- DL manuals
- Accton Technology
- Switch
- ES4626
- Management Manual
Accton Technology ES4626 Management Manual
Summary of ES4626
Page 1
1 es4626/es4650 layer 3 gigabit switch management guide www.Edge-core.Com.
Page 2
2 preface es4626/es4650 is a routing switch that can be deployed as the core layer device for campus and enterprise networks, or as an aggregation device for ip metropolitan area networks (man). The es4626 provides 24 fixed 1000mb port (4 of which are fixed 1000mb combo fiber cable port/copper cable...
Page 3: Contents
3 contents preface 2 contents 3 chapter 1 switch management _________________________________________ 12 1.1 management options ____________________________________________ 12 1.1.1 out-of-band management ____________________________________________ 12 1.1.2 in-band management ______________________...
Page 4
4 2.2.4 traceroute _________________________________________________________ 46 2.2.5 show ______________________________________________________________ 47 2.2.6 debug _____________________________________________________________ 53 2.3 configuring switch ip addresses ______________________________...
Page 5
5 3.4.1 monitor and debug commands _______________________________________115 3.4.2 port troubleshooting help____________________________________________116 3.5 web management ______________________________________________ 116 3.5.1 ethenet port configuration ________________________________________...
Page 6
6 5.4 vlan troubleshooting help _____________________________________ 160 5.4.1 monitor and debug information______________________________________ 160 5.4.2 vlan troubleshooting help _________________________________________ 162 5.5 web management ______________________________________________ 162 ...
Page 7
7 8.2 802.1x configuration ____________________________________________ 211 8.2.1 802.1x configuration task sequence ___________________________________211 8.2.2 802.1x configuration command _____________________________________ 216 8.3 802.1x apply example __________________________________________...
Page 8
8 10.3 port channel example _________________________________________ 262 10.4 port channel troubleshooting help ____________________________ 264 10.4.1 monitor and debug commands ______________________________________ 264 10.4.2 port channel troubleshooting help ___________________________________ ...
Page 9
9 12.4.3 time difference _______________________________________________________ 308 12.4.4 show sntp ___________________________________________________________ 308 chapter 13 qos configuration _________________________________________ 309 13.1 qos __________________________________________________...
Page 10
10 15.3.2 rip configuration _________________________________________________ 369 15.3.3 typical rip scenario _______________________________________________ 385 15.3.4 rip troubleshooting help ___________________________________________ 387 15.4 ospf ________________________________________________...
Page 11
11 16.6 igmp _________________________________________________________ 485 16.6.1 introduction to igmp ______________________________________________ 485 16.6.2 igmp configuration ________________________________________________ 486 16.6.3 typical igmp scenario ______________________________________...
Page 12: 1.1
12 chapter 1 switch management 1.1 management options after purchasing the switch, the user needs to configure the switch for network management. Es4626/es4650 provides two management options: in-band management and out-of-band management. 1.1.1 out-of-band management out-of-band management is the m...
Page 13
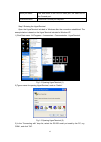
13 serial port cable one end attach to the rs-232 serial port, the other end to the console port. Es4626/es4650 functional console port required. Step 2 entering the hyperterminal open the hyperterminal included in windows after the connection established. The example below is based on the hyperterm...
Page 14
14 fig 1-4 opening hyperterminal (3) 4) com1 property appears, select “9600” for “baud rate”, “8” for “data bits”, “none” for “parity checksum”, “1” for stop bit and “none” for traffic control; or, you can also click “revert to default” and click “ok”. Fig 1-5 opening hyperterminal (4) step 3 enteri...
Page 15: 1.1.2 In-Band Management
15 power on the switch. The following appears in the hyperterminal windows, that is the cli configuration mode for es4626. Es4626 management switch copyright (c) 2001-2004 by accton technology corporation. All rights reserved. Reset chassis ... Done. Testing ram... 134,217,728 ram ok. Initializing.....
Page 16
16 the switch. In the case when in-band management fails due to switch configuration changes, out-of-band management can be used for configuring and managing the switch. 1.1.2.1 management via telnet to manage the switch with telnet, the following conditions should be met: 1) switch has an ip addres...
Page 17
17 management (i.E. Console mode), the configuration commands are as follows (all switch configuration prompts are assumed to be “switch” hereafter if not otherwise specified): switch> switch>en switch#config switch(config)#interface vlan 1 switch(config-if-vlan1)#ip address 10.1.128.251 255.255.255...
Page 18
18 will be able to enter the switch’s cli configuration interface. The commands used in the telnet cli interface after login is the same as in that in the console interface. Fig 1-8 telnet configuration interface 1.1.2.2 management via http to manage the switch via http, the following conditions sho...
Page 19
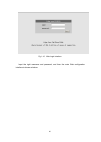
19 switch(config)#ip http server step 2: run http protocol on the host. Open the web browser on the host and type the ip address of the switch. Or run directly the http protocol on the windows. For example, the ip address of the switch is “10.1.128.251”. Fig 1-9 run http protocol step 3: logon to th...
Page 20
20 fig 1-10 web login interface input the right username and password, and then the main web configuration interface is shown as below..
Page 21: 1.2
21 fig 1-11 main web configuration interface 1.2 management interface 1.2.1 cli interface cli interface is familiar to most users. As aforementioned, out-of-band management and telnet login are all performed through cli interface to manage the switch. Cli interface is supported by shell program, whi...
Page 22: 1.2.1.1.1 User
22 z input verification z fuzzy match support 1.2.1.1 configuration modes fig 1-12 shell configuration modes 1.2.1.1.1 user mode on entering the cli interface, entering user entry system first. If as common user, it is defaulted to user mode. The prompt shown is “switch>”, the symbol “>” is the prom...
Page 23: 1.2.1.1.3 Global
23 mode, it will also return to the admin mode. Es4626/es4650 also provides a shortcut key sequence "ctrl+z”, this allows an easy way to exit to admin mode from any configuration mode (except user mode). Under admin mode, when disable command is run, it will return to user mode. When exit command is...
Page 24
24 port-channel mber> command under global mode. Port-channelx)# port-channel related settings such as duplex mode, speed, etc. Command to return to global mode. 1.2.1.1.3.2 vlan mode using the vlan command under global mode can enter the corresponding vlan mode. Under vlan mode the user can configu...
Page 25
25 1.2.1.1.3.5 acl mode acl type entry prompt operates exit standard ip acl mode type access-list ip command under global mode. Switch(config-std-nacl- a)# configure parameters for standard ip acl mode use the “ exit” command to return to global mode. Extended ip acl mode type access-list ip command...
Page 26: 1.2.1.4 Help Function
26 1.2.1.3 shortcut key support es4626/es4650 provides several shortcut keys to facilitate user configuration, such as up, down, left, right and blank space. If the terminal does not recognize up and down keys, ctrl+p and ctrl+n can be used instead. Key(s) function backspace delete a character befor...
Page 27: 1.2.1.5 Input Verification
27 “?” 1. Under any command line prompt, enter “?” to get a command list of the current mode and related brief description. 2. Enter a “?” after the command keyword with a embedded space. If the position should be a parameter, a description of that parameter type, scope, etc, will be returned; if th...
Page 28: 1.2.2 Web Interface
28 es4626/es4650 shell support fuzzy match in searching command and keyword. Shell will recognize commands or keywords correctly if the entered string causes no conflict. For example: 1. For admin configuration command “show interfaces status ethernet 1/1”, typing “sh in status e 1/1” will work 2. H...
Page 29: 1.2.2.2 Interface Panel
29 1.2.2.2 interface panel on the top of the management page, the switch interface shows the current status of the ports. Click the ports which are in the state of “link up”, the port statistics are shown on the right..
Page 30: 2.1
30 chapter 2 basic switch configuration 2.1 basic switch configuration commands the basic configuration for the switch including all the commands for entering and exiting the admin mode and interface mode, setting and displaying switch clock and displaying system version information. 2.1.1 calendar ...
Page 31: 2.1.3 Enable
31 2.1.3 enable command : enable function: enter admin mode from user mode. Parameter: 0 and 15 are user access levels. 0 is normal user level. In this level, users can enter admin mode and conduct major commands such as show, ping and traceroute etc. But users can‘t enter global mode. 15 is privile...
Page 32: 2.1.6 Exec Timeout
32 function: modify the password to enter admin mode from the user mode, press enter after type in this command displays and parameter for the users to configure. Parameter: 0 is normal user access level, users can enter admin mode and conduct major commands such as show, ping and trace route etc. B...
Page 33: 2.1.7 Exit
33 0 exec timeout value indicate the system will never exit admin mode automatically. Example: set timeout value for the switch to exit admin mode to 6 minutes. Switch(config)#exec timeout 6 2.1.7 exit command: exit function: exit the current mode to the previous mode. Under global mode, this comman...
Page 34: 2.1.10
34 parameter of this command will delete the mapping. Parameter: is the host name, up to 15 characters are allowed; is the corresponding ip address for the host name, takes a dot decimal format. Command mode: global mode usage guide: set the association between host and ip address, which can be used...
Page 35: 2.1.12
35 example: set username as “admin” and set password as “admin” switch(config)#username admin password 0 admin switch(config)# related command: username nopassword 、 username access-level 、 show users 2.1.12 username nopassword command: username nopassword function: set the username for logging on t...
Page 36: 2.1.15
36 2.1.15 set default command: set default function: reset the switch to factory settings. Command mode: admin mode usage guide: reset the switch to factory settings. That is to say, all configurations made by the user to the switch will disappear. When the switch is restarted, the prompt will be th...
Page 37: 2.2
37 command: write function: save the currently configured parameters to the flash memory. Command mode: admin mode usage guide: after a set of configuration with desired functions, the setting should be saved to the flash memory, so that the system can revert to the saved configuration automatically...
Page 38: 2.2.2 Telnet
38 packets (i.E. Ping failed), the last two packets are replied successfully, the successful rate is 40%. The switch represent ping failure with a “.”, for unreachable target; and ping success with “!” , for reachable target. Switch#ping protocol [ip]: target ip address: 10.1.128.160 repeat count [5...
Page 39: 2.2.2.3 Telnet Commands
39 remote host. If a connection to another remote host is desired, the current tcp connection must be dropped. 2.2.2.2 telnet task sequence 1. Configuring telnet server 2. Telnet to a remote host from the switch. 1. Configuring telnet server command explanation global mode ip telnet server no ip tel...
Page 40: 2.2.2.3.2 Telnet
40 command: monitor no monitor function: enable debug information for telnet client login to the switch, the console end debug display will be disabled at the same time; the “no monitor” command disables the debug information and re-enables the console end debug display. . Command mode: admin mode u...
Page 41: 2.2.2.3.4 Telnet-Server
41 no ip telnet server function: enable the telnet server function in the switch: the “ no telnet-server enable” command disables the telnet function in the switch. Default: telnet server function is enabled by default. Command mode: global mode usage guide: this command is available in console only...
Page 42
42 connection is protected from being intercepted and decrypted. The switch meets the requirements of ssh2.0. It supports ssh2.0 client software such as ssh secure client and putty. Users can run the above software to manage the switch remotely. The switch presently supports rsa authentication, 3des...
Page 43: 2.2.3.3.1
43 2.2.3.3.1 ssh-server enable command: ssh-server enable no ssh-server enable function: enable ssh function on the switch; the “ no ssh-server enable ” command disables ssh function. Command mode: global mode default: ssh function is disabled by default. Usage guide: in order that the ssh client ca...
Page 44: 2.2.3.3.4
44 parameter: is timeout value; valid range is 10 to 600 seconds. Command mode: global mode default: ssh authentication timeout is 180 seconds by default. Example: set ssh authentication timeout to 240 seconds. Switch(config)#ssh-server timeout 240 2.2.3.3.4 ssh-server authentication-retries command...
Page 45: 2.2.3.3.6
45 2.2.3.3.6 monitor command: monitor no monitor function: display ssh debug information on the ssh client side and stop displaying ssh debug information on the console; the “ no monitor ” command stops displaying ssh debug information on the ssh client side and enables to display ssh debug informat...
Page 46: 2.2.3.5.1 Show
46 2.2.3.5.1 show ssh-user command: show ssh-user function: display the configured ssh usernames. Parameter: admin mode example: switch#show ssh-user test related command: ssh-user 2.2.3.5.2 show ssh-server command: show ssh-server function: display ssh state and users which log on currently. Comman...
Page 47: 2.2.5 Show
47 sector. Parameter: is the target host ip address in dot decimal format. Is the hostname for the remote host. Is the maximum gateway number allowed by traceroute command. Is the timeout value for test packets in milliseconds, between 100 – 10000. Default: the default maximum gateway number is 16, ...
Page 48: 2.2.5.3 Dir
48 command mode: admin mode example: check for currently enabled debug switch. Switch#show debugging stp: stp input packet debugging is on stp output packet debugging is on stp basic debugging is on switch# related command: debug 2.2.5.3 dir command: dir function: display the files and their sizes i...
Page 49: 2.2.5.5 Show Memory
49 2.2.5.5 show memory command: show memory function: display the contents in the memory. Command mode: admin mode usage guide: this command is used for switch debug purposes. The command will interactively prompt the user to enter start address of the desired information in the memory and output wo...
Page 50
50 2.2.5.7 show startup-config command: show startup-config function: display the switch parameter configurations written into the flash memory at the current operation, those are usually also the configuration files used for the next power-up. Default: if the configuration parameters read from the ...
Page 51: 2.2.5.9 Show Tcp
51 port vid : 1 vlan number belong to the current interface trunk allowed vlan : all vlan allowed to be crossed by trunk. 2.2.5.9 show tcp command: show tcp function: display the current tcp connection status established to the switch. Command mode: admin mode example: switch#show tcp localaddress l...
Page 52: 2.2.5.11 Show Users
52 2.2.5.11 show users command: show users function: display all user information that can login the switch . Usage guide: this command can be used to check for all user information that can login the switch . Example: switch#show users user level havepasword admin 0 1 online user info: user ip logi...
Page 53: 2.2.6 Debug
53 2.2.6 debug all the protocols es4626/es4650 supports have their corresponding debug commands. The users can use the information from debug command for troubleshooting. Debug commands for their corresponding protocols will be introduced in the later chapters. 2.3 configuring switch ip addresses al...
Page 54: Addresses
54 no ip address [secondary] [secondary]” command deletes vlan interface ip address. 2. Bootp configuration command explanation ip address bootp no ip address bootp enable the switch to be a bootp client and obtain ip address and gateway address through bootp negotiation; the “ no ip bootp-client en...
Page 55
55 switch(config)#interface vlan 1 switch(config-if-vlan1)#ip address 10.1.128.1 255.255.255.0 switch(config-if-vlan1)#exit switch(config)# related command: ip address bootp 、 ip address dhcp 2.3.2.2 ip address bootp command: ip address bootpno ip address bootp function: enable the switch to be a bo...
Page 56: 2.4
56 switch (config)#interface vlan 1 switch (config-if-vlan1)# ip address dhcp switch (config-if-vlan1)#exit switch (config)# related command: ip address, ip address bootp 2.4 snmp 2.4.1 introduction to snmp snmp (simple network management protocol) is a standard network management protocol widely us...
Page 57: 2.4.2 Introduction to Mib
57 requests, replies with get-response message. On some special situations, like network device ports are on up/down status or the network topology changes, agents can send trap messages to nms to inform the abnormal events. Besides, nms can also be set to alert to some abnormal events by enabling r...
Page 58: 2.4.3 Introduction to Rmon
58 fig 2-1 asn.1 tree instance in this figure, the oid of the object a is 1.2.1.1. Nms can locate this object through this unique oid and gets the standard variables of the object. Mib defines a set of standard variables for monitored network devices by following this structure. If the variable info...
Page 59: 2.4.4 Snmp Configuration
59 group 1, 2, 3 and 9: statistics: maintain basic usage and error statistics for each subnet monitored by the agent. History: record periodical statistic samples available from statistics. Alarm: allow management console users to set any count or integer for sample intervals and alert thresholds fo...
Page 60
60 community string. 3. Configure ip address of snmp management base command explanation snmp-server securityip no snmp-server securityip configure the secure ip address which is allowed to access the switch on the nms; the “ no snmp-server securityip ” command deletes configured secure address. Snm...
Page 63: 2.4.4.2.5 Snmp-Server
63 no snmp-server engineid function: configure the engine id; the “ no snmp-server engineid ” command restores the default engine id. Parameter: > is the engine id which is 1-32 hexadecimal characters. Command mode: global mode default: the engine id is manufacturer number + local mac address by def...
Page 66: 2.4.4.2.10 Snmp-Server
66 used for snmp v1 and snmp v2. Example 1: set the secure ip address to 1.1.1.5 switch(config)#snmp-server securityip 1.1.1.5 example 2: delete the secure ip address switch(config)#no snmp-server securityip 1.1.1.5 2.4.4.2.10 snmp-server securityip enable command: snmp-server securityip enable snmp...
Page 67: 2.4.6.1.1 Show
67 switch(config)#snmp-server community private rw switch(config)#snmp-server community public ro switch(config)#snmp-server securityip 1.1.1.5 the nms can use “private” as the community string to access the switch with read-write permission, or use “public” as the community string to access the swi...
Page 68
68 function: display all snmp counter information. Command mode: admin mode example: switch#show snmp 0 snmp packets input 0 bad snmp version errors 0 unknown community name 0 illegal operation for community name supplied 0 encoding errors 0 number of requested variables 0 number of altered variable...
