- DL manuals
- Accton Technology
- Switch
- 24/48 10/100 Ports + 2GE
- Management Manual
Accton Technology 24/48 10/100 Ports + 2GE Management Manual
Summary of 24/48 10/100 Ports + 2GE
Page 1
Powered by accton www.Edge-core.Com management guide 24/48 10/100 ports + 2ge intelligent layer 2 fast ethernet switch.
Page 3: Fast Ethernet Switch
Management guide fast ethernet switch layer 2 standalone switch with 24/48 10/100base-tx (rj-45) ports, and 2 combination gigabit ports (rj-45/sfp).
Page 4
Es3526xa es3552xa f2.2.6.3 e122006-cs-r02 149100005500h.
Page 5: Contents
I contents chapter 1: introduction 1-1 key features 1-1 description of software features 1-2 system defaults 1-5 chapter 2: initial configuration 2-1 connecting to the switch 2-1 configuration options 2-1 required connections 2-2 remote connections 2-3 basic configuration 2-3 console connection 2-3 ...
Page 6
Contents ii saving or restoring configuration settings 3-22 downloading configuration settings from a server 3-23 console port settings 3-24 telnet settings 3-26 configuring event logging 3-28 system log configuration 3-28 remote log configuration 3-30 displaying log messages 3-31 sending simple mai...
Page 7
Contents iii access control lists 3-82 configuring access control lists 3-82 setting the acl name and type 3-83 configuring a standard ip acl 3-84 configuring an extended ip acl 3-85 configuring a mac acl 3-87 binding a port to an access control list 3-88 port configuration 3-89 displaying connectio...
Page 8
Contents iv displaying current private vlans 3-153 configuring private vlans 3-154 associating vlans 3-154 displaying private vlan interface information 3-155 configuring private vlan interfaces 3-156 class of service configuration 3-158 layer 2 queue settings 3-158 setting the default priority for ...
Page 9
Contents v chapter 4: command line interface 4-1 using the command line interface 4-1 accessing the cli 4-1 console connection 4-1 telnet connection 4-1 entering commands 4-3 keywords and arguments 4-3 minimum abbreviation 4-3 command completion 4-3 getting help on commands 4-3 showing commands 4-4 ...
Page 10
Contents vi prompt 4-25 hostname 4-26 user access commands 4-26 username 4-27 enable password 4-28 ip filter commands 4-29 management 4-29 show management 4-30 web server commands 4-31 ip http port 4-31 ip http server 4-31 ip http secure-server 4-32 ip http secure-port 4-33 telnet server commands 4-...
Page 11
Contents vii sntp client 4-54 sntp server 4-55 sntp poll 4-56 show sntp 4-56 ntp client 4-57 ntp server 4-57 ntp poll 4-58 ntp authenticate 4-59 ntp authentication-key 4-59 show ntp 4-60 clock timezone 4-61 calendar set 4-62 show calendar 4-62 system status commands 4-63 show startup-config 4-63 sho...
Page 12
Contents viii 802.1x port authentication 4-85 dot1x system-auth-control 4-86 dot1x default 4-86 dot1x max-req 4-87 dot1x port-control 4-87 dot1x operation-mode 4-88 dot1x re-authenticate 4-88 dot1x re-authentication 4-89 dot1x timeout quiet-period 4-89 dot1x timeout re-authperiod 4-90 dot1x timeout ...
Page 13
Contents ix snmp-server 4-117 show snmp 4-117 snmp-server community 4-118 snmp-server contact 4-119 snmp-server location 4-119 snmp-server host 4-120 snmp-server enable traps 4-122 snmp-server engine-id 4-123 show snmp engine-id 4-124 snmp-server view 4-125 show snmp view 4-126 snmp-server group 4-1...
Page 14
Contents x clear mac-address-table dynamic 4-158 show mac-address-table 4-158 mac-address-table aging-time 4-159 show mac-address-table aging-time 4-159 spanning tree commands 4-160 spanning-tree 4-161 spanning-tree mode 4-161 spanning-tree forward-time 4-163 spanning-tree hello-time 4-163 spanning-...
Page 15
Contents xi private-vlan 4-189 private vlan association 4-190 switchport mode private-vlan 4-191 switchport private-vlan host-association 4-191 switchport private-vlan isolated 4-192 switchport private-vlan mapping 4-193 show vlan private-vlan 4-193 gvrp and bridge extension commands 4-194 bridge-ex...
Page 16
Contents xii ip igmp snooping query-max-response-time 4-218 ip igmp snooping router-port-expire-time 4-218 static multicast routing commands 4-219 ip igmp snooping vlan mrouter 4-219 show ip igmp snooping mrouter 4-220 igmp filtering and throttling commands 4-221 ip igmp filter (global configuration...
Page 17
Contents xiii cluster commander 4-250 cluster ip-pool 4-250 cluster member 4-251 rcommand 4-252 show cluster 4-252 show cluster members 4-253 show cluster candidates 4-253 appendix a: software specifications a-1 software features a-1 management features a-2 standards a-2 management information bases...
Page 18
Contents xiv.
Page 19: Tables
Xv tables table 1-1 key features 1-1 table 1-2 system defaults 1-5 table 3-1 configuration options 3-3 table 3-2 main menu 3-4 table 3-3 logging levels 3-29 table 3-6 https system support 3-59 table 3-7 802.1x statistics 3-73 table 3-8 lacp port counters 3-99 table 3-9 lacp internal configuration in...
Page 20
Tables xvi table 4-27 authentication commands 4-76 table 4-28 authentication sequence 4-76 table 4-29 radius client commands 4-78 table 4-30 tacacs commands 4-81 table 4-31 port security commands 4-84 table 4-32 802.1x port authentication 4-85 table 4-33 network access 4-94 table 4-35 ip acls 4-103 ...
Page 21
Tables xvii table 4-72 igmp filtering and throttling commands 4-221 table 4-73 multicast vlan registration commands 4-228 table 4-74 show mvr - display description 4-231 table 4-76 show mvr members - display description 4-232 table 4-75 show mvr interface - display description 4-232 table 4-77 dns c...
Page 22
Tables xviii.
Page 23: Figures
Xix figures figure 3-1 home page 3-2 figure 3-2 panel display 3-3 figure 3-3 system information 3-10 figure 3-4 displaying switch information 3-12 figure 3-5 bridge extension configuration 3-13 figure 3-6 manual ip configuration 3-15 figure 3-7 ip configuration using dhcp 3-16 figure 3-8 dhcp relay ...
Page 24
Figures xx figure 3-43 network access configuration 3-76 figure 3-44 network access port configuration 3-77 figure 3-45 network access mac address information 3-78 figure 3-46 network access mac filter configuration 3-79 figure 3-47 creating a web ip filter list 3-81 figure 3-48 selecting acl type 3...
Page 25
Figures xxi figure 3-88 port priority configuration 3-159 figure 3-89 traffic classes 3-161 figure 3-90 queue mode 3-162 figure 3-91 configuring queue scheduling 3-163 figure 3-92 ip precedence/dscp priority status 3-164 figure 3-93 mapping ip precedence priority values 3-165 figure 3-94 mapping ip ...
Page 26
Figures xxii.
Page 27: Chapter 1: Introduction
1-1 chapter 1: introduction this switch provides a broad range of features for layer 2 switching. It includes a management agent that allows you to configure the features listed in this manual. The default configuration can be used for most of the features provided by this switch. However, there are...
Page 28
Introduction 1-2 1 description of software features the switch provides a wide range of advanced performance enhancing features. Flow control eliminates the loss of packets due to bottlenecks caused by port saturation. Broadcast storm suppression prevents broadcast traffic storms from engulfing the ...
Page 29
Description of software features 1-3 1 port mirroring – the switch can unobtrusively mirror traffic from any port to a monitor port. You can then attach a protocol analyzer or rmon probe to this port to perform traffic analysis and verify connection integrity. Port trunking – ports can be combined i...
Page 30
Introduction 1-4 1 virtual lans – the switch supports up to 255 vlans. A virtual lan is a collection of network nodes that share the same collision domain regardless of their physical location or connection point in the network. The switch supports tagged vlans based on the ieee 802.1q standard. Mem...
Page 31: System Defaults
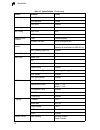
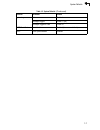
System defaults 1-5 1 system defaults the switch’s system defaults are provided in the configuration file “factory_default_config.Cfg.” to reset the switch defaults, this file should be set as the startup configuration file (page 3-24). The following table lists some of the basic system defaults. Ta...
Page 32
Introduction 1-6 1 port configuration admin status enabled auto-negotiation enabled flow control disabled rate limiting input and output limits disabled port trunking static trunks none lacp (all ports) disabled broadcast storm protection status disabled (all ports) broadcast limit rate 32,000 octet...
Page 33
System defaults 1-7 1 system log status enabled messages logged levels 0-7 (all) messages logged to flash levels 0-6 smtp email alerts event handler enabled (but no server defined) sntp clock synchronization disabled table 1-2 system defaults (continued) function parameter default.
Page 34
Introduction 1-8 1.
Page 35: Connecting to The Switch
2-1 chapter 2: initial configuration connecting to the switch configuration options the switch includes a built-in network management agent. The agent offers a variety of management options, including snmp, rmon and a web-based interface. A pc may also be connected directly to the switch for configu...
Page 36: Required Connections
Initial configuration 2-2 2 • configure up to 4 static or lacp trunks • enable port mirroring • set broadcast storm control on any port • display system information and statistics required connections the switch provides an rs-232 serial port that enables a connection to a pc or terminal for monitor...
Page 37: Remote Connections
Basic configuration 2-3 2 remote connections prior to accessing the switch’s onboard agent via a network connection, you must first configure it with a valid ip address, subnet mask, and default gateway using a console connection, dhcp or bootp protocol. The ip address for this switch is obtained vi...
Page 38: Setting Passwords
Initial configuration 2-4 2 setting passwords note: if this is your first time to log into the cli program, you should define new passwords for both default user names using the “username” command, record them and put them in a safe place. Passwords can consist of up to 8 alphanumeric characters and...
Page 39
Basic configuration 2-5 2 before you can assign an ip address to the switch, you must obtain the following information from your network administrator: • ip address for the switch • default gateway for the network • network mask for this network to assign an ip address to the switch, complete the fo...
Page 40
Initial configuration 2-6 2 5. Wait a few minutes, and then check the ip configuration settings by typing the “show ip interface” command. Press . 6. Then save your configuration changes by typing “copy running-config startup-config.” enter the startup file name and press . Enabling snmp management ...
Page 41
Basic configuration 2-7 2 the default strings are: • public - with read-only access. Authorized management stations are only able to retrieve mib objects. • private - with read-write access. Authorized management stations are able to both retrieve and modify mib objects. To prevent unauthorized acce...
Page 42
Initial configuration 2-8 2 configuring access for snmp version 3 clients to configure management access for snmpv3 clients, you need to first create a view that defines the portions of mib that the client can read or write, assign the view to a group, and then assign the user to a group. The follow...
Page 43: Managing System Files
Managing system files 2-9 2 managing system files the switch’s flash memory supports three types of system files that can be managed by the cli program, web interface, or snmp. The switch’s file system allows files to be uploaded and downloaded, copied, deleted, and set as a start-up file. The three...
Page 44
Initial configuration 2-10 2.
Page 45: Using The Web Interface
3-1 chapter 3: configuring the switch using the web interface this switch provides an embedded http web agent. Using a web browser you can configure the switch and view statistics to monitor network activity. The web agent can be accessed by any computer on the network using a standard web browser (...
Page 46: Home Page
Configuring the switch 3-2 3 navigating the web browser interface to access the web-browser interface you must first enter a user name and password. The administrator has read/write access to all configuration parameters and statistics. The default user name and password for the administrator is “ad...
Page 47: Configuration Options
Panel display 3-3 3 configuration options configurable parameters have a dialog box or a drop-down list. Once a configuration change has been made on a page, be sure to click on the apply button to confirm the new setting. The following table summarizes the web page configuration buttons. Notes: 1. ...
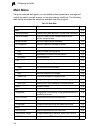
Page 48: Main Menu
Configuring the switch 3-4 3 main menu using the onboard web agent, you can define system parameters, manage and control the switch, and all its ports, or monitor network conditions. The following table briefly describes the selections available from this program. Table 3-2 main menu menu descriptio...
Page 49
Main menu 3-5 3 ssh 3-61 host-key settings generates the host key pair (public and private) 3-63 settings configures secure shell server settings 3-65 port security configures per port security, including status, response for security breach, and maximum allowed mac addresses 3-66 802.1x port authen...
Page 50
Configuring the switch 3-6 3 trunk broadcast control sets the broadcast storm threshold for each trunk 3-105 mirror port configuration sets the source and target ports for mirroring 3-106 rate limit 3-107 granularity enables or disables the rate limit feature 3-107 input port configuration sets the ...
Page 51
Main menu 3-7 3 private vlan 3-152 information displays private vlan feature information 3-153 configuration this page is used to create/remove primary or community vlans 3-154 association each community vlan must be associated with a primary vlan 3-154 port information shows vlan port type, and ass...
Page 52
Configuring the switch 3-8 3 igmp snooping 3-170 igmp configuration enables multicast filtering; configures parameters for multicast query 3-171 igmp filter configuration enables igmp filtering and throttling for the switch, creates filter profile numbers 3-178 igmp immediate leave enables the immed...
Page 53
Main menu 3-9 3 member configuration adds switch members to the cluster 3-195 member information displays cluster member switch information 3-196 candidate information displays network candidate switch information 3-197 table 3-2 main menu (continued) menu description page.
Page 54: Basic Configuration
Configuring the switch 3-10 3 basic configuration displaying system information you can easily identify the system by displaying the device name, location and contact information. Field attributes • system name – name assigned to the switch system. • object id – mib ii object id for switch’s network...
Page 55
Basic configuration 3-11 3 cli – specify the hostname, location and contact information. Displaying switch hardware/software versions use the switch information page to display hardware/firmware version numbers for the main board and management software, as well as the power status of the system. Fi...
Page 56
Configuring the switch 3-12 3 these additional parameters are displayed for the cli. • unit - this is unit 1. • redundant power status – displays the status of the redundant power supply. Web – click system, switch information. Figure 3-4 displaying switch information cli – use the following command...
Page 57
Basic configuration 3-13 3 displaying bridge extension capabilities the bridge mib includes extensions for managed devices that support multicast filtering, traffic classes, and virtual lans. You can access these extensions to display default settings for the key variables. Field attributes • extend...
Page 58
Configuring the switch 3-14 3 cli – enter the following command. Setting the switch’s ip address this section describes how to configure an ip interface for management access over the network. The ip address for this switch is obtained via dhcp by default. To manually configure an address, you need ...
Page 59
Basic configuration 3-15 3 manual configuration web – click system, ip configuration. Select the vlan through which the management station is attached, set the ip address mode to “static,” enter the ip address, subnet mask and gateway, then click apply. Figure 3-6 manual ip configuration cli – speci...
Page 60
Configuring the switch 3-16 3 using dhcp/bootp if your network provides dhcp/bootp services, you can configure the switch to be dynamically configured by these services. Web – click system, ip configuration. Specify the vlan to which the management station is attached, set the ip address mode to dhc...
