- DL manuals
- ABB
- Control Unit
- FPBA-01 PROFIBUS DP
- User Manual
ABB FPBA-01 PROFIBUS DP User Manual
Summary of FPBA-01 PROFIBUS DP
Page 1
Options for abb drives, converters and inverters user’s manual fpba-01 profibus dp adapter module.
Page 2
List of related manuals you can find manuals and other product documents in pdf format on the internet. See section document library on the internet on the inside of the back cover. For manuals not available in the document library, contact your local abb representative. Drive user’s manuals code (e...
Page 3: User’S Manual
6. Start-up user’s manual fpba-01 profibus dp adapter module 3afe68573271 rev f en effective: 2017-01-25 2017 abb oy all rights reserved. 1. Safety instructions table of contents 4. Mechanical installation 5. Electrical installation.
Page 5: Table Of Contents
Table of contents 5 table of contents 1. Safety instructions what this chapter contains . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11 use of warnings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11 safety in installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ....
Page 6: 5. Electrical Installation
6 table of contents 5. Electrical installation what this chapter contains . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31 general cabling instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31 connecting the module to the profibus network . . . . . . . . . . 32 switchin...
Page 7: 7. Communication Profiles
Table of contents 7 parameter setting examples – acs850 and acq810 . . . . . 75 speed control using the profidrive communication profile with ppo type 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75 starting up acs880 and acs880-m04 drives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78 parameter se...
Page 8: 8. Communication Protocol
8 table of contents actual values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117 scaling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117 8. Communication protocol what this chapter contains . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ....
Page 9: 9. Diagnostics
Table of contents 9 164 example 2a: writing a drive parameter (one array element) 166 example 2b: writing 2 drive parameters (multi-parameter) 168 example 3: reading a profidrive parameter. . . . . . . 170 example 4: configuring the process data written to the drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ....
Page 10
10 table of contents document library on the internet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195.
Page 11: Safety Instructions
Safety instructions 11 1 safety instructions what this chapter contains the chapter contains the warning symbols used in this manual and the safety instructions which you must obey when you install or connect an optional module to a drive, converter or inverter. If you ignore the safety instructions...
Page 12: Safety In Installation
12 safety instructions safety in installation these instructions are for all who install or connect an optional module to a drive, converter or inverter and need to open its front cover or door to do the work. Warning! Obey these instructions. If you ignore them, injury or death, or damage to the eq...
Page 13: About The Manual
About the manual 13 2 about the manual what this chapter contains this chapter introduces this manual. Applicability this manual applies to the fpba-01 profibus dp adapter module, sw version 3.10 or later. Compatibility the fpba-01 profibus dp adapter module is compatible with the following drives: ...
Page 14: Purpose Of The Manual
14 about the manual purpose of the manual the manual provides information on installing, commissioning and using an fpba-01 profibus dp adapter module. Related manuals see list of related manuals on the inside of front cover. Cyber security disclaimer this product is designed to be connected to and ...
Page 15: Contents
About the manual 15 contents the manual consists of the following chapters: • safety instructions presents the safety instructions which you must follow when installing a fieldbus adapter module. • about the manual introduces this manual. • overview of the profibus network and the fpba-01 module con...
Page 16: Term/abbreviation
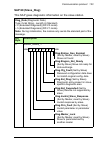
16 about the manual terms and abbreviations used in this manual general terms and abbreviations term/abbreviation explanation communication module communication module is a name for a device (eg, a fieldbus adapter) through which the drive is connected to an external communication network (eg, a fie...
Page 17: Profibus Terms
About the manual 17 profibus terms term explanation acyclic communication communication in which messages are sent only once on request array parameter consisting of data fields of equal data type broadcast non-acknowledged message from master to all bus participants (compare multicast) cyclic commu...
Page 18: Profibus Abbreviations
18 about the manual profibus abbreviations the text in italics is the original german term. Process data data that contains control word and reference value or status word and actual value. May also contain other (user-definable) control information. Request label coded information specifying the re...
Page 19: Abbreviation
About the manual 19 pa process automation prozessautomatisierung pd process data prozessdaten pke parameter identification parameter-kennung pkw parameter identification value parameter-kennung-wert pnu parameter number parameternummer ppo parameter/process data object parameter-/prozessdaten-objekt...
Page 20
20 about the manual.
Page 21: Overview Of The Profibus
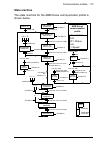
Overview of the profibus network and the fpba-01 module 21 3 overview of the profibus network and the fpba-01 module what this chapter contains this chapter contains a short description of the profibus network and the fpba-01 profibus dp adapter module. Profibus network profibus is an open serial co...
Page 22
22 overview of the profibus network and the fpba-01 module in profibus communication, the master station – usually a programmable logic controller (plc) – polls the nodes which respond and take the actions requested by the master. It is also possible to send a command to several nodes at the same br...
Page 23
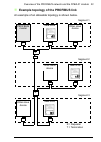
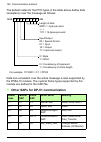
Overview of the profibus network and the fpba-01 module 23 example topology of the profibus link an example of an allowable topology is shown below. Profibus master segment 1 segment 2 segment 3 r other slave device other slave device other slave device r = repeater t = termination t t t abb drive t...
Page 24
24 overview of the profibus network and the fpba-01 module fpba-01 profibus dp adapter module the fpba-01 profibus dp adapter module is an optional device for abb drives which enables the connection of the drive to a profibus network. The drive is considered a slave on the profibus network. Through ...
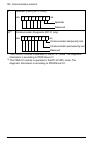
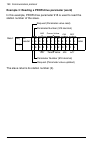
Page 25
Overview of the profibus network and the fpba-01 module 25 layout of the adapter module diagnostic leds (see chapter diagnostics ) bus connector x1 (see chapter electrical installation ) host module network network x1 mounting screw.
Page 26
26 overview of the profibus network and the fpba-01 module.
Page 27: Mechanical Installation
Mechanical installation 27 4 mechanical installation what this chapter contains this chapter contains a delivery checklist and instructions on mounting the adapter module. Warning! Follow the safety instructions given in this manual and the drive documentation. Delivery check the option package for ...
Page 28
28 mechanical installation installing the adapter module warning! Obey the safety instructions. See chapter safety instructions on page 11 . If you ignore the safety instructions, injury or death can occur. The adapter module has a specific position in the drive. Plastic pins, a lock and one screw t...
Page 29
Mechanical installation 29 3. Push in the lock. 4. Tighten the screw to torque 0.8 n·m. Note: it is necessary to tighten the screw properly to fulfill the emc requirements and to ensure the proper operation of the module. See the applicable drive manual for further instructions on how to install the...
Page 30
30 mechanical installation.
Page 31: Electrical Installation
Electrical installation 31 5 electrical installation what this chapter contains this chapter contains: • general cabling instructions • instructions on connecting the module to the profibus dp network • instructions on switching on the bus termination. Warning! Before installation, switch off the dr...
