- DL manuals
- ABB
- Protection Device
- REG650 ANSI
- Technical Manual
ABB REG650 ANSI Technical Manual
Summary of REG650 ANSI
Page 1
Relion ® 650 series generator protection reg650 ansi technical manual.
Page 3
Document id: 1mrk 502 043-uus issued: june 2012 revision: b product version: 1.2 © copyright 2012 abb. All rights reserved.
Page 4
Copyright this document and parts thereof must not be reproduced or copied without written permission from abb, and the contents thereof must not be imparted to a third party, nor used for any unauthorized purpose. The software and hardware described in this document is furnished under a license and...
Page 5
Disclaimer the data, examples and diagrams in this manual are included solely for the concept or product description and are not to be deemed as a statement of guaranteed properties. All persons responsible for applying the equipment addressed in this manual must satisfy themselves that each intende...
Page 6
Conformity this product complies with the directive of the council of the european communities on the approximation of the laws of the member states relating to electromagnetic compatibility (emc directive 2004/108/ec) and concerning electrical equipment for use within specified voltage limits (low-...
Page 7
Table of contents section 1 introduction..........................................................................29 this manual............................................................................................29 intended audience...............................................................
Page 8
Function block...................................................................................56 signals...............................................................................................56 basic part for led indication module......................................................57 id...
Page 9
Elimination of zero sequence currents.........................................89 restrained and unrestrained limits of the differential protection......................................................................................90 fundamental frequency negative sequence differential currents.......
Page 10
Functionality....................................................................................133 function block.................................................................................134 signals................................................................................................
Page 11
Signals.............................................................................................162 settings............................................................................................162 operation principle............................................................................
Page 12
Function block.................................................................................195 signals.............................................................................................196 settings............................................................................................
Page 13
Operation principle..........................................................................221 pole discrepancy signaling from circuit breaker.........................223 unsymmetrical current detection................................................224 technical data.................................
Page 14
Operation principle..........................................................................240 pickup sensitivity........................................................................242 alarm function.............................................................................242 logic diagram....
Page 15
Monitored data.................................................................................260 operation principle..........................................................................260 measurement principle...............................................................261 time delay.........
Page 16
Signals.............................................................................................283 settings............................................................................................284 monitored data.................................................................................
Page 17
Measurement principle...............................................................300 time delay..................................................................................301 design........................................................................................302 technical data.......
Page 18
Energizing check........................................................................327 fuse failure supervision..............................................................327 voltage selection........................................................................328 voltage selection for a s...
Page 19
Operation principle..........................................................................344 selector mini switch vsggio...............................................................345 identification....................................................................................345 functio...
Page 20
Function commands user defined for iec 60870-5-103 i103usrcmd.......................................................................................356 functionality....................................................................................356 function block....................................
Page 21
Controllable gate function block gate.......................................371 exclusive or function block xor..............................................372 loop delay function block loopdelay....................................373 timer function block timerset......................................
Page 22
Integer to boolean 16 conversion with logic node representation ib16fcvb.............................................................................................387 identification....................................................................................387 functionality...................
Page 23
Settings.......................................................................................407 monitored data............................................................................408 phase-neutral voltage measurement vnmmxu..............................409 identification .....................
Page 24
Settings.......................................................................................432 analog input signals a4radr.........................................................436 identification...............................................................................436 function block.....
Page 25
Functionality....................................................................................459 function block.................................................................................459 signals................................................................................................
Page 26
Function block.................................................................................469 signals.............................................................................................470 settings............................................................................................
Page 27
Settings............................................................................................481 ssiml settings...........................................................................481 operation principle..........................................................................482 techni...
Page 28
Signals.............................................................................................502 settings............................................................................................502 function status fault protection for iec 60870-5-103 i103fltprot...............................
Page 29
Monitored data.................................................................................516 operation principle..........................................................................516 technical data.................................................................................517 secti...
Page 30
Functionality....................................................................................530 function block.................................................................................530 signals................................................................................................
Page 31
Time system, summer time begin dstbegin................................545 identification...............................................................................545 settings.......................................................................................546 time system, summer time ends...
Page 32
Settings............................................................................................559 operation principle..........................................................................559 ied identifiers terminalid.................................................................560 iden...
Page 33
Functionality....................................................................................576 function block.................................................................................576 signals................................................................................................
Page 34
Connection diagrams for reg650 b01a.........................................603 connection diagrams for reg650 b05a.........................................612 section 19 technical data...................................................................621 dimensions.....................................
Page 35
Section 1 introduction 1.1 this manual the technical manual contains application and functionality descriptions and lists function blocks, logic diagrams, input and output signals, setting parameters and technical data sorted per function. The manual can be used as a technical reference during the e...
Page 36
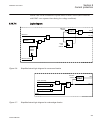
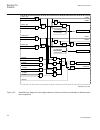
1.3 product documentation 1.3.1 product documentation set p la nni n g & p ur cha se e n gi nee ring in st al ling c om m iss io n ing o p e ra tio n m a in te na nc e d ec om m issi oni n g de inst a lli n g & d is pos a l application manual operation manual installation manual service manual engin...
Page 37
During the testing phase. The manual provides procedures for checking of external circuitry and energizing the ied, parameter setting and configuration as well as verifying settings by secondary injection. The manual describes the process of testing an ied in a substation which is not in service. Th...
Page 38
1.3.3 related documents documents related to reg650 identity number application manual 1mrk 502 042-uus technical manual 1mrk 502 043-uus commissioning manual 1mrk 502 044-uus product guide 1mrk 502 045-bus type test certificate 1mrk 502 045-tus rotor ground fault protection with injection unit rxtt...
Page 39
The information icon alerts the reader of important facts and conditions. The tip icon indicates advice on, for example, how to design your project or how to use a certain function. Although warning hazards are related to personal injury, it is necessary to understand that under certain operational ...
Page 40
34.
Page 41
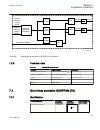
Section 2 available functions 2.1 main protection functions iec 61850/ function block name ansi function description generator reg650 reg650 (b01a) gen diff reg650 (b05a) gen+trafo diff differential protection t3wpdif 87t transformer differential protection, three winding 0–1 1 hzpdif 87 1ph high im...
Page 42
Iec 61850/ function block name ansi function description generator reg650 reg650 (b01a) gen diff reg650 (b05a) gen+trafo diff trpttr 49 thermal overload protection, two time constants 0–2 2 2 ccrbrf 50bf breaker failure protection, 3–phase activation and output 0–1 1 1 ccrpld 52pd pole discordance p...
Page 43
Iec 61850/function block name ansi function description generator reg650 reg650 (b01 a) gen diff reg650 (b05 a) gen+trafo diff locrem handling of lr-switch positions 1 1 1 locremctrl lhmi control of permitted source to operate (psto) 1 1 1 cbc1 circuit breaker for 1cb 0–1 1 slggio logic rotating swi...
Page 44
Iec 61850/function block name ansi function description generator reg650 reg650 (b01 a) gen diff reg650 (b05 a) gen+trafo diff b16ifcvi boolean 16 to integer conversion with logic node representation 16 16 16 ib16a integer to boolean 16 conversion 16 16 16 ib16fcvb integer to boolean 16 conversion w...
Page 45
Iec 61850/function block name ansi function description generator reg650 reg650 (b01a) gen diff reg650 (b05a) gen+trafo diff i103meas measurands for iec60870-5-103 1 1 1 i103measusr measurands user defined signals for iec60870-5-103 3 3 3 i103ar function status auto-recloser for iec60870-5-103 1 1 1...
Page 46
Iec 61850/function block name ansi function description generator reg650 reg650 (b01a) gen diff reg650 (b05a) gen+trafo diff mst2tcp dnp3.0 for tcp/ip communication protocol 1 1 1 mst3tcp dnp3.0 for tcp/ip communication protocol 1 1 1 mst4tcp dnp3.0 for tcp/ip communication protocol 1 1 1 rs485gen r...
Page 47
Iec 61850/function block name function description actvgrp parameter setting groups 1 testmode test mode functionality 1 chnglck change lock function 1 terminalid ied identifiers 1 prodinf product information 1 systemtime system time 1 runtime ied runtime comp 1 primval primary system values 1 smai_...
Page 48
42.
Page 49
Section 3 analog inputs 3.1 introduction analog input channels are already configured inside the ied. However the ied has to be set properly to get correct measurement results and correct protection operations. For power measuring and all directional and differential functions the directions of the ...
Page 50
• forward means direction into the object. • reverse means direction out from the object. Protected object line , transformer, etc forward reverse definition of direction for directional functions measured quantity is positive when flowing towards the object e.G . P , q , i reverse forward definitio...
Page 51
Table 1: aisvbas non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description phaseangleref trm - channel 1 trm - channel 2 trm - channel 3 trm - channel 4 trm - channel 5 trm - channel 6 trm - channel 7 trm - channel 8 trm - channel 9 trm - channel 10 - - trm - channel 1 reference c...
Page 52
Name values (range) unit step default description vtprim8 0.001 - 9999.999 kv 0.001 132 rated vt primary voltage vtsec9 0.001 - 999.999 v 0.001 110.000 rated vt secondary voltage vtprim9 0.001 - 9999.999 kv 0.001 132.000 rated vt primary voltage vtsec10 0.001 - 999.999 v 0.001 110 rated vt secondary...
Page 53
Name values (range) unit step default description ctprim8 1 - 99999 a 1 1000 rated ct primary current vtsec9 0.001 - 999.999 v 0.001 110.000 rated vt secondary voltage vtprim9 0.001 - 9999.999 kv 0.001 132.000 rated vt primary voltage vtsec10 0.001 - 999.999 v 0.001 110 rated vt secondary voltage vt...
Page 54
Table 5: aim_6i_4u non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description ct_wyepoint1 fromobject toobject - - toobject toobject= towards protected object, fromobject= the opposite ctsec1 0.1 - 10.0 a 0.1 1 rated ct secondary current ctprim1 1 - 99999 a 1 1000 rated ct primary ...
Page 55
Section 4 binary input and output modules 4.1 binary input 4.1.1 binary input debounce filter the debounce filter eliminates bounces and short disturbances on a binary input. A time counter is used for filtering. The time counter is increased once in a millisecond when a binary input is high, or dec...
Page 56
4.1.3 settings 4.1.3.1 setting parameters for binary input modules table 6: bio_9bi non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description batteryvoltage 24 - 250 v 1 110 station battery voltage table 7: bio_9bi non group settings (advanced) name values (range) unit step defaul...
Page 57
Name values (range) unit step default description oscillationtime6 0.000 - 600.000 s 0.001 0.000 oscillation time for input 6 threshold7 6 - 900 %vb 1 65 threshold in percentage of station battery voltage for input 7 debouncetime7 0.000 - 0.100 s 0.001 0.005 debounce time for input 7 oscillationcoun...
Page 58
Name values (range) unit step default description oscillationcount3 0 - 255 - 1 0 oscillation count for input 3 oscillationtime3 0.000 - 600.000 s 0.001 0.000 oscillation time for input 3 threshold4 6 - 900 %vb 1 65 threshold in percentage of station battery voltage for input 4 debouncetime4 0.000 -...
Page 59
Name values (range) unit step default description debouncetime11 0.000 - 0.100 s 0.001 0.005 debounce time for input 11 oscillationcount11 0 - 255 - 1 0 oscillation count for input 11 oscillationtime11 0.000 - 600.000 s 0.001 0.000 oscillation time for input 11 threshold12 6 - 900 %vb 1 65 threshold...
Page 60
54.
Page 61
Section 5 local human-machine-interface lhmi 5.1 local hmi screen behaviour 5.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number local hmi screen behaviour screen - - 5.1.2 settings table 10: screen non group settings (basic) name ...
Page 62
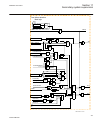
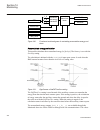
5.2 local hmi signals 5.2.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number local hmi signals lhmictrl - - 5.2.2 function block lhmictrl clrleds hmi-on red-s yellow-s yellow-f clrpulse ledsclrd iec09000320-1-en.Vsd iec09000320 v1 en...
Page 63
5.3 basic part for led indication module 5.3.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number basic part for led indication module ledgen - - basic part for led indication module grp1_led1 - grp1_led15 grp2_led1 - grp2_led15 grp3_l...
Page 64
Table 14: grp1_led1 input signals name type default description hm1l01r boolean 0 red indication of led1, local hmi alarm group 1 hm1l01y boolean 0 yellow indication of led1, local hmi alarm group 1 hm1l01g boolean 0 green indication of led1, local hmi alarm group 1 table 15: ledgen output signals n...
Page 65
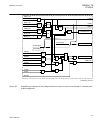
5.4 lcd part for hmi function keys control module 5.4.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number lcd part for hmi function keys control module fnkeymd1 - fnkeymd5 - - 5.4.2 function block fnkeymd1 ^ledctl1 ^fkeyout1 iec090003...
Page 66
Table 21: fnkeyty1 non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description type disabled menu shortcut control - - disabled function key type menushortcut main menu events measurements diagnostics disturbance records clear single line diagram - - main menu 5.5 operation principl...
Page 67
Guid-97da85dd-db01-449b-ad1f-eec75a955d25 v3 en figure 8: display layout 1 path 2 content 3 status 4 scroll bar (appears when needed) • the path shows the current location in the menu structure. If the path is too long to be shown, it is truncated from the beginning, and the truncation is indicated ...
Page 68
Guid-1ecf507d-322a-4b94-b09c-49f6a0085384 v1 en figure 9: truncated path the number before the function instance, for example 1:ethfrnt, indicates the instance number. The function button panel shows on request what actions are possible with the function buttons. Each function button has a led indic...
Page 69
Guid-d20bb1f1-fdf7-49ad-9980-f91a38b2107d v1 en figure 11: alarm led panel the function button and alarm led panels are not visible at the same time. Each panel is shown by pressing one of the function buttons or the multipage button. Pressing the esc button clears the panel from the display. Both t...
Page 70
The keypad also contains programmable push-buttons that can be configured either as menu shortcut or control buttons. Ansi11000247 v1 en figure 12: lhmi keypad with object control, navigation and command push buttons and rj-45 communication port 1...5 function button 6 close 7 open 8 escape 9 left 1...
Page 71
5.5.2 led 5.5.2.1 functionality the function blocks ledgen and grp1_ledx, grp2_ledx and grp3_ledx (x=1-15) controls and supplies information about the status of the indication leds. The input and output signals of the function blocks are configured with pcm600. The input signal for each led is selec...
Page 72
Acknowledgment/reset • from local hmi • the active indications can be acknowledged/reset manually. Manual acknowledgment and manual reset have the same meaning and is a common signal for all the operating sequences and leds. The function is positive edge triggered, not level triggered. The acknowled...
Page 73
= no indication = steady light = flash g = green y = yellow r = red iec09000311.Vsd iec09000311 v1 en figure 13: symbols used in the sequence diagrams sequence 1 (follow-s) this sequence follows all the time, with a steady light, the corresponding input signals. It does not react on acknowledgment o...
Page 74
Sequence 3 (latchedack-f-s) this sequence has a latched function and works in collecting mode. Every led is independent of the other leds in its operation. At the activation of the input signal, the indication starts flashing. After acknowledgment the indication disappears if the signal is not prese...
Page 75
Activating signal red led acknow. Iec09000314-1-en.Vsd activating signal yellow g y r r y activating signal green iec09000314 v1 en figure 18: operating sequence 3, three colors involved, alternative 1 if an indication with higher priority appears after acknowledgment of a lower priority indication ...
Page 76
Sequence 3 and 4 is that indications that are still activated will not be affected by the reset that is, immediately after the positive edge of the reset has been executed a new reading and storing of active signals is performed. Every led is independent of the other leds in its operation. Iec010002...
Page 77
Signals is performed. Leds set for sequence 6 are completely independent in its operation of leds set for other sequences. Timing diagram for sequence 6 figure 22 shows the timing diagram for two indications within one disturbance. Iec01000239_2-en.Vsd activating signal 2 led 2 manual reset activati...
Page 78
Iec01000240_2_en.Vsd activating signal 2 led 2 manual reset activating signal 1 automatic reset led 1 disturbance trestart disturbance trestart iec01000240 v2 en figure 23: operating sequence 6 (latchedreset-s), two different disturbances figure 24 shows the timing diagram when a new indication appe...
Page 79
Iec01000241_2_en.Vsd activating signal 2 led 2 manual reset activating signal 1 automatic reset led 1 disturbance trestart iec01000241 v2 en figure 24: operating sequence 6 (latchedreset-s), two indications within same disturbance but with reset of activating signal between figure 25 shows the timin...
Page 80
Iec01000242_2_en.Vsd activating signal 2 led 2 manual reset activating signal 1 automatic reset led 1 disturbance trestart iec01000242 v2 en figure 25: operating sequence 6 (latchedreset-s), manual reset 5.5.3 function keys 5.5.3.1 functionality local human-machine-interface (lhmi) has five function...
Page 81
Fnkeymd1 - fnkeymd5 function block also has a number of settings and parameters that control the behavior of the function block. These settings and parameters are normally set using the pst. Operating sequence the operation mode is set individually for each output, either off, toggle or pulsed. Mode...
Page 82
Note that the third positive edge on the input attribute does not cause a pulse, since the edge was applied during pulse output. A new pulse can only begin when the output is zero; else the trigger edge is lost. Input value t pulse t pulse output value iec09000332_1_en.Vsd iec09000332 v1 en figure 2...
Page 83
Section 6 differential protection 6.1 transformer differential protection 6.1.1 functionality transformer differential protection, three-winding (t3wpdif, 87t) is provided with internal ct ratio matching and phase shift compensation. In addition, zero sequence elimination is also provided. The funct...
Page 84
Without load tap changer as well as for shunt reactors including local feeders within the station. An adaptive stabilizing feature is included to avoid misoperations during for heavy through-faults. Harmonic restraint is included for inrush currents as well as for overexcitation conditions. Adaptive...
Page 85
6.1.2.3 signals table 22: t3wpdif (87t) input signals name type default description i3pw1ct1 group signal - three phase current connection winding 1 (w1) ct1 i3pw2ct1 group signal - three phase current connection winding 2 (w2) ct1 i3pw3ct1 group signal - three phase current connection winding 3 (w3...
Page 86
6.1.2.4 settings table 24: t3wpdif (87t) group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation disabled enabled - - disabled operation disable / enable idmin 0.10 - 0.60 ib 0.01 0.30 section 1 sensitivity current, usually w1 current endsection1 0.20 - 1.50 ib 0.01 1.25 e...
Page 87
Name values (range) unit step default description connecttypew2 wye (y) delta (d) - - wye (y) connection type of winding 2: y-wye or d-delta connecttypew3 wye (y) delta (d) - - delta (d) connection type of winding 3: y-wye or d-delta clocknumberw2 0 [0 deg] 1 [30 deg lag] 2 [60 deg lag] 3 [90 deg la...
Page 88
6.1.2.5 monitored data table 26: t3wpdif (87t) monitored data name type values (range) unit description idmag_a real - a magnitude of fundamental frequency differential current, phase a idmag_b real - a magnitude of fundamental frequency differential current, phase b idmag_c real - a magnitude of fu...
Page 89
Due to the ratio of the number of turns of the windings and the connection group of the protected transformer, the current between two windings can not be directly compared to each other. Therefore the differential protection must first correlate all currents to each other before any calculation can...
Page 90
These are internal compensation algorithms within the differential function. The protected power transformer data are always entered as they are given on the nameplate. Differential function will by it self adapt nameplate data and select proper reference windings. _ _ 1 _ _ 2 _ 2 _ _ 1 _ _ 2 _ 1 _ ...
Page 91
I_a_w1 is the fundamental frequency phase current in phasea on w1 side i_b_w1 is the fundamental frequency phase current in phaseb on w1 side i_c_w1 is the fundamental frequency phase current in phasec on w1 side i_a_w2 is the fundamental frequency phase current in phasea on w2 side i_b_w2 is the fu...
Page 92
For the phase reference, the highest voltage wye (y) connected winding is used. For example, if the power transformer is a yd1 power transformer, the hv winding (y) is taken as the phase reference winding. If the power transformer is a yy0 power transformer the hv winding (y) is taken as the phase r...
Page 93
Matrix with zero sequence reduction set to on matrix with zero sequence reduction set to off matrix for winding with 120° lagging 1 1 2 1 2 1 1 3 1 2 1 - - × - - - - é ù ê ú ê ú ê ú ë û equation1233 v1 en (equation 9) 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 é ù ê ú ê ú ê ú ë û equation1234 v1 en (equation 10) matrix for ...
Page 94
By using this table we can derive a complete calculation for all common transformer configuration. For example when considering a ynd5 power transformer the following can be concluded: 1. Hv wye (y) connected winding will be used as reference winding and zero sequence currents shall be subtracted on...
Page 95
The fundamental frequency differential currents are the magnitudes which are applied in a phase segregated manner to the operate - restrain characteristic of the differential protection. The magnitudes of the differential currents can be read as service values from the function and they are availabl...
Page 96
• the protected power transformer cannot transform the zero sequence currents to the other side, for any reason. • the zero sequence currents can only flow on one side of the protected power transformer. In most cases, power transformers do not properly transform the zero sequence current to the oth...
Page 97
1. Idmin (sensitivity in section 1, multiple of trans. Reference side rated current set under the parameter ibase in globalbaseselw1) 2. Endsection1 (end of section 1, as multiple of transformer reference side rated current set under the parameter ibase in globalbaseselw1) 3. Endsection2 (end of sec...
Page 98
Section 1 operate conditionally unrestrainedlimit section 2 section 3 restrain operate unconditionally 5 4 3 2 1 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 idmin endsection1 endsection2 restrain current [ times ibase ] operate current [ times ibase ] slopesection2 slopesection3 en05000187-2.Vsd iec05000187 v2 en figure 32: desc...
Page 99
Changer is a typical reason for existence of the false differential currents in this section. Slope in section 1 is always zero percent. Section 2: in section 2, a certain minor slope is introduced which is supposed to cope with false differential currents due to higher than normal currents through ...
