- DL manuals
- Airlink101
- Wireless Access Point
- HOMEPLUG TURBO
- User Manual
Airlink101 HOMEPLUG TURBO User Manual
Summary of HOMEPLUG TURBO
Page 1
User’s manual homeplug turbo wireless g access point.
Page 2
1 index fcc part 68....................................................................................................................................................... 2 fcc part 15.......................................................................................................................
Page 3
2 fcc part 68 this equipment complies with part 68 of the fcc rules. On the bottom of this equipment is a label that contains the fcc registration number and ringer equivalence number (ren) for this equipment. You must provide this information to the telephone company upon request. The ren is useful...
Page 4
3 fcc part 15 the modem generates and uses radio frequency energy. If it is not installed and used properly in strict accordance with the user's manual, it may cause interference with radio and television reception. The modem has been tested and found to comply with the limits for class b computing ...
Page 5
4 chapter 1 introduction congratulations on your purchase of an instant homeplug turbo wireless g ap. The homeplug turbo wireless g ap is the perfect option to connect a small group of pcs or small wireless clients. Integrated wireless to powerline networks, the device can extend large coverage and ...
Page 6
5 http web-based management ‧firmware upgrade by ui ‧password protected access 1.3 system requirements 1) personal computer (pc) 2) pentium ii 233 mhz processor minimum 3) 32 mb ram minimum 4) 20 mb of free disk space minimum 5) ethernet network interface controller (nic) rj45 port 6) internet brows...
Page 7
6 chapter 2 installation this chapter offers information about installing your router. If you are not familiar with the hardware or software parameters presented here, please consult your service provider for the values needed. 2.1 checklist check the shipping box carefully to ensure that the conten...
Page 8
7 2.2 the front leds led state description power on press the button to power one the router. Op flashing the router running well. Pl flashing when the device detect other powerline devices on link flashing tx or rx activity lan 1-4 off no link these four lan (local area network) ports are where you...
Page 9
8 connector description power connect to power cord. Lan (1-4) router is successfully connected to a device through the corresponding port (1, 2, 3 or 4). If the led is flashing, the router is actively sending or receiving data over that port. Antenna there are two kind of connecter, fixed or r/sma ...
Page 10
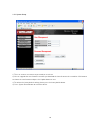
9 chapter 3 configuration 3.1 determine your connection settings before you configure the router; you need to know the connection information supplied by your service provider. 3.2 connecting the powerline extender to your network unlike a simple hub or switch, the setup of the powerline extender co...
Page 11
10 you can use " quick setup" to setup the device, and choose the connect mode you prefer..
Page 12
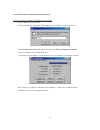
11 3.3.1 lan interface configuration you can set static ip address at here...
Page 13
12 3.4.1 wireless settings wireless mode support auto, 802.11b only, 802.11g only, disable modes. Ssid the identifier set for the wireless network. You can change the ssid. Only devices with the same ssid can interconnect. Channel id the channel number is used for wireless network. The channel setti...
Page 14
13 3.4.2 wireless security the authentication type supports “open system”, “shared key”, “wpa-psk”, “wpa2-psk” and "wpa-psk/wpa2-psk"..
Page 15
14 3.4.3 wireless advance you can change some wireless advanced parameters at this page. Keep the setting as the default if you are not the professional user..
Page 16
15 3.4.4 wireless mac acl you can set which wireless client’s mac addresses is allowed or rejected to link to the router via wireless. For advanced security issue, you can enable this function..
Page 17
16 3.5.1 system setup 1) the user account can rename or password can reset here. 2) you can upgrade the new firmware here while you download the latest firmware via our website. Click browser to choose the new firmware and press the update button to start. 3) to retrieve the factory default settings...
Page 18
17 3.6.1 tcp/ip settings for windows operating system 1. How can i find my ip address in windows 95, 98, or me? ‧click on start, then click on run. ‧the run dialogue box will appear. Type winipcfg in the window as shown then click ok ‧the ip configuration window will appear, displaying your ethernet...
Page 19
18 2. How can i find my ip address in windows 2000/xp? ‧click on start and select run. ‧type cmd then click ok. ‧from the command prompt, enter ipconfig. It will return your ip address, subnet mask, and default router. ‧type exit to close the command prompt. ‧make sure you take note of your computer...
Page 20
19 3. How can i assign a static ip address in windows 98/me? ‧from the desktop, right-click on the network neighborhood icon (win me - my network places) and select properties. ‧highlight tcp/ip and click the properties button. If you have more than 1 adapter, then there will be a tcp/ip “binding” f...
Page 21
20 ‧click specify an ip address. ‧enter in an ip address that is on the same subnet as the lan ip address on your router. Example: if the router ´s lan ip address is 192.168.0.1, make your ip address 192.168.0.X where x is between 2-99. Make sure that the number you choose is not in use on the netwo...
Page 22
21 ‧click on the dns configuration tab. ‧click enable dns. Type in a host (can be any word). Under dns server search order, enter the lan ip address of your router (192.168.0.1). Click add. ‧click ok twice. ‧when prompted to reboot your computer, click yes. After you reboot, the computer will now ha...
Page 23
22 4. How can i assign a static ip address in windows 2000? ‧right-click on my network places and select properties. ‧right-click on the local area connection which represents your network card and select properties. ‧highlight internet protocol (tcp/ip) and click properties..