Page 32: Description
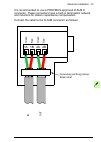
32 electrical installation connecting the module to the profibus network connect the bus cable to connector x1 on the adapter module. The connector pin allocation described below follows the profibus standard. X1 description 1 shld alternate cable shield connection. Connected to connector housing. 2...
Page 33
Electrical installation 33 it is recommended to use a profibus-approved d-sub 9 connector. These connectors have a built-in termination network and inductors for station capacitance compensation. Connect the cable to the d-sub connector as follows: 1a 1b 2a 2b re d re d gre en gre en ou t in groundi...
Page 34
34 electrical installation switching on the bus termination bus termination is required to prevent signal reflections from the bus cable ends. The adapter module is not equipped with internal bus termination. Therefore, the d-sub connectors at the first and last modules of the bus must have built-on...
Page 35: Start-Up
Start-up 35 6 start-up what this chapter contains this chapter contains: • information on configuring the drive for operation with the adapter module • drive-specific instructions on starting up the drive with the adapter module • examples of configuring the master station for communication with the...
Page 36: Drive Configuration
36 start-up drive configuration the following information applies to all drive types compatible with the adapter module, unless otherwise stated. Profibus connection configuration after the adapter module is mechanically and electrically installed according to the instructions in chapters mechanical...
Page 37: Emulation Modes
Start-up 37 emulation modes fpba-01 supports emulation modes for rpba-01, npba-02, npba-12 and vik-namur. Emulation modes change the fpba-01 identification information so that fpba-01 accepts connection from plc configuration made for rpba-01, npba-02, npba-12 or vik-namur. Emulation mode can be use...
Page 38: No. Name/value
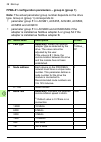
38 start-up fpba-01 configuration parameters – group a (group 1) note: the actual parameter group number depends on the drive type. Group a (group 1) corresponds to: • parameter group 51 in acsm1, acs355, acs380, acs580, acs850 and acq810 • parameter group 51 in acs880 and acs880-m04 if the adapter ...
Page 39: Msg Type
Start-up 39 93 93.75 kbit/s 45 45.45 kbit/s 19 19.2 kbit/s 9 9.6 kbit/s 04 msg type read-only. Indicates the telegram type selected for profibus communication. The adapter module automatically detects the telegram type used. For more information on the supported ppo message types, see section ppo ty...
Page 40: Profile
40 start-up 05 profile selects the communication profile used. For more information on the communication profiles, see chapter communication profiles . 1 = abb drives 0 = profidrive profidrive profile selected. See also virtual address allocation with acsm1 on page 50 . 1 = abb drives abb drives pro...
Page 41: T16 Scale
Start-up 41 06 t16 scale defines the reference multiplier/actual value divisor for the adapter module. Note: the parameter is effective only when • transparent 16 profile is selected • drive is using the native communication profile (for example, dcu or fba) • a 16-bit transparent reference 1/actual...
Page 42: Emul Mode
42 start-up 07 emul mode enables the emulation mode for the drive. When the mode is enabled, it is possible to replace a drive using modules rpba-01, npba-02 or npba-12 in the profibus network with a drive using the fpba-01 module, without modifying the plc hardware configuration. The vik-namur mode...
Page 43: Fba Par Refresh
Start-up 43 3 = map_err_wro ng_idx wrong mapping index (e.G. Index of pzd 10) is used when ppo type 2 is in use 4 = map_err_in parameter number or virtual index number is not supported for input mapping 5 = map_err_out parameter number or virtual index number is not supported for output mapping 6 = ...
Page 44: Fba Drive Type
44 start-up parameter table revision 29 fba drive type code read-only. Displays the drive type code of the fieldbus adapter module mapping file stored in the memory of the drive. N/a drive type code of the fieldbus adapter module mapping file 30 fba mapping file ver read-only. Displays the fieldbus ...
Page 45: Fba A Comm Sw
Start-up 45 32 fba a comm sw ver read-only. Displays firmware patch and build number of the adapter module in format xxyy, where: xx = patch number yy = build number. Example: c80d ≥ 200.13 or 0 ≥ 0.0 0 hex 0...0xffff firmware patch and build number of the adapter module. 33 fba appl sw ver read-onl...
Page 46: No.
46 start-up fpba-01 configuration parameters – group b (group 2) note: the actual parameter group number depends on the drive type. Group b (group 2) corresponds to: • parameter group 55 in acs355 • parameter group 53 in acsm1, acs380, acs580, acs850, acq580, and acq810 • parameter group 53 in acs88...
Page 47: 13 = Ref2 32Bit
Start-up 47 13 = ref2 32bit reference ref2 (32 bits) 21 = cw2 16bit control word 2 (16 bits) 101…9999 parameter index with format xxyy, where • xx is the parameter group number (1…99) • yy is the parameter number index within that group (01…99). Other path to parameter area selection. 03… 12 fba dat...
Page 48: No.
48 start-up fpba-01 configuration parameters – group c (group 3) note: the actual parameter group number depends on the drive type. Group c (group 3) corresponds to: • parameter group 54 in acs355 • parameter group 52 in acsm1, acs380, acs580, acs850, acq580, and acq810 • parameter group 52 in acs88...
Page 49: 24 = Sw2 16Bit
Start-up 49 24 = sw2 16bit status word 2 (16 bits) 101…9999 parameter index with format xxyy, where • xx is the parameter group number (1…99) • yy is the parameter number index within that group (01…99). Other path to parameter area selection. 03… 12 fba data in 3… fba data in12 see parameter 01 fba...
Page 50: 50.04/50.05.)
50 start-up virtual address allocation with acsm1 when the profidrive profile or profidrive positioning mode is used with an acsm1 drive, the virtual addresses shown below are recommended. (fba refx mode is selected with drive parameter 50.04/50.05.) the information in the table is applicable only i...
Page 51: Control Locations
Start-up 51 control locations abb drives can receive control information from multiple sources including digital inputs, analog inputs, the drive control panel and a communication module (for e.G., the adapter module). Abb drives allow the user to separately determine the source for each type of con...
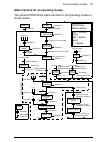
Page 52: Starting Up Acs355 Drives
52 start-up starting up acs355 drives 1. Power up the drive. 2. Enable the communication between the adapter module and the drive by setting parameter 9802 comm prot sel to ext fba. 3. Set the fpba-01 configuration parameters in group 51. At the minimum, set the required node address in parameter 51...
Page 53: With Ppo Type 2
Start-up 53 parameter setting examples – acs355 speed control using the profidrive communication profile with ppo type 2 this example shows how to configure a basic speed control application that uses the profidrive profile. In addition, some application-specific data is added to the communication. ...
