- DL manuals
- Anritsu
- Measuring Instruments
- ms9710b
- Operation Manual
Anritsu ms9710b Operation Manual
Summary of ms9710b
Page 1
Document no.: m-w1283ae-14.0 anritsu corporation ms9710b optical spectrum analyzer operation manual for safety and warning information, please read this manual before attempting to use the equipment. Keep this manual with the equipment. 14th edition.
Page 2: Danger
Ii safety symbols to prevent the risk of personal injury or loss related to equipment malfunction, anritsu corporation uses the following safety symbols to indicate safety-related information. Ensure that you clearly understand the meanings of the symbols before using the equipment. Some or all of t...
Page 3: Warning
For safety iii warning 1. Always refer to the operation manual when working near locations at which the alert mark shown on the left is attached. If the advice in the operation manual is not followed there is a risk of personal injury or reduced equipment performance. The alert mark shown on the lef...
Page 4: Warning
For safety iv warning 3. Laser radiation warning • never look directly into the cable connector on the equipment nor into the end of a cable connected to the equipment. There is a risk of injury if laser radiation enters the eye. • the laser safety label is attached to the equipment for safety use a...
Page 5: Caution
For safety v caution 1. Always remove the mains power cable from the power outlet before replacing blown fuses. There is a risk of electric shock if fuses are replaced with the power cable connected. Always use new fuses of the type and rating specified on the rear panel of the instrument. There is ...
Page 6: Caution
For safety vi the laser in this equipment is classified as class 1 according to the iec 60825-1:2001 specifications, or as class i according to the 21 cfr 1040.10:1995 specifications. These classes of lasers are safe under reasonably foreseeable operating conditions. Table 1 standard name model numb...
Page 7: Laser Radiation Markings
For safety vii laser radiation markings.
Page 8: Caution
For safety viii caution this equipment uses a poly-carbomonofluoride lithium battery to backup the memory. This battery must be replaced by service personnel when it has reached the end of its useful life; contact the anritsu sales section or your nearest representative. Note: the battery used in th...
Page 9: Equipment Certificate
Ix equipment certificate anritsu corporation certifies that this equipment was tested before shipment using calibrated measuring instruments with direct traceability to public testing organizations recognized by national research laboratories, including the national institute of advanced industrial ...
Page 10
X notes on export management this product and its manuals may require an export license/approval by the government of the product's country of origin for re-export from your country. Before re-exporting the product or manuals, please contact us to confirm whether they are export-controlled items or ...
Page 11
Xi crossed-out wheeled bin symbol equipment marked with the crossed-out wheeled bin symbol complies with council directive 2002/96/ec (the “weee directive”) in european union. For products placed on the eu market after august 13, 2005, please contact your local anritsu representative at the end of t...
Page 12: Ce Conformity Marking
Xii ce conformity marking anritsu affixes the ce conformity marking on the following product(s) in accordance with the council directive 93/68/eec to indicate that they conform to the emc and lvd directive of the european union (eu). Ce marking 1. Product model model: ms9710b optical spectrum analyz...
Page 13: C-Tick Conformity Marking
Xiii c-tick conformity marking anritsu affixes the c-tick marking on the following product(s) in accordance with the regulation to indicate that they conform to the emc framework of australia/new zealand. C-tick marking 1. Product model model: ms9710b optical spectrum analyzer 2. Applied standards e...
Page 14: Power Line Fuse Protection
Xiv power line fuse protection for safety, anritsu products have either one or two fuses in the ac power lines as requested by the customer when ordering. Single fuse: a fuse is inserted in one of the ac power lines. Double fuse: a fuse is inserted in each of the ac power lines. Example 1: an exampl...
Page 15: About This Manual
I 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 appendix index about this manual this manual explains the operation, calibration and maintenance of the ms9710b optical spectrum analyzer. The basic functions and operations of this analyzer are outlined in section 4 “operation.” for an in-depth explanation of each menu screen refer ...
Page 16: Contents
Ii for safety ................................................................. Iii about this manual ................................................... I section 1 introduction ........................................... 1-1 1.1 ms9710b optical spectrum analyzer ........................ 1-2 1.2 ma...
Page 17: Contents
Iii 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 appendix index section 4 operation ............................................... 4-1 4.1 connecting optical fiber ............................................ 4-2 4.2 switching power on ................................................... 4-3 4.3 basic function and example of the ...
Page 18: Contents
Iv contents . Section 7 maintenance and troubleshooting ..... 7-1 7.1 periodic maintenance ................................................. 7-2 7.2 storage precautions ................................................... 7-4 7.3 transporting .............................................................
Page 19: Section 1
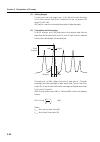
1-1 this section is an outline of the ms9710b optical spectrum analyzer and re- lated equipments. 1.1 ms9710b optical spectrum analyzer ............. 1-2 1.2 main functions ................................................ 1-3 1.3 features ........................................................... 1...
Page 20: 1.1
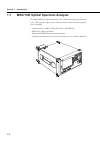
1-2 section 1 introduction 1.1 ms9710b optical spectrum analyzer the ms9710b optical spectrum analyzer is a diffraction grating spectrum ana- lyzer. This rugged, compact unit is ideal for field as well as laboratory applica- tions, including: • characterization of led’s, fabry-perot lds, and dfb lds...
Page 21: 1.2
1-3 1.2 main functions optical levels in the wavelength range from 600 to 1750 nm can be measured with a maximum resolution of 0.07 nm. The level measurement range is -90 to +10 dbm and this can be increased to +20 dbm by using the internal attenuator. This performance varies with the measurement ra...
Page 22: 1.3
1-4 section 1 introduction 1.3 features the features of the ms9710b are listed below. (1) fast and accurate measurement of polarization dependency and level lin- earity in 1.55 µ m band (2) wide dynamic range (70 db), high sensitivity (–90 dbm) and measure- ment up to +20 dbm using optical attenuato...
Page 23: 1.4
1-5 1.4 standard configuration standard accessories of the ms9710b optical spectrum analyzer • ac power cord • t3.15 fuses power supply • operation manual (this manual) • front cover • printer paper • remote control operation manual • labview measuring instruments driver for rs-232c • labview measur...
Page 24: 1.5
1-6 section 1 introduction 1.5 options two or more than two of those ms9710b-02, -05, -13, -14 optional equipments cannot be installed simultaneity. (1) ms9710b-02 white light source a low-cost white light source can be installed in the main unit for mea- surements not requiring wide dynamic range. ...
Page 25: 1.6
1-7 1.6 related parts rs-232c cable (9 p to 9 p) ...................................... J0654a rs-232c cable (9 p to 25 p) .................................... J0655a gpib cable ............................................................... J0007 replaceable optical connector • fc connector ..........
Page 26: 1.7
1-8 section 1 introduction 1.7 main specifications to obtain stable operation, allow at least 5 minutes to elapse after power-on. The following specifications are guaranteed 2 hours after power-on. If the in- strument is out-of-specification, perform automatic optical-axis alignment (auto align) and...
Page 27
1-9 level no ref. Light source with ref. Light source measurement level range 0 to 30 ° c 0 to 30 ° c (600 to 1000 nm) –65 to +10 dbm (1100 to 1600 nm) –70 to +20 dbm (1000 to 1250 nm) –85 to +10 dbm (1250 to 1600 nm) –90 to +10 dbm (1600 to 1700 nm) –75 to +10 dbm (1700 to 1750 nm) –55 to +10 dbm m...
Page 28
1-10 section 1 introduction others sweep speed 0.5 s max./500 nm (vbw: 10 hz, normal dynamic range mode, center wavelength: 1200 nm, from sweep start to sweep end, no optical input, 501 sampling points max.) white light source (option 02) optical output ≥ –59 dbm/1 nm (multi mode/fiber input) wavele...
Page 29
1-11 dimensions and mass dimensions 177 (h) x 320 (w) x 350 (d) mm mass ≤ 16.5 kg 1.7 main specifications.
Page 30: 1.8
1-12 section 1 introduction 1.8 user interface the measurement settings of the ms9710b are screens from the displays called “cards” which can be flipped back and force like a stuck of cards. The cards are selected by pressing the f1 to f7 card selection keys along the bottom of the screen. Each card...
Page 31
1-13 for the names of each part of each screen, refer to section 2.5 “screen dis- plays,” for more details on each screen, refer to section 5 “explanation of screens.” to improve the functionality, the ms9710b also has a number of keys corre- sponding to major functions called shortcut keys. These c...
Page 32
1-14 section 1 introduction prior f 1 f 2 f 3 f 4 f 5 f 6 f 7 f 8 f 7 f 6 f 5 f 4 f 3 f 2 f 1 marker select screen prior f 1 f 2 f 3 f 4 f 5 f 6 f 7 f 8 f 7 f 6 f 5 f 4 f 3 f 2 f 1 zone marker screen ..
Page 33: Section 2
2-1 this section describes each part of the front and back panels of the ms9710b optical spectrum analyzer. Section 4 “operation” gives examples of the main measurement functions. Section 5 “explanation of screens” gives a detailed explanation of how to use each card screen. 2.1 unpacking .............
