- DL manuals
- Accton Technology
- Network Router
- CheetahSwitch Workgroup-3514F
- Management Manual
Accton Technology CheetahSwitch Workgroup-3514F Management Manual - Contents
i
Contents
Chapter 1: Switch Management
1-1
Configuration Options
1-1
Required Connections
1-1
Console Port (Out-of-Band) Connections
1-1
Remote Management via the Console Port
1-2
Configure the Switch Site
1-2
Configure the Remote Site
1-2
In-Band Connections
1-2
Chapter 2: Using the System Configuration Program
2-1
Login Screen
2-1
Main Menu
2-3
System Information Menu
2-5
Displaying System Information
2-6
Displaying Switch Version Information
2-7
Management Setup Menu
2-8
Changing the Network Configuration
2-9
IP Configuration
2-10
IP Connectivity Test (Ping)
2-11
HTTP Configuration
2-12
Configuring the Serial Port
2-13
Assigning SNMP Parameters
2-14
Configuring Community Names
2-15
Configuring IP Trap Managers
2-16
Console Login Configuration
2-17
Downloading System Software
2-18
Using TFTP to Download Over the Network
2-18
Configuring the Switch
2-19
Configuring Port Parameters
2-20
Viewing the Current Port Configuration
2-21
Using the Spanning Tree Algorithm
2-22
Configuring Bridge STA
2-22
Configuring STA for Ports
2-24
Viewing the Current Spanning Tree Information
2-25
Displaying the Current Bridge STA
2-26
Displaying the Current STA for Ports
2-27
Using a Mirror Port for Analysis
2-28
Configuring Port Trunks
2-29
IGMP Multicast Filtering
2-31
Configuring IGMP
2-31
Configuring Bridge MIB Extensions
2-32
Summary of CheetahSwitch Workgroup-3514F
Page 1
Cheetahswitch workgroup-3514f cheetahswitch workgroup-3526f cheetahswitch workgroup-3526g management guide.
Page 3
Management guide cheetahswitch workgroup-3514f intelligent/stackable fast ethernet switch with 12 10base-t / 100base-tx (rj-45) ports, and optional media expansion and stack modules cheetahswitch workgroup-3526f intelligent/stackable fast ethernet switch with 24 10base-t / 100base-tx (rj-45) ports, ...
Page 4
Accton is a trademark of accton technology corporation. Other trademarks or brand names mentioned herein are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective companies. International headquarters no. 1 creation road iii, science-based industrial park hsinchu 300, taiwan, r.O.C. Phone: 886-3-5...
Page 5: Contents
I contents chapter 1: switch management 1-1 configuration options 1-1 required connections 1-1 console port (out-of-band) connections 1-1 remote management via the console port 1-2 configure the switch site 1-2 configure the remote site 1-2 in-band connections 1-2 chapter 2: using the system configu...
Page 6
Contents ii configuring traffic classes 2-33 port priority configuration 2-34 802.1p port traffic class information 2-35 configuring virtual lans 2-36 802.1q vlan base information 2-36 802.1q vlan current table information 2-37 802.1q vlan static table configuration 2-38 802.1q vlan port configurati...
Page 7
Contents iii spanning tree configuration 3-16 switch 3-16 when the switch becomes root 3-16 sta port configuration 3-17 configuring bridge mib extensions 3-18 bridge capability 3-18 bridge settings 3-19 priority 3-20 port priority configuration 3-20 port traffic class information 3-21 configuring vi...
Page 8
Contents iv appendix a: troubleshooting a-1 troubleshooting chart a-1 upgrading firmware via the serial port a-2 appendix b: pin assignments b-1 console port pin assignments b-1 db-9 port pin assignments b-1 console port to 9-pin com port on pc b-2 console port to 25-pin dce port on modem b-2 consol...
Page 9
1-1 chapter 1: switch management configuration options for advanced management capability, the snmp/rmon module provides a menu-driven system configuration program. This program can be accessed by a direct or modem connection to the serial port on the rear panel (out-of-band), or by a telnet connect...
