno. Parameter name and significance min max default unit (1) custom. Setting grp 2 operation mode (continued) 2.05 signal main ctrl word the main ctrl word maps the control bits of the drive. This parameter indicates the control bits of the terminal block or of the ...
Page 74
Ii k 4-50 overview of software parno. Parameter name and significance min max default unit (1) custom. Setting grp 2 operation mode (continued) long parameter menu 2.07 comm fault mode selection of the desired operating response to a communication failure: 0 = ramp motor is decelerated in accord. To...
Page 75
Ii k 4-51 overview of software parno. Parameter name and significance min max default unit (1) custom. Setting grp 3 armature 3.01 signal arm cur ref armature current reference value in amperes. - - - a 3.02 signal arm cur act measured armature current actual value in amperes. - - - a 3.03 signal ar...
Page 76
Ii k 4-52 overview of software parno. Parameter name and significance min max default unit (1) custom. Setting grp 3 armature (continued) 3.10 auto- tuning arm cur reg ti integration time constant of the armature current controller (pi controller) in milliseconds. 0.0 1000.0 50.0 ms 3.11 auto- tunin...
Page 77
Ii k 4-53 overview of software parno. Parameter name and significance min max default unit (1) custom. Setting grp 3 armature (continued) 3.15 torque ref sel selection of the desired torque reference location: 0 = macro depend / dependent on the select. Macro 1 = ai1 / analog input 1 (x2:1-2) 2 = ai...
Page 78
Ii k 4-54 overview of software parno. Parameter name and significance min max default unit (1) custom. Setting grp 4 field 4.01 signal field cur ref field current reference value in amperes. - - - a 4.02 signal field cur act measured field current actual value in amperes. - - - a 4.03 auto- tuning f...
Page 79
Ii k 4-55 overview of software parno. Parameter name and significance min max default unit (1) custom. Setting grp 5 speed controller 5.01 speed ref sel selection of the desired speed reference location: 0 = macro depend / dependent on the selected macro 1 = ai1 / analog input 1 (x2:1-2) 2 = ai2 / a...
Page 80
Ii k 4-56 overview of software parno. Parameter name and significance min max default unit (1) custom. Setting grp 5 speed controller (continued) long parameter menu 5.12 ramp shape 0 = linear >0 = ramp shape time setting the ramp shape: this parameter adds a filter to the output of the ramp generat...
Page 81
Ii k 4-57 overview of software parno. Parameter name and significance min max default unit (1) custom. Setting grp 5 speed controller (continued) 5.15 wizard zero speed lev zero speed signal. Speed level below which the signal is issued that the motor has reached zero speed. Is used for stall protec...
Page 82
Ii k 4-58 overview of software parno. Parameter name and significance min max default unit (1) custom. Setting grp 5 speed controller (continued) 5.22 alt speed kp proportional gain of the speed controller (pi controller) for the alternative parameter set. 0.000 19.000 0.200 integer 5.23 alt speed t...
Page 83
Ii k 4-59 overview of software parno. Parameter name and significance min max default unit (1) custom. Setting grp 5 speed controller (continued) 5.30 act filt 2 time filter time constant 2 for smoothing speed deviation at the input of the speed regulator. 0.00 10.00 0.00 s 5.31 speed lim fwd speed ...
Page 84
Ii k 4-60 overview of software parno. Parameter name and significance min max default unit (1) custom. Setting grp 6 input / output 6.01 ai1 scale 100% scaling of analog input 1: input of a voltage value in volts, which correspond to 100% reference. 2.50 11.00 10.00 v 6.02 ai1 scale 0% scaling of an...
Page 85
Ii k 4-61 overview of software parno. Parameter name and significance min max default unit (1) custom. Setting grp 6 input / output (continued) 6.11 wizard do1 assign desired assignment of digital output 1: 0 = none 0 constant (for test purposes) 1 = constant 1 1 constant (for test purposes) 2 = mac...
Page 86
Ii k 4-62 overview of software parno. Parameter name and significance min max default unit (1) custom. Setting grp 6 input / output (continued) 6.12 wizard do2 assign d esired assignment of digital output 2: assignment identical with do1 (6.11). 0 64 2 text 6.13 wizard do3 assign desired assignment ...
Page 87
Ii k 4-63 overview of software parno. Parameter name and significance min max default unit (1) custom. Setting grp 6 input / output (continued) 6.20 dataset 2.2 asn selection of the desired assignment for fieldbus dataset 2.2: 0 = speed act / speed actual value (5.05) 1 = speed ref / speed reference...
