- DL manuals
- ABB
- Protection Device
- REG670 2.0 IEC
- Commissioning Manual
ABB REG670 2.0 IEC Commissioning Manual
Summary of REG670 2.0 IEC
Page 1
Relion ® 670 series generator protection reg670 2.0 iec commissioning manual.
Page 3
Document id: 1mrk502053-uen issued: july 2016 revision: b product version: 2.0 © copyright 2014 abb. All rights reserved.
Page 4
Copyright this document and parts thereof must not be reproduced or copied without written permission from abb, and the contents thereof must not be imparted to a third party, nor used for any unauthorized purpose. The software and hardware described in this document is furnished under a license and...
Page 5
Disclaimer the data, examples and diagrams in this manual are included solely for the concept or product description and are not to be deemed as a statement of guaranteed properties. All persons responsible for applying the equipment addressed in this manual must satisfy themselves that each intende...
Page 6
Conformity this product complies with the directive of the council of the european communities on the approximation of the laws of the member states relating to electromagnetic compatibility (emc directive 2004/108/ec) and concerning electrical equipment for use within specified voltage limits (low-...
Page 7
Table of contents section 1 introduction.....................................................................11 this manual...................................................................................... 11 intended audience.........................................................................
Page 8
Binary input circuits..................................................................... 50 binary output circuits................................................................... 50 checking optical connections........................................................... 50 section 5 configuring ...
Page 9
Section 9 establishing connection and verifying the lon communication............................................................... 89 communication via the rear ports ....................................................89 lon communication..............................................................
Page 10
Completing the test.............................................................. 109 impedance protection..................................................................... 109 full scheme distance protection, mho characteristic zmhpdis109 distance protection zones, quadrilateral characteristic z...
Page 11
Completing the test.............................................................. 150 instantaneous residual overcurrent protection efpioc ...........150 measuring the operate limit of set values.............................151 completing the test........................................................
Page 12
Accidental energizing protection for synchronous generator aegpvoc.................................................................................170 verifying the settings............................................................ 170 voltage-restrained time overcurrent protection vrpvoc............
Page 13
Rate-of-change frequency protection sapfrc ........................190 verifying the settings............................................................ 190 completing the test.............................................................. 191 frequency time accumulation protection function ftaqfvr....
Page 14
Check the normal voltage regulation function...................... 215 check the undervoltage block function................................ 215 check the upper and lower busbar voltage limit.................. 216 check the overcurrent block function................................... 216 single tra...
Page 15
Basic ied functions........................................................................ 235 parameter setting group handling setgrps........................... 235 verifying the settings............................................................ 235 completing the test.............................
Page 16
10
Page 17
Section 1 introduction 1.1 this manual the commissioning manual contains instructions on how to commission the ied. The manual can also be used by system engineers and maintenance personnel for assistance during the testing phase. The manual provides procedures for the checking of external circuitry...
Page 18
1.3 product documentation 1.3.1 product documentation set iec07000220-4-en.Vsd p la n n in g & p u rc h a se e n gi n e e rin g in st a lli n g c o m m is si o n in g o p e ra tio n m ai n te n a n ce d e co m m is si o n in g d e in st a lli n g & d is p o sa l application manual operation manual i...
Page 19
Well as verifying settings by secondary injection. The manual describes the process of testing an ied in a substation which is not in service. The chapters are organized in the chronological order in which the ied should be commissioned. The relevant procedures may be followed also during the servic...
Page 20
1.3.3 related documents documents related to reg670 identify number application manual 1mrk 502 051-uen commissioning manual 1mrk 502 053-uen product guide 1mrk 502 054-ben technical manual 1mrk 502 052-uen type test certificate 1mrk 502 054-ten 670 series manuals identify number operation manual 1m...
Page 21
The caution icon indicates important information or warning related to the concept discussed in the text. It might indicate the presence of a hazard which could result in corruption of software or damage to equipment or property. The information icon alerts the reader of important facts and conditio...
Page 22
• signals in frames with a shaded area on their right hand side represent setting parameter signals that are only settable via the pst or lhmi. • if an internal signal path cannot be drawn with a continuous line, the suffix -int is added to the signal name to indicate where the signal starts and con...
Page 23
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes busptrc_b11 busptrc busptrc busptrc_b12 busptrc busptrc busptrc_b13 busptrc busptrc busptrc_b14 busptrc busptrc busptrc_b15 busptrc busptrc busptrc_b16 busptrc busptrc busptrc_b17 busptrc busptrc busptrc_b18 busptrc busptrc busptrc_...
Page 24
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes cbpgapc cbplln0 cbpmmxu cbpptrc holptov hph1ptov ph3ptuc ph3ptoc rp3pdop cbpmmxu cbpptrc holptov hph1ptov ph3ptoc ph3ptuc rp3pdop ccpdsc ccrpld ccpdsc ccrbrf ccrbrf ccrbrf ccrwrbrf ccrwrbrf ccrwrbrf ccsrbrf ccsrbrf ccsrbrf ccsspvc c...
Page 25
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes ftaqfvr ftaqfvr ftaqfvr fufspvc sddrfuf fufspvc sddspvc genpdif genpdif gengapc genpdif genphar genptrc goosebinrcv bingrec - goosedprcv dpgrec - gooseintlkrcv intgrec - gooseintrcv intsgrec - goosemvrcv mvgrec - goosesprcv binsgrec...
Page 26
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes ldrgfc stsggio ldrgfc lexpdis lexpdis lexpdis lexptrc lfpttr lfpttr lfpttr lmbrflo lmbrflo lmbrflo lovptuv lovptuv lovptuv lphd lphd lpttr lpttr lpttr lt3cpdif lt3cpdif lt3cgapc lt3cpdif lt3cphar lt3cptrc lt6cpdif lt6cpdif lt6cgapc ...
Page 27
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes qcbay qcbay qcrsv qcrsv qcrsv refpdif refpdif refpdif rotiphiz rotiphiz rotiphiz rotiptrc rov2ptov gen2lln0 ph1ptrc rov2ptov ph1ptrc rov2ptov sapfrc sapfrc sapfrc saptof saptof saptof saptuf saptuf saptuf sccvptoc sccvptoc sccvptoc ...
Page 28
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes tclyltc tclyltc tclyltc tcsltc tcmyltc tcmyltc tcmyltc teigapc teiggio teigapc teiggio teilgapc teilggio teilgapc tmagapc tmaggio tmagapc tppioc tppioc tppioc tr1atcc tr1atcc tr1atcc tr8atcc tr8atcc tr8atcc trpttr trpttr trpttr u2rw...
Page 29
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes zmfpdis zmflln0 psfpdis zmfpdis zmfptrc zmmmxu psfpdis psfpdis zmfpdis zmfptrc zmmmxu zmhpdis zmhpdis zmhpdis zmmapdis zmmapdis zmmapdis zmmpdis zmmpdis zmmpdis zmqapdis zmqapdis zmqapdis zmqpdis zmqpdis zmqpdis zmrapdis zmrapdis zm...
Page 30
24.
Page 31
Section 2 safety information 2.1 symbols on the product all warnings must be observed. Read the entire manual before doing installation or any maintenance work on the product. All warnings must be observed. Class 1 laser product. Take adequate measures to protect your eyes and do not view directly w...
Page 32
Always use suitable isolated test pins when measuring signals in open circuitry. Potentially lethal voltages and currents are present. Never connect or disconnect a wire and/or a connector to or from a ied during normal operation. Hazardous voltages and currents are present that may be lethal. Opera...
Page 33
2.3 caution signs whenever changes are made in the ied, measures should be taken to avoid inadvertent tripping. The ied contains components which are sensitive to electrostatic discharge. Esd precautions shall always be observed prior to touching components. Always transport pcbs (modules) using cer...
Page 34
2.4 note signs observe the maximum allowed continuous current for the different current transformer inputs of the ied. See technical data. Section 2 1mrk502053-uen b safety information 28 generator protection reg670 2.0 iec commissioning manual.
Page 35
Section 3 available functions 3.1 main protection functions 2 = number of basic instances 0-3 = option quantities 3-a03 = optional function included in packages a03 (refer to ordering details) iec 61850 ansi function description generator reg670 reg670 (a20) reg670 (b30) reg670 (c30) differential pr...
Page 36
3.2 back-up protection functions iec 61850 ansi function description generator reg670 reg670 (a20) reg670 (b30) reg670 (c30) current protection phpioc 50 instantaneous phase overcurrent protection 0-4 1 2 2 oc4ptoc 51_67 1) four step phase overcurrent protection 0-6 4 4 4 efpioc 50n instantaneous re...
Page 37
Iec 61850 ansi function description generator reg670 reg670 (a20) reg670 (b30) reg670 (c30) rov2ptov 59n two step residual overvoltage protection 0-3 3 3 3 oexpvph 24 overexcitation protection 0-2 1 1 2 vdcptov 60 voltage differential protection 0-2 2 2 2 stefphiz 59thd 100% stator earth fault prote...