Page 54: 5104 Fb Par 4
54 start-up 5104 fb par 4 (telegram type) 2 (= ppo2) 1) displays the telegram type selected by the plc configuration tool. 5105 fb par 5 (profile) 0 (= profidrive) selects the control word according to the profidrive profile (speed control mode). 3018 comm fault func 3 = last speed enables fieldbus ...
Page 55: 1601 Run Enable
Start-up 55 the start sequence for the parameter example above is given below. Speed and torque control using the abb drives communication profile with ppo type 4 this example shows how to configure a speed and torque control application that uses the abb drives profile. From the plc programming poi...
Page 56: Direction Pzd1
56 start-up the minimum and maximum 16-bit integer values that can be given through the fieldbus are -32768 and 32767 respectively. The table below gives the recommended drive parameter settings. Direction pzd1 pzd2 pzd3 pzd4 pzd5 pzd6 out control word speed reference torque reference n/a n/a n/a in...
Page 57: 5402 Fba Data In 2
Start-up 57 5402 fba data in 2 5 (= act1 16bit) 1) actual value 1 (speed) 5403 fba data in 3 6 (= act2 16bit) 2) actual value 2 (torque) 5501 fba data out 1 1 (= cw 16bit) 1) control word 5502 fba data out 2 2 (= ref1 16bit) 1) reference 1 (speed) 5503 fba data out 3 3 (= ref2 16bit) 2) reference 2 ...
Page 58: 1604 Fault Reset Sel
58 start-up the start sequence for the parameter example above is given below. 1604 fault reset sel 8 = comm selects the fieldbus interface as the source for the fault reset signal. 1) read-only or automatically detected/set 2) example control word start sequence 47eh (1150 decimal) ready to switch ...
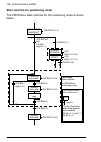
Page 59: Starting Up Acsm1 Drives
Start-up 59 starting up acsm1 drives 1. Power up the drive. 2. Enable the communication between the adapter module and the drive by setting parameter 50.01 fba enable to enable. 3. With parameter 50.02 comm loss func, select how the drive reacts to a fieldbus communication break. Note that this func...
Page 60: With Ppo Type 2
60 start-up parameter setting examples – acsm1 speed control using the profidrive communication profile with ppo type 2 this example shows how to configure a basic speed control application that uses the profidrive profile. In addition, some application-specific data is added to the communication. T...
Page 61: 51.02 Fba Par2
Start-up 61 51.02 fba par2 (node address) 3 2) defines the profibus node address of the fieldbus adapter module. 51.03 fba par3 (baud rate) 12000 1) displays the current baud rate on the profibus network in kbit/s. 51.04 fba par4 (telegram type) 2 (= ppo2) 1) displays the telegram type selected by t...
Page 62: With Ppo Type 4
62 start-up the start sequence for the parameter example above is given below. Position control using the profidrive communication profile with ppo type 4 this example shows how to configure a basic positioning application. The start/stop commands and reference are according to the profidrive profil...
Page 63: Drive Parameter
Start-up 63 the table below gives the recommended drive parameter settings. Drive parameter setting for acsm1 drives description 50.01 fba enable enable enables communication between the drive and the fieldbus adapter module. 50.02 comm loss func fault enables fieldbus communication fault monitoring...
Page 64: 51.27 Fba Par
64 start-up 53.02 fba data out2 12 (= ref1 32bit) reference 1 53.04 fba data out4 13 (= ref2 32bit) reference 2 51.27 fba par refresh refresh validates the fpba-01 configuration parameter settings. 10.01 ext1 start func fba selects the fieldbus interface as the source of the start and stop commands ...
Page 65: 65.03 Pos Start 1
Start-up 65 the position set point is scaled as follows: 65.03 pos start 1 c.False selects the fieldbus as the position start1 source. 65.04 pos ref 1 sel fba ref 1 selects the fba reference 1 as the position reference source. 65.11 pos start 2 c.False selects the fieldbus as the position start2 sou...
Page 66: Drive Parameter
66 start-up the position set point and actual values are scaled with the above example values as follows: example for velocity set point scale: the velocity set point and actual values are scaled with the above example values as follows: pay attention to the following parameter groups: drive paramet...
Page 67: Control Word
Start-up 67 the start sequence for the above parameter example is given below: speed and torque control using the abb drives communication profile with ppo type 4 this example shows how to configure a speed and torque control application that uses the abb drives profile. From the plc programming poi...
Page 68: Drive Parameter
68 start-up the table below gives the recommended drive parameter settings. Drive parameter setting for acsm1 drives description 50.01 fba enable enable enables communication between the drive and the fieldbus adapter module. 50.02 comm loss func fault enables fieldbus communication fault monitoring...
Page 69: 53.02 Fba Data
Start-up 69 53.02 fba data out2 2 (= ref1 16bit 2) reference 1 53.03 fba data out3 3 (= ref2 16bit 2) reference 2 51.27 fba par refresh refresh validates the fpba-01 configuration parameter settings. 10.01 ext1 start func fba selects the fieldbus interface as the source of the start and stop command...
Page 70: Control Word
70 start-up the start sequence for the parameter example above is given below. Control word start sequence 47eh (1150 decimal) ready to switch on 47fh (1151 decimal) operating (speed mode) c7fh (3199 decimal) operating (torque mode).
Page 71: Starting Up Acs380 Drives
Start-up 71 starting up acs380 drives the acs380 software automatically sets the relevant parameters when the fieldbus adapter module is connected to the drive. Automatic configuration is only minimum configuration, and you can change these parameters later, e.G., node address. Parameter general set...
Page 72: Control Word
72 start-up the start sequence for the parameter example above is given below. Setting up the drive for fieldbus control manually the fieldbus adapter module is typically pre-installed. The device automatically recognizes the module. If the adapter is not pre- installed, you can install it mechanica...
Page 73
Start-up 73 9. Save the valid parameter values to permanent memory by setting parameter 96.07 parameter save manually to save. 10. Validate the settings made in parameter groups 51, 52 and 53 by setting parameter 51.27 fba a par refresh to configure. 11. Configure control locations ext1 and ext2 to ...
Page 74
74 start-up starting up acs850 and acq810 drives 1. Power up the drive. 2. Enable the communication between the adapter module and the drive by setting parameter 50.01 fba enable to enable. 3. With parameter 50.02 comm loss func, select how the drive reacts to a fieldbus communication break. Note th...
Page 75: With Ppo Type 2
Start-up 75 parameter setting examples – acs850 and acq810 speed control using the profidrive communication profile with ppo type 2 this example shows how to configure a basic speed control application that uses the profidrive profile. In addition, some application-specific data is added to the comm...
Page 76: 50.21 Comm Loss
76 start-up (acq810 only) 50.21 comm loss enable bit 0 = 1 enables communication loss detection for ext 1. 51.01 fba type profibus-dp 1) displays the type of the fieldbus adapter module. 51.02 fba par2 (node address) 3 2) defines the profibus node address of the fieldbus adapter module. 51.03 fba pa...