Page 10
Switch management 1-2 remote management via the console port configure the switch site connect the switch’s db9 serial port to the modem’s serial port using standard cabling. For most modems which use a 25-pin port, you will have to provide an rs-232 cable with a 9-pin connector on one end and a 25-...
Page 11
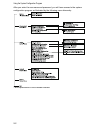
2-1 chapter 2: using the system configuration program login screen once a direct connection to the serial port or a telnet connection is established, the login screen for the on-board configuration program appears as shown below. If this is your first time to log into the configuration program, then...
Page 12
Using the system configuration program 2-2 after you enter the user name and password, you will have access to the system configuration program as illustrated by the following menu hierarchy: * not implemented in this firmware release..
Page 13
Main menu 2-3 main menu with the system configuration program you can define system parameters, manage and control the switch, the connected stack and all its ports, or monitor network conditions. The figure below of the main menu and the following table briefly describe the selections available fro...
Page 14
Using the system configuration program 2-4 device control menu port configuration enables any port, enables/disables flow control, and sets communication mode to auto-negotiation, full duplex or half duplex. Port information displays operational status, including link state, flow control method, and...
Page 15
System information menu 2-5 system information menu use the system information menu to display a basic description of the switch, including contact information, and hardware/firmware versions. System information menu ======================= system information ... Switch information ... Use or arrow ...
Page 16
Using the system configuration program 2-6 displaying system information use the system information screen to display descriptive information about the switch, or for quick system identification as shown in the following figure and table. System information ================== system description : ch...
Page 17
System information menu 2-7 displaying switch version information use the switch information screen to display hardware/firmware version numbers for the main board, as well as the power status. Switch information : unit 1 ================== main board hardware version : v3.0 firmware version : v1.11...
Page 18
Using the system configuration program 2-8 management setup menu after initially logging onto the system, adjust the communication parameters for your console to ensure a reliable connection (serial port configuration). Specify the ip addresses for the switch (network configuration / ip configuratio...
Page 19
Management setup menu 2-9 changing the network configuration use the network configuration menu to set the bootup option, configure the switch’s internet protocol (ip) parameters, enable the on-board web agent, or to set the number of concurrent telnet sessions allowed. The screen shown below is des...
Page 20
Using the system configuration program 2-10 ip configuration use the ip configuration screen to set the bootup option, or configure the switch’s ip parameters. The screen shown below is described in the following table. Network configuration : ip configuration =======================================...
Page 21
Management setup menu 2-11 ip connectivity test (ping) use the ip connectivity test to see if another site on the internet can be reached. The screen shown below is described in the following table. Network configuration : ip connectivity test (ping) =================================================...
Page 22
Using the system configuration program 2-12 http configuration use the http configuration screen to enable/disable the on-board web agent, and to specify the tcp port that will provide http service. The screen shown below is described in the following table. Network configuration : http configuratio...
Page 23
Management setup menu 2-13 configuring the serial port you can access the on-board configuration program by attaching a vt100 compatible device to the switch’s serial port. (for more information on connecting to this port, see “required connections” on page 1-1.) the communication parameters for thi...
Page 24
Using the system configuration program 2-14 assigning snmp parameters use the snmp configuration screen to display and modify parameters for the simple network management protocol (snmp). The switch includes an on-board snmp agent which monitors the status of its hardware, as well as the traffic pas...
Page 25
Management setup menu 2-15 configuring community names the following figure and table describe how to configure the community strings authorized for management access. Up to 5 community names may be entered. Note: the default community string is “public” with read/write access. Snmp configuration : ...
Page 26
Using the system configuration program 2-16 configuring ip trap managers the following figure and table describe how to specify management stations that will receive authentication failure messages or other trap messages from the switch. Up to 5 trap managers may be entered. Snmp configuration : ip ...
Page 27
Management setup menu 2-17 console login configuration use the management setup: console login configuration to restrict management access based on specified user names and passwords, or to set the invalid password threshold and time-out. There are two user types, administrator and guest. Only the a...
Page 28
Using the system configuration program 2-18 downloading system software using tftp to download over the network use the tftp download menu to load software updates into the switch. The download file should be an es3514f/26f or es3526g binary file from accton; otherwise the agent will not accept it. ...
