- DL manuals
- Banner
- Controller
- SC26-2
- Instruction Manual
Banner SC26-2 Instruction Manual
Summary of SC26-2
Page 1
Xs/sc26-2 safety controller instruction manual original instructions 174868 rev. E 20 june 2014 174868.
Page 2: Contents
Contents 1 about this document .....................................................................................................4 1.1 important . . . Read this before proceeding! .................................................................................4 1.1.1 use of warnings and cautions...
Page 3
6.3.2 safety input device properties ........................................................................................ 69 6.4 safety input device function ................................................................................................... 71 6.4.1 safety circuit integrity leve...
Page 4: 1 About This Document
1 about this document 1.1 important . . . Read this before proceeding! It is the responsibility of the machine designer, controls engineer, machine builder, and/or maintenance electrician to apply and maintain this device in full compliance with all applicable regulations and standards. The device c...
Page 5
1.4 contact us corporate headquarters address: banner engineering corporate 9714 tenth avenue north minneapolis, minnesota 55441, usa phone: +1 763 544 3164 website: www.Bannerengineering.Com europe address: banner engineering emea park lane culliganlaan 2f diegem b-1831, belgium phone: +32 (0)2 456...
Page 6: 2 Overview
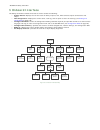
2 overview the banner xs/sc26-2 safety controllers are easy-to-use, configurable, and expandable modules (xs26-2xx models) designed to monitor multiple safety and non-safety input devices, providing safe stop and start functions for machines with hazardous motion. The safety controller can replace m...
Page 7
2.2 design and testing the xs/sc26-2 safety controllers are designed for up to category 4 pl e (iso 13849-1) and safety integrity level 3 (iec 61508 and iec 62061) safeguarding applications. It has been extensively tested to ensure that it meets these standards as well as iec 61131-2 and ul 61131-2 ...
Page 8
2.7 input and output connections 2.7.1 safety and non-safety input devices the base controller has 26 input terminals that can be used to monitor either safety or non-safety devices; these devices may incorporate either solid-state or contact-based outputs. Some of the input terminals can be configu...
Page 9
Functional stops according to iec 60204-1 and ansi nfpa79 the controller is capable of performing two functional stop types: • category 0: an uncontrolled stop with the immediate removal of power from the guarded machine • category 1: a controlled stop with a delay before power is removed from the g...
Page 10
2.10 confirming a configuration confirmation is a verification process where the safety controller analyzes the configuration generated by the pc interface for logical integrity and completeness. The user must review and approve the results before the configuration can be saved and used by the devic...
Page 11
3 specifications and requirements 3.1 specifications base controller and expansion modules mechanical stress shock: 15 g for 11 ms, half sine, 18 shocks total (per iec 61131-2) vibration: 3.5 mm occasional / 1.75 mm continuous at 5 hz to 9 hz, 1.0 g occasional and 0.5 g continuous at 9 hz to 150 hz:...
Page 12
Xs1ro and xs2ro safety relay modules bus power xs1ro 0.125 a (outputs on) xs2ro: 0.15 a (outputs on) maximum power 2000 va, 240 w electrical life 50,000 at full resistive load overvoltage category iii pollution degree 2 mechanical life 40,000,000 operations note: transient suppression is recommended...
Page 13: 4 Pc Interface
4 pc interface the xs26-2 expandable safety controller pc interface is a software application with real-time display and diagnostic tools that are used to: • design and edit configurations • write a configuration to the safety controller • read the current configuration from the safety controller • ...
Page 14
4.2 abbreviations abbreviation1 description avm adjustable valve monitoring input node of the safety outputs avmx adjustable valve monitoring input bp bypass input node of the bypass blocks and muting blocks bpx bypass switch input cd cancel delay input node of the safety outputs cdx cancel delay in...