Page 34: 2.1
2-2 section 2 front and back panel description 2.1 unpacking remove the main unit and accessories from the packing case and check that all the parts described on the enclosed packing list are present. If anything is miss- ing or damaged, please contact anritsu corporation or your sales representativ...
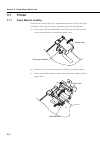
Page 35: 2.2
2-3 2.2 instrument overview this section describes the names and functions of each parts of the ms9710b. (5) printer (6) back panel (8) front panel (9) floppy disk drive(fdd) (1) power switch (7) optical input connector (2) feed key (3) copy key (4) handle 2.2 instrument overview front and back pane...
Page 36
2-4 section 2 front and back panel description (1) power switch (2) feed key feed feeds printer paper while pressed (3) copy key copy prints hard copy of screen to internal or external printer when pressed section 5.14 (4) handles handles are on each side of this analyzer for carriage always carry t...
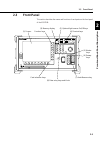
Page 37: 2.3
2-5 2.3 front panel this section describes the names and functions of each parts on the front panel of the ms9710b. Ms9710b o p t i c a l s p e c t r u m a n a l y z e r 0 . 6 – 1 . 7 5 µ m copy feed prior f 1 f 2 f 3 f 4 f 5 f 6 f 7 f 8 f 7 f 6 f 5 f 4 f 3 f 2 f 1 printer memory a b optical input m...
Page 38
2-6 section 2 front and back panel description (1) screen in addition to displaying the measured spectrum, the screen displays the cards for selecting this analyzer’s functions. Eight cards of which names are aligned along the bottom of the screen can be displayed using the card selection keys f1 to...
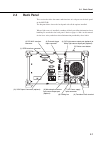
Page 39: 2.4
2-7 2.4 back panel this section describes the names and functions of each parts on the back panel of the ms9710b. The diagram below shows the back panel with all the options installed. When a light source is installed, a number of labels providing information about handling are attached to the back ...
Page 40
2-8 section 2 front and back panel description (1) gpib interface connector this connector connects the external computer or printer. (2) rs-232c interface connector this connector connects the external computer, also used as dedicated interface for the mg9637/mg9638 in the tracking measurement. (3)...
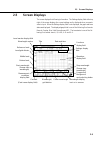
Page 41: 2.5
2-9 2.5 screen displays the screen displays the following information. The settings display field at the top right of the screen displays the current settings and is displayed when a numeric value is input. When the settings display field is not displayed, the graph and trace status are displayed. T...
Page 42: 2.6
2-10 section 2 front and back panel description 2.6 shortcut keys center sets center wavelength section 5.1 span sets wavelength sweep width section 5.1 center sets spectrum peak point to center wavelength section 5.1 ref lvl sets level of spectrum peak point to reference level section 5.2 log (div)...
Page 43: 2.7
2-11 2.7 sweep keys single executes one sweep measurement from start wavelength to stop wavelength repeat executes repeated sweep measurement from start wavelength to stop wave- length stop stops measurement 2.8 marker keys marker select displays marker selection screen section 5.15 zone marker disp...
Page 44: 2.9
2-12 section 2 front and back panel description 2.9 data entry keys and knob knob data entry keys 7 8 9 data entry 4 5 6 1 2 3 0 . – bs 2.9.1 data entry keys the data entry keys include the numerics 0 to 9 keys, the period (.) key, the minus (–) symbol key, and the backspace key (bs). They are used ...
Page 45
2-13 (3) the input value is confirmed when the units are selected and the new cen- ter wavelength is displayed on the screen. (4) the set value can be changed until either another shortcut key is pressed or until a different function card is selected. To input another value from the data entry keys ...
Page 46
2-14 section 2 front and back panel description ..
Page 47: Section 3
3-1 3 this section describes the preparations that must be made before using ms9710b optical spectrum analyzer. These steps are important to ensure to keep this analyzer functions properly and safely. 3.1 installation conditions ..................................... 3-2 3.2 power connection ...........
Page 48: 3.1
3-2 section 3 preparations before use 3.1 installation conditions orientation use this analyzer in a horizontal position. Ms9710c o p t i c a l s p e c t r u m a n a l y z e r 0 . 6 – 1 . 7 5 µ m copy feed prior f 1 f 2 f 3 f 4 f 5 f 6 f 7 f 8 f 7 f 6 f 5 f 4 f 3 f 2 f 1 printer memory a b optical i...
Page 49: 3.2
3-3 3 3.2 power connection this section describes the procedures for supplying power. 3.2.1 power requirements for normal operation of the instrument, observe the power voltage range de- scribed below. Power source voltage range frequency 100 vac system 100 to 120 v 47.5 to 63 hz 200 vac system 200 ...
Page 50: Caution
3-4 section 3 preparations before use caution if an emergency arises causing the instrument to fail or malfunction, disconnect the instrument from the power supply by either turning off the power switch on the front panel (switch to the (o) side), or by pulling out the power cord or the power inlet....
Page 51: 3.3
3-5 3 3.3 vibration precautions the heart of this analyzer is a diffraction grating with a precision on the order of several microns. When using, maintaining and transporting this analyzer, it is important to take precautions against excessive vibration and mechanical shock. Always carry this analyz...
Page 52: 3.5
3-6 section 3 preparations before use 3.5 floppy disk (fd) the ms9710b uses 3.5-inch fd to save data. When attempting to save data to a new fd, the fd must be formatted first. This analyzer formats fds in the ms- dos format. Both double-density (2dd) and high-density (2hd) fds can be used. High- den...
Page 53: 3.6
3-7 3 3.6 optical attenuator the optical attenuator can be switched between insert (on) and not insert (off) by opening the level scale card and pressing the f2 card selection key. When the attenuator is off, the maximum input power is +10 dbm; when it is on, the maximum input power is +20 dbm. The ...
Page 54: 3.7
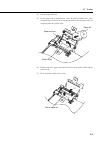
3-8 section 3 preparations before use 3.7 printer 3.7.1 paper manual loading check that the printer paper roll is installed in the printer at the top left of the back panel. If the paper has run out, load more paper as described below. (1) on the upper side of the ms9710b, rotate the printer cover b...
Page 55
3-9 3 (4) lift the paper roll lever. (5) set the paper roll as shown below. Note the paper feed direction. Next, return the paper roll lever to its original position so that the paper roll is set straight against the printer head. Printer head paper roll lever paper roll (4) (5) (6) pull the end of ...
Page 56: Caution
3-10 section 3 preparations before use (8) feed the end of the paper roll through the slit of the printer cover. (9) return the printer cover back to its original position, and then lock it by rotating the printer cover button clockwise or counterclockwise. Slit (9) (8) caution only use the specifie...
Page 57: 3.8
3-11 3 3.8 optional light sources wavelength reference light source and sld light source the level reference light (sld light source) for measuring transmission charac- teristics is output from port 1, and the reference light for wavelength calibration is output from port 2. White light source the w...
Page 58: 3.9
3-12 section 3 preparations before use 3.9 changing optical connector 3.9.1 replaceable optical connectors unless otherwise specified, the fc connector (ms9710b-37) is supplied as the standard connector with the main unit. The following connectors are also avail- able and can be changed by the opera...
Page 59
3-13 3 3.9.2 connectors not replaceable at user site please contact your service representative for replacing the following connec- tors. Name model e2000 (diamond) connector ms9710b-27 3.9 changing optical connector.
Page 60: 3.10
3-14 section 3 preparations before use 3.10 changing fuses if a fuse blows, first find the reason why and perform the repair. Then change the fuse following the steps in the caution below. Caution 1. Before changing a fuse, always disconnect the power cord from the power outlet. If the fuse is chang...
Page 61: Section 4
4-1 this section describes the basic functions and how to operate the ms9710b optical spectrum analyzer. It explains some measurement procedures as well as the composition of the operation panels and screens. Refer to section 5 “ex- planation of screen” for more details on each screen. 4.1 connectin...
Page 62: 4.1
4-2 section 4 operation 4.1 connecting optical fiber open the cover of the optical input connector and connect the optical fiber to the connector. Optical input ma x + 10d bm (at t o ff) ma x + 20d bm (at t o n) marker sweep optical input connector optical fiber caution 1. Before connecting the opti...
Page 63: 4.2
4-3 4.2 switching power on (1) when using the 3-wire power cord, supplied as an accessory with the con- version adapter, always either connect the green wire from the conver- sion adapter to ground, or ground the frame ground terminal on the back panel, before supplying power to the ms9710b. (2) che...
Page 64: 4.3
4-4 section 4 operation 4.3 basic function and example of the operation as an example of a basic operation, measurement of an ld light source is de- scribed. An fp-ld with a peak level of about –20 to –10 dbm in the 1.55 µ m wavelength band is used. (1) return the measurement conditions to the facto...
Page 65
4-5 prior f 1 f 2 f 3 f 4 f 5 f 6 f 7 f 8 f 7 f 6 f 5 f 4 f 3 f 2 f 1 (5) set the span (sweep width) to 50 nm. Section 5.1 (a) either press the f1 key to select the wavelength card and press the span function key f 2 , or press the span key span of shortcut keys. Actual value of span is displayed in...
