- DL manuals
- Anritsu
- Remote Control
- MT9083 Series
- Operation Manual
Anritsu MT9083 Series Operation Manual
Document No.: M-W3636AE-4.0
ANRITSU CORPORATION
MT9083 Series
ACCESS Master
Remote Control
Operation manual
Fourth Edition
• For safety and warning information, please read this
manual before attempting to use the equipment.
• Additional safety and warning information is provided
within the MT9083A2/B2/C2 ACCESS Master
Operation Manual. Please also refer to this document
before using the equipment.
• Keep this manual with the equipment.
Summary of MT9083 Series
Page 1
Document no.: m-w3636ae-4.0 anritsu corporation mt9083 series access master remote control operation manual fourth edition • for safety and warning information, please read this manual before attempting to use the equipment. • additional safety and warning information is provided within the mt9083a2...
Page 2: Danger
Ii safety symbols to prevent the risk of personal injury or loss related to equipment malfunction, anritsu corporation uses the following safety symbols to indicate safety-related information. Ensure that you clearly understand the meanings of the symbols before using the equipment. Some or all of t...
Page 3: About This Manual
I about this manual this operation manual describes the scpi (standard commands for programmable instruments) commands for the mt9083a2/b2/c2 access master. Operations for the mt9083 series access master main frame are described. Mt9083 series access master operation manual operation manuals for mt9...
Page 4: Table Of Contents
Ii table of contents about this manual ....................................... I chapter 1 overview ................................... 1-1 1.1 about remote control ............................................... 1-2 1.2 applications ................................................................ 1...
Page 5: Appendix A Recommended
1 iii 2 3 4 app end ix appendix a recommended usb-ethernet converter ........... A-1.
Page 6
Iv.
Page 7
Chapter 1 overview 1-1 1 o ver view this chapter explains remote control of the mt9083a2/b2/c2 access master. 1.1 about remote control .................................................. 1-2 1.2 applications ................................................................... 1-2.
Page 8: 1.1 About Remote Control
Chapter 1 outline 1-2. 1.1 about remote control the remote control function sends commands via the communications interface from the remote control pc to set the measuring instrument and read the measurement results and measuring instrument conditions. The mt9083a2/b2/c2 access master (this instrume...
Page 9
Chapter 2 before use 2-1 2 before use this chapter explains the preparations for using remote control. 2.1 preparing equipment .................................................... 2-2 2.2 connecting equipment ................................................. 2-3 2.2.1 connecting usb-ethernet convert...
Page 10: 2.1 Preparing Equipment
Chapter 2 before use 2-2 2.1 preparing equipment the following equipment is required to perform remote control. pc usb-ethernet converter ethernet cable program development tools pc the pc must be able to run the program development tools. Usb-ethernet converter we recommend using the anrits...
Page 11: 2.2 Connecting Equipment
2.2 connecting equipment 2-3 2 before use 2.2 connecting equipment 2.2.1 connecting usb-ethernet converter connect the usb-ethernet converter to the usb down port on the top edge of the access master. Figure 2.2.1-1 access master and usb-ethernet converter if the converter is connected while the pow...
Page 12
Chapter 2 before use 2-4 2.2.2 connecting external equipment connect the external equipment with a lan cable to the lan port of the usb-ethernet converter connected to the instrument. Use a crossover cable to connect one pc controller. When connecting multiple pieces of external equipment, use a net...
Page 13: 2.3 Setting Ethernet
2.3 setting ethernet 2-5 2 before use 2.3 setting ethernet instrument settings such as ip address are set at the remote setup screen. The remote screen is displayed by the following two methods. press remote setup (f1) at the top menu. With the power on, connect the usb-ethernet converter to the u...
Page 14
Chapter 2 before use 2-6 1. Set the ip address. The input setting range is 0.0.0.1 to 255.255.255.254. Use the instrument’s numeric keypad or the left/right/up/down arrow keys to input the numeric values. The default setting is 192.168.1.2. 2. Set the ip netmask. The input setting range is 0.0.0.0 t...
Page 15: 2.4 Checking Connection
2.4 checking connection 2-7 2 before use 2.4 checking connection check that the link between the pc and instrument has been established. 1. Click programs at the windows start menu. 2. Click accessories. 3. Click command prompt. 4. Input the commands shown in the screen below. This example shows how...
