- DL manuals
- Accton Technology
- Wireless Access Point
- WA6102X
- User Manual
Accton Technology WA6102X User Manual
Summary of WA6102X
Page 1
User guide wlan 11a+b/g access point 2.4ghz/5ghz wireless access point model: wa6102x / wa6102y accton.
Page 2
User guide guide 2.4ghz/5ghz wireless access point ieee 802.11g and 802.11a dual-band access point with 1 10/100base-tx (rj-45) port.
Page 3
I c ompliances federal communication commission interference statement this equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a class b digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the fcc rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a r...
Page 4
C ompliances ii high power radars are allocated as primary users (meaning they have priority) of the 5250-5350 mhz and 5650-5850 mhz bands. These radars could cause interference and /or damage to the access point when used in canada. The term “ic:” before the radio certification number only signifie...
Page 5
C ompliances iii important! Before making connections, make sure you have the correct cord set. Check it (read the label on the cable) against the following: power cord set u.S.A. And canada the cord set must be ul-approved and csa certified. The minimum specifications for the flexible cord are: - n...
Page 6
C ompliances iv veuillez lire à fond l'information de la sécurité suivante avant d'installer l’appareil: avertissement: l’installation et la dépose de ce groupe doivent être confiés à un personnel qualifié. • ne branchez pas votre appareil sur une prise secteur (alimentation électrique) lorsqu'il n'...
Page 7
C ompliances v bitte unbedingt vor dem einbauen des geräts die folgenden sicherheitsanweisungen durchlesen (germany) : warnung: die installation und der ausbau des geräts darf nur durch fachpersonal erfolgen. • das gerät sollte nicht an eine ungeerdete wechselstromsteckdose angeschlossen werden. • d...
Page 8
C ompliances vi stromkabel . Dies muss von dem land, in dem es benutzt wird geprüft werden: u.S.A und canada der cord muß das ul gepruft und war das csa beglaubigt. Das minimum spezifikation fur der cord sind: - nu. 18 awg - nicht mehr als 2 meter, oder 16 awg. - der typ sv oder sj - 3-leiter der co...
Page 9
Vii t able of c ontents 1 introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1 package checklist . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2 hardware description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3 component description . ...
Page 10
1-1 chapter 1 introduction the 2.4ghz/5ghz wireless access point is an ieee 802.11a/g access point that provides transparent, wireless high-speed data communications between a wired lan and fixed, portable or mobile devices equipped with an 802.11a, 802.11b or 802.11g wireless adapter. This solution...
Page 11: Package Checklist
Introduction 1-2 the access point supports a 54 mbps half-duplex connection to ethernet networks for each active channel . Package checklist the 2.4ghz/5ghz wireless access point package includes: • one 2.4ghz/5ghz wireless access point • one category 5 network cable • one rs-232 console cable • one...
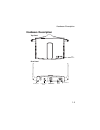
Page 12: Hardware Description
Hardware description 1-3 hardware description top panel rear panel wlan a wlan g led indicators security slot rj-45 port, poe connector reset button console port 5 vdc power socket antennas.
Page 13
Introduction 1-4 component description antennas the access point includes integrated diversity antennas for wireless communications. A diversity antenna system uses two identical antennas to receive and transmit signals, helping to avoid multipath fading effects. When receiving, the access point che...
Page 14
Hardware description 1-5 security slot the access point includes a kensington security slot on the rear panel. You can prevent unauthorized removal of the access point by wrapping the kensington security cable (not provided) around an unmovable object, inserting the lock into the slot, and turning t...
Page 15
Introduction 1-6 console port this port is used to connect a console device to the access point through a serial cable. This connection is described under “console port pin assignments” on page b-4. The console device can be a pc or workstation running a vt-100 terminal emulator, or a vt-100 termina...
Page 16: Features and Benefits
Features and benefits 1-7 reset button this button is used to reset the access point or restore the factory default configuration. If you hold down the button for less than 5 seconds, the access point will perform a hardware reset. If you hold down the button for 5 seconds or more, any configuration...
Page 17: Applications
Introduction 1-8 • advanced security through 64/128/152-bit wired equivalent protection (wep) encryption, ieee 802.1x port authentication, wi-fi protected access (wpa), remote authentication via radius server, and mac address filtering features to protect your sensitive data and authenticate only au...