Page 29
Configuring the switch 2-19 configuring the switch the device control menu is used to control a broad range of functions, including port configuration, spanning tree, port mirroring, multicast filtering, and virtual lans. Each of the setup screens provided by these configuration menus is described i...
Page 30
Using the system configuration program 2-20 configuring port parameters use the port configuration menus to set or display communication parameters for any port or module in the stack. Port configuration : unit 1 port 1 - 12 ================== flow control on all ports : [enable] [disable] port type...
Page 31
Configuring the switch 2-21 viewing the current port configuration the port information screen displays the port type, status, link state, and flow control in use, as well as the communication speed and duplex mode. To change any of the port settings, use the port configuration menu. Port informatio...
Page 32
Using the system configuration program 2-22 using the spanning tree algorithm the spanning tree algorithm can be used to detect and disable network loops, and to provide backup links between switches, bridges or routers. This allows the switch to interact with other bridging devices (that is, an sta...
Page 33
Configuring the switch 2-23 hello time 2 time interval (in seconds) at which the root device transmits a configuration message. The minimum value is1. The maximum value is the lower of 10 or [(max. Message age / 2) -1]. Max (message) age 20 the maximum time (in seconds) a device can wait without rec...
Page 34
Using the system configuration program 2-24 configuring sta for ports the following figure and table describe port sta configuration. Note: fast forwarding enables end-node workstations and servers to overcome time-out problems when the spanning tree algorithm is implemented in a network. Therefore,...
Page 35
Configuring the switch 2-25 viewing the current spanning tree information the spanning tree information screen displays a summary of the sta information for the overall bridge or for a specific port. To make any changes to the parameters for the spanning tree, use the spanning tree configuration men...
Page 36
Using the system configuration program 2-26 displaying the current bridge sta the parameters shown in the following figure and table describe the current bridge sta information. Spanning tree information : bridge sta information ================================================== priority : 32768 hel...
Page 37
Configuring the switch 2-27 displaying the current sta for ports the parameters shown in the following figure and table are for port sta information. Spanning tree port information : unit 1 port 1 - 12 ============================== port type status designated designated designated cost bridge port ...
Page 38
Using the system configuration program 2-28 using a mirror port for analysis you can mirror traffic from any source port to a target port for real-time analysis. You can then attach a logic analyzer or rmon probe to the target port and study the traffic crossing the source port in a completely unobt...
Page 39
Configuring the switch 2-29 configuring port trunks port trunks can be used to increase the bandwidth of a network connection or to ensure fault recovery. You can configure up to four trunk connections (combining 2~4 ports into a fat pipe) between any two es3514f, es3526f or es3526g switches. Howeve...
Page 40
Using the system configuration program 2-30 you can use the port trunking configuration screen set up port trunks as shown below: port trunking configuration =========================== trunk id status member list 1 2 3 4 --------- -------- ----------- ----------- ----------- ----------- -- --------...
Page 41
Configuring the switch 2-31 the rj-45 ports used for one side of a trunk must all be on the same internal switch chip. The port groups permitted include: the 100base-fx fiber ports used for one side of a trunk must all be on the same module. However, the 1000base-sx ports used for one side of a trun...
Page 42
Using the system configuration program 2-32 igmp multicast filtering multicasting is used to support real-time applications such as video conferencing or streaming audio. A multicast server does not have to establish a separate connection with each client. It merely broadcasts its service to the net...
Page 43
Configuring the switch 2-33 configuring bridge mib extensions the bridge mib includes extensions for managed devices that support traffic classes and virtual lans. To display and configure these extensions, use the extended bridge configuration screen as shown below. Extended bridge configuration ==...
Page 44
Using the system configuration program 2-34 configuring traffic classes ieee 802.1p defines up to 8 separate traffic classes. This switch supports quality of service (qos) by using two priority queues, with weighted fair queuing for each port. You can use the 802.1p configuration menu to configure t...
Page 45
Configuring the switch 2-35 port priority configuration inbound frames that do not have any vlan tags are tagged with the input port’s default vlan id (pvid) and the default ingress user priority as shown in the following menu, and then sorted into the appropriate priority queue at the output port. ...
