- DL manuals
- Accton Technology
- Switch
- ES4512C
- Management Manual
Accton Technology ES4512C Management Manual
Summary of ES4512C
Page 1
Www.Edge-core.Com management guide powered by accton es4512c es4524c es4548c 12/24/48-port gigabit intelligent switch.
Page 2
Command line interface 4-206 4 ip igmp snooping version this command configures the igmp snooping version. Use the no form to restore the default. Syntax ip igmp snooping version { 1
Page 3
Installation guide es4512c 12-port gigabit intelligent switch layer 2 workgroup switch with 12 1000base-t (rj-45) ports, and 4 combination (rj-45/sfp) ports es4524c 24-port gigabit intelligent switch layer 2 workgroup switch with 24 1000base-t (rj-45) ports, and 4 combination (rj-45/sfp) ports es454...
Page 4
Es4512c es4524c es4548c e052005-r02.
Page 5: Contents
I contents chapter 1: introduction 1-1 key features 1-1 description of software features 1-2 system defaults 1-5 chapter 2: initial configuration 2-1 connecting to the switch 2-1 configuration options 2-1 required connections 2-2 remote connections 2-3 basic configuration 2-3 console connection 2-3 ...
Page 6
Contents ii system log configuration 3-19 remote log configuration 3-20 displaying log messages 3-22 sending simple mail transfer protocol alerts 3-23 resetting the system 3-25 setting the system clock 3-26 configuring sntp 3-26 setting the time zone 3-27 simple network management protocol 3-28 sett...
Page 7
Contents iii displaying lacp settings and status for the local side 3-77 displaying lacp settings and status for the remote side 3-79 setting broadcast storm thresholds 3-80 configuring port mirroring 3-82 configuring rate limits 3-83 showing port statistics 3-84 address table settings 3-88 setting ...
Page 8
Contents iv mapping cos values to acls 3-136 changing priorities based on acl rules 3-137 multicast filtering 3-139 layer 2 igmp (snooping and query) 3-139 configuring igmp snooping and query parameters 3-140 displaying interfaces attached to a multicast router 3-142 specifying static interfaces for...
Page 9
Contents v disconnect 4-18 show line 4-19 general commands 4-20 enable 4-20 disable 4-21 configure 4-21 show history 4-22 reload 4-22 end 4-23 exit 4-23 quit 4-24 system management commands 4-24 device designation commands 4-25 prompt 4-25 hostname 4-25 user access commands 4-26 username 4-26 enable...
Page 10
Contents vi logging facility 4-45 logging trap 4-46 clear logging 4-46 show logging 4-47 smtp alert commands 4-48 logging sendmail host 4-49 logging sendmail level 4-49 logging sendmail source-email 4-50 logging sendmail destination-email 4-50 logging sendmail 4-51 show logging sendmail 4-51 time co...
Page 11
Contents vii tacacs-server host 4-74 tacacs-server port 4-74 tacacs-server key 4-75 show tacacs-server 4-75 port security commands 4-76 port security 4-76 802.1x port authentication 4-78 authentication dot1x default 4-78 dot1x default 4-79 dot1x max-req 4-79 dot1x port-control 4-80 dot1x operation-m...
Page 12
Contents viii acl information 4-111 show access-list 4-111 show access-group 4-111 snmp commands 4-112 snmp-server community 4-112 snmp-server contact 4-113 snmp-server location 4-113 snmp-server host 4-114 snmp-server enable traps 4-115 show snmp 4-115 dns commands 4-117 ip host 4-117 clear host 4-...
Page 13
Contents ix lacp admin-key (port channel) 4-142 lacp port-priority 4-142 show lacp 4-143 address table commands 4-147 mac-address-table static 4-148 clear mac-address-table dynamic 4-149 show mac-address-table 4-149 mac-address-table aging-time 4-150 show mac-address-table aging-time 4-150 spanning ...
Page 14
Contents x switchport allowed vlan 4-177 switchport forbidden vlan 4-178 displaying vlan information 4-179 show vlan 4-179 configuring private vlans 4-180 pvlan 4-180 show pvlan 4-181 configuring protocol-based vlans 4-181 protocol-vlan protocol-group (configuring groups) 4-182 protocol-vlan protoco...
Page 15
Contents xi igmp query commands (layer 2) 4-206 ip igmp snooping querier 4-206 ip igmp snooping query-count 4-206 ip igmp snooping query-interval 4-207 ip igmp snooping query-max-response-time 4-208 ip igmp snooping router-port-expire-time 4-208 static multicast routing commands 4-209 ip igmp snoopi...
Page 16
Contents xii.
Page 17: Tables
Xiii tables table 1-1. Key features 1-1 table 1-2. System defaults 1-5 table 3-1. Web page configuration buttons 3-3 table 3-2. Switch main menu 3-4 table 3-3. Logging levels 3-19 table 3-4. Https system support 3-35 table 3-5. 802.1x statistics 3-48 table 3-6. Lacp port counters 3-76 table 3-7. Lac...
Page 18
Xiv tables table 4-27. Authentication sequence commands 4-69 table 4-28. Radius client commands 4-71 table 4-29. Tacacs+ client commands 4-74 table 4-30. Port security commands 4-76 table 4-31. 802.1x port authentication commands 4-78 table 4-32. Access control list commands 4-87 table 4-33. Ip acl ...
Page 19: Figures
Xv figures figure 3-1. Home page 3-2 figure 3-2. Front panel indicators 3-3 figure 3-3. System information 3-9 figure 3-4. Switch information 3-11 figure 3-5. Displaying bridge extension configuration 3-12 figure 3-6. Ip interface configuration - manual 3-14 figure 3-7. Ip interface configuration - ...
Page 20
Figures xvi figure 3-43. Lacp - aggregation port 3-74 figure 3-44. Lacp - port counters information 3-76 figure 3-45. Lacp - port internal information 3-78 figure 3-46. Lacp - port neighbors information 3-79 figure 3-47. Port broadcast control 3-81 figure 3-48. Mirror port configuration 3-82 figure ...
Page 21
Figures xvii figure 3-88. Dns general configuration 3-147 figure 3-89. Dns static host table 3-149 figure 3-90. Dns cache 3-150
Page 22
Figures xviii.
Page 23: Chapter 1: Introduction
1-1 chapter 1: introduction this switch provides a broad range of features for layer 2 switching. It includes a management agent that allows you to configure the features listed in this manual. The default configuration can be used for most of the features provided by this switch. However, there are...
Page 24
Introduction 1-2 1 description of software features the switch provides a wide range of advanced performance enhancing features. Flow control eliminates the loss of packets due to bottlenecks caused by port saturation. Broadcast storm suppression prevents broadcast traffic storms from engulfing the ...
Page 25
Description of software features 1-3 1 port mirroring – the switch can unobtrusively mirror traffic from any port to a monitor port. You can then attach a protocol analyzer or rmon probe to this port to perform traffic analysis and verify connection integrity. Port trunking – ports can be combined i...
Page 26
Introduction 1-4 1 multiple spanning tree protocol (mstp, ieee 802.1s) – this protocol is a direct extension of rstp. It can provide an independent spanning tree for different vlans. It simplifies network management, provides for even faster convergence than rstp by limiting the size of each region,...
Page 27: System Defaults
System defaults 1-5 1 system defaults the switch’s system defaults are provided in the configuration file “factory_default_config.Cfg.” to reset the switch defaults, this file should be set as the startup configuration file (page 3-18). The following table lists some of the basic system defaults. Ta...
Page 28
Introduction 1-6 1 port configuration admin status enabled auto-negotiation enabled flow control disabled port capability 1000base-t – 10 mbps half duplex 10 mbps full duplex 100 mbps half duplex 100 mbps full duplex 1000 mbps full duplex full-duplex flow control disabled symmetric flow control disa...
Page 29
System defaults 1-7 1 ip settings ip address 0.0.0.0 subnet mask 255.0.0.0 default gateway 0.0.0.0 dhcp client: enabled bootp disabled dns server lookup disabled multicast filtering igmp snooping snooping: enabled querier: enabled system log status enabled messages logged levels 0-7 (all) messages l...
Page 30
Introduction 1-8 1.
Page 31: Connecting To The Switch
2-1 chapter 2: initial configuration connecting to the switch configuration options the switch includes a built-in network management agent. The agent offers a variety of management options, including snmp, rmon and a web-based interface. A pc may also be connected directly to the switch for configu...
Page 32: Required Connections
Initial configuration 2-2 2 • enable port mirroring • set broadcast storm control on any port • display system information and statistics required connections the switch provides an rs-232 serial port that enables a connection to a pc or terminal for monitoring and configuring the switch. A null-mod...
Page 33: Remote Connections
Basic configuration 2-3 2 remote connections prior to accessing the switch’s onboard agent via a network connection, you must first configure it with a valid ip address, subnet mask, and default gateway using a console connection, dhcp or bootp protocol. The ip address for this switch is obtained vi...
Page 34: Setting Passwords
Initial configuration 2-4 2 setting passwords note: if this is your first time to log into the cli program, you should define new passwords for both default user names using the “username” command, record them and put them in a safe place. Passwords can consist of up to 8 alphanumeric characters and...
Page 35
Basic configuration 2-5 2 before you can assign an ip address to the switch, you must obtain the following information from your network administrator: • ip address for the switch • default gateway for the network • network mask for this network to assign an ip address to the switch, complete the fo...
Page 36
Initial configuration 2-6 2 5. Wait a few minutes, and then check the ip configuration settings by typing the “show ip interface” command. Press . 6. Then save your configuration changes by typing “copy running-config startup-config.” enter the startup file name and press . Enabling snmp management ...
Page 37
Basic configuration 2-7 2 to configure a community string, complete the following steps: 1. From the privileged exec level global configuration mode prompt, type “snmp-server community string mode ,” where “string” is the community access string and “mode” is rw (read/write) or ro (read only). Press...
Page 38: Managing System Files
Initial configuration 2-8 2 2. Enter the name of the start-up file. Press . Managing system files the switch’s flash memory supports three types of system files that can be managed by the cli program, web interface, or snmp. The switch’s file system allows files to be uploaded and downloaded, copied...
Page 39: Using The Web Interface
3-1 chapter 3: configuring the switch using the web interface this switch provides an embedded http web agent. Using a web browser you can configure the switch and view statistics to monitor network activity. The web agent can be accessed by any computer on the network using a standard web browser (...
Page 40: Home Page
Configuring the switch 3-2 3 navigating the web browser interface to access the web-browser interface you must first enter a user name and password. The administrator has read/write access to all configuration parameters and statistics. The default user name and password for the administrator is “ad...
Page 41: Configuration Options
Navigating the web browser interface 3-3 3 configuration options configurable parameters have a dialog box or a drop-down list. Once a configuration change has been made on a page, be sure to click on the “apply” button to confirm the new setting. The following table summarizes the web page configur...
Page 42: Main Menu
Configuring the switch 3-4 3 main menu using the onboard web agent, you can define system parameters, manage and control the switch, and all its ports, or monitor network conditions. The following table briefly describes the selections available from this program. Table 3-2. Switch main menu menu de...
Page 43
Navigating the web browser interface 3-5 3 802.1x port authentication 3-43 information displays global configuration settings 3-44 configuration configures protocol parameters 3-46 port configuration sets the authentication mode for individual ports 3-47 statistics displays protocol statistics for t...
Page 44
Configuring the switch 3-6 3 address table 3-88 static addresses displays entries for interface, address or vlan 3-88 dynamic addresses displays or edits static entries in the address table 3-89 address aging sets timeout for dynamically learned entries 3-91 spanning tree 3-91 sta 3-91 information d...
Page 45
Navigating the web browser interface 3-7 3 protocol vlan 3-123 configuration creates a protocol group, specifying the supported protocols 3-123 port configuration maps a protocol group to a vlan 3-123 priority 3-125 default port priority sets the default priority for each port 3-125 default trunk pr...
Page 46
Configuring the switch 3-8 3 dns 3-146 general configuration enables dns; configures domain name and domain list; and specifies ip address of name servers for dynamic lookup 3-146 static host table configures static entries for domain name to address mapping 3-148 cache displays cache entries discov...
Page 47: Basic Configuration
Basic configuration 3-9 3 basic configuration displaying system information you can easily identify the system by displaying the device name, location and contact information. Field attributes • system name – name assigned to the switch system. • object id – mib ii object id for switch’s network man...
Page 48
Configuring the switch 3-10 3 cli – specify the hostname, location and contact information. Displaying switch hardware/software versions use the switch information page to display hardware/firmware version numbers for the main board and management software, as well as the power status of the system....
