- DL manuals
- Baldor
- PCI Card
- NextMove PCI
- Installation Manual
Baldor NextMove PCI Installation Manual
Summary of NextMove PCI
Page 1
Nextmove pci motion controller motion control installation manual 3/02 mn1903.
Page 3
Contents i mn1903 contents 1 general information 1-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 introduction 2-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.1 nextmove pci features 2-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 4
Ii contents mn1903 4.6 can connections 4-20 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.6.1 can1 (canopen) - x17 4-21 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.6.2 can2 (baldor can) - x18 4-22 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ....
Page 5
Contents iii mn1903 6 troubleshooting 6-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6.1 introduction 6-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6.1.1 problem diagnosis 6-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ....
Page 6
Iv contents mn1903.
Page 7
General information 1-1 mn1903 lt0166a00 copyright baldor (c) 2002. All rights reserved. This manual is copyrighted and all rights are reserved. This document or attached software may not, in whole or in part, be copied or reproduced in any form without the prior written consent of baldor. Baldor ma...
Page 8: Safety Notice
1-2 general information mn1903 safety notice only qualified personnel should attempt the start-up procedure or troubleshoot this equipment. This equipment may be connected to other machines that have rotating parts or parts that are controlled by this equipment. Improper use can cause serious or fat...
Page 9: 2.1 Nextmove Pci Features
Introduction 2-1 mn1903 2.1 nextmove pci features nextmove pci is a high speed multi-axis intelligent motion controller for use in pci bus based pc systems. Nextmove pci features the mintmt motion control language. Mintmt is a structured form of basic, custom designed for stepper or servo motion con...
Page 10
2-2 introduction mn1903 included with nextmove pci is the baldor motion toolkit cd. This contains a number of utilities and useful resources to get the most from you mintmt controller. These include: h mint workbench v5 this is the user interface for communicating with the nextmove pci. Installing m...
Page 11
Introduction 2-3 mn1903 2.2 receiving and inspection when you receive your nextmove pci, there are several things you should do immediately: 1. Check the condition of the packaging and report any damage immediately to the carrier that delivered your nextmove pci. 2. Remove the nextmove pci from the ...
Page 12
2-4 introduction mn1903 2.3 units and abbreviations the following units and abbreviations may appear in this manual: v volt (also vac and vdc) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . W watt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A ampere . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Ω ohm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . µf microfarad . ....
Page 13: 3.1 Introduction
Basic installation 3-1 mn1903 3.1 introduction you should read all the sections in basic installation. It is important that the correct steps are followed when installing the nextmove pci. This section describes the mechanical and electrical installation of the nextmove pci. 3.1.1 hardware requireme...
Page 14: 3.2 Location Requirements
3-2 basic installation mn1903 3.2 location requirements it is essential that you read and understand this section before beginning the installation. Caution: to prevent equipment damage, be certain that input and output signals are powered and referenced correctly. Caution: to ensure reliable perfor...
Page 15: 3.3 Installation
Basic installation 3-3 mn1903 3.3 installation nextmove pci can be installed into an at style personal computer that has a free 7 inch pci card slot. The baldor motion toolkit cd supports the following operating systems: windows 95, windows 98, windows me, windows nt4 and windows 2000. 3.3.1 install...
Page 16
3-4 basic installation mn1903.
Page 17: 4.1 Outline
Input / output 4-1 mn1903 4.1 outline this section describes the digital and analog input and output capabilities of the nextmove pci. The following conventions will be used to refer to the inputs and outputs: i/o input / output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Din digital input . . . . . . . . . . . . ....
Page 18
4-2 input / output mn1903 4.2.1 100-pin connector pin assignment pin signal pin signal 1 ain0+ 51 ain1+ 2 ain0- 52 ain1- 3 ain2+ 53 ain3+ 4 ain2- 54 ain3- 5 demand0 55 demand1 6 demand2 56 demand3 7 analog gnd 57 gnd 8 gnd 58 +5v out 9 can1 transmit 59 can2 transmit 10 can1 receive 60 can2 receive 1...