Page 61
Basic configuration 3-17 3 web – if the address assigned by dhcp is no longer functioning, you will not be able to renew the ip settings via the web interface. You can only restart dhcp service via the web interface if the current address is still available. Cli – enter the following command to rest...
Page 62
Configuring the switch 3-18 3 • drop – discards the option 82 information in a packet and then floods it to the entire vlan. • dhcp relay server – ip addresses of dhcp servers to be used by the switch’s dhcp relay agent in order of preference. Up to five servers can be specified. Web – click system,...
Page 63: Managing Firmware
Basic configuration 3-19 3 managing firmware you can upload/download firmware to or from a tftp server. By saving runtime code to a file on a tftp server, that file can later be downloaded to the switch to restore operation. You can also set the switch to use new firmware without overwriting the pre...
Page 64
Configuring the switch 3-20 3 downloading system software from a server when downloading runtime code, you can specify the destination file name to replace the current image, or first download the file using a different name from the current runtime code file, and then set the new file as the startu...
Page 65
Basic configuration 3-21 3 to delete a file select system, file, delete. Select the file name from the given list by checking the tick box and click apply. Note that t he file currently designated as the startup code cannot be deleted. Figure 3-11 deleting files cli – to download new firmware form a...
Page 66
Configuring the switch 3-22 3 saving or restoring configuration settings you can upload/download configuration settings to/from a tftp server. The configuration files can be later downloaded to restore the switch’s settings. Command attributes • file transfer method – the configuration copy operatio...
Page 67
Basic configuration 3-23 3 downloading configuration settings from a server you can download the configuration file under a new file name and then set it as the startup file, or you can specify the current startup configuration file as the destination file to directly replace it. Note that the file ...
Page 68: Console Port Settings
Configuring the switch 3-24 3 cli – enter the ip address of the tftp server, specify the source file on the server, set the startup file name on the switch, and then restart the switch. To select another configuration file as the start-up configuration, use the boot system command and then restart t...
Page 69
Basic configuration 3-25 3 • speed – sets the terminal line’s baud rate for transmit (to terminal) and receive (from terminal). Set the speed to match the baud rate of the device connected to the serial port. (range: 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, or 115200 baud, auto; default: 9600 bps) • stop bits – s...
Page 70: Telnet Settings
Configuring the switch 3-26 3 cli – enter line configuration mode for the console, then specify the connection parameters as required. To display the current console port settings, use the show line command from the normal exec level. Telnet settings you can access the onboard configuration program ...
Page 71
Basic configuration 3-27 3 • password threshold – sets the password intrusion threshold, which limits the number of failed logon attempts. When the logon attempt threshold is reached, the system interface becomes silent for a specified amount of time (set by the silent time parameter) before allowin...
Page 72: Configuring Event Logging
Configuring the switch 3-28 3 cli – enter line configuration mode for a virtual terminal, then specify the connection parameters as required. To display the current virtual terminal settings, use the show line command from the normal exec level. Configuring event logging the switch allows you to con...
Page 73
Basic configuration 3-29 3 • ram level – limits log messages saved to the switch’s temporary ram memory for all levels up to the specified level. For example, if level 7 is specified, all messages from level 0 to level 7 will be logged to ram. (range: 0-7, default: 6) note: the flash level must be e...
Page 74
Configuring the switch 3-30 3 remote log configuration the remote logs page allows you to configure the logging of messages that are sent to syslog servers or other management stations. You can also limit the error messages sent to only those messages below a specified level. Command attributes • re...
Page 75
Basic configuration 3-31 3 cli – enter the syslog server host ip address, choose the facility type and set the logging trap. Displaying log messages the logs page allows you to scroll through the logged system and event messages. The switch can store up to 2048 log entries in temporary random access...
Page 76
Configuring the switch 3-32 3 sending simple mail transfer protocol alerts to alert system administrators of problems, the switch can use smtp (simple mail transfer protocol) to send email messages when triggered by logging events of a specified level. The messages are sent to specified smtp servers...
Page 77
Basic configuration 3-33 3 web – click system, log, smtp. Enable smtp, specify a source email address, and select the minimum severity level. To add an ip address to the smtp server list, type the new ip address in the smtp server field and click add. To delete an ip address, click the entry in the ...
Page 78: Resetting The System
Configuring the switch 3-34 3 cli – enter the ip address of at least one smtp server, set the syslog severity level to trigger an email message, and specify the switch (source) and up to five recipient (destination) email addresses. Enable smtp with the logging sendmail command to complete the confi...
Page 79: Setting The System Clock
Basic configuration 3-35 3 setting the system clock simple network time protocol (sntp) allows the switch to set its internal clock based on periodic updates from a network time protocol (ntp) server. Maintaining an accurate time on the switch enables the system log to record meaningful dates and ti...
Page 80
Configuring the switch 3-36 3 cli – this example configures the switch to operate as an sntp unicast client and then displays the current time and settings. Configuring ntp the ntp client allows you to configure up to 50 ntp servers to poll for time updates. You can also enable authentication to ens...
Page 81
Basic configuration 3-37 3 figure 3-22 ntp client configuration cli – this example configures the switch to operate as an ntp client and then displays the current settings. Console(config)#ntp authentication-key 19 md5 thisiskey19 4-59 console(config)#ntp authentication-key 30 md5 ntpkey30 console(c...
Page 82
Configuring the switch 3-38 3 setting the time zone sntp uses coordinated universal time (or utc, formerly greenwich mean time, or gmt) based on the time at the earth’s prime meridian, zero degrees longitude. To display a time corresponding to your local time, you must indicate the number of hours a...
Page 83
Simple network management protocol 3-39 3 the format of the mib specifications and the protocol used to access this information over the network. The switch includes an onboard agent that supports snmp versions 1, 2c, and 3. This agent continuously monitors the status of the switch hardware, as well...
Page 84: Enabling The Snmp Agent
Configuring the switch 3-40 3 enabling the snmp agent enables snmpv3 service for all management clients (i.E., versions 1, 2c, 3). Command attributes snmp agent status – enables snmp on the switch. Web – click snmp, agent status. Enable the snmp agent by marking the enabled checkbox, and click apply...
Page 85
Specifying trap managers and trap types 3-41 3 web – click snmp, configuration. Add new community strings as required, select the access rights from the access mode drop-down list, then click add. Figure 3-25 configuring snmp community strings cli – the following example adds the string “spiderman” ...
Page 86
Configuring the switch 3-42 3 to send an inform to a snmpv2c host, complete these steps: 1.Enable the snmp agent (page 3-54). 2.Enable trap informs as described in the following pages. 3.Create a view with the required notification messages (page 3-53). 4.Create a group that includes the required no...
Page 87
Configuring snmpv3 management access 3-43 3 • enable authentication traps 5 – issues a notification message to specified ip trap managers whenever authentication of an snmp request fails. (default: enabled) • enable link-up and link-down traps – issues a notification message whenever a port link is ...
Page 88: Setting A Local Engine Id
Configuring the switch 3-44 3 v2c or v3) and security level (i.E., authentication and privacy). 4. Assign snmp users to groups, along with their specific authentication and privacy passwords. Setting a local engine id an snmpv3 engine is an independent snmp agent that resides on the switch. This eng...
Page 89: Configuring Snmpv3 Users
Configuring snmpv3 management access 3-45 3 configure the remote agent’s snmp engine id before you can send proxy requests or informs to it. (see “specifying trap managers and trap types” on page 3-41 and “configuring remote snmpv3 users” on page 3-47.) the engine id can be specified by entering 1 t...
Page 90
Configuring the switch 3-46 3 available for the snmpv3 security model). • authentication protocol – the method used for user authentication. (options: md5, sha; default: md5) • authentication password – a minimum of eight plain text characters is required. • privacy protocol – the encryption algorit...
Page 91
Configuring snmpv3 management access 3-47 3 cli – use the snmp-server user command to configure a new user name and assign it to a group. Configuring remote snmpv3 users each snmpv3 user is defined by a unique name. Users must be configured with a specific security level and assigned to a group. The...
Page 92
Configuring the switch 3-48 3 • privacy protocol – the encryption algorithm use for data privacy; only 56-bit des is currently available. • privacy password – a minimum of eight plain text characters is required. Web – click snmp, snmpv3, remote users. Click new to configure a user name. In the new ...
Page 93: Configuring Snmpv3 Groups
Configuring snmpv3 management access 3-49 3 cli – use the snmp-server user command to configure a new user name and assign it to a group. Configuring snmpv3 groups an snmpv3 group sets the access policy for its assigned users, restricting them to specific read, write, and notify views. You can use t...
Page 94
Configuring the switch 3-50 3 table 3-5 supported notification messages object label object id description rfc 1493 traps newroot 1.3.6.1.2.1.17.0.1 the newroot trap indicates that the sending agent has become the new root of the spanning tree; the trap is sent by a bridge soon after its election as...
Page 95
Configuring snmpv3 management access 3-51 3 private traps - swpowerstatus changetrap 1.3.6.1.4.1.259.6.10.95.2.1.0.1 this trap is sent when the power state changes. Swfanfailuretrap 1.3.6.1.4.1.259.6.10.95.2.1.0.17 this trap is sent when the fan fails. Swfanrecovertrap 1.3.6.1.4.1.259.6.10.95.2.1.0....
Page 96
Configuring the switch 3-52 3 web – click snmp, snmpv3, groups. Click new to configure a new group. In the new group page, define a name, assign a security model and level, and then select read, write, and notify views. Click add to save the new group and return to the groups list. To delete a group...
Page 97: Setting Snmpv3 Views
Configuring snmpv3 management access 3-53 3 setting snmpv3 views snmpv3 views are used to restrict user access to specified portions of the mib tree. The predefined view “defaultview” includes access to the entire mib tree. Command attributes • view name – the name of the snmp view. (range: 1-64 cha...
Page 98: User Authentication
Configuring the switch 3-54 3 cli – use the snmp-server view command to configure a new view. This example view includes the mib-2 interfaces table, and the wildcard mask selects all index entries. User authentication you can restrict management access to this switch using the following options: • u...
Page 99
User authentication 3-55 3 • new account – displays configuration settings for a new account. - user name – the name of the user. (maximum length: 8 characters) - access level – specifies the user level. (options: normal and privileged) - password – specifies the user password. (range: 0-8 character...
Page 100
Configuring the switch 3-56 3 configuring local/remote logon authentication use the authentication settings menu to restrict management access based on specified user names and passwords. You can manually configure access rights on the switch, or you can use a remote access authentication server bas...
Page 101
User authentication 3-57 3 command attributes • authentication – select the authentication, or authentication sequence required: - local – user authentication is performed only locally by the switch. - radius – user authentication is performed using a radius server only. - tacacs – user authenticati...
Page 102
Configuring the switch 3-58 3 web – click security, authentication settings. To configure local or remote authentication preferences, specify the authentication sequence (i.E., one to three methods), fill in the parameters for radius or tacacs+ authentication if selected, and click apply. Figure 3-3...
Page 103: Configuring Https
User authentication 3-59 3 configuring https you can configure the switch to enable the secure hypertext transfer protocol (https) over the secure socket layer (ssl), providing secure access (i.E., an encrypted connection) to the switch’s web interface. Command usage • both the http and https servic...
Page 104
Configuring the switch 3-60 3 web – click security, https settings. Enable https and specify the port number, then click apply. Figure 3-35 https settings cli – this example enables the http secure server and modifies the port number. Replacing the default secure-site certificate when you log onto t...
Page 105
User authentication 3-61 3 configuring the secure shell the berkley-standard includes remote access tools originally designed for unix systems. Some of these tools have also been implemented for microsoft windows and other environments. These tools, including commands such as rlogin (remote login), ...
Page 106
Configuring the switch 3-62 3 3. Import client’s public key to the switch – use the copy tftp public-key command (page 4-70) to copy a file containing the public key for all the ssh client’s granted management access to the switch. (note that these clients must be configured locally on the switch vi...
Page 107
User authentication 3-63 3 generating the host key pair a host public/private key pair is used to provide secure communications between an ssh client and the switch. After generating this key pair, you must provide the host public key to ssh clients and import the client’s public key to the switch a...
Page 108
Configuring the switch 3-64 3 web – click security, ssh, host-key settings. Select the host-key type from the drop-down box, select the option to save the host key from memory to flash (if required) prior to generating the key, and then click generate. Figure 3-36 ssh host-key settings cli – this ex...
Page 109
User authentication 3-65 3 configuring the ssh server the ssh server includes basic settings for authentication. Field attributes • ssh server status – allows you to enable/disable the ssh server on the switch. (default: disabled) • version – the secure shell version number. Version 2.0 is displayed...
Page 110: Configuring Port Security
Configuring the switch 3-66 3 cli – this example enables ssh, sets the authentication parameters, and displays the current configuration. It shows that the administrator has made a connection via shh, and then disables this connection. Configuring port security port security is a feature that allows...
Page 111
User authentication 3-67 3 • if a port is disabled (shut down) due to a security violation, it must be manually re-enabled from the port/port configuration page (page 3-91). Command attributes • port – port number. • name – descriptive text (page 4-132). • action – indicates the action to be taken w...
Page 112
Configuring the switch 3-68 3 configuring 802.1x port authentication network switches can provide open and easy access to network resources by simply attaching a client pc. Although this automatic configuration and access is a desirable feature, it also allows unauthorized personnel to easily intrud...
Page 113
User authentication 3-69 3 • the radius server and 802.1x client support eap. (the switch only supports eapol in order to pass the eap packets from the server to the client.) • the radius server and client also have to support the same eap encryption method for passing authentication messages – md5,...
Page 114
Configuring the switch 3-70 3 configuring 802.1x global settings the 802.1x protocol includes port authentication. The 802.1x protocol must be enabled globally for the switch system before port settings are active. Command attributes • 802.1x system authentication control – sets the global setting f...
Page 115
User authentication 3-71 3 • re-authen – sets the client to be re-authenticated after the interval specified by the re-authentication period. Re-authentication can be used to detect if a new device is plugged into a switch port. (default: disabled) • max-req – sets the maximum number of times the sw...
Page 116
Configuring the switch 3-72 3 cli – this example sets the 802.1x parameters on port 2. For a description of the additional fields displayed in this example, see “show dot1x” on page 4-90. Console(config)#interface ethernet 1/2 4-131 console(config-if)#dot1x port-control auto 4-87 console(config-if)#...
Page 117
User authentication 3-73 3 displaying 802.1x statistics this switch can display statistics for dot1x protocol exchanges for any port. Table 3-7 802.1x statistics parameter description rx eapol start the number of eapol start frames that have been received by this authenticator. Rx eapol logoff the n...
Page 118: Mac Address Authentication
Configuring the switch 3-74 3 web – select security, 802.1x, statistics. Select the required port and then click query. Click refresh to update the statistics. Figure 3-42 displaying 802.1x port statistics cli – this example displays the 802.1x statistics for port 4. Mac address authentication some ...
Page 119
User authentication 3-75 3 address is forwarded by the switch only if the source mac address is successfully authenticated by a central radius server. While authentication for a mac address is in progress, all traffic is blocked until authentication is completed. On successful authentication, the ra...