Page 49
Basic configuration 3-11 3 • redundant power status* – displays the status of the redundant power supply. * cli only. Management software • loader version – version number of loader code. • boot-rom version – version of power-on self-test (post) and boot code. • operation code version – version numb...
Page 50
Configuring the switch 3-12 3 displaying bridge extension capabilities the bridge mib includes extensions for managed devices that support multicast filtering, traffic classes, and virtual lans. You can access these extensions to display default settings for the key variables. Field attributes • ext...
Page 51
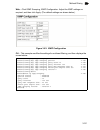
Basic configuration 3-13 3 cli – enter the following command. Setting the switch’s ip address this section describes how to configure an ip interface for management access over the network. The ip address for this switch is obtained via dhcp by default. To manually configure an address, you need to ...
Page 52
Configuring the switch 3-14 3 manual configuration web – click system, ip configuration. Select the vlan through which the management station is attached, set the ip address mode to “static,” enter the ip address, subnet mask and gateway, then click apply. Figure 3-6. Ip interface configuration - ma...
Page 53
Basic configuration 3-15 3 using dhcp/bootp if your network provides dhcp/bootp services, you can configure the switch to be dynamically configured by these services. Web – click system, ip configuration. Specify the vlan to which the management station is attached, set the ip address mode to dhcp o...
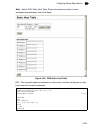
Page 54: Managing Firmware
Configuring the switch 3-16 3 cli – enter the following command to restart dhcp service. Managing firmware you can upload/download firmware to or from a tftp server. By saving runtime code to a file on a tftp server, that file can later be downloaded to the switch to restore operation. You can also ...
Page 55
Basic configuration 3-17 3 if you download to a new destination file, then select the file from the drop-down box for the operation code used at startup, and click apply changes. To start the new firmware, reboot the system via the system/reset menu. Figure 3-9. Setting the startup code cli – enter ...
Page 56
Configuring the switch 3-18 3 downloading configuration settings from a server you can download the configuration file under a new file name and then set it as the startup file, or you can specify the current startup configuration file as the destination file to directly replace it. Note that the fi...
Page 57: Configuring Event Logging
Basic configuration 3-19 3 if you download the startup configuration file under a new file name, you can set this file as the startup file at a later time, and then restart the switch. Configuring event logging the switch allows you to control the logging of error messages, including the type of eve...
Page 58
Configuring the switch 3-20 3 • ram level – limits log messages saved to the switch’s temporary ram memory for all levels up to the specified level. For example, if level 7 is specified, all messages from level 0 to level 7 will be logged to ram. (range: 0-7, default: 7) note: the flash level must b...
Page 59
Basic configuration 3-21 3 • logging trap – limits log messages that are sent to the remote syslog server for all levels up to the specified level. For example, if level 3 is specified, all messages from level 0 to level 3 will be sent to the remote server. (range: 0-7, default: 7) • host ip list – ...
Page 60
Configuring the switch 3-22 3 cli – enter the syslog server host ip address, choose the facility type and set the logging trap. Displaying log messages use the logs page to scroll through the logged system and event messages. The switch can store up to 2048 log entries in temporary random access mem...
Page 61
Basic configuration 3-23 3 cli – this example shows that system logging is enabled, the message level for flash memory is “errors” (i.E., default level 3 - 0), the message level for ram is “debugging” (i.E., default level 7 - 0), and lists one sample error. Sending simple mail transfer protocol aler...
Page 62
Configuring the switch 3-24 3 web – click system, log, smtp. Enable smtp, specify a source email address, and select the minimum severity level. To add an ip address to the smtp server list, type the new ip address in the smtp server field and click add. To delete an ip address, click the entry in t...
Page 63: Resetting The System
Basic configuration 3-25 3 cli – enter the ip address of at least one smtp server, set the syslog severity level to trigger an email message, and specify the switch (source) and up to five recipient (destination) email addresses. Enable smtp with the logging sendmail command to complete the configur...
Page 64: Setting The System Clock
Configuring the switch 3-26 3 setting the system clock simple network time protocol (sntp) allows the switch to set its internal clock based on periodic updates from a time server (sntp or ntp). Maintaining an accurate time on the switch enables the system log to record meaningful dates and times fo...
Page 65
Basic configuration 3-27 3 cli – this example configures the switch to operate as an sntp client and then displays the current time and settings. Setting the time zone sntp uses coordinated universal time (or utc, formerly greenwich mean time, or gmt) based on the time at the earth’s prime meridian,...
Page 66
Configuring the switch 3-28 3 cli - this example shows how to set the time zone for the system clock. Simple network management protocol simple network management protocol (snmp) is a communication protocol designed specifically for managing devices on a network. Equipment commonly managed with snmp...
Page 67
Simple network management protocol 3-29 3 web – click snmp, configuration. Add new community strings as required, select the access rights from the access mode drop-down list, then click add. Figure 3-19. Configuring snmp community strings cli – the following example adds the string “spiderman” with...
Page 68: User Authentication
Configuring the switch 3-30 3 web – click snmp, configuration. Fill in the ip address and community string for each trap manager that will receive these messages, specify the snmp version, mark the trap types required, and then click add. Figure 3-20. Configuring snmp trap managers cli – this exampl...
Page 69
User authentication 3-31 3 command attributes • user name* – the name of the user. (maximum length: 8 characters) • access level* – specifies the user level. (options: normal and privileged) • password – specifies the user password. (range: 0-8 characters plain text, case sensitive) * cli only. Web ...
Page 70
Configuring the switch 3-32 3 radius uses udp while tacacs+ uses tcp. Udp only offers best effort delivery, while tcp offers a connection-oriented transport. Also, note that radius encrypts only the password in the access-request packet from the client to the server, while tacacs+ encrypts the entir...
Page 71
User authentication 3-33 3 note: the local switch user database has to be set up by manually entering user names and passwords using the cli. (see “username” on page 4-26.) web – click security, authentication settings. To configure local or remote authentication preferences, specify the authenticat...
Page 72: Configuring Https
Configuring the switch 3-34 3 cli – specify all the required parameters to enable logon authentication. Configuring https you can configure the switch to enable the secure hypertext transfer protocol (https) over the secure socket layer (ssl), providing secure access (i.E., an encrypted connection) ...
Page 73
User authentication 3-35 3 • the following web browsers and operating systems currently support https: • to specify a secure-site certificate, see “replacing the default secure-site certificate” on page 3-35. Command attributes • https status – allows you to enable/disable the https server feature o...
Page 74
Configuring the switch 3-36 3 caution: for maximum security, we recommend you obtain a unique secure sockets layer certificate at the earliest opportunity. This is because the default certificate for the switch is not unique to the hardware you have purchased. When you have obtained these, place the...
Page 75
User authentication 3-37 3 to use the ssh server, complete these steps: 1. Generate a host key pair – on the ssh host key settings page, create a host public/private key pair. 2. Provide host public key to clients – many ssh client programs automatically import the host public key during the initial...
Page 76
Configuring the switch 3-38 3 e. The switch compares the decrypted bytes to the original bytes it sent. If the two sets match, this means that the client's private key corresponds to an authorized public key, and the client is authenticated. Notes: 1. To use ssh with only password authentication, th...
Page 77
User authentication 3-39 3 web – click security, ssh host-key settings. Select the host-key type from the drop-down box, select the option to save the host key from memory to flash (if required) prior to generating the key, and then click generate. Figure 3-23. Ssh host-key settings cli – this examp...
Page 78
Configuring the switch 3-40 3 configuring the ssh server the ssh server includes basic settings for authentication. Field attributes • ssh server status – allows you to enable/disable the ssh server on the switch. (default: disabled) • version – the secure shell version number. Version 2.0 is displa...
Page 79: Configuring Port Security
User authentication 3-41 3 cli – this example enables ssh, sets the authentication parameters, and displays the current configuration. It shows that the administrator has made a connection via shh, and then disables this connection. Configuring port security port security is a feature that allows yo...
Page 80
Configuring the switch 3-42 3 • if a port is disabled (shut down) due to a security violation, it must be manually re-enabled from the port/port configuration page (page 3-67). Command attributes • port – port number. • name – descriptive text (page 4-126). • action – indicates the action to be take...
Page 81
User authentication 3-43 3 cli – this example selects the target port, sets the port security action to send a trap and disable the port, specifies a maximum address count, and then enables port security for the port. Configuring 802.1x port authentication network switches can provide open and easy ...
Page 82
Configuring the switch 3-44 3 the operation of 802.1x on the switch requires the following: • the switch must have an ip address assigned. • radius authentication must be enabled on the switch and the ip address of the radius server specified. • each switch port that will be used must be set to dot1...
Page 83
User authentication 3-45 3 web – click security, 802.1x, information. Figure 3-26. 802.1x information cli – this example shows the default protocol settings for 802.1x. For a description of the additional entries displayed in the cli, see “show dot1x” on page 4-83. Console#show dot1x 4-83 global 802...
Page 84
Configuring the switch 3-46 3 configuring 802.1x global settings the dot1x protocol includes global parameters that control the client authentication process that runs between the client and the switch (i.E., authenticator), as well as the client identity lookup process that runs between the switch ...
Page 85
User authentication 3-47 3 web – select security, 802.1x, configuration. Enable dot1x globally for the switch, modify any of the parameters required, and then click apply. Figure 3-27. 802.1x configuration cli – this enables re-authentication and sets all of the global parameters for 802.1x. Configu...
Page 86
Configuring the switch 3-48 3 • authorized – - yes – connected client is authorized. - no – connected client is not authorized. - blank – displays nothing when dot1x is disabled on a port. • supplicant – indicates the mac address of a connected client. • trunk – indicates if the port is configured a...
Page 87
User authentication 3-49 3 web – select security, 802.1x, statistics. Select the required port and then click query. Click refresh to update the statistics. Figure 3-29. 802.1x port statistics rx eap resp/oth the number of valid eap response frames (other than resp/id frames) that have been received...
Page 88
Configuring the switch 3-50 3 cli – this example displays the 802.1x statistics for port 4. Filtering ip addresses for management access you can create a list of up to 16 ip addresses or ip address groups that are allowed management access to the switch through the web interface, snmp, or telnet. Co...
Page 89
User authentication 3-51 3 web – click security, ip filter. Enter the addresses that are allowed management access to an interface, and click add ip filtering entry. Figure 3-30. Ip filter cli – this example allows snmp access for a specific client. Console(config)#management snmp-client 10.1.2.3 4-...
Page 90: Access Control Lists
Configuring the switch 3-52 3 access control lists access control lists (acl) provide packet filtering for ip frames (based on address, protocol, layer 4 protocol port number or tcp control code) or any frames (based on mac address or ethernet type). To filter incoming packets, first create an acces...
Page 91
Access control lists 3-53 3 setting the acl name and type use the acl configuration page to designate the name and type of an acl. Command attributes • name – name of the acl. (maximum length: 16 characters) • type – there are three filtering modes: - standard: ip acl mode that filters packets based...
Page 92
Configuring the switch 3-54 3 the mask is bitwise anded with the specified source ip address, and compared with the address for each ip packet entering the port(s) to which this acl has been assigned. Web – specify the action (i.E., permit or deny). Select the address type (any, host, or ip). If you...
Page 93
Access control lists 3-55 3 configuring an extended ip acl command attributes • action – an acl can contain either all permit rules or all deny rules. (default: permit rules) • src/dst ip – specifies the source or destination ip address. Use “any” to include all possible addresses, “host” to specify...
Page 94
Configuring the switch 3-56 3 web – specify the action (i.E., permit or deny). Specify the source and/or destination addresses. Select the address type (any, host, or ip). If you select “host,” enter a specific address. If you select “ip,” enter a subnet address and the mask for an address range. Se...
Page 95
Access control lists 3-57 3 configuring a mac acl command attributes • action – an acl can contain all permit rules or all deny rules. (default: permit rules) • source/destination mac – use “any” to include all possible addresses, “host” to indicate a specific mac address, or “mac” to specify an add...
Page 96
Configuring the switch 3-58 3 web – specify the action (i.E., permit or deny). Specify the source and/or destination addresses. Select the address type (any, host, or mac). If you select “host,” enter a specific address (e.G., 11-22-33-44-55-66). If you select “mac,” enter a base address and a hexid...
Page 97: Configuring Acl Masks
Access control lists 3-59 3 configuring acl masks you can specify optional masks that control the order in which acl rules are checked. The switch includes two system default masks that pass/filter packets matching the permit/deny rules specified in an ingress acl. You can also configure up to seven...
Page 98
Configuring the switch 3-60 3 configuring an ip acl mask this mask defines the fields to check in the ip header. Command usage • masks that include an entry for a layer 4 protocol source port or destination port can only be applied to packets with a header length of exactly five bytes. Command attri...