Page 66
4-6 section 4 operation (6) set the resolution to 0.1 nm. Section 5.3 (a) either press the f3 key to select the res/vbw/avg card and press the res function key f 1 , or press the res key res of shortcut keys. The current resolution is displayed in the settings display field. The value of resolution ...
Page 67
4-7 (7) set the video bandwidth (vbw) to 1 khz. Section 5.3 (a) either press the f3 key to select the res/vbw/avg card and press the vbw function key f 2 , or press the vbw key vbw of shortcut keys. The current vbw is displayed in the settings display field. The vbw can be selected from the function...
Page 68
4-8 section 4 operation (8) execute the measurement. Section 2.7 press the single key single of sweep keys to execute one measurement sweep and display the measured waveform on the screen. Prior f 1 f 2 f 3 f 4 f 5 f 6 f 7 f 8 f 7 f 6 f 5 f 4 f 3 f 2 f 1 (9) set the peak level wavelength as the cent...
Page 69
4-9 (10) set the peak level as the reference level. Section 2.6 press the peak → ref level ref lvl of shortcut keys to set the peak level to the reference level. Prior f 1 f 2 f 3 f 4 f 5 f 6 f 7 f 8 f 7 f 6 f 5 f 4 f 3 f 2 f 1 4.3 basic function and example of the operation.
Page 70
4-10 section 4 operation (11) set the span (sweep width) to 20 nm. Section 5.1 (a) either press the f1 key to select the wavelength card and press the span function key f 2 , or press the span key span of shortcut keys. Actual value of span is displayed in the settings display field. The value of sp...
Page 71
4-11 (13) use the repeat sweep function. Section 2.7 press the repeat key repeat of the sweep keys to take measurements continu- ously using the repeat sweep function, and change measurement conditions during a repeat sweep to optimize the displayed trace. Alternatery, the auto measurement function ...
Page 72: 4.4
4-12 section 4 operation 4.4 analyzing measured waveforms this section explains how to analyze the waveform obtained in the previous section. (1) execute rms analysis. The basic operation of rms analysis, which is one of the analysis function of the ms9710b, is as follows. Section 5.5 press the f5 k...
Page 73
4-13 (2) execute peak search. Section 5.4 find the peak point of the waveform using peak search. Either press the f4 key to select the peak/dip search card and press the peak search func- tion key f 1 , or press the peak search key peak search of shortcut keys. The peak point on the waveform is foun...
Page 74
4-14 section 4 operation (3) use the zone marker. Section 2.8 and 5.16 press the zone marker key zone marker of shortcut keys to display the zone marker is displayed on the screen. Press zone width function key f 2 to set the zone marker to a width of about 1 grid division on the screen, and use zon...
Page 75: 4.5
4-15 4.5 saving and recalling measured waveforms this section explains how to save and recall measured waveforms. (1) format the floppy disk. This analyzer can save measured data to fd. In addition, previously saved data can be read and analyzed. Section 5.7 before saving the waveform to fd, the fd ...
Page 76
4-16 section 4 operation (2) save measured data. To save measured data, press f7 key to select the save/recall card, and press the save function key f 1 to input the file name or number. Section 5.7 prior f 1 f 2 f 3 f 4 f 5 f 6 f 7 f 8 f 7 f 6 f 5 f 4 f 3 f 2 f 1 this example explains how to save t...
Page 77
4-17 (3) recall saved data. For an example of recalling data, recall the data saved in the example of (2) “save measured data.” to recall saved data, press the f7 to select the save/ recall card, and press the recall function key f 2 . A list of saved files is displayed; move the cursor to the recal...
Page 78: 4.6
4-18 section 4 operation 4.6 printing waveforms when the copy key copy is pressed, the screen displayed at that instant is hard copied by either the internal printer or an external printer. A sample of printout is shown below. To set the print output destination, press the f7 key to display other ca...
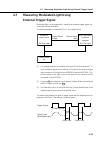
Page 79: 4.7
4-19 4.7 measuring modulated light using external trigger signal modulated light can be measured by inputting an external trigger signal syn- chronized with the modulation. The setting example of measuring dfb-ll is as shown below. Optical signal output optical signal input signal output sg mg9001a ...
Page 80: 4.8
4-20 section 4 operation 4.8 peak hold measurement when a synchronization signal cannot be obtained for measuring modulated light, the modulated light can be measured by setting a gate time longer than the modulation cycle and holding the peak point for that interval. This measure- ment method is ca...
Page 81: 4.9
4-21 4.9 use of the optional light sources there are four optional light sources, white light source, and wavelength refer- ence and sld light sources. White light source (option 02) this light source is light from a small halogen lamp coupled to the optical fiber and output. The light has wide rang...
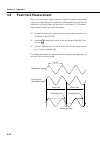
Page 82: 4.10
4-22 section 4 operation 4.10 transmission characteristics the transmission characteristics can be measured by using the light source with wide range spectrum and the subtraction function with memory a and memory b. In the beginning, a measuring system without device under test (dut) is measured and...
Page 83: 4.11
4-23 4.11 tracking measurement the mg9637/mg9638 tunable light source can be used for tracking measure- ment in combination with the ms9710b. The tracking measurement and output wavelength of the tunable light source is controlled by the ms9710b; the side sending the set wavelength (mg9637/mg9638) a...
Page 84
4-24 section 4 operation 4.11.3 execute tracking wavelength calibration (adjust to tls) calibrate the tracking wavelength of the ms9710b and the mg9637/mg9638. Connect the ms9710b and the mg9637/mg9638 directly with an optical fiber cord. After setting the center wavelength of the ms9710b to the cen...
Page 85
4-25 4.11.4 tracking measurement now, necessary setup has been completed for the tracking measurement. Refer to section 4.10. “transmission characteristics” for more details on measure- ment of transmission. An example of filter measurement by tracking measurement is as shown below. Prior f 1 f 2 f ...
Page 86
4-26 section 4 operation ..
Page 87: Section 5
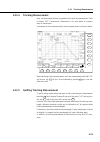
5-1 this section explains how to select functions of ms9710b optical spectrum analyzer from its screens. The most-commonly-used functions have dedicated keys (shortcut keys) on the front panel. This analyzer has a number of function screens each called a “card”, that are switched using the card sele...
Page 88
5-2 section 5 explanation of screens the tabs of foreground cards appear at the bottom of the ms9710b screen. The background cards are displayed by pressing the f8 key to select the change button . Prior f 1 f 2 f 3 f 4 f 5 f 6 f 7 f 8 f 7 f 6 f 5 f 4 f 3 f 2 f 1 5.1 setting wavelength (wavelength c...
Page 89
5-3 5.4 peak/dip search (peak/dip search card f4 ) ................... 5-22 5.4.1 searching for peak points (peak search f 1 ) .... 5-22 5.4.2 searching for dip points (dip search f 2 ) .......... 5-22 5.4.3 searching for next largest/smallest peak/dip point ( ↓ : next f 4 ) ...........................
Page 90
5-4 section 5 explanation of screens the tabs of background cards appear at the bottom of the ms9710b screen. The foreground cards are displayed by pressing the f8 key to select the change button . Prior f 1 f 2 f 3 f 4 f 5 f 6 f 7 f 8 f 7 f 6 f 5 f 4 f 3 f 2 f 1 5.8 setting graph type (graph card f...
Page 91
5-5 5.10.4 interval measurement (interval f 4 ) .................... 5-92 5.10.5 tracking measurement (tls tracking f 5 ) ........ 5-93 5.10.6 power monitor measurement (power monitor f 6 ) ............................................. 5-94 5.11 setting titles (title card f4 ) .........................
Page 92
5-6 section 5 explanation of screens the screen shown below is displayed when the marker select key marker select of the marker keys is pressed. To select a foreground card, press any of the f1 to f7 card selection keys. To go back to the graph card (the f1 key) press f8 key. Prior f 1 f 2 f 3 f 4 f...
Page 93
5-7 the screen shown below is displayed when the zone marker key zone marker of the marker keys is pressed. To select a foreground card, press any of the f1 to f7 card selection keys. To go back to the graph card (the f1 key) press f8 key. Prior f 1 f 2 f 3 f 4 f 5 f 6 f 7 f 8 f 7 f 6 f 5 f 4 f 3 f ...
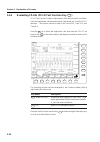
Page 94: 5.1
5-8 section 5 explanation of screens 5.1 setting wavelength (wavelength card f1 ) the wavelength card displayed by pressing the f1 key is used to set the mea- surement conditions related to wavelength. (horizontal axis of the screen) prior f 1 f 2 f 3 f 4 f 5 f 6 f 7 f 8 f 7 f 6 f 5 f 4 f 3 f 2 f 1 ...
Page 95
5-9 5.1.2 setting sweep width (span function key f 2 ) this key sets the wavelength range to be displayed on the horizontal axis of the screen. This wavelength range is called the sweep width or span. When the span is changed, the center wavelength is centered and the start and stop wave- lengths ar...