Page 120
Configuring the switch 3-76 3 web – click security, network access, configuration. Figure 3-43 network access configuration cli – this example sets and displays the reauthentication time. Configuring mac authentication for ports configures mac authentication on switch ports, including setting the ma...
Page 121
User authentication 3-77 3 note: mac authentication cannot be configured on trunk ports. Ports configured as trunk members are indicated on the network access port configuration page in the “trunk” column. Web – click security, network access, port configuration. Figure 3-44 network access port conf...
Page 122
Configuring the switch 3-78 3 • query by – specifies parameters to use in the mac address query. • port – specifies a port interface. • mac address – specifies a single mac address information. • attribute – displays static or dynamic addresses. • address table sort key – sorts the information displ...
Page 123
User authentication 3-79 3 cli – this example displays all entries currently in the secure mac address table. Configuring mac address filters mac address filters are used to specify mac addresses to be excluded from network access authentication. Mac addresses in a filter are not authenticated by a ...
Page 124
Configuring the switch 3-80 3 cli – this example configures filter id 1 with three mac addresses, then applies the filter to port 1. Filtering addresses for management access you create a list of up to 16 ip addresses or ip address groups that are allowed access to the switch through the web interfa...
Page 125
User authentication 3-81 3 web – click security, ip filter. Enter the ip addresses or range of addresses that are allowed management access to an interface, and click add ip filtering entry to update the filter list. Figure 3-47 creating a web ip filter list cli – this example allows snmp access for...
Page 126: Access Control Lists
Configuring the switch 3-82 3 access control lists access control lists (acl) provide packet filtering for ip frames (based on address, protocol, layer 4 protocol port number or tcp control code) or any frames (based on mac address or ethernet type). To filter incoming packets, first create an acces...
Page 127
Access control lists 3-83 3 the order in which active acls are checked is as follows: 1. User-defined rules in the ingress mac acl for ingress ports. 2. User-defined rules in the ingress ip acl for ingress ports. 3. Explicit default rule (permit any any) in the ingress ip acl for ingress ports. 4. E...
Page 128
Configuring the switch 3-84 3 configuring a standard ip acl command attributes • action – an acl can contain any combination of permit or deny rules. • address type – specifies the source ip address. Use “any” to include all possible addresses, “host” to specify a specific host address in the addres...
Page 129
Access control lists 3-85 3 configuring an extended ip acl command attributes • action – an acl can contain any combination of permit or deny rules. • source/destination address type – specifies the source or destination ip address. Use “any” to include all possible addresses, “host” to specify a sp...
Page 130
Configuring the switch 3-86 3 web – specify the action (i.E., permit or deny). Specify the source and/or destination addresses. Select the address type (any, host, or ip). If you select “host,” enter a specific address. If you select “ip,” enter a subnet address and the mask for an address range. Se...
Page 131
Access control lists 3-87 3 configuring a mac acl command attributes • action – an acl can contain any combination of permit or deny rules. • source/destination address type – use “any” to include all possible addresses, “host” to indicate a specific mac address, or “mac” to specify an address range...
Page 132
Configuring the switch 3-88 3 binding a port to an access control list after configuring access control lists (acl), you should bind them to the ports that need to filter traffic. You can assign one ip access list to any port, but you can only assign one mac access list to all the ports on the switc...
Page 133: Port Configuration
Port configuration 3-89 3 cli – this example assigns an ip and mac access list to port 1, and an ip access list to port 3. Port configuration displaying connection status you can use the port information or trunk information pages to display the current connection status, including link state, speed...
Page 134
Configuring the switch 3-90 3 web – click port, port information or trunk information. Figure 3-53 displaying port/trunk information field attributes (cli) basic information: • port type – indicates the port type. (100base-tx, 1000base-t, or sfp) • mac address – the physical layer address for this p...
Page 135
Port configuration 3-91 3 • max mac count – shows the maximum number of mac address that can be learned by a port. (0 - 1024 addresses) • port security action – shows the response to take when a security violation is detected. (shutdown, trap, trap-and-shutdown, or none) current status: • link statu...
Page 136
Configuring the switch 3-92 3 • flow control – allows automatic or manual selection of flow control. • autonegotiation (port capabilities)– allows auto-negotiation to be enabled/ disabled. When auto-negotiation is enabled, you need to specify the capabilities to be advertised. When auto-negotiation ...
Page 137: Creating Trunk Groups
Port configuration 3-93 3 cli – select the interface, and then enter the required settings. Creating trunk groups you can create multiple links between devices that work as one virtual, aggregate link. A port trunk offers a dramatic increase in bandwidth for network segments where bottlenecks exist,...
Page 138
Configuring the switch 3-94 3 • when configuring static trunks on switches of different types, they must be compatible with the cisco etherchannel standard. • the ports at both ends of a trunk must be configured in an identical manner, including communication mode (i.E., speed, duplex mode and flow ...
Page 139
Port configuration 3-95 3 cli – this example creates trunk 2 with ports 1 and 2. Just connect these ports to two static trunk ports on another switch to form a trunk. Enabling lacp on selected ports command usage • to avoid creating a loop in the network, be sure you enable lacp before connecting th...
Page 140
Configuring the switch 3-96 3 command attributes • member list (current) – shows configured trunks (unit, port). • new – includes entry fields for creating new trunks. - port – port identifier. (range: 1-26/52) web – click port, lacp, configuration. Select any of the switch ports from the scroll-dow...
Page 141
Port configuration 3-97 3 configuring lacp parameters dynamically creating a port channel – ports assigned to a common port channel must meet the following criteria: • ports must have the same lacp system priority. • ports must have the same lacp port admin key. • however, if the “port channel” admi...
Page 142
Configuring the switch 3-98 3 web – click port, lacp, aggregation port. Set the system priority, admin key, and port priority for the port actor. You can optionally configure these settings for the port partner. (be aware that these settings only affect the administrative state of the partner, and w...
Page 143
Port configuration 3-99 3 cli – the following example configures lacp parameters for ports 1-4. Ports 1-4 are used as active members of the lag. Displaying lacp port counters you can display statistics for lacp protocol messages. Console(config)#interface ethernet 1/1 4-131 console(config-if)#lacp a...
Page 144
Configuring the switch 3-100 3 web – click port, lacp, port counters information. Select a member port to display the corresponding information. Figure 3-58 lacp - port counters information cli – the following example displays lacp counters for port channel 1. Lacpdus unknown pkts number of frames r...
Page 145
Port configuration 3-101 3 displaying lacp settings and status for the local side you can display configuration settings and the operational state for the local side of an link aggregation. Table 3-9 lacp internal configuration information field description oper key current operational value of the ...
Page 146
Configuring the switch 3-102 3 web – click port, lacp, port internal information. Select a port channel to display the corresponding information. Figure 3-59 lacp - port internal information cli – the following example displays the lacp configuration settings and operational state for the local side...
Page 147
Port configuration 3-103 3 displaying lacp settings and status for the remote side you can display configuration settings and the operational state for the remote side of an link aggregation. Web – click port, lacp, port neighbors information. Select a port channel to display the corresponding infor...
Page 148
Configuring the switch 3-104 3 cli – the following example displays the lacp configuration settings and operational state for the remote side of port channel 1. Console#show lacp 1 neighbors 4-152 port channel 1 neighbors ------------------------------------------------------------------------- eth ...
Page 149
Port configuration 3-105 3 setting broadcast storm thresholds broadcast storms may occur when a device on your network is malfunctioning, or if application programs are not well designed or properly configured. If there is too much broadcast traffic on your network, performance can be severely degra...
Page 150: Configuring Port Mirroring
Configuring the switch 3-106 3 cli – specify any interface, and then enter the threshold. The following disables broadcast storm control for port 1, and then sets broadcast suppression at 600 octets per second for port 2 (which applies to all ports). Configuring port mirroring you can mirror traffic...
Page 151: Configuring Rate Limits
Port configuration 3-107 3 web – click port, mirror port configuration. Specify the source port, the traffic type to be mirrored, and the monitor port, then click add. Figure 3-62 mirror port configuration cli – use the interface command to select the monitor port, then use the port monitor command ...
Page 152
Configuring the switch 3-108 3 web – click port, rate limit, granularity. Select the required rate limit granularity for fast ethernet and gigabit ethernet, and click apply. Figure 3-63 rate limit granularity configuration cli - this example sets and displays fast ethernet and gigabit ethernet granu...
Page 153: Showing Port Statistics
Port configuration 3-109 3 web – click port, rate limit, input/output port/trunk configuration. Enable the rate limit status for the required interfaces, set the rate limit level, and click apply. Figure 3-64 output rate limit port configuration cli - this example sets the rate limit level for input...
Page 154
Configuring the switch 3-110 3 table 3-11 port statistics parameter description interface statistics received octets the total number of octets received on the interface, including framing characters. Received unicast packets the number of subnetwork-unicast packets delivered to a higher-layer proto...
Page 155
Port configuration 3-111 3 excessive collisions a count of frames for which transmission on a particular interface fails due to excessive collisions. This counter does not increment when the interface is operating in full-duplex mode. Single collision frames the number of successfully transmitted fr...
Page 156
Configuring the switch 3-112 3 fragments the total number of frames received that were less than 64 octets in length (excluding framing bits, but including fcs octets) and had either an fcs or alignment error. 64 bytes frames the total number of frames (including bad packets) received and transmitte...
Page 157
Port configuration 3-113 3 web – click port, port statistics. Select the required interface, and click query. You can also use the refresh button at the bottom of the page to update the screen. Figure 3-65 port statistics.
Page 158: Address Table Settings
Configuring the switch 3-114 3 cli – this example shows statistics for port 13. Address table settings switches store the addresses for all known devices. This information is used to pass traffic directly between the inbound and outbound ports. All the addresses learned by monitoring traffic are sto...
Page 159
Address table settings 3-115 3 web – click address table, static addresses. Specify the interface, the mac address and vlan, then click add static address. Figure 3-66 static addresses cli – this example adds an address to the static address table, but sets it to be deleted when the switch is reset....
Page 160
Configuring the switch 3-116 3 web – click address table, dynamic addresses. Specify the search type (i.E., mark the interface, mac address, or vlan checkbox), select the method of sorting the displayed addresses, and then click query. Figure 3-67 dynamic addresses cli – this example also displays t...
Page 161: Changing The Aging Time
Spanning tree algorithm configuration 3-117 3 changing the aging time you can set the aging time for entries in the dynamic address table. Command attributes • aging status – enables/disables the function. • aging time – the time after which a learned entry is discarded. (range: 10-30000 seconds; de...
Page 162
Configuring the switch 3-118 3 ports, and disables all other ports. Network packets are therefore only forwarded between root ports and designated ports, eliminating any possible network loops. Once a stable network topology has been established, all bridges listen for hello bpdus (bridge protocol d...
Page 163: Displaying Global Settings
Spanning tree algorithm configuration 3-119 3 mstp then builds a internal spanning tree (ist) for the region containing all commonly configured mstp bridges. An mst region consists of a group of interconnected bridges that have the same mst configuration identifiers (including the region name, revis...
Page 164
Configuring the switch 3-120 3 • bridge id – a unique identifier for this bridge, consisting of the bridge priority, the mst instance id 0 for the common spanning tree when spanning tree mode is set to mstp (page 3-123), and mac address (where the address is taken from the switch system). • max age ...
Page 165
Spanning tree algorithm configuration 3-121 3 • root maximum age – the maximum time (in seconds) this device can wait without receiving a configuration message before attempting to reconfigure. All device ports (except for designated ports) should receive configuration messages at regular intervals....
Page 166
Configuring the switch 3-122 3 cli – this command displays global sta settings, followed by settings for each port. Note: the current root port and current root cost display as zero when this device is not connected to the network. Console#show spanning-tree 4-176 spanning-tree information ---------...
Page 167: Configuring Global Settings
Spanning tree algorithm configuration 3-123 3 configuring global settings global settings apply to the entire switch. Command usage • spanning tree protocol 9 uses rstp for the internal state machine, but sends only 802.1d bpdus. This creates one spanning tree instance for the entire network. If mul...
Page 168
Configuring the switch 3-124 3 address will then become the root device. (note that lower numeric values indicate higher priority.) • default: 32768 • range: 0-61440, in steps of 4096 • options: 0, 4096, 8192, 12288, 16384, 20480, 24576, 28672, 32768, 36864, 40960, 45056, 49152, 53248, 57344, 61440 ...
Page 169
Spanning tree algorithm configuration 3-125 3 configuration settings for mstp • max instance numbers – the maximum number of mstp instances to which this switch can be assigned. • configuration digest – an md5 signature key that contains the vlan id to mst id mapping table. In other words, this key ...
Page 170
Configuring the switch 3-126 3 web – click spanning tree, sta, configuration. Modify the required attributes, and click apply. Figure 3-70 sta global configuration.
Page 171
Spanning tree algorithm configuration 3-127 3 cli – this example enables spanning tree protocol, sets the mode to mst, and then configures the sta and mstp parameters. Displaying interface settings the sta port information and sta trunk information pages display the current status of ports and trunk...
Page 172
Configuring the switch 3-128 3 • oper path cost – the contribution of this port to the path cost of paths towards the spanning tree root which include this port. • oper link type – the operational point-to-point status of the lan segment attached to this interface. This parameter is determined by ma...
Page 173
Spanning tree algorithm configuration 3-129 3 • internal path cost – the path cost for the mst. See the preceding item. • priority – defines the priority used for this port in the spanning tree algorithm. If the path cost for all ports on a switch is the same, the port with the highest priority (i.E...
Page 174
Configuring the switch 3-130 3 cli – this example shows the sta attributes for port 5. Configuring interface settings you can configure rstp and mstp attributes for specific interfaces, including port priority, path cost, link type, and edge port. You may use a different priority or path cost for po...
Page 175
Spanning tree algorithm configuration 3-131 3 the following interface attributes can be configured: • spanning tree – enables/disables sta on this interface. (default: enabled) • priority – defines the priority used for this port in the spanning tree protocol. If the path cost for all ports on a swi...
Page 176
Configuring the switch 3-132 3 other sta-related timeout problems. However, remember that edge port should only be enabled for ports connected to an end-node device. (default: disabled) • migration – if at any time the switch detects stp bpdus, including configuration or topology change notification...
Page 177
Spanning tree algorithm configuration 3-133 3 to use multiple spanning trees: 1. Set the spanning tree type to mstp (sta configuration, page 3-123). 2. Enter the spanning tree priority for the selected mst instance (mstp vlan configuration). 3. Add the vlans that will share this msti (mstp vlan conf...
Page 178
Configuring the switch 3-134 3 web – click spanning tree, mstp, vlan configuration. Select an instance identifier from the list, set the instance priority, and click apply. To add the vlan members to an msti instance, enter the instance identifier, the vlan identifier, and click add. Figure 3-73 mst...
Page 179
Spanning tree algorithm configuration 3-135 3 cli – this example sets the priority for msti 1, and adds vlans 1-5 to this msti. --------------------------------------------------------------- eth 1/ 7 information --------------------------------------------------------------- admin status: enabled r...
Page 180
Configuring the switch 3-136 3 displaying interface settings for mstp the mstp port information and mstp trunk information pages display the current status of ports and trunks in the selected mst instance. Field attributes mst instance id – instance identifier to configure. (range: 0-4094; default: ...