Page 88
Ii k 4-64 overview of software parno. Parameter name and significance min max default unit (1) custom. Setting grp 6 input / output (continued) 6.22 msw bit 11 asn function assignement for bit 11 in the main fieldbus status word (2.06): 0 = none 0 constant (for test purposes) 1 = constant 1 1 consta...
Page 89
Ii k 4-65 overview of software parno. Parameter name and significance min max default unit (1) custom. Setting grp 6 input / output (continued) 6.23 msw bit 12 asn function assignment for bit 12 in the main fieldbus status word (2.06): assignment identical with msw bit 11 asn (6.22) 0 67 2 text 6.24...
Page 90
Ii k 4-66 overview of software parno. Parameter name and significance min max default unit (1) custom. Setting grp 7 maintenance 7.01 wizard language selection of the panel language: 0 = english 1 = deutsch 2 = français 3 = italiano 4 = español 0 4 0 text 7.02 action contr service selection of the d...
Page 91
Ii k 4-67 overview of software parno. Parameter name and significance min max default unit (1) custom. Setting grp 7 maintenance (continued) 7.03 signal diagnosis display of all diagnostic messages: further information see chapter ’troubleshooting’ 0 = none 1…10 = 1…10 (internal software causes) 11 ...
Page 92
Ii k 4-68 overview of software parno. Parameter name and significance min max default unit (1) custom. Setting grp 7 maintenance (continued) 7.06 const. Conv nom cur display of the converter’s nominal current in amperes. - - - a 7.07 const. Conv nom volt display of the converter’s nominal voltage in...
Page 93
Ii k 4-69 overview of software parno. Parameter name and significance min max default unit (1) custom. Setting grp 7 maintenance (continued) 7.12 signal alarm word 1 alarm word 1. Significance of the individual bits: all the pending alarms are displayed if the corresponding bits are set to log. "1"....
Page 94
Ii k 4-70 overview of software parno. Parameter name and significance min max default unit (1) custom. Setting grp 7 maintenance (continued) 7.15 commis ref 1 commissioning reference value 1 scaling: field current 0…100% = 0…4096 torque 0…100% = 0…4096 armature current 0…100% = 0…4096 speed 0…max = ...
Page 95
Ii k 4-71 overview of software parno. Parameter name and significance min max default unit (1) custom. Setting grp 8 fieldbus long parameter menu 8.01 fieldbus par 1 0 = disable no communication with plc 1 = fieldbus plc communication via fieldbus adapter 2 = rs232-port plc communication via rs232 p...
Page 96
Ii k 4-72 overview of software parno. Parameter name and significance min max default unit (1) custom. Setting grp 9 macro adaptation long parameter menu 9.01 macpargrpaction before a new function can be assigned to a digital input or control bit, the actual function has to be disabled. This can be ...
Page 97
Ii k 4-73 overview of software parno. Parameter name and significance min max default unit (1) custom. Setting grp 9 macro adaptation (continued) 9.05 user fault fault function will be controlled from a binary signal which is assigned in this parameter: 0=macro depend 1=disable 2=di1 3=di2 4=di3 5=d...
Page 98
Ii k 4-74 overview of software parno. Parameter name and significance min max default unit (1) custom. Setting grp 9 macro adaptation (continued) 9.10 motpot incr motorpot increase speed function will be controlled from a binary signal which is assigned in this parameter. Assignment identical with 9...
Page 99
Ii k 4-75 overview of software parno. Parameter name and significance min max default unit (1) custom. Setting grp 9 macro adaptation (continued) 9.14 alternativparam alternative parameter set will be controlled from a binary signal which is assigned in this parameter. Assignment identical with 9.05...
Page 100
Ii k 4-76 overview of software parno. Parameter name and significance min max default unit (1) custom. Setting grp 9 macro adaptation (continued) 9.19 disable bridge1 bridge 1 will be controlled from binary signal which is assigned in this parameter. Assignment identical with 9.05 state of binary si...
Page 101: Installation
Ii k 5-1 installation 5 installation general incoming inspection check the contents of delivery • dcs 400 • manual • mounting template • quick installation & commissioning guide check the consignment for any signs of damage. If you find any, please contact the insurance company or the supplier. Chec...
Page 102
Ii k 5-2 installation 5.1 safety instructions 1. General in operation, drive converters, depending on their degree of protec- tion, may have live, uninsulated, and possibly also moving or rotating parts, as well as hot surfaces. In case of inadmissible removal of the required covers, of improper use...
Page 103
Ii k 5-3 installation warnings warnings provide information on states which if the specified procedure for the state concerned is not meticulously complied with may result in a serious error, in major damage to the unit, in injury to persons and even in death. They are identified by the following sy...