Page 16: 2.5 Message Format
Chapter 2 before use 2-8 2.5 message format messages are composed of character strings for executing commands and character strings indicating the message end. When sending messages to this instrument, terminate the line with cr/lf; received messages are terminated with cr/lf. Messages are composed ...
Page 17
2.5 message format 2-9 2 before use example: *esr? Topmenu:unit:catalog? Sour:puls:enh? When linking multiple program messages, separate the message using semicolons (;).The maximum number of linked messages is 12.If 13 or more messages are sent, the 13th and subsequent messages are discarded. Examp...
Page 18: 2.6.1 Register
Chapter 2 before use 2-10 2.6 checking instrument status this instrument has registers indicating the status, such as errors and command execution status. This section explains these registers. 2.6.1 register structure figure 2.6.1-1 shows the structure of the registers indicating the instrument sta...
Page 19
2.6 checking instrument status 2-11 2 before use each register uses 8-bit data. The register output values are the binary totals for each bit shown in figure 2.6.1-1. Table 2.6.1-1 register bit binary conversion values bit binary value bit binary value 0 1 4 16 1 2 5 32 2 4 6 64 3 8 7 128 to read th...
Page 20: 2.6.2 Status
Chapter 2 before use 2-12 2.6.2 status byte register the meaning of each bit of the status byte register is shown in the following table. Table 2.6.2-1 meaning of status byte register bit explanation 7 osr (operation status register) displays the equipment’s operation status. Currently only 1 can be...
Page 21: 2.6.3 Event
2.6 checking instrument status 2-13 2 before use 2.6.3 event register standard event status register the meaning of each bit of the standard event status register is listed in the table below. Table 2.6.3-1 meaning of standard event status register bit explanation 7 power-on becomes 1 at power-on an...
Page 22
Chapter 2 before use 2-14 2.7 controlling message sync the following messages (12 types max.) can be received during measurement by this instrument and analysis of measurement results. However, if a message is sent to change the measurement parameters before the previous processing is completed, the...
Page 23
2.7 controlling message sync 2-15 2 before use using *wai the *wai common command instructs processing to wait until processing of the message sent before the *wai command is completed before executing the next command. Example of use: init ; *wai ; sour:wav 1550; init time me ssa ge re ce iv ed ini...
Page 24
Chapter 2 before use 2-16 using *opc and *esr? The *opc common command sets the standard event status register bit to 0 and displays the opc bit. Examples of use: *cls sets the opc bit to 0. *ese 1 sets standard event status enable bit to 1 init executes averaging measurement *opc sets so as to chan...
Page 25
2.7 controlling message sync 2-17 2 before use querying measurement end the instrument program messages query the end of processing execution. These queries send the following messages after confirming the processing end. Example of use, 1: when averaging measurement is 60 s init executes averaging ...
Page 26
Chapter 2 before use 2-18 2.8 switching sm unit and mm unit two otdr units for single mode fiber (measurement wavelength: 1310/1550 nm ) and multimode fiber (measurement wavelength: 850/1300 nm) can be installed in this instrument according to the number of the option unit (e.G. Mt9083b2 option 063)...
Page 27: Menu
2.9 moving to another measurement mode from top menu 2-19 2 before use 2.9 moving to another measurement mode from top menu in addition to otdr measurement, this instrument has other built-in measurement mode functions such as light source and power meter. To use these measurements, it is necessary ...
Page 28
Chapter 2 before use 2-20. Example of use 2: to measure with mm unit after measuring with sm unit using mt9083b2-063 (mm 850/1300 nm/sm 1310/1550 nm) instrument:nselect? Queries current measurement mode >2 at 2 response: otdr (standard) mode inst:nsel 1 moves to top menu topmenu:unit:catalog:full? Q...
Page 29
Chapter 3 platform scpi commands 3-1 3 pla tf or m s c pi c om ma nd s this chapter details the scpi commands for the mt9083a2/b2/c2 platform. 3.1 star (ieee 488.2) subsystem commands ................... 3-4 3.1.1 *cls clear status command .......................... 3-4 3.1.2 *ese standard event sta...
