- DL manuals
- ABB
- Touch terminals
- REL 551-C1*2.5
- Technical Reference Manual
ABB REL 551-C1*2.5 Technical Reference Manual - (Time)
32
Real-time clock with external time
synchronization (TIME)
Chapter 3
Common functions
1
Real-time clock with external time synchronization
(TIME)
1.1
Application
Use the time synchronization source selector to select a common source of absolute time for the
terminal when it is a part of a protection system. This makes comparison of events and distur-
bance data between all terminals in a SA system possible.
1.2
Function block
1.3
Input and output signals
Table 23:
Input signals for the TIME (TIME-) function block
Path in local HMI: ServiceReport/Functions/Time
Table 24:
Output signals for the TIME (TIME-) function block
1.4
Setting parameters
Path in local HMI: Configuration/Time
xx00000171.vsd
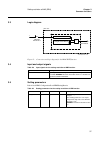
TIME-
TIME
MINSYNC
SYNCSRC
RTCERR
SYNCERR
Signal
Description
MINSYNC
Minute pulse input
SYNCSRC
Synchronization source selector input. See settings for details.
Signal
Description
RTCERR
Real time clock error
SYNCERR
Time synchronisation error
Summary of REL 551-C1*2.5
Page 1
Technical reference manual protect it line differential protection terminal rel 551-c1*2.5.
Page 2: Technical Reference Manual
© copyright 2006 abb. All rights reserved. Technical reference manual line differential protection terminal rel 551-c1*2.5 about this manual document no: 1mrk 506 207-uen issued: december 2006 revision: c.
Page 3
Copyright we reserve all rights to this document, even in the event that a patent is issued and a different commercial proprietary right is registered. Improper use, in particular reproduction and dissemination to third parties, is not permitted. This document has been carefully checked. However, in...
Page 4: Contents
Contents page chapter chapter 1 introduction ..................................................................... 1 introduction to the technical reference manual.................................... 2 about the complete set of manuals for a terminal .......................... 2 design of the techni...
Page 5: Contents
Contents application .................................................................................... 38 logic diagram ............................................................................... 38 function block............................................................................... ...
Page 6: Contents
Contents application .................................................................................... 64 functionality ................................................................................. 64 function block ................................................................................
Page 7: Contents
Contents technical data .............................................................................. 87 event function (ev) ............................................................................ 88 application .....................................................................................
Page 8: Contents
Contents technical data ....................................................................... 117 short range galvanic module ...................................................... 118 application ............................................................................. 118 technical data .......
Page 9: Contents
Contents i/o module (iom) ............................................................................. 143 application .................................................................................. 143 design..........................................................................................
Page 10: Chapter 1 Introduction
1 about this chapter chapter 1 introduction chapter 1 introduction about this chapter this chapter introduces you to the manual as such..
Page 11
2 introduction to the technical reference manual chapter 1 introduction 1 introduction to the technical reference manual 1.1 about the complete set of manuals for a terminal the users manual (um) is a complete set of four different manuals: the application manual (am) contains descriptions, such as ...
Page 12
3 introduction to the technical reference manual chapter 1 introduction functionality/design presents the general concept of a function. Function block each function block is imaged by a graphical symbol. Input signals are always on the left side, and output signals on the right side. Settings are n...
Page 13
4 introduction to the technical reference manual chapter 1 introduction figure 2: simplified logic diagram example the names of the configurable logic signals consist of two parts divided by dashes. The first part consists of up to four letters and presents the abbreviated name for the corresponding...
Page 14
5 introduction to the technical reference manual chapter 1 introduction configuration purposes. The user can configure them to binary outputs from the terminal or to inputs of different functions. Typical examples are signals tuv--trip, tuv--start etc. Other internal signals configurated to other fu...
Page 15
6 introduction to the technical reference manual chapter 1 introduction 1.3 intended audience 1.3.1 general this manual addresses system engineers, installation and commissioning personnel, who use technical data during engineering , installation and commissioning, and in normal service. 1.3.2 requi...
Page 16
7 introduction to the technical reference manual chapter 1 introduction awg american wire gauge standard bim binary input module blkdel block of delayed fault clearing bom binary output module br binary transfer receive over ldcm bs british standard bsr binary signal receive (smt) over ldcm bst bina...
Page 17
8 introduction to the technical reference manual chapter 1 introduction cvt capacitive voltage transformer dar delayed auto-reclosing db dead band dbdl dead bus dead line dbll dead bus live line dc direct current din-rail rail conforming to din standard dip-switch small switch mounted on a printed c...
Page 18
9 introduction to the technical reference manual chapter 1 introduction hdlc protocol high level data link control, protocol based on the hdlc standard hfbr connector type fibre connector receiver hmi human-machine interface hsar high-speed auto-reclosing hv high voltage hvdc high voltage direct cur...
Page 19
10 introduction to the technical reference manual chapter 1 introduction inampl present magnitude of residual current instmagn magnitude of instantaneous value instname instance name in signal matrix tool iom binary input/output module iposim imaginary part of positive sequence current iposre real c...
Page 20
11 introduction to the technical reference manual chapter 1 introduction mvb multifunction vehicle bus. Standardized serial bus originally developed for use in trains mvsubena enable substitution negseqroa operate angle for internal/external negative sequence fault discrimina- tor. Nsangle angle bet...
Page 21
12 introduction to the technical reference manual chapter 1 introduction rtc real time clock sa substation automation sc switch or push-button to close scs station control system slm serial communication module. Used for spa/lon/iec communication sma connector sub miniature version a connector sms s...