Page 19
Input / output 4-3 mn1903 pin signal pin signal 29 direction output 1 79 direction output 3 30 step output 3 80 dout11 31 dout10 81 usr v+ 32 dout9 82 dout8 33 dout7 83 usr v+ 34 dout6 84 dout5 35 dout4 85 cgnd 36 dout3 86 dout2 37 dout1 87 cgnd 38 dout0 88 common2 39 din19 89 din17 40 din18 90 din1...
Page 20: 4.3 Analog I/o
4-4 input / output mn1903 4.3 analog i/o the nextmove pci provides: h four 12-bit resolution analog inputs. The inputs are available on connector x6 on the nextmove pci breakout module. H four 14-bit resolution analog outputs. The outputs are available on connector x7 on the nextmove pci breakout mo...
Page 21
Input / output 4-5 mn1903 4.3.1 analog inputs - x6 location breakout module, connector x6 pin name mintmt keyword / description 1 agnd analog ground 2 ain0+ ain0 3 ain0- ain0 4 ain1+ ain1 5 ain1- ain1 6 shield shield connection 7 agnd analog ground 8 ain2+ ain2 9 ain2- ain2 10 ain3+ ain3 11 ain3- ai...
Page 22
4-6 input / output mn1903 nextmove pci - + ain0+ ain0- agnd mintmt adc.0 breakout module 3 1 2 x6 100 pin cable - + figure 1 - analog input wiring, ain0 shown for differential inputs connect input lines to ain+ and ain-. Leave agnd unconnected. For single ended inputs, connect signal to ain+. Connec...
Page 23
Input / output 4-7 mn1903 4.3.2 analog outputs (drive demand/command) - x7 location breakout module, connector x7 pin name description 1 demand0 demand output signal for axis 0 2 agnd analog ground 3 shield shield connection 4 demand1 demand output signal for axis 1 5 agnd analog ground 6 shield shi...
Page 24: 4.4 Digital I/o
4-8 input / output mn1903 4.4 digital i/o there are a total of 20 general purpose digital inputs. Inputs can be configured in mintmt for any of the following functions: h forward limit (end of travel) input on any axis h reverse limit (end of travel) input on any axis h home input on any axis h driv...
Page 25
Input / output 4-9 mn1903 inputs can be shared between axes, and are programmable in mintmt (using the keywords inputactivelevel, inputmode, inputpostrigger and inputnegtrigger) to determine their active level and if they should be edge triggered. Four of the inputs, din0-din3, are fast position lat...
Page 26
4-10 input / output mn1903 4.4.1 digital inputs - x1 location breakout module, connector x1 pin name mintmt keyword / description common 1 shield shield connection 2 din12 inx.12 3 din13 inx.13 4 din14 inx.14 5 din15 inx.15 common2 6 din16 inx.16 common2 7 din17 inx.17 8 din18 inx.18 9 din19 inx.19 ...
Page 27
Input / output 4-11 mn1903 the inputs are conditioned using low pass rc filters and schmitt trigger buffers. If an input is configured as edge triggered, the triggering pulse must have a duration of at least 1ms (one software scan) to guarantee acceptance by mintmt. Voltages below 2v are considered ...
Page 28
4-12 input / output mn1903 4.4.3 digital inputs - x3 digital inputs din0 to din3 can be used as high speed position latches. The fast position inputs are routed through a programmable cross-point switch which allows any input to cause the position of any combination of axes to be captured (by the ha...
Page 29
Input / output 4-13 mn1903 4.4.4 digital outputs - x4 location breakout module, connector x4 pin name mintmt keyword / description 1 shield shield connection 2 dout6 outx.6 3 dout7 outx.7 4 dout8 outx.8 5 dout9 outx.9 6 dout10 outx.10 7 dout11 outx.11 8 - (nc) 9 - (nc) 10 shield shield connection 11...
Page 30
4-14 input / output mn1903 outx.6 usr v+ nextmove pci dout6 output module cgnd output load breakout module 2 11 x4 100 pin cable 12 figure 6 - digital output circuit with optional ‘npn’ current sinking module - dout6 shown 4.4.5 digital outputs - x5 location breakout module, connector x5 pin name mi...
