- DL manuals
- Access
- Barcode Reader
- ATR110
- Product Manual
Access ATR110 Product Manual
Access-IS
18 Suttons Business Park, Reading
Berkshire, RG6 1AZ, United Kingdom
Tel: +44 (0) 118 966 3333
Web: www.access-is.com
Email: support@access-is.com
Product names
mentioned herein are for
identification purposes
only and may be
trademarks and/or
registered trademarks of
their respective
companies.
© Copyright 2016
ALL RIGHTS
RESERVED
Subject: ATR110 Manual
Revision: 1.4
Issue Date: 15/03/2016
ATR110
1D/2D Barcode Imager
(Barcode Only Version)
Product Manual
Summary of ATR110
Page 1
Access-is 18 suttons business park, reading berkshire, rg6 1az, united kingdom tel: +44 (0) 118 966 3333 web: www.Access-is.Com email: support@access-is.Com product names mentioned herein are for identification purposes only and may be trademarks and/or registered trademarks of their respective comp...
Page 2
Page 2 of 39 copyright © access-is 2016 warnings this manual contains important information regarding the installation and operation of the atr110 1d/2d barcode imager. For safe and reliable operation of the imager, installers must ensure that they are familiar with and fully understand all instruct...
Page 3
Page 3 of 39 copyright © access-is 2016 contents 1. Overview .................................................................................................................... 4 2. Specifications .........................................................................................................
Page 4
Page 4 of 39 copyright © access-is 2016 figure 1. Atr110 1d/2d barcode imager 1. Overview the atr110 is a compact and fast barcode reader, which can process a wide range of electronic ticketing across a variety of media. The device reads all popular linear, pdf417 and 2d barcode symbologies, includi...
Page 5
Page 5 of 39 copyright © access-is 2016 2. Specifications specification details dimensions (l x w x h) 120.6 mm x 96.0 mm x 81.2 mm weight 443 g (with cable) environmental operating temperature: -25ºc to 50ºc storage temperature: -30ºc to 70ºc humidity: 95% non-condensing designed to meet ip54 body ...
Page 6
Page 6 of 39 copyright © access-is 2016 3. Installation 3.1 unpack the atr110 unpack the atr110 and ensure that you have the following items: advisory notice card. Atr110 device with attached serial or usb cable. Serial unit: usb power injector cable or power supply (iec cable not supplied). Report ...
Page 7
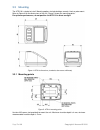
Page 7 of 39 copyright © access-is 2016 3.3 mounting the atr110 is simple to install. Mounting options include desktop, console, kiosk or pole-mount. Refer to figure 4 for the dimensions of the unit. Figure 5 shows the mounting points. For optimum performance, do not position the atr110 in direct su...
Page 8
Page 8 of 39 copyright © access-is 2016 figure 6. Pole-mount cable connection 3.3.2 pole mounting an optional pole-mount kit allows you to mount the device on a 1.25 inch or 1.5 inch diameter pole. If the mounting bracket is pre-fitted to the unit, attach the unit to the pole as follows: 1. Remove t...
Page 9
Page 9 of 39 copyright © access-is 2016 3.4 interface options 3.4.1 serial connection connect a serial atr110 device using an rs232 interface directly into a com port. You must specify the baud rate, parity, data bits and stop bits. Note: a serial atr110 communicates directly with the com port and d...
Page 10
Page 10 of 39 copyright © access-is 2016 3.5 serial installation a serial atr110 communicates directly with the com port and does not require any special software or drivers to be loaded. 1. Switch off the computer. 2. Connect the serial cable to a com port on the computer and finger-tighten the two...
Page 11
Page 11 of 39 copyright © access-is 2016 3.7 test the device once you have connected the device and installed the relevant drivers, if applicable, you can test the device. To do this, wave a piece of paper in front of the glass; the reader’s leds should illuminate. If the device fails to respond whe...
Page 12
Page 12 of 39 copyright © access-is 2016 4. Operating modes the atr110 operates in one of three ways, as defined by the aisomd command. Refer to the command reference on page 18 for a list of commands that you can send to configure the atr110. 4.1 mode summary 4.1.1 dumb mode the atr110 is a one-way...