Page 99
Access control lists 3-61 3 web – configure the mask to match the required rules in the ip ingress or egress acls. Set the mask to check for any source or destination address, a specific host address, or an address range. Include other criteria to search for in the rules, such as a protocol type or ...
Page 100
Configuring the switch 3-62 3 configuring a mac acl mask this mask defines the fields to check in the packet header. Command usage you must configure a mask for an acl rule before you can bind it to a port. Command attributes • source/destination mac – use “any” to match any address, “host” to speci...
Page 101
Access control lists 3-63 3 cli – this example shows how to create an ingress mac acl and bind it to a port. You can then see that the order of the rules have been changed by the mask. Binding a port to an access control list after configuring the access control lists (acl), you can bind the ports t...
Page 102: Port Configuration
Configuring the switch 3-64 3 web – click security, acl, port binding. Mark the enable field for the port you want to bind to an acl for ingress or egress traffic, select the required acl from the drop-down list, then click apply. Figure 3-38. Acl port binding cli – this examples assigns an ip and m...
Page 103
Port configuration 3-65 3 • forced mode 1 – shows the forced/preferred port type to use for combination ports 21-24 or 45-48. (copper-forced, copper-preferred-auto, sfp-forced, sfp-preferred-auto) • trunk member 1 – shows if port is a trunk member. • creation 2 – shows if a trunk is manually configu...
Page 104
Configuring the switch 3-66 3 • broadcast storm – shows if broadcast storm control is enabled or disabled. • broadcast storm limit – shows the broadcast storm threshold. (500 - 262143 packets per second) • flow control – shows if flow control is enabled or disabled. • lacp – shows if lacp is enabled...
Page 105
Port configuration 3-67 3 configuring interface connections you can use the port configuration or trunk configuration page to enable/disable an interface, set auto-negotiation and the interface capabilities to advertise, or manually fix the speed, duplex mode, and flow control. Command attributes • ...
Page 106
Configuring the switch 3-68 3 • trunk – indicates if a port is a member of a trunk. To create trunks and select port members, see “creating trunk groups” on page 3-69. Note: auto-negotiation must be disabled before you can configure or force the interface to use the speed/duplex mode or flow control...
Page 107: Creating Trunk Groups
Port configuration 3-69 3 creating trunk groups you can create multiple links between devices that work as one virtual, aggregate link. A port trunk offers a dramatic increase in bandwidth for network segments where bottlenecks exist, as well as providing a fault-tolerant link between two devices. Y...
Page 108
Configuring the switch 3-70 3 statically configuring a trunk command usage • when configuring static trunks, you may not be able to link switches of different types, depending on the manufacturer’s implementation. However, note that the static trunks on this switch are cisco etherchannel compatible....
Page 109
Port configuration 3-71 3 cli – this example creates trunk 2 with ports 1 and 2. Just connect these ports to two static trunk ports on another switch to form a trunk. Enabling lacp on selected ports command usage • to avoid creating a loop in the network, be sure you enable lacp before connecting th...
Page 110
Configuring the switch 3-72 3 web – click port, lacp, configuration. Select any of the switch ports from the scroll-down port list and click add. After you have completed adding ports to the member list, click apply. Figure 3-42. Lacp trunk configuration cli – the following example enables lacp for ...
Page 111
Port configuration 3-73 3 configuring lacp parameters dynamically creating a port channel – ports assigned to a common port channel must meet the following criteria: • ports must have the same lacp system priority. • ports must have the same lacp port admin key. • however, if the “port channel” admi...
Page 112
Configuring the switch 3-74 3 web – click port, lacp, aggregation port. Set the system priority, admin key, and port priority for the port actor. You can optionally configure these settings for the port partner. (be aware that these settings only affect the administrative state of the partner, and w...
Page 113
Port configuration 3-75 3 cli – the following example configures lacp parameters for ports 1-6. Ports 1-4 are used as active members of the lag; ports 5 and 6 are set to backup mode. Console(config)#interface ethernet 1/1 4-125 console(config-if)#lacp actor system-priority 3 4-142 console(config-if)...
Page 114
Configuring the switch 3-76 3 displaying lacp port counters you can display statistics for lacp protocol messages. Web – click port, lacp, port counters information. Select a member port to display the corresponding information. Figure 3-44. Lacp - port counters information cli – the following examp...
Page 115
Port configuration 3-77 3 displaying lacp settings and status for the local side you can display configuration settings and the operational state for the local side of an link aggregation. Table 3-7. Lacp internal configuration information field description oper key current operational value of the ...
Page 116
Configuring the switch 3-78 3 web – click port, lacp, port internal information. Select a port channel to display the corresponding information. Figure 3-45. Lacp - port internal information cli – the following example displays the lacp configuration settings and operational state for the local side...
Page 117
Port configuration 3-79 3 displaying lacp settings and status for the remote side you can display configuration settings and the operational state for the remote side of an link aggregation. Web – click port, lacp, port neighbors information. Select a port channel to display the corresponding inform...
Page 118
Configuring the switch 3-80 3 cli – the following example displays the lacp configuration settings and operational state for the remote side of port channel 1. Setting broadcast storm thresholds broadcast storms may occur when a device on your network is malfunctioning, or if application programs ar...
Page 119
Port configuration 3-81 3 web – click port, port/trunk broadcast control. Check the enabled box for any interface, set the threshold and click apply. Figure 3-47. Port broadcast control cli – specify any interface, and then enter the threshold. The following disables broadcast storm control for port...
Page 120: Configuring Port Mirroring
Configuring the switch 3-82 3 configuring port mirroring you can mirror traffic from any source port to a target port for real-time analysis. You can then attach a logic analyzer or rmon probe to the target port and study the traffic crossing the source port in a completely unobtrusive manner. Comma...
Page 121: Configuring Rate Limits
Port configuration 3-83 3 configuring rate limits this function allows the network manager to control the maximum rate for traffic transmitted or received on an interface. Rate limiting is configured on interfaces at the edge of a network to limit traffic coming out of the switch. Traffic that falls...
Page 122: Showing Port Statistics
Configuring the switch 3-84 3 showing port statistics you can display standard statistics on network traffic from the interfaces group and ethernet-like mibs, as well as a detailed breakdown of traffic based on the rmon mib. Interfaces and ethernet-like statistics display errors on the traffic passi...
Page 123
Port configuration 3-85 3 transmit discarded packets the number of outbound packets which were chosen to be discarded even though no errors had been detected to prevent their being transmitted. One possible reason for discarding such a packet could be to free up buffer space. Transmit errors the num...
Page 124
Configuring the switch 3-86 3 received frames the total number of frames (bad, broadcast and multicast) received. Broadcast frames the total number of good frames received that were directed to the broadcast address. Note that this does not include multicast packets. Multicast frames the total numbe...
Page 125
Port configuration 3-87 3 web – click port, port statistics. Select the required interface, and click query. You can also use the refresh button at the bottom of the page to update the screen. Figure 3-50. Port statistics.
Page 126: Address Table Settings
Configuring the switch 3-88 3 cli – this example shows statistics for port 13. Address table settings switches store the addresses for all known devices. This information is used to pass traffic directly between the inbound and outbound ports. All the addresses learned by monitoring traffic are stor...
Page 127
Address table settings 3-89 3 web – click address table, static addresses. Specify the interface, the mac address and vlan, then click add static address. Then set this as a permanent address or to be deleted on reset. Figure 3-51. Static addresses cli – this example adds an address to the static ad...
Page 128
Configuring the switch 3-90 3 web – click address table, dynamic addresses. Specify the search type (i.E., mark the interface, mac address, or vlan checkbox), select the method of sorting the displayed addresses, and then click query. Figure 3-52. Dynamic addresses cli – this example also displays t...
Page 129: Changing The Aging Time
Spanning tree algorithm configuration 3-91 3 changing the aging time you can set the aging time for entries in the dynamic address table. Command attributes • aging status – enables or disables the aging time. • aging time – the time after which a learned entry is discarded. (range: 10-1000000 secon...
Page 130: Displaying Global Settings
Configuring the switch 3-92 3 once a stable network topology has been established, all bridges listen for hello bpdus (bridge protocol data units) transmitted from the root bridge. If a bridge does not get a hello bpdu after a predefined interval (maximum age), the bridge assumes that the link to th...
Page 131
Spanning tree algorithm configuration 3-93 3 • hello time – interval (in seconds) at which the root device transmits a configuration message. • forward delay – the maximum time (in seconds) the root device will wait before changing states (i.E., discarding to learning to forwarding). This delay is r...
Page 132
Configuring the switch 3-94 3 information that would make it return to a discarding state; otherwise, temporary data loops might result. • root hold time – the interval (in seconds) during which no more than two bridge configuration protocol data units shall be transmitted by this node. • max hops –...
Page 133: Configuring Global Settings
Spanning tree algorithm configuration 3-95 3 cli – this command displays global sta settings, followed by settings for each port. Note: the current root port and current root cost display as zero when this device is not connected to the network. Configuring global settings global settings apply to t...
Page 134
Configuring the switch 3-96 3 • multiple spanning tree protocol - to allow multiple spanning trees to operate over the network, you must configure a related set of bridges with the same mstp configuration, allowing them to participate in a specific set of spanning tree instances. - a spanning tree i...
Page 135
Spanning tree algorithm configuration 3-97 3 • forward delay – the maximum time (in seconds) this device will wait before changing states (i.E., discarding to learning to forwarding). This delay is required because every device must receive information about topology changes before it starts to forw...
Page 136
Configuring the switch 3-98 3 web – click spanning tree, sta, configuration. Modify the required attributes, and click apply. Figure 3-55. Sta configuration.
Page 137
Spanning tree algorithm configuration 3-99 3 cli – this example enables spanning tree protocol, sets the mode to mst, and then configures the sta and mstp parameters. Displaying interface settings the sta port information and sta trunk information pages display the current status of ports and trunks...
Page 138
Configuring the switch 3-100 3 • oper link type – the operational point-to-point status of the lan segment attached to this interface. This parameter is determined by manual configuration or by auto-detection, as described for admin link type in sta port configuration on page 3-102. • oper edge port...
Page 139
Spanning tree algorithm configuration 3-101 3 • priority – defines the priority used for this port in the spanning tree algorithm. If the path cost for all ports on a switch is the same, the port with the highest priority (i.E., lowest value) will be configured as an active link in the spanning tree...
Page 140
Configuring the switch 3-102 3 cli – this example shows the sta attributes for port 5. Configuring interface settings you can configure rstp and mstp attributes for specific interfaces, including port priority, path cost, link type, and edge port. You may use a different priority or path cost for po...
Page 141
Spanning tree algorithm configuration 3-103 3 protocol is detecting network loops. Where more than one port is assigned the highest priority, the port with lowest numeric identifier will be enabled. • default: 128 • range: 0-240, in steps of 16 • path cost – this parameter is used by the stp to dete...
Page 142
Configuring the switch 3-104 3 web – click spanning tree, sta, port configuration or trunk configuration. Modify the required attributes, then click apply. Figure 3-57. Sta port configuration cli – this example sets sta attributes for port 7. Configuring multiple spanning trees mstp generates a uniq...
Page 143
Spanning tree algorithm configuration 3-105 3 to ensure that the msti maintains connectivity across the network, you must configure a related set of bridges with the same msti settings. Command attributes • mst instance – instance identifier of this spanning tree. (default: 0) • priority – the prior...
Page 144
Configuring the switch 3-106 3 cli – this displays sta settings for instance 1, followed by settings for each port. Cli – this example sets the priority for msti 1, and adds vlans 1-5 to this msti. Console#show spanning-tree mst 1 4-170 spanning-tree information -------------------------------------...
Page 145
Spanning tree algorithm configuration 3-107 3 displaying interface settings for mstp the mstp port information and mstp trunk information pages display the current status of ports and trunks in the selected mst instance. Field attributes • mst instance id – instance identifier to configure. (range: ...
Page 146
Configuring the switch 3-108 3 configuring interface settings for mstp you can configure the sta interface settings for an mst instance using the mstp port configuration and mstp trunk configuration pages. Field attributes the following attributes are read-only and cannot be changed: • sta state – d...
Page 147
Spanning tree algorithm configuration 3-109 3 • mst path cost – this parameter is used by the mstp to determine the best path between devices. Therefore, lower values should be assigned to ports attached to faster media, and higher values assigned to ports with slower media. (path cost takes precede...