Page 100
1 2 3 2 2 _ 2 1 1 _ 1 1 0 1 _ 2 1 _ 2 1 _ 1 2 1 _ 1 1 1 0 _ 2 3 _ 1 3 _ 1 1 2 0 1 1 _ 1 _ 2 idns a ins w ins w vn w idns b a ins w a ins w vn w idns c a ins w a ins w - - - = × - - × × + × × - × × - - - × × é ù é ù é ù é ù é ù ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ê ú ë û ë û ë û ë...
Page 101
As marked in equation 23 , the first term on the right hand side of the equation, represents the total contribution of the negative sequence current from w1 side compensated for eventual power transformer phase shift. The second term on the right hand side of the equation, represents the total contr...
Page 102
Sequence current contributions, respectively, defined by expression shown in equation 23 . It performs a directional comparison between these two phasors. Taking into account the phase rotation transformation the relative phase displacement between the two negative sequence current phasors is calcul...
Page 103
Above the limit, the phase angle between these two phasors is checked. If any of the negative sequence current contributions are too small (less than the set value for iminnegseq), no directional comparison is made in order to avoid the possibility to produce a wrong decision. The setting negseqroa ...
Page 104
En05000189.Vsd 0.1 ka 30 210 60 240 90 270 150 330 180 0 0.2 ka 0.3 ka 0.4 ka "steady state" for hv side neg. Seq. Phasor 10 ms 10 ms "steady state" for lv side neg. Seq. Phasor contribution to neg. Seq. Differential current from hv side contribution to neg. Seq. Differential current from lv side ie...
Page 105
En05000190.Vsd 0.5 ka 30 210 60 240 90 270 120 300 150 330 180 0 hv s ide contribution to the total negative s equence differential current in ka directional limit (within the region delimited by ± 60 degrees is internal fault) 1.0 ka 1.5 ka definitely an internal fault internal fault declared 7 ms ...
Page 106
Operate region on the operate - restrain characteristic. So, this protection is not independent of the traditional restrained differential protection - it is activated after the first start signal has been placed. If the fault is positively recognized as internal, then the unrestrained negative sequ...
Page 107
6.1.3.10 instantaneous differential currents the instantaneous differential currents are calculated from the instantaneous values of the input currents in order to perform the harmonic analysis and waveform analysis upon each one of them (see section "harmonic and waveform block criteria" for more i...
Page 108
I_a i_b i_c en05000343_ansi.Vsd time [cycles] 400kv currents c ur re nt [ % ] ansi05000343 v1 en figure 36: inrush currents to a transformer as seen by a protection ied. Typical is a high amount of the 2 nd harmonic, and intervals of low current, and low rate-of-change of current within each period....
Page 109
A transformer is energized with a more severe (minor faults cannot be discovered) internal fault (for example, forgotten grounding on transformer lv side for example, after a regular service). The feature is based on the waveform check. If a severe internal fault exists, then, during energization th...
Page 110
Adm a/ d co nv er si on sc al in g w ith c t ra tio a/ d co nv er si on sc al in g w ith c t ra tio ph as or ca lc ul at io n of in di vi du al ph as e cu rr en t ph as or ca lc ul at io n of in di vi du al ph as e cu rr en t differential function d er iv e eq ua tio n to ca lc ul at e di ffe re nt ...
Page 111
1. Instantaneous values of currents (samples) from hv, and lv sides for two- winding power transformers, and from the hv, the first lv, and the second lv sides for three-winding power transformers. 2. Currents from all power transformer sides expressed as fundamental frequency phasors, with their re...
Page 112
Idunre idmag_a 2nd harmonic 5th harmonic wave block ida and cross block from b or c phases or ibias tripunre_a pu_a tripres_a blk2h_a blk5h_a blkwav_a ansi05000168_2_en.Vsd a b b>a or and cross block to b or c phases and and and blkunres block blkres not crossblocken=enabled ansi05000168 v2 en figur...
Page 113
Internal/ external fault discrimin ator t pu_a pu_b pu_c or and extfault intfault trnssens trnsunr en05000167_ansi.Vsd constant ibias a b b>a neg.Seq. Diff current contributions opnegseqdiff=on and blknssen blknsunr block 0 ansi05000167 v1 en figure 39: transformer differential protection simplified...
Page 114
En05000279_ansi.Vsd pu_a pu_b pu_c or pickup blk2h_a blk2h_b blk2h_c or blk2h blkwav_a blkwav_b blkwav_c or blkwav blk5h_a blk5h_b blk5h_c or blk5h ansi05000279 v1 en figure 41: transformer differential protection internal grouping of logical signals logic in figures 38 , 39 , 40 and 41 can be summa...
Page 115
Common trip trip are issued. This feature is called the sensitive negative sequence differential protection. 5. If a pickup signal is issued in a phase (see signal pu_a), even if the fault has been classified as an external fault, then the instantaneous differential current of that phase (see signal...
Page 116
6.1.4 technical data table 28: t2wpdif, t3wpdif (87t) technical data function range or value accuracy operating characteristic adaptable ± 1.0% of in for i ± 1.0% of i for i > in reset ratio >94% - unrestrained differential current limit (1.00-50.00)x ibase on high voltage winding ± 1.0% of set valu...
Page 117
6.2.2 introduction the 1ph high impedance differential protection (hzpdif, 87) function can be used when the involved cts have the same turns ratio and similar magnetizing characteristics. It utilizes an external summation of the currents in the interconnected cts, a series resistor, and a voltage d...
Page 118
6.2.5 settings table 31: hzpdif (87) group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation disabled enabled - - disabled disable/enable operation alarmpickup 2 - 500 v 1 10 alarm voltage level on ct secondary talarm 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 5.000 time delay to activate ala...
Page 119
Alarmpickup alarmpickup 0-talarm 0 0.03s 0 en05000301_ansi.Vsd ansi05000301 v1 en figure 44: logic diagram for 1ph high impedance differential protection hzpdif (87) 6.2.8 technical data table 33: hzpdif (87)technical data function range or value accuracy operate voltage (20-400) v i=v/r ± 1.0% of i...
Page 120
6.3.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number generator differential protection genpdif i d > symbol-nn v1 en 87g 6.3.2 functionality short circuit between the phases of the stator windings causes normally very large fault c...
Page 121
An open ct circuit condition creates unexpected operations for generator differential protection under the normal load conditions. It is also possible to damage secondary equipment due to high voltage produced from open ct circuit outputs. Therefore, it may be a requirement from security and reliabi...
Page 122
Table 35: genpdif (87g) output signals name type description trip boolean general, common trip signal tripres boolean trip signal from restrained differential protection tripunre boolean trip signal from unrestrained differential protection trnsunr boolean trip signal from unrestrained negative sequ...
Page 123
Table 37: genpdif (87g) group settings (advanced) name values (range) unit step default description endsection1 0.20 - 1.50 ib 0.01 1.25 end of section 1, multiple of generator rated current endsection2 1.00 - 10.00 ib 0.01 3.00 end of section 2, multiple of generator rated current slopesection2 10....
Page 124
Iec06000430-2-en.Vsd iec06000430 v2 en figure 46: position of current transformers; the recommended (default) orientation if the fault is internal, the faulty generator must be quickly tripped, that is, disconnected from the network, the field breaker tripped and the power to the prime mover interru...
Page 125
6.3.6.1 function calculation principles to make a differential protection as sensitive and stable as possible, the restrained differential characteristic is used. The protection must be provided with a proportional bias, which makes the protection operate for a certain percentage differential curren...
Page 126
Ian iat ian iat idiff ansi0700018_3_en.Vsd ansi07000018 v3 en figure 47: internal fault ian iat external fault: ian = - iat ian iat idiff = 0 en07000019-2_ansi.Vsd ansi07000019 v2 en figure 48: external fault generator differential protection genpdif (87g) function uses two mutually independent char...
Page 127
• the non-stabilized (instantaneous unrestrained) differential protection • the stabilized differential protection the non-stabilized (instantaneous) differential protection is used for very high differential currents, where it must be beyond any doubt, that the fault is internal. This limit, (defin...
Page 128
The protected machine at rated load, the restrain, bias current will be around 1 p.U., that is, equal to the machine rated current. In section 2, a certain minor slope is introduced which is supposed to cope with false differential currents proportional to higher than normal currents through the cur...
Page 129
Section 1 operate conditionally unrestrainedlimit section 2 section 3 restrain operate unconditionally 5 4 3 2 1 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 idmin endsection1 endsection2 restrain current [ times ibase ] operate current [ times ibase ] slopesection2 slopesection3 en06000637.Vsd tempidmin iec06000637 v2 en figure ...
Page 130
This dc desensitization is not active, if a disturbance has been detected and characterized as internal fault. 6.3.6.3 supplementary criteria to relieve the burden of constructing an exact optimal operate-restrain characteristic, two special features supplement the basic stabilized differential prot...
Page 131
Sequence system, faults can be distinguished as internal or external, even for three- phase faults. The internal or external fault discriminator responds to the relative phase angles of the negative sequence fault currents at both ends of the stator winding. Observe that the source of the negative s...
Page 132
Internal fault region 0 deg 180 deg 90 deg 270 deg 120 deg angle could not be measured. One or both currents too small negseqroa (relay operate angle) iminnegseq internal / external fault boundary. Default ± 60 deg external fault region the characteristic is defined by the settings: iminnegseq and n...
Page 133
Protected generator. Operation of this protection is signaled on the output of the function as trnsens. 6.3.6.4 harmonic restrain harmonic restrain is the classical restrain method traditionally used with power transformer differential protections. The goal there was to prevent an unwanted trip comm...
Page 134
6.3.6.6 simplified block diagrams the principle design of the generator differential protection is shown in figure 52 . Calculation idiff and ibias calculation instantaneous idiff pickup and trip logic trip signals pickup signals block signals intern/ extern fault phasors ian, ibn,icn phasors iat, i...
Page 135
Idunre idmag_a 2nd and 5th harmonic id_a and cross block from b or c opcrossblock=yes or not ibias tripunre_a pu_a tripres_a blkh ansi07000020-3-en.Vsd a b b>a and and and and blkunres block blkres cross block to b or c ansi07000020 v3 en figure 53: generator differential logic diagram 1. Internal/ ...
Page 136
En07000022_ansi.Vsd pu_a pu_b pu_c or pickup blkh_a blkh_b blkh_c or blkh ansi07000022 v1 en figure 55: generator differential logic diagram 3. En07000023_ansi.Vsd tripres_a tripres_b tripres_c or tripres tripunre_a tripunre_b tripunre_c or tripunre or trip trnsunr trnssens ansi07000023 v1 en figure...
Page 137
Function range or value accuracy operate time, unrestrained function 20 ms typically at 0 to 5 x set level - reset time, unrestrained function 40 ms typically at 5 to 0 x set level - operate time, negative sequence unrestrained function 15 ms typically at 0 to 5 x set level - critical impulse time, ...
Page 138
132.
Page 139
Section 7 impedance protection 7.1 underimpedance protection for generators and transformers zgcpdis (21g) 7.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number underimpedance protection for generators and transformers zgcpdis 21g 7...
Page 140
En07000117.Vsd jx operation area operation area r operation area no operation area no operation area iec07000117 v1 en figure 57: load encroachment influence on the offset mho z3 characteristic 7.1.3 function block ansi10000122-2-en.Vsd zgcpdis (21g) i3p* v3p* block blkz ldcnd trip trz1 trz2 trz3 pi...
Page 141
Table 41: zgcpdis (21g) output signals name type description trip boolean general trip trz1 boolean trip signal zone1 trz2 boolean trip signal zone2 trz3 boolean trip signal zone3 pickup boolean pickup pu_z1 boolean start signal zone1 pu_z2 boolean start signal zone2 z3_pu boolean start signal zone3...
Page 142
Table 44: zgcpdis (21g) non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description globalbasesel 1 - 6 - 1 1 selection of one of the global base value groups 7.1.6 operation principle 7.1.6.1 full scheme measurement the execution of the different fault loops for phase-to-phase faul...
Page 143
R jx mho, zone3 mho, zone2 mho, zone1 iec09000172_1_en.Vsd iec09000172 v1 en figure 59: mho, offset mho characteristic zone 3 can be equipped with a load encroachment function which cuts off a section of the characteristic when enabled. The function is activated by setting the parameter loadenchmodz...
Page 144
Impedanceang x r z1 fw d z1 re v iec10000176-2-en.Vsd iec10000176 v2 en figure 60: mho, offset mho characteristic for zone 1 with setting parameters z1fwd, z1rev and impedanceang the measuring loops can be time delayed individually by setting the parameter tzx (where x is 1-3 depending on selected z...
Page 145
7.1.6.4 theory of operation the mho algorithm is based on the phase comparison of a operating phasor and a polarizing phasor. When the operating phasor leads the polarizing phasor by more than 90 degrees, the function operates and gives a trip output. The characteristic for offset mho is a circle wh...
Page 146
ß v i ab· x i ab· r × zxfwd ab i - × zxrev ab i 2 ( ) = + × zxrev ab ab vcomp v i 1 ( ) = - × zxfwd ab ab vcomp v i ansi09000174_2_en.Vsd ansi09000174 v2 en figure 61: simplified offset mho characteristic and voltage vectors for phase a-to- b fault. Operation occurs if 90≤β≤270. 7.1.7 technical data...
Page 147
7.2 loss of excitation lexpdis (40) 7.2.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number loss of excitation lexpdis symbol-mm v1 en 40 7.2.2 functionality there are limits for the low excitation of a synchronous machine. A reductio...
Page 148
7.2.4 signals table 46: lexpdis (40) input signals name type default description i3p group signal - current group connection v3p group signal - voltage group connection block boolean 0 block of function blktrz1 boolean 0 block trip of zone z1 blktrz2 boolean 0 block trip of zone z2 table 47: lexpdis...
Page 149
Name values (range) unit step default description operationz2 disabled enabled - - enabled operation disable/enable zone z2 xoffsetz2 -1000.00 - 1000.00 % 0.01 -10.00 offset of z2 circle top point along x axis in % of zbase z2diameter 0.01 - 3000.00 % 0.01 200.00 diameter of imedance circle for z2 i...
Page 150
Measured mode measured apparent impedance z posseq posseq posseq v i = equation2051-ansi v1 en (equation 31) there are three characteristics in lexpdis (40) protection as shown in figure 63 . Naimly: • offset mho circle for z1 • offset mho circle for z2 • directional blinder r x underexcitation prot...
Page 151
In lexpdis (40) function the zone measurement is done as shown in figure 64 . R offset z1 or z2 xoffsetz1 z1diameter z (apparent impedance) z1 = z - (xoffsetz1 + z1diameter/2) en06000456-2.Vsd iec06000456 v2 en figure 64: zone measurement in lexpdis (40) protection function the impedance z1 is const...
Page 152
R x underexcitation protection restrain area dirangle xoffsetdirline z (apparent impedance) en06000457.Vsd iec06000457 v1 en figure 65: impedance constructed as xoffsetdirline in lexpdis (40) protection lexpdis (40) function is schematically described in figure 66 . Section 7 1mrk 502 043-uus b impe...
Page 153
En06000458- 2_ansi.Vsd apparent impedance calculation positive sequence current phasor positive sequence voltage phasor z z in z1 char. Z in z2 char. Dir. Restrain or dir.Restrain enabled and and pickupz1 0 tripz1 tripz2 tz1 tz2 0 pickupz2 ansi06000458 v2 en figure 66: simplified logic diagram of le...
Page 154
7.3.2 functionality out-of-step protection (oosppam, 78) function in the ied can be used both for generator protection application as well as, line protection applications. The main purpose of the oosppam, 78 function is to detect, evaluate, and take the required action during pole slipping occurren...
Page 155
7.3.4.2 oosppam outputsignals table 54: output signals for the function block oosppam (psp1-) signal description trip common trip, issued when either zone 1 or zone 2 give trip tripz1 zone 1 trip tripz2 zone 2 trip start set when measured impedance enters lens characteristic genmode generator rotate...
Page 156
Table 56: advanced general settings for the function oosppam (psp1-) parameter range step default unit description startangle 90.0 - 130.0 0.1 110.0 deg angle between two rotors to get the start signal, in deg tripangle 15.0 - 90.0 0.1 60.0 deg maximum rotor angle to allow trip signals, in deg table...
Page 157
7.3.6 monitored data table 59: oosppam (78) monitored data name type values (range) unit description voltage real - kv magnitude of the measured positive-sequence voltage, in v current real - a magnitude of the measured positive-sequence current, in a r real - ohm real part of measured positive-sequ...
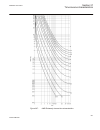
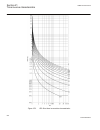
Page 158
-1.5 -1 -0.5 0 0.5 1 1.5 -1 -0.5 0 0.5 1 1.5 ------- ------ ------ ----- ----- ----- ----- ----- --- -- --- - --- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- ---- ---- ---- ---- ------ real part (r) of z in ohms im a g in a ry p a rt ( x ) o f z in o h m s ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ...
Page 159
Rotor (power) angle δ can be thought of as the angle between the two lines, connecting point 0 in figure 68 , that is, z(r, x) under normal load, with the points se and re, respectively. These two lines are not shown in figure 68 . Normal values of the power angle, that is, under stable, steady-stat...
Page 160
-1 -0.5 0 0.5 1 1.5 -1 -0.8 -0.6 -0.4 -0.2 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 ------ ------ ----- ---- ---- ---- ----- ----- ----- ---- --- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- ---- ---- ---- --- real part (r) of z in ohms → im ag ina ry pa rt (x ) o f z in o hm s → ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ...
Page 161
-0.8 -0.6 -0.4 -0.2 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 -0.6 -0.4 -0.2 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 ---- --- --- --- --- --- --- -- -- -- -- -- --- -- --- --- -- - -- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -- - -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --- --- --- --- - real part (r) of z in ohms im a g in a ry p a r...
Page 162
Zeq(req, xeq), and the setting pickupangle, for example 120 degrees. All impedances must be referred to the voltage level where the out-of-step protection relay is placed; in this case shown in figure 72 this is the generator nominal voltage level. The impedances from the position of the out-of-step...
Page 163
Results in a tendency to miss the 1st pole-slip, that one immediately after the fault has been cleared.) the above timing is used to discriminate a fault from an out-of-step condition. In figure 68 , some important points on the trajectory of z(r, x) are designated. Point 0: the pre-fault, normal lo...
Page 164
Pickupangle = 130° → fsmax = 25 ⋅ 0.277 = 6.944 hz the minimum value of fsmax is 6.994 hz. When pickupangle = 110degrees, fsmax = 7.777hz. This implies, that the default pickupangle = 110 degrees covers 90% of cases as, the typical final slip frequency is between 2 - 5hz. In practice, however, befor...
Page 165
The second method this method is more exact. If the break-time of the circuit breaker is known, (and specified as the setting tbreaker) than it is possible to initiate a trip (break) command almost exactly tbreaker milliseconds before the rotor (power) angle reaches 0 degrees, where the currents are...
Page 166
0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 -5 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 c urr en t i n ka , t rip c om m and to c b , r ot or ang le in ra d → time in milliseconds → pos. Seq. Current in ka trip command to cb rotor angle in radian fault occurs ← normal load current ← min. Current very high currents due to out-of-step ...
Page 167
Iec10000116-2-en.Vsd genmode calculation of r and x parts of the complex positive - sequence impedance z(r, x) upsre upsim upsmag r ipsre ipsim z(r,x) z(r,x) within limit of reach? X no return yes z(r,x) within lens characteristic? No yes z(r,x) entered lens from? Function alert right left z(r,x) ex...
Page 168
7.4.2 functionality heavy load transfer is common in many power networks and may make fault resistance coverage difficult to achieve. In such a case, load encroachment (lepdis) function can be used to prevent operation of the of the underimpedance measuring zones during heavy loads. 7.4.3 function b...
Page 169
Table 64: lepdis non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description globalbasesel 1 - 6 - 1 1 selection of one of the global base value groups 7.4.6 operation principle the basic impedance algorithm for the operation of load encroachment lepdis is the same as for the distan...
Page 170
R x rld rld ldangle ldangle ldangle ldangle ansi10000144-2-en.Vsd ansi10000144 v2 en figure 77: characteristic of load encroachment function the reach is limited by the minimum operation current and the distance measuring zones. 7.4.6.2 simplified logic diagrams figure 78 schematically presents the ...
Page 171
Ansi10000226-2-en.Vsd & & & bool to integer dlecnd block & block 0 3 0.1 i 0 3 0.4 phmax i i × & or 0 3 0.05 i ³ 0 3 0.2 phmax i i ³ × r x a ab & 0 10 ms 20 ms 0 ansi10000226 v2 en figure 78: phase-to-phase ab operating conditions (residual current criteria) special attention is paid to correct phas...
Page 172
166.
Page 173
Section 8 current protection 8.1 four step phase overcurrent protection 3-phase output oc4ptoc (51/67) 8.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number four step phase overcurrent protection 3-phase output oc4ptoc 4 4 alt 3i> t...
Page 174
8.1.3 function block ansi08000002-2-en.Vsd oc4ptoc (51_67) i3p* v3p* block blk1 blk2 blk3 blk4 trip trst1 trst2 trst3 trst4 pickup pu_st1 pu_st2 pu_st3 pu_st4 pu_a pu_b pu_c 2ndharm ansi08000002 v2 en figure 79: oc4ptoc (51/67) function block 8.1.4 signals table 66: oc4ptoc (51_67) input signals nam...
Page 175
Name type description pu_st1 boolean start signal from step 1 pu_st2 boolean start signal from step 2 pu_st3 boolean start signal from step 3 pu_st4 boolean start signal from step 4 pu_a boolean pickup signal from phase a pu_b boolean pickup signal from phase b pu_c boolean pickup signal from phase ...
Page 176
Name values (range) unit step default description dirmodesel2 disabled non-directional forward reverse - - non-directional directional mode of step 2 off / non- directional / forward / reverse pickup2 5 - 2500 %ib 1 500 phase current operate level for step 2 in % of ibase t2 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0...
