- DL manuals
- Baotian
- Scooter
- BT49QT-28
- Service Manual
Baotian BT49QT-28 Service Manual
Summary of BT49QT-28
Page 1
Bt49qt-28 model service manual.
Page 2: Contents
Contents chapter one maintenance of the motorcycle Ⅰ. Items of maintenance 1 Ⅱ. Periodic maintenance schedule and maintenance locations 1 Ⅲ. Maintenance specifications 4 Ⅳ. Throttle actuation inspection 5 Ⅴ. Air filter inspection and cleaning 6 Ⅵ. Brake blocks inspection 6 Ⅶ. Brake system inspection...
Page 3
Ⅲ. Front shock absorber service 48 Ⅳ. Front fork service 48 Ⅴ. Handlebar service 50 Ⅵ. Rear wheel service 51 Ⅶ. Rear brake service (disk brake) 52 Ⅷ. Rear shock absorber service 53 Ⅸ. Coolant system 53 chapter five electric part troubleshooting section one electric part common troubles and trouble d...
Page 4: Summary
Summary this 2-stroke scooter bt49qt-28 is with low weight, enough power, low oil consumption and good operating performance. This manual is for maintenance men to repair and maintain bt49qt-28 and it is also useful when maintain other models. This manual holds the latest technical information. We r...
Page 5
1 chapter one maintenance of the motorcycle Ⅰ Ⅰ Ⅰ Ⅰ. Items of maintenance when the motorcycle is used, parts loose and mechanical wear inevitably occur to varied extents. Neglecting of timely maintenance not only reduces its mechanical function, economic performance, stability and durability, but al...
Page 6
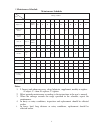
2 1. Maintenance schedule maintenance schedule time item mileage 1000km 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000 8000 9000 10000 11000 12000 engine oil new r 300km r r r r r r r r r r r engine oil strainer c c gasoline strainer r gear oil note 4 new r 300km r r throttle play a a a a carburetor i i c air f...
Page 7
3 Ⅲ Ⅲ Ⅲ Ⅲ. Maintenance specifications the basic methods of motorcycle maintenance include inspection, adjustment, tightening, lubrication, cleaning, supplementing and replacement, which constitute the main elements of maintenance. 1. Inspection inspection refers to basic inspecting operations in acc...
Page 8
4 iv. Throttle actuation inspection inspect throttle grip for easy and smooth movement. Inspect throttle free travel. Free travel: 2-6mm the main adjusting position is beside the carburetor. Remove rear store case inner cover. Adjust by loosening the fastening nut and turning the adjusting nut. Fine...
Page 9
5 Ⅴ Ⅴ Ⅴ Ⅴ. Air filter inspection and cleaning after a certain mileage, dust and impurities will gather in air filter case and strainer, which will clog strainer pores and reduce inlet of air and thus lead to excessive concentration of mixed gas and reduce the performance of engine. That’s why the st...
Page 10
6 vii. Brake system inspection, adjustment and replacement 1. Front brake (disk brake) remove the bolts linking brake caliper and front shock absorber. Remove brake caliper. * do not pull brake lever when brake caliper is removed so as to prevent jamming of brake blocks. If brake blocks are jammed, ...
Page 11
7 2. Rear brake (disk brake) remove the exhaust muffler. Remove the black dust cover. Remove the rear wheel nut. Remove the three mounting bolts of the rear wheel mounting base. Remove the rear wheel. Remove the bolts linking rear brake caliper and engine. Remove the rear brake caliper. * do not pul...
Page 12
8 2. Rear shock absorber press rear shock absorber to inspect actuation. Inspect rear shock absorber to see if there is oil leakage and if there is damage or loosening in machine parts. Lift rear wheel, press rear wheel right and left to inspect if engine suspension lug buffer bush is loose. Ix. Fro...
Page 13
9 inspect tire pressure by means of a tire pressure gauge * tire pressure should be inspected when the motorcycle is in a cold state. Specified pressure unit: kpa front tire 250 rear tire 250 tire specifications: front tire 130/60-13 rear tire 130/60-13 inspect if front wheel nut is loose. Inspect i...
Page 14
10 chapter two maintenance information i. Frame number and engine number location ii. Precautions in operation removed washers, 0-rings, elastic retaining rings and split pins must be replaced with new ones. When mounting bolts, nuts and screws, proceed from trial tightening, from larger diameters t...
Page 15
11 connectors must be inserted home. When connecting connectors with locks, confirm that their locks are fastened. Confirm that the wires are not loose. Confirm that connectors’ plastic sleeves completely cover the connectors without fail. Before connecting the connectors, confirm that their sleeves...
Page 16
12 engine: tighten part number screw specification torsion quadrature: n·m cyclinder head bolt a 2 m 7 9 cyclinder head boltb 2 m 7 9 oil filter cap 1 m 30 15 muffler flange fixing bolt 2 m 6 9 camshaft flange nut 4 m 7 16~18 valve adjusting bolt 2 m 5 9 chain tensioner bolt 1 m 6 10 leaking oil bol...