Page 148: Vlan Configuration
Configuring the switch 3-110 3 vlan configuration ieee 802.1q vlans in large networks, routers are used to isolate broadcast traffic for each subnet into separate domains. This switch provides a similar service at layer 2 by using vlans to organize any group of network nodes into separate broadcast ...
Page 149
Vlan configuration 3-111 3 note: vlan-tagged frames can pass through vlan-aware or vlan-unaware network interconnection devices, but the vlan tags should be stripped off before passing it on to any end-node host that does not support vlan tagging. Vlan classification – when the switch receives a fra...
Page 150
Configuring the switch 3-112 3 these hosts, and core switches in the network, enable gvrp on the links between these devices. You should also determine security boundaries in the network and disable gvrp on the boundary ports to prevent advertisements from being propagated, or forbid those ports fro...
Page 151
Vlan configuration 3-113 3 enabling or disabling gvrp (global setting) garp vlan registration protocol (gvrp) defines a way for switches to exchange vlan information in order to register vlan members on ports across the network. Vlans are dynamically configured based on join messages issued by host ...
Page 152
Configuring the switch 3-114 3 cli – enter the following command. Displaying current vlans the vlan current table shows the current port members of each vlan and whether or not the port supports vlan tagging. Ports assigned to a large vlan group that crosses several switches should use vlan tagging....
Page 153
Vlan configuration 3-115 3 command attributes (cli) • vlan – id of configured vlan (1-4094, no leading zeroes). • type – shows how this vlan was added to the switch. - dynamic : automatically learned via gvrp. - static : added as a static entry. • name – name of the vlan (1 to 32 characters). • stat...
Page 154
Configuring the switch 3-116 3 web – click vlan, 802.1q vlan, static list. To create a new vlan, enter the vlan id and vlan name, mark the enable checkbox to activate the vlan, and then click add. Figure 3-64. Vlan static list - creating vlans cli – this example creates a new vlan. Adding static mem...
Page 155
Vlan configuration 3-117 3 command attributes • vlan – id of configured vlan (1-4094, no leading zeroes). • name – name of the vlan (1 to 32 characters). • status – enables or disables the specified vlan. - enable : vlan is operational. - disable : vlan is suspended; i.E., does not pass packets. • p...
Page 156
Configuring the switch 3-118 3 cli – the following example adds tagged and untagged ports to vlan 2. Adding static members to vlans (port index) use the vlan static membership by port menu to assign vlan groups to the selected interface as a tagged member. Command attributes • interface – port or tr...
Page 157
Vlan configuration 3-119 3 configuring vlan behavior for interfaces you can configure vlan behavior for specific interfaces, including the default vlan identifier (pvid), accepted frame types, ingress filtering, gvrp status, and garp timers. Command usage • gvrp – garp vlan registration protocol def...
Page 158
Configuring the switch 3-120 3 or leaveall message has been issued, the applicants can rejoin before the port actually leaves the group. (range: 60-3000 centiseconds; default: 60) • garp leaveall timer * – the interval between sending out a leaveall query message for vlan group participants and the ...
Page 159: Configuring Private Vlans
Vlan configuration 3-121 3 cli – this example sets port 3 to accept only tagged frames, assigns pvid 3 as the native vlan id, enables gvrp, sets the garp timers, and then sets the switchport mode to hybrid. Configuring private vlans private vlans provide port-based security and isolation between por...
Page 160
Configuring the switch 3-122 3 configuring uplink and downlink ports use the private vlan link status page to set ports as downlink or uplink ports. Ports designated as downlink ports can not communicate with any other ports on the switch except for the uplink ports. Uplink ports can communicate wit...
Page 161
Vlan configuration 3-123 3 configuring protocol groups create a protocol group for one or more protocols. Command attributes • protocol group id – group identifier of this protocol group. (range: 1-2147483647) • frame type – frame type used by this protocol. (options: ethernet, rfc_1042, llc_other) ...
Page 162
Configuring the switch 3-124 3 - if the frame is untagged and the protocol type matches, the frame is forwarded to the appropriate vlan. - if the frame is untagged but the protocol type does not match, the frame is forwarded to the default vlan for this interface. Command attributes • interface – po...
Page 163: Layer 2 Queue Settings
Class of service configuration 3-125 3 class of service configuration class of service (cos) allows you to specify which data packets have greater precedence when traffic is buffered in the switch due to congestion. This switch supports cos with eight priority queues for each port. Data packets in a...
Page 164
Configuring the switch 3-126 3 web – click priority, default port priority or default trunk priority. Modify the default priority for any interface, then click apply. Figure 3-72. Default port priority cli – this example assigns a default priority of 5 to port 3. Console(config)#interface ethernet 1...
Page 165
Class of service configuration 3-127 3 mapping cos values to egress queues this switch processes class of service (cos) priority tagged traffic by using eight priority queues for each port, with service schedules based on strict or weighted round robin (wrr). Up to eight separate traffic priorities ...
Page 166
Configuring the switch 3-128 3 web – click priority, traffic classes. Mark an interface and click select to display the current mapping of cos values to output queues. Assign priorities to the traffic classes (i.E., output queues) for the selected interface, then click apply. Figure 3-73. Traffic cl...
Page 167
Class of service configuration 3-129 3 selecting the queue mode you can set the switch to service the queues based on a strict rule that requires all traffic in a higher priority queue to be processed before lower priority queues are serviced, or use weighted round-robin (wrr) queuing that specifies...
Page 168
Configuring the switch 3-130 3 web – click priority, queue scheduling. Select the interface, highlight a traffic class (i.E., output queue), enter a weight, then click apply. Figure 3-75. Queue scheduling cli – the following example shows how to assign wrr weights to each of the priority queues. Con...
Page 169: Layer 3/4 Priority Settings
Class of service configuration 3-131 3 layer 3/4 priority settings mapping layer 3/4 priorities to cos values this switch supports several common methods of prioritizing layer 3/4 traffic to meet application requirements. Traffic priorities can be specified in the ip header of a frame, using the pri...
Page 170
Configuring the switch 3-132 3 mapping ip precedence the type of service (tos) octet in the ipv4 header includes three precedence bits defining eight different priority levels ranging from highest priority for network control packets to lowest priority for routine traffic. The default ip precedence ...
Page 171
Class of service configuration 3-133 3 cli – the following example globally enables ip precedence service on the switch, maps ip precedence value 1 to cos value 0 (on port 1), and then displays the ip precedence settings. * mapping specific values for ip precedence is implemented as an interface con...
Page 172
Configuring the switch 3-134 3 web – click priority, ip dscp priority. Select an entry from the dscp table, enter a value in the class of service value field, then click apply. Figure 3-78. Ip dscp priority cli – the following example globally enables dscp priority service on the switch, maps dscp v...
Page 173
Class of service configuration 3-135 3 mapping ip port priority you can also map network applications to class of service values based on the ip port number (i.E., tcp/udp port number) in the frame header. Some of the more common tcp service ports include: http: 80, ftp: 21, telnet: 23 and pop3: 110...
Page 174
Configuring the switch 3-136 3 cli – the following example globally enables ip port priority service on the switch, maps http traffic on port 5 to cos value 0, and then displays the ip port priority settings for that port. * mapping specific values for ip precedence is implemented as an interface co...
Page 175
Class of service configuration 3-137 3 web – click priority, acl cos priority. Enable mapping for any port, select an acl from the scroll-down list, then click apply. Figure 3-81. Acl cos priority cli – this example assigns a cos value of zero to packets matching rules within the specified acl on po...
Page 176
Configuring the switch 3-138 3 command attributes • port – port identifier. • name * – name of acl. • type – type of acl (ip or mac). • precedence – ip precedence value. (range: 0-7) • dscp – differentiated services code point value. (range: 0-63) • 802.1p priority – class of service value in the ie...
Page 177: Multicast Filtering
Multicast filtering 3-139 3 multicast filtering multicasting is used to support real-time applications such as videoconferencing or streaming audio. A multicast server does not have to establish a separate connection with each client. It merely broadcasts its service to the network, and any hosts th...
Page 178
Configuring the switch 3-140 3 configuring igmp snooping and query parameters you can configure the switch to forward multicast traffic intelligently. Based on the igmp query and report messages, the switch forwards traffic only to the ports that request multicast traffic. This prevents the switch f...
Page 179
Multicast filtering 3-141 3 web – click igmp snooping, igmp configuration. Adjust the igmp settings as required, and then click apply. (the default settings are shown below.) figure 3-83. Igmp configuration cli – this example modifies the settings for multicast filtering, and then displays the curre...
Page 180
Configuring the switch 3-142 3 displaying interfaces attached to a multicast router multicast routers that are attached to ports on the switch use information obtained from igmp, along with a multicast routing protocol such as dvmrp or pim, to support ip multicasting across the internet. These route...
Page 181
Multicast filtering 3-143 3 specifying static interfaces for a multicast router depending on your network connections, igmp snooping may not always be able to locate the igmp querier. Therefore, if the igmp querier is a known multicast router/ switch connected over the network to an interface (port ...
Page 182
Configuring the switch 3-144 3 displaying port members of multicast services you can display the port members associated with a specified vlan and multicast service. Command attribute • vlan id – selects the vlan for which to display port members. • multicast ip address – the ip address for a specif...
Page 183
Multicast filtering 3-145 3 assigning ports to multicast services multicast filtering can be dynamically configured using igmp snooping and igmp query messages as described in “configuring igmp snooping and query parameters” on page 3-140. For certain applications that require tighter control, you m...
Page 184
Configuring the switch 3-146 3 configuring domain name service the domain naming system (dns) service on this switch allows host names to be mapped to ip addresses using static table entries or by redirection to other name servers on the network. When a client device designates this switch as a dns ...
Page 185
Configuring domain name service 3-147 3 web – select dns, general configuration. Set the default domain name or list of domain names, specify one or more name servers to use to use for address resolution, enable domain lookup status, and click apply. Figure 3-88. Dns general configuration cli - this...
Page 186
Configuring the switch 3-148 3 configuring static dns host to address entries you can manually configure static entries in the dns table that are used to map domain names to ip addresses. Command usage • static entries may be used for local devices connected directly to the attached network, or for ...
Page 187
Configuring domain name service 3-149 3 web – select dns, static host table. Enter a host name and one or more corresponding addresses, then click apply. Figure 3-89. Dns static host table cli - this example maps two address to a host name, and then configures an alias host name for the same address...
Page 188: Displaying The Dns Cache
Configuring the switch 3-150 3 displaying the dns cache you can display entries in the dns cache that have been learned via the designated name servers. Field attributes • no – the entry number for each resource record. • flag – the flag is always “4” indicating a cache entry and therefore unreliabl...
Page 189
Configuring domain name service 3-151 3 cli - this example displays all the resource records learned from the designated name servers. Console#show dns cache 4-123 no flag type ip ttl domain 0 4 cname 207.46.134.222 51 www.Microsoft.Akadns.Net 1 4 cname 207.46.134.190 51 www.Microsoft.Akadns.Net 2 4...
Page 190
Configuring the switch 3-152 3.
Page 191: Accessing The Cli
4-1 chapter 4: command line interface this chapter describes how to use the command line interface (cli). Using the command line interface accessing the cli when accessing the management interface for the switch over a direct connection to the server’s console port, or via a telnet connection, the s...
Page 192
Command line interface 4-2 4 to access the switch through a telnet session, you must first set the ip address for the switch, and set the default gateway if you are managing the switch from a different ip subnet. For example, if your corporate network is connected to another network outside your off...
Page 193: Entering Commands
Entering commands 4-3 4 entering commands this section describes how to enter cli commands. Keywords and arguments a cli command is a series of keywords and arguments. Keywords identify a command, and arguments specify configuration parameters. For example, in the command “show interfaces status eth...
Page 194
Command line interface 4-4 4 showing commands if you enter a “?” at the command prompt, the system will display the first level of keywords for the current command class (normal exec or privileged exec) or configuration class (global, acl, interface, line, vlan database, or mstp). You can also displ...
Page 195: Partial Keyword Lookup
Entering commands 4-5 4 partial keyword lookup if you terminate a partial keyword with a question mark, alternatives that match the initial letters are provided. (remember not to leave a space between the command and question mark.) for example “ s? ” shows all the keywords starting with “s.” negati...
Page 196: Understanding Command Modes
Command line interface 4-6 4 understanding command modes the command set is divided into exec and configuration classes. Exec commands generally display information on system status or clear statistical counters. Configuration commands, on the other hand, modify interface parameters or enable certai...
Page 197: Configuration Commands
Entering commands 4-7 4 configuration commands configuration commands are privileged level commands used to modify switch settings. These commands modify the running configuration only and are not saved when the switch is rebooted. To store the running configuration in non-volatile storage, use the ...