Page 15
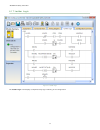
4.3 pc interface overview figure 4. Xs26-2 expandable safety controller pc interface xs/sc26-2 safety controller 15.
Page 16
(1) navigation toolbar starts a new project or opens a recent project and sample configurations displays project settings opens an existing project opens password manager saves (or saves as) the project to the user-defined location reads the data, such as fault log, configuration, network settings, ...
Page 17
4.4 creating a configuration the following steps are required to complete and confirm (write to controller) the configuration: 1. Install xs26-2 expandable safety controller software. See installation on page 13. 2. Become familiar with the pc interface options. See pc interface overview on page 15....
Page 18
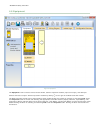
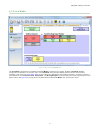
4.6 equipment figure 6. Equipment the equipment view is used to select the base model, add the expansion modules (input and output), and add input devices and status outputs. Add the expansion modules by clicking to the right of the base controller module. The base controller module can be customize...
Page 19
Figure 7. Module properties 4.7 adding inputs and status outputs safety and non-safety inputs can be added from either the equipment view or the functional view. Status outputs can be added from the equipment view only. When inputs are added on the equipment view, they are automatically placed in th...
Page 20
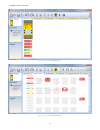
Figure 9. Non-safety inputs 3. Select appropriate device settings: basic settings: figure 10. Basic safety input settings • name—input device name; generated automatically and can be changed by the user • circuit type—the circuit and signal convention options appropriate for the selected input devic...
Page 21
Advanced settings (where applicable): figure 11. Advanced safety input settings • simultaneity (where applicable)—simultaneous or concurrent (see glossary on page 115 for definitions) • debounce times—the signal state transition time • monitored/non-monitored (where applicable) 4.7.2 adding status o...
Page 22
Figure 13. Status output properties • name • module • i/o (where applicable) • terminal • input or output (where applicable) • signal convention xs/sc26-2 safety controller 22.
Page 23
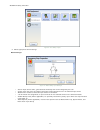
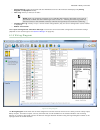
4.8 functional view figure 14. Functional view the functional view is used to create the control logic. The left column of the functional view is used for safety and non-safety inputs; the middle area is used for logic and function blocks and the right column is reserved for safety outputs. Safety a...
Page 24
• navigate between pages by clicking the left and right arrows within the page navigation area in the top right corner of the pc interface • modify properties of all blocks by either double-clicking a block or by selecting a block and clicking edit under the properties table • delete any block or co...
Page 25
Nand (us) (eu) input 1 input 2 output 0 x 1 x 0 1 1 1 0 the output value is based on inverting the logical and of 2 to 5 inputs. Output is off when all inputs are on. Nor (us) (eu) input 1 input 2 output 0 0 1 1 x 0 x 1 0 the output value is based on inverting the logical or of 2 to 5 inputs. Output...
Page 26
Sr flip-flop input 1 (set) input 2 (reset) output 0 0 value remains the same 0 1 0 (reset) 1 0 1 (set) 1 1 1 (set has priority) this block is set dominant (set has priority if both inputs are on). 4.8.2 function blocks function blocks provide built-in functionality for most common applications in on...
Page 27
Lockout/tagout hazardous energy (lockout/tagout) must be controlled in machine maintenance and servicing situations in which the unexpected energization, start up, or release of stored energy could cause injury. Refer to osha 29cfr 1910.147, ansi 2244.1, iso 14118 , iso 12100 or other relevant stand...
Page 28
E1 enabling mode starts when the enabling device ed1 is switched to the run state. Ed1 and es input devices have on/off control authority while in enable mode. When mr1 is used to perform a reset, the normal run mode is re-established and os1 and es1 have the on/off control authority. Enabling devic...