Page 77: 10.01 Ext1 Start Func
Start-up 77 the start sequence for the parameter example above is given below. 10.01 ext1 start func fb selects the fieldbus interface as the source of the start and stop commands for external control location 1. 10.08 fault reset sel p.Fba main cw.8 selects fieldbus interface as the source for faul...
Page 78: 53.01 Fba A Data Out1.
78 start-up starting up acs880 and acs880-m04 drives 1. Power up the drive. 2. Enable communication between the adapter module and the drive by setting parameter 50.01 fba a enable, option slot 1, 2 or 3 depending on the slot the adapter module is attached to. 3. With parameter 50.02 fba a comm loss...
Page 79: M04
Start-up 79 10. Set the relevant drive control parameters to control the drive according to the application. Examples of appropriate values are shown in the tables below. Parameter setting examples – acs880 and acs880- m04 speed control using the profidrive communication profile with ppo type 2 this...
Page 80: 51.01 Fba A Type
80 start-up 51.01 fba a type 1 = fpba 1) displays the type of the fieldbus adapter module. 51.02 fba a par2 3 2) defines the profibus node address of the fieldbus adapter module. 51.03 baud rate 12000 1) displays the current baud rate on the profibus network in kbit/s. 51.04 msg type 1 = ppo1 1) dis...
Page 81: 20.02 Ext1 Start Trigger
Start-up 81 the start sequence for the parameter example above is given below. 20.01 ext1 commands 12 = fieldbus a selects the fieldbus a interface as the source of the start and stop commands for external control location 1. 20.02 ext1 start trigger type 1 = level selects the start trigger type to ...
Page 82: Downloading The Gsd File
82 start-up configuring the master station after the adapter module is initialized by the drive, prepare the master station for communication with the module. See examples of an abb ac500 plc and siemens simatic s7 plc given below. If you are using another master system, refer to its documentation f...
Page 83
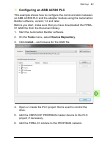
Start-up 83 configuring an abb ac500 plc this example shows how to configure the communication between an abb ac500 plc and the adapter module using the automation builder software, version 1.2 and later. Before you start, make sure that you have downloaded the fpba- 01 gsd file from the document li...
Page 84
84 start-up 7. Add the dp module, for example, ppo type 4 to the fpba-01 module to define cyclical communication between the adapter module and the plc. 8. Define the cm572-dp master properties, such as the baud rate, node address (station address) and the highest station address..
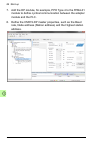
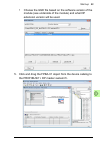
Page 85: On The Dp-Parameters Tab,
Start-up 85 9. Define the fpba-01 properties: on the dp-parameters tab, • select the node address (station address) and the dp mode • configure the fail-safe functionality..
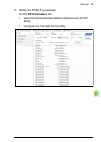
Page 86
86 start-up 10. Define the dp module properties: on the dp-module i/o mapping tab, type names for the variables that refer to the drive's signals in the plc program. 11. Open the plc program and create a program that controls the drive..
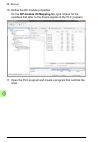
Page 87
Start-up 87 12. Compile the project and download it to the plc. Note: make sure that the variable names defined for the drive signals are used in the plc program. Otherwise the communication will not work..
Page 88: Click New.
88 start-up configuring a siemens simatic s7 plc this example shows how to configure the communication between a siemens simatic s7 plc and the adapter module using simatic manager step 7. Before you start, make sure that you have downloaded the fpba- 01 gsd files from the document library. 1. Start...
Page 89
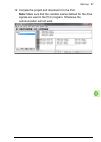
Start-up 89 • choose the gsd file based on the software version of the module (see underside of the module) and what dp extension version will be used. 5. Click and drag the fpba-01 object from the device catalog to the profibus(1): dp master system(1)..
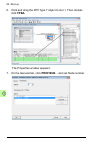
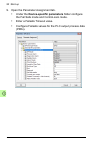
Page 90: Click Fpba.
90 start-up 6. Click and drag the pp0 type 7 object to slot 1. Then double- click fpba. The properties window appears. 7. On the general tab, click profibus... And set node number..
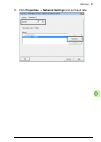
Page 91: 8. Click Properties
Start-up 91 8. Click properties → network settings and set baud rate..
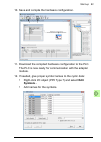
Page 92
92 start-up 9. Open the parameter assignment tab. • under the device-specific parameters folder configure the fail safe mode and control-zero mode. • enter a failsafe timeout value. • configure failsafe values for the plc output process data (pzds)..
Page 93: Symbols...
Start-up 93 10. Save and compile the hardware configuration. 11. Download the compiled hardware configuration to the plc. The plc is now ready for communication with the adapter module. 12. If needed, give proper symbol names to the cyclic data: • right-click i/o object (pp0 type 7) and select edit ...
Page 94: 2. Go To Options
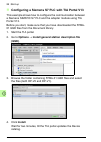
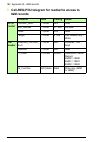
94 start-up configuring a siemens s7 plc with tia portal v13 this example shows how to configure the communication between a siemens simatic s7 plc and the adapter module using tia portal v13. Before you start, make sure that you have downloaded the fpba- 01 gsd files from the document library. 1. S...
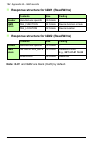
Page 95
Start-up 95 5. In tia portal, go to network view. Drag and drop fpba-01 from the device catalog to the network view. 6. Click on not assigned text and select the master to create link between the master and fpba-01. 7. Go to device view and select slave_1 (fpba-01). Drag and drop the telegram from c...
Page 96
96 start-up 8. In the general tab, set fpba-01 node address. 9. In the device-specific parameters, set fail-safe mode, time out and fail-safe values. 10. Compile and download the project. After the plc starts, node 3 (fpba-01) goes online with ppo- 08..
Page 97: Cyclic Data Handling
Start-up 97 cyclic data handling with fpba-01, both data-consistent and non-consistent communication can be used, data-consistent meaning that the whole cyclic data frame is transmitted during a single program cycle. Some plcs handle this internally, but others must be programmed to transmit data-co...
Page 98
98 start-up.
Page 99: Communication Profiles
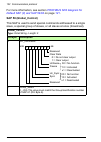
Communication profiles 99 7 communication profiles what this chapter contains this chapter describes the communication profiles used in the communication between the profibus network, the adapter module and the drive. Communication profiles communication profiles are ways of conveying control comman...
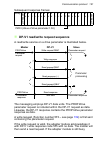
Page 100: Fpba-01
100 communication profiles the figure below illustrates the profile selection: the following sections describe the control word, the status word, references and actual values for the profidrive and abb drives communication profiles. Refer to the drive manuals for details on the native profiles. Fpba...