Page 177
Table 69: oc4ptoc (51_67) group settings (advanced) name values (range) unit step default description 2ndharmstab 5 - 100 %ib 1 20 pickup of second harm restraint in % of fundamental harmrestrain1 disabled enabled - - disabled enable block of step 1 from harmonic restrain harmrestrain2 disabled enab...
Page 178
8.1.7 operation principle the protection design can be decomposed in four parts: • the direction element • the harmonic restraint blocking function • the four step over current function • the mode selection if vt inputs are not available or not connected, setting parameter dirmodeselx shall be left ...
Page 179
Overcurrent protection 3-phase output function oc4ptoc (51/67), it is possible to select the type of the measurement used for all overcurrent stages. It is possible to select either discrete fourier filter (dft) or true rms filter (rms). If dft option is selected then only the rms value of the funda...
Page 180
_ _ ref ca c a dir ca c a v v v i i i = - = - ansiequation1451 v1 en (equation 35) phase-ground short circuit: _ _ ref a a dir a a v v i i = = ansiequation1452 v1 en (equation 36) _ _ ref b b dir b b v v i i = = ansiequation1453 v1 en (equation 37) _ _ ref c c dir c c v v i i = = ansiequation1454 v1...
Page 181
V ref i dir ansi09000636-1-en.Vsd 1 2 2 3 4 ansi09000636 v1 en figure 81: directional characteristic of the phase overcurrent protection 1 rca = relay characteristic angle 55° 2 roa = relay operating angle 80° 3 reverse 4 forward if no blockings are given the pickup signals will start the timers of ...
Page 183
Function setting range accuracy reset time, directional pickup function 35 ms typically at 2 to 0 x i set - critical impulse time 10 ms typically at 0 to 2 x i set - impulse margin time 15 ms typically - 1) note: timing accuracy only valid when 2nd harmonic blocking is turned off 8.2 four step resid...
Page 184
Other setting combinations are possible, but not recommended. Second harmonic blocking restraint level can be set for the function and can be used to block each step individually. 8.2.3 function block ansi08000004-2-en.Vsd ef4ptoc (51n_67n) i3p* v3p* i3ppol* i3pdir* block blk1 blk2 blk3 blk4 trip tr...
Page 185
Table 74: ef4ptoc (51n_67n) output signals name type description trip boolean common trip signal trst1 boolean trip signal from step 1 trst2 boolean trip signal from step 2 trst3 boolean trip signal from step 3 trst4 boolean trip signal from step 4 pickup boolean general pickup signal pu_st1 boolean...
Page 186
Name values (range) unit step default description dirmodesel1 disabled non-directional forward reverse - - non-directional directional mode of step 1 (off, non- directional, forward, reverse) characterist1 ansi ext. Inv. Ansi very inv. Ansi norm. Inv. Ansi mod. Inv. Ansi def. Time l.T.E. Inv. L.T.V....
Page 187
Name values (range) unit step default description harmrestrain3 disabled enabled - - enabled enable block of step 3 from harmonic restrain dirmodesel4 disabled non-directional forward reverse - - non-directional directional mode of step 4 (off, non- directional, forward, reverse) characterist4 ansi ...
Page 188
8.2.6 monitored data table 77: ef4ptoc (51n_67n) monitored data name type values (range) unit description stdir integer 0=no direction 1=forward 2=reverse 3=both - fault direction coded as integer iop real - a operating current level vpol real - kv polarizing voltage level ipol real - a polarizing c...
Page 189
• parallel connection of current instrument transformers in all three phases (holm-green connection). • one single core balance, current instrument transformer (cable ct). • one single current instrument transformer located between power system wye point and ground (that is, current transformer loca...
Page 190
Voltage polarizing when voltage polarizing is selected the protection will use either the residual voltage 3v 0 or the negative sequence voltage v 2 as polarizing quantity v3p. The residual voltage can be: 1. Directly measured (when a dedicated vt input of the ied is connected in pcm600 to the fourt...
Page 191
The polarizing phasor is used together with the phasor of the operating directional current, in order to determine the direction to the ground fault (forward/reverse). In order to enable voltage polarizing the magnitude of polarizing voltage shall be bigger than a minimum level defined by setting pa...
Page 192
2 ipol = (ia+alpha ib+alpha ic)/3 × × ansiequation2406 v2 en (equation 44) where: ia, ib and ic are fundamental frequency phasors of three individual phase currents. Alpha phasor with an angle of 120 degrees. The polarizing current is pre-processed by a discrete fourier filter. Thus the phasor of th...
Page 193
Point and ground (current transformer located in the wye point of a wye connected transformer winding). • for some special line protection applications this dedicated ied ct input can be connected to parallel connection of current transformers in all three phases (holm-green connection). 2. Calculat...
Page 194
1. Distance protection directional function. 2. Negative sequence based overcurrent function. 8.2.7.5 base quantities within the protection the base quantities are entered as global settings for all functions in the ied. Base current (ibase) shall be entered as rated phase current of the protected o...
Page 195
Available. For the complete list of available inverse curves please refer to section "inverse time characteristics" . • time delay related settings. By these parameter settings the properties like definite time delay, minimum operating time for inverse curves and reset time delay are defined. • supe...
Page 196
Setting polmethod. The polarizing quantity will be selected by the function in one of the following three ways: 1. When polmethod = voltage, vpol will be used as polarizing quantity. 2. When polmethod = current, ipol will be used as polarizing quantity. 3. Whenpolmethod = dual, vpol + ipol · znpol w...
Page 198
Purev 0.6 * idirpu pufw -rca -85 deg 40% of idir idir rca 65 deg v pol = - v 2 i = 3i op 2 rca +85 deg rca -85 deg characteristic for purev operating area operating area characteristic for pufw characteristic for reverse release of measuring steps characteristic for forward release of measuring step...
Page 199
1. Pufw=1 when operating quantity magnitude iop x cos(φ - anglerca) is bigger than setting parameter idirpu and directional supervision element detects fault in forward direction. 2. Purev=1 when operating quantity magnitude iop x cos(φ - anglerca) is bigger than 60% of setting parameter idirpu and ...
Page 200
8.2.8 technical data table 78: ef4ptoc (51n/67n) technical data function range or value accuracy operate current (1-2500)% of lbase ± 1.0% of i n at i n ± 1.0% of i at i > i n reset ratio > 95% - operate current for directional comparison, zero sequence (1–100)% of lbase ± 2.0% of i n operate curren...
Page 201
8.3 sensitive directional residual overcurrent and power protection sdepsde (67n) 8.3.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number sensitive directional residual over current and power protection sdepsde - 67n 8.3.2 functionali...
Page 202
8.3.4 signals table 79: sdepsde (67n) input signals name type default description i3p group signal - three phase group signal for current inputs v3p group signal - three phase group signal for voltage inputs block boolean 0 block of function blkvn boolean 0 blocks the non-directional voltage residua...
Page 203
Name values (range) unit step default description rcadir -179 - 180 deg 1 -90 relay characteristic angle rca rcacomp -10.0 - 10.0 deg 0.1 0.0 relay characteristic angle compensation roadir 0 - 90 deg 1 90 relay open angle roa used as release in phase mode incosphipu 0.25 - 200.00 %ib 0.01 1.00 set l...
Page 204
Name values (range) unit step default description tvn 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.100 time delay for non-directional residual overvoltage inrelpu 0.25 - 200.00 %ib 0.01 1.00 residual release current for all directional modes, in % of ibase vnrelpu 1.00 - 300.00 %vb 0.01 3.00 residual release volt for a...
Page 205
8.3.7.2 directional residual current protection measuring 3i 0 ·cos φ φ is defined as the angle between the residual current 3i 0 and the reference voltage. Vref = -3v 0 e jrcadir , that is -3v 0 rotated by the set characteristic angle rcadir (φ=ang(3i 0 )-ang(v ref ) ). Rcadir is normally set equal...
Page 206
-3v 0 3i 0 rca = -90 °, roa = 90° = ang(3i 0 ) – ang(v ref ) 3i 0 cos v ref en06000649_ansi.Vsd ansi06000649 v1 en figure 91: rcadir set to -90° for trip, both the residual current 3i 0 ·cos φ and the release voltage 3v 0 , must be larger than the set levels: incosphipu and vnrelpu. When the functio...
Page 207
-3v 0 =v ref 3i 0 rca = 0 ° 3i 0 cos operate area roa en06000650_ansi.Vsd ansi06000650-2- vsd v ref =- 3v o ansi06000650 v2 en figure 92: characteristic with roadir restriction the function indicates forward/reverse direction to the fault. Reverse direction is defined as 3i 0 ·cos (φ + 180°) ≥ the s...
Page 208
-3v 0 =v ref rca = 0 ° operate area instrument transformer angle error 3i 0 (prim) 3i 0 (to prot) a characteristic after angle compensation rcacomp en06000651_ansi.Vsd ansi06000651 v1 en figure 93: explanation of rcacomp 8.3.7.3 directional residual power protection measuring 3i 0 · 3v 0 · cos φ φ i...
Page 209
This sub-function has the possibility of choice between definite time delay and inverse time delay. The inverse time delay is defined as: t tdsn i v reference i v measured inv = ⋅ ⋅ ⋅ ⋅ ⋅ ( cos ( )) cos ( ) 3 3 3 3 0 0 0 0 ϕ ϕ equation2032-ansi v2 en (equation 49) 8.3.7.4 directional residual curren...
Page 210
The function indicate forward/reverse direction to the fault. Reverse direction is defined as φ is within the angle sector: rcadir + 180° ± roadir this sub-function has definite time delay. 8.3.7.5 directional functions for all the directional functions there are directional pickup signals pufw: fau...
Page 211
When the function is activated binary output signal puvn is activated. If the output signals are active after the set delay tvnnondir trip and trun are activated. A simplified logical diagram of the total function is shown in figure 95 . En06000653_ansi.Vsd innondirpu un_pu opmode=incosphi pickup_n ...
Page 212
8.3.8 technical data table 84: sdepsde (67n) technical data function range or value accuracy operate level for 3i 0 ·cosj directional residual overcurrent (0.25-200.00)% of lbase at low setting: (2.5-10) ma (10-50) ma ± 1.0% of i n at i £ i n ± 1.0% of i at i > i n ± 0.5 ma ± 1.0 ma operate level fo...
Page 213
Function range or value accuracy operate time, non-directional residual overvoltage 70 ms typically at 0.8 to 1.5 x u set - reset time, non-directional residual overvoltage 120 ms typically at 1.2 to 0.8 x u set - operate time, directional residual over current 260 ms typically at 0.5 to 2 x i set -...
Page 214
Two warning pickup levels are available. This enables actions in the power system to be done before dangerous temperatures are reached. If the temperature continues to increase to the trip value, the protection initiates a trip of the protected transformer/ generator. 8.4.3 function block ansi080000...
Page 215
8.4.5 settings table 87: trpttr (49) group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation disabled enabled - - disabled disable/enable operation iref 10.0 - 1000.0 %ib 1.0 100.0 reference current in % of ibase ibase1 30.0 - 250.0 %ib 1.0 100.0 base current ibase1 withou...
Page 216
8.4.6 monitored data table 89: trpttr (49) monitored data name type values (range) unit description ttrip real - - estimated time to trip (in min) ttripcal integer - - calculated time status to trip: not active/long time/active trescal integer - - calculated time status to reset: not active/long tim...
Page 217
If final n q > q equation1172 v1 en (equation 51) ( ) 1 1 1 t n n final n e t d - - - æ ö q = q + q - q × - ç ÷ è ø equation1173 v1 en (equation 52) if final n q equation1174 v1 en (equation 53) ( ) 1 t n final final n e t d - - q = q - q - q × equation1175 v1 en (equation 54) where: q n is the calc...
Page 218
After a trip, caused by the thermal overload protection, there can be a lockout to reconnect the tripped circuit. The output lockout signal lockout is activated when the temperature of the object is above the set lockout release temperature setting reslo. The time to lockout release is calculated, t...
Page 219
Calculation of final temperature i3p calculation of heat content final temp > triptemp actual heat comtent actual temp > alarm1,alarm2 temp actual temp > triptemp alarm1 trip actual temp temp pickup calculation of time to trip calculation of time to reset of lockout ttrip treslo management of settin...
Page 220
8.4.8 technical data table 90: trpttr (49) technical data function range or value accuracy base current 1 and 2 (30–250)% of ibase ± 1.0% of i n operate time: 2 2 2 2 ln p b i i t i i t æ ö - ç ÷ = × ç ÷ - è ø equation1356 v1 en (equation 57) i = i measured i p = load current before overload occurs ...
Page 221
Current check with extremely short reset time is used as check criterion to achieve high security against unnecessary operation. Contact check criteria can be used where the fault current through the breaker is small. Breaker failure protection, 3-phase activation and output (ccrbrf, 50bf) current c...
Page 222
8.5.5 settings table 93: ccrbrf (50bf) group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation disabled enabled - - disabled disable/enable operation functionmode current contact current&contact - - current detection principle for back-up trip butripmode 2 out of 4 1 out o...
Page 223
8.5.7 operation principle breaker failure protection, 3-phase activation and output ccrbrf (50bf) is initiated from protection trip command, either from protection functions within the ied or from external protection devices. The initiate signal is general for all three phases. A re-trip attempt can...
Page 224
And and and and and or or or a b a>b and a b a>b and time out a bfp started a reset a 52a_a i_a current high a contact closed a ansi09000977-1-en.Vsd functionmode or or current contact current and contact 1 cb closed a pickup_ph pickup_blkcont ansi09000977 v1 en figure 99: simplified logic scheme of...
Page 225
Function range or value accuracy phase current pickup for blocking of contact function (5-200)% of lbase ± 1.0% of i n at i £ i n ± 1.0% of i at i > i n reset ratio > 95% - timers (0.000-60.000) s ± 0.5% ±10 ms operate time for current detection 35 ms typically - reset time for current detection 10 ...
Page 226
8.6.3 function block ansi08000041-1-en.Vsd ccrpld (52pd) i3p* block closecmd opencmd extpdind trip pickup ansi08000041 v1 en figure 101: ccrpld (52pd) function block 8.6.4 signals table 98: ccrpld (52pd) input signals name type default description i3p group signal - three phase group signal for curr...
Page 227
Name values (range) unit step default description currentsel disabled cb oper monitor continuous monitor - - disabled current function selection currunsympu 0 - 100 % 1 80 unsym magn of lowest phase current compared to the highest. Currrelpu 0 - 100 %ib 1 10 current magnitude for release of the func...
Page 228
Ansi_en05000287.Vsd polediscrepancy signal from c.B. + c.B. 52b 52b 52b 52a 52a 52a ansi05000287 v1 en figure 102: pole discrepancy external detection logic this binary signal is connected to a binary input of the ied. The appearance of this signal will start a timer that will give a trip signal aft...
Page 229
Block pd signal from cb and extpdind unsymmetrical current detection or closecmd opencmd ttrip+200 ms and or and trip 150 ms cb oper monitor ansi08000014-2-en.Vsd 0 0-trip ansi08000014 v2 en figure 103: simplified block diagram of pole discrepancy function - contact and current based the pole discre...
Page 230
8.6.7.2 unsymmetrical current detection unsymmetrical current indicated if: • any phase current is lower than currunsympu of the highest current in the three phases. • the highest phase current is greater than currrelpu of ibase. If these conditions are true, an unsymmetrical condition is detected. ...
Page 231
Reactive power flow in the power system. There are a number of applications where such functionality is needed. Some of them are: • detection of reversed active power flow • detection of high reactive power flow each function has two steps with definite time delay. Reset times for both steps can be ...
Page 232
8.7.2.3 signals table 104: goppdop (32) input signals name type default description i3p group signal - three phase group signal for current inputs v3p group signal - three phase group signal for voltage inputs block boolean 0 block of function blk1 boolean 0 block of step 1 blk2 boolean 0 block of s...
Page 233
Name values (range) unit step default description power2 0.0 - 500.0 % 0.1 1.0 power setting for stage 2 in % of calculated power base value angle2 -180.0 - 180.0 deg 0.1 0.0 characteristic angle for stage 2 tripdelay2 0.010 - 6000.000 s 0.001 1.000 trip delay for stage 2 table 107: goppdop (32) gro...
Page 234
8.7.3.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number directional underpower protection guppdup p symbol-ll v1 en 37 8.7.3.2 function block ansi08000507-1-en.Vsd guppdup (37) i3p* v3p* block blk1 blk2 trip trip1 trip2 bfi_3p picku...
Page 235
Name type description pickup1 boolean pickup signal from stage 1 pickup2 boolean pickup signal from stage 2 p real active power ppercent real active power in % of calculated power base value q real reactive power qpercent real reactive power in % of calculated power base value 8.7.3.4 settings table...
Page 236
Table 114: guppdup (37) non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description globalbasesel 1 - 6 - 1 1 selection of one of the global base value groups mode a, b, c arone pos seq ab bc ca a b c - - pos seq mode of measurement for current and voltage 8.7.3.5 monitored data tab...
Page 237
Chosen current phasors chosen voltage phasors complex power calculation p derivation of s( composant) in char angle s( angle) s( angle) power1 t trip 1 pickup1 q p = powre q = powim s( angle) power2 trip2 pickup2 0 t 0 ansi06000438-2-en.Vsd ansi06000438 v2 en figure 106: simplified logic diagram of ...
Page 238
Set value: mode formula used for complex power calculation ca * * ( ) ca c a s v i i = × - equation2060-ansi v1 en (equation 63) a * 3 a a s v i = × × equation2061-ansi v1 en (equation 64) b * 3 b b s v i = × × equation2062-ansi v1 en (equation 65) c * 3 c c s v i = × × equation2063-ansi v1 en (equa...
Page 239
Will make slower measurement response to the step changes in the measured quantity. Filtering is performed in accordance with the following recursive formula: s td s td s old calculated = ⋅ + − ( ) ⋅ 1 equation1959-ansi v1 en (equation 67) where s is a new measured value to be used for the protectio...
Page 240
8.8.2 functionality inadvertent or accidental energizing of off-line generators has occurred often enough due to operating errors, breaker head flashovers, control circuit malfunctions, or a combination of these causes. Inadvertently energized generator operates as induction motor drawing a large cu...
Page 241
8.8.5 settings table 120: aeggapc (50ae) group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation disabled enabled - - disabled disable/enable operation ipickup 2 - 900 %ib 1 120 phase current pickup in % of ibase toc 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.030 trip time daly for overcurr...
Page 242
Three phases is larger than ipickup for the period toc then the trip signal becomes activated. Also pickup signal becomes activated when overcurrent is detected. When the maximum phase-to-phase voltage is larger than 59_drop_out for the period tdisarm, it is ensured generator is on line. During this...
Page 243
Function range or value accuracy impulse margin time, overcurrent 15 ms typically - operate value, undervoltage (2-200)% of vbase ± 0.5% of v n at v n ± 0.5% of v at v>v n critical impulse time, undervoltage 10 ms typically at 2 to 0 x v set - impulse margin time, undervoltage 15 ms typically - oper...
Page 244
To provide an effective protection for the generator for external unbalanced conditions, ns2ptoc (46i2) is able to directly measure the negative sequence current. Ns2ptoc (46i2) also has a time delay characteristic which matches the heating characteristic of the generator 2 2 i t k = as defined in s...
Page 245
Table 125: ns2ptoc (46i2) output signals name type description trip boolean common trip signal trst1 boolean trip signal for step 1 trst2 boolean trip sognal for step 2 pickup boolean common start signal pu_st1 boolean pickup signal for step 1 pu_st2 boolean pickup signal for step2 alarm boolean ala...
Page 246
Table 127: ns2ptoc (46i2) non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description globalbasesel 1 - 6 - 1 1 selection of one of the global base value groups 8.9.6 monitored data table 128: ns2ptoc (46i2) monitored data name type values (range) unit description nscurr real - a ne...
Page 247
When the parameter curvetype1 is set to inverse, an inverse curve is selected according to selected value for parameter k1. The minimum trip time setting of parameter t1min and reset time parameter resetmultip1 also influence step operation. However, to match the heating characteristics of the gener...
Page 248
Resettime s resetmultip i i ns pickup [ ] − = ⋅ 2 1 k k1 ansiequation2111 v1 en (equation 68) where i ns is the measured negative sequence current i pickup is the desired pickup level in pu of rated generator current resetmultip is multiplier of the generator capability constant k equal to setting...
Page 249
8.9.7.3 logic diagram ansi08000466-3-en.Vsd operation=enabled blk1 inverse time selected inverse dt time selected pu_st1 trst1 and or block a b a>b negative sequence current i2-1> 0 0-t1 ansi08000466 v3 en figure 111: simplified logic diagram for step 1 of negative sequence time overcurrent protecti...
Page 250
Function range or value accuracy time characteristics definite or inverse - inverse time characteristic step 1, 2 2 i t k = k=1.0-99.0 ± 3% or ± 40 ms 1 ≤ k ≤ 20 reset time, inverse characteristic step 1, 2 2 i t k = k=0.01-20.00 ± 10% or ± 50 ms 1 ≤ k ≤ 20 maximum trip delay, step 1 idmt (0.00-6000...
Page 251
8.10.3 function block vr2pvoc (51v) i3p* v3p* block blkoc blkuv trip troc 27 trip pickup pu_oc 27 pu imax vumin ansi10000118-1-en.Vsd ansi10000118 v2 en figure 113: vr2pvoc(51v) function block 8.10.4 signals table 130: input signals for the function block vr2pvoc (vrc1-) signal description i3p three...
Page 252
Table 133: basic parameter group settings for the function vr2pvoc (vrc1-) parameter range step default unit description operation off on - off - operation off / on startcurr 2.0 - 5000.0 1.0 120.0 %ib start current level in % of ibase characterist ansi ext. Inv. Ansi very inv. Ansi norm. Inv. Ansi ...
Page 253
8.10.6 monitored data table 135: vr2pvoc(51v) monitored data name type values (range) unit description imax real - a maximum phase current magnitude vumin real - kv minimum ph-to-ph voltage magnitude 8.10.7 operation principle 8.10.7.1 measured quantities the voltage-restrained time overcurrent prot...