Page 30
Chapter 3 platform scpi commands 3-2 3.3.15 status:operation:instrument :isummary#:enable? ................................... 3-14 3.3.16 status:operation:instrument :isummary#[:event]? .................................. 3-14 3.3.17 status:questionable[:event]? .................. 3-15 3.3.18 status...
Page 31
Chapter 3 platform scpi commands 3-3 3 pla tf or m s c pi c om ma nd s 3.5.6 topmenu:unit:nselect? ........................... 3-23.
Page 32
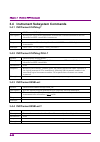
Chapter 3 platform scpi commands 3-4 3.1 star (ieee 488.2) subsystem commands 3.1.1 *cls clear status command syntax: *cls description: the clear status command *cls clears all the event registers summarized in the status byte register. Except for the output queue, all queues summarized in the statu...
Page 33
3.1 star (ieee 488.2) subsystem commands 3-5 3 pla tf or m s c pi c om ma nd s 3.1.4 *esr? Standard event status register query syntax: *esr? Description: the standard event status register query *esr? Returns the contents of the standard event status register. The register is cleared after being re...
Page 34
Chapter 3 platform scpi commands 3-6 3.1.7 *opc? Operation complete query syntax: *opc? Description: a device is in the operation complete query active state (oqas) after it has executed *opc?. The device returns to the operation complete query idle state (oqis) whenever the no operation pending fla...
Page 35
3.1 star (ieee 488.2) subsystem commands 3-7 3 pla tf or m s c pi c om ma nd s 3.1.9 *sre service request enable command syntax: *sre description: the standard service request enable command (*sre) sets bits in the service request enable register. A 1 in a bit in the enable register enables the corr...
Page 36
Chapter 3 platform scpi commands 3-8 3.1.11 *stb? Read status byte query syntax: *stb? Description: the status byte query *stb? Returns the contents of the status byte register. The master summary status (mss) bit is true when any enabled bit of the stb register is set (excluding bit 6). The status ...
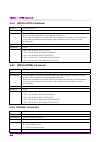
Page 37: 3.2.1 System:error?
3.2 system subsystem commands 3-9 3 pla tf or m s c pi c om ma nd s 3.2 system subsystem commands 3.2.1 system:error? Syntax: system:error? Description: returns the contents of the scpi error queue. Removes the returned entry from the queue. Parameters: none response: the number of the latest error,...
Page 38: 3.2.5 System:light?
Chapter 3 platform scpi commands 3-10 3.2.5 system:light? Syntax: system:light? Description: checks if the backlight is turned on or off. Parameters: none response: possible responses are: 0 = the backlight is off. 1 = the backlight is on . Example: syst:ligh? -> 0 3.2.6 system:light syntax: system:...
Page 39
3.3 status subsystem commands 3-11 3 pla tf or m s c pi c om ma nd s 3.3 status subsystem commands all commands in this section are prepared for future functions. All the registers regarding these commands are set to 0 now. 3.3.1 status:operation[:event]? Syntax: status:operation[:event]? Descriptio...
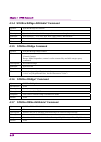
Page 40
Chapter 3 platform scpi commands 3-12 3.3.5 status:operation:bit#:enable? Syntax: status:operation:bit:enable? Description: returns the operation enable mask for the event register specified bit. The value of is restricted from 8 to 12 and represents bits 8 through 12 parameters: none response: the ...
Page 41
3.3 status subsystem commands 3-13 3 pla tf or m s c pi c om ma nd s 3.3.9 status:operation:instrument:condition? Syntax: status:operation:instrument:condition? Description: queries the instrument operation condition register. Parameters: none response: the bit value for the operation condition regi...
Page 42
Chapter 3 platform scpi commands 3-14 3.3.13 status:operation:instrument:isummary#:condition? Syntax: status:operation:instrument:isummary:condition? Description: queries the instrument operation condition register of the specified instrument. The value of is restricted from 1 to 14 and represents t...
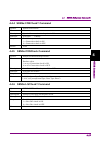
Page 43
3.3 status subsystem commands 3-15 3 pla tf or m s c pi c om ma nd s 3.3.17 status:questionable[:event]? Syntax: status:questionable[:event]? Description: queries the questionable event register parameters: none response: the bit value for the questionable event register as a short value (0 .. +3276...