Page 101: Parameter 968).
Communication profiles 101 profidrive communication profile control word and status word the control word (profidrive parameter 967) is the principal means for controlling the drive from a fieldbus system. It is sent by the fieldbus master station to the drive through the adapter module. The drive s...
Page 102: Inhibit.
102 communication profiles 2 off3 1 continue operation (off3 inactive). 0 emergency stop, stop according to fastest possible deceleration mode. Proceed to off3 active; proceed further to switch-on inhibit. Warning: ensure motor and driven machine can be stopped using this stop mode. 3 operation_ ena...
Page 103: Operating.
Communication profiles 103 6 1 normal operation. Proceed to operating. Note: this bit is effective only if the fieldbus interface is set as the source for this signal by drive parameters. Activate traversing task (0 → 1). This is a toggle bit; each rising edge of signal enables a traversing task or ...
Page 104: Profidrive Parameter 936
104 communication profiles 14 vendor-specific bit as defined by profidrive parameter 936 15 vendor-specific bit as defined by profidrive parameter 937 bit name value state/description speed control mode positioning mode.
Page 105: Status Word Contents
Communication profiles 105 status word contents the table below shows the contents of the status word for the profidrive communication profile (profidrive parameter 968). The upper case boldface text refers to the states shown in the state machine on page 107 . Bit name value state/description speed...
Page 106: Parameter 939
106 communication profiles 10 1 actual frequency or speed value equals or is greater than supervision limit. Target position reached 0 actual frequency or speed value is within supervision limit. Not at target position 11 1 vendor-specific bit as defined by profidrive parameter 939 homing procedure ...
Page 107
Communication profiles 107 state machine for all operating modes the general profidrive state machine for all operating modes is shown below. ‘n=0 or f =0’ and ‘i=0’ and pause expired jogging 1 or 2 off (cw bit8=0 or bit9=0) mains off power on off1 (cw bit0=0) switch-on inhibit (sw bit6=1) not ready...
Page 108
108 communication profiles state machine for positioning mode the profidrive state machine for the positioning mode is shown below. State condition e f (sw bit10,13=1) (cw bit4,5=1 and cw bit6 edge 0 1) cw= control word sw = status word profidrive state machine for profidrive positioning mode (cw b...
Page 109: References
Communication profiles 109 references abb drives can receive control information from multiple sources including analog and digital inputs, the drive control panel and a communication module (for example, fpba-01). In order to have the drive controlled through profibus, the communication module must...
Page 110: Actual Values
110 communication profiles actual values actual values are 16-bit or 32-bit words containing information on the operation of the drive. The functions to be monitored are selected with a drive parameter. Actual values in speed control mode the scaling of 16-bit actual speed values (act or nist_a) in ...
Page 111: Control Word Contents
Communication profiles 111 abb drives communication profile control word and status word the control word is the principal means for controlling the drive from a fieldbus system. It is sent by the fieldbus master station to the drive through the adapter module. The drive switches between its states ...
Page 112: Operation Inhibited.
112 communication profiles 3 inhibit_ operation 1 proceed to operation enabled. Note: run enable signal must be active; see drive documentation. If the drive is set to receive the run enable signal from the fieldbus, this bit activates the signal. 0 inhibit operation. Proceed to operation inhibited....
Page 113: Status Word Contents
Communication profiles 113 status word contents the table below shows the contents of the status word for the abb drives communication profile. The upper case boldface text refers to the states shown on page 115 . 10 remote_ cmd 1 fieldbus control enabled 0 control word and reference not getting thr...
Page 114: Bit
114 communication profiles 7 alarm 1 warning/alarm 0 no warning/alarm 8 at_setpoint 1 operation. Actual value equals reference value (= is within tolerance limits, i.E., in speed control, speed error is 10% maximum of the nominal motor speed). Note that tolerance limit can be configured in the drive...
Page 115: State Machine
Communication profiles 115 state machine the state machine for the abb drives communication profile is shown below. Power on (cw bit0=0) (sw bit6=1) (sw bit0=0) from any state (cw=xxxx x1xx xxxx x110) (sw bit1=1) n(f)=0 / i=0 (sw bit2=0) a b c d (cw bit3=0) operation inhibited off1 (cw bit0=0) (sw b...
Page 116: References
116 communication profiles references references are 16-bit words containing a sign bit and a 15-bit integer. A negative reference (indicating reversed direction of rotation) is formed by calculating the two’s complement from the corresponding positive reference. Abb drives can receive control infor...
Page 117: Actual Values
Communication profiles 117 actual values actual values are 16-bit words containing information on the operation of the drive. The functions to be monitored are selected with a drive parameter. Scaling actual values are scaled as shown below. Note: the values of ref1 max and ref2 max are set with dri...
Page 118
118 communication profiles.
Page 119: Communication Protocol
Communication protocol 119 8 communication protocol what this chapter contains this chapter describes the profibus messaging used in the communication with the drive and in profibus slave device configuration messages. Profibus dp the fpba-01 module supports the profibus dp-v0 and dp-v1 protocols ac...
Page 120: Communication Start-Up
120 communication protocol service access points (saps) the services of the profibus data link layer (layer 2) are used by profibus dp through service access points (saps). Precisely defined functions are assigned to individual saps. For further information on saps, refer to the manual of the profib...
Page 121: Output Data
Communication protocol 121 profibus sd2 telegram for default sap (0) and sap 58-62 profibus typically uses sd2 telegrams for dp communication. The structure of an sd2 telegram is shown below. Default sap (sap 0) (data_exch) this sap allows the master to send output data to a slave station and to sim...
Page 122: Sap 58 (Global_Control)
122 communication protocol for more information, see section profibus sd2 telegram for default sap (0) and sap 58-62 on page 121 . Sap 58 (global_control) this sap is used to send special commands addressed to a single slave, a special group of slaves, or all slaves at once (broadcast). Global_contr...
Page 123: Sap 60 (Slave_Diag)
Communication protocol 123 sap 60 (slave_diag) this sap gives diagnostic information on the slave station. Diag_data (diagnostic data) type: octet string - length: 6 (standard) + 2 (extended diagnosis) (dp-v0 mode) + 5 (extended diagnosis) (dp-v1 mode) note: during initialization, the module only se...
Page 124: Diag.Master_Add
124 communication protocol 1 station_status_2 2 station_status_3 3 diag.Master_add the address of the master that parameterized this slave 4…5 ident_number (for fpba-01: 0959h) 6 2) ext_diag_data (0x02) (dp-v0 only) the number of bytes (including this byte) reserved for extended diagnosis x 0 x x x ...