Page 38
Iec 61850 ansi function description generator reg670 reg670 (a20) reg670 (b30) reg670 (c30) locrem handling of lrswitch positions 1+5/apc30 1+5/ apc3 0 1+5/ apc3 0 1+5/ apc3 0 locremctrl lhmi control of psto 1+5/apc30 1+5/ apc3 0 1+5/ apc3 0 1+5/ apc3 0 tcmyltc 84 tap changer control and supervision...
Page 39
Iec 61850 ansi function description generator reg670 reg670 (a20) reg670 (b30) reg670 (c30) and, or, inv, pulsetimer, gate, timerset, xor, lld, srmemory, rsmemory configurable logic blocks 40-280 40-28 0 40-28 0 40-28 0 andqt, orqt, inverterqt, xorqt, srmemoryqt, rsmemoryqt, timersetqt, pulsetimerqt...
Page 40
Iec 61850 ansi function description generator reg670 reg670 (a20) reg670 (b30) reg670 (c30) drprdre, a1radr, a2radr, a3radr, a4radr, b1rbdr, b2rbdr, b3rbdr, b4rbdr, b5rbdr, b6rbdr disturbance report 1 1 1 1 spgapc generic communication function for single point indication 64 64 64 64 sp16gapc generi...
Page 41
3.4 communication iec 61850 ansi function description generator reg670 reg670 (a20) reg670 (b30) reg670 (c30) station communication lonspa, spa spa communication protocol 1 1 1 1 ade lon communication protocol 1 1 1 1 horzcomm network variables via lon 1 1 1 1 protocol operation selection between sp...
Page 42
Iec 61850 ansi function description generator reg670 reg670 (a20) reg670 (b30) reg670 (c30) multicmdrcv, multicmdsnd multiple command and transmit 60/10 60/10 60/10 60/10 front, lanabi, lanab, lancdi, lancd ethernet configuration of links 1 1 1 1 gateway ethernet configuration of link one 1 1 1 1 op...
Page 43
3.5 basic ied functions table 2: basic ied functions iec 61850 or function name description interrsig self supervision with internal event list selfsupevlst self supervision with internal event list timesynchgen time synchronization module synchbin, synchcan, synchcmpps, synchlon, synchpph, synchpps...
Page 44
Iec 61850 or function name description altrk service tracking activlog activity logging parameters fstaccs field service tool access via spa protocol over ethernet communication pcmaccs ied configuration protocol secalarm component for mapping security events on protocols such as dnp3 and iec103 dnp...
Page 45
Section 4 starting up 4.1 factory and site acceptance testing testing the proper ied operation is carried out at different occasions, for example: • acceptance testing • commissioning testing • maintenance testing this manual describes the workflow and the steps to carry out the commissioning testin...
Page 46
• pc with pcm600 installed along with the connectivity packages corresponding to the ieds to be tested. • administration rights on the pc, to set up ip addresses • product documentation (engineering manual, installation manual, commissioning manual, operation manual, technical manual and communicati...
Page 47
• software version, main menu/diagnostics/ied status/product identifiers. • serial number, main menu/diagnostics/ied status/product identifiers. • installed modules and their ordering number, main menu/diagnostics/ied status/installed hw. 4.4.2 ied start-up sequence when the ied is energized, the gr...
Page 48
The communication media is always ethernet and the used protocol is tcp/ip. Each ied has an rj-45 ethernet interface connector on the front. The front ethernet connector shall be used for communication with pcm600.. When an ethernet-based station protocol is used, pcm600 communication can use the sa...
Page 49
Iec09000096-2-en.Vsd tx tx rx rx rj-45 ied pcm600 iec09000096 v2 en figure 3: point-to-point link between ied and pcm600 using a null-modem cable the following description is an example valid for standard pcs using microsoft windows operating system. The example is taken from a laptop with one ether...
Page 50
Iec13000057-1-en.Vsd iec13000057 v1 en figure 4: select: search programs and files 2. Type view network connections and click on the view network connections icon. Section 4 1mrk502053-uen b starting up 44 generator protection reg670 2.0 iec commissioning manual.
Page 51
Iec13000058-1-en.Vsd iec13000058 v1 en figure 5: click view network connections 3. Right-click and select properties. Iec13000059-1-en.Vsd iec13000059 v1 en figure 6: right-click local area connection and select properties 4. Select the tcp/ipv4 protocol from the list of configured components using ...
Page 52
Iec13000060-1-en.Vsd iec13000060 v1 en figure 7: select the tcp/ipv4 protocol and open properties 5. Select use the following ip address and define ip address and subnet mask if the front port is used and if the ip address is not set to be obtained automatically by the ied, see figure 8 . The ip add...
Page 53
Iec13000062-1-en.Vsd iec13000062 v1 en figure 8: select: use the following ip address 6. Use the ping command to verify connectivity with the ied. 7. Close all open windows and start pcm600. Setting up the pc to access the ied via a network this task depends on the used lan/wan network. The pc and i...
Page 54
4.8 checking ct circuits check that the wiring is in strict accordance with the supplied connection diagram. The cts must be connected in accordance with the circuit diagram provided with the ied, both with regards to phases and polarity. The following tests shall be performed on every primary ct co...
Page 55
4.9 checking vt circuits check that the wiring is in strict accordance with the supplied connection diagram. Correct possible errors before continuing to test the circuitry. Test the circuitry. • polarity check when applicable; this test is often omitted for cvts • vt circuit voltage measurement (pr...
Page 56
Verify that the contact sockets have been crimped correctly and that they are fully inserted by tugging on the wires. Never do this with current circuits in service. Current circuit 1. Verify that the contacts are of current circuit type. 2. Verify that the short circuit jumpers are located in the c...
Page 57
An ied equipped with optical connections has an minimum space requirement of 180 mm for plastic fiber cables and 275 mm for glass fiber cables. Check the allowed minimum bending radius from the optical cable manufacturer. 1mrk502053-uen b section 4 starting up generator protection reg670 2.0 iec 51 ...
Page 58
52.
Page 59
Section 5 configuring the ied and changing settings 5.1 overview the customer specific values for each setting parameter and a configuration file have to be available before the ied can be set and configured, if the ied is not delivered with a configuration. Use the configuration tools in pcm600 to ...
Page 60
5.2 configuring analog ct inputs the analog input channels must be configured to get correct measurement results as well as correct protection functionality. Because all protection algorithms in the ied utilize the primary system quantities, it is extremely important to make sure that connected curr...
Page 61
Each logical i/o module has an error flag that indicates signal or module failure. The error flag is also set when the physical i/o module of the correct type is not detected in the connected slot. 1mrk502053-uen b section 5 configuring the ied and changing settings generator protection reg670 2.0 i...
Page 62
56.
Page 63
Section 6 calibrating injection based sensitive rotor earth fault protection 6.1 commissioning process the commissioning process utilizes the commissioning tool ict. The instructions for the process cover installation, calibration, commissioning, monitoring and auditing for the sensitive rotor earth...
Page 64
Injection frequency (for example, due to accuracy of the rex060 hardware). Set manually the actual frequency value measured by ict in the ied via pst. The high accuracy of this frequency is essential for proper operation of the protection under different operating conditions. Calibrating the calibra...
Page 65
After the three measurements ict calculates the complex factors k1 and k2. The reference impedance refr1 + jrefx1 is also calculated. After this the values are downloaded to the parameter setting in pcm600. From pcm600 the settings are downloaded to ied. During the three measurements described above...
Page 66
Iec11000222-1-en.Vsd iec11000222 v1 en figure 10: ict toolbar 3. Select the installing tab if it was not already selected by default after the ict was launched. The first thing that needs to be ensured prior to calibration is that the measured voltage and current signal on the injected frequency is ...
Page 67
6.4 performing calibration 1. From the calibration tab, select the first sub tab, i.E. Step1: calibration step 1. 2. Make sure you have not attached any additional impedance in parallel with the rotor. 3. From the ict toolbar, select the start reading from ied button. Ict now performs continuous mea...
Page 68
8. Once again, wait until the stability criteria is fulfilled, then select the submit button. Ict automatically shifts to the third calibration tab, step3: calibration step 3. 9. Remove the known fault resistance attached earlier and apply a short circuit instead. 10. In the ict toolbar, select the ...
Page 69
6.5 acquiring references to detect different operation conditions of the generator and select proper impedance reference requires logic outside the injection function. Therefore changing/switching impedance reference is not described here but in a separate application note 1mrg005030 application exa...
Page 70
Settled, and also if the average impedance is based on enough values so that statistically the signal noise is “filtered out”. This results in a fairly accurate impedance measurement which can be used as an alternative reference. 5. Click the select button when the standard deviation has converged s...
Page 71
By default the measured absolute impedance is plotted, however there are several items that can be viewed when monitoring. To see these, select the available quantities under the viewed quantity drop-down menu under the monitoring tab. 4. Observe the fault conductance while applying known faults. Bo...