Page 44
Chapter 3 platform scpi commands 3-16 3.3.21 status:questionable:bit#:enable? Syntax: status:questionable:bit:enable? Description: returns the questionable enable mask for the event register specified bit. The value of is restricted from 9 to 12 and represents bits 9 through 12 parameters: none resp...
Page 45
3.3 status subsystem commands 3-17 3 pla tf or m s c pi c om ma nd s 3.3.25 status:questionable:instrument:condition? Syntax: status:questionable:instrument:condition? Description: queries the questionable instrument condition register. Parameters: none response: the bit value for the questionable c...
Page 46
Chapter 3 platform scpi commands 3-18 3.3.29 status:questionable:instrument:isummary#:condition? Syntax: status:questionable:instrument:isummary:condition? Description: queries the specified logical instrument questionable instrument condition register. The value of is restricted from 1 to 14 and re...
Page 47: 3.3.33 Status:preset
3.3 status subsystem commands 3-19 3 pla tf or m s c pi c om ma nd s 3.3.33 status:preset syntax: status:preset description: resets both the operation enable mask and questionable enable mask to 0 parameters: none response: none example: stat:pres.
Page 48: 3.4.1 Instrument:catalog?
Chapter 3 platform scpi commands 3-20 3.4 instrument subsystem commands 3.4.1 instrument:catalog? Syntax: instrument:catalog? Description: returns the list of scpi controllable instruments on mt9083a2/b2/c2 that are identified as scpi controllable instruments parameters: none response: comma-separat...
Page 49: 3.4.5 Instrument[:select]
3.4 instrument subsystem commands 3-21 3 pla tf or m s c pi c om ma nd s 3.4.5 instrument[:select] syntax: instrument:select description: sets the specified logical instrument to be currently selected instrument parameters: the string instrument identifier assigned by the instrument subsystem for th...
Page 50
Chapter 3 platform scpi commands 3-22 3.5 topmenu subsystem commands 3.5.1 topmenu:unit:catalog? Syntax: topmenu:unit:catalog? Description: returns the list of units installed on mt9083a2/b2/c2 that can be selected prior to starting otdr instrument parameters: none response: comma-separated list of ...
Page 51
3.5 topmenu subsystem commands 3-23 3 pla tf or m s c pi c om ma nd s 3.5.5 topmenu:unit:nselect syntax: topmenu:nselect description: sets the specified unit to be currently selected to run with otdr instrument. Parameters: the numeric value identifier assigned by the topmenu subsystem for the unit ...
Page 52
Chapter 3 platform scpi commands 3-24..
Page 53
Chapter 4 otdr commands 4-1 4 otdr commands this chapter details the scpi commands for the mt9083a2/b2/c2 standard otdr application. The command summary section presents a brief summary of each command, while each command is detailed in the subsequent sections. 4.1 command summary .....................
Page 54
Chapter 4 otdr commands 4-2 4.4.11 sense:fiber:bsc? Command ...................... 4-17 4.4.12 sense:hoffset command .......................... 4-17 4.4.13 sense:hoffset? Command ........................ 4-17 4.4.14 sense:voffset command ........................... 4-18 4.4.15 sense:voffset? Command...
Page 55
Chapter 4 otdr commands4.1 command summary 4-3 4 otdr commands 4.6.10 display:scale:vertical command ............ 4-35 4.6.11 display:scale:vertical? Command .......... 4-35.
Page 56: 4.1 Command
Chapter 4 otdr commands 4-4 4.1 command summary the command summary section provides a list of the scpi commands for the mt9083a2/b2/c2 standard otdr application, and a brief description for each command. Commands and queries in this section can be received only in the otdr (standard) mode. Root lev...
Page 57
4.1 command summary 4-5 4 otdr commands sense:trace:ready? - queries if the trace data is ready. Sense:concheck - sets connection check option on or off. Sense:concheck? - queries if the connection check option enabled. Sense:livcheck - sets live fiber check option on or off. Sense:livcheck? - queri...
Page 58
Chapter 4 otdr commands 4-6 display subsystem commands display:mode – sets current display mode (from a, from b, from origin). Display:mode? – queries current display mode. Display:zoom:full – sets zoom to view full trace in current display mode. Display:zoom:horizontal – set the display zoom level ...