Page 17
13 standard torques: designations torques: n·m bolt, nut m5 5 bolt, nut m6 10 bolt, nutm8 21.5 bolt, nut m10 35 bolt, nut m12 55 screw m5 4 screw m6 9 flange bolt, nut m6 12 flange bolt, nut m8 27 flange bolt, nut m10 40 Ⅳ Ⅳ Ⅳ Ⅳ. Tools tools number flywheel disassemble ware z01 valve adjusting gripe...
Page 18
14 chapter four body troubleshooting section one body common troubles and trouble detection body part common troubles and possible causes are as follows: troubles causes details (reference) handlebar rotation not easy (strenuous turning or unstable tightness) over tightening of handlebar adjusting n...
Page 19
15 chart continued troubles causes details (reference) disk brake failure feeble brake lever inadequate liquid refer to “brake system inspection, adjustment and replacement, front brake service or rear brake service” contaminated brake block and brake disc bent or deformed brake disc contaminated br...
Page 20
16 chart continued troubles causes details (reference) deviation of motorcycle direction (inclining to roadside) steering stem rotation not easy refer to “front fork service” bent shock absorber refer to “front shock absorber service” shock absorber oil leakage bent front axle, incorrect wheel mount...
Page 21
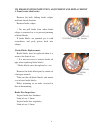
17 section two detailed description of body parts malfunction precautions in operation: forced mounting or dismounting of body cover parts will cause damage to claws and slots of corresponding hoods. When mounting body cover parts, be sure to align the corresponding parts of hoods. When mounting bod...
Page 22
18 axle bending inspection place axle on a v-seat and measure with a dial gauge. The dial gauge indicates a 1/2 bending value. Limit of use: replace if >0.2mm. Wheel rim oscillation inspection measure oscillation value on a correcting bench. Limit of use: replace if >2.0mm. Traverse direction: repla...
Page 23
19 front wheel mounting mount brake disc, tighten brake disc mounting bolts. Torque: 27n·m spread front axle with a thin film of grease. Mount front axle from left side. Mount in order small bush, left front shock absorber, front axle bush, front wheel, transmission gearbox, right front shock absorb...
Page 24
20 connect a transparent hose to exhaust valve. Grip brake lever fast and open exhaust valve 1/2 turn to let out air and lock exhaust valve. Repeat this operation till no bubbles are exhausted from brake oil passage. ·do not release brake lever before exhaust valve is closed. At the completion of ad...
Page 25
21 inspection inspect for wear or ageing of main and auxiliary cups on pistons. Inspect for scratches and other damages on main cylinder and piston. Measure main cylinder bore. Measure the outside diameter of piston at the end of auxiliary cup. Mounting apply pure brake oil to piston, main cup and a...
Page 26
22 absorber arm and if there is damage or loosening of any part. Mounting mount front shock absorber on front fork and mount 2 bolts. Torque: upper bolt 40n·m. Mount bodycovering parts. Mount front wheel. Mount front fender and front brake caliper. Ⅳ Ⅳ Ⅳ Ⅳ. Front fork service dismounting remove fron...
Page 27
23 inspection inspect if there is slot or pit in bearing cup and bearing top. If there is, effect replacemented. Inspect for completeness of bearing balls and if there is, effect replacement with new ones. Inspect for proper tightness of steering stem and if not, effect adjustment and fasten it. Ins...
Page 28
24 Ⅴ Ⅴ Ⅴ Ⅴ. Handlebar service dismounting remove covering parts of front part, rear part, upper cover and nether cover of handlebar. Remove the meter assy. Remove two bolts of rear brake main cylinder and remove brake main cylinder. Remove connectors of left handlebar switch. Remove 2 screws of left...
Page 29
25 mounting mount nether cover of handlebar. Mount handlebar on steering stem guide tube, fit bush, setting bolt and nut. Torque: 45 n·m mount upper cover of handlebar. Mount front and rear brake main cylinder. Mount left and right handlebar switch. Apply grease to throttle cable. Mount throttle gri...
Page 30
26 rear wheel oscillation inspection measure oscillation value on a correcting bench by means of micrometers. Limit of use: longitudinal >2.0 mm traverse >2.0 mm mounting mount rear brake disc and fasten the bolts. Torque: 27n·m mount rear wheel in an order reversed to that of dismounting. Torque: 1...
Page 31
27 inspection inspect rear shock absorber oil seal for oil leakage, inspect buffer bar and spring for deformation and other parts for damage and loosening. Mounting mount rear shock absorber. Torque: upper mounting bolt: 40n·m lower mounting bolt: 25n·m mount motorcycle body covering parts..
Page 32
28 chapter five electric part troubleshooting section one electric part common troubles and trouble detection troubles causes details no power voltage battery discharge no electrolyte whitened electrode plate battery short circuit (overdischarging) poor adjusting rectifier refer to “power supply sys...
Page 33
29 troubles causes details generator running not easy poor primary ignition loop poor ignition coil poor contact of wire or connector poor main switch refer to “ignition system service’ poor secondary ignition loop poor ignition coil poor contact of wire or connector poor main switch poor ignition t...