Page 22
13 introduction to the technical reference manual chapter 1 introduction ttrip estimated time to trip (in minutes) ubase base setting for phase-phase voltage in kilovolts u/i-pisa process interface components that delivers measured voltage and cur- rent values unom nominal voltage in % of ubase for ...
Page 23
14 introduction to the technical reference manual chapter 1 introduction.
Page 24: Chapter 2 General
15 about this chapter chapter 2 general chapter 2 general about this chapter this chapter describes the terminal in general..
Page 25
16 terminal identification rated and base values chapter 2 general 1 terminal identification rated and base values 1.1 general terminal parameters use the terminal identifiers to name the individual terminal for identification purposes. Use the terminal reports to check serial numbers of the termina...
Page 26
17 terminal identification rated and base values chapter 2 general table 6: rated voltages path in local hmi: configuration/analoginputs/u1-u5 table 7: analog inputs - voltage parameter range default unit description ur * 10.000 - 500.000 step: 0.001 110.000 v rated voltage of transformer module u1r...
Page 27
18 terminal identification rated and base values chapter 2 general path in local hmi: configuration/analoginputs/trafoinpmodule table 8: rated currents u3scale 1.000 - 20000.000 step: 0.001 2000.000 - main voltage transformer ratio, input u3 name_u3 0 - 13 u3 char user-defined name of input u3 u4b 3...
Page 28
19 terminal identification rated and base values chapter 2 general path in local hmi: configuration/analoginputs/i1-i5 table 9: analog inputs - current path in local hmi: configuration/analoginputs/u, i, p, q, s, f table 10: labels for service values parameter range default unit description i1b 0.1 ...
Page 29
20 terminal identification rated and base values chapter 2 general 1.3 calendar and clock table 11: calendar and clock name_i 0 - 13 i char name for analogue input i name_p 0 - 13 p char name for analogue input p name_q 0 - 13 q char name for analogue input q name_s 0 - 13 s char name for analogue i...
Page 30: Technical Data
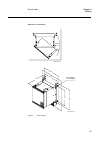
21 technical data chapter 2 general 2 technical data 2.1 case dimensions figure 3: case without rear cover figure 4: case without rear cover with 19” rack mounting kit a b c d e xx02000646.Vsd f g h j k xx02000647.Vsd case size a b c d e f g h j k 6u, 1/2 x 19” 265.9 223.7 204.1 252.9 205.7 190.5 20...
Page 31
22 technical data chapter 2 general figure 5: case with rear cover. Figure 6: case with rear cover and 19” rack mounting kit. Figure 7: rear cover case with details. A b c d e f xx02000648.Vsd j i h g k xx02000649.Vsd xx02000650.Vsd.
Page 32
23 technical data chapter 2 general case size a b c d e f g h j k 6u, 1/2 x 19” 265.9 223.7 242.1 252.9 205.7 190.5 203.7 - 186.6 - the h and k dimensions are defined by the 19” rack mounting kit. All dimensions are in millimeters. Panel cut-outs for rex 500 series, single case flush mounting semi-f...
Page 33
24 technical data chapter 2 general the flush mounting kit consists of four fasteners (2) with appropriate mounting details (4) and a sealing strip (5) for fastening to the ied (3). To receive ip54 class protection, an additional sealing (1) must be ordered with the ied. This sealing is factory moun...
Page 34
25 technical data chapter 2 general dimensions, wall mounting figure 9: wall mounting 80 mm xx02000653.Vsd e a b c d screws m6 or corresponding en02000654.Vsd.
Page 35
26 technical data chapter 2 general 2.2 weight table 12: weight 2.3 unit table 13: case 2.4 power consumption table 14: power consumption, basic terminal 2.5 environmental properties table 15: temperature and humidity influence case size (mm) a b c d e 6u, 1/2 x 19” 292 267.1 272.8 390 247 case size...
Page 36
27 technical data chapter 2 general table 16: auxiliary dc supply voltage influence on functionality during operation table 17: frequency influence table 18: electromagnetic compatibility dependence on within nominal range influence ripple, in dc auxiliary voltage max 12% 0.01% / % interrupted auxil...
Page 37
28 technical data chapter 2 general table 19: electromagnetic compatibility for rs485 interface table 20: insulation radiated electromagnetic field disturbance 10 v/m, 80-1000 mhz, 1.4-2.0 ghz iec 61000-4-3, class iii radiated electromagnetic field disturbance 35 v/m 26-1000 mhz ieee/ansi c37.90.2 c...
Page 38
29 technical data chapter 2 general table 21: ce compliance table 22: mechanical tests test according to immunity en 61000-6-2 emissivity en 61000-6-4 low voltage directive en 50178 test type test values reference standards vibration class i iec 60255-21-1 shock and bump class i iec 60255-21-2 seism...
Page 39
30 technical data chapter 2 general.
Page 40: Chapter 3 Common Functions
31 about this chapter chapter 3 common functions chapter 3 common functions about this chapter this chapter presents the common functions in the terminal..
Page 41: (Time)
32 real-time clock with external time synchronization (time) chapter 3 common functions 1 real-time clock with external time synchronization (time) 1.1 application use the time synchronization source selector to select a common source of absolute time for the terminal when it is a part of a protecti...
Page 42
33 real-time clock with external time synchronization (time) chapter 3 common functions table 25: setting parameters for the time synchronization source selector function 1.5 technical data table 26: time - time synchronisation parameter range default unit description syncsrc 0-5 0 - selects the tim...