Page 181
Spanning tree algorithm configuration 3-137 3 configuring interface settings for mstp you can configure the sta interface settings for an mst instance using the mstp port configuration and mstp trunk configuration pages. Field attributes the following attributes are read-only and cannot be changed: ...
Page 182
Configuring the switch 3-138 3 • admin mst path cost – this parameter is used by the mstp to determine the best path between devices. Therefore, lower values should be assigned to ports attached to faster media, and higher values assigned to ports with slower media. (path cost takes precedence over ...
Page 183: Vlan Configuration
Vlan configuration 3-139 3 vlan configuration ieee 802.1q vlans in large networks, routers are used to isolate broadcast traffic for each subnet into separate domains. This switch provides a similar service at layer 2 by using vlans to organize any group of network nodes into separate broadcast doma...
Page 184
Configuring the switch 3-140 3 note: vlan-tagged frames can pass through vlan-aware or vlan-unaware network interconnection devices, but the vlan tags should be stripped off before passing it on to any end-node host that does not support vlan tagging. Vlan classification – when the switch receives a...
Page 185
Vlan configuration 3-141 3 these hosts, and core switches in the network, enable gvrp on the links between these devices. You should also determine security boundaries in the network and disable gvrp on the boundary ports to prevent advertisements from being propagated, or forbid those ports from jo...
Page 186
Configuring the switch 3-142 3 enabling or disabling gvrp (global setting) garp vlan registration protocol (gvrp) defines a way for switches to exchange vlan information in order to register vlan members on ports across the network. Vlans are dynamically configured based on join messages issued by h...
Page 187
Vlan configuration 3-143 3 cli – enter the following command. Displaying current vlans the vlan current table shows the current port members of each vlan and whether or not the port supports vlan tagging. Ports assigned to a large vlan group that crosses several switches should use vlan tagging. How...
Page 188
Configuring the switch 3-144 3 web – click vlan, 802.1q vlan, current table. Select any id from the scroll-down list. Figure 3-78 vlan current table command attributes (cli) • vlan – id of configured vlan (1-4094, no leading zeroes). • type – shows how this vlan was added to the switch. - dynamic: a...
Page 189
Vlan configuration 3-145 3 cli – current vlan information can be displayed with the following command. Creating vlans use the vlan static list to create or remove vlan groups. To propagate information about vlan groups used on this switch to external network devices, you must specify a vlan id for e...
Page 190
Configuring the switch 3-146 3 web – click vlan, 802.1q vlan, static list. To create a new vlan, enter the vlan id and vlan name, mark the enable checkbox to activate the vlan, and then click add. Figure 3-79 vlan static list - creating vlans cli – this example creates a new vlan. Console(config)#vl...
Page 191
Vlan configuration 3-147 3 adding static members to vlans (vlan index) use the vlan static table to configure port members for the selected vlan index. Assign ports as tagged if they are connected to 802.1q vlan compliant devices, or untagged they are not connected to any vlan-aware devices. Or conf...
Page 192
Configuring the switch 3-148 3 web – click vlan, 802.1q vlan, static table. Select a vlan id from the scroll-down list. Modify the vlan name and status if required. Select the membership type by marking the appropriate radio button in the list of ports or trunks. Click apply. Figure 3-80 vlan static...
Page 193
Vlan configuration 3-149 3 web – open vlan, 802.1q vlan, static membership by port. Select an interface from the scroll-down box (port or trunk). Click query to display membership information for the interface. Select a vlan id, and then click add to add the interface as a tagged member, or click re...
Page 194
Configuring the switch 3-150 3 configuring vlan behavior for interfaces you can configure vlan behavior for specific interfaces, including the default vlan identifier (pvid), accepted frame types, ingress filtering, gvrp status, and garp timers. Command usage • gvrp – garp vlan registration protocol...
Page 195
Vlan configuration 3-151 3 • garp leave timer 10 – the interval a port waits before leaving a vlan group. This time should be set to more than twice the join time. This ensures that after a leave or leaveall message has been issued, the applicants can rejoin before the port actually leaves the group...
Page 196: Private Vlans
Configuring the switch 3-152 3 cli – this example sets port 3 to accept only tagged frames, assigns pvid 3 as the native vlan id, enables gvrp, sets the garp timers, and then sets the switchport mode to hybrid. Private vlans private vlans provide port-based security and isolation between ports withi...
Page 197
Vlan configuration 3-153 3 2. Use the private vlan port configuration menu (page 3-156) to set the port type to promiscuous (i.E., the single channel to the external network), or isolated (i.E., having access only to the promiscuous port in its own vlan). Then assign the promiscuous port and all hos...
Page 198
Configuring the switch 3-154 3 configuring private vlans the private vlan configuration page is used to create/remove primary, community, or isolated vlans. Command attributes • vlan id – id of configured vlan (1-4094). • type – there are three types of vlans within a private vlan: - primary vlans –...
Page 199
Vlan configuration 3-155 3 web – click vlan, private vlan, association. Select the required primary vlan from the scroll-down box, highlight one or more community vlans in the non-association list box, and click add to associate these entries with the selected primary vlan. (a community vlan can onl...
Page 200
Configuring the switch 3-156 3 web – click vlan, private vlan, port information or trunk information. Figure 3-86 private vlan port information cli – this example shows the switch configured with primary vlan 5 and community vlan 6. Port 3 has been configured as a promiscuous port and mapped to vlan...
Page 201
Vlan configuration 3-157 3 • community vlan – a community vlan conveys traffic between community ports, and from community ports to their designated promiscuous ports. Set pvlan port type to “host,” and then specify the associated community vlan. • isolated vlan – conveys traffic only between the vl...
Page 202: Layer 2 Queue Settings
Configuring the switch 3-158 3 class of service configuration class of service (cos) allows you to specify which data packets have greater precedence when traffic is buffered in the switch due to congestion. This switch supports cos with four priority queues for each port. Data packets in a port’s h...
Page 203
Class of service configuration 3-159 3 web – click priority, default port priority or default trunk priority. Modify the default priority for any interface, then click apply. Figure 3-88 port priority configuration cli – this example assigns a default priority of 5 to port 3. Console(config)#interfa...
Page 204
Configuring the switch 3-160 3 mapping cos values to egress queues this switch processes class of service (cos) priority tagged traffic by using four priority queues for each port, with service schedules based on strict or weighted round robin (wrr). Up to eight separate traffic priorities are defin...
Page 205
Class of service configuration 3-161 3 web – click priority, traffic classes. Assign priorities to the traffic classes (i.E., output queues), then click apply. Figure 3-89 traffic classes cli – the following example shows how to change the cos assignments. * mapping specific values for cos prioritie...
Page 206
Configuring the switch 3-162 3 selecting the queue mode you can set the switch to service the queues based on a strict rule that requires all traffic in a higher priority queue to be processed before lower priority queues are serviced, or use weighted round-robin (wrr) queuing that specifies a relat...
Page 207
Class of service configuration 3-163 3 setting the service weight for traffic classes this switch uses the weighted round robin (wrr) algorithm to determine the frequency at which it services each priority queue. As described in “mapping cos values to egress queues” on page 3-160, the traffic classe...
Page 208: Layer 3/4 Priority Settings
Configuring the switch 3-164 3 layer 3/4 priority settings mapping layer 3/4 priorities to cos values this switch supports several common methods of prioritizing layer 3/4 traffic to meet application requirements. Traffic priorities can be specified in the ip header of a frame, using the priority bi...
Page 209
Class of service configuration 3-165 3 mapping ip precedence the type of service (tos) octet in the ipv4 header includes three precedence bits defining eight different priority levels ranging from highest priority for network control packets to lowest priority for routine traffic. The default ip pre...
Page 210
Configuring the switch 3-166 3 cli – the following example globally enables ip precedence service on the switch, maps ip precedence value 1 to cos value 0 (on port 1), and then displays the ip precedence settings. Note: mapping specific values for ip precedence is implemented as an interface configu...
Page 211
Class of service configuration 3-167 3 command attributes • dscp priority table – shows the dscp priority to cos map. • class of service value – maps a cos value to the selected dscp priority value. Note that “0” represents low priority and “7” represent high priority. Note: ip dscp settings apply t...
Page 212
Configuring the switch 3-168 3 mapping ip port priority you can also map network applications to class of service values based on the ip port number (i.E., tcp/udp port number) in the frame header. Some of the more common tcp service ports include: http: 80, ftp: 21, telnet: 23 and pop3: 110. Comman...
Page 213
Class of service configuration 3-169 3 cli* – the following example globally enables ip port priority service on the switch, maps http traffic on port 5 to cos value 0, and then displays all the ip port priority settings for that port. Note: mapping specific values for ip port priority is implemente...
Page 214: Multicast Filtering
Configuring the switch 3-170 3 web – click priority, acl cos priority. Enable mapping for any port, select an acl from the scroll-down list, then click add. Figure 3-97 acl cos priority cli – this example assigns a cos value of zero to packets matching rules within the specified acl on port 24. Mult...
Page 215
Multicast filtering 3-171 3 requesting to join the service and sends data out to those ports only. It then propagates the service request up to any neighboring multicast switch/router to ensure that it will continue to receive the multicast service. This procedure is called multicast filtering. The ...
Page 216
Configuring the switch 3-172 3 command attributes • igmp status — when enabled, the switch will monitor network traffic to determine which hosts want to receive multicast traffic. This is also referred to as igmp snooping. (default: enabled) • act as igmp querier — when enabled, the switch can serve...
Page 217
Multicast filtering 3-173 3 cli – this example modifies the settings for multicast filtering, and then displays the current status. Enabling igmp immediate leave the igmp snooping immediate-leave feature enables a layer 2 lan interface to be removed from the multicast forwarding table without first ...
Page 218
Configuring the switch 3-174 3 cli – this example enables igmp immediate leave for vlan 1 and then displays the current igmp snooping status. Displaying interfaces attached to a multicast router multicast routers that are attached to ports on the switch use information obtained from igmp, along with...
Page 219
Multicast filtering 3-175 3 cli – this example shows that port 11 has been statically configured as a port attached to a multicast router. Specifying static interfaces for a multicast router depending on your network connections, igmp snooping may not always be able to locate the igmp querier. There...
Page 220
Configuring the switch 3-176 3 displaying port members of multicast services you can display the port members associated with a specified vlan and multicast service. Command attributes • vlan id – selects the vlan for which to display port members. • multicast ip address – the ip address for a speci...
Page 221
Multicast filtering 3-177 3 assigning ports to multicast services multicast filtering can be dynamically configured using igmp snooping and igmp query messages as described in “configuring igmp snooping and query parameters” on page 3-133. For certain applications that require tighter control, you m...
Page 222
Configuring the switch 3-178 3 cli – this example assigns a multicast address to vlan 1, and then displays all the known multicast services supported on vlan 1. Igmp filtering and throttling in certain switch applications, the administrator may want to control the multicast services that are availab...
Page 223
Multicast filtering 3-179 3 web – click igmp snooping, igmp filter configuration. Create a profile number by entering the number in text box and clicking add. Enable the igmp filter status, then click apply. Figure 3-104 enabling igmp filtering and throttling cli – this example enables igmp filterin...
Page 224
Configuring the switch 3-180 3 command attributes • profile id – selects an existing profile number to configure. After selecting an id number, click the query button to display the current configuration. • access mode – sets the access mode of the profile; either permit or deny. (default: deny) • n...
Page 225
Multicast filtering 3-181 3 cli – this example configures profile number 19 by setting the access mode to “permit” and then specifying a range of multicast groups that a user can join. The current profile configuration is then displayed. Configuring igmp filtering and throttling for interfaces once ...
Page 226
Configuring the switch 3-182 3 • trunk – indicates if a port is a trunk member. Web – click igmp snooping, igmp filter/throttling port configuration or igmp filter/throttling trunk configuration. Select a profile to assign to an interface, then set the throttling number and action. Click apply. Figu...
Page 227: Multicast Vlan Registration
Multicast vlan registration 3-183 3 multicast vlan registration multicast vlan registration (mvr) is a protocol that controls access to a single network-wide vlan most commonly used for transmitting multicast traffic (such as television channels or video-on-demand) across a service provider’s networ...
Page 228
Configuring the switch 3-184 3 4. For multicast streams that will run for a long term and be associated with a stable set of hosts, you can statically bind the multicast group to the participating interfaces (see “assigning static multicast groups to interfaces” on page 3-188). Configuring global mv...
Page 229
Multicast vlan registration 3-185 3 cli – this example first enables igmp snooping, enables mvr globally, and then configures a range of mvr group addresses. Displaying mvr interface status you can display information about the interfaces attached to the mvr vlan. Field attributes • type – shows the...
Page 230
Configuring the switch 3-186 3 displaying port members of multicast groups you can display the multicast groups assigned to the mvr vlan either through igmp snooping or static configuration. Field attributes • group ip – multicast groups assigned to the mvr vlan. • group port list – shows the interf...
Page 231
Multicast vlan registration 3-187 3 configuring mvr interface status each interface that participates in the mvr vlan must be configured as an mvr source port or receiver port. If only one subscriber attached to an interface is receiving multicast services, you can enable the immediate leave functio...
Page 232
Configuring the switch 3-188 3 web – click mvr, port or trunk configuration. Figure 3-110 mvr port configuration cli – this example configures an mvr source port and receiver port, and then enables immediate leave on the receiver port. Assigning static multicast groups to interfaces for multicast st...
Page 233
Configuring domain name service 3-189 3 web – click mvr, group member configuration. Select a port or trunk from the “interface” field, and click query to display the assigned multicast groups. Select a multicast address from the displayed lists, and click the add or remove button to modify the memb...
Page 234
Configuring the switch 3-190 3 • if there is no domain list, the default domain name is used. If there is a domain list, the default domain name is not used. • when an incomplete host name is received by the dns service on this switch and a domain name list has been specified, the switch will work t...
Page 235
Configuring domain name service 3-191 3 web –select dns, general configuration. Set the default domain name or list of domain names, specify one or more name servers to use to use for address resolution, enable domain lookup status, and click apply. Figure 3-112 dns general configuration cli - this ...
Page 236
Configuring the switch 3-192 3 configuring static dns host to address entries you can manually configure static entries in the dns table that are used to map domain names to ip addresses. Command usage • static entries may be used for local devices connected directly to the attached network, or for ...
Page 237: Displaying The Dns Cache
Configuring domain name service 3-193 3 cli - this example maps two address to a host name, and then configures an alias host name for the same addresses. Displaying the dns cache you can display entries in the dns cache that have been learned via the designated name servers. Field attributes • no –...
Page 238: Switch Clustering
Configuring the switch 3-194 3 cli - this example displays all the resource records learned from the designated name servers. Switch clustering switch clustering is a method of grouping switches together to enable centralized management through a single unit. Switches that support clustering can be ...
Page 239
Switch clustering 3-195 3 • role – indicates the current role of the switch in the cluster; either commander, member, or candidate. • cluster ip pool – an “internal” ip address pool that is used to assign ip addresses to member switches in the cluster. Internal cluster ip addresses are in the form 1...