Page 254
Vbase current pickup level pickupcurr vdepfact * pickupcurr vhighlimit 0,25 ansi10000123-1-en.Vsd ansi10000123 v1 en figure 114: example for current pickup level variation as function of measured voltage magnitude in slope mode of operation • voltage controlled overcurrent (when setting parameter vd...
Page 255
Current value for the calculation of operate times for idmt curves (the overcurrent with idmt curve operates faster during low voltage conditions). 8.10.7.4 logic diagram pickupcurr x a b a>b voltage control or restraint feature inverse def time selected inverse time selected or ansi10000214-2-en.Vs...
Page 256
8.10.7.5 undervoltage protection the undervoltage step simply compares the magnitude of the measured voltage quantity with the set pickup level. The undervoltage step picks up if the magnitude of the measured voltage quantity is smaller than the set level. The pickup signal starts a definite time de...
Page 257
Section 9 voltage protection 9.1 two step undervoltage protection uv2ptuv (27) 9.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number two step undervoltage protection uv2ptuv 2u symbol-r-2u-greater-than v1 en 27 9.1.2 functionality u...
Page 258
9.1.4 signals table 137: uv2ptuv (27) input signals name type default description v3p group signal - three phase group signal for voltage inputs block boolean 0 block of function blk1 boolean 0 block of step 1 blk2 boolean 0 block of step 2 table 138: uv2ptuv (27) output signals name type descriptio...
Page 259
Name values (range) unit step default description t1min 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 5.000 minimum operate time for inverse curves for step 1 td1 0.05 - 1.10 - 0.01 0.05 time multiplier for the inverse time delay for step 1 operationstep2 disabled enabled - - enabled enable execution of step 2 opmode2 1 o...
Page 260
Settable for step 1 and can be either definite or inverse time delayed. Step 2 is always definite time delayed. Uv2ptuv (27) can be set to measure phase-to-ground fundamental value, phase-to- phase fundamental value, phase-to-ground true rms value or phase-to-phase true rms value. The choice of the ...
Page 261
Td t vpickup v vpickup = ansiequation1431 v1 en (equation 71) the type b curve is described as: 2.0 480 0.055 vpickup 32 0.5 vpickup td t × = + × - æ ö ç ÷ è ø equation1608 v1 en (equation 72) the lowest voltage is always used for the inverse time delay integration. The details of the different inve...
Page 262
Pickup pu_st1_a pu_st1_b pu_st1_c trst1 pickup pu_st2 trst2 trip minvoltselector pickup & trip output logic step 1 pickup & trip output logic step 2 phase c phase b phase a phase c phase b phase a timer t2 voltage phase selector opmode2 time integrator t1 voltage phase selector opmode1 1 out of 3 2 ...
Page 263
9.1.8 technical data table 142: uv2ptuv (27) technical data function range or value accuracy operate voltage, low and high step (1–100)% of vbase ± 0.5% of v n reset ratio - inverse time characteristics for low and high step, see table 505 - see table 505 definite time delay, step 1 (0.00 - 6000.00)...
Page 264
Ov2ptov (59) has two voltage steps, where step 1 can be set as inverse or definite time delayed. Step 2 is always definite time delayed. Ov2ptov (59) has an extremely high reset ratio to allow settings close to system service voltage. 9.2.3 function block ansi09000278-1-en.Vsd ov2ptov (59) v3p* bloc...
Page 265
9.2.5 settings table 145: ov2ptov (59) group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation disabled enabled - - disabled disable/enable operation operationstep1 disabled enabled - - enabled enable execution of step 1 characterist1 definite time inverse curve a inverse ...
Page 266
9.2.6 monitored data table 147: ov2ptov (59) monitored data name type values (range) unit description v_a real - kv voltage in phase a v_b real - kv voltage in phase b v_c real - kv voltage in phase c 9.2.7 operation principle two step overvoltage protection ov2ptov (59) is used to detect high power...
Page 267
When phase-to-ground voltage measurement is selected the function automatically introduces division of the base value by the square root of three. 9.2.7.1 measurement principle all the three voltages are measured continuously, and compared with the set values, pickup1 and pickup2. The parameters opm...
Page 268
The highest phase (or phase-to-phase) voltage is always used for the inverse time delay integration, see figure 121 . The details of the different inverse time characteristics are shown in section "inverse time characteristics" en05000016_ansi.Vsd voltage inverse time voltage time va vb vc ansi05000...
Page 269
9.2.7.4 design the voltage measuring elements continuously measure the three phase-to-ground voltages or the three phase-to-phase voltages. Recursive fourier filters filter the input voltage signals. The phase voltages are individually compared to the set value, and the highest voltage is used for t...
Page 270
Pickup pu_st1_a pu_st1_b pu_st1_c pu_st1 trst1 pickup pu_st2 trst2 trip comparator v > pickup1 comparator v > pickup1 comparator v > pickup1 maxvoltselector comparator v > pickup2 comparator v > pickup2 comparator v > pickup2 pickup & trip output logic step 1 pickup & trip output logic step 2 phase ...
Page 271
9.2.8 technical data table 148: ov2ptov (59) technical data function range or value accuracy operate voltage, low and high step (1-200)% of vbase ± 0.5% of v n at v n ± 0.5% of v at v > v n reset ratio >95% - inverse time characteristics for low and high step, see table 504 - see table 504 definite ...
Page 272
Two step residual overvoltage protection rov2ptov (59n) function calculates the residual voltage from the three-phase voltage input transformers or measures it from a single voltage input transformer fed from a broken delta or neutral point voltage transformer. Rov2ptov (59n) has two voltage steps, ...
Page 273
9.3.5 settings table 151: rov2ptov (59n) group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation disabled enabled - - disabled disable/enable operation operationstep1 disabled enabled - - enabled enable execution of step 1 characterist1 definite time inverse curve a invers...
Page 274
Adding the input phase voltages. 3v 0 may also be input single phase by either measuring directly from a voltage transformer in the neutral of a power transformer, or from a secondary broken delta connection of a transformer with a wye-grounded primary. Rov2ptov (59n) has two steps with separate tim...
Page 275
T td v vpickup vpickup = ⋅ ⋅ − > > − + 480 32 0 5 0 035 . . Ansiequation2288 v2 en (equation 80) the details of the different inverse time characteristics are shown in section "inverse time characteristics" . Trip signal issuing requires that the residual overvoltage condition continues for at least...
Page 276
Ansi08000013-1-en.Vsd vn pu_st1 trst1 pu_st2 trst2 pickup trip comparator vn > pickup1 pickup & trip output logic step 2 phase 1 phase 1 timer t2 pickup pickup & trip output logic step 1 time integrator t1 comparator vn > pickup2 pickup trip trip or or ansi08000013 v1 en figure 124: schematic design...
Page 277
9.3.8 technical data table 154: rov2ptov (59n) technical data function range or value accuracy operate voltage, step 1 (1-200)% of vbase ± 0.5% of v n at v n ± 0.5% of v at v > v n operate voltage, step 2 (1–100)% of vbase ± 0.5% of v n at v n ± 0.5% of v at v > v n reset ratio >95% - inverse time c...
Page 278
9.4.2 functionality when the laminated core of a power transformer or generator is subjected to a magnetic flux density beyond its design limits, stray flux will flow into non-laminated components not designed to carry flux and cause eddy currents to flow. The eddy currents can cause excessive heati...
Page 279
9.4.5 settings table 157: oexpvph (24) group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation disabled enabled - - disabled operation disable / enable pickup1 100.0 - 180.0 %vb/f 0.1 110.0 operate level of v/hz at no load and rated freq in % of (vbase/frated) pickup2 100....
Page 280
9.4.7 operation principle the importance of overexcitation protection (oexpvph, 24) function is growing as the power transformers as well as other power system elements today operate most of the time near their designated limits. Modern design transformers are more sensitive to overexcitation than e...
Page 281
Step-up transformer), and if this fails, or if this is not possible, the trip signal will disconnect the transformer from the source after a delay ranging from seconds to minutes, typically 5-10 seconds. Overexcitation protection may be of particular concern on directly connected generator unit tran...
Page 282
Overexcited as long as the relative excitation is m ≤ pickup1, pickup1 expressed in % of vn/fn. It is assumed that overexcitation is a symmetrical phenomenon, caused by events such as loss-of-load, etc. It will be observed that a high phase-to-ground voltage does not mean overexcitation. For example...
Page 283
Op 2 2 0.18 0.18 t m 1 puv hz td td overexcitation × × = - = æ ö ç ÷ è ø ansiequation2298 v2 en (equation 86) where: m the relative excitation pickup1 operate level of over-excitation function at no load in % of (/f rated ) td is time multiplier for inverse time functions, see figure 127 . The relat...
Page 284
Be allowed. In case the inverse delay is longer than 1800 seconds, oexpvph (24) trips t_maxtripdelay, see figure 126 . A definite minimum time, t_mintripdelay, can be used to limit the operate time at high degrees of overexcitation for pickup1. In case the inverse delay is shorter than t_mintripdela...
Page 285
( ) pickup2 f m 1.40 vn/fn = = ansiequation2286 v1 en (equation 88) 9.4.7.3 cooling overexcitation protection function (oexpvph, 24) is basically a thermal protection; therefore a cooling process has been introduced. Exponential cooling process is applied, with a default time constant of 20 minutes....
Page 286
At low degrees of overexcitation, the very long delay is limited by 30 minutes, then the trip output signal of oexpvph (24) will be set to 1 and tmtotrip will reach 0 seconds before thermsta reaches 100%. 9.4.7.5 overexcitation alarm a separate step, alarmpickup, is provided for alarming purpose. It...
Page 287
9.4.8 technical data table 160: oexpvph (24) technical data function range or value accuracy pickup value, pickup (100–180)% of ( vbase /f n ) ± 0.5% of v pickup value, alarm (50–120)% of pickup level ± 0.5% of v n at v ≤ v n ± 0.5% of v at v > v n pickup value, high level (100–200)% of ( vbase /f n...
Page 288
In normal non-faulted operation of the generating unit the neutral point voltage is close to zero, and there is no zero sequence current flow in the generator. When a phase-to- ground fault occurs the neutral point voltage will increase and there will be a current flow through the neutral point resi...
Page 289
9.5.3 function block ansi07000033 -3-en.Vsd stefphiz (59thd) neutvolt* termvolt* 52a block block3rd blockvn trip trip3h trip_vn pickup pu_3h pu_vn dv3 bv3 ansi07000033 v3 en figure 130: stefphiz (59thd) function block 9.5.4 signals table 161: stefphiz (59thd) input signals name type default descript...
Page 290
9.5.5 settings table 163: stefphiz (59thd) group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation disabled enabled - - disabled disable/enable operation beta 0.50 - 10.00 - 0.01 3.00 portion of 3rd harm voltage in neutral point used as bias cbexists no yes - - no defines ...
Page 291
9.5.6 monitored data table 165: stefphiz (59thd) monitored data name type values (range) unit description vt3 real - kv mag. Of 3rd harm. Voltage at generator terminal side vn3 real - kv mag. Of 3rd harm. Voltage at generator neutral side e3 real - kv total induced stator 3rd harmonic voltage angle ...
Page 292
En06000448_ansi.Vsd v 3n v 3t - dv 3 + - v 3 + - v 3n + + v 3t,a - + v 3t,b - + v 3t,c - ansi06000448 v1 en figure 131: generator 3 rd harmonic voltage characteristic at normal operation the generator is modeled as parts of a winding where a 3 rd harmonic voltage is induced along the winding, repres...
Page 293
3t 3n 3n v v v beta + ³ equation2359-ansi v1 en (equation 91) v 3n , and v 3t are third harmonic phasors with real and imaginary parts. The factor beta must be set not to risk operation under non-faulted conditions. The voltage v 3n is measured via a voltage transformer between the generator neutral...
Page 294
Ansi10000240-2-en.Vsd samples: generator terminal voltage 3rd harmonic fourier filtering giving vt3 complex vt3 samples: generator neutral point voltage 3rd harmonic fourier filtering giving vn3 complex vn3 stator ground fault detection 3rd harmonic based pickup pickup and trip logic trip trip3h tri...
Page 295
Beta ç v3n+v3t ç x a b ç v3n ç b ³ a vt3blklevel a b a ³ b ç v3t ç and pu3h t trip3h vnfundpu a b b ³ a v_n pu_vn tripvn or or pickup trip ansi07000001-2-en.Vsd 0 t 0 ansi07000001 v2 en figure 133: simplified pickup and trip logical diagram of the stefphiz (59thd) protection there are two different ...
Page 296
With the circuit breaker open, the total capacitance will be smaller compared to normal operating conditions. This means that the neutral point 3 rd harmonic voltage will be reduced compared to the normal operating condition. Therefore, there is a possibility to reduce the sensitivity of the protect...
Page 297
Section 10 frequency protection 10.1 underfrequency protection saptuf (81) 10.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number underfrequency protection saptuf f symbol-p v1 en 81 10.1.2 functionality underfrequency occurs as a r...
Page 298
10.1.4 signals table 167: saptuf (81) input signals name type default description v3p group signal - three phase group signal for voltage inputs block boolean 0 block of function table 168: saptuf (81) output signals name type description trip boolean common trip signal pickup boolean general pickup...
Page 299
The set time delay the trip signal is issued. To avoid an unwanted trip due to uncertain frequency measurement at low voltage magnitude, a voltage controlled blocking of the function is available from the preprocessing function, that is, if the voltage is lower than the set blocking voltage in the p...
Page 300
10.1.7.4 design the design of underfrequency protection saptuf (81) is schematically described in figure 136 . Frequency comparator f pickup pickup trip block comparator f > restorefreq block or definitetimedelay timedlyoperate timedlyrestore restore 100 ms pickup & trip output logic ansi09000034-1-...
Page 301
10.2 overfrequency protection saptof (81) 10.2.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number overfrequency protection saptof f > symbol-o v1 en 81 10.2.2 functionality overfrequency protection function saptof (81) is applicable ...
Page 302
Table 173: saptof (81) output signals name type description trip boolean common trip signal bfi boolean general pickup signal blkdmagn boolean measurement blocked due to low amplitude 10.2.5 settings table 174: saptof (81) group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description oper...
Page 303
Preprocessing function, which is discussed in the basic ied functions chapter and is set as a percentage of a global base voltage parameter vbase, saptof (81) is blocked, and the output blkdmagn is issued. All voltage settings are made in percent of the global parameter vbase. To avoid oscillations ...
Page 304
Pickup pickup trip pickup & trip output logic definite time delay timedlyoperate block ansi09000033-1-en.Vsd frequency comparator f > pufrequency trip blkdmagn block or freqnotvalid ansi09000033 v1 en figure 138: schematic design of overfrequency protection saptof (81) 10.2.8 technical data table 17...
Page 305
10.3.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number rate-of-change frequency protection sapfrc df/dt > symbol-n v1 en 81 10.3.2 functionality rate-of-change frequency protection function (sapfrc,81) gives an early indication of a...
Page 306
Table 178: sapfrc (81) output signals name type description trip boolean operate/trip signal for frequency gradient pickup boolean start/pick-up signal for frequency gradient restore boolean restore signal for load restoring purposes blkdmagn boolean blocking indication due to low magnitude 10.3.5 s...
Page 307
Negative value, and a trip signal has been issued, then a 100 ms pulse is issued on the restore output, when the frequency recovers to a value higher than the setting restorefreq. A positive setting of pufreqgrad, sets sapfrc (81) to pickup and trip for frequency increases. To avoid oscillations of ...
Page 308
10.3.6.3 design ansi08000009_en_1.Vsd restore pickup pickup trip pickup & trip output logic block frequency 100 ms comparator if [pufreqgrad and df/dt or [pufreqgrad>0 and df/dt > pufreqgrad] then pickup comparator f > restorefreq or definite time delay ttrip trestore blkdmagn rate-of-change of freq...
Page 309
Section 11 secondary system supervision 11.1 fuse failure supervision sddrfuf 11.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number fuse failure supervision sddrfuf - - 11.1.2 functionality the aim of the fuse failure supervision f...
Page 310
A criterion based on delta current and delta voltage measurements can be added to the fuse failure supervision function in order to detect a three phase fuse failure, which in practice is more associated with voltage transformer switching during station operations. 11.1.3 function block ansi08000220...
Page 311
11.1.5 settings table 183: sddrfuf group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation disabled enabled - - enabled disable/enable operation opmodesel disabled v2i2 v0i0 v0i0 or v2i2 v0i0 and v2i2 optimzsns - - v0i0 operating mode selection 3v0pu 1 - 100 %vb 1 30 picku...
Page 312
11.1.6 monitored data table 185: sddrfuf monitored data name type values (range) unit description 3i0 real - a magnitude of zero sequence current 3i2 real - a magnitude of negative sequence current 3v0 real - kv magnitude of zero sequence voltage 3v2 real - kv magnitude of negative sequence voltage ...
Page 313
Ia ib ic zero sequence filter negative sequence filter va vb vc zero sequence filter negative sequence filter currzeroseq currnegseq a b a>b a b a>b a b a>b a b a>b 3i0pu 3i2pu voltzeroseq voltnegseq and and fusefaildetzeroseq fusefaildetnegseq sequence detection 3v0pu 3v2pu 3i0 3i2 3v0 3v2 ansi1000...
Page 314
• the magnitude of the phase-ground voltage has been above vppu for more than 1.5 cycle • the magnitude of dv is higher than the setting dvpu • the magnitude of di is below the setting dipu and at least one of the following conditions are fulfilled: • the magnitude of the phase current in the same p...
Page 316
11.1.7.3 dead line detection a simplified diagram for the functionality is found in figure 144 . A dead phase condition is indicated if both the voltage and the current in one phase is below their respective setting values vdldpu and idldpu. If at least one phase is considered to be dead the output ...
Page 317
• v0i0 or v2i2; both negative and zero sequence is activated and working in parallel in an or-condition • v0i0 and v2i2; both negative and zero sequence is activated and working in series (and-condition for operation) • optimzsns; optimum of negative and zero sequence (the function that has the high...
Page 318
Prolongs the presence of mcbop signal to prevent the unwanted operation of voltage dependent function due to non simultaneous closing of the main contacts of the miniature circuit breaker. The input signal 89b is supposed to be connected via a terminal binary input to the n.C. Auxiliary contact of t...
Page 319
Sealin = enabled all vp sealinpu any vp sealinpu and 3ph mcbop all vp > vsealinpu 52a block and test test active and blocfuse = yes opmodesel and and or 89b blkv blkz and and fusefaildetzeroseq v0i0 or v2i2 v0i0 and v2i2 v0i0 v2i2 optimzsns and fusefaildetnegseq or and and currzeroseq currnegseq a b...
Page 320
Figure 145: simplified logic diagram for fuse failure supervision function, main logic 11.1.8 technical data table 186: sddrfuf technical data function range or value accuracy operate voltage, zero sequence (1-100)% of vbase ± 1.0% of v n operate current, zero sequence (1–100)% of ibase ± 1.0% of i ...
Page 321
11.2.3 function block guid-6f85bd70-4d18-4a00-a410-313233025f3a v2 en figure 146: function block 11.2.4 signals table 187: tcsscbr input signals name type default description tcs_state boolean 0 trip circuit fail indication from i/o-card block boolean 0 block of function table 188: tcsscbr output si...
Page 322
Block timer alarm tcs status tcs_state 0 0-t ansi11000289 v1 en figure 147: functional module diagram trip circuit supervision generates a current of approximately 1.0 ma through the supervised circuit. It must be ensured that this current will not cause a latch up of the controlled object. To prote...
Page 323
Section 12 control 12.1 synchronism check, energizing check, and synchronizing sesrsyn (25) 12.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number synchrocheck, energizing check, and synchronizing sesrsyn sc/vc symbol-m v1 en 25 12....
Page 324
12.1.3 function block sesrsyn (25) v3pb1* v3pb2* v3pl1* v3pl2* block blksynch blksc blkenerg bus1_op bus1_cl bus2_op bus2_cl line1_op line1_cl line2_op line2_cl vb1ok vb1ff vb2ok vb2ff vl1ok vl1ff vl2ok vl2ff startsyn tstsynch tstsc tstenerg aenmode menmode synok autosyok autoenok mansyok manenok ts...
Page 325
Name type default description bus1_op boolean 0 open status for cb or disconnector connected to bus1 bus1_cl boolean 0 close status for cb and disconnector connected to bus1 bus2_op boolean 0 open status for cb or disconnector connected to bus2 bus2_cl boolean 0 close status for cb and disconnector ...
Page 326
Name type description b2sel boolean bus2 selected l1sel boolean line1 selected l2sel boolean line2 selected synprogr boolean synchronizing in progress synfail boolean synchronizing failed frdifsyn boolean frequency difference out of limit for synchronizing frderiva boolean frequency derivative out o...
Page 327
Name values (range) unit step default description operationsynch disabled enabled - - disabled operation for synchronizing function off/on freqdiffmin 0.003 - 0.250 hz 0.001 0.010 minimum frequency difference limit for synchronizing freqdiffmax 0.050 - 0.500 hz 0.001 0.200 maximum frequency differen...
Page 328
Table 194: sesrsyn (25) non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description gblbaseselbus 1 - 6 - 1 1 selection of one of the global base value groups, bus gblbaseselline 1 - 6 - 1 1 selection of one of the global base value groups, line selphasebus1 phase l1 phase l2 phase ...
Page 329
12.1.7 operation principle 12.1.7.1 basic functionality the synchronism check function measures the conditions across the circuit breaker and compares them to set limits. The output is only given when all measured quantities are simultaneously within their set limits. The energizing check function m...
Page 330
If both sides are higher than the set values, the measured values are compared with the set values for acceptable frequency, phase angle and voltage difference: freqdiff, phasediffand vdiffsc. If a compensation factor is set due to the use of different voltages on the bus and line, the factor is ded...
Page 331
Tstsc blksc block tstautsy autosyok phdiffme frdiffme vdiffme phdiffa voksc vdiffsc or and and and and and and phaseangledifferencevalue frequencydifferencevalue voltagedifferencevalue 1 1 and note! Similar logic for manual synchrocheck. 1 frdiffa ansi08000018-2-en.Vsd operationsc = enabled vdiffsc ...