Page 18
Applications 1-9 • temporary lans for special projects or peak times trade shows, exhibitions and construction sites which need temporary setup for a short time period. Retailers, airline and shipping companies that need additional workstations for a peak period. Auditors who require workgroups at c...
Page 19: System Defaults
Introduction 1-10 system defaults the following table lists some of the access point’s basic system defaults. To reset the access point defaults, use the cli command “reset configuration” from the exec level prompt. Feature parameter default identification system name meap administration user name a...
Page 20
System defaults 1-11 mac authentication mac local mac authentication session timeout 0 seconds (disabled) local mac system default allowed local mac permission allowed 802.1x authentication status disabled broadcast key refresh 0 minutes (disabled) session key refresh 0 minutes (disabled) reauthenti...
Page 21
Introduction 1-12 system logging syslog disabled logging host disabled logging console disabled ip address / host name 0.0.0.0 logging level informational logging facility type 16 ethernet interface speed and duplex auto wireless interface 802.11a iapp enabled ssid meap turbo mode disabled status en...
Page 22
System defaults 1-13 wireless security 802.11a authentication type open system wep encryption disabled wep key length 128 bits wep key type hexadecimal wep transmit key number 1 wep keys null wpa configuration mode all clients wpa key management wpa authentication over 802.1x multicast cipher wep wi...
Page 23
Introduction 1-14 wireless security 802.11b/g authentication type open system wep encryption disabled wep key length 128 bits wep key type hexadecimal wep transmit key number 1 wep keys null wpa configuration mode all clients wpa key management wpa authentication over 802.1x multicast cipher wep fea...
Page 24
2-1 chapter 2 hardware installation 1. Select a site – choose a proper place for the access point. In general, the best location is at the center of your wireless coverage area, within line of sight of all wireless devices. Try to place the access point in a position that can best cover its basic se...
Page 25
Hardware installation 2-2 3. Lock the access point in place – to prevent unauthorized removal of the access point, you can use a kensington slim microsaver security cable (not included) to attach the access point to a fixed object. 4. Connect the power cord – connect the power adapter to the access ...
Page 26
Hardware installation 2-3 6. Connect the ethernet cable – the access point can be wired to a 10/100 mbps ethernet through a network device such as a hub or a switch. Connect your network to the rj-45 port on the back panel with category 3, 4, or 5 utp ethernet cable. When the access point and the co...
Page 27
Hardware installation 2-4.
Page 28
3-1 chapter 3 network configuration the wireless solution supports a stand-alone wireless network configuration as well as an integrated configuration with 10/100 mbps ethernet lans. Wireless network cards, adapters, and access points can be configured as: • ad hoc for departmental, soho or enterpri...
Page 29: Network Topologies
Network configuration 3-2 network topologies ad hoc wireless lan (no ap or bridge) an ad hoc wireless lan consists of a group of computers, each equipped with a wireless adapter, connected via radio signals as an independent wireless lan. Computers in a specific ad hoc wireless lan must therefore be...
Page 30
Network topologies 3-3 infrastructure wireless lan the access point also provides access to a wired lan for wireless workstations. An integrated wired/wireless lan is called an infrastructure configuration. A basic service set (bss) consists of a group of wireless pc users, and an access point that ...
Page 31
Network configuration 3-4 infrastructure wireless lan for roaming wireless pcs the basic service set (bss) defines the communications domain for each access point and its associated wireless clients. The bss id is a 48-bit binary number based on the access point’s wireless mac address, and is set au...
Page 32
Network topologies 3-5 a wireless infrastructure can also support roaming for mobile workers. More than one access point can be configured to create an extended service set (ess). By placing the access points so that a continuous coverage area is created, wireless users within this ess can roam free...
Page 33: General Specifications
4 -1 chapter 4 specifications general specifications maximum channels 802.11a: us & canada: 13 (normal mode), 5 (turbo mode) japan: 4 (normal mode), 1 (turbo mode) etsi: 11 channels (normal mode), 4 (turbo mode) taiwan: 8 (normal mode), 3 (turbo mode) 802.11b/g: fcc/ic: 1-11 ,1 (turbo mode) , etsi: ...
Page 34
Specifications 4 -2 network configuration infrastructure operating frequency 802.11a: 5.15 ~ 5.25 ghz (lower band) us/canada, japan 5.25 ~ 5.35 ghz (middle band) us/canada 5.725 ~ 5.825 ghz (upper band) us/canada 5.50 ~ 5.70 ghz europe 5.25 ~ 5.35 ghz (middle band) taiwan 5.725 ~ 5.825 ghz (high ban...
