- DL manuals
- Basler
- Camera Accessories
- slA1000-30fm
- User Manual
Basler slA1000-30fm User Manual - 1.4
Specifications, Requirements, and Precautions
Basler scout light
7
1.4
Mechanical Specifications
The camera housing conforms to protection class IP30 provided the lens mount is covered by a lens
or by the cap that is shipped with the camera.
1.4.1
Camera Dimensions and Mounting Points
The cameras are manufactured with high precision. Planar, parallel, and angular sides guarantee
precise mounting with high repeatability.
The camera dimensions in millimeters are as shown in Figure 5.
Camera housings are equipped with four mounting holes on the top and four mounting holes on the
bottom as shown in the drawings.
Summary of slA1000-30fm
Page 1
Basler scout light user’s manual (for scout light cameras used with basler’s pylon api) document number: aw000753 version: 02 language: 000 (english) release date: 17 june 2009.
Page 2
For customers in the u.S.A. This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a class a digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the fcc rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial en...
Page 3
Contacting basler support worldwide europe: basler ag an der strusbek 60 - 62 22926 ahrensburg germany tel.: +49-4102-463-500 fax.: +49-4102-463-599 bc.Support.Europe@baslerweb.Com americas: basler, inc. 855 springdale drive, suite 160 exton, pa 19341 u.S.A. Tel.: +1-877-934-8472 fax.: +1-610-280-76...
Page 5
Table of contents basler scout light i table of contents 1 specifications, requirements, and precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 1.1 models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 1.2 genera...
Page 6
Table of contents ii basler scout light 5.7 input and output lines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32 5.7.1 i/o schematic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32 5.7.2 input...
Page 7
Table of contents basler scout light iii 7 pixel data formats . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75 7.1 setting the pixel data format . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75 7.2 pixel data for...
Page 8
Table of contents iv basler scout light 9.12 configuration sets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127 9.12.1 saving user sets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128 9.12.2 sel...
Page 9: And Precautions
Specifications, requirements, and precautions basler scout light 1 1 specifications, requirements, and precautions this section lists the camera models covered by the manual. It provides the general specifications for those models and the basic requirements for using them. This section also includes...
Page 10: 1.2
Specifications, requirements, and precautions 2 basler scout light 1.2 general specifications specification sla750-60fm sla1000-30fm sensor size (h x v pixels) 752 x 480 1034 x 779 sensor type aptina mt9v022 (formerly known as the micron mt9v022) progressive scan cmos sony icx204 al progressive scan...
Page 11
Specifications, requirements, and precautions basler scout light 3 specification sla1390-17fm sla1600-14fm sensor size (h x v pixels) 1392 x 1040 1626 x 1236 sensor type sony icx267 al progressive scan ccd sony icx274 al progressive scan ccd optical size 1/2" 1/1.8" pixel size 4.65 µm x 4.65 µm 4.4 ...
Page 12: 1.3
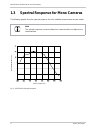
Specifications, requirements, and precautions 4 basler scout light 1.3 spectral response for mono cameras the following graphs show the spectral response for each available monochrome camera model. Fig. 1: sla750-60fm spectral response note the spectral response curves excludes lens characteristics ...
Page 13
Specifications, requirements, and precautions basler scout light 5 fig. 2: sla1000-30fm spectral response fig. 3: sla1390-17fm spectral response wave length (nm) rela ti ve r espon se wave length (nm) relative response.
Page 14
Specifications, requirements, and precautions 6 basler scout light fig. 4: sla1600-14fm spectral response wave length (nm) rela ti ve r espon se.
Page 15: 1.4
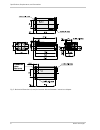
Specifications, requirements, and precautions basler scout light 7 1.4 mechanical specifications the camera housing conforms to protection class ip30 provided the lens mount is covered by a lens or by the cap that is shipped with the camera. 1.4.1 camera dimensions and mounting points the cameras ar...
Page 16
Specifications, requirements, and precautions 8 basler scout light fig. 5: mechanical dimensions (in mm) for cameras with the standard c-mount lens adapter.