Page 332
Difference between bus and line is acceptable, the measured values are also compared with the set values for acceptable frequency freqdiffmax and freqdiffmin, rate of change of frequency freqratechange and phase angle, which has to be smaller than the internally preset value of 15 degrees. Measured ...
Page 333
12.1.7.4 energizing check voltage values are measured in the ied centrally and are available for evaluation by the synchronism check function. The function measures voltages on the busbar and the line to verify whether they are live or dead. To be considered live, the value must be above 80% of gblb...
Page 334
12.1.7.6 voltage selection the voltage selection module including supervision of included voltage transformer fuses for the different arrangements is a basic part of the sesrsyn (25) function and determines the parameters fed to the synchronizing, synchrocheck and energizing check functions. This in...
Page 335
And and and bus1voltage or or or vl1ff vl1ok vb1ff vb1ok vb2ff vb2ok bus2_cl bus2_op bus1_cl bus1_op selectedfuseok block bus2voltage busvoltage and invalidselection b2sel b1sel and and and vselfail en05000779_ansi.Vsd or not ansi05000779 v1 en figure 151: logic diagram for the voltage selection fun...
Page 336
The fuse supervision is connected to vl1ok-vl1ff, vl2ok-vl2ff and with alternative healthy or failing fuse signals depending on what is available from each fuse (mcb). The tie circuit breaker is connected either to bus 1 or line 1 on one side and the other side is connected either to bus 2 or line 2...
Page 337
And and or or vl1ff vl1ok vb1ff vb1ok vb2ff vb2ok bus1_cl bus1_op line1_cl line1_op selectedfuseok block linevoltage invalidselection l1sel and and vselfail vl2ff vl2ok or and and bus2_cl bus2_op line2_cl line2_op and and l2sel or and b2sel and and and en05000780_ansi.Vsd or or line2voltage bus2volt...
Page 338
And and or or vl1ff vl1ok vb1ff vb1ok vb2ff vb2ok bus1_cl bus1_op line1_cl line1_op selectedfuseok block line1voltage l1sel and and vselfail vl2ff vl2ok or and and and and and b1sel bus1voltage busvoltage and and and bus2_cl bus2_op line2_cl line2_op bus2voltage l2sel and and b2sel line2voltage line...
Page 339
12.1.8 technical data table 196: sesrsyn (25) technical data function range or value accuracy phase shift, j line - j bus (-180 to 180) degrees - voltage ratio, v bus /v line 0.500 - 2.000 - reset ratio, synchronism check > 95% - frequency difference limit between bus and line for synchrocheck (0.00...
Page 340
Function range or value accuracy operate time for energizing function 80 ms typically - minimum time to accept synchronizing conditions (0.000-60.000) s ± 0.5% ± 10 ms maximum allowed frequency rate of change (0.000-0.500) hz/s ± 10.0 mhz/s 12.2 apparatus control 12.2.1 functionality the apparatus c...
Page 341
12.2.2.3 function block qcbay lr_off lr_loc lr_rem lr_valid bl_upd bl_cmd psto upd_blkd cmd_blkd loc rem iec09000080_1_en.Vsd iec09000080 v1 en figure 154: qcbay function block 12.2.2.4 signals table 197: qcbay input signals name type default description lr_off boolean 0 external local/remote switch...
Page 342
12.2.3 local remote locrem 12.2.3.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number local remote locrem - - 12.2.3.2 functionality the signals from the local hmi or from an external local/remote switch are applied via the function b...
Page 343
12.2.3.5 settings table 202: locrem non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description controlmode internal lr-switch external lr-switch - - internal lr-switch control mode for internal/external lr-switch 12.2.4 local remote control locremctrl 12.2.4.1 identification functi...
Page 344
12.2.4.4 signals table 203: locremctrl input signals name type default description psto1 integer 0 psto input channel 1 psto2 integer 0 psto input channel 2 psto3 integer 0 psto input channel 3 psto4 integer 0 psto input channel 4 psto5 integer 0 psto input channel 5 psto6 integer 0 psto input chann...
Page 345
12.2.5 operation principle 12.2.5.1 bay control qcbay the functionality of the bay control (qcbay) function is not defined in the iec 61850– 8–1 standard, which means that the function is a vendor specific logical node. The function sends information about the permitted source to operate (psto) and ...
Page 346
Table 205: psto values for different local panel switch positions local panel switch positions psto value allpstovalid (configuration parameter) possible locations that shall be able to operate 0 = off 0 -- not possible to operate 1 = local 1 false local panel 1 = local 5 true local or remote level ...
Page 347
Locremctrl psto1 psto2 psto3 psto4 psto5 psto6 psto7 psto8 psto9 psto10 psto11 psto12 hmictr1 hmictr2 hmictr3 hmictr4 hmictr5 hmictr6 hmictr7 hmictr8 hmictr9 hmictr10 hmictr11 hmictr12 qcbay lr_ off lr_ loc lr_ rem lr_ valid bl_ upd bl_ cmd psto upd_ blkd cmd_ blkd locrem ctrloff locctrl remctrl lhm...
Page 348
12.3.2 functionality the logic rotating switch for function selection and lhmi presentation (slggio) (or the selector switch function block) is used to get a selector switch functionality similar to the one provided by a hardware selector switch. Hardware selector switches are used extensively by ut...
Page 349
Table 207: slggio output signals name type description p01 boolean selector switch position 1 p02 boolean selector switch position 2 p03 boolean selector switch position 3 p04 boolean selector switch position 4 p05 boolean selector switch position 5 p06 boolean selector switch position 6 p07 boolean...
Page 350
12.3.5 settings table 208: slggio non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation disabled enabled - - disabled operation enable/disable nrpos 2 - 32 - 1 32 number of positions in the switch outtype pulsed steady - - steady output type, steady or pulse tpulse 0...
Page 351
Through the psto input. If any operation is allowed the signal intone from the fixed signal function block can be connected. Slggio function block has also an integer value output, that generates the actual position number. The positions and the block names are fully settable by the user. These name...
Page 352
Table 211: vsggio output signals name type description blocked boolean the function is active but the functionality is blocked position integer position indication, integer pos1 boolean position 1 indication, logical signal pos2 boolean position 2 indication, logical signal cmdpos12 boolean execute ...
Page 353
It is important for indication in the sld that the a symbol is associated with a controllable object, otherwise the symbol won't be displayed on the screen. A symbol is created and configured in gde tool in pcm600. The psto input is connected to the local remote switch to have a selection of operato...
Page 354
12.5.3 function block dpggio open close valid position iec09000075_1_en.Vsd iec09000075 v1 en figure 159: dpggio function block 12.5.4 signals table 213: dpggio input signals name type default description open boolean 0 open indication close boolean 0 close indication valid boolean 0 valid indicatio...
Page 355
12.6 single point generic control 8 signals spc8ggio 12.6.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number single point generic control 8 signals spc8ggio - - 12.6.2 functionality the single point generic control 8 signals (spc8ggi...
Page 356
Table 216: spc8ggio output signals name type description out1 boolean output 1 out2 boolean output2 out3 boolean output3 out4 boolean output4 out5 boolean output5 out6 boolean output6 out7 boolean output7 out8 boolean output8 12.6.5 settings table 217: spc8ggio non group settings (basic) name values...
Page 357
12.6.6 operation principle the psto input selects the operator place (local, remote or all). One of the eight outputs is activated based on the command sent from the operator place selected. The settings latchedx and tpulsex (where x is the respective output) will determine if the signal will be pul...
Page 358
12.7.3 function block iec09000030-1-en.Vsd autobits block psto ^cmdbit1 ^cmdbit2 ^cmdbit3 ^cmdbit4 ^cmdbit5 ^cmdbit6 ^cmdbit7 ^cmdbit8 ^cmdbit9 ^cmdbit10 ^cmdbit11 ^cmdbit12 ^cmdbit13 ^cmdbit14 ^cmdbit15 ^cmdbit16 ^cmdbit17 ^cmdbit18 ^cmdbit19 ^cmdbit20 ^cmdbit21 ^cmdbit22 ^cmdbit23 ^cmdbit24 ^cmdbi...
Page 359
Name type description cmdbit4 boolean command out bit 4 cmdbit5 boolean command out bit 5 cmdbit6 boolean command out bit 6 cmdbit7 boolean command out bit 7 cmdbit8 boolean command out bit 8 cmdbit9 boolean command out bit 9 cmdbit10 boolean command out bit 10 cmdbit11 boolean command out bit 11 cm...
Page 360
12.7.6 operation principle automation bits function (autobits) has 32 individual outputs which each can be mapped as a binary output point in dnp3. The output is operated by a "object 12" in dnp3. This object contains parameters for control-code, count, on-time and off-time. To operate an autobits o...
Page 361
12.8.3 signals table 221: i103cmd input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of commands table 222: i103cmd output signals name type description 16-ar boolean information number 16, block of autorecloser 17-diff boolean information number 17, block of differential protection 1...
Page 362
12.9.3 signals table 224: i103iedcmd input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of commands table 225: i103iedcmd output signals name type description 19-ledrs boolean information number 19, reset leds 23-grp1 boolean information number 23, activate setting group 1 24-grp2 boo...
Page 363
12.10.2 function block iec10000284-1-en.Vsd i103usrcmd block ^output1 ^output2 ^output3 ^output4 ^output5 ^output6 ^output7 ^output8 iec10000284 v1 en figure 164: i103usrcmd function block 12.10.3 signals table 227: i103usrcmd input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of comm...
Page 364
Name values (range) unit step default description infno_2 1 - 255 - 1 2 information number for output 2 (1-255) infno_3 1 - 255 - 1 3 information number for output 3 (1-255) infno_4 1 - 255 - 1 4 information number for output 4 (1-255) infno_5 1 - 255 - 1 5 information number for output 5 (1-255) in...
Page 365
12.11.4 settings table 232: i103gencmd non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description functiontype 1 - 127 - 1 1 function type (1-255) pulselength 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.400 pulse length infno 32 - 239 - 1 32 information number for command output (1-255) 12.12 ied com...
Page 366
12.12.4 settings table 234: i103poscmd non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description functiontype 1 - 255 - 1 1 fucntion type (1-255) infno 160 - 196 - 4 160 information number for command output (1-255) section 12 1mrk 502 043-uus b control 360 technical manual.
Page 367
Section 13 logic 13.1 tripping logic common 3-phase output smpptrc (94) 13.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number tripping logic common 3-phase output smpptrc i->o symbol-k v1 en 94 13.1.2 functionality a function block...
Page 368
13.1.4 signals table 235: smpptrc (94) input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function trinp_3p boolean 0 trip all phases setlkout boolean 0 input for setting the circuit breaker lockout function rstlkout boolean 0 input for resetting the circuit breaker lockout functio...
Page 369
Binary inputs, are routed. It has a single trip output (trip) for connection to one or more of the ieds binary outputs, as well as to other functions within the ied requiring this signal. Ansi05000789 v2 en figure 168: simplified logic diagram for three pole trip lockout can be activated either by a...
Page 370
13.2.2 functionality the trip matrix logic tmaggio function is used to route trip signals and other logical output signals to the tripping logics smpptrc and sptptrc or to different output contacts on the ied. Tmaggio output signals and the physical outputs allows the user to adapt the signals to th...
Page 371
13.2.4 signals table 240: tmaggio input signals name type default description input1 boolean 0 binary input 1 input2 boolean 0 binary input 2 input3 boolean 0 binary input 3 input4 boolean 0 binary input 4 input5 boolean 0 binary input 5 input6 boolean 0 binary input 6 input7 boolean 0 binary input ...
Page 372
Table 241: tmaggio output signals name type description output1 boolean or function betweeen inputs 1 to 16 output2 boolean or function between inputs 17 to 32 output3 boolean or function between inputs 1 to 32 13.2.5 settings table 242: tmaggio group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step d...
Page 373
Always active and will delay the input to output transition by the set time. The modeoutput for respective output decides whether the output shall be steady with an drop-off delay as set by offdelay or if it shall give a pulse with duration set by pulsetime. Note that for pulsed operation since the ...
Page 374
13.3 configurable logic blocks 13.3.1 standard configurable logic blocks 13.3.1.1 functionality a number of logic blocks and timers are available for the user to adapt the configuration to the specific application needs. • or function block. • inverter function blocks that inverts the input signal. ...
Page 375
13.3.1.2 or function block identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number or function block or - - functionality the or function is used to form general combinatory expressions with boolean variables. The or function block has six ...
Page 376
Settings the function does not have any parameters available in local hmi or protection and control ied manager (pcm600). 13.3.1.3 inverter function block inverter identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number inverter function bl...
Page 377
Functionality the pulse function can be used, for example for pulse extensions or limiting of operation of outputs. The pulsetimer has a settable length. Function block pulsetimer input out iec09000291-1-en.Vsd iec09000291 v1 en figure 173: pulsetimer function block signals table 247: pulsetimer inp...
Page 378
Function block gate input out iec09000295-1-en.Vsd iec09000295 v1 en figure 174: gate function block signals table 250: gate input signals name type default description input boolean 0 input signal table 251: gate output signals name type description out boolean output signal settings table 252: gat...
Page 379
Function block xor input1 input2 out nout iec09000292-1-en.Vsd iec09000292 v1 en figure 175: xor function block signals table 253: xor input signals name type default description input1 boolean 0 input signal 1 input2 boolean 0 input signal 2 table 254: xor output signals name type description out b...
Page 380
Signals table 255: loopdelay input signals name type default description input boolean 0 input signal table 256: loopdelay output signals name type description out boolean output signal, signal is delayed one execution cycle settings the function does not have any parameters available in local hmi o...
Page 381
Function block timerset input on off iec09000290-1-en.Vsd iec09000290 v1 en figure 178: timerset function block signals table 257: timerset input signals name type default description input boolean 0 input signal table 258: timerset output signals name type description on boolean output signal, pick...
Page 382
Default value on all four inputs are logical 1 which makes it possible for the user to just use the required number of inputs and leave the rest un-connected. The output out has a default value 0 initially, which suppresses one cycle pulse if the function has been put in the wrong execution order. F...
Page 383
Functionality the set-reset function srmemory is a flip-flop with memory that can set or reset an output from two inputs respectively. Each srmemory function block has two outputs, where one is inverted. The memory setting controls if the flip-flop after a power interruption will return the state it...
Page 384
Settings table 265: srmemory group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description memory off on - - on operating mode of the memory function 13.3.1.11 reset-set with memory function block rsmemory identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identificati...
Page 385
Signals table 267: rsmemory input signals name type default description set boolean 0 input signal to set reset boolean 0 input signal to reset table 268: rsmemory output signals name type description out boolean output signal nout boolean inverted output signal settings table 269: rsmemory group se...
Page 386
13.4 fixed signals fxdsign 13.4.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number fixed signals fxdsign - - 13.4.2 functionality the fixed signals function (fxdsign) generates a number of pre-set (fixed) signals that can be used in ...
Page 387
Name type description strnull string string signal with no characters zerosmpl group signal channel id for zero sample grp_off group signal group signal fixed off 13.4.5 settings the function does not have any settings available in local hmi or protection and control ied manager (pcm600). 13.4.6 ope...
Page 388
13.5.3 function block b16i block in1 in2 in3 in4 in5 in6 in7 in8 in9 in10 in11 in12 in13 in14 in15 in16 out iec09000035-1-en.Vsd iec09000035 v1 en figure 183: b16i function block 13.5.4 signals table 272: b16i input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function in1 boolean ...
Page 389
Table 273: b16i output signals name type description out integer output value 13.5.5 settings the function does not have any parameters available in local hmi or protection and control ied manager (pcm600) 13.5.6 monitored data table 274: b16i monitored data name type values (range) unit description...
Page 390
13.6.3 function block b16ifcvi block in1 in2 in3 in4 in5 in6 in7 in8 in9 in10 in11 in12 in13 in14 in15 in16 out iec09000624-1-en.Vsd iec09000624 v1 en figure 184: b16ifcvi function block 13.6.4 signals table 275: b16ifcvi input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function ...
Page 391
Table 276: b16ifcvi output signals name type description out integer output value 13.6.5 settings the function does not have any parameters available in local hmi or protection and control ied manager (pcm600) 13.6.6 monitored data table 277: b16ifcvi monitored data name type values (range) unit des...
Page 392
13.7.3 function block ib16a block inp out1 out2 out3 out4 out5 out6 out7 out8 out9 out10 out11 out12 out13 out14 out15 out16 iec09000036-1-en.Vsd iec09000036 v1 en figure 185: ib16a function block 13.7.4 signals table 278: ib16a input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of fu...
Page 393
Name type description out14 boolean output 14 out15 boolean output 15 out16 boolean output 16 13.7.5 settings the function does not have any parameters available in local hmi or protection and control ied manager (pcm600) 13.7.6 operation principle integer to boolean 16 conversion function (ib16a) i...
Page 394
13.8.3 function block ib16fcvb block psto out1 out2 out3 out4 out5 out6 out7 out8 out9 out10 out11 out12 out13 out14 out15 out16 iec09000399-1-en.Vsd iec09000399 v1 en figure 186: ib16fcvb function block 13.8.4 signals table 280: ib16fcvb input signals name type default description block boolean 0 b...
Page 395
Name type description out13 boolean output 13 out14 boolean output 14 out15 boolean output 15 out16 boolean output 16 13.8.5 settings the function does not have any parameters available in local hmi or protection and control ied manager (pcm600) 13.8.6 operation principle integer to boolean conversi...
Page 396
390
Page 397
Section 14 monitoring 14.1 measurements 14.1.1 functionality measurement functions is used for power system measurement, supervision and reporting to the local hmi, monitoring tool within pcm600 or to station level for example, via iec 61850. The possibility to continuously monitor measured values o...
Page 398
• p, q and s: three phase active, reactive and apparent power • pf: power factor • v: phase-to-phase voltage magnitude • i: phase current magnitude • f: power system frequency the output values are displayed in the local hmi under main menu/tests/function status/monitoring/cvmmxn/outputs the measuri...
Page 399
14.1.2.2 function block the available function blocks of an ied are depending on the actual hardware (trm) and the logic configuration made in pcm600. Cvmmxn i3p* v3p* s s_range p_inst p p_range q_inst q q_range pf pf_range ilag ilead v v_range i i_range f f_range ansi10000051-1-en.Vsd ansi10000051 ...
Page 400
Name type description pf real power factor magnitude of deadband value pf_range integer power factor range ilag boolean current is lagging voltage ilead boolean current is leading voltage v real calculated voltage magnitude of deadband value v_range integer calcuated voltage range i real calculated ...
Page 401
Name values (range) unit step default description pmax -2000.0 - 2000.0 %sb 0.1 200.0 maximum value in % of sbase preptyp cyclic dead band int deadband - - cyclic reporting type qmin -2000.0 - 2000.0 %sb 0.1 -200.0 minimum value in % of sbase qmax -2000.0 - 2000.0 %sb 0.1 200.0 maximum value in % of...
Page 402
Name values (range) unit step default description pdbrepint 1 - 300 type 1 10 cycl: report interval (s), db: in % of range, int db: in %s pzerodb 0 - 100000 m% 1 500 zero point clamping philim -2000.0 - 2000.0 %sb 0.1 120.0 high limit in % of sbase plowlim -2000.0 - 2000.0 %sb 0.1 -120.0 low limit i...
Page 403
Name values (range) unit step default description ilowlim 0.0 - 500.0 %ib 0.1 80.0 low limit in % of ibase ilowlowlim 0.0 - 500.0 %ib 0.1 60.0 low low limit in % of ibase ilimhyst 0.000 - 100.000 % 0.001 5.000 hysteresis value in % of range (common for all limits) frdbrepint 1 - 300 type 1 10 cycl: ...
Page 404
Name type values (range) unit description v real - kv calculated voltage magnitude of deadband value i real - a calculated current magnitude of deadband value f real - hz system frequency magnitude of deadband value 14.1.3 phase current measurement cmmxu 14.1.3.1 identification function description ...
Page 405
Table 288: cmmxu output signals name type description i_a real ia amplitude ia_range integer phase a current magnitude range ia_angl real ia angle i_b real ib amplitude ib_range integer phase b current magnitude range ib_angl real ib angle i_c real ic amplitude ic_range integer phase c current magni...
Page 406
Name values (range) unit step default description imagcomp5 -10.000 - 10.000 % 0.001 0.000 magnitude factor to calibrate current at 5% of in imagcomp30 -10.000 - 10.000 % 0.001 0.000 magnitude factor to calibrate current at 30% of in imagcomp100 -10.000 - 10.000 % 0.001 0.000 magnitude factor to cal...
Page 407
Ansi08000223-1-en.Vsd vmmxu v3p* v_ab vab_rang vab_angl v_bc vbc_rang vbc_angl v_ca vca_rang vca_angl ansi08000223 v1 en figure 189: vmmxu function block 14.1.4.3 signals table 292: vmmxu input signals name type default description v3p group signal - three phase group signal for voltage inputs table...
Page 408
14.1.4.4 settings table 294: vmmxu non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation disabled enabled - - disabled operation disable / enable globalbasesel 1 - 6 - 1 1 selection of one of the global base value groups vldbrepint 1 - 300 type 1 10 cycl: report inte...
Page 409
14.1.5 current sequence component measurement cmsqi 14.1.5.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number current sequence component measurement cmsqi i1, i2, i0 symbol-vv v1 en - 14.1.5.2 function block the available function bl...
Page 410
Name type description i1rang integer i1amplitude range i1angl real i1 angle i2 real i2 amplitude i2rang integer i2 magnitude range i2angl real i2angle 14.1.5.4 settings table 299: cmsqi non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation disabled enabled - - disabl...
Page 411
Table 300: cmsqi non group settings (advanced) name values (range) unit step default description 3i0zerodb 0 - 100000 m% 1 500 zero point clamping 3i0hihilim 0 - 500000 a 1 3600 high high limit (physical value) 3i0hilim 0 - 500000 a 1 3300 high limit (physical value) 3i0lowlim 0 - 500000 a 1 0 low l...