Page 29
The manual reset input device can be configured for one of two types of reset signals: monitored & non-monitored manual reset input monitored reset >.5s time non-monitored reset monitored reset non-monitored reset m0:es1 m0:mr1 monitored m0:so1 m0:es1 m0:mr1 non-monitored m0:so1 figure 20. Timing di...
Page 30
In the figure below, reference signal a3 is on page 1 of the function block diagram and the a3 and block is on page 2. The output node on the a3 and block can also be used on page 2 for other safety control logic. Reference signals reference signal a3 on page 1 and logic block a3 on page 2 figure 22...
Page 31
Manual reset of safety outputs sets the output to on if the output block configured for latch reset is on. Exceptions: • a safety output cannot be configured to use a manual reset when associated with a two hand control input or an enabling device function block. System fault reset sets the system t...
Page 32
Force a sequenced reset routine, which can be used to reduce or eliminate pass-through hazards in perimeter guarding applications (see safety input device properties on page 69). If the controlling inputs to a latch reset block or a safety output block are not in the run state, the reset for that bl...
Page 33
In the mute block properties menu in the advanced settings, if the bypass check box is checked, the option to select a bypass or a mute dependent override is possible. The mute dependent override is used to temporarily restart an incomplete mute cycle (for example after the mute time limit expires)....
Page 34
Mute bypass bypasstime expired bypasstime expired on or off m0:os1 m0:msp1-1 m0:msp1-2 m0:bp1 m0:so1 figure 27. Mute bypass mute function one way - 1 sensor pair max. Time max. Time max. Time max. Time mute ends due to defined area going clear mute ends due to defined area going clear note: mo:os1 m...
Page 35
Max. Time max. Time m0:msp2-1 m0:msp2-2 mute time limit m0:so1 m0:os1 m0:me1 m0:msp1-1 m0:msp1-2 mute function one way - 2 sensor pair on or off on or off figure 29. Timing diagram—one-way muting block, two muting sensor pairs mute function two way - 1 sensor pair m0:so1 m0:os1 m0:msp1 m0:me1 on or ...
Page 36
Mute function two way - 2 sensor pair max. Time max. Time max. Time max. Time m0:msp2-1 m0:msp2-2 mute time limit m0:so1 m0:os1 m0:me1 m0:msp1-1 m0:msp1-2 on or off on or off figure 31. Timing diagram—two-way muting block, two muting sensor pairs improper e-stop control not recommended the configura...
Page 37
To mute the primary safeguard appropriately, the design of a muting system must: 1. Identify the non-hazardous portion of the machine cycle 2. Involve the selection of the proper muting devices 3. Include proper mounting and installation of those devices warning: mute and bypass mute and bypass oper...
Page 38
Mute enable on or off safety input mute sensor pair safety output figure 33. Timing logic—one mute sensor pair with mute enable simultaneity timer reset function the mute enable input can also be used to reset the simultaneity timer of the mute sensor inputs. If one input is active for longer than t...
Page 39
Mute on power-up this function initiates a mute cycle after power is applied to the safety controller. If selected, the mute on power-up function will initiate a mute when: • the mute enable input is on (if configured) • the safety device inputs are active (in run mode) • mute sensors m1-m2 (or m3-m...
Page 40
Two-hand control block default nodes additional nodes notes tc (up to 4 tc nodes) in mp1 me two-hand control inputs must connect either directly to a two-hand control block or indirectly through a bypass block connected to a two-hand control block. It is not possible to use a two-hand control input ...
Page 41
Two-hand control & bypass function blocks if both tc1 actuators and the bp1 bypass switch active at the same time, the b1 bypass function block output and the two-hand control function block output turn off. The outputs for b1 and t1 will only turn on when either the tc1 actuators or the bp1 switch ...
Page 42
To configure the two-hand control mute option, the tc actuators first need to be connected to the two-hand control function block in the function view. Check boxes (blue square above) in the properties menu will display the names of all tc actuator input devices. Only those thc station boxes that ar...