Page 17: 1.4.2
Specifications, requirements, and precautions basler scout light 9 1.4.2 mechanical stress test results scout cameras were submitted to an independent mechanical testing laboratory and subjected to the stress tests listed below. The mechanical stress tests were performed on selected camera models wi...
Page 18: 1.5
Specifications, requirements, and precautions 10 basler scout light 1.5 software licensing information the software in the camera includes the lwip tcp/ip implementation. The copyright information for this implementation is as follows: copyright (c) 2001, 2002 swedish institute of computer science. ...
Page 19: 1.6
Specifications, requirements, and precautions basler scout light 11 1.6 avoiding emi and esd problems the cameras are frequently installed in industrial environments. These environments often include devices that generate electromagnetic interference (emi) and they are prone to electrostatic dischar...
Page 20: 1.7
Specifications, requirements, and precautions 12 basler scout light 1.7 environmental requirements 1.7.1 temperature and humidity housing temperature during operation: 0 °c ... +50 °c (+32 °f ... +122 °f) humidity during operation: 20 % ... 80 %, relative, non-condensing storage temperature: -20 °c ...
Page 21: 1.8
Specifications, requirements, and precautions basler scout light 13 1.8 precautions avoid dust on the sensor the camera is shipped with a cap on the lens mount. To avoid collecting dust on the camera’s sensor, make sure that you always put the cap in place when there is no lens mounted on the camera...
Page 22
Specifications, requirements, and precautions 14 basler scout light warranty precautions to ensure that your warranty remains in force: do not remove the camera’s serial number label if the label is removed and the serial number can’t be read from the camera’s registers, the warranty is void. Do not...
Page 23: 2 Software and Hardware
Software and hardware installation basler scout light 15 2 software and hardware installation the information you will need to install and operate the camera is included in the installation and setup guide for cameras used with basler’s pylon api, (aw000611xx000). You can download the guide from the...
Page 24
Software and hardware installation 16 basler scout light.
Page 25: 3 Tools For Changing Camera
Tools for changing camera parameters basler scout light 17 3 tools for changing camera parameters this section explains the options available for changing the camera’s parameters. The available options let you change parameters either by using stand-alone tools that access the camera via a gui or by...
Page 26
Tools for changing camera parameters 18 basler scout light.
Page 27: 4 Functional Description
Functional description basler scout light 19 4 functional description this section provides an overview of the camera’s functionality from a system perspective. The overview will aid your understanding when you read the more detailed information included in the next chapters of the user’s manual. 4....
Page 28
Functional description 20 basler scout light fig. 6: ccd sensor architecture ccd sensor vert. Shift reg. Vert. Shift reg. Vert. Shift reg. Vert. Shift reg. Pixels pixels pixels pixels horizontal shift register adc vgc.
Page 29: 4.2
Functional description basler scout light 21 4.2 overview (sla750-60fm only) each camera provides features such as a full frame shutter and electronic exposure time control. The sensor chip includes gain controls, adcs, and other digital devices. Exposure start, exposure time, and charge readout can...
Page 30
Functional description 22 basler scout light fig. 7: cmos sensor architecture cmos sensor pixel array digitized pixel data adcs analog processing digital processing.
Page 31: 5 Physical Interface
Physical interface basler scout light 23 5 physical interface this section provides detailed information, such as pinouts and voltage requirements, for the physical interface on the camera. This information will be especially useful during your initial design-in process. 5.1 general description of t...
Page 32: 5.2
Physical interface 24 basler scout light 5.2 connector pin assignments and numbering 5.2.1 ieee 1394b socket pin assignments the ieee 1394b socket is used to supply power to the camera and to interface video data and control signals. The pin assignments for the socket are as shown in table 4. Note t...
Page 33: 5.2.2
Physical interface basler scout light 25 5.2.2 12-pin receptacle pin assignments the 12 pin receptacle is used to access the one physical input line and one physical output line available on the camera. The pin assignments for the receptacle are shown in table 5. Pin numbering for the 12-pin recepta...
Page 34: 5.2.3
Physical interface 26 basler scout light 5.2.3 pin numbering fig. 9: pin numbering for the ieee 1394b socket and the 12-pin receptacle 1 12 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9.