Page 46
Using the system configuration program 2-36 802.1p port traffic class information this switch provides two priority levels with weighted fair queuing for port egress. This means that any frames with a priority tag from 0~3 are sent to the low priority queue “0” while those from 4~7 are sent to the h...
Page 47
Configuring the switch 2-37 configuring virtual lans you can use the vlan configuration menu to assign any port on the switch to any of up to 255 lan groups. In conventional networks with routers, broadcast traffic is split up into separate domains. Switches do not inherently support broadcast domai...
Page 48
Using the system configuration program 2-38 802.1q vlan current table information this screen shows the current port members of each vlan and whether or not the port supports vlan tagging. Ports assigned to a large vlan group that crosses several switches should use vlan tagging. However, if you jus...
Page 49
Configuring the switch 2-39 802.1q vlan static table configuration use this screen to create a new vlan or modify the settings for an existing vlan. You can add/delete port members for a vlan from any unit in the stack as a tagged or untagged member. Or you can prevent a port from being automaticall...
Page 50
Using the system configuration program 2-40 for example, the following screen displays settings for vlan 2, which includes untagged ports 1-6, and forbidden port 8. Notes: 1. To allow this switch to participate in a vlan group that extends beyond this switch, you must add the vlan id for the require...
Page 51
Configuring the switch 2-41 802.1q vlan port configuration use this screen to configure port-specific settings for ieee 802.1q vlan features. 802.1q vlan port configuration : unit 1 port 1 - 12 =============================== port pvid acceptable ingress gvrp gvrp failed gvrp last frame type filteri...
Page 52
Using the system configuration program 2-42 monitoring the switch the network monitor menu provides access to port statistics, rmon statistics, ip multicast addresses, and the static address table. Each of the screens provided by these menus is described in the following sections. Network monitor me...
Page 53
Monitoring the switch 2-43 displaying port statistics port statistics display key statistics from the ethernet-like mib for each port. Error statistics on the traffic passing through each port are displayed. This information can be used to identify potential problems with the switch (such as a fault...
Page 54
Using the system configuration program 2-44 displaying rmon statistics use the rmon statistics screen to display key statistics for each port from rmon group 1. (rmon groups 2, 3 and 9 can only be accessed using snmp management software such as accview.) the following screen displays the overall sta...
Page 55
Monitoring the switch 2-45 fragments the total number of frames received that were less than 64 octets in length (excluding framing bits, but including fcs octets) and had either an fcs or alignment error. Jabbers the total number of frames received that were longer than 1518 octets (excluding frami...
Page 56
Using the system configuration program 2-46 displaying the unicast address table the address table contains the mac addresses and vlan identifier associated with each port (that is, the source port associated with the address and vlan), sorted by mac address or vlan id. You can search for a specific...
Page 57
Monitoring the switch 2-47 displaying the ip multicast registration table use the ip multicast registration table to display all the multicast groups active on this switch, including multicast ip addresses and the corresponding vlan id. Ip multicast registration table ===============================...
Page 58
Using the system configuration program 2-48 configuring static unicast addresses use the static unicast address table configuration screen to manually configure host mac addresses in the unicast table. You can use this screen to associate a mac address with a specific vlan id and switch port as show...
Page 59
Resetting the system 2-49 resetting the system use the restart command under the main menu to reset the management agent. The reset screen includes options as shown in the following figure and table. Logging off the system use the exit command under the main menu to exit the configuration program an...
Page 60
Using the system configuration program 2-50
Page 61
3-1 chapter 3: web-based management web-based configuration and monitoring as well as the menu-driven system configuration program, the agent module provides an embedded http web agent. This agent can be accessed by any computer on the network using a standard web browser (internet explorer 4.0 or a...
Page 62
Web-based management 3-2 navigating the web browser interface to access the web-browser interface you must first enter a user name and password. The default user name is “admin,” with no password. The administrator has read/write access to all configuration parameters and statistics. Home page when ...