Page 96
5-10 section 5 explanation of screens 5.1.3 setting start wavelength (start function key f 4 ) this key sets the wavelength displayed at the left side of the screen. This wave- length is called the start wavelength. When the start wavelength is changed, the stop wavelength remains unchanged but the ...
Page 97
5-11 5.1.5 switching marker frequency display [option] (mkr value wl/freq function key f 6 ) this key switches the wavelength value of the trace marker and the analysis part to the frequency value. The display items that can be switched between wavelength and frequency dis- play are the trace marker...
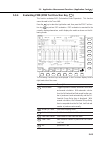
Page 98: 5.2
5-12 section 5 explanation of screens 5.2 setting level (level scale card f2 ) the level scale card displayed by pressing the f2 key used to set measure- ment conditions related to the power level. (vertical axis of the screen) prior f 1 f 2 f 3 f 4 f 5 f 6 f 7 f 8 f 7 f 6 f 5 f 4 f 3 f 2 f 1 5.2.1 ...
Page 99
5-13 5.2.2 setting reference level (ref level function key f 2 ) this key sets the reference display level (ref value displayed on vertical axis) when the vertical axis is set to log scale. However, when linear scale is se- lected, the origin of the vertical axis becomes 0 and it is not possible to ...
Page 100
5-14 section 5 explanation of screens 5.2.3 setting linear scale (linear level function key f 4 ) this key sets the vertical axis to a liner unit, and sets the value [w] of top end of the scale. (1) setting linear scale press the f2 key to select the level scale card, then press the linear level fun...
Page 101: Caution
5-15 5.2.4 optical attenuator on/off (opt. Att off/on function key f 6 ) this key sets whether or not to insert the optical attenuator, permitting measure- ment of high-level optical inputs. The optical attenuator is inserted each time the function key f 6 is pressed. At on, the optical attenuator i...
Page 102: 5.3
5-16 section 5 explanation of screens 5.3 setting resolution and averaging (res/vbw/avg card f3 ) the res/vbw/avg card displayed by pressing the f3 key is used to set mea- surement conditions related to resolution, averaging, smoothing, and number of sample points. Prior f 1 f 2 f 3 f 4 f 5 f 6 f 7 ...
Page 103
5-17 5.3.1 setting resolution (res function key f 1 ) this key sets the wavelength resolution. When measuring the optical input of narrow spectra such as lds, etc., it is necessary to set a small resolution value. Moreover, when a large resolution is set for input of wide spectra such as leds, etc.,...
Page 104
5-18 section 5 explanation of screens 5.3.2 setting video band width (vbw function key f 2 ) this key sets the video bandwidth. When a wide-band vbw is set, measure- ment can be performed at high speed. Conversely, when a narrow vbw is set, sweep speeds are slower but sensitivity is improved due to ...
Page 105
5-19 5.3.4 setting sweep average (sweep average function key f 4 ) this key is used to activate the sweep avg function. A user-specified number of traces are average together and the results are displayed. This is commonly known as a “sweep-to sweep” averaging technique. This function cannot be used...
Page 106
5-20 section 5 explanation of screens 5.3.5 setting smoothing (smooth function key f 5 ) this key smooths the level of a data point based on the levels on both sides of the point. It is possible to set correction based on only the preceding and suc- ceeding points, or based on a number of data point...
Page 107
5-21 5.3.6 setting sampling points (sampling points function key f 6 ) this key sets the number of measured data points (sampling point number) within the span. When the sampling point number is small, measurement can be performed at high speed, but to measure with good resolution over a wide range,...
Page 108: 5.4
5-22 section 5 explanation of screens 5.4 peak/dip search (peak/dip search card f4 ) the peak/dip search card displayed by pressing the f4 key is used to search for peak (maximum) points and dip (minimum) point in the measured spec- trum. Prior f 1 f 2 f 3 f 4 f 5 f 6 f 7 f 8 f 7 f 6 f 5 f 4 f 3 f 2...
Page 109
5-23 5.4.3 searching for next largest/smallest peak/dip point ( ↓↓↓↓↓ : next function key f 4 ) press the f4 key to select the peak/dip search card, then press the ↓ , or next function key, f 4 to move the trace marker to the next highest peak point or next smallest dip point. This operation is the ...
Page 110
5-24 section 5 explanation of screens 5.4.6 searching for next right peak/dip point ( → → → → → : right function key f 7 ) press the f4 key to select the peak/dip search card, then press the → , or right function key, f 7 to move the trace marker to the peak or dip point to the right of the current ...
Page 111: 5.5
5-25 5.5 analyzing waveforms (analysis card f5 ) the analysis card displayed by pressing f5 key is used for analyzing mea- sured spectra. Prior f 1 f 2 f 3 f 4 f 5 f 6 f 7 f 8 f 7 f 6 f 5 f 4 f 3 f 2 f 1 5.5 analyzing waveforms (analysis card f5 ).
Page 112
5-26 section 5 explanation of screens 5.5.1 threshold analysis (threshold function key f 1 ) press the f5 key to select the analysis card, then press the threshold function key f 1 to perform threshold analysis on measured spectrum. This analysis is useful for finding the spectrum half width, etc. T...
Page 113
5-27 the cut level can be set with the data entry keys, the knob, or function keys. The following values are displayed in the functions display field at the right side of the screen and can be input using the function keys. F 1 f 2 f 3 f 4 3 db 6 db 10 db 20 db (1) calculation and processing of thre...
Page 114
5-28 section 5 explanation of screens 5.5.2 ndb-loss analysis (ndb-loss function key f 2 ) press the f5 key to select the analysis card, then press the ndb-loss function key f 2 to perform ndb-loss analysis on the measured spectrum. The ndb- loss analysis is for analysis of multimode spectra. If the...
Page 115
5-29 the cut level can be set with the data entry keys, the knob, or function keys. The following values are displayed in the functions display field at the right side of the screen and can be input using the function keys. F 1 f 2 f 3 f 4 3 db 6 db 10 db 20 db (1) calculation and processing of ndb-...
Page 116
5-30 section 5 explanation of screens 5.5.3 side mode suppression ratio analysis (smsr function key f 3 ) press the f5 key to select the analysis card, then press the smsr function key f 3 to perform a side mode suppression ratio analysis of the measured spectrum. Smsr specifies the level ratio betw...
Page 117
5-31 three side modes can be selected with the function keys as follows: function key side mode f 1 : 2nd next largest level from peak point side mode f 2 : left peak immediately to left of peak point side mode f 3 : right peak immediately to right of peak point side mode (1) calculation and process...
Page 118
5-32 section 5 explanation of screens 5.5.4 envelope analysis (envelope function key f 4 ) press the f5 key to select the analysis card, then press the envelope function key f 4 to perform an envelope analysis of the measured spectrum. This analysis finds the envelope from the peak points of several...
Page 119
5-33 the cut level can be set with the data entry keys, the knob, or the function keys. The following values are displayed in the functions display field at the right side of the screen and can be input using the function keys. F 1 f 2 f 3 f 4 3 db 6 db 10 db 20 db (1) calculation and processing of ...
Page 120
5-34 section 5 explanation of screens 5.5.5 rms analysis (rms function key f 5 ) press the f5 key to select the analysis card, then press the rms function key f 5 to perform a root mean square analysis (hereinafter referred as rms analysis) of the measured spectrum. Rms analysis is for analyzing mul...
Page 121
5-35 (1) calculation and processing of rms analysis when setting the wavelength and level of the peaks of spectrum exceeding the level which lowers from the maximum peak by the preset level to “an” and “ λ n ” (n = 1, 2, 3 ... I), you can calculate center wavelength “ λ c ” and spectrum width σ as b...
Page 122
5-36 section 5 explanation of screens 5.5.6 spectrum power analysis (spectrum power function key f 6 ) press the f5 key to select the analysis card, then press the spectrum power function key f 6 to perform a spectrum power analysis. Spectrum analysis finds the power distribution of the measured spe...
Page 123
5-37 the total power pow is found from the following equation. P ow = α∆λ r es l k where, α is the correction factor depending on the slit, res is the actual resolution and ∆λ is the sampling wavelength interval. 5.5.7 deleting analysis results (off function key f 7 ) press the f5 key to select the ...
Page 124: 5.6
5-38 section 5 explanation of screens 5.6 trace memory (trace card f6 ) the trace card f6 is used to switch the memory in which the measured data is stored or change the display (trace) method. The unit has two memories: memory a and memory b. You can use each of them individually or combine the two...
Page 125
5-39 5.6.1 selecting memory a (memory a function key f 1 ) to store the spectrum measurement data in memory a, select memory a func- tion key f 1 from trace card f6 . The screen which displays the data stored in memory a is called trace a. When selecting memory a function key f 1 while trace b is di...
Page 126
5-40 section 5 explanation of screens 5.6.7 comparing trace b–a (trace b–a function key f 7 ) press the f6 key to select the trace card, then press the trace b–a function key f 7 to subtract the trace-a data from the trace-b data and display the result when a log scale is displayed. The subtraction ...