Page 24
23 ‧click use the following ip address and enter an ip address that is on the same subnet as the lan ip address on your router. Example: if the router ´s lan ip address is 192.168.0.1, make your ip address 192.168.0.X where x = 2-99. Make sure that the number you choose is not in use on the network....
Page 25
24 chapter 4. Powerline networking utility note. The device can auto detect the other powerline bridges which plug in the same power circuit, you don’t need to use this powerline utility except you want to encryption all the powerline devices as the same group or you can not access the other compute...
Page 26
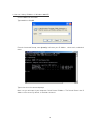
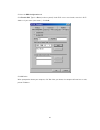
25 4.2 windows configuration utility in order to run the utility, double-click the utility icon. Figure 2 shows the main screen of the configuration utility. This screen shot shows a powerline ethernet device connected as a local device and other powerline ethernet devices as remote devices. Figure ...
Page 27
26 figure 3 : main screen with low-speed powerline ethernet device local 4.3 user interface 4.3.1 main screen the main screen essentially provides a list of all powerline ethernet devices logically connected to the computer where the utility is running. The top panel shows all local powerline ethern...
Page 28
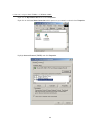
27 figure 4: multiple local device connection.
Page 29
28 the lower panel displays all the powerline ethernet devices, discovered on the current logical network (remote devices). Displayed immediately above this panel is the number of remote devices found, the type of logical network (public or private), and a message area that reports connectivity and ...
Page 30
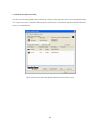
29 the add button is used to add a remote device to your network that is not on the displayed list in the lower panel, for example, a device currently on another logical network. Users are advised to locate the passwords for all devices they wish to manage and add them to the local logical network b...
Page 31
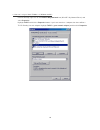
30 figure 7: main screen of the configuration utility 4.3.2 privacy screen the privacy dialog screen provides a means for managing the local network and providing additional security. All powerline ethernet devices are shipped using a default logical network (network name), which is normally “homepl...
Page 32
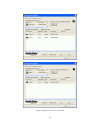
31 figure 8: privacy screen the set local device only button is used to change the network name (network password) for the local device only. After doing this, all the devices seen on the main panel prior to this will no longer be able to communicate or respond to the computer, as they will be on a ...
Page 33
32 ‧ operating system type/version ‧ host network name ‧ user name ‧ mac address of all nics (network interface card) ‧ identify versions of all driver dlls and libraries used (ndis) and optionally ‧ powerline ethernet device chipset manufacturer name (85mbps version only) ‧ mac firmware version (85...
Page 34
33 ‧ adapter last known rate ‧ adapter last known network ‧ homeplug chipset manufacturer name ‧ date device last scanned ‧ mac firmware version (85mbps version only) the diagnostics information displayed may be saved to a text file for later emailing to technical support of a manufacturer, or print...
Page 35
34 4.5 troubleshooting this section will introduce how to solve the connect problem for management remote powerline devices. 4.5.1 when the remote powerline devices can not connect or access? When you find that the computer can not connect to another or the remote powerline device can not found by p...
Page 36
35 step 2: connect to the other powerline bridge or router directly which can not detect at main tab at step 1. On the privacy page, you can change the private network name as the same name with other powerline device or just press the use default (public network). Please press the set local device ...
Page 37
36 appendix a glossary address mask a bit mask used to select bits from an internet address for subnet addressing. The mask is 32 bits long and selects the network portion of the internet address and one or more bits of the local portion. Sometimes called subnet mask. Aal5 atm adaptation layer - thi...
Page 38
37 customer premises equipment located in a user's premises. Dhcp (dynamic host configuration protocol) dhcp is software that automatically assigns ip addresses to client stations logging onto a tcp/ip network. Dhcp eliminates having to manually assign permanent ip addresses to every device on your ...
Page 39
38 hop count a measure of distance between two points on the internet. It is equivalent to the number of routers that separate the source and destination. Html hypertext markup language - the page-coding language for the world wide web. Html browser a browser used to traverse the internet, such as n...
Page 40
39 mib management information base - a collection of objects can be accessed via a network management protocol, such as snmp and cmip (common management information protocol). Nat network address translation - a proposal for ip address reuse, where the local ip address is mapped to a globally unique...
Page 41
40 route the path that network traffic takes from its source to its destination. The route a datagram may follow can include many routers and many physical networks. In the internet, each datagram is routed separately. Router a system responsible for making decisions about which of several paths net...
Page 42
41 static ip addresses a static ip address is an ip address permanently assigned to computer in a tcp/ip network. Static ip addresses are usually assigned to networked devices that are consistently accessed by multiple users, such as server pcs, or printers. If you are using your router to share you...
Page 43
42 virtual connection (vc) a link that seems and behaves like a dedicated point-to-point line or a system that delivers packets in sequence, as happens on an actual point-to-point network. In reality, the data is delivered across a network via the most appropriate route. The sending and receiving de...
Page 44
43 appendix b cabling / connection network cables connect pcs in an ethernet network category 5, called "cat5" for short is commonly used type of network cable today. Cat 5 cables are tipped with rj-45 connectors, which fit into rj-45 port. Straight-through vs. Crossover cables: lan connection: to c...