Page 63
Panel display 3-3 configuration options configurable parameters have a dialog box or a drop-down list. Once a configuration change has been made on a page, be sure to click on the “apply” button at the bottom of the page to confirm the new setting. The following table summarizes the web page configu...
Page 64
Web-based management 3-4 port state display click on any port to display a summary or port status as shown below, as well as etherlike statistics (page 3-36) and rmon statistics (page 3-37). Parameter description type shows port type as: 10/100tx : 10base-t / 100base-tx 100fx : 100base-fx 1000sx : 1...
Page 65
Panel display 3-5 console configuration if you are having difficulties making an out-of-band console connection to the serial port on the agent module, you can display or modify the current settings for the serial port through the web agent. Click on the serial port icon in the switch image to displ...
Page 66
Web-based management 3-6 main menu using the on-board web agent, you can define system parameters, manage and control the switch, the connected stack and all its ports, or monitor network conditions. The following table briefly describes the selections available from this program. Menu description s...
Page 67
System information 3-7 system information use the system information screen to display descriptive information about the switch, or for quick system identification as shown in the following figure and table. Parameter description system name* name assigned to the switch system. Ip address ip address...
Page 68
Web-based management 3-8 switch information use the switch information screen to display hardware/firmware version numbers for the main board, as well as the power status and modules plugged into the system. Main board agent module expansion slot parameter description serial number serial number of ...
Page 69
Ip configuration 3-9 ip configuration use the ip configuration screen to set the bootup option, configure the ip address for the on-board management agent, or set the number or concurrent telnet sessions allowed. The screen shown below is described in the following table. Parameter default descripti...
Page 70
Web-based management 3-10 snmp configuration use the snmp configuration screen to display and modify parameters for the simple network management protocol (snmp). The stack should include an snmp agent module which monitors the status of its hardware, as well as the traffic passing through its ports...
Page 71
Security configuration 3-11 trap managers the following figure and table describe how to specify management stations that will receive authentication failure messages or other trap messages from the switch. Up to 5 trap managers may be entered. Security configuration use the security configuration s...
Page 72
Web-based management 3-12 firmware upgrade options you can upgrade system firmware via a web browser, a tftp server, or a direct connection to the console port. Web upload management use the web upload management menu to load software updates into the switch. The upload file should be an es3514f/26f...
Page 73
Address table configuration 3-13 address table configuration the address table contains the unicast mac addresses and vlan identifier associated with each port (that is, the source port), sorted by mac address or vlan. You can also clear the entire address table, or information associated with a spe...
Page 74
Web-based management 3-14 spanning tree algorithm (sta) the spanning tree algorithm can be used to detect and disable network loops, and to provide backup links between switches, bridges or routers. This allows the switch to interact with other bridging devices (that is, sta compliant switch, bridge...
Page 75
Spanning tree algorithm (sta) 3-15 ports the parameters shown in the following figure and table are for port sta information. Parameter description port status displays the current state of this port within the spanning tree: broken no link has been established on this port. Disabled port has been d...
Page 76
Web-based management 3-16 spanning tree configuration the following figures and tables describe bridge sta configuration. Switch when the switch becomes root parameter default description usage enabled enable this parameter to participate in an sta compliant network. Priority 32,768 device priority ...
Page 77
Spanning tree algorithm (sta) 3-17 sta port configuration the following figure and table describe sta configuration for ports or modules. Parameter default description fast forwarding mode (all ports) enabled see “fast forward” in this table. Priority 128 defines the priority for the use of a port i...
Page 78
Web-based management 3-18 configuring bridge mib extensions the bridge mib includes extensions for managed devices that support traffic classes and virtual lans. To display and configure these extensions, use the bridge extension screen as shown below: bridge capability parameter description extende...
Page 79
Configuring bridge mib extensions 3-19 bridge settings parameter description traffic classes* multiple traffic classes are supported by this switch as indicated under bridge capabilities. However, this switch supports just two priority queues and only the default port priority can be configured. The...
Page 80
Web-based management 3-20 priority ieee 802.1p defines up to 8 separate traffic classes. This switch supports quality of service (qos) by using two priority queues, with weighted fair queuing for each port. You can use the priority menu to configure the default priority for each port, or to display ...