Page 125: Diagnostic Type
Communication protocol 125 6 1) header byte (dp-v1 only) the complete header consists of 5 bytes with fpba-01. 7 2) communication diagnostic (dp-v0 only) 7 1) status type = status message (0x81) (dp-v1 only) 8 1) slot number (0x00) (dp-v1 only) slot number (0…244). 0 0 x x x x x x msb lsb block leng...
Page 126
126 communication protocol 9 1) specifier (0x00) (dp-v1 only) 10 1) communication diagnostic (dp-v1 only) 1) the fpba-01 module is operated in the dp-v1 mode. The diagnostic information is according to profidrive 3.1. 2) the fpba-01 module is operated in the dp-v0 (dp) mode. The diagnostic informati...
Page 127: Sap 61 (Set_Prm)
Communication protocol 127 sap 61 (set_prm) this sap is used in the parameterization of the drive. Prm_data (parameter data standard) type: octet string total length: 37 – prm_data length: 14 – user_prm_data length: 23 du byte value description 0 b8h (recom- mended default value) station status 1…2 ...
Page 128: Dis_Start_Control
128 communication protocol 7 dpv1_status_1 (dp-v1 only) x 0 x 0 0 x x x dis_start_control (disable stop-bit control) 0 = start bit monitoring in receiver enabled 1 = start bit monitoring in receiver disabled msb lsb wd_base (watchdog time base) 0 = 10 ms 1 = 1 ms dis_stop_control (disable stop-bit c...
Page 129: Chk_Cfg_Mode
Communication protocol 129 8 dpv1_status_2 (dp-v1 only) (not supported) x x x x x x 0 x chk_cfg_mode 0 = chk_cfg according to en 50170 (default state) 1 = user-specific evaluation of chk_cfg msb lsb enable_update_alarm 0 = enable_update_alarm disabled 1 = enable_update_alarm enabled reserved. To be ...
Page 130: Structured_Length
130 communication protocol 9 dpv1_status_3 (dp-v1 only) 10 1bh (default) structured_length length of the structured prm telegram. (user parameter length is 23 bytes + 4 header bytes.) 11 81h structure_type 129: user_prm_data 12 0 slot_number set to 0 13 0 reserved 0 0 0 x 1 x x x alarm_mode. Not sup...
Page 131: Fail-Safe Mode.
Communication protocol 131 user_prm_data (parameter data extended) type: octet string - length: 23 14 00h (default) header byte 15… 16 0… 65536 cut off time out in milliseconds. 0 = cut off disabled. 17… 18 0… 65536 fail-safe, pzd1 (typically cw) 19… 20 0… 65536 fail-safe, pzd2 (typically ref) 0 0 0...
Page 132: Sap 62 (Chk_Cfg)
132 communication protocol the extended parameter data bytes are configured through the profibus network configuration tool. The functions are defined in the gsd file. Sap 62 (chk_cfg) with this telegram, the master sends the selected data exchange (write_read_data) telegram type code to the slave. ...
Page 133: Telegram
Communication protocol 133 ppo 5 4 pkw + 10 pzd in/out f3 f9 dp-v0 / dp-v1 1) ppo 6 0 pkw + 10 pzd in/out f9 dp-v1 1) ppo 7 4 pkw + 12 pzd in/out 0xf3, 0xfb dp-v0 / dp-v1 1) ppo 8 0 pkw + 12 pzd in/out 0xfb dp-v1 1) st 1 2 pzd in / 2 pzd out c3 c1 c1 fd 00 01 dp-v1 st 2 4 pzd in / 4 pzd out c3 c3 c3...
Page 134: Master
134 communication protocol the default codes for the ppo types in the table above define data consistency over the message as follows: data non-consistent over the entire message is also supported by the fpba-01 module. The cyclical frame types supported by the module are defined in the gsd file. Ot...
Page 135: Cyclical Message Types
Communication protocol 135 cyclical message types ppo types out area – data sent from master to slave (control data) in area – data sent from slave to master (actual data) parameter identification: id – parameter identification ind – index for arrays value – parameter value (max. 4 bytes) pkw – para...
Page 136: St1
136 communication protocol standard telegram (st) types (dp-v1) note: for the contents of the control word, the status word, references and actual values, see chapter communication profiles . St1 pzd1 pzd2 out area stw1 control word 1 nsoll_a speed set point a in area zsw1 status word 1 nist_a speed...
Page 137: Request
Communication protocol 137 parameter handling in cyclic communication (dp) in cyclic profibus dp communication, parameter data is transferred in ppo message types 1, 2 and 5, as shown in section ppo types on page 135 . The parameter identification part consists of eight bytes, as shown below. The re...
Page 138: Ackn.
138 communication protocol 7 change parameter value (array word) 4 7, 8 8 change parameter value (array double word) 5 7, 8 9 request number of array elements 6 7 response label (acknowledgement from slave to master) ackn. Function 0 no response 1 transfer parameter value (word) 2 transfer parameter...
Page 139: Ackn.
Communication protocol 139 7 task cannot be executed, followed by error number 8 no parameter change rights for pkw interface 9 parameter data signal (word) 10 parameter data signal (double word) response label (acknowledgement from slave to master) ackn. Function 0 = illegal parameter number 1 = pa...
Page 140: Virtual Drive Control Area
140 communication protocol the allocation of drive control/actual words, drive parameters and profidrive parameters to the parameter identification part of the ppo type is shown below. • the index column corresponds to the parameter number (pnu) in the id part of parameter identification. • the sub-...
Page 141: Profidrive Parameters
Communication protocol 141 for a complete profidrive parameter list, see appendix a – profidrive parameters . Note: continuous (cyclic) writing of profidrive parameters should be avoided as the values of these parameters are stored in the flash memory of the adapter module. The estimated lifetime of...
Page 142
142 communication protocol parameter data transfer examples (dp-v0) note: only the ‘data unit’ part of the telegram is presented in the examples. See section profibus sd2 telegram for default sap (0) and sap 58-62 on page 121 . Example 1: reading a drive parameter (or data set) to determine the para...
Page 143
Communication protocol 143 error response resp d p h ead er 7 0 5 4 0 b 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 3 0 3 3 7 3 4 1 5 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 dp tr aile r sw act pzd3 pzd4 pzd5 pzd6 error number (3: erroneous subindex) subindex 1) parameter number response (negative acknowledgement) 1) 2nd byte reserv...
Page 144
144 communication protocol example 2: writing a drive parameter (or data set) to determine the parameter number and subindex for drive parameter writing, convert the drive parameter group number and the parameter index number to hexadecimal. The index number is the subindex (ind), and the group numb...
Page 145
Communication protocol 145 the following is an example of writing a 32-bit parameter: req d p h ead er 8 0 0 c 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 6 4 0 4 7 f 3 4 1 5 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 dp tr aile r resp 5 0 0 c 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 6 4 0 3 3 7 3 4 1 5 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 cw ref pzd3 pzd4 pz...