Page 31: 4.5 Other I/o
Input / output 4-15 mn1903 4.5 other i/o 4.5.1 encoder interfaces - x12, x13, x14, x15, x16 location breakout module, connectors x12, x13, x14, x15, x16 pin name description 1 encoder v+ power supply to encoder 2 chz+ index channel signal 3 chb- channel b signal complement 4 shield shield connection...
Page 32
4-16 input / output mn1903 4.5.2 encoder input frequency the maximum encoder input frequency is affected by the length of the encoder cables. The theoretical maximum frequency is 7.5 million quadrature counts per second. This is equivalent to a maximum frequency for the a and b signals of 1.87mhz. H...
Page 33
Input / output 4-17 mn1903 4.5.3 power - x9 location breakout module, connector x9 pin name description 1 vcc +5v supply source from the host pc 2 vcc +5v supply source from the host pc 3 encoder v+ power to the encoder connectors 4 encoder v+ power to the encoder connectors 5 gnd digital ground fro...
Page 34
4-18 input / output mn1903 4.5.4 relay and can power - x8 location breakout module, connector x8 pin name description 1 can1 v+ power input for can1 (canopen) network (12-24v) 2 can1 gnd ground for can1 (canopen) network 3 can2 v+ power input for can2 (baldor can) network (12-24v) 4 can2 gnd ground ...
Page 35
Input / output 4-19 mn1903 4.5.5 stepper drive outputs - x10, x11 location connectors x10, x11 pin x10 name x11 name description 1 step0+ step2+ step signal 2 dir0+ dir2+ direction signal 3 gnd gnd signal ground 4 dir1+ dir3+ direction signal 5 step1+ step3+ step signal 6 step0- step2- step signal c...
Page 36: 4.6 Can Connections
4-20 input / output mn1903 4.6 can connections can (controller area network) is a 1mb/s local area network. Two can channels are supported by nextmove pci - canopen and baldor can. Access to both channels is configured by a 10-pin 2mm pin header, j11, mounted along the top edge of the nextmove pci c...
Page 37
Input / output 4-21 mn1903 h terminators must only be fitted at both ends of the network, not at intermediate nodes. H the 0v connection of all of the nodes on the network must be tied together through the can cabling. This ensures that the can signal levels transmitted by nextmove pci or can periph...
Page 38
4-22 input / output mn1903 4.6.2 can2 (baldor can) - x18 baldor can connections are made using the breakout module connector x18. Location breakout module, connector x18 pin name description 1 - (nc) 2 - (nc) 3 - (nc) 4 can2 0v ground/earth reference for can signal 5 can2 v+ can remote node power v+...
Page 39: 4.7 Other I/o
Input / output 4-23 mn1903 4.7 other i/o 4.7.1 emulator connection an 11-pin footprint on the rear of the card marked ‘ice’ provides access to the processor for boundary scan emulation. To connect the texas instruments emulator pod, a two row 12-pin 0.1in pitch surface mount pin header with pin 8 mi...
Page 40
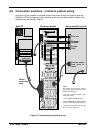
4-24 input / output mn1903 4.9 connection summary - minimum system wiring as a guide, figure 9 shows an example of the typical minimum wiring required to allow the nextmove pci and a single axis servo amplifier (motor drive) to work together. Details of the connector pins are shown in table 4. Nextm...
Page 41
Input / output 4-25 mn1903 the pin connections in the example are described below: breakout module connector pin name of signal function connection on drive (note: drive may be labelled differently) x7 1 demand0 command signal for axis 0 demand+ input 2 agnd command signal for axis 0 demand- input x...
Page 42
4-26 input / output mn1903.
Page 43: 5.1 Introduction
Operation 5-1 mn1903 5.1 introduction the software provided includes a number of applications and utilities to allow you to configure, tune and program the nextmove pci. If you do not have experience of software installation or windows applications you will need to seek further assistance for this s...
Page 44
5-2 operation mn1903 5.1.2 installing the driver software - windows nt windows nt does not support ‘plug and play’ so there will be no indication that a new card has been installed. The device driver for nextmove pci must be installed from the baldor motion toolkit cd. 1. Place the baldor motion too...