Page 35
General specifications 4 -3 led indicators pwr (power), ethernet link (ethernet link/activity), .11a and .11g (wireless link/activity) network management web-browser, rs232 console, telnet, snmp temperature operating: 0 to 50 ° c (32 to 122 ° f) storage: 0 to 70 ° c (32 to 158 ° f) humidity 15% to 9...
Page 36
5-1 chapter 5 system configuration before continuing with advanced configuration, first complete the initial configuration steps described in chapter 4 to set up an ip address for the access point. The access point can be managed by any computer using a web browser (internet explorer 5.0 or above, o...
Page 37: Advanced Configuration
System configuration 5-2 the information in this chapter is organized to reflect the structure of the web screens for easy reference. However, we recommend that you configure a user name and password as the first step under advanced configuration to control management access to this device (page 5-3...
Page 38
Advanced configuration 5-3 system log controls logging of error messages; sets the system clock via sntp server or manual configuration 5-36 radio interface 1 configures the ieee 802.11a interface 5-42 radio settings configures radio signal parameters, such as radio channel, transmission rate, and b...
Page 39
System configuration 5-4 system identification the system information parameters for the access point can be left at their default settings. However, modifying these parameters can help you to more easily distinguish different devices in your network. You should set a service set identification (ssi...
Page 40
Advanced configuration 5-5 cli commands for system identification – enter the global configuration mode, and use the system name command to specify a new system name. Enter the wireless configuration mode (either 11a or 11g), and use the ssid command to set the service set identifier. Then return to...
Page 41
System configuration 5-6 tcp / ip settings configuring the access point with an ip address expands your ability to manage the access point. A number of access point features depend on ip addressing to operate. Note: you can use the web browser interface to access ip addressing only if the access poi...
Page 42
Advanced configuration 5-7 dhcp client (enable) – select this option to obtain the ip settings for the access point from a dhcp (dynamic host configuration protocol) server. The ip address, subnet mask, default gateway, and domain name server (dns) address are dynamically assigned to the access poin...
Page 43
System configuration 5-8 cli commands for tcp/ip settings – from the global configuration mode, enter the interface configuration mode with the interface ethernet command. Use the ip dhcp command to enable the dhcp client, or no ip dhcp to disable it. To manually configure an address, specify the ne...
Page 44
Advanced configuration 5-9 radius remote authentication dial-in user service (radius) is an authentication protocol that uses software running on a central server to control access to radius-aware devices on the network. An authentication server contains a database of user credentials for each user ...
Page 45
System configuration 5-10 primary radius server setup – configure the following settings to use radius authentication on the access point. • ip address: specifies the ip address or host name of the radius server. • port: the udp port number used by the radius server for authentication messages. (ran...
Page 46
Advanced configuration 5-11 cli commands for radius – from the global configuration mode, use the radius-server address command to specify the address of the primary or secondary radius servers. (the following example configures the settings for the primary radius server.) configure the other parame...
Page 47
System configuration 5-12 pppoe settings the access point can use a point-to-point protocol over ethernet (pppoe) connection, or tunnel, for management traffic between the access point and a remote pppoe server (typically at an isp). Examples of management traffic that may be initiated by the access...
Page 48
Advanced configuration 5-13 confirm password – use this field to confirm the pppoe password. Pppoe service name – the service name assigned for the pppoe tunnel. The service name is normally optional, but may be required by some service providers. (range: 1-63 alphanumeric characters) ip allocation ...
Page 49
System configuration 5-14 authentication wireless clients can be authenticated for network access by checking their mac address against the local database configured on the access point, or by using a database configured on a central radius server. Alternatively, authentication can be implemented us...
Page 50
Advanced configuration 5-15 • local mac: the mac address of the associating station is compared against the local database stored on the access point. The local mac authentication section enables the local database to be set up. • radius mac: the mac address of the associating station is sent to a c...
Page 51
System configuration 5-16 - update: enters the specified mac address and permission setting into the local database. • mac authentication table: displays current entries in the local mac database. Note: client station mac authentication occurs prior to the ieee 802.1x authentication procedure config...
Page 52
Advanced configuration 5-17 the 802.1x eap packets are also used to pass dynamic unicast session keys and static broadcast keys to wireless clients. Session keys are unique to each client and are used to encrypt and correlate traffic passing between a specific client and the access point. You can al...
