- DL manuals
- ABB
- Relays
- RELION 650 SERIES
- Technical Manual
ABB RELION 650 SERIES Technical Manual
Summary of RELION 650 SERIES
Page 1
Relion® 650 series — line differential protection red650 version 2.2 technical manual.
Page 3
Document id: 1mrk 505 394-uen issued: october 2017 revision: a product version: 2.2.1 © copyright 2017 abb. All rights reserved.
Page 4
Copyright this document and parts thereof must not be reproduced or copied without written permission from abb, and the contents thereof must not be imparted to a third party, nor used for any unauthorized purpose. The software and hardware described in this document is furnished under a license and...
Page 5
Disclaimer the data, examples and diagrams in this manual are included solely for the concept or product description and are not to be deemed as a statement of guaranteed properties. All persons responsible for applying the equipment addressed in this manual must satisfy themselves that each intende...
Page 6
Conformity this product complies with the directive of the council of the european communities on the approximation of the laws of the member states relating to electromagnetic compatibility (emc directive 2004/108/ec) and concerning electrical equipment for use within specified voltage limits (low-...
Page 7
Table of contents section 1 introduction.....................................................................31 this manual...................................................................................... 31 presumptions for technical data................................................ 31 inte...
Page 8
Local hmi signals............................................................................. 61 identification................................................................................ 61 function block............................................................................. 61 signals.....
Page 9
Line differential protection logic ldlpsch ......................... 106 technical data........................................................................... 109 section 7 impedance protection...................................................111 distance protection zmfpdis........................
Page 10
Technical data........................................................................... 158 section 8 current protection.........................................................159 instantaneous phase overcurrent protection phpioc .................. 159 identification.................................
Page 11
Four residual overcurrent steps............................................195 directional supervision element with integrated directional comparison function............................................197 second harmonic blocking element..................................... 199 switch on to fault f...
Page 12
Monitored data...........................................................................231 operation principle.................................................................... 231 measurement principle......................................................... 232 time delay.........................
Page 13
Voltage dependent time delay..............................................270 blocking................................................................................271 design.................................................................................. 271 technical data..........................
Page 14
Monitored data...........................................................................290 operation principle.................................................................... 290 zero and negative sequence detection................................ 290 delta current and delta voltage detection....
Page 15
Error handling............................................................................350 bay control qcbay...................................................................353 functionality......................................................................... 354 function block................
Page 16
Selector mini switch vsgapc........................................................387 identification.............................................................................. 387 functionality.............................................................................. 388 function block.........
Page 17
Settings......................................................................................403 operation principle.................................................................... 403 blocking scheme.................................................................. 404 delta blocking scheme......
Page 18
Identification.............................................................................. 423 functionality.............................................................................. 424 function block........................................................................... 424 signals.........
Page 19
Logic for group warning wrncalh...............................................455 identification.............................................................................. 455 functionality.............................................................................. 455 function block..............
Page 20
Reset-set with memory function block rsmemory.................466 function block...................................................................... 466 signals..................................................................................466 settings...............................................
Page 21
Monitored data...........................................................................477 operation principle.................................................................... 478 technical data........................................................................... 479 integer to boolean 16...
Page 22
Signals.......................................................................................493 settings......................................................................................493 operation principle.................................................................... 493 technical da...
Page 23
Signals.......................................................................................540 settings......................................................................................541 monitored data...........................................................................543 operation p...
Page 24
Identification.............................................................................. 590 functionality.............................................................................. 590 function block........................................................................... 591 signals.........
Page 25
Technical data........................................................................... 613 function for energy calculation and demand handling etpmmtr 613 identification.............................................................................. 613 functionality...................................
Page 26
Generic communication function for single point indication spgapc, sp16gapc...............................................................642 functionality......................................................................... 642 function block........................................................
Page 27
Function block...................................................................... 654 signals..................................................................................654 settings................................................................................ 654 operation principle ........
Page 28
Communication ports........................................................... 704 technical data........................................................................... 705 iec 60870-5-103 communication protocol..................................... 706 introduction..................................
Page 29
Identification......................................................................... 716 function block...................................................................... 716 signals..................................................................................716 settings.....................
Page 30
Ied commands with position for iec 60870-5-103 i103poscmdv......................................................................... 727 functionality......................................................................... 727 identification..............................................................
Page 31
Functionality.............................................................................. 755 operation principle ................................................................... 756 authorization with central account management enabled ied..........................................................
Page 32
Synchronization alternatives................................................ 783 process bus iec/uca 61850-9-2le synchronization.......... 786 precision time protocol (ptp) ............................................ 786 technical data...................................................................
Page 33
Signals.......................................................................................804 settings......................................................................................805 operation principle ................................................................... 806 global base ...
Page 34
Signals..................................................................................826 settings................................................................................ 827 monitored data..................................................................... 827 technical data...............
Page 35
Mounting procedure for wall mounting................................. 855 how to reach the rear side of the ied.................................. 855 side-by-side 19” rack mounting.................................................856 overview..............................................................
Page 36
30
Page 37
Section 1 introduction 1.1 this manual guid-ab423a30-13c2-46af-b7fe-a73bb425eb5f v18 the technical manual contains operation principle descriptions, and lists function blocks, logic diagrams, input and output signals, setting parameters and technical data, sorted per function. The manual can be used...
Page 38
1.2 intended audience guid-c9b8127f-5748-4bea-9e4f-cc762fe28a3a v11 this manual addresses system engineers and installation and commissioning personnel, who use technical data during engineering, installation and commissioning, and in normal service. The system engineer must have a thorough knowledg...
Page 39
Instructions on how to set up a pcm600 project and insert ieds to the project structure. The manual also recommends a sequence for the engineering of protection and control functions, lhmi functions as well as communication engineering for iec 60870-5-103, iec 61850, dnp3, lon and spa. The installat...
Page 40
1.3.2 document revision history guid-c8027f8a-d3cb-41c1-b078-f9e59bb73a6c v4 document revision/date history –/may 2017 first release 1.3.3 related documents guid-94e8a5ca-be1b-45af-81e7-5a41d34ee112 v5 documents related to red650 document numbers application manual 1mrk 505 393-uen commissioning man...
Page 41
1.4 document symbols and conventions 1.4.1 symbols guid-2945b229-dab0-4f15-8a0e-b9cf0c2c7b15 v12 the electrical warning icon indicates the presence of a hazard which could result in electrical shock. The warning icon indicates the presence of a hazard which could result in personal injury. The cauti...
Page 42
1.4.2 document conventions guid-96dfab1a-98fe-4b26-8e90-f7ceb14b1ab6 v6 • abbreviations and acronyms in this manual are spelled out in the glossary. The glossary also contains definitions of important terms. • push button navigation in the lhmi menu structure is presented by using the push button ic...
Page 43
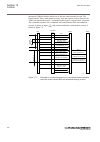
Table 1: iec 61850 edition 1 / edition 2 mapping function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes agsal agsal seclln0 agsal almcalh almcalh almcalh altim - altim altms - altms altrk - altrk brcptoc brcptoc brcptoc btigapc b16ifcvi btigapc ccpdsc ccrpld ccpdsc ccrbrf ccrbrf ccrbrf ...
Page 44
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes lt3cpdif lt3cpdif lt3cgapc lt3cpdif lt3cphar lt3cptrc mvgapc mvggio mvgapc ns4ptoc ef4lln0 ef4ptrc ef4rdir gen4phar ph1ptoc ef4ptrc ef4rdir ph1ptoc oc4ptoc oc4lln0 gen4phar ph3ptoc ph3ptrc gen4phar ph3ptoc ph3ptrc ov2ptov gen2lln0 o...
Page 45
Function block name edition 1 logical nodes edition 2 logical nodes t3wpdif t3wpdif t3wgapc t3wpdif t3wphar t3wptrc teigapc teiggio teigapc teilgapc teilggio teilgapc tmagapc tmaggio tmagapc trpttr trpttr trpttr uv2ptuv gen2lln0 ph1ptrc uv2ptuv ph1ptrc uv2ptuv vmmxu vmmxu vmmxu vmsqi vmsqi vmsqi vnm...
Page 46
40
Page 47
Section 2 available functions guid-f5776dd1-bd04-4872-bb89-a0412b4b5cc3 v1 the following tables list all the functions available in the ied. Those functions that are not exposed to the user or do not need to be configured are not described in this manual. 2.1 main protection functions guid-66baad98-...
Page 48
2.2 back-up protection functions guid-a8d0852f-807f-4442-8730-e44808e194f0 v13 iec 61850 or function name ansi function description line differential red650 (a11) current protection phpioc 50 instantaneous phase overcurrent protection 1 oc4ptoc 51_67 1) directional phase overcurrent protection, four...
Page 49
Iec 61850 or function name ansi function description line differential red650 (a11) sxcbr circuit breaker 3 scilo interlocking 1 scswi switch controller 1 xlnproxy proxy for signals from switching device via goose 3 slgapc logic rotating switch for function selection and lhmi presentation 15 vsgapc ...
Page 50
Iec 61850 or function name ansi function description line differential red650 (a11) teigapc elapsed time integrator with limit transgression and overflow supervision 12 intcomp comparator for integer inputs 30 realcomp comparator for real inputs 30 table 3: total number of instances for basic config...
Page 51
Iec 61850 or function name ansi function description line differential red650 (a11) mvgapc generic communication function for measured values 24 binstatrep logical signal status report 3 range_xp measured value expander block 66 lmbrflo fault locator 1 i103meas measurands for iec 60870-5-103 1 i103m...
Page 52
Iec 61850 or function name ansi function description line differential red650 (a11) mst1tcp, mst2tcp, mst3tcp, mst4tcp dnp3.0 for tcp/ip communication protocol 1 dnpfrec dnp3.0 fault records for tcp/ip and eia-485 communication protocol 1 iec 61850-8-1 iec 61850 1 gooseintlkrcv horizontal communicat...
Page 53
Iec 61850 or function name ansi function description line differential red650 (a11) binsignrec1_1, binsignrec1_2, binsignreceive2, binsigntrans1_1, binsigntrans1_2, binsigntransm2 binary signal transfer receive/transmit 3/3/6 ldcmtrn transmission of analog data from ldcm 1 ldcmrecbinstat1, ldcmrecbi...
Page 54
Iec 61850 or function name description 3phsum summation block 3 phase athstat authority status athchck authority check authman authority management ftpaccs ftp access with password gbasval global base values for settings altms time master supervision altim time management comstatus protocol diagnost...
Page 55
Section 3 analog inputs semod55010-1 v3 3.1 introduction semod55003-5 v11 analog input channels must be configured and set properly in order to get correct measurement results and correct protection operations. For power measuring, all directional and differential functions, the directions of the in...
Page 56
3.3 signals pid-3923-outputsignals v7 table 6: trm_7i_5u output signals name type description status boolean analogue input module status ch1(i) string analogue current input 1 ch2(i) string analogue current input 2 ch3(i) string analogue current input 3 ch4(i) string analogue current input 4 ch5(i)...
Page 57
Pid-6598-outputsignals v6 table 8: trm_10i_2u output signals name type description status boolean analogue input module status ch1(i) string analogue current input 1 ch2(i) string analogue current input 2 ch3(i) string analogue current input 3 ch4(i) string analogue current input 4 ch5(i) string ana...
Page 58
Pid-4153-settings v7 table 9: aisvbas non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description phaseangleref trm40-ch1 - ch12 trm41-ch1 - ch12 mu1-l1i mu1-l2i mu1-l3i mu1-l4i mu1-l1u mu1-l2u mu1-l3u mu1-l4u mu2-l1i mu2-l2i mu2-l3i mu2-l4i mu2-l1u mu2-l2u mu2-l3u mu2-l4u mu3-l1i m...
Page 59
Pid-3923-settings v7 table 10: trm_7i_5u non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description ctstarpoint1 fromobject toobject - - toobject toobject= towards protected object, fromobject= the opposite ctsec1 1 - 10 a 1 1 rated ct secondary current ctprim1 1 - 99999 a 1 3000 r...
Page 60
Pid-3924-settings v7 table 11: trm_9i_3u non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description ctstarpoint1 fromobject toobject - - toobject toobject= towards protected object, fromobject= the opposite ctsec1 1 - 10 a 1 1 rated ct secondary current ctprim1 1 - 99999 a 1 3000 r...
Page 61
Name values (range) unit step default description vtprim11 0.05 - 2000.00 kv 0.05 400.00 rated vt primary voltage vtsec12 0.001 - 999.999 v 0.001 110.000 rated vt secondary voltage vtprim12 0.05 - 2000.00 kv 0.05 400.00 rated vt primary voltage pid-6598-settings v6 table 12: trm_10i_2u non group set...
Page 62
Name values (range) unit step default description ctstarpoint10 fromobject toobject - - toobject toobject= towards protected object, fromobject= the opposite ctsec10 1 - 10 a 1 1 rated ct secondary current ctprim10 1 - 99999 a 1 3000 rated ct primary current vtsec11 0.001 - 999.999 v 0.001 110.000 r...
Page 63
3.6 operation principle semod55028-5 v9 the direction of a measured current depends on the connection of the ct. The main cts are typically star connected and can be connected with the star point towards the object or away from the object. This information must be set in the ied. Once the ct directi...
Page 64
The ct and vt ratio and the name on respective channel is done under ied configuration/hw configuration/adm in the parameter settings tool or under main menu/configuration/analog modules in the hmi. 3.7 technical data semod55412-1 v1 m16988-1 v11 table 17: trm - energizing quantities, rated values a...
Page 65
Section 4 binary input and output modules 4.1 binary input 4.1.1 binary input debounce filter guid-ae43976c-e966-484c-af39-89b2b12f56dc v5 the debounce filter eliminates bounces and short disturbances on a binary input. A time counter is used for filtering. The time counter is increased once in a mi...
Page 66
4.1.3.1 setting parameters for binary input modules pid-3473-settings v2 table 19: bim non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - on operation off/on debouncetime 0.001 - 0.020 s 0.001 0.001 debounce time for binary inputs oscblock 1 - 40 hz 1 4...
Page 67
Section 5 local human-machine-interface lhmi 5.1 local hmi screen behaviour 5.1.1 identification guid-84392eff-4d3f-4a67-a6ed-34c6e98574d6 v1 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number local hmi screen behaviour screen - - 5.2 local hmi signa...
Page 68
Pid-3992-outputsignals v6 table 22: lhmictrl output signals name type description hmi-on boolean backlight of the lcd display is active red-s boolean red led on the lcd-hmi is steady yellow-s boolean yellow led on the lcd-hmi is steady yellow-f boolean yellow led on the lcd-hmi is flashing clrpulse ...
Page 69
5.3.3 signals pid-4114-inputsignals v5 table 23: ledgen input signals name type default description block boolean 0 input to block the operation of the leds reset boolean 0 input to acknowledge/reset the indication leds pid-4114-outputsignals v5 table 24: ledgen output signals name type description ...
Page 70
Pid-1697-settings v18 table 27: grp1_led1 non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description sequencetype follow-s follow-f latchedack-f-s latchedack-s-f latchedcoll-s latchedreset-s - - follow-s sequence type for led 1, local hmi alarm group 1 labeloff 0 - 18 - 1 g1l01_off...
Page 71
Pid-1657-outputsignals v19 table 29: fnkeymd1 output signals name type description fkeyout1 boolean output controlled by function key 5.4.4 settings pid-1657-settings v19 table 30: fnkeymd1 non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description mode off toggle pulsed - - off ou...
Page 72
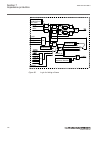
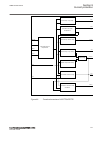
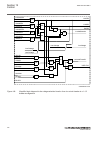
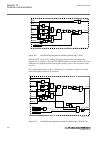
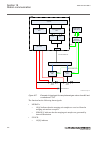
5.5 operation principle 5.5.1 local hmi amu0600442 v14 iec13000239-3-en.Vsd iec13000239 v3 en-us figure 7: local human-machine interface the lhmi of the ied contains the following elements: • keypad • display (lcd) • led indicators • communication port for pcm600 section 5 1mrk 505 394-uen a local h...
Page 73
The lhmi is used for setting, monitoring and controlling. 5.5.1.1 keypad amu0600428 v17 the lhmi keypad contains push-buttons which are used to navigate in different views or menus. The push-buttons are also used to acknowledge alarms, reset indications, provide help and switch between local and rem...
Page 74
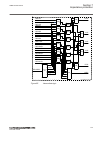
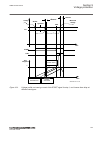
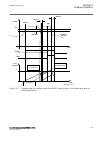
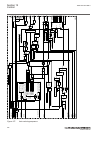
1 18 19 7 6 5 4 3 2 8 20 21 22 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 23 24 iec15000157-2-en.Vsd iec15000157 v2 en-us figure 8: lhmi keypad with object control, navigation and command push- buttons and rj-45 communication port 1...5 function button 6 close 7 open 8 escape 9 left 10 down 11 up 12 right 13 key 14 ...
Page 75
20 clear 21 help 22 communication port 23 programmable indication leds 24 ied status leds 5.5.1.2 display guid-55739d4f-1da5-4112-b5c7-217aaf360ea5 v11 the lhmi includes a graphical monochrome liquid crystal display (lcd) with a resolution of 320 x 240 pixels. The character size can vary. The amount...
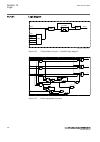
Page 76
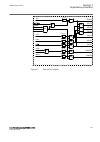
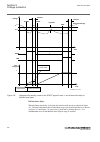
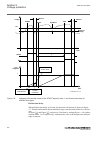
Iec15000270-1-en.Vsdx iec15000270 v1 en-us figure 9: display layout 1 path 2 content 3 status 4 scroll bar (appears when needed) • the path shows the current location in the menu structure. If the path is too long to be shown, it is truncated from the beginning, and the truncation is indicated with ...
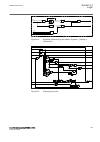
Page 77
Iec15000138-1-en.Vsdx iec15000138 v1 en-us figure 10: truncated path the number after : (colon sign) at the end of the function instance, for example, 1 in smai1:1, indicates the number of that function instance. The function key button panel shows on request what actions are possible with the funct...
Page 78
Iec13000281-1-en.Vsd guid-c98d972d-d1d8-4734-b419-161dbc0dc97b v1 en-us figure 11: function button panel the indication led panel shows on request the alarm text labels for the indication leds. Three indication led pages are available. Iec13000240-1-en.Vsd guid-5157100f-e8c0-4fab-b979-fd4a971475e3 v...
Page 79
There are 15 programmable indication leds on the front of the lhmi. Each led can indicate three states with the colors: green, yellow and red. The texts related to each three-color led are divided into three panels. There are 3 separate panels of leds available. The 15 physical three-color leds in o...
Page 80
5.5.2 led configuration alternatives 5.5.2.1 functionality guid-1a03e0ef-c10f-4797-9d9f-5cca86ca29eb v5 the function blocks ledgen and grp1_ledx, grp2_ledx and grp3_ledx (x=1-15) controls and supplies information about the status of the indication leds. The input and output signals of the function b...
Page 81
• leds that are used in the collecting mode of operation are accumulated continuously until the unit is acknowledged manually. This mode is suitable when the leds are used as a simplified alarm system. When all three inputs (red, yellow and green) are connected to different sources of events for the...
Page 82
When the automatic reset of the leds has been performed, still persisting indications will be indicated with a steady light. Operating sequence guid-dfca880b-308c-4334-94df-97c7765e8c13 v5 the sequences can be of type follow or latched. For the follow type, the led follows the input signal completel...
Page 83
Activating signal led iec01000228_2_en.Vsd iec01000228 v2 en-us figure 15: operating sequence 1 (follow-s) guid-107fe952-3b4c-4c01-831a-3147e652327c v4 if inputs for two or more colors are active at the same time to the same led, the priority color it shows is in accordance with the color described ...
Page 84
The sequence described below is valid only if the same function block is used for all three colour leds. When an acknowledgment is performed, all indications that appear before the indication with higher priority has been reset, will be acknowledged, independent of if the low priority indication app...
Page 85
If an indication with higher priority appears after acknowledgment of a lower priority indication the high priority indication will be shown as not acknowledged according to figure 20 . Activating signal red led acknow. Iec09000315-1-en.Vsd activating signal yellow g g r r y activating signal green ...
Page 86
Activating signal red led reset iec09000316_1_en.Vsd activating signal green r g iec09000316 v1 en-us figure 22: operating sequence 5, two colors sequence 6 latchedreset-s semod56072-75 v4 in this mode all activated leds, which are set to sequence 6 (latchedreset-s), are automatically reset at a new...
Page 87
Iec01000239_2-en.Vsd activating signal 2 led 2 manual reset activating signal 1 automatic reset led 1 disturbance trestart iec01000239 v2 en-us figure 23: operating sequence 6 (latchedreset-s), two indications within same disturbance figure 24 shows the timing diagram for a new indication after tres...
Page 88
Figure 25 shows the timing diagram when a new indication appears after the first one has reset but before trestart has elapsed. Iec01000241_2_en.Vsd activating signal 2 led 2 manual reset activating signal 1 automatic reset led 1 disturbance trestart iec01000241 v2 en-us figure 25: operating sequenc...
Page 89
5.5.3 function keys 5.5.3.1 functionality guid-bed38e9a-c90d-4b7f-aa20-42821c4f6a1c v3 local human-machine-interface (lhmi) has five function buttons, directly to the left of the lcd, that can be configured either as menu shortcut or control buttons. Each button has an indication led that can be con...
Page 90
Input value output value iec09000331_1_en.Vsd 500ms 500ms 500ms iec09000331 v2 en-us figure 28: sequence diagram for setting toggle setting pulsed in this mode the output sets high (1) when the function key has been pressed for more than 500ms and remains high according to set pulse time. After this...
Page 91
Section 6 differential protection 6.1 line differential protection ip13934-1 v1 6.1.1 identification m14844-1 v4 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number line differential protection 3 ct sets, with in-zone transformers, 2-3 line ends lt3cp...
Page 92
6.1.2.2 analog signal transfer for line differential protection m13647-3 v8 the line differential protection function can be arranged as a master-master system or a master-slave system alternatively. In the former, current samples are exchanged between all ieds, and an evaluation is made in each ied...
Page 93
6.1.3 function block semod54630-1 v1 m14937-3 v3 iec06000254-3-en.Vsd lt3cpdif i3p1* i3p2* i3p3* trip trl1 trl2 trl3 startres startunr startenh start stl1 stl2 stl3 intfault extfault blk2h blk2hl1 blk2hl2 blk2hl3 blk5h blk5hl1 blk5hl2 blk5hl3 alarm openct openctal idl1 idl2 idl3 idl1mag idl2mag idl3...
Page 94
6.1.4 signals pid-3701-inputsignals v4 table 32: lt3cpdif input signals name type default description i3p1 group signal - three phase current grp1 samples and dft values i3p2 group signal - three phase current grp2 samples and dft values i3p3 group signal - three phase current grp3 samples and dft v...
Page 95
Name type description idl3 real instantaneous differential current, phase l3 idl1mag real magnitude of fund. Freq. Differential current, phase l1 idl2mag real magnitude of fund. Freq. Differential current, phase l2 idl3mag real magnitude of fund. Freq. Differential current, phase l3 ibias real magni...
Page 96
6.1.5 settings pid-6605-settings v3 table 36: lt3cpdif group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off / on idmin 0.20 - 2.00 ib 0.01 0.30 oper - restr charact., section 1 sensitivity, multiple ibase idminhigh 0.20 - 10.00 ib 0.01 0.80 ...
Page 97
Name values (range) unit step default description k 0.05 - 1.10 - 0.01 1.00 time multiplier setting (tms) for inverse delays idiffalarm 0.05 - 1.00 ib 0.01 0.15 sustained differential current alarm, factor of ibase talarmdelay 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 10.000 delay for alarm due to sustained differenti...
Page 98
Name values (range) unit step default description traaoninpch no transf a 1 2 3 - - no transf a power transformer a applied on input channel x ratvoltw1traa 1.0 - 9999.9 kv 0.1 130.0 transformer a rated voltage (kv) on winding 1 (hv winding) ratvoltw2traa 1.0 - 9999.9 kv 0.1 130.0 transformer a rate...
Page 99
6.1.6 monitored data pid-3701-monitoreddata v3 table 40: lt3cpdif monitored data name type values (range) unit description openctin integer - - open ct on input : 1 for input 1, 2 for input 2 openctph integer - - open ct in phase : 1 for l1, 2 for l2, 3 for l3 idl1mag real - a magnitude of fund. Fre...
Page 100
Iec05000294-4-en.Vsd calculation of instantaneous differential currents (3x) calculation of fundamental frequency differential currents (3x) & bias current magnitudes of differential currents bias current [magnitude] [samples] instantaneous differential currents (samples) differential and bias curre...
Page 101
In the preprocessing block, the real and imaginary parts of the fundamental frequency phase currents and negative sequence currents are derived by means of fundamental frequency numerical fourier filters. Together with the current samples, which are required to internally estimate the 2 nd and the 5...
Page 102
Section 1 unrestrainedlimit section 2 section 3 restrain operate unconditionally 5 4 3 2 1 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 idmin endsection1 endsection2 restrain current [ in pu of ibase] operate current [ in pu of ibase] slopesection2 slopesection3 en05000300.Vsd operate conditionally idminhigh a c b iec05000300 v1 ...
Page 103
Harmonics blocking based on 2 nd and 5 th harmonics is used only used if one of the following conditions are fulfilled: • when a power transformer is included in the protected zone. • when the bias current is less than 125 % ibase. • when an external fault has been detected by the negative sequence ...
Page 104
An internal fault can be suspected. In the opposite case, when one negative sequence current is entering and the other is leaving the protected object, the phase difference will ideally be 180 degrees. An external fault can be suspected. If either the local or the sum of the remote negative sequence...
Page 105
Start l1 start l3 start l2 st l1 idminhigh st l3 idminhigh st l2 idminhigh diff curr l1 2 nd harm diff curr l3 2 nd harm diff curr l2 2 nd harm diff curr l3 5 th harm diff curr l2 5 th harm diff curr l1 5 th harm line energizing and and and crossblocken external fault internal fault or tidminhigh t ...
Page 106
As the harmonic is above the set level. However, when a line is energized the current setting value idminhigh is used. Effectively this means that the line a- b-c in figure 34 forms the characteristic. The harmonic block scheme is generally not applied if there are no in-line or shunt power transfor...
Page 107
Note that all small pre-fault differential currents are subtracted, regardless of their origin. Besides the true charging currents, the following currents are eliminated: • small false differential currents due to small errors (inequalities) of current transformers. • small false differential curren...
Page 108
2 1 4 3 ( ) ( ) 2 d t t t t t - + - = equation1358 v1 en-us (equation 2) 1 4 2 3 ( ) ( ) 2 t t t t t + - + d = equation1359 v1 en-us (equation 3) Δt is calculated every time a telegram is received, and the time difference is then used to adjust and interpolate the current measurements from the remot...
Page 109
The master-slave configuration is achieved by setting parameter operation in the slaves to off for line differential protection function, and setting parameter channelmode to on for the ldcms in the slaves. Test mode semod52415-48 v2 line differential protection function in one ied can be set in tes...
Page 110
Ld cm ld cm telecom. Network telecom. Network primary channel secondary redundant channel ld cm ld cm en05000289.Vsd iec05000289 v1 en-us figure 39: direct fibre optical connection between two ieds with ldom over longer distances. If communication is lost on the primary channel, switchover to the se...
Page 111
And if the load in the protected circuit is relatively high, about the nominal load, the unwanted trip cannot always be prevented. Still, the information about what was the cause of the open ct secondary circuit, is vital. The principle applied to detect an open ct is a simple pattern recognition me...
Page 112
1. Output openct provides instant information to indicate that an open ct circuit has been detected. 2. Output openctal provides a time-delayed alarm that the open ct circuit has been detected. Time delay is defined by the parameter toctalarmdelay. 3. Integer output openctin provides information on ...
Page 113
When the line differential protection function in local ied is set to test mode, ldlpsch sets the remote ieds in a remote test mode and block the trip outputs in the remote ieds. Figure 40 shows a simplified block diagram which illustrates block signal handling by ldlpsch. The following figures indi...
Page 114
>=1 0 0 0 0 0 & 0 0 0 & 0 0 0 >=1 0 0 0 & 0 0 0 >=1 0 0 0 0 0 & 0 0 0 & 0 0 0 >=1 0 0 0 & 0 0 0 >=1 0 0 0 0 0 & 0 0 0 & 0 0 0 >=1 0 0 0 & 0 0 0 trip signal logic of ldlpsch 1 1 >=1 0 0 0 0 >=1 0 0 0 0 >=1 0 0 0 0 difftripl1 difftripl2 difftripl3 tripl1remoteterm1 tripl1remoteterm2 tripl1remoteterm3 ...
Page 115
Internal signals source of destination description blockremoteterm2 signal from ldcm block from remote terminal 2 testmodeinput signal from test mode function input for forcing the function into test mode difftripl1 signal from differential function trip from local differential function in phase l1 ...
Page 116
Function range or value accuracy unrestrained limit function (100–5000)% of ibase ±1.0% of i r at i ≤ i r ±1.0% of i at i > i r second harmonic blocking (5.0–100.0)% of fundamental ±1.0% of i r note: fundamental magnitude = 100% of i r fifth harmonic blocking (5.0–100.0)% of fundamental ±2.0% of i r...
Page 117
Section 7 impedance protection 7.1 distance protection zmfpdis guid-cc4f7338-2281-411d-b55a-67bf03f31681 v4 7.1.1 identification guid-8acd3565-c607-4399-89d2-a05657840e6d v3 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number distance protection zone ...
Page 118
The directional element utilizes a set of well-established quantities to provide fast and correct directional decision during various power system operating conditions, including close-in three-phase faults, simultaneous faults and faults with only zero- sequence in-feed. 7.1.3 function block guid-3...
Page 119
7.1.4 signals pid-6815-inputsignals v3 table 43: zmfpdis input signals name type default description i3p group signal - group signal for current input u3p group signal - group signal for voltage input block boolean 0 blocks and resets timers and outputs of entire function vtsz boolean 0 blocks and r...
Page 120
Name type description trl3z1 boolean trip in phase l3 from zone 1 - forward direction trz2 boolean trip in any phase or phases from zone 2 - forward direction trl1z2 boolean trip in phase l1 from zone 2 - forward direction trl2z2 boolean trip in phase l2 from zone 2 - forward direction trl3z2 boolea...
Page 121
Name type description stndzrv boolean start in any phase or phases from zone rv - any direction stnd boolean fault detected in any phase or phases - any direction stndl1 boolean fault detected in phase l1 - any direction stndl2 boolean fault detected in phase l2 - any direction stndl3 boolean fault ...
Page 122
Table 46: zmfpdis non group settings (advanced) name values (range) unit step default description zzerodb 0 - 100000 m% 100 0 zero point clamping zhihilim 0.0 - 5000.0 ohm 0.1 800.0 high high limit in ohm zhilim 0.0 - 5000.0 ohm 0.1 150.0 high limit in ohm zlowlim 0.0 - 5000.0 ohm 0.1 50.0 low limit...
Page 123
Name type values (range) unit description l23x real - ohm reactance in phase l2- l3 l31r real - ohm resistance in phase l3- l1 l31x real - ohm reactance in phase l3- l1 zl1imag real - ohm zl1 amplitude, magnitude of instantaneous value zl1angim real - deg zl1 angle, magnitude of instantaneous value ...
Page 124
7.1.7.1 filtering guid-16b5060b-101c-402a-bf25-06e70fdd7836 v2 practically all voltage, current and impedance quantities used within the zmfpdis function are derived from fundamental frequency phasors filtered by a half cycle filter. The phasor filter is frequency adaptive in the sense that its coef...
Page 125
Thus providing the advantage of knowing how performance should be optimized, even during the first turbulent milliseconds of the fault period. There are two types of cvts from the function point of view, the passive and the active type, which refers to the type of ferro-resonance suppression device ...
Page 126
Zero sequence current is relatively high due to a source with low z0/z1 ratio. In these situations zone measurement will be released both for the related phase-to- earth loops and the phase-to-phase loop simultaneously. On the other hand, simultaneous faults closer to the remote bus will gradually t...
Page 127
Since the polarizing voltage is also used for the mho distance characteristics, the magnitude of the voltage is just as interesting as the phase. If there are symmetrical conditions and the measured per phase positive sequence voltage magnitude is above 75% of the base voltage before the fault, the ...
Page 128
R1zx rfppzx x1zx x1zx rfppzx r1zx rfppzx rfppzx rfppzx rfppzx r x (ohm/phase) (ohm/phase) iec11000416-2-en.Vsdx 2 2 2 2 2 2 iec11000416 v2 en-us figure 44: zmfpdis characteristic for phase-to-phase measuring, ohm/loop domain section 7 1mrk 505 394-uen a impedance protection 122 line differential pro...
Page 129
Rfpezx x1zx+xnzx x1zx+xnzx rfpezx r1zx+rnzx rfpezx rfpezx rfpezx rfpezx r r1zx+rnzx (ohm/loop) iec11000415-2-en.Vsdx x0zx-x1zx xnzx 3 = r0zx-r1zx rnzx 3 = x (ohm/loop) n φ n φ iec11000415 v2 en-us figure 45: zmfpdis characteristic for phase-to-earth measuring, ohm/loop domain the faulty loop in rela...
Page 130
Ul1 r1zx + j x1zx il1 rfpezx phase-to-earth fault in phase l1 phase-to-phase fault in phase l1-l2 three-phase fault or phase-to- phase-earth fault (arc + tower resistance) 0 (r0zx-r1zx)/3 + j (x0zx-x1zx)/3 ) in ul1 r1zx + j x1zx il1 ul2 r1zx + j x1zx il2 rfppzx ul1 r1zx + j x1zx il1 ul3 r1zx + j x1z...