Page 127: 5.7
5-41 5.7 saving and recalling measured data (save/recall card f7 ) the save/recall card displayed by pressing f7 key is used to save/recall mea- sured data to/from a fd. In addition to using its own file format, this analyzer can create ms-windows bitmapped and ms-dos text formats files so that the ...
Page 128
5-42 section 5 explanation of screens 5.7.1 saving measured data (save function key f 1 ) press the f7 key to select the save/recall card, then press the save function key f 1 to save the measured data to fd. The data is saved to the standard analyzer proprietary format (.Dat). To save the data in a...
Page 129
5-43 (1) saving as file name press the f7 key to select the save/recall card, then press the save func- tion key f 1 to display the following screen. Enter a file name of up to 8 alphanumeric characters using the data entry key and function keys and press the save function key f 5 to complete the sa...
Page 130
5-44 section 5 explanation of screens (2) saving as file number press the f7 key to select the save/recall card, then press the save func- tion key f 1 to display the following screen. Enter a file number using the data entry key and press the save function key f 5 to complete the saving. This assum...
Page 131
5-45 5.7.2 recalling saved data (recall function key f 2 ) press the f7 key to select the save/recall card, then press the recall function key f 2 to recall a file saved in the analyzer format from the fd. However, the files saved in bitmap format of ms-windows™ and text format of ms-dos™ cannot be ...
Page 132
5-46 section 5 explanation of screens 5.7.3 setting options (file option function key f 4 ) the following options related to saving data can be set. Saved file format the file can be saved in the analyzer format, bitmapped format or text format. File name input the file can be saved as a file name o...
Page 133
5-47 (1) selecting data addition (additional save file) when saving a file, in addition to the standard format, the file format can be selected from the following four items. The additional file name(s) has the same name as the standard format file but the extension is different. The meanings of the...
Page 134
5-48 section 5 explanation of screens 5.7.4 deleting files (file delete function key f 5 ) press the f7 key to select the save/recall card, then press the file delete func- tion key f 5 to delete a standard format file saved on the fd. Files deleted with this function cannot be recovered. Making a b...
Page 135
5-49 5.7.5 formatting floppy disk (file format function key f 6 ) press the f7 key to select the save/recall card, then press the file format function key f 6 to format the fd. When attempting to save data to a new fd, the fd must be formatted first. Note that formatting a fd erases all current data...
Page 136: 5.8
5-50 section 5 explanation of screens 5.8 setting graph type (graph card f1 ) the graph card displayed by pressing f1 key is used to select the graph display format. The user can choose from five display formats: normal, overlap, max hold, normalize, and 3d. Prior f 1 f 2 f 3 f 4 f 5 f 6 f 7 f 8 f 7...
Page 137
5-51 5.8.3 max hold display (max hold function key f 3 ) press the f1 key to select the graph card, then press the max hold function key f 3 to display the peak level at each measurement point for multiple sweeps. This is useful for monitoring the peak values of a changing spectrum. To delete the gr...
Page 138
5-52 section 5 explanation of screens 5.8.5 3d display (3d function key f 5 ) press the f1 key to select the graph card, then press the 3d function key f 5 to display repeatedly measured spectra as a 3d graph. The display format can be selected from type 1, type 2, or type 3. Prior f 1 f 2 f 3 f 4 f...
Page 139
5-53 (2) type 2 graph display format in the type 2 graph display format, wavelength is displayed on the x-axis, level on the y-axis, and time (number of times) on the z-axis. The z-axis display angle can be selected from 30 ° , 45 ° , 60 ° and 90 ° using the f 4 to f 7 function keys, respectively. P...
Page 140
5-54 section 5 explanation of screens 5.8.6 clearing graphs (clear function key f 6 ) press the f1 key to select the graph card, then press the clear function key f 6 to clear the displayed graphs. When the graphs are cleared, both memories a and b are cleared as well..
Page 141: 5.9
5-55 5.9 application measurement functions (application card f2 ) the application card displayed by pressing the f2 key has a variety of conve- nient functions for use in device and wdm system evaluations. • dfb-ld test ..... Evaluates dfb-lds • fp-ld test ......... Evaluates fp-lds (fabry-perot lds...
Page 142
5-56 section 5 explanation of screens 5.9.1 evaluating dfb-lds (dfb-ld test function key f 1 ) this function determines the smsr, spectrum width (ndb width), stop band, mode offset, and center offset, etc., from the dfb-ld spectrum. This function cannot be used with trace a&b, trace a–b, or trace b–...
Page 143
5-57 the names and descriptions of the data collected by this function is explained below. Data name description peak displays wavelength and level of peak point 2nd peak left peak displays wavelength and level for each side mode right peak ndb width width of spectrum at level ndb lower than peak po...
Page 144
5-58 section 5 explanation of screens 5.9.2 evaluating fp-lds (fp-ld test function key f 2 ) fp-ld test function is used to find the peak, rms analysis results, oscillation vertical mode number, vertical mode interval, total power, etc., from the fp-ld spectrum. This function cannot be used in the t...
Page 145
5-59 the names and descriptions of the data collected by this function is explained below. Data name description peak displays wavelength and level of peak point mean w1 center wavelength calculated by rms analysis fwhm (2.35 σ ) half width calculated by rms analysis total power total power mode (nd...
Page 146
5-60 section 5 explanation of screens 5.9.3 evaluating leds (led test function key f 3 ) this function finds the peak, center wavelength, spectrum width (ndb width), total power and power per nm, etc. This function cannot be used in the trace a&b, trace a–b, and trace b–a. Press the f2 key to select...
Page 147
5-61 the names and descriptions of the data collected by this function are explained below. Data name description peak displays wavelength and level of peak point mean w1 (ndb) center wavelength calculated by threshold analysis mean w1 (fwhm) center wavelength calculated by averaging pro- cessing nd...
Page 148
5-62 section 5 explanation of screens (2) calculation and processing mean wl (ndb) and ndb width use the same calculation method used in threshold analysis. Section 5.5 mean wl (fwhm), fwhm, total power, and pk dens (/1nm) are calcu- lated from all the measured points in the displayed spectrum. • me...
Page 149
5-63 5.9.4 evaluating pmd (pmd test function key f 4 ) this function evaluates pmd (polarization mode dispersion). This function cannot be used in the trace a&b. Press the f2 key to select the application card, then press the pdm test func- tion key f 4 to perform pmd evaluation. Pmd evaluation is e...
Page 150
5-64 section 5 explanation of screens the names and descriptions of the data collected by this function are explained below. Data name description diff. Group delay differential group delay time 1st peak wavelength of first peak in analysis range last peak wavelength of last peak in analysis range p...
Page 151
5-65 (3) measurement example the following diagram shows a setup for performing a simple pmd test. Polarization controller optical analyzer device under test (optical fiber cable, etc.) ms9710b optical spectrum analyzer sld, etc., wideband light source convert the light from a wideband light source ...
Page 152
5-66 section 5 explanation of screens (5) manual calculation measurement procedure (a) set pmd test to manual. Press the f2 key to select the application card and press the pmd function key f 4 . Select manual by pressing the auto/manual func- tion key f 1 . (b) measure the spectrum. Adjust the meas...
Page 153
5-67 5.9.5 evaluating optical amplifiers (opt. Amp test function key f 5 ) this function evaluates optical amplifiers. This function cannot be used in the trace a–b, trace b–a. Press the f2 key to select the application card, then press the opt. Amp test function key f 5 to display the following scr...
Page 154
5-68 section 5 explanation of screens the following function keys are displayed in the functions display field at right-hand side of the screen. Key name description f 1 : prmtr opens window for setting various test parameters. F 2 : method sets evaluation method. The following five meth- ods can be...
Page 155
5-69 press the f2 key to select the application card and press the opt. Amp test function key f 5 to display the prmtr function. When the prmtr function key f 1 is pressed, the following screen is displayed. Prior f 1 f 2 f 3 f 4 f 5 f 6 f 7 f 8 f 7 f 6 f 5 f 4 f 3 f 2 f 1 the following function key...
Page 156
5-70 section 5 explanation of screens the descriptions of each parameters are as follows. Parameter description nf select selects the types of noise included in the noise figure calculation. In the s-ase setting, only the beat noise between the optical signal (signal) and the amplified spontaneous e...
Page 157
5-71 parameter description o. Bpf bw sets optical passband filter bandwidth. The band- width is centered around the wavelength of the signal. O. Bpf bw can only be used when calcu- lating the total nf; it is not displayed for s-ase. Set 999 nm when the filter is not inserted. Pol loss only displayed...
Page 158
5-72 section 5 explanation of screens (1) settable range the ext. Trig delay can be set in the range of 0 to 5 s. The setting ranges of other parameters are as follows. Parameter setting range fitting span 0.10 to 100.00 [nm] masked span 0.10 to 100.00 [nm] (masked span pin loss –10.00 to 10.00 [db]...
Page 159
5-73 the descriptions of the symbols used in the formulas above are as fol- lows. λ sv : wavelength of output optical signal in vacuum [nm] v: signal frequency [hz] res real : actual resolution (calibrated by res cal) [nm] ∆ vs: frequency band of analyzer at pase measurement [hz] h: planck’s constan...