Page 43
34 four parameter setting groups (grp) chapter 3 common functions 2 four parameter setting groups (grp) 2.1 application use the four sets of settings to optimize the terminals operation for different system conditions. By creating and switching between fine tuned setting sets, either from the human-...
Page 44
35 four parameter setting groups (grp) chapter 3 common functions 2.4 input and output signals table 27: input signals for the activegroup (grp--) function block path in local hmi: servicereport/functions/activegroup/funcoutputs table 28: output signals for the activegroup (grp--) function block sig...
Page 45
36 setting restriction of hmi (srh) chapter 3 common functions 3 setting restriction of hmi (srh) 3.1 application use the setting restriction function to prevent unauthorized setting changes and to control when setting changes are allowed. Unpermitted or uncoordinated changes by unauthorized personn...
Page 46
37 setting restriction of hmi (srh) chapter 3 common functions 3.3 logic diagram figure 11: connection and logic diagram for the blockset function 3.4 input and output signals table 29: input signals for the setting restriction of hmi function 3.5 setting parameters path in local hmi: configuration/...
Page 47: I/o System Configurator
38 i/o system configurator chapter 3 common functions 4 i/o system configurator 4.1 application the i/o system configurator must be used in order for the terminal’s software to recognize added modules and to create internal address mappings between modules and protections and other functions. 4.2 lo...
Page 48
39 i/o system configurator chapter 3 common functions 4.3 function block 4.4 input and output signals table 31: output signals for the i/oposition (iopn-) function block xx00000238.Vsd iop1- i/oposition s11 s12 s13 s14 s15 s16 s17 s18 s19 s20 s21 s22 s23 s24 s25 s26 s27 s28 s29 s30 s32 s33 s34 s35 s...
Page 49
40 self supervision with internal event recorder (int) chapter 3 common functions 5 self supervision with internal event recorder (int) 5.1 application use the local hmi, sms or scs to view the status of the self-supervision function. The self-su- pervision operates continuously and includes: • norm...
Page 50
41 self supervision with internal event recorder (int) chapter 3 common functions 5.3 logic diagram figure 13: hardware self-supervision, potential-free alarm contact. Power supply fault w atchdog tx overflow master resp. Supply fault reboot i/o checksum fault supply fault parameter check power supp...
Page 51
42 self supervision with internal event recorder (int) chapter 3 common functions figure 14: software self-supervision, function block internal signals 5.4 input and output signals path in local hmi: servicereport/functions/internsignals checksum node reports synch error no rx data no tx clock check...
Page 52
43 self supervision with internal event recorder (int) chapter 3 common functions table 32: output signals for the internsignals (int--) function block 5.5 technical data table 33: internal event list signal description fail internal fail status warning internal warning status cpufail cpu module fai...
Page 53
44 configurable logic blocks (cl1) chapter 3 common functions 6 configurable logic blocks (cl1) 6.1 application the user can with the available logic function blocks build logic functions and configure the ter- minal to meet application specific requirements. Different protection, control, and monit...
Page 54
45 configurable logic blocks (cl1) chapter 3 common functions table 36: input signals for the or (onnn-) function block path in local hmi: servicereport/functions/or1n table 37: output signals for the or (onnn-) function block 6.4 and function block (and) the and function is used to form general com...
Page 55
46 configurable logic blocks (cl1) chapter 3 common functions table 39: output signals for the and (annn-) function block 6.5 timer function block (tm) the function block tm timer has drop-out and pick-up delayed outputs related to the input sig- nal. The timer has a settable time delay (parameter t...
Page 56
47 configurable logic blocks (cl1) chapter 3 common functions table 43: input signals for the timerlong (tlnn-) function block path in local hmi: servicereport/functions/timerlong table 44: output signals for the timerlong (tlnn-) function block 6.6.1 setting parameters table 45: setting parameters ...
Page 57
48 configurable logic blocks (cl1) chapter 3 common functions table 47: output signals for the tp (tpnn-) function block 6.7.1 setting parameters table 48: setting parameters for the pulse (tpnn-) function 6.8 extended length pulse function block (tq) the function block tq pulse timer with extended ...
Page 58
49 configurable logic blocks (cl1) chapter 3 common functions 6.9 exclusive or function block (xo) the exclusive or function xor is used to generate combinatory expressions with boolean vari- ables. The function block xor has two inputs and two outputs. One of the outputs is inverted. The output sig...
Page 59
50 configurable logic blocks (cl1) chapter 3 common functions table 55: output signals for the sr (srnn-) function block 6.11 set-reset with memory function block (sm) the set-reset function sm is a flip-flop with memory that can set or reset an output from two inputs respectively. Each sm function ...
Page 60
51 configurable logic blocks (cl1) chapter 3 common functions table 59: input signals for the gt (gtnn-) function block path in local hmi: servicereport/functions/controlgates1/funcoutputs table 60: output signals for the gt (gtnn-) function block 6.12.1 setting parameters path in local hmi: setting...
Page 61
52 configurable logic blocks (cl1) chapter 3 common functions table 63: output signals for the ts (tsnn-) function block 6.13.1 setting parameters path in local hmi: settings/functions/group1/timerset1/timersetnn table 64: setting parameters for the ts (tsn-) function 6.14 technical data table 65: c...
Page 62
53 blocking of signals during test (bst) chapter 3 common functions 7 blocking of signals during test (bst) 7.1 application the protection and control terminals have a complex configuration with many included func- tions. To make the testing procedure easier, the terminals include the feature to ind...