Page 146
146 communication protocol example 3: reading a profidrive parameter (word) in this example, profidrive parameter 918 is used to read the station number of the slave. The slave returns its station number (2). Read: req dp header 1 3 9 6 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 4 7 f 3 4 1 5 dp trailer resp 1 3 9 6...
Page 147
Communication protocol 147 example 4: writing a profidrive parameter (word) in this example, current parameter settings are saved to the flash memory of the drive. This is done by setting the value of profidrive parameter 971 (3cbh) to 1. Note that the drive always observes the control word (cw) and...
Page 148
148 communication protocol example 5: reading a profidrive parameter (array) in this example, profidrive parameter 945 is used to read the code of the active fault. As shown on page 187 , parameter 945 is of the array type with subindexes 0 and 1. The slave returns the code of the active fault (2300...
Page 149
Communication protocol 149 example 6: configuring the process data written to the drive profidrive parameter 915 can be used to define which data is written cyclically to a drive parameter as application-specific process data. In the example below, the value of drive parameter 12.02 (0ch.02h) is sel...
Page 150
150 communication protocol example 7: configuring the process data read from the drive profidrive parameter 916 can be used to define which data is read cyclically from the drive as application-specific process data. In the example below, drive parameter 1.04 (01h.04h) is selected to be transmitted ...
Page 151: Master
Communication protocol 151 subsequent response frames: dp-v1 read/write request sequence a read/write service on a drive parameter is illustrated below. The messaging employs dp-v1 data units. The profidrive parameter request is included within the dp-v1 request as data. Likewise, the dp-v1 response...
Page 152
152 communication protocol performing the internal parameter request, it will return a negative response with the dp-v1 error code b5h (state conflict). In this case, the read request will be repeated by the master until the adapter module has the profidrive response data ready. If the write request...
Page 153: Data Unit
Communication protocol 153 profibus sd2 telegram for sap 51 the read/write service uses a variable-length profibus sd2 telegram shown below. Dp header dp trailer sd le ler sd da sa fc dsap ssap du fcs ed 68h x x 68h xx xx x xx xx x… xx 16h sd = start delimiter le = length ler = length repeated da = ...
Page 154: Value
154 communication protocol the table below lists the dp-v1 function numbers. The table below lists the dp-v1 error responses. Value meaning 0x48 idle req, res 0x51 data transport req, res 0x56 resource manager req 0x57 initiate req, res 0x58 abort req 0x5c alarm req, res 0x5e read req, res 0x5f writ...
Page 155: Error Class
Communication protocol 155 the table below lists the error codes for the dp-v1 error responses. Error class meaning error code 0…9 (reserved) 10 (0x0a) application 0 = read error 1 = write error 2 = module failure 3…7 = reserved 8 = version conflict 9 = feature not supported 10…15 = user-specific 11...
Page 156: Field(S)
156 communication protocol the table below shows the contents of the profidrive request header. Field(s) description range byte/word request reference unique identification set by the master. Changed for each new request. 1…255 byte request id request type for the issued block request parameter (01h...
Page 157: Field(S)
Communication protocol 157 subindex addresses • the first array element of the parameter or • the beginning of a string access or • the text array or • the description element that is being accessed. 0…65535 word format 1) see the table on page 159 . See the table on page 159 . Byte number of values...
Page 158: Field(S)
158 communication protocol the table below shows the contents of the profidrive response header. Field(s) description range request reference (mirrored) mirrored from the request 1…255 response id response from the slave. In case any requested services fail, a “not acknowledged” (nak) response will ...
Page 159: Code
Communication protocol 159 the table below shows the data types for the format field. Code type 0x00 (reserved) 0x01…0x36 standard data types 1 boolean (not supported) 2 integer8 (not supported) 3 integer16 4 integer32 5 unsigned8 (not supported) 6 unsigned16 7 unsigned32 8 floating point (not suppo...
Page 160: Error #
160 communication protocol the table below shows the profidrive parameter request error codes . Error # meaning used at 00h impermissible parameter number access to an unavailable parameter 01h parameter value cannot be changed change access to a parameter value that cannot be changed 02h low or hig...
Page 161: Error #
Communication protocol 161 15h response too long the length of the current response exceeds the maximum transmittable length. 16h parameter address impermissible illegal value or value that is not supported for the attribute, number of elements, parameter number or sub-index, or a combination 17h il...
Page 162: Error #
162 communication protocol parameter data transfer examples (dp-v1) the following examples show how parameter data is transferred using the dp-v1 mechanisms read and write. Note: only the “data unit” part of the sd2 telegram is presented in the examples. See profibus sd2 telegram for sap 51 on page ...
Page 163
Communication protocol 163 • positive read response to dp-v1 read request: • negative response to profidrive read request: dp header 5e 01 2f 08 05 01 01 01 42 01 05 64 dp trailer dp-v1 response profidrive v3 parameter channel dp header 5e 01 2f 08 05 01 01 01 44 01 00 01 dp trailer dp-v1 response p...
Page 164
164 communication protocol example 1b: reading 3 drive parameters (multi-parameter) in this example, three parameters (12.04, 20.08 and 30.19) are read using one telegram. • dp-v1 write request (read parameter value): dp header 5 f 0 1 2 f 1 6 0 6 0 1 0 1 0 3 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 c 0 0 0 4 ••• dp-v1 comman...
Page 165
Communication protocol 165 • positive read response to dp-v1 read request: the values 190h (400), 1f4h (500) and 1eh (30) are returned. Dp header 5 f 0 1 2 f 1 0 0 6 0 1 0 1 0 3 4 2 01 0 1 9 0 ••• dp-v1 response profidrive v3 parameter channel ••• 4 2 01 0 1 f 4 ••• (par. Channel cont’d) ••• 4 2 01 ...
Page 166: Parameter 12.02 (0C.02H).
166 communication protocol example 2a: writing a drive parameter (one array element) drive parameters are addressed so that the drive parameter group corresponds to the parameter index (pnu), and the drive parameter number within that group corresponds to the subindex (ind). In the following example...
Page 167
Communication protocol 167 dp header 5e 01 2f 04 07 02 01 01 dp trailer dp-v1 response profidrive v3 parameter channel slot number slot number index data length request reference (mirrored) response id drive object id (mirrored) number of parameters.
Page 168
168 communication protocol example 2b: writing 2 drive parameters (multi-parameter) in this example, the values 300 (12ch) and 500 (1f4h) are written to drive parameters 12.02 (0c.02h) and 20.08 (14.08h) respectively using one telegram. Dp header 5 f 0 1 2 f 1 4 0 8 0 2 0 1 0 2 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 c 0 0 0...
Page 169
Communication protocol 169 dp header 5e 01 2f 04 08 02 01 02 dp trailer dp-v1 response profidrive v3 parameter channel slot number slot number index data length request reference (mirrored) response id drive object id (mirrored) number of parameters.