Page 43
4.8.3 error codes the following table lists error codes that are encountered when attempting to make an invalid connection between blocks on the functional view. Pc interface code error a.1 this connection creates a loop. A.2 a connection from this block already exists. A.3 connecting a block to its...
Page 44
Pc interface code error l.3 a safety output block that has lr (latch reset) function enabled cannot be connected to two-hand control blocks or enabling device blocks. L.4 a safety output block that has power up mode set to "manual reset" cannot be connected to two-hand control blocks or enabling dev...
Page 45
4.10 industrial ethernet figure 40. Industrial ethernet view the industrial ethernet view of the pc interface allows configuration of the virtual status outputs, which offer the same functionality as status outputs (added on the equipment view) over the network (see status output signal conventions ...
Page 46
4.10.1 network settings figure 41. Network settings click network settings on the pc interface to open the network settings window. The default port (ethernet tcp) is 502 (tcp502); this is an internal value and is not listed in the network settings window. Table 1: default network settings setting n...
Page 47
4.10.2 ethernet/ip input assembly objects input (t->o) assembly objects instance id data length (16-bit words) description 100 (0x64) 8 used to access the basic information about the virtual status outputs 101 (0x65) 104 used to access the advanced information (including the basic information) about...
Page 48
Seconds since boot the time in seconds since power was applied to the safety controller. May be used in conjunction with the timestamp in the fault log and a real time clock reference to establish the time when a fault occurred. String (ethernet/ip and pccc protocol) the default format ethernet/ip s...
Page 49
System information type length (words) starting register configname string 8 388 config crc word 2 396 pccc fault log type length (words) starting register fault log entry 1 (most recent) see fault log entry table below 15 232 fault log entry 2 15 247 fault log entry 3 15 262 fault log entry 4 15 27...
Page 50
Fault log entry type length (words) timestamp udint 2 name length dword 2 name string string 6 error code word 1 advanced error code word 1 error message index word 1 reserved word 2 system information type length (words) class 0x72 instance 1 attribute seconds since boot udint 2 1 operating mode wo...
Page 51
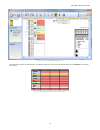
4.11 configuration summary figure 42. Configuration summary the configuration summary view displays the detailed information about all configured inputs, function and logic blocks, safety outputs, status outputs, and the related response times in a text format. Xs/sc26-2 safety controller 51.
Page 52
4.12 print options figure 43. Print options the pc interface provides several options to print the configuration. Click print on the toolbar to access the print options. The following print choices are available: • all—prints all views, including network settings (in ethernet-enabled versions) • equ...
Page 53
4.13 password manager figure 44. Password manager click password manager on the pc interface toolbar to edit the configuration access rights. The safety controller stores up to three user passwords to manage different levels of access to the configuration settings. The password for user1 provides fu...
Page 54
Note: network settings are sent separately from the configuration settings. Click send from the network settings window to write the network settings to the controller. 7. Reset the safety controller for the changes to take effect. 4.15 viewing and importing controller data the xs26-2 expandable saf...
Page 55
• wiring diagram (removes all other tabs and worksheets from the pc interface and displays only wiring diagram and equipment views) • fault log—history of the last 10 faults. Note: fault log numbering increases up to 4,294,967,295 unless the controller power cycle is performed, in which case the num...
Page 56
4.17 ladder logic figure 47. Ladder logic the ladder logic view displays a simplified relay logic rendering of the configuration. Xs/sc26-2 safety controller 56.
Page 57
4.18 live mode figure 48. Run time—live mode view the live mode view becomes accessible when live mode is clicked on the toolbar. Enabling live mode disables configuration modification on all other views. The live mode view provides additional device and fault information, including a fault code (se...
Page 58
Figure 49. Run time—equipment view figure 50. Run time—functional view xs/sc26-2 safety controller 58.