Page 69: 2.4.6.1.2
69 snmp packets output total number of snmp packet outputs. Too big errors number of “too_ big” error snmp packets. Maximum packet size maximum length of snmp packets. No such name errors number of packets requesting for non-existent mib objects. Bad values errors number of “bad_values” error snmp p...
Page 70: 2.4.6.1.3
70 2.4.6.1.3 show snmp engineid command: show snmp engineid function: display snmp engine id information. Command mode: admin mode example: switch#show snmp engineid snmp engineid: 3138633303f1276c engine boots is: 1 displayed information description snmp engineid snmp engine id engine boots the num...
Page 71: 2.4.6.1.6
71 example: switch#show snmp group group name: initial security level: noauthnopriv read view: one write view: notify view: one displayed information description group name group name security level security level read view read view name write view write view name notify view notify view name users...
Page 72: 2.5
72 command: show snmp mib function: display all the mib supported on the switch. Command mode: admin mode 2.4.6.2 snmp troubleshooting help when users configure the snmp, the snmp server may fail to run properly due to physical connection failure and wrong configuration, etc. Users can troubleshoot ...
Page 73
73 there are two methods for bootrom upgrade: tftp and ftp, which can be selected at bootrom command settings. Fig -2-2 typical topology for switch upgrade in bootrom mode the upgrade procedures are listed below: step 1: as shown in the figure, a pc is used as the console for the switch. A console c...
Page 74
74 bootrom version: 1.0.4 creation date: jun 9 2006, 14: 54: 12 attached tcp/ip interface to lnpci0. [boot]: step 3: under bootrom mode, run “setconfig” to set the ip address and mask of the switch under bootrom mode, server ip address and mask, and select tftp or ftp upgrade. Suppose the switch add...
Page 75: 2.5.2 Ftp/tftp Upgrade
75 [boot]: step 6: after successful upgrade, execute “run” command in bootrom mode to return to cli configuration interface. [boot]: run ( or reboot ) other commands in bootrom mode 1. Dir command used to list existing files in the flash. [boot]: dir boot.Rom 327,440 1900-01-01 00: 00: 00 --sh boot....
Page 76
76 there are two types of data connections: active connection and passive connection. In active connection, the client transmits its address and port number for data transmission to the sever, the management connection maintains until data transfer is complete. Then, using the address and port numbe...
Page 77: 2.5.2.2.1
77 allowed to save in rom only. Es4626/es4650 mandates the name of the boot file to be boot.Rom. Configuration file: including start up configuration file and active configuration file. The distinction between start up configuration file and active configuration file can facilitate the backup and up...
Page 79: 2.5.2.2.2
79 command explanation global mode tftp-server retransmission-number number > set maximum retransmission time within timeout interval. ( 3 ) modify tftp server connection retransmission time command explanation global mode tftp-server retransmission-number number > set maximum retransmission time wi...
Page 80: 2.5.2.2.4
80 usage guide: the command provides command line prompt messages. If the user enters a command like copy ftp: // or copy ftp: // and press enter, the following prompt will appear: ftp server ip address [x.X.X.X] : ftp username> ftp password> ftp filename> this prompts for the ftp server address, us...
Page 81: 2.5.2.2.6
81 no ftp-server enable function: start ftp server, the “ no ftp-server enable ” command shuts down ftp server and prevents ftp user from logging in. Default: ftp server is not started by default. Command mode: global mode usage guide: when ftp server function is enabled, the switch can still perfor...
Page 82: 2.5.2.2.8 Tftp-Server
82 keyword source/target ip address running-config active configuration file startup-config start up configuration file nos.Img system file boot.Rom system boot file command mode: admin mode usage guide: the command provides command line prompt messages. If the user enters a command like copy tftp: ...
Page 83: 2.5.2.2.9 Tftp-Server
83 related command: tftp-server timeout 2.5.2.2.9 tftp-server retransmission-number command: tftp-server retransmission-number number> function: set the retransmission time for tftp server parameter: is the time to re-transfer, the valid range is 1 to 20. Default: the default value is 5 retransmissi...
Page 84
84 scenario 1: the switch is used as ftp/tftp client. The switch connects from one of its ports to a computer, which is a ftp/tftp server with an ip address of 10.1.1.1; the switch acts as a ftp/tftp client, the ip address of the switch management vlan is 10.1.1.2. Download “nos.Img” file in the com...
Page 85
85 switch (config-if-vlan1)#no shut switch (config-if-vlan1)#exit switch (config)#ftp-server enable switch(config)# username switch password 0 admin computer side configuration: login to the switch with any ftp client software, with the username “admin” and password “switch”, use the command “get no...
Page 86
86 switch (config-if-vlan1)#exit switch (config)#exit switch#copy ftp: //switch: admin@10.1.1.1/profile1 profile1 switch#copy ftp: //switch: admin@10.1.1.1/profile2 profile2 switch#copy ftp: //switch: admin@10.1.1.1/profile3 profile3 with the above commands, the switch will have the user profile con...
Page 87: 2.5.2.4.1
87 230 user logged in, proceed. 200 port command successful. 150 opening ascii mode data connection for /bin/ls. Recv total = 480 nos.Img nos.Rom parsecommandline.Cpp position.Doc qmdict.Zip shell maintenance statistics.Xls … (some display omitted here) show.Txt snmp.Txt 226 transfer complete. Switc...
Page 88: 2.5.2.4.2 Ftp
88 default: no display by default. Command mode: admin mode example: switch#show tftp timeout : 60 retry times : 10 displayed information explanation timeout timeout time. Retry times retransmission times. 2.5.2.4.2 ftp troubleshooting help when upload/download system file with ftp protocol, the con...
Page 89: 2.5.2.4.3
89 150 opening ascii mode data connection for nos.Img (1526037 bytes). 226 transfer complete. & if the switch is upgrading system file or system start up file through ftp, the switch must not be restarted until “close ftp client” or “226 transfer complete.” is displayed, indicating upgrade is succes...
Page 90: 2.6
90 2.6 web management click switch basic configuration. Users can deploy the switch basic configuration such as enter or quit privileged mode, enter or quit interface mode, show switch clock and show switch system version etc. 2.6.1 switch basic configuration click switch basic configuration, switch...
Page 91: 2.6.2 Snmp Configuration
91 2.6.2 snmp configuration click switch basic configuration, snmp configuration. The switch snmp configuration is shown. Users can configure snmp. 2.6.2.1 snmp manager configuration click switch basic configuration, snmp configuration, snmp manager configuration. Configure switch community string. ...
Page 92: 2.6.2.4 Snmp Statistics
92 2.6.2.3 configure ip address of snmp manager click switch basic configuration, snmp configuration. Users can configure the secure ip address for nms allowed to access the switch. See the equivalent cli command at 2.4.4.2.6 & security ip address - nms secure ip address & state - valid means to set...
Page 93: 2.6.3 Switch Upgrade
93 click switch basic configuration, snmp configuration, rmon and trap configuration. Users can configure switch rmon: & snmp agent state - enable/disable the switch as snmp agent. See the equivalent cli command at 2.4.4.2.3 & rmon state - enable/disable rmon on the switch. See the equivalent cli co...
Page 94
94 file in binary format for example: get system file nos.Img from tftp server 10.1.1.1. Input the information as below, and then click apply 2.6.3.2 tftp server configuration click tftp server service. The configuration page is shown. See the equivalent cli command at 2.2.2.2 the explanation of eac...
Page 95
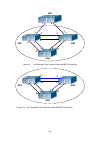
95 server file name - server file name operation type – upload means to upload file, download means to download file. Transmission type - ascii means to transmit file in ascii format, binary means to transmit file in binary format 2.6.3.4 ftp server configuration click ftp server service. The config...
Page 96: 2.6.4.1 Debug Command
96 debug command - debug command show clock - show clock. See the equivalent cli command at 2.2.4.1 show flash - show flash file information. See the equivalent cli command at 2.2.4.3 show history - show recent user input history. See the equivalent cli command at 2.2.4.4 show running-config - show ...
Page 97: 2.6.4.3 Other
97 click show switchport interface. The configuration page is shown. See the equivalent cli command at 2.2.4.8 the explanation of each field is as below: port - port list select port1/1, and then click apply. The port vlan information is shown. 2.6.4.3 other other parts are quite straight forward. C...
Page 98: 2.6.7 Switch Maintenance
98 prompt - command line prompt messages 2.6.6 switch on-off configuration click switch on-off information node. The configuration page is shown. The explanation of each field is as below: rip status - enable or disable rip. See the equivalent cli command at 15.3.2.2.17 igmp snooping – enable or dis...
Page 99: 2.6.9 Username Service
99 2.6.8 telnet service configuration on the mainpage, click talent server configuration on the left column users can configure telnet service. Click telnet server user configuration to configure telnet service. See the equivalent cli command at 2.2.2.3.3: telnet server state – enable or disable tel...
Page 100
100 2.6.10 basic host configuration & basic host configuration - set the mapping relationship between the host and ip address. See the equivalent cli command at 2.1.8 set hostname to london, set ip address to 200.121.1.1,and then click apply. The configuration is applied on the switch..
Page 101: 3.1
101 chapter 3 port configuration 3.1 introduction to port the front panel of es4626 provide 4 combo ports (these combo ports can be configured as either 1000mb copper ports or 1000mb sfp fiber ports, but only one type can be selected), 20 1000mb copper ports and 2 xfp 10gb fiber port. If the user ne...
Page 104
104 command mode: interface mode default: the default setting for combo mode of combo ports is fiber cable port first. Usage guide: the combo mode of combo ports and the port connection condition determines the active port of the combo ports. A combo port consists of one fiber port and a copper cabl...
Page 105: 3.2.1.2.3
105 3.2.1.2.3 flow control command: flow control no flow control function: enable the flow control function for the port: the “ no flow control” command disables the flow control function for the port . Command mode: interface mode default: port flow control is disabled by default. Usage guide: afte...
Page 106: 3.2.1.2.6
106 command: loopback no loopback function: enable the loopback test function in ethernet port; the “ no loopback ” command disables the loopback test on ethernet port. Command mode: interface mode default: loopback test is disabled in ethernet port by default. Usage guide: loopback test can be used...
Page 107: 3.2.1.2.8
107 parameter: is a string, up to 32 characters are allowed. Command mode: interface mode default: no name is set by default. Usage guide: this command facilitates the management of the switch. The user can name the ports according to their usage, for example, 1/1-2 ports used by the financial depar...
Page 108: 3.2.1.2.10
108 to pass through the switch at line speed. Parameter: use dlf to limit unicast traffic for unknown destination; multicast to limit multicast traffic; broadcast to limit broadcast traffic. S tands for the number of packets allowed to pass through per second for non-10gb ports; for 10 gb ports, thi...
Page 110: 3.2.2.2.1 Interface
110 1. Enter vlan mode 2. Configure the ip address for vlan interface and enables vlan interface. 1. Enter vlan mode 2. Configure the ip address for vlan interface and enables vlan interface. Command explanation vlan mode ip address [secondary] no ip address [ ] configure the vlan interface ip addre...
Page 112
112 3.2.3 port mirroring configuration 3.2.3.1 introduction to port mirroring port mirroring refers to duplicate the data frames sent/received on a port to another port, where the duplicated port is referred to as mirror source port, and the duplicating port is referred to as mirror destination port...
Page 114: 3.2.3.5.2
114 switch#show port monitor 3.2.3.5.2 device mirroring troubleshooting help if problems occur configuring port mirroring, please check the following first for causes: & whether the mirror destination port is a member of a trunk group or not, if yes, modify the trunk group. & if the throughput of mi...
Page 116: 3.5
116 duplex mode, traffic control on/off, broadcast storm control and statistics for packets sent/received. Usage guide: if no port is specified, then information for all ports will be displayed. Example: display information about port 4/1. Switch#show interfaces status ethernet 4/1 3.4.2 port troubl...
Page 117
117 cable is support; normal means that only the straight cable is support. See the equivalent cli command at 3.2.1.2.6 & admin status – enable or disable port. See the equivalent cli command at 3.2.1.2.9 & speed/duplex status – set port duplex. The supported types include: auto, 10m/half, 10m/full,...
Page 118
118 click port configuration, ethernet port configuration, bandwidth control. Users can configure port bandwidth control. See the equivalent cli command at 3.2.1.2.1 & port – specify the port & bandwidth control level – port bandwidth control; valid ranges is 1 to 10000 in mbps. & control type –inpu...
Page 119
119 click port configuration, vlan interface configuration. The vlan port configuration page is shown. Users can configure port layer 3 information such as ip address and network mask etc. 3.5.2.1 allocate ip address for l3 port click port configuration, vlan interface configuration, allocate ip add...
Page 120
120 3.5.3 port mirroring configuration click port configuration, port mirroring configuration. Users can configure port mirroring. 3.5.3.1 mirror configuration click port configuration, port mirroring configuration, mirror configuration. Users can configure port mirroring for source interface and de...
Page 121
121 3.5.4.1 show port information click port configuration, port debug and maintenance, show port information. The port statistics information is shown. See the equivalent cli command at 3.4.1.2 for example: select to display ethernet1/1, and then click refresh. The statistics information of port et...
Page 122
122.
Page 123: 4.1
123 chapter 4 mac table configuration 4.1 introduction to mac table mac table is a table identifies the mapping relationship between destination mac addresses and switch ports. Mac addresses can be categorized as static mac addresses and dynamic mac addresses. Static mac addresses are manually confi...
Page 124
124 pc1 mac : 00-01-11-11-11-11 pc4 mac : 00-01-44-44-44-44 pc3 mac : 00-01-33-33-33-33 pc2 mac : 00-01-22-22-22-22 1/5 1/12 fig 4-1 mac table dynamic learning the topology of the figure above: 4 pcs connected to es4626/es4650, where pc1 and pc2 belongs to a same physical segment (same collision dom...
Page 125: 4.1.2 Forward Or Filter
125 for mac address entry in es4626/es4650. Aging time can be modified in es4626/es4650. 4.1.2 forward or filter the switch will forward or filter received data frames according to the mac table. Take the above figure as an example, assuming es4626/es4650 has learnt the mac address of pc1 and pc3, a...
Page 126: 4.2
126 ports; when the destination mac address in a unicast frame is not found in the mac table, the switch will broadcast the unicast frame. When vlans are configured, the switch will forward unicast frame within the same vlan. If the destination mac address is found in the mac table but belonging to ...
Page 127
127 function: add or modify static address entry , the “ no mac-address-table ” command delete static address entries and dynamic address entries. Parameter: static stands for static address entry; dynamic for dynamic address entry; for mac address to add or delete; for port name to forward the mac ...
Page 128: 4.3
128 4.3 typical configuration examples 1/7 1/9 1/11 1/5 pc1 mac : 00-01-11-11-11-11 pc4 mac : 00-01-44-44-44-44 pc3 mac : 00-01-33-33-33-33 pc2 mac : 00-01-22-22-22-22 fig 4-2 mac table typical configuration example scenario: four pcs as shown in the above figure connect to port 1/5, 1/7, 1/9, 1/11 ...
Page 130: 4.5.1.2.1
130 the mac address again to forward data in the new port. However, in some cases, security or management policy may require mac addresses to be bound with the ports, only data stream from the binding mac are allowed to be forwarded in the ports. That is to say, after a mac address is bound to a por...
Page 131: Commands
131 switchport port-security timeout no switchport port-security timeout enable port locking timer function; the “ no switchport port-security timeout ” restores the default setting. Switchport port-security mac-address mac-address> no switchport port-security mac-address mac-address> add static sec...
Page 132
132 enabled, the spanning tree and port aggregation functions must be disabled, and the port enabling mac address binding must not be a trunk port. Example: enable mac address binding function for port 1and and lock the port. When a port is locked, the mac address learning function for the port will...
Page 133
133 switch(config-ethernet1/1)# switchport port-security timeout 30 4.5.1.2.2.4 switchport port-security mac-address command: switchport port-security mac-address mac-address> no switchport port-security mac-address mac-address> function: add static secure mac address; the “ no switchport port-secur...
Page 134: 4.5.1.3.1
134 parameter: is the up limit for static secure mac address, the valid range is 1 to 128. Default: the default maximum port secure mac address number is 1. Usage guide: the mac address binding function must be enabled before maximum secure mac address number can be set. If secure static mac address...
Page 135
135 4.5.1.3.1.1 show port-security command: show port-security function: display the global configuration of secure ports. Command mode: admin mode default: configuration of secure ports is not displayed by default. Usage guide: this command displays the information for ports that are currently conf...
Page 136
136 usage guide: this command displays the detailed configuration information for the secure port. Example: switch# show port-security interface ethernet 1/1 ethernet1/1 port security : enabled port status : security up violation mode : protect maximum mac addresses : 1 total mac addresses : 1 confi...
Page 137: 4.5.1.3.2
137 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- vlan mac address type ports 1 0000.0000.1111 secureconfigured ethernet1/3 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- total addresses : 1 disp...
Page 138
138 4.6.1.1 unicast address configuration click mac address table configuration, mac address table configuration, unicast address configuration. Users can add and delete mac address. See the equivalent cli command at 4.2.2: & mac address – specify mac address & vid – vlan number of the mac address &...
Page 139
139 for example: select vid 1; select interface ethernet1/1; select port status to static, and then click apply. All the static mac addresses on the interface ethernet 1/1 are deleted. 4.6.1.3 static mac query click mac address table configuration, mac address table configuration, static mac query. ...