Page 35: 5.3
Physical interface basler scout light 27 5.3 connector types 5.3.1 ieee 1394b connector the 1394b socket on the camera is a standard, 9-pin ieee 1394b bilingual socket. The recommended mating connector is any standard, 9-pin ieee 1394b plug. 5.3.2 12-pin connector the 12-pin connector on the camera ...
Page 36: 5.4
Physical interface 28 basler scout light 5.4 cabling requirements 5.4.1 ieee 1394b cable the maximum length of the ieee 1394b cable used between the camera and the adapter in your pc or between the camera and a 1394b hub is 4.5 meters as specified in the ieee 1394 standard. Standard, 9-pin, shielded...
Page 37
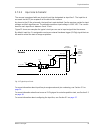
Physical interface basler scout light 29 fig. 10: i/o cable avoid applying voltage to the non-functional pins applying incorrect voltages to the non-functional pins in the 12 pin connector may damage the electronic components in the camera. We recommend that you do not apply signals of any kind to t...
Page 38: 5.5
Physical interface 30 basler scout light 5.5 ieee 1394b device information the camera uses an ieee1394b - 2002 compliant physical layer device that can transmit at speeds up to 800 mbit/s (s800). The device is backward compatible with ieee 1394a - 2000 devices. Detailed spec sheets for ieee 1394b - ...
Page 39: 5.6
Physical interface basler scout light 31 5.6 camera power camera power must be supplied to the camera via the ieee 1394b cable. Power consumption is as shown in the specification tables in section 1 of this manual. If your camera is connected to an ieee 1394b adapter in a desktop computer, consult t...
Page 40: 5.7
Physical interface 32 basler scout light 5.7 input and output lines 5.7.1 i/o schematic fig. 11: i/o line schematic 5.7.2 input line description 5.7.2.1 voltage requirements the following voltage requirements apply to the camera’s i/o input (pin 3 of the 12-pin receptacle): voltage significance +0 t...
Page 41
Physical interface basler scout light 33 5.7.2.2 input line schematic the camera is equipped with one physical input line designated as input line 1. The input line is accessed via the 12-pin receptacle on the back of the camera. As shown in the i/o line schematic, the input line is opto-isolated. S...
Page 42: 5.7.3
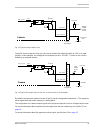
Physical interface 34 basler scout light 5.7.3 output line description 5.7.3.1 voltage requirements the following voltage requirements apply to the i/o output vcc (pin 10 of the 12-pin receptacle): 5.7.3.2 output line schematic the camera is equipped with one physical output line designated as outpu...
Page 43
Physical interface basler scout light 35 fig. 13: typical voltage output circuit figure 14 shows a typical circuit you can use to monitor the output line with an led or an opto- coupler. In this example, the voltage for the external circuit is +24 vdc. Current in the circuit is limited by an externa...
Page 44
Physical interface 36 basler scout light for more information about assigning camera output signals to the physical output line, see section 8.2 on page 88 ..
Page 45: 6 Image Acquisition Control
Image acquisition control basler scout light 37 6 image acquisition control this section provides detailed information about controlling image acquisition. You will find details about setting the exposure time for each acquired image and about how the camera’s maximum allowed acquisition frame rate ...
Page 46: 6.1.2
Image acquisition control 38 basler scout light 6.1.2 acquiring one image at a time in “single frame” operation, the camera acquires and transmits a single image. To select single frame operation, the camera’s acquisition mode parameter must be set to single frame. To begin image acquisition, execut...
Page 47
Image acquisition control basler scout light 39 // set camera in continous mode camera.Acquisitionmode.Setvalue( acquisitionmode_continuous ); // set a frame rate and getting the resulting frame rate camera.Acquisitionframerateenable.Setvalue( true ); camera.Acquisitionframerateabs.Setvalue( 20.5 );...
Page 48: 6.2
Image acquisition control 40 basler scout light 6.2 controlling image acquisition with a software trigger you can configure the camera so that image acquisition will be controlled by issuing a software trigger. The software trigger is issued by executing a trigger software command. Image acquisition...
Page 49: 6.2.2
Image acquisition control basler scout light 41 you can also use the basler pylon viewer application to easily set the parameters. For more information about the pylon viewer, see section 3.1 on page 17 . 6.2.2 acquiring a single image by applying one software trigger you can set the camera to react...