Page 59: 4.2 Root Level Commands
4.2 root level commands 4-7 4 otdr commands 4.2 root level commands these commands start/stop otdr test sequence 4.2.1 abort command syntax: abort parameters: none description: aborts the active test. The trace data will be lost. Example: abor response: none errors: (–200, "std_execgen, test is inac...
Page 60: 4.2.4 Initiate:auto
Chapter 4 otdr commands 4-8 4.2.4 initiate:auto command syntax: initiate:auto parameters: none description: starts otdr auto-test. All test parameters are automatically obtained during the pre-scan. This command is an overlapped command. When this command is executed with “wavelength all” selected, ...
Page 61: Command
4.3 source subsystem commands 4-9 4 otdr commands 4.3 source subsystem commands the source subsystem controls/query otdr’s optical source parameters. 4.3.1 source:wavelength:available? Command syntax: source:wavelength:available? Parameters: none description: queries the list of available wavelength...
Page 62: 4.3.5 Source:range
Chapter 4 otdr commands 4-10 4.3.4 source:range:available? Command syntax: source:range:available? Parameters: none description: queries the list of available ranges for current wavelength settings. Example: sour:ran:ava? --- 5.0, 10.0, 20.0, 50.0, 100.0, 200.0, 300.0 response: list of available ran...
Page 64
Chapter 4 otdr commands 4-12 4.3.11 source:pulse command syntax: source:pulse parameters: numeric format range: integer pw value returned by querying available pulse width command. Available pulse width values are dependant on current range/resolution settings. Description: set current pulse width. ...
Page 66: 4.4.1 Sense:averages?
Chapter 4 otdr commands 4-14 4.4 sense subsystem commands the sense subsystem lets you control/query otdr’s measurement parameters. 4.4.1 sense:averages? Command syntax: sense:averages? Parameters: none description: queries number of averages that have been completed on the trace or since the test s...
Page 67: 4.4.5 Sense:concheck
4.4 sense subsystem commands 4-15 4 otdr commands 4.4.4 sense:concheck? Command syntax: sense:concheck? Parameters: none description: queries if connection check option is on. Example: sens:conc? --- 1 response: possible response values: 1 = connection check is on. 0 = connection check is off. Error...
Page 68: 4.4.7 Sense:livcheck:command
Chapter 4 otdr commands 4-16 4.4.7 sense:livcheck:command syntax: sense:livcheck parameters: boolean value 1 or on = live fiber check is on. 0 or off = live fiber check is off. Description: sets live fiber check option on or off. Example: sens:livc on response: none errors: (–200, "std_execgen, test...
Page 69
4.4 sense subsystem commands 4-17 4 otdr commands 4.4.10 sense:fiber:bsc command syntax: sense:fiber:bsc parameters: floating point format range: –90.0 - –40.0 description: sets backscatter coefficient. This value will be used for the next test. Example: sens:fib:bsc –83.0 response: none errors: (–2...
Page 70
Chapter 4 otdr commands 4-18 4.4.14 sense:voffset command syntax: sense:voffset parameters: floating point format range: offset value can be set plus/minus current dynamic range. (–64.0 to 64.0) description: set vertical offset for the displayed trace(s). Offset value units – db. Example: sens:voff ...
Page 71
4.4 sense subsystem commands 4-19 4 otdr commands 4.4.18 sense:bcursor command syntax: sense:bcursor parameters: floating point format range: 0.0 – current distance range. Description: set b cursor position. Cursor position units – km. Example: sens:bcur 20.5 response: none errors: (–224, "std_illeg...
Page 72
Chapter 4 otdr commands 4-20 4.4.21 sense:lsaleft? Command syntax: sense:lsaleft? Parameters: none description: query left lsa values. Example: sens:lsal? --- 0.0, 0.5 response: start and stop for left lsa marker. Start and stop units – kilometers (km). Errors: (–400, "std_querygen, lsa inactive sta...
Page 75
4.4 sense subsystem commands 4-23 4 otdr commands 4.4.29 sense:analyze:parameters? Command syntax: sense:analyze:parameters? Parameters: none description: query current analysis parameters. Example: sens:anal:par? --- 0.050000, –60.000000, 3.000000,10.000000 response: loss>,,, errors: none 4.4.30 se...
Page 76: 4.5.1 Trace:parameters?