Page 140: 4.6.2.1.1
140 mac-address-table. The current mac address information is shown. See the equivalent cli command at 4.4.1.1: 4.6.2 mac address table configuration click mac address table configuration, mac address binding configuration. Users can configure secure port features. 4.6.2.1 enbale port mac-binding cl...
Page 141: 4.6.2.2.2
141 lock port. User can lock the secure port. See the equivalent cli command at 4.5.1.2.2.3 & port – specify port for example: select port ethernet1/1, and then click apply. The port ethernet1/1 is locked. Click remove to disable port mac address binding. 4.6.2.2.2 dynamic mac converting click mac a...
Page 142: 4.6.2.2.5
142 cli command at 4.5.1.2.2.5: & port – specify the port & port security mac –port security mac address & operation type – add static security address; remove static security address for example: select port ethernet1/1; set mac address to 00-11-11-11-11-11; select add static security address, and ...
Page 143: 4.6.2.3.2
143 4.5.1.2.2.7 & port – specify the port & max security mac number (1-128) – maximum mac number for example: select port ethernet1/1; set max security mac number to 30, and then click apply. The configuration is applied on the switch. Click remove to restore the default setting. 4.6.2.3.2 port viol...
Page 144
144 specified port. See the equivalent cli command at 4.5.1.3.1.3 & show all port-security – show secure port configuration. See the equivalent cli command at 8.5.1.3.1.1 & show all port-security address – show secure port mac address. See the equivalent cli command at 4.5.1.3.1.3 click show port co...
Page 145: 5.1
145 chapter 5 vlan configuration 5.1 introduction to vlan vlan (virtual local area network) is a technology that divides the logical addresses of devices within the network to separate network segments basing on functions, applications or management requirements. This way, virtual workgroups can be ...
Page 146: 5.2
146 z enhancing network security vlan and gvrp (garp vlan registration protocol) defined by 802.1q are implemented in es4626/es4650. The chapter will describe the use and configuration of vlan and gvrp in details. 5.2 vlan configuration 5.2.1 vlan configuration task sequence 1. Creating or deleting ...
Page 148: 5.2.2.1 Vlan
148 5.2.2 vlan configuration commands 5.2.2.1 vlan command: vlan vlan-id>[name vlan-name>] no vlan vlan-id>[name] function: create a vlan and enter vlan configuration mode, and can set vlan name. In vlan mode, the user can assign the switch port to the vlan. The “ no vlan vlan-id> ” command deletes ...
Page 149: 5.2.2.4 Switchport Mode
149 switch(config-ethernet1/8)#switchport mode access switch(config-ethernet1/8)#switchport access vlan 100 switch(config-ethernet1/8)#exit 5.2.2.3 switchport interface command: switchport interface interface-list> no switchport interface interface-list> function: specify ethernet port to vlan; the ...
Page 151: 5.2.2.8 Private-Vlan
151 switch(config-ethernet1/5)#exit 5.2.2.7 switchport ingress-filtering command: switchport ingress-filtering no switchport ingress-filtering function: enable the vlan ingress rule for a port; the “ no vlan ingress disable ” command disable the ingress rule. Command mode: interface mode default: vl...
Page 152
152 example: set vlan100, vlan200 and vlan300 to private vlan. Set vlan100 to primary vlan; set vlan200 to isolated vlan; set vlan300 to community vlan. 5.2.2.9 private-vlan association command: private-vlan association no private-vlan association function: set private vlan association; the “ no pri...
Page 153
153 fig 5-2 typical vlan application topology the existing lan is required to be partitioned to 3 vlans due to security and application requirements. The three vlans are vlan2, vlan100 and vlan200. Those three vlans must cross location a and b. One switch is placed in each site, and cross-location r...
Page 154: 5.3
154 switch(config)#vlan 2 switch(config-vlan2)#switchport interface ethernet 1/2-4 switch(config-vlan2)#exit switch(config)#vlan 100 switch(config-vlan100)#switchport interface ethernet 1/5-7 switch(config-vlan100)#exit switch(config)#vlan 200 switch(config-vlan200)#switchport interface ethernet 1/8...
Page 155
155 and population of such register information to the other switches. Switches support gvrp can receive vlan dynamic register information from the other switches, and update local vlan register information according the information received. Gvrp enabled switch can also populate their won vlan regi...
Page 156: 5.3.2 Gvrp Commands
156 5.3.2 gvrp commands 5.3.2.1 garp timer join command: garp timer join timer-value> no garp timer join function: set the join timer for garp; the “ no garp timer join ” command restores the default timer setting. Parameter: is the value for join timer, the valid range is 100 to 327650 ms. Command ...
Page 157: 5.3.2.5 Bridge-Ext Gvrp
157 5.3.2.3 garp timer hold command: garp timer hold timer-value> no garp timer hold function: set the hold timer for garp; the “ no garp timer hold” command restores the default timer setting. Parameter: is the value for garp hold timer, the valid range is 100 to 327650 ms. Command mode: interface ...
Page 158
158 no bridge-ext gvrp function: enable the gvrp function for the switch or the current trunk port; the “ no gvrp” command disables the gvrp function globally or for the port . Command mode: interface mode and global mode. Default: gvrp is disabled by default. Usage guide: port gvrp can only be enab...
Page 159
159 to enable dynamic vlan information register and update among switches, gvrp protocol is to be configured in the switch. Configure gvrp in switch a, b and c, enable switch b to learn vlan100 dynamically so that the two workstation connected to vlan100 in switch a and c can communicate with each o...
Page 160: 5.4
160 switch(config)# bridge-ext gvrp switch(config)#vlan 100 switch(config-vlan100)#switchport interface ethernet 1/2-6 switch(config-vlan100)#exit switch(config)#interface ethernet 1/11 switch(config-ethernet1/11)#switchport mode trunk switch(config-ethernet1/11)# bridge-ext gvrp switch(config-ether...
Page 161
161 the max. Vlan entrys: 4094 universal vlan: 1 2 total existing vlans is: 2 displayed information explanation vlan vlan number name vlan name type vlan property, of statically configured or dynamically leaned. Media vlan interface type: ethernet ports access port within a vlan universal vlan unive...
Page 162: 5.4.1.4 Debug Gvrp
162 gvrp timers(milliseconds) leaveall : 10000 5.4.1.4 debug gvrp command: debug gvrp no debug gvrp function: enable the gvrp debug function: the “ no debug gvrp ” command disables this debug function . Command mode: admin mode default: gvrp debug information is disabled by default. Usage guide: use...
Page 163: 5.5.1.1.1
163 click vlan configuration, vlan configuration, create/remove vlan. User can add or remove vlan. 5.5.1.1.1 vid allocation click vlan configuration, vlan configuration, create/remove vlan, vid allocation. Users can add or remove vlan. See the equivalent cli command at 5.2.2.1: operation type – add ...
Page 164: 5.5.1.2.1
164 5.5.1.2 allocate port for vlan click vlan configuration, vlan configuration, allocate ports for vlan. Users can configure the vlan information on the switch. 5.5.1.2.1 allocate port for vlan click vlan configuration, vlan configuration, allocate ports for vlan, allocate port for vlan. Users can ...
Page 165: 5.5.1.4.1
165 port – specify the port type – specify port type: access, trunk. See the equivalent cli command at 5.2.2.5 vlan ingress rules – enable or disable vlan ingress rule. See the equivalent cli command at 5.2.2.8 for example: select port ethernet1/1; select type to trunk; select enable vlan ingress ru...
Page 166: 5.5.1.5.1
166 trunk port. Users can configure vlan attributes of trunk ports: set trunk native vlan: set the native vlan of the port. See the equivalent cli command at 5.2.2.7: port – specify the port trunk native vlan – specify native vlan id operation type – set native vlan: add new vlan; remove native vlan...
Page 167: 5.5.1.6.1
167 for access port. Users can add access port to the specified vlan, or delete access port from the specified vlan: port – specify the port vlan id – specify vlan id for example: select port ethernet1/1; select vlan id 1, and then click apply. The port ethernet 1/1 is added to vlan 1. The results a...
Page 168: 5.5.2 Gvrp Configuration
168 5.5.2 gvrp configuration click vlan configuration, gvrp configuration. Users can configure gvrp. 5.5.2.1 enable global gvrp click vlan configuration, gvrp configuration, enable global gvrp. Users can enable or disable gvrp globally. See the equivalent cli command at 5.3.2.5. For example: select ...
Page 169: 5.5.3.1 Show Vlan
169 applied on the switch. 5.5.3 vlan debug and maintenance click vlan configuration, vlan debug and maintenance. Users can view vlan information on the switch. 5.5.3.1 show vlan click vlan configuration, vlan debug and maintenance, show vlan. The vlan information is shown on information display win...
Page 170: 5.5.3.3 Show Gvrp
170 5.5.3.3 show gvrp click vlan configuration, vlan debug and maintenance, show gvrp. The gvrp information is shown on information display window. See the equivalent cli command at 5.4.1.3.
Page 171: 6.1
171 chapter 6 mstp configuration 6.1 mstp introduction the mstp (multiple stp) is a new spanning-tree protocol which is based on the stp and the rstp. It runs on all the bridges of a bridged-lan. It calculates a common and internal spanning tree (cist) for the bridge-lan which consists of the bridge...
Page 172
172 figure 6-1 example of cist and mst region in the above network, if the bridges are running the stp other the rstp, one port between bridge m and bridge b should be blocked. But if the bridges in the yellow range run the mstp and are configured in the same mst region, mstp will treat this region ...
Page 173: 6.1.2 Port Roles
173 region to become the cst. The msti is only valid within its mst region. An msti has nothing to do with mstis in other mst regions. The bridges in a mst region receive the mst bpdu of other regions through boundary ports. They only process cist related information and abandon msti information. 6....
Page 175
175 4. Configure mstp time parameters 5. Configure the fast migrate feature for mstp command explanation global mode spanning-tree mst configuration no spanning-tree mst configuration enter mstp region mode. The “ no spanning-tree mst configuration ” command restores the default setting. Mstp region...
Page 176: 6.2.2.1 Abort
176 6.2.2 mstp configuration command 6.2.2.1 abort command: abort function: abort the current mstp region configuration, quit mstp region mode and return to global mode. Command mode: mstp region mode usage guide: this command is to quit mstp region mode without saving the current configuration. The...
Page 177: 6.2.2.4 Name
177 no instance [vlan ] function: in mstp region mode, create the instance and set the mappings between vlans and instances; the command “ no instance [vlan ] ” removes the specified instance and the specified mappings between the vlans and instances. Parameter: normally, sets the instance number. T...
Page 178: 6.2.2.6 Spanning-Tree
178 command: revision-level no revision-level function: in mstp region mode, this command is to set revision level for mstp configuration; the command “ no revision-level ” restores the default setting to 0. Parameter: is revision level. The valid range is from 0 to 65535. Command mode: mstp region ...
Page 179
179 blocking to forwarding. This delay is called the forward delay. The forward delay is co working with hello time and max age. The parameters should meet the following conditions. Otherwise, the mstp may work incorrectly. 2 * (bridge_forward_delay - 1.0 seconds) >= bridge_max_age bridge_max_age >=...
Page 180: 6.2.2.10 Spanning-Tree
180 switch(config-port-range)#spanning-tree link-type p2p force-true 6.2.2.10 spanning-tree maxage command: spanning-tree maxage no spanning-tree maxage function: set the max aging time for bpdu; the command “ no spanning-tree maxage ” restores the default setting. Parameter: is max aging time in se...
Page 181: 6.2.2.13 Spanning-Tree
181 function: force the port to run in the mstp mode. Command mode: interface mode default: the port is in the mstp mode by default. Usage guide: if a network which is attached to the current port is running ieee 802.1d stp, the port converts itself to run in stp mode. The command is used to force t...
Page 182
182 name mac address of the bridge revision 0 usage guide: whether the switch is in the mstp region mode or not, users can enter the mstp mode, configure the attributes, and save the configuration. When the switch is running in the mstp mode, the system will generate the mst configuration identifier...
Page 183: 6.2.2.18 Spanning-Tree
183 6.2.2.16 spanning-tree mst port-priority command: spanning-tree mst port-priority no spanning-tree mst port-priority function: set the current port priority for the specified instance; the command “ no spanning-tree mst port-priority ” restores the default setting. Parameter: sets the instance i...
Page 184: 6.3
184 function: set the current port as boundary port; the command “ no spanning-tree portfast ” sets the current port as non-boundary port. Command mode: interface mode default: all the ports are non-boundary ports by default when enabling mstp. Usage guide: when a port is set to be a boundary port, ...
Page 185
185 address bridge priority 32768 32768 32768 32768 port 1 128 128 128 port 2 128 128 128 port 3 128 128 port 4 128 128 port 5 128 128 port 6 128 128 port priority port 7 128 128 port 1 200000 200000 200000 port 2 200000 200000 200000 port 3 200000 200000 port 4 200000 200000 port 5 200000 200000 po...
Page 186
186 sw2(config)#vlan 30 sw2(config-vlan30)#exit sw2(config)#vlan 40 sw2(config-vlan40)#exit sw2(config)#vlan 50 sw2(config-vlan50)#exit sw2(config)#spanning-tree mst configuration sw2(config-mstp-region)#name mstp sw2(config-mstp-region)#instance 3 vlan 20;30 sw2(config-mstp-region)#instance 4 vlan ...
Page 187
187 sw4(config-vlan20)#exit sw4(config)#vlan 30 sw4(config-vlan30)#exit sw4(config)#vlan 40 sw4(config-vlan40)#exit sw4(config)#vlan 50 sw4(config-vlan50)#exit sw4(config)#spanning-tree mst configuration sw4(config-mstp-region)#name mstp sw4(config-mstp-region)#instance 3 vlan 20;30 sw4(config-mstp-...
Page 188
188 sw1 sw2 sw3 sw4 1 1 2 2 3 5 4 2 3 1 6 7 5 4 6 7 x x x x x figure 6-3 the topology of the instance 0 after the mstp calculation sw2 sw3 sw4 2 3 5 4 2 3 6 7 5 4 6 7 x x x x figure 6-4 the topology of the instance 3 after the mstp calculation.
Page 189: 6.4
189 sw2 sw3 sw4 2 3 5 4 2 3 6 7 5 4 6 7 x x x x figure 6-5 the topology of the instance 4 after the mstp calculation mstp troubleshooting 6.4 mstp troubleshooting 6.4.1 monitoring and debugging command 6.4.1.1 show spanning-tree command: show spanning-tree [mst []] [interface ] [detail] function: di...
Page 190
190 force version: 3 ########################### instance 0 ########################### self bridge id : 32768 - 00: 03: 0f: 01: 0e: 30 root id : 16384.00: 03: 0f: 01: 0f: 52 ext.Rootpathcost : 200000 region root id : this switch int.Rootpathcost : 0 root port id : 128.1 current port list in instanc...
Page 191
191 portname id intrpc state role dsgbridge dsgport -------------- ------- --------- --- ---- ------------------ ------- ethernet1/1 128.001 0 fwd mstr 32768.00030f010e30 128.001 ethernet1/2 128.002 0 blk altr 32768.00030f010e30 128.002 displayed information description bridge information standard s...
Page 192: 6.4.1.3 Show Mst-Pending
192 function: display the configuration of the mstp in the privileged mode. Command mode: privileged mode usage guide: in the privileged mode, this command can show the parameters of the mstp configuration such as mstp name, revision, vlan and instance mapping. Example: display the configuration of ...
Page 193: 6.4.1.4 Debug Spanning-Tree
193 switch(config-mstp-region)# 6.4.1.4 debug spanning-tree command: debug spanning-tree no debug spanning-tree function: enable the mstp debugging information; the command “ no debug spanning-tree ” disables the mstp debugging information command mode: privileged mode usage guide: this command is t...
Page 194: Chapter 7 Igmp Snooping
194 chapter 7 igmp snooping configuration 7.1 introduction to igmp snooping igmp (internet group management protocol) is a protocol used in ip multicast. Igmp is used by multicast enabled network devices (such as routers) for host membership query, and by hosts that are joining a multicast group to ...
Page 195
195 2. Configure igmp snooping command explanation global mode ip igmp snooping vlan no ip igmp snooping vlan enable igmp snooping for specified vlan ip igmp snooping vlan mrouter interface no ip igmp snooping vlan mrouter set in the specified vlan the port for connecting m-router ip igmp snooping v...
Page 196: 7.2.2.1
196 query max-response-time 7.2.2 igmp snooping configuration command 7.2.2.1 ip igmp snooping command: ip igmp snooping no ip igmp snooping function: enable the igmp snooping function in the switch: the “ no ip igmp snooping ” command disables the igmp snooping function. Command mode: global mode d...
Page 197: 7.2.2.4
197 function: specify static multicast router port in the vlan; the “ no ip igmp snooping vlan mrouter ” command deletes multicast router port. Parameter: is the specified vlan number; is the specified multicast router port number. Command mode: global mode default: no m-router port is set in the de...
Page 198: 7.2.2.6
198 snooping vlan immediate-leave ” command disables the igmp fast leave function. Parameter: is the vlan number specified. Command mode: global mode default: this function is disabled by default. Usage guide: enabling igmp fast leave function speeds up the process for port to leave multicast group....
Page 199: 7.2.2.8
199 usage guide: larger robustness; parameter means worse network conditions; smaller robustness; parameter means better network conditions. The user can set the robustness parameter according to their network conditions. Example: set the robustness parameter for the igmp query of vlan 100 to 3. Swi...