Page 240: Cluster Member Information
Configuring the switch 3-196 3 web – click cluster, member configuration. Figure 3-116 cluster member configuration cli – this example creates a new cluster member by specifying the candidate switch mac address and setting a member id. Cluster member information displays current cluster member switc...
Page 241
Switch clustering 3-197 3 cli – this example shows information about cluster member switches. Cluster candidate information displays information about discovered switches in the network that are already cluster members or are available to become cluster members. Command attributes • role – indicates...
Page 242
Configuring the switch 3-198 3.
Page 243: Accessing The Cli
4-1 chapter 4: command line interface this chapter describes how to use the command line interface (cli). Using the command line interface accessing the cli when accessing the management interface for the switch over a direct connection to the server’s console port, or via a telnet connection, the s...
Page 244
Command line interface 4-2 4 to access the switch through a telnet session, you must first set the ip address for the switch, and set the default gateway if you are managing the switch from a different ip subnet. For example, if your corporate network is connected to another network outside your off...
Page 245: Entering Commands
Entering commands 4-3 4 entering commands this section describes how to enter cli commands. Keywords and arguments a cli command is a series of keywords and arguments. Keywords identify a command, and arguments specify configuration parameters. For example, in the command “show interfaces status eth...
Page 246: Showing Commands
Command line interface 4-4 4 showing commands if you enter a “?” at the command prompt, the system will display the first level of keywords for the current command class (normal exec or privileged exec) or configuration class (global, acl, interface, line or vlan database). You can also display a li...
Page 247: Partial Keyword Lookup
Entering commands 4-5 4 partial keyword lookup if you terminate a partial keyword with a question mark, alternatives that match the initial letters are provided. (remember not to leave a space between the command and question mark.) for example “s?” shows all the keywords starting with “s.” negating...
Page 248: Exec Commands
Command line interface 4-6 4 current mode. The command classes and associated modes are displayed in the following table: exec commands when you open a new console session on the switch with the user name and password “guest,” the system enters the normal exec command mode (or guest mode), displayin...
Page 249: Configuration Commands
Entering commands 4-7 4 configuration commands configuration commands are privileged level commands used to modify switch settings. These commands modify the running configuration only and are not saved when the switch is rebooted. To store the running configuration in non-volatile storage, use the ...
Page 250: Command Line Processing
Command line interface 4-8 4 command line processing commands are not case sensitive. You can abbreviate commands and parameters as long as they contain enough letters to differentiate them from any other currently available commands or parameters. You can use the tab key to complete partial command...
Page 251: Command Groups
Command groups 4-9 4 command groups the system commands can be broken down into the functional groups shown below . Table 4-4 command groups command group description page line sets communication parameters for the serial port and telnet, including baud rate and console time-out 4-11 general basic c...
Page 252
Command line interface 4-10 4 the access mode shown in the following tables is indicated by these abbreviations: ne (normal exec) ic (interface configuration) pe (privileged exec) lc (line configuration) gc (global configuration) vc (vlan database configuration) acl (access control list configuratio...
Page 253: Line Commands
Line commands 4-11 4 line commands you can access the onboard configuration program by attaching a vt100 compatible device to the server’s serial port. These commands are used to set communication parameters for the serial port or telnet (i.E., a virtual terminal). Line this command identifies a spe...
Page 254
Command line interface 4-12 4 command usage telnet is considered a virtual terminal connection and will be shown as “vty” in screen displays such as show users. However, the serial communication parameters (e.G., databits) do not affect telnet connections. Example to enter console line mode, enter t...
Page 256
Command line interface 4-14 4 timeout login response this command sets the interval that the system waits for a user to log into the cli. Use the no form to restore the default. Syntax timeout login response [seconds] no timeout login response seconds - integer that specifies the timeout interval. (...
Page 257
Line commands 4-15 4 command mode line configuration command usage • if user input is detected within the timeout interval, the session is kept open; otherwise the session is terminated. • this command applies to both the local console and telnet connections. • the timeout for telnet cannot be disab...
Page 258
Command line interface 4-16 4 related commands silent-time (4-16) timeout login response (4-13) silent-time this command sets the amount of time the management console is inaccessible after the number of unsuccessful logon attempts exceeds the threshold set by the password-thresh command. Use the no...
Page 259
Line commands 4-17 4 command usage the databits command can be used to mask the high bit on input from devices that generate 7 data bits with parity. If parity is being generated, specify 7 data bits per character. If no parity is required, specify 8 data bits per character. Example to specify 7 dat...
Page 260
Command line interface 4-18 4 speed this command sets the terminal line’s baud rate. This command sets both the transmit (to terminal) and receive (from terminal) speeds. Use the no form to restore the default setting. Syntax speed bps no speed bps - baud rate in bits per second. (options: 9600, 192...
Page 261
Line commands 4-19 4 disconnect this command terminates an ssh, telnet, or console connection. Syntax disconnect session-id session-id – the session identifier for an ssh, telnet or console connection. (range: 0-4) command mode privileged exec command usage specifying session identifier “0” will dis...
Page 262: General Commands
Command line interface 4-20 4 example to show all lines, enter this command: general commands enable this command activates privileged exec mode. In privileged mode, additional commands are available, and certain commands display additional information. See “understanding command modes” on page 4-5....
Page 263
General commands 4-21 4 default setting level 15 command mode normal exec command usage • “super” is the default password required to change the command mode from normal exec to privileged exec. (to set this password, see the enable password command on page 4-28.) • the “#” character is appended to ...
Page 264
Command line interface 4-22 4 configure this command activates global configuration mode. You must enter this mode to modify any settings on the switch. You must also enter global configuration mode prior to enabling some of the other configuration modes, including interface configuration, line conf...
Page 265
General commands 4-23 4 the ! Command repeats commands from the execution command history buffer when you are in normal exec or privileged exec mode, and commands from the configuration command history buffer when you are in any of the configuration modes. In this example, the !2 command repeats the...
Page 266
Command line interface 4-24 4 exit this command returns to the previous configuration mode or exit the configuration program. Default setting none command mode any example this example shows how to return to the privileged exec mode from the global configuration mode, and then quit the cli session: ...
Page 267: System Management Commands
System management commands 4-25 4 system management commands these commands are used to control system logs, passwords, user names, browser configuration options, and display or configure a variety of other system information. Device designation commands prompt this command customizes the cli prompt...
Page 268: User Access Commands
Command line interface 4-26 4 example hostname this command specifies or modifies the host name for this device. Use the no form to restore the default host name. Syntax hostname name no hostname name - the name of this host. (maximum length: 255 characters) default setting none command mode global ...
Page 269
System management commands 4-27 4 username this command adds named users, requires authentication at login, specifies or changes a user's password (or specify that no password is required), or specifies or changes a user's access level. Use the no form to remove a user name. Syntax username name {ac...
Page 270
Command line interface 4-28 4 enable password after initially logging onto the system, you should set the privileged exec password. Remember to record it in a safe place. This command controls access to the privileged exec level from the normal exec level. Use the no form to reset the default passwo...
Page 273: Web Server Commands
System management commands 4-31 4 web server commands ip http port this command specifies the tcp port number used by the web browser interface. Use the no form to use the default port. Syntax ip http port port-number no ip http port port-number - the tcp port to be used by the browser interface. (r...
Page 274
Command line interface 4-32 4 example related commands ip http port (4-31) ip http secure-server this command enables the secure hypertext transfer protocol (https) over the secure socket layer (ssl), providing secure access (i.E., an encrypted connection) to the switch’s web interface. Use the no f...
Page 275
System management commands 4-33 4 example related commands ip http secure-port (4-33) copy tftp https-certificate (4-70) ip http secure-port this command specifies the udp port number used for https/ssl connection to the switch’s web interface. Use the no form to restore the default port. Syntax ip ...
Page 276: Telnet Server Commands
Command line interface 4-34 4 telnet server commands ip telnet port this command specifies the tcp port number used by the telnet interface. Use the no form to use the default port. Syntax ip telnet port port-number no ip telnet port port-number - the tcp port to be used by the browser interface. (r...
Page 277: Secure Shell Commands
System management commands 4-35 4 related commands ip telnet port (4-34) secure shell commands the berkley-standard includes remote access tools originally designed for unix systems. Some of these tools have also been implemented for microsoft windows and other environments. These tools, including c...
Page 278
Command line interface 4-36 4 the ssh server on this switch supports both password and public key authentication. If password authentication is specified by the ssh client, then the password can be authenticated either locally or via a radius or tacacs+ remote authentication server, as specified by ...
Page 279
System management commands 4-37 4 corresponding to the public keys stored on the switch can gain access. The following exchanges take place during this process: a. The client sends its public key to the switch. B. The switch compares the client's public key to those stored in memory. C. If a match i...
Page 280
Command line interface 4-38 4 ip ssh timeout this command configures the timeout for the ssh server. Use the no form to restore the default setting. Syntax ip ssh timeout seconds no ip ssh timeout seconds – the timeout for client response during ssh negotiation. (range: 1-120) default setting 10 sec...
Page 281
System management commands 4-39 4 example related commands show ip ssh (4-41) ip ssh server-key size this command sets the ssh server key size. Use the no form to restore the default setting. Syntax ip ssh server-key size key-size no ip ssh server-key size key-size – the size of server key. (range: ...
Page 283
System management commands 4-41 4 command mode privileged exec command usage • this command clears the host key from volatile memory (ram). Use the no ip ssh save host-key command to clear the host key from flash memory. • the ssh server must be disabled before you can execute this command. Example ...
Page 284
Command line interface 4-42 4 example show ssh this command displays the current ssh server connections. Command mode privileged exec example console#show ip ssh ssh enabled - version 1.99 negotiation timeout: 120 secs; authentication retries: 3 server key size: 768 bits console# console#show ssh co...
Page 286: Event Logging Commands
Command line interface 4-44 4 event logging commands logging on this command controls logging of error messages, sending debug or error messages to switch memory. The no form disables the logging process. Syntax [no] logging on default setting none command mode global configuration command usage the...
Page 288
Command line interface 4-46 4 logging host this command adds a syslog server host ip address that will receive logging messages. Use the no form to remove a syslog server host. Syntax [no] logging host host_ip_address host_ip_address - the ip address of a syslog server. Default setting none command ...
Page 289
System management commands 4-47 4 logging trap this command enables the logging of system messages to a remote server, or limits the syslog messages saved to a remote server based on severity. Use this command without a specified level to enable remote logging. Use the no form to disable remote logg...
Page 292: Smtp Alert Commands
Command line interface 4-50 4 example the following example shows sample messages stored in ram. Smtp alert commands these commands configure smtp event handling, and forwarding of alert messages to the specified smtp servers and email recipients. Logging sendmail host this command specifies smtp se...
Page 293
System management commands 4-51 4 command mode global configuration command usage • you can specify up to three smtp servers for event handing. However, you must enter a separate command to specify each server. • to send email alerts, the switch first opens a connection, sends all the email alerts w...
Page 294
Command line interface 4-52 4 logging sendmail source-email this command sets the email address used for the “from” field in alert messages. Use the no form to delete the source email address. Syntax [no] logging sendmail source-email email-address email-address - the source email address used in al...
Page 295
System management commands 4-53 4 logging sendmail this command enables smtp event handling. Use the no form to disable this function. Syntax [no] logging sendmail default setting enabled command mode global configuration example show logging sendmail this command displays the settings for the smtp ...
Page 296: Time Commands
Command line interface 4-54 4 time commands the system clock can be dynamically set by polling a set of specified ntp time servers. Maintaining an accurate time on the switch enables the system log to record meaningful dates and times for event entries. If the clock is not set, the switch will only ...
Page 297
System management commands 4-55 4 example related commands sntp server (4-55) sntp poll (4-56) show sntp (4-56) sntp server this command sets the ip address of the servers to which sntp time requests are issued. Use this command with no arguments to clear all time servers from the current list. Synt...
Page 298
Command line interface 4-56 4 sntp poll this command sets the interval between sending time requests when the switch is set to sntp client mode. Use the no form to restore to the default. Syntax sntp poll seconds no sntp poll seconds - interval between time requests. (range: 16-16384 seconds) defaul...
Page 299
System management commands 4-57 4 ntp client this command enables ntp client requests for time synchronization from ntp time servers specified with the ntp servers command. Use the no form to disable ntp client requests. Syntax [no] ntp client default setting disabled command mode global configurati...
Page 300
Command line interface 4-58 4 default setting version number: 3 command mode global configuration command usage • this command specifies time servers that the switch will poll for time updates when set to ntp client mode. It issues time synchronization requests based on the interval set with the ntp...
Page 301
System management commands 4-59 4 example related commands ntp client (4-57) ntp authenticate this command enables authentication for ntp client-server communications. Use the no form to disable authentication. Syntax [no] ntp authenticate default setting disabled command mode global configuration c...
Page 302
Command line interface 4-60 4 • key - an md5 authentication key string. The key string can be up to 32 case-sensitive printable ascii characters (no spaces). Default setting none command mode global configuration command usage • the key number specifies a key value in the ntp authentication key list...
Page 304
Command line interface 4-62 4 related commands show sntp (4-56) calendar set this command sets the system clock. It may be used if there is no time server on your network, or if you have not configured the switch to receive signals from a time server. Syntax calendar set hour min sec {day month year...
Page 305: System Status Commands
System management commands 4-63 4 system status commands show startup-config this command displays the configuration file stored in non-volatile memory that is used to start up the system. Default setting none command mode privileged exec command usage • use this command in conjunction with the show...
Page 306
Command line interface 4-64 4 example related commands show running-config (4-65) console#show startup-config building startup-config, please wait..... ! ! Username admin access-level 15 username admin password 0 admin ! Username guest access-level 0 username guest password 0 guest ! Enable password...
Page 307
System management commands 4-65 4 show running-config this command displays the configuration information currently in use. Default setting none command mode privileged exec command usage • use this command in conjunction with the show startup-config command to compare the information in running mem...
Page 308
Command line interface 4-66 4 example related commands show startup-config (4-63) console#show running-config building running-config, please wait..... ! Sntp server 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 ! Clock timezone hours 0 minute 0 after-utc ! ! Snmp-server community private rw snmp-server community public ...
Page 309
System management commands 4-67 4 show system this command displays system information. Default setting none command mode normal exec, privileged exec command usage • for a description of the items shown by this command, refer to “displaying system information” on page 3-10. • the post results shoul...
Page 310
Command line interface 4-68 4 command usage the session used to execute this command is indicated by a “*” symbol next to the line (i.E., session) index number. Example show version this command displays hardware and software version information for the system. Default setting none command mode norm...
Page 311: Frame Size Commands
System management commands 4-69 4 example frame size commands jumbo frame this command enables support for jumbo frames. Use the no form to disable it. Syntax [no] jumbo frame default setting disabled command mode global configuration command usage • this switch provides more efficient throughput fo...
Page 312: Flash/file Commands
Command line interface 4-70 4 • enabling jumbo frames will limit the maximum threshold for broadcast storm control. (see the switchport broadcast command on page 4-137.) • the current setting for jumbo frames can be displayed with the show system command (page 4-67). Example flash/file commands thes...
Page 313
Flash/file commands 4-71 4 • public-key - keyword that allows you to copy a ssh key from a tftp server. (“secure shell commands” on page 4-35) default setting none command mode privileged exec command usage • the system prompts for data required to complete the copy command. • the destination file n...