Page 131
R x z3 z2 z1 z4 z5 zrv r x z s =0 z s =z1 z s =2z1 iec15000056-1-en.Vsdx iec15000056 v1 en-us figure 47: mho, offset mho characteristics and the source impedance influence on the mho characteristic the mho characteristic has a dynamic expansion due to the source impedance. Instead of crossing the or...
Page 132
R r x r x r r x r forward reverse non-directional (a) (b) (c) x x rset xset rset xset x r rset xset (a) and (c) are for zone 1, zone 2 and zone 3-5 when dirmodez3-5 = forward. (b) and (d) are for zonerv and zone 3-5 when dirmodez3-5 = reverse (c) and (f) are for zone 3-5 when dirmodez3-5 = non-direc...
Page 133
The plain mho circle has the characteristic as in figure 49 . The condition for deriving the angle β is according to equation 6 . β = − ( ) − ( ) ⋅ arg arg u i z u l l l l set pol 1 2 1 2 1 iecequation15027 v1 en-us (equation 6) where u l1l2 equation1790 v2 en-us is the voltage vector difference bet...
Page 134
2 1l l u 1 2 1 l l set i z set l l l l comp z i u u 1 2 1 2 1 pol u jx i l l 2 1 r i l l 2 1 iec15000060-1-en.Vsdx iec15000060 v1 en-us figure 49: simplified mho characteristic and vector diagram for phase l1-to- l2 fault offset mho guid-3e13e6d5-0832-4386-9677-9a40bff42f8f v2 the characteristic for...
Page 135
1 2 l l u 1 2 1 l l set i z 2 1 2 1 2 ( 1 ) comp l l l l set u u i z 1 1 2 1 2 1 comp l l l l set u u i z 1 2 l l i jx 1 2 l l i r 1 2 1 l l set i z iec15000058-2-en.Vsdx iec15000058 v2 en-us figure 50: simplified offset mho characteristic and voltage vector for phase l1 to l2 fault operation occurs...
Page 136
K z z z n set set set = − ⋅ 0 1 3 1 iecequation15017 v1 en-us z r zx j x zx set 0 0 0 = + ⋅ iecequation15018 v1 en-us for zone 1, z r pez j x pez set 1 1 1 1 1 = + ⋅ iecequation15019 v1 en-us for zone 2-5 and rv, z r zx j x zx set 1 1 1 = + ⋅ iecequation15020 v1 en-us (equation 10) where z set 0 is ...
Page 137
1 l u set n z k i 1 0 3 set n l l comp z k i i u u 1 ) 0 3 ( 1 1 pol u i l1 •r i l1 •jx set l z i 1 1 iec15000059-1-en.Vsdx iec15000059 v1 en-us figure 51: simplified offset mho characteristic and vector diagram for phase l1-to-earth fault operation occurs if 90°≤β≤270°. Offset mho guid-b1ef3931-7b8...
Page 138
1 l u 1 ( 3 0 ) 1 l n set i i k z i l1 • jx 2 1 1 ( ( 3 0 ) 1 ) comp l l n set u u i i k z 1 1 1 ( 3 0 ) 1 comp l l n set u u i i k z i l1 • r 1 ( 3 0 ) 1 l n set i i k z iec15000057-2-en.Vsdx iec15000057 v2 en-us figure 52: simplified offset mho characteristic and voltage vector for phase l1-to-ear...
Page 139
The possibility to detect high fault resistances, especially for phase-to-earth faults at the remote line end. For example, for a given setting of the load angle argld, the resistive blinder for the zone measurement can be set according to figure 53 affording higher fault resistance coverage without...
Page 140
Ibase. However, if current transformer saturation is detected, this criterion is changed to residual voltage (3u0) exceeding 5% of ubase/sqrt(3) instead. Dirmodez3-5 forward reverse true (1) fw(ln & lmln) rv(ln & lmln) fw(ln & lmln) fw(ln & lmln) rv(ln & lmln) iec12000137-2-en.Vsd iec12000137 v3 en-...
Page 141
Zml1zx ndzx phsl1 or zml2zx phsl2 zml3zx phsl3 zml1l2zx phsl1l2 zml2l3zx phsl2l3 zml3l1zx phsl3l1 or dirl1zx and dirl2zx and and or and and and dirl3zx dirl1l2zx dirl2l3zx dirl3l1zx l1zx pezx l2zx ppzx or or or and and and and and and integer to bool l1n l2n l3n l1l2 l2l3 l1l3 relcndzx iec12000140-2...
Page 142
T tppzx t tpezx block ppzx pezx timerlinkszx looplink (tpp-tpe) looplink & zonelink no links false (0) timerlinkszx = looplink & zonelink lnkz2 lnkzx or lnkz4 lnkz5 zonelinkstart phase selection 1st starting zone vtsz blkzx blktrzx or or or or or and and or and and and timermodezx = enable phph or p...
Page 143
T 15 ms stl1zx t 15 ms tripzx and and and and trl1zx trl2zx trl3zx t 15 ms t 15 ms startzx stl2zx stl3zx and and and tzx block vtsz blkzx t 15 ms and t 15 ms and stndzx or or l1zx l2zx ppzx ndzx or pezx iec12000138-2-en.Vsd iec12000138 v2 en-us figure 57: start and trip outputs 1mrk 505 394-uen a se...
Page 144
Phsl1l2 block vtsz or t 15 ms and or or or or t 15 ms and t 15 ms and startnd or or t 15 ms and stphs t 15 ms and stpp stpe iec12000133-2-en.Vsd iec12000133 v2 en-us figure 58: additional start outputs 1 section 7 1mrk 505 394-uen a impedance protection 138 line differential protection red650 2.2 ie...
Page 145
Phsl1 phsl1l2 phsl2l3 stfwl2 stfwl3 fwl1 fwl2 fwl1l2 fwl3 fwl2l3 fwl3l1 block vtsz or t 15 ms and and and and and and and or or or or in present t 15 ms and t 15 ms and stfwpe and =1 =2 =3 stfw1ph stfw2ph stfw3ph iec12000134-2-en.Vsd iec12000134 v2 en-us figure 59: additional start outputs 2 phsl1 p...
Page 146
7.1.7.10 measurement measurement supervision semod54417-130 v4 the protection, control, and monitoring ieds have functionality to measure and further process information for currents and voltages obtained from the pre- processing blocks. The number of processed alternate measuring quantities depends...
Page 147
Iec05000657-3-en.Vsdx x_range= 1 x_range = 3 x_range=0 hysteresis high-high limit high limit low limit low-low limit x_range=2 x_range=4 y t x_range=0 y = magnitude of the measured quantity iec05000657 v3 en-us figure 61: presentation of operating limits each analogue output has one corresponding su...
Page 148
In addition to the normal cyclic reporting the ied also report spontaneously when measured value passes any of the defined threshold limits. Iec05000500-2-en.Vsdx v a lu e 1 y t v a lu e 2 v a lu e 3 v a lu e 4 value reported (1st) value reported v a lu e 5 value reported y1 y2 y5 value reported val...
Page 149
Iec99000529-2-en.Vsdx y t value reported (1st) value reported value reported y1 y2 y3 y y y y y y value reported iec99000529 v2 en-us figure 63: amplitude dead-band supervision reporting after the new value is reported, the ±Δy limits for dead-band are automatically set around it. The new value is r...
Page 150
Iec99000530-2-en.Vsdx y t value reported (1st) y1 value reported a1 y2 value reported y3 y4 a value reported a2 y5 a3 a4 a5 a7 a6 value reported a2 >= pre-set value a1 >= pre-set value a >= pre-set value a3 + a4 + a5 + a6 + a7 >= pre-set value iec99000530 v2 en-us figure 64: reporting with integral ...
Page 151
7.1.8 technical data guid-6c2ef52a-8166-4a23-9861-38931682aa7d v7 table 48: zmfpdis technical data function range or value accuracy number of zones 3 selectable directions, 3 fixed directions - minimum operate current, ph-ph and ph-e (5-6000)% of ibase ±1.0% of i r positive sequence reactance reach,...
Page 152
7.2 power swing detection zmrpsb ip14499-1 v3 7.2.1 identification m14853-1 v3 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number power swing detection zmrpsb zpsb symbol-ee v1 en-us 68 7.2.2 functionality m13873-3 v12 power swings may occur after di...
Page 153
Name type default description blki01 boolean 0 block inhibit of start output for slow swing condition blki02 boolean 0 block inhibit of start output for subsequent residual current detection blk1ph boolean 0 block one-out-of-three-phase operating mode rel1ph boolean 0 release one-out-of-three-phase ...
Page 154
Name values (range) unit step default description kldrfw 0.50 - 0.90 mult 0.01 0.75 multiplication factor for inner resistive load boundary, forward kldrrv 0.50 - 0.90 mult 0.01 0.75 multiplication factor for inner resistive load boundary, reverse tef 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 3.000 timer for overcomin...
Page 155
R jx argld argld rldoutfw rldinfw r1finfw r1finrv rldinrv rldoutrv x1infw x1outfw zl r1lin x1inrv x1outrv iec09000222_1_en.Vsd d rv d rv d rv d rv d rv d fw d fw d fw d fw d fw d fw j j j iec09000222 v1 en-us figure 66: operating characteristic for zmrpsb function (setting parameters in italic) the ...
Page 156
Rldinfw = kldrfw·rldoutfw equation1185 v2 en-us (equation 15) where: kldrfw is a settable multiplication factor less than 1 the slope of the load encroachment inner and outer boundary is defined by setting the parameter argld. The load encroachment in the fourth quadrant uses the same settings as in...
Page 157
The inner resistive characteristic in the third quadrant outside the load encroachment zone consist of the sum of the settings r1finrv and the line resistance r1lin. The argument of the tilted lines outside the load encroachment is the same as the tilted lines in the first quadrant. The distance bet...
Page 158
Of figure 67 (internal input signal zoutl1, zinl1, and-gates and tp-timers) are duplicated for phase l2 and l3. All tp1 and tp2 timers in the figure have the same settings. Iec05000113-2-en.Vsd and zinl1 and det-l1 or and and zoutl1 -loop zoutl2 zoutl3 or detected or -loop 0-tp1 0 0-tp2 0 0 0-tw iec...
Page 159
En05000114.Vsd trsp t tef i0check and blki02 t 10 ms and blki01 block inhibit zoutl3 zoutl2 zoutl1 det1of3 - int. Rel1ph blk1ph and det2of3 - int. Rel2ph blk2ph and external and start zout zinl1 zinl2 zinl3 zin and t tr1 t tr2 or and and or or or or or t th -loop -loop iec05000114 v1 en-us figure 69...
Page 160
• logical 1 on functional input block inhibits the output start signal instantaneously. • the inhibit internal signal is activated, if the power swing has been detected and the measured impedance remains within its operate characteristic for the time, which is longer than the time delay set on tr2 t...
Page 161
7.3.2 functionality semod153644-5 v9 automatic switch onto fault logic zcvpsof is a function that gives an instantaneous trip when closing the breaker onto a fault. A dead-line detection check is provided to activate zcvpsof when the line is de-energized. Mho distance protections cannot operate for ...
Page 162
Pid-3875-outputsignals v9 table 56: zcvpsof output signals name type description trip boolean trip output 7.3.5 settings ip15016-1 v2 pid-3875-settings v10 table 57: zcvpsof group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off / on autoinitm...
Page 163
Name type values (range) unit description ul1 real - kv voltage in phase l1 ul2 real - kv voltage in phase l2 ul3 real - kv voltage in phase l3 7.3.7 operation principle semod153665-4 v8 the automatic switch onto fault logic zcvpsof can be activated externally (by the breaker-closed input) or intern...
Page 164
The measured phase voltages and currents are provided as service values. Block trip zacc start_dlyd i3p u3p autoinitmode mode = impedance mode = uilevel mode = uilvl&imp uilevel detector iph uph bc t ≥1 tsotf 15ms t & t tdld ≥1 deadline sotfuilevel toperate t tduration t ≥1 & & & ≥1 & iec07000084 v3...
Page 165
Section 8 current protection 8.1 instantaneous phase overcurrent protection phpioc ip14506-1 v6 8.1.1 identification m14880-1 v5 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number instantaneous phase overcurrent protection phpioc 3i>> symbol-z v1 en-...
Page 166
Pid-6914-outputsignals v3 table 62: phpioc output signals name type description trip boolean trip signal from any phase trl1 boolean trip signal from phase l1 trl2 boolean trip signal from phase l2 trl3 boolean trip signal from phase l3 8.1.5 settings ip11434-1 v2 pid-6914-settings v3 table 63: phpi...
Page 167
8.1.7 operation principle m12913-3 v8 the sampled analogue phase currents are pre-processed in a discrete fourier filter (dft) block. The rms value of each phase current is derived from the fundamental frequency components, as well as sampled values of each phase current. These phase current values ...
Page 168
8.1.8 technical data ip11435-1 v1 m12336-1 v13 table 67: phpioc technical data function range or value accuracy operate current (5-2500)% of lbase ± 1.0% of i r at i ≤ i r ± 1.0% of i at i > i r reset ratio > 95% at (50–2500)% of ibase - operate time at 0 to 2 x i set min. = 15 ms max. = 25 ms - res...
Page 169
The directional function needs voltage as it is voltage polarized with memory. The function can be set to be directional or non-directional independently for each of the steps. A second harmonic blocking level can be set for the function and can be used to block each step individually. 8.2.3 functio...
Page 170
8.2.4 signals pid-6973-inputsignals v3 table 68: oc4ptoc input signals name type default description i3p group signal - group signal for current input u3p group signal - group signal for voltage input block boolean 0 block of function blktr boolean 0 block of trip blkst1 boolean 0 block of step1 blk...
Page 171
Name type description tr3l3 boolean trip signal from step3 phase l3 tr4l1 boolean trip signal from step4 phase l1 tr4l2 boolean trip signal from step4 phase l2 tr4l3 boolean trip signal from step4 phase l3 start boolean general start signal st1 boolean common start signal from step1 st2 boolean comm...
Page 172
Name values (range) unit step default description startphsel 1 out of 3 2 out of 3 3 out of 3 - - 1 out of 3 number of phases required for op (1 of 3, 2 of 3, 3 of 3) dirmode1 off non-directional forward reverse - - non-directional directional mode of step 1 (off, nodir, forward, reverse) characteri...
Page 173
Name values (range) unit step default description characterist2 ansi ext. Inv. Ansi very inv. Ansi norm. Inv. Ansi mod. Inv. Ansi def. Time l.T.E. Inv. L.T.V. Inv. L.T. Inv. Iec norm. Inv. Iec very inv. Iec inv. Iec ext. Inv. Iec s.T. Inv. Iec l.T. Inv. Iec def. Time reserved programmable ri type rd...
Page 174
Name values (range) unit step default description k3 0.05 - 999.00 - 0.01 0.05 time multiplier for the inverse time delay for step 3 imin3 1 - 10000 %ib 1 33 minimum operate current for step3 in % of ibase t3min 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.000 minimum operate time for inverse curves for step 3 i3mult 1...
Page 175
Name values (range) unit step default description i1>max 5 - 2500 %ib 1 2500 maximum used operating phase current level for step 1 in % of ibase, if i1> is greater than i1>max then i1> is set to i1>max resettypecrv1 instantaneous iec reset ansi reset - - instantaneous selection of reset curve type f...
Page 176
Name values (range) unit step default description harmblock2 off on - - off enable block of step 2 from harmonic restrain i3>min 5 - 2500 %ib 1 5 minimum used operating phase current level for step 3 in % of ibase, if i3> is less than i3>min then i3> is set to i3>min i3>max 5 - 2500 %ib 1 2500 maxim...
Page 177
Name values (range) unit step default description tprcrv4 0.005 - 3.000 - 0.001 0.500 parameter pr for customer programmable curve for step 4 ttrcrv4 0.005 - 100.000 - 0.001 13.500 parameter tr for customer programmable curve for step 4 tcrcrv4 0.1 - 10.0 - 0.1 1.0 parameter cr for customer programm...
Page 178
• the direction element • the harmonic restraint blocking function • the four step overcurrent function • the mode selection if vt inputs are not available or not connected, setting parameter dirmodex shall be left to default value, non-directional. Iec05000740-3-en.Vsdx direction element 4 step ove...
Page 179
In a comparator, the dft or rms values are compared to the set operation current value of the function (i1>, i2>, i3> or i4>) for each phase current. If a phase current is larger than the set operation current, outputs start, stx, stl1, stl2 and stl3 are activated without delay. Output signals stl1,...
Page 180
The polarizing voltage is available as long as the positive-sequence voltage exceeds 5% of the set base voltage ubase. So the directional element can be used for all unsymmetrical faults including close-in faults. For close-in three-phase faults, the u1 l1m memory voltage, based on the same positive...
Page 181
The default value of anglerca is –55°. The parameter angleroa gives the angular distance from anglerca to define the directional borders. A minimum current for the directional phase start current signal can be set. Iminopphsel is the start level for the directional evaluation of il1, il2 and il3. Th...
Page 182
Iminopphsel anglerca angleroa iec15000266-2-en.Vsdx greater comparator directional element i3p u3p directional release block dfwdlx dfwdlxx drevlx drevlxx stlx forward_int reverse_int x‐ means three phases 1,2 and 3 xx – means phase to phase 12,23,31 iec15000266 v2 en-us figure 78: oc4 directional r...
Page 183
The stdircnd output provides an integer signal that depends on the start and directional evaluation and is derived from a binary coded signal as described in table 74 . Table 74: code description for stdircnd output signal stdircnd description bit 0 (1) general start bit 1 (2) direction detected in ...
Page 184
A b a>b block and i op extract second harmonic current component extract fundamental current component x 2ndharmstab a b a>b a b a>b 0.07*ibase iec13000014-2-en.Vsd 2ndh_block_int iec13000014 v2 en-us figure 80: second harmonic blocking 8.2.8 technical data m12342-1 v20 table 75: oc4ptoc technical d...
Page 185
8.3 instantaneous residual overcurrent protection efpioc ip14508-1 v3 8.3.1 identification m14887-1 v4 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number instantaneous residual overcurrent protection efpioc in>> ief v1 en-us 50n 8.3.2 functionality m...
Page 186
Pid-6915-outputsignals v4 table 77: efpioc output signals name type description trip boolean trip signal 8.3.5 settings ip11449-1 v2 pid-6915-settings v4 table 78: efpioc group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off / on in>> 5 - 250...
Page 187
Current value is fed to the instantaneous residual overcurrent protection (efpioc). In a comparator the rms value is compared to the set operation current value of the function (in>>). If the residual current is larger than the set operation current a signal from the comparator is set to true. This ...
Page 188
Function range or value accuracy critical impulse time 10 ms typically at 0 to 2 x i set - operate time at 0 to 10 x i set min. = 5 ms max. = 15 ms - reset time at 10 x i set to 0 min. = 25 ms max. = 35 ms - critical impulse time 2 ms typically at 0 to 10 x i set - dynamic overreach - 8.4 directiona...
Page 189
The residual current can be calculated by summing the three-phase currents or taking the input from the neutral ct. 8.4.3 function block m12619-3 v8 ef4ptoc i3p* u3p* i3ppol* i3pdir* block blktr blkst1 blkst2 blkst3 blkst4 enmult1 enmult2 enmult3 enmult4 cbpos closecb opencb trip trin1 trin2 trin3 t...
Page 190
Name type default description enmult4 boolean 0 when activated, the current multiplier is in use for step4 cbpos boolean 0 breaker position closecb boolean 0 breaker close command opencb boolean 0 breaker open command pid-6967-outputsignals v3 table 84: ef4ptoc output signals name type description t...
Page 191
Name values (range) unit step default description ipolmin 2 - 100 %ib 1 5 minimum current level for polarization in % of ibase rnpol 0.50 - 1000.00 ohm 0.01 5.00 real part of source impedance used for current polarisation xnpol 0.50 - 3000.00 ohm 0.01 40.00 imaginary part of source imp. Used for cur...
Page 192
Name values (range) unit step default description characterist1 ansi ext. Inv. Ansi very inv. Ansi norm. Inv. Ansi mod. Inv. Ansi def. Time l.T.E. Inv. L.T.V. Inv. L.T. Inv. Iec norm. Inv. Iec very inv. Iec inv. Iec ext. Inv. Iec s.T. Inv. Iec l.T. Inv. Iec def. Time reserved programmable ri type rd...
Page 193
Name values (range) unit step default description t2 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.400 def time delay or add time delay for inverse char of step 2 k2 0.05 - 999.00 - 0.01 0.05 time multiplier for the step 2 selected time characteristic imin2 1.00 - 10000.00 %ib 1.00 50 minimum operate residual current fo...
Page 194
Name values (range) unit step default description characterist4 ansi ext. Inv. Ansi very inv. Ansi norm. Inv. Ansi mod. Inv. Ansi def. Time l.T.E. Inv. L.T.V. Inv. L.T. Inv. Iec norm. Inv. Iec very inv. Iec inv. Iec ext. Inv. Iec s.T. Inv. Iec l.T. Inv. Iec def. Time reserved programmable ri type rd...
Page 195
Name values (range) unit step default description tbcrv1 0.00 - 20.00 - 0.01 0.00 param b for customized inverse trip time curve for step 1 tccrv1 0.1 - 10.0 - 0.1 1.0 param c for customized inverse trip time curve for step 1 tprcrv1 0.005 - 3.000 - 0.001 0.500 param pr for customized inverse reset ...
Page 196
Name values (range) unit step default description tacrv3 0.005 - 200.000 - 0.001 13.500 param a for customized inverse trip time curve for step 3 tbcrv3 0.00 - 20.00 - 0.01 0.00 param b for customized inverse trip time curve for step 3 tccrv3 0.1 - 10.0 - 0.1 1.0 param c for customized inverse trip ...
Page 197
8.4.6 monitored data pid-6967-monitoreddata v3 table 88: ef4ptoc monitored data name type values (range) unit description iop real - a operating current level upol real - kv polarizing voltage level ipol real - a polarizing current level upoliang real - deg polarizing angle between voltage and curre...
Page 198
• parallel connection of current instrument transformers in all three phases (holm-green connection). • one single core balance current instrument transformer (cable ct). • one single current instrument transformer located between power system star point and earth (current transformer located in the...
Page 199
This voltage can be: 1. Directly measured (when a dedicated vt input of the ied is connected in pcm600 to the fourth analog input of the pre-processing block connected to ef4ptoc function input u3p). This dedicated ied vt input shall be then connected to the open delta winding of a three-phase main ...
Page 200
• for some special line protection applications, this dedicated ied ct input can be connected to a parallel connection of current transformers in all three phases (holm-green connection). 2. Calculated from three phase current input within the ied (when the fourth analog input into the pre-processin...
Page 201
8.4.7.3 external polarizing for earth-fault function m13941-144 v6 the individual steps within the protection can be set as non-directional. When this setting is selected, it is possible via the function binary input blkstx to provide external directional control (that is, torque control) by, for ex...
Page 202
• directional mode can be set to off/non-directional/forward/reverse. By this parameter setting the directional mode of the step is selected. • residual current start value. • type of operating characteristic (inverse or definite time). By this parameter setting it is possible to select inverse or d...
Page 204
The operating and polarizing quantity are then used inside the directional element, as shown in figure 86 , in order to determine the direction of the earth fault. Strv 0.6 * in>dir stfw -rca -85 deg 40% of in>dir in>dir rca 65° u = -3u pol 0 i = 3i op 0 rca +85 deg rca -85 deg characteristic for st...
Page 205
These signals shall be used for communication based earth-fault teleprotection communication schemes (permissive or blocking). Simplified logic diagram for directional supervision element with integrated directional comparison step is shown in figure 87 : x a a>b b in>dir polmethod=voltage polmethod...
Page 206
1. The fundamental frequency component of the current > 1% of ibase 2. The second harmonic component > 1% of ibase 3. The ratio of the 2nd harmonic component in relation to the fundamental frequency component in the residual current exceeds the preset level defined by the parameter 2ndharmstab setti...
Page 207
A b a>b block and i op extract second harmonic current component extract fundamental current component x 2ndharmstab a b a>b a b a>b 0.07*ibase iec13000015-4-en.Vsdx usestartvalue in1> in2> in3> in4> a b a>b t t=70ms or and blkpartransf=on q -1 or 2ndh_block_int q -1 = unit delay iec13000015 v4 en-u...
Page 208
Setting) the function will give a trip after a set delay tsotf. This delay is normally set to a short time (default 200 ms). The under-time logic acts as a circuit breaker pole-discordance protection, but it is only active immediately after breaker switching. The under-time logic can only be used in...
Page 209
Directio n elemen t 4 step over current elemen t one ele me nt fo r ea ch step harmonic restrain t mode sele ction earthfaultdir ection harmrestrb lock ena bledir ena blestep1-4 directio nalmode1-4 trip elemen t ena bledir ang levalid directio nal che ck ope ratin gcurrent switcho nto fa ult star t ...
Page 210
Function range or value accuracy inverse time characteristics, see table 660 , table 662 and table 664 16 curve types see table 660 , table 662 and table 664 second harmonic blocking (5–100)% of fundamental ±2.0% of i r minimum polarizing voltage (1–100)% of ubase ±0.5% of u r minimum polarizing cur...
Page 211
A thermal overload will often not be detected by other protection functions and the introduction of the thermal overload protection can allow the protected circuit to operate closer to the thermal limits. The three-phase current measuring protection has an i 2 t characteristic with settable time con...
Page 212
Pid-3909-inputsignals v9 table 91: lfpttr input signals name type default description i3p group signal - group signal for current input block boolean 0 block of function blktr boolean 0 block of trip enmult boolean 0 current multiplyer used when thol is for two or more lines ambtemp real 0 ambient t...
Page 213
Name values (range) unit step default description tau 1 - 1000 min 1 45 time constant of the line in minutes. Alarmtemp 0 - 200 deg c 1 80 temperature level for start (alarm) triptemp 0 - 300 deg c 1 90 temperature level for trip recltemp 0 - 300 deg c 1 75 temperature for reset of lockout after tri...
Page 214
Table 97: lfpttr non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description globalbasesel 1 - 12 - 1 1 selection of one of the global base value groups 8.5.6 monitored data pid-3908-monitoreddata v7 table 98: lcpttr monitored data name type values (range) unit description ttrip int...
Page 215
2 final ref ref i t i æ ö q = × ç ÷ ç ÷ è ø equation1167 v1 en-us (equation 30) where: i is the largest phase current, i ref is a given reference current and t ref is steady state temperature rise corresponding to i ref the ambient temperature is added to the calculated final temperature. If this te...
Page 216
Ln final operate operate final n t t æ ö q - q = - × ç ÷ ç ÷ q - q è ø equation1169 v1 en-us (equation 32) the calculated time to trip is available as a real figure signal, ttrip. After a trip, caused by the thermal overload protection, there can be a lockout to reconnect the tripped circuit. The ou...
Page 217
Calculation of final temperature final temp > trip temp actual temp > alarm temp actual temp > trip temp actual temp calculation of time to trip calculation of time to reset of lockout calculation of actual temperature lockout logic ambtemp start temp trip lockout ttrip tenrecl i3p enmult sensflt al...
Page 218
8.5.8 technical data m12352-1 v14 table 100: lcpttr/lfpttr technical data function range or value accuracy reference current (2-400)% of ibase ±1.0% of i r reference temperature (0-300)°c, (0 - 600)°f ± 1.0°c, ±2.0°f operate time: 2 2 2 2 2 ln p trip amb p ref ref i i t t t i i i t t - = - - - × é ù...
Page 219
A current check with extremely short reset time is used as check criterion to achieve high security against unwanted operation. Contact check criteria can be used where the fault current through the breaker is small. Ccrbrf can be single- or three-phase initiated to allow use with single phase tripp...
Page 220
Pid-3562-outputsignals v7 table 102: ccrbrf output signals name type description trbu boolean back-up trip by breaker failure protection function trbu2 boolean second back-up trip by breaker failure protection function trret boolean retrip by breaker failure protection function trretl1 boolean retri...
Page 221
Table 104: ccrbrf group settings (advanced) name values (range) unit step default description i>blkcont 5 - 200 %ib 1 20 i> in % of ibase block operation using function mode contact t3 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.030 additional time delay to t2 for a second back-up trip tcbalarm 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 ...
Page 222
Table 107: dependencies between parameters retripmode and functionmode retripmode functionmode description retrip off n/a the re-trip function is not activated. Cb pos check current the re-trip will follow the function mode. Contact current/contact no cbpos check current the re-trip is done uncondit...
Page 223
S r sr q or and and 30 ms t 150 ms start stl1 or backuptrip l1 bfp started l1 reset l1 block retrip time out l1 iec09000976-2-en.Vsd time out l1 iec09000976 v2 en-us figure 94: simplified logic scheme of the ccrbrf starting logic and and and and and or or or a b a>b and a b a>b i>blkcont and time ou...
Page 224
Iec09000979-4-en.Vsd bfp started l1 t t2 and or bfp started l2 bfp started l3 from other phases or or and t t2mph cbflt and and a b a>b in in> 1 out of 4 and or 1 out of 3 current high l2 current high l3 from other phases and current high l1 or contact closed l1 or backup trip l1 tpulse backup trip ...
Page 225
Function range or value accuracy time delay for re-trip at 0 to 2 x i set (0.000-60.000) s ±0.2% or ±15 ms whichever is greater time delay for back-up trip at 0 to 2 x i set (0.000-60.000) s ±0.2% or ±15 ms whichever is greater time delay for back-up trip at multi-phase start at 0 to 2 x i set (0.00...
Page 226
8.7.3 function block m17149-3 v6 ccpdsc i3p* block blkdbyar closecmd opencmd extpdind pole1opn pole1cl pole2opn pole2cl pole3opn pole3cl trip start iec13000305-1-en.Vsd iec13000305 v1 en-us figure 98: ccpdsc function block 8.7.4 signals pid-3525-inputsignals v8 table 109: ccpdsc input signals name t...
Page 227
8.7.5 settings pid-3525-settings v8 table 111: ccpdsc group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off / on ttrip 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.300 time delay between trip condition and trip signal contsel off pd signal from cb pole pos aux c...
Page 228
Pole discordance signal from circuit breaker + circuit breaker en05000287.Vsd iec05000287 v2 en-us figure 99: pole discordance external detection logic this binary signal is connected to a binary input of the ied. The appearance of this signal will start a timer that will give a trip signal after th...
Page 229
Set to be active either continuously or only directly in connection to breaker open or close command. The function also has a binary input that can be configured from the autoreclosing function, so that the pole discordance function can be blocked during sequences with a single pole open if single p...
Page 230
Is connected to a signalization “1phase autoreclosing in progress” from the external autoreclosing device. If the pole discordance protection is enabled, then two different criteria can generate a trip signal trip: • pole discordance signaling from the circuit breaker. • unsymmetrical current detect...
Page 231
8.7.8 technical data m13279-1 v10 table 114: ccpdsc technical data function range or value accuracy operate current (0–100)% of ibase ±1.0% of i r independent time delay between trip condition and trip signal (0.000-60.000) s ±0.2% or ± 30 ms whichever is greater 1mrk 505 394-uen a section 8 current...
Page 232
226.
Page 233
Section 9 voltage protection 9.1 two step undervoltage protection uv2ptuv ip14544-1 v3 9.1.1 identification m16876-1 v7 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number two step undervoltage protection uv2ptuv 3u symbol-r-2u-greater-than v2 en-us 2...
Page 234
9.1.3 function block m13794-3 v6 iec06000276-2-en.Vsd uv2ptuv u3p* block blktr1 blkst1 blktr2 blkst2 trip tr1 tr1l1 tr1l2 tr1l3 tr2 tr2l1 tr2l2 tr2l3 start st1 st1l1 st1l2 st1l3 st2 st2l1 st2l2 st2l3 iec06000276 v2 en-us figure 102: uv2ptuv function block 9.1.4 signals pid-3586-inputsignals v7 table...
Page 235
Name type description start boolean general start signal st1 boolean common start signal from step1 st1l1 boolean start signal from step1 phase l1 st1l2 boolean start signal from step1 phase l2 st1l3 boolean start signal from step1 phase l3 st2 boolean common start signal from step2 st2l1 boolean st...
Page 236
Name values (range) unit step default description characterist2 definite time inverse curve a inverse curve b prog. Inv. Curve - - definite time selection of time delay curve type for step 2 opmode2 1 out of 3 2 out of 3 3 out of 3 - - 1 out of 3 number of phases required for op (1 of 3, 2 of 3, 3 o...
Page 237
Name values (range) unit step default description tireset2 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.025 time delay in idmt reset (s), step 2 acrv2 0.005 - 200.000 - 0.001 1.000 parameter a for customer programmable curve for step 2 bcrv2 0.50 - 100.00 - 0.01 1.00 parameter b for customer programmable curve for step...
Page 238
Available: if the voltage is lower than the set blocking level, the function is blocked and no start or trip signal is generated. The time delay characteristic is individually chosen for each step and can be either definite time delay or inverse time delay. To avoid oscillations of the output start ...
Page 239
Where: un set value for step 1 and step 2 u measured voltage the type b curve is described as: n n k t u u u 2.0 480 0.055 32 0.5 × = + æ ö × - ç ÷ è ø equation1432 v2 en-us (equation 38) the customer programmable curve can be created as: p n n k a t d u u b c u é ù ê ú ê ú × = + ê ú æ ö ê ú × - ç ÷...