Page 200
200 fig 7-1 enabling igmp snooping function as shown in the above figure, a vlan 100 is configured in the switch, including port 1, 2, 6, 10 and 12 on slot 1. Four hosts are connected to port 2, 6, 10, 12 respectively and the multicast router is connected to port 1. As igmp snooping is disabled by d...
Page 201
201 traffic of program 2 and port 12 will not receive traffic of program 1. Scenario2igmpquery fig 7-2 the switches as igmp queriers the configuration of switch2 is the same as the switch in scenario 1, switch1 takes the place of multicast router in scenario 1. Let’s assume vlan 60 is configured in ...
Page 202: 7.4
202 multicast configuration the same as scenario 1. Igmp snooping listening result: similar to scenario 1. 7.4 igmp snooping troubleshooting help 7.4.1 monitor and debug commands 7.4.1.1 show ip igmp snooping command: show ip igmp snooping [vlan vlan-id> ] parameter: is id of vlan to display the igm...
Page 203
203 igmp snooping vlan status : disabled igmp snooping vlan query : disabled igmp snooping vlan mrouter port : (null) -------------------------------- igmp information for vlan 4: igmp snooping vlan status : disabled igmp snooping vlan query : disabled igmp snooping vlan mrouter port : (null) ------...
Page 204
204 igmp snooping status : enabled igmp snooping vlan status : enabled igmp snooping vlan mrouter port : ethernet1/4 igmp snooping vlan mrouter state : up igmp snooping vlan mrouter present : yes igmp snooping vlan immediate leave : no igmp snooping vlan query : disabled igmp snooping vlan robustnes...
Page 205: 7.4.1.2 Show
205 port igmp snooping vlan mrouter state all m-router port (if any) status of all vlans in the switch, this will not be displayed if no m-router port is specified. Igmp snooping vlan mrouter present whether query packets present in the m-router igmp snooping vlan query tx query packet number sent b...
Page 206: 7.5
206 processing information can be displayed. Example: enable igmp snooping debug. Switch# debug ip igmp snooping 7.4.2 igmp snooping troubleshooting help & igmp snooping function cannot be used with igmp query, snooping is not available when query is enabled. The user must make sure whether igmp sno...
Page 207: 7.5.2.3 Igmp Configuration
207 the explanation of each field is as below: vlan id – configure query vlan id query state – query state: open or close. See the equivalent cli command at 7.2.2.6 robustness – robustness. See the equivalent cli command at 7.2.2.7 query interval – query interval. See the equivalent cli command at 7...
Page 208
208 7.5.3 igmp snooping static multicast configuration click igmp snooping static multicast configuration. Users can configure igmp snooping static multicast. 7.5.3.1 igmp snooping static multicast configuration the explanation of each field is as below: vlan id – configure vlan id multicast group m...
Page 209
209.
Page 210: 8.1
210 chapter 8 802.1x configuration 8.1 802.1x introduction ieee 802.1x is a kind of port-based network access control technology. The access equipment is authenticated and controlled at the physical access level of lan equipment. The physical access level used here means the ports of switch equipmen...
Page 211: 8.2
211 eapol protocol defined in 802.1x is adopted between user access equipment (pc) and access control unit (access switch); eap protocol is also adopted between access control unit and authentication server. Authentication data is sealed in eap messages, which are included in other high-layer protoc...
Page 212
212 1) configure port authorization status 2) configure port access control method: base on mac address or base on port 3) configure switch 802.1x extend function 3. The configuration of something about user access equipment ( not required ) 4. The configuration of something about radius server 1) c...
Page 214
214 3. Some interrelated configuration about supplicant command explanation global configuration mode dot1x max-req count> no dot1x max-req configure the maximum times of sending eap-request/md5 frame when switch did not receive suppliant response before reload authentication; use the “no” command t...
Page 215
215 dot1x timeout tx-period seconds> no dot1x timeout tx-period configure the timeout interval of switch resending eap-request/identity frame to suppliant; use the “no” command to restore default. Privileged configuration mode dot1x re-authenticate [interface interface-name>] configure the 802.1x re...
Page 216: 8.2.2.1 Aaa Enable
216 radius-server retransmit no radius-server retransmit configure radius retransmit times; use the “no” command to restore default configuration. Radius-server timeout no radius-server timeout configure radius server timeout timer; use the “no” command to restore default configuration. 8.2.2 802.1x...
Page 217: 8.2.2.3 Dot1X Accept-Mac
217 while the user is offline, an “offline” message will not inform radius authentication server. Example: enable the switch aaa accounting function. Switch(config)#aaa-accounting enable 8.2.2.3 dot1x accept-mac command: dot1x accept-mac mac-address> [interface interface-name>] no dot1x accept-mac m...
Page 218: 8.2.2.5 Dot1X Enable
218 8.2.2.5 dot1x enable command: dot1x enable no dot1x enable function: enable switch global and port 802.1x function; use the “no” command to disable 802.1x function . Command mode: global configuration mode and port configuration mode default: switch without enable 802.1x function in global mode;...
Page 219: 8.2.2.8 Dot1X Max-Req
219 command: dot1x macfilter enable no dot1x macfilter enable function: enable switch dot1x address filter function; use the “no” command to disable dot1x address filter function. Command mode: global configuration mode default: switch disable dot1x address filter function. Instructions : while enab...
Page 221: 8.2.2.13 Dot1X
221 command: dot1x re-authenticate [interface interface-name>] function: configure the 802.1x re-authenticate to all port or some specific port in time, not need to wait for time to expire. Parameter: interface-name> is port id, if there’s no parameter, it means all port. Command mode: privilege con...
Page 222: 8.2.2.17 Radius-Server
222 8.2.2.15 dot1x timeout re-authperiod command: dot1x timeout re-authperiod seconds> no dot1x timeout re-authperiod function: configure switch re-authenticate time interval to supplicant; use the “no” command to restore default. Parameter: seconds> re-authenticate time interval, unit is second, th...
Page 223: 8.2.2.18 Radius-Server
223 according to configuration gradation; if configure primary , will use this radius server first. Command mode: global configuration mode default: system without configure radius accounting server. Instructions: this command for specify accounting radius server ip address and port id which connect...
Page 224: 8.2.2.19 Radius-Server
224 8.2.2.19 radius-server dead-time command: radius-server dead-time no radius-server dead-time function: configure the recover time after radius server dead; use the “no” command to restore default configuration. Parameter: is the recover time after radius server dead in minutes, the range: 1~255....
Page 225: 8.2.2.22 Radius-Server
225 function: configure radius authentication message retransmit times; use the “no” command to restore default configuration. Parameter: is radius server retransmit times, the range: 0~100. Command mode: global configuration mode default: default is 3 times. Instructions : after this command specif...
Page 226: 8.3
226 8.3 802.1x apply example 1 0 . 1 . 1 . 1 1 0 . 1 . 1 . 2 ra d i u s se r v e r 1 0 . 1 . 1 . 3 figure 8-2 ieee802.1x configuration example topology figure computer connect to switch port 1/2, ieee802.1x authentication function in port 1/2 is enabled, the access method adopt default method is bas...
Page 227: 8.4
227 8.4 802.1x trouble shooting 8.4.1 802.1x debug and monitor command 8.4.1.1 show aaa config command: show aaa config function: displays the existing configuration commands while the switch works as radius client. Command mode: privilege mode instructions: display switch whether is enable aaa auth...
Page 228
228 .Socket no = 0 accounting server[1].Host ip = 192.168.1.208 .Udp port = 1813 .Is primary = 0 .Is server dead = 0 .Socket no = 0 time out = 3 retransmit = 3 dead time = 5 account time interval = 0 display content description is aaa enabled display aaa authentication function whether is enable. 1 ...
Page 229
229 8.4.1.2 show aaa authenticated-user command: show aaa authenticated-user function: displays the online authenticated users. Command mode: privilege mode instructions: other online user information is typically used for technical support engineers for diagnosis and troubleshooting. Example: switc...
Page 230: 8.4.1.5 Show Dot1X
230 example: 1. Show radius authenticated-user statistics information. Switch #show radius authenticated-user count --------------------- radius user statistic--------------------- the authenticated online user num is: 1 the total user num is: 1 2. Show radius authenticating-user statistics informat...
Page 231
231 802.1x is enabled on ethernet 1 authentication method: port based status authorized port-control auto supplicant 00-03-0f-fe-2e-d3 authenticator state machine state authenticated backend state machine state idle reauthentication state machine state stop display content explanation global 802.1x ...
Page 232: 8.4.1.6 Debug Aaa
232 backend state machine backend state machine status reauthentication state machine reauthentication state machine status 8.4.1.6 debug aaa command: debug aaa no debug aaa function: enable aaa debug information; use the “no” command to close aaa debug information. Command mode: privilege configura...
Page 233: 8.5
233 port. For enabling the 802.1x authentication function, it is necessary to disable the trunk functions of the port. Z if the switch is configured correctly and the authentication is still not passed, it is recommended to examine whether links are established between the switch and radius server, ...
Page 234
234 authentication and accounting ) it is equivalent to cli command 8.2.2.19. Z system recovery time (1-255 minute) - configure the recover time after radius server dead. It is equivalent to 8.2.2.18. Z radius retransmit times(0-100) - configure radius authentication message retransmit times. It is ...
Page 235
235 8.5.1.3 radius accounting configuration click authentication configuration, radius client configuration, radius accounting configuration. Configure radius accounting server ip address and monitor port id. It is equivalent to cli command 8.2.2.16. Z accounting server ip - server ip address. Z acc...
Page 236
236 click authentication configuration, 802.1x configuration, open 802.1x function configuration management list, user may configure switch 802.1x function. 8.5.2.1 802.1x configuration click authentication configuration, 802.1x configuration, 802.1x configuration. Configure 802.1x global configurat...
Page 237
237 8.5.2.2 802.1x port authentication configuration click authentication configuration, 802.1x configuration, 802.1x port authentication configuration. Configure port 802.1xfunction: z port – assign port z 802.1x status – port 802.1x status, enable, 802.1x function is enable; close, 802.1x function...
Page 238
238 click authentication configuration, 802.1x configuration, 802.1x port mac configuration. Add a mac address table to dot1x address filter. It is equivalent to cli command 8.2.2.3. Z port –if specify port, the added list only suitable for specific port, specify all ports, the added list suitable f...
Page 239: 9.1
239 chapter 9 acl configuration 9.1 introduction to acl acl (access control list) is an ip packet filtering mechanism employed in switches, providing network traffic control by granting or denying access through the switches, effectively safeguards the security of networks. The user can lay down a s...
Page 240: 9.2
240 decide whether to permit or deny access. 9.1.3 access list action and global default action there are two access list action and default action: “permit” or “deny”. The following rules apply: z an access list can consist of several rules. Filtering of packets is to compare packet conditions to t...
Page 244
244 firewall disable disable global packet filtering function (2) configure default action. Command explanation global mode firewall default permit set default action to “permit” firewall default deny set default action to “deny” 3. Bind access-list to a specific direction of the specified port. Com...
Page 245: 9.2.2.2 Access
245 [tos ] no access-list function: create a numbered extended ip access rule for specific ip protocol or all ip protocols; if the numbered extended access list of specified number does not exist, then an access list will be created using this number. The “no” form command deletes a numbered extende...
Page 246: 9.2.2.3 Firewall
246 be created, and entries can be added to that acl. Example: create a standard ip access list numbered 20, allowing packets from 10.1.1.0/24 and deny packets from 10.1.1.0/16. Switch(config)#access list 20 permit 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 switch(config)#access list 20 deny 10.1.1.0 0.0.255.255 9.2.2.3 fi...
Page 247: 9.2.2.6
247 function: create a name-based extended ip access list; the “ no ip access extended ” command delete the name-based extended ip access list parameter: is the name for access list, the character string length is 1 – 8, pure digit sequence is not allowed. Command mode: global mode default: no ip ad...
Page 250: 9.4
250 switch#show firewall firewall status: enable. Firewall default rule: permit. Switch#show access lists access list 110(used 1 time(s)) access list 110 deny tcp 10.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 any-destination d-port 21 switch#show access-group interface ethernet 1/10 interface name: ethernet1/10 the ingress ac...
Page 251: 9.4.1.2 Show
251 access list 10 deny any-source deny all ip packets passage. Access list 100(used 1 time(s)) numbered acl100, reference time: 1. Access list 100 deny ip any-source any-destination deny ip packets of any source addresses and destination addresses. Access list 100 deny tcp any-source any-destinatio...
Page 252: 9.5
252 command mode: admin mode usage guide: example: switch#show firewall firewall status: enable. Firewall default rule: permit. Displayed information explanation firewall status: enable. Enable packet filtering function firewall default rule: permit. The default action for packet filtering is “permi...
Page 253
253 acl name configuration – configure name acl, including standard acl and extended acl filter configuration - enable filter globally. Acl filter is binded to the port by default. 9.5.1 add standard numeric ip acl configuration click numeric acl configuration, add standard numeric. Users can config...
Page 254
254 users can configure the following types of numeric acl: add icmp numeric extended acl - add icmp numeric extended acl add igmp numeric extended acl - add igmp numeric extended acl add tcp numeric extended acl - add tcp numeric extended acl add udp numeric extended acl - add udp numeric extended ...
Page 255
255 target port – specify the target port for other protocols, the following fields need to be configured: matched protocol – specify the matched protocol: ip, eigrp, ospf, ipinip and input protocol manually. When “input protocol manually, users can imput protocol number. For example: configure an e...
Page 256
256 source address type - specified ip address or allow any address source ip address – specify source ip address reverse network mask – specify reverse network mask operation type – add; remove for example: add a stanard name acl. Set acl name to ac1; configure other fields; set operation type to a...
Page 257
257 firewall default action – configure firewall default action. “accept” is used to allow packets to pass; “refuse” is used to deny packets to pass. See the equivalent cli command at 9.2.2.4 for example: set packet filtering to enable; set firewall default action to accept, and then click apply. 9....
Page 258: 10.1
258 chapter 10 port channel configuration 10.1 introduction to port channel to understand port channel, port group should be introduced first: port group is a group of physical ports in the configuration level, only physical ports in the port group can take part in link aggregation and become a memb...
Page 259: 10.2
259 for port channel to work properly, member ports of the port channel must have the same properties as the following: ) all ports in full duplex mode. ) ports are of the same speed. ) all ports are access ports and belong to the same vlan or are all trunk ports. ) if the ports are trunk ports, the...
Page 262: 10.3
262 saved and will be restored until the ports are aggregated. Note such restoration will be performed only once, if an aggregated group is ungrouped and aggregated again, the initial user configuration will not be restored. If it is the configuration to other modules, such as shutdown or speed conf...
Page 263
263 switch2 (config)#port-group 2 switch2 (config)#interface eth 1/6 switch2 (config-ethernet1/6)#port-group 2 mode passive switch2 (config-ethernet1/6)#exit switch2 (config)# interface eth 1/8-9 switch2 (config-port-range)#port-group 2 mode passive switch2 (config-port-range)#exit switch2 (config)#...
Page 264: 10.4
264 switch1 (config-ethernet1/2)#exit switch1 (config)#interface eth 1/3 switch1 (config-ethernet1/3)# port-group 1 mode on switch1 (config-ethernet1/3)#exit switch2#config switch2 (config)#port-group 2 switch2 (config)#interface eth 1/6 switch2 (config-ethernet1/6)#port-group 2 mode on switch2 (con...
Page 265
265 “port-channel” displays port aggregation information. Command mode: admin mode usage guide: if “port-group-number” is not specified, then information for all port groups will be displayed. Example: add port 1/1 and 1/2 to port-group1. 1. Display summary information for port-group1. Switch# show ...
Page 266
266 port ethernet1/2 : both of the port and the agg attributes are not equal the general information of the port are as follows: portnumber: 2 actor_port_agg_id: 0 partner_oper_sys: 0x000000000000 partner_oper_key: 0x0002 actor_oper_port_key: 0x0102 mode of the port: active lacp_aware: enable begin:...
Page 267
267 4. Display member port information for port-group1. Switch# show port-group 1 port sorted by the ports in the group 1 : -------------------------------------------- the portnum is 1 port ethernet1/1 related information: actor part administrative operational port number 1 port priority 0x8000 agg...
Page 268
268 expired . . Selected unselected displayed information explanation portnumber port number port priority port priority system system id system priority system priority lacp activety whether port is added to the group in “active” mode, 1 for yes. Lacp timeout port timeout mode, 1 for short timeout....
Page 269: 10.4.1.2 Debug
269 number of port port number in the port-channel. Standby port port that is in “standby” status, which means the port is qualified to join the channel but cannot join the channel due to the maximum port limit, thus the port status is “standby” instead of “selected”. 10.4.1.2 debug lacp command: de...
Page 270: 10.5
270 otherwise lacp packet wouldn’t be initialed. & lacp cannot be used on port enabled security and 802.1x, therefore it cannot be enabled if those two protocols are present on the port. & port channel configuration 10.5 web management click port channel configuration. Lacp port group configuration ...
Page 271
271 10.5.2 lacp port configuration click lacp port configuration. The configuration page is shown. See the equivalent cli command at 10.2.2.2 the explanation of each field is as below: group num - group number port - specify the port port mode - configure port mode: active, passive or on operation t...
Page 272: 11.1
272 chapter 11 dhcp configuration 11.1 introduction to dhcp dhcp [rfc2131] is the acronym for dynamic host configuration protocol. It is a protocol that assigns ip address dynamically from the address pool as well as other network configuration parameters such as default gateway, dns server, default...