Page 34
30 section two detailed description of electric assemblies and parts service i. Precautions in electric circuit service 1. Main switch must be set at position “off” before wires are connected or disconnected. 2. When connectors with locks are disconnected, locks must be pressed or lifted. 3. Connect...
Page 35
31 1. Storage battery precautions in using storage battery ○, 1 do not effect the first starting of a new motorcycle by electric starter as a new storage battery has only 80% of full capacity. The difficulty in starting a new motorcycle often causes overdischarging of storage battery. ○, 2 mf storag...
Page 36
32 in the following cases, effect replenishing charging of new storage battery case for replenishing replenishing method 0 ℃ and below in winter charge for 2-3 hours at the charging current value (standard current) indicated on storage battery cover. Stored in high-temperature and high- humidity env...
Page 37
33 charging current: standard: 0.6a quick: 6.0a charging time: standard: 5~10 hours quick : 30 minutes at completion of charging: open circuit: 12.8v and above 2 22 2、 、 、 、charging system inspection electric leakage inspection remove earthing wire from storage battery, connect voltmeter between sto...
Page 38
34 3. Voltage adjusting rectifier troubles causes inspection method troubleshooting parameter burnt bulb in lighting system damaged voltage adjusting part of voltage adjusting rectifier start engine and measure lighting coil voltage. In case voltage rises with the rise of engine speed, trouble exist...
Page 39
35 main wire terminal loop inspection remove front cover. Remove voltage adjusting rectifier plug 4p and measure conductivity between main wire terminals. Item (wire color) judgment between storage (red) and motorcycle earthing with storage battery voltage between earthing wire (green) and motorcycl...
Page 40
36 iii. Ignition system service troubles causes (inspect and judge from ○ ○ ○ ○, 1 ) ignition coil voltage too low ○, 1 inner resistance too low, inspect with a specified circuit tester. ○, 2 crankshaft speed too low (storage battery voltage too low, or starting rod too feeble when tread on) ○, 3 ci...
Page 41
37 ignition and charging coils ○, 2 poor ignition and charging coils troubles causes (inspect and judge from ○ ○ ○ ○, 1 ) trigger coil voltage too low ○, 1 inner resistance too low, measuree with specified circuit tester. ○, 2 crankshaft speed too low (storage battery voltage too low or starting rod...
Page 42
38 ignition primary coil voltage remove spark plug as illustrated and mount a faultless spark plug. Connect spark plug with engine earthling. Note: effect correct connection of wires and their measurements。 cylinder compression pressure measurement is effected in normal condition (measure with spark...
Page 43
39 ignition and charging coil note: mount spark plug on cylinder head, inspect at normal compression pressure. Remove cdi set connector 6p, connect distributor between ignition and charging coil at wire terminal (black/red terminal) and green terminal. Actuate starting motor or tread on starting rod...
Page 44
40 3. 3. 3. 3. Cdi check cdi check cdi check cdi check troubles causes 1. Poor contact 2. Absence of high-voltage 3. Occasional misfire 4. Poor acceleration 5. Effective kick starting, elctronic starting failure 1. Damaged terminal, poor connecting or contact 2. Punctured or damaged diode 3. Punctur...
Page 45
41 primary coil inspection measure resistance between primary terminals. Standard value: 0.21Ω±10% (20℃) resistance within standard value indicates good state. Resistance “∞” (infinity) indicates open circuit of coil. Replace coil. Secondary coil inspection measure primary coil resistance between te...
Page 46
42 Ⅳ Ⅳ Ⅳ Ⅳ. Electric starting system service troubles causes electric starting failure with normal circuit and normal starting motor rotation one-way clutch spring fatigue or breakage starting relay failure without closing sound when started but with other electric circuits normal damaged brake swit...
Page 47
43 starting relay earthing loop inspection remove starting relay connector. Inspect conductivity between wire connector terminal yellow/red wire and motorcycle earthing. Conductivity between terminal yellow/red wire and motorcycle earthing when starting button is pressed. Inspect conductivity of sta...
Page 48
44 1.Headlight adjustment and dismounting loosen headlight fastening bolt and turn headlight to adjust headlight beam. Remove headlight fastening bolt. Remove headlight cover. Remove headlight bulb. Mounting is effected in an order reversed to that of dismounting. (if want to change healight bulb, t...
Page 49
45 remove front head cover. Remove main switch wire connector. Inspect conductivity between connector terminals. 5. Horn voltage supplied current supplied horn condition location of trouble troubleshooting 10~ 14.5v 0~2a no sound horn increase horn current, turn out adjusting screw counterclockwise ...
Page 50
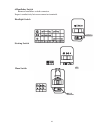
46 6.Handlebar switch remove handlebar switch connector. Inspect conductivity between connector terminals. Headlight switch starting switch horn switch.
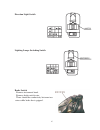
Page 51
47 direction light switch lighting lamps switching switch brake switch remove instrument hood. Remove brake switch wire. There should be conductivity between two wires while brake bar is gripped..
Page 52
48 Ⅵ Ⅵ Ⅵ Ⅵ. Circuit diagram.