Page 314
Command line interface 4-72 4 the following example shows how to copy the running configuration to a startup file. The following example shows how to download a configuration file: this example shows how to copy a secure-site certificate from an tftp server. It then reboots the switch to activate th...
Page 315
Flash/file commands 4-73 4 delete this command deletes a file or image. Syntax delete filename filename - name of the configuration file or image name. Default setting none command mode privileged exec command usage • if the file type is used for system startup, then this file cannot be deleted. • “...
Page 316
Command line interface 4-74 4 • file information is shown below: example the following example shows how to display all file information: whichboot this command displays which files were booted when the system powered up. Syntax whichboot default setting none command mode privileged exec example thi...
Page 318: Authentication Commands
Command line interface 4-76 4 authentication commands you can configure this switch to authenticate users logging into the system for management access using local or radius authentication methods. You can also enable port-based authentication for network client access using ieee 802.1x. Authenticat...
Page 319
Authentication commands 4-77 4 • radius and tacacs+ logon authentication assigns a specific privilege level for each user name and password pair. The user name, password, and privilege level must be configured on the authentication server. • you can specify three authentication methods in a single c...
Page 320: Radius Client
Command line interface 4-78 4 authentication is attempted on the tacacs+ server. If the tacacs+ server is not available, the local user name and password is checked. Example related commands enable password - sets the password for changing command modes (4-28) radius client remote authentication dia...
Page 321
Authentication commands 4-79 4 • retransmit - number of times the switch will try to authenticate logon access via the radius server. (range: 1-30) • key - encryption key used to authenticate logon access for client. Do not use blank spaces in the string. (maximum length: 20 characters) default sett...
Page 322
Command line interface 4-80 4 default setting none command mode global configuration example radius-server retransmit this command sets the number of retries. Use the no form to restore the default. Syntax radius-server retransmit number_of_retries no radius-server retransmit number_of_retries - num...
Page 323: Tacacs+ Client
Authentication commands 4-81 4 example show radius-server this command displays the current settings for the radius server. Default setting none command mode privileged exec example tacacs+ client terminal access controller access control system (tacacs+) is a logon authentication protocol that uses...
Page 324
Command line interface 4-82 4 tacacs-server host this command specifies the tacacs+ server. Use the no form to restore the default. Syntax tacacs-server host host_ip_address no tacacs-server host host_ip_address - ip address of a tacacs+ server. Default setting 10.11.12.13 command mode global config...
Page 325
Authentication commands 4-83 4 syntax tacacs-server key key_string no tacacs-server key key_string - encryption key used to authenticate logon access for the client. Do not use blank spaces in the string. (maximum length: 20 characters) default setting none command mode global configuration example ...
Page 326: Port Security Commands
Command line interface 4-84 4 port security commands these commands can be used to enable port security on a port. When using port security, the switch stops learning new mac addresses on the specified port when it has reached a configured maximum number. Only incoming traffic with source addresses ...
Page 327: 802.1X Port Authentication
Authentication commands 4-85 4 command usage • if you enable port security, the switch stops learning new mac addresses on the specified port when it has reached a configured maximum number. Only incoming traffic with source addresses already stored in the dynamic or static address table will be acc...
Page 328
Command line interface 4-86 4 dot1x system-auth-control this command enables 802.1x port authentication globally on the switch. Use the no form to restore the default. Syntax [no] system-auth-control default setting disabled command mode global configuration example dot1x default this command sets a...
Page 329
Authentication commands 4-87 4 dot1x max-req this command sets the maximum number of times the switch port will retransmit an eap request/identity packet to the client before it times out the authentication session. Use the no form to restore the default. Syntax dot1x max-req count no dot1x max-req ...
Page 330
Command line interface 4-88 4 dot1x operation-mode this command allows single or multiple hosts (clients) to connect to an 802.1x-authorized port. Use the no form with no keywords to restore the default to single host. Use the no form with the multi-host max-count keywords to restore the default max...
Page 331
Authentication commands 4-89 4 command mode privileged exec example dot1x re-authentication this command enables periodic re-authentication globally for all ports. Use the no form to disable re-authentication. Syntax [no] dot1x re-authentication command mode interface configuration example dot1x tim...
Page 332
Command line interface 4-90 4 dot1x timeout re-authperiod this command sets the time period after which a connected client must be re-authenticated. Syntax dot1x timeout re-authperiod seconds no dot1x timeout re-authperiod seconds - the number of seconds. (range: 1-65535) default 3600 seconds comman...
Page 333
Authentication commands 4-91 4 syntax show dot1x [statistics] [interface interface] • statistics - displays dot1x status for each port. • interface • ethernet unit/port - unit - this is unit 1. - port - port number. (range: 1-26/52) command mode privileged exec command usage this command displays th...
Page 334
Command line interface 4-92 4 - port-control – shows the dot1x mode on a port as auto, force-authorized, or force-unauthorized (page 4-87). - supplicant – mac address of authorized client. - current identifier – the integer (0-255) used by the authenticator to identify the current authentication ses...
Page 335
Authentication commands 4-93 4 example console#show dot1x global 802.1x parameters system-auth-control: enable 802.1x port summary port name status operation mode mode authorized 1/1 disabled single-host forceauthorized n/a 1/2 enabled single-host auto yes . . . 1/26 disabled single-host forceauthor...
Page 336: Network Access
Command line interface 4-94 4 network access the network access feature controls host access to the network by authenticating its mac address on the connected switch port. Traffic received from a specific mac address is forwarded by the switch only if the source mac address is successfully authentic...
Page 337
Authentication commands 4-95 4 command usage • when enabled on a port interface, the authentication process sends a password authentication protocol (pap) request to a configured radius server. The username and password are both equal to the mac address being authenticated. • on the radius server, p...
Page 338
Command line interface 4-96 4 command mode interface configuration command usage the maximum number of mac addresses per port is 1024, and the maximum number of secure mac addresses supported for the switch system is 1024. When the limit is reached, all new mac addresses are treated as authenticatio...
Page 339
Authentication commands 4-97 4 example the following example creates mac filter 1 and adds mac address 00-00-e8-12-11-01 to the filter. Network-access port-mac-filter use this command to apply a mac address filter to a port interface. Use the no form of this command to remove a mac address filter fr...
Page 340
Command line interface 4-98 4 command usage • when enabled, the vlan identifiers returned by the radius server will be applied to the port, providing the vlans have been already created on the switch. Gvrp is not used to create the vlans. • the vlan settings specified by the first authenticated mac ...
Page 342
Command line interface 4-100 4 example show network-access mac-filter use this command to display mac authentication filters. Syntax show network-access mac-filter [filter-id] filter-id - specifies a filter number. (range: 1-64) default setting displays all filters. Command mode privileged exec exam...
Page 343
Authentication commands 4-101 4 • ethernet unit/port - unit - this is unit 1. - port - port number. (range: 1-26/52) • sort - sorts displayed entries by either mac address or interface. Default setting displays all filters. Command mode privileged exec command usage when using a bit mask to filter d...
Page 344
Command line interface 4-102 4 access control list commands access control lists (acl) provide packet filtering for ip frames (based on address, protocol, layer 4 protocol port number or tcp control code) or any frames (based on mac address or ethernet type). To filter packets, first create an acces...
Page 346
Command line interface 4-104 4 command usage • when you create a new acl or enter configuration mode for an existing acl, use the permit or deny command to add new rules to the bottom of the list. To create an acl, you must add at least one rule to the list. • to remove a rule, use the no permit or ...
Page 347
Access control list commands 4-105 4 example this example configures one permit rule for the specific address 10.1.1.21 and another rule for the address range 168.92.16.X – 168.92.31.X using a bitmask. Related commands access-list ip (4-103) permit, deny (extended acl) this command adds a rule to an...
Page 348
Command line interface 4-106 4 default setting none command mode extended acl command usage • all new rules are appended to the end of the list. • address bitmasks are similar to a subnet mask, containing four integers from 0 to 255, each separated by a period. The binary mask uses 1 bits to indicat...
Page 350
Command line interface 4-108 4 command usage • a port can only be bound to one acl. • if a port is already bound to an acl and you bind it to a different acl, the switch will replace the old binding with the new one. • you must configure a mask for an acl rule before you can bind it to a port. Examp...
Page 351
Access control list commands 4-109 4 command usage a packet matching a rule within the specified acl is mapped to one of the output queues as shown in the following table. For information on mapping the cos values to output queues, see queue cos-map on page 4-201. Example related commands queue cos-...
Page 352: Mac Acls
Command line interface 4-110 4 mac acls access-list mac this command adds a mac access list and enters mac acl configuration mode. Use the no form to remove the specified acl. Syntax [no] access-list mac acl_name acl_name – name of the acl. (maximum length: 16 characters) default setting none comman...
Page 353
Access control list commands 4-111 4 related commands permit, deny (mac acl) (4-111) mac access-group (4-112) show mac access-list (4-112) permit, deny (mac acl) this command adds a rule to a mac acl. The rule filters packets matching a specified mac source or destination address (i.E., physical lay...
Page 354
Command line interface 4-112 4 example this rule permits packets from any source mac address to the destination address 00-e0-29-94-34-de where the ethernet type is 0800. Related commands access-list mac (4-110) show mac access-list this command displays the rules for configured mac acls. Syntax sho...
Page 355
Access control list commands 4-113 4 command usage • a port can only be bound to one acl. • if a port is already bound to an acl and you bind it to a different acl, the switch will replace the old binding with the new one. Example related commands show mac access-list (4-112) show mac access-group t...
Page 356
Command line interface 4-114 4 command usage • you must configure an acl mask before you can map cos values to the rule. • a packet matching a rule within the specified acl is mapped to one of the output queues as shown below. Example related commands queue cos-map (4-201) show map access-list mac (...
Page 357: Acl Information
Access control list commands 4-115 4 acl information show access-list this command shows all acls and associated rules, as well as all the user-defined masks. Command mode privileged exec command usage once the acl is bound to an interface (i.E., the acl is active), the order in which the rules are ...
Page 358: Snmp Commands
Command line interface 4-116 4 snmp commands controls access to this switch from management stations using the simple network management protocol (snmp), as well as the error types sent to trap managers. Snmp version 3 also provides security features that cover message integrity, authentication, and...
Page 359: Snmp-Server
Snmp commands 4-117 4 snmp-server this command enables the snmpv3 engine and services for all management clients (i.E., versions 1, 2c, 3). Use the no form to disable the server. Syntax [no] snmp-server default setting enabled command mode global configuration example show snmp this command can be u...
Page 361: Snmp-Server Contact
Snmp commands 4-119 4 • private - read/write access. Authorized management stations are able to both retrieve and modify mib objects. Command mode global configuration example snmp-server contact this command sets the system contact string. Use the no form to remove the system contact information. S...
Page 362: Snmp-Server Host
Command line interface 4-120 4 command mode global configuration example related commands snmp-server contact (4-119) snmp-server host this command specifies the recipient of a simple network management protocol notification operation. Use the no form to remove the specified host. Syntax snmp-server...
Page 363
Snmp commands 4-121 4 • snmp version: 1 • udp port: 162 command mode global configuration command usage • if you do not enter an snmp-server host command, no notifications are sent. In order to configure the switch to send snmp notifications, you must enter at least one snmp-server host command. In ...
Page 364: Snmp-Server Enable Traps
Command line interface 4-122 4 supports. If the snmp-server host command does not specify the snmp version, the default is to send snmp version 1 notifications. • if you specify an snmp version 3 host, then the community string is interpreted as an snmp user name. If you use the v3 “auth” or “priv” ...
Page 365: Snmp-Server Engine-Id
Snmp commands 4-123 4 conjunction with the corresponding entries in the notify view assigned by the snmp-server group command (page 4-126). Example related commands snmp-server host (4-120) snmp-server engine-id this command configures an identification string for the snmpv3 engine. Use the no form ...
Page 366: Show Snmp Engine-Id
Command line interface 4-124 4 • a local engine id is automatically generated that is unique to the switch. This is referred to as the default engine id. If the local engine id is deleted or changed, all snmp users will be cleared. You will need to reconfigure all existing users (page 4-128). Exampl...
Page 369: Show Snmp Group
Snmp commands 4-127 4 default setting • default groups: public 23 (read only), private 24 (read/write) • readview - every object belonging to the internet oid space (1.3.6.1). • writeview - nothing is defined. • notifyview - nothing is defined. Command mode global configuration command usage • a gro...
Page 372: Show Snmp User
Command line interface 4-130 4 show snmp user this command shows information on snmp users. Command mode privileged exec example console#show snmp user engineid: 800000ca030030f1df9ca00000 user name: steve authentication protocol: md5 privacy protocol: des56 storage type: nonvolatile row status: act...
Page 373: Interface Commands
Interface commands 4-131 4 interface commands these commands are used to display or set communication parameters for an ethernet port, aggregated link, or vlan. Interface this command configures an interface type and enter interface configuration mode. Use the no form to remove a trunk. Syntax inter...
Page 374
Command line interface 4-132 4 command mode global configuration example to specify port 24, enter the following command: description this command adds a description to an interface. Use the no form to remove the description. Syntax description string no description string - comment or a description...
Page 375
Interface commands 4-133 4 default setting • auto-negotiation is enabled by default. • when auto-negotiation is disabled, the default speed-duplex setting is 100half for 100base-tx ports and 1000full for gigabit ethernet ports. Command mode interface configuration (ethernet, port channel) command us...
Page 376
Command line interface 4-134 4 • if autonegotiation is disabled, auto-mdi/mdi-x pin signal configuration will also be disabled for the rj-45 ports. Example the following example configures port 11 to use autonegotiation. Related commands capabilities (4-134) speed-duplex (4-132) capabilities this co...
Page 377
Interface commands 4-135 4 example the following example configures ethernet port 5 capabilities to 100half, 100full and flow control. Related commands negotiation (4-133) speed-duplex (4-132) flowcontrol (4-135) flowcontrol this command enables flow control. Use the no form to disable flow control....
Page 378
Command line interface 4-136 4 example the following example enables flow control on port 5. Related commands negotiation (4-133) capabilities (flowcontrol, symmetric) (4-134) shutdown this command disables an interface. To restart a disabled interface, use the no form. Syntax [no] shutdown default ...
Page 379
Interface commands 4-137 4 switchport broadcast packet-rate this command configures broadcast storm control. Use the no form to disable broadcast storm control. Syntax switchport broadcast octet-rate rate no switchport broadcast rate - threshold level as a rate; i.E., octets per second. (range: 64-9...
Page 380
Command line interface 4-138 4 command mode privileged exec command usage statistics are only initialized for a power reset. This command sets the base value for displayed statistics to zero for the current management session. However, if you log out and back into the management interface, the stati...
Page 381
Interface commands 4-139 4 example show interfaces counters this command displays interface statistics. Syntax show interfaces counters [interface] interface • ethernet unit/port - unit - this is unit 1. - port - port number. (range: 1-26/52) • port-channel channel-id (range: 1-4) default setting sh...
Page 382
Command line interface 4-140 4 example show interfaces switchport this command displays the administrative and operational status of the specified interfaces. Syntax show interfaces switchport [interface] interface • ethernet unit/port - unit - this is unit 1. - port - port number. (range: 1-26/52) ...