Page 63
54 blocking of signals during test (bst) chapter 3 common functions.
Page 64: Chapter 4 Line Differential
55 about this chapter chapter 4 line differential protection chapter 4 line differential protection about this chapter this chapter describes how the line differential function works and includes tables with data re- lated to this function..
Page 65: (Difl)
56 line differential protection, phase segregated (difl) chapter 4 line differential protection 1 line differential protection, phase segregated (difl) 1.1 application current line-differential protection compares the currents entering and leaving the protected overhead line or cable. The differenti...
Page 66
57 line differential protection, phase segregated (difl) chapter 4 line differential protection figure 15: operating characteristic the communication delay is continuously measured and automatically compensated for, in the differential measurement. This function enables the terminal to use a communi...
Page 67
58 line differential protection, phase segregated (difl) chapter 4 line differential protection 1.3 function block figure 16: difl function block for three phase tripping. Figure 17: difl function block for single two and/or three phase tripping. En03000099.Vsd rtcsend1 difl- differential block ctsu...
Page 68
59 line differential protection, phase segregated (difl) chapter 4 line differential protection 1.4 logic diagram figure 18: simplified block diagram, line differential protection function 1.5 input and output signals table 69: input signals for the difl (difl-) function block 1 communication interf...
Page 69
60 line differential protection, phase segregated (difl) chapter 4 line differential protection path in local hmi: servicereport/functions/differential/funcoutputs table 70: output signals for the difl (difl-) function block 1.6 setting parameters path in local hmi-tree: settings/functions/groupn/di...
Page 70
61 line differential protection, phase segregated (difl) chapter 4 line differential protection path in local hmi-tree: configuration/terminalcom/remtermcom table 72: setting parameters for remote terminal communication path in local hmi-tree: configuration/difffunction table 73: setting parameter f...
Page 71
62 line differential protection, phase segregated (difl) chapter 4 line differential protection.
Page 72: Chapter 5 Current
63 about this chapter chapter 5 current chapter 5 current about this chapter this chapter describes the current protection functions..
Page 73: Protection (Ioc)
64 instantaneous non-directional overcurrent protection (ioc) chapter 5 current 1 instantaneous non-directional overcurrent protection (ioc) 1.1 application different system conditions, such as source impedance and the position of the faults on long transmission lines influence the fault currents to...
Page 74
65 instantaneous non-directional overcurrent protection (ioc) chapter 5 current figure 20: ioc function block, phase + n with 3 phase trip figure 21: ioc function block phase with 1, 2, 3 phase trip figure 22: ioc function block, phase with 3 phase trip figure 23: ioc function block, n + 3 phase tri...
Page 75
66 instantaneous non-directional overcurrent protection (ioc) chapter 5 current 1.4 logic diagram figure 24: ioc function, logic diagram 1.5 input and output signals table 75: input signals for the ioc (ioc--) function block path in local hmi: servicereport/functions/instantoc/funcoutputs ioc--block...
Page 76
67 instantaneous non-directional overcurrent protection (ioc) chapter 5 current table 76: output signals for the ioc (ioc--) function block 1.6 setting parameters path in local hmi: settings/functions/group n /instantoc (where n =1-4) table 77: setting parameters for the instantaneous phase and resi...
Page 77: Protection (Toc)
68 definite time non-directional overcurrent protection (toc) chapter 5 current 2 definite time non-directional overcurrent protection (toc) 2.1 application the time delayed overcurrent protection, toc, operates at different system conditions for cur- rents exceeding the preset value and which remai...
Page 78
69 definite time non-directional overcurrent protection (toc) chapter 5 current 2.3 function block figure 25: toc function block, phase + n figure 26: toc function block, phase figure 27: toc function block, n xx00000197.Vsd toc-- toc block blktr trip trp trn stp stl1 stl2 stl3 stn xx00000681.Vsd to...
Page 79
70 definite time non-directional overcurrent protection (toc) chapter 5 current 2.4 logic diagram figure 28: toc function, logic diagram 2.5 input and output signals table 79: input signals for the toc (toc--) function block path in local hmi: servicereport/functions/timedelayoc/funcoutputs table 80...
Page 80
71 definite time non-directional overcurrent protection (toc) chapter 5 current 2.6 setting parameters path in local hmi: settings/functions/group n /timedelayoc (where n =1-4) table 81: setting parameters for the time delayed phase and residual overcurrent pro- tection toc (toc--) function 2.7 tech...
Page 81: (Tef)
72 time delayed residual overcurrent protection (tef) chapter 5 current 3 time delayed residual overcurrent protection (tef) 3.1 application use the inverse and definite time delayed residual overcurrent functions in solidly earthed sys- tems to get a sensitive and fast fault clearance of phase to e...
Page 82
73 time delayed residual overcurrent protection (tef) chapter 5 current 3.4 logic diagram figure 30: simplified logic diagram for the residual overcurrent protection 3.5 input and output signals table 83: input signals for the tef (tef--) function block path in local hmi: servicereport/functions/ear...
Page 83
74 time delayed residual overcurrent protection (tef) chapter 5 current table 84: output signals for the tef (tef--) function block 3.6 setting parameters path in local hmi: settings/functions/groupn/earthfault/tef table 85: settings for the tef (tef--) function signal description trip trip by tef t...
Page 84
75 time delayed residual overcurrent protection (tef) chapter 5 current 3.7 technical data table 86: tef - time delayed non-directional residual overcurrent protection parameter setting range accuracy start current, definite time or inverse time delay, in> 5-300% of ib in steps of 1% ± 5% of set val...