Page 59
Figure 51. Run time—wiring diagram view the table below shows the differences in the display method of the device statuses between the live mode view and all other views. Live mode equipment functional view wiring diagram bypassed fault inactive muted not used off off-delay on-delay ready run stop f...
Page 60
4.19 sample configuration external device monitoring (edm) external device monitoring (edm) external device monitoring (edm) gate switch optical sensor (x3) emergency stop on/off switch enabling device manual reset safety output devices mute enable (x3) mute sensor pair (x3) gate switch figure 53. S...
Page 61
Tip: you may notice that not all inputs are placed on page 1. There are two solutions to keep the configuration on one page. Perform one of the following steps: 1. Add a reference to the block located on a different page—click any of the empty placeholders in the middle area, select reference and se...
Page 62
Figure 54. Sample configuration—functional view xs/sc26-2 safety controller 62.
Page 63
4.20 application note important: the configuration software incorporates reference signals that represent the state of controller outputs, input devices and both function and logic blocks. A safety output reference signal can be used to control another safety output. In this type of configuration, t...
Page 64: 5 Onboard Interface
5 onboard interface the safety controller's onboard interface is used to access the following: • system status—displays the current status of safety outputs, and, when selected, inputs connected to that output • fault diagnostics—displays the current faults, fault log, and an option to clear the fau...
Page 65
5.1 configuration mode configuration mode provides options to send the current configuration to an sc-xm2 drive and to receive a configuration from the sc-xm2 drive. Note: a password is required to access the configuration mode menu. Important: entering the configuration mode turns off safety output...
Page 66: 6 System Installation
6 system installation 6.1 appropriate application the correct application of the safety controller depends on the type of machine and the safeguards that are to be interfaced with the controller. If there is any concern about whether or not your machinery is compatible with this controller, contact ...
Page 67
To remove the xs/sc26-2 safety controllers: 1. Push up on the bottom of the module. 2. Tilt the top of the module slightly forward. 3. Lower the module after the top rigid clip is clear of the din rail. Note: to remove an expansion module, pull apart other modules on each side of the desired module ...
Page 68
6.3.1 safety circuit integrity and iso 13849-1 safety circuit principles safety circuits involve the safety-related functions of a machine that minimize the level of risk of harm. These safety- related functions can prevent initiation, or they can stop or remove a hazard. The failure of a safety-rel...
Page 69
Fault exclusion an important concept within the requirements of iso 13849-1 is the probability of the occurrence of a failure, which can be reduced using a technique termed "fault exclusion." the rationale assumes that the possibility of certain well-defined failure(s) can be reduced via design, ins...
Page 70
Input circuit input signal cos timing rules stop state—so turns off when3: run state—so turns on when4: 2x complementary a and b 4 terminals 5 terminals pnp 24v off on off on at least 1 channel (a or b) within a pair of contacts is in the stop state. Simultaneous: a and b are concurrently in the sto...
Page 71
6.4 safety input device function es gs os rp ps sm thc ed 1 & 2 terminal single channel (see note 1) cat 2 cat 2 cat 2 cat 2 cat 2 2 & 3 terminal dual channel (see note 2) cat 3 cat 3 cat 3 cat 3 cat 3 type iiia cat 1 type iiib cat 3 cat 3 2 terminal dual channel pnp w/ integral monitoring (see note...
Page 72
6.4.1 safety circuit integrity levels the application requirements for safeguarding devices vary for the level of control reliability or safety category per iso 13849-1 (en954-1). While banner engineering always recommends the highest level of safety in any application, the user is responsible to sa...
Page 73
Rope pull emergency stop switches have many of the same requirements as emergency stop push buttons, such as positive (direct) opening operation, as described by iec 60947-5-1. See emergency stop push buttons on page 72 for additional information. In emergency stop applications, the rope pull switch...
Page 74
Protective (safety) stop requirements the required safety circuit integrity level is determined by a risk assessment and indicates the level of control performance that is acceptable, for example, category 4, control reliability (see safety circuit integrity and iso 13849-1 safety circuit principles...