Page 72
• after completion of the calibration step • before leaving the ict tool 6.7 auditing during installations, calibrations and commissions the ict generates reports for each of the steps and collects them under the auditing tab. See the procedures below on how to view and delete reports as well as gen...
Page 73
• in the short cut menu, right click and select generate log. • click the generate log button. Besides generating a report you can also generate a log file with the same information as for the report. Open and see the details of the file in notepad or ms excel. After a successful generation of the l...
Page 74
Iec11000052-1-en.Vsd guid-261171b2-59cd-4248-b873-39a2bc3cd1f1 v1 en figure 18: zooming via area selection of a part of the graph • press pgup key on the keyboard to zoom in and pgdn to zoom out. 2. Cancel a zoom in the following ways: • right click a graph and select cancel zoom in the shortcut men...
Page 75
Ict continuously logs data to this file with logging interval set under graph update period. Notice that there is a field named log period and its default value is 1 hour. The period can be adjusted before the logging is started, if needed. 5. The logging can be stopped by selecting the stop button....
Page 76
70
Page 77
Section 7 calibrating injection based 100% stator earth fault protection 7.1 commissioning process the commissioning process utilizes the commissioning tool ict. The instructions for the process cover installation, calibration, commissioning, monitoring and auditing for the 100% stator earth fault s...
Page 78
Injection frequency (e.G. Due to accuracy of the rex060 hardware). Set manually the actual frequency value measured by ict in the ied via pst.Check that the selected injection frequency setting on rex060 is equal to the freqinjected setting in parameter setting. Also verify that the measured injecti...
Page 79
Diagram. The user stops the sequence by acceptance of the measurement. The result is stored for later calculations. • calibration sequence 2: a known resistor is connected to the generator neutral point in parallel with the stator neutral point resistor. The value of the resistance is input to ict. ...
Page 80
If more than one reference impedance is to be used there must be a logic configured to detect such changes in the operation states when the reference impedance must be changed, and when a change in the function block must be initiated. The following automatic choices can for example be made: 1. Gene...
Page 81
5. Activate the injection by turning the injection switch to on position on the injection unit rex060. 6. Select the start reading from ied button from the ict toolbar to start performing continuous measurements. 7. Verify that the bars/voltage levels for both the voltage and current on the injected...
Page 82
It is very important that calibration steps 1 to 3 is performed in the proper order. If not, the calibration might fail. 4. When the bar has reached the stability region (turned green), select the submit button. Ict automatically shifts to the second calibration sub tab, step2: calibration step 2. S...
Page 83
Iec11000048-2-en.Vsd guid-d024d8b7-45f3-42d1-aaa3-488a2996267b v1 en figure 23: ict calibration tab 4 13. Before proceeding any further make sure that you have removed the short-circuit that was applied during calibration step 3. 14. To finish the calibration process, select the submit to parameter ...
Page 84
1. Ensure that the generator is in a state where the reference must be set (for example normal operation). 2. To start, select the commissioning tab. 3. In the reference impedance selection drop-down menu. Select reference 2. 4. To start reading the measurements, click the start reading from ied but...
Page 85
7.6 verifying calibration after the calibration is performed, it is appropriate to verify that known faults are measured as expected and that the function is indicating trips and alarms when it should, in other words that the calibration was successful. For this purpose the monitoring feature can be...
Page 86
Due to the fact that no fault theoretically equals infinite fault resistance and viewing this only plots unreliable values, it is better to view the fault conductance, which is zero in this case. As no fault is applied, the measured fault conductance must be close to zero. Confirm this by viewing th...
Page 87
1. To view the reports, go to the auditing tab. Iec11000049-1-en.Vsd guid-8348f60b-9bf5-4018-9740-0fa3371b0f9f v1 en figure 26: auditing tab 2. Open and view each report. 3. View reports in one of the following ways: • in the short cut menu, right click and select view report. • click the view repor...
Page 88
7.8 editing features in graph you can do the following operations on the graph during calibration, commissioning and monitoring: • zoom in • zoom out • cancel zoom • enable x-zooming • enable y-zooming 1. Zoom in one of the following ways: • right click a graph and select zoom in or zoom out in the ...
Page 89
2. Cancel a zoom in the following ways: • right click a graph and select cancel zoom in the shortcut menu. The graph area is squeezed to the original size. • press esc. 3. Enable x and y zooming • to enable and disable x zooming, right click the graph and select or deselect enable x zooming in the s...
Page 90
84.
Page 91
Section 8 establishing connection and verifying the spa/iec communication 8.1 entering settings if the ied is connected to a monitoring or control system via the rear spa/iec port, the spa/iec port has to be set either for spa or iec use. 8.1.1 entering spa settings the spa/iec port is located on th...
Page 92
1. Set the operation of the rear spa/iec port to “iec”. The operation of the rear spa/iec port can be found on the local hmi under main menu/configuration/communication/slm configuration/rear optical spa-iec-dnp port/protocol:1 when the setting is entered the ied restarts automatically. After the re...
Page 93
1. Check that the master system time-out for response from the ied, for example after a setting change, is > 40 seconds. 2. Use a protocol analyzer and record the communication between the ied and the iec master. Check in the protocol analyzer’s log that the ied answers the master messages. 3. Gener...
Page 94
88.
Page 95
Section 9 establishing connection and verifying the lon communication 9.1 communication via the rear ports 9.1.1 lon communication lon communication is normally used in substation automation systems. Optical fiber is used within the substation as the physical communication link. The test can only be...
Page 96
The fibre optic lon bus is implemented using either glass core or plastic core fibre optic cables. Table 6: specification of the fibre optic connectors glass fibre plastic fibre cable connector st-connector snap-in connector cable diameter 62.5/125 m 1 mm max. Cable length 1000 m 10 m wavelength 820...
Page 97
• the node addresses of the other connected ieds. • the network variable selectors to be used. This is organized by lnt. The node address is transferred to lnt via the local hmi by setting the parameter servicepinmsg = yes. The node address is sent to lnt via the lon bus, or lnt can scan the network...
Page 98
Path in the local hmi under main menu/configuration/communication/slm configuration/rear optical lon port table 9: ade non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation timerclass slow normal fast - - slow timer class path in the local hm...
Page 99
Section 10 establishing connection and verifying the iec 61850 communication 10.1 overview the rear oem ports are used for: • substation bus (iec 61850-8-1) communication. For iec 61850-8-1 redundant communication, both rear oem ports are utilized. 10.2 setting the station communication to enable ie...
Page 100
The ied will restart after confirmation. Menu items lanab:1 and lancd:1 are hidden in local hmi after restart but are visible in pst where the values for parameter mode is set to duo. 10.3 verifying the communication to verify that the communication is working a test/analyzing tool, for example itt6...
Page 101
Section 11 testing ied operation 11.1 preparing for test 11.1.1 requirements ied test requirements: • calculated settings • application configuration diagram • signal matrix (smt) configuration • terminal connection diagram • technical manual • three-phase test equipment • pcm600 the setting and con...
Page 102
Chapter. The functions can be tested in any order according to user preferences. Only the functions that are used (operation is set to on) should be tested. The response from a test can be viewed in different ways: • binary outputs signals • service values on the local hmi (logical signals or phasor...
Page 103
Amplitudes and phase angles. In addition, pcm600 contains the disturbance handling tool. The content of reports generated by the disturbance handling tool can be configured which makes the work more efficient. For example, the tool may be configured to only show time tagged events and to exclude ana...
Page 104
The yellow startled above the lcd will start flashing when the ied is in test mode. 11.3 preparing the connection to the test equipment the ied can be equipped with a test switch of type rtxp8, rtxp18 or rtxp24. The test switch and its associated test plug handle (rtxh8, rtxh18 or rtxh24) are a part...
Page 105
Connect the current and voltage terminals. Pay attention to the current polarity. Make sure that the connection of input and output current terminals and the connection of the residual current conductor is correct. Check that the input and output logical signals in the logic diagram for the function...
Page 106
Which depends on the configuration. Ensure that the logical status of the block input signal is equal to 0 for the function to be tested. Event function blocks can also be individually blocked to ensure that no events are reported to a remote station during the test. This is done by setting the para...
Page 107
If some setting deviates, check the analog input settings under main menu/settings/general settings/analog modules 11.7 testing the protection functionality each protection function must be tested individually by secondary injection. • verify operating levels (trip) and timers. • verify alarm and bl...
Page 108
102.
Page 109
Section 12 testing functionality by secondary injection 12.1 testing disturbance report 12.1.1 introduction the following sub-functions are included in the disturbance report function: • disturbance recorder • event list • event recorder • trip value recorder • indications if the disturbance report ...
Page 110
A new recording begins. The view is updated if you leave the menu and return. 1.2. Navigate to general information or to trip values to obtain more detailed information. 2. Open the disturbance handling tool for the ied in the plant structure in pcm600. 2.1. Right-click and select execute manual tri...
Page 111
Internal event list or main menu/clear/clear process event list. It is not possible to clear the event lists from pcm600. When testing binary inputs, the event list (el) might be used instead. No uploading or analyzing of registrations is then needed since the event list keeps running, independent o...