Page 198
Command line interface 4-8 4 to enter the other modes, at the configuration prompt type one of the following commands. Use the exit or end command to return to the privileged exec mode. For example, you can use the following commands to enter interface configuration mode, and then return to privileg...
Page 199: Command Line Processing
Entering commands 4-9 4 command line processing commands are not case sensitive. You can abbreviate commands and parameters as long as they contain enough letters to differentiate them from any other currently available commands or parameters. You can use the tab key to complete partial commands, or...
Page 200: Command Groups
Command line interface 4-10 4 command groups the system commands can be broken down into the functional groups shown below . Table 4-4. Command group index command group description page line sets communication parameters for the serial port and telnet, including baud rate and console time-out 4-11 ...
Page 201: Line Commands
Line commands 4-11 4 the access mode shown in the following tables is indicated by these abbreviations: ne (normal exec) ic (interface configuration) pe (privileged exec) lc (line configuration) gc (global configuration) vc (vlan database configuration) acl (access control list configuration) mst (m...
Page 203
Line commands 4-13 4 command usage • there are three authentication modes provided by the switch itself at login: - login selects authentication by a single global password as specified by the password line configuration command. When using this method, the management interface starts in normal exec...
Page 204
Command line interface 4-14 4 number of times a user can enter an incorrect password before the system terminates the line connection and returns the terminal to the idle state. • the encrypted password is required for compatibility with legacy password settings (i.E., plain text or encrypted) when ...
Page 205
Line commands 4-15 4 password-thresh this command sets the password intrusion threshold which limits the number of failed logon attempts. Use the no form to remove the threshold value. Syntax password-thresh [ threshold ] no password-thresh threshold - the number of allowed password attempts. (range...
Page 206
Command line interface 4-16 4 example to set the silent time to 60 seconds, enter this command: related commands password-thresh (4-15) databits this command sets the number of data bits per character that are interpreted and generated by the console port. Use the no form to restore the default valu...
Page 208
Command line interface 4-18 4 command usage set the speed to match the baud rate of the device connected to the serial port. Some baud rates available on devices connected to the port might not be supported. The system indicates if the speed you selected is not supported. If you select the “auto” op...
Page 209
Line commands 4-19 4 command usage specifying session identifier “0” will disconnect the console connection. Specifying any other identifiers for an active session will disconnect an ssh or telnet connection. Example related commands show ssh (4-41) show users (4-61) show line this command displays ...
Page 210: General Commands
Command line interface 4-20 4 general commands enable this command activates privileged exec mode. In privileged mode, additional commands are available, and certain commands display additional information. See “understanding command modes” on page 4-6. Syntax enable [ level ] level - privilege leve...
Page 211
General commands 4-21 4 example related commands disable (4-21) enable password (4-27) disable this command returns to normal exec mode from privileged mode. In normal access mode, you can only display basic information on the switch's configuration or ethernet statistics. To gain access to all comm...
Page 212
Command line interface 4-22 4 related commands end (4-23) show history this command shows the contents of the command history buffer. Default setting none command mode normal exec, privileged exec command usage the history buffer size is fixed at 10 execution commands and 10 configuration commands. ...
Page 213
General commands 4-23 4 command mode privileged exec command usage this command resets the entire system. Example this example shows how to reset the switch: end this command returns to privileged exec mode. Default setting none command mode global configuration, interface configuration, line config...
Page 214: System Management Commands
Command line interface 4-24 4 quit this command exits the configuration program. Default setting none command mode normal exec, privileged exec command usage the quit and exit commands can both exit the configuration program. Example this example shows how to quit a cli session: system management co...
Page 215: Device Designation Commands
System management commands 4-25 4 device designation commands prompt this command customizes the cli prompt. Use the no form to restore the default prompt. Syntax prompt string no prompt string - any alphanumeric string to use for the cli prompt. (maximum length: 255 characters) default setting cons...
Page 216: User Access Commands
Command line interface 4-26 4 example user access commands the basic commands required for management access are listed in this section. This switch also includes other options for password checking via the console or a telnet connection (page 4-11), user authentication via a remote authentication s...
Page 217
System management commands 4-27 4 command mode global configuration command usage the encrypted password is required for compatibility with legacy password settings (i.E., plain text or encrypted) when reading the configuration file during system bootup or when downloading the configuration file fro...
Page 218: Ip Filter Commands
Command line interface 4-28 4 example related commands enable (4-20) ip filter commands management this command specifies the client ip addresses that are allowed management access to the switch through various protocols. Use the no form to restore the default setting. Syntax [ no ] management { all...
Page 219
System management commands 4-29 4 • when entering addresses for the same group (i.E., snmp, web or telnet), the switch will not accept overlapping address ranges. When entering addresses for different groups, the switch will accept overlapping address ranges. • you cannot delete an individual addres...
Page 220: Web Server Commands
Command line interface 4-30 4 web server commands ip http port this command specifies the tcp port number used by the web browser interface. Use the no form to use the default port. Syntax ip http port port-number no ip http port port-number - the tcp port to be used by the browser interface. (range...
Page 221
System management commands 4-31 4 example related commands ip http port (4-30) ip http secure-server this command enables the secure hypertext transfer protocol (https) over the secure socket layer (ssl), providing secure access (i.E., an encrypted connection) to the switch’s web interface. Use the ...
Page 222
Command line interface 4-32 4 example related commands ip http secure-port (4-32) copy tftp https-certificate (4-63) ip http secure-port this command specifies the udp port number used for https/ssl connection to the switch’s web interface. Use the no form to restore the default port. Syntax ip http...
Page 223: Telnet Server Commands
System management commands 4-33 4 telnet server commands ip telnet port this command specifies the tcp port number used by the telnet interface. Use the no form to use the default port. Syntax ip telnet port port-number no ip telnet port port-number - the tcp port to be used by the browser interface...
Page 224: Secure Shell Commands
Command line interface 4-34 4 related commands ip telnet port (4-33) secure shell commands the berkley-standard includes remote access tools originally designed for unix systems. Some of these tools have also been implemented for microsoft windows and other environments. These tools, including comma...
Page 225
System management commands 4-35 4 the ssh server on this switch supports both password and public key authentication. If password authentication is specified by the ssh client, then the password can be authenticated either locally or via a radius or tacacs+ remote authentication server, as specified...
Page 226
Command line interface 4-36 4 corresponding to the public keys stored on the switch can gain access. The following exchanges take place during this process: a. The client sends its public key to the switch. B. The switch compares the client's public key to those stored in memory. C. If a match is fo...
Page 227
System management commands 4-37 4 ip ssh timeout use this command to configure the timeout for the ssh server. Use the no form to restore the default setting. Syntax ip ssh timeout seconds no ip ssh timeout seconds – the timeout for client response during ssh negotiation. (range: 1-120) default sett...
Page 228
Command line interface 4-38 4 example related commands show ip ssh (4-40) ip ssh server-key size use this command to set the ssh server key size. Use the no form to restore the default setting. Syntax ip ssh server-key size key-size no ip ssh server-key size key-size – the size of server key. (range...
Page 230
Command line interface 4-40 4 command mode privileged exec command usage • this command clears the host key from volatile memory (ram). Use the no ip ssh save host-key command to clear the host key from flash memory. • the ssh server must be disabled before you can execute this command. Example rela...
Page 231
System management commands 4-41 4 example show ssh use this command to display the current ssh server connections. Command mode privileged exec example console#show ip ssh ssh enabled - version 1.99 negotiation timeout: 120 secs; authentication retries: 3 server key size: 768 bits console# console#s...
Page 233: Event Logging Commands
System management commands 4-43 4 event logging commands logging on this command controls logging of error messages, sending debug or error messages to switch memory. The no form disables the logging process. Syntax [ no ] logging on default setting none command mode global configuration command usa...
Page 235
System management commands 4-45 4 logging host this command adds a syslog server host ip address that will receive logging messages. Use the no form to remove a syslog server host. Syntax [ no ] logging host host_ip_address host_ip_address - the ip address of a syslog server. Default setting none co...
Page 236
Command line interface 4-46 4 logging trap this command enables the logging of system messages to a remote server, or limits the syslog messages saved to a remote server based on severity. Use this command without a specified level to enable remote logging. Use the no form to disable remote logging....
Page 238: Smtp Alert Commands
Command line interface 4-48 4 the following example displays settings for the trap function. Related commands show logging sendmail (4-51) smtp alert commands these commands configure smtp event handling, and forwarding of alert messages to the specified smtp servers and email recipients. Console#sh...
Page 239
System management commands 4-49 4 logging sendmail host this command specifies smtp servers that will be sent alert messages. Use the no form to remove an smtp server. Syntax [ no ] logging sendmail host ip_address ip_address - ip address of an smtp server that will be sent alert messages for event ...
Page 240
Command line interface 4-50 4 command usage the specified level indicates an event threshold. All events at this level or higher will be sent to the configured email recipients. (for example, using level 7 will report all events from level 7 to level 0.) example this example will send email alerts f...
Page 241
System management commands 4-51 4 command usage you can specify up to five recipients for alert messages. However, you must enter a separate command to specify each recipient. Example logging sendmail this command enables smtp event handling. Use the no form to disable this function. Syntax [ no ] l...
Page 242: Time Commands
Command line interface 4-52 4 time commands the system clock can be dynamically set by polling a set of specified time servers (ntp or sntp), or by using information broadcast by local time servers. Sntp client this command enables sntp client requests for time synchronization from ntp or sntp time ...
Page 243
System management commands 4-53 4 example related commands sntp server (4-53) sntp poll (4-54) show sntp (4-54) sntp server this command sets the ip address of the servers to which sntp time requests are issued. Use the this command with no arguments to clear all time servers from the current list. ...
Page 244
Command line interface 4-54 4 sntp poll this command sets the interval between sending time requests when the switch is set to sntp client mode. Use the no form to restore to the default. Syntax sntp poll seconds no sntp poll seconds - interval between time requests. (range: 16-16384 seconds) defaul...
Page 246
Command line interface 4-56 4 default setting none command mode privileged exec example this example shows how to set the system clock to 15:12:34, february 1st, 2004. Show calendar this command displays the system clock. Default setting none command mode normal exec, privileged exec example console...
Page 247: System Status Commands
System management commands 4-57 4 system status commands show startup-config this command displays the configuration file stored in non-volatile memory that is used to start up the system. Default setting none command mode privileged exec command usage • use this command in conjunction with the show...
Page 248
Command line interface 4-58 4 example related commands show running-config (4-58) show running-config this command displays the configuration information currently in use. Default setting none command mode privileged exec command usage • use this command in conjunction with the show startup-config c...
Page 249
System management commands 4-59 4 - vlan configuration settings for each interface - multiple spanning tree instances (name and interfaces) - ip address configured for vlans - spanning tree settings - any configured settings for the console port and telnet example console#show running-config buildin...
Page 250
Command line interface 4-60 4 related commands show startup-config (4-57) show system this command displays system information. Default setting none command mode normal exec, privileged exec command usage • for a description of the items shown by this command, refer to “displaying system information...
Page 251
System management commands 4-61 4 show users shows all active console and telnet sessions, including user name, idle time, and ip address of telnet client. Default setting none command mode normal exec, privileged exec command usage the session used to execute this command is indicated by a “*” symb...
Page 252: Frame Size Commands
Command line interface 4-62 4 example frame size commands jumbo frame this command enables support for jumbo frames. Use the no form to disable it. Syntax [ no ] jumbo frame default setting disabled command mode global configuration command usage • this switch provides more efficient throughput for ...
Page 253: Flash/file Commands
Flash/file commands 4-63 4 example flash/file commands these commands are used to manage the system code or configuration files. Copy this command moves (upload/download) a code image or configuration file between the switch’s flash memory and a tftp server. When you save the system code or configur...
Page 254
Command line interface 4-64 4 command mode privileged exec command usage • the system prompts for data required to complete the copy command. • the destination file name should not contain slashes (\ or /), the leading letter of the file name should not be a period (.), and the maximum length for fi...
Page 255
Flash/file commands 4-65 4 the following example shows how to download a configuration file: this example shows how to copy a secure-site certificate from an tftp server. It then reboots the switch to activate the certificate: this example shows how to copy a public-key used by ssh from an tftp serv...
Page 256
Command line interface 4-66 4 command usage • if the file type is used for system startup, then this file cannot be deleted. • “factory_default_config.Cfg” cannot be deleted. Example this example shows how to delete the test2.Cfg configuration file from flash memory. Related commands dir (4-66) dele...
Page 257
Flash/file commands 4-67 4 example the following example shows how to display all file information: whichboot this command displays which files were booted when the system powered up. Default setting none command mode privileged exec example this example shows the information displayed by the whichb...