Page 75
Optical safety devices must be placed at an appropriate safety distance (minimum distance), according to the application standards. Refer to the applicable standards and to manufacturer documentation specific to your device for the appropriate calculations. The response time of the safety controller...
Page 76
Caution: machine control must provide anti-repeat control appropriate anti-repeat control must be provided by the machine control and is required by u.S. And international standards for single-stroke or single-cycle machines. This banner device can be used to assist in accomplishing anti-repeat cont...
Page 77
European applications s the minimum distance (in millimeters) k the iso 13855 recommended hand-speed constant (in millimeters per second), in most cases is calculated at 1600 mm/sec, but may vary between 1600 to 2500 mm/sec based on the application circumstances; · not a conclusive determination; co...
Page 78
The environmental rating of the sensor must meet a minimum of ip54. When the sensor is specified for immersion in water, the sensor’s minimum enclosure level must be ip67. The interconnect cabling may require special attention. A wicking action may result in the ingress of liquid into the mat, possi...
Page 79
Safety mat safety distance (minimum distance) as a stand-alone safeguard, the safety mat must be installed at a safety distance (minimum distance) so that the exterior edge of the sensing surface is at or beyond that distance, unless it is solely used to prevent start/restart, or solely used for cle...
Page 80
The safety mat, its safety controller, and any output signal switching devices must meet, at a minimum, the category 1 safety requirements. See iso 13856-1 (en 1760-1) and iso 13849-1 (en 954-1) for relevant requirement details. The safety controller is designed to monitor 4-wire safety mats and is ...
Page 81
Mute device requirements the muting devices must, at a minimum, comply with the following requirements: 1. There must be a minimum of two independent hard-wired muting devices. 2. The muting devices must have one of the following: normally open contacts, pnp outputs (both of which must fulfill the i...
Page 82
6.4.12 adjustable valve monitoring (avm) function the adjustable valve (device) monitoring (avm) function is similar in function to one-channel external device monitoring (1-channel edm, see external device monitoring (edm) on page 90). The avm function monitors the state of the device(s) that are c...
Page 83
Caution: adjustable valve monitoring (avm) operation when an input is configured with automatic reset logic and is quickly cycled (from run to stop to run), the safety output(s) will not turn on until the avm input is satisfied. This could result in an on- delay up to the configured avm monitoring t...
Page 84
Safety inputs latch reset input cancel delay input so1 on off off delay time limit figure 63. Keep output on function for safety inputs with the latch reset off delay started off delay ended off delay normal end cancel delay performed safety inputs cancel delay input so1 off delay on off figure 64. ...
Page 85
Power up mode the safety output can be configured for three power-up scenarios (operational characteristics when power is applied): • normal power-up mode (default) • manual power-up mode • automatic power-up mode see manual reset input and latch reset block on page 30 for more information. Split (s...
Page 86
3. Set the desired output delay time. 4. Click ok. 5. Open the properties window of the safety output that will link to the safety output with an off-delay. 6. From link to safety output drop-down list, select the safety output with an off-delay to which you wish to link this safety output. Note: th...
Page 87
Gs so1 so2 figure 66. Timing diagram—linked safety outputs 6.6.1 solid-state safety outputs the solid-state safety outputs, for example, so1a and b, and so2a and b, are actively monitored to detect short circuits to the supply voltage, to each other, and to other voltage sources and are designed for...
Page 88
The level of the safety circuit integrity must be determined by risk assessment; this level is dependent on the configuration, proper installation of external circuitry, and the type and installation of the devices under control (fsds and mpces). The solid-state safety outputs are suitable for categ...
Page 89
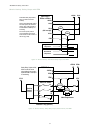
0v 24v 0v 24v * xs2so solid state safety output module xs26-2 base controller power supply power supply #1 #2 power supply 0v 24v 24v 0v* functional earth (optional) preferred 0v routing plan when a single power supply is used preferred 0v routing plan when separate power supplies are used +/- 30v p...