Page 85
76 thermal phase overload protection (thol) chapter 5 current 4 thermal phase overload protection (thol) 4.1 application load currents that exceed the permissible continuous value may cause damage to the conductors and isolation due to overheating. The permissible load current will vary with the amb...
Page 86
77 thermal phase overload protection (thol) chapter 5 current 4.4 logic diagram figure 31: thermal overload protection, simplified logic diagram 4.5 input and output signals table 87: input signals for the thol (thol-) function block path in local hmi: servicereport/functions/thermoverload/funcoutpu...
Page 87
78 thermal phase overload protection (thol) chapter 5 current table 89: settings for the thermal overload protection thol (thol-) function table 90: settings for thermal overload protection (thol), ma input parameter range default unit description operation off, noncomp, comp off - operating mode fo...
Page 88
79 thermal phase overload protection (thol) chapter 5 current 4.7 technical data table 91: thol - thermal phase overload protection table 92: thermal overload protection ma input function setting range accuracy mode of operation off / noncomp / comp ( function blocked/no temp. Com- pensation/temp. C...
Page 89
80 thermal phase overload protection (thol) chapter 5 current.
Page 90: Chapter 6 Secondary System
81 about this chapter chapter 6 secondary system supervision chapter 6 secondary system supervision about this chapter this chapter describes the secondary system supervision functions..
Page 91
82 current circuit supervision, current based (ctsu) chapter 6 secondary system supervision 1 current circuit supervision, current based (ctsu) 1.1 application faulty information about current flows in a protected element might influence the security (line differential protection) or dependability (...
Page 92
83 current circuit supervision, current based (ctsu) chapter 6 secondary system supervision 1.4 logic diagram figure 32: simplified logic diagram for the current circuit supervision 1.5 input and output signals table 93: input signals for the ctsu (ctsu-) function block path in local hmi: servicerep...
Page 93
84 current circuit supervision, current based (ctsu) chapter 6 secondary system supervision 1.7 technical data table 96: ctsu - current circuit supervision, current based function setting range accuracy operate current, iminop 5-100% of i1b in steps of 1% ± 5.0 % of i r.
Page 94: Chapter 7 Logic
85 about this chapter chapter 7 logic chapter 7 logic about this chapter this chapter describes the logic functions..
Page 95: Tripping Logic (Tr)
86 tripping logic (tr) chapter 7 logic 1 tripping logic (tr) 1.1 application the main purpose of the tr trip logic function is to serve as a single node through which all tripping for the entire terminal is routed. To meet the different single, double, 1 and 1/2 or other multiple circuit breaker arr...
Page 96
87 tripping logic (tr) chapter 7 logic table 99: setting parameters for the trip logic tr (tr---) function 1.5 technical data table 100: tr - tripping logic parameter range default unit description operation off / on off - operating mode for tr function ttripmin 0.000-60.000 step. 0.001 0.150 s mini...
Page 97: Event Function (Ev)
88 event function (ev) chapter 7 logic 2 event function (ev) 2.1 application when using a substation automation system, events can be spontaneously sent or polled from the terminal to the station level. These events are created from any available signal in the termi- nal that is connected to the eve...
Page 98
89 event function (ev) chapter 7 logic 2.3 function block xx00000235.Vsd ev01- event input1 input2 input3 input4 input5 input6 input7 input8 input9 input10 input11 input12 input13 input14 input15 input16 t_supr01 t_supr03 t_supr05 t_supr07 t_supr09 t_supr11 t_supr13 t_supr15 name01 name02 name03 nam...
Page 99
90 event function (ev) chapter 7 logic 2.4 input and output signals table 101: input signals for the event (evnn-) function block 2.5 setting parameters table 102: setting parameters for the event (evnn-) function signal description inputy event input y, y=1-16 namey user name of signal connected to...
Page 100
91 event function (ev) chapter 7 logic t_supr11 0.000-60.000 step: 0.001 0.000 s suppression time for event input 11 and 12. Can only be set using the cap 540 configu- ration tool. T_supr13 0.000-60.000 step: 0.001 0.000 s suppression time for event input 13 and 14. Can only be set using the cap 540...
Page 101
92 event function (ev) chapter 7 logic.
Page 102: Chapter 8 Monitoring
93 about this chapter chapter 8 monitoring chapter 8 monitoring about this chapter this chapter describes the monitoring functions..
Page 103: Disturbance Report (Drp)
94 disturbance report (drp) chapter 8 monitoring 1 disturbance report (drp) 1.1 application use the disturbance report to provide the network operator with proper information about dis- turbances in the primary network. The function comprises several subfunctions enabling differ- ent types of users ...
Page 104
95 disturbance report (drp) chapter 8 monitoring disturbance overview is a summary of all the stored disturbances. The overview is available only on a front-connected pc or via the station monitoring system (sms). The overview con- tains: • disturbance index • date and time • trip signals • trig sig...
Page 105
96 disturbance report (drp) chapter 8 monitoring 1.3 function block xx00000229.Vsd drp1- disturbreport clrleds input1 input2 input3 input4 input5 input6 input7 input8 input9 input10 input11 input12 input13 input14 input15 input16 name01 name02 name03 name04 name05 name06 name07 name08 name09 name10 ...
Page 106
97 disturbance report (drp) chapter 8 monitoring 1.4 input and output signals table 103: input signals for the disturbreport (drpn-) function blocks path in local hmi: servicereport/functions/disturbreport table 104: output signals for the disturbreport (drp1-) function block 1.5 setting parameters ...