Page 112
8. Connect the timer and set the current to twice the operate value. 9. Switch on the current and note the operate time. 10. Check in the same way the measuring circuits connected to the cts on the lv side and other current inputs to the transformer differential protection. 11. Finally check that tr...
Page 113
A slightly higher operating value is no problem as the sensitivity is not influenced much. 2. Increase the voltage and make note of the operate value u>trip. This is done by manual testing and without trip of the test set. 3. Connect the trip contact to the test set to stop the test set for measurem...
Page 114
As the generator differential protection, are set off. Make sure that the generator differential function is unblocked. 2. Connect the test set for injection of three-phase current to the current ieds, which are connected to the cts on the hv side of the generator. 3. Increase the current in phase l...
Page 115
4. Decrease the current slowly from operate value and note the reset value. 5. Connect the timer and set the current to ten times the value of the idmin setting. 6. Switch on the current and note the operate time. 7. Connect the test set to terminal l1 and neutral of the three-phase current input co...
Page 116
12.4.2 distance protection zones, quadrilateral characteristic zmfpdis prepare the ied for verification of settings outlined in section "requirements" and section "preparing for test" in this chapter. Measure operating characteristics during constant current conditions. Keep the measured current as ...
Page 117
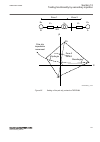
X1 x r (ohm/phase) 50% 80% 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 80% of rldfw 40% of rldfw 0.5 x rfpp 12 13 120° 20° a c iec05000368-3-en b = ar gld iec05000368 v3 en figure 31: distance protection characteristic with test points for phase-to-phase measurements table 12: test points for phase-to-phase loops l1-l2...
Page 118
Test point reach set value comments 11 x 0.8 x x1 set exact –0.5 x r1 set x tan(argnegres=30°) r –0.37 x x1 set 12 x 0.5 x x1 set r 0.5 x r1 set 13 x 0 only used when operationldcmp setting is 0 (off) r 0.5 x rfpp table 12 is used in conjunction with figure 31 . X1+xn x r (ohm/loop) 50% 80% 1 2 3 4 ...
Page 119
Test point reach value comments 5 x 0.85 x rfpe set x tan(argldset) argld = angle for the maximal load transfer r 0.85 x rfpe 6 x rldfwset x tan(argldset) r rldfw set 7 x 0 r rldfw set 8 x –02143 x rldfw set exact: 0.8 x rfpe x tan (argdir=20°) r 0.8 x rldfw set 9 x –0.8 x rldfw set x tan(argdir=20°...
Page 120
Function for all 5 measuring zones, it is only necessary to test points 6, 7, 8 and 9 once, in the forward direction (the largest reverse zone can be used to facilitate the test) in order to test the accuracy of directionality (directional angles). Directional functionality testing (trip inside, no-...
Page 121
The test procedure has to take into consideration that the shaped load encroachment characteristic is active. It is therefore necessary to check the setting. To verify the settings with the shaped load encroachment characteristic the test should be carried out according to figures 31 and 32 and tabl...
Page 122
Table 14: test points for phase-to-phase loops l1-l2 (ohm/loop) test point reach set value comments 1 x x1 set r 0 2 x x1 set r r1 set 3 x 0.8 x x1 set r 0.8 x r1 set + rfpp/2 4 x 0.5 x x1 set r 0.5 x r1 set + rfpp/2 5 x 0.85 x rfpp x tan (argld) argld = angle for the maximal load transfer r 0.85 x ...
Page 123
X1+xn x r (ohm/loop) 50% 80% 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 80% of rldfw 40% of rldfw rfpe 12 13 c b = ar gld alt. 80% of rfpe (load encroachment) 120° 20° a iec05000369-3-en.Vsd iec05000369 v3 en figure 34: distance protection characteristic with test points for phase-to-earth measurements table 13 is use...
Page 124
Test point reach value comments 10 x 0.17 x (2 x x1 set + x0 set ) exact: 0.5 x (2 x x1 set x0 set )/3 r -0.36 x (2 x x1 set + x0 set ) exact: 0.5 x (2x1 set + x0 set )/(3 x tan(agnegdir=30°) 11 x 0.27 x (2 x x1 set +x0 set ) exact: 0.8 x (2 x x1 set + x0 set )/3 r –0.57 x (2 x x1 set + x0 set ) exa...
Page 125
1. Subject the ied to healthy normal load conditions for at least two seconds. 2. Apply the fault condition to find the operating time for the phase-to-phase fault according to test point 10 in figure 31 and table 12 for zone 1. Compare the result of the measurement with the setting t1pp. 3. Repeat ...
Page 126
This is done with a speed so that the final impedance is reached after 1 second. As the injected voltage is higher than 0.92 ubase no start signal should be activated. 3. With reduced amplitude of the injected voltage to 0.8 ubase the current amplitude and angle is changed to a value zc/2. This is d...
Page 127
Ied b a e b e a x’ d x t z s zone 1 zone 2 jx r zb za pole slip impedance movement zone 2 zone 1 warnangle tripangle f zc iec07000099_2_en.Vsd iec07000099 v2 en figure 35: setting of the pole slip protection pspppam 1mrk502053-uen b section 12 testing functionality by secondary injection generator p...
Page 128
0.2 £ f(ucos) £ 8hz and and start z cross line za - zc z cross line zc - zb and and zone1 zone2 counter a b a ³ b and trip1 counter a b a ³ b and trip2 or trip iec07000100_2_en.Vsd imin > 0.10 ibase umax d ³ startangle n1limit d £ tripangle n2limit iec07000100 v2 en figure 36: logic diagram of the p...
Page 129
Two current channels i3p1 and i3p2 are available in oosppam function to allow the direct connection of two groups of three-phase currents; that may be needed for very powerful generators, with stator windings split into two groups per phase, when each group is equipped with current transformers. The...
Page 130
If the rated secondary current i rs of the analog channel is 1 a, then the maximum current test i ts is i i i a ts ovrl rs ≤ = × = 4 4 equation14041 v1 en (equation 1) if the ct of the generator has ratio 9000/1 a, then in primary values i i i i i a t ovrl p ovrl rp rs ≤ = × = × = , 4 9000 1 36000 e...
Page 131
R forwardr zbase fwdr = × = × = 100 8 19 100 0 9522 0 078 . . . Ω equation14048 v1 en (equation 8) x forwardx zbase fwdx = × = × = 100 59 33 100 0 9522 0 565 . . . Ω equation14049 v1 en (equation 9) r reverser zbase rvsr = × = × = 100 0 29 100 0 9522 0 003 . . . Ω equation14050 v1 en (equation 10) x...
Page 132
Test sets usually do not have a feature to simulate a real network during a power swing and apply the related analog quantities at the terminal of the generator. The scope of the present test is not a simulation of a real network. Voltages and currents are supplied in order to measure an impedance t...
Page 133
For the test as motor the frequency current may have 50.5 hz in the quadrant 1 and 2 of the r-x plane and 49.5 hz in the quadrant 3 and 4. Verifying the settings by secondary injection it is advised to connect the analog output channels of the function block oosppam to the internal disturbance recor...
Page 134
I i i i a s cts ctp 50 50 10459 1 9000 1 162 = × = × = . Equation14059 v1 en (equation 19) ∠i 50s =0° frequency of i 50s = 50 hz it i i i a fs cts ctp tf = × = × = 10459 1 9000 1 162 . Equation14062 v1 en (equation 20) ∠i tfs =0° frequency of i tfs = 50 hz • check that the service values (voltage, c...
Page 135
Define the following three-phase symmetrical quantities (the phase angle is related to phase l1): v v v v v ts t fwdz vt s vt p = × × = × × = 1 1 1 1 11931 0 1 13 8 95 1 . . . . . , , , equation14057 v1 en (equation 23) ∠ = = = v forwardx forwardr ts arctan arctan . . 59 33 8 19 82..14° equation...
Page 136
I i i i a s cts ctp 50 50 10459 1 9000 1 162 = × = × = . Equation14059 v1 en (equation 29) ∠i 50s = 0º frequency of i 50s = 50 hz it i i i a fs cts ctp tf = × = × = 10459 1 9000 1 162 . Equation14062 v1 en (equation 30) ∠i tfs = 0º frequency of i tf = 50 hz • check that the service values (voltage, ...
Page 137
Define the following three-phase symmetrical quantities (the phase angle is related to phase l1): v v v v v ts t fwdz vt s vt p = × × = × × = 0 9 0 9 11931 0 1 13 8 77 81 . . . . . , , , equation14063 v1 en (equation 33) ∠ = = = v forwardx forwardr ts arctan arctan . . 59 33 8 19 82..14° equatio...