Page 81
Priority 3-21 port traffic class information this switch provides two priority levels with weighted fair queuing for port egress. This means that any frames with a default or user priority from 0~3 are sent to the low priority queue “0” while those from 4~7 are sent to the high priority queue “1” as...
Page 82
Web-based management 3-22 configuring virtual lans you can use the vlan configuration menu to assign any port on the switch to any of up to 255 lan groups. In conventional networks with routers, broadcast traffic is split up into separate domains. Switches do not inherently support broadcast domains...
Page 83
Configuring virtual lans 3-23 vlan current table this screen shows the current port members of each vlan and whether or not the port supports vlan tagging. Ports assigned to a large vlan group that crosses several switches should use vlan tagging. However, if you just want to create a small port-bas...
Page 84
Web-based management 3-24 vlan static list use this screen to create or remove vlan groups. Parameter description current lists all the current vlan groups created for this system. Up to 255 vlan groups can be defined. To allow this switch to participate in a vlan group that extends beyond this swit...
Page 85
Configuring virtual lans 3-25 vlan static table use this screen to modify the settings for an existing vlan. You can add/delete port members for a vlan from any unit in the stack. (note that vlan1 is fixed as an untagged vlan containing all ports in the stack, and cannot be modified via this screen....
Page 86
Web-based management 3-26 use the menu shown below to prevent a port from being dynamically added to the displayed vlan group through gvrp. Use the menu shown below to assign ports to the specified vlan group as an ieee 802.1q tagged or untagged port. Assign ports as tagged if they are connected to ...
Page 87
Configuring virtual lans 3-27 vlan static membership by port use the screen shown below to assign vlan groups to the selected port. To perform detailed port configuration for a specific vlan, use the vlan static table (page 3-25). Parameter description port number port number on the switch selected ...
Page 88
Web-based management 3-28 vlan port configuration use this screen to configure port-specific settings for ieee 802.1q vlan features. Parameter description pvid the vlan id assigned to untagged frames received on this port. Use the pvid to assign ports to the same untagged vlan. Acceptable frame type...
Page 89
Igmp multicast filtering 3-29 igmp multicast filtering multicasting is used to support real-time applications such as video conferencing or streaming audio. A multicast server does not have to establish a separate connection with each client. It merely broadcasts its service to the network, and any ...
Page 90
Web-based management 3-30 ip multicast registration table use the ip multicast registration table to display all the multicast groups active on this switch, including multicast ip addresses and the corresponding vlan id. Parameter description vlan id vlan id assigned to this multicast group. Multica...
Page 91
Port menus 3-31 port menus port information the port information screen displays the port status, link state, the communication speed and duplex mode, as well as the flow control in use. To change any of the port settings, use the port configuration menu. The parameters are shown in the following fi...
Page 92
Web-based management 3-32 port configuration use the port configuration menu to configure any port on the switch. Note: 100base-fx is fixed at 100 mbps, full-duplex. 1000base-sx is fixed at 1000 mbps, but auto-negotiates duplex mode and flow control. Parameter default description flow control (on al...
Page 93
Using a port mirror for analysis 3-33 using a port mirror for analysis you can mirror traffic from any source port to a target port for real-time analysis. You can then attach a logic analyzer or rmon probe to the target port and study the traffic crossing the source port in a completely unobtrusive...
Page 94
Web-based management 3-34 port trunk configuration port trunks can be used to increase the bandwidth of a network connection or to ensure fault recovery. You can configure up to four trunk connections (combining 2~4 ports into a fat pipe) between any two es3514f, es3526f or es3526g switches. However...
Page 95
Port trunk configuration 3-35 use the port trunking configuration screen to set up port trunks as shown below: the rj-45 ports used for one side of a trunk must all be on the same internal switch chip. The port groups permitted include: the 100base-fx fiber ports used for one side of a trunk must al...
Page 96
Web-based management 3-36 port statistics use the port statistics menu to display etherlike or rmon statistics for any port on the switch. The statistics displayed are indicated in the following figure and table. Etherlike statistics etherlike statistics display key statistics from the ethernet-like...