Page 273: 11.2
273 dhcp packets so that the dhcp packets exchange can be completed between the dhcp client and server. Es4626/es4650 can act as both a dhcp server and a dhcp relay. Dhcp server supports not only dynamic ip address assignment, but also manual ip address binding (i.E. Specify a specific ip address to...
Page 276: 11.2.2.2 Client-Identifier
276 on bootup. This command is together with the “next sever”. Example: the path and filename for the file to be imported is “c: \tempos.Img”. Switch(dhcp-1-config)#bootfile c: \tempos.Img related command: next-server 11.2.2.2 client-identifier command: client-identifier no client-identifier fun...
Page 277: 11.2.2.5 Dns-Server
277 command: default-router [[…]] no default-router function: configure default gateway(s) for dhcp clients; the “ no default-router ” command deletes the default gateway. Parameter: address1…address8 are ip addresses, in dotted decimal format. Default: no default gateway is configured for dhcp clie...
Page 279
279 system will assign a mask automatically according to the ip address class. This command is used with “hardware address” command or “client identifier” command when binding address manually. If the identifier or hardware address of the requesting client matches the specified identifier or hardwar...
Page 280: 11.2.2.11 Ip Dhcp Pool
280 command mode: global mode usage guide: this command can be used to exclude one or several consecutive addresses in the pool from being assigned dynamically so that those addresses can be used by the administrator for other purposes. Example: reserve addresses from 10.1.128.1 to 10.1.128.10 from ...
Page 282: 11.2.2.16 Network-Address
282 function: set the node type for the specified port; the “ no netbios-node-type ” command cancels the setting. Parameter: b-node stands for broadcasting node, h-node for hybrid node that broadcasts after point-to-point communication; m-node for hybrid node communicates in point-to-point after bro...
Page 283: 11.2.2.18 Option
283 command: next-server [[…]] no next-server function: set the server address for storing the client import file; the “ no next-server ” command cancels the setting. Parameter: address1…address8 are ip addresses, in the dotted decimal format. Command mode: dhcp address pool mode usage guide: this c...
Page 284: 11.3
284 default: dhcp service is disabled by default. Command mode: global mode usage guide: both dhcp server and dhcp relay are included in the dhcp service. When dhcp service enables, both dhcp server and dhcp relay are enabled. Es4626/es4650 can only assign ip address for the dhcp clients and enable ...
Page 285
285 dhcp relay can not only send dhcp broadcasting packets to the specified dhcp servers, but can also send other specified udp broadcast packet to specified servers. 11.3.1 dhcp relay configuration task sequence 1. Enable dhcp relay. 2. Configure dhcp relay to forward dhcp broadcast packet. 3. Conf...
Page 286: 11.3.2.2 Ip
286 11.3.2.1 ip forward-protocol udp command: ip forward-protocol udp no ip forward-protocol udp function: set dhcp relay to forward upd broadcast packets on the port; the “ no ip forward-protocol udp ” command cancels the service. Default: dhcp relay forwards dhcp broadcast packet by default (udp p...
Page 287: 11.4
287 command to stop the dhcp message forwarding. The command “ no ip dhcp relay information policy drop ” restores the dhcp message forwarding. Default: dhcp relay forwards dhcp broadcasting messages by default. Command mode: global mode usage guide: when dhcp messages shouldn’t be forwarded for cer...
Page 288
288 switch(dhcp-a-config)#dns-server 10.16.1.202 switch(dhcp-a-config)#netbios-name-server 10.16.1.209 switch(dhcp-a-config)#netbios-node-type h-node switch(dhcp-a-config)#exit switch(config)#ip dhcp excluded-address 10.16.1.200 10.16.1.210 switch(config)#ip dhcp pool b switch(dhcp-b-config)#network...
Page 289: 11.5
289 switch (config)#vlan 2 switch (config-vlan-2)#exit switch (config)#interface ethernet 1/2 switch (config-erthernet1/2)#switchport access vlan 2 switch (config-erthernet1/2)#exit switch (config)#interface vlan 2 switch (config-if-vlan2)#ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 switch (config-if-vlan2)#e...
Page 291
291 related command: ip dhcp conflict logging , show ip dhcp conflict 11.5.1.3 clear ip dhcp server statistics command: clear ip dhcp server statistics function: delete the statistics for dhcp server, clear the dhcp server count. Command mode: admin mode usage guide: dhcp count statistics can be vie...
Page 292
292 11.5.1.5 show ip dhcp conflict command: show ip dhcp conflict function: display log information for address that has conflict record. Command mode: admin mode example: switch# show ip dhcp conflict ip address detection method detection time 10.1.1.1 ping fri jan 02 00: 07: 01 2002 displayed info...
Page 293
293 message send bootreply 1911 dhcpoffer 6 dhcpack 6 dhcpnak 0 dhcprelay 1907 dhcpforward 0 switch# displayed information explanation address pools number of dhcp address pools configured. Database agents number of database agents. Automatic bindings number of addresses assigned automatically manua...
Page 295: 11.6.1.1 Enable Dhcp
295 11.6.1.1 enable dhcp click dhcp configuration, dhcp server configuration, enable dhcp. Users can enable or disable dhcp server, and configure logging server: dhcp server status – enable or disable dhcp server. See the equivalent cli command at 11.2.2.19 conflict logging status – enable or disabl...
Page 296
296 www.Edge-core.Com; for address range for allocating, set ip address to 10.1.128.0; set network mask to 255.255.255.0; set dhcp client node type to broadcast node; set address lease timeout to 3 day 12 hour 30 minute, and then click apply. The configuration is applied on the switch. 11.6.1.3 clie...
Page 297
297 click dhcp configuration, dhcp server configuration, client dns server configuration. Users can configure dhcp client dns server. See the equivalent cli command at 11.2.2.5: dhcp pool name – select dhcp pool dns server - configure dns server. Users can configure maximum eight dns servers. Dns se...
Page 298
298 11.6.1.6 dhcp file server address configuration click dhcp configuration, dhcp server configuration, dhcp file server address configuration. Users can configure dhcp client bootfile name and file server: dhcp pool name – select dhcp pool name dhcp client bootfile name (1-128 character) – specify...
Page 299
299 11.6.1.7 dhcp network parameter configuration click dhcp configuration, dhcp server configuration, dhcp network parameter configuration. Users can specify dhcp network parameters. See the equivalent cli command at 11.2.2.18: dhcp pool name – select dhcp pool name code(0-254) – specify network co...
Page 300: 11.6.1.9 Excluded
300 11.6.1.9 excluded address click dhcp configuration, dhcp server configuration, manual address pool configuration.Users can configure the exclusive addresses on the dchp pool. See the equivalent cli command at 11.2.2.10: starting address – specify starting address ending address - specify ending ...
Page 301: 11.6.2
301 11.6.2 dhcp relay configuration click dhcp configuration, dhcp relay configuration. Users can configure dhcp relay. 11.6.2.1 dhcp relay configuration click dhcp configuration, dhcp relay configuration, dhcp relay configuration. Users can configure dhcp relay: dhcp forward udp configuration: conf...
Page 302: 11.6.3
302 packet. See the equivalent cli command at 11.3.2.2: ip address – specify server ip address l3 interface – specify layer 2 interface for example: set ip address to 192.168.1.5; set l3 interface to vlan1, and then click add. The configuration is applied on the switch. Configure the relay policy to...
Page 303: 11.6.3.5 Show
303 11.6.3.3 delete dhcp server statistics log click dhcp configuration, dhcp debugging, delete dhcp server statistics log. Users can delete dhcp server statistics and restore the counter to zero. For example: click apply. All the dhcp statistics are deleted. 11.6.3.4 show ip-mac binding click dhcp ...
Page 304: 12.1
304 chapter 12 sntp configuration the network time protocol (ntp) is widely used for clock synchronization for global computers connected to the internet. Ntp can assess packet sending/receiving delay in the network, and estimate computer clock deviation independently, so as to achieve high accuracy...
Page 305: 12.1.3 Clock
305 command: sntp poll no sntp poll function: set the interval for sntp client to send request to ntp/sntp; the “ no sntp polltime ” command cancels polltime set and restores the default setting. Parameter: is the interval value from 16 to 16284. Default: the default poll is 64 seconds. Command mode...
Page 306: 12.2
306 12.2 typical sntp configuration examples switch1 switch2 switch3 sntp/ntp server sntp/ntp server fig 12-1 typical sntp configuration all es4626/es4650 switches in the autonomous zone are required to perform time synchronization, which is done through two redundant sntp/ntp servers. For time to b...
Page 308: 12.4.3 12.4.3
308 interval of sending request from sntp client to ntp/sntp server. See the equivalent cli command at 12.1.2 for example: set interval to 128, and then click apply. The configuration is applied on the switch. 12.4.3 12.4.3 time difference click sntp configuration, time difference. Users can configu...
Page 309: 13.1
309 chapter 13 qos configuration 13.1 qos 13.1.1 introduction to qos qos (quality of service) is a set of capabilities that allow you to create differentiated services for network traffic, thereby providing better service for selected network traffic. Qos is a guarantee for service quality of consis...
Page 310: 13.1.1.2 Qos
310 dscp: differentiated services code point, classification information carried in layer 3 ip packet header, occupying 6 bits, in the range of 0 to 63, and is downward compatible with ip precedence. Classification: the entry action of qos, classifying packet traffic according to the classification ...
Page 311: 13.1.1.3 Basic Qos Model
311 may discard some low priority packets in case of bandwidth shortage. If devices of each hop in a network support differentiated service, an end-to-end qos solution can be created. Qos configuration is flexible, the complexity or simplicity depends on the network topology and devices and analysis...
Page 312
312 classify the data stream. Different classes of data streams will be processed with different policies. 3 . configure a policy map. After data steam classification, a policy map can be created to associate with the class map created earlier and enter class mode. Then different policies (such as b...
Page 313
313 global mode policy-map policy-map-name> no policy-map policy-map-name> create a policy map and enter policy map mode; the “ no policy-map policy-map-name> ” command deletes the specified policy map. Class class-map-name> no class class-map-name> after a policy map is created, it can be associate...
Page 317: 13.1.2.2.5 Class
317 policy map configuration mode. Example: create and delete a policy map named “p1”. Switch(config)#policy-map p1 switch(config-policymap)#exit switch(config)#no policy-map p1 13.1.2.2.5 class command: class no class class-map-name> function: associate a class to a policy map and enter the policy ...
Page 319: 13.1.2.2.9
319 no mls qos aggregate-policer aggregate-policer-name> function: define a policy set that can be used in one policy map by several classes; the “ no mls qos aggregate-policer aggregate-policer-name> ” command deletes the specified policy set. Parameter: aggregate-policer-name> is the name of the p...
Page 321: 13.1.2.2.12 Service-Policy
321 default: the default cos value is 0. Command mode: interface mode example: set the default cos value of port ethernet 1/1 to 5, i.E., packets coming in through this port will be assigned a default cos value of 5 if no cos value present. Switch(config)#interface ethernet 1/1 switch(config-etherne...
Page 322: 13.1.2.2.14 Queue
322 default: there is no policy by default. Command mode: interface mode usage guide : for configuration of dscp mutation mapping on the port to take effect, the trust status of that port must be “trust dscp”. Applying dscp mutation mapping allows dscp value specified directly convert to new dscp va...
Page 323: 13.1.2.2.16 Wrr-Queue
323 queue mode wrr function: queue mode strict configure the queue out. Configure the queue to the output queue queue mode wrr restores wrr queue out default: non-queue mode. Command mode: interface mode usage guide: when queue queue out mode is used, packets are no longer sent with wrr weighted alg...
Page 325: 13.1.3 Qos
325 1 2 3 4 5 6 7. Switch(config)#mls qos map cos-dscp 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 13.1.3 qos example scenario 1: enable qos function, change the queue out weight of port ethernet 1/1 to 1: 1: 2: 2: 4: 4: 8: 8, and set the port in trust cos mode without changing dscp value, and set the default cos value of the ...
Page 326
326 switch(config-policymap)#class c1 switch(config--policy-class)#police 10000 4000 exceed-action drop switch(config--policy-class)#exit switch(config-policymap)#exit switch(config)#interface ethernet 1/2 switch(config-ethernet1/2)#service-policy input p1 configuration result: an acl name 1 is set ...
Page 327: 13.1.4.1.1 Show
327 precedence. Thus inside the qos domain, packets of different priority will go to different queues and get different bandwidth. The configuration steps are listed below: qos configuration in switch1: switch#config switch(config)#access-list 1 permit 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 switch(config)#mls qos sw...
Page 328: 13.1.4.1.2
328 usage guide: this command indicates whether qos is enabled or not. Example: switch #show mls-qos qos is enabled displayed information explanation qos is enabled qos is enabled. 13.1.4.1.2 show mls qos aggregate-policer command: show mls qos aggregate-policer [aggregate-policer-name>] function: d...
Page 329
329 example: switch #show mls qos interface ethernet 1/2 ethernet1/2 default cos: 0 dscp mutation map: default dscp mutation map attached policy-map for ingress: p1 displayed information explanation ethernet1/2 port name default cos: 0 default cos value of the port. Dscp mutation map: default dscp m...
Page 330: 13.1.4.1.4
330 queue and weight type: queue to weight mapping. Qtype wfq or pq queue out method switch # show mls qos interface policers ethernet 1/2 ethernet1/2 attached policy-map for ingress: p1 displayed information explanation ethernet1/2 port name attached policy-map for ingress: p1 policy map bound to t...
Page 331: 13.1.4.1.5
331 ipprecedence-dscp map: ipprec: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 ------------------------------------- dscp: 0 8 16 24 32 40 48 56 dscp-cos map: d1 : d2 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1: 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2: 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 3 3 3: 3 3 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4: 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 6 6 5: 6 6 6 6 6 6 7 7 7 7 6: ...
Page 332: 13.1.4.1.6
332 match acl name: 1 displayed information explanation class map name: c1 name of the class map match acl name: 1 classifying rule for the class map. 13.1.4.1.6 show policy-map command: show policy-map [policy-map-name>] function: display policy map of qos. Parameter: policy-map-name> is the policy...
Page 333: 13.1.5 Web
333 & policy map can only be bound to ingress direction, egress is not supported yet. & if the policy is too complex to be configured due to hardware resource limit, error massages will be provided. 13.1.5 web management select qos configuration and it consist of six sections as following: z enable ...
Page 334: 13.1.5.2.1 Add/remove
334 13.1.5.2.1 add/remove class-map click add/remove class-map then entry the configure page. It is equivalent to cli command 13.1.2.2.2. All sections describe as following: z class - map name z operation type - create class table and remove class table. Adding class-map name, specify the class-map ...
Page 335: 13.1.5.3 Policy-Map
335 13.1.5.3 policy-map configuration click policy-map configuration to display the extension, including five sections: z add/remove policy-map z policy-map priority configuration z policy-map bandwidth configuration z add/remove aggregate policer z apply aggregate policer 13.1.5.3.1 add/remove poli...
Page 336: 13.1.5.3.2 Policy-Map
336 13.1.5.3.2 policy-map priority configuration click policy-map priority configuration to entry configure page. It is equivalent to cli command 13.1.2.2.6. All sections describe as following: z policy-map name z class-map name z priority type. Dscp value or ip precedence value z priority value z o...
Page 337: 13.1.5.3.4 Add/remove
337 drop and policied-dscp-transmit, the latter is by a mapping function between given dscp and corresponding policy and mark the dscp into the packet. Z operation type - set or remove. To configure policy-map bandwidth configuration, select p1 to policy-map name, input c1 to class-map name, all sec...
Page 338: 13.1.5.4.1
338 click apply aggregate policer to entry the configure page. It is equivalent to cli command 13.1.2.2.9. All sections describe as following: z aggregate policer name z policy-map name z class-map name to apply the aggregate policer agg1 by c1 class-map, input the graphic presentation value, then c...
Page 339: 13.1.5.4.2
339 z default - will back to startup setting. This command will modify the configuration. The parameter will take effect alternative port trust status and port priority. To configure the port ethernet 1/1 with trust mode, should set the packet by cos value classification first and keep it without ch...
Page 340: 13.1.5.4.4
340 z operation - set or remove z reset - will set column as startup defaults. This command will not modify the configuration. Apply - will take effort to all setting. This command will modify the configuration. If would like to set the policy-map in port ethernet 1/1. Choosing ethernet1/1 for port ...
Page 341: 13.1.5.5.2
341 click egress-queue wrr weight configuration to entry the configure page. It is equivalent to cli command 13.1.2.2.14. All sections describe as following: z port nameweight for queue 0-7 z operation - set or remove z reset - will set column as startup defaults. This command will not modify the co...
Page 342: 13.1.5.6 Qos
342 click mapping cos values to egress queue to entry the configure page. It is equivalent to cli command 13.1.2.2.16. All sections describe as following: z queue-id z cos value - mapping cos values to egress queue. Up to 8 queue to be supported. Z reset - will set column as startup defaults. This c...
Page 343: 13.1.5.6.2 Dscp-to-Cos
343 z operation - set or remove if would like applying cos value 2 to map dscp value 20, it should input the dscp value 20 in cos value 2 column, selecting set for operation type, then click apply. 13.1.5.6.2 dscp-to-cos mapping click dscp-to-cos mapping to entry configure page. All sections describ...
Page 344: 13.1.5.6.5
344 to configure the dscp mutation mapping should input the required value first, selecting set for operation type, then click apply. 13.1.5.6.4 ip-precedence-to-dscp mapping click ip-precedence-to-dscp mapping to entry the configure page. All sections describe as following: z ip-precedence - ip pre...