Page 138
Frequency of v ts = 50 hz i i i i a s cts ctp 50 50 10459 1 9000 1 162 = × = × = . Equation14059 v1 en (equation 39) ∠i 50s = 0º frequency of i 50s = 50 hz it i i i a fs cts ctp tf = × = × = 10459 1 9000 1 162 . Equation14062 v1 en (equation 40) ∠i tfs = 0º frequency of i tfs = 50 hz • check that th...
Page 139
I tfs = 0 a • state 2: main test step. Define the following three-phase symmetrical quantities (the phase angle is related to phase l1): v v v v v ts t rz vt s vt p = × × = × × = 1 1 1 1 1435 0 1 13 8 11 44 1 . . . . . , , , equation14065 v1 en (equation 43) ∠ = = = v forwardx forwardr ts arctan...
Page 140
Frequency of v ts = 50 hz i i i i a s cts ctp 50 50 10459 1 9000 1 162 = × = × = . Equation14059 v1 en (equation 49) ∠i 50s = 0º frequency of i 50s = 50 hz it i i i a fs cts ctp tf = × = × = 10459 1 9000 1 162 . Equation14062 v1 en (equation 50) ∠i tfs = 0º frequency of i tf = 50 hz • check that the...
Page 141
I tfs = 0 a • state 2: main test step. Define the following three-phase symmetrical quantities (the phase angle is related to phase l1): v v v v v ts t rz vt s vt p = × × = × × = 0 9 0 9 1435 0 1 13 8 9 36 1 . . . . . , , , equation14066 v1 en (equation 53) ∠ = = = v forwardx forwardr ts arctan ...
Page 142
29.60 arctan 180 arctan 180 90.56 0.29 ts reversex v reverser Ð = - ° = - ° = - ° æ ö æ ö ç ÷ ç ÷ è ø è ø equation14068 v1 en (equation 58) frequency of v ts = 50 hz i i i i a s cts ctp 50 50 10459 1 9000 1 162 = × = × = . Equation14059 v1 en (equation 59) ∠i 50s = 0º frequency of i 50s = 50 hz it i...
Page 143
Frequency of v ts = 50 hz i 50s = 0 a i tfs = 0 a • state 2: main test step. Define the following three-phase symmetrical quantities (the phase angle is related to phase l1): v v v v v ts t rvsz vt s vt p = × × = × × = 0 9 0 9 5899 0 1 13 8 38 47 . . . . . , , , equation14067 v1 en (equation 63) 29....
Page 144
29.60 arctan 180 arctan 180 90.56 0.29 ts reversex v reverser Ð = - ° = - ° = - ° æ ö æ ö ç ÷ ç ÷ è ø è ø equation14068 v1 en (equation 68) frequency of v ts = 50 hz i i i i a s cts ctp 50 50 10459 1 9000 1 162 = × = × = . Equation14059 v1 en (equation 69) ∠i 50s = 0º frequency of i 50s = 50 hz it i...
Page 145
Frequency of v ts = 50 hz i 50s = 0 a i tfs = 0 a • state 2: main test step. Define the following three-phase symmetrical quantities (the phase angle is related to phase l1): v v v v v ts t rvsz vt s vt p = × × = × × = 1 1 1 1 5899 0 1 13 8 47 02 . . . . . , , , equation14069 v1 en (equation 73) 29....
Page 146
Iec10000142-1-en.Vsd 0 1 2 common trip command (trip) -1 0 1 tripz1 (tripzone1) 0 1 2 tripz2 (tripzone2) 0 1 2 start (start) 0 1 2 genmode (generatormode) 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 -1 0 1 time in seconds → motmode (motormode) iec10000142 v1 en figure 38: boolean output signals for the injected...
Page 147
That this reading corresponds to the injected impedance. No start or trip signals shall be activated. 3. Feed the ied with current and voltage corresponding to the apparent impedance: test #3, as shown in figure 39 . Read the analog outputs for r and x and check that this reading corresponds to the ...
Page 148
12.4.6.2 completing the test continue to test another function or end the test by changing the testmode setting to off. Restore connections and settings to their original values, if they were changed for testing purposes. 12.4.7 under impedance protection for generator zgvpdis prepare the ied for ve...
Page 149
P1 p3 p4 x r lineangle z1fwd z1rev p2 iec11000312-2-en.Vsd iec11000312 v2 en figure 40: proposed four test points for phase-to-phase fault where, z1fwd is the forward positive sequence impedance setting for zone 1 z1rev is the reverse positive sequence impedance setting for zone 1 lineangle is the i...
Page 150
P1 p3 p4 x r lineangle zxfwd zxrev p2 iec11000313-1-en.Vsd iec11000313 v2 en figure 41: proposed four test points for phase-to-earth fault where, zxfwd is the forward positive sequence impedance setting for zone x (where, x is 2- 3 depending on the zone selected) zxrev is the reverse positive sequen...
Page 151
Load encroachment load encroachment operates on the same measuring principles as the impedance measuring zones. Thus, it is necessary to follow the same principles as for distance protection when performing the secondary injection tests. Measure operating characteristics during constant current cond...
Page 152
12.4.8 rotor earth fault protection with rxtte4 and general current and voltage protection cvgapc prepare the ied for verification of settings as outlined in section "requirements" and section "preparing for test" in this chapter. 12.4.8.1 testing the protection function uses injection of an ac volt...
Page 153
En06000498.Vsd reg 670 rxtte 4 i u 230 v ac 120 v ac 0 generator rotor winding g 313 314 315 421 428 324 325 221 222 optional external resistor connection to be done by the panel builder iec06000498 v1 en figure 42: ten times amplification of current via a current transformer the test described in s...
Page 154
4. Close the switch to the station earth and check that the trip from the rotor earth fault will be given after the set delay time. 5. Open the switch to the station earth and check that the trip signal resets instantaneously. 6. Connect an adjustable resistor to the field circuit (221 on rxtte4). D...
Page 155
Observe: do not exceed the maximum permitted overloading of the current circuits in the ied. 5. Compare the measured operating current with the set value. 6. Set the operation mode to 2 out of 3 and inject current into one of the phases. Check - no operation. 12.5.1.2 completing the test continue to...
Page 156
If reverse directional function is selected, set the injection current to lag the polarizing voltage by an angle equal to 260° (equal to 80° + 180°). 4. Increase the injected current and note the operate value of the tested step of the function. 5. Decrease the current slowly and note the reset valu...
Page 157
Ensure that the maximum continuous current, supplied from the current source used for the test of the ied, does not exceed four times the rated current value of the ied. 12.5.3.1 measuring the operate limit of set values 1. Inject a phase current into the ied with an initial value below that of the ...
Page 158
7. Connect a trip output contact to a timer. 8. Set the injected current to 200% of the operate level of the tested step, switch on the current and check the time delay. For inverse time curves, check the operate time at a current equal to 110% of the operate current for txmin. 9. Check that all tri...
Page 159
1. Connect the test set for injection of three-phase currents and voltages to the appropriate ct and vt inputs of the ied. 2. Inject pure negative sequence current, that is, phase currents with exactly same magnitude, reversed sequence and exactly 120° phase displaced into the ied with an initial va...
Page 160
Iec09000021-2-en.Vsd ied test set ni ied ni l1u l2u l3u nu u1 u2 u3 nu trip iec09000021 v2 en figure 43: principle connection of the test set values of the logical signals belonging to the sensitive directional residual overcurrent and power protection are available on the local hmi under main menu/...
Page 161
5. Measure the operate time of the timer by injecting a current two times the set incosphi> value and the polarizing voltage 1.2 · unrel>. ( ) 0 0 cos 3 3 test test ksn sref tinv i u j × = × × iecequation2402 v2 en (equation 77) 6. Compare the result with the expected value. The expected value depen...
Page 162
-3u 0 =u ref operate area instrument transformer angle error 3i 0 (prim) 3i 0 (to prot) characteristic after angle compensation rcacomp iec06000651-3-en.Vsd rcadir = 0º iec06000651 v3 en figure 45: explanation of rcacomp operation mode 3i 0 · 3u 0 · cos φ 1. Set the polarizing voltage to 1.2 · unrel...
Page 163
5. Measure the operate time of the timer by injecting 1.2 · unrel> and a current to get two times the set sn> operate value. ( ) 0 0 / 3 3 cos test test tinv ksn sref i u j = × × × iecequation2403 v1 en (equation 78) 6. Compare the result with the expected value. The expected value depends on whethe...
Page 164
-3u 0 operate area 3i 0 rcadir = 0º roadir = 80º iec06000652-3-en.Vsd iec06000652 v3 en figure 46: example characteristic non-directional earth fault current protection procedure 1. Measure that the operate current is equal to the innondir> setting. The function activates the start and stdirin outpu...
Page 165
12.5.6.2 completing the test continue to test another function or end the test by changing the testmode setting to off. Restore connections and settings to their original values, if they were changed for testing purposes. 12.5.7 thermal overload protection, two time constants trpttr prepare the ied ...
Page 166
13. Switch off the injection current and check from the service menu readings of thermal status and lockout that the lockout resets at the set percentage of heat content. 14. Activate the cooling input signal to switch over to base current ibase2. Wait 5 minutes to empty the thermal memory and set t...