Page 97
Port statistics 3-37 rmon statistics rmon statistics display key statistics for each port or media module from rmon group 1. (rmon groups 2, 3 and 9 can only be accessed using snmp management software such as accview.) the following screen displays overall statistics on traffic passing through each ...
Page 98
Web-based management 3-38 256-511 byte frames the total number of packets (including bad packets) received and transmitted that were between 256 and 511 octets in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but including fcs octets). 512-1023 byte frames the total number of packets (including bad packe...
Page 99: Chapter 4: Advanced Topics
4-1 chapter 4: advanced topics the cheetahswitch workgroup-3514f/26f/26g supports layer 2 switching and other advanced features, which are described in this chapter. Layer-2 switching when a frame enters a port, its destination mac address is checked in the address database to see which port leads t...
Page 100
Advanced topics 4-2 once a stable network topology has been established, all bridges listen for hello bpdus (bridge protocol data units) transmitted from the root bridge. If a bridge does not get a hello bpdu after a predefined interval (maximum age), the bridge assumes that the link to the root bri...
Page 101
Virtual lans 4-3 this switch supports the following vlan features: • up to 255 vlans based on the ieee 802.1q standard • distributed vlan learning across multiple switches using explicit or implicit tagging and gvrp protocol • port overlapping, allowing a port to participate in multiple vlans • end ...
Page 102
Advanced topics 4-4 gvrp-compliant devices to be automatically configured for vlan groups based solely on endstation requests. Forwarding traffic with unknown vlan tags this switch only supports 255 vlans, but up to 4094 vlans are supported by the ieee 802.1q vlan protocol. Therefore, if this switch...
Page 103
Multicast filtering 4-5 multicast filtering multicasting sends data to a group of nodes instead of a single destination. The simplest way to implement multicasting is to broadcast data to all nodes on the network. However, such an approach wastes a lot of bandwidth if the target group is small compa...
Page 104
Advanced topics 4-6 class-of-service (cos) support the cheetahswitch workgroup-3514f/26f/26g provides two transmit queues on each port, with a weighted fair queuing scheme. This function can be used to provide independent priorities for various types of data such as real-time video or voice, and bes...
Page 105
Remote monitoring 4-7 remote monitoring remote monitoring (rmon) provides a cost-effective way to monitor large networks by placing embedded or external probes on distributed network equipment (hubs, switches or routers). Accton’s accview network management software can access the probes embedded in...
Page 106
Advanced topics 4-8.
Page 107: Appendix A: Troubleshooting
A-1 appendix a: troubleshooting troubleshooting chart troubleshooting chart symptom action cannot connect using telnet, web browser, or snmp software • be sure to have configured the agent with a valid ip address, subnet mask and default gateway. • check that you have a valid network connection to t...
Page 108
Troubleshooting a-2 upgrading firmware via the serial port you can upgrade system firmware by connecting your computer to the serial port on the switch, and using a console interface package that supports the xmodem protocol. (see “required connections” on page 1-1.) 1. Restart the system by using t...
Page 109
Upgrading firmware via the serial port a-3 3. After the file has been downloaded, the console screen will display information similar to that shown below. Press “s” to start the management interface, change the baud rate back to 19200, and press enter. The logon screen will then appear. For details ...
Page 110
Troubleshooting a-4.
Page 111: Appendix B: Pin Assignments
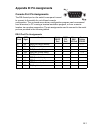
B-1 appendix b: pin assignments console port pin assignments the db-9 serial port on the switch’s rear panel is used to connect to the switch for out-of-band console configuration. The on-board menu-driven configuration program can be accessed from a terminal, a pc running a terminal emulation progr...
Page 112
Pin assignments b-2 console port to 9-pin com port on pc console port to 25-pin dce port on modem console port to 25-pin dte port on pc switch’s 9-pin serial port ccitt signal pc’s 9-pin com port 1 dcd ----------- dcd ------------ 1 2 rxd txd ------------ 3 3 txd ----------- rxd ----------> 2 4 dtr ...
Page 114
Es3514f es3526f es3526g e072000-r04 f2.2 150074-102.