Chapter 4 otdr commands 4-24 4.5 trace subsystem commands the trace subsystem provides access to the trace analysis and trace data. 4.5.1 trace:parameters? Command syntax: trace:parameters? Parameters: none description: get main otdr parameters used to collect the trace data. , , , , , , , example: ...
Page 77: 4.5.4 Trace:analyze:orl
4.5 trace subsystem commands 4-25 4 otdr commands 4.5.4 trace:analyze:orl command syntax: trace:analyze:orl parameters: description: performs orl calculations on the trace. This command is an overlapped command. Example: trac:anal:orl response: none errors: (–200, "std_execgen, test is active") (–20...
Page 78: 4.5.7 Trace:load:sor?
Chapter 4 otdr commands 4-26 4.5.7 trace:load:sor? Command syntax: trace:load:sor? Parameters: none description: get sor trace object. Refer to section 2.5 “message format – binary data” for further details. Example: trac:load:sor? --- “binary array” #524047 //scpi data size message for binary data ...
Page 79
4.5 trace subsystem commands 4-27 4 otdr commands (cont’d) example: trac:load:text? #6140479 //scpi data size message for binary data transfer wl = 1310 nm //wavelength fbr = sm //fiber type dr = 5 km // pw = 50 ns [er] //pulse width and resolution type avg = 6144 //number of hardware averages ior =...
Page 80: 4.5.9 Trace:load:data?
Chapter 4 otdr commands 4-28 4.5.9 trace:load:data? Command syntax: trace:load:data?,, parameters: starting distance (km) floating point format range: 0.0 - (current distance range - *resolution) ending distance (km) floating point format range: (+*resolution) - (current distance range). Data point ...
Page 81: 4.5.10 Trace:header Command
4.5 trace subsystem commands 4-29 4 otdr commands 4.5.10 trace:header command syntax: trace:header,,,, ,,,, parameters: bc, rc, ot up to 30 characters up to 30 characters up to 30 characters up to 30 characters up to 30 characters 0: a->b, 1-> b->a up to 30 characters up to 30 characters description...
Page 82
Chapter 4 otdr commands 4-30 4.5.12 trace:store:sor command syntax: trace:store:sor parameters: file path and file name to save the sor file description: store the sor file in internal memory of mt9083. Example: trac:stor:sor test.Sor test.Sor file is stored in root folder of internal memory. Trac:s...
Page 84: Command
Chapter 4 otdr commands 4-32 4.6.4 display:zoom:horizontal command syntax: display:zoom:horizontal parameters: zoom level numeric format range: 0 – (6 - 16) depends on current distance range 0 – full zoom in, (6 – 16) – full zoom out note: the maximum value for each distance is as follows. 0.5 km : ...
Page 85: 4.6.6 Display:zoom:vertical
4.6 display subsystem commands 4-33 4 otdr commands 4.6.6 display:zoom:vertical command syntax: display:zoom:vertical parameters: zoom level numeric format range: 0 – 7 0 – full zoom in, 7 – full zoom out description: set vertical display zoom to specified level example: disp:zoom:vert 2 response: n...
Page 86: Command
Chapter 4 otdr commands 4-34 4.6.8 display:scale:horizontal command syntax: display:scale:horizontal parameters: horizontal scale range value in km floating point format range: 0.0096 – (0.5040 - 300.0000) depends on current distance range (0.5 – 300) km 0.0096 – full zoom in, (0.5040 - 300.0000) – ...
Page 87
4.6 display subsystem commands 4-35 4 otdr commands 4.6.10 display:scale:vertical command syntax: display:scale:vertical parameters: vertical scale range value in db floating point format range: 0.5 – 65 0.5 – full zoom in, 65 – full zoom out note: there are 8 predefined scale ranges (0.5, 1.25, 2.5...
Page 88
Chapter 4 otdr commands 4-36..
Page 89
Appendix a recommended usb-ethernet converter a-1 a pp en dix a ppe ndi x a these usb-ethernet converters manufactured by other companies are confirmed to work. Manufacturer model name planex ue-200tx-g buffalo lua-u2-ktx buffalo lua2-u2-atx d-link dub-e100 linksys usb200m linksys usb300m.
Page 90
Appendix a recommended usb-ethernet converter a-2..