Page 53
System configuration 5-18 • session key refresh rate: the interval at which the access point refreshes unicast session keys for associated clients. (range: 0-1440 minutes; default: 0 means disabled) • 802.1x re-authentication refresh rate: the time period after which a connected client must be re-au...
Page 54
Advanced configuration 5-19 cli commands for local mac authentication – use the mac-authentication server command from the global configuration mode to enable local mac authentication. Set the default for mac addresses not in the local table using the address filter default command, then enter mac a...
Page 55
System configuration 5-20 cli commands for radius mac authentication – use the mac-authentication server command from the global configuration mode to enable remote mac authentication. Set the timeout value for re-authentication using the mac-authentication session-timeout command. Be sure to also c...
Page 56
Advanced configuration 5-21 cli commands for 802.1x authentication – use the 802.1x supported command from the global configuration mode to enable 802.1x authentication. Set the session and broadcast key refresh rate, and the re-authentication timeout. To display the current settings, use the show a...
Page 57
System configuration 5-22 filter control the access point can employ vlan id and network traffic frame filtering to control access to network resources and increase security. Native vlan id – the vlan id assigned to wireless clients that are not assigned to a specific vlan by radius server configura...
Page 58
Advanced configuration 5-23 a vlan id (1-4095) is assigned to a client after successful authentication using ieee 802.1x and a central radius server. The user vlan ids must be configured on the radius server for each user authorized to access the network. If a user does not have a configured vlan id...
Page 59
System configuration 5-24 • enable: blocks wireless-to-wireless communications between clients through the access point. Ap management filter – controls management access to the access point from wireless clients. Management interfaces include the web, telnet, or snmp. • disabled: allows management ...
Page 60
Advanced configuration 5-25 to view the current vlan settings, use the show system command. Ap#show system system information =========================================================== serial number : a252014354 system up time : 0 days, 1 hours, 28 minutes, 9 seconds system name : meap system locat...
Page 61
System configuration 5-26 cli commands for bridge filtering – use the filter local-bridge command from the global configuration mode to prevent wireless-to-wireless communications through the access point. Use the filter ap-manage command to restrict management access from wireless clients. To confi...
Page 62
Advanced configuration 5-27 snmp you can use a network management application such as hp’s openview to manage the access point via the simple network management protocol (snmp) from a network management station. To implement snmp management, the access point must have an ip address and subnet mask, ...
Page 63
System configuration 5-28 location – a text string that describes the system location. (maximum length: 20 characters) contact – a text string that describes the system contact. (maximum length: 255 characters) community name (read only) – defines the snmp community access string that has read-only ...
Page 64
Advanced configuration 5-29 cli commands for snmp – use the snmp-server enable server command from the global configuration mode. To set read/write and read-only community names, use the snmp-server community command. Use the snmp-server location and snmp-server contact commands to indicate the phys...
Page 65
System configuration 5-30 administration changing the password management access to the web and cli interface on the access point is controlled through a single user name and password. You can also gain additional access security by using control filters (see “filter control” on page 5-22). To prote...
Page 66
Advanced configuration 5-31 cli commands for the user name and password – use the username and password commands from the cli configuration mode. Ap(config)#username bob 6-21 ap(config)#password admin 6-22 ap#.
Page 67
System configuration 5-32 upgrading firmware you can upgrade new access point software from a local file on the management workstation, or from an ftp or tftp server. New software may be provided periodically from your distributor. After upgrading new software, you must reboot the access point to im...
Page 68
Advanced configuration 5-33 if you need to download from an ftp or tftp server, take the following additional steps: • obtain the ip address of the ftp or tftp server where the access point software is stored. • if upgrading from an ftp server, be sure that you have an account configured on the serv...
Page 69
System configuration 5-34 firmware upgrade remote – downloads an operation code image file from a specified remote ftp or tftp server. After filling in the following fields, click start upgrade to proceed. • new firmware file: specifies the name of the code file on the server. The new firmware file ...
Page 70
Advanced configuration 5-35 cli commands for downloading software from a tftp server – use the copy tftp file command from the exec mode and then specify the file type, name, and ip address of the tftp server. When the download is complete, the dir command can be used to check that the new file is p...
Page 71
System configuration 5-36 system log the access point can be configured to send event and error messages to a system log server. The system clock can also be synchronized with a time server, so that all the messages sent to the syslog server are stamped with the correct time and date. Enabling syste...