Page 258: Authentication Commands
Command line interface 4-68 4 default setting none command mode global configuration command usage • a colon (:) is required after the specified file type. • if the file contains an error, it cannot be set as the default file. Example related commands dir (4-66) whichboot (4-67) authentication comma...
Page 259: Authentication Sequence
Authentication commands 4-69 4 authentication sequence authentication login this command defines the login authentication method and precedence. Use the no form to restore the default. Syntax authentication login {[ local ] [ radius ] [ tacacs ]} no authentication login • local - use local password....
Page 260
Command line interface 4-70 4 authentication enable this command defines the authentication method and precedence to use when changing from exec command mode to privileged exec command mode with the enable command (see page 4-20). Use the no form to restore the default. Syntax authentication enable ...
Page 261: Radius Client
Authentication commands 4-71 4 radius client remote authentication dial-in user service (radius) is a logon authentication protocol that uses software running on a central server to control access to radius-aware devices on the network. An authentication server contains a database of multiple user n...
Page 262
Command line interface 4-72 4 default setting 1812 command mode global configuration example radius-server key this command sets the radius encryption key. Use the no form to restore the default. Syntax radius-server key key_string no radius-server key key_string - encryption key used to authenticat...
Page 263
Authentication commands 4-73 4 example radius-server timeout this command sets the interval between transmitting authentication requests to the radius server. Use the no form to restore the default. Syntax radius-server timeout number_of_seconds no radius-server timeout number_of_seconds - number of...
Page 264: Tacacs+ Client
Command line interface 4-74 4 tacacs+ client terminal access controller access control system (tacacs+) is a logon authentication protocol that uses software running on a central server to control access to tacacs-aware devices on the network. An authentication server contains a database of multiple...
Page 265
Authentication commands 4-75 4 command mode global configuration example tacacs-server key this command sets the tacacs+ encryption key. Use the no form to restore the default. Syntax tacacs-server key key_string no tacacs-server key key_string - encryption key used to authenticate logon access for ...
Page 266: Port Security Commands
Command line interface 4-76 4 port security commands these commands can be used to enable port security on a port. When using port security, the switch stops learning new mac addresses on the specified port when it has reached a configured maximum number. Only incoming traffic with source addresses ...
Page 267
Authentication commands 4-77 4 command usage • if you enable port security, the switch stops learning new mac addresses on the specified port when it has reached a configured maximum number. Only incoming traffic with source addresses already stored in the dynamic or static address table will be acc...
Page 268: 802.1X Port Authentication
Command line interface 4-78 4 802.1x port authentication the switch supports ieee 802.1x (dot1x) port-based access control that prevents unauthorized access to the network by requiring users to first submit credentials for authentication. Client authentication is controlled centrally by a radius ser...
Page 269
Authentication commands 4-79 4 dot1x default this command sets all configurable dot1x global and port settings to their default values. Syntax dot1x default command mode global configuration example dot1x max-req this command sets the maximum number of times the switch port will retransmit an eap re...
Page 271
Authentication commands 4-81 4 command usage • the “max-count” parameter specified by this command is only effective if the dot1x mode is set to “auto” by the dot1x port-control command (page 4-105). • in “multi-host” mode, only one host connected to a port needs to pass authentication for all other...
Page 272
Command line interface 4-82 4 dot1x timeout quiet-period this command sets the time that a switch port waits after the max request count has been exceeded before attempting to acquire a new client. Use the no form to reset the default. Syntax dot1x timeout quiet-period seconds no dot1x timeout quiet...
Page 273
Authentication commands 4-83 4 dot1x timeout tx-period this command sets the time that the switch waits during an authentication session before re-transmitting an eap packet. Use the no form to reset to the default value. Syntax dot1x timeout tx-period seconds no dot1x timeout tx-period seconds - th...
Page 274
Command line interface 4-84 4 (page 4-79). It also displays the following global parameters which are set to a fixed value, including the following items: - supp-timeout – supplicant timeout. - server-timeout – server timeout. - reauth-max – maximum number of reauthentication attempts. • 802.1x port...
Page 275
Authentication commands 4-85 4 example console#show dot1x global 802.1x parameters reauth-enabled: yes reauth-period: 3600 quiet-period: 60 tx-period: 30 supp-timeout: 30 server-timeout: 30 reauth-max: 2 max-req: 2 802.1x port summary port name status operation mode mode authorized 1/1 disabled sing...
Page 276: Access Control List Commands
Command line interface 4-86 4 access control list commands access control lists (acl) provide packet filtering for ip frames (based on address, protocol, layer 4 protocol port number or tcp control code) or any frames (based on mac address or ethernet type). To filter packets, first create an access...
Page 277: Ip Acls
Access control list commands 4-87 4 3. User-defined rules in the ingress mac acl for ingress ports. 4. User-defined rules in the ingress ip acl for ingress ports. 5. Explicit default rule (permit any any) in the ingress ip acl for ingress ports. 6. Explicit default rule (permit any any) in the ingre...
Page 280
Command line interface 4-90 4 permit , deny (extended acl) this command adds a rule to an extended ip acl. The rule sets a filter condition for packets with specific source or destination ip addresses, protocol types, source or destination protocol ports, or tcp control codes. Use the no form to rem...
Page 281
Access control list commands 4-91 4 command usage • all new rules are appended to the end of the list. • address bitmasks are similar to a subnet mask, containing four integers from 0 to 255, each separated by a period. The binary mask uses 1 bits to indicate “match” and 0 bits to indicate “ignore.”...
Page 283
Access control list commands 4-93 4 command usage • a mask can only be used by all ingress acls or all egress acls. • the precedence of the acl rules applied to a packet is not determined by order of the rules, but instead by the order of the masks; i.E., the first mask that matches a rule will dete...
Page 284
Command line interface 4-94 4 command mode ip mask command usage • packets crossing a port are checked against all the rules in the acl until a match is found. The order in which these packets are checked is determined by the mask, and not the order in which the acl rules were entered. • first creat...
Page 285
Access control list commands 4-95 4 this shows how to create a standard acl with an ingress mask to deny access to the ip host 171.69.198.102, and permit access to any others. This shows how to create an extended acl with an egress mask to drop packets leaving network 171.69.198.0 when the layer 4 s...
Page 286
Command line interface 4-96 4 this is a more comprehensive example. It denies any tcp packets in which the syn bit is on, and permits all other packets. It then sets the ingress mask to check the deny rule first, and finally binds port 1 to this acl. Note that once the acl is bound to an interface (...
Page 288
Command line interface 4-98 4 related commands ip access-group (4-97) map access-list ip this command sets the output queue for packets matching an acl rule. The specified cos value is only used to map the matching packet to an output queue; it is not written to the packet itself. Use the no form to...
Page 289
Access control list commands 4-99 4 show map access-list ip this command shows the cos value mapped to an ip acl for the current interface. (the cos value determines the output queue for packets matching an acl rule.) syntax show map access-list ip [ interface ] interface • ethernet unit / port - un...
Page 290
Command line interface 4-100 4 command usage • you must configure an acl mask before you can change frame priorities based on an acl rule. • traffic priorities may be included in the ieee 802.1p priority tag. This tag is also incorporated as part of the overall ieee 802.1q vlan tag. To specify this ...
Page 291: Mac Acls
Access control list commands 4-101 4 mac acls access-list mac this command adds a mac access list and enters mac acl configuration mode. Use the no form to remove the specified acl. Syntax [ no ] access-list mac acl_name acl_name – name of the acl. (maximum length: 16 characters) default setting non...
Page 292
Command line interface 4-102 4 example related commands permit, deny 4-102 mac access-group (4-107) show mac access-list (4-103) permit , deny (mac acl) this command adds a rule to a mac acl. The rule filters packets matching a specified mac source or destination address (i.E., physical layer addres...
Page 293
Access control list commands 4-103 4 • destination – destination mac address range with bitmask. • address-bitmask* – bitmask for mac address (in hexidecimal format). • vid – vlan id. (range: 1-4095) • vid-bitmask* – vlan bitmask. (range: 1-4095) • protocol – a specific ethernet protocol number. (ra...
Page 294
Command line interface 4-104 4 example related commands permit, deny 4-102 mac access-group (4-107) access-list mac mask-precedence this command changes to mac mask mode used to configure access control masks. Use the no form to delete the mask table. Syntax [ no ] access-list ip mask-precedence { i...
Page 296
Command line interface 4-106 4 example this example shows how to create an ingress mac acl and bind it to a port. You can then see that the order of the rules have been changed by the mask. This example creates an egress mac acl. Console(config)#access-list mac m4 console(config-mac-acl)#permit any ...
Page 298
Command line interface 4-108 4 related commands show mac access-list (4-103) show mac access-group this command shows the ports assigned to mac acls. Command mode privileged exec example related commands mac access-group (4-107) map access-list mac this command sets the output queue for packets matc...
Page 299
Access control list commands 4-109 4 example related commands queue cos-map (4-194) show map access-list mac (4-109) show map access-list mac this command shows the cos value mapped to a mac acl for the current interface. (the cos value determines the output queue for packets matching an acl rule.) ...
Page 300
Command line interface 4-110 4 match access-list mac this command changes the ieee 802.1p priority of a layer 2 frame matching the defined acl rule. (this feature is commonly referred to as acl packet marking.) use the no form to remove the acl marker. Syntax match access-list mac acl_name set prior...
Page 301: Acl Information
Access control list commands 4-111 4 acl information show access-list this command shows all acls and associated rules, as well as all the user-defined masks. Command mode privileged exec command usage once the acl is bound to an interface (i.E., the acl is active), the order in which the rules are ...
Page 302: Snmp Commands
Command line interface 4-112 4 snmp commands controls access to this switch from management stations using the simple network management protocol (snmp), as well as the error types sent to trap managers. Snmp-server community this command defines the community access string for the simple network ma...
Page 303
Snmp commands 4-113 4 example snmp-server contact this command sets the system contact string. Use the no form to remove the system contact information. Syntax snmp-server contact string no snmp-server contact string - string that describes the system contact information. (maximum length: 255 charac...
Page 304
Command line interface 4-114 4 related commands snmp-server contact (4-113) snmp-server host this command specifies the recipient of a simple network management protocol notification operation. Use the no form to remove the specified host. Syntax snmp-server host host-addr community-string [ version...
Page 305
Snmp commands 4-115 4 related commands snmp-server enable traps (4-115) snmp-server enable traps this command enables this device to send simple network management protocol traps (snmp notifications). Use the no form to disable snmp notifications. Syntax [ no ] snmp-server enable traps [ authenticat...
Page 306
Command line interface 4-116 4 command usage this command provides information on the community access strings, counter information for snmp input and output protocol data units, and whether or not snmp logging has been enabled with the snmp-server enable traps command. Example console#show snmp sys...
Page 307: Dns Commands
Dns commands 4-117 4 dns commands these commands are used to configure domain naming system (dns) services. You can manually configure entries in the dns domain name to ip address mapping table, configure default domain names, or specify one or more name servers to use for domain name to address tra...
Page 308
Command line interface 4-118 4 command usage servers or other network devices may support one or more connections via multiple ip addresses. If more than one ip address is associated with a host name using this command, a dns client can try each address in succession, until it establishes a connecti...
Page 309
Dns commands 4-119 4 default setting none command mode global configuration example related commands ip domain-list (4-119) ip name-server (4-120) ip domain-lookup (4-121) ip domain-list this command defines a list of domain names that can be appended to incomplete host names (i.E., host names passe...
Page 310
Command line interface 4-120 4 example this example adds two domain names to the current list and then displays the list. Related commands ip domain-name (4-118) ip name-server this command specifies the address of one or more domain name servers to use for name-to-address resolution. Use the no for...
Page 311
Dns commands 4-121 4 example this example adds two domain-name servers to the list and then displays the list. Related commands ip domain-name (4-118) ip domain-lookup (4-121) ip domain-lookup this command enables dns host name-to-address translation. Use the no form to disable dns. Syntax [ no ] ip...
Page 312
Command line interface 4-122 4 example this example enables dns and then displays the configuration. Related commands ip domain-name (4-118) ip name-server (4-120) show hosts this command displays the static host name-to-address mapping table. Command mode privileged exec example note that a host na...
Page 313
Dns commands 4-123 4 show dns this command displays the configuration of the dns server. Command mode privileged exec example show dns cache this command displays entries in the dns cache. Command mode privileged exec example console#show dns domain lookup status: dns enabled default domain name: sa...
Page 314
Command line interface 4-124 4 clear dns cache this command clears all entries in the dns cache. Command mode privileged exec example console#clear dns cache console#show dns cache no flag type ip ttl domain console#.