Page 104
Ii k 5-4 installation 5.2 emc compliant installation and configuration for a power drive system remark this is a part of the man- ual thyristor power con- verters emc compliant installation and configu- ration for a power drive system - technical guide note in order to make the description in this c...
Page 105
Ii k 5-5 installation definitions earth, earthing for safety ground, grounding for emc, connection with chassis or housing with low inductance important instructions for plants with line fil- ters filter in an earthed line (tn or tt network) the filters are suitable for earthed lines only, for examp...
Page 106
Ii k 5-6 installation 1 classification 0 0 0 0 0 0 6hfrqghqylurqphqw (1 )luvwhqylurqphqwzlwkuhvwulfwlrq (domestic and light industry) (1 /hjhqg unscreened cable with limitation, see screened cable, see line filter line choke to other loads which must be protected against line pollution caused by con...
Page 107
Ii k 5-7 installation 2 three-phase filters emc filters are necessary to fulfil en 50081 if a converter shall be run at a public low voltage line, in europe for example with 400 v between the phases. Such lines have an earthed neutral conduc- tor. Abb offers suitable three - phase filters for 400 v ...
Page 108
Ii k 5-8 installation due to the maximum power of public 400 v transformers (p max = 1.2 mva Õ i max = 1732 a) and due to their relative short circuit voltage v sc of 6% or 4% the maximum ac current which is available for a converter is 346 a or 520 a (i dc ≤ 422 a or 633 a). For v sc = 4 %: i dc ≤ ...
Page 109
Ii k 5-9 installation 5 separation transformers a separation transformer makes line chokes unnecessary because of its leakage inductance, and a grounded screen between its windings saves an emc filter, see 1 and 4 . The screen and the iron core must be well connected with the mounting plate of the c...
Page 110
Ii k 5-10 installation 11 screening 12 signal cables the cables for digital signals, which are longer than 3 m and all ca- bles for analogue signals, must be screened. Each screen must be connected at both ends by metal clamps (see figure 5.2-4) or comparable means directly on clean metal surfaces, ...
Page 111
Ii k 5-11 installation 14 power cables without screens if a screen is not necessary (see 13 ) the armature current cable must be a four-wire cable because two wires are needed as con- ductors for the parasitic rf currents from the motor to the rf filter in the cubicle. The unscreened field current c...
Page 112
Ii k 5-12 installation 17 others 18 earthed public low voltage lines the rated voltages of a public european low voltage line are 400 v between the 3 phases and 230 v between a phase and the neutral conductor. These voltages are provided by a transformer with its 3- phase secondary winding in star c...
Page 113
Ii k 5-13 installation 20 industrial low voltage lines industrial low voltage lines are local lines in plants or factories. They have own supply transformers (see 6 ). In most cases they are insulated (it network / no earthed star point) and their voltages are often higher than 400 v. The loads tole...
Page 114
Ii k 5-14 installation 24 connection exam- ple in accordance with emc see figure 5.2 - 7. 25 armature and field cables with screens for “first environ- ment” see figure 5.2 - 7. 26 armature and field cables without screens for “second en- vironment” see figure 5.2 - 7. 27 encoder inputs and analogue...
Page 115
Ii k 5-15 installation 0 a1 a2 f1 f2 a1 a2 f1 f2 l1 l2 l3 pe u1 v1 w1 c1 d1 u1 v1 f- f+ pe pe pe pe $ ) $ ) 7dfkr $ ) 7dfkr t $ ) $ ) i/ o mounting plate dc motor 6fuhhqv contact to the motor housing at the whole screen perimeter filter mounting plate with pe bar and terminals pe bar dc motor mounti...
Page 116
Ii k 5-16 installation important hint the example shows the principle structure of a dc drive and its connections. It is not a binding recommendation, and it cannot re- spect all conditions of a plant. Therefore each drive must be con- sidered separately and with respect to the special application. ...
Page 117
Ii k 5-17 installation 5.3.1 connection example for digital and analogue coupling of a plc fig. 5.3/1: connection example for digital and analogue coupling of a plc installation 5.3 connection examples remark the drive is controlled via digital inputs/outputs. Speed reference is given via analogue i...
Page 118
Ii k 5-18 installation installation fig. 5.3/2: connection example for a serial communication of a plc 5.3.2 connection example for serial communication of a plc remark the drive is controlled serial via maincontrolword and mainstatusword. Speed reference and aux speed reference is given via two 16 ...