Page 160
5-74 section 5 explanation of screens (c) ase (p ase ) [dbm] is approximated by mean fitting. Set wavelength of the data point, which is one of two points innermost in the approximated data of amplified optical spectra (data obtained by removing the range set in masked span from the range set in fit...
Page 161
5-75 (d) ase (p ase ) [dbm] approximated by gauss fitting points ( λ 1 , l 1 ) and ( λ 2 , l 2 ) are used to calculate p ase ( λ s ) using a least square fit. The points ( λ 1 , l 1 ) and ( λ 2 , l 2 ) correspond to the end points of the masked span region masked span fitting span λ s λ 1 λ 2 p ase ...
Page 162
5-76 section 5 explanation of screens (3) measurement procedure and example press the key to select the application card and press the opt. Amp test function key . Press the method function key and select the evaluation method. Refer to the following pages for more details. Select each parameter. To...
Page 163
5-77 note *1 : when calibrating resolution, always use a single-mode light source such as a dfb-ld, and match the center wavelength to the peak wavelength of the dfb-ld spectrum. When the resolution setting is changed during measurement, the resolu- tion data becomes void; execute the calibration pr...
Page 164
5-78 section 5 explanation of screens (c) plzn null lvl method in this method, the optical amplifier is evaluated by eliminating polar- ization. Both input light and output light of the optical amplifier are measured. Then, the signal light is cut off from output light through the polarization nulli...
Page 165
5-79 strongly modulated light modulation signal input terminal modulation signal modulation signal input terminal output light sg signal generator ms9710b optical spectrum analyzer ext-trig dut a measurement is taken τ msec after the ext. Trig signal rising edge. This τ is called the ext. Trig delay...
Page 166
5-80 section 5 explanation of screens (e) wdm method this method is a variation on the pulse method which is useful for wdm systems. One channel in the wdm system is pulsed. The amplified optical level and the ase output level for this channel are measured using the same technique described previous...
Page 167
5-81 5.9.6 wdm evaluation (wdm f 6 ) this function is used to find the snr of signal peaks as well as the wavelength and level differences between peaks, which are important parameters in wdm analysis. A maximum of 300 peaks from the short wavelength side can be de- tected. Evaluation is performed u...
Page 168
5-82 section 5 explanation of screens there are three display modes for wdm signal analysis: multipeak, snr, and relative. (when option 10 is installed, the table display mode is added to these three modes.) the items displayed for each mode are different. To change the display mode, press the displ...
Page 169
5-83 in the snr mode, the wavelength, level, and snr of up to 8 peaks can be dis- played simultaneously. In the relative mode, the wavelength, level, and wavelength spacing, or the wavelength and level relative to a reference peak, can be displayed for up to 5 peaks simultaneously. 5.9 application m...
Page 170
5-84 section 5 explanation of screens (option) in the table mode, the wavelength, level, snr, and spacing of up to 16 peaks can be displayed simultaneously. In addition, the peak wavelength and spacing can be displayed as frequency. The frequency f is found from the wavelength λ in a vacuum using th...
Page 171
5-85 the following table lists the names of the data found by this function and the meaning. Item (key name) operation and setting next page scrolls detected-peak data display range to next page last page scrolls detected-peak data display range to previ- ous page display mode selects display mode f...
Page 172
5-86 section 5 explanation of screens === peak prmtr ========= s.Level ..... 30 db peak type ..... Max threshold threshold cut level ..... 3.0 db set the target for peaks to be analyzed up to x db below the maximum peak at s.Level in the peak prmtr window. Select whether to use the wavelength of the...
Page 173
5-87 the following table lists the names of the data found by this function and the meaning. Data name meaning no. Peak no. Appends sequential number from short wavelength side to detected peak. Wl (nm) or signal (nm) peak wavelength. Displays peak wavelength. Signal (ghz) peak wavelength. Calculate...
Page 174
5-88 section 5 explanation of screens (1) setting ranges s. Level can be set in the range from 1 to 50. ∆λ can be set in the range 0.01 to 20 nm and the peak prmtr threshold cut level can be set in the range 0.1 to 50.0 db. Ref peak no. Cannot be set outside the number of detected peaks. (2) calcula...
Page 175
5-89 when ∆λ is off, if dip type of dip prmtr is set to left, the noise level lnlin is the level of dip point b at the short wavelength side of the peak; if dip type of dip prmtr is set to right, it is the level of dip point c at the long wavelength side of the peak. When higher is set, the level of...
Page 176: 5.10
5-90 section 5 explanation of screens 5.10 special measurement modes (measure mode card f3 ) the measure mode card selected by pressing f3 key is used to set the measure- ment environment. Prior f 1 f 2 f 3 f 4 f 5 f 6 f 7 f 8 f 7 f 6 f 5 f 4 f 3 f 2 f 1 5.10.1 wide dynamic range measurement (d. Ran...
Page 177
5-91 5.10.2 peak hold measurement (peak hold function key f 2 ) the measurement method for measuring the peak level at each measurement point during the set gate time is called peak hold measurement. Peak hold measurement can be used at the same time as measurement of external modula- tion light. Pr...
Page 178
5-92 section 5 explanation of screens 5.10.3 modulated light measurement (ext. Trig function key f 3 ) by using the ext. Trigger function, it is possible for the analyzer to monitor modulated light. The signal used to modulate the light is input to the ext. Trig- ger terminal on the back panel of th...
Page 179
5-93 5.10.5 tracking measurement (tls tracking function f 5 ) tracking measurement can be performed with the mg9637/mg9638a. The output wavelength of the tunable light source is controlled from the ms9710b and tracking measurement is performed. In the tracking measurement mode, the wavelength offset...
Page 180
5-94 section 5 explanation of screens 5.10.6 power monitor measurement (power monitor function key f 6 ) this function sets this analyzer to the power monitor mode. (1) measuring total power of optical input press the f3 key to select the measure mode card, then press the power monitor function key ...
Page 181: 5.11
5-95 5.11 setting titles (title card f4 ) this function inputs titles of up to 30 characters at the top of the screen. Prior f 1 f 2 f 3 f 4 f 5 f 6 f 7 f 8 f 7 f 6 f 5 f 4 f 3 f 2 f 1 when the title card is selected by pressing the f4 key, the character selection window shown above is displayed. Us...
Page 182
5-96 section 5 explanation of screens for example, set the title “you” as follows: (1) select the title card by pressing f4 key. The character selection window is displayed in the middle of the screen. (2) use the knob to move the cursor in the character selection window to the y. (3) move the curso...
Page 183: 5.12
5-97 5.12 calibration function (cal card f5 ) the cal card displayed by pressing f5 key is used to calibrate the ms9710b. Calibration makes it possible to obtain higher-accuracy measurement results. Prior f 1 f 2 f 3 f 4 f 5 f 6 f 7 f 8 f 7 f 6 f 5 f 4 f 3 f 2 f 1 caution if this function is used wh...
Page 184
5-98 section 5 explanation of screens 5.12.1 setting wavelength offset (wl offset function key f 1 ) when the wavelength offset component is input, the spectrum is displaced hori- zontally left/right. When a positive value is input to the wavelength offset data, the displayed spectrum of the subsequ...
Page 185
5-99 5.12.3 calibrating wavelength using external wavelength reference (wl cal (ext) function key f 3 ) this function uses an external wavelength reference to calibrate wavelength. Press the f5 key to select the cal card and press the wl cal (ext) function key f 3 to display execute and cancel in th...
Page 186: Caution
5-100 section 5 explanation of screens 5.12.5 initializing wavelength calibration data (wl cal (init) function key f 5 ) this function initializes the wavelength calibration data to the factory default values. If the wavelength calibration fails for some reason, use this function to return the calib...
Page 187: 5.13
5-101 5.13 saving and recalling measurement conditions (condition card f6 ) up to five different measurement conditions can be saved to internal memory. The measurement conditions can also be returned to the factory default settings. Prior f 1 f 2 f 3 f 4 f 5 f 6 f 7 f 8 f 7 f 6 f 5 f 4 f 3 f 2 f 1 ...
Page 188: Caution
5-102 section 5 explanation of screens optical att on/off interval time dynamic range graph mod. Mode analysis/application 5.13.1 saving measurement conditions (condition save function key f 1 ) the current measurement conditions can be saved to memory number 1 to 5. Press the f6 key to select the c...
Page 189: Caution
5-103 5.13.2 recalling and initializing measurement conditions (recall function key f 2 ) this function recalls saved measurement conditions. Press the f6 key to select the condition card, then press the recall function key f 2 to display the recall screen as shown below. Prior f 1 f 2 f 3 f 4 f 5 f...
Page 190
5-104 section 5 explanation of screens 5.13.3 listing current measurement conditions (view function key f 4 ) this function displays the currently-set measurement conditions. Press the f6 key to select the condition card, then press the view function key f 4 to display condition view screen as shown...