Page 240
Voltage idmt voltage time ul1 ul2 ul3 iec12000186-1-en.Vsd iec12000186 v1 en-us figure 103: voltage used for the inverse time characteristic integration trip signal issuing requires that the undervoltage condition continues for at least the user set time delay. This time delay is set by the paramete...
Page 241
Voltage time hystabs1 start trip u1 start trip t tireset1 time time integrator t frozen timer linearly decreased instantaneous measured voltage tireset1 iec05000010-4-en.Vsd iec05000010 v4 en-us figure 104: voltage profile not causing a reset of the start signal for step 1, and inverse time delay at...
Page 242
Voltage time hystabs1 start trip start u1 start trip t tireset1 time time integrator t frozen timer linearly decreased instantaneous measured voltage tireset1 iec05000011-en-3.Vsd iec05000011 v3 en-us figure 105: voltage profile causing a reset of the start signal for step 1, and inverse time delay ...
Page 243
A a b u1 u tr1 st1 iec09000785-3-en.Vsd t t1 treset1 r t and iec09000785 v3 en-us figure 106: logic diagram for step 1, dt operation u1 st1 tr1 treset1 t1 iec10000039-3-en.Vsd iec10000039 v3 en-us figure 107: example for definite time delay stage1 reset 1mrk 505 394-uen a section 9 voltage protectio...
Page 244
U1 st1 tr1 treset1 t1 iec10000040-3-en.Vsd iec10000040 v3 en-us figure 108: example for definite time delay stage1 operation 9.1.7.3 blocking m15326-20 v8 it is possible to block two step undervoltage protection uv2ptuv partially or completely, by binary input signals or by parameter settings, where...
Page 245
Time u normal voltage u1 u2 intblkstval1 intblkstval2 disconnection tblkuv1 t1,t1min tblkuv2 t2,t2min block step 1 block step 2 en05000466.Vsd iec05000466 v1 en-us figure 109: blocking function 9.1.7.4 design m15326-35 v9 the voltage measuring elements continuously measure the three phase-to-neutral...
Page 246
Start st1l1 st1l2 st1l3 tr1l1 tr1l2 tr1l3 st1 tr1 start st2l1 st2l2 st2l3 tr2l1 tr2l2 tr2l3 st2 tr2 trip comparator ul1 comparator ul2 comparator ul3 minvoltselector comparator ul1 comparator ul2 ul3 minvoltselector start t1 & trip output logic step 1 start t2 & trip output logic step 2 phase 3 phas...
Page 247
Function range or value accuracy inverse time characteristics for step 1 and step 2, see table 675 - see table 675 definite time delay, step 1 at 1.2 x u set to 0 (0.00-6000.00) s ±0.2% or ±40ms whichever is greater definite time delay, step 2 at 1.2 x u set to 0 (0.000-60.000) s ±0.2% or ±40ms whic...
Page 248
Ov2ptov has a high reset ratio to allow settings close to system service voltage. 9.2.3 function block m13803-3 v6 iec06000277-2-en.Vsd ov2ptov u3p* block blktr1 blkst1 blktr2 blkst2 trip tr1 tr1l1 tr1l2 tr1l3 tr2 tr2l1 tr2l2 tr2l3 start st1 st1l1 st1l2 st1l3 st2 st2l1 st2l2 st2l3 iec06000277 v2 en-...
Page 249
Name type description tr2l2 boolean trip signal from step2 phase l2 tr2l3 boolean trip signal from step2 phase l3 start boolean general start signal st1 boolean common start signal from step1 st1l1 boolean start signal from step1 phase l1 st1l2 boolean start signal from step1 phase l2 st1l3 boolean ...
Page 250
Name values (range) unit step default description opmode2 1 out of 3 2 out of 3 3 out of 3 - - 1 out of 3 number of phases required for op (1 of 3, 2 of 3, 3 of 3) from step 2 u2> 1.0 - 200.0 %ub 0.1 150.0 voltage setting/start val (dt & idmt) in % of ubase, step 2 t2 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 5.000 de...
Page 251
Name values (range) unit step default description dcrv2 0.000 - 60.000 - 0.001 0.000 parameter d for customer programmable curve for step 2 pcrv2 0.000 - 3.000 - 0.001 1.000 parameter p for customer programmable curve for step 2 crvsat2 0 - 100 % 1 0 tuning param for prog. Over voltage idmt curve, s...
Page 252
The setting of the analog inputs are given as primary phase-to-earth or phase-to- phase voltage. Ov2ptov will operate if the voltage gets higher than the set percentage of the set base voltage ubase. This means operation for phase-to-earth voltage over: (%) ( ) 3 u ubase kv > × equation1434 v1 en-us...
Page 253
Where: un> set value for step 1 and step 2 u measured voltage the type b curve is described as: 2.0 480 0.035 32 0.5 n n k t u u u iecequation2423 v2 en-us (equation 44) the type c curve is described as: 3.0 480 0.035 32 0.5 n n k t u u u × = + æ ö - > × - ç ÷ > è ø iecequation2425 v1 en-us (equatio...
Page 254
Iec05000016-2-en.Vsd voltage idmt voltage time ul1 ul2 ul3 iec05000016 v2 en-us figure 112: voltage used for the inverse time characteristic integration operation of the trip signal requires that the overvoltage condition continues for at least the user set time delay. This time delay is set by the ...
Page 255
Trip u1> trip t time time integrator t frozen timer instantaneous voltage voltage time hystabs1 start start tireset1 measured tireset1 linearly decreased iec09000055-2-en.Vsd iec09000055 v2 en-us figure 113: voltage profile not causing a reset of the start signal for step 1, and inverse time delay a...
Page 256
Time integrator voltage time start trip start u1> start trip t tireset1 time t frozen timer linearly decreased instantaneous measured voltage tireset1 iec05000020-3-en.Vsd hystabs1 iec05000020 v3 en-us figure 114: voltage profile causing a reset of the start signal for step 1, and inverse time delay...
Page 257
U1> u a>b a b t treset1 t t1 and tr1 st1 off delay on delay iec10000100-2-en.Vsd iec10000100 v2 en-us figure 115: logic diagram for step 1, definite time delay, dt operation treset1 u1> start trip t1 iec10000037-2-en.Vsd iec10000037 v2 en-us figure 116: example for step 1, definite time delay stage ...
Page 258
Treset1 u1> start trip t1 iec10000038-2-en.Vsd iec10000038 v2 en-us figure 117: example for definite time delay stage 1 operation 9.2.7.3 blocking m15330-20 v8 it is possible to block two step overvoltage protection ov2ptov partially or completely, by binary input signals where: block: blocks all ou...
Page 259
Start st1l1 st1l2 st1l3 tr1l1 tr1l2 tr1l3 st1 tr1 start st2l1 st2l2 st2l3 tr2l1 tr2l2 tr2l3 st2 tr2 start trip comparator ul1 > u1> comparator ul2 > u1> comparator ul3 > u1> maxvoltselect comparator ul1 > u2> comparator ul2 > u2> comparator ul3 > u2> maxvoltselect start t1 t1reset & trip output logi...
Page 260
Function range or value accuracy definite time delay, low step (step 1) at 0 to 1.2 x u set (0.00 - 6000.00) s ±0.2% or ±45 ms whichever is greater definite time delay, high step (step 2) at 0 to 1.2 x u set (0.000-60.000) s ±0.2% or ±45 ms whichever is greater minimum operate time, inverse characte...
Page 261
9.3.3 function block m13812-3 v6 iec06000278-2-en.Vsd rov2ptov u3p* block blktr1 blkst1 blktr2 blkst2 trip tr1 tr2 start st1 st2 iec06000278 v2 en-us figure 119: rov2ptov function block 9.3.4 signals pid-3531-inputsignals v5 table 129: rov2ptov input signals name type default description u3p group s...
Page 262
9.3.5 settings pid-3531-settings v5 table 131: rov2ptov group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off / on operationstep1 off on - - on enable execution of step 1 characterist1 definite time inverse curve a inverse curve b inverse cur...
Page 263
Name values (range) unit step default description acrv1 0.005 - 200.000 - 0.001 1.000 parameter a for customer programmable curve for step 1 bcrv1 0.50 - 100.00 - 0.01 1.00 parameter b for customer programmable curve for step 1 ccrv1 0.0 - 1.0 - 0.1 0.0 parameter c for customer programmable curve fo...
Page 264
9.3.7 operation principle m15331-3 v8 two step residual overvoltage protection rov2ptov is used to detect a high residual voltage. The residual voltage can be measured directly from a voltage transformer in the neutral of a power transformer or from a three-phase voltage transformer, where the secon...
Page 265
The type b curve is described as: 2.0 480 0.035 32 0.5 n n k t u u u iecequation2423 v2 en-us (equation 49) the type c curve is described as: 3.0 480 0.035 32 0.5 n k t u u u × = + - > æ ö × - ç ÷ > è ø iecequation2421 v1 en-us (equation 50) the customer programmable curve can be created as: p n n k...
Page 266
Here it should be noted that after leaving the hysteresis area, the start condition must be fulfilled again and it is not sufficient for the signal to only return back to the hysteresis area. Also, notice that for the overvoltage function, idmt reset time is constant and does not depend on the volta...
Page 267
Time integrator voltage time start trip start u1> start trip t tireset1 time t frozen timer linearly decreased instantaneous measured voltage tireset1 iec05000020-3-en.Vsd hystabs1 iec05000020 v3 en-us figure 121: voltage profile causing a reset of the start signal for step 1, and inverse time delay...
Page 268
U1> u a>b a b t treset1 t t1 and tr1 st1 off delay on delay iec10000100-2-en.Vsd iec10000100 v2 en-us figure 122: logic diagram for step 1, definite time delay, dt operation u1 st1 tr1 treset1 t1 iec10000039-3-en.Vsd iec10000039 v3 en-us figure 123: example for definite time delay stage 1 reset sect...
Page 269
U1 st1 tr1 treset1 t1 iec10000040-3-en.Vsd iec10000040 v3 en-us figure 124: example for definite time delay stage 1 operation 9.3.7.3 blocking m15331-18 v7 it is possible to block two step residual overvoltage protection rov2ptov partially or completely by binary input signals where: block: blocks a...
Page 270
Iec05000748_2_en.Vsd un st1 tr1 st2 tr2 start trip comparator un > u1> start t2 treset2 & trip output logic step 2 phase 1 phase 1 time integrator tireset2 resettypecrv2 start start t1 treset1 & trip output logic step 1 time integrator tireset1 resettypecrv1 comparator un > u2> start trip trip or or...
Page 271
Function range or value accuracy minimum operate time (0.000-60.000) s ± 0.2% or ± 45 ms whichever is greater operate time, start at 0 to 2 x u set min. = 15 ms max. = 30 ms - reset time, start at 2 x u set to 0 min. = 15 ms max. = 30 ms - operate time, start at 0 to 1.2 x u set min. = 20 ms max. = ...
Page 272
266.
Page 273
Section 10 frequency protection 10.1 underfrequency protection saptuf ip15746-1 v3 10.1.1 identification m14865-1 v5 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number underfrequency protection saptuf f symbol-p v1 en-us 81 10.1.2 functionality m1334...
Page 274
10.1.4 signals pid-6752-inputsignals v2 table 136: saptuf input signals name type default description u3p group signal - three phase group signal for voltage inputs block boolean 0 block of function blktrip boolean 0 blocking operate output blkrest boolean 0 blocking restore output pid-6752-outputsi...
Page 275
Table 139: saptuf non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description globalbasesel 1 - 12 - 1 1 selection of one of the global base value groups 10.1.6 operation principle m13354-3 v9 underfrequency protection saptuf is used to detect low power system frequency. Saptuf can ...
Page 276
Hysteresis area, the start condition must be fulfilled again and it is not sufficient for the signal to only return back to the hysteresis area. The total time delay consists of the set value for time delay plus the minimum operate time of the start function (80-90 ms). On the restore output of sapt...
Page 277
90 95 100 0 0.5 1 en05000075.Vsd t im ed ly o pe ra te [s ] u [% of ubase] exponenent 0 1 2 3 4 iec05000075 v1 en-us figure 127: voltage dependent inverse time characteristics for underfrequency protection saptuf. The time delay to operate is plotted as a function of the measured voltage, for the ex...
Page 278
Frequency f voltage start trip restore u block f > restorefreq block or definite timer or voltage based timer treset tdelay trestore restore iec16000041-1-en.Vsdx trip start blktrip and start & trip output logic blkrest and blkdmagn iec16000041 v1 en-us figure 128: simplified logic diagram for saptu...
Page 279
Function range or value accuracy reset time, definite time function at f set - 0.02 hz to f set + 0.02 hz (0.000-60.000)s ±0.2% or ±120 ms whichever is greater voltage dependent time delay settings: unom=(50-150)% of u base umin=(50-150)% of u base exponent=0.0-5.0 tmax=(0.010–60.000)s tmin=(0.010–6...
Page 280
How to connect analog inputs, refer to application manual/ied application/ analog inputs/setting guidelines. 10.2.3 function block m14956-3 v5 iec06000280_2_en.Vsd saptof u3p* block blktrip trip start blkdmagn freq iec06000280 v2 en-us figure 129: saptof function block 10.2.4 signals pid-6751-inputs...
Page 281
Table 144: saptof non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description globalbasesel 1 - 12 - 1 1 selection of one of the global base value groups 10.2.6 operation principle m14958-3 v7 overfrequency protection saptof is used to detect high power system frequency. Saptof has ...
Page 282
10.2.6.3 blocking m14958-13 v7 it is possible to block overfrequency protection saptof partially or completely, by binary input signals or by parameter settings, where: block: blocks the start and trip outputs blktrip: blocks the trip output if the measured voltage level decreases below the setting ...
Page 283
10.2.7 technical data m14964-1 v12 table 145: saptof technical data function range or value accuracy operate value, start function at symmetrical three-phase voltage (35.00-90.00) hz ±2.0 mhz operate time, start at f set -0.02 hz to f set +0.02 hz fn = 50hz min. = 80 ms max. = 95 ms - fn = 60 hz min...
Page 284
Analog inputs, refer to application manual/ied application/analog inputs/ setting guidelines. 10.3.3 function block m14968-3 v6 iec06000281-2-en.Vsd sapfrc u3p* block blktrip blkrest trip start restore blkdmagn iec06000281 v2 en-us figure 131: sapfrc function block 10.3.4 signals pid-6754-inputsigna...
Page 285
Name values (range) unit step default description restorefreq 45.00 - 65.00 hz 0.01 49.90 restore frequency value trestore 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.000 restore time delay treset 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.000 time delay for reset table 149: sapfrc non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit st...
Page 286
Trip signal issuing requires that the rate-of-change of frequency condition continues for at least the user set time delay, tdelay. If the start condition, with respect to the measured frequency ceases during the delay time, and is not fulfilled again within a user defined reset time, treset, the st...
Page 287
Iec16000040-1-en.Vsdx restore voltage start start trip block if [startfreqgrad and df/dt or [startfreqgrad>0 and df/dt > startfreqgrad] then start u blkdmagn rate-of-change of frequency block or blkrest > f > restorefreq trestore restore and blktrip trip and start start & trip output logic definite ...
Page 288
282.
Page 289
Section 11 secondary system supervision 11.1 current circuit supervision ccsspvc ip14555-1 v5 11.1.1 identification m14870-1 v5 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number current circuit supervision ccsspvc - 87 11.1.2 functionality m12444-3 ...
Page 290
11.1.4 signals pid-6806-inputsignals v2 table 151: ccsspvc input signals name type default description i3p group signal - group signal for three phase current input iref group signal - residual reference current input block boolean 0 block of function pid-6806-outputsignals v2 table 152: ccsspvc out...
Page 293
11.2.2 functionality semod113820-4 v12 the aim of the fuse failure supervision function (fufspvc) is to block voltage measuring functions at failures in the secondary circuits between the voltage transformer and the ied in order to avoid inadvertent operations that otherwise might occur. The fuse fa...
Page 294
11.2.4 signals pid-3492-inputsignals v9 table 157: fufspvc input signals name type default description i3p group signal - current connection u3p group signal - voltage connection block boolean 0 block of function cbclosed boolean 0 active when circuit breaker is closed mcbop boolean 0 active when ex...
Page 295
11.2.5 settings pid-3492-settings v9 table 159: fufspvc group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off / on opmode off unsins uzsizs uzsizs or unsins uzsizs and unsins optimzsns - - uzsizs operating mode selection 3u0> 1 - 100 %ub 1 30...
Page 296
11.2.6 monitored data pid-3492-monitoreddata v8 table 161: fufspvc monitored data name type values (range) unit description 3i0 real - a magnitude of zero sequence current 3i2 real - a magnitude of negative sequence current 3u0 real - kv magnitude of zero sequence voltage 3u2 real - kv magnitude of ...
Page 297
Il1 il2 il3 zero sequence filter negative sequence filter ul1 ul2 ul3 zero sequence filter negative sequence filter currzeroseq currnegseq a b a>b a b a>b a b a>b a b a>b 3i2 t 100 ms t 100 ms voltzeroseq voltnegseq and and fusefaildetzeroseq fusefaildetnegseq sequence detection 3u0> 3u2> 3i0 3i2 3u...
Page 298
The opening of the breaker, which might cause unbalance conditions for which the fuse failure might operate. The output signal blkz will also be blocked if the internal dead line detection is activated. The dead line detection signal has a 200 ms drop-out time delay. The input signal mcbop is suppos...
Page 299
• the magnitude of the phase-ground voltage has been above uph> for more than 1.5 cycles (i.E. 30 ms in a 50 hz system) • the magnitudes of du in three phases are higher than the corresponding setting du> • the magnitudes of di in three phases are below the setting di in addition to the above condit...
Page 300
Di ul1 du> a b a>b t 20 ms t 1.5 cycle and dudi detection phase 1 uph> dudi detection phase 2 same logic as for phase 1 il1 dudi detection phase 3 same logic as for phase 1 ul3 a b a ul1 il1 a b a>b iph> and and cbclosed or or and a b a ul2 il2 a b a>b and and or or and a b a ul3 il3 a b a>b and and...
Page 301
Deltail1 deltaul1 deltail2 deltaul2 deltail3 deltaul3 stdil1 stdil2 stdil3 stdi stdu stdul1 stdul2 stdul3 iec12000165-1-en.Vsd intblock or or 20 ms 20 ms or t 20 ms t 20 ms t 20 ms and and and and and and and and t 20 ms t 20 ms t 20 ms t 20 ms t t iec12000165 v1 en-us figure 139: internal signals d...
Page 302
Il1 il2 il3 a b a a b a a b a idld ul1 ul2 ul3 a b a a b a a b a udld or and and and and and and and allcurrlow deadlinedet1ph dld3ph dld1ph intblock dead line detection iec10000035-1-en.Vsd iec10000035 v2 en-us figure 140: simplified logic diagram for dead line detection part 11.2.7.4 main logic gu...
Page 303
As soon as any fuse failure situation is detected, signals fusefaildetzeroseq, fusefaildetnegseq or fusefaildetdudi, and the specific functionality is released, the function will activate the output signal blku. The output signal blkz will be activated as well if the internal dead phase detection, d...
Page 304
Sealin = on all ul usealin any ul usealin t 5 s and 3ph mcbop all ul > usealin t 60 s cbclosed block and test test active and blocfuse = yes opmode and t 200 ms and or discpos blku blkz and and fusefaildetzeroseq uzsizs or unsins uzsizs and unsins uzsizs unsins optimzsns and fusefaildetnegseq or and...
Page 305
11.2.8 technical data m16069-1 v12 table 162: fufspvctechnical data function range or value accuracy operate voltage, zero sequence (1-100)% of ubase ±0.5% of u r operate current, zero sequence (1–100)% of ibase ±0.5% of i r operate voltage, negative sequence (1-100)% of ubase ±0.5% of u r operate c...
Page 306
300
Page 307
Section 12 control 12.1 synchrocheck, energizing check, and synchronizing sesrsyn ip14558-1 v4 12.1.1 identification m14889-1 v4 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number synchrocheck, energizing check, and synchronizing sesrsyn sc/vc symbol...
Page 308
12.1.3 function block m12431-3 v7 sesrsyn u3pbb1* u3pbb2* u3pln1* u3pln2* block blksynch blksc blkenerg b1qopen b1qcld b2qopen b2qcld ln1qopen ln1qcld ln2qopen ln2qcld ub1ok ub1ff ub2ok ub2ff uln1ok uln1ff uln2ok uln2ff startsyn tstsynch tstsc tstenerg aenmode menmode synok autosyok autoenok mansyok...
Page 309
Name type default description b1qopen boolean 0 open status for cb or disconnector connected to bus1 b1qcld boolean 0 close status for cb or disconnector connected to bus1 b2qopen boolean 0 open status for cb or disconnector connected to bus2 b2qcld boolean 0 close status for cb or disconnector conn...
Page 310
Name type description tstenok boolean energizing check ok test output uselfail boolean selected voltage transformer fuse failed b1sel boolean bus1 selected b2sel boolean bus2 selected ln1sel boolean line1 selected ln2sel boolean line2 selected synprogr boolean synchronizing in progress synfail boole...
Page 311
12.1.5 settings pid-6724-settings v2 table 165: sesrsyn group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off / on operationsynch off on - - off operation for synchronizing function off/on uhighbussynch 50.0 - 120.0 %ubb 1.0 80.0 voltage high...
Page 312
Name values (range) unit step default description autoenerg off dllb dbll both - - dllb automatic energizing check mode manenerg off dllb dbll both - - both manual energizing check mode manenergdbdl off on - - off manual dead bus, dead line energizing uhighbusenerg 50.0 - 120.0 %ubb 1.0 80.0 voltage...
Page 313
Name values (range) unit step default description selphaseline1 phase l1 phase l2 phase l3 phase l1l2 phase l2l3 phase l3l1 positive sequence - - phase l1 select phase for line1 selphaseline2 phase l1 phase l2 phase l3 phase l1l2 phase l2l3 phase l3l1 positive sequence - - phase l1 select phase for ...
Page 314
The energizing check feature measures the bus and line voltages and compares them to both high and low threshold detectors. The output is given only when the actual measured quantities match the set conditions. The synchronizing feature measures the conditions across the circuit breaker, and also de...
Page 315
The frequency on both sides of the circuit breaker is also measured. The frequencies must not deviate from the rated frequency more than ±5hz. The frequency difference between the bus frequency and the line frequency is measured and may not exceed the set value freqdiff. Two sets of settings for fre...
Page 316
Operationsc = on or t 0-60 s and and and and and and t 50 ms uhighlinesc uhighbussc udiffsc phaseangledifferencevalue frequencydifferencevalue voltagedifferencevalue 1 1 1 and tsca phasediffa freqdiffa note! Similar logic for manual synchrocheck. Phdiff > 60° phdiff and 32 ms t and 100 ms invalidsel...
Page 317
Calculation of the operation pulse sent in advance is using the measured slipfrequency and the set tbreaker time. To prevent incorrect closing pulses, a maximum closing angle between bus and line is set with closeanglemax. Table 169 below shows the maximum settable value for tbreaker when closeangle...
Page 318
Or and s r udiffsynch uhighbussynch uhighlinesynch freqdiffmax freqdiffmin freqratechange and t 50 ms and and and and tclosepulse and startsyn blksynch synprogr synok synfail tmaxsynch tstsynok =iec06000636=5=en=original.Vsd fbus&fline ± 5hz phasediff=close pulse in advance tbreaker freqdiff tstsync...
Page 319
Block (b16i). Integers supplied shall be 1=off, 2=dllb, 3=dbll and 4= both. Not connected input will mean that the setting is done from parameter setting tool. The active position can be read on outputs modeaen resp modemen. The modes are 0=off, 1=dllb, 2=dbll and 3=both. The inputs block and blkene...
Page 320
Fbus and fline ±5 hz autoenerg uhighbusenerg ulowlineenerg and ulowbusenerg uhighlineenerg and or and or t tautoenerg and and umaxenerg autoenok tstenok selectedfuseok or block blkenerg tstenerg dllb dbll iec14000030-1-en.Vsd both iec14000030 v1 en-us figure 146: automatic energizing manenerg cbconf...
Page 321
Fuse failure supervision m14837-3 v11 external fuse failure signals or signals from a tripped fuse switch/mcb are connected to binary inputs that are configured to the inputs of sesrsyn function in the ied. Alternatively, the internal signals from fuse failure supervision can be used when available....
Page 322
Bus 1 voltage is used. All other combinations use the bus 2 voltage. The outputs b1sel and b2sel respectively indicate the selected bus voltage. The function checks the fuse-failure signals for bus 1, bus 2 and line voltage transformers. Inputs ub1ok-ub1ff supervise the mcb for bus 1 and ub2ok- ub2f...
Page 323
With the setting parameter cbconfig the selection of actual cb location in the 1 1/2 circuit breaker switchgear is done. The settings are: 1 1/2 bus cb, 1 1/2 alt. Bus cb or tie cb. This voltage selection function uses the binary inputs from the disconnectors and circuit breakers auxiliary contacts ...
Page 324
And and or or uln1ff uln1ok ub1ff ub1ok ub2ff ub2ok b1qcld b1qopen ln1qcld ln1qopen block ln1sel and and uselfail uln2ff uln2ok or and and b2qcld b2qopen ln2qcld ln2qopen and and ln2sel or and b2sel and and and en05000780-2.Vsd or or line2voltage bus2voltage line1voltage invalidselection linevoltage...
Page 325
And and or or uln1ff uln1ok ub1ff ub1ok ub2ff ub2ok b1qcld b1qopen ln1qcld ln1qopen block line1voltage ln1sel and and uselfail uln2ff uln2ok or and and and and and 1 b1sel bus1voltage and and and b2qcld b2qopen ln2qcld ln2qopen bus2voltage ln2sel and and 1 b2sel line2voltage or en05000781-2.Vsd or o...
Page 326
12.1.8 technical data m12359-1 v15 table 170: sesrsyn technical data function range or value accuracy phase shift, j line - j bus (-180 to 180) degrees - voltage high limit for synchronizing and synchrocheck (50.0-120.0)% of ubase ±0.5% of u r at u ≤ u r ±0.5% of u at u > u r reset ratio, synchroche...
Page 327
Function range or value accuracy maximum voltage for energizing (50.0-180.0)% of ubase ±0.5% of u r at u ≤ u r ±0.5% of u at u > u r time delay for energizing check when voltage jumps from 0 to 90% of urated (0.000-60.000) s ±0.2% or ±100 ms whichever is greater operate time for synchrocheck functio...
Page 328
Each auto reclosing function can be configured to co-operate with the synchrocheck function. 12.2.3 function block m12633-3 v6 iec06000189-3-en.Vsd smbrrec on off blkon blkoff reset inhibit start starths trsotf skiphs zonestep tr2p tr3p tholhold cbready cbclosed plclost sync wait rstcount modeint bl...
Page 329
Name type default description zonestep boolean 0 coordinate local ar with down stream devices tr2p boolean 0 two phase trip occurred tr3p boolean 0 three phase trip occurred tholhold boolean 0 hold ar in wait state cbready boolean 0 circuit breaker is ready cbclosed boolean 0 circuit breaker status ...
Page 330
Name type description count3p3 integer number of three-phase shot 3 reclosings count3p4 integer number of three-phase shot 4 reclosings count3p5 integer number of three-phase shot 5 reclosings countar integer number of total reclosing shots mode integer integer output for reclosing mode aborted bool...
Page 331
Name values (range) unit step default description priority none low high - - none priority selection between adjacent terminals twaitformaster 0.00 - 6000.00 s 0.01 60.00 maximum wait time for release from master longstartinhib off on - - on to be set on if ar is to be used with maximum allowed star...
Page 332
Name values (range) unit step default description zoneseqcoord off on - - off coordination of down stream devices to local protection unit’s ar tsuccessful 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 1.000 delay time before indicating successful reclosing tslavedeadtime 0.100 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.400 wait time for the sla...
Page 333
“ready” guid-04f154ec-e236-40a4-a3e0-7624a2f6b132 v1 the function is in “ready” status when the following conditions are fulfilled: • the circuit breaker is ready • the circuit breaker must have been closed for more that the set time in setting: tcbclosedmin • the function is not in “blocked” status...
Page 334
The empty cells in the table indicate that no such transition is possible. Table 175: status transition matrix to → inactive ready in progress (dead time) reclaim time blocked from ↓ inactive activate cbclosed and cbready activate blkon ready deactivate cbclosed or cbready or activate inhibit or res...
Page 335
• input signal sync is true, which typically indicates that power systems on the two sides of the circuit breaker are in synchronism • and that input signal cbready is true, typically indicating that circuit breaker springs are charged. If a circuit breaker close command is given successfully at the...
Page 336
Iec16000153-1-en.Vsdx trsotf operation and s r externalctrl and or s r and and or startbycbopen and and and and 100ms 100ms or or t 120ms t tcbclosedmin and or and and or and and seton on off initiate start cbready cbclosed ready starths startthermal inhibit inhibit start count0 cbready cbclosed iec...
Page 337
Table 176: type of reclosing shots at different settings of “armode” or integer inputs to "modeint" modeint (integer) armode type of fault 1st shot 2nd - 5th shot 1 3ph 1ph 3ph 3ph 2ph 3ph 3ph 3ph 3ph 3ph 2 1/2/3ph 1ph 1ph 3ph 2ph 2ph 3ph 3ph 3ph 3ph 3 1/2ph 1ph 1ph 3ph 2ph 2ph 3ph 3ph - - 4 1ph+1x2...
Page 338
A time extension delay, textended t1, can be added to the dead time delay for the first shot. It is intended to come into use if the communication channel for permissive line protection is lost. In a case like this there can be a significant time difference in fault clearance at the two line ends, w...
Page 339
• cbready: circuit breaker is ready for a reclosing cycle, for example, charged operating gear. • cbclosed: to ensure that the circuit breaker was closed when the line fault occurred and start was applied. The cbclosed condition must be present for more that the settable time tcbclosedmin. • no blko...
Page 340
Open (no) shall be connected to the cbclosed and start inputs. Then the circuit breaker status change from closed to open will generate an auto reclosing start pulse of limited length (100ms) subject to the usual auto recloser checks. The auto reclosing sequence continues then as usual. Signals from...
Page 341
• inhibitwaitformaster: after expiration of the twaitformaster time for the wait input to reset, the reclosing cycle of the slave is inhibited. • longstartinhibit: if start pulse duration is longer than the tlongstartinh time, the reclosing cycle is inhibited. The aborted output indicates that the a...
Page 342
Auto reclosing sequence guid-78aae7cd-702e-407b-94d2-6a70bafc8e70 v1 when the function has started and the dead time has elapsed during the auto reclosing sequence, certain conditions must be fulfilled before the circuit breaker closing command is issued. In three-phase reclosing, a synchrocheck and...
Page 343
Iec16000157-1-en.Vsdx and cbclosed t tunsuccl and initiate reclaimtimestarted or and s r or and unsuccl unsuccessful or unsucclbycbchk t tunsuccl commandclosecb or and and s r t tsuccessful count0 succl iec16000157 v1 en-us figure 156: successful/unsuccessful figure 157 shows the logic for most part...
Page 344
Iec16000158-1-en.Vsdx a n d zo n es e q c oo rd a n d de ad t im e t te xt e n d ed t 1 te xt e n d ed t 1 is ad d e d t o t 1 1 ph o r t1 2 p h o r t1 3 ph t1 1 ph t1 2 ph t1 3 ph t2 3 ph t3 3 ph t4 3 ph t5 3 ph t t ts la ve de ad tim e sk ip s h ig h -s p e ed s h o t (t 1 3 p h h s) an d co n tin...
Page 345
A number of outputs from the function keeps track of the actual state in the auto reclosing sequence. The outputs are: • inprogr: any dead time is in progress • 1pt1, 2pt1, 3pt1, 3pt2, 3pt3, 3pt4 and 3pt5: dead time is in progress for respective shot and fault type • active: during dead time + recla...
Page 346
There are several counters within the function. One for each shot and type of fault and one overall counter for total number of circuit breaker closing commands. All counters can be reset to zero using either the hmi command or the rstcount input or by an iec 61850 command. The circuit breaker closi...
Page 347
Iec16000159-1-en.Vsdx and or q -1 and 20ms start tholhold inhibit startthermal inhibitthermalstart and s r iec16000159 v1 en-us figure 158: thermal protection hold the auto recloser is set as master or slave in multi-breaker arrangements with sequential reclosing with the setting priority. The auto ...
Page 348
Iec16000160-1-en.Vsdx priority and or high (master) inprogress unsuccessful wfmaster master: slave: priority low (slave) and and start wait t twaitformaster and and s r or inhibit commandclosecb reclaimtimestarted inhibitwaitformaster slavedeadtime wait iec16000160 v1 en-us figure 159: master-slave ...
Page 349
Cbready fault succl prep3p closecb active 1pt1 inprogr ready sync start cbclosed closed open closed tpulse t1 1ph treclaim time iec04000196-4-en.Vsd iec04000196 v4 en-us figure 160: transient single-phase fault, single-phase reclosing cbready fault unsuccl active 3pt2 3pt1 inprogr ready sync tr3p st...
Page 350
Cbready fault unsuccl 3pt2 3pt1 1pt1 inprogr ready sync tr3p start cbclosed iec04000198-3-en.Vsd prep3p closecb t1 1ph treclaim iec04000198 v3 en-us figure 162: permanent single-phase fault, single-phase trip, single-shot reclosing, armode=1/2/3ph section 12 1mrk 505 394-uen a control 344 line diffe...
Page 351
Cbready cbclosed iec04000199-3-en.Vsd t1 1ph t2 3ph treclaim fault unsuccl 3pt2 3pt1 1pt1 inprogr ready sync tr3p start prep3p closecb iec04000199 v3 en-us figure 163: permanent single-phase fault, single-phase trip, two-shot reclosing, armode=1ph + 1*2ph 12.2.7 technical data m12379-1 v13 table 180...