Page 119
Ii k 5-19 installation 5.3.3 connection example for emergeny off (valid for all macros) general situation fig. 5.3/3: connection example for emergeny off - general situation installation remark in cases of emergency off it is necessary to have an off-delay relais (k22) in the emergency off circuit a...
Page 120
Ii k 5-20 installation installation fig. 5.3/4: connection example with dc breaker and controlled deceleration 5.3.4 connection example with dc breaker and controlled deceleration remark in cases of emergency off it is necessary to have an off-delay relais (k22) in the emergency off circuit and an a...
Page 121
Ii k 5-21 installation 5.3.5 connection example with dc breaker and drive coasting fig. 5.3/5: connection example for emergeny stop - dc breaker with drive coasting installation remark switch main contactor (k1) on and off is controlled by digital output do5. In case of emergency off the main contac...
Page 122
Ii k 5-22 installation 5.3.6 connection example for motor fan and converter fan (useful for all macros) general situation fig. 5.3/6: connection example for motor and converter fan _ + in ou t c 1 d 1 x9 8 : do 5 12 34 4 5 x 9 9 : 123 u1 w 1 v1 pe x1 0 : 1 2 ai t a c a i1 ai 2 + 1 0 v -1 0 v ao1 a o...
Page 123: Operating Instructions
Ii k 6-1 operating instructions (17(5 0(18 /2& 5(0 5(6(7 1500rpm 440v 368a 1500rpm output menu auto off hand rem loc $%% 6 operating instructions general this manual is designed to help those responsible for planning, installing, start-up and servicing the thyris- tor power converter. These people s...
Page 124
Ii k 6-2 operating instructions 6.1 panel panel mode: menu selection if output is indicated in the status line of the panel display, press the 0(18 key to change over to menu selection. The menu selection mode allows you to access the parameter groups as well as the functions available. After pressi...
Page 125
Ii k 6-3 operating instructions panel mode: parameter programming the first nine menu items or parameter groups are used for setting the drive parameters. To access the desired parameter group, select the group concerned using the scrolling functions and confirm by pressing (17(5 . The display now s...
Page 126
Ii k 6-4 operating instructions cancel function, back to select type with (17(5 . Read faultlogger output menu auto off hand rem loc faultlogger empty press enter output menu auto off hand rem loc clear faultlogger no yes output menu auto off hand rem loc eme stop pending 02: -a 09 external alarm 03...
Page 127
Ii k 6-5 operating instructions lcd contrast press arrows output menu auto off hand rem loc commissioning output menu auto off hand rem loc change the lcd contast by using the keys. The result will be shown immediately. See chapter: guided commissioning panel lock lcd contrast commissioning disabled...
Page 128
Ii k 6-6 operating instructions drive control from the panel caution: appropriate safety precautions must be taken before starting the drive. Before the drive can be controlled from the panel, the panel first must be given permission to take control. The panel’s ability to control the drive is deter...
Page 129
Ii k 6-7 operating instructions 6.2 guided commissioning the dcs 400 converters of abb offer the possibility to have a guided commissioning by means of interac- tive dialogue through the parameter programming. One guarantees with it, that the drive is set up right and is optimized. This section desc...
Page 130
Ii k 6-8 operating instructions parameter entries the entries required during the guided commission- ing procedure are divided into selection parameters and value parameters. Selection parameters are selected from a prede- fined text list and confirmed. The control panel display only shows one line ...
Page 131
Ii k 6-9 operating instructions commissioning step comments language select and confirm. Macro select and confirm. Detailed information abaut mac- ros see ch. 4.2 application mac- ros nominal armature voltage see motor name plate nominal armature current see motor name plate nominal field voltage se...
Page 132
Ii k 6-10 operating instructions 1.06 max speed is set to the value of 1.05 base speed field weakening yes/no maximum speed for field- weakening operation see motor name plate selection of desired operat- ing response at stop mode acceleration ramp deceleration ramp selection of desired operat- ing ...
Page 133
Ii k 6-11 operating instructions caution observe safety instructions field current controller opti- mization press key on panel to apply field voltage to the motor. Optimization running. If any faults or alarms have oc- cured during optimization, fur- ther action depends on the mes- sages displayed;...
Page 134
Ii k 6-12 operating instructions caution observe safety instructions armature current controller optimization commissioning step comments armature autotuning? No output menu auto off hand rem loc yes start drive press (i) output menu auto off hand rem loc please wait output menu auto off hand rem lo...
Page 135
Ii k 6-13 operating instructions commissioning step no speed meas adjust? Yes output menu auto off hand rem loc 5.02 speed meas mode emf analog tacho encoder output menu auto off hand rem loc turn pot near zero yyy output menu auto off hand rem loc warning max speed press (i) output menu auto off ha...