Page 45
Operation 5-3 mn1903 5.1.4 installing workbench v5 you will need to install workbench v5 to configure and tune the nextmove pci. 1. Insert the cdrom into the drive. 2. After a few seconds the setup wizard should start automatically. If the setup wizard does not appear, select run... From the windows...
Page 46
5-4 operation mn1903 5.1.5 starting workbench v5 1. On the windows start menu, select programs, workbench v5, workbench v5. Workbench v5 will start, and the tip of the day dialog will be displayed. You can prevent the tip of the day dialog appearing next time by removing the check mark next to show ...
Page 47
Operation 5-5 mn1903 3. In the select controller dialog, go to the drop down box near the top and select do not scan serial ports. Click scan to search for the nextmove pci. When the search is complete, click ‘nextmove pci card 0’ and then click select. 4. A dialog box will appear to tell you that t...
Page 48
5-6 operation mn1903 5. In the open dialog, look in the sub folder ‘nextmove pci’. Select the file with extension ‘.Chx’ and click open to download the firmware. The firmware will be downloaded to the nextmove pci. (a dialog box may be displayed to tell you that workbench v5 has detected the new fir...
Page 49: 5.2 Workbench V5
Operation 5-7 mn1903 5.2 workbench v5 workbench v5 is a fully featured application for programming and controlling the nextmove pci. The main workbench window contains a menu system, the toolbox and other toolbars. Many functions can be accessed from the menu or by clicking a button - use whichever ...
Page 50: 5.3 Configuring An Axis
5-8 operation mn1903 5.3 configuring an axis the nextmove pci is capable of controlling servo and stepper axes. This section describes the basic setup for both types of axis. Commands typed in the command window have immediate effect - they do not need to be separately downloaded to the nextmove pci...
Page 51
Operation 5-9 mn1903 5.3.3 selecting a scale mintmt defines all positional and speed related motion keywords in terms of encoder quadrature counts (for servo motors) or steps for stepper motors. The number of quadrature counts (or steps) is divided by the scale factor allowing you to use units more ...
Page 52
5-10 operation mn1903 5.3.4 setting the drive enable output the drive enable output allows nextmove pci to disable the drive in the event of an error. Each axis can be configured with its own drive enable output, or can share an output with other axes. If an output is shared, an error on any of the ...
Page 53
Operation 5-11 mn1903 4. If you are going to use the relay, drag the grey relay0 icon to the grey x axis icon on the right of the screen. To configure multiple axes to use the relay, repeat this step for the other axes. If you are using a digital output, drag the bright blue out icon to the grey x a...
Page 54
5-12 operation mn1903 5.4 servo axis - testing and tuning this section describes the method for testing and tuning a servo axis. To test a stepper axes, go straight to section 5.8. 5.4.1 testing the drive command output this section tests the operation and direction of the axis command output. It is...
Page 55
Operation 5-13 mn1903 6. To remove the demand and stop the test, type: stop.0 this should cause the demand produced at the demand 0 output to become 0v. 5.4.2 an introduction to closed loop control this section describes the basic principles of closed loop control. If you are familiar with closed lo...
Page 56
5-14 operation mn1903 this problem is overcome by using a term called integral gain (kint). This sums the error over time, so that the motor torque is gradually increased until the positional error is reduced to zero [ like a person gradually pushing harder and harder on your car until they’ve pushe...
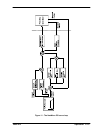
Page 57
Operation 5-15 mn1903 figure 11 - the nextmove pci servo loop.
Page 58
5-16 operation mn1903 5.5 servo axis - tuning for current control 5.5.1 selecting servo loop gains all servo loop parameters default to zero, meaning that the demand output will be zero at power up. Most servo amplifiers can be set to current (torque) control mode or velocity control mode; check tha...
Page 59
Operation 5-17 mn1903 3. Click in the kprop box and enter a value that is approximately one quarter of the value of kderiv. If the motor begins to vibrate, decrease the value of kprop or increase the value of kderiv until the vibration stops. Small changes may be all that is necessary. 4. In the mov...
Page 60
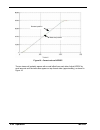
5-18 operation mn1903 5.5.2 underdamped response if the graph shows that the response is underdamped (it overshoots the demand, as shown in figure 12) then the value for kderiv should be increased to add extra damping to the move. If the overshoot is excessive or oscillation has occurred, it may be ...