Page 72
Advanced configuration 5-37 logging console – enables the logging of error messages to the console. Logging level – sets the minimum severity level for event logging. The system allows you to limit the messages that are logged by specifying a minimum severity level. The following table lists the err...
Page 73
System configuration 5-38 cli commands for system logging – to enable logging on the access point, use the logging on command from the global configuration mode. The logging level command sets the minimum level of message to log. Use the logging console command to enable logging to the console. Use ...
Page 74
Advanced configuration 5-39 configuring sntp simple network time protocol (sntp) allows the access point to set its internal clock based on periodic updates from a time server (sntp or ntp). Maintaining an accurate time on the access point enables the system log to record meaningful dates and times ...
Page 75
System configuration 5-40 enable daylight saving – the access point provides a way to automatically adjust the system clock for daylight savings time changes. To use this feature you must define the month and date to begin and to end the change from standard time. During this period the system clock...
Page 76
Advanced configuration 5-41 cli commands for the system clock – the following example shows how to manually set the system time when sntp server support is disabled on the access point. Ap(config)#no sntp-server enable 6-29 ap(config)#sntp-server date-time 6-30 enter year: 2003 enter month: 10 enter...
Page 77: Radio Interface
System configuration 5-42 radio interface the ieee 802.11a and 802.11g interfaces include configuration options for radio signal characteristics and wireless security features. The configuration options are nearly identical, and are therefore both covered in this section of the manual. The access po...
Page 78
Radio interface 5-43 radio settings (802.11a) the ieee 802.11a interface operates within the 5 ghz band, at up to 54 mbps in normal mode or up to 108 mbps in turbo mode. Enable – enables radio communications on the access point. (default: enabled) turbo mode – the normal 802.11a wireless operation m...
Page 79
System configuration 5-44 radio channel – the radio channel that the access point uses to communicate with wireless clients. When multiple access points are deployed in the same area, set the channel on neighboring access points at least four channels apart to avoid interference with each other. For...
Page 80
Radio interface 5-45 beacon interval – the rate at which beacon signals are transmitted from the access point. The beacon signals allow wireless clients to maintain contact with the access point. They may also carry power-management information. (range: 20-1000 tus; default: 100 tus) data beacon rat...
Page 81
System configuration 5-46 the access points contending for the medium may not be aware of each other. The rts/cts mechanism can solve this “hidden node problem.” (range: 0-2347 bytes: default: 2347 bytes) cli commands for the 802.11a wireless interface – from the global configuration mode, enter the...
Page 82
Radio interface 5-47 ap#show interface wireless a 6-107 wireless interface 802.11a information ========================================================== ----------------identification---------------------------- description : enterprise 802.11a access point ssid : r&d turbo mode : on channel : 42 (...
Page 83
System configuration 5-48 radio settings (802.11g) the ieee 802.11g standard operates within the 2.4 ghz band at up to 108 mbps (include turbo mode) . Also note that because the ieee 802.11g standard is an extension of the ieee 802.11b standard, it allows clients with 802.11b wireless network cards ...
Page 84
Radio interface 5-49 set to the same as that used by the access point to which it is linked. (range: 1-11; default: 1) auto channel select – enables the access point to automatically select an unoccupied radio channel. (default: enabled) maximum supported rate – the maximum data rate at which a clie...
Page 85
System configuration 5-50 cli commands for the 802.11 g wireless interface – from the global configuration mode, enter the interface wireless g command to access the 802.11g radio interface. Set the interface ssid using the ssid command and, if required, configure a name for the interface using the ...
Page 86
Radio interface 5-51 ap#show interface wireless g 6-107 wireless interface information =========================================================== ----------------identification----------------------------- description : enterprise 802.11g access point ssid : r&d channel : 11 (auto) status : enabled...
Page 87
System configuration 5-52 security the access point is configured by default as an “open system,” which broadcasts a beacon signal including the configured ssid. Wireless clients can read the ssid from the beacon, and automatically reset their ssid to allow immediate connection to the nearest access...
Page 88
Radio interface 5-53 the security mechanisms that may be employed depend on the level of security required, the network and management resources available, and the software support provided on wireless clients. A summary of wireless security considerations is listed in the following table. Note: alt...
Page 89
System configuration 5-54 wired equivalent privacy (wep) wep provides a basic level of security, preventing unauthorized access to the network and encrypting data transmitted between wireless clients and the access point. Wep uses static shared keys (fixed-length hexadecimal or alphanumeric strings)...