Page 167
Note! If no cbpos check or retrip off is set, only back-up trip can be used to check set ip>. 12.5.8.2 checking the residual (earth fault) current operate value in> set below ip> check the low set in> current where setting functionmode = current and setting butripmode = 1 out of 4 1. Apply the fault...
Page 168
1. Set retripmode = cb pos check. 2. Apply the fault condition, including start of ccrbrf, well above the set current value. 3. Verify that re-trip is achieved after set time t1 and back-up trip after time t2 4. Apply the fault condition, including the start of ccrbrf, with the current below the set...
Page 169
Checking the case butripmode = 2 out of 4 the earth-fault current setting in> may be equal to or below phase-current setting ip>. 1. Set butripmode = 2 out of 4. 2. Apply the fault condition, including start of ccrbrf, with one-phase current above set ip> and residual (earth fault) above set in>. 3....
Page 170
12.5.8.8 verifying the function mode current&contact to be made only when functionmode = current&contact is selected. It is suggested to make the tests in one phase only, or at three-phase trip applications for just three- phase tripping. Checking the case with fault current above set value ip> the ...
Page 171
12.5.9.1 verifying the settings 1. External detection logic, contact function selection = contsel setting equals ccpdsc signal from cb. Activate the extpdind binary input, and measure the operating time of ccpdsc. Use the trip signal from the configured binary output to stop the timer. 2. Compare th...
Page 172
12.5.10 directional underpower protection guppdup prepare the ied for verification of settings outlined in section "requirements" and section "preparing for test" in this chapter. 12.5.10.1 verifying the settings the underpower protection shall be set to values according to the real set values to be...
Page 173
Set value: mode formula used for complex power calculation l1 * 1 1 3 l l s u i = × × equation1703 v1 en (equation 86) l2 * 2 2 3 l l s u i = × × equation1704 v1 en (equation 87) l3 * 3 3 3 l l s u i = × × equation1705 v1 en (equation 88) 2. Adjust the injected current and voltage to the set values ...
Page 174
1. Connect the test set for injection of voltage and current corresponding to the mode to be used in the application. If a three phase test set is available this could be used for all the modes. If a single phase current/voltage test set is available the test set should be connected to a selected in...
Page 175
1. Connect the test set for injection of three-phase currents to the appropriate current terminals of the ied. 2. Go to main menu/settings/setting group n/current protection/ negseqovercurr2step/nson/general and make sure that the function is enabled, that is operation is set to on. 3. Inject curren...
Page 176
To 10% of rated generator current, then tr1 and trip signals operates at time equal to 250 sec ± tolerance. 10. Repeat the above-described tests for the step 2 of the function excluding the inverse time testing. 11. Finally check that start and trip information is stored in the event menu. Example t...
Page 177
7. Check that all trip and start contacts operate according to the configuration (signal matrises). 8. Finally check that start and trip information is stored in the event menu. 9. Inject rated symmetric three phase voltage to the ied. 10. Set the injected current to 200% of the operate level of the...
Page 178
Startcurr ibase ct ctprim 100 × × sec iecequation2434 v1 en (equation 91) example (rated secondary current = 1a): ct ratio 10 000/1a vt ratio 10 kv/100 v startcurr 100% vdepfact 25% uhighlimit 100% ibase 10 000 a 10 kv a test for each section of the characteristic of the function vrpvoc may be perfo...
Page 179
6. Repeat steps 4 and 5 applying voltages that are related to the second and the last section of the characteristic; the function operates when il1 is slightly higher than: 0.5 a in the second section; 1a in the last section. 7. Connect the trip output contact to the input channel of the test set in...
Page 180
14. Note the operate value. The set operate value in secondary volts is calculated according to the following equation: startvolt ubase vt vtprim 100 3 × × sec iecequation2436 v1 en (equation 93) if the vrpvoc function is used as an overcurrent protection with undervoltage seal-in, it is necessary t...
Page 181
Two shots, or reset this memory by setting the reset input into the function to value true 1. Connect the test set for the appropriate three-phase current injection to the ied phases l1, l2 and l3. The protection shall be fed with a symmetrical three- phase current. 2. Set the injected current to 11...
Page 182
1. Connect the test set for the appropriate three-phase current injection to the ied phases l1, l2 and l3. The protection shall be fed with a symmetrical three- phase current. 2. Set the injected current to 113% of ibase, switch on the current and check operate time of the trip, 120 s. 3. Decrease t...
Page 183
1. Check that the ied settings are appropriate, especially the start value, the definite time delay and the 1 out of 3 operation mode. 2. Supply the ied with three-phase voltages at their rated values. 3. Slowly decrease the voltage in one of the phases, until the start signal appears. 4. Note the o...
Page 184
For example, if the measured voltage jumps from the rated value to 0.8 times the set start voltage level and time multiplier k1 is set to 0.05 s (default value), then the tr1 and trip signals operate at a time equal to 0.250 s ± tolerance. 10. The test above can be repeated to check the inverse time...
Page 185
6. Measure the time delay for the tr1 signal and compare it with the set value. 7. Check the inverse time delay by injecting a voltage corresponding to 1.2 × u1>. 8. Repeat the test to check the inverse time characteristic at different over-voltage levels. 9. Repeat the above-described steps for ste...
Page 186
Where: t(s) operate time in seconds k1 settable time multiplier of the function for step 1 u measured voltage u1> set start voltage for step 1 for example, if the measured voltage jumps from 0 to 1.2 times the set start voltage level and time multiplier k1 is set to 0.05 s (default value), then the ...
Page 187
11. Check that trip and alarm contacts operate according to the configuration logic. 12. Set the cooling time constant temporarily to min value (1min.) to quickly lower the thermal content. 13. Wait for a period equal to 6 times tcooling switch 20 minutes on a voltage 1.15 · v/hz> and check the inve...
Page 188
Ul1 ul2 ul3 un ul1 ul1 ul2 ul3 ie d t e s t s e t ie d iec07000106-1-en.Vsd ul2 ul3 un 1 2 iec07000106 v2 en figure 47: connection of the test set to the ied for test of u1 block level where: 1 is three-phase voltage group1 (u1) 2 is three-phase voltage group2 (u2) 3. Decrease slowly the voltage in ...
Page 189
Ul1 ul2 ul3 un ul1 ul1 ul2 ul3 ie d t e s t s e t ie d iec07000107-1-en.Vsd ul2 ul3 un 1 2 iec07000107 v2 en figure 48: connection of the test set to the ied for test of u2 block level where: 1 is three-phase voltage group1 (u1) 2 is three-phase voltage group2 (u2) 2. Apply voltage higher than the h...
Page 190
Ul1 ul2 ul3 un ul1 ul1 ul2 ul3 ie d t e s t s e t ie d iec07000108-1-en.Vsd ul2 ul3 un 1 2 iec07000108 v2 en figure 49: connection of the test set to the ied for test of alarm levels, trip levels and trip timer where: 1 is three-phase voltage group1 (u1) 2 is three-phase voltage group2 (u2) 2. Apply...
Page 191
1. Connect voltages to the ied according to valid connection diagram and figure 49 . 2. Set ur (rated voltage) to the u1 inputs and increase u2 voltage until differential voltage is 1.5 · operating level (udtrip). 3. Switch on the test set. Measure the time from activation of the start signal until ...
Page 192
12.6.6.1 testing the protection function uses measurement of the third-harmonic voltages in the neutral point of the generator and on the generator terminal (broken delta voltage transformer connection to the ied). The test set shall be capable to generate third-harmonic voltages. One voltage (u n3 ...
Page 193
3 n du u beta = equation2072 v2 en (equation 102) considering stated accuracy (beta is a setting parameter) 4. Increase the voltage u 3n so that the sart signal falls. After that, switch the voltage u 3n to zero and measure the time delay for the activation of the signals trip and trip3h. The 100% s...
Page 194
12.6.6.3 completing the test continue to test another function or end the test by changing the testmode setting to off. Restore connections and settings to their original values, if they were changed for testing purposes. 12.7 frequency protection 12.7.1 underfrequency protection saptuf prepare the ...
Page 195
1. Check that the ied settings are appropriate, for example the startfrequency, umin , and the tdelay. 2. Supply the ied with three-phase voltages at rated values. 3. Slowly decrease the magnitude of the applied voltage, until the blkdmagn signal appears. 4. Note the voltage magnitude value and comp...
Page 196
Verification of the low voltage magnitude blocking 1. Check that the settings in the ied are appropriate, for example the startfrequency, umin, and the tdelay. 2. Supply the ied with three-phase voltages at their rated values. 3. Slowly decrease the magnitude of the applied voltage, until the blkdma...
Page 197
1. The test above can be repeated to check a positive setting of startfreqgrad. 2. The tests above can be repeated to check the time to reset. 3. The tests above can be repeated to test the restore signal, when the frequency recovers from a low value. 12.7.3.2 completing the test continue to test an...