Page 50: 6.2.3
Image acquisition control 42 basler scout light 6.2.3 acquiring images by applying a series of software triggers you can set the camera to react to multiple applications of the software trigger and then apply a series of software triggers to acquire images. To do so, follow this sequence: 1. Access ...
Page 51
Image acquisition control basler scout light 43 camera.Acquisitionframerateabs.Setvalue( 60.0 ); double resultingframerate = camera.Resultingframerateabs.Getvalue( ); // how to disable the framerateabs parameter camera.Acquisitionframerateenable.Setvalue( false ); for detailed information about usin...
Page 52: 6.3
Image acquisition control 44 basler scout light 6.3 controlling image acquisition with a hardware trigger you can configure the camera so that an external hardware trigger (extrig) signal applied to the camera’s input line will control image acquisition. A rising edge or a falling edge of the extrig...
Page 53: 6.3.1
Image acquisition control basler scout light 45 6.3.1 exposure modes if you are triggering exposure start with an extrig signal, two exposure modes are available, "timed" and "trigger width." timed exposure mode when timed mode is selected, the exposure time for each image is determined by the value...
Page 54
Image acquisition control 46 basler scout light when you operate the camera in trigger width exposure mode, you must use the camera’s exposure setting to set an exposure time. The exposure time setting will be used by the camera to operate the trigger ready signal. You should adjust the exposure set...
Page 55: 6.3.2
Image acquisition control basler scout light 47 camera.Exposuretimeabs.Setvalue( 3000 ); // set for the width exposure mode, set minimum exposure time to 3000 µs camera.Exposuremode.Setvalue( exposuremode_triggerwidth ); camera.Exposuretimeabs.Setvalue( 3000 ); for detailed information about using t...
Page 56: 6.3.3
Image acquisition control 48 basler scout light 6.3.3 acquiring a single image by applying one hardware trigger transition you can set the camera to react to a single transition of an external hardware trigger (extrig) signal and then you can transition the extrig signal to begin image acquisition. ...
Page 57: 6.3.4
Image acquisition control basler scout light 49 for more information about the pylon viewer, see section 3.1 on page 17 . For more information about the trigger ready signal, see section 6.7 on page 57 . For more information about the camera’s exposure time parameter, see section 6.4 on page 51 . 6....
Page 58
Image acquisition control 50 basler scout light you can set the exposure time and the acquisition mode parameter values from within your application software by using the pylon api. You can also execute the acquisition start and stop commands. The following code snippet illustrates using the api to ...
Page 59: 6.4
Image acquisition control basler scout light 51 6.4 exposure time parameters many of the camera’s image acquisition modes require you to specify an exposure time. There are two ways to set exposure time: by setting "raw" values or by setting an "absolute value". The two methods are described below. ...
Page 60
Image acquisition control 52 basler scout light changing the exposure time base normally, the exposure time is adjusted by setting the value of the exposure time raw parameter as explained above. However, if you require an exposure time that is longer than what you can achieve by changing the value ...
Page 61: 6.4.2
Image acquisition control basler scout light 53 6.4.2 setting the exposure time using "absolute" settings you can also set the exposure time by using an "absolute" value. This is accomplished by setting the exposure time abs parameter. The units for setting this parameter are µs and the value can be...
Page 62: 6.5
Image acquisition control 54 basler scout light 6.5 overlapping exposure and sensor readout (all models except sla750-60fm) the image acquisition process on the camera includes two distinct parts. The first part is the exposure of the pixels in the imaging sensor. Once exposure is complete, the seco...
Page 63: 6.5.1
Image acquisition control basler scout light 55 fig. 20: overlapped exposure determining whether your camera is operating with overlapped or non-overlapped exposures is not a matter of issuing a command or switching a setting on or off. Rather the way that you operate the camera will determine wheth...
Page 64: 6.6
Image acquisition control 56 basler scout light for more detailed guidelines about using an external trigger signal with the trigger width exposure mode and overlapped exposure, refer to the application notes called "using a specific external trigger signal with overlapped exposure" (aw000565xx000)....