Page 107
98 disturbance report (drp) chapter 8 monitoring table 107: parameters for recording time path in local hmi: settings/disturbreport/binarysignals/inputn table 108: parameters for reporting of binary signals path in local hmi: settings/disturbreport/analogsignals/un table 109: voltage parameters for ...
Page 108
99 disturbance report (drp) chapter 8 monitoring table 110: current parameters for disturbance recorder table 111: disturbance report settings 1.6 technical data table 112: drp - disturbance report setting performance parameter range default unit description operation off, on on - determines if the ...
Page 109: Indications
100 indications chapter 8 monitoring 2 indications 2.1 application use the indications list to view the state of binary signals during the fault. All binary input sig- nals to the disturbance report function are listed. 2.2 functionality the indications list tracks zero-to-one changes of binary sign...
Page 110: Disturbance Recorder (Dr)
101 disturbance recorder (dr) chapter 8 monitoring 3 disturbance recorder (dr) 3.1 application use the disturbance recorder to record analog and binary signals during fault conditions in order to analyze disturbances. The analysis may include fault severity, fault duration and protection performance...
Page 111
102 disturbance recorder (dr) chapter 8 monitoring 3.3 technical data table 113: dr - disturbance recorder setting performance table 114: dr - disturbance recorder performance function setting range overcurrent triggering 0-5000% of inb in steps of 1% undercurrent triggering 0-200% of inb in steps o...
Page 112: Event Recorder (Er)
103 event recorder (er) chapter 8 monitoring 4 event recorder (er) 4.1 application use the event recorder to obtain a list of binary signal events that occurred during the distur- bance. 4.2 design when a trigger condition for the disturbance report is activated, the event recorder collects time tag...
Page 113: Trip Value Recorder (Tvr)
104 trip value recorder (tvr) chapter 8 monitoring 5 trip value recorder (tvr) 5.1 application use the trip value recorder to record fault and prefault phasor values of voltages and currents to be used in detailed analysis of the severity of the fault and the phases that are involved. The re- corded...
Page 114
105 supervision of ac input quantities (da) chapter 8 monitoring 6 supervision of ac input quantities (da) 6.1 application use the ac monitoring function to provide three phase or single phase values of voltage and current. At three phase measurement, the values of apparent power, active power, reac...
Page 115
106 supervision of ac input quantities (da) chapter 8 monitoring 6.4 input and output signals table 117: input signals for the ac monitoring (dann-) function block use cap configuration tool to se status of the output signals. Table 118: output signals for the ac monitoring (dann-) function block 6....
Page 116
107 supervision of ac input quantities (da) chapter 8 monitoring table 119: setting parameters for the ac monitoring (dann-) function block parameter range default unit description for each voltage input channels u1 - u5: da01--da05 operation off, on off - operating mode for dann function hysteres 0...
Page 117
108 supervision of ac input quantities (da) chapter 8 monitoring enalarms off, on off - set to 'on' to activate alarm supervision for i1 - i5 (produces an immediate event at oper- ation of any alarm monitoring element, when on) hialarm 0-99999 step: 1 900 a high alarm level for i1 - i5 hiwarn 0-9999...
Page 118
109 supervision of ac input quantities (da) chapter 8 monitoring repint 0-3600 step: 1 0 s time between reports for u in seconds. Zero = off (duration of time interval between two reports at periodic reporting function. Setting to 0 disables the periodic reporting endeadb off, on off - enable amplit...
Page 119
110 supervision of ac input quantities (da) chapter 8 monitoring active power measuring channel p: da13- operation off, on off - operating mode for dann function hysteres 0.0-9999.9 step. 0.1 5.0 mw alarm hysteresis for p enalrem off, on on - immediate event when an alarm is disabled for p (produces...
Page 120
111 supervision of ac input quantities (da) chapter 8 monitoring enalarms off, on off - set to 'on' to activate alarm supervision for q (produces an immediate event at opera- tion of any alarm monitoring element, when on) hialarm 0.0-9999.9 step: 0.1 300.0 mvar high alarm level for q hiwarn 0.0-9999...
Page 121
112 supervision of ac input quantities (da) chapter 8 monitoring repint 0-3600 step: 1 0 s time between reports for f in seconds. Zero = off (duration of time interval between two reports at periodic reporting function. Setting to 0 disables the periodic reporting) endeadb off, on off - enable ampli...
Page 122
113 supervision of ac input quantities (da) chapter 8 monitoring endeadbp off, on off - enable periodic dead band reporting s reporting of events to the station control system (scs) through lon port : eventmask u1 no events, report events no events - enables (report events) or disables (no events) t...
Page 123
114 supervision of ac input quantities (da) chapter 8 monitoring 6.6 technical data table 120: mean values (ac-monitoring) eventmask i no events, report events no events - enables (report events) or disables (no events) the reporting of events from channel da12 to the scs eventmask p no events, repo...
Page 124: Chapter 9 Data
115 about this chapter chapter 9 data communication chapter 9 data communication about this chapter this chapter describes the data communication and the associated hardware..
Page 125
116 remote end data communication chapter 9 data communication 1 remote end data communication 1.1 application the remote terminal communication modules can be used either for differential line protection applications or for binary signal transfer of up to 32 signals in both directions between, for ...