Page 412
14.1.6 voltage sequence measurement vmsqi 14.1.6.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number voltage sequence measurement vmsqi u1, u2, u0 symbol-tt v1 en - 14.1.6.2 function block the available function blocks of an ied are d...
Page 413
Name type description v1rang integer v1 magnitude range v1angl real u1 angle v2 real u2 amplitude v2rang integer v2 magnitude range v2angl real u2 angle 14.1.6.4 settings table 304: vmsqi non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation disabled enabled - - disa...
Page 414
Table 305: vmsqi non group settings (advanced) name values (range) unit step default description 3v0zerodb 0 - 100000 m% 1 500 zero point clamping 3v0hihilim 0 - 2000000 v 1 288000 high high limit (physical value) 3v0hilim 0 - 2000000 v 1 258000 high limit (physical value) 3v0lowlim 0 - 2000000 v 1 ...
Page 415
14.1.7 phase-neutral voltage measurement vnmmxu 14.1.7.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number phase-neutral voltage measurement vnmmxu u symbol-uu v1 en - 14.1.7.2 function block the available function blocks of an ied ar...
Page 416
Name type description vb_range integer v_b amplitude range vb_angl real v_b angle, magnitude of reported value v_c real v_c amplitude, magnitude of reported value vc_range integer v_c amplitude range vc_angl real vc angle, magnitude of reported value 14.1.7.4 settings table 309: vnmmxu non group set...
Page 417
14.1.7.5 monitored data table 311: vnmmxu monitored data name type values (range) unit description v_a real - kv v_a amplitude, magnitude of reported value va_angl real - deg v_a angle, magnitude of reported value v_b real - kv v_b amplitude, magnitude of reported value vb_angl real - deg v_b angle,...
Page 418
Zero point clamping might be overridden by the zero point clamping used for the measurement values within cvmmxn. Continuous monitoring of the measured quantity users can continuously monitor the measured quantity available in each function block by means of four defined operating thresholds, see fi...
Page 419
Actual value of the measured quantity the actual value of the measured quantity is available locally and remotely. The measurement is continuous for each measured quantity separately, but the reporting of the value to the higher levels depends on the selected reporting mode. The following basic repo...
Page 420
Magnitude dead-band supervision if a measuring value is changed, compared to the last reported value, and the change is larger than the ±Δy pre-defined limits that are set by user (xzerodb), then the measuring channel reports the new value to a higher level, if this is detected by a new measured val...
Page 421
Absolute values of these integral values are added until the pre-set value is exceeded. This occurs with the value y2 that is reported and set as a new base for the following measurements (as well as for the values y3, y4 and y5). The integral dead-band supervision is particularly suitable for monit...
Page 422
Set value for parameter “mode” formula used for complex, three- phase power calculation formula used for voltage and current magnitude calculation comment 1 a, b, c * * * a a b b c c s v i v i v i = × + × + × equation1561 v1 en ( ) ( ) / 3 / 3 a b c a b c v v v v i i i i = + + = + + equation1562 v1 ...
Page 423
Set value for parameter “mode” formula used for complex, three- phase power calculation formula used for voltage and current magnitude calculation comment 8 b * 3 b b s v i = × × equation1575 v1 en (equation 104) 3 b b v v i i = × = equation1576 v1 en (equation 105) used when only v b phase-to- grou...
Page 424
Each analog output has a corresponding supervision level output (x_range). The output signal is an integer in the interval 0-4, see section "measurement supervision" . Calibration of analog inputs measured currents and voltages used in the cvmmxn function can be calibrated to get class 0.5 measuring...
Page 425
The measured quantity. Filtering is performed in accordance with the following recursive formula: (1 ) old calculated x k x k x = × + - × equation1407 v1 en (equation 112) where: x is a new measured value (that is p, q, s, v, i or pf) to be given out from the function x old is the measured value giv...
Page 426
Directionality ctstartpoint defines if the cts grounding point is located towards or from the protected object under observation. If everything is properly set power is always measured towards protection object. Busbar protected object p q ansi05000373_2_en.Vsd 52 ied ansi05000373 v2 en figure 198: ...
Page 427
Outputs and iec 61850. This is achieved by magnitude and angle compensation at 5, 30 and 100% of rated current. The compensation below 5% and above 100% is constant and linear in between, see figure 197 . Phase currents (magnitude and angle) are available on the outputs and each magnitude output has...
Page 428
Function range or value accuracy reactive power, q 0.1 x v n n 0.2 x i n n ± 1.0% of s n at s ≤ s n ± 1.0% of s at s > s n apparent power, s 0.1 x v n n 0.2 x i n n ± 1.0% of s n at s ≤ s n ± 1.0% of s at s > s n apparent power, s three phase settings cos phi = 1 ± 0.5% of s at s > s n ± 0.5% of s n...
Page 429
14.2.4 signals table 313: cntggio input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function counter1 boolean 0 input for counter 1 counter2 boolean 0 input for counter 2 counter3 boolean 0 input for counter 3 counter4 boolean 0 input for counter 4 counter5 boolean 0 input for cou...
Page 430
Name type values (range) unit description value4 integer - - output of counter 4 value5 integer - - output of counter 5 value6 integer - - output of counter 6 14.2.7 operation principle event counter (cntggio) has six counter inputs. Cntggio stores how many times each of the inputs has been activate...
Page 431
14.3 disturbance report 14.3.1 functionality complete and reliable information about disturbances in the primary and/or in the secondary system together with continuous event-logging is accomplished by the disturbance report functionality. Disturbance report drprdre, always included in the ied, acqu...
Page 432
14.3.2.2 function block drprdre drpoff recstart recmade cleared memused iec09000346-1-en.Vsd iec09000346 v1 en figure 200: drprdre function block 14.3.2.3 signals table 318: drprdre output signals name type description drpoff boolean disturbance report function turned off recstart boolean disturbanc...
Page 433
14.3.2.5 monitored data table 320: drprdre monitored data name type values (range) unit description memoryused integer - % memory usage (0-100%) untrigstatch1 boolean - - under level trig for analog channel 1 activated ovtrigstatch1 boolean - - over level trig for analog channel 1 activated untrigst...
Page 434
Name type values (range) unit description untrigstatch11 boolean - - under level trig for analog channel 11 activated ovtrigstatch11 boolean - - over level trig for analog channel 11 activated untrigstatch12 boolean - - under level trig for analog channel 12 activated ovtrigstatch12 boolean - - over...
Page 435
Name type values (range) unit description untrigstatch22 boolean - - under level trig for analog channel 22 activated ovtrigstatch22 boolean - - over level trig for analog channel 22 activated untrigstatch23 boolean - - under level trig for analog channel 23 activated ovtrigstatch23 boolean - - over...
Page 436
Name type values (range) unit description untrigstatch33 boolean - - under level trig for analog channel 33 activated ovtrigstatch33 boolean - - over level trig for analog channel 33 activated untrigstatch34 boolean - - under level trig for analog channel 34 activated ovtrigstatch34 boolean - - over...
Page 437
14.3.3 analog input signals axradr 14.3.3.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number analog input signals a1radr - - analog input signals a2radr - - analog input signals a3radr - - 14.3.3.2 function block a1radr ^grpinput1 ^g...
Page 438
Table 322: a1radr input signals name type default description grpinput1 group signal - group signal for input 1 grpinput2 group signal - group signal for input 2 grpinput3 group signal - group signal for input 3 grpinput4 group signal - group signal for input 4 grpinput5 group signal - group signal ...
Page 439
Name values (range) unit step default description operation05 disabled enabled - - disabled operation on/off operation06 disabled enabled - - disabled operation on/off operation07 disabled enabled - - disabled operation on/off operation08 disabled enabled - - disabled operation on/off operation09 di...
Page 440
Name values (range) unit step default description funtype9 0 - 255 - 1 0 function type for analog channel 9 (iec-60870-5-103) infno9 0 - 255 - 1 0 information number for analog channel 9 (iec-60870-5-103) funtype10 0 - 255 - 1 0 function type for analog channel 10 (iec-60870-5-103) infno10 0 - 255 -...
Page 441
Name values (range) unit step default description overtrigop04 disabled enabled - - disabled use over level trigger for analog channel 4 (on) or not (off) overtrigle04 0 - 5000 % 1 200 over trigger level for analog channel 4 in % of signal nomvalue05 0.0 - 999999.9 - 0.1 0.0 nominal value for analog...
Page 442
Name values (range) unit step default description undertrigle09 0 - 200 % 1 50 under trigger level for analog channel 9 in % of signal overtrigop09 disabled enabled - - disabled use over level trigger for analog channel 9 (on) or not (off) overtrigle09 0 - 5000 % 1 200 over trigger level for analog ...
Page 443
14.3.4.3 signals table 325: a4radr input signals name type default description input31 real 0 analog channel 31 input32 real 0 analog channel 32 input33 real 0 analog channel 33 input34 real 0 analog channel 34 input35 real 0 analog channel 35 input36 real 0 analog channel 36 input37 real 0 analog c...
Page 444
Name values (range) unit step default description infno31 0 - 255 - 1 0 information number for analog channel 31 (iec-60870-5-103) funtype32 0 - 255 - 1 0 function type for analog channel 32 (iec-60870-5-103) infno32 0 - 255 - 1 0 information number for analog channel 32 (iec-60870-5-103) funtype33 ...
Page 445
Table 327: a4radr non group settings (advanced) name values (range) unit step default description nomvalue31 0.0 - 999999.9 - 0.1 0.0 nominal value for analog channel 31 undertrigop31 disabled enabled - - disabled use under level trigger for analog channel 31 (on) or not (off) undertrigle31 0 - 200 ...
Page 446
Name values (range) unit step default description overtrigop35 disabled enabled - - disabled use over level trigger for analog channel 35 (on) or not (off) overtrigle35 0 - 5000 % 1 200 over trigger level for analog channel 35 in % of signal nomvalue36 0.0 - 999999.9 - 0.1 0.0 nominal value for anal...
Page 447
Name values (range) unit step default description undertrigle40 0 - 200 % 1 50 under trigger level for analog channel 40 in % of signal overtrigop40 disabled enabled - - disabled use over level trigger for analog channel 40 (on) or not (off) overtrigle40 0 - 5000 % 1 200 over trigger level for analo...
Page 448
14.3.5.3 signals b1rbdr - b6rbdr input signals tables for input signals for b1rbdr - b6rbdr are all similar except for input and description number. • b1rbdr, input1 - input16 • b2rbdr, input17 - input32 • b3rbdr, input33 - input48 • b4rbdr, input49 - input64 • b5rbdr, input65 - input80 • b6rbdr, in...
Page 449
• b4rbdr, channel49 - channel64 • b5rbdr, channel65 - channel80 • b6rbdr, channel81 - channel96 table 329: b1rbdr non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description trigdr01 disabled enabled - - disabled trigger operation on/off setled01 disabled start trip pick up and trip...
Page 450
Name values (range) unit step default description trigdr08 disabled enabled - - disabled trigger operation on/off setled08 disabled start trip pick up and trip - - disabled set led on hmi for binary channel 8 trigdr09 disabled enabled - - disabled trigger operation on/off setled09 disabled start tri...
Page 451
Name values (range) unit step default description trigdr16 disabled enabled - - disabled trigger operation on/off setled16 disabled start trip pick up and trip - - disabled set led on hmi for binary channel 16 funtype1 0 - 255 - 1 0 function type for binary channel 1 (iec -60870-5-103) infno1 0 - 25...
Page 452
Name values (range) unit step default description funtype11 0 - 255 - 1 0 function type for binary channel 11 (iec -60870-5-103) infno11 0 - 255 - 1 0 information number for binary channel 11 (iec -60870-5-103) funtype12 0 - 255 - 1 0 function type for binary channel 12 (iec -60870-5-103) infno12 0 ...
Page 453
Name values (range) unit step default description triglevel05 trig on 0 trig on 1 - - trig on 1 trigger on positive (1) or negative (0) slope for binary input 5 indicationma05 hide show - - hide indication mask for binary channel 5 triglevel06 trig on 0 trig on 1 - - trig on 1 trigger on positive (1...
Page 454
Name values (range) unit step default description indicationma15 hide show - - hide indication mask for binary channel 15 triglevel16 trig on 0 trig on 1 - - trig on 1 trigger on positive (1) or negative (0) slope for binary input 16 indicationma16 hide show - - hide indication mask for binary chann...
Page 455
Trip value rec sequential of events event recorder indications disturbance recorder a1-4radr b1-6rbdr disturbance report binary signals analog signals a4radr b6rbdr drprdre ansi09000337-1-en.Vsd ansi09000337 v1 en figure 204: disturbance report functions and related function blocks the whole disturb...
Page 456
The ied flash disk should not be used to store any user files. This might cause disturbance recordings to be deleted due to lack of disk space. 14.3.6.1 disturbance information date and time of the disturbance, the indications, events, fault location and the trip values are available on the local hm...
Page 457
14.3.6.7 time tagging the ied has a built-in real-time calendar and clock. This function is used for all time tagging within the disturbance report 14.3.6.8 recording times disturbance report drprdre records information about a disturbance during a settable time frame. The recording times are valid ...
Page 458
14.3.6.9 analog signals up to 40 analog signals can be selected for recording by the disturbance recorder and triggering of the disturbance report function. Out of these 40, 30 are reserved for external analog signals from analog input modules via preprocessing function blocks (smai) and summation b...
Page 459
The preprocessor function block (smai) calculates the residual quantities in cases where only the three phases are connected (ai4-input not used). Smai makes the information available as a group signal output, phase outputs and calculated residual output (ain-output). In situations where ai4-input i...
Page 460
Fulfilled, there is no disturbance report, no indications, and so on. This implies the importance of choosing the right signals as trigger conditions. A trigger can be of type: • manual trigger • binary-signal trigger • analog-signal trigger (over/under function) manual trigger a disturbance report ...
Page 461
Under certain circumstances the fault condition may reoccur during the post-fault recording, for instance by automatic reclosing to a still faulty power line. In order to capture the new disturbance it is possible to allow retriggering (postretrig = enabled) during the post-fault time. In this case ...
Page 462
14.4 indications 14.4.1 functionality to get fast, condensed and reliable information about disturbances in the primary and/ or in the secondary system it is important to know, for example binary signals that have changed status during a disturbance. This information is used in the short perspective...
Page 463
Function controlled by setledn setting in disturbance report function. Indication list: the possible indication signals are the same as the ones chosen for the disturbance report function and disturbance recorder. The indication function tracks 0 to 1 changes of binary signals during the recording p...
Page 464
The event recorder logs all selected binary input signals connected to the disturbance report function. Each recording can contain up to 150 time-tagged events. The event recorder information is available for the disturbances locally in the ied. The event recording information is an integrated part ...
Page 465
14.5.5 technical data table 333: drprdre technical data function value buffer capacity maximum number of events in disturbance report 150 maximum number of disturbance reports 100 resolution 1 ms accuracy depending on time synchronizing 14.6 sequential of events 14.6.1 functionality continuous event...
Page 466
The list can be configured to show oldest or newest events first with a setting on the local hmi. The sequential of events function runs continuously, in contrast to the event recorder function, which is only active during a disturbance, and each event record is an integral part of its associated dr...
Page 467
14.7.3 signals 14.7.3.1 input signals the trip value recorder function uses analog input signals connected to a1radr to a3radr (not a4radr). 14.7.4 operation principle trip value recorder calculates and presents both fault and pre-fault magnitudes as well as the phase angles of all the selected anal...
Page 468
14.8 disturbance recorder 14.8.1 functionality the disturbance recorder function supplies fast, complete and reliable information about disturbances in the power system. It facilitates understanding system behavior and related primary and secondary equipment during and after a disturbance. Recorded ...
Page 469
Disturbance recorder collects analog values and binary signals continuously, in a cyclic buffer. The pre-fault buffer operates according to the fifo principle; old data will continuously be overwritten as new data arrives when the buffer is full. The size of this buffer is determined by the set pre-...
Page 470
The header file (optional in the standard) contains basic information about the disturbance, that is, information from the disturbance report sub-functions. The disturbance handling tool use this information and present the recording in a user- friendly way. General: • station name, object name and ...
Page 471
14.8.6 technical data table 336: drprdre technical data function value buffer capacity maximum number of analog inputs 40 maximum number of binary inputs 96 maximum number of disturbance reports 100 maximum total recording time (3.4 s recording time and maximum number of channels, typical value) 340...
Page 472
14.9.4 signals table 337: spggio input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function in boolean 0 input status 14.9.5 settings the function does not have any parameters available in local hmi or protection and control ied manager (pcm600). 14.9.6 operation principle upon re...
Page 473
14.10.3 function block sp16ggio block ^in1 ^in2 ^in3 ^in4 ^in5 ^in6 ^in7 ^in8 ^in9 ^in10 ^in11 ^in12 ^in13 ^in14 ^in15 ^in16 iec09000238_en_1.Vsd iec09000238 v1 en figure 208: sp16ggio function block 14.10.4 signals table 338: sp16ggio input signals name type default description block boolean 0 bloc...
Page 474
14.10.5 settings the function does not have any parameters available in local hmi or protection and control ied manager (pcm600). 14.10.6 monitoreddata table 339: sp16ggio monitored data name type values (range) unit description out1 group signal - - output 1 status out2 group signal - - output 2 st...
Page 475
14.10.7 operation principle upon receiving signals at its inputs, iec 61850 generic communication i/o functions 16 inputs (sp16ggio) function will send the signals over iec 61850-8-1 to the equipment or system that requests this signals. To be able to get the signal, one must use other tools, descri...
Page 476
14.11.4 signals table 340: mvggio input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function in real 0 analog input value table 341: mvggio output signals name type description value real magnitude of deadband value range integer range 14.11.5 settings table 342: mvggio non group ...
Page 477
14.11.6 monitored data table 343: mvggio monitored data name type values (range) unit description value real - - magnitude of deadband value range integer 0=normal 1=high 2=low 3=high-high 4=low-low - range 14.11.7 operation principle upon receiving an analog signal at its input, iec61850 generic co...
Page 478
14.12.3 function block mvexp range* highhigh high normal low lowlow iec09000215-1-en.Vsd iec09000215 v1 en figure 209: mvexp function block 14.12.4 signals table 344: mvexp input signals name type default description range integer 0 measured value range table 345: mvexp output signals name type desc...
Page 479
Table 346: input integer value converted to binary output signals measured supervised value is: below low-low limit between low‐ low and low limit between low and high limit between high- high and high limit above high-high limit output: lowlow high low high normal high high high highhigh high 14.13...
Page 480
In the definite time (dt) mode, spvnzbat operates after a predefined operate time and resets when the battery undervoltage or overvoltage condition disappears after reset time. 14.13.4 signals table 347: spvnzbat input signals name type default description v_batt real 0.00 battery terminal voltage t...
Page 481
14.13.6 measured values table 350: spvnzbat measured values name type default description v_batt real 0.00 battery terminal voltage that has to be supervised block boolean 0 blocks all the output signals of the function 14.13.7 monitored data table 351: spvnzbat monitored data name type values (rang...
Page 482
It is possible to block the function outputs by the block input. Low level detector the level detector compares the battery voltage v_batt with the set value of the battvoltlowlim setting. If the value of the v_batt input drops below the set value of the battvoltlowlim setting, the pickup signal pu_...
Page 483
14.14.2 functionality insulation gas monitoring function ssimg (63) is used for monitoring the circuit breaker condition. Binary information based on the gas pressure in the circuit breaker is used as input signals to the function. In addition, the function generates alarms based on received informa...
Page 484
14.14.4.2 ssimg outputsignals table 354: output signals for the function block ssimg (gm01-) signal description pressure pressure service value pres_alm pressure below alarm level pres_lo pressure below lockout level temp temperature of the insulation medium temp_alm temperature above alarm level te...
Page 485
14.14.6 operation principle insulation gas monitoring function ssimg (63) is used to monitor gas pressure in the circuit breaker. Two binary output signals are used from the circuit breaker to initiate alarm signals, pressure below alarm level and pressure below lockout level. If the input signal pr...
Page 486
14.15.2 functionality insulation liquid monitoring function ssiml (71) is used for monitoring the circuit breaker condition. Binary information based on the oil level in the circuit breaker is used as input signals to the function. In addition, the function generates alarms based on received informa...
Page 487
14.15.4.2 ssiml outputsignals table 358: output signals for the function block ssiml (lm1-) signal description level level service value lvl_alm level below alarm level lvl_lo level below lockout level temp temperature of the insulation medium temp_alm temperature above alarm level temp_lo temperatu...
Page 488
14.15.6 operation principle insulation liquid monitoring function ssiml (71) is used to monitor oil level in the circuit breaker. Two binary output signals are used from the circuit breaker to initiate alarm signals, level below alarm level and level below lockout level. If the input signal lvl_alm ...
Page 489
14.16.2 functionality the circuit breaker condition monitoring function sscbr is used to monitor different parameters of the circuit breaker. The breaker requires maintenance when the number of operations has reached a predefined value. For proper functioning of the circuit breaker, it is essential ...
Page 490
Name type default description sprchrgn boolean 0 cb spring charging started input sprchrgd boolean 0 cb spring charged input cbcntrst boolean 0 reset input for cb remaining life and operation counter iaccrst boolean 0 reset accumulated currents power spchtrst boolean 0 reset spring charge time trvtr...
Page 491
Name values (range) unit step default description acccurralmlvl 0.00 - 20000.00 - 0.01 2500.00 setting of alarm level for accumulated currents power acccurrlo 0.00 - 20000.00 - 0.01 2500.00 lockout limit setting for accumulated currents power dircoef -3.00 - -0.50 - 0.01 -1.50 directional coefficien...
Page 492
Name type values (range) unit description nooprday integer - - the number of days cb has been inactive cblife_a integer - - cb remaining life phase a cblife_b integer - - cb remaining life phase b cblife_c integer - - cb remaining life phase c iacc_a real - - accumulated currents power (iyt), phase ...