Page 136
Ii k 6-14 operating instructions caution observe safety instructions speed controller optimization select and confirm. Commissioning step comments start drive press (i) output menu auto off hand rem loc please wait output menu auto off hand rem loc success press enter output menu auto off hand rem l...
Page 137
Ii k 6-15 operating instructions commissioning step comments yes flux adaptation? No output menu auto off hand rem loc caution observe safety instructions flux optimization only available in field weaken- ing mode. Press key on panel to switch on and enable the drive. Optimization running. The drive...
Page 138
Ii k 6-16 operating instructions stall protection commissioning step comments (17(5 to terminate the guided commissioning procedure. Yes stall protection? No output menu auto off hand rem loc 3.17 stall torque 100% output menu auto off hand rem loc 3.18 stall time 0.0s output menu auto off hand rem ...
Page 139
Ii k 6-17 operating instructions manually commissioning short description for manual commissioning a dcs400 via control panel. Follow this guide if panel commissioning wizard has failed. Valid for software version 108.0 and higher. Set parameters arm cur nom (1.01): see motor name plate arm volt nom...
Page 140
Ii k 6-18 operating instructions set parameters arm cur nom (1.01): see motor name plate arm volt nom (1.02): see motor name plate field cur nom (1.03): see motor name plate field volt nom (1.04): see motor name plate base speed (1.05): see motor name plate max speed (1.06): same as base speed with ...
Page 141
Ii k 6-19 operating instructions set parameters arm cur nom (1.01): see motor name plate arm volt nom (1.02): see motor name plate field cur nom (1.03): see motor name plate field volt nom (1.04): see motor name plate base speed (1.05): see motor name plate with encoder feedback start the panel wiza...
Page 142
Ii k 6-20 operating instructions 6.3 useful hints for commissioning 1. Select emf and confirm, even if analog tacho or encoder is in use. 2. Caution! Start the drive and stop the drive using (i) button as soon as the motor will turn. 3. Drive can be started and stopped alternately us- ing (i) button...
Page 143
Ii k 6-21 operating instructions n hints for speed controller autotuning only successfully commissioned selftuning will change parameters of the speed controller speed reg kp (5.07) and speed reg ti (5.08), other-wise parame- ters remain unchanged. After selftuning the behav- iour of the drive must ...
Page 144
Ii k 6-22 operating instructions n motor drifts at zero speed reference eliminate speed offset via tacho offset (5.34) • switch drive off • read speed actual from panel • set tacho offset (5.34) to this value incl. Polarity • switch drive on and finetune tacho offset (5.34) eliminate speed offset vi...
Page 145
Ii k 6-23 operating instructions n soft network in regenerative mode soft network in regenerative mode is a specific prob- lem of dc technology. If emf of the motor is greater than (mains voltage * 1,35 * 0,866) then fuses and thyristors can be destroyed. To protect the drive against damage as far a...
Page 146
Ii k 6-24 operating instructions 6.4 troubleshooting 6.4.1 display of status, alarm and fault si- gnals the available signals (messages) for thyristor power converters series dcs 400 are subdivided: • converter's 7-segment led (located behind the panel) general messages starting errors fault signals...
Page 147
Ii k 6-25 operating instructions red led green led dcs 400 state remarks off off no rdy on on command prevented possible causes and remedies: l state caused by emergency stop or coast. Close emergency stop or coast. Switch on and run off and on again. L zero speed lev (5.15) = 0 rpm or too low, incr...
Page 148
Ii k 6-26 operating instructions fault message fault no. Definition / possible source pa ra m. F 1 aux voltage fault auxiliary voltage fault (not implemented yet) 7.09 bit 0 f 2 hardware fault hardware fault something is wrong with flashprom or thyristor diagnosis has detected a short circuit. 7.09 ...
Page 149
Ii k 6-27 operating instructions fault message fault no. Definition / possible source pa ra m. F 7 converter overtemp see also a4 converter over temperature temperature of the converter too high. Please wait until the temperature of the converter has cooled down. After that you can clear the fault b...
Page 150
Ii k 6-28 operating instructions fault message fault no. Definition / possible source pa ra m. F 17 tacho polarity fault tacho polarity fault polarity of feed back signal from tacho generator incorrect. Please check • the polarity of tacho gene- rator cable • polarity of armature and field cable • d...
Page 151
Ii k 6-29 operating instructions fault message fault no. Definition / possible source pa ra m. F 21 local control lost local control lost during operation in local control mode no message has been received for a time longer than the value that has been set in parameter comm fault time (2.08). Please...