Page 65: 6.7
Image acquisition control basler scout light 57 6.7 trigger ready signal 6.7.1 trigger ready signal (all models except sla750-60fm) as described in the previous section, the cameras can operate in an “overlapped” acquisition fashion. When the camera is operated in this manner, it is especially impor...
Page 66
Image acquisition control 58 basler scout light fig. 22: trigger ready signal you should be aware that if the acquisition frame rate abs parameter is enabled, the operation of the trigger ready signal will be influenced by the value of the parameter: if the value of the parameter is greater than zer...
Page 67: 6.7.2
Image acquisition control basler scout light 59 6.7.2 trigger ready signal (sla750-60fm only) as described in an earlier section, on these cameras the exposure for an image acquisition must not begin until readout of the previously acquired image has ended. The camera supplies a “trigger ready” (tri...
Page 68
Image acquisition control 60 basler scout light you should be aware that if the acquisition frame rate abs parameter is enabled, the operation of the trigger ready signal will be influenced by the value of the parameter: if the value of the parameter is greater than zero but less than the maximum al...
Page 69: 6.8
Image acquisition control basler scout light 61 6.8 exposure active signal the camera’s “exposure active” (expac) signal goes high when the exposure time for each image acquisition begins and goes low when the exposure time ends as shown in figure 24. This signal can be used as a flash trigger and i...
Page 70: 6.9
Image acquisition control 62 basler scout light 6.9 acquisition timing chart figure 25 shows a timing chart for image acquisition and transmission. The chart assumes that exposure is triggered with an extrig signal with rising edge activation and that the camera is set for programmable exposure mode...
Page 71
Image acquisition control basler scout light 63 total start delay = 50.33 µs fig. 25: exposure start controlled with an extrig signal you can calculate the frame readout time by using this formula: frame readout time = t r = ( aoi height x c 1 ) + c 2 where the values for the constants c 1 and c 2 a...
Page 72
Image acquisition control 64 basler scout light if t b ≤ t r , then t e = t r + 250 µs if t b > t r , then t e = t b + 250 µs you can determine the value of the payload size and packet size parameters from within your application software by using the pylon api. The following code snippet illustrate...
Page 73: Rate
Image acquisition control basler scout light 65 6.10 maximum allowed acquisition frame rate (all models except sla750-60fm) in general, the maximum allowed acquisition frame rate can be limited by three factors: the amount of time it takes to read an acquired image out of the imaging sensor and into...
Page 74
Image acquisition control 66 basler scout light increasing the maximum allowed frame rate you may find that you would like to acquire frames at a rate higher than the maximum allowed with the camera’s current settings. In this case, you must first use the three formulas described below to determine ...
Page 75
Image acquisition control basler scout light 67 formula 2: calculates the maximum frame rate based on the exposure time for the acquired frames: where the constant c 3 depends on the camera model as shown in the table below: formula 3: calculates the maximum frame rate based on the number of packets...
Page 76: Allowed Frame Rate
Image acquisition control 68 basler scout light formula 2: max frames/s = 491.0 frames/s formula 3: packets per frame = 39.9 (round the result up to 40.) max frames/s = 200 frames/s formula one returns the lowest value. So in this case, the limiting factor is the sensor readout time and the maximum ...
Page 77
Image acquisition control basler scout light 69 maximum frame rate with the current camera settings. If you gradually decrease the setting for the packet size parameter, you will eventually find that the value of the resulting frame rate abs parameter will also decrease. If you are operating a singl...
Page 78: Rate
Image acquisition control 70 basler scout light 6.11 maximum allowed acquisition frame rate (sla750-60fm only) in general, the maximum allowed acquisition frame rate can be limited by two factors: the sum of the exposure time plus the amount of time it takes to read the acquired image out of the ima...
Page 79
Image acquisition control basler scout light 71 increasing the maximum allowed frame rate you may find that you would like to acquire frames at a rate higher than the maximum allowed with the camera’s current settings. In this case, you must first use the two formulas described below to determine wh...
Page 80
Image acquisition control 72 basler scout light formula 2: calculates the maximum frame rate based on the number of packets needed to transmit a captured frame from the camera to your host pc via the ieee 1394 bus: (round the result up to the nearest integer) example assume that you are using a mono...