Page 345: 13.2
345 value 30 first and policed dscp 1/2 for value10/20, selecting set for operation type, then click apply. 13.2 pbr this chapter describes how to configure the pbr through the examples. 13.2.1 pbr introduction the pbr (policy-based routing) allows modifying the next hop of the packets according to ...
Page 346: 13.2.2.2 Pbr
346 the policy has to apply to the port. 13.2.2.2 pbr command 13.2.2.2.1 mls qos commands: mls qos no mls qos function: enable the qos globally, and the pbr is enabled automatically; the command “ no mls qos ” disables the qos and the pbr globally. Command mode: global mode default: the pbr is disab...
Page 347: 13.2.2.2.4 Policy-Map
347 deletes the specified match. Parameter: access-group acl-index-or-name> specifies the acl. The attribute is the acl number or name. Default: by default, there is no match. Command mode: class-map mode usage guide: only one match can be set in one class-map. When the acl applies to the pbr, the a...
Page 348: 13.2.2.2.6
348 default: by default, there is no policy-map. Command mode: policy-map mode usage guide: before create a policy-map class, users must create a policy-map and enter the policy mode; inside a policy-map, users can set the next hop according to the traffic. The priority of the classes is decided by ...
Page 349: 13.2.3 Pbr
349 parameter: input policy-map-name> applies the specified policy-map to the current port for the inbound traffic; output policy-map-name> applies the specified policy-map to the current port for the outbound traffic. Default: by default, there is no bound policy-map. Command mode: interface mode u...
Page 350
350 configuration result: set the acl a1 which includes 2 policies. The first policy allows the traffic which has the source ip address as 192.168.1.0/24. The second policy denies the traffic which has the source ip address as 192.168.1.0/24 and has the destination ip address as 192.168.0.0/16. Then...
Page 351: Chapter 14 Layer 3 Forward
351 chapter 14 layer 3 forward configuration es4626/es4650 supports layer3 forwarding. Layer3 forwarding is to forward layer3 protocol packets (ip packets) across vlans. Such forwarding addresses using ip address, when a port receives an ip packet, it will index in its own route table and decide the...
Page 352: 14.1.2.1 Layer3
352 14.1.2 layer3 interface configuration 14.1.2.1 layer3 interface configuration task sequence create layer3 interface command explanation global mode interface vlan no interface vlan create a vlan interface (vlan interface is a layer3 interface); the “ no interface vlan ” command deletes the vlan ...
Page 353: 14.2
353 14.2 ip forwarding 14.2.1 introduction to ip forwarding gateway devices can forward ip packets from one subnet to another; such forwarding uses the route to find a path. Ip forwarding of es4626/es4650 is done with the participation of hardware and wire speed forwarding can be achieved. In additi...
Page 354: 14.2.3.1.1
354 command mode: global mode usage guide: this command is used to optimize the aggregation algorithm: if the route table contains no default route, the next hop most frequently referred to will be used to construct a virtual default route to simplify the aggregation result. This method has the bene...
Page 355
355 0 mask requests, 0 mask replies, 0 quench 0 parameter, 0 timestamp, 0 timestamp replies sent: 0 total 0 errors 0 time exceeded 0 redirects, 0 unreachable, 0 echo, 0 echo replies 0 mask requests, 0 mask replies, 0 quench 0 parameter, 0 timestamp, 0 timestamp replies tcp statistics: tcpactiveopens...
Page 356: 14.2.3.1.2
356 quench 0 parameter, 0 timestamp, 0 timestamp replies sent: 0 total 0 errors 0 time exceeded 0 redirects, 0 unreachable, 0 echo, 0 echo replies 0 mask requests, 0 mask replies, 0 quench 0 parameter, 0 timestamp, 0 timestamp replies statistics of total icmp packets sent and classified information ...
Page 357: 14.3.2 Arp
357 resolution. Es4626/es4650 supports both dynamic arp and static configuration. Furthermore, es4626/es4650 supports the configuration of proxy arp for some applications. For instance, when an arp request is received on the port, requesting an ip address in the same ip segment of the port but not t...
Page 358: 14.3.2.2.2 Ip
358 default: no static arp entry is set by default. Command mode: vlan interface mode usage guide: static arp entries can be configured in the switch. Example: configure static arp for interface vlan1. Switch(config-if-vlan1)#arp 1.1.1.1 00-03-0f-f0-12-34 eth 1/2 14.3.2.2.2 ip proxy-arp command: ip ...
Page 359: 14.3.3.1.2 Clear
359 identifier of specified vlan; hw-addr> for entry of specified mac address; “static” for static arp entry; “dynamic” for dynamic arp entry; “count” displays number of arp entries. Command mode: admin mode usage guide: displays the content of current arp table such as ip address, mac address, hard...
Page 360: 14.3.3.1.3 Debug
360 14.3.3.1.3 debug arp command: debug arp no debug arp function: enable the arp debug function: the “ no debug arp ” command disables this debug function. Default: arp debug is disabled by default. Command mode: admin mode usage guide: display contents for arp packets received/sent, including type...
Page 361: Chapter 15 Routing Protocol
361 chapter 15 routing protocol configuration to communicate with a remote host over the internet, a host must choose a proper route via a set of routers/l3 switches. Both routers or layer3 switches calculate the route using cpu, the difference is that layer3 switch adds the calculated route to the ...
Page 362: 15.2
362 layer3 switch has its own route table containing all routes used by that switch. Each route entry in the route table specifies the vlan interface should be used for forwarding packet to reach a destination host or the next hop layer3 switch to the host. The route table mainly consists of the fol...
Page 363
363 convenient for load balance and route backup. However, it also has its own defects. Static route, as its name indicates, is static. It won’t modify the route automatically on network failure, and manual configuration is required on such occasions, therefore it is not suitable for mid and large-s...
Page 364: 15.2.3.2.1 Ip
364 ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 [] no ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 [] configures a default route; the “ no ip route []” command deletes a default route entry. 15.2.3.2 static route configuration commands z ip route z show ip route 15.2.3.2.1 ip route command: ip route [] no ip route [] function: configures...
Page 366: 15.2.4 Configuration
366 mask mask of the destination network nexthop next hop ip address interface the layer3 switch interface to next hop. Pref route priority, if route of the other types exist to the destination network, only the route of the higher priority will be displayed in the core route table. 15.2.4 configura...
Page 367: 15.2.5 Troubleshooting
367 ! next hop use the partner ip address switch(config)#ip route 10.1.4.0 255.255.255.0 10.1.3.1 configuration of layer3 switch switch-2 switch#config switch(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.1.3.2 this way, ping connectivity can be established between pc1 and pc3, and pc2 and pc3 15.2.5 troubles...
Page 368
368 rip is first introduced in arpanet, this is a protocol dedicated to small, simple networks. Rip is a distance vector routing protocol based on the bellman-ford algorithm. Network devices running vector routing protocol send 2 kind of information to the neighboring devices regularly: • number of ...
Page 369: 15.3.2 Rip
369 224.0.0.9). Subnet mask field and rip authentication filed (simple plaintext password and md5 password authentication are supported), and support variable length subnet mask. Rip-ii used some of the zero field of rip-i and require no zero field verification. Layer3 switches send rip-ii packets i...
Page 370
370 b. Configure rip advertisement (2) configure rip routing parameters. A. Configure route aggregation b. Configure route introduction (default route metric, configure routes of the other protocols to be introduced in rip) c. Enable interface to send/receive additional routing metric of rip packets...
Page 371
371 [no] rip broadcast indicates rip layer3 switch allow all ports to send broadcast/multicast packets; the “ no rip broadcast ” command disables all ports to send broadcast/multicast packets 2) configure rip routing parameters. A. Configure route aggregation command explanation rip configuration mo...
Page 372
372 ip rip authentication key no ip rip authentication key sets the authentication key; the “ no ip rip authentication key-chain ” command means no authentication key is used. 3) configure other rip parameters a. Configure rip routing priority b. Configure zero field verification for rip packets c. ...
Page 374: 15.3.2.2.1 Auto-Summary
374 z router rip z timer basic z version z show ip protocols z show ip rip z debug ip rip packet z debug ip rip recv z debug ip rip send 15.3.2.2.1 auto-summary command: auto-summary no auto-summary function: configure route aggregation; the “ no auto-summary” command disables route aggregation. Par...
Page 375: 15.3.2.2.3
375 introducing routes from the other routing protocols to rip. When using “ redistribute ” command to introduce routes of the other protocols without specifying detailed route metric, the default route metric set by “ default-metric ” command applies. Example: set the default route metric for intro...
Page 376: 15.3.2.2.5
376 related command: ip rip authentication key 15.3.2.2.5 ip rip metricin command: ip rip metricin value> no ip rip metricin function: set the additional route metric receiving rip packets on the interface; the “ no ip rip metricin ” command restores the default setting. Parameter: is the additional...
Page 377: 15.3.2.2.8
377 related command: no ip rip send version 15.3.2.2.8 ip rip send version none command: ip rip send version none function: disable sending rip packets on the interface default: sending rip packet is enabled by default. Command mode: interface mode usage guide: this command is used with the other tw...
Page 378: 15.3.2.2.11
378 in multicast by default, packets are only broadcasted when v2-broadcast is set on the interface. 15.3.2.2.11 ip rip work command: ip rip work no ip rip work function: configure the interface to run rip or not; the “ no ip rip work ” command disables rip packet sending/receiving on the interface....
Page 379: 15.3.2.2.14 Rip
379 default: other routes are not introduced to rip by default. If routes of the other routing protocols are introduced without metric value, the default metric value is used. Command mode: rip configuration mode usage guide: use this command to introduce routes of the other routing protocols as rip...
Page 380: 15.3.2.2.17 Router
380 function: set the route priority of rip; the “ no rip preference ” command restores the default setting. Parameter: is the priority value, ranging from 0 to 255. Default: the default rip priority is 120. Command mode : rip configuration mode usage guide: each routing protocol has its own priorit...
Page 381: 15.3.2.2.19 Version
381 command mode: rip configuration mode usage guide: the system advertises rip update packets every 30 seconds by default. If no update packet form a route is received after 180 seconds, this route is considered to be invalid. However, the route will be kept in the route table for another 120 secon...
Page 382: 15.3.2.2.21 Show
382 and perform routing troubleshooting according to the output of this command. Example: switch#sh ip protocols rip information rip is turning on default metrict 16 neighbour is: null preference is 100 rip version information is: interface send version receive version vlan2 v2bc v12 vlan3 v2bc v12 ...
Page 383: 15.3.2.2.22
383 rip information rip is turning on default metric 16 neighbour is preference is 100 displayed information explanation rip is turning on rip routing is enabled default metric 16 the default metric for introduced route is 16. Neighbour is the specified destination address. Preference is 100 rip rou...
Page 384: 15.3.2.2.23
384 2: 11.11.11.2 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 2 00: 04: 20: start at 260********************* received a rip packet from 159.226.42.1 rip packet cmd : 2 version: 1 15.3.2.2.23 debug ip rip recv command: debug ip rip recv no debug ip rip recv function: enable the rip packet debug function for receiving: the “ no...
Page 385: 15.3.3 Typical
385 function: enable the rip packet debug function for sending: the “ no debug ip rip send ” command disables the debug function. Default: debug is disabled by default. Command mode: admin mode example: switch#debug ip rip send 00: 02: 50: start at 170********************* send packets to 11.11.11.2...
Page 386
386 the configuration for switcha, switchb and switchc is shown below: a) configuration of layer3 switch switcha !Configuration of the ip address for interface vlan1 switcha#config switcha(config)# interface vlan 1 switcha(config-if-vlan1)# ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 switcha (config-if-vlan1)...
Page 387
387 switchc(config)# interface vlan 2 switchc(config-if-vlan2)# ip address 20.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 switchc (c config-if-vlan2)#exit ! enable rip switchc(config)#router rip switchc(config-router-rip)#exit ! enable vlan2 to send/receive rip packets switchc(config)#interface vlan 2 switchc (config-if-vl...
Page 388
388 preference is : 100 explanation to displayed information: displayed information explanation automatic network summarization is not in effect disable rip auto aggregation default metric for redistribute is : 16 the default metric for introduced route is 16. Neigbour is the specified destination a...
Page 389: 15.4
389 displayed information explanation automatic network summarization is not in effect disable rip auto aggregation default metric for redistribute is : rip protocol default metric value. Neigbour is: the neighbor layer3 switch connecting to this rip switch. Preference rip routing priority. Rip vers...
Page 390
390 algorithm to generate a route table based on that database. Autonomous system (as) is a self-managed interconnected network. In large networks, such as the internet, a giant interconnected network is broken down to autonomous systems. Big enterprise networks connecting to the internet are indepe...
Page 391
391 autonomous system, they can be grouped as internal switches, edge switches, as edge switches and backbone switches). Ospf supports load balance and multiple routes to the same destination of equal costs. Ospf supports 4 level routing mechanisms (process routing according to the order of route in...
Page 392: 15.4.2 Ospf
392 to be configured as stub areas to reduce the topology database size. Type4 lsa (asbr summary lsa) and type5 lsa (as exterior lsa) are not allowed to flood into/through stub areas. Stub areas must use the default routes, the layer3 switches on stub area edge advertise the default routes to stub a...
Page 393
393 (1) configure ospf packet sending mechanism parameters a. Configure ospf packet verification b. Set the ospf interface to receive only c. Configure the cost for sending packets from the interface d. Configure ospf packet sending timer parameter (timer of broadcast interface sending hello packet ...
Page 394
394 ip ospf enable area area_id> no ip ospf enable area sets an area for the specified interface; the “ no ip ospf enable area ” command cancels the setting. (required) 2. Configure ospf sub-parameters (1) configure ospf packet sending mechanism parameters a. Configure ospf packet verification b. Se...
Page 395
395 default redistribute tag tag> no default redistribute tag sets the default tag value for introducing external routes; the “ no default redistribute tag ” command cancels the tag value setting. Default redistribute cost cost> no default redistribute cost sets the default cost for introducing exte...
Page 396: 15.4.2.2 Ospf
396 virtuallink neighborid router_id> transitarea area_id> [ hellointerval time> ] [ deadinterval time> ] [ retransmit time> ] [ transitdelay time> ] no virtuallink neighborid router_id> transitarea area_id> creates and configures virtual link; the “ no virtuallink neighborid router_id> transitarea ...
Page 397: 15.4.2.2.1
397 z router ospf z stub cost z virtuallink neighborid z show ip ospf z show ip ospfase z show ip ospf cumulative z show ip ospf database z show ip ospf interface z show ip ospf neighbor z show ip ospf routing z show ip ospf virtual-links z show ip protocols z debug ip ospf event z debug ip ospf lsa...
Page 398: 15.4.2.2.3
398 default: the default interval in ospf for introducing exterior routes is 1 second. Command mode: ospf protocol configuration mode usage guide: ospf introduces exterior routing information regularly and advertise the information throughout the autonomous system. This command is used to modify the...
Page 400: 15.4.2.2.8
400 function: set the cost for running ospf on the interface; the “ no ip ospf cost ” command restores the default setting. Parameter: is the ospf cost, ranging from 1 to 65535. Default: the default cost for ospf protocol is 1. Command mode: interface mode example: set the ospf route cost of interfa...
Page 401: 15.4.2.2.10
401 interface. Example: specify interface vlan1 to area 1. Switch(config-if-vlan1)#ip ospf enable area 1 15.4.2.2.10 ip ospf hello-interval command: ip ospf hello-interval no ip ospf hello-interval function: configure the interval for sending hello packets from the interface; the “ no ip ospf hello-...
Page 402: 15.4.2.2.12
402 15.4.2.2.12 ip ospf priority command: ip ospf priority no ip ospf priority function: set the priority of the interface in “designated layer3 switch” (dr) election; the “ no ip ospf priority ” command restores the default setting. Parameter: is the priority value, ranging from 0 to 255. Defaulted...
Page 403: 15.4.2.2.15 Network
403 command: ip ospf tranmsit-delay no ip ospf transmit-delay function: set the delay time before sending link-state advertisement (lsa); the “ no ip ospf transmit-delay ” command restores the default setting. Parameter: is the delay time for the link-state advertisement transmission in seconds, ran...
Page 404: 15.4.2.2.17 Redistribute
404 for as exterior routes introduced; the “ no preference [ ase ] ” command restores the default setting. Parameter: ase means the priority is used when introducing exterior routes outside the as; is the priority value ranging from 1 to 255. Default: the default priority of ospf protocol is 110; th...
Page 405: 15.4.2.2.19 Router
405 command: router id no router id function: configure the id number for the layer3 switch running ospf; the “ no router id ” command cancels the id number. Parameter: is the id number for the layer3 switch in dotted decimal format. Default: no layer3 switch id number is configured by default, an a...
Page 406: 15.4.2.2.21 Virtuallink
406 command mode: ospf protocol configuration mode usage guide: an area can be configured to a stub area if the area has only one egress point (connect to one layer3 switch only), or need not select egress point for each exterior destination. Type4 lsa (asbr summary lsa) and type5 lsa (as exterior l...
Page 407: 15.4.2.2.23
407 command mode: admin mode example: switch#show ip ospf my router id is 11.11.4.1 preference=10 ase perference=150 export metric=1 export tag=-2147483648 area id 0 interface count: 1 80times spf has been run for this area net range: lsrefreshtime is1800 area id 1 interface count: 1 41times spf has...