Page 352
Function range or value accuracy reclaim time ”treclaim” (0.00-6000.00) s ±0.2% or ±15 ms whichever is greater maximum wait time for release from master “twaitformaster” (0.00-6000.00) s ±0.2% or ±15 ms whichever is greater reset time for reclosing inhibit “tinhibit” (0.000-60.000) s ±0.2% or ±45 ms...
Page 353
12.3.1.4 signals pid-3487-inputsignals v7 table 181: scilo input signals name type default description posopen boolean 0 open position of switch device posclose boolean 0 closed position of switch device open_en boolean 0 open operation from interlocking logic is enabled close_en boolean 0 close ope...
Page 354
12.4 apparatus control apc ip14560-1 v2 12.4.1 functionality m13444-3 v15 the apparatus control functions are used for control and supervision of circuit breakers, disconnectors and earthing switches within a bay. Permission to operate is given after evaluation of conditions from other functions suc...
Page 355
In normal security, the command is processed and the resulting position is not supervised. However with enhanced security, the command is processed and the resulting position is supervised. Normal security means that only the command is evaluated and the resulting position is not supervised. Enhance...
Page 356
Control function reflecting the switchyard configuration. The total number used depends on the switchyard configuration. These types are: • bay control qcbay • switch controller scswi • circuit breaker sxcbr another function block type for supervision and control is the xlnproxy. It is used for inte...
Page 357
Cause number name description supported 7 step-limit control action is blocked, because tap changer has reached the limit (endposr or endposl in yltc) x 8 blocked-by-mode control action is blocked, because the ln (cswi or xcbr) is in a mode (mod) which doesn’t allow any switching x 9 blocked-by-proc...
Page 358
Cause number name description supported -25 blocked-for-close- cmd blocked for close command x -30 long-operation-time operation time too long x -31 switch-not-start- moving switch did not start moving x -32 persistent- intermediate-state switch stopped in intermediate state x -33 switch-returned-to...
Page 359
Internal cause number addcause in iec 61850-8-1 name ed 2 ed 1 -22 0 -22 wrong-ctl-model -24 9 -24 blocked-for-open-cmd -25 9 -25 blocked-for-close-cmd -30 16 -30 long-operation-time -31 16 -31 switch-not-start-moving -32 4 -32 persistent-intermediate-state -33 22 -33 switch-returned-to-init-pos -34...
Page 360
12.4.4.1 functionality m13447-3 v8 the bay control (qcbay) function is used together with local remote and local remote control functions to handle the selection of the operator place per bay. Qcbay also provides blocking functions that can be distributed to different apparatuses within the bay. 12....
Page 361
12.4.4.4 settings pid-4086-settings v8 table 188: qcbay non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description allpstovalid priority no priority - - priority override priority of originators, commands from both local, station and remote are allowed remoteincstation no yes - - n...
Page 362
Operate from local, station and remote level without any priority. When the external panel switch is in off position, the psto output shows the actual state of the switch that is, 0. In this case, it is not possible to control anything. The locsta command value is forced to false if allpstovalid is ...
Page 363
• blocking of position indications, bl_upd. This input will block all inputs related to apparatus positions for all configured functions within the bay. • blocking of commands, bl_cmd. This input will block all commands for all configured functions within the bay. The switching of the local/remote s...
Page 364
12.4.5.2 signals pid-3944-inputsignals v7 table 190: locrem input signals name type default description ctrloff boolean 0 disable control locctrl boolean 0 local in control remctrl boolean 0 remote in control lhmictrl integer 0 lhmi control pid-3944-outputsignals v7 table 191: locrem output signals ...
Page 365
Name type description hmictr4 integer bitmask output 4 to local remote lhmi input hmictr5 integer bitmask output 5 to local remote lhmi input hmictr6 integer bitmask output 6 to local remote lhmi input hmictr7 integer bitmask output 7 to local remote lhmi input hmictr8 integer bitmask output 8 to lo...
Page 366
Qcbay lr_ off lr_ loc lr_ rem lr_ valid bl_ upd bl_ cmd psto upd_ blkd cmd_ blkd locrem ctrloff locctrl remctrl lhmictrl off local remote valid locremctrl psto1 psto2 psto3 psto4 psto5 psto6 psto7 psto8 psto9 psto 10 psto 11 psto 12 hmictr1 hmictr2 hmictr3 hmictr4 hmictr5 hmictr6 hmictr7 hmictr8 hmi...
Page 367
12.4.6.1 functionality m13486-3 v8 the switch controller (scswi) initializes and supervises all functions to properly select and operate switching primary apparatuses. The switch controller may handle and operate on one multi-phase device or up to three one-phase devices. 12.4.6.2 function block m13...
Page 368
Name type default description xposl1 group signal - group signal from xcbr/xswi per phase xposl2 group signal - group signal from xcbr/xswi per phase xposl3 group signal - group signal from xcbr/xswi per phase pid-6798-outputsignals v3 table 196: scswi output signals name type description selected b...
Page 369
L_open or l_close is operated, if the control model is select before operate. If one multi-phase xcbr or two single-phase xcbr is used for a two- or three-phase system, two or more of the inputs xposl1, xposl2 and xposl3 are connected to the same source. 12.4.6.4 settings pid-6798-settings v3 table ...
Page 370
Parameter ctlmodel defines which one of the two control models is used. The control model "direct with normal security" does not require a select whereas, the "sbo with enhanced security" command model requires a select before execution. The command sequence for a command with control mode sbo with ...
Page 371
Client reservation core switchctrl core switch core res_grt = true exe_cl operateack/addcause = 0 position = 00, timestamp res_grt = false operateack/addcause = 0 requestedposition = 10 oprcvd = true opok = true, topok position = 00, timestamp position = 10, timestamp res_rq res_rq = false tre serva...
Page 372
All switches in open position: switch control position = open all switches in closed position: switch control position = closed at least one switch in open position and the other(s) in closed position: switch control position = intermediate any switch in intermediate position: switch control positio...
Page 373
And au_close, the operator place is not evaluated. If the operator place is set to off, the commands through the inputs au_open and au_close are not accepted. Interaction with synchrocheck and synchronizing functions m13484-47 v5 the switch controller (scswi) works in conjunction with the synchroche...
Page 374
The timer tselect is used for supervising the time between the select and the execute command signal, that is, the time the operator has to perform the command execution after the selection of the object to operate. Select tselect timer execute command t1 t1>tselect, then long- operation-time in 'ca...
Page 375
Execute command position l1 t1>texecutionfb, then long-operation-time in 'cause' is set open close close open position l3 close open position l2 t1 texecutionfb timer cmd termination l1 cmd termination l2 cmd termination l3 cmd termination position open close * the cmd termination will be delayed on...
Page 376
Execute command sy_inpro sync_ok t2>tsynchronizing, then blocked-by-synchrocheck in 'cause' is set tsynchrocheck t1 start_sy tsynchronizing t2 en05000095.Vsd iec05000095 v1 en-us figure 177: tsynchrocheck and tsynchronizing 12.4.6.6 interaction with switch on process bus guid-1e243260-55fc-4da6-a314...
Page 377
Client reservation logic scswi select tse le ct tr es erv ati on r es po n se tex ec uti on f b res_grt = true sel_cl = true selected = true selectack/addcause = 0 res_grt = false operateack/addcause = 0 requestedposition = 10 oprcvd = true opok = true, topok position = 00, timestamp position = 10, ...
Page 378
12.4.7.2 function block m13500-3 v5 sxcbr block lr_swi open close bl_open bl_close bl_upd posop en posclose cbopcap tr_open tr_close rs_cnt eeh_warn eeh_alm xin* xpos exe_op exe_cl op_blkd cl_blkd upd_blkd openp os closepos tr_pos cnt_val l_cause eehealth cbopcap iec05000338-4-en.Vsdx iec05000338 v5...
Page 379
Pid-6799-outputsignals v2 table 199: sxcbr output signals name type description xpos group signal group connection to cswi for xcbr and xswi exe_op boolean executes the command for open direction exe_cl boolean executes the command for close direction op_blkd boolean indication that the function is ...
Page 380
Allowed, the function performs the execution command. In case of erroneous conditions, the function indicates an appropriate "cause" value, see table 183 . Sxcbr has an operation counter for closing and opening commands. The counter value can be read remotely from the operator place. The value is re...
Page 381
The above blocking outputs are stored in a non-volatile memory. Substitution m13487-22 v5 the substitution part in sxcbr is used for manual set of the position and quality of the switch. The typical use of substitution is that an operator enters a manual value because that the real process value is ...
Page 382
Exe_cl tstartmove timer openpos closepos tintermediate timer t1 t2 tstartmove tintermediate if t1 > tstartmove then "switch-not-start-moving" attribute in 'cause' is set if t2 > tintermediate then "persisting-intermediate-state" attribute in 'cause' is set close pulse duration adaptivepulse = true e...
Page 383
• the new expected final position is reached and the configuration parameter adaptivepulse is set to true • the timer topenpulse or tclosepulse has elapsed • an error occurs due to the switch does not start moving, that is, tstartmove has elapsed. If the breaker reaches the final position before the...
Page 384
12.4.8 proxy for signals from switching device via goose xlnproxy 12.4.8.1 functionality guid-11f9ca1c-8e20-489b-822b-34dacc59553a v1 the proxy for signals from switching device via goose (xlnproxy) gives an internal representation of the position status and control response for a switch modelled in...
Page 385
Name type default description blkcls_vld boolean 0 valid data on blkcls input posval integer 0 switch position, pos.Stval posval_vld boolean 0 valid data on posval input opcnt integer -1 operation counter opcnt_vld boolean 0 valid data on opcnt input blk boolean 0 dynamic blocking of function descri...
Page 386
12.4.8.4 settings pid-6712-settings v3 table 203: xlnproxy non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description switchtype circuit breaker load break disconnector earthing switch hs earth switch - - circuit breaker 0 = cb, 1 = load break, 2 = disconnector, 3 = earthing switch...
Page 387
Desired position within the two time limits tstartmove and tintermediate. The default values for tstartmove and tintermediate are for a breaker. The typical values for a disconnector are: • tstartmove = 3s • tintermediate = 15s in most cases, tstartmove and tintermediate can be set to the same value...
Page 388
If the quality of the position or the communication becomes bad, the command evaluation replaces the uncertain position value with intermediate position. Thus, as long as the quality is bad, all commands will result in the cause persistant- intermediate-state, -32. If the switch in the merging unit ...
Page 389
Sources for maintenance issues, lower system reliability and an extended purchase portfolio. The selector switch function eliminates all these problems. 12.5.3 function block semod114954-4 v6 slgapc block psto up down ^p01 ^p02 ^p03 ^p04 ^p05 ^p06 ^p07 ^p08 ^p09 ^p10 ^p11 ^p12 ^p13 ^p14 ^p15 ^p16 ^p...
Page 390
Pid-6641-outputsignals v3 table 206: slgapc output signals name type description p01 boolean selector switch position 1 p02 boolean selector switch position 2 p03 boolean selector switch position 3 p04 boolean selector switch position 4 p05 boolean selector switch position 5 p06 boolean selector swi...
Page 391
12.5.5 settings pid-6641-settings v3 table 207: slgapc non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off/on nrpos 2 - 32 - 1 32 number of positions in the switch outtype pulsed steady - - steady output type, steady or pulse tpulse 0.0...
Page 392
Slgapc function block has also an integer value output, that generates the actual position number. The positions and the block names are fully settable by the user. These names will appear in the menu, so the user can see the position names instead of a number. 12.5.7.1 graphical display semod114931...
Page 393
From the graphical display: iec06000421-3-en.Vsdx i ../control/sld/switch smbrrec control wfm pilo t se tup off damage control dal ../control/sld/switch smbrrec control wfm pilo t se tup off p: disc n: disc fe ok cancel ../control/sld/switch smbrrec control wfm pilo t se tup off damage control dfw c...
Page 394
12.6.2 functionality semod158756-5 v9 the selector mini switch (vsgapc) function block is a multipurpose function used for a variety of applications, as a general purpose switch. Vsgapc can be controlled from the menu, from a symbol on the single line diagram (sld) on the local hmi or from binary in...
Page 395
12.6.5 settings pid-6504-settings v6 table 211: vsgapc non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off / on ctlmodel dir norm sbo enh - - dir norm specifies the type for control model according to iec 61850 mode steady pulsed - - pu...
Page 396
The following table shows the relationship between ipos1/ipos2 inputs and the name of the string that is shown on the sld. The value of the strings are set in pst. Ipos1 ipos2 name of displayed string default string value 0 0 posundefined p00 1 0 position1 p01 0 1 position2 p10 1 1 posbadstate p11 1...
Page 397
12.7.4 signals semod55883-1 v2 pid-4139-inputsignals v12 table 212: dpgapc input signals name type default description open boolean 0 open indication close boolean 0 close indication valid boolean 0 valid indication pid-4139-outputsignals v11 table 213: dpgapc output signals name type description po...
Page 398
Table 214: description of the input-output relationship valid open close position value description 0 - - 0 intermediate 1 0 0 0 intermediate 1 1 0 1 open 1 0 1 2 closed 1 1 1 3 bad state 12.8 single point generic control 8 signals spc8gapc semod176448-1 v3 12.8.1 identification semod176456-2 v3 fun...
Page 399
12.8.4 signals pid-3575-inputsignals v8 table 215: spc8gapc input signals name type default description block boolean 0 blocks the function operation psto integer 1 operator place selection pid-3575-outputsignals v8 table 216: spc8gapc output signals name type description out1 boolean command output...
Page 400
Name values (range) unit step default description pulsemode6 pulsed latched - - pulsed setting for pulsed/latched mode for output 6 tpulse6 0.01 - 6000.00 s 0.01 0.10 pulse time output 6 pulsemode7 pulsed latched - - pulsed setting for pulsed/latched mode for output 7 tpulse7 0.01 - 6000.00 s 0.01 0...
Page 401
Autobits function plays the same role as functions goosebinrcv (for iec 61850) and multicmdrcv (for lon). 12.9.3 function block semod158603-4 v3 iec09000925-1-en.Vsd autobits block psto ^cmdbit1 ^cmdbit2 ^cmdbit3 ^cmdbit4 ^cmdbit5 ^cmdbit6 ^cmdbit7 ^cmdbit8 ^cmdbit9 ^cmdbit10 ^cmdbit11 ^cmdbit12 ^cm...
Page 402
Name type description cmdbit5 boolean command out bit 5 cmdbit6 boolean command out bit 6 cmdbit7 boolean command out bit 7 cmdbit8 boolean command out bit 8 cmdbit9 boolean command out bit 9 cmdbit10 boolean command out bit 10 cmdbit11 boolean command out bit 11 cmdbit12 boolean command out bit 12 ...
Page 403
12.9.6 operation principle semod158597-4 v5 automationbits function (autobits) has 32 individual outputs which each can be mapped as a binary output point in dnp3. The output is operated by a "object 12" in dnp3. This object contains parameters for control-code, count, on-time and off-time. To opera...
Page 404
12.10.3 function block semod116040-4 v2 iec05000698-2-en.Vsd singlecmd block ^out1 ^out2 ^out3 ^out4 ^out5 ^out6 ^out7 ^out8 ^out9 ^out10 ^out11 ^out12 ^out13 ^out14 ^out15 ^out16 iec05000698 v3 en-us figure 191: singlecmd function block 12.10.4 signals pid-6189-inputsignals v6 table 221: singlecmd ...
Page 405
12.10.5 settings pid-6189-settings v6 table 223: singlecmd non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off steady pulsed - - off operation off / on 12.10.6 operation principle m12447-3 v3 single command, 16 signals (singlecmd) function has 16 binary output ...
Page 406
400
Page 407
Section 13 scheme communication 13.1 scheme communication logic for distance or overcurrent protection zcpsch ip15749-1 v3 13.1.1 identification m14854-1 v4 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number scheme communication logic for distance or...
Page 408
13.1.4 signals pid-3766-inputsignals v7 table 224: zcpsch input signals name type default description i3p group signal - current group connection u3p group signal - voltage group connection block boolean 0 block of function blktr boolean 0 signal for block of trip output from communication logic blk...
Page 409
13.1.5 settings pid-3766-settings v7 table 226: zcpsch group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off / on schemetype intertrip permissive ur permissive or blocking deltablocking - - permissive ur scheme type tcoord 0.000 - 60.000 s 0....
Page 410
On a received signal for a fast trip, so its dependability is lower than that of a blocking scheme. 13.1.6.1 blocking scheme m13893-6 v7 the principle of operation for a blocking scheme is that an overreaching zone is allowed to trip instantaneously after the settable co-ordination time tcoord has e...
Page 411
If the fault inception function has detected a system fault, a block signal cs will be issued and sent to remote end in order to block the overreaching zones. Different criteria has to be fulfilled for sending the cs signal: 1. The breaker has to be in closed condition, that is, the input signal cbo...
Page 412
The function can be totally blocked by activating the input block. Tripping can be blocked by activating the input blktr. Signal send can be blocked by activating the input blkcs. 13.1.6.4 permissive overreaching scheme m13893-22 v6 in a permissive overreaching scheme, a forward directed overreachin...
Page 413
Crg t 200 ms 1 tsecurity t 150 ms >1 cr crl lcg and or t and en05000746.Vsd iec05000746 v1 en-us figure 197: guard signal logic with unblocking scheme and with setting unblock = restart or t 1 cr crg crl tsecurity iec11000253-1-en.Vsd iec11000253 v1 en-us figure 198: guard signal logic with unblocki...
Page 414
In case of single-pole tripping in multi-phase systems, a phase selection is performed. 13.1.6.7 simplified logic diagram m13893-40 v4 the simplified logic diagram for the complete logic is shown in figure 199 . Iec05000515-2-en.Vsd crg cr crl crl 1 tsecurit y t 200 ms t 150 ms lcg unblock = restart...
Page 415
13.1.7 technical data m16038-1 v14 table 229: zcpsch technical data function range or value accuracy scheme type off intertrip permissive ur permissive or blocking deltablocking - operate voltage, delta u (0–100)% of ubase ±5.0% of Δu operate current, delta i (0–200)% of ibase ±5.0% of Δi operate ze...
Page 416
Permissive tripping at the local end. This blocking condition is maintained long enough to ensure that no unwanted operation will occur as a result of the current reversal. On verification of a weak end infeed condition, the weak end infeed logic provides an output for sending the received teleprote...
Page 417
Pid-3521-outputsignals v8 table 231: zcrwpsch output signals name type description irvl boolean operation of current reversal logic trwei boolean trip signal from weak end infeed logic trweil1 boolean trip signal from weak end infeed logic in phase l1 trweil2 boolean trip signal from weak end infeed...
Page 418
Has been activated (even if only for a short time), it prevents sending of a communication signal and tripping through the scheme communication logic after a settable time tpickuprev. The prevention will last for tpickuprev + 10 ms + tdelayrev after the irev reset. This makes it possible for the rec...
Page 419
Block vtsz weiblk1 weiblk2 crl t tpickupwei t 200 ms cbopen t 1500 ms t 50 ms t 200 ms echo or or and and and and or wei = echo iec05000123-3-en.Vsd iec05000123 v3 en-us figure 202: simplified logic diagram for weak-end infeed logic — echo when an echo function is used in both ieds (should generally...
Page 420
13.2.7 technical data m16039-1 v16 table 234: zcrwpsch technical data function range or value accuracy detection level phase-to-neutral voltage (10-90)% of ubase ±0.5% of u r detection level phase-to-phase voltage (10-90)% of ubase ±0.5% of u r operate time for current reversal logic (0.000-60.000) ...
Page 421
13.3.4 signals pid-3511-inputsignals v6 table 235: zclcpsch input signals name type default description i3p group signal - group signal for current input block boolean 0 block of function arready boolean 0 autoreclosure ready, releases function used for fast trip ndst boolean 0 non directional crite...
Page 422
Table 238: zclcpsch non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description globalbasesel 1 - 12 - 1 1 selection of one of the global base value groups 13.3.6 operation principle 13.3.6.1 zone extension m13819-3 v2 the overreaching zone is connected to the input exacc. For this ...
Page 423
Currents have been above the set value mincurr for more than setting tlowcurr, an overreaching zone will be allowed to trip "instantaneously" during a fault condition when one or two of the phase currents will become low due to a three-phase trip at the opposite ied, see figure 206 . The current mea...
Page 424
Of the protection including a channel transmission time, can be achieved. This short operate time enables rapid autoreclosing function after the fault clearance. The communication logic module for directional residual current protection enables blocking as well as permissive under/overreaching, and ...
Page 425
Pid-3581-outputsignals v6 table 240: ecpsch output signals name type description trip boolean trip signal by communication scheme logic cs boolean carrier send by communication scheme logic crl boolean carrier receive from communication scheme logic lcg boolean loss of carrier guard signal 13.4.5 se...
Page 426
• input signal cacc is used for tripping of the communication scheme, normally the start signal of a forward overreaching step of stfw. • input signal csblk is used for sending block signal in the blocking communication scheme, normally the start signal of a reverse overreaching step of strv. • inpu...
Page 427
Iec05000448 v1 en-us figure 208: simplified logic diagram for blocking scheme 13.4.6.2 permissive under/overreaching scheme m13922-17 v6 in the permissive scheme the forward directed earth-fault measuring element sends a permissive signal to the other end, if an earth fault is detected in the forwar...
Page 428
In the overreaching alternative, an overreaching directional residual overcurrent measurement element will be used as sending criterion of the permissive input signal csor. Also the underreaching input signal csur can initiate sending. Block cr cacc blkcs crl overreach csor t 0 - 60 s tcoord t 25 ms...
Page 429
Crg t 200 ms 1 tsecurity t 150 ms >1 cr crl lcg and or t and en05000746.Vsd iec05000746 v1 en-us figure 209: guard signal logic with unblocking scheme the unblocking function can be set in three operation modes (setting unblock): off: the unblocking function is out of operation no restart: communica...
Page 430
13.5.2 functionality m13928-3 v8 the current reversal and weak-end infeed logic for residual overcurrent protection (ecrwpsch) is a supplement to scheme communication logic for residual overcurrent protection ecpsch. To achieve fast fault clearing for all earth faults on the line, the directional ea...
Page 431
13.5.4 signals pid-3522-inputsignals v9 table 244: ecrwpsch input signals name type default description u3p group signal - group signal for voltage input block boolean 0 block of function irvblk boolean 0 block of current reversal function irv boolean 0 activation of current reversal logic weiblk1 b...
Page 432
Table 247: ecrwpsch non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description globalbasesel 1 - 12 - 1 1 selection of one of the global base value groups 13.5.6 operation principle 13.5.6.1 directional comparison logic function m13929-4 v6 the directional comparison function conta...
Page 433
And block irvblk t tpickuprev t tpickuprev t 10 ms irv currrev = on t tdelayrev irvl iec09000031-4-en.Vsd iec09000031 v4 en-us figure 211: simplified logic diagram for current reversal 13.5.6.3 weak-end infeed logic m13929-24 v10 the weak-end infeed function can be set to send only an echo signal (w...
Page 434
And or or or and and t tpickupwei t 200 ms and and t 1500 ms cbopen vtsz weiblk1 weiblk2 crl block t 50 ms t 200 ms wei = echo echo cr iec09000032-6-en.Vsd iec09000032 v6 en-us figure 212: simplified logic diagram for weak-end infeed logic - echo with the wei= echo & trip setting, the logic sends an...
Page 435
The weak-end infeed echo sent to the strong line end has a maximum duration of 200 ms. When this time period has elapsed, the conditions that enable the echo signal to be sent are set to zero for a time period of 50 ms. This avoids ringing action if the weak-end echo is selected for both line ends. ...
Page 436
430
Page 437
Section 14 logic 14.1 tripping logic smpptrc ip14576-1 v4 14.1.1 identification semod56226-2 v7 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number tripping logic smpptrc 1 -> 0 iec15000314 v1 en-us 94 14.1.2 functionality m12275-3 v12 a function bloc...
Page 438
14.1.3 function block m12638-3 v7 smpptrc block blklkout trin trinl1 trinl2 trinl3 psl1 psl2 psl3 1ptrz 1ptref p3ptr setlkout rstlkout stdi r trip trl1 trl2 trl3 tr1p tr2p tr3p cllkou t start stl1 stl2 stl3 stn fw rev iec05000707-4-en.Vsdx iec05000707 v4 en-us figure 214: smpptrc function block 14.1...
Page 439
Guid-d6b3dfe3-f7df-4602-b57e-764dc9eb0d4a v1 table 250: smpptrc output signals name type description trip boolean general trip output signal trl1 boolean trip signal from phase l1 trl2 boolean trip signal from phase l2 trl3 boolean trip signal from phase l3 tr1p boolean trip single-pole tr2p boolean...
Page 440
14.1.6 operation principle m12255-3 v12 the duration of the trip output signal is settable (ttripmin). The pulse length should be long enough to secure the opening of the circuit breaker. There is a single input (trin) through which all trip output signals from the protection functions within the ie...
Page 441
Blklkout tripall tripl1 tripl2 tripl3 setlkout rstlkout trip final tripping circuits trl1 trl2 trl3 tr1p tr2p tr3p cllkout simplified logic where setting program = 3 phase block blklkout trin trinl1 trinl2 trinl3 1ptrz 1ptref setlkout rstlkout trip trl1 trl2 trl3 tr3p cllkout block trin trinl1 trinl...
Page 442
Residual overcurrent protection. The smpptrc function has two inputs for these functions, one for impedance tripping (1ptrz used for carrier-aided tripping commands from the scheme communication logic), and one for earth fault tripping (1ptref used for tripping from a residual overcurrent protection...
Page 443
B2= rev (reverse) b3= stl1 (start l1) b4= fwl1 (forward l1) b5= revl1 (reverse l1) b6= stl2 (start l2) b7= fwl2 (forward l2) b8= revl2 (reverse l2) b9= stl3 (start l3) b10= fwl3 (forward l3) b11= revl3 (reverse l3) b12= stn (start n) b13= fwn (forward n) b14= revn (reverse n) the indications for gen...
Page 444
14.1.6.1 logic diagram m12258-7 v6 iec05000517=4=en=original..Vsdx tripall block and trinl1 t ttripmin or trinl2 trinl3 trin 1ptref 1ptrz or iec05000517 v4 en-us figure 216: three-phase front logic — simplified logic diagram iec10000056=4=en=original.Vsdx l1trip trin or 1ptref t twaitforphs or trinl...
Page 445
Tripl1 block and l1trip t tevolvingfault t ttripmin l2trip l3trip p3ptr or or or and trip iec17000065-2-en.Vsdx iec17000065 v2 en-us figure 218: simplified additional logic per phase, program = 1ph/3ph or 1ph/2ph/3ph iec17000066=1=en=original.Vsdx trl1 t 3ms blklkout or or tripl1 and tripl3 tripl2 t...
Page 446
Start stl1 and fw and rev fwl1 revl1 start fw stl1 dirl1 stl2 stl3 stdir xor and and fwl2 revl2 xor and and fwl3 revl3 xor stl2 directional logic b0 b1 out bitstoint b0 b1 out bitstoint dirl2 b0 b1 out bitstoint dirl3 b0 b1 out bitstoint rev dir dirgeneral (61850 standard) 0 = unknown 1 = forward 2 ...
Page 447
14.2 general start matrix block smagapc 14.2.1 identification guid-c6d3de50-03d2-4f27-82ff-623e81d019f4 v1 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number generat start matrix block smagapc - - 14.2.2 functionality guid-ba516165-96de-4cd9-979b-294...
Page 448
Name type default description stdir4 integer 0 start direction input 4 stdir5 integer 0 start direction input 5 stdir6 integer 0 start direction input 6 stdir7 integer 0 start direction input 7 stdir8 integer 0 start direction input 8 stdir9 integer 0 start direction input 9 stdir10 integer 0 start ...
Page 449
B3= stl1 (startl1) b4= fwl1 (forwardl1) b5= revl1 (reversel1) b6= stl2 (startl2) b7= fwl2 (forwardl2) b8= revl2 (reversel2) b9= stl3 (startl3) b10= fwl3 (forwardl3) b11= revl3 (reversel3) b12= stn (startn) b13= fwn (forwardn) b14= revn (reversen) the startmatrix function contains two function: the s...
Page 450
Start criteria stdirx stdirout direction criteria stdirin stdir start criteria stdirx stdirout start criteria stdirx stdirout start criteria stdirx stdirout start criteria stdirx stdirout start criteria stdirx stdirout start criteria stdirx stdirout start criteria stdirx stdirout start criteria stdi...
Page 451
Start (in) stl1 (in) stl3 (in) & fw (in) & rev (in) & fwl1 (in) & revl1 (in) & fwl2 (in) & revl2 (in) & fwl3 (in) & revl3 (in) start (out) fw (out) rev (out) stl1 (out) fwl1 (out) revl1 (out) stl2 (out) fwl2 (out) revl2 (out) stl3 (out) fwl3 (out) revl3 (out) stdirout stl2 (in) start criteria start ...
Page 452
Startcomb to make it possible to provide the directional information from a protection function, a startcomb block is used in between the application function and the start matrix function. The startcomb function has one block input and 14 boolean inputs that convert the 14 boolean inputs into a wor...
Page 453
• protection 1: general start, fw and rev • protection 2: phase-wise stlx, fwlx and revlx (where x = 1, 2 and 3) • protection 3: stn, fwn and revn • protection 4: stdir connection example in figure 226 below is an example how to connect start and directional signals from protection functions via sta...
Page 454
14.3 trip matrix logic tmagapc ip15121-1 v4 14.3.1 identification semod167882-2 v3 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number trip matrix logic tmagapc - - 14.3.2 functionality m15321-3 v12 the trip matrix logic tmagapc function is used to ro...
Page 455
14.3.3 function block semod54400-4 v6 tmagapc block blk1 blk2 blk3 input1 input2 input3 input4 input5 input6 input7 input8 input9 input10 input11 input12 input13 input14 input15 input16 input17 input18 input19 input20 input21 input22 input23 input24 input25 input26 input27 input28 input29 input30 in...
Page 456
Name type default description input8 boolean 0 binary input 8 input9 boolean 0 binary input 9 input10 boolean 0 binary input 10 input11 boolean 0 binary input 11 input12 boolean 0 binary input 12 input13 boolean 0 binary input 13 input14 boolean 0 binary input 14 input15 boolean 0 binary input 15 in...
Page 457
14.3.5 settings pid-6513-settings v4 table 259: tmagapc group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off / on pulsetime 0.050 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.150 output pulse time ondelay 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.000 output on delay time offdelay 0.0...
Page 458
Pulsetime ondelay output 1 pulsetime ondelay output 2 pulsetime ondelay output 3 input 17 input 32 input 1 input 16 iec09000612-3-en.Vsd ³1 ³1 ³1 ³1 & & & & & & ³1 ³1 t t t offdelay t t t t offdelay t offdelay t modeoutput1=pulsed modeoutput2=pulsed modeoutput3=pulsed iec09000612 v3 en-us figure 228...
Page 459
14.4.2 functionality guid-16e60e27-f7a8-416d-8648-8174aac49bb5 v4 the group alarm logic function (almcalh) is used to route several alarm signals to a common indication, led and/or contact, in the ied. 14.4.3 function block guid-ea192656-71dd-4d44-a1d5-96b1b4937971 v1 almcalh block input1 input2 inp...
Page 460
Pid-6510-outputsignals v5 table 262: almcalh output signals name type description alarm boolean or function betweeen inputs 1 to 16 14.4.5 settings pid-6510-settings v5 table 263: almcalh group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off ...
Page 461
14.5 logic for group warning wrncalh 14.5.1 identification guid-3ebd3d5b-f506-4557-88d7-dfc0bd21c690 v4 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number logic for group warning wrncalh - - 14.5.2 functionality guid-f7d9a012-3ad4-4d86-be97-df2a99be5...
Page 462
Name type default description input9 boolean 0 binary input 9 input10 boolean 0 binary input 10 input11 boolean 0 binary input 11 input12 boolean 0 binary input 12 input13 boolean 0 binary input 13 input14 boolean 0 binary input 14 input15 boolean 0 binary input 15 input16 boolean 0 binary input 16 ...
Page 463
14.5.7 technical data guid-70b7357d-f467-4cf5-9f73-641a82d334f5 v1 table 268: number of wrncalh instances function quantity with cycle time 3 ms 8 ms 100 ms wrncalh - - 5 14.6 logic for group indication indcalh 14.6.1 identification guid-3b5d4371-420d-4249-b6a4-5a168920d635 v4 function description i...
Page 464
14.6.4 signals pid-4128-inputsignals v4 table 269: indcalh input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function input1 boolean 0 binary input 1 input2 boolean 0 binary input 2 input3 boolean 0 binary input 3 input4 boolean 0 binary input 4 input5 boolean 0 binary input 5 inp...
Page 465
When any one of 16 input signals (input1 to input16) has logical value 1, the ind output signal will get logical value 1. The function has a drop-off delay of 200 ms when all inputs are reset to provide a steady signal. Ind ³1 200 ms t iec13000193-1-en.Vsd input1 input16 iec13000193 v1 en-us 14.6.7 ...
Page 466
• or function block. The or function is used to form general combinatory expressions with boolean variables. The or function block has up to six inputs and two outputs. One of the outputs is inverted. • pulsetimer function block can be used, for example, for pulse extensions or limiting of operation...
Page 467
14.7.1.2 signals pid-3437-inputsignals v7 table 273: and input signals name type default description input1 boolean 1 input signal 1 input2 boolean 1 input signal 2 input3 boolean 1 input signal 3 input4 boolean 1 input signal 4 pid-3437-outputsignals v7 table 274: and output signals name type descr...