Page 493
Lopres posclose block iaccrst posopen cbopen 52a opralm oprloalm iaccalm iaccloal noopralm prelo presalm sprchral almpres sprchrgn sprchrgd cbcntrst operation monitoring cblifeal operation counter cbinvpos trvtoal trvtcal circuit breaker status breaker contact travel time accumula- ted energy breake...
Page 494
The breaker status monitoring can be described by using a module diagram. All the modules in the diagram are explained in the next sections. Contact position indicator posclose posopen 52a cbopen phase current check cbinvpos i3p i_a i_b i_c guid-60adc120-4b5a-40d8-b1c5-475e4634214b-ansi v1 en figure...
Page 495
Guid-82c88b52-1812-477f-8b1a-3011a300547a v1 en figure 217: functional module diagram for calculating inactive days and alarm for circuit breaker operation monitoring inactivity timer the module calculates the number of days the circuit breaker has remained inactive, that is, has stayed in the same ...
Page 496
Traveling time calculator the contact travel time of the breaker is calculated from the time between auxiliary contacts' state change. The open travel time is measured between the opening of the posclose auxiliary contact and the closing of the posopen auxiliary contact. Travel time is also measured...
Page 497
14.16.7.4 operation counter the operation counter subfunction calculates the number of breaker operation cycles. Both open and close operations are included in one operation cycle. The operation counter value is updated after each open operation. The operation of the subfunction can be described by ...
Page 498
Accumula- ted energy calculator posclose iaccrst block blk_alm alarm limit check iaccloal iaccalm i3p i_a i_b i_c guid-dac3746f-dfbf-4186-a99d-1d972578d32a-ansi v1 en figure 220: functional module diagram for calculating accumulative energy and alarm accumulated energy calculator this module calcula...
Page 499
Can be reset by setting the clear accum. Breaking curr setting to true in the clear menu from lhmi. Alarm limit check the iaccalm alarm is activated when the accumulated energy exceeds the value set with the acccurralmlvl threshold setting. However, when the energy exceeds the limit value set with t...
Page 500
Of operations the breaker can perform at the rated current and at the rated fault current, respectively. The remaining life is calculated separately for all three phases and it is available as a monitored data value cblife_a (_b, _c). The values can be cleared by setting the parameter cb wear values...
Page 501
Spring charge time measurement two binary inputs, sprchrgn and sprchrgd, indicate spring charging started and spring charged, respectively. The spring charging time is calculated from the difference of these two signal timings. The spring charging time sprchrt is available through the monitored data...
Page 502
The binary input block can be used to block the function. The activation of the block input deactivates all outputs and resets internal timers. The alarm signals from the function can be blocked by activating the binary input blk_alm. 14.16.8 technical data table 365: sscbr technical data function r...
Page 503
Guid-b8a3a04c-430d-4488-9f72-8529fab0b17d v1 en figure 225: settings for cmmxu: 1 all input signals to iec 60870-5-103 i103meas must be connected in application configuration. Connect an input signals on iec 60870-5-103 i103meas that is not connected to the corresponding output on mmxu function, to ...
Page 504
14.17.3 signals table 366: i103meas input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of service value reporting i_a real 0.0 service value for current phase a i_b real 0.0 service value for current phase b i_c real 0.0 service value for current phase c in real 0.0 service value for ...
Page 505
14.18 measurands user defined signals for iec 60870-5-103 i103measusr 14.18.1 functionality i103measusr is a function block with user defined input measurands in monitor direction. These function blocks include the functiontype parameter for each block in the private range, and the information numbe...
Page 506
14.18.4 settings table 369: i103measusr non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description functiontype 1 - 255 - 1 25 function type (1-255) infno 1 - 255 - 1 1 information number for measurands (1-255) maxmeasur1 0.05 - 10000000000.00 - 0.05 1000.00 maximum value for measu...
Page 507
14.19.2 function block iec10000289-1-en.Vsd i103ar block 16_aract 128_cbon 130_unsu iec10000289 v1 en figure 228: i103ar function block 14.19.3 signals table 370: i103ar input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of status reporting 16_aract boolean 0 information number 16, au...
Page 508
14.20.2 function block iec10000290-1-en.Vsd i103ef block 51_effw 52_efrev iec10000290 v1 en figure 229: i103ef function block 14.20.3 signals table 372: i103ef input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of status reporting 51_effw boolean 0 information number 51, ground-fault ...
Page 509
14.21.2 function block i103fltprot block 64_pu_a 65_pu_b 66_pu_c 67_stin 68_trgen 69_tr_a 70_tr_b 71_tr_c 72_trbkup 73_scl 74_fw 75_rev 76_trans 77_recev 78_zone1 79_zone2 80_zone3 81_zone4 82_zone5 84_stgen 85_bfp 86_mtr_a 87_mtr_b 88_mtr_c 89_mtrn 90_ioc 91_ioc 92_ief 93_ief arinprog fltloc ansi10...
Page 510
Name type default description 73_scl real 0 information number 73, fault location in ohm 74_fw boolean 0 information number 74, forward/line 75_rev boolean 0 information number 75, reverse/busbar 76_trans boolean 0 information number 76, signal transmitted 77_recev boolean 0 information number 77, s...
Page 511
14.22 ied status for iec 60870-5-103 i103ied 14.22.1 functionality i103ied is a function block with defined ied functions in monitor direction. This block uses parameter as functiontype, and information number parameter is defined for each input signal. 14.22.2 function block iec10000292-1-en.Vsd i1...
Page 512
14.23 supervison status for iec 60870-5-103 i103superv 14.23.1 functionality i103superv is a function block with defined functions for supervision indications in monitor direction. This block includes the functiontype parameter, and the information number parameter is defined for each output signal....
Page 513
14.24 status for user defined signals for iec 60870-5-103 i103usrdef 14.24.1 functionality i103usrdef is a function blocks with user defined input signals in monitor direction. These function blocks include the functiontype parameter for each block in the private range, and the information number pa...
Page 514
14.24.3 signals table 380: i103usrdef input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of status reporting input1 boolean 0 binary signal input 1 input2 boolean 0 binary signal input 2 input3 boolean 0 binary signal input 3 input4 boolean 0 binary signal input 4 input5 boolean 0 bin...
Page 515
Section 15 metering 15.1 pulse counter pcggio 15.1.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number pulse counter pcggio s00947 v1 en - 15.1.2 functionality pulse counter (pcggio) function counts externally generated binary pulses,...
Page 516
15.1.4 signals table 382: pcggio input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function read_val boolean 0 initiates an additional pulse counter reading bi_pulse boolean 0 connect binary input channel for metering rs_cnt boolean 0 resets pulse counter value table 383: pcggio o...
Page 517
15.1.6 monitored data table 385: pcggio monitored data name type values (range) unit description cnt_val integer - - actual pulse counter value scal_val real - - scaled value with time and status information 15.1.7 operation principle the registration of pulses is done according to setting of countc...
Page 518
Read_val performs readings according to the setting of parameter countcriteria. The signal must be a pulse with a length >1 second. The bi_pulse input is connected to the used input of the function block for the binary input output module (bio). The rs_cnt input is used for resetting the counter. Ea...
Page 519
15.2 energy calculation and demand handling etpmmtr 15.2.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number energy calculation and demand handling etpmmtr wh iec10000169 v1 en - 15.2.2 functionality outputs from the measurements (cvm...
Page 520
15.2.4 signals table 387: etpmmtr input signals name type default description p real 0 measured active power q real 0 measured reactive power stacc boolean 0 start to accumulate energy values rstacc boolean 0 reset of accumulated enery reading rstdmd boolean 0 reset of maximum demand reading table 3...
Page 521
15.2.5 settings table 389: etpmmtr non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation disabled enabled - - disabled operation enable/disable startacc disabled enabled - - disabled activate the accumulation of energy values tenergy 1 minute 5 minutes 10 minutes 15 ...
Page 522
15.2.6 monitored data table 391: etpmmtr monitored data name type values (range) unit description eafacc real - mwh accumulated forward active energy value earacc real - mwh accumulated reverse active energy value erfacc real - mvarh accumulated forward reactive energy value erracc real - mvarh accu...
Page 523
P q stacc rstacc rstdmd true false false cvmmxn iec09000106.Vsd etpmmtr p_inst q_inst iec09000106 v1 en figure 237: connection of energy calculation and demand handling function (etpmmtr) to the measurements function (cvmmxn) 15.2.8 technical data table 392: etpmmtr technical data function range or ...
Page 524
518.
Page 525
Section 16 station communication 16.1 dnp3 protocol dnp3 (distributed network protocol) is a set of communications protocols used to communicate data between components in process automation systems. For a detailed description of the dnp3 protocol, see the dnp3 communication protocol manual. 16.2 ie...
Page 526
Interoperates with other iec 61850-compliant ieds, tools, and systems and simultaneously reports events to five different clients on the iec 61850 station bus. The event system has a rate limiter to reduce cpu load. The event channel has a quota of 10 events/second. If the quota is exceeded the even...
Page 527
16.2.5 technical data table 395: communication protocol function value protocol tcp/ip ethernet communication speed for the ieds 100 mbit/s protocol iec 61850–8–1 communication speed for the ieds 100base-fx protocol dnp3.0/tcp communication speed for the ieds 100base-fx protocol, serial iec 60870–5–...
Page 528
16.3.2 function block gooseintlkrcv block ^resreq ^resgrant ^app1_op ^app1_cl app1val ^app2_op ^app2_cl app2val ^app3_op ^app3_cl app3val ^app4_op ^app4_cl app4val ^app5_op ^app5_cl app5val ^app6_op ^app6_cl app6val ^app7_op ^app7_cl app7val ^app8_op ^app8_cl app8val ^app9_op ^app9_cl app9val ^app10...
Page 529
Table 397: gooseintlkrcv output signals name type description resreq boolean reservation request resgrant boolean reservation granted app1_op boolean apparatus 1 position is open app1_cl boolean apparatus 1 position is closed app1val boolean apparatus 1 position is valid app2_op boolean apparatus 2 ...
Page 530
Name type description app12_op boolean apparatus 12 position is open app12_cl boolean apparatus 12 position is closed app12val boolean apparatus 12 position is valid app13_op boolean apparatus 13 position is open app13_cl boolean apparatus 13 position is closed app13val boolean apparatus 13 position...
Page 531
16.4.2 function block goosebinrcv block ^out1 out1val ^out2 out2val ^out3 out3val ^out4 out4val ^out5 out5val ^out6 out6val ^out7 out7val ^out8 out8val ^out9 out9val ^out10 out10val ^out11 out11val ^out12 out12val ^out13 out13val ^out14 out14val ^out15 out15val ^out16 out16val iec09000236_en.Vsd iec...
Page 532
Name type description out3 boolean binary output 3 out3val boolean valid data on binary output 3 out4 boolean binary output 4 out4val boolean valid data on binary output 4 out5 boolean binary output 5 out5val boolean valid data on binary output 5 out6 boolean binary output 6 out6val boolean valid da...
Page 533
16.5 goose function block to receive a double point value goosedprcv 16.5.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number goose function block to receive a double point value goosedprcv - - 16.5.2 functionality goosedprcv is used ...
Page 534
16.5.5 settings table 404: goosedprcv non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation disabled enabled - - disabled operation enable/disable 16.5.6 operation principle the datavalid output will be high if the incoming message is with valid data. The commvalid o...
Page 535
16.6.2 functionality gooseintrcv is used to receive an integer value using iec61850 protocol via goose. 16.6.3 function block iec10000250-1-en.Vsd gooseintrcv block ^intout datavalid commvalid test iec10000250 v1 en figure 241: gooseintrcv function block 16.6.4 signals table 405: gooseintrcv input s...
Page 536
The commvalid output will become low when the sending ied is under total failure condition and the goose transmission from the sending ied does not happen. The test output will go high if the sending ied is in test mode. The input of this goose block must be linked in smt by means of a cross to rece...
Page 537
16.7.4 signals table 408: goosemvrcv input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function table 409: goosemvrcv output signals name type description mvout real measurand value output datavalid boolean data valid for measurand value output commvalid boolean communication vali...
Page 538
16.8 goose function block to receive a single point value goosesprcv 16.8.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number goose function block to receive a single point value goosesprcv - - 16.8.2 functionality goosesprcv is used ...
Page 539
16.8.5 settings table 413: goosesprcv non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation disabled enabled - - disabled operation off/on 16.8.6 operation principle the datavalid output will be high if the incoming message is with valid data. The commvalid output wi...
Page 540
Iec 60870-5-103 protocol can be configured to use either the optical serial or rs485 serial communication interface on the com05 communication module. The functions operation selection for optical serial (opticalprot) and operation selection for rs485 (rs485prot) are used to select the communication...
Page 541
Name values (range) unit step default description mastertimedomain utc local local with dst - - utc master time domain timesyncmode iedtime linmasttime iedtimeskew - - iedtime time synchronization mode evaltimeaccuracy disabled 5ms 10ms 20ms 40ms - - 5ms evaluate time accuracy for invalid time event...
Page 542
536.
Page 543
Section 17 basic ied functions 17.1 self supervision with internal event list 17.1.1 functionality the self supervision with internal event list (interrsig and selfsupevlst) function reacts to internal system events generated by the different built-in self- supervision elements. The internal events ...
Page 544
17.1.2.3 signals table 416: interrsig output signals name type description fail boolean internal fail warning boolean internal warning tsyncerr boolean time synchronization error rtcerr boolean real time clock error disable boolean application disable 17.1.2.4 settings the function does not have any...
Page 545
Menu/diagnostics/internal events or main menu/diagnostics/ied status/general. The information from the self-supervision function is also available in the event viewer in pcm600. Both events from the event list and the internal events are listed in time consecutive order in the event viewer. A self-s...
Page 546
Time synch error internal warning gents sync error gents sync ok s r gents rtc error s r or internal fail liodev stopped s r real time clock error e.G. Bio1- error settings changed settings changed rte fatal error wdog starved sw watchdog error gents rtc ok gents time reset or liodev started or liod...
Page 547
17.1.4.1 internal signals selfsupevlst function provides several status signals, that tells about the condition of the ied. As they provide information about the internal status of the ied, they are also called internal signals. The internal signals can be divided into two groups. • standard signals...
Page 548
Table 419: explanations of internal signals name of signal reasons for activation internal fail this signal will be active if one or more of the following internal signals are active; real time clock error, runtime app error, runtime exec error, sw watchdog error, file system error internal warning ...
Page 549
U 1 x 2 x 1 u 1 x 2 x 1 adx controller adx_high adx_low adx iec05000296-3-en.Vsd iec05000296 v3 en figure 247: simplified drawing of a/d converter for the ied. The technique to split the analog input signal into two a/d converter(s) with different amplification makes it possible to supervise the a/d...
Page 550
17.2 time synchronization 17.2.1 functionality the time synchronization source selector is used to select a common source of absolute time for the ied when it is a part of a protection system. This makes it possible to compare event and disturbance data between all ieds in a station automation syste...
Page 551
17.2.3.2 settings table 422: sntp non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description serverip-add 0 - 255 ip address 1 0.0.0.0 server ip-address redservip-add 0 - 255 ip address 1 0.0.0.0 redundant server ip-address 17.2.4 time system, summer time begin dstbegin 17.2.4.1 id...
Page 552
17.2.4.2 settings table 423: dstbegin non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description monthinyear january february march april may june july august september october november december - - march month in year when daylight time starts dayinweek sunday monday tuesday wedne...
Page 553
17.2.5.2 settings table 424: dstend non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description monthinyear january february march april may june july august september october november december - - october month in year when daylight time ends dayinweek sunday monday tuesday wednesd...
Page 554
17.2.7 time synchronization via irig-b 17.2.7.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number time synchronization via irig-b irig-b - - 17.2.7.2 settings table 426: irig-b non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step ...
Page 555
Design of the time system (clock synchronization) sw-time protection and control functions time tagging and general synchronization commu - nication events ansi09000210-1-en.Vsd external synchronization sources disabled sntp dnp irig-b time- regulator iec60870-5-103 ansi09000210 v1 en figure 248: de...
Page 556
• the maximum error of the last used synchronization message • the time since the last used synchronization message • the rate accuracy of the internal clock in the function. 17.2.8.2 real-time clock (rtc) operation the ied has a built-in real-time clock (rtc) with a resolution of one second. The cl...
Page 557
Rate accuracy in the ied, the rate accuracy at cold start is 100 ppm but if the ied is synchronized for a while, the rate accuracy is approximately 1 ppm if the surrounding temperature is constant. Normally, it takes 20 minutes to reach full accuracy. Time-out on synchronization sources all synchron...
Page 558
If the x in 00x is 4, 5, 6 or 7, the time message from irig-b contains information of the year. If x is 0, 1, 2 or 3, the information contains only the time within the year, and year information has to come from the tool or local hmi. The irig-b input also takes care of ieee1344 messages that are se...
Page 559
17.3.2 setting group handling setgrps 17.3.2.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number setting group handling setgrps - - 17.3.2.2 settings table 428: setgrps non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default ...
Page 560
17.3.3.3 signals table 429: actvgrp input signals name type default description actgrp1 boolean 0 selects setting group 1 as active actgrp2 boolean 0 selects setting group 2 as active actgrp3 boolean 0 selects setting group 3 as active actgrp4 boolean 0 selects setting group 4 as active table 430: a...
Page 561
More than one input may be activated at the same time. In such cases the lower order setting group has priority. This means that if for example both group four and group two are set to activate, group two will be the one activated. Every time the active group is changed, the output signal grp_chgd i...
Page 562
17.4.2 functionality when the test mode functionality testmode is activated, all the functions in the ied are automatically blocked. It is then possible to unblock every function(s) individually from the local hmi to perform required tests. When leaving testmode, all blockings are removed and the ie...
Page 563
17.4.5 settings table 433: testmode non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description testmode disabled enabled - - disabled test mode in operation (enabled) or not (disabled) eventdisable disabled enabled - - disabled event disable during testmode cmdtestbit off on - - of...
Page 564
When a binary input is used to set the ied in test mode and a parameter, that requires restart of the application, is changed, the ied will re-enter test mode and all functions will be blocked, also functions that were unblocked before the change. During the re-entering to test mode, all functions w...
Page 565
17.5.3 function block chnglck lock* active override iec09000062-1-en.Vsd iec09000062 v1 en figure 253: chnglck function block 17.5.4 signals table 434: chnglck input signals name type default description lock boolean 0 activate change lock table 435: chnglck output signals name type description acti...
Page 566
• set system time • enter and exit from test mode • change of active setting group the binary input signal lock controlling the function is defined in act or smt: binary input function 1 activated 0 deactivated 17.6 ied identifiers terminalid 17.6.1 identification function description iec 61850 iden...
Page 567
Name values (range) unit step default description unitname 0 - 18 - 1 unit name unit name unitnumber 0 - 99999 - 1 0 unit number technicalkey 0 - 18 - 1 aa0j0q0a0 technical key 17.7 product information 17.7.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/...
Page 568
17.8 primary system values primval 17.8.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number primary system values primval - - 17.8.2 functionality the rated system frequency and phasor rotation are set under main menu/ configuration/ ...
Page 569
To a smai function block shall always have the same cycle time as the smai block. 17.9.2 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number signal matrix for analog inputs smai_20_x - - 17.9.3 function block ansi09000137-1-en.Vsd smai_...
Page 570
17.9.4 signals table 438: smai_20_1 input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block group 1 dftspfc real 20.0 number of samples per fundamental cycle used for dft calculation revrot boolean 0 reverse rotation group 1 grp1_a string - first analog input used for phase l1 or l1-l2 qua...
Page 571
Table 441: smai_20_12 output signals name type description ai3p group signal grouped three phase signal containing data from inputs 1-4 ai1 group signal quantity connected to the first analog input ai2 group signal quantity connected to the second analog input ai3 group signal quantity connected to ...
Page 572
Table 443: smai_20_1 non group settings (advanced) name values (range) unit step default description negation disabled negaten negate3ph negate3ph+n - - disabled negation minvalfreqmeas 5 - 200 % 1 10 limit for frequency calculation in % of vbase even if the analoginputtype setting of a smai block i...
Page 573
Even if the analoginputtype setting of a smai block is set to current, the minvalfreqmeas setting is still visible. This means that the minimum level for current amplitude is based on vbase. For example, if vbase is 20000, the minimum amplitude for current is 20000 * 10% = 2000. This has practical a...
Page 574
• it is not mandatory to connect all the inputs of smai function. However, it is very important that same set of three phase analog signals should be connected to one smai function. • the sequence of input connected to smai function inputs grpx_a, grpx_b, grpx_c and grpx_n should normally represent ...
Page 575
Based on the set system frequency. Dftreference set to dftrefgrpx uses dft reference from the selected group block, when own group selected adaptive dft reference will be used based on the calculated signal frequency from own group. Dftreference set to external dft ref will use reference based on in...
Page 576
Task time group 1 (5ms) task time group 2 (20ms) task time group 1 (5ms) smai instance 3 phase group smai_20_1:1 1 smai_20_2:1 2 smai_20_3:1 3 smai_20_4:1 4 smai_20_5:1 5 smai_20_6:1 6 smai_20_7:1 7 smai_20_8:1 8 smai_20_9:1 9 smai_20_10:1 10 smai_20_11:1 11 smai_20_12:1 12 task time group 2 (20ms) ...
Page 577
For smai_20_1:2 to smai_20_12:2 dftreference set to external dft ref to use dftspfc input as reference. 17.10 summation block 3 phase 3phsum 17.10.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number summation block 3 phase 3phsum - - ...
Page 578
Table 447: 3phsum output signals name type description ai3p group signal linear combination of two connected three phase inputs ai1 group signal linear combination of input 1 signals from both smai blocks ai2 group signal linear combination of input 2 signals from both smai blocks ai3 group signal l...
Page 579
17.11.1 identification function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number global base values gbasval - - 17.11.2 functionality global base values function (gbasval) is used to provide global values, common for all applicable functions within the ied....
Page 580
17.12.2 functionality to safeguard the interests of our customers, both the ied and the tools that are accessing the ied are protected, by means of authorization handling. The authorization handling of the ied and the pcm600 is implemented at both access points to the ied: • local, through the local...