Page 126
117 remote end data communication chapter 9 data communication 1.3.2 technical data table 122: dcm-fom - fibre optical communication module 1.4 galvanic interface 1.4.1 application the galvanic data communication modules according to v35/36 dcm-v36 contra, dcm-v36 co, x.21 dcm-x21, rs530/422 dcm-rs ...
Page 127
118 remote end data communication chapter 9 data communication 1.5 short range galvanic module 1.5.1 application the short-range galvanic module dcm-sgm can be used for communication over galvanic pi- lot wires and can operate over distances of up to 3 km depending on pilot wire cable. Twist- ed-pai...
Page 128
119 remote end data communication chapter 9 data communication 1.6.2 technical data table 125: dcm-sfom - short-range fibre optical module 1.7 co-directional g. 703 galvanic interface 1.7.1 application the galvanic data communication module dcm-g.703 according to g.703 is not recommended for distanc...
Page 129
120 remote end data communication chapter 9 data communication figure 33: block diagram for the carrier module. Micro- controller memory can sub-module bac k p lane c onnec to r 99000520.Vsd.
Page 130: Serial Communication
121 serial communication chapter 9 data communication 2 serial communication 2.1 application, common one or two optional serial interfaces with lon protocol, spa protocol or iec 60870-5-103 pro- tocol, for remote communication, enables the terminal to be part of a substation control system (scs) and...
Page 131
122 serial communication chapter 9 data communication • report of analog service values (measurements) • fault location • command handling - autorecloser on/off - teleprotection on/off - protection on/off - led reset - characteristics 1 - 4 (setting groups) • file transfer (disturbance files) • time...
Page 132
123 serial communication chapter 9 data communication remote communication over the telephone network also requires a telephone modem. The software needed in the pc, either local or remote, is cap 540. Spa communication is applied when using the front communication port, but for this purpose, no spe...
Page 133
124 serial communication chapter 9 data communication table 131: serial communication (rs485) table 132: serial communication (spa) via front 2.5 serial communication, iec (iec 60870-5-103 protocol) 2.5.1 application this communication protocol is mainly used when a protection terminal communicates ...
Page 134
125 serial communication chapter 9 data communication • time synchronization the events created in the terminal available for the iec protocol are based on the event function blocks ev01 - ev06 and disturbance function blocks drp1 - drp3. The commands are repre- sented in a dedicated function block ...
Page 135
126 serial communication chapter 9 data communication 28 auxiliary input 2 yes 29 auxiliary input 3 yes 30 auxiliary input 4 yes 32 measurand supervision i yes 33 measurand supervision v yes 35 phase sequence supervision no 36 trip circuit supervision yes 37 i>> backup operation yes 38 vt fusefailur...
Page 136
127 serial communication chapter 9 data communication table 134: information numbers in control direction 85 breaker failure yes 86 trip measuring system l1 no 87 trip measuring system l2 no 88 trip measuring system l2 no 89 trip measuring system e no 90 trip i> yes 91 trip i>> yes 92 trip in> yes 9...
Page 137
128 serial communication chapter 9 data communication table 135: measurands table 136: interoperability, physical layer 245 general interrogation on generic data no 248 write entry no 249 write entry with confirmation no 250 write entry with execution no 251 write entry abort no measurand rated valu...
Page 138
129 serial communication chapter 9 data communication table 137: interoperability, application layer supported selection of standard asdus in monitoring direction asdu 1 time-tagged message yes 2 time-tagged message with rel. Time yes 3 measurands i yes 4 time-taggedmeasurands with rel.Time yes 5 id...
Page 139
130 serial communication chapter 9 data communication 2.5.4 function block 2.5.5 input and output signals table 138: input signals for the iec (icom-) function block path in local hmi: servicereport/functions/iec103command table 139: output signals for the iec (icom-) function block 2.5.6 setting pa...
Page 140
131 serial communication chapter 9 data communication path in local hmi: configuration/terminalcom/ieccom/commands/arblock table 141: setting parameters for controlling autorecloser command path in local hmi: configuration/terminalcom/ieccom/commands/zcommblock table 142: configuration/terminalcom/i...
Page 141
132 serial communication chapter 9 data communication table 146: setting parameters for main function types path in local hmi: configuration/terminalcom/ieccom/communication table 147: setting parameters for iec communication path in local hmi: configuration/terminalcom/ieccom/blockofinfocmd table 1...
Page 142
133 serial communication chapter 9 data communication 2.6.2 design an optical serial interface with lon protocol enables the terminal to be part of a substation control system (scs) and/or substation monitoring system (sms). This interface is located at the rear of the terminal. The hardware needed ...
Page 143
134 serial communication chapter 9 data communication table 153: setting parameters for the session timers path in local hmi: configuration/terminalcom/loncom table 154: lon commands 2.6.4 technical data table 155: lon - serial communication 2.7 serial communication modules (scm) 2.7.1 design, spa/i...
Page 144
135 serial communication chapter 9 data communication the fibre optic spa/iec port can be connected point-to-point, in a loop, or with a star coupler. The incoming optical fibre is connected to the rx receiver input and the outgoing optical fibre to the tx transmitter output. The module is identifie...
Page 145
136 serial communication chapter 9 data communication table 158: lon - optical fibre connection requirements for lon bus glass fibre plastic fibre cable connector st-connector hfbr, snap-in connector fibre diameter 62.5/125 μ m 50/125 μ m 1 mm max. Cable length 1000 m 25 m.
Page 146: Chapter 10 Hardware Modules
137 about this chapter chapter 10 hardware modules chapter 10 hardware modules about this chapter this chapter describes the different hardware modules..