Page 61
Operation 5-19 mn1903 5.5.3 overdamped response if the graph shows that the response is overdamped (it reaches the demand too slowly, as shown in figure 13) then the value for kderiv should be decreased to reduce the damping of the move. If the overdamping is excessive, it may be necessary to increa...
Page 62
5-20 operation mn1903 5.5.4 critically damped response if the graph shows that the response reaches the demand quickly and only overshoots the demand by a small amount, this can be considered an ideal response for most systems. See figure 14. Measured position demand position figure 14 - critically ...
Page 63
Operation 5-21 mn1903 5.6 servo axis - eliminating steady-state errors in systems where precise positioning accuracy is required, it is often necessary to position within one encoder count. Proportional gain, kprop, is not normally able to achieve this because a very small following error will only ...
Page 64
5-22 operation mn1903 5.7 servo axis - tuning for velocity control drives designed for velocity control incorporate their own velocity feedback term to provide system damping. For this reason, kderiv (and kvel) can be set to zero. Correct setting of the velocity feed forward gain kvelff is important...
Page 65
Operation 5-23 mn1903 the analog demand output is controlled by a 12-bit dac, which can create output voltages in the range -10v to +10v. This means a maximum output of +10v corresponds to a dac value of 2048. The value of kvelff is calculated by dividing 2048 by the number of quadrature counts per ...
Page 66
5-24 operation mn1903 9. Using the check boxes below the graph, select the measured velocity and demand velocity traces. Measured velocity demand velocity figure 15 - correct value of kvelff it may be necessary to make changes to the calculated value of kvelff. If the trace for measured velocity app...
Page 67
Operation 5-25 mn1903 5.7.2 adjusting kprop the kprop term can be used to reduce following error. Its value will usually be much smaller than the value used for an equivalent current controlled system. A fractional value, for example 0.1, will probably give the best response. 1. Click in the kprop b...
Page 68
5-26 operation mn1903 measured position demand position figure 16 - correct value of kprop the two traces will probably appear with a small offset from each other. Adjust kprop by small amounts until the two traces appear on top of each other (approximately), as shown in figure 16..
Page 69
Operation 5-27 mn1903 5.8 stepper axis - testing this section describes the method for testing a stepper axis. The stepper control is an open loop system so no tuning is necessary. 5.8.1 testing the drive command output this section tests the operation and direction of the axis command output. It is...
Page 70
5-28 operation mn1903 5.9 digital input/output configuration the digital i/o window can be used to setup other digital inputs and outputs. 5.9.1 digital input configuration the digital inputs tab allows you to define how each digital input will be triggered and, optionally, if it is to be allocated ...
Page 71
Operation 5-29 mn1903 4. Now drag the in1 icon onto the fwd limit icon . This will setup in1 as the forward limit input of axis 0. 5. Click apply to send the changes to the nextmove pci. Note: if required, multiple inputs can be configured before clicking apply. 5.9.2 digital output configuration th...
Page 72
5-30 operation mn1903 5.10 saving setup information when power is removed from the nextmove pci all data, including configuration and tuning parameters, is lost. You should therefore save this information in a file, which can be loaded when the card is next used. Alternatively, the information can b...
Page 73
Operation 5-31 mn1903 4. On the main menu, choose file, save file. Locate a folder, enter a filename and click save. 5.10.1loading saved information 1. In the toolbox, click the edit & debug icon. 2. On the main menu, choose file, open file... Locate the file and click open. A startup block should b...
Page 74
5-32 operation mn1903.
Page 75: 6.1 Introduction
Troubleshooting 6-1 mn1903 6.1 introduction this section explains common problems and their solutions. If you want to know the meaning of the led indicators, see section 6.2. 6.1.1 problem diagnosis if you have followed all the instructions in this manual in sequence, you should have few problems in...
Page 76
6-2 troubleshooting mn1903 6.2 nextmove pci indicators 6.2.1 status and can leds the backplate of the nextmove pci contains four leds. S1 and s2 represent general status information. C1 and c2 are can traffic indicators. The leds may illuminate red or green and can be continuous or flashing. Led sta...