Page 383
Interface commands 4-141 4 example this example shows the configuration setting for port 24. Console#show interfaces switchport ethernet 1/24 broadcast threshold: enabled, 600 octets/second lacp status: enabled ingress rate limit: disable, level: 30 egress rate limit: disable, level: 30 vlan members...
Page 385
Mirror port commands 4-143 4 example the following example configures the switch to mirror received packets from port 6 to 11: show port monitor this command displays mirror information. Syntax show port monitor [interface] interface - ethernet unit/port (source port) • unit - this is unit 1. • port...
Page 386: Rate Limit Commands
Command line interface 4-144 4 rate limit commands this function allows the network manager to control the maximum rate for traffic transmitted or received on an interface. Rate limiting is configured on interfaces at the edge of a network to limit traffic into or out of the network. Traffic that fa...
Page 388: Link Aggregation Commands
Command line interface 4-146 4 command usage • for fast ethernet interfaces, the rate limit granularity is 512 kbps, 1 mbps, or 3.3 mbps. • for gigabit ethernet interfaces, the rate limit granularity is 33.3 mbps. Example link aggregation commands ports can be statically grouped into an aggregate li...
Page 389
Link aggregation commands 4-147 4 guidelines for creating trunks general guidelines – • finish configuring port trunks before you connect the corresponding network cables between switches to avoid creating a loop. • a trunk can have up to eight ports. • the ports at both ends of a connection must be...
Page 390
Command line interface 4-148 4 command usage • when configuring static trunks, the switches must comply with the cisco etherchannel standard. • use no channel-group toremove a port group from a trunk. • use no interfaces port-channel to remove a trunk from the switch. Example the following example c...
Page 391
Link aggregation commands 4-149 4 example the following shows lacp enabled on ports 11-13. Because lacp has also been enabled on the ports at the other end of the links, the show interfaces status port-channel 1 command shows that trunk 1 has been established. Lacp system-priority this command confi...
Page 392
Command line interface 4-150 4 command mode interface configuration (ethernet) command usage • port must be configured with the same system priority to join the same lag. • system priority is combined with the switch’s mac address to form the lag identifier. This identifier is used to indicate a spe...
Page 393
Link aggregation commands 4-151 4 • once the remote side of a link has been established, lacp operational settings are already in use on that side. Configuring lacp settings for the partner only applies to its administrative state, not its operational state, and will only take effect the next time a...
Page 395
Link aggregation commands 4-153 4 default setting port channel: all command mode privileged exec example console#show lacp 1 counters channel group : 1 ------------------------------------------------------------------------- eth 1/ 1 -----------------------------------------------------------------...
Page 396
Command line interface 4-154 4 console#show lacp 1 internal port channel : 1 ------------------------------------------------------------------------- oper key : 4 admin key : 0 eth 1/1 ------------------------------------------------------------------------- lacpdus internal : 30 sec lacp system pr...
Page 397
Link aggregation commands 4-155 4 console#show lacp 1 neighbors port channel 1 neighbors ------------------------------------------------------------------------- eth 1/1 ------------------------------------------------------------------------- partner admin system id : 32768, 00-00-00-00-00-00 part...
Page 398: Address Table Commands
Command line interface 4-156 4 address table commands these commands are used to configure the address table for filtering specified addresses, displaying current entries, clearing the table, or setting the aging time. Console#show lacp sysid port channel system priority system mac address ---------...
Page 399
Address table commands 4-157 4 mac-address-table static this command maps a static address to a destination port in a vlan. Use the no form to remove an address. Syntax mac-address-table static mac-address interface interface vlan vlan-id [action] no mac-address-table static mac-address vlan vlan-id...
Page 400
Command line interface 4-158 4 clear mac-address-table dynamic this command removes any learned entries from the forwarding database and clears the transmit and receive counts for any static or system configured entries. Default setting none command mode privileged exec example show mac-address-tabl...
Page 401
Address table commands 4-159 4 means to match a bit and “1” means to ignore a bit. For example, a mask of 00-00-00-00-00-00 means an exact match, and a mask of ff-ff-ff-ff-ff-ff means “any.” • the maximum number of address entries is 8191. Example mac-address-table aging-time this command sets the a...
Page 402: Spanning Tree Commands
Command line interface 4-160 4 spanning tree commands this section includes commands that configure the spanning tree algorithm (sta) globally for the switch, and commands that configure sta for the selected interface. Table 4-55 spanning tree commands command function mode page spanning-tree enable...
Page 403: Spanning-Tree
Spanning tree commands 4-161 4 spanning-tree this command enables the spanning tree algorithm globally for the switch. Use the no form to disable it. Syntax [no] spanning-tree default setting spanning tree is enabled. Command mode global configuration command usage the spanning tree algorithm (sta) ...
Page 404: Spanning-Tree Forward-Time
Command line interface 4-162 4 - this creates one spanning tree instance for the entire network. If multiple vlans are implemented on a network, the path between specific vlan members may be inadvertently disabled to prevent network loops, thus isolating group members. When operating multiple vlans,...
Page 405: Spanning-Tree Hello-Time
Spanning tree commands 4-163 4 global configuration command usage this command sets the maximum time (in seconds) the root device will wait before changing states (i.E., discarding to learning to forwarding). This delay is required because every device must receive information about topology changes...
Page 406: Spanning-Tree Max-Age
Command line interface 4-164 4 spanning-tree max-age this command configures the spanning tree bridge maximum age globally for this switch. Use the no form to restore the default. Syntax spanning-tree max-age seconds no spanning-tree max-age seconds - time in seconds. (range: 6-40 seconds) the minim...
Page 407
Spanning tree commands 4-165 4 command mode global configuration command usage bridge priority is used in selecting the root device, root port, and designated port. The device with the highest priority (i.E., lower numeric value) becomes the sta root device. However, if all devices have the same pri...
Page 408
Command line interface 4-166 4 spanning-tree transmission-limit this command configures the minimum interval between the transmission of consecutive rstp/mstp bpdus. Use the no form to restore the default. Syntax spanning-tree transmission-limit count no spanning-tree transmission-limit count - the ...
Page 409: Mst Vlan
Spanning tree commands 4-167 4 mst vlan this command adds vlans to a spanning tree instance. Use the no form to remove the specified vlans. Using the no form without any vlan parameters to remove all vlans. Syntax [no] mst instance_id vlan vlan-range • instance_id - instance identifier of the spanni...
Page 410: Mst Priority
Command line interface 4-168 4 mst priority this command configures the priority of a spanning tree instance. Use the no form to restore the default. Syntax mst instance_id priority priority no mst instance_id priority • instance_id - instance identifier of the spanning tree. (range: 0-4094) • prior...
Page 411: Revision
Spanning tree commands 4-169 4 the mst region name and revision number (page 4-169) are used to designate a unique mst region. A bridge (i.E., spanning-tree compliant device such as this switch) can only belong to one mst region. And all bridges in the same region must be configured with the same ms...
Page 412: Spanning-Tree Cost
Command line interface 4-170 4 default setting 20 command mode mst configuration command usage an msti region is treated as a single node by the stp and rstp protocols. Therefore, the message age for bpdus inside an msti region is never changed. However, each spanning tree instance within a region, ...
Page 413: Spanning-Tree Port-Priority
Spanning tree commands 4-171 4 the recommended range is: •ethernet: 200,000-20,000,000 •fast ethernet: 20,000-2,000,000 •gigabit ethernet: 2,000-200,000 default setting by default, the system automatically detects the speed and duplex mode used on each port, and configures the path cost according to...
Page 414: Spanning-Tree Edge-Port
Command line interface 4-172 4 command usage • this command defines the priority for the use of a port in the spanning tree algorithm. If the path cost for all ports on a switch are the same, the port with the highest priority (that is, lowest value) will be configured as an active link in the spann...
Page 415: Spanning-Tree Portfast
Spanning tree commands 4-173 4 spanning-tree portfast this command sets an interface to fast forwarding. Use the no form to disable fast forwarding. Syntax [no] spanning-tree portfast default setting disabled command mode interface configuration (ethernet, port channel) command usage • this command ...
Page 416: Spanning-Tree Mst Cost
Command line interface 4-174 4 default setting auto command mode interface configuration (ethernet, port channel) command usage • specify a point-to-point link if the interface can only be connected to exactly one other bridge, or a shared link if it can be connected to two or more bridges. • when a...
Page 417
Spanning tree commands 4-175 4 command mode interface configuration (ethernet, port channel) command usage • each spanning-tree instance is associated with a unique set of vlan ids. • this command is used by the multiple spanning-tree algorithm to determine the best path between devices. Therefore, ...
Page 418: Show Spanning-Tree
Command line interface 4-176 4 example related commands spanning-tree mst cost (4-174) spanning-tree protocol-migration this command re-checks the appropriate bpdu format to send on the selected interface. Syntax spanning-tree protocol-migration interface interface • ethernet unit/port - unit - stac...
Page 419
Spanning tree commands 4-177 4 • port-channel channel-id (range: 1-32) • instance_id - instance identifier of the multiple spanning tree. (range: 0-4094, no leading zeroes) default setting none command mode privileged exec command usage • use the show spanning-tree command with no parameters to disp...
Page 420
Command line interface 4-178 4 show spanning-tree mst configuration this command shows the configuration of the multiple spanning tree. Command mode privileged exec example --------------------------------------------------------------- eth 1/ 1 information ------------------------------------------...
Page 421: Vlan Commands
Vlan commands 4-179 4 vlan commands a vlan is a group of ports that can be located anywhere in the network, but communicate as though they belong to the same physical segment. This section describes commands used to create vlan groups, add port members, specify how vlan tagging is used, and enable a...
Page 423: Configuring Vlan Interfaces
Vlan commands 4-181 4 configuring vlan interfaces interface vlan this command enters interface configuration mode for vlans, which is used to configure vlan parameters for a physical interface. Syntax interface vlan vlan-id vlan-id - id of the configured vlan. (range: 1-4094, no leading zeroes) defa...
Page 425
Vlan commands 4-183 4 command mode interface configuration (ethernet, port channel) command usage when set to receive all frame types, any received frames that are untagged are assigned to the default vlan. Example the following example shows how to restrict the traffic received on port 1 to tagged ...
Page 426
Command line interface 4-184 4 example the following example shows how to set the interface to port 1 and then enable ingress filtering: switchport native vlan this command configures the pvid (i.E., default vlan id) for a port. Use the no form to restore the default. Syntax switchport native vlan v...
Page 430: Configuring Private Vlans
Command line interface 4-188 4 configuring private vlans private vlans provide port-based security and isolation between ports within the assigned vlan. This switch supports two types of private vlans: primary/ secondary associated groups, and stand-alone isolated vlans. A primary vlan contains prom...
Page 431
Vlan commands 4-189 4 3. Use the switchport mode private-vlan command to configure ports as promiscuous (i.E., having access to all ports in the primary vlan) or host (i.E., community port). 4. Use the switchport private-vlan host-association command to assign a port to a secondary vlan. 5. Use the ...
Page 432
Command line interface 4-190 4 an associated “primary” vlan that contains promiscuous ports. When using an isolated vlan, it must be configured to contain a single promiscuous port. • port membership for private vlans is static. Once a port has been assigned to a private vlan, it cannot be dynamical...
Page 434
Command line interface 4-192 4 command mode interface configuration (ethernet, port channel) command usage all ports assigned to a secondary (i.E., community) vlan can pass traffic between group members, but must communicate with resources outside of the group via promiscuous ports in the associated...
Page 435
Vlan commands 4-193 4 switchport private-vlan mapping use this command to map an interface to a primary vlan. Use the no form to remove this mapping. Syntax switchport private-vlan mapping primary-vlan-id no switchport private-vlan mapping primary-vlan-id – id of primary vlan. (range: 1-4094, no lea...
Page 436
Command line interface 4-194 4 example gvrp and bridge extension commands garp vlan registration protocol defines a way for switches to exchange vlan information in order to automatically register vlan members on interfaces across the network. This section describes how to enable gvrp for individual...
Page 437
Gvrp and bridge extension commands 4-195 4 example show bridge-ext this command shows the configuration for bridge extension commands. Default setting none command mode privileged exec command usage see “enabling or disabling gvrp (global setting)” on page 3-142 and “displaying bridge extension capa...
Page 438
Command line interface 4-196 4 show gvrp configuration this command shows if gvrp is enabled. Syntax show gvrp configuration [interface] interface • ethernet unit/port - unit - this is unit 1. - port - port number. (range: 1-26/52) • port-channel channel-id (range: 1-4) default setting shows both gl...
Page 439
Gvrp and bridge extension commands 4-197 4 command usage • group address registration protocol is used by gvrp and gmrp to register or deregister client attributes for client services within a bridged lan. The default values for the garp timers are independent of the media access method or data rate...
Page 440: Priority Commands
Command line interface 4-198 4 related commands garp timer (4-196) priority commands the commands described in this section allow you to specify which data packets have greater precedence when traffic is buffered in the switch due to congestion. This switch supports cos with four priority queues for...
Page 442
Command line interface 4-200 4 default setting the priority is not set, and the default value for untagged frames received on the interface is zero. Command mode interface configuration (ethernet, port channel) command usage • the precedence for priority mapping is ip port, ip precedence or ip dscp,...
Page 443
Priority commands 4-201 4 command mode global configuration command usage wrr controls bandwidth sharing at the egress port by defining scheduling weights. Example this example shows how to assign wrr weights to priority queues 1 - 3: related commands show queue bandwidth (4-202) queue cos-map this ...
Page 444
Command line interface 4-202 4 command usage • cos values assigned at the ingress port are also used at the egress port. • this command sets the cos priority for all interfaces. Example the following example shows how to map cos values 0, 1 and 2 to egress queue 0, value 3 to egress queue 1, values ...
Page 445
Priority commands 4-203 4 example show queue cos-map this command shows the class of service priority map. Syntax show queue cos-map [interface] interface • ethernet unit/port - unit - this is unit 1. - port - port number. (range: 1-26/52) • port-channel channel-id (range: 1-4) default setting none ...
Page 446
Command line interface 4-204 4 priority commands (layer 3 and 4) map ip port (global configuration) this command enables ip port mapping (i.E., class of service mapping for tcp/udp sockets). Use the no form to disable ip port mapping. Syntax [no] map ip port default setting disabled command mode glo...
Page 447
Priority commands 4-205 4 map ip port (interface configuration) this command set ip port priority (i.E., tcp/udp port priority). Use the no form to remove a specific setting. Syntax map ip port port number cos cos-value no map ip port port-number • port-number - 16-bit tcp/udp port number.(range 1-6...
Page 448
Command line interface 4-206 4 example the following example shows how to enable ip precedence mapping globally: map ip precedence (interface configuration) this command sets ip precedence priority (i.E., ip type of service priority). Use the no form to restore the default table. Syntax map ip prece...
Page 449
Priority commands 4-207 4 map ip dscp (global configuration) this command enables ip dscp mapping (i.E., differentiated services code point mapping). Use the no form to disable ip dscp mapping. Syntax [no] map ip dscp default setting disabled command mode global configuration command usage • the pre...