Page 468
Pid-3801-outputsignals v5 table 277: gate output signals name type description out boolean output from gate 14.7.2.3 settings pid-3801-settings v6 table 278: gate group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off/on 14.7.2.4 technical dat...
Page 469
14.7.3.3 technical data guid-0ec4192a-ef03-47c0-aec1-09b68b411a98 v2 table 282: number of inv instances logic block quantity with cycle time 3 ms 8 ms 100 ms inv 90 90 240 14.7.4 loop delay function block lld guid-05d959b5-a55b-437c-8e8f-831a4a357e24 v2 guid-64b24094-010d-4b8f-8b7b-ddd49499aae5 v3 t...
Page 470
14.7.5 or function block ip11012-1 v3 m11449-3 v2 the or function is used to form general combinatory expressions with boolean variables. The or function block has up to six inputs and two outputs. One of the outputs is inverted. 14.7.5.1 function block m11448-3 v1 iec04000405_2_en.Vsd or input1 inp...
Page 471
14.7.6 pulse timer function block pulsetimer ip11016-1 v2 m11466-3 v3 the pulse (pulsetimer) function can be used, for example, for pulse extensions or limiting the operation time of outputs. The pulsetimer has a settable length. When the input is 1, the output will be 1 for the time set by the time...
Page 472
14.7.7 reset-set with memory function block rsmemory guid-9c93669f-078b-49ea-85b8-c4bb6a434734 v1 guid-4c804dea-3c83-4c20-82c6-bad03bd48242 v4 the reset-set with memory function block (rsmemory) is a flip-flop with memory that can reset or set an output from two inputs respectively. Each rsmemory fu...
Page 473
14.7.7.3 settings pid-3811-settings v5 table 296: rsmemory group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description memory off on - - on operating mode of the memory function 14.7.7.4 technical data guid-be6fd540-e96e-4f15-b2a2-12ffae6c51db v1 table 297: number of rsmemory instances ...
Page 474
14.7.8.2 signals pid-3813-inputsignals v5 table 299: srmemory input signals name type default description set boolean 0 input signal to set reset boolean 0 input signal to reset pid-3813-outputsignals v5 table 300: srmemory output signals name type description out boolean output signal nout boolean ...
Page 475
On off t tdelay tdelay iec08000289-2-en.Vsd input iec08000289 v2 en-us figure 238: timerset status diagram 14.7.9.1 function block m11495-3 v3 iec04000411-2-en.Vsd timerset input on off iec04000411 v2 en-us figure 239: timerset function block 14.7.9.2 signals pid-6976-inputsignals v1 table 303: time...
Page 476
14.7.9.3 settings pid-6976-settings v1 table 305: timerset group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off/on t 0.000 - 90000.000 s 0.001 0.000 delay for settable timer n 14.7.9.4 technical data guid-c6c98fe0-f559-45ee-b853-464516775417...
Page 477
14.7.10.2 signals pid-3817-inputsignals v2 table 308: xor input signals name type default description input1 boolean 0 input 1 to xor gate input2 boolean 0 input 2 to xor gate pid-3817-outputsignals v2 table 309: xor output signals name type description out boolean output from xor gate nout boolean ...
Page 478
Function blocks to a certain level/value, or for creating certain logic. Boolean, integer, floating point, string types of signals are available. One fxdsign function block is included in all ieds. 14.9.3 function block semod54909-4 v4 fxdsign off on intzero intone intalone realzero strnull zerosmpl...
Page 479
• off is a boolean signal, fixed to off (boolean 0) value • on is a boolean signal, fixed to on (boolean 1) value • intzero is an integer number, fixed to integer value 0 • intone is an integer number, fixed to integer value 1 • intalone is an integer value ffff (hex) • realzero is a floating point ...
Page 480
14.10.4 signals pid-3606-inputsignals v4 table 312: b16i input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function in1 boolean 0 input 1 in2 boolean 0 input 2 in3 boolean 0 input 3 in4 boolean 0 input 4 in5 boolean 0 input 5 in6 boolean 0 input 6 in7 boolean 0 input 7 in8 boolean...
Page 481
14.10.7 operation principle semod175737-4 v5 the boolean 16 to integer conversion function (b16i) will transfer a combination of up to 16 binary inputs inx, where 1≤x≤16, to an integer. Each inx represents a value according to the table below from 0 to 32768. This follows the general formula: inx = ...
Page 482
14.10.8 technical data guid-65a2876a-f779-41c4-acd7-7662d1e7f1f2 v2 table 315: number of b16i instances function quantity with cycle time 3 ms 8 ms 100 ms b16i 6 4 8 14.11 boolean to integer conversion with logical node representation, 16 bit btigapc semod175753-1 v4 14.11.1 identification semod1757...
Page 483
14.11.4 signals pid-6944-inputsignals v2 table 316: btigapc input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function in1 boolean 0 input 1 in2 boolean 0 input 2 in3 boolean 0 input 3 in4 boolean 0 input 4 in5 boolean 0 input 5 in6 boolean 0 input 6 in7 boolean 0 input 7 in8 bool...
Page 484
14.11.7 operation principle semod158425-4 v6 the boolean 16 to integer conversion with logic node representation function (btigapc) will transfer a combination of up to 16 binary inputs inx, where 1≤x≤16, to an integer. Each inx represents a value according to the table below from 0 to 32768. This f...
Page 485
14.11.8 technical data guid-3820f464-d296-4cad-8491-f3f997359d79 v1 table 319: number of btigapc instances function quantity with cycle time 3 ms 8 ms 100 ms btigapc 4 4 8 14.12 integer to boolean 16 conversion ib16 14.12.1 identification semod167941-2 v2 function description iec 61850 identificatio...
Page 486
14.12.4 signals pid-6938-inputsignals v1 table 320: ib16 input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function inp integer 0 integer input pid-6938-outputsignals v1 table 321: ib16 output signals name type description out1 boolean output 1 out2 boolean output 2 out3 boolean o...
Page 487
In the above example when integer 15 is on the input inp the out1 has a value =1, out2 has a value =2, out3 has a value =4 and out4 has a value =8. The sum of these outx is equal to 1 + 2 + 4 + 8 = 15. This follows the general formulae: the sum of the values of all outx = 2 x-1 where 1≤x≤16 will be ...
Page 488
14.12.7 technical data guid-b45901f4-b163-4696-8220-7f8cac84d793 v1 table 322: number of ib16 instances function quantity with cycle time 3 ms 8 ms 100 ms ib16 6 4 8 14.13 integer to boolean 16 conversion with logic node representation itbgapc semod158419-1 v3 14.13.1 identification semod167944-2 v4...
Page 489
14.13.3 function block semod158435-4 v4 itbgapc block psto out1 out2 out3 out4 out5 out6 out7 out8 out9 out10 out11 out12 out13 out14 out15 out16 iec14000012-1-en.Vsd iec14000012 v1 en-us figure 245: itbgapc function block 14.13.4 signals pid-3627-inputsignals v7 table 323: itbgapc input signals nam...
Page 490
14.13.5 settings guid-f573ca16-4821-4203-970a-f7d01af5e63b v1 this function does not have any setting parameters. 14.13.6 operation principle semod176587-4 v6 an example is used to explain the principle of operation: with integer 15 sent to and received by the itbgapc function on the iec 61850 the o...
Page 491
Name of outx type description value when activated value when deactivated out11 boolean output 11 1024 0 out12 boolean output 12 2048 0 out13 boolean output 13 4096 0 out14 boolean output 14 8192 0 out15 boolean output 15 16384 0 out16 boolean output 16 32768 0 the sum of the numbers in column “valu...
Page 492
Time integration with retain block acctime reset in twarning talarm overflow warning alarm q -1 a>b a b a>b a b a>b a b and and and q -1 = unit delay iec13000290-2-en.Vsd 999 999 s iec13000290 v2 en-us figure 246: teigapc logics the main features of teigapc • applicable to long time integration up t...
Page 493
Pid-6836-outputsignals v2 table 328: teigapc output signals name type description warning boolean indicator of the integrated time has reached the warning limit alarm boolean indicator of the integrated time has reached the alarm limit overflow boolean indicator of the integrated time has reached th...
Page 494
Time integration transgression supervision plus retain block acctime reset in talarm overflow warning alarm iec12000195-4-en.Vsd loop delay loop delay twarning iec12000195 v4 en-us figure 248: teigapc simplified logic teigapc main functionalities • integration of the elapsed time when in has been hi...
Page 495
Talarm and twarning are possible to be defined with a resolution of 10 ms, depending on the level of the defined values for the parameters. The limit for the overflow supervision is fixed at 999999.9 seconds. The outputs freeze if an overflow occurs. 14.14.6.1 operation accuracy guid-e0772193-9f6e-4...
Page 496
14.15.2 functionality guid-a93564fa-0017-4939-a9c1-095da0fd9832 v1 the function gives the possibility to monitor the level of integer values in the system relative to each other or to a fixed value. It is a basic arithmetic function that can be used for monitoring, supervision, interlocking and othe...
Page 497
14.15.6 monitored data pid-6928-monitoreddata v1 table 335: intcomp monitored data name type values (range) unit description inequal boolean - - input value is equal to the reference value inhigh boolean - - input value is higher than the reference value inlow boolean - - input value is lower than t...
Page 498
Abs input ref inhigh inequal inlow t f abs enaabs refsource setvalue a > b a b a a b a = b b a iec15000129-3-en.Vsdx t f t f iec15000129 v4 en-us figure 249: function logic diagram for intcomp 14.15.8 technical data guid-cea332ff-838d-42b7-aefc-c1e87809825e v2 table 336: number of intcomp instances ...
Page 499
14.16.4 signals pid-6897-inputsignals v2 table 337: realcomp input signals name type default description input real 0.000 input value to be compared with reference value ref real 0.000 reference value to be compared with input value pid-6897-outputsignals v2 table 338: realcomp output signals name t...
Page 500
Comparison is taken from second input signal (ref). If refsource is selected as set value then the reference value for comparison is taken from setting (setvalue). Generally the inputs to the function are in si units, but when the comparison is to be done with respect to set level, then the user can...
Page 501
Internal hysteresis for equal band equal band equalbandhigh equalbandlow ref or setvalue inequal reset / inhigh set inequal set / inhigh reset inequal reset / inlow set inequal set / inlow reset iec15000261-1-en.Vsdx iec15000261 v1 en-us figure 251: operation principle of realcomp when enaabs is set...
Page 502
496.
Page 503
Section 15 monitoring 15.1 measurements ip14593-1 v3 15.1.1 identification semod56123-2 v8 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number power system measurements cvmmxn p, q, s, i, u, f symbol-rr v1 en-us - phase current measurement cmmxu i sym...
Page 504
Provides to the system operator fast and easy overview of the present status of the power system. Additionally, it can be used during testing and commissioning of protection and control ieds in order to verify proper operation and connection of instrument transformers (cts and vts). During normal se...
Page 505
It is possible to calibrate the measuring function above to get better then class 0.5 presentation. This is accomplished by angle and amplitude compensation at 5, 30 and 100% of rated current and at 100% of rated voltage. The power system quantities provided, depends on the actual hardware, (trm) an...
Page 506
Iec05000701-2-en.Vsd vmmxu u3p* ul12 ul12rang ul12angl ul23 ul23rang ul23angl ul31 ul31rang ul31angl iec05000701 v2 en-us figure 254: vmmxu function block iec05000703-2-en.Vsd cmsqi i3p* 3i0 3i0rang 3i0angl i1 i1rang i1angl i2 i2rang i2angl iec05000703 v2 en-us figure 255: cmsqi function block iec05...
Page 507
15.1.4 signals pid-6713-inputsignals v3 table 341: cvmmxn input signals name type default description i3p group signal - group signal for current input u3p group signal - group signal for voltage input pid-6713-outputsignals v3 table 342: cvmmxn output signals name type description s real apparent p...
Page 508
Pid-6735-outputsignals v3 table 344: cmmxu output signals name type description il1 real il1 amplitude, magnitude of reported value il1rang integer il1 amplitude range il1angl real il1 angle, magnitude of reported value il2 real il2 amplitude, magnitude of reported value il2rang integer il2 amplitud...
Page 509
Pid-6736-outputsignals v3 table 348: cmsqi output signals name type description 3i0 real 3i0 amplitude, magnitude of reported value 3i0rang integer 3i0 amplitude range 3i0angl real 3i0 angle, magnitude of reported value i1 real i1 amplitude, magnitude of reported value i1rang integer i1 amplitude ra...
Page 510
Pid-6737-outputsignals v2 table 352: vnmmxu output signals name type description ul1 real ul1 amplitude, magnitude of reported value ul1rang integer ul1 amplitude range ul1angl real ul1 angle, magnitude of reported value ul2 real ul2 amplitude, magnitude of reported value ul2rang integer ul2 amplitu...
Page 511
Name values (range) unit step default description pmin -2000.0 - 2000.0 %sb 0.1 -200.0 minimum value in % of sbase pmax -2000.0 - 2000.0 %sb 0.1 200.0 maximum value in % of sbase preptyp cyclic deadband int deadband db & cyclic 5s db & cyclic 30s db & cyclic 1min - - cyclic reporting type qmin -2000...
Page 512
Name values (range) unit step default description mode l1, l2, l3 arone pos seq l1l2 l2l3 l3l1 l1 l2 l3 - - l1, l2, l3 selection of measured current and voltage powampfact 0.000 - 6.000 - 0.001 1.000 amplitude factor to scale power calculations powangcomp -180.0 - 180.0 deg 0.1 0.0 angle compensatio...
Page 513
Name values (range) unit step default description pfdbrepint 1 - 100000 type 1 10 cycl: report interval (s), db: in 0,001% of range, int db: in 0,001%s pfzerodb 0 - 100000 m% 100 500 magnitude zero point clamping in 0,001% of range pfhihilim -1.000 - 1.000 - 0.001 1.000 high high limit (physical val...
Page 514
Name values (range) unit step default description uampcomp30 -10.000 - 10.000 % 0.001 0.000 amplitude factor to calibrate voltage at 30% of ur uampcomp100 -10.000 - 10.000 % 0.001 0.000 amplitude factor to calibrate voltage at 100% of ur iampcomp5 -10.000 - 10.000 % 0.001 0.000 amplitude factor to c...
Page 515
Name values (range) unit step default description il3max 0.0 - 500.0 %ib 0.1 200.0 maximum value in % of ibase il3reptyp cyclic deadband int deadband db & cyclic 5s db & cyclic 30s db & cyclic 1min - - cyclic reporting type il3angdbrepint 1 - 100000 s 1 10 cyclic report interval (s) table 356: cmmxu...
Page 516
Pid-6738-settings v2 table 357: vmmxu non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description ul12dbrepint 1 - 100000 type 1 10 cycl: report interval (s), db: in 0,001% of range, int db: in 0,001%s operation off on - - off operation mode on / off ul12zerodb 0 - 100000 m% 500 100...
Page 517
Table 358: vmmxu non group settings (advanced) name values (range) unit step default description ul12hihilim 0.0 - 200.0 %ub 0.1 150.0 high high limit in % of ubase ul12hilim 0.0 - 200.0 %ub 0.1 120.0 high limit in % of ubase ul12lowlim 0.0 - 200.0 %ub 0.1 80.0 low limit in % of ubase ul12lowlowlim ...
Page 518
Name values (range) unit step default description i1dbrepint 1 - 100000 type 1 10 cycl: report interval (s), db: in 0,001% of range, int db: in 0,001%s i1zerodb 0 - 100000 m% 500 1000 magnitude zero point clamping in 0,001% of range i1min 0.0 - 500.0 %ib 0.1 50.0 minimum value in % of ibase i1max 0....
Page 519
Pid-6739-settings v2 table 361: vmsqi non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description 3u0dbrepint 1 - 100000 type 1 10 cycl: report interval (s), db: in 0,001% of range, int db: in 0,001%s 3u0zerodb 0 - 100000 m% 500 1000 magnitude zero point clamping in 0,001% of range ...
Page 520
Name values (range) unit step default description u2angdbrepint 1 - 100000 s 1 10 cyclic report interval (s) uampprecomp5 -10.000 - 10.000 % 0.001 0.000 amplitude factor to pre-calibrate voltage at 5% of ur uampprecomp30 -10.000 - 10.000 % 0.001 0.000 amplitude factor to pre-calibrate voltage at 30%...
Page 521
Name values (range) unit step default description ul1angdbrepint 1 - 100000 s 1 10 cyclic report interval (s) ul2dbrepint 1 - 100000 type 1 10 cycl: report interval (s), db: in 0,001% of range, int db: in 0,001%s ul2zerodb 0 - 100000 m% 500 1000 magnitude zero point clamping in 0,001% of range ul2mi...
Page 522
Name values (range) unit step default description ul3hilim 0.0 - 200.0 %ub 0.1 120.0 high limit in % of ubase ul3lowlim 0.0 - 200.0 %ub 0.1 80.0 low limit in % of ubase ul3lowlowlim 0.0 - 200.0 %ub 0.1 60.0 low low limit in % of ubase 15.1.6 monitored data pid-6713-monitoreddata v3 table 365: cvmmxn...
Page 523
Pid-6738-monitoreddata v2 table 367: vmmxu monitored data name type values (range) unit description ul12 real - kv ul12 amplitude, magnitude of reported value ul12angl real - deg ul12 angle, magnitude of reported value ul23 real - kv ul23 amplitude, magnitude of reported value ul23angl real - deg ul...
Page 524
Name type values (range) unit description u1angl real - deg u1 angle, magnitude of reported value u2 real - kv u2 amplitude, magnitude of reported value u2angl real - deg u2 angle, magnitude of reported value pid-6737-monitoreddata v2 table 370: vnmmxu monitored data name type values (range) unit de...
Page 525
Phase angle reference semod54417-303 v5 all phase angles are presented in relation to a defined reference channel. The general setting parameter phaseangleref defines the reference, see section "analog inputs" . Zero point clamping semod54417-137 v4 measured value below zero point clamping limit is ...
Page 526
The logical value of the functional output signals changes according to figure 258 . The user can set the hysteresis (xlimhyst), which determines the difference between the operating and reset value at each operating point, in wide range for each measuring channel separately. The hysteresis is commo...
Page 527
Iec05000500-2-en.Vsdx v a lu e 1 y t v a lu e 2 v a lu e 3 v a lu e 4 value reported (1st) value reported v a lu e 5 value reported y1 y2 y5 value reported value reported y3 y4 (*)set value for t: xdbrepint t (*) t (*) t (*) t (*) iec05000500 v2 en-us figure 259: periodic reporting amplitude dead-ba...
Page 528
Iec99000529-2-en.Vsdx y t value reported (1st) value reported value reported y1 y2 y3 y y y y y y value reported iec99000529 v2 en-us figure 260: amplitude dead-band supervision reporting after the new value is reported, the ±Δy limits for dead-band are automatically set around it. The new value is ...
Page 529
Iec99000530-2-en.Vsdx y t value reported (1st) y1 value reported a1 y2 value reported y3 y4 a value reported a2 y5 a3 a4 a5 a7 a6 value reported a2 >= pre-set value a1 >= pre-set value a >= pre-set value a3 + a4 + a5 + a6 + a7 >= pre-set value iec99000530 v2 en-us figure 261: reporting with integral...
Page 530
Iec16000109-1-en.Vsdx y1...Y7 : cyclic reported values, depending upon time Δt. Y’ and y” : deadband reported value, change is greater than setting Δt Δt Δt Δt Δt Δt y1 y2 y3 y4 y5 y6 y7 +Δy -Δy value time y’ y” value reported iec16000109 v1 en-us figure 262: example of value reporting in mode dead ...
Page 531
Set value for parameter “mode” formula used for complex, three- phase power calculation formula used for voltage and current magnitude calculation comment 1 l1, l2, l3 * * * 1 1 2 2 3 3 = × + × + × l l l l l l s u i u i u i equation1385 v1 en-us (equation 55) 1 2 3 1 2 3 ( ) / 3 ( ) / 3 = + + = + + ...
Page 532
Set value for parameter “mode” formula used for complex, three- phase power calculation formula used for voltage and current magnitude calculation comment 8 l2 * 2 2 3 = × × l l s u i equation1399 v1 en-us (equation 69) 2 2 3 = × = l l u u i i equation1400 v1 en-us (equation 70) used when only u l2 ...
Page 533
Calibration of analog inputs semod54417-293 v5 measured currents and voltages used in the cvmmxn function can be calibrated to get 0.5 class measuring accuracy. This is achieved by amplitude and angle compensation at 5, 30 and 100% of rated current and voltage. The compensation below 5% and above 10...
Page 534
(1 ) old calculated x k x k x = × + - × equation1407 v1 en-us (equation 77) where: x is a new measured value (that is p, q, s, u, i or pf) to be given out from the function x old is the measured value given from the measurement function in previous execution cycle x calculated is the new calculated ...
Page 535
Busbar protected object p q iec09000038-1-en.Vsd ied iec09000038-1-en v1 en-us figure 264: internal ied directionality convention for p & q measurements practically, it means that active and reactive power will have positive values when they flow from the busbar towards the protected object and they...
Page 536
Phase currents (amplitude and angle) are available on the outputs and each amplitude output has a corresponding supervision level output (ilx_rang). The supervision output signal is an integer in the interval 0-4, see section "measurement supervision" . 15.1.7.4 phase-phase and phase-neutral voltage...
Page 537
Function range or value accuracy reactive power, q (10 to 300) v (0.1-4.0) x i r ± 0.5% of s r at s ≤0.5 x s r ± 0.5% of s at s > 0.5 x s r (100 to 220) v (0.5-2.0) x i r cos φ> 0.7 ± 0.2% of q apparent power, s (10 to 300) v (0.1-4.0) x i r ± 0.5% of s r at s ≤0.5 x s r ± 0.5% of s at s >0.5 x s r ...
Page 538
Guid-47094054-a828-459b-be6a-d7fa1b317da7 v6 table 375: vmsqitechnical data function range or value accuracy voltage positive sequence, u1 (10 to 300) v ± 0.5% of u at u ≤ 50 v ± 0.2% of u at u > 50 v voltage zero sequence, 3u0 (10 to 300) v ± 0.5% of u at u ≤ 50 v ± 0.2% of u at u > 50 v voltage ne...
Page 539
15.2.3 function block guid-94b75a6d-973d-4f1f-8643-f2128ad31cc4 v3 ssimg block blkalm senpres sentemp senpresalm senpreslo setplo settlo resetlo lockout preslo templo alarm presalm tempalm pressure temp iec09000129-2-en.Vsdx iec09000129 v2 en-us figure 265: ssimg function block 15.2.4 signals guid-8...
Page 540
15.2.5 settings pid-6950-settings v6 table 379: ssimg group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off / on presalmlimit 1.00 - 100.00 - 0.01 5.00 alarm setting for pressure preslolimit 1.00 - 100.00 - 0.01 3.00 pressure lockout setting ...
Page 541
Goes below the settings for more than these time delays, the corresponding alarm presalm or lockout preslo will be initiated. The setplo binary input is used for setting the gas pressure lockout preslo. The preslo output retains the last value until it is reset by using the binary input resetlo. The...
Page 542
Function range or value accuracy time delay for temperature alarm (0.000-60.000) s ±0.2% or ±250ms whichever is greater reset time delay for temperature alarm (0.000-60.000) s ±0.2% or ±250ms whichever is greater time delay for temperature lockout (0.000-60.000) s ±0.2% or ±250ms whichever is greate...
Page 543
Pid-6951-inputsignals v7 table 382: ssiml input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function blkalm boolean 0 block all the alarms senlevel real 0.0 level input from cb sentemp real 0.0 temperature of the insulation medium from cb senlvlalm boolean 0 level alarm signal sen...
Page 544
Name values (range) unit step default description ttemplockout 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.000 time delay for temperture lockout tresetlevelalm 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.000 reset time delay for level alarm tresetlevello 0.000 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.000 reset time delay for level lockout tresettemplo 0.000 ...
Page 545
Alarm, two time delays ttempalarm or ttemplockouthave been included. If the temperature goes above the settings for more than these time delays, the corresponding alarm tempalm or lockout templo will be initiated. The settlo binary input is used for setting the temperature lockout templo. The templo...
Page 546
15.4.2 functionality guid-e1fd74c3-b9b6-4e11-aa1b-7e7f822fb4dd v11 the circuit breaker condition monitoring function (sscbr) is used to monitor different parameters of the breaker condition. The breaker requires maintenance when the number of operations reaches a predefined value. For a proper funct...
Page 547
Name type default description rsttrvt boolean 0 reset of cb closing and opening travel times rstipow boolean 0 reset of accumulated i^currexponent rstspcht boolean 0 reset of cb spring charging time pid-3267-outputsignals v10 table 388: sscbr output signals name type description openpos boolean cb i...
Page 548
Name values (range) unit step default description opernofault 1 - 10000 - 1 1000 number of operations possible at rated fault current ttropenalm 0.000 - 0.200 s 0.001 0.040 alarm level for open travel time ttrclosealm 0.000 - 0.200 s 0.001 0.040 alarm level for close travel time operalmlevel 0 - 999...
Page 549
15.4.6 monitored data pid-3267-monitoreddata v7 table 391: sscbr monitored data name type values (range) unit description ttrvop real - ms travel time of the cb during opening operation ttrvcl real - ms travel time of the cb during closing operation nooper integer - - number of cb operation cycle cb...
Page 550
I3p-ilrmsph posclose posopen block blkalm cb contact travel time ttrvop trvtopal trvtclal rsttrvt operalm cb gas pressure indication sprchrst sprchrd cblifeph ttrvcl nooper cblifeal i3p-il ipowph trind openpos closepos invdpos cb status cb operation monitoring cb operation cycles accumulated energy ...
Page 551
15.4.7.1 circuit breaker contact travel time guid-3af0ee8d-aa8e-4f83-9916-61b5d0d6b05b v12 the circuit breaker contact travel time subfunction calculates the breaker contact travel time for opening and closing operations. The operation of the breaker contact travel time measurement is described in f...
Page 552
The closing time is calculated by adding the value set with the closetimecorr (t3+t4) setting to the measured closing time. The last measured opening travel time (ttrvop) and the closing travel time (ttrvcl) are given as service values. The values can be reset using the clear menu on the lhmi or by ...
Page 553
Contacts have the same value or if the auxiliary input contact posclose is low and the posopen input is high but the current is above the setting accstopcurr. The status of the breaker is indicated with the binary outputs openpos, closepos and invdpos for open, closed and error position respectively...
Page 554
The old circuit breaker operation counter value can be used by adding the value to the initcbremlife parameter. The value can be reset using the clear menu from lhmi or by activating the input rstcbwr. 15.4.7.4 accumulated energy guid-0163ff0f-6e18-4cdc-87aa-578304e0872e v11 the accumulated energy s...
Page 555
Main contact close open posclose 1 0 energy accumulation starts conttrcorr (negative) main contact close posclose energy accumulation starts conttrcorr (positive) 1 0 open iec12000618_1_en.Vsd iec12000618 v1 en-us figure 274: significance of correction factor setting accumulated energy can also be c...
Page 556
Posclose posopen rstcbwr block blkalm operation counter alarm limit check nooper operalm operlo iec12000617 v2 en-us figure 275: functional module diagram for circuit breaker operation cycles operation counter the operation counter counts the number of operations based on the state of change of the ...
Page 557
Inactive timer the inactive timer module calculates the number of days the circuit breaker has remained in the same open or closed state. The value is calculated by monitoring the states of the posopen and posclose auxiliary contacts. The number of inactive days inadays is available as a service val...
Page 558
Alarm limit check if the time taken by the spring to charge is more than the value set with the spchalmtime setting, the subfunction generates the spchalm alarm. It is possible to block the spchalm alarm signal by activating the blkalm binary input. 15.4.7.8 circuit breaker gas pressure indication g...
Page 559
Function range or value accuracy independent time delay for gas pressure alarm (0.00 – 60.00) s ±0.2% or ±30 ms whichever is greater independent time delay for gas pressure lockout (0.00 – 60.00) s ±0.2% or ±30 ms whichever is greater cb contact travel time, opening and closing ±3 ms remaining life ...
Page 560
15.5.3 function block semod116030-4 v2 iec05000697-2-en.Vsd event block ^input1 ^input2 ^input3 ^input4 ^input5 ^input6 ^input7 ^input8 ^input9 ^input10 ^input11 ^input12 ^input13 ^input14 ^input15 ^input16 iec05000697 v2 en-us figure 279: event function block 15.5.4 signals ip11335-1 v2 pid-4145-in...
Page 561
Name type default description input13 group signal 0 input 13 input14 group signal 0 input 14 input15 group signal 0 input 15 input16 group signal 0 input 16 15.5.5 settings ip11336-1 v2 pid-4145-settings v6 table 394: event non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default descriptio...
Page 562
Name values (range) unit step default description eventmask7 noevents onset onreset onchange autodetect - - autodetect reporting criteria for input 7 eventmask8 noevents onset onreset onchange autodetect - - autodetect reporting criteria for input 8 eventmask9 noevents onset onreset onchange autodet...
Page 563
Name values (range) unit step default description minrepintval6 0 - 3600 s 1 2 minimum reporting interval input 6 minrepintval7 0 - 3600 s 1 2 minimum reporting interval input 7 minrepintval8 0 - 3600 s 1 2 minimum reporting interval input 8 minrepintval9 0 - 3600 s 1 2 minimum reporting interval in...
Page 564
• noevents • onset • onreset • onchange • autodetect it is possible to define which part of the event function generates the events. This can be performed individually for communication types spachannelmask and lonchannelmask. For each communication type these settings are available: • off • channel...
Page 565
Disturbance report (drprdre), always included in the ied, acquires sampled data of all selected analog input and binary signals connected to the function block with a maximum of 40 analog and 352 binary signals. The disturbance report functionality is a common name for several functions: • event lis...
Page 566
Semod54837-4 v4 iec05000430-4-en.Vsdx a1radr ^grp input1 ^grp input2 ^grp input3 ^grp input4 ^grp input5 ^grp input6 ^grp input7 ^grp input8 ^grp input9 ^grp input10 iec05000430 v4 en-us figure 281: a1radr function block example for a1radr-a3radr semod54843-4 v3 iec05000431-3-en.Vsd a4radr ^input31 ...
Page 567
15.6.4 signals pid-3949-outputsignals v2 table 395: drprdre output signals name type description drpoff boolean disturbance report function turned off recstart boolean disturbance recording started recmade boolean disturbance recording made cleared boolean all disturbances in the disturbance report ...
Page 568
Pid-4017-inputsignals v6 table 397: a4radr input signals name type default description input31 real 0 analog channel 31 input32 real 0 analog channel 32 input33 real 0 analog channel 33 input34 real 0 analog channel 34 input35 real 0 analog channel 35 input36 real 0 analog channel 36 input37 real 0 ...
Page 569
• b6rbdr: input81 to input96 (binary channels 81 to 96) • b7rbdr: input97 to input112 (binary channels 97 to 112) • b8rbdr: input113 to input128 (binary channels 113 to 128) • b9rbdr: input129 to input144 (binary channels 129 to 144) • b10rbdr: input145 to input160 (binary channels 145 to 160) • b11...
Page 570
Pid-4014-settings v7 table 400: a1radr non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation01 off on - - off operation on/off operation02 off on - - off operation on/off operation03 off on - - off operation on/off operation04 off on - - off operation on/off operatio...
Page 571
Name values (range) unit step default description undertrigle03 0 - 200 % 1 50 under trigger level for analog channel 3 in % of signal overtrigop03 off on - - off use over level trigger for analog channel 3 (on) or not (off) overtrigle03 0 - 5000 % 1 200 overtrigger level for analog channel 3 in % o...
Page 572
Name values (range) unit step default description overtrigop08 off on - - off use over level trigger for analog channel 8 (on) or not (off) overtrigle08 0 - 5000 % 1 200 over trigger level for analog channel 8 in % of signal nomvalue09 0.0 - 999999.9 - 0.1 0.0 nominal value for analog channel 9 unde...
Page 573
Pid-3798-settings v6 table 402: b1rbdr non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description trigdr01 off on - - off trigger operation on/off setled01 off start trip start and trip - - off set led on hmi for binary channel 1 trigdr02 off on - - off trigger operation on/off set...
Page 574
Name values (range) unit step default description setled09 off start trip start and trip - - off set led on hmi for binary channel 9 trigdr10 off on - - off trigger operation on/off setled10 off start trip start and trip - - off set led on hmi for binary channel 10 trigdr11 off on - - off trigger op...
Page 575
Name values (range) unit step default description infno2 0 - 255 - 1 0 information number for binary channel 2 (iec -60870-5-103) funtype3 0 - 255 - 1 0 function type for binary channel 3 (iec -60870-5-103) infno3 0 - 255 - 1 0 information number for binary channel 3 (iec -60870-5-103) funtype4 0 - ...
Page 576
Name values (range) unit step default description infno14 0 - 255 - 1 0 information number for binary channel 14 (iec -60870-5-103) funtype15 0 - 255 - 1 0 function type for binary channel 15 (iec -60870-5-103) infno15 0 - 255 - 1 0 information number for binary channel 15 (iec -60870-5-103) funtype...
Page 577
Name values (range) unit step default description indicationma09 hide show - - show indication mask for binary channel 9 triglevel10 trig on 0 trig on 1 - - trig on 1 trigger on positive (1) or negative (0) slope for binary input 10 indicationma10 hide show - - show indication mask for binary channe...
Page 578
• b15rbdr: 225 to 240 (setled225, set led on hmi for binary channel 225) • b16rbdr: 241 to 256 (setled241, set led on hmi for binary channel 241) • b17rbdr: 257 to 272 (setled257, set led on hmi for binary channel 257) • b18rbdr: 273 to 288 (setled273, set led on hmi for binary channel 273) • b19rbd...