Page 152
Ii k 6-30 operating instructions 6.4.6 alarm signals (a) the alarm signals will be shown on the seven segment display of the control board sdcs-con-3 as codes a . . As well as on the lcd of the control panel dcs 400 pan as clear text. Alarm signals will only be displayed, if there is no fault signal...
Page 153
Ii k 6-31 operating instructions alarm message alarm no. Definition / possible source pa ra m. A 7 field volt limited alarm field voltage at limit this alarm is issued if the field voltage reaches the value that was set in parameter field volt nom (1.04) and therefore the field current cannot be set...
Page 154
Ii k 6-32 operating instructions alarm message alarm no. Definition / possible source pa ra m. A 14 up/download failed alarm upload download fai- led the checksum verification failed during uploading or downloading between drive and control panel. Try again. 7.12 bit 13 a 15 pantxt not uptodate alar...
Page 155
Ii k 6-33 operating instructions 7.03 diagnosis diagn. Message int e rn a l code ai2 vs ptc 74 arm cur 0 15 arm data 73 arm l meas 16 a arm r meas 17 e enc polarity 26 field l meas 18 field r meas 19 field range 72 fld cur 0 14 fld low lim 70 f flux char 71 ground fault 103 g grp9 disable 76 no acce...
Page 156
Ii k 6-34 operating instructions int e rn a l code 7.03 diagnosis diagn. Message definition / possible source 31 31 upload or download start timeout. Please contact your abb local service center. 32 updn aborted uploading or downloading data transfer timeout. Data was not uploaded or downloaded in t...
Page 157
Ii k 6-35 operating instructions int e rn a l code 7.03 diagnosis diagn. Message definition / possible source 74 ai2 vs ptc ai2 is set as ptc evaluation and ref- erence value source. If ptc is allocated to ai2 this input will not be available to other functions anymore. Ai2 is normally parameter- iz...
Page 158
Ii k 6-36 operating instructions.
Page 159: Serial Interfaces
Ii k 7-1 serial interfaces 7 serial interfaces general the dcs 400 is equipped with the following serial interfaces: • panel-port (standard, built-in) • rs232-port (standard, built-in) • fieldbus-interface (adapter available as option) the fieldbus interface is designed for control via an external p...
Page 160
Ii k 7-2 serial interfaces fig.: 7/2 overview dataset 2. Monitoring the drive via fieldbus communication 8.01 nx xx -01 x xx xx x xx ada pter bu s te rm i na ti on o n off r xd tx d pe shf dg d(n) d(p) x1 x2 pe shf dg d(n) d(p) sh xm i t r ec er r or +24v 0v sh 15 14 13 12 11 10 09 08 07 06 05 04 03...
Page 161
Ii k 7-3 serial interfaces fig.: 7/3 overview dataset 3 and 4. Monitoring the drive via fieldbus communication 8.01 dataset 4.1 )og&xu$fw 3/& r s 232 -b us p ane l b u s dataset 4.2 3rzhu$fw dataset 4.3 7rutxh$fw d is abl e do1 $x[6s5hi6ho $x[6s5hi6ho speed act (5.05) speed ref (5.04) arm volt act (...
Page 162
Ii k 7-4 serial interfaces necessary parameter-settings for fieldbus communication parameter parameter name possible settings recommended 2.02 cmd location 0=macro depend 1=terminals 2=bus 3=key 2=bus 2.07 comm fault mode 0=ramp 1=torque lim 2=coast 0=ramp 2.08 comm fault time 0.00s=no supervision 0...
Page 163
Ii k 7-5 serial interfaces telegram structure the serial communication with a plc can be carried out via a field bus adapter, a rs232 port or a panel port. Irrespective of the bus protocol, these ports communicate with the dcs400 software via specified data sets. Four data sets are available with th...
Page 164
Ii k 7-6 serial interfaces 7.1 panel-port the panel port is normally used for connection of the control panel. The default settings of this interface are as follows: signal level: +12v / 0v data format: uart message format: modbus-protocoll transmission method: half-duplex baudrate: 9.600 baud numbe...
Page 165
Ii k 7-7 serial interfaces 7.2 rs232-port the rs232 interface is normally used for setting parameter in the drive via the pc tool drive window light. The default settings of this interface are as follows: signal level: rs232 (+12v / -12v) data format: uart message format: modbus-protocol transmissio...