Page 77
Troubleshooting 6-3 mn1903 6.2.2 communication if the problem is not listed below please contact baldor technical support. An oscilloscope will be useful for many of the electrical tests described below. Symptom check cannot detect nextmove pci check that the nextmove pci driver has been installed. ...
Page 78
6-4 troubleshooting mn1903 symptom check motor runs uncontrollably when controller is switched on and servo loop gains are applied or when a move is set in progress. Motor then stops after a short time. Check that the axis’ corresponding encoder and demand signals are connected to the same axes of m...
Page 79: 7.1 Introduction
Specifications 7-1 mn1903 7.1 introduction this section provides technical specifications of the nextmove pci 7.1.1 mechanical specifications description value input power (from host pc) +5v at 1200ma ±12v at 250ma additional current will be required when powering the encoders from the host pc’s +5v...
Page 80
7-2 specifications mn1903 7.1.3 analog outputs (drive demand/command - x7) description unit value type bipolar output voltage range vdc ±10 output current (max) ma 1 output dac resolution bits 14 (includes sign bit) equivalent resolution mv ±1.22 update interval immediate 7.1.4 digital inputs (x1 & ...
Page 81
Specifications 7-3 mn1903 7.1.6 digital outputs (x4) description unit value output current (maximum, each output) ma 50 update interval immediate 7.1.7 relay output (x8) description unit value contacts normally closed contact rating (resistive) 1a @ 24vdc or 0.5a @ 125vac maximum carrying current a ...
Page 82
7-4 specifications mn1903 7.1.9 stepper outputs (x10 & x11) description unit value output type pulse (step) and direction maximum output frequency mhz 3 output voltage 5v output current ma 20 max. 7.1.10canopen interface (x17) description unit value signal 2-wire, isolated channels 1 bit rate kbit/s...
Page 83: A.1 Introduction
Accessories a-1 mn1903 a.1 introduction nextmove pci is supplied with a software license to control 1, 2 ,3, 4 or 8 axes. Similarly, the nextmove pci expansion card is supplied with a software license to control a further 4 or 8 axes. A license cannot be upgraded. A.1.1 nextmove pci expansion card t...
Page 84
A-2 accessories mn1903 a description of the catalog numbers are shown in the following table: catalog number description pci002-501 nextmove pci expansion card with pnp digital outputs, 4 axis pci002-502 nextmove pci expansion card with pnp digital outputs, 8 axis pci002-503 nextmove pci expansion c...
Page 85
Accessories a-3 mn1903 a.1.3 expansion card status leds the backplate of the nextmove pci expansion card contains two leds, s1 and s2. These represent general status information. The leds may illuminate red or green and can be continuous or flashing. Expansion card led state(s) meaning both off the ...
Page 86
A-4 accessories mn1903 a.1.4 nextmove pci breakout module breakout modules are available for use with the nextmove pci and expansion cards, providing one or two part screw-down terminals for the i/o, power and relay connections, with 9-pin d-type connectors for the encoders and steppers. Can connect...
Page 87
Accessories a-5 mn1903 a.1.5 digital output modules the digital output drive on nextmove pci is in the form of a removable module which allows different types of outputs for different applications. Currently there are two modules available: catalog number description opt025-508 npn - n-channel unpro...
Page 88
A-6 accessories mn1903 a.1.8 baldor can nodes digital i/o can be expanded easily on nextmove pci using the baldor can (can2) connection. This provides a high speed serial bus interface to a range of i/o devices, including: h inputnode 8: 8 opto isolated digital inputs. H relaynode 8: 8 relay outputs...
Page 89
Accessories a-7 mn1903 a.1.9 nextmove pci can bracket board this is a compact alternative to using the breakout module when the nextmove pci controller is being used only as a can network manager. Both can channels are presented on 9-pin d-type connectors. The board is connected to the nextmove pci ...
Page 90
A-8 accessories mn1903.
Page 92
Printed in uk e baldor uk ltd baldor electric company p.O. Box 2400 ft. Smith, ar 72902-2400 tel: (479) 646-4711 fax: (479) 648-5792 www.Baldor.Com lt0166a00