Page 315: Interface Commands
Interface commands 4-125 4 interface commands these commands are used to display or set communication parameters for an ethernet port, aggregated link, or vlan. Interface this command configures an interface type and enter interface configuration mode. Use the no form to remove a trunk. Syntax inter...
Page 316
Command line interface 4-126 4 command mode global configuration example to specify port 24, enter the following command: description this command adds a description to an interface. Use the no form to remove the description. Syntax description string no description string - comment or a description...
Page 317
Interface commands 4-127 4 default setting • auto-negotiation is enabled by default. • when auto-negotiation is disabled, the default speed-duplex setting is 100half for 100base-tx ports and 1000full for gigabit ethernet ports. Command mode interface configuration (ethernet, port channel) command us...
Page 318
Command line interface 4-128 4 • if autonegotiation is disabled, auto-mdi/mdi-x pin signal configuration will also be disabled for the rj-45 ports. Example the following example configures port 11 to use autonegotiation. Related commands capabilities (4-128) speed-duplex (4-126) capabilities this co...
Page 319
Interface commands 4-129 4 example the following example configures ethernet port 5 capabilities to 100half, 100full and flow control. Related commands negotiation (4-127) speed-duplex (4-126) flowcontrol (4-129) flowcontrol this command enables flow control. Use the no form to disable flow control....
Page 320
Command line interface 4-130 4 example the following example enables flow control on port 5. Related commands negotiation (4-127) capabilities (flowcontrol, symmetric) (4-128) combo-forced-mode this command forces the port type selected for combination ports 21-24/45-48. Use the no form to restore t...
Page 321
Interface commands 4-131 4 default setting all interfaces are enabled. Command mode interface configuration (ethernet, port channel) command usage this command allows you to disable a port due to abnormal behavior (e.G., excessive collisions), and then reenable it after the problem has been resolved...
Page 322
Command line interface 4-132 4 example the following shows how to configure broadcast storm control at 600 packets per second: clear counters this command clears statistics on an interface. Syntax clear counters interface interface • ethernet unit / port - unit - this is device 1. - port - port numb...
Page 323
Interface commands 4-133 4 show interfaces status this command displays the status for an interface. Syntax show interfaces status [ interface ] interface • ethernet unit / port - unit - this is device 1. - port - port number. • port-channel channel-id (range: 1-6) • vlan vlan-id (range: 1-4094) def...
Page 324
Command line interface 4-134 4 show interfaces counters this command displays interface statistics. Syntax show interfaces counters [ interface ] interface • ethernet unit / port - unit - this is device 1. - port - port number. • port-channel channel-id (range: 1-6) default setting shows the counter...
Page 325
Interface commands 4-135 4 show interfaces switchport this command displays the administrative and operational status of the specified interfaces. Syntax show interfaces switchport [ interface ] interface • ethernet unit / port - unit - this is device 1. - port - port number. • port-channel channel-...
Page 327
Mirror port commands 4-137 4 command usage • you can mirror traffic from any source port to a destination port for real-time analysis. You can then attach a logic analyzer or rmon probe to the destination port and study the traffic crossing the source port in a completely unobtrusive manner. • the d...
Page 328: Rate Limit Commands
Command line interface 4-138 4 example the following shows mirroring configured from port 6 to port 11: rate limit commands this function allows the network manager to control the maximum rate for traffic transmitted or received on an interface. Rate limiting is configured on interfaces at the edge ...
Page 329: Link Aggregation Commands
Link aggregation commands 4-139 4 example link aggregation commands ports can be statically grouped into an aggregate link (i.E., trunk) to increase the bandwidth of a network connection or to ensure fault recovery. Or you can use the link aggregation control protocol (lacp) to automatically negotia...
Page 330
Command line interface 4-140 4 • all the ports in a trunk have to be treated as a whole when moved from/to, added or deleted from a vlan via the specified port-channel. • stp, vlan, and igmp settings can only be made for the entire trunk via the specified port-channel. Dynamically creating a port ch...
Page 331
Link aggregation commands 4-141 4 lacp this command enables 802.3ad link aggregation control protocol (lacp) for the current interface. Use the no form to disable it. Syntax [ no ] lacp default setting disabled command mode interface configuration (ethernet) command usage • the ports on both ends of...
Page 334
Command line interface 4-144 4 lacp admin-key (port channel) this command configures a port channel's lacp administration key string. Use the no form to restore the default setting. Syntax lacp admin-key key [ no ] lacp admin-key key - the port channel admin key is used to identify a specific link a...
Page 335
Link aggregation commands 4-145 4 command mode interface configuration (ethernet) command usage • setting a lower value indicates a higher effective priority. • if an active port link goes down, the backup port with the highest priority is selected to replace the downed link. However, if two or more...
Page 336
Command line interface 4-146 4 example console#show lacp 1 counters channel group : 1 ------------------------------------------------------------------------- eth 1/ 1 ------------------------------------------------------------------------- lacpdus sent : 21 lacpdus received : 21 marker sent : 0 m...
Page 337
Link aggregation commands 4-147 4 console#show lacp 1 internal channel group : 1 ------------------------------------------------------------------------- oper key : 4 admin key : 0 eth 1/1 ------------------------------------------------------------------------- lacpdus internal : 30 sec lacp syste...
Page 338
Command line interface 4-148 4 console#show lacp 1 neighbors channel group 1 neighbors ------------------------------------------------------------------------- eth 1/1 ------------------------------------------------------------------------- partner admin system id : 32768, 00-00-00-00-00-00 partne...
Page 339: Address Table Commands
Address table commands 4-149 4 address table commands these commands are used to configure the address table for filtering specified addresses, displaying current entries, clearing the table, or setting the aging time. Console#show lacp sysid channel group system priority system mac address --------...
Page 340
Command line interface 4-150 4 mac-address-table static this command maps a static address to a destination port in a vlan. Use the no form to remove an address. Syntax mac-address-table static mac-address interface interface vlan vlan-id [ action ] no mac-address-table static mac-address vlan vlan-...
Page 341
Address table commands 4-151 4 clear mac-address-table dynamic this command removes any learned entries from the forwarding database and clears the transmit and receive counts for any static or system configured entries. Default setting none command mode privileged exec example show mac-address-tabl...
Page 342
Command line interface 4-152 4 00-00-00-00-00-00 means an exact match, and a mask of ff-ff-ff-ff-ff-ff means “any.” • the maximum number of address entries is 8191. Example mac-address-table aging-time this command sets the aging time for entries in the address table. Use the no form to restore the ...
Page 343: Spanning Tree Commands
Spanning tree commands 4-153 4 spanning tree commands this section includes commands that configure the spanning tree algorithm (sta) globally for the switch, and commands that configure sta for the selected interface. Table 4-51. Spanning tree commands command function mode page spanning-tree enabl...
Page 344
Command line interface 4-154 4 spanning-tree this command enables the spanning tree algorithm globally for the switch. Use the no form to disable it. Syntax [ no ] spanning-tree default setting spanning tree is enabled. Command mode global configuration command usage the spanning tree algorithm (sta...
Page 345
Spanning tree commands 4-155 4 command usage • spanning tree protocol uses rstp for the internal state machine, but sends only 802.1d bpdus. - this creates one spanning tree instance for the entire network. If multiple vlans are implemented on a network, the path between specific vlan members may be...
Page 346
Command line interface 4-156 4 default setting 15 seconds command mode global configuration command usage this command sets the maximum time (in seconds) the root device will wait before changing states (i.E., discarding to learning to forwarding). This delay is required because every device must re...
Page 347
Spanning tree commands 4-157 4 spanning-tree max-age this command configures the spanning tree bridge maximum age globally for this switch. Use the no form to restore the default. Syntax spanning-tree max-age seconds no spanning-tree max-age seconds - time in seconds. (range: 6-40 seconds) the minim...
Page 348
Command line interface 4-158 4 command mode global configuration command usage bridge priority is used in selecting the root device, root port, and designated port. The device with the highest priority becomes the sta root device. However, if all devices have the same priority, the device with the l...
Page 349
Spanning tree commands 4-159 4 spanning-tree transmission-limit this command configures the minimum interval between the transmission of consecutive rstp/mstp bpdus. Use the no form to restore the default. Syntax spanning-tree transmission-limit count no spanning-tree transmission-limit count - the ...
Page 350
Command line interface 4-160 4 mst vlan this command adds vlans to a spanning tree instance. Use the no form to remove the specified vlans. Using the no form without any vlan parameters to remove all vlans. Syntax [ no ] mst instance_id vlan vlan-range • instance_id - instance identifier of the span...
Page 351
Spanning tree commands 4-161 4 mst priority this command configures the priority of a spanning tree instance. Use the no form to restore the default. Syntax mst instance_id priority priority no mst instance_id priority • instance_id - instance identifier of the spanning tree. (range: 0-4094) • prior...
Page 352
Command line interface 4-162 4 command usage the mst region name and revision number (page 4-162) are used to designate a unique mst region. A bridge (i.E., spanning-tree compliant device such as this switch) can only belong to one mst region. And all bridges in the same region must be configured wi...
Page 353
Spanning tree commands 4-163 4 max-hops this command configures the maximum number of hops in the region before a bpdu is discarded. Use the no form to restore the default. Syntax max-hops hop-number hop-number - maximum hop number for multiple spanning tree. (range: 1-40) default setting 20 command...
Page 354
Command line interface 4-164 4 spanning-tree cost this command configures the spanning tree path cost for the specified interface. Use the no form to restore the default. Syntax spanning-tree cost cost no spanning-tree cost cost - the path cost for the port. (range: 1-200,000,000)) the recommended r...
Page 355
Spanning tree commands 4-165 4 default setting 128 command mode interface configuration (ethernet, port channel) command usage • this command defines the priority for the use of a port in the spanning tree algorithm. If the path cost for all ports on a switch are the same, the port with the highest ...
Page 356
Command line interface 4-166 4 example related commands spanning-tree portfast (4-166) spanning-tree portfast this command sets an interface to fast forwarding. Use the no form to disable fast forwarding. Syntax [ no ] spanning-tree portfast default setting disabled command mode interface configurat...
Page 358
Command line interface 4-168 4 default setting • ethernet – half duplex: 2,000,000; full duplex: 1,000,000; trunk: 500,000 • fast ethernet – half duplex: 200,000; full duplex: 100,000; trunk: 50,000 • gigabit ethernet – full duplex: 10,000; trunk: 5,000 command mode interface configuration (ethernet...
Page 359
Spanning tree commands 4-169 4 interface with the highest priority (that is, lowest value) will be configured as an active link in the spanning tree. • where more than one interface is assigned the highest priority, the interface with lowest numeric identifier will be enabled. Example related comman...
Page 361
Spanning tree commands 4-171 4 example console#show spanning-tree spanning-tree information --------------------------------------------------------------- spanning tree mode :mstp spanning tree enable/disable :enable instance :0 vlans configuration :1-4094 priority :32768 bridge hello time (sec.) :...
Page 362: Vlan Commands
Command line interface 4-172 4 show spanning-tree mst configuration this command shows the configuration of the multiple spanning tree. Syntax show spanning-tree mst configuration command mode privileged exec example vlan commands a vlan is a group of ports that can be located anywhere in the networ...
Page 363: Editing Vlan Groups
Vlan commands 4-173 4 editing vlan groups vlan database this command enters vlan database mode. All commands in this mode will take effect immediately. Default setting none command mode global configuration command usage • use the vlan database command mode to add, change, and delete vlans. After fi...
Page 365: Configuring Vlan Interfaces
Vlan commands 4-175 4 configuring vlan interfaces interface vlan this command enters interface configuration mode for vlans, which is used to configure vlan parameters for a physical interface. Syntax interface vlan vlan-id vlan-id - id of the configured vlan. (range: 1-4094, no leading zeroes) defa...
Page 367
Vlan commands 4-177 4 command mode interface configuration (ethernet, port channel) command usage when set to receive all frame types, any received frames that are untagged are assigned to the default vlan. Example the following example shows how to restrict the traffic received on port 1 to tagged ...
Page 368
Command line interface 4-178 4 example the following example shows how to set the interface to port 1 and then enable ingress filtering: switchport native vlan this command configures the pvid (i.E., default vlan id) for a port. Use the no form to restore the default. Syntax switchport native vlan v...
Page 372: Configuring Private Vlans
Command line interface 4-182 4 configuring private vlans private vlans provide port-based security and isolation between ports within the assigned vlan. This section describes commands used to configure private vlans. Pvlan this command enables or configures a private vlan. Use the no form to disabl...