Page 579
15.6.6 monitored data pid-3949-monitoreddata v2 table 404: drprdre monitored data name type values (range) unit description memoryused integer - % memory usage (0-100%) untrigstatch1 boolean - - under level trig for analog channel 1 activated ovtrigstatch1 boolean - - over level trig for analog chan...
Page 580
Name type values (range) unit description untrigstatch10 boolean - - under level trig for analog channel 10 activated ovtrigstatch10 boolean - - over level trig for analog channel 10 activated untrigstatch11 boolean - - under level trig for analog channel 11 activated ovtrigstatch11 boolean - - over...
Page 581
Name type values (range) unit description untrigstatch20 boolean - - under level trig for analog channel 20 activated ovtrigstatch20 boolean - - over level trig for analog channel 20 activated untrigstatch21 boolean - - under level trig for analog channel 21 activated ovtrigstatch21 boolean - - over...
Page 582
Name type values (range) unit description untrigstatch30 boolean - - under level trig for analog channel 30 activated ovtrigstatch30 boolean - - over level trig for analog channel 30 activated untrigstatch31 boolean - - under level trig for analog channel 31 activated ovtrigstatch31 boolean - - over...
Page 583
Name type values (range) unit description untrigstatch40 boolean - - under level trig for analog channel 40 activated ovtrigstatch40 boolean - - over level trig for analog channel 40 activated faultnumber integer - - disturbance fault number 15.6.7 operation principle m12155-6 v10 disturbance report...
Page 584
Trip value rec fault locator event list event recorder indications disturbance recorder disturbance report binary signals analog signals drprdre fl iec09000336-3-en.Vsdx axradr bxrbdr iec09000336 v3 en-us figure 284: disturbance report functions and related function blocks the whole disturbance repo...
Page 585
Disturbance report record no. N record no. N+1 record no. N+100 general dist. Information & setting infotrmation indications trip values event recordings disturbance recording fault locator event list iec05000125-2-en.Vsdx iec05000125 v2 en-us figure 285: disturbance report structure up to 100 distu...
Page 586
The maximum number of recordings depend on each recordings total recording time. Long recording time will reduce the number of recordings to less than 100. The ied flash disk should not be used to store any user files. This might cause disturbance recordings to be deleted due to lack of disk space. ...
Page 587
And the behavior of each component are compared between the trigger and the post processing time. If there are any differences, then it will be added in the header file under section changed_settings. In the hdr file, section tag settings has an attribute tag called function which includes parameter...
Page 588
Prefaultrect timelimit postfaultrect en05000487.Vsd 1 2 3 trig point iec05000487 v1 en-us figure 287: the recording times definition prefaultrect, 1 pre-fault or pre-trigger recording time. The time before the fault including the operate time of the trigger. Use the setting prefaultrect to set this ...
Page 589
Iec10000029-1-en.Vsd a3radr a2radr a1radr smai ai1 ai2 ai3 ai4 ai3p ^grp2l1 ^grp2l2 ^grp2l3 block ^grp2n input1 input2 input3 input4 input5 input6 ... A4radr input31 input32 input33 input34 input35 input36 ... Input40 internal analogue signals external analogue signals ain type iec10000029 v1 en-us ...
Page 590
If operation = off, no waveform (samples) will be recorded and reported in graph. However, trip value, pre-fault and fault value will be recorded and reported. The input channel can still be used to trig the disturbance recorder. If operation = on, waveform (samples) will also be recorded and report...
Page 591
Generate a trigger from a logic zero, the selected signal will not be listed in the indications list of the disturbance report. Analog-signal trigger m12155-171 v6 all analog signals are available for trigger purposes, no matter if they are recorded in the disturbance recorder or not. The settings a...
Page 592
Function range or value accuracy maximum total recording time (3.4 s recording time and maximum number of channels, typical value) 340 seconds (100 recordings) at 50 hz, 280 seconds (80 recordings) at 60 hz - sampling rate 1 khz at 50 hz 1.2 khz at 60 hz - recording bandwidth (5-300) hz - 15.7 logic...
Page 593
15.7.4 signals pid-4144-inputsignals v6 table 406: binstatrep input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function input1 boolean 0 single status report input 1 input2 boolean 0 single status report input 2 input3 boolean 0 single status report input 3 input4 boolean 0 singl...
Page 594
15.7.5 settings pid-4144-settings v6 table 408: binstatrep non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description t 0.0 - 60.0 s 0.1 10.0 time delay of function 15.7.6 operation principle guid-537921ca-82b9-4a02-bad1-67e3ac61ae96 v3 the logical signal status report (binstatrep)...
Page 595
Supervised with four settable limits: low-low limit, low limit, high limit and high- high limit. The measure value expander block (range_xp) has been introduced to enable translating the integer output signal from the measuring functions to 5 binary signals: below low-low limit, below low limit, nor...
Page 596
Table 411: input integer value converted to binary output signals measured supervised value is: below low-low limit between low‐ low and low limit between low and high limit between high- high and high limit above high- high limit output: lowlow high low high normal high high high highhigh high 15.9...
Page 597
15.9.3 function block m16684-3 v6 lmbrflo phsell1* phsell2* phsell3* calcdist* calcmade flt_x bcd_80 bcd_40 bcd_20 bcd_10 bcd_8 bcd_4 bcd_2 bcd_1 iec05000679-4-en.Vsd iec05000679 v4 en-us figure 292: flo function block 15.9.4 signals pid-3906-inputsignals v1 table 412: lmbrflo input signals name typ...
Page 598
15.9.5 settings pid-3906-settings v2 table 414: lmbrflo group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description r1a 0.001 - 1500.000 ohm/p 0.001 2.000 source resistance a (near end) x1a 0.001 - 1500.000 ohm/p 0.001 12.000 source reactance a (near end) r1b 0.001 - 1500.000 ohm/p 0.00...
Page 599
15.9.6 monitored data pid-3906-monitoreddata v1 table 416: lmbrflo monitored data name type values (range) unit description flt_rel real - - distance to fault, relative flt_dist real - - distance to fault in line length unit flt_x real - ohm reactive distance to fault flt_r real - ohm resistive dist...
Page 600
If source impedance in the near and far end of the protected line have changed in a significant manner relative to the set values at fault location calculation time (due to exceptional switching state in the immediate network, power generation out of order, and so on), new values can be entered via ...
Page 601
Z a pz l a u a i f r f (1-p).Z l b z b f l i b i a xx01000171.Vsd iec01000171 v1 en-us figure 294: fault on transmission line fed from both ends from figure 294 it is evident that: u a i a p z l i f r f × + × × = equation95 v1 en-us (equation 78) where: i a is the line current after the fault, that ...
Page 602
U a i a p z l i fa d a -------- r f × + × × = equation98 v1 en-us (equation 81) table 417: expressions for u a , i a and i fa for different types of faults fault type: u a i a i fa l1-n u l1a i l1a + k n x i na 3 2 --- d i l1a i 0a – ( ) ´ equation110 v1 en-us l2-n u l2a i l2a + k n x i na 3 2 --- d...
Page 603
D a 1 p – ( ) z a z a l z b + + ( ) z b + × 2 z a z l 2 z b × + + × ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- = equation101 v1 en-us (equation 84) the k n compensation factor for the double line becomes: k n z 0l z 1l – 3 z 1l × ------------------------ z 0m 3 z 1...
Page 604
P 2 p re k 1 ( ) re k 2 ( ) r f re k 3 ( ) 0 = × – + × – equation107 v1 en-us (equation 90) p im k 1 ( ) im k 2 ( ) r f im k 3 ( ) 0 = × × – × + × × – equation108 v1 en-us (equation 91) if the imaginary part of k 3 is not zero, r f can be solved according to equation 91 , and then inserted to equati...
Page 605
15.9.8 technical data m14987-1 v6 table 418: lmbrflo technical data function value or range accuracy reactive and resistive reach (0.001-1500.000) Ω/phase ±2.0% static accuracy conditions: voltage range: (0.1-1.1) x u r current range: (0.5-30) x i r phase selection according to input signals - maxim...
Page 606
15.10.3.1 design guid-b643c994-d0ba-4be9-bacb-adea0197cae4 v1 figure 295 illustrates the general logic diagram of the function. Block counttype input reset error overflow limit1 … 4 counterlimit1...4 maxvalue onmaxvalue initialvalue value operation counter overflow detection limit check error detect...
Page 607
The input and all the outputs except the error output remains at zero state. The error condition remains until the correct settings for counter limits and/or initial value setting(s) are applied. The function can be blocked through a block input. During the block time, input is not counted and outpu...
Page 608
Pid-6966-outputsignals v2 table 420: l4ufcnt output signals name type description error boolean error indication on counter limit and/or initial value settings overflow boolean overflow indication on count of greater than maxvalue limit1 boolean counted value is larger than or equal to counterlimit1...
Page 609
15.10.8 technical data guid-c43b8654-60fe-4e20-8328-754c238f4ad0 v3 table 423: l4ufcnt technical data function range or value accuracy counter value 0-65535 - max. Count up speed 30 pulses/s (50% duty cycle) - 15.11 running hour-meter teilgapc 15.11.1 identification guid-3f9ef4fa-74fa-4d1d-88a0-e948...
Page 610
• possibilities for blocking and reset • possibility for manual addition of accumulated time • reporting of the accumulated time 15.11.3 function block guid-d0e9688b-c9d9-44b7-bd95-81132cca5e4f v1 teilgapc block in addtime reset alarm warning overflow acc_hour acc_day iec15000323.Vsdx iec15000323 v1...
Page 611
15.11.5 settings pid-6998-settings v1 table 426: teilgapc group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off / on talarm 1.0 - 99999.9 hour 0.1 90000.0 time limit for alarm supervision twarning 1.0 - 99999.9 hour 0.1 50000.0 time limit for...
Page 612
• applicable to very long time accumulation (≤99999.9 hours) • output acc_hour presents accumulated value in hours and acc_day presents accumulated value in days • accumulated value is retained in a non-volatile memory • any retained value is used as initiation value for the integration following by...
Page 613
• the pulse length • the number of pulses, that is, the number of rising and falling flank pairs in principle, more pulses may lead to reduced accuracy. 15.11.6.2 memory storage guid-b49698ff-0ab2-4792-a7cb-5534313b6ca0 v2 the value of the accumulated time is retained in a non-volatile memory, • at ...
Page 614
608.
Page 615
Section 16 metering 16.1 pulse-counter logic pcfcnt ip14600-1 v3 16.1.1 identification m14879-1 v4 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number pulse-counter logic pcfcnt s00947 v1 en-us - 16.1.2 functionality m13394-3 v7 pulse-counter logic (p...
Page 616
16.1.4 signals pid-6509-inputsignals v4 table 428: pcfcnt input signals name type default description bi_pulse boolean 0 connect binary input channel for metering block boolean 0 block of function read_val boolean 0 initiates an additional pulse counter reading rs_cnt boolean 0 resets pulse counter ...
Page 617
16.1.6 monitored data pid-6509-monitoreddata v4 table 431: pcfcnt monitored data name type values (range) unit description scal_val real - - scaled value with time and status information 16.1.7 operation principle ip14087-1 v2 m13397-3 v5 the registration of pulses is done for positive transitions (...
Page 618
En05000744.Vsd pulsecounter block read_val bi_pulse pulse input out database pulse counter value: 0...2147483647 sms settings 1.Operation = off/on 2.Treporting = 0s...60min 3.Event mask = no events/report events singlecmdfunc outx singlecmdfunc outx i/o-module pulse length >1s invalid restart blocke...
Page 619
The new_val signal is a pulse signal. The signal is set if the counter value was updated since last report. Note, the pulse is short, one cycle. The scal_val signal consists of scaled value (according to parameter scale), time and status information. 16.1.8 technical data ip14092-1 v1 m13404-2 v5 ta...
Page 620
The values of active and reactive energies are calculated from the input power values by integrating them over a selected time tenergy. The integration of active and reactive energy values will happen in both forward and reverse directions. These energy values are available as output signals and als...
Page 621
Pid-6872-outputsignals v3 table 434: etpmmtr output signals name type description accinprg boolean accumulation of energy values in progress eafpulse boolean accumulated forward active energy pulse earpulse boolean accumulated reverse active energy pulse erfpulse boolean accumulated forward reactive...
Page 622
Name values (range) unit step default description tenergyoffpls 0.100 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.500 energy accumulated pulse off time in secs eafaccplsqty 0.001 - 10000.000 mwh 0.001 100.000 pulse quantity for active forward accumulated energy value earaccplsqty 0.001 - 10000.000 mwh 0.001 100.000 pulse qu...
Page 623
16.2.6 monitored data pid-6872-monitoreddata v3 table 437: etpmmtr monitored data name type values (range) unit description eafacc real - mwh accumulated forward active energy value earacc real - mwh accumulated reverse active energy value erfacc real - mvarh accumulated forward reactive energy valu...
Page 624
Zero clamping detection p q maximum power demand calculation energy accumulation calculation startacc stopacc rstdmd maxpafd maxpard maxprfd maxprrd eafalm earalm erfalm erralm eafacc earacc erfacc erracc accinprg eafpulse earpulse erfpulse errpulse rstacc iec13000185-2-en.Vsd iec13000185 v2 en-us f...
Page 625
T f t f t f x 60.0 q -1 0.0 q -1 & rstacc eafprestval accinprg p* (active forward) eafacc a>b a b 1000 gwh q -1 = unit delay iec13000187-5-en.Vsdx iec13000187 v5 en-us figure 306: logic for integration of active forward energy the energy pulses generated by using internally calculated accumulated en...
Page 626
A>b a b counter rst cu cv x q -1 ÷ ÷ r i r i a>b a b 0 counter rst cu cv q -1 eafpulse rstacc eafacc t f t toff tp 0 q -1 tenergyoffpls 1000 gwh eafaccplsqty tenergyonpls q -1 = unit delay iec13000188-5-en.Vsdx iec13000188 v5 en-us figure 307: logic for pulse generation of integrated active forward ...
Page 627
16.2.8 technical data 16.2.8.1 technical data guid-da0a8ab5-755d-4f35-8c69-ffaa951fe374 v1 table 438: function range or value accuracy energy metering mwh export/import, mvarh export/import input from mmxu. No extra error at steady load 1mrk 505 394-uen a section 16 metering line differential protec...
Page 628
622.
Page 629
Section 17 ethernet 17.1 access point 17.1.1 introduction guid-6e5d2696-a8ee-43e7-a94b-69c3d0612127 v1 an access point is an ethernet communication interface for single or redundant station communication. Each access point is allocated with one physical ethernet port, two physical ethernet ports are...
Page 630
Name values (range) unit step default description pcm600access off on - - on pcm600 access ftp off on - - on ftp and ftps access mms off on - - on iec61850-8-1 mms goose off on - - on iec61850-8-1 goose dnp3 off on - - on dnp3 slave sntpserver off on - - on sntp server fstaccess off on - - on field ...
Page 631
Name values (range) unit step default description dnp3 off on - - on dnp3 slave sntpserver off on - - on sntp server fstaccess off on - - on field service tool access c37.118tcp off on - - on ieee 1344 and c37.118 tcp server c37.118udp1 off on - - on ieee 1344 and c37.118 udp stream and the tcp cont...
Page 632
17.2.2 function block guid-727bf536-1d60-4060-a674-5d73f252ccb7 v1 schlcch linkup dosalarm iec16000044-1-en.Vsdx iec16000044 v1 en-us figure 310: schlcch function block rchlcch redlinka redlinkb dosalarm iec16000045-1-en.Vsdx iec16000045 v1 en-us figure 311: rchlcch function block frontstatus linkup...
Page 633
17.2.4 monitored data pid-6818-monitoreddata v2 table 445: schlcch monitored data name type values (range) unit description gatewayconfig integer 0=ok 1=error -1=off 2=invalid - gateway configuration status pid-6819-monitoreddata v2 table 446: rchlcch monitored data name type values (range) unit des...
Page 634
17.3.2 functionality guid-494facf7-4be0-4b9f-a18f-47cd1e92c0f9 v1 prp iec 62439-3 redundant communication redundant communication according to iec 62439-3 prp-0 and iec 62439-3 prp-1 parallel redundancy protocol (prp) is available as an option when ordering ieds. Prp according to iec 62439-3 uses tw...
Page 635
Iec09000758-4-en.Vsd switch a ap1 phyportb phyporta ap1 phyporta phyportb ap1 phyportb phyporta ap1 phyporta phyportb switch b device 1 device 2 device 3 device 4 iec09000758 v4 en-us figure 313: redundant station bus iec 62439-3 high-availabillity seamless redundancy (hsr) hsr applies the principle...
Page 636
Iec16000038-1-en.Vsdx ap1 phyportb phyporta ap1 phyporta phyportb ap1 phyporta phyportb ap1 phyportb phyporta device 1 device 2 device 3 device 4 iec16000038 v1 en-us figure 314: hsr ring 17.4 merging unit 17.4.1 introduction guid-e630c16f-edb8-40ae-a8a2-94189982d15f v1 the iec/uca 61850-9-2le proce...
Page 637
17.4.2 settings pid-6770-settings v2 table 448: mu1 non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description samplevalueid 0 - 34 - 1 abb_mu0101 sample value id (svid) for the merging unit [0-34 char] apconnection none ap1 ap2 ap3 ap4 - - none access point connection for the merg...
Page 638
Name type values (range) unit description simmode boolean 1=yes 0=no - mu delivers simulated data accepted by ied badreference boolean 1=yes 0=no - badreference indication output for i1 derived boolean 1=yes 0=no - derived indication output for i1 failure boolean 1=yes 0=no - failure indication outp...
Page 639
Name type values (range) unit description source boolean 0=process 1=substituted - source indication output for i2 test boolean 1=yes 0=no - test indication output for i2 validity integer 0=good 2=reserved 1=invalid 3=questionable - validity indication output i2 badreference boolean 1=yes 0=no - bad...
Page 640
Name type values (range) unit description oscillatory boolean 1=yes 0=no - oscillatory indication output for i4 outofrange boolean 1=yes 0=no - outofrange indication output for i4 overflow boolean 1=yes 0=no - overflow indication output for i4 source boolean 0=process 1=substituted - source indicati...
Page 641
Name type values (range) unit description inconsistent boolean 1=yes 0=no - inconsistent indication output for u2 olddata boolean 1=yes 0=no - olddata indication output for u2 operatorblocked boolean 1=yes 0=no - operatorblocked indication output for u2 oscillatory boolean 1=yes 0=no - oscillatory i...
Page 642
Name type values (range) unit description derived boolean 1=yes 0=no - derived indication output for u4 failure boolean 1=yes 0=no - failure indication output for u4 inaccurate boolean 1=yes 0=no - inaccurate indication output for u4 inconsistent boolean 1=yes 0=no - inconsistent indication output f...
Page 643
Gateway source destination default gateway iec16000095-1-en.Vsdx iec16000095 v1 en-us figure 315: route from source to destination through gateway 17.5.2 settings pid-6761-settings v2 table 451: route_1 non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - -...
Page 644
638.
Page 645
Section 18 station communication 18.1 communication protocols m14815-3 v13 each ied is provided with several communication interfaces enabling it to connect to one or many substation level systems or equipment, either on the substation automation (sa) bus or substation monitoring (sm) bus. Available...
Page 646
Iec15000400-1-en.Vsd iec15000400 v1 en-us figure 316: protocol diagnostic screen in lhmi 18.3 dnp3 protocol guid-54a54716-23bd-4e7c-8245-de2b4c75e8dc v1 dnp3 (distributed network protocol) is a set of communications protocols used to communicate data between components in process automation systems....
Page 647
The front port is only intended for pcm600 communication, maintenance, training and test purposes due to risk of interference during normal operation. 18.4.2 communication interfaces and protocols guid-35c845d3-574a-40d1-aef1-9e0d330e31de v7 table 453: supported station communication interfaces and ...
Page 648
18.4.4 technical data ip14434-1 v1 m15031-1 v8 table 455: communication protocols function value protocol iec 61850-8-1 communication speed for the ieds 100base-fx protocol iec 60870–5–103 communication speed for the ieds 9600 or 19200 bd protocol dnp3.0 communication speed for the ieds 300–115200 b...
Page 649
Sp16gapc block ^in1 ^in2 ^in3 ^in4 ^in5 ^in6 ^in7 ^in8 ^in9 ^in10 ^in11 ^in12 ^in13 ^in14 ^in15 ^in16 iec14000020-1-en.Vsd iec14000020 v1 en-us figure 318: sp16gapc function block 18.4.5.3 signals semod55830-1 v2 pid-3780-inputsignals v6 table 456: spgapc input signals name type default description ...
Page 650
18.4.5.4 settings abbd8e283673 v3 the function does not have any parameters available in the local hmi or pcm600. 18.4.5.5 monitored data pid-3780-monitoreddata v3 table 458: spgapc monitored data name type values (range) unit description out group signal - - output status pid-3781-monitoreddata v3 ...
Page 651
18.4.5.6 operation principle semod55725-5 v7 upon receiving a signal at its input, generic communication function for single point indication (spgapc) function sends the signal over iec 61850-8-1 to the equipment or system that requests this signal. Additional configuration is needed with pcm600 or ...
Page 652
18.4.6.4 settings semod55954-1 v2 pid-6753-settings v1 table 462: mvgapc non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description baseprefix micro milli unit kilo mega giga tera - - unit base prefix (multiplication factor) mv db 1 - 100000 type 1 10000 cycl: report interval (s), ...
Page 653
18.4.6.6 operation principle semod55936-5 v7 upon receiving an analog signal at its input, generic communication function for measured value (mvgapc) will give the instantaneous value of the signal and the range, as output values. Additional configuration is needed with pcm600 or iet600 to get the i...
Page 654
Pid-6828-inputsignals v3 table 464: goosedprcv input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function srcdpout integer 0 source to double point output pid-6828-outputsignals v3 table 465: goosedprcv output signals name type description dpout integer double point output dataval...
Page 655
Data value data valid comm valid test receiver in test mode and incoming data with q= normal updated 1 1 0 receiver in test mode and incoming data with q= test updated 1 1 1 communication error 0 0 0 0 the input of this goose block must be linked either in smt by means of a cross or in act by means ...
Page 656
18.4.8.4 signals guid-2dc54788-86af-4b4b-8e57-a89e30f0c433 v1 except for the block input, the rest of the inputs of this goose function block are used for goose connections. These connections are visible and possible to make only if easy goose engineering is enabled. For instructions on how to enabl...
Page 657
Data value data valid comm valid test incoming data with q=normal updated 1 1 0 incoming data with q=olddata freeze 0 1 0 incoming data with q=invalid freeze 0 1 0 incoming data with q=test freeze 0 1 1 incoming data with q=test+olddata freeze 0 1 1 receiver in block freeze 0 1 0 receiver in block a...
Page 658
18.4.9.3 function block guid-a0b333cc-aef4-40ea-b152-364648ab78d3 v1 iec10000251-2-en.Vsd goosemvrcv block ^srcmvout ^mvout datavalid commvalid test iec10000251 v2 en-us figure 322: goosemvrcv function block 18.4.9.4 signals guid-2dc54788-86af-4b4b-8e57-a89e30f0c433 v1 except for the block input, th...
Page 659
The commvalid output will become low when the sending ied is under total failure condition and the goose transmission from the sending ied does not happen. The test output will go high if the sending ied is in test mode. Data value data valid comm valid test incoming data with q=normal updated 1 1 0...
Page 660
18.4.10.2 functionality guid-0c99a106-c131-45d3-9b81-6b188e35eb34 v3 goosesprcv is used to receive a single point value using iec 61850 protocol via goose. 18.4.10.3 function block guid-a414f31a-323f-4684-bada-46f9c5e2b0e8 v1 iec10000248-2-en.Vsd goosesprcv block ^srcspout ^spout datavalid commvalid...
Page 661
18.4.10.6 operation principle guid-0e25a3fb-41bd-4efe-9ca0-1262b9cd14cd v4 the datavalid output will be high if the incoming message is with valid data. The commvalid output will become low when the sending ied is under total failure condition and the goose transmission from the sending ied does not...
Page 662
18.4.11 horizontal communication via goose for interlocking gooseintlkrcv semod173197-1 v2 18.4.11.1 functionality guid-92ece152-892c-4214-95de-b92718689434 v2 goose communication can be used for exchanging information between ieds via the iec 61850-8-1 station communication bus. This is typically u...
Page 663
18.4.11.3 signals semod173205-1 v2 guid-2dc54788-86af-4b4b-8e57-a89e30f0c433 v1 except for the block input, the rest of the inputs of this goose function block are used for goose connections. These connections are visible and possible to make only if easy goose engineering is enabled. For instructio...
Page 664
Name type description app3_op boolean apparatus 3 position is open app3_cl boolean apparatus 3 position is closed app3val boolean apparatus 3 position is valid app4_op boolean apparatus 4 position is open app4_cl boolean apparatus 4 position is closed app4val boolean apparatus 4 position is valid ap...
Page 665
Name type description app15val boolean apparatus 15 position is valid commvalid boolean communication valid test boolean test output 18.4.11.4 settings semod173168-1 v2 pid-6831-settings v3 table 478: gooseintlkrcv non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operatio...
Page 666
The implementation for iec 61850 quality data handling is restricted to a simple level. If quality data validity is good then the appxval output will be high. If quality data validity is invalid, questionable, overflow, failure or old data then the appxval output will be low. 18.4.12 goose binary re...
Page 667
Pid-6827-inputsignals v3 table 479: goosebinrcv input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of output signals srcout1 boolean 0 source to binary output 1 srcout2 boolean 0 source to binary output 2 srcout3 boolean 0 source to binary output 3 srcout4 boolean 0 source to binary o...
Page 668
Name type description out9 boolean binary output 9 dvalid9 boolean valid data on binary output 9 out10 boolean binary output 10 dvalid10 boolean valid data on binary output 10 out11 boolean binary output 11 dvalid11 boolean valid data on binary output 11 out12 boolean binary output 12 dvalid12 boole...
Page 669
Data value data valid comm valid test incoming data with q=test+olddata 0 0 1 1 receiver in block 0 0 1 0 receiver in block and communication error 0 0 0 0 receiver in test mode and incoming data with q= normal updated 1 1 0 receiver in test mode and incoming data with q= test updated 1 1 1 communic...
Page 670
18.4.13.3 function block guid-690fd935-5344-4d6f-ab94-f9fd5fd35b23 v1 iec16000036-1-en.Vsdx goosexlnrcv block ^srcbeh ^srcloc ^srcblkopn ^srcblkcls ^srcpos ^srcopcnt ^srcblk ^srcstseld ^srcoprcvd ^srcopok ^srceehlt ^srcopcap ^beh beh_valid ^loc loc_valid ^blkopn blkopn_valid ^blkcls blkcls_valid ^po...
Page 671
Name type default description srcoprcvd boolean 0 source to operate command for a controllable data object received srcopok boolean 0 source to operate command for a controllable data object accepted srceehlt integer 0 source to external equipment health srcopcap integer 0 source to operating capabi...
Page 672
18.4.13.5 settings pid-6643-settings v3 table 484: goosexlnrcv non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation off/on 18.4.13.6 operation principle guid-903b5e3f-dc92-4d0a-b4d5-59dd01f36458 v1 the xxx_valid outputs will be high if the i...
Page 673
Are included in the configuration with the ethernet configuration tool. In the smt tool they can be mapped to the desired virtual input (smai) of the ied and used internally in the configuration. 18.5.3 signals 18.5.3.1 output signals semod166622-1 v1 guid-942c81ad-22d9-438f-95fa-1972ba2be2e5 v1 the...
Page 674
18.5.4 settings semod166625-1 v2 pid-6850-settings v3 table 486: mu1_hw non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description ctstarpoint1 fromobject toobject - - toobject toobject= towards protected object, fromobject= the opposite ctstarpoint2 fromobject toobject - - toobjec...
Page 675
Name type values (range) unit description olddata boolean 1=yes 0=no - olddata indication output for i1 operatorblocked boolean 1=yes 0=no - operatorblocked indication output for i1 oscillatory boolean 1=yes 0=no - oscillatory indication output for i1 outofrange boolean 1=yes 0=no - outofrange indic...
Page 676
Name type values (range) unit description failure boolean 1=yes 0=no - failure indication output for i3 inaccurate boolean 1=yes 0=no - inaccurate indication output for i3 inconsistent boolean 1=yes 0=no - inconsistent indication output for i3 olddata boolean 1=yes 0=no - olddata indication output f...
Page 677
Name type values (range) unit description validity integer 0=good 2=reserved 1=invalid 3=questionable - validity indication output i4 badreference boolean 1=yes 0=no - badreference indication output for u1 derived boolean 1=yes 0=no - derived indication output for u1 failure boolean 1=yes 0=no - fai...
Page 678
Name type values (range) unit description overflow boolean 1=yes 0=no - overflow indication output for u2 source boolean 0=process 1=substituted - source indication output for u2 test boolean 1=yes 0=no - test indication output for u2 validity integer 0=good 2=reserved 1=invalid 3=questionable - val...
Page 679
Name type values (range) unit description operatorblocked boolean 1=yes 0=no - operatorblocked indication output for u4 oscillatory boolean 1=yes 0=no - oscillatory indication output for u4 outofrange boolean 1=yes 0=no - outofrange indication output for u4 overflow boolean 1=yes 0=no - overflow ind...
Page 680
Ct ct combi sensor merging unit merging unit ethernet switch combi sensor conventional vt iec/uca 61850-9-2le iec/uca 61850-9-2le iec/uca 61850-9-2le splitter electrical-to- optical converter 1pps 1pps 1pps 110 v 1 a station wide gps clock iec080000723enoriginal.Vsd preprocessing blocks smai applica...
Page 681
• when synclostmode = block, and the time quality of the hardware is within the set value [syncacclevel=1us, 4us or unspecified] • when synclostmode = blockonlostutc, the time quality of the hardware is within the set value [syncacclevel=1us, 4us or unspecified] [and] ied receives global common time...
Page 682
• no[0] indicates that normal data is received and are accepted • yes[1] indicates that the received datastream is tagged as simulated and are accepted internal substitution can happen during the following conditions: 1. Transient block after receive error (sample loss) 2. Transient block after simu...
Page 683
Trm f1 f2 f3 f4 mu2 mu1 lost data blocked function iec16000049-1-en.Vsdx smai3 smai2 smai1 iec16000049 v1 en-us figure 328: an example of function blocking 18.5.6.1 iec 61850 quality expander qualexp guid-9c5dc78e-041b-422b-9668-320e62b847a2 v1 the quality expander component is used to display the d...
Page 684
The derived quality is the extension to iec 61850-7-3. If the derived bit is set to 1, it indicates that there is no physical sensor within the system to determine the value, but the value is derived from a combination of values from other physical sensors. Typically, i4 or u4 are derived if they ar...
Page 685
Follows the reference model for open system interconnection (osi) designed by the international standardization organization (iso). In this document the most common addresses for commands and events are available. For other addresses, refer to section related documents . It is assumed that the reade...
Page 686
Messages, such as measuring values, status information, and interlocking/blocking signals. Explicit messages are used to transfer longer pieces of information, such as events and explicit read and write messages to access device data. The benefits achieved from using the lon bus in protection and co...
Page 687
Binary events are generated in event function blocks event:1 to event:20 in the ieds. The event function blocks have predefined lon addresses. Table 491 shows the lon addresses to the first input on the event function blocks. Addresses to the other inputs on the event function block are consecutive ...
Page 688
Function block first lon address in function block event:17 1280 event:18 1296 event:19 1312 event:20 1328 event masks m15083-78 v4 event mask for each input can be set individually from parameter setting tool (pst) under: settings/ied settings/ monitoring / event function or via parameter setting t...
Page 689
Only one spa-bus message at a time to one node and waits for the reply before sending the next message. For commands from the operator workplace to the ied for apparatus control, that is the function blocks type scswi 1 to 30, sxcbr 1 to 18 and sxswi 1 to 24, the spa addresses are according to table...
Page 690
Name function block spa address description bl_cmd scswi20 1 i 5571 spa parameters for block command bl_cmd scswi21 1 i 5594 spa parameters for block command bl_cmd scswi22 1 i 5619 spa parameters for block command bl_cmd scswi23 1 i 5643 spa parameters for block command bl_cmd scswi24 1 i 5667 spa ...
Page 691
Name function block spa address description cancel scswi12 1 i 5371 spa parameters for cancel command cancel scswi13 1 i 5395 spa parameters for cancel command cancel scswi14 1 i 5419 spa parameters for cancel command cancel scswi15 1 i 5443 spa parameters for cancel command cancel scswi16 1 i 5467 ...
Page 692
Name function block spa address description selectopen=00, selectclose=01, so on. Scswi02 1 i 5129 spa parameters for select (open/ close) command selectopen=00, selectclose=01, so on. Scswi03 1 i 5151 spa parameters for select (open/ close) command selectopen=00, selectclose=01, so on. Scswi04 1 i ...
Page 693
Name function block spa address description selectopen=00, selectclose=01, so on. Scswi26 1 i 5705 spa parameters for select (open/ close) command selectopen=00, selectclose=01, so on. Scswi27 1 i 5729 spa parameters for select (open/ close) command selectopen=00, selectclose=01, so on. Scswi28 1 i ...
Page 694
Name function block spa address description excopen=00, excclose=01, so on. Scswi16 1 i 5466 spa parameters for operate (open/close) command excopen=00, excclose=01, so on. Scswi17 1 i 5490 spa parameters for operate (open/close) command excopen=00, excclose=01, so on. Scswi18 1 i 5514 spa parameter...