Page 166
Ii k 7-8 serial interfaces sdcs-con-3 gnd +24 v/ ≤ 150 ma nxxx-01 xxxx xx xx adapter bus termination on off rxd txd pe shf dg d(n) d(p) x1 x2 pe shf dg d(n) d(p) sh xmit r ec error +24v 0v sh +24v 0v '&6 1 2 x8 rxd txd eo xh eo xh ju h\ ju h\ fieldbus cable 7.3 fieldbus interface for connection to e...
Page 167
Ii k 7-9 serial interfaces parameter overview for the most commonly used fieldbuses for parameter setting, with the control panel, intially switch to long par list, in the menu selection, in profibus (including parameter transfer) parameter meaning alternative settings typical settings 8.01 module t...
Page 168
Ii k 7-10 serial interfaces modbus (including parameter transfer) parameter meaning alternative settings typical settings 8.01 module type 0 = disable 1 = fieldbus 2 = rs232-port 3 = panel-port 4 = res feldbus fieldbus 8.02 modbus mode 0 = rtu wdg:flt 1 = rtu wdg:rst 0 = rtu wdg:flt 8.03 station num...
Page 169
Ii k 7-11 serial interfaces cs31 (without parameter transfer) parameter meaning alternative settings typical settings 8.01 module type 0 = disable 1 = fieldbus 2 = rs232-port 3 = panel-port 4 = res feldbus fieldbus 8.02 protocol 1 1 = abb cs31 8.03 modul id 0 = word 1 = binary 0 = word 8.04 station ...
Page 170
Ii k 7-12 serial interfaces for detailed information please refer to the related fieldbus adapter description. In the case you need a fieldbus other than shown, please contact your local abb sales office. Abb is continuously developing on new solutions. Devicenet (including parameter transfer) param...
Page 171
Ii k 7-13 serial interfaces dcs 400 fieldbus parameter profibus modbus, can-bus dcs400 dcs-400 par.Name remark par. No modbus+ par.No. 1 - motor settings 100 40101 3065 101 arm cur nom 101 40102 3066 102 arm volt nom 102 40103 3067 103 field cur nom 103 40104 3068 104 field volt nom 104 40105 3069 1...
Page 172
Ii k 7-14 serial interfaces profibus modbus, can-bus dcs400 dcs-400 par.Name remark par. No modbus+ par.No. 4 - field 199 40401 3191 401 field cur ref 200 40402 3192 402 field cur act 201 40403 3193 403 field cur kp 202 40404 3194 404 field cur ti 203 40405 3195 405 fld ov cur trip 204 40406 3196 40...
Page 173
Ii k 7-15 serial interfaces profibus modbus, can-bus dcs400 dcs-400 par.Name remark par. No modbus+ par.No. 6 - input/output 265 40601 3259 601 ai1 scale 100% 266 40602 325a 602 ai1 scale 0% 267 40603 325b 603 ai2 scale 100% 268 40604 325c 604 ai2 scale 0% 269 40605 325d 605 ao1 assign 270 40606 325...
Page 174
Ii k 7-16 serial interfaces profibus modbus, can-bus dcs400 dcs-400 par.Name remark par. No modbus+ par.No. 8 - fieldbus 331 40801 3321 801 fieldbus par 1 332 40802 3322 802 fieldbus par 2 333 40803 3323 803 fieldbus par 3 334 40804 3324 804 fieldbus par 4 335 40805 3325 805 fieldbus par 5 336 40806...
Page 175: Appendix
Appendix appendix a - accessories ii k a-1 dcs type type of fig. 500v reactor 2-quadrant converter dcs401.0020 nd01 1 dcs401.0045 nd02 1 dcs401.0065 nd04 1 dcs401.0090 nd05 1 dcs401.0125 nd06 1 dcs401.0180 nd07 2 dcs401.0230 nd07 2 dcs401.0315 nd09 2 dcs401.0405 nd10 2 dcs401.0500 nd10 2 dcs401.0610...
Page 176
A, b, c 300 100 0 x, y, z b a a1 c a x b y c z a b c x y z 3 a, b, c x, y, z d e g f ii k a-2 appendix a type choke weight power loss l i rms i peak fe cu [ mh] [a] [a] [kg] [w] [w] nd 01 512 18 27 2.0 5 16 nd 02 250 37 68 3.0 7 22 nd 04 168 55 82 5.8 10 33 nd 05 135 82 122 6.4 5 30 nd 06 90 102 153...
Page 177
Ii k a-3 appendix a type a b c d e f g h i k nd 07 285 230 86 115 253 176 65 80 9x17 385 nd 09 327 290 99 120 292 224 63 100 11x21 423 nd 10 408 290 99 120 373 224 63 100 11x21 504 nd 12 458 290 120 145 423 224 63 100 11x21 554 line chokes type nd 07...Nd 12 c ±1 max d b ±1 f ±0.3 h ±2 15 7 3 ast 4 ...