Page 90
Whenever possible, incorporating external device monitoring (edm) and/or adjustable valve monitoring (avm) is highly recommended to monitor devices under control (fsds and mpces) for unsafe failures. See external device monitoring (edm) on page 90 for more information. Output connections—when used, ...
Page 91
+24v dc mpce 1 so1 mpce1 safety input device edm safety controller mpce 2 mpce2 single-channel edm used to monitor both mpce feedback signals. If one or both channels do not close, the system enters a lockout mode. Figure 69. One-channel edm hookup +24v dc mpce 1 so1 mpce1 safety input device edm ed...
Page 92
Safety output 250 ms max. 250 ms max. 250 ms max. 250 ms max. 250 ms max. 250 ms max. Don’t care closed open closed open edm 1 edm 2 figure 72. Timing logic: two-channel edm, timing between channels safety output must match edm 2 must match edm 2 on off closed open edm 1 must match edm 1 must match ...
Page 93
• routing interconnecting control wires with low voltage or neutral that cannot result in energizing the hazard • locating all elements (modules, switches, devices under control, etc.) within the same control panel, adjacent to each other, and directly connected with short wires • properly installin...
Page 94
Generic hookup: safety output with edm xs/sc26-2xx xs2so or xs4so single-channel stop circuit dual-channel stop circuit +24vdc +24vdc 0vdc 0vdc so1a (so1 not split) so1b edm fsd1 fsd2 solid-state safety outputs so2, so3, and so4 can be wired similarily. When a solid-state safety output has been spli...
Page 95
6.7 status outputs 6.7.1 status output signal conventions there are two signal conventions selectable for each status output: "pnp on" (sourcing 24 v dc), or "pnp off" (non- conducting). The default convention is active = pnp on. Table 4: status output signal conventions function signal conventions ...
Page 96
Track output indicates the physical state of a particular safety output (on or off). Track output fault indicates when a particular safety output has a fault. Track output fault all indicates a fault from any safety output. Track output logical state indicates the logical state of a particular safet...
Page 97: 7 System Checkout
7 system checkout 7.1 schedule of required checkouts verifying the configuration and proper functioning of the safety controller includes checking each safety and non-safety input device, along with each output device. As the inputs are individually switched from the run state to the stop state, the...
Page 98
2. Whenever any maintenance or modification is performed on the system or on the machine being guarded by the system, to ensure continued proper controller function (see schedule of required checkouts on page 97) for the initial part of the commissioning checkout, the controller and associated safet...
Page 99
• if no latch reset functions are used, verify that the safety output turns on important: always test the safeguarding devices according to the recommendations of the device manufacture. In the sequence of steps below, if a particular function or device is not part of the application, skip that step...
Page 100
B. Change the muted safeguarding device to the stop state. C. Activate muting sensor pair 2. D. Deactivate muting sensor pair 1. 2. Verify the associated safety output remains on throughout the process. 3. Repeat the test in the wrong direction (muting sensor pair 2, then the safeguarding device, th...
Page 101
A. The associated safety outputs turn on b. The associated safety outputs turn off when the bypass timer expires. 3. Change the bypass switch to the run state and verify that the associated safety outputs turn on. 4. One at a time, switch the non-bypassed input devices to the stop state and verify t...
Page 102
1. With enabling device and jog button in run state in control of the primary safety output, verify that the output turns off when either the enabling device or the jog button is switched to the stop state. 2. With the enabling device in control of the primary safety output and the jog button in con...
Page 103: 8 Operating Instructions
8 operating instructions the safety controller can be operated using either the onboard or pc interface to monitor ongoing status. 8.1 led status led status meaning all off initialization mode sequence: green on for 0.5 s red on for 0.5 s off for 0.5 s min power applied power/fault off power off gre...