Page 695
Name function block spa address description sub value sxcbr07 2 i 7961 spa parameter for position to be substituted sub value sxcbr08 2 i 7980 spa parameter for position to be substituted sub value sxcbr09 3 i 7 spa parameter for position to be substituted sub value sxcbr10 3 i 26 spa parameter for ...
Page 696
Name function block spa address description sub value sxswi13 3 i 416 spa parameter for position to be substituted sub value sxswi14 3 i 435 spa parameter for position to be substituted sub value sxswi15 3 i 454 spa parameter for position to be substituted sub value sxswi16 3 i 473 spa parameter for...
Page 697
Name function block spa address description sub enable sxcbr08 2 i 7979 spa parameter for substitute enable command sub enable sxcbr09 3 i 8 spa parameter for substitute enable command sub enable sxcbr10 3 i 25 spa parameter for substitute enable command sub enable sxcbr11 3 i 46 spa parameter for s...
Page 698
Name function block spa address description sub enable sxswi14 3 i 436 spa parameter for substitute enable command sub enable sxswi15 3 i 455 spa parameter for substitute enable command sub enable sxswi16 3 i 474 spa parameter for substitute enable command sub enable sxswi17 3 i 493 spa parameter fo...
Page 699
Name function block spa address description update block sxcbr10 3 i 27 spa parameter for update block command update block sxcbr11 3 i 44 spa parameter for update block command update block sxcbr12 3 i 57 spa parameter for update block command update block sxcbr13 3 i 73 spa parameter for update bl...
Page 700
Name function block spa address description update block sxswi16 3 i 472 spa parameter for update block command update block sxswi17 3 i 491 spa parameter for update block command update block sxswi18 3 i 510 spa parameter for update block command update block sxswi19 3 i 529 spa parameter for updat...
Page 701
Multicmdsnd: 7 bay e1 multicmdsnd: 9 bay e3 lon bay e4 multicmdsnd: 9 en05000718.Vsd iec05000718 v2 en-us figure 330: examples connections between multicmdsnd and multicmdrcv function blocks in three ieds the network variable connections are done from the nv connection window. From lnt window select...
Page 702
En05000720.Vsd iec05000720 v1 en-us figure 332: the download configuration window in lnt communication ports m15083-97 v5 the serial communication module (slm) is a mezzanine module placed on the first analog digital conversion module (adm), and it is used for lon, spa, iec 60870-5-103 and dnp commu...
Page 703
Iec16000079-1-en.Vsd iec16000079 v1 en-us figure 333: rear view of 1/2 x 19” casing with 1 trm slot there are two types of io connectors: snap-in connectors for plastic fibre cables and st/bayonet connectors for glass fibre cables. The slm can be equipped with either type of connector or a combinati...
Page 704
18.7 spa communication protocol ip14614-1 v1 18.7.1 functionality m11897-3 v6 in this section the most common addresses for commands and events are available. For other addresses, refer to section related documents . It is assumed that the reader is familiar with the spa communication protocol in ge...
Page 705
Pid-6194-settings v5 table 495: lonspa non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - off operation slaveaddress 1 - 899 - 1 30 slave address 18.7.4 operation principle ip14401-1 v3 m11880-3 v2 the spa bus uses an asynchronous serial communications ...
Page 706
Function block spa address cnt_val spa address new_val pcfcnt:11 6-o-2848 6-o-2847 pcfcnt:12 6-o-2854 6-o-2853 pcfcnt:13 6-o-2860 6-o-2859 pcfcnt:14 6-o-2866 6-o-2865 pcfcnt:15 6-o-2872 6-o-2871 pcfcnt:16 6-o-2878 6-o-2877 i/o modules m11880-16 v4 to read binary inputs, the spa-addresses for the out...
Page 707
Function block spa address cmd input spa address cmd output singlecmd1-cmd12 4-s-4650 5-o-522 singlecmd1-cmdt13 4-s-4651 5-o-523 singlecmd1-cmd14 4-s-4652 5-o-524 singlecmd1-cmd15 4-s-4653 5-o-525 singlecmd1-cmd16 4-s-4654 5-o-526 singlecmd2-cmd1 4-s-4672 5-o-527 singlecmd2-cmd2 4-s-4673 5-o-528 sin...
Page 708
Function block spa address cmd input spa address cmd output singlecmd4-cmd3 4-s-4740 5-o-561 singlecmd4-cmd4 4-s-4741 5-o-562 singlecmd4-cmd5 4-s-4742 5-o-563 singlecmd4-cmd6 4-s-4743 5-o-564 singlecmd4-cmd7 4-s-4744 5-o-565 singlecmd4-cmd8 4-s-4745 5-o-566 singlecmd4-cmd9 4-s-4746 5-o-567 singlecmd...
Page 709
Event function event m11880-82 v6 the event function (event) sends time-tagged events to the station level (for example, operator workplace) over the station bus. On the station level, events are presented in an event list. Events can be created from both internal logical signals and binary input ch...
Page 710
Event block ^input1 ^input2 ^input3 ^input4 ^input5 ^input6 ^input7 ^input8 ^input9 ^input10 ^input11 ^input12 ^input13 ^input14 ^input15 ^input16 block ilrang psto ul12rang ul31rang ul23rang 3i0rang 3u0rang false iec07000065-2-en.Vsd iec07000065 v2 en-us figure 335: connection of protection signals...
Page 711
Iec16000079-1-en.Vsd iec16000079 v1 en-us figure 336: rear view of 1/2 x 19” casing with 1 trm slot there are two types of io connectors: snap-in connector for plastic fibre cables and st/bayonet connector for glass fibre cables. The slm can be equipped with either type or connector or with a combin...
Page 712
18.8 iec 60870-5-103 communication protocol ip14615-1 v2 18.8.1 introduction m11910-3 v3 iec 60870-5-103 communication protocol is mainly used when a protection ied communicates with a third party control or monitoring system. This system must have software that can interpret the iec 60870-5-103 com...
Page 713
18.8.2.3 function block guid-ec5f1c83-0f47-4548-86e3-ffe056571241 v2 iec10000287-1-en.Vsd i103meas block il1 il2 il3 in ul1 ul2 ul3 ul1l2 un p q f iec10000287 v1 en-us figure 337: i103meas function block 18.8.2.4 signals pid-6625-inputsignals v4 table 500: i103meas input signals name type default de...
Page 714
Name values (range) unit step default description maxin 1 - 99999 a 1 3000 maximum residual current in maxul1 0.05 - 2000.00 kv 0.05 230.00 maximum voltage for phase l1 maxul2 0.05 - 2000.00 kv 0.05 230.00 maximum voltage for phase l2 maxul3 0.05 - 2000.00 kv 0.05 230.00 maximum voltage for phase l3...
Page 715
18.8.3.4 signals pid-3791-inputsignals v5 table 502: i103measusr input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of service value reporting input1 real 0.0 service value for measurement on input 1 input2 real 0.0 service value for measurement on input 2 input3 real 0.0 service valu...
Page 716
18.8.4 function status auto-recloser for iec 60870-5-103 i103ar 18.8.4.1 functionality guid-7a132276-35a2-402c-9722-6259d65998f5 v1 i103ar is a function block with defined functions for autorecloser indications in monitor direction. This block includes the functiontype parameter, and the information...
Page 717
18.8.5 function status earth-fault for iec 60870-5-103 i103ef guid-f23b392e-b55d-4bc3-a0a6-b7992d551092 v1 18.8.5.1 functionality guid-13f90e95-7c8c-4dcb-a9d8-2489b66db81a v2 i103ef is a function block with defined functions for earth fault indications in monitor direction. This block includes the f...
Page 718
18.8.6 function status fault protection for iec 60870-5-103 i103fltprot 18.8.6.1 functionality guid-6d52f442-1592-4ba7-919c-0cd79046cae5 v1 i103fltprot is used for fault indications in monitor direction. Each input on the function block is specific for a certain fault type and therefore must be conn...
Page 719
18.8.6.3 function block guid-f0ed13b8-6b82-4ca7-8f22-c200c33ebb7e v2 i103fltprot block 64_stl1 65_stl2 66_stl3 67_stin 68_trgen 69_trl1 70_trl2 71_trl3 72_trbkup 73_scl 74_fw 75_rev 76_trans 77_recev 78_zone1 79_zone2 80_zone3 81_zone4 82_zone5 83_zone6 84_stgen 85_bfp 86_mtrl1 87_mtrl2 88_mtrl3 89_...
Page 720
Name type default description 74_fw boolean 0 information number 74, forward/line 75_rev boolean 0 information number 75, reverse/busbar 76_trans boolean 0 information number 76, signal transmitted 77_recev boolean 0 information number 77, signal received 78_zone1 boolean 0 information number 78, zo...
Page 721
18.8.7 ied status for iec 60870-5-103 i103ied 18.8.7.1 functionality guid-52ac7d0f-33c5-46fc-983e-5cb4b3517d88 v1 i103ied is a function block with defined ied functions in monitor direction. This block uses parameter as functiontype, and information number parameter is defined for each input signal....
Page 722
18.8.7.5 settings pid-3975-settings v5 table 511: i103ied non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description functiontype 1 - 255 - 1 1 function type (1-255) 18.8.8 supervison status for iec 60870-5-103 i103superv 18.8.8.1 functionality guid-e7a28d8d-398e-437c-9b58-ae125bc3...
Page 723
Name type default description 37_ibkup boolean 0 information number 37, i high-high back-up protection 38_vtff boolean 0 information number 38, fuse failure vt 46_grwa boolean 0 information number 46, group warning 47_gral boolean 0 information number 47, group alarm 18.8.8.5 settings pid-3976-setti...
Page 724
18.8.9.3 function block guid-b8312e77-514d-4117-bb31-b9907755580c v1 i103usrdef block ^input1 ^input2 ^input3 ^input4 ^input5 ^input6 ^input7 ^input8 rt_start iec10000294-3-en.Vsdx iec10000294 v3 en-us figure 344: i103usrdef function block 18.8.9.4 signals pid-6485-inputsignals v5 table 514: i103usr...
Page 725
18.8.9.5 settings pid-6485-settings v5 table 515: i103usrdef non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description functiontype 1 - 255 - 1 5 function type (1-255) infno1 1 - 255 - 1 1 information number for binary input 1 (1-255) infno2 1 - 255 - 1 2 information number for bi...
Page 726
Name values (range) unit step default description gino6 excluded included - - included response and status change (gi) gino7 excluded included - - included response and status change (gi) gino8 excluded included - - included response and status change (gi) guid-86de9dba-be2f-4cc9-b447-1d2d86849eff v...
Page 727
18.8.10.4 signals pid-3969-inputsignals v5 table 516: i103cmd input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of commands pid-3969-outputsignals v5 table 517: i103cmd output signals name type description 16-ar boolean information number 16, off/on of autorecloser 17-diff boolean in...
Page 728
18.8.11.3 function block guid-52d27cda-8805-48fa-99be-2e05a438b0c7 v1 iec10000283-1-en.Vsd i103iedcmd block 19-ledrs 23-grp1 24-grp2 25-grp3 26-grp4 iec10000283 v1 en-us figure 346: i103iedcmd function block 18.8.11.4 signals pid-3788-inputsignals v5 table 519: i103iedcmd input signals name type def...
Page 729
18.8.12.2 identification guid-9d6d1636-36c6-4c4e-b157-2d827820ddc7 v1 function description function block name iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number function commands user defined for iec 60870-5-103 i103usrcmd - - 18.8.12.3 function block guid-5ebeaed5-abd9-4257-b879-df7fd9f7805a v...
Page 730
18.8.12.5 settings pid-3790-settings v5 table 524: i103usrcmd non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description functiontype 1 - 255 - 1 1 function type (1-255) pulsemode steady pulsed - - pulsed pulse mode pulselength 0.200 - 60.000 s 0.001 0.400 pulse length infno_1 1 - ...
Page 731
18.8.13.3 function block guid-6ec8453e-0d00-4720-95a6-156c41ca46bb v1 iec10000285-1-en.Vsd i103gencmd block ^cmd_off ^cmd_on iec10000285 v1 en-us figure 348: i103gencmd function block 18.8.13.4 signals pid-3970-inputsignals v5 table 525: i103gencmd input signals name type default description block b...
Page 732
Input position is a double-indication signal, and it is gi enabled. This means that any state transition, that is to on, off, intermediate and faulty, is reported spontaneously. However, the intermediate and faulty states may be suppressed by setting the report intermediate position = off. See the s...
Page 733
18.8.14.5 settings pid-6997-settings v1 table 529: i103poscmd non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description functiontype 1 - 255 - 1 1 function type infno 160 - 236 - 4 160 information number for command output 18.8.15 ied commands with position for iec 60870-5-103 i10...
Page 734
18.8.15.3 function block guid-031c0f49-bebd-40fe-a33f-18f1d94bb4b0 v1 i103poscmdv block position iec15000081-2-en.Vsdx iec15000081 v2 en-us figure 350: i103poscmdv function block 18.8.15.4 signals pid-6578-inputsignals v5 table 530: i103poscmdv input signals name type default description block boole...
Page 735
• autorecloser on/off • teleprotection on/off • protection on/off • led reset • characteristics 1 - 4 (setting groups) • file transfer (disturbance files) • time synchronization for detailed information about iec 60870-5-103, refer to the iec 60870 standard part 5: transmission protocols, and to the...
Page 736
Information number is defined for each output signals. Table 533: pre-defined i103cmd supported indications inf description 16 auto-recloser on/off 17 teleprotection on/off 18 protection on/off function commands in control direction, user-defined, i103usrcmd m11874-72 v6 function command blocks in c...
Page 737
Table 535: i103ied supported functions inf description 19 led reset 21 testmode 22 local parameter setting 23 setting group 1 active 24 setting group 2 active 25 setting group 3 active 26 setting group 4 active function status indications in monitor direction, user-defined, i103usrdef m11874-137 v7 ...
Page 738
Table 537: i103superv supported functions inf description typ gi cot 32 measurand supervision i 1 y 1,7,9 33 measurand supervision u 1 y 1,7,9 37 i>>back-up operation 1 y 1,7,9 38 vt fuse failure 1 y 1,7,9 46 group warning 1 y 1,7,9 47 group alarm 1 y 1,7,9 earth fault indications in monitor directi...
Page 739
Table 540: i103fltprot supported functions inf description typ gi cot 64 start phase l1 2 y 1,7,9 65 start phase l2 2 y 1,7,9 66 start phase l3 2 y 1,7,9 67 start residual current in 2 y 1,7,9 68 trip general 2 n 1,7 69 trip phase l1 2 n 1,7 70 trip phase l2 2 n 1,7 71 trip phase l3 2 n 1,7 72 back ...
Page 740
Upper limit for measured currents, active/reactive-power is 2.4 times rated value. Upper limit for measured voltages and frequency is 1.2 times rated value. The upper limit is the maximum value that can be encoded into the asdu (application service data unit). Any value higher than this value will b...
Page 741
Table 542: i103measusr supported indications inf fun gi typ cot description * 1) * 2) no, polled with cl2 * 3) 2,7 meas1 * * no, polled with cl2 * 2,7 meas2 * * no, polled with cl2 * 2,7 meas3 * * no, polled with cl2 * 2,7 meas4 * * no, polled with cl2 * 2,7 meas5 * * no, polled with cl2 * 2,7 meas6...
Page 742
Channel number used for the remaining 32 analog signals are numbers in the private range 64 to 95. Binary signals, 128-channels: for each channel the user can specify a function type and an information number. M11874-629 v7 disturbance upload all analog and binary signals that are recorded with dist...
Page 743
Action. Fan is equal to disturbance number, which is incremented for each disturbance. Asdu26 / asdu31 when a disturbance has been selected by the master by sending asdu24, the protection equipment answers by sending asdu26, which contains an information element named nof (number of grid faults). Th...
Page 744
Supported 10 generic data no 11 generic identification no 23 list of recorded disturbances yes 26 ready for transm. Of disturbance data yes 27 ready for transm. Of a channel yes 28 ready for transm of tags yes 29 transmission of tags yes 30 transmission fo disturbance data yes 31 end of transmission...
Page 745
18.8.17 technical data ip14417-1 v1 m11921-1 v4 table 543: iec 60870-5-103 communication protocol function value protocol iec 60870-5-103 communication speed 9600, 19200 bd 18.9 multicmdrcv and multicmdsnd semod119881-1 v3 guid-1a6e066c-6399-4d37-8ca5-3074537e48b2 v3 function description iec 61850 i...
Page 746
18.9.3 function block semod119978-1 v1 semod119976-5 v2 iec06000007-2-en.Vsd multicmdrcv block error newdata output1 output2 output3 output4 output5 output6 output7 output8 output9 output10 output11 output12 output13 output14 output15 output16 valid iec06000007 v2 en-us figure 351: multicmdrcv funct...
Page 747
Pid-399-inputsignals v10 table 545: multicmdsnd input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block of function input1 boolean 0 input 1 input2 boolean 0 input 2 input3 boolean 0 input 3 input4 boolean 0 input 4 input5 boolean 0 input 5 input6 boolean 0 input 6 input7 boolean 0 input 7...
Page 748
Name type description output15 boolean output 15 output16 boolean output 16 valid boolean output data is valid pid-399-outputsignals v10 table 547: multicmdsnd output signals name type description error boolean multisend error 18.9.5 settings semod119927-1 v2 pid-400-settings v10 table 548: multicmd...
Page 749
Function, which sets the output connector "valid" to 0 (zero) if its block does not receive any data within the time defined by tmaxcycletime. Lon connections are established using lon network tool (lnt). 18.10 security events on protocols secalarm 18.10.1 security alarm secalarm guid-205b0024-da06-...
Page 750
18.11.2 settings pid-6908-settings v2 table 552: activlog non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description extlogsrv1type off syslog udp/ip syslog tcp/ip cef tcp/ip - - off external log server 1 type extlogsrv1port 1 - 65535 - 1 514 external log server 1 port number extlo...
Page 751
Section 19 remote communication 19.1 binary signal transfer ip12423-1 v2 19.1.1 identification m14849-1 v3 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number binary signal transfer, receive binsignrec1_1 binsignrec1_2 binsignreceive2 - - binary signa...
Page 752
Pid-6471-outputsignals v2 table 553: ldcmrecbinstat1 output signals name type description comfail boolean detected error in the differential communication addrerr boolean incoming message from non-valid address crcerror boolean identified error by crc check in incoming message remblkdf boolean remot...
Page 753
Pid-6473-outputsignals v2 table 555: ldcmrecbinstat3 output signals name type description ch1 string remote communication channel 1 ch2 string remote communication channel 2 ch3 string remote communication channel 3 ch4 string remote communication channel 4 comfail boolean detected error in the diff...
Page 754
Name values (range) unit step default description optopower lowpower highpower - - lowpower transmission power for ldcm comalarmdel 5 - 10000 ms 5 100 time delay before communication alarm signal is activated comalrmresdel 5 - 10000 ms 5 100 reset delay before communication alarm signal is reset pid...
Page 755
Pid-6473-settings v2 table 558: ldcmrecbinstat3 non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description channelmode blocked normal outofservice - - normal channel mode of ldcm terminalno 0 - 255 - 1 0 terminal number used for line differential communication remotetermno 0 - 255 ...
Page 756
19.1.5 monitored data pid-6471-monitoreddata v2 table 559: ldcmrecbinstat1 monitored data name type values (range) unit description commstatus boolean 0=ok 1=syncerr 2=no rxd 3=localgpserr 4=remgpserr 5=locandremg pserr 6=localaderr 7=remaderr 8=locandrema derr 9=addresserr 10=freqconferr 11=latency...
Page 757
19.1.6 operation principle m12452-14 v5 in 64 kbit mode, communication takes place in standard itu (ccitt) pcm digital 64 kbit/s channels. Communication is two-way, and telegrams are sent every 5 ms (same in 50 hz and 60 hz) to exchange information between two ieds. The format used is c37.94, and on...
Page 758
19.2 transmission of local analog data via ldcm to remote end, function block ldcmtrn called ldcmtransmit guid-b057c0dd-4ea8-4f6a-b57c-3395dfb38463 v2 19.2.1 identification guid-3387f71e-020e-4556-aa55-8204340efa47 v1 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c...
Page 759
Name type default description ct2l2 string 0 input to be used for transmit ct-group2 line l2 to remote end ct2l3 string 0 input to be used for transmit ct-group2 line l3 to remote end ct2n string 0 input to be used for transmit ct-group2 neutral n to remote end 1mrk 505 394-uen a section 19 remote c...
Page 760
754.
Page 761
Section 20 security 20.1 authority check athchck 20.1.1 identification guid-fbef319b-94e6-41fb-bb9f-d870e0425128 v2 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number authority check athchck - - 20.1.2 functionality semod117051-23 v6 to safeguard the...
Page 762
Iec12000202-2-en.Vsd iec12000202 v2 en-us figure 355: pcm600 user management tool 20.1.3 operation principle guid-b555edd0-baf1-4f0e-9162-bdb3a3468cf2 v8 there are different levels (or types) of users that can access or operate different areas of the ied and tools functionality. The pre-defined user...
Page 763
Table 563: pre-defined user types access rights guest super user spa guest system operator protection engineer design engineer user administrator basic setting possibilities (change setting group, control settings, limit supervision) r r/w r r/w r/w r/w r advanced setting possibilities (for example ...
Page 764
Only characters a - z, a - z and 0 - 9 should be used in user names and passwords. The maximum of characters in a password is 18. At least one user must be included in the useradministrator group to be able to write users, created in pcm600, to ied. Semod176296-5 v9 at delivery the default user is t...
Page 765
One user can have one or several user roles. By default, the users in table 564 are created in the ied, and when creating new users in the sdm600 server, the predefined roles from table 565 can be used. At delivery, the ied user has full access as superuser when using the lhmi and as administrator w...
Page 766
The successfully activation of central account management will disable built-in users or remove all local created users from pcm600. Management of user credentials and roles is handled on the central account management server e.G. Sdm600 the ied employs two strategies to ensure availability of the a...
Page 767
For more information on the functions authority management (authman), authority status (athstat), and authority check (athchck) functions, refer to chapter “basic ied functions” in the technical manual. 20.2 authority management authman 20.2.1 identification guid-7925e6a3-301d-44a5-982f-167805eea473...
Page 768
The automatic negotiation mode acts on configured port number 21 and server features, it tries to negotiate with explicit tls via auth tls. If the specified port is any other, it tries to negotiate in a similar way. Using ftp without tls encryption gives the ftp client reduced capabilities. This mod...
Page 769
20.4.3 function block semod158547-4 v4 iec06000503-2-en.Vsd athstat usrblked loggedon iec06000503 v2 en-us figure 356: athstat function block 20.4.4 signals pid-3773-outputsignals v6 table 569: athstat output signals name type description usrblked boolean at least one user is blocked by invalid pass...
Page 770
20.5 self supervision with internal event list interrsig ip1721-1 v2 20.5.1 functionality m11399-3 v7 self supervision with internal event list function listens and reacts to internal system events, generated by the different built-in self-supervision elements. The internal events are saved in an in...
Page 771
• normal micro-processor watchdog function. • checking of digitized measuring signals. • other alarms, for example hardware and time synchronization. The self-supervision function status can be monitored from the local hmi or from the event viewer in pcm600. Under the diagnostics menu in the local h...
Page 772
Module. This contact is closed when the ied either does not have auxiliary power, or when one or more error conditions are present in the ied (for example harware error). Some output signals are available from the interrsig function block. The signals from this function block are sent as events via ...
Page 773
Name of signal description displayed on local hmi as reasons for activation iec61850error iec 61850 error status iec61850 this signal will be active if the iec 61850 stack did not succeed in some actions like reading iec 61850 configuration, startup, for example dnp3 dnp3 error status dnp3 this sign...
Page 774
Card name of signal description displayed on local hmi as reasons for activation adm adm-error a/d module error status adm32 activated if the module has a hardware error. Ldcm ldcm-error line differentia l communi cation module error status ldcm3nn activated if the module has a hardware error. N = s...
Page 775
20.6.2 function block guid-15aa1d42-912e-4085-8166-33fdc327ceb5 v2 iec09000946.Vsd chnglck lock* active override iec09000946 v2 en-us figure 360: chnglck function block 20.6.3 signals guid-1b253577-c81b-40e3-b406-1f6586dce545 v2 pid-3786-inputsignals v6 table 574: chnglck input signals name type def...
Page 776
Binary input function 1 activated 0 deactivated 20.7 denial of service dos 20.7.1 functionality guid-407250ca-0076-41e1-ad2d-434077ac3f1d v5 the denial of service functionality limits overload on the ied produced by heavy ethernet network traffic. The communication facilities must not be allowed to ...
Page 777
The dos functionality activates when the inbound traffic rate exceeds 3000 packets per second. 1mrk 505 394-uen a section 20 security line differential protection red650 2.2 iec 771 technical manual.
Page 778
772.
Page 779
Section 21 basic ied functions 21.1 time synchronization timesynchgen ip1750-1 v2 21.1.1 functionality m11344-3 v10 the time synchronization function is used to select a common source of absolute time for the synchronization of the ied when it is a part of a protection system. This makes it possible...
Page 780
Pid-6638-settings v3 table 576: timesynchgen non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description coarsesyncsrc off spa lon dnp iec103 - - off coarse time synchronization source finesyncsource off spa lon bin gps gps+spa gps+lon gps+bin sntp gps+sntp irig-b gps+irig-b pps - -...
Page 781
Guid-cd154442-0f80-4b69-8c43-22445fd7f865 v1 gps settings are not supported by 650 due to hardware restrictions. Pid-6188-settings v6 table 577: bininput non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description moduleposition 3 - 16 - 1 3 hardware position of io module for time s...
Page 782
Pid-3967-settings v7 table 580: dstbegin non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description monthinyear january february march april may june july august september october november december - - march month in year when daylight time starts dayinweek sunday monday tuesday we...
Page 783
Pid-3968-settings v7 table 581: dstend non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description monthinyear january february march april may june july august september october november december - - october month in year when daylight time ends dayinweek sunday monday tuesday wedn...
Page 784
Pid-4138-settings v5 table 582: timezone non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description timezone -12:00 -11:00 -10:00 -9:30 -9:00 -8:00 -7:00 -6:00 -5:00 -4:30 -4:00 -3:30 -3:00 -2:00 -1:00 0:00 1:00 2:00 3:00 3:30 4:00 4:30 5:00 5:30 5:45 6:00 6:30 7:00 8:00 8:45 9:00 ...
Page 785
Pid-6630-settings v2 table 584: ptp non group settings (advanced) name values (range) unit step default description domain 0 - 127 - 1 0 0 = default domain, 1-3 = alternative domain, 4-127 = user defined priority1 0 - 255 - 1 128 the clock with the lowest priority 1 becomes the reference clock (gran...
Page 786
Sw time time regulator (fast or slow) time tagging and general synchronization time regulator (setting: see technical manual) commu- nication events synchronization for differential protection (echo mode) diff. Commu- nication *iec 61850-9-2 iec16000002-2-en.Vsdx external synchronization sources mer...
Page 787
Fast clock synchronization mode at start-up and after interruptions in the irig b time signals, the deviation between the external time system and the internal differential time system can be substantial. A new start-up is also required, for example, after maintenance of the auxiliary voltage system...
Page 788
• the maximum error of the last used synchronization message • the time since the last used synchronization message • the rate accuracy of the internal clock in the function. 21.1.3.2 real-time clock (rtc) operation m11346-57 v3 the ied has a built-in real-time clock (rtc) with a resolution of one s...
Page 789
Time-out on synchronization sources m11346-96 v3 all synchronization interfaces have a time-out, and a configured interface must receive time synchronization messages regularly in order not to give an error signal (tsyncerr) that is reported from the interrsig function block. The time-out is such th...
Page 790
Synchronization via binary input m11346-42 v6 the ied accepts minute pulses to a binary input. These minute pulses can be generated from, for example station master clock. If the station master clock is not synchronized from a world wide source, time will be a relative time valid for the substation....
Page 791
If contact bounce occurs, only the first pulse will be detected as a minute pulse. The next minute pulse will be registered first 60 s - 50 ms after the last contact bounce. If the minute pulses are perfect, for example, it is exactly 60 seconds between the pulses, contact bounces might occur 49 ms ...
Page 792
The irig-b module also takes care of ieee1344 messages that are sent by irig-b clocks, as irig-b previously did not have any year information. Ieee1344 is compatible with irig-b and contains year information and information of the time-zone. 21.1.3.4 process bus iec/uca 61850-9-2le synchronization g...
Page 793
The ied connects the access points via a boundary clock. If ptp is “on” on redundant access points, the ied acts as a “transparent clock”. In a network there may be variety of possible masters that are connected together where the masters by selection, using the priority of ptp (also called the best...
Page 794
Guid-8aeb81d0-1731-46df-a206-d2e758823575 v1 table 586: time synchronization ptp: iec/ieee 61850-9-3 supported types of clock boundary clock (bc), ordinary clock (oc), transparent clock (tc) accuracy according to standard iec/ieee 61850-9-3 number of nodes according to standard iec/ieee 61850-9-3 po...
Page 795
Pid-6558-outputsignals v6 table 588: actvgrp output signals name type description grp1 boolean setting group 1 is active grp2 boolean setting group 2 is active grp3 boolean setting group 3 is active grp4 boolean setting group 4 is active grp5 boolean setting group 5 is active grp6 boolean setting gr...
Page 796
More than one input may be activated at the same time. In such cases the lower order setting group has priority. This means that if for example both group four and group two are set to be activated, group two will be the one activated. Every time a setting is changed, the output signal setchgd is se...
Page 797
21.3 test mode functionality testmode ip1647-1 v3 21.3.1 functionality m4803-3 v10 when entering ied test mode there is an option to block all functions. Active test mode is indicated by a flashing yellow start led on the lhmi. After that, it is possible to unblock arbitrarily selected functions fro...
Page 798
Name type description noevent boolean event disabled during test mode input boolean ied test input is active setting boolean ied test mode setting is on iec61850 boolean active when ld0 mode is in blocked, test or test blocked 21.3.4 settings ip11343-1 v2 pid-6730-settings v1 table 592: testmode non...
Page 799
If the ied is restarted while set to ied testmode by a binary input all functions will be temporarily unblocked during startup, which might cause unwanted operations. The testmode function block might be used to automatically block functions when a test handle is inserted in a test switch. A contact...
Page 800
21.5 product information prodinf guid-f67243ca-2429-4118-bbff-3d62bf55e080 v2 21.5.1 functionality guid-d78786e6-c34a-4e63-9d1e-0582c8f1f7e1 v8 product information contains unchangeable data that uniquely identifies the ied. Product information data is visible on the local hmi under main menu/ diagn...
Page 801
Firmware versions depending on the small issues corrected in between releases. • productver • describes the product version. Example: 2.1.0 1 is the major version of the manufactured product this means, new platform of the product 2 is the minor version of the manufactured product this means, new fu...
Page 802
21.6.3 signals semod55814-1 v2 pid-3940-inputsignals v5 table 594: smbi input signals name type default description bi1 boolean 0 smt connect input bi2 boolean 0 smt connect input bi3 boolean 0 smt connect input bi4 boolean 0 smt connect input bi5 boolean 0 smt connect input bi6 boolean 0 smt connec...
Page 803
21.7 signal matrix for binary outputs smbo semod55215-1 v2 21.7.1 functionality m15311-3 v5 the signal matrix for binary outputs (smbo) function is used within the application configuration tool (act) in direct relation with the signal matrix tool (smt), see the application manual to get information...
Page 804
21.7.4 operation principle semod55864-4 v7 the signal matrix for binary outputs (smbo) function , see figure 368 , receives logical signal from the ied configuration, which is transferring to the real (hardware) outputs, via the signal matrix tool (smt) or act. The inputs in smbo are bo1 to bo10 and...
Page 805
Semod54997-4 v10 smai2 block revrot ^grp2l1 ^grp2l2 ^grp2l3 ^grp2n g2ai3p g2ai1 g2ai2 g2ai3 g2ai4 g2n iec14000028-1-en.Vsd iec14000028 v1 en-us figure 370: smai2 function block figure 370 is an example of smai2:n to smai12:m in each of the three task time groups 1, 2 or 3 where: • n=2 and m=12 in ta...
Page 806
Name type description g1ai3 group signal group 1 analog input 3 g1ai4 group signal group 1 analog input 4 g1n group signal group parameter for residual sample pid-3406-inputsignals v6 table 599: smai2 input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block group 2 revrot boolean 0 reverse ...
Page 807
Pid-3405-settings v5 table 601: smai1 non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description globalbasesel 1 - 12 - 1 1 selection of one of the global base value groups dftrefextout internaldftref dftrefgrp1 dftrefgrp2 dftrefgrp3 dftrefgrp4 dftrefgrp5 dftrefgrp6 dftrefgrp7 dftr...
Page 808
Pid-3406-settings v5 table 603: smai2 non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description globalbasesel 1 - 12 - 1 1 selection of one of the global base value groups dftreference internaldftref dftrefgrp1 dftrefgrp2 dftrefgrp3 dftrefgrp4 dftrefgrp5 dftrefgrp6 dftrefgrp7 dftr...
Page 809
Note that all other functions, with a few exceptions, use this output in configuration. Note that the smai function will always calculate the residual sum of current/voltage if the input grpxn is not connected in smt. Applications with a few exceptions shall always be connected to ai3p. 21.8.5.1 fre...
Page 810
The outputs from the above configured smai block shall only be used for overfrequency protection (saptof), underfrequency protection (saptuf) and rate-of-change frequency protection (sapfrc) due to that all other information except frequency and positive sequence voltage might be wrongly calculated....