Page 147: Modules
138 modules chapter 10 hardware modules 1 modules table 159: basic, always included, modules table 160: application specific modules module description backplane module (bpm) carries all internal signals between modules in a termi- nal. The size of the module depends on the size of the case. Power s...
Page 148: A/d Module (Adm)
139 a/d module (adm) chapter 10 hardware modules 2 a/d module (adm) 2.1 design the inputs of the a/d-conversion module (adm) are fed with voltage and current signals from the transformer module. The current signals are adapted to the electronic voltage level with shunts. To gain dynamic range for th...
Page 149: Transformer Module (Trm)
140 transformer module (trm) chapter 10 hardware modules 3 transformer module (trm) 3.1 design a transformer input module can have up to 10 input transformers. The actual number depends on the type of terminal. Terminals including only current measuring functions only have current inputs. Fully equi...
Page 150: Binary I/o Capabilities
141 binary i/o capabilities chapter 10 hardware modules 4 binary i/o capabilities 4.1 application input channels with high emi immunity can be used as binary input signals to any function. Sig- nals can also be used in disturbance or event recording. This enables extensive monitoring and evaluation ...
Page 151
142 binary i/o capabilities chapter 10 hardware modules table 164: power consumption breaking capacity for dc with l/r 48 v/1 a 48 v/1 a 110 v/0.4 a 110 v/0.4 a 220 v/0.2 a 220 v/0.2 a 250 v/0.15 a 250 v/0.15 a maximum capacitive load - 10 nf power consumption for each output relay ≤ 0.15 w module p...
Page 152: I/o Module (Iom)
143 i/o module (iom) chapter 10 hardware modules 5 i/o module (iom) 5.1 application the binary input/output module is used when only a few input and output channels are needed. The ten standard output channels are used for trip output or any signalling purpose. The two high speed signal output chann...
Page 153
144 i/o module (iom) chapter 10 hardware modules 5.4 input and output signals table 165: input signals for i/o module iom path in local hmi: servicereport/i/o/slotnn-iomn/funcoutputs table 166: output signals for i/o module iom signal description position i/o module slot position bo1-bo12 binary out...
Page 154: Power Supply Module (Psm)
145 power supply module (psm) chapter 10 hardware modules 6 power supply module (psm) 6.1 application the power supply module, psm, with built in binary i/o is used in 1/2 and 3/4 of full width 19” units. It has four optically isolated binary inputs and five binary outputs, out of which one binary o...
Page 155
146 power supply module (psm) chapter 10 hardware modules table 168: output signals for the i/o-module (io02-) function block (i/o on psm) 6.5 technical data table 169: psm - power supply module signal description error i/o-module fail bi1-bi4 binary input data quantity rated value nominal range aux...
Page 156
147 local lcd human machine interface (lcd-hmi) chapter 10 hardware modules 7 local lcd human machine interface (lcd-hmi) 7.1 application the human machine interface is used to monitor and in certain aspects affect the way the product operates. The configuration designer can add functions for alerti...
Page 157
148 local lcd human machine interface (lcd-hmi) chapter 10 hardware modules the number of buttons used on the hmi module is reduced to a minimum to allow a communi- cation as simple as possible for the user. The buttons normally have more than one function, depending on actual dialogue..
Page 158
149 serial communication modules (scm) chapter 10 hardware modules 8 serial communication modules (scm) 8.1 spa/iec refer to chapter data communication. 8.2 lon refer to chapter data communication..
Page 159
150 data communication modules (dcm) chapter 10 hardware modules 9 data communication modules (dcm) for more informaton about the data communication modules, refer to the previous chapter 9 "data communication" . Note! Instructions how to configure the digital communication modules, see chapter conf...
Page 160: Chapter 11 Diagrams
151 chapter 11 diagrams chapter 11 diagrams this chapter contains the terminal diagrams for the terminal..
Page 161: Terminal Diagrams
152 terminal diagrams chapter 11 diagrams 1 terminal diagrams 1.1 terminal diagram, rex5xx figure 37: hardware structure of the 1/2 of full width 19” case.
Page 162
153 terminal diagrams chapter 11 diagrams 1.2 terminal diagram, rel 551-c1 figure 38: rel 551-c1.
Page 163
154 terminal diagrams chapter 11 diagrams figure 39: rel 551-c1 with dc-switch.
Page 164
155 terminal diagrams chapter 11 diagrams figure 40: rel 551-c1, transformer input module and a/d conversion module 3 phase sys- tem.
Page 165
156 terminal diagrams chapter 11 diagrams figure 41: rel 551-c1, transformer input module and a/d conversion module 3 phase sys- tem with rtxp 24, internal earthing.
Page 166
157 terminal diagrams chapter 11 diagrams figure 42: rel 551-c1, transformer input module and a/d conversion module 3 phase sys- tem with rtxp 24, external earthing.
Page 167
158 terminal diagrams chapter 11 diagrams.
Page 168: Chapter 12 Configuration
159 about this chapter chapter 12 configuration chapter 12 configuration about this chapter this chapter refer to the configuration in cap 540..
Page 169: Configuration
160 configuration chapter 12 configuration 1 configuration configuration of rel 551 c1 is available as templates in the latest version of cap 540..
Page 170
Abb power technologies ab substation automation products se-721 59 västerås sweden telephone: +46 (0) 21 34 20 00 facsimile: +46 (0) 21 14 69 18 internet: www.Abb.Com/substationautomation 1m r k 5 0 6 20 7- u e n printed on recycled and ecolabelled paper at elanders novum.