Page 450
Command line interface 4-208 4 default setting the dscp default values are defined in the following table. Note that all the dscp values that are not specified are mapped to cos value 0. Command mode interface configuration (ethernet, port channel) command usage • the precedence for priority mapping...
Page 451
Priority commands 4-209 4 default setting none command mode privileged exec example the following shows that http traffic has been mapped to cos value 0: related commands map ip port (global configuration) (4-204) map ip port (interface configuration) (4-205) show map ip precedence this command show...
Page 452
Command line interface 4-210 4 example related commands map ip port (global configuration) (4-204) map ip precedence (interface configuration) (4-206) show map ip dscp this command shows the ip dscp priority map. Syntax show map ip dscp [interface] interface • ethernet unit/port - unit - this is uni...
Page 453: Multicast Filtering Commands
Multicast filtering commands 4-211 4 example related commands map ip dscp (global configuration) (4-207) map ip dscp (interface configuration) (4-207) multicast filtering commands this switch uses igmp (internet group management protocol) to query for any attached hosts that want to receive a specif...
Page 454
Command line interface 4-212 4 ip igmp snooping this command enables igmp snooping on this switch. Use the no form to disable it. Syntax [no] ip igmp snooping default setting enabled command mode global configuration example the following example enables igmp snooping. Ip igmp snooping vlan static t...
Page 455
Multicast filtering commands 4-213 4 command mode global configuration example the following shows how to statically configure a multicast group on a port: ip igmp snooping version this command configures the igmp snooping version. Use the no form to restore the default. Syntax ip igmp snooping vers...
Page 456
Command line interface 4-214 4 default setting disabled command mode interface configuration (vlan) command usage the igmp snooping immediate-leave feature enables a layer 2 lan interface to be removed from the multicast forwarding table without first sending an igmp group-specific query to the inte...
Page 458
Command line interface 4-216 4 igmp query commands (layer 2) ip igmp snooping querier this command enables the switch as an igmp querier. Use the no form to disable it. Syntax [no] ip igmp snooping querier default setting enabled command mode global configuration command usage if enabled, the switch...
Page 459
Multicast filtering commands 4-217 4 default setting 2 times command mode global configuration command usage the query count defines how long the querier waits for a response from a multicast client before taking action. If a querier has sent a number of queries defined by this command, but a client...
Page 460
Command line interface 4-218 4 ip igmp snooping query-max-response-time this command configures the query report delay. Use the no form to restore the default. Syntax ip igmp snooping query-max-response-time seconds no ip igmp snooping query-max-response-time seconds - the report delay advertised in...
Page 461
Multicast filtering commands 4-219 4 default setting 300 seconds command mode global configuration command usage the switch must use igmpv2 for this command to take effect. Example the following shows how to configure the default timeout to 300 seconds: related commands ip igmp snooping version (4-2...
Page 462
Command line interface 4-220 4 command usage depending on your network connections, igmp snooping may not always be able to locate the igmp querier. Therefore, if the igmp querier is a known multicast router/switch connected over the network to an interface (port or trunk) on your router, you can ma...
Page 463
Multicast filtering commands 4-221 4 igmp filtering and throttling commands in certain switch applications, the administrator may want to control the multicast services that are available to end users. For example, an ip/tv service based on a specific subscription plan. The igmp filtering feature fu...
Page 464
Command line interface 4-222 4 • igmp filtering and throttling only applies to dynamically learned multicast groups, it does not apply to statically configured groups. • the igmp filtering feature operates in the same manner when mvr is used to forward the multicast traffic. Example ip igmp profile ...
Page 465
Multicast filtering commands 4-223 4 command usage • each profile has only one access mode; either permit or deny. • when the access mode is set to permit, igmp join reports are processed when a multicast group falls within the controlled range. When the access mode is set to deny, igmp join reports...
Page 466
Command line interface 4-224 4 default setting none command mode interface configuration command usage • the igmp filtering profile must first be created with the ip igmp profile command before being able to assign it to an interface. • only one profile can be assigned to an interface. • a profile c...
Page 468
Command line interface 4-226 4 command mode privileged exec example show ip igmp profile this command displays igmp filtering profiles created on the switch. Syntax show ip igmp profile [profile-number] profile-number - an existing igmp filter profile number. (range: 1-4294967295) default setting no...
Page 469
Multicast filtering commands 4-227 4 • port-channel channel-id (range: 1-4) default setting none command mode privileged exec command usage using this command without specifying an interface displays all interfaces. Example multicast vlan registration commands this section describes commands used to...
Page 470
Command line interface 4-228 4 mvr (global configuration) this command enables multicast vlan registration (mvr) globally on the switch, statically configures mvr multicast group ip address(es) using the group keyword, or specifies the mvr vlan identifier using the vlan keyword. Use the no form of t...
Page 471
Multicast filtering commands 4-229 4 mvr (interface configuration) this command configures an interface as an mvr receiver or source port using the type keyword, enables immediate leave capability using the immediate keyword, or configures an interface as a static member of the mvr vlan using the gr...
Page 472
Command line interface 4-230 4 response to determine if there are any remaining subscribers for that multicast group before removing the port from the group list. • using immediate leave can speed up leave latency, but should only be enabled on a port attached to one multicast subscriber to avoid di...
Page 473
Multicast filtering commands 4-231 4 command usage enter this command without any keywords to display the global settings for mvr. Use the interface keyword to display information about interfaces attached to the mvr vlan. Or use the members keyword to display information about multicast groups assi...
Page 474
Command line interface 4-232 4 the following shows information about the interfaces associated with multicast groups assigned to the mvr vlan: domain name service commands these commands are used to configure domain naming system (dns) services. You can manually configure entries in the dns domain n...
Page 475: Ip Host
Domain name service commands 4-233 4 ip host this command creates a static entry in the dns table that maps a host name to an ip address. Use the no form to remove an entry. Syntax [no] ip host name address1 [address2 … address8] • name - name of the host. (range: 1-64 characters) • address1 - corre...
Page 476: Ip Domain-Name
Command line interface 4-234 4 • * - removes all entries. Default setting none command mode privileged exec example this example clears all static entries from the dns table. Ip domain-name this command defines the default domain name appended to incomplete host names (i.E., host names passed from a...
Page 477: Ip Domain-List
Domain name service commands 4-235 4 ip domain-list this command defines a list of domain names that can be appended to incomplete host names (i.E., host names passed from a client that are not formatted with dotted notation). Use the no form to remove a name from this list. Syntax [no] ip domain-li...
Page 478: Ip Name-Server
Command line interface 4-236 4 ip name-server this command specifies the address of one or more domain name servers to use for name-to-address resolution. Use the no form to remove a name server from this list. Syntax [no] ip name-server server-address1 [server-address2 … server-address6] • server-a...
Page 479: Show Hosts
Domain name service commands 4-237 4 default setting disabled command mode global configuration command usage • at least one name server must be specified before you can enable dns. • if all name servers are deleted, dns will automatically be disabled. Example this example enables dns and then displ...
Page 480: Show Dns
Command line interface 4-238 4 show dns this command displays the configuration of the dns service. Command mode privileged exec example show dns cache this command displays entries in the dns cache. Command mode privileged exec example console#show dns domain lookup status: dns enabled default doma...
Page 481: Clear Dns Cache
Domain name service commands 4-239 4 clear dns cache this command clears all entries in the dns cache. Command mode privileged exec example console#clear dns cache console#show dns cache no flag type ip ttl domain console#.
Page 482: Dhcp Commands
Command line interface 4-240 4 dhcp commands these commands are used to configure dynamic host configuration protocol (dhcp) relay and option 82 functions. The switch can be configured to relay dhcp client configuration requests to a dhcp server on another network and include information about the s...
Page 484: Show Ip Dhcp-Relay
Command line interface 4-242 4 usage guidelines you must specify the ip address for at least one dhcp server. Otherwise, the switch’s dhcp relay agent will not operate and all dhcp request and reply packets will be flooded to the entire vlan. Example show ip dhcp-relay this command shows the current...
Page 485: Ip Interface Commands
Ip interface commands 4-243 4 ip interface commands an ip addresses may be used for management access to the switch over your network. The ip address for this switch is obtained via dhcp by default. You can manually configure a specific ip address, or direct the device to obtain an address from a bo...
Page 486: Ip Default-Gateway
Command line interface 4-244 4 command usage • you must assign an ip address to this device to gain management access over the network. You can manually configure a specific ip address, or direct the device to obtain an address from a bootp or dhcp server. Valid ip addresses consist of four numbers,...
Page 487: Ip Dhcp Restart
Ip interface commands 4-245 4 example the following example defines a default gateway for this device: related commands show ip redirects (4-246) ip dhcp restart this command submits a bootp or dhcp client request. Default setting none command mode privileged exec command usage • this command issues...
Page 488: Show Ip Redirects
Command line interface 4-246 4 example related commands show ip redirects (4-246) show ip redirects this command shows the default gateway configured for this device. Default setting none command mode privileged exec example related commands ip default-gateway (4-244) ping this command sends icmp ec...
Page 489
Ip interface commands 4-247 4 - normal response - the normal response occurs in one to ten seconds, depending on network traffic. - destination does not respond - if the host does not respond, a “timeout” appears in ten seconds. - destination unreachable - the gateway for this destination indicates ...
Page 490: Switch Cluster Commands
Command line interface 4-248 4 switch cluster commands switch clustering is a method of grouping switches together to enable centralized management through a single unit. A switch cluster has a “commander” unit that is used to manage all other “member” switches in the cluster. The management station...
Page 491: Cluster Commander
Switch cluster commands 4-249 4 example cluster commander this command enables the switch as a cluster commander. Use the no form to disable the switch as cluster commander. Syntax [no] cluster commander default setting disabled command mode global configuration command usage • once a switch has bee...
Page 492: Cluster Member
Command line interface 4-250 4 command usage • an “internal” ip address pool is used to assign ip addresses to member switches in the cluster. Internal cluster ip addresses are in the form 10.X.X.Member-id. Only the base ip address of the pool needs to be set since member ids can only be between 1 a...
Page 493: Show Cluster
Switch cluster commands 4-251 4 command mode privileged exec command usage • this command only operates through a telnet connection to the commander switch. Managing cluster members using the local console cli on the commander is not supported. • there is no need to enter the username and password f...
Page 494: Show Cluster Candidates
Command line interface 4-252 4 show cluster candidates this command shows the discovered candidate switches in the network. Command mode privileged exec example console#show cluster candidates cluster candidates: role mac description --------------- ----------------- --------------------------------...
Page 495: Software Features
A-1 appendix a: software specifications software features authentication local, radius, tacacs, port (802.1x), https, ssh, port security access control lists ip, mac (up to 88 lists) dhcp client port configuration 100base-tx: 10/100 mbps, half/full duplex 1000base-t: 10/100 mbps at half/full duplex,...
Page 496: Management Features
Software specifications a-2 a additional features bootp client sntp (simple network time protocol) snmp (simple network management protocol) rmon (remote monitoring, groups 1,2,3,9) smtp email alerts management features in-band management telnet, web-based http or https, snmp manager, or secure shel...
Page 497
Management information bases a-3 a management information bases bridge mib (rfc 1493) entity mib (rfc 2737) ether-like mib (rfc 2665) extended bridge mib (rfc 2674) extensible snmp agents mib (rfc 2742) forwarding table mib (rfc 2096) igmp mib (rfc 2933) interface group mib (rfc 2233) interfaces evo...
Page 498
Software specifications a-4 a.
Page 499: Appendix B: Troubleshooting
B-1 appendix b: troubleshooting problems accessing the management interface table b-1 troubleshooting chart symptom action cannot connect using telnet, web browser, or snmp software • be sure the switch is powered up. • check network cabling between the management station and the switch. • check tha...
Page 500: Using System Logs
Troubleshooting b-2 b using system logs if a fault does occur, refer to the installation guide to ensure that the problem you encountered is actually caused by the switch. If the problem appears to be caused by the switch, follow these steps: 1. Enable logging. 2. Set the error messages reported to ...
Page 501: Glossary
Glossary-1 glossary access control list (acl) acls can limit network traffic and restrict access to certain users or devices by checking each packet for certain ip or mac (i.E., layer 2) information. Boot protocol (bootp) bootp is used to provide bootup information for network devices, including ip ...
Page 502
Glossary glossary-2 garp vlan registration protocol (gvrp) defines a way for switches to exchange vlan information in order to register necessary vlan members on ports along the spanning tree so that vlans defined in each switch can work automatically over a spanning tree network. Generic attribute ...
Page 503
Glossary-3 glossary igmp snooping listening to igmp query and igmp report packets transferred between ip multicast routers and ip multicast host groups to identify ip multicast group members. Igmp query on each subnetwork, one igmp-capable device will act as the querier — that is, the device that as...
Page 504
Glossary glossary-4 md5 message-digest algorithm an algorithm that is used to create digital signatures. It is intended for use with 32 bit machines and is safer than the md4 algorithm, which has been broken. Md5 is a one-way hash function, meaning that it takes a message and converts it into a fixe...
Page 505
Glossary-5 glossary remote monitoring (rmon) rmon provides comprehensive network monitoring capabilities. It eliminates the polling required in standard snmp, and can set alarms on a variety of traffic conditions, including specific error types. Rapid spanning tree protocol (rstp) rstp reduces the c...
Page 506
Glossary glossary-6 user datagram protocol (udp) udp provides a datagram mode for packet-switched communications. It uses ip as the underlying transport mechanism to provide access to ip-like services. Udp packets are delivered just like ip packets – connection-less datagrams that may be discarded b...
Page 507: Index
Index-1 numerics 802.1x, port authentication 3-68 a acceptable frame type 3-150, 4-182 access control list see acl acl extended ip 3-83, 4-102, 4-103, 4-105 mac 3-83, 4-102, 4-110, 4-110–4-112 standard ip 3-83, 4-102, 4-103, 4-104 address table 3-114, 4-156 aging time 3-117, 4-159 b bootp 3-16, 4-24...
Page 508
Index-2 index g garp vlan registration protocol see gvrp gateway, default 3-14, 4-245 gvrp global setting 4-194 interface configuration 3-150, 4-195 gvrp, global setting 3-142 h hardware version, displaying 3-11, 4-68 https 3-59, 4-32 https, secure server 3-59, 4-32 i ieee 802.1d 3-117, 4-162 ieee 8...
Page 509
Index-3 index path cost 3-120, 3-128 method 3-124, 4-165 sta 3-120, 3-128, 4-165 port authentication 3-68 port priority configuring 3-158, 4-198 default ingress 3-158, 4-199 sta 3-129, 4-171 port security, configuring 3-66, 4-84 port, statistics 3-109, 4-139 ports autonegotiation 3-92, 4-133 broadca...
Page 510
Index-4 index t tacacs+, logon authentication 3-56, 4-81 time, setting 3-35, 4-54 traffic class weights 3-163, 4-200 trap manager 2-7, 3-41, 4-120 troubleshooting b-1 trunk configuration 3-93, 4-146 lacp 3-95, 4-148 static 3-94, 4-147 u upgrading software 3-20, 4-70 user password 3-54, 4-27, 4-28 v ...
Page 512
Es3526xa es3552xa e122006-cs-r02d 149100005500h.