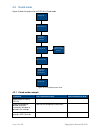
Page 13
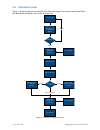
Page 13 of 39 copyright © access-is 2016 4.2 dumb mode figure 9 shows the process for an atr110 in dumb mode. Figure 9. Dumb mode process flow 4.2.1 dumb mode example comments atr command to host host command to atr media placed in front of atr110. - - imager activated and barcode scanned. Illuminat...
Page 14
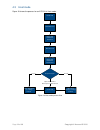
Page 14 of 39 copyright © access-is 2016 4.3 host mode figure 10 shows the process for an atr110 in host mode. Figure 10. Host mode process flow media detected imager and illumination activated barcode read data sent to host. Imager and illumination deactivated accept or reject? Lights ‘bad read’ (a...
Page 15
Page 15 of 39 copyright © access-is 2016 4.3.1 host mode example 4.3.1.1 accept comments atr command to host host command to atr media placed in front of atr110. - - imager activated and barcode scanned. Illumination activated as defined in the settings. Data sent as configured (usb/serial) - host d...
Page 16
Page 16 of 39 copyright © access-is 2016 4.4 interactive mode figure 11 shows the process for an atr110 in interactive mode. The host can send ‘good read’ and ‘bad read’ commands to the atr110 at any time. Figure 11. Interactive mode process flow media detected, message sent requesting trigger send ...
Page 17
Page 17 of 39 copyright © access-is 2016 4.4.1 interactive mode example 4.4.1.1 ‘good read’ initiated by atr110 detecting media comments atr command to host host command to atr media placed in front of atr110. The atr110 sends commands to host notifying of media. [0x16][0x0d]trig:1[0x16][0x0a] - hos...
Page 18
Page 18 of 39 copyright © access-is 2016 5. Command reference commands are sent with a prefix of [0x16][0x4d][0x0d] causing the command sequence to take the form [0x16][0x4d][0x0d] . The menu commands are six characters long with a parameter (if required). To send a command to modify a configuration...
Page 19
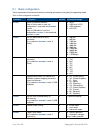
Page 19 of 39 copyright © access-is 2016 5.1 basic configuration these commands set the device interface, connection parameters and specify the operating mode. Table 2. Basic configuration commands command description default parameters/range aisinf selects the device interface. When a serial cable ...
Page 20
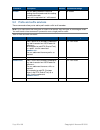
Page 20 of 39 copyright © access-is 2016 command description default parameters/range dlygrd sets the delay between successful reading of one barcode and the reading of another barcode. Each unit is equivalent to 1 millisecond. 0 0 –25000 5.2 prefix and suffix solutions these commands allow you to a...
Page 21
Page 21 of 39 copyright © access-is 2016 5.3 atr110 illumination the standard method of reading barcodes cycles the illumination on and off. You can control illumination for various different applications using the commands in table 4. For example, it is often beneficial to turn off the illumination...
Page 22
Page 22 of 39 copyright © access-is 2016 command description default parameters/range aisofm illumination off mode. When set to 0, the timing for the illumination off period is set to a single value, aisoft . When set to 1, the illumination off period cycles continuously (while triggered) through th...
Page 23
Page 23 of 39 copyright © access-is 2016 5.4 indicator control these commands control the behaviour of the ‘good read’ and ‘bad read’ leds, device leds and sounder. 5.4.1 indicator leds these commands control the behaviour of the ‘good read’ and ‘bad read’ leds. Table 5. Indicator led commands comma...
Page 24
Page 24 of 39 copyright © access-is 2016 enhanced method the enhanced method extends the functionality of the lsr110 method with a permanent power led and on/off control of the ‘good’, ‘bad’ and ‘busy’ leds. In dumb mode, successfully reading a barcode causes the ‘good read’ leds to illuminate and t...
Page 25
Page 25 of 39 copyright © access-is 2016 command description default parameters aislct led control. Used in enhanced mode. 0 - turn all leds off 1 - turn on ‘bad read’ led(s) 2 - turn on ‘good read’ led(s) 4 - turn on ‘busy’ led(s) aislcd led control direct. Used in direct mode (on page 26) aissbu s...
Page 26
Page 26 of 39 copyright © access-is 2016 5.4.4 led control direct parameter format the parameter is a 16-character string. The string consists of eight character pairs, each of which represents the state of an led. The first four pairs represent the leds in led bank 1 (front leds in desktop orientat...