Page 581
17.12.4.1 authorization handling in the ied at delivery the default user is the superuser. No log on is required to operate the ied until a user has been created with the ied user management.. Once a user is created and written to the ied, that user can perform a log on, using the password assigned ...
Page 582
17.13.2 functionality authority status (athstat) function is an indication function block for user log-on activity. 17.13.3 function block athstat usrblked loggedon iec09000235_en_1.Vsd iec09000235 v1 en figure 258: athstat function block 17.13.4 signals table 452: athstat output signals name type d...
Page 583
17.14 denial of service 17.14.1 functionality the denial of service functions (doslan1 and dosfrnt) are designed to limit overload on the ied produced by heavy ethernet network traffic. The communication facilities must not be allowed to compromise the primary functionality of the device. All inboun...
Page 584
17.14.2.4 settings the function does not have any parameters available in the local hmi or pcm600. 17.14.2.5 monitored data table 454: dosfrnt monitored data name type values (range) unit description state integer 0=off 1=normal 2=throttle 3=discardlow 4=discardall 5=stoppoll - frame rate control st...
Page 585
17.14.3.2 function block doslan1 linkup warning alarm iec09000134-1-en.Vsd iec09000134 v1 en figure 260: doslan1 function block 17.14.3.3 signals table 455: doslan1 output signals name type description linkup boolean ethernet link status warning boolean frame rate is higher than normal state alarm b...
Page 586
Name type values (range) unit description nonippackrecnorm integer - - number of non ip packets received in normal mode nonippackrecpoll integer - - number of non ip packets received in polled mode nonippackdisc integer - - number of non ip packets discarded 17.14.4 operation principle the denial of...
Page 587
Section 18 ied physical connections 18.1 protective ground connections the ied shall be grounded with a 6 gauge flat copper cable. The ground lead should be as short as possible, less than 59.06 inches (1500 mm). Additional length is required for door mounting. Ansi11000286 v2 en figure 261: the pro...
Page 588
18.2 inputs 18.2.1 measuring inputs table 457: analog input modules terminal trm 6i + 4u trm 8i + 2u trm 4i + 1i + 5u trm 4i + 6u aim 6i + 4u aim 4i + 1i + 5u x101-1, 2 1/5a 1/5a 1/5a 1/5a 1/5a 1/5a x101-3, 4 1/5a 1/5a 1/5a 1/5a 1/5a 1/5a x101-5, 6 1/5a 1/5a 1/5a 1/5a 1/5a 1/5a x101-7, 8 1/5a 1/5a 1...
Page 589
Table 459: auxiliary voltage supply of 48-125 v dc case terminal description 3u full 19” x420-1 - input x420-2 + input 18.2.3 binary inputs the binary inputs can be used, for example, to generate a blocking signal, to unlatch output contacts, to trigger the digital fault recorder or for remote contr...
Page 590
Table 461: binary inputs x324, 3u full 19” terminal description pcm600 info hardware module instance hardware channel x324-1 - for input 1 bio_3 bi1 x324-2 binary input 1 + bio_3 bi1 x324-3 - x324-4 common - for inputs 2-3 x324-5 binary input 2 + bio_3 bi2 x324-6 binary input 3 + bio_3 bi3 x324-7 - ...
Page 591
Terminal description pcm600 info hardware module instance hardware channel x329-12 common - for inputs 6-7 x329-13 binary input 6 + bio_4 bi6 x329-14 binary input 7 + bio_4 bi7 x329-15 - x329-16 common - for inputs 8-9 x329-17 binary input 8 + bio_4 bi8 x329-18 binary input 9 + bio_4 bi9 table 463: ...
Page 592
Table 464: binary inputs x339, 3u full 19” terminal description pcm600 info hardware module instance hardware channel x339-1 - for input 1 bio_6 bi1 x339-2 binary input 1 + bio_6 bi1 x339-3 - x339-4 common - for inputs 2-3 x339-5 binary input 2 + bio_6 bi2 x339-6 binary input 3 + bio_6 bi3 x339-7 - ...
Page 593
Table 465: terminal description pcm600 info hardware module instance hardware channel power output 1, normally open (tcm) x317-1 - psm_102 bo1_po_tcm x317-2 + power output 2, normally open (tcm) x317-3 - psm_102 bo2_po_tcm x317-4 + power output 3, normally open (tcm) x317-5 - psm_102 bo3_po_tcm x317...
Page 594
Terminal description pcm600 info hardware module instance hardware channel x326-4 x326-5 power output 3, normally open bio_4 bo3_po x326-6 table 468: output contacts x331, 3u full 19” terminal description pcm600 info hardware module instance hardware channel x331-1 power output 1, normally open bio_...
Page 595
Table 470: output contacts x317, 3u full 19” terminal description pcm600 info hardware module instance hardware channel x317-13 signal output 1, normally open psm_102 bo7_so x317-14 x317-15 signal output 2, normally open psm_102 bo8_so x317-16 x317-17 signal output 3, normally open psm_102 bo9_so x3...
Page 596
Terminal description pcm600 info hardware module instance hardware channel x326-14 signal output 5, normally open bio_4 bo8_so x326-15 signal outputs 4 and 5, common x326-16 signal output 6, normally closed bio_4 bo9_so x326-17 signal output 6, normally open x326-18 signal output 6, common table 473...
Page 597
Terminal description pcm600 info hardware module instance hardware channel x336-16 signal output 6, normally closed bio_6 bo9_so x336-17 signal output 6, normally open x336-18 signal output 6, common 18.3.3 irf the irf contact functions as a change-over output contact for the self-supervision system...
Page 598
Pc has to be configured in a way that it obtains the ip address automatically if the dhcpserver is enabled in lhmi. There is a dhcp server inside ied for the front interface only. The events and setting values and all input data such as memorized values and disturbance records can be read via the fr...
Page 599
Pin description 7 rs485 rxterm 8 rs485 tx- 9 rs485 gnd 10 rs485 gnd 11 irig-b - 12 irig-b + 13 gndc 14 gnd 18.4.5 communication interfaces and protocols table 477: supported station communication interfaces and protocols protocol ethernet serial 100base-fx lc glass fibre (st connector) eia-485 iec 6...
Page 600
18.5.1 connection diagrams for 650 series iec12000584 v1 en section 18 1mrk 502 043-uus b ied physical connections 594 technical manual.
Page 601
Iec12000585 v1 en 1mrk 502 043-uus b section 18 ied physical connections 595 technical manual.
Page 602
Iec12000586 v1 en section 18 1mrk 502 043-uus b ied physical connections 596 technical manual.
Page 603
Iec12000587 v1 en 1mrk 502 043-uus b section 18 ied physical connections 597 technical manual.
Page 604
Iec12000588 v1 en section 18 1mrk 502 043-uus b ied physical connections 598 technical manual.
Page 605
Iec12000589 v1 en 1mrk 502 043-uus b section 18 ied physical connections 599 technical manual.
Page 606
Iec12000590 v1 en section 18 1mrk 502 043-uus b ied physical connections 600 technical manual.
Page 607
Iec12000591 v1 en 1mrk 502 043-uus b section 18 ied physical connections 601 technical manual.
Page 608
Iec12000592 v1 en section 18 1mrk 502 043-uus b ied physical connections 602 technical manual.
Page 609
18.5.2 connection diagrams for reg650 b01a 1mrk006502-nc-1-1.2-ansi v1 en 1mrk 502 043-uus b section 18 ied physical connections 603 technical manual.
Page 610
1mrk006502-nc-2-1.2-ansi v1 en section 18 1mrk 502 043-uus b ied physical connections 604 technical manual.
Page 611
1mrk006502-nc-3-1.2-ansi v1 en 1mrk 502 043-uus b section 18 ied physical connections 605 technical manual.
Page 612
1mrk006502-nc-4-1.2-ansi v1 en section 18 1mrk 502 043-uus b ied physical connections 606 technical manual.
Page 613
1mrk006502-nc-5-1.2-ansi v1 en 1mrk 502 043-uus b section 18 ied physical connections 607 technical manual.
Page 614
1mrk006502-nc-6-1.2-ansi v1 en section 18 1mrk 502 043-uus b ied physical connections 608 technical manual.
Page 615
1mrk006502-nc-7-1.2-ansi v1 en 1mrk 502 043-uus b section 18 ied physical connections 609 technical manual.
Page 616
1mrk006502-nc-8-1.2-ansi v1 en section 18 1mrk 502 043-uus b ied physical connections 610 technical manual.
Page 617
1mrk006502-nc-9-1.2-ansi v1 en 1mrk 502 043-uus b section 18 ied physical connections 611 technical manual.
Page 618
18.5.3 connection diagrams for reg650 b05a 1mrk006502-pc-1-1.2-ansi v1 en section 18 1mrk 502 043-uus b ied physical connections 612 technical manual.
Page 619
1mrk006502-pc-2-1.2-ansi v1 en 1mrk 502 043-uus b section 18 ied physical connections 613 technical manual.
Page 620
1mrk006502-pc-3-1.2-ansi v1 en section 18 1mrk 502 043-uus b ied physical connections 614 technical manual.
Page 621
1mrk006502-pc-4-1.2-ansi v1 en 1mrk 502 043-uus b section 18 ied physical connections 615 technical manual.
Page 622
1mrk006502-pc-5-1.2-ansi v1 en section 18 1mrk 502 043-uus b ied physical connections 616 technical manual.
Page 623
1mrk006502-pc-6-1.2-ansi v1 en 1mrk 502 043-uus b section 18 ied physical connections 617 technical manual.
Page 624
1mrk006502-pc-7-1.2-ansi v1 en section 18 1mrk 502 043-uus b ied physical connections 618 technical manual.
Page 625
1mrk006502-pc-8-1.2-ansi v1 en 1mrk 502 043-uus b section 18 ied physical connections 619 technical manual.
Page 626
1mrk006502-pc-9-1.2-ansi v1 en section 18 1mrk 502 043-uus b ied physical connections 620 technical manual.
Page 627
Section 19 technical data 19.1 dimensions table 478: dimensions of the ied - 3u full 19" rack description value width 17.40 inches (442 mm) height 5.20 inches (132 mm), 3u depth 9.82 inches (249.5 mm) weight box weight lhmi 2.87 lbs (1.3 kg) 19.2 power supply table 479: power supply description 600p...
Page 628
19.3 energizing inputs table 480: energizing inputs description value rated frequency 50/60 hz operating range rated frequency ± 5 hz current inputs rated current, i n 0.1/0.5 a 1) 1/5 a 2) thermal withstand capability: • continuously 4 a 20 a • for 1 s 100 a 500 a *) • for 10 s 20 a 100 a dynamic c...
Page 629
19.5 signal outputs table 482: signal output and irf output description value rated voltage 250 v ac/dc continuous contact carry 5 a make and carry for 3.0 s 10 a make and carry 0.5 s 30 a breaking capacity when the control-circuit time constant l/r ≤0.5 a/≤0.1 a/≤0.04 a 19.6 power outputs table 483...
Page 630
19.7 data communication interfaces table 485: ethernet interfaces ethernet interface protocol cable data transfer rate 100base-tx - cat 6 s/ftp or better 100 mbits/s 100base-fx tcp/ip protocol fibre-optic cable with lc connector 100 mbits/s table 486: fibre-optic communication link wave length fibre...
Page 631
Table 489: eia-485 interface type value conditions minimum differential driver output voltage 1.5 v — maximum output current 60 ma — minimum differential receiver input voltage 0.2 v — supported bit rates 300, 600, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, 115200 — maximum number of 650 ieds supp...
Page 632
19.9 environmental conditions and tests table 494: environmental conditions description value operating temperature range -25...+55ºc (continuous) short-time service temperature range -40...+70ºc ( note: degradation in mtbf and hmi performance outside the temperature range of -25...+55ºc relative hu...
Page 633
Section 20 ied and functionality tests 20.1 electromagnetic compatibility tests table 496: electromagnetic compatibility tests description type test value reference 100 khz and 1 mhz burst disturbance test iec 61000-4-18, level 3 iec 60255-22-1 ansi c37.90.1-2002 • common mode 2.5 kv • differential ...
Page 634
Description type test value reference • 3 s 1000 a/m • continuous 100 a/m pulse magnetic field immunity test 1000a/m iec 61000–4–9, level 5 power frequency immunity test iec 60255-22-7, class a iec 61000-4-16 • common mode 300 v rms • differential mode 150 v rms voltage dips and short interruptionsc...
Page 635
20.2 insulation tests table 497: insulation tests description type test value reference dielectric tests: iec 60255-5 ansi c37.90-2005 • test voltage 2 kv, 50 hz, 1 min 1 kv, 50 hz, 1 min, communication impulse voltage test: iec 60255-5 ansi c37.90-2005 • test voltage 5 kv, unipolar impulses, wavefo...
Page 636
Table 499: product safety description reference lv directive 2006/95/ec standard en 60255-27 (2005) 20.5 emc compliance table 500: emc compliance description reference emc directive 2004/108/ec standard en 50263 (2000) en 60255-26 (2007) section 20 1mrk 502 043-uus b ied and functionality tests 630 ...
Page 637
Section 21 time inverse characteristics 21.1 application in order to assure time selectivity between different overcurrent protections in different points in the network different time delays for the different relays are normally used. The simplest way to do this is to use definite time delay. In mo...
Page 638
En05000131.Vsd time fault point position iec05000131 v1 en figure 264: inverse time overcurrent characteristics with inst. Function the inverse time characteristic makes it possible to minimize the fault clearance time and still assure the selectivity between protections. To assure selectivity betwe...
Page 639
En05000132_ansi.Vsd 51 51 a1 b1 feeder time axis t=0 t=t 1 t=t 2 t=t 3 ansi05000132 v1 en figure 265: selectivity steps for a fault on feeder b1 where: t=0 is the fault occurs t=t 1 is protection b1 trips t=t 2 is breaker at b1 opens t=t 3 is protection a1 resets in the case protection b1 shall oper...
Page 640
• if there is a risk of intermittent faults. If the current relay, close to the faults, picks up and resets there is a risk of unselective trip from other protections in the system. • delayed resetting could give accelerated fault clearance in case of automatic reclosing to a permanent fault. • over...
Page 641
For inverse time characteristics a time will be initiated when the current reaches the set pickup level. From the general expression of the characteristic the following can be seen: ( ) - × - × æ ö æ ö × ç ÷ = ç ÷ ç ÷ è ø è ø p op i t b td c a td pickupn equation1642 v1 en (equation 114) where: t op...
Page 642
For the iec curves there is also a setting of the minimum time-lag of operation, see figure 266 . Iec05000133-3-en.Vsd tmin current operate time imin iec05000133 v2 en figure 266: minimum time-lag operation for the iec curves in order to fully comply with iec curves definition setting parameter tmin...
Page 643
[ ] = - × æ ö ç ÷ ç ÷ ç ÷ ç ÷ è ø 0.339 0.235 td t s pickupn i equation1647 v1 en (equation 118) where: pickupn is the set pickup current for step n td is set time multiplier for step n i is the measured current the rd inverse curve gives a logarithmic delay, as used in the combiflex protection rxid...
Page 644
Table 501: ansi inverse time characteristics function range or value accuracy operating characteristic: ( ) = + × - æ ö ç ÷ ç ÷ è ø 1 p a t b td i equation1651 v1 en i = i measured /i set td = (0.05-999) in steps of 0.01 - ansi extremely inverse a=28.2, b=0.1217, p=2.0 ansi very inverse a=19.61, b=0...
Page 645
Table 503: ri and rd type inverse time characteristics function range or value accuracy ri type inverse characteristic = × - 1 0.236 0.339 t td i equation1656 v1 en i = i measured /i set td = (0.05-999) in steps of 0.01 rd type logarithmic inverse characteristic = - × æ ö ç ÷ è ø 5.8 1.35 t i in td ...
Page 646
Table 505: inverse time characteristics for undervoltage protection function range or value accuracy type a curve: = - æ ö ç ÷ è ø td t vpickup v vpickup equation1658 v1 en v = v measured td = (0.05-1.10) in steps of 0.01 ±5% +60 ms type b curve: × = + - × - æ ö ç ÷ è ø 2.0 480 0.055 32 0.5 td t vpi...
Page 647
A070750 v2 en figure 267: ansi extremely inverse time characteristics 1mrk 502 043-uus b section 21 time inverse characteristics 641 technical manual.
Page 648
A070751 v2 en figure 268: ansi very inverse time characteristics section 21 1mrk 502 043-uus b time inverse characteristics 642 technical manual.
Page 649
A070752 v2 en figure 269: ansi normal inverse time characteristics 1mrk 502 043-uus b section 21 time inverse characteristics 643 technical manual.
Page 650
A070753 v2 en figure 270: ansi moderately inverse time characteristics section 21 1mrk 502 043-uus b time inverse characteristics 644 technical manual.
Page 651
A070817 v2 en figure 271: ansi long time extremely inverse time characteristics 1mrk 502 043-uus b section 21 time inverse characteristics 645 technical manual.
Page 652
A070818 v2 en figure 272: ansi long time very inverse time characteristics section 21 1mrk 502 043-uus b time inverse characteristics 646 technical manual.
Page 653
A070819 v2 en figure 273: ansi long time inverse time characteristics 1mrk 502 043-uus b section 21 time inverse characteristics 647 technical manual.
Page 654
A070820 v2 en figure 274: iec normal inverse time characteristics section 21 1mrk 502 043-uus b time inverse characteristics 648 technical manual.
Page 655
A070821 v2 en figure 275: iec very inverse time characteristics 1mrk 502 043-uus b section 21 time inverse characteristics 649 technical manual.
Page 656
A070822 v2 en figure 276: iec inverse time characteristics section 21 1mrk 502 043-uus b time inverse characteristics 650 technical manual.
Page 657
A070823 v2 en figure 277: iec extremely inverse time characteristics 1mrk 502 043-uus b section 21 time inverse characteristics 651 technical manual.
Page 658
A070824 v2 en figure 278: iec short time inverse time characteristics section 21 1mrk 502 043-uus b time inverse characteristics 652 technical manual.
Page 659
A070825 v2 en figure 279: iec long time inverse time characteristics 1mrk 502 043-uus b section 21 time inverse characteristics 653 technical manual.
Page 660
A070826 v2 en figure 280: ri-type inverse time characteristics section 21 1mrk 502 043-uus b time inverse characteristics 654 technical manual.
Page 661
A070827 v2 en figure 281: rd-type inverse time characteristics 1mrk 502 043-uus b section 21 time inverse characteristics 655 technical manual.
Page 662
Guid-acf4044c-052e-4cbd-8247-c6abe3796fa6 v1 en figure 282: inverse curve a characteristic of overvoltage protection section 21 1mrk 502 043-uus b time inverse characteristics 656 technical manual.
Page 663
Guid-f5e0e1c2-48c8-4dc7-a84b-174544c09142 v1 en figure 283: inverse curve b characteristic of overvoltage protection 1mrk 502 043-uus b section 21 time inverse characteristics 657 technical manual.
Page 664
Guid-a9898db7-90a3-47f2-aef9-45ff148cb679 v1 en figure 284: inverse curve c characteristic of overvoltage protection section 21 1mrk 502 043-uus b time inverse characteristics 658 technical manual.
Page 665
Guid-35f40c3b-b483-40e6-9767-69c1536e3cbc v1 en figure 285: inverse curve a characteristic of undervoltage protection 1mrk 502 043-uus b section 21 time inverse characteristics 659 technical manual.
Page 666
Guid-b55d0f5f-9265-4d9a-a7c0-e274aa3a6bb1 v1 en figure 286: inverse curve b characteristic of undervoltage protection section 21 1mrk 502 043-uus b time inverse characteristics 660 technical manual.
Page 667
Section 22 glossary ac alternating current act application configuration tool within pcm600 a/d converter analog-to-digital converter adbs amplitude deadband supervision ai analog input ansi american national standards institute ar autoreclosing asct auxiliary summation current transformer asd adapt...
Page 668
Comtrade standard common format for transient data exchange format for disturbance recorder according to ieee/ansi c37.111, 1999 / iec60255-24 contra-directional way of transmitting g.703 over a balanced line. Involves four twisted pairs, two of which are used for transmitting data in both direction...
Page 669
Emc electromagnetic compatibility emf (electric motive force) emi electromagnetic interference enfp end fault protection epa enhanced performance architecture esd electrostatic discharge fcb flow control bit; frame count bit fox 20 modular 20 channel telecommunication system for speech, data and pro...
Page 670
Iec 61850 substation automation communication standard iec 61850–8–1 communication protocol standard ieee institute of electrical and electronics engineers ieee 802.12 a network technology standard that provides 100 mbits/s on twisted-pair or optical fiber cable ieee p1386.1 pci mezzanine card (pmc)...
Page 671
Lan local area network lib 520 high-voltage software module lcd liquid crystal display ldd local detection device led light-emitting diode mcb miniature circuit breaker mcm mezzanine carrier module mvb multifunction vehicle bus. Standardized serial bus originally developed for use in trains. Ncc nat...
Page 672
Rca relay characteristic angle rfpp resistance for phase-to-phase faults resistance for phase-to-ground faults risc reduced instruction set computer rms value root mean square value rs422 a balanced serial interface for the transmission of digital data in point-to-point connections rs485 serial link...
Page 673
Tcp/ip transmission control protocol over internet protocol. The de facto standard ethernet protocols incorporated into 4.2bsd unix. Tcp/ip was developed by darpa for internet working and encompasses both network layer and transport layer protocols. While tcp and ip specify two protocols at specific...
Page 674
3v o three times the zero sequence voltage. Often referred to as the residual voltage or the neutral point voltage section 22 1mrk 502 043-uus b glossary 668 technical manual.
Page 675
669.
Page 676
Contact us abb inc. 1021 main campus drive raleigh, nc 27606, usa phone toll free: 1-800-help-365, menu option #8 abb inc. 3450 harvester road burlington, on l7n 3w5, canada phone toll free: 1-800-help-365, menu option #8 abb mexico s.A. De c.V. Paseo de las americas no. 31 lomas verdes 3a secc. 531...