Page 811
Pid-6428-outputsignals v4 table 606: 3phsum output signals name type description spfcout real number of samples per fundamental cycle from internal dft reference function ai3p group signal linear combination of two connected three phase inputs ai1 group signal linear combination of input 1 signals f...
Page 812
21.9.5 operation principle semod55749-4 v5 summation block 3 phase 3phsum receives the three-phase signals from signal matrix for analog inputs function (smai). In the same way, the block input will reset all the outputs of the function to 0. 21.10 global base values gbasval guid-2fdb0a2c-10fe-4954-...
Page 813
21.11 primary system values primval 21.11.1 identification guid-b8b3535d-227b-4151-9e98-beb85f4d54de v1 function description iec 61850 identification iec 60617 identification ansi/ieee c37.2 device number primary system values primval - - 21.11.2 functionality m15288-3 v6 the rated system frequency ...
Page 814
808.
Page 815
Section 22 ied hardware 22.1 overview ip14270-1 v1 22.1.1 variants of case size with local hmi display m15024-3 v5 iec04000458-2-en.Psd iec04000458 v2 en-us figure 373: 1/2 19” case with local hmi display. 1mrk 505 394-uen a section 22 ied hardware line differential protection red650 2.2 iec 809 tec...
Page 816
22.1.2 case from the rear side ip16286-1 v1 m16105-3 v8 table 611: designations for 1/2 x 19” casing with 1 trm slot front view 1/2x19" p40 p31 p30 p5 p4 p3 p1 p31 :1 p 30:4 p 3 0 :3 p 30 :2 p 30:1 p31 :2 p30 :5 p31 :3 p30 :6 rear view x11 x31 x41 x51 x401 x301 x302 x303 x304 x311 a b c d x305 x312 ...
Page 817
22.2 hardware modules ip14529-1 v1 22.2.1 overview m11562-3 v9 table 612: basic modules module description power supply module (psm) including a regulated dc/dc converter that supplies auxiliary voltage to all static circuits. • an internal fail alarm output is available. Numerical module (num) modu...
Page 818
Module description galvanic rj45 ethernet sfps small form factor pluggable for ethernet communication galvanic rs485 communication module (rs485) module used for dnp3 and iec 60870-5-103 communication irig-b time synchronization module (irig-b) module with 2 inputs. One is used for handling both pul...
Page 819
22.2.2.3 technical data semod55319-1 v1 semod55310-2 v11 table 614: sfp - optical ethernet port quantity rated value number of channels 4 single or 2 redundant can be used for single or redundant communication using any protocol standard ieee 802.3u 100base-fx type of fiber 62.5/125 mm multimode fib...
Page 820
22.2.3.2 design ip14278-1 v1 m6377-3 v2 there are two types of the power supply module. They are designed for different dc input voltage ranges see table 617 . The power supply module contains a built- in, self-regulated dc/dc converter that provides full isolation between the terminal and the exter...
Page 821
22.2.5.1 introduction m14875-3 v9 the transformer input module is used to galvanically separate and adapt the secondary currents and voltages generated by the measuring transformers. The module has twelve inputs in different combinations of currents and voltage inputs. Alternative connectors of ring...
Page 822
1mrk006501-af-trm-iec-6502p1 v1 en-us figure 375: trm connection diagram 22.2.5.3 technical data semod55412-1 v1 m16988-1 v11 table 618: trm - energizing quantities, rated values and limits for protection transformer description value frequency rated frequency f r 50/60 hz operating range f r ± 10% ...
Page 823
Description value voltage inputs **) rated voltage u r 110 or 220 v operating range 0 - 340 v thermal withstand 450 v for 10 s 420 v continuously burden **) all values for individual voltage inputs note! All current and voltage data are specified as rms values at rated frequency 22.2.6 analog digita...
Page 824
Pmc pci to pci pc-mip pc-mip ad3 ad1 ad2 ad4 channel 1 channel 2 channel 3 channel 4 channel 5 channel 6 channel 7 channel 8 channel 9 channel 10 channel 11 channel 12 1.2v 2.5v level shift en05000474.Vsd iec05000474 v1 en-us figure 376: the adm layout section 22 1mrk 505 394-uen a ied hardware 818 ...
Page 825
22.2.7 binary input module (bim) ip14535-1 v1 22.2.7.1 introduction m1769-3 v4 the binary input module has 16 optically isolated inputs and is available in two versions, one standard and one with enhanced pulse counting capabilities on the inputs to be used with the pulse counter function. The binar...
Page 826
300 176 144 88 72 38 32 19 17 24/30v 48/60v 110/125v 220/250v [v] xx06000391-2-en.Vsd iec06000391 v2 en-us figure 377: voltage dependence for the binary inputs iec99000517-abc v1 en-us operation operation uncertain no operation this binary input module communicates with the numerical module (num). T...
Page 827
En07000104-3.Vsd 50 55 [ms] [ma] iec07000104 v3 en-us figure 378: approximate binary input inrush current for the standard version of bim. En07000105-1.Vsd 50 5.5 [ms] [ma] iec07000105 v2 en-us figure 379: approximate binary input inrush current for the bim version with enhanced pulse counting capab...
Page 828
Iec99000503 v3 en-us figure 380: connection diagram 22.2.7.3 signals pid-6435-outputsignals v5 table 620: bim output signals name type description status boolean binary input module status bi1 boolean binary input 1 value bi2 boolean binary input 2 value bi3 boolean binary input 3 value bi4 boolean ...
Page 829
Name type description bi7 boolean binary input 7 value bi8 boolean binary input 8 value bi9 boolean binary input 9 value bi10 boolean binary input 10 value bi11 boolean binary input 11 value bi12 boolean binary input 12 value bi13 boolean binary input 13 value bi14 boolean binary input 14 value bi15...
Page 830
22.2.7.6 technical data semod55338-1 v1 m12576-1 v9 table 623: bim - binary input module quantity rated value nominal range binary inputs 16 - dc voltage, rl 24/30 v 48/60 v 110/125 v 220/250 v rl ±20% rl ±20% rl ±20% rl ±20% power consumption 24/30 v, 50 ma 48/60 v, 50 ma 110/125 v, 50 ma 220/250 v...
Page 831
22.2.8.2 design m1819-3 v4 the binary output module (bom) has 24 software supervised output relays. Each pair of relays have a common power source input to the contacts, see figure 381 . This should be considered when connecting the wiring to the connection terminal on the back of the ied. The high ...
Page 832
Iec99000505 v3 en-us figure 382: connection diagram 22.2.8.3 signals pid-3439-inputsignals v2 table 625: bom input signals name type default description block boolean 0 block binary outputs bo1 boolean 0 binary output 1 bo2 boolean 0 binary output 2 bo3 boolean 0 binary output 3 bo4 boolean 0 binary...
Page 833
Name type default description bo13 boolean 0 binary output 13 bo14 boolean 0 binary output 14 bo15 boolean 0 binary output 15 bo16 boolean 0 binary output 16 bo17 boolean 0 binary output 17 bo18 boolean 0 binary output 18 bo19 boolean 0 binary output 19 bo20 boolean 0 binary output 20 bo21 boolean 0...
Page 834
Name type values (range) unit description bo2force boolean 0=normal 1=forced - binary output 2 force bo2 boolean 0=normal 1=forced 2=blocked - binary output 2 status bo3value boolean 1=1 0=0 - binary output 3 value bo3force boolean 0=normal 1=forced - binary output 3 force bo3 boolean 0=normal 1=for...
Page 835
Name type values (range) unit description bo9 boolean 0=normal 1=forced 2=blocked - binary output 9 status bo10value boolean 1=1 0=0 - binary output 10 value bo10force boolean 0=normal 1=forced - binary output 10 force bo10 boolean 0=normal 1=forced 2=blocked - binary output 10 status bo11value bool...
Page 836
Name type values (range) unit description bo16 boolean 0=normal 1=forced 2=blocked - binary output 16 status bo17value boolean 1=1 0=0 - binary output 17 value b017force boolean 0=normal 1=forced - binary output 17 force bo17 boolean 0=normal 1=forced 2=blocked - binary output 17 status bo18value bo...
Page 837
Name type values (range) unit description bo23 boolean 0=normal 1=forced 2=blocked - binary output 23 status bo24value boolean 1=1 0=0 - binary output 24 value bo24force boolean 0=normal 1=forced - nary output 24 force bo24 boolean 0=normal 1=forced 2=blocked - binary output 24 status 22.2.8.6 techn...
Page 838
22.2.9 binary input/output module (iom) ip15582-1 v1 22.2.9.1 introduction m6939-3 v6 the binary input/output module is used when only a few input and output channels are needed. The ten standard output channels are used for trip output or any signaling purpose. The two high speed signal output chan...
Page 839
Iec1mrk002801-aa11-utan-ram v2 en-us figure 383: binary in/out module (iom), input contacts named xa corresponds to rear position x31, x41, and so on, and output contacts named xb to rear position x32, x42, and so on semod175370-4 v1 the binary input/output module version with mov protected contacts...
Page 840
Xx04000069.Vsd iec04000069 v1 en-us figure 384: iom with mov protection, relay example 22.2.9.3 signals pid-6434-outputsignals v4 table 630: iomin output signals name type description status boolean binary input part of iom module status bi1 boolean binary input 1 value bi2 boolean binary input 2 va...
Page 841
22.2.9.4 settings pid-4050-settings v2 table 632: iomin non group settings (basic) name values (range) unit step default description operation off on - - on binary input/output module in operation (on) or not (off) debouncetime 0.001 - 0.020 s 0.001 0.001 debounce time for binary inputs oscblock 1 -...
Page 842
Name type values (range) unit description bo4 boolean 0=normal 1=forced 2=blocked - binary output 4 status bo5value boolean 1=1 0=0 - binary output 5 value bo5force boolean 0=normal 1=forced - binary output 5 force bo5 boolean 0=normal 1=forced 2=blocked - binary output 5 status bo6value boolean 1=1...
Page 843
Name type values (range) unit description bo11 boolean 0=normal 1=forced 2=blocked - binary output 11 status bo12value boolean 1=1 0=0 - binary output 12 value bo12force boolean 0=normal 1=forced - binary output 12 force bo12 boolean 0=normal 1=forced 2=blocked - binary output 12 status 22.2.9.6 tec...
Page 844
Function or quantity trip and signal relays fast signal relays (parallel reed relay) making capacity at inductive load with l/r > 10 ms 0.2 s 1.0 s 30 a 10 a 0.4 a 0.4 a making capacity at resistive load 0.2 s 1.0 s 30 a 10 a 220–250 v/0.4 a 110–125 v/0.4 a 48–60 v/0.2 a 24–30 v/0.1 a breaking capac...
Page 845
22.2.10 serial and lon communication module (slm) ip15583-1 v2 22.2.10.1 introduction m14933-3 v5 the serial and lon communication module (slm) is used for spa, iec 60870-5-103, dnp3 and lon communication. Slm has two optical communication ports for plastic/plastic, plastic/glass or glass/glass fibr...
Page 846
When the slm connectors are viewed from the rear side of the ied, contact 4 is in the topmost position and contact 1 in the lowest position. 22.2.10.3 technical data semod117454-1 v1 m12589-1 v4 table 638: slm – lon port quantity range or value optical connector glass fiber: type st plastic fiber: t...
Page 847
22.2.11.2 design semod158668-1 v1 semod158670-4 v3 rs485 is a pc-mip card, and it is factory mounted as a mezzanine card on the analog digital conversion module (adm). Rs485 connector pinouts semod158670-10 v1 the arrangement for the pins in the rs485 connector (figure 386 ) are presented in table 6...
Page 848
Soft ground connector pinouts semod158670-45 v1 a second 2-pole screw connector is used for the connection of io-ground. It can be used in two combinations like: • unconnected: no ground of the io-part · . • soft grounded: the io is connected to the gnd with an rc net parallel with a mov 22.2.11.3 t...
Page 849
• adm • num st st io -c o n n e c to r iec07000087-3-en.Vsdx 1 2 iec07000087 v3 en-us figure 387: sr-ldcm layout with two pci connectors and one i/o st type connector 1. Receiver 2. Transmitter c iec06000393-3-en.Vsdx iec06000393 v3 en-us figure 388: mr-ldcm layout with two pci connectors and one i/...
Page 850
Table 642: line data communication module characteristic range or value type of ldcm short range (sr) medium range (mr) type of fiber graded-index multimode 62.5/125 µm singlemode 9/125 µm peak emission wave length nominal maximum minimum 820 nm 865 nm 792 nm 1310 nm 1330 nm 1290 nm optical budget g...
Page 851
St y2 t a1 iec06000304=1=en=original.Ai iec06000304 v2 en-us figure 389: irig-b pc-mip board with top left st connector for optical irig-b 00x 820 nm multimode fibre optic signal input and lower left bnc connector for irig-b signal input 22.2.13.3 settings pid-5187-settings v5 table 643: irig-b non ...
Page 852
Quantity rated value amplitude modulated – low level – high level 1-3 vpp 3 x low level, max 9 vpp supported formats irig-b 00x, irig-b 12x accuracy +/-10μs for irig-b 00x and +/-100μs for irig-b 12x input impedance 100 k ohm optical connector: optical connector irig-b type st type of fibre 62.5/125...
Page 853
Iec05000502 v2 en-us figure 391: case with rear cover and 19” rack mounting kit iec15000448-1-en.Vsd iec15000448 v1 en-us figure 392: rear cover case with details m11985-120 v4 case size (mm) a b c d e f g h j k 6u, 1/2 x 19” 265.9 223.7 242.1 255.8 205.7 190.5 203.7 465.1 228.6 482.6 the h and k di...
Page 854
22.3.2 case without rear cover semod53195-1 v1 m2152-3 v5 iec04000448-3-en.Vsdx c d e a b iec04000448 v3 en-us figure 393: case without rear cover g f k h j iec04000464-3-en.Vsdx iec04000464 v3 en-us figure 394: case without rear cover with 19” rack mounting kit section 22 1mrk 505 394-uen a ied har...
Page 855
M2152-11 v4 case size (mm) a b c d e f g h j k 6u, 1/2 x 19” 266.7 224.0 204.1 249.9 205.8 190.5 204.0 242.3 188.9 259.1 the h and k dimensions are defined by the 19” rack mounting kit 22.3.3 flush mounting dimensions m11571-3 v6 c a iec04000465-3-en.Vsd b e d iec04000465 v3 en-us figure 395: flush ...
Page 856
22.3.4 side-by-side flush mounting dimensions m11984-3 v6 iec06000182-2-en.Vsd iec06000182 v2 en-us figure 396: a 1/2 x 19” size ied side-by-side with rhgs6 xx05000505.Vsd b a c g d e f iec05000505 v1 en-us figure 397: panel-cut out dimensions for side-by-side flush mounting case size (mm) tolerance...
Page 857
22.3.5 wall mounting dimensions m11569-3 v4 iec04000471-2-en.Vsd iec04000471 v2 en-us figure 398: wall mounting case size (mm) a b c d e 6u, 1/2 x 19” 292.0 267.1 272.8 390.0 243.0 22.4 mounting alternatives ip11721-1 v1 22.4.1 flush mounting ip10303-1 v1 22.4.1.1 overview m11967-3 v5 the flush moun...
Page 858
To obtain ip54 class protection, an additional factory mounted sealing must be ordered when ordering the ied. 22.4.1.2 mounting procedure for flush mounting m11942-2 v5 1 5 6 3 iec16000080=1=en.Vsd 2 4 iec16000080 v1 en-us figure 399: flush mounting details. Posno description quantity type 1 sealing...
Page 859
The mounting angles are reversible which enables mounting of the ied either to the left or the right side of the cubicle. A separately ordered rack mounting kit for side-by-side mounted ieds or ieds together with rhgs cases should be selected so that the total size equals 19”. Use only the screws in...
Page 860
Posno description quantity type 1a, 1b mounting angles, can be mounted either to the left or the right side of the case 2 - 2 screw 8 m4x6 3 washer 8 m4x6 22.4.3 wall mounting ip10316-1 v1 22.4.3.1 overview m11973-3 v6 the ied can be mounted on a wall, a panel or in a cubicle. Use only the screws in...
Page 861
22.4.3.2 mounting procedure for wall mounting m11949-2 v2 iec130 00266-1-en.Vsd 1 2 3 4 5 6 iec13000266 v1 en-us figure 401: wall mounting details. Posno description quantity type 1 bushing 4 - 2 screw 8 m4x10 3 screw 4 m6x12 or corresponding 4 mounting bar 2 - 5 screw 6 m5x8 6 side plate 2 - 22.4.3...
Page 862
80 mm 1 3 2 iec06000135-2-en.Vsd iec06000135 v3 en-us figure 402: how to reach the connectors on the rear side of the ied. Posno description type 1 screw m4x10 2 screw m5x8 3 rear protection cover (ordered separately) 22.4.4 side-by-side 19” rack mounting ip10323-1 v1 22.4.4.1 overview m11974-3 v3 i...
Page 863
22.4.4.2 mounting procedure for side-by-side rack mounting m11955-2 v3 iec040004563enoriginal.Vsdx 1 2 3 4 3 iec04000456 v3 en-us figure 403: side-by-side rack mounting details. The required torque for the screws is 3.5 nm. Posno description quantity type 1 mounting plate 2 - 2, 3 screw 16 m4x6 4 mo...
Page 864
8 8 8 7 5 6 3 4 2 7 5 6 7 5 6 3 4 2 3 4 2 1 1 2 1 1 1 8 7 5 6 3 4 2 2 1 iec06000180-2-en.Vsd iec06000180 v2 en-us figure 404: ied (1/2 x 19”) mounted with a rhgs6 case containing a test switch module equipped with only a test switch and a rx2 terminal base 22.4.5 side-by-side flush mounting ip10329-...
Page 865
22.4.5.2 mounting procedure for side-by-side flush mounting m12730-6 v4 1 2 3 4 iec06000181-2-en.Vsd iec06000181 v2 en-us figure 405: side-by-side flush mounting details (rhgs6 side-by-side with 1/2 x 19” ied). The required torque for the screws is 3.5 nm. Posno description quantity type 1 mounting ...
Page 866
M12327-1 v4 table 646: water and dust protection level according to iec 60529 front ip40 (ip54 with sealing strip) sides, top and bottom ip40 rear side ip20 with screw compression type ip10 with ring lug terminals m11777-1 v5 table 647: weight case size weight 6u, 1/2 x 19” £ 10 kg/22 lb 22.5.2 elec...
Page 867
Table 651: binary i/o connectors connector type rated voltage maximum conductor area screw compression type 250 v ac 2.5 mm 2 (awg14) 2 × 1 mm 2 (2 x awg18) 22.5.4 influencing factors semod52785-1 v1 m16705-1 v12 table 652: temperature and humidity influence parameter reference value nominal range i...
Page 868
22.5.5 type tests according to standard ip16288-1 v1 m16706-1 v9 table 655: electromagnetic compatibility test type test values reference standards 1 mhz burst disturbance 2.5 kv iec 60255-26 100 khz slow damped oscillatory wave immunity test 2.5 kv iec 61000-4-18, class iii ring wave immunity test,...
Page 869
Table 657: environmental tests test type test value reference standard cold operation test test ad for 16 h at -25°c iec 60068-2-1 cold storage test test ab for 16 h at -40°c iec 60068-2-1 dry heat operation test test bd for 16 h at +70°c iec 60068-2-2 dry heat storage test test bb for 16 h at +85°c...
Page 870
864.
Page 871
Section 23 labels 23.1 labels on ied semod168249-4 v4 front view of ied iec16000081=1=en.Vsdx 9 8 7 6 5 4 1 2 3 10 iec16000081 v1 en-us figure 406: example of ied label 1 qr-code containing the complete ordering code 2 power supply module (psm) 3 ordering and serial number 4 manufacturer 5 transform...
Page 872
Rear view of ied iec15000573=2=en=original.Wsdx 1 2 2 3 iec15000573 v2 en-us 1 warning label 2 caution label 3 class 1 laser product label it is used when an optical sfp or an mr ldcm is configured in the product. Iec06000575 v1 en-us section 23 1mrk 505 394-uen a labels 866 line differential protec...
Page 873
Section 24 connection diagrams guid-cf4effa5-3081-4fc7-9a14-ed127c3c0fde v6 the connection diagrams are delivered in the ied connectivity package as part of the product delivery. The latest versions of the connection diagrams can be downloaded from http://www.Abb.Com/protection-control . Connection ...
Page 874
868.
Page 875
Section 25 inverse time characteristics 25.1 application m16686-3 v5 in order to assure time selectivity between different overcurrent protections at different points in the network different time delays for the different protections are normally used. The simplest way to do this is to use definite ...
Page 876
En05000131.Vsd time fault point position iec05000131 v1 en-us figure 409: inverse time overcurrent characteristics with inst. Function the inverse time characteristic makes it possible to minimize the fault clearance time and still assure the selectivity between protections. To assure selectivity be...
Page 877
En05000132.Vsd i> i> a1 b1 feeder time axis t=0 t=t 1 t=t 2 t=t 3 iec05000132 v1 en-us figure 410: selectivity steps for a fault on feeder b1 where: t=0 is the fault occurs t=t 1 is protection b1 trips t=t 2 is breaker at b1 opens t=t 3 is protection a1 resets in the case protection b1 shall operate...
Page 878
• if there is a risk of intermittent faults. If the current ied, close to the faults, starts and resets there is a risk of unselective trip from other protections in the system. • delayed resetting could give accelerated fault clearance in case of automatic reclosing to a permanent fault. • overcurr...
Page 879
For inverse time characteristics a time will be initiated when the current reaches the set start level. From the general expression of the characteristic the following can be seen: ( ) - × × - = × > æ ö æ ö ç ÷ ç ÷ è ø è ø p op i t b k c a k in equation1190 v1 en-us (equation 94) where: t op is the ...
Page 880
Iec05000133-3-en.Vsd tmin current operate time imin iec05000133 v2 en-us figure 411: minimum time-lag operation for the iec curves in order to fully comply with iec curves definition setting parameter tmin shall be set to the value which is equal to the operating time of the selected iec inverse tim...
Page 881
The rd inverse curve gives a logarithmic delay, as used in the combiflex protection rxidg. The curve enables a high degree of selectivity required for sensitive residual earth-fault current protection, with ability to detect high-resistive earth faults. The curve is described by equation 98 : [ ] 5....
Page 882
[ ] 2 1 r t t s k i in = × - > æ ö ç ÷ ç ÷ ç ÷ æ ö ç ÷ ç ÷ è ø è ø equation1197 v2 en-us (equation 100) where: the set value t r is the reset time in case of zero current after fault clearance. The possibility of choice of reset characteristics is to some extent dependent of the choice of time delay...
Page 883
25.3 inverse characteristics ip15797-1 v2 m12388-1 v21 table 660: ansi inverse time characteristics function range or value accuracy operating characteristic: ( ) 1 p a t b k tdef i æ ö ç ÷ = + × + ç ÷ ç - ÷ è ø equation1249-small v2 en-us reset characteristic: ( ) 2 1 = × - tr t k i equation1250-sm...
Page 884
Table 661: ansi inverse time characteristics for line differential protection function range or value accuracy operating characteristic: ( ) 1 p a t b k tdef i æ ö ç ÷ = + × + ç ÷ ç - ÷ è ø equation1249-small v2 en-us reset characteristic: ( ) 2 1 = × - tr t k i equation1250-small v1 en-us i = i mea...
Page 885
Table 662: iec inverse time characteristics function range or value accuracy operating characteristic: ( ) 1 = × - æ ö ç ÷ ç ÷ è ø p a t k i equation1251-small v1 en-us i = i measured /i set 0.10 ≤ k ≤ 3.00 1.5 x i set ≤ i ≤ 20 x i set iec 60255-151, ±2.0% or ±40 ms whichever is greater iec normal i...
Page 886
Table 663: iec inverse time characteristics for line differential protection function range or value accuracy operating characteristic: ( ) 1 = × - æ ö ç ÷ ç ÷ è ø p a t k i equation1251-small v1 en-us i = i measured /i set 0.10 ≤ k ≤ 3.00 1.5 x i set ≤ i ≤ 20 x i set iec 60255-151, ±5.0% or ±40 ms ...
Page 887
Table 665: ri and rd type inverse time characteristics for line differential protection function range or value accuracy ri type inverse characteristic 1 0.236 0.339 = × - t k i equation1137-small v1 en-us i = i measured /i set 0.10 ≤ k ≤ 3.00 1.5 x i set ≤ i ≤ 20 x i set iec 60255-151, ±5.0% or ±40...
Page 888
Table 667: iec inverse time characteristics for line differential protection function range or value accuracy operating characteristic: ( ) 1 = × - æ ö ç ÷ ç ÷ è ø p a t k i equation1251-small v1 en-us i = i measured /i set k = (0.05-2.00) in steps of 0.01 iec 60255-151, ± 5.0% or ± 40 ms whichever ...
Page 889
Guid-19f8e187-4ed0-48c3-92f6-0d9eaa2b39bb v3 table 669: ansi inverse time characteristics for sensitive directional residual overcurrent and power protection function range or value accuracy operating characteristic: ( ) 1 p a t b k tdef i æ ö ç ÷ = + × + ç ÷ ç - ÷ è ø equation1249-small v2 en-us re...
Page 890
Table 670: iec inverse time characteristics for sensitive directional residual overcurrent and power protection function range or value accuracy operating characteristic: ( ) 1 = × - æ ö ç ÷ ç ÷ è ø p a t k i equation1251-small v1 en-us i = i measured /i set 0.10 ≤ k ≤ 2.00 1.5 x i set ≤ i ≤ 20 x i ...
Page 891
Table 671: ri and rd type inverse time characteristics for sensitive directional residual overcurrent and power protection function range or value accuracy ri type inverse characteristic 1 0.236 0.339 = × - t k i equation1137-small v1 en-us i = i measured /i set 0.10 ≤ k ≤ 2.00 1.5 x i set ≤ i ≤ 20 ...
Page 892
Table 673: iec inverse time characteristics for voltage restrained time overcurrent protection function range or value accuracy operating characteristic: ( ) 1 = × - æ ö ç ÷ ç ÷ è ø p a t k i equation1251-small v1 en-us i = i measured /i set 0.10 ≤ k ≤ 3.00 iec 60255-151, ±5.0% or ±40 ms whichever i...
Page 893
Table 675: inverse time characteristics for undervoltage protection function range or value accuracy type a curve: = æ ö ç ÷ è ø k t u u u equation1431-small v1 en-us u set u = u measured k = (0.05-1.10) in steps of 0.01 ±5.0% or ±45 ms whichever is greater type b curve: 2.0 480 0.055 32 0.5 × = + ×...
Page 894
Table 676: inverse time characteristics for residual overvoltage protection function range or value accuracy type a curve: = - > > æ ö ç ÷ è ø t k u u u equation1436-small v1 en-us u> = u set u = u measured k = (0.05-1.10) in steps of 0.01 ±5.0% or ±45 ms whichever is greater type b curve: 2.0 480 3...
Page 895
Semod118114-4 v4 a070750 v2 en-us figure 412: ansi extremely inverse time characteristics 1mrk 505 394-uen a section 25 inverse time characteristics line differential protection red650 2.2 iec 889 technical manual.
Page 896
A070751 v2 en-us figure 413: ansi very inverse time characteristics section 25 1mrk 505 394-uen a inverse time characteristics 890 line differential protection red650 2.2 iec technical manual.
Page 897
A070752 v2 en-us figure 414: ansi normal inverse time characteristics 1mrk 505 394-uen a section 25 inverse time characteristics line differential protection red650 2.2 iec 891 technical manual.
Page 898
A070753 v2 en-us figure 415: ansi moderately inverse time characteristics section 25 1mrk 505 394-uen a inverse time characteristics 892 line differential protection red650 2.2 iec technical manual.
Page 899
A070817 v2 en-us figure 416: ansi long time extremely inverse time characteristics 1mrk 505 394-uen a section 25 inverse time characteristics line differential protection red650 2.2 iec 893 technical manual.
Page 900
A070818 v2 en-us figure 417: ansi long time very inverse time characteristics section 25 1mrk 505 394-uen a inverse time characteristics 894 line differential protection red650 2.2 iec technical manual.
Page 901
A070819 v2 en-us figure 418: ansi long time inverse time characteristics 1mrk 505 394-uen a section 25 inverse time characteristics line differential protection red650 2.2 iec 895 technical manual.
Page 902
A070820 v2 en-us figure 419: iec normal inverse time characteristics section 25 1mrk 505 394-uen a inverse time characteristics 896 line differential protection red650 2.2 iec technical manual.
Page 903
A070821 v2 en-us figure 420: iec very inverse time characteristics 1mrk 505 394-uen a section 25 inverse time characteristics line differential protection red650 2.2 iec 897 technical manual.
Page 904
A070822 v2 en-us figure 421: iec inverse time characteristics section 25 1mrk 505 394-uen a inverse time characteristics 898 line differential protection red650 2.2 iec technical manual.
Page 905
A070823 v2 en-us figure 422: iec extremely inverse time characteristics 1mrk 505 394-uen a section 25 inverse time characteristics line differential protection red650 2.2 iec 899 technical manual.
Page 906
A070824 v2 en-us figure 423: iec short time inverse time characteristics section 25 1mrk 505 394-uen a inverse time characteristics 900 line differential protection red650 2.2 iec technical manual.
Page 907
A070825 v2 en-us figure 424: iec long time inverse time characteristics 1mrk 505 394-uen a section 25 inverse time characteristics line differential protection red650 2.2 iec 901 technical manual.
Page 908
A070826 v2 en-us figure 425: ri-type inverse time characteristics section 25 1mrk 505 394-uen a inverse time characteristics 902 line differential protection red650 2.2 iec technical manual.
Page 909
A070827 v2 en-us figure 426: rd-type inverse time characteristics 1mrk 505 394-uen a section 25 inverse time characteristics line differential protection red650 2.2 iec 903 technical manual.
Page 910
Guid-acf4044c-052e-4cbd-8247-c6abe3796fa6 v1 en-us figure 427: inverse curve a characteristic of overvoltage protection section 25 1mrk 505 394-uen a inverse time characteristics 904 line differential protection red650 2.2 iec technical manual.
Page 911
Guid-f5e0e1c2-48c8-4dc7-a84b-174544c09142 v1 en-us figure 428: inverse curve b characteristic of overvoltage protection 1mrk 505 394-uen a section 25 inverse time characteristics line differential protection red650 2.2 iec 905 technical manual.
Page 912
Guid-a9898db7-90a3-47f2-aef9-45ff148cb679 v1 en-us figure 429: inverse curve c characteristic of overvoltage protection section 25 1mrk 505 394-uen a inverse time characteristics 906 line differential protection red650 2.2 iec technical manual.
Page 913
Guid-35f40c3b-b483-40e6-9767-69c1536e3cbc v1 en-us figure 430: inverse curve a characteristic of undervoltage protection 1mrk 505 394-uen a section 25 inverse time characteristics line differential protection red650 2.2 iec 907 technical manual.
Page 914
Guid-b55d0f5f-9265-4d9a-a7c0-e274aa3a6bb1 v1 en-us figure 431: inverse curve b characteristic of undervoltage protection section 25 1mrk 505 394-uen a inverse time characteristics 908 line differential protection red650 2.2 iec technical manual.
Page 915
Section 26 glossary m14893-1 v16 ac alternating current acc actual channel act application configuration tool within pcm600 a/d converter analog-to-digital converter adbs amplitude deadband supervision adm analog digital conversion module, with time synchronization ai analog input ansi american nati...
Page 916
Ccitt consultative committee for international telegraph and telephony. A united nations-sponsored standards body within the international telecommunications union. Ccm can carrier module ccvt capacitive coupled voltage transformer class c protection current transformer class as per ieee/ ansi cmpps...
Page 917
Dhcp dynamic host configuration protocol dip-switch small switch mounted on a printed circuit board di digital input dllb dead line live bus dnp distributed network protocol as per ieee std 1815-2012 dr disturbance recorder dram dynamic random access memory drh disturbance report handler dsp digital...
Page 918
Gde graphical display editor within pcm600 gi general interrogation command gis gas-insulated switchgear goose generic object-oriented substation event gps global positioning system gsal generic security application gse generic substation event hdlc protocol high-level data link control, protocol ba...
Page 919
I-gis intelligent gas-insulated switchgear iom binary input/output module instance when several occurrences of the same function are available in the ied, they are referred to as instances of that function. One instance of a function is identical to another of the same kind but has a different numbe...
Page 920
Nof number of grid faults num numerical module oco cycle open-close-open cycle ocp overcurrent protection oltc on-load tap changer otev disturbance data recording initiated by other event than start/pick-up ov overvoltage overreach a term used to describe how the relay behaves during a fault conditi...
Page 921
Rtu remote terminal unit sa substation automation sbo select-before-operate sc switch or push button to close scl short circuit location scs station control system scada supervision, control and data acquisition sct system configuration tool according to standard iec 61850 sdu service data unit sfp ...
Page 922
Transport layer protocols. While tcp and ip specify two protocols at specific protocol layers, tcp/ip is often used to refer to the entire us department of defense protocol suite based upon these, including telnet, ftp, udp and rdp. Tef time delayed earth-fault protection function tls transport laye...
Page 923
3i o three times zero-sequence current.Often referred to as the residual or the earth-fault current 3u o three times the zero sequence voltage. Often referred to as the residual voltage or the neutral point voltage 1mrk 505 394-uen a section 26 glossary line differential protection red650 2.2 iec 91...
Page 924
918.
Page 925
919.
Page 926
— abb ab grid automation products 721 59 västerås, sweden phone: +46 (0) 21 32 50 00 abb.Com/protection-control © copyright 2017 abb. All rights reserved. Specifications subject to change without notice. 1mrk 505 394-uen.