Page 27
Page 27 of 39 copyright © access-is 2016 5.4.6 sounder commands these commands control the atr110 ’s sounder (beep). Table 8. Sounder commands command description default parameters/range aisgbf ‘good beep’ frequency. 2 0 - 700 hz 1 - 1400 hz 2 - 2800 hz aisgbd ‘good beep’ active duration. Each unit...
Page 28
Page 28 of 39 copyright © access-is 2016 5.5 development commands 5.5.1 firmware and imager levels the firmware levels identify the release and build of a unit. Send the command aisfwv? To obtain this information. For example: sb 01.00.00 is a first generation atr110. To check the latest firmware ve...
Page 29
Page 29 of 39 copyright © access-is 2016 5.5.2 status leds the atr110 contains two small orange leds on the main circuit board, typically used for debug purposes only. We recommend turning these off in normal use. A typical configuration will have these turned off, but the default values will be as ...
Page 30
Page 30 of 39 copyright © access-is 2016 5.6 triggering these commands control triggering and untriggering of the atr110. Table 11. Triggering commands command description default parameters/range aistut automatically untrigger. 0 0 –25000 milliseconds aistmd convert trigger modes. Warning: this is ...
Page 31
Page 31 of 39 copyright © access-is 2016 5.7 counter these commands display the number of ‘good’ or ‘bad’ reads made by the device. Table 13. Counter commands command description default parameters/range aisgrc ‘good read’ counter. Cannot be reset. 0 - aisbrc ‘bad read’ counter. Cannot be reset. 0 -.
Page 32
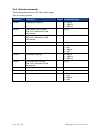
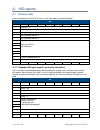
Page 32 of 39 copyright © access-is 2016 a. Hid reports a.1 receive data data received from the atr110 will be in a hid input report, structured as below: bit byte 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 0 report id = 2 1 length of data field 2 aim symbology identifier (always ‘]’) 3 aim symbology identifier 1 4 aim symbol...
Page 33
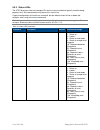
Page 33 of 39 copyright © access-is 2016 bit byte 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 0 [0x02] 1 [0x04] 2 [0x5d] - ‘]’ 3 [0x51] - ‘q’ 4 [0x30] - ‘0’ 5 [0x20]100 [0x00] [0x00] ... [0x00] [0x00] .. .. 60 61 [0x73] - ‘s’ 62 [0x00] 63 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 a.2 send commands to send commands to the atr110, use a hid out report wi...
Page 34
Page 34 of 39 copyright © access-is 2016 a.3 trigger controls to set the device status or to sound flash the ‘read’ lights on the device, send a hid output report with the following structure: bit byte 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 0 report id = 4 1 - flash ‘good read ’ light (green) flash ‘bad read ’ light (red)...
Page 35
Page 35 of 39 copyright © access-is 2016 b. Ascii character reference dec hex symbol description 0 00 nul null char 1 01 soh start of heading 2 02 stx start of text 3 03 etx end of text 4 04 eot end of transmission 5 05 enq enquiry 6 06 ack acknowledgment 7 07 bel bell 8 08 bs back space 9 09 ht hor...
Page 36
Page 36 of 39 copyright © access-is 2016 dec hex symbol description 37 25 % percent sign 38 26 & ampersand 39 27 ' single quote 40 28 ( open parenthesis (or open bracket) 41 29 ) close parenthesis (or close bracket) 42 2a * asterisk 43 2b + plus 44 2c , comma 45 2d - hyphen 46 2e . Period, dot or fu...
Page 37
Page 37 of 39 copyright © access-is 2016 dec hex symbol description 77 4d m uppercase m 78 4e n uppercase n 79 4f o uppercase o 80 50 p uppercase p 81 51 q uppercase q 82 52 r uppercase r 83 53 s uppercase s 84 54 t uppercase t 85 55 u uppercase u 86 56 v uppercase v 87 57 w uppercase w 88 58 x uppe...
Page 39
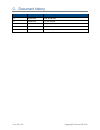
Page 39 of 39 copyright © access-is 2016 c. Document history issue date description 1.0 05/03/2015 initial distribution 1.1 05/06/2015 first full release 1.2 21/08/2015 typographical update 1.3 01/02/2016 style and content updates 1.4 15/03/2016 minor changes.