Page 191: 5.14
5-105 5.14 other functions (others card f7 ) the following items can be set in this card: • printer parameters • display colors • gpib address • backlight on/off • system date-time • buzzer on/off prior f 1 f 2 f 3 f 4 f 5 f 6 f 7 f 8 f 7 f 6 f 5 f 4 f 3 f 2 f 1 5.14 other functions (others card f7 ...
Page 192
5-106 section 5 explanation of screens 5.14.1 setting printer (printer prmtr function key f 1 ) this function switches between the internal and external printer, and selects the type of external printer. Press the f7 key to select the others card, then press the printer prmtr function key f 1 to dis...
Page 193
5-107 5.14.2 setting gpib address (gpib address function key f 2 ) this function sets the gpib address of the ms9710b. Press the f7 key to select the others card and press the gpib address function key f 2 to input the address using the data entry keys or knob. When the data entry keys are used, pre...
Page 194
5-108 section 5 explanation of screens 5.14.3 setting date and time (date/time function key f 3 ) this function sets the date and time of the internal timer. Press the f7 key to select the others, then and press the date/time function key f 3 to display the following screen. Prior f 1 f 2 f 3 f 4 f ...
Page 195
5-109 the descriptions of each settings are as follows. Setting item descriptions display sets whether or not to display the date and time on the screen on ............ Date/time displayed off ............ Date/time not displayed date sets date time sets time 5.14 other functions (others card f7 ).
Page 196
5-110 section 5 explanation of screens 5.14.4 setting screen display color (display color function key f 4 ) this function sets the display color. Press the f7 key to select the others card, then press the display color func- tion key f 4 to display the following screen. The following function keys ...
Page 197
5-111 (1) settable range the range can be set from 0 to 7. 5.14.5 setting backlight off time (backlight function key f 5 ) this function sets the keypad idling time before the lcd screen is turned off. When the backlighting is off, it is switched on as soon as any key is pressed. Press the f7 key to...
Page 198
5-112 section 5 explanation of screens 5.14.7 setting rs-232c (rs-232c prmtr function key f 7 ) this function switches the remote-control interface to either rs-232c or gpib and sets the rs-232c communication conditions. Press the f7 key to select the other card, then press the rs-232c prmtr func- t...
Page 199
5-113 the descriptions of each settings are as follows. Setting item description interface selects remote control interface from gpib and rs-232c. Rs-232c cannot be used for remote control interface in tracking measurement with tls. Speed selects communication speed from 9600, 4800, 2400, 1200, and ...
Page 200: 5.15
5-114 section 5 explanation of screens 5.15 marker select screen (marker select key marker select ) to make waveform analysis easier, the ms9710b has wavelength markers a and b, level markers c and d, trace marker tmkr, and delta marker ∆ mkr. When the marker select key marker select is pressed, the...
Page 201
5-115 5.15.1 setting wavelength markers ( λλλλλ mkr_a function key f 1 , λλλλλ mkr_b function key f 2 ) wavelength markers a and b ( λ mkr_a, λ mkr_b) are displayed as vertical lines in the wavelength display field. The wavelengths at the markers a and b as well as the difference between the two mar...
Page 202
5-116 section 5 explanation of screens 5.15.2 setting level markers (lmkr_c function key f 3 , lmkr_d function key f 4 ) level markers c and d (lmkr_c, lmkr_d) are displayed as horizontal lines in the wavelength display field. The difference between the two markers (c–d) (relative scale) or (c/d) (l...
Page 203
5-117 5.15.4 setting delta marker ( ∆ mkr function key f 6 ) the delta marker ( ∆ mkr) is a marker for tracing the spectrum in the same way as the trace marker, but it displays wavelength difference and level difference from the trace marker in the marker display field. ∆ mkr can be used with trace ...
Page 204: 5.16
5-118 section 5 explanation of screens 5.16 zone marker screen (zone marker key zone marker ) press the zone marker key zone marker of the marker keys to display the zone marker card as shown below and activate the zone marker. The zone marker specifies a subset of the wavelength range for measureme...
Page 205
5-119 5.16 zone marker screen (zone marker key zone marker ) 5.16.2 setting zone width (zone width function key f 2 ) this function sets the interval between the two lines of the zone marker. It cannot be used at 3d displays. Press the zone marker key zone marker of the marker keys to display the zo...
Page 206
5-120 section 5 explanation of screens ..
Page 207: Section 6
6-1 this section describes how to calibrate the level and wavelength measurement accuracy, and execute the performance test of the ms9710b optical spectrum analyzer. 6.1 calibrating level .............................................. 6-2 6.2 calibrating wavelength .....................................
Page 208: 6.1
6-2 section 6 calibration and testing performance 6.1 calibrating level (1) inputting reference level light connect the output of a single-mode oscillation light source (calibrated with an optical power meter to a level of –30 dbm minimum) to the input of the ms9710b. A suitable light source would b...
Page 209
6-3 (3) adjusting level offset (a) connect the tester and measuring instruments as shown below. Ms9710b optical spectrum analyzer mn9610b tunable optical attenuator mg9001a stabilized light source ml9001a optical power meter (b) set the wavelength output mode of the mg9001a stabilized light source t...
Page 210: 6.2
6-4 section 6 calibration and testing performance 6.2 calibrating wavelength 6.2.1 calibration using internal wavelength reference (1) inputting reference wavelength light to adjust the optical axis, connect the output of a single-mode oscillation light source with a level of –30 dbm minimum to the ...
Page 211
6-5 6.2.2 calibration using external wavelength reference (1) inputting reference wavelength light connect the output of a single-mode light source calibrated with an optical wavelength meter to the input of the ms9710b. A suitable light source would be a 1.3 µ m or 1.55 µ m dfb-ld with output power...
Page 212: 6.3
6-6 section 6 calibration and testing performance 6.3 testing performance the following items are tested to confirm the performance of the tester. (1) wavelength accuracy (2) level accuracy clean all connectors before testing performance. In addition, allow the tester to warm up sufficiently and alw...
Page 213
6-7 6.3.1 checking wavelength (1) setup connect the tester and measuring instruments as shown below. Ms9710b optical spectrum analyzer mf9630a optical wavelength meter mg9637a tunable light source optical coupler (2) test procedure (a) set the wavelength output mode of the mg9637a tunable light sour...
Page 214
6-8 section 6 calibration and testing performance . 6.3.2 checking level (1) setup connect the tester and measuring instruments as shown below. Ms9710b optical spectrum analyzer mn9610b tunable optical attenuator mg9001a stabilized light source ml9001a optical power meter (2) test procedure (a) set ...
Page 215: Section 7
7-1 this section describes the periodic maintenance procedures, storage precau- tions, transporting and troubleshooting of the ms9710b optical spectrum ana- lyzer. 7.1 periodic maintenance ...................................... 7-2 7.1.1 cleaning exterior ............................... 7-2 7.1.2 cl...
Page 216: 7.1
7-2 section 7 maintenance and troubleshooting 7.1 periodic maintenance 7.1.1 cleaning exterior if the exterior of this analyzer becomes soiled, or before long-term storage, clean off using a soft cloth lightly moistened with soapy water. Do not use thinners or benzene solvents which will damage the ...
Page 217: Caution
7-3 (3) carefully wipe any dirt from the end face of the ferrule. End face of the ferrule ma rke r op tica l in pu t max +10dbm(a tt of f) max +20dbm(a tt on) sw ee p (4) carefully refit the optical input connector taking care not to scratch or otherwise damage the end face of the ferrule. 7.1.4 cle...
Page 218: 7.2
7-4 section 7 maintenance and troubleshooting 7.2 storage precautions do not store this analyzer where: • the temperature exceeds 60 ° c or is less than –20 ° c • it will be exposed to direct sunlight • it is very dusty • high humidity will cause condensation • there are active gases. 7.3 transporti...
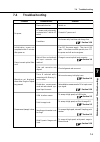
Page 219: 7.4
7-5 7.4 troubleshooting problem no power initialization screen not completed within 2 minutes after power-on cannot connect optical fiber cord waveform not displayed when either single or repeat key pressed measurement (sweep) is slow. Probable case power switch not on ac power cord not properly con...
Page 220
7-6 section 7 maintenance and troubleshooting problem probable case solution measurement (sweep) is slow. (continue) measured spectrum is incor- rect. Measured spectrum wave- length is incorrect. Measured spectrum level is incorrect (low). Measurement is impossible due to the noise when measuring lo...
Page 221
7-7 problem probable case solution measurement is impossible due to the noise when measuring low-level light. (continue) method does not change when peak/dip search is set to off. Peak point is not found in peak search. Waveform analysis is not executed for whole waveform. Unable to save/delete meas...
Page 222
7-8 section 7 maintenance and troubleshooting . Problem probable case solution screen color is unusual. Gpib/rs-232c is not operating. Gpib/rs-232c does not work. Tracking measurement is not possible. Measurement results is incorrect (in tls tracking). Error is in adjust to tls. Screen color setting...
Page 223: Appendix
Appn -1 appendix appendix appendix a specifications ..................................... A-1 appendix b initial settings ..................................... B-1 appendix c error codes ........................................ C-1 appendix d relationship between the resolution, vbw, and sensitivity...
Page 224
Appn -2 appendix ..