Page 198
Verification of the accalarm value and time delay to operation 1. Connect the test set for the injection of three-phase currents and three-phase voltages to the appropriate current and voltage terminals of the ied. 2. Ensure that the settings in the ied are appropriate for the default settings, espe...
Page 199
6. Slowly decrease the positive-sequence voltage of the injected voltage below the ulowlimit value until the start signal disappears. 7. Check that the voltok signal disappears. 8. Compare the reset value to the set voltage low limit value. 9. Readjust the positive-sequence voltage of the applied vo...
Page 200
12.8.1.1 built-in overcurrent feature (non-directional) procedure 1. Go to main menu/test/function test modes/multipurpose protection/ generalcurrentvoltage(gapc)/cvgapc:x and make sure that cvgapc to be tested is unblocked and other functions that might disturb the evaluation of the test are blocke...
Page 201
1. Connect the test set for injection of three-phase currents and three-phase voltages to the appropriate current and voltage terminals of the ied. 2. Inject current(s) and voltage(s) in a way that relevant measured (according to setting parameter currentinput and voltageinput) currents and voltages...
Page 202
12.8.1.5 over/undervoltage feature procedure 1. Connect the test set for injection three-phase voltages to the appropriate voltage terminals of the ied. 2. Inject voltage(s) in a way that relevant measured (according to setting parameter voltageinput) voltages are created from the test set. 3. Overa...
Page 203
12.9.1.2 completing the test continue to test another function or end the test by changing the testmode setting to off. Restore connections and settings to their original values, if they were changed for testing purposes. 12.9.2 fuse failure supervision fufspvc prepare the ied for verification of se...
Page 204
• signal 3ph after about 25ms • signal blku after about 50ms • signal blkz after about 200ms 12.9.2.2 measuring the operate value for the negative sequence function measure the operate value for the negative sequence function, if included in the ied. 1. Simulate normal operating conditions with the ...
Page 205
2 3 3 1 0, 5 2 j a e j p × = × = - + . Iecequation00022 v2 en 7. Compare the result with the set value of the negative-sequence operating current. Consider that the set value 3i2 ibase. 12.9.2.3 measuring the operate value for the zero-sequence function measure the operate value for the zero-sequenc...
Page 206
12.9.2.4 measuring the operate value for the dead line detection function 1. Apply three-phase voltages with their rated value and zero currents. 2. Decrease the measured voltage in one phase until the dld1ph signal appears. 3. This is the point at which the dead line condition is detected. Check th...
Page 207
8. Change the magnitude of the voltage and current for phase 1 to a value greater than the set value for du> and di. 9. Check that the start output signals stdul1 and stdil1 and the general start signals stdu or stdi are activated. 10. Check that the start output signals for the current and voltage ...
Page 208
7. After more than 5 seconds increase the measured voltage back to the value slightly below usealin level. Mainfuf signal should not reset. 8. Slowly increase measured voltage to the value slightly above usealin until mainfuf signal resets. 9. Record the measured voltage and compare with the set val...
Page 209
To use different phases, phase to earth or phase to phase. Use the set voltages instead of what is indicated below. Figure 51 shows the general test connection principle, which can be used during testing. This description describes the test of the version intended for one bay. Figure 52 shows the ge...
Page 210
U-bus1 u-line1 n test equipment ied u3pbb1 n iec05000481-5-en.Vsd n umeasure ph/n ph/ph u-bus2 u-line2 u3pbb2 u3pln2 u3pln1 n n input phase l1,l2,l3 l12,l23,l31 umeasure ph/n ph/ph input phase l1,l2,l3 l12,l23,l31 iec05000481 v5 en figure 52: general test connection for a 1½ breaker diameter with on...
Page 212
Testing the phase angle difference the phase angle differences phasediffm and phasediffa respectively are set to their final settings and the test should verify that operation is achieved when the phase angle difference is lower than this value both leading and lagging. Test with no voltage differen...
Page 213
1. Apply voltages u-line equal to 100% gblbaseselline and u-bus equal to 100% gblbaseselbus, with a frequency difference equal to 0 mhz and a phase difference lower than the set value. 2. Check that the autosyok and mansyok outputs are activated. 3. Apply voltage to the u-line equal to 100% gblbases...
Page 214
1. Apply a single-phase voltage 100% gblbaseselbus to the u-bus, and a single- phase voltage 30% gblbaseselline to the u-line. 2. Check that the autoenok and manenok outputs are activated after set tautoenerg respectively tmanenerg. 3. Increase the u-line to 60% gblbaseselline and u-bus to be equal ...
Page 215
4. Check that the manenok output is activated after set tmanenerg. 5. Increase the u-bus to 80% gblbaseselbus and keep the u-line equal to 30% gblbaseselline. The outputs should not be activated. 6. Repeat the test with manenerg set to dllb with different values on the u-bus and the u-line voltage. ...
Page 216
Be considered as wa2 and line2 as line1. The voltage is selected by activation of different inputs in the voltage selection logic as shown in table 17 and figure 54 . Table 17: voltage selection logic sesrsyn cbconfig setting section to be synchroniz ed activated b1qcld input on ied from activated b...
Page 217
Wa1 wa2 wa1_qa1 (sesrsyn 1) wa2_qa1 (sesrsyn 3) tie_qa1 (sesrsyn 2) line1 line2 line1_qb9 line2_qb9 iec11000274-3-en.Vsd iec11000274 v3 en figure 54: objects used in the voltage selection logic 12.10.1.5 completing the test continue to test another function or end the test by changing the testmode s...
Page 218
12.10.3 voltage control (vctr) tr1atcc, tr8atcc, tcmyltc, tclyltc prepare the ied for verification of settings outlined in section "requirements" and section "preparing for test" in this chapter. The automatic voltage control for tap changer, single control tr1atcc is based on a transformer configur...
Page 219
Transformervoltagecontrol(atcc,90)/tr1atcc:x/tr8atcc:x/ xr2. • confirm that the setting for tcmyltc or tclyltc is in accordance with transformer data: • tap change timeout duration - effectively the maximum transformer tap change time, ttctimeout, available on the local hmi under main menu/ settings...
Page 220
Control/transformervoltagecontrol(atcc,90)/tr1atcc:x/ tr8atcc:x/time/t1 and t2l. For cases where single-mode voltage control is implemented, the parameter setting menu structure includes tr1atcc:1 instead of the parallel designator tr8atcc:1. 12.10.3.1 secondary test the voltage control function per...
Page 221
Main menu/settings/general settings/control/ transformertapchanger(yltc,84)/tcmyltc:x/tclyltc:x/ enabtapcmd while the test set is connected to the ied but no voltage is applied, the voltage control functions will detect an undervoltage condition that may result in an alarm or blocking of the voltage...
Page 222
General settings/control/transformervoltagecontrol(atcc,90)/ tr1atcc:x/tr8atcc:x/uvbk that may cause an alarm, total or automatic block of the voltage control function to be displayed on the local hmi. 3. Apply a voltage slightly below ublock and confirm the response of the voltage control function....
Page 223
12.10.3.7 single transformer load drop compensation 1. Confirm that operationldc is set to on. 2. Confirm settings for rline and xline. 3. Calculate the expected load voltage u l (displayed as a measured value on the local hmi) based on secondary injection of transformer secondary voltage (u b = use...
Page 224
7. Confirm that the calculated value for load voltage, displayed on the local hmi, is equal to that derived through hand calculations. 8. When setting operationldc set to on, the voltage regulation algorithm uses the calculated value for load voltage as the regulating quantity to compare against use...
Page 225
Settings/setting group n/control/transformervoltagecontrol(atcc, 90)/tr1atcc:x/tr8atcc:x/time/t1 and t2 6. Apply a voltage 1% below u1 and wait for the issue of a raise command from the voltage control after the expiry of a constant or inverse time delay set by t1. Detection of this command will inv...
Page 226
The parameter corresponding to the own ied must not be set. T1rxop should thus not be set in ied t1, t2rxopnot in ied t2 and so on. 3. Review the settings for udeadband (based on percentage of nominal bus voltage) and calculate the upper (u2) and lower (u1) voltage regulation limits for which a tap ...
Page 227
Equation2092 v2 en (equation 121) equation2094 v2 en (equation 122) (for the purposes of this test procedure) therfore: _ 2 ci icc i xi u uset × × > - equation2096 v1 en (equation 123) ( ) ( ) 2 _ u uset icc i ci xi - > × equation2098 v1 en (equation 124) 10. Using the settings for uset, udeadband, ...
Page 228
4. Review the setting for circcurrbk to confirm whether a circulating current limit will result in an alarm state, auto block or auto&man block of the automatic voltage control for tap changer, for parallel control function tr8atcc. 5. Inject a voltage u b equal to uset for each transformer. 6. Inje...
Page 229
Values of the logical signals are available on the local hmi under main menu/tests/ function status/control/apparatus control/interlocking. The signal monitoring in pcm600 shows the same signals that are available on the local hmi. The interlocking function consists of a bay-level part and a station...