Page 104
8.4 lockout conditions input lockout conditions are generally resolved by repairing the fault and cycling the input off and then back on. Output lockout conditions (including edm and avm faults) are resolved by repairing the fault and then cycling the reset input connected to the fr node on the safe...
Page 105: 9 Troubleshooting
9 troubleshooting the controller is designed and tested to be highly resistant to a wide variety of electrical noise sources that are found in industrial settings. However, intense electrical noise sources that produce emi or rfi beyond these limits may cause a random trip or lockout condition. If r...
Page 106
9.1.1 verifying driver installation windows 7 and 8 1. Click start. 2. Type "device manager" in the search for programs and files field at the bottom and click device manager when windows locates it. 3. Expand the ports (com & lpt) dropdown menu. 4. Find xs26-2 expandable safety controller followed ...
Page 107
Windows xp and vista 1. Click start. 2. Right-click my computer and click properties. 3. Click device manager. Xs/sc26-2 safety controller drivers 1. Expand the ports (com & lpt) dropdown menu. 2. Find xs26-2 expandable safety controller followed by a com port number (for example, com3). It must not...
Page 108
To resolve an exclamation mark, a red ×, or a down arrow indicator: 1. Make sure your device is enabled: a. Right-click on the entry that has the indicator. B. If you see disable, the device is enabled; if you see enable, the device is disabled. • if the device is enabled, continue with troubleshoot...
Page 109
Fault code displayed message additional message steps to resolve 2.1 concurrency fault cycle input on a dual-channel input with both inputs in the run state, one input went to the stop state then back to run: • check the wiring • check the input signals • consider adjusting the debounce times 2.2 si...
Page 110
Fault code displayed message additional message steps to resolve 3.2 edmxx fault check terminal xx edm contact(s) failed to close within 250 ms after the safety outputs turned off: • check for a slow or stuck on contactor or relay • check for an open wire 3.3 edmxx fault check terminal xx edm contac...
Page 111
Fault code displayed message additional message steps to resolve 4.49-4.55 internal fault - internal failure—contact banner engineering (see repairs and warranty service repairs warranty on page 111). 4.56 display comm failure - display communication failure: • cycle power to the controller. If faul...
Page 112
10 components, models, and accessories 10.1 models all expandable and non-expandable base modules have 18 safety inputs, 8 convertible safety i/os, and 2 solid-state safety output pairs. Up to eight expansion modules, in any combination of input and output modules, can be added to the expandable mod...
Page 113
10.3 ethernet cordsets cat5e shielded cordsets cat5e crossover shielded cordsets length stp07 stpx07 2.1 m (7 ft) stp25 stpx25 7.62 m (25 ft) stp50 stpx50 15.2 m (50 ft) stp75 stpx75 22.9 m (75 ft) 10.4 interface modules note: external device monitoring (edm) is required to be wired separately to th...
Page 114: 11 Standards and Regulations
11 standards and regulations the list of standards below is included as a convenience for users of this banner device. Inclusion of the standards below does not imply that the device complies specifically with any standard, other than those specified in the specifications section of this manual. 11....
Page 115: 12 Glossary
12 glossary a automatic reset the safety input device control operation setting where the assigned safety output will automatically turn on when all of its associated input devices are in the run state. C change of state (cos) the change of an input signal when it switches from run-to-stop or stop-t...
Page 116
P pass-through hazard a pass-through hazard is associated with applications where personnel may pass through a safeguard (which issues a stop command to remove the hazard), and then continues into the guarded area, such as in perimeter guarding. Subsequently, their presence is no longer detected, an...
Page 117: Index
Index a abbreviations 14 accessories 112 add input 19 add safety input 19 add status output 21 and 24 auto configure 45 b bypass block 26 c checkout 97 cleaning 111 commissioning checkout 97 configuration 7, 44 configuration mode 64, 65 configuration summary 51, 64 confirmation 10 confirming a confi...