Page 81: Allowed Frame Rate
Image acquisition control basler scout light 73 6.11.1 effect of the packet size setting on the maximum allowed frame rate after a camera acquires a frame, the image data is read out from the sensor into a buffer. Once the frame has been read out to the buffer, the data is packetized and transmitted...
Page 82
Image acquisition control 74 basler scout light.
Page 83: 7 Pixel Data Formats
Pixel data formats basler scout light 75 7 pixel data formats by selecting a pixel data format, you determine the format (layout) of the image data transmitted by the camera. This section provides detailed information about the available pixel data formats. 7.1 setting the pixel data format the sett...
Page 84: 7.2
Pixel data formats 76 basler scout light 7.2 pixel data formats 7.2.1 mono 8 format (equivalent to dcam mono 8) when a monochrome camera is set for the mono 8 pixel data format, it outputs 8 bits of brightness data per pixel. The table below describes how the pixel data for a received frame will be ...
Page 85
Pixel data formats basler scout light 77 with the camera set for mono8, the pixel data output is 8 bit data of the “unsigned char” type. The available range of data values and the corresponding indicated signal levels are as shown in the table below. This data value (hexadecimal) indicates this sign...
Page 86: 7.2.2
Pixel data formats 78 basler scout light 7.2.2 mono 16 format (equivalent to dcam mono 16) when a monochrome camera is set for the mono16 pixel data format, it outputs 16 bits of brightness data per pixel with 12 bits effective. The 12 bits of effective pixel data fill from the least significant bit...
Page 87
Pixel data formats basler scout light 79 when the camera is set for mono 16, the pixel data output is 16 bit data of the “unsigned short (little endian)” type. The available range of data values and the corresponding indicated signal levels are as shown in the table below. Note that for 16 bit data,...
Page 88: 7.2.3
Pixel data formats 80 basler scout light 7.2.3 mono 12 packed format when a monochrome camera is set for the mono 12 packed pixel data format, it outputs 12 bits of brightness data per pixel. Every three bytes transmitted by the camera contain data for two pixels. The table below describes how the p...
Page 89
Pixel data formats basler scout light 81 when a monochrome camera is set for mono 12 packed, the pixel data output is 12 bit data of the “unsigned” type. The available range of data values and the corresponding indicated signal levels are as shown in the table below. This data value (hexadecimal) in...
Page 90: 7.2.4
Pixel data formats 82 basler scout light 7.2.4 yuv 4:2:2 packed format (equivalent to dcam yuv 4:2:2) when a monochrome camera is set for the yuv 4:2:2 packed pixel data format, the camera transmits y, u, and v values in a fashion that mimics the output from a color camera set for yuv 4:2:2 packed. ...
Page 91: 7.2.5
Pixel data formats basler scout light 83 when the camera is set for yuv 4:2:2 packed output, the pixel data output for the y component is 8 bit data of the “unsigned char” type. The range of data values for the y component and the corresponding indicated signal levels are shown below. The pixel data...
Page 92
Pixel data formats 84 basler scout light p n = the last pixel transmitted by the camera b 0 = the first byte in the buffer b m = the last byte in the buffer when a color camera is set for yuv 4:2:2 (yuyv) output, the pixel data output for the y component is 8 bit data of the “unsigned char” type. Th...
Page 93
Pixel data formats basler scout light 85 the pixel data output for the u component or the v component is 8 bit data of the “straight binary” type. The data values for a u or a v component will always be zero..
Page 94: 7.3
Pixel data formats 86 basler scout light 7.3 pixel transmission sequence for each captured image, pixel data is transmitted from the camera in the following sequence: where row 0 col 0 is the upper left corner of the sensor the columns are numbered 0 through m from the left side to the right side of...
Page 95: 8 I/o Control
I/o control basler scout light 87 8 i/o control this section describes how to configure the camera’s physical input line and physical output line. It also provides information about monitoring the state of the input and output lines. For more detailed information about the physical and electrical ch...
Page 96: 8.2
I/o control 88 basler scout light 8.2 configuring the output line 8.2.1 assigning a camera output signal to the physical output line the camera is equipped with one physical output line designated as output line 1. You can use the camera’s output signal assignment capability to assign one of the cam...