Page 178
Converter type manufacturer/ type fuse holder 2-quadrant converter dcs401.0020 bussman 170m 1564 ofax 00 s3l dcs401.0045 bussman 170m 1566 ofax 00 s3l dcs401.0065 bussman 170m 1568 ofax 00 s3l dcs401.0090 bussman 170m 1568 ofax 00 s3l dcs401.0125 bussman 170m 3815 ofax 1 s3 dcs401.0180 bussman 170m ...
Page 179
Manufacturer/ type loss [w] resistance [m w] fuse f1 size fuse holder caliper [mm] bussman 170m 1564 15 6 50a 660v ur 0 ofax 00 s3l 78.5 bussman 170m 1566 19 3 80a 660v ur 0 ofax 00 s3l 78.5 bussman 170m 1568 28 1 , .8 125a 660v ur 0 ofax 00 s3l 78.5 bussman 170m 3815 35 0 , .87 200a 660v ur 1 ofax ...
Page 180
Emc filters ii k a-6 appendix a three-phase filters emc mains filters are necessary so as to comply with en 50 081 if a power converter is to be operated at a public low-voltage grid, in europe, for example, with 400 v between the phases. Grids of this kind have an earthed neutral conductor. For the...
Page 181
Ii k b-1 appendix b - declaration of conformity.
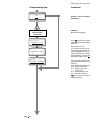
Page 182: Dcs 400
Ii k c-1 appendix c - quick installation & commissioning guide ➊ enter menu reset loc rem ➋ dcs 400 quick installation & commissioning guide before starting installation check box contents: dcs 400, manual, mounting template, quick inst. & commissg. Guide check installation site: see manual tools ne...
Page 183
Ii k c-2 appendix c 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 x2 1 10 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 x4 +ai1 -ai1 +ai2 -ai2 0v +10v -10v ao1 ao2 di1 di2 di3 di4 di5 di6 di7 di8 +24v 0v ➐ (1 7(5 0(1 8 /2 & 5( 0 5 (6( 7 15 00 rpm 44 0 v 368 a 1 5 0 0 rp m ou tpu t me nu a u to off ha nd r em lo c run > $% % 0( 1 8 (1 7( 5 ● electronic supp...
Page 184
Appendix d - examples for basic parameter programming ii k d-1 the experience has shown that certain parameters must be adapted in most applications. These parameters show the following tables. Table 1: operation for armature control mode table 2: operation for field control mode table 3: operation ...
Page 185
Ii k d-2 appendix d operation for field control mode p n base speed p norm armature control range field control range max speed 106 105 table 2 parameter number parameter name significance contents entry 101 arm cur nom nominal armature current ia nom 102 arm volt nom nominal armature voltage ua nom...
Page 186
Appendix d ii k d-3 operation for field control mode with speed-dependent current limiting p n base speed p norm armature control range field control range cur lim speed max speed 105 112 106 speed-dependent current limiting table 3 parameter number parameter name significance contents entry 101 arm...
Page 187
Appendix d ii k d-4 common parameters for the three operating modes table 4 parameter number parameter name significance contents entry 304 arm cur max maximum current limit % i a 305 overload time overload time sec 306 recovery time recovery time sec 307 torque lim pos positive torque limit % m nom...
Page 188
Symbole 7-segment display 2-5, 3-7, 6-24, 6-26, 6-30 a alarm signals (a) 6-30 alternative parameters for speed controller 4-2, 4-36 analogue tacho feedback 6-17 application macros 4-2 armature current controller 4-32, 4-37, 4-51 auto reclosing 4-29 automatic field weakening 4-30 autotuning 4-37 b ba...
Page 189
O operating instructions 6-1 overload 2-4 overtemperature protection 4-31 overview of software 4-1 p paint finish 2-2 panel dcs400pan 1-4, 2-5, 6-1, 6-7, 6-24, 6-25, 7-6 panel leds 6-25 panel lock 6-5 panel mode 6-2 drive control 6-6 function selection 6-3 menu selection 6-2 parameter programming 6-...
Page 190
Notices.
Page 191
Notices.
Page 192
Since we aim to always meet the latest state-of- the-art standards with our products, we are sure you will understand when we reserve the right to alter particulars of design, figures, sizes, weights, etc. For our equipment as specified in this bro- chure. 3adw 000 095 r0501 rev e 11_00 abb automati...