Page 230
Single-phase tripping will only be allowed when an autoreclose attempt will follow. The autorecloser function smbrrec has the functionality such as the long trip time, cb ready and so on, which can prevent a proper single-phase tripping and autoreclose. To by-pass this problem the fault initiation s...
Page 231
Take an adequate time interval between faults into consideration, to overcome a reclaim time, which is activated by the autorecloser function smbrrec. Only a single-phase trip should occur for each separate fault and only one of the trip outputs (trln) should be activated at a time. Functional outpu...
Page 232
12.11.1.4 circuit breaker lockout the following tests should be carried out when the built-in lockout function is used in addition to possible other tests, which depends on the complete configuration of an ied. 1. Check that autolock and triplockout are both set to off. 2. Activate shortly the set l...
Page 233
12.12 monitoring 12.12.1 gas medium supervision ssimg prepare the ied for verification of settings as outlined in section "testing the liquid medium supervision for alarm and lock out conditions" and section "completing the test" in this chapter. Check that the input logical signal block is logical ...
Page 234
Check that the input logical signal block is logical zero and that on the local hmi, the logical signals lvl_alm, lvl_lo, temp_alm and temp_lo are equal to logical zero. 12.12.2.1 testing the liquid medium supervision for alarm and lock out conditions 1. Connect the binary inputs to consider liquid ...
Page 235
12.12.3.1 verifying the settings 1. Connect the test set for the injection of a three-phase current to the appropriate current terminals of the ied. 2. If current need to be injected for a particular test, it should be done in the phase selected by the phsel parameter. 3. Follow the sequence for pos...
Page 236
7.1. Test the actual set values defined by accselcal to aux contact, conttrcorr and almacccurrpwr. 7.2. Inject phase current in the selected phase such that its value is greater than set accstopcurr value. 7.3. When the breaker goes to open position, accumulated energy ipowph is calculated. The calc...
Page 237
12.12.4 event function event prepare the ied for verification of settings as outlined in section "preparing for test" in this chapter. During testing, the ied can be set when in test mode from pst. The functionality of the event reporting during test mode is set in the parameter setting tool in pcm6...
Page 238
12.13.2.1 verifying the settings common test equipment can be used to determine the injection of current and voltage and time measurement. Verification of eafacc & erfacc output 1. Connect the test set for injection of three-phase currents and three phase voltage to the appropriate current and volta...
Page 239
1. Repeat the above test steps 1 to 2. 2. Set tenergy setting as 1 minute and supply the ied with three phase currents and voltages at their rated value till 1 minute. 3. Ensure that the active and reactive energy values are less than the ealim and erlim setting default values respectively. 4. Check...
Page 240
To perform a test of binary signal transfer function (binsignreceive/ binsigntransm), the hardware (ldcm) and binary input and output signals to transfer must be configured as required by the application. There are two types of internal self supervision of binsignreceive/binsigntransm • the i/o-circ...
Page 241
Iec07000188 v1 en figure 55: test of rtc with i/o 12.16 basic ied functions 12.16.1 parameter setting group handling setgrps prepare the ied for verification of settings as outlined in section "preparing for test" in this chapter. 12.16.1.1 verifying the settings 1. Check the configuration of binary...
Page 242
12.16.1.2 completing the test continue to test another function or end the test by changing the testmode setting to off. Restore connections and settings to their original values, if they were changed for testing purposes. 12.17 exit test mode the following procedure is used to return to normal oper...
Page 243
Section 13 checking the directionality 13.1 overview before starting this process, all individual devices that are involved in the fault clearance process of the protected object must have been individually tested and must be set in operation. The circuit breaker must be ready for an open-close-open...
Page 244
• for forward (exported) load: -15 deg • for reverse (imported) load: 165 deg the settings for forward load: - argdir argnegres and the settings for reverse load: 180 deg - argdir argnegres included in the directional functions zdrdir or zdmrdir are available under the hmi menu: • main menu/settings...
Page 245
If the directional function shows “no direction” for only some of the three phases, this probably means a wrong cts/vts connection. 4. The measured impedance information is available under the same menu. These values are not affected by the minimum operating current setting of zdrdir or zdmrdir and ...
Page 246
240
Page 247
Section 14 commissioning and maintenance of the fault clearing system 14.1 commissioning tests during commissioning all protection functions shall be verified with the setting values used at each plant. The commissioning tests must include verification of all circuits by green-lining the circuit dia...
Page 248
Every four to six years • periodic maintenance test for protection ieds of objects with redundant protection system. First maintenance test should always be carried out after the first half year of service. When protection ieds are combined with built-in control, the test interval can be increased d...
Page 249
• test instructions for protection ieds to be tested • test records from previous commissioning and maintenance tests • list of valid settings • blank test records to fill in measured values 14.2.2.2 recording it is of utmost importance to carefully record the test results. Special test sheets cover...
Page 250
Is really closed when the test-plug handle has been removed by using a high-ohmic voltmeter and measuring between the plus and the trip output on the panel. The measurement is then done through the trip coil of the circuit breaker and therefore the complete trip circuit is checked. Note that the bre...
Page 251
14.2.2.8 restoring maintenance is very important to improve the availability of the protection system by detecting failures before the protection is required to operate. There is however little point in testing healthy equipment and then putting it back into service with an open terminal, with a rem...
Page 252
246.
Page 253
Section 15 troubleshooting 15.1 checking the self supervision signals 15.1.1 checking the self supervision function 15.1.1.1 determine the cause of an internal failure this procedure describes how to navigate the menus in order to find the cause of an internal failure when indicated by the flashing ...
Page 254
Indicated result possible reason proposed action adc-module ok no problem detected. None. Adc-module fail the ad conversion module has failed. Contact your abb representative for service. (protocol name) ready no problem detected. None. (protocol name) fail protocol has failed. (i/o module name) rea...
Page 255
Hmi signal name: status description time sync ready / fail this signal will be active when the source of the time synchronization is lost, or when the time system has to make a time reset. Application ready / fail this signal will be active if one or more of the application threads are not in the st...
Page 256
The internal events in this list not only refer to faults in the ied, but also to other activities, such as change of settings, clearing of disturbance reports, and loss of external time synchronization. The information can only be retrieved from the parameter setting software package. The pc can be...
Page 257
Cause a massive potential build up that may damage the transformer and may cause injuries to humans. Never connect or disconnect a wire and/or a connector to or from a ied during normal service. Hazardous voltages and currents are present that may be lethal. Operation may be disrupted and ied and me...
Page 258
15.4 repair support if an ied needs to be repaired, the whole ied must be removed and sent to an abb logistic center. Before returning the material, an inquiry must be sent to the abb logistic center. E-mail: offer.Selog@se.Abb.Com 15.5 maintenance the ied is self-supervised. No special maintenance ...
Page 259
Section 16 glossary ac alternating current acc actual channel act application configuration tool within pcm600 a/d converter analog-to-digital converter adbs amplitude deadband supervision adm analog digital conversion module, with time synchronization ai analog input ansi american national standard...
Page 260
Ccitt consultative committee for international telegraph and telephony. A united nations-sponsored standards body within the international telecommunications union. Ccm can carrier module ccvt capacitive coupled voltage transformer class c protection current transformer class as per ieee/ ansi cmpps...
Page 261
Dhcp dynamic host configuration protocol dip-switch small switch mounted on a printed circuit board di digital input dllb dead line live bus dnp distributed network protocol as per ieee std 1815-2012 dr disturbance recorder dram dynamic random access memory drh disturbance report handler dsp digital...
Page 262
Gis gas-insulated switchgear goose generic object-oriented substation event gps global positioning system gsal generic security application gse generic substation event hdlc protocol high-level data link control, protocol based on the hdlc standard hfbr connector type plastic fiber connector hmi hum...
Page 263
Function. One instance of a function is identical to another of the same kind but has a different number in the ied user interfaces. The word "instance" is sometimes defined as an item of information that is representative of a type. In the same way an instance of a function in the ied is representa...
Page 264
Ocp overcurrent protection oem optical ethernet module oltc on-load tap changer otev disturbance data recording initiated by other event than start/pick-up ov overvoltage overreach a term used to describe how the relay behaves during a fault condition. For example, a distance relay is overreaching w...
Page 265
Scl short circuit location scs station control system scada supervision, control and data acquisition sct system configuration tool according to standard iec 61850 sdu service data unit slm serial communication module. Sma connector subminiature version a, a threaded connector with constant impedanc...
Page 266
Tnc connector threaded neill-concelman, a threaded constant impedance version of a bnc connector tp trip (recorded fault) tpz, tpy, tpx, tps current transformer class according to iec trm transformer module. This module transforms currents and voltages taken from the process into levels suitable for...
Page 267
261.
Page 268
Contact us for more information please contact: abb ab substation automation products se-721 59 västerås, sweden phone +46 (0) 21 32 50 00 www.Abb.Com/substationautomation note: we reserve the right to make technical changes or modify the contents of this document without prior notice. Abb ab does n...