Page 408: 15.4.2.2.24
408 displayed information explanation destination target network segment or address advrouter route election nexthop next hop address age aging time. Seqnumber sequence number. Type exterior routes type for introduction. Cost cost for introducing exterior routes 15.4.2.2.24 show ip ospf cumulative c...
Page 409: 15.4.2.2.25
409 ls_rtr 3 ls_net 3 ls_sum_net 1 ls_sum_asb 0 ls_ase 3 as internal route 4 as external route 0 displayed information explanation io cumulative statistics for ospf packets in/out. Type packet type: including hello packet, dd packet, ls request, update and acknowledging packet, etc. In packet in sta...
Page 410
410 11.11.4.2 11.11.4.2 1 2147483662 1 35126 summary network lsas ls id adv rtr age sequence cost checksum (net's ip) 11.11.1.0 11.11.4.1 0 2147483656 1 6777215 11.11.2.255 11.11.4.1 0 2147483649 1 6777215 11.11.3.255 11.11.4.1 0 2147483680 1 6777215 asbr summary lsas ls id adv rtr age sequence cost...
Page 411: 15.4.2.2.26
411 ls id route type adv rtr age sequence cost checksu forw addr routetag (ext net's ip) displayed information explanation ospf router id the id of the layer3 switch. Area 1>>>>>>>> area id: 0 represent the lsa database information from area 1 to area 0. Router lsas route lsa network lsas network ls...
Page 412: 15.4.2.2.27
412 type layer3 switch type, such as designated layer3 switch. Priority configure the priority in electing designated layer3 switch. Transit delay the delay value for interface to transfer las. Dr the designated layer3 switch. Bdr backup designated layer3 switch. Authentication key ospf packet authe...
Page 413: 15.4.2.2.28
413 interface ip 51.1.1.1 area id 0 interface ip 52.1.1.1 area id 0 interface ip 100.1.1.1 area id 0 interface ip 110.1.1.1 area id 0 interface ip 150.1.1.1 area id 0 router id 12.2.0.0 router ip addr 150.1.1.2 state nfull priority 0 dr 150.1.1.1 bdr 0.0.0.0 last hello 59011 last exch 49607 displaye...
Page 414: 15.4.2.2.29
414 as external routes: destination cost dest type next hop adv rtr displayed information explanation as internal routes autonomous system interior route. As external routes autonomous system exterior route. Destination destination network segment area area number. Cost cost value. Dest type route t...
Page 415: 15.4.2.2.31
415 interface count: 2 7times spf has been run for this area net range: lsrefreshtime is1800 rip information rip is shutting down displayed information explanation ospf is running the running routing protocol is ospf protocol. My router id the id number of the layer3 switch running. Preference ospf ...
Page 416: 15.4.2.2.33
416 default: debug is disabled by default. Command mode: admin mode 15.4.2.2.33 debug ip ospf packet command: debug ip ospf packet no debug ip ospf packet function: enable the ospf packet debug function; the “ no debug ip ospf packet ” command disables this debug function. Default: debug is disabled...
Page 417: 15.4.3 Typical
417 15.4.3 typical ospf scenario scenario 1: ospf autonomous system. This scenario takes an ospf autonomous system consists of five es4626/es4650 layer3 switches for example, where layer3 switch switch1 and switch5 make up ospf area 0, layer3 switch switch2 and switch3 form ospf area 1 (assume vlan1...
Page 418
418 switch1(config)#interface vlan2 switch1 (config-if-vlan2)#ip ospf enable area 0 switch1 (config-if-vlan2)#exit switch1(config)#exit switch1# layer3 switch switch2: !Configure the ip address for interface vlan1 and vlan2. Switch2#config switch2(config)# interface vlan 1 switch2(config-if-vlan1)# ...
Page 419
419 switch3(config-if-vlan3)#exit switch3(config)#exit switch3# layer3 switch switch4: !Configuration of the ip address for interface vlan3 switch4#config switch4(config)# interface vlan 3 switch4(config-if-vlan3)# ip address30.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 switch4(config-if-vlan3)#no shut-down switch4(config...
Page 420
420 switch5(config-if-vlan3)#exit switch5(config)#exit switch5# scenario 2: typical ospf protocol complex topology. Domai n 2 domai n 3 domai n 1 n3 n1 n8 n5 n6 n9 n10 n4 n2 n15 n14 n7 n12 n13 n11 domai n 0 switch1 switch2 switch3 switch4 switch5 switch6 switch9 switch12 switch11 switch10 switch7 sw...
Page 421
421 floods in area 1, those lsa are included in the area 1 database to get the routes to network n11 and n15. In addition, layer3 switch switch3 and switch4 must summary the topology of area 1 to the backbone area (area 0, all non-0 areas must be connected via area 0, direct connections are not allo...
Page 422
422 switch1(config-if-vlan2)exit !Configuration of the ip address and area number for interface vlan1 switch1(config)# interface vlan 1 switch1(config-if-vlan1)#ip address 20.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 switch1(config-if-vlan1)#ip ospf enable area 1 switch1(config-if-vlan1)#exit 2)switch2: !Configuration of...
Page 423
423 switch3(config-if-vlan2)#exit !Configuration of the ip address and area number for interface vlan3 switch3(config)# interface vlan 3 switch3(config-if-vlan3)#ip address 20.1.3.1 255.255.255.0 switch3(config-if-vlan3)#ip ospf enable area 1 switch3(config-if-vlan3)#exit !Configuration of the ip ad...
Page 424
424 15.4.4 ospf troubleshooting help 1. Monitor and debugging commands 2. Ospf troubleshooting help 15.4.4.1 monitor and debugging commands command explanation admin mode show interface status displays interface information to verify the interface and datalink layer protocols are up. Show ip ospf di...
Page 425
425 ( 1 ) show ip ospf example: switch#show ip ospf my router id is 11.11.4.1 preference=10 ase perference=150 export metric=1 export tag=-2147483648 area id 0 interface count: 1 80times spf has been run for this area net range: lsrefreshtime is1800 area id 1 interface count: 1 41times spf has been ...
Page 426
426 a 5.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 12.1.1.2 vlan12 150 a 5.1.2.0 255.255.255.0 12.1.1.2 vlan12 150 a 5.1.3.0 255.255.255.0 12.1.1.2 vlan12 150 a 5.1.4.0 255.255.255.0 12.1.1.2 vlan12 150 a 5.1.5.0 255.255.255.0 12.1.1.2 vlan12 150 a 5.1.6.0 255.255.255.0 12.1.1.2 vlan12 150 a 5.1.7.0 255.255.255.0 12.1.1.2...
Page 427
427 switch#show ip ospf cumulative io cumulative type in out hello 1048 253 dd 338 337 ls req 62 219 ls update 753 295 ls ack 495 308 ase count 0 checksum 0 original lsa 340 ls_rtr 179 ls_net 1 ls_sum_net 160 ls_sum_asb 0 ls_ase 0 received lsa 325 areaid 0 nbr count 1 interface count 1 spf times 120...
Page 428
428 (router id) 11.11.4.1 11.11.4.1 0 2147483808 0 42401 11.11.4.2 11.11.4.2 18 2147483863 1 6777215 router lsa 11.11.4.1 11.11.4.1 0 2147483808 0 42401 11.11.4.2 11.11.4.2 18 2147483863 1 6777215 network lsas ls id adv rtr age sequence cost checksum (dr's ip) 11.11.4.2 11.11.4.2 1 2147483662 1 3512...
Page 429
429 (dr's ip) 11.11.1.1 11.11.4.1 0 2147483649 1 6777215 11.11.1.3 14.14.14.1 15 2147483705 1 53384 summary network lsas ls id adv rtr age sequence cost checksum (net's ip) 11.11.4.255 11.11.4.1 0 2147483677 1 6777215 asbr summary lsas ls id adv rtr age sequence cost checksum (asbr's rtr id) as exte...
Page 430
430 area the area of the interface net type network type, such as broadcast, p2mp, etc. Cost cost value. State status type layer3 switch type, such as designated layer3 switch. Priority configure the priority in electing designated layer3 switch. Transit delay the delay value for interface to transf...
Page 431
431 state nfull priority 0 dr 150.1.1.1 bdr 0.0.0.0 last hello 66289 last exch 49607 displayed information explanation interface ip the ip address of an interface in the current layer3 switch. Area id the id of the area for the interface router id the id of the neighbor layer3 switch. Router ip addr...
Page 432: 15.4.4.2 Ospf
432 for example, displayed information can be: switch#show ip ospf virtual-links no virtual-link ( 10 ) show ip protocols “show ip protocols” command can be used to display the information of the routing protocols running in the switch. For example, displayed information can be: switch#sh ip protoco...
Page 433: 15.5
433 all interface and link protocols are in the up state (use “show interface status” command). Then ip addresses of different network segment should be configured in all interfaces. Enable ospf(use “router rip” command) first, then configure ospf areas for appropriate interfaces to reside in. Next,...
Page 434: 15.5.2 Rip
434 15.5.2 rip click rip configuration. Users can configure rip: enable rip – enable rip, including: enable rip – enable rip enable port to receive/transmit rip packet – configure the port to receive/transmit rip packet rip parameter configuration – configure rip parameters, including: enable import...
Page 435: 15.5.2.3 Configuring
435 the equivalent cli command at 15.3.2.2.11 the explanation of each field is as below: port – port name enable port to receive/transmit rip packet – set; cancel for example: disable to receive/transmit rip packet on vlan2. Select vlan1; select vlan1; select cancel, and then click apply. 15.5.2.3 c...
Page 436
436 15.5.2.5 rip port configuration click rip port imported route. The configuration page is shown. The explanation of each field is as below: port – specify the port receiving rip version – configure receiving rip version on the port: version 1, version 2 and version 1 and 2. See the equivalent cli...
Page 437
437 15.5.2.6 global rip mode configuration click rip mode configuration. The configuration page is shown. The explanation of each field is as below: set receiving/sending rip version for all ports – configure receiving/sending rip version for all ports: version1, version2 and cancel (default version...
Page 438: 15.5.3 Ospf
438 15.5.2.7 rip timer configuration click rip timer configuration. The configuration page is shown. See the equivalent cli command at 15.3.2.2.18 the explanation of each field is as below: update timer – update packet timer invalid timer – rip route invalid timer holddown timer – time length of a r...
Page 439: 15.5.3.1.1 Enable/disable
439 15.5.3.1.1 enable/disable ospf click ospf enable. The configuration page is shown. See the equivalent cli command at 15.4.2.2.19 the explanation of each field is as below: ospf enable - ospf enable; ospf disable reset – clear the selection for example: enable ospf protocol. Select ospf enable, a...
Page 440: 15.5.3.1.4
440 15.5.3.1.4 configure ospf area for port click ospf area configuration for port. The configuration page is shown. See the equivalent cli command at 15.4.2.2.9 the explanation of each field is as below: vlan port – vlan port list area id – area id reset – reset default – restore the default value ...
Page 441: 15.5.3.2.2
441 reset - reset for example: set osfp port vlan1 to use md5 authentication with the password of 123abc and with keyid of 1. Select vlan port to vlan1; set authentication mode to md5; set authentication key to 123abc; set keyid to 1, and then click apply. 15.5.3.2.2 ospf passive interface configura...
Page 442: 15.5.3.3.1
442 equivalent cli command at 18.4.2.2.8 sending link-state packet delay – configure sending link-state packet delay on the port. See the equivalent cli command at 18.4.2.2.14 sending link-state packet retransmit interval – specify sending link-state packet retransmit interval to neighbor router. Se...
Page 443: Configuration
443 15.5.3.3.2 import external routing information configuration click import external routing information. The configuration page is shown. See the equivalent cli command at 15.4.2.2.17. The explanation of each field is as below: imported type – configure imported route type: static, rip, connected...
Page 444: 15.5.3.4.2 Ospf
444 ospf priority relative to other routing protocols. Priority – set priority value 15.5.3.4.2 ospf stub area and default route cost configuration click ospf stub area and default route cost. The configuration page is shown. See the equivalent cli command at 15.4.2.2.20 the explanation of each fiel...
Page 445: 15.5.3.4.4
445 15.5.3.4.4 port dr priority configuration click port dr priority configuration. The configuration page is shown. See the equivalent cli command at 15.4.2.2.12 the explanation of each field is as below: vlan port – specify vlan port priority – specify priority 15.5.3.5 ospf debug click ospf debug...
Page 446
446.
Page 447: Configuration
447 chapter 16 multicast protocol configuration 16.1 multicast protocol overview 16.1.1 introduction to multicast when sending information (including data, voice and video) to a small number of users in the network, there are several ways of transmission, for instance, the unicast method that establ...
Page 448: 16.1.2 Multicast
448 16.1.2 multicast address the multicast packets uses class d ip address as their destination addresses, ranging from 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255. Class d addresses cannot be used in the source ip address field of an ip packet. In unicast, the path a packet travels is from the source address to t...
Page 449
449 224.0.0.17 all sbms 224.0.0.18 vrrp when transferring unicast ip packets on ethernet, the destination mac address is the mac of the receiver. However, in transferring multicast packets, as the destination is no longer one specific recipient but a group with unknown members, the destination addre...
Page 450: 16.2
450 network, and can significantly save the network bandwidth and reduce network traffic. The multicast feature can be conveniently used to provide some new value-added services, including online live broadcast, network tv, remote education, remote medical service, network radio, realtime video/audi...
Page 451: 16.3
451 239.255.0.1 7.1.1.100 vlan4 0 2005: 1 239.255.0.1 1.1.1.100 vlan1 0 2006: 1 2007: 1 switch # displayed information explanation name the interface list used by the multicast protocol and basic information for the interfaces. Index index number for the interface group multicast forwarding entry gr...
Page 452: 16.3.2 Pim-Dm
452 upstream nodes to inform the upstream node that no more forwarding for that multicast group is necessary. The upstream nodes will delete the corresponding interface, multicast forwarding entry(s,g), from the outgoing interface list. Hence a shortest path tree (spt) rooted by source s is establis...
Page 453: 16.3.2.2 Pim-Dm
453 pim-dm in the appropriate interfaces. Command explanation interface mode ip pim dense-mode no ip pim dense-mode enable pim-dm protocol; the “ no ip pim dense-mode ” command disables pim-dm protocol (required) 2. Configure pim-dm sub-parameters configure pim-dm interface parameters a. Configure p...
Page 454: 16.3.3 Typical
454 command disables pim-dm protocol on the interface. Parameter: n/a. Default: pim-dm protocol is disabled by default. Command mode: interface mode usage guide: example: enable pim-dm protocol on interface vlan1. Switch (config)#interface vlan 1 switch(config-if-vlan1)#ip pim dense-mode 16.3.2.4 ip...
Page 455
455 switcha switchb et her net 1/1 vl an2 et her net 1/ 1 vl an1 et her net 1/2 vl an2 et her net 1/ 2 vl an1 fig 16-1 typical pim-dm environment the followings are the configurations of switcha and switchb. (1) configuration of switcha: switch (config)#interface vlan 1 switch(config-if-vlan1)# ip p...
Page 456: 16.3.4.1.1
456 show ip pim interface display pim-dm interface information debug ip pim enable the debug function for displaying detailed pim information; the “ no ” format of this command disables this debug function. 16.3.4.1.1 show ip pim mroute dm command: show ip pim mroute dm function: display the pim-dm ...
Page 457: 16.3.4.1.2
457 displayed information explanation (5.1.1.100, 225.0.0.1) forwarding entry. Incoming interface incoming interface or rpf interface. Outgoing interface list outgoing interface list. Prune interface list downstream prune interface list. 16.3.4.1.2 show ip pim neighbor command: show ip pim neighbor ...
Page 458: 16.3.4.1.4
458 function: display information for the pim interface. Parameter: is the interface name, i.E. Display pim information of the specified interface. Default: pim information is displayed by default on all interfaces. Command mode: admin mode example: display pim information of interface vlan 1. Switc...
Page 459: 16.4
459 16.3.4.2 pim-dm troubleshooting help in configuring and using pim-dm protocol, the pim-dm protocol may fail to run properly due to reasons such as physical connection failure or wrong configurations. The user should ensure the following: good condition of the physical connection. All interface a...
Page 460: 16.4.2 Pim-Sm
460 sends a join message to the upstream node in the rp direction. Each routers between the leaf router and the rp will created a (*, g) entry in their forwarding table, indicating packets sent by any source to multicast group g applies to this entry. When rp receives a packet sending to multicast g...
Page 461
461 (1) configure pim-sm interface parameters 1 ) configure pim-sm hello packet interval 2 ) configure a interface as the pim-sm area border (2) configure pim-sm global parameters 1) configure a switch as the candidate bsr. 2) configure a switch as the candidate rp. 3. Disable pim-sm protocol 1. Ena...
Page 462: 16.4.2.2 Pim-Sm
462 ip pim bsr-candidate ifname> [hashlength] [priority] no ip pim bsr-candidate this command is a global candidate bsr configuration command. It is used to configure information for pim-sm candidate bsr and to comtend for the bsr router with the other candidate bsrs; the “ no ip pim bsr-candidate ”...
Page 463: 16.4.2.2.1
463 16.4.2.2.1 ip pim sparse-mode command: ip pim sparse-mode no ip pim sparse-mode function: enable pim-sm protocol on the interface; the “ no ip pim sparse-mode ” command disables pim-sm protocol on the interface. Parameter: n/a. Default: pim-sm protocol is disabled by default. Command mode: inter...
Page 464: 16.4.2.2.4
464 parameter: hello-interval-second> is the interval for sending pim hello packets, ranging from 1 to 18724s. Parameter: the default interval for sending pim hello is 30s. Command mode: interface mode usage guide: the hello message enables pim-dm switches to locate each other and establish the neig...