Page 373
Vlan commands 4-183 4 show pvlan this command displays the configured private vlan. Command mode privileged exec example configuring protocol-based vlans the network devices required to support multiple protocols cannot be easily grouped into a common vlan. This may require non-standard devices to p...
Page 375
Vlan commands 4-185 4 command usage • when creating a protocol-based vlan, only assign interfaces via this command. If you assign interfaces using any of the other vlan commands (such as vlan on page 4-174), these interfaces will admit traffic of any protocol type into the associated vlan. • when a ...
Page 376
Command line interface 4-186 4 show interfaces protocol-vlan protocol-group this command shows the mapping from protocol groups to vlans for the selected interfaces. Syntax show interfaces protocol-vlan protocol-group [ interface ] interface • ethernet unit / port - unit - this is device 1. - port -...
Page 377
Gvrp and bridge extension commands 4-187 4 gvrp and bridge extension commands garp vlan registration protocol defines a way for switches to exchange vlan information in order to automatically register vlan members on interfaces across the network. This section describes how to enable gvrp for indivi...
Page 378
Command line interface 4-188 4 show bridge-ext this command shows the configuration for bridge extension commands. Default setting none command mode privileged exec command usage see “displaying basic vlan information” on page 3-113 and “displaying bridge extension capabilities” on page 3-12 for a d...
Page 379
Gvrp and bridge extension commands 4-189 4 show gvrp configuration this command shows if gvrp is enabled. Syntax show gvrp configuration [ interface ] interface • ethernet unit / port - unit - this is device 1. - port - port number. • port-channel channel-id (range: 1-6) default setting shows both g...
Page 380
Command line interface 4-190 4 command usage • group address registration protocol is used by gvrp and gmrp to register or deregister client attributes for client services within a bridged lan. The default values for the garp timers are independent of the media access method or data rate. These valu...
Page 381: Priority Commands
Priority commands 4-191 4 related commands garp timer (4-189) priority commands the commands described in this section allow you to specify which data packets have greater precedence when traffic is buffered in the switch due to congestion. This switch supports cos with eight priority queues for eac...
Page 383
Priority commands 4-193 4 switchport priority default this command sets a priority for incoming untagged frames. Use the no form to restore the default value. Syntax switchport priority default default-priority-id no switchport priority default default-priority-id - the priority number for untagged ...
Page 384
Command line interface 4-194 4 queue bandwidth this command assigns weighted round-robin (wrr) weights to the eight class of service (cos) priority queues. Use the no form to restore the default weights. Syntax queue bandwidth weight1...Weight4 no queue bandwidth weight1...Weight4 - the ratio of wei...
Page 385
Priority commands 4-195 4 default setting this switch supports class of service by using eight priority queues, with weighted round robin queuing for each port. Eight separate traffic classes are defined in ieee 802.1p. The default priority levels are assigned according to recommendations in the iee...
Page 386
Command line interface 4-196 4 example show queue bandwidth this command displays the weighted round-robin (wrr) bandwidth allocation for the eight priority queues. Default setting none command mode privileged exec example show queue cos-map this command shows the class of service priority map. Synt...
Page 387: Priority Commands
Priority commands 4-197 4 example priority commands (layer 3 and 4) map ip port (global configuration) this command enables ip port mapping (i.E., class of service mapping for tcp/udp sockets). Use the no form to disable ip port mapping. Syntax [ no ] map ip port default setting disabled command mod...
Page 388
Command line interface 4-198 4 example the following example shows how to enable tcp/udp port mapping globally: map ip port (interface configuration) this command enables ip port mapping (i.E., tcp/udp port priority). Use the no form to remove a specific setting. Syntax map ip port port number cos c...
Page 389
Priority commands 4-199 4 command usage • the precedence for priority mapping is ip port, ip precedence or ip dscp, and default switchport priority. • ip precedence and ip dscp cannot both be enabled. Enabling one of these priority types will automatically disable the other type. Example the followi...
Page 390
Command line interface 4-200 4 map ip dscp (global configuration) this command enables ip dscp mapping (i.E., differentiated services code point mapping). Use the no form to disable ip dscp mapping. Syntax [ no ] map ip dscp default setting disabled command mode global configuration command usage • ...
Page 391
Priority commands 4-201 4 default setting the dscp default values are defined in the following table. Note that all the dscp values that are not specified are mapped to cos value 0. Command mode interface configuration (ethernet, port channel) command usage • the precedence for priority mapping is i...
Page 392
Command line interface 4-202 4 default setting none command mode privileged exec example the following shows that http traffic has been mapped to cos value 0: related commands map ip port (global configuration) (4-197) map ip port (interface configuration) (4-198) show map ip precedence this command...
Page 393
Priority commands 4-203 4 example related commands map ip port (global configuration) (4-197) map ip precedence (interface configuration) (4-199) show map ip dscp this command shows the ip dscp priority map. Syntax show map ip dscp [ interface ] interface • ethernet unit / port - unit - this is devi...
Page 394: Multicast Filtering Commands
Command line interface 4-204 4 example related commands map ip dscp (global configuration) (4-200) map ip dscp (interface configuration) (4-200) multicast filtering commands this switch uses igmp (internet group management protocol) to query for any attached hosts that want to receive a specific mul...
Page 395
Multicast filtering commands 4-205 4 ip igmp snooping this command enables igmp snooping on this switch. Use the no form to disable it. Syntax [ no ] ip igmp snooping default setting enabled command mode global configuration example the following example enables igmp snooping. Ip igmp snooping vlan ...
Page 398: Igmp Query Commands
Command line interface 4-208 4 igmp query commands (layer 2) ip igmp snooping querier this command enables the switch as an igmp querier. Use the no form to disable it. Syntax [ no ] ip igmp snooping querier default setting enabled command mode global configuration command usage if enabled, the swit...
Page 399
Multicast filtering commands 4-209 4 default setting 2 times command mode global configuration command usage the query count defines how long the querier waits for a response from a multicast client before taking action. If a querier has sent a number of queries defined by this command, but a client...
Page 400
Command line interface 4-210 4 ip igmp snooping query-max-response-time this command configures the query report delay. Use the no form to restore the default. Syntax ip igmp snooping query-max-response-time seconds no ip igmp snooping query-max-response-time seconds - the report delay advertised in...
Page 401
Multicast filtering commands 4-211 4 default setting 300 seconds command mode global configuration command usage the switch must use igmpv2 for this command to take effect. Example the following shows how to configure the default timeout to 300 seconds: related commands ip igmp snooping version (4-2...
Page 402
Command line interface 4-212 4 command usage depending on your network connections, igmp snooping may not always be able to locate the igmp querier. Therefore, if the igmp querier is a known multicast router/switch connected over the network to an interface (port or trunk) on your router, you can ma...
Page 403: Ip Interface Commands
Ip interface commands 4-213 4 ip interface commands an ip addresses may be used for management access to the switch over your network. The ip address for this switch is obtained via dhcp by default. You can manually configure a specific ip address, or direct the device to obtain an address from a bo...
Page 404: Ip Dhcp Restart
Command line interface 4-214 4 • if you select the bootp or dhcp option, ip is enabled but will not function until a bootp or dhcp reply has been received. Requests will be broadcast periodically by this device in an effort to learn its ip address. (bootp and dhcp values can include the ip address, ...
Page 405: Ip Default-Gateway
Ip interface commands 4-215 4 related commands ip address (4-213) ip default-gateway this command establishes a static route between this switch and management stations that exist on another network segment. Use the no form to remove the static route. Syntax ip default-gateway gateway no ip default-...
Page 406: Show Ip Redirects
Command line interface 4-216 4 related commands show ip redirects (4-216) show ip redirects this command shows the default gateway configured for this device. Default setting none command mode privileged exec example related commands ip default-gateway (4-215) ping this command sends icmp echo reque...
Page 407
Ip interface commands 4-217 4 - network or host unreachable - the gateway found no corresponding entry in the route table. • press to stop pinging. Example related commands interface (4-125) console#ping 10.1.0.9 type esc to abort. Ping to 10.1.0.9, by 5 32-byte payload icmp packets, timeout is 5 se...
Page 408
Command line interface 4-218 4.
Page 409: Software Features
A-1 appendix a: software specifications software features authentication local, radius, tacacs, port (802.1x), https, ssh, port security access control lists ip, mac (up to 32 lists) dhcp client dns server port configuration 1000base-t: 10/100 mbps at half/full duplex, 1000 mbps at full duplex 1000b...
Page 410: Management Features
Software specifications a-2 a additional features bootp client sntp (simple network time protocol) snmp (simple network management protocol) rmon (remote monitoring, groups 1, 2, 3, 9) smtp email alerts management features in-band management telnet, web-based http or https, snmp manager, or secure s...
Page 411: Management Information Bases
Management information bases a-3 a rmon (rfc 1757 groups 1,2,3,9) snmp (rfc 1157) snmpv2 (rfc 1907) sntp (rfc 2030) ssh (version 2.0) tftp (rfc 1350) management information bases bridge mib (rfc 1493) entity mib (rfc 2737) ether-like mib (rfc 2665) extended bridge mib (rfc 2674) extensible snmp agen...
Page 412
Software specifications a-4 a.
Page 413: Appendix B: Troubleshooting
B-1 appendix b: troubleshooting problems accessing the management interface table b-1 troubleshooting chart symptom action cannot connect using telnet, web browser, or snmp software • be sure the switch is powered up. • check network cabling between the management station and the switch. • check tha...
Page 414: Using System Logs
Troubleshooting b-2 b using system logs if a fault does occur, refer to the installation guide to ensure that the problem you encountered is actually caused by the switch. If the problem appears to be caused by the switch, follow these steps: 1. Enable logging. 2. Set the error messages reported to ...
Page 415: Glossary
Glossary-1 glossary access control list (acl) acls can limit network traffic and restrict access to certain users or devices by checking each packet for certain ip or mac (i.E., layer 2) information. Boot protocol (bootp) bootp is used to provide bootup information for network devices, including ip ...
Page 416
Glossary glossary-2 garp vlan registration protocol (gvrp) defines a way for switches to exchange vlan information in order to register necessary vlan members on ports along the spanning tree so that vlans defined in each switch can work automatically over a spanning tree network. Generic attribute ...
Page 417
Glossary-3 glossary ieee 802.3x defines ethernet frame start/stop requests and timers used for flow control on full-duplex links. Igmp snooping listening to igmp query and igmp report packets transferred between ip multicast routers and ip multicast host groups to identify ip multicast group members...
Page 418
Glossary glossary-4 management information base (mib) an acronym for management information base. It is a set of database objects that contains information about a specific device. Multicast switching a process whereby the switch filters incoming multicast frames for services for which no attached h...
Page 419
Glossary-5 glossary rapid spanning tree protocol (rstp) rstp reduces the convergence time for network topology changes to about 10% of that required by the older ieee 802.1d stp standard. Secure shell (ssh) a secure replacement for remote access functions, including telnet. Ssh can authenticate user...
Page 420
Glossary glossary-6 user datagram protocol (udp) udp provides a datagram mode for packet-switched communications. It uses ip as the underlying transport mechanism to provide access to ip-like services. Udp packets are delivered just like ip packets – connection-less datagrams that may be discarded b...
Page 421: Index
Index-1 symbols 3-31 numerics 802.1x, port authentication 3-43, 4-78 a acceptable frame type 3-119, 4-174 access control list see acl acl extended ip 3-53, 4-86, 4-87, 4-90 mac 3-53, 4-86, 4-101, 4-101–4-103 standard ip 3-53, 4-86, 4-87, 4-89 address table 3-88, 4-147 aging time 3-91, 4-150 b bootp ...
Page 422
Index-2 index h hardware version, displaying 3-10, 4-61 https 3-34, 4-31 https, secure server 3-34, 4-31 i ieee 802.1d 3-91, 4-152 ieee 802.1s 4-152 ieee 802.1w 3-91, 4-152 ieee 802.1x 3-43, 4-78 igmp groups, displaying 3-144, 4-205 layer 2 3-139, 4-202 query 3-139, 4-206 query, layer 2 3-140, 4-206...
Page 423
Index-3 index q queue weights 3-129, 4-192 r radius, logon authentication 3-31, 4-71 rate limits, setting 3-83, 4-136 restarting the system 3-25, 4-22 rstp 3-91, 4-152 global configuration 3-92, 4-152 s secure shell 3-36, 4-34 configuration 3-36, 4-37 secure shell configuration 4-37 serial port conf...
Page 424
Index-4 index w web interface access requirements 3-1 configuration buttons 3-3 home page 3-2 menu list 3-3, 3-4 panel display 3-3.
Page 426
Es4512c es4524c es4548c e052005-r02.