Page 170
170 communication protocol example 3: reading a profidrive parameter in this example, profidrive parameter 918 (396h) is used to read the station number of the slave. • dp-v1 write request (reading a profidrive parameter): • dp-v1 read response: the slave returns the station number of the slave (000...
Page 171
Communication protocol 171 example 4: configuring the process data written to the drive profidrive parameter 915 (393h) can be used to define which data is written cyclically to a drive parameter as application-specific process data. In the example below, the value of drive parameter 12.06 (0c.06h) ...
Page 172
172 communication protocol • dp-v1 read response: subsequently, the contents of pzd3 in each request frame are written to drive parameter 12.06 until a different selection is made. Dp header 5e 01 2f 08 0a 01 01 01 42 01 00 68 dp trailer dp-v1 response profidrive v3 parameter channel function number...
Page 173: The Drive
Communication protocol 173 example 5: determining the source of process data read from the drive profidrive parameter 916 (394h) can be used to define which data is read cyclically from the drive as application-specific process data. In the example below, the parameter is used to determine which dri...
Page 174
174 communication protocol • dp-v1 read response: value indicates the source of pzd3 as drive parameter 12.05 (0c.05h). Dp header 5e 01 2f 08 0b 01 01 01 42 01 0c 05 dp trailer dp-v1 response profidrive v3 parameter channel function number slot number index data length request reference (mirrored) r...
Page 175: Diagnostics
Diagnostics 175 9 diagnostics what this chapter contains this chapter explains how to trace faults with the status leds on the adapter module..
Page 176: Led Indications
176 diagnostics led indications the adapter module is equipped with three bicolor diagnostic leds. The leds are described below. Name color function host green connection to host ok blinking red establishing communication to host, or communication to host lost flashing orange, alternating with the m...
Page 177: Name
Diagnostics 177 module green module status ok blinking red configuration mismatch blinking red in unison with host (blinking red) establishing communication to host blinking green in unison with network (blinking red) network connection lost blinking green once per second with network steady green n...
Page 178
178 diagnostics.
Page 179: Technical Data
Technical data 179 10 technical data what this chapter contains this chapter contains the technical data of the adapter module and the profibus link. Fpba-01 enclosure: host module network x1 network.
Page 180: Connectors:
180 technical data mounting: into the option slot on the drive degree of protection: ip20 ambient conditions: the applicable ambient conditions specified for the drive in its manuals are in effect. Indicators: three bicolor leds (host, module, network) connectors: • 20-pin connector to drive (x2) • ...
Page 181: Profibus Link
Technical data 181 profibus link compatible devices: all profibus-compliant devices medium: shielded twisted pair rs-485 cable (profibus- approved cable recommended) • termination:220 ohms, or active termination circuitry at each end of trunk cable (termination not built in the fpba-01 module) • spe...
Page 182
182 technical data.
Page 183: Appendix A – Profidrive
Appendix a – profidrive parameters 183 11 appendix a – profidrive parameters what this chapter contains this chapter contains a list of the profidrive profile parameters. Profidrive parameters par. No. R/w 1) data type description 915 r/w array [10] unsigned16 assignment pzd1 to pzd10 in ppo- write ...
Page 184: Par. No. R/w
184 appendix a – profidrive parameters 923 r array [n] unsigned16 list of all parameters for signals. Mandatory if process data normalization is used and/or parameters 915 and 916 are implemented. Par. No. R/w 1) data type description no. Signal name type 1 control word 1 (stw1) unsigned16 2 status ...
Page 185: Par. No. R/w
Appendix a – profidrive parameters 185 927 r/w unsigned16 operator control rights (parameter identification, pkw) 928 r/w unsigned16 control rights (process data, pzd). 929 r unsigned16 selected ppo type par. No. R/w 1) data type description value mode 0 parameters cannot be written, only read (927 ...
Page 186: Par. No. R/w
186 appendix a – profidrive parameters 930 r/w unsigned16 selection switch for communication profile. 933 r/w unsigned16 selection switch for control word, bit 11. 934 r/w unsigned16 selection switch for control word, bit 12. (see parameter 933 for coding.) 935 r/w unsigned16 selection switch for co...
Page 187: 0 = 9.6 Kbit/s
Appendix a – profidrive parameters 187 945 r array[64] unsigned16 fault code (coded according to drivecom profile). Supported with acs355 drives only. Note: the drive may limit the actual number of the faults recorded. 947 r array [64] unsigned16 fault number. 950 r unsigned16 scaling of fault buffe...
Page 188: Par. No. R/w
188 appendix a – profidrive parameters 964 r array [7] unsigned16 965 r octet string2 profile number of this device. E.G.: 0302h = profile 3, version 2 967 r unsigned16 control word (cw) 968 r unsigned16 status word (sw) 970 r/w unsigned16 load parameter record the parameter must do a zero-to-one tr...
Page 189: Par. No. R/w
Appendix a – profidrive parameters 189 972 r/w unsigned16 software reset the parameter must do a zero-to-one transition and the motor must be stopped. 975 r array[n] unsigned16 do identification. For subindexes 0…4, see parameter 964 . 980 981 r array[n] unsigned16 number list of the defined paramet...
Page 190
190 appendix a – profidrive parameters.
Page 191: Appendix B – I&m Records
Appendix b – i&m records 191 12 appendix b – i&m records what this chapter contains this chapter contains the telegram and response structures for i&m (identification & maintenance) records. I&m records i&m records can be read, for example, with the dtm tool. The fpba-01 module supports the mandator...
Page 192: I&m Records
192 appendix b – i&m records call-req-pdu telegram for read/write access to i&m records contents size coding notes dp-v1 header function_num 1 octet 5fh fixed slot_number 1 octet 0…255 variable index 1 octet 255 fixed length 1 octet 4 / 68 call header only / write call header extended_function_ num ...
Page 193: Contents
Appendix b – i&m records 193 response structure for i&m0 (read-only) contents size coding header manufacturer-specific 10 octets “fpba-01” i&m block manufacturer_id 2 octets 0x1a = abb automation order_id 20 octets “68469325” (for fpba- 01 kit) serial_number 16 octets serial number of fpba module ha...
Page 194: Contents
194 appendix b – i&m records response structure for i&m1 (read/write) response structure for i&m2 (read/write) note: i&m1 and i&m2 are blank (0x20) by default. Contents size coding header manufacturer-specific 10 octets – i&m0 block tag_function 32 octets device function or task tag_location 22 octe...
Page 195
Further information product and service inquiries address any inquiries about the product to your local abb representative, quoting the type designation and serial number of the unit in question. A listing of abb sales, support and service contacts can be found by navigating to www.Abb.Com/searchcha...
Page 196: Www.Abb.Com/drives
Contact us www.Abb.Com/drives www.Abb.Com/solar www.Abb.Com/windpower www.Abb.Com/drivespartners 3afe68573271f 3afe68573271 rev f (en) 2017-01-25.