Page 225: Appendix A
A-1 this section describes the specification of the ms9710b optical spectrum ana- lyzer. A.1 wavelength ...................................................... A-2 a.2 resolution ........................................................ A-2 a.3 level ......................................................
Page 226: A.1
A-2 appendix a specifications to obtain stable operation, allow at least 5 minutes to elapse after power-on. The following specifications are guaranteed 2 hours after power-on. If the in- strument is out-of-specification, perform automatic optical-axis alignment (auto align) and then keep the instru...
Page 227: A.3
A-3 a.3 level level no ref. Light source with ref. Light source measurement level range 0 to 30 ° c 0 to 30 ° c (600 to 1000 nm) –65 to +10 dbm (1100 to 1600 nm) –70 to +20 dbm (1000 to 1250 nm) –85 to +10 dbm (1250 to 1600 nm) –90 to +10 dbm (1600 to 1700 nm) –75 to +10 dbm (1700 to 1750 nm) –55 to...
Page 228: A.4
A-4 appendix a specifications a.4 others others sweep speed 0.5 s max./500 nm (vbw: 10 hz, normal dynamic range mode, center wavelength: 1200 nm, from sweep start to sweep end, no optical input, 501 sampling points max.) a.5 white light source (option 02) white light source (option 02) optical outpu...
Page 229: A.7
A-5 a.7 functions functions measurement functions auto measure, pulse light measurement (external trigger, peak hold), power monitor, traking measurement with tls display functions zoom, overlap, normalize, max. Hold, 3d, wavelength in vacuum/air, actual resolution, display clear, title, date/time, ...
Page 230
A-6 appendix a specifications ..
Page 231: Appendix B
Appendix b initial settings b-1 appendix this section lists the factory default settings of the ms9710b optical spectrum analyzer. The factory defaults can be returned at any time by pressing the f6 key in con- dition card, pressing the recall function key f 2 , and selecting memory num- ber 0. B.1 ...
Page 232: B.1
B-2 appendix b initial settings b.1 wavelength card setting item factory default setting center 1350 nm span 500 nm start 1100 nm stop 1600 nm mkr value wl/freq wl value in air/vac air b.2 level scale card setting item factory default setting scale select log log (/div) 10 db/div reference level 20 ...
Page 233: B.5
Appendix b initial settings b-3 appendix b.5 analysis card setting item factory default setting status off threshold cut lvl: 3 db ndb loss ndb: 3 db smsr side mode: 2nd peak envelope cut lvl: 3 db rms k: 2.35 s-level: 20 db b.6 save/recall card setting item factory default setting file option file ...
Page 234: B.8
B-4 appendix b initial settings b.8 application card setting item factory default setting status off dfb-id ndb width: 20 db side mode: 2nd peak fp-ld mode cut lvl: 3 db led ndb width: 3 db power cal factor: 1 pmd auto/manual: auto mode cal factor: 1 o. Amp nf select: s-ase spect div: on ase fitting...
Page 235: B.9
Appendix b initial settings b-5 appendix b.9 measure mode card setting item factory default setting dynamic range normal peak hold off gate time: 1 ms ext. Trigger off delay time: 0 µ s interval time 0 s (off) power monitor off wavelength: 1550 nm b.10 title card (blank) b.11 cal card setting item f...
Page 236
B-6 appendix b initial settings ..
Page 237: Appendix C
Appendix c error codes c-1 appendix this section describes the error cards. C.1 system error codes (000 to 009) ................... C-2 c.2 measurement-related errors (100 to 199) ...... C-2 c.3 key operation errors (200 to 299) .................. C-3 c.4 device-related errors (300 to 499) ............
Page 238: C.1
C-2 appendix c error codes c.1 system error codes (000 to 009) 000 001 002 003 004 005 006 007 008 009 010 no. No error optical error (ram) optical error (slit-1) optical error (slit-2) optical error (wl align) optical error (opt att) not used optical error (light source) optical error (grating) opt...
Page 239: C.3
Appendix c error codes c-3 appendix c.3 key operation errors (200 to 299) no. Error message status output condition 200 201 202 to 204 205 206 207 208 to 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 not used input value error not...
Page 240
C-4 appendix c error codes no. Error message status output condition 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 260 261 invalid in analysis invalid in swp-avg set a trace or b trace invalid in a–b, b–a trace invalid in a–b trace invalid in b–a trace invalid in a&b trace inva...
Page 241: C.4
Appendix c error codes c-5 appendix c.4 device-related errors (300 to 499) no. Error message status output condition 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 320 321 322 324 325 400 401 402 403 404 405 406 407 408 to 419 420 421 ¥ errors relating to fd fd does not exist fd format error can t find file fd memory ...
Page 242
C-6 appendix c error codes ..
Page 243
Appendix d relationship between the resolution, vbw, and sensitivity d-1 appendix the relationship between the vbw, sweep speed and minimum received light sensitivity is shown in the following table. Vbw 10 hz 100 hz 1 khz 10 khz 100 khz 1 mhz sweep speed (typ) 30 s 5 s 0.5 s 0.5 s 0.5 s 0.5 s minim...
Page 244
D-2 appendix d relationship between the resolution, vbw, and sensitivity ..
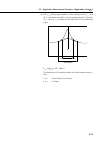
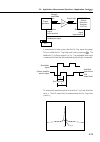
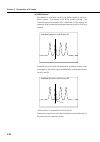
Page 245: Appendix E
Appendix e checking actual display resolution e-1 appendix this section explains improvement of display resolution accuracy. Upgrading from the ms9710a to the ms9710b improves the accuracy of the actual display resolution in the 1530 to 1570 nm band. In addition, the defini- tion of resolution has b...
Page 246: E.1
E-2 appendix e checking actual display resolution e.1 previous definition of resolution in the ms9710a, as shown in the diagram below, the half width of the spectrum of a single-mode oscillation light source was used as the resolution width. In this method, the accuracy of the resolution measurement...
Page 247: Appendix F
Appendix f optical fiber cord f-1 appendix the ms9710b uses a 10/125 µ m optical fiber cord at the optical input. At mea- surement, if the core eccentricity of the optical fiber cord connector is large, there is a possibility that the specified level accuracy may not be met. Anritsu uses a specified...
Page 248
F-2 appendix f optical fiber cord ..
Page 249
Appendix g example of performance test result record sheet g-1 appendix record no. : test location: test date: tester: tested model: ms9710b optical spectrum analyzer serial no.: power supply frequency: hz ambient temperature: ° c relative humidity: % remarks ms9710b optical spectrum analyzer wavele...
Page 250
G-2 appendix g example of performance test result record sheet ..
Page 251: Appendix H
H-1 appendix appendix h automatic measurement processing the automatic measurement processing function of this equipment has been optimized for measurement of input light in the range of 1300 to 1550 nm. However, measurement is possible in the range of 900 to 1650 nm. The auto- matic measurement fun...
Page 252
H-2 appendix h automatic measurement processing ..
Page 253: Appendix I
I-1 appendix appendix i switching marker frequency display the marker frequency display switching function of this instrument switches the display of the trace marker, ∆ marker and analysis part between a wave- length value and frequency value. The items that can be switched between the wavelength a...
Page 254
I-2 appendix i switching marker frequency display ..
Page 255: Appendix J
J-1 appendix appendix j option 10 installing option 10 adds a marker frequency display function and a table dis- play mode function for wdm applications. Note that these functions cannot be used when option 10 is not installed. The following functions are added by installing option 10: marker freque...
Page 256
J-2 appendix j option 10 ..
Page 257: Appendix K
K-1 appendix appendix k limited life span parts the ms9710b uses consumable parts for which the life span is determined ac- cording to the usage frequency (times). A fee will be charged for replacement of such parts due to end of life even if it is within the warranty period of the mt9080 series. Ta...
Page 258
K-2 appendix k limited life span parts ..
Page 259: Index
Index-1 index index index 3d display 5-52 3d function key 5-52 ↓: next function key 5-23 ∆ mkr function key 5-117 ←: left function key 5-23 ↑: last function key 5-23 →: right function key 5-24 a act-res off/on function key 5-21 analysis card 5-25 analyzing measured waveforms 4-12 analyzing waveforms...
Page 260
Index-2 index i initializing wavelength calibration data 5-100 interval function key 5-92 interval measurement 5-92 l l mkr_a function key 5-115 l mkr_b function key 5-115 laser safety vi led test function key 5-60 level offset function key 5-98 level scale card 5-12 linear level function key 5-14 l...
Page 261
Index-3 index index s sampling points function key 5-21 save function key 5-42 save/recall card 5-41 saving and recalling measured data 5-41 saving and recalling measured waveforms 4-15 saving and recalling measurement conditions 5-101 saving measured data 5-42 saving measurement conditions 5-102 se...
Page 262
Index-4 index t testing performance 6-1, 6-5 threshold analysis 5-26 threshold function key 5-26 title card 5-95 tls tracking function 5-93 tmkr function key 5-116 tmkrÆcenter key 5-117 trace a function key 5-39 trace a&b function key 5-39 trace a–b function key 5-39 trace b function key 5-39 trace ...