Page 90
Radio interface 5-55 if you choose to use wep shared keys instead of an open system, be sure to define at least one static wep key for user authentication and data encryption. Also, be sure that the wep shared keys are the same for each client in the wireless network. Authentication type setup – set...
Page 91
System configuration 5-56 shared key setup – select 64 bit, 128 bit, or 152 bit key length. Note that the same size of encryption key must be supported on all wireless clients. 152 bit key length is only supported on 802.11a radio. (default: 128 bit) key type – select the preferred method of enterin...
Page 92
Radio interface 5-57 cli commands for wep shared key security – from the 802.11a or 802.11g interface configuration mode, use the authentication command to enable wep shared-key authentication and the encryption command to enable wep encryption. Use the multicast-cipher command to select wep cipher ...
Page 93
System configuration 5-58 note: the index and length values used in the key command must be the same values used in the encryption and transmit-key commands. Cli commands for wep over 802.1x security – from the 802.11a or 802.11g interface configuration mode, use the authentication command to select...
Page 94
Radio interface 5-59 wi-fi protected access (wpa) wpa employs a combination of several technologies to provide an enhanced security solution for 802.11 wireless networks. The access point supports the following wpa components and features: ieee 802.1x and the extensible authentication protocol (eap)...
Page 95
System configuration 5-60 note: to implement wpa on wireless clients requires a wpa-enabled network card driver and 802.1x client software that supports the eap authentication type that you want to use. Windows xp provides native wpa support, other systems require additional software. Temporal key i...
Page 96
Radio interface 5-61 multicast and broadcast traffic must be the same for all clients, therefore it restricts encryption to a wep key. When access is opened to both wpa and wep clients, no authentication is provided for the wep clients through shared keys. To support authentication for wep clients i...
Page 97
System configuration 5-62 wpa key management – wpa can be configured to work in an enterprise environment using ieee 802.1x and a radius server for user authentication. For smaller networks, wpa can be enabled using a common pre-shared key for client authentication with the access point. • wpa authe...
Page 98
Radio interface 5-63 wpa pre-shared key type – if the wpa pre-shared-key mode is used, all wireless clients must be configured with the same key to communicate with the access point. • hexadecimal: enter a key as a string of 64 hexadecimal numbers. • alphanumeric: enter a key as an easy-to-remember ...
Page 99
System configuration 5-64 cli commands for wpa pre-shared key security – from the 802.11a or 802.11g interface configuration mode, use the authentication command to set the access point to “open system.” use the wep encryption command to enable all types of encryption. To enable wpa to be required f...
Page 100
Radio interface 5-65 cli commands for wpa over 802.1x security – from the 802.11a or 802.11g interface configuration mode, use the authentication command to set the access point to “open system.” use the wep encryption command to enable all types of encryption. Use the wpa-clients command to set wpa...
Page 101: Status Information
System configuration 5-66 status information the status page includes information on the following items: access point status the ap status window displays basic system configuration settings, as well as the settings for the wireless interface. Menu description page ap status displays configuration ...
Page 102
Status information 5-67 ap system configuration – the ap system configuration table displays the basic system configuration settings: • system up time: length of time the management agent has been up. • mac address: the physical layer address for this device. • system name: name assigned to this sys...
Page 103
System configuration 5-68 • 802.1x: shows if ieee 802.1x access control for wireless clients is enabled. Cli commands for displaying system settings – to view the current access point system settings, use the show system command from the exec mode. To view the current radio interface settings, use t...
Page 104
Status information 5-69 station status the station status window shows the wireless clients currently associated with the access point. The station configuration page displays basic connection information for all associated stations as described below. Note that this page is automatically refreshed ...
Page 105
System configuration 5-70 • associated: shows if the station has been successfully associated with the access point. Once authentication is completed, stations can associate with the current access point, or reassociate with a new access point. The association procedure allows the wireless system to...
Page 106
Status information 5-71 event logs the event logs window shows the log messages generated by the access point and stored in memory. The event logs table displays the following information: • log time: the time the log message was generated. • event level: the logging level associated with this messa...
Page 107
System configuration 5-72 • access point was set to “shared key authentication,” but a client sent an authentication frame for “open system.” • wep keys do not match: when the access point uses “shared key authentication,” but the key used by client and access point are not the same, the frame will ...