Page 465: 16.4.3 Typical
465 router with the other candidate rps; the “ no ip pim rp-candidate [ifname>] ” command cancels the rp configuration. Parameter: ifname> is the name of specified interface; access-list is the number of group range list can be used as the rp in the switch, ranging from 1 to 99, if this parameter is...
Page 466
466 the followings are the configurations of switcha, switchb, switchc, and switchd. (1) configuration of switcha: switch (config)#interface vlan 1 switch(config-if-vlan1)# ip pim sparse-mode switch(config-if-vlan1)#exit switch (config)#interface vlan 2 switch(config-if-vlan2)# ip pim sparse-mode (2...
Page 467: 16.4.4.1.1
467 switch(config-if-vlan3)# ip pim sparse-mode 16.4.4 pim-sm troubleshooting help 16.4.4.1 monitor and debug commands 16.4.4.1.1 show ip pim bsr-router command: show ip pim bsr-router function: display pim bsr-router information. Parameter: n/a. Default: no display by default. Command mode: admin m...
Page 468: 16.4.4.1.3
468 function: display pim information of interface vlan 2. Switch #show ip pim interface vlan2 switch # interface vlan2 : 192.3.1.2 owner is pimsm, vif is 1, hello interval is 30, pim sm jp interval is (60) neighbor-address interface uptime expires 192.3.1.3 vlan2 00: 12: 18 00: 01: 38 switch # disp...
Page 469: 16.4.4.1.4
469 incoming interface : vlan1, rpf nbr 0.0.0.0, pref 0, metric 0 outgoing interface list: (vlan2), protos: 0x2, uptime: 00: 10: 18, exp: 00: 03: 18 switch # displayed information explanation (192.1.1.1, 225.0.0.1) forwarding entry. Incoming interface incoming interface, or rpf interface. Outgoing i...
Page 471: 16.4.4.1.7
471 16.4.4.1.7 debug ip pim bsr command: debug ip pimbsr function: enable the pim candidate rp/bsr informaiton debug function; the “ no ” format of the command disables this debug function. Parameter: n/a. Default: disabled. Command mode: admin mode usage guide: if detailed information about pim can...
Page 472: 16.5
472 16.5 dvmrp 16.5.1 introduction to dvmrp distance vector multicast routing protocol (dvmrp) is a dense mode multicast routing protocol. It employs a rip like route exchange mechanism to establish a forwarding broadcast tree for each source, then a truncated broadcast tree (short path tree to the ...
Page 473: 16.5.2 Dvmrp
473 way like the rip. That is to say, route advertisements are sent between dvmrp neighbors periodically (every 60 seconds by default). The routing information in the dvmrp route selection table is used to establish the source distribution tree, which can be used to determine which neighbor can reac...
Page 474
474 [no] ip dvmrp enable dvmrp; the “ no ip dvmrp enable ” command disables dvmrp (required) 2. Configure connectivity with cisco routers/switches cisco does not really implemented dvmrp, but provides connectivity with dvmrp. As cisco routers/switches send report packet but not probe packets, neighb...
Page 475: 16.5.2.2 Dvmrp
475 ip dvmrp report-interval time_val> no ip dvmrp report-interval set the interval for sending dvmrp report messages; the “ no ip dvmrp report interval ” command restores the default setting. D. Configuring dvmrp route timeout time command explanation global mode ip dvmrp route-timeout time_val> no...
Page 476: 16.5.2.2.1
476 16.5.2.2.1 ip dvmrp cisco-compatible command: ip dvmrp cisco-compatible no ip dvmrp cisco-compatible function: enable connectivity with cisco neighbor a, b, c, d; the “ no ip dvmrp cisco-compatible ” command disables connectivity with cisco neighbors. Parameter: are the neighboring ip addresses ...
Page 477: 16.5.2.2.4
477 graft-interval ” command restores the default setting. Parameter: time_val> is the interval for sending dvmrp graft packets, ranging from 5 to 3600s. Parameter: the default interval for sending dvmrp graft messages is 5s. Command mode: global mode usage guide: if a new receiver joins that interf...
Page 478: 16.5.2.2.6
478 command mode: interface mode usage guide: when neighborhood established in dvmrp, a neighbor is considered nonsexist if no probe message from that neighbor is received in the neighbor timeout interval, and the neighborhood is terminated. Neighbor timeout interval must be greater than the interva...
Page 479: 16.5.2.2.8
479 updating report message for a route from the neighbor of the route is received in the specified interval, then the route is considered to be invalid. This interval configured must be no greater than the timeout interval for the route. Example: set the interval for sending dvmrp route report mess...
Page 480: 16.5.3 Typical
480 multicast-enabled switch. Dvmrp treats tunneling interface the same way as common physical interfaces. Example: configure a dvmrp tunnel on ethernet interface vlan1 to the remote neighbor 1.1.1.1. Switch(config-if-vlan1)#ip dvmrp tunnel 1.1.1.1 metric 10 16.5.3 typical dvmrp scenario as shown in...
Page 481: 16.5.4.1.1
481 16.5.4.1 monitor and debug commands 16.5.4.1.1 show ip dvmrp mroute command: show ip dvmrp mroute function: display the dvmrp packet forwarding entries.. Parameter: n/a. Default: not displayed. Command mode: admin mode usage guide: this command is used to display dvmrp multicast forwarding entri...
Page 482: 16.5.4.1.3
482 function: display information for dvmrp neighbors. Parameter: is the interface name, i.E. Display neighbor information of the specified interface. Default: not displayed. Command mode: admin mode example: display neighbor information of ethernet interface vlan1. Switch #show ip dvmrp neighbor vl...
Page 483: 16.5.4.1.4
483 mask. Nexthop next hop address interface the interface on which the route is discovered. Gateway gateway address metric route metric value state route state (active, hold, etc) 16.5.4.1.4 show ip dvmrp tunnel command: show ip dvmrp tunnel [ifname>] function: display information for a dvmrp tunne...
Page 484: 16.5.4.1.6
484 command mode: admin mode usage guide: if detailed information about dvmrp packets (except prune and graft) is required, this debug command can be used. Example: switch#debug ip dvmrp detail dvmrp detail debug is on switch#01: 18: 09: 35: dvmrp: received probe on vlan1 from 192.168.1.22 01: 18: 0...
Page 485: 16.6
485 02: 22: 20: 40: dvmrp: graft source 192.168.1.105, group 224.1.1.1 02: 22: 20: 40: dvmrp: send graft-ack on vlan1 to 105.1.1.2, len 16 02: 22: 20: 40: dvmrp: graft-ack vers: majorv 3, minorv 255 02: 22: 20: 40: dvmrp: graft-ack source 192.168.1.105, group 224.1.1.1 16.5.4.2 dvmrp troubleshooting...
Page 486: 16.6.2 Igmp
486 by the multicast switches, i.E., respond with membership report packets. The switches send membership query packets in regular interval, and decide whether hosts of their subnet join some group or not; on receiving quit group reports from the hosts, they send query of associated group (igmp v2) ...
Page 487
487 (2) configure igmp query parameters. A. Configure transmission interval of query packets in igmp b. Configure maximum response time for igmp queries c. Configure timeout setting for igmp queries (3) configure igmp version 2 、 disable igmp 1. Enable igmp there is no special command for enabling i...
Page 488
488 interface mode ip igmp query-interval time_val> no ip igmp query-interval set the interval for sending igmp query messages; the “ no ip igmp query interval ” command restores the default setting. Ip igmp query-max-response-time time_val> no ip igmp query-max-response-time set the maximum time fo...
Page 490: 16.6.2.2.4
490 command: ip igmp query-interval time_val> no ip igmp query-interval function: set the interval for sending igmp query messages; the “ no ip igmp query interval ” command restores the default setting. Parameter: time_val> is the interval for sending igmp query packets, ranging from 1 to 65535s. D...
Page 491: 16.6.2.2.6
491 300s. Default: the default value is 265 seconds. Command mode: interface mode usage guide: in a shared network with several routers running igmp, one switch will be selected as the querier for that shared network, the other switches act as timers monitoring the status of the querier; if no query...
Page 492: 16.6.3 Typical
492 command mode: interface mode usage guide: this command is used to provide forward compatibility between different versions. It should be noted that v1 and v2 are not interconnectable, and the same version of igmp must be ensured for the same network. Example: configure the igmp running on the in...
Page 493: 16.6.4.1.1
493 1. Monitor and debug commands 2.Igmp troubleshooting help 16.6.4.1 monitor and debug commands 16.6.4.1.1 show ip igmp groups command: show ip igmp groups [{}] function: display igmp group information. Parameter: is the interface name, i.E. Display group information of the specified interface; is...
Page 494: 16.6.4.1.3
494 switch # show ip igmp interface vlan1 vlan1 is up, line protocol is up internet address is 192.168.1.11, subnet mask is 255.255.255.0 igmp is enabled, i am querier igmp current version is v2 igmp query interval is 125s igmp querier timeout is 265s igmp max query response time is 10s inboud igmp ...
Page 495: 16.6.4.2 Igmp
495 used. Example: switch# debug ip igmp packet igmp packet debug is on switch #02: 17: 38: 58: igmp: send membership query on dvmrp2 for 0.0.0.0 02: 17: 38: 58: igmp: received membership query on dvmrp2 from 192.168.1.11 for 0.0.0.0 02: 17: 39: 26: igmp: send membership query on vlan1 for 0.0.0.0 0...
Page 496: 16.7.2 Pim-Dm
496 packets forwarding. See the equivalent cli command at 16.2.1.1.1. Users don’t need to configure the parameters. For the detailed explanation of the displayed information, see chapter 16.2.1.1.1 16.7.2 pim-dm configuration in pim-dm configuration mode, users can enable pim-dm or disable pim-dm pr...
Page 497
497 pim-sm protocol. Vlan port - specify the layer 3 port apply – apply the configuration default – disable pim-sm on the layer 3 interface click pim-sm parameter configuration. Users can configure pim-sm parameters on the layer 3 port. See the equivalent cli command at 16.4.2.2.3: hello-interval – ...
Page 498: 16.7.4 Dvmrp
498 click set router as rp candidate. Users can configure candidate rp for pim-sm. See the equivalent cli command at 16.4.2.2.5: set router as rp candidate – “yes” is used to set the switch as rp candidate; “yes” is used to cancel the switch as rp candidate port – specify layer 3 vlan id group-list ...
Page 499
499 click dvmrp parameter configuration. Users can configure dvmrp interface parameters: see the equivalent cli command at 16.5.2.2.4 and 16.5.2.2.5: vlan port - specify the layer 3 port dvmrp report metric configuration – configure dvmrp report metric for the port. See the equivalent cli command at...
Page 500: 16.7.5 Igmp
500 click dvmrp tunnel configuration. Users can create and delete dvmrp tunnel. See the equivalent cli command at 16.5.2.2.9: neighbor ip address – specify neighbor ip address metric – specify metric to neighbor vlan port –specify the layer 3 port apply – create dvmrp tunnel to neighbor delete tunne...
Page 501
501 command at 16.6.2.2.5 vlan port –specify the layer 3 port apply – apply the configuration default – restore the default settings (including acl for igmp group, igmp query interval, max-response igmp request time and igmp query timeout. If users have configured static group and join group, the st...
Page 502
502 click show ip dvmrp route. See the equivalent cli command at 16.5.4.1.3 click show ip dvmrp tunnel. See the equivalent cli command at 16.5.4.1.4.
Page 503: 17.1
503 chapter 17 vrrp configuration 17.1 introduction to vrrp vrrp (virtual router redundancy protocol) is a redundancy protocol. It uses a backup mechanism to increase reliability of the router (or the layer 3 switch) to connect the outside network. It is designed for the local area network which sup...
Page 504: 17.2
504 17.2 vrrp configuration 17.2.1 vrrp configuration task sequence 1. Create/delete virtual router (required) 2. Configure vrrp virtual ip address and vrrp interface (required) 3. Enable/disable virtual router (required) 4. Configure vrrp authentication (optional) 5. Configure vrrp accessorial para...
Page 505: 17.2.2.1 Router
505 ip vrrp authentication mode text no ip vrrp authentication mode configure authentication mode of vrrp messages sent by the current interface; the “ no ip vrrp authentication mode ” command restores the default authentication mode. Ip vrrp authentication string string> no ip vrrp authentication s...
Page 506: 17.2.2.2 Virtual-Ip
506 command mode: global mode usage guide: this command is used to create or delete the virtual router. The virtual router is identified by the sequence numbers. Users have to create the virtual router before they configure the virtual router parameters. Example: configure the virtual router with se...
Page 507: 17.2.2.4 Enable
507 switch(config-router-vrrp)# interface vlan 1 17.2.2.4 enable command: enable function: enable the vrrp command mode: vrrp mode usage guide: enable the virtual router. Users have to configure the vrrp virtual ip address and the vrrp interface before they enable the vrrp. After this configuration,...
Page 508: 17.2.2.8 Preempt
508 the routers in the same standby group should set to the same authentication mode. Example: set the vrrp authentication mode to plain text mode. Switch(config)#interface vlan 1 switch(config-if-vlan1)# ip vrrp authentication mode text 17.2.2.7 vrrp authentication string command: ip vrrp authentic...
Page 509
509 no priority function: configure vrrp priority; the “ no priority ” command restores to its default value 100. Ip owner’s vrrp priority is always 255. Parameter: value> is the vrrp priority, valid range is 1 to 255. Command mode: vrrp mode default: the vrrp priority for the backup routers (or the...
Page 510: 17.2.2.11 Circuit-Failover
510 users can set greater adver_interval value or set greater preempt delay time. Example: set vrrp timer to 3 seconds switch(config-router-vrrp)# advertisement-interval 3 17.2.2.11 circuit-failover command: circuit-failover ifname> value_reduced> no circuit-failover function: configure the vrrp mon...
Page 511: 17.2.4.1.1 Show
511 fig 17-1 typical vrrp application topology switcha and switchb are layer 3 lan switches in the same standby group. Set switcha to master switch. The configuration steps are listed below: switcha: switcha(config)#interface vlan 1 switcha (config-if-vlan1)# ip address 10.1.1.5 255.255.255.0 switch...
Page 512: 17.2.4.1.2 Debug
512 interface is vlan2 priority is 100 advertisement interval is 1 sec preempt mode is true vrid state is initialize virtual ip is 10.1.10.1 (ip owner) interface is vlan1 configured priority is 255, current priority is 255 advertisement interval is 1 sec preempt mode is true circuit failover interfa...
Page 513: 17.2.4.2 Vrrp
513 17.2.4.2 vrrp troubleshooting help vrrp may not work properly due to bad physical connection or wrong configuration. Users can troubleshoot the problems by following the guide below: make sure the physical connection is good use “show interfaces status” command to make sure the interface and lin...
Page 514: Chapter 18 Cluster Network
514 chapter 18 cluster network management 18.1 introduction to cluster network management cluster network management is an in-band configuration management. Unlike cli, snmp and web config which implement a direct management of the target switches through a management workstation, cluster network ma...
Page 515: 18.2
515 18.2 basic cluster network management configuration 18.2.1 cluster network management configuration sequence enable or disable cluster function create cluster create or delete cluster configure private ip address pool for member switches of the cluster add or remove a member switch configure att...
Page 516
516 3 . configure attributes of the cluster in the commander switch 4. Configure attributes of the cluster in the candidate switch 5. Remote cluster network management command explanation global mode cluster commander [vlan] no cluster commander create or delete a cluster cluster ip-pool no cluster ...
Page 517: 18.2.2.1 Cluster Run
517 18.2.2 cluster configuration commands 18.2.2.1 cluster run command: cluster run no cluster run function: enable cluster function; the “ no cluster run ” command disables cluster function. Command mode: global mode default: cluster function is disabled by default. Usage guide: this command enable...
Page 518: 18.2.2.3 Cluster
518 function: sets interval of sending cluster registration packet; the “ no cluster register timer ” command restores the default setting. Parameter: is interval of sending cluster registration packet in seconds, valid range is 30 to 65535. Command mode: global mode default: cluster register timer ...
Page 519: 18.2.2.5 Cluster
519 parameter: is the cluster’s name; is the vlan of the layer 3 device which the cluster belongs to. If it is omitted, the cluster belongs to vlan1. Command mode: global mode default: there is no cluster by default. Usage guide: this command sets the switch as a commander switch and creates a clust...
Page 520: 18.2.2.6 Cluster
520 18.2.2.6 cluster auto-add command: cluster auto-add enable no cluster auto-add enable function: when this command is executed in the commander switch, the newly discovered candidate switches will be added to the cluster as a member switch automatically; the “ no cluster auto-add enable ” command...
Page 521
521 usage guide: this command is used to configure the commander switch remotely. Users have to telnet the commander switch by passing the authentication. The command “ exit ” is used to quit the configuration interface of the commander switch. If this command is executed in the commander switch, an...
Page 522: 18.2.2.11 Cluster Holdtime
522 keyword source address or destination address startup-config startup configuration file nos.Img system file boot.Rom system startup file command mode: admin mode usage guide: the commander switch sends the remote upgrade command to the member switch. The member switch is upgraded and reset. If t...
Page 523
523 no cluster heartbeat function: in the commander switch, set interval of sending heartbeat packets among the switches of the cluster; the “ no cluster heartbeat ” command restores the default setting. Parameter: is the interval of heartbeat of the cluster, valid range is 1 to 65535. Command mode:...