Page 97: 8.2.2
I/o control basler scout light 89 8.2.2 setting the state of a user settable output line as mentioned in the previous section, you can designate the camera’s output line as "user settable". If you have designated the output line as user settable, you can use camera parameters to set the state of the...
Page 98
I/o control 90 basler scout light you can set the line selector and the line inverter parameter value from within your application software by using the pylon api. The following code snippet illustrates using the api to set the selector and the parameter value: // enable the inverter on output line ...
Page 99: 8.2.4
I/o control basler scout light 91 8.2.4 working with the timer signal the camera a timer output signal available called timer 1. The timer works as follows: a trigger source event occurs that starts the timer. A delay period begins to expire. When the delay expires, the timer signal goes high and a ...
Page 100
I/o control 92 basler scout light 8.2.4.2 setting the timer delay time there are two ways to set the delay time for timer 1: by setting "raw" values or by setting an "absolute value". You can use whichever method you prefer to set the delay time. Setting the delay time with raw values when the delay...
Page 101
I/o control basler scout light 93 setting the delay time with an absolute value you can also set the timer 1 delay by using an "absolute" value. This is accomplished by setting the timer delay abs parameter. The units for setting this parameter are µs and the value can be set in increments of 1 µs. ...
Page 102
I/o control 94 basler scout light 8.2.4.3 setting the timer duration time there are two ways to set the duration time for timer 1: by setting "raw" values or by setting an "absolute value". You can use whichever method you prefer to set the duration time. Setting the duration time with raw values wh...
Page 103
I/o control basler scout light 95 setting the timer duration with an absolute value you can also set the timer 1 duration by using an "absolute" value. This is accomplished by setting the timer duration abs parameter. The units for setting this parameter are µs and the value can be set in increments...
Page 104: 8.3
I/o control 96 basler scout light 8.3 checking the state of the i/o lines 8.3.1 checking the state of the output line you can determine the current state of the output line. To check the state of the output line: use the line selector parameter to select output line 1. Read the value of the line sta...
Page 105
I/o control basler scout light 97 the state of the associated line is currently low. If a bit is 1, it indicates that the state of the associated line is current high. Fig. 27: line status all parameter bits indicates output line 1 state indicates input line 1 state.
Page 106
I/o control 98 basler scout light.
Page 107: 9 Standard Features
Standard features basler scout light 99 9 standard features this section provides detailed information about the standard features available on each camera. It also includes an explanation of their operation and the parameters associated with each feature. 9.1 gain the camera’s gain setting is adjus...
Page 108
Standard features 100 basler scout light setting the gain (all models except sla750-60fm) the camera’s gain is determined by the value of the gain raw parameter. Gain raw is adjusted on a decimal scale. The minimum decimal setting varies depending on the camera model (see table 12). The maximum sett...
Page 109
Standard features basler scout light 101 for gain raw settings from 110 to 511: for gain raw settings from 512 to 1023: where: example: assume that you are working with an sla1390-17fm camera that is set for the mono 8 pixel format and has a gain raw setting of 500. Calculating the gain is a two ste...
Page 110
Standard features 102 basler scout light setting the gain (sla750-60fm only) the camera’s gain is determined by the value of the gain raw parameter. Gain raw is adjusted on a decimal scale. The range for the gain raw parameter setting is from 0 to 22. To set the gain raw parameter value: set the gai...
Page 111
Standard features basler scout light 103 if you know the current decimal setting for the gain raw, you can use the following formula to calculate the db of gain that will result from that setting: example: assume that you are working with an sla750-60fm camera that has a gain raw setting of 18. The ...
Page 112: 9.2
Standard features 104 basler scout light 9.2 black level adjusting the camera’s black level will result in an offset to the pixel values output by the camera. Increasing the black level setting will result in a positive offset in the digital values output for the pixels. Decreasing the black level s...
Page 113: 9.3
Standard features basler scout light 105 9.3 digital shift the digital shift feature lets you change the group of bits that is output from the adc in the camera. Using the digital shift feature will effectively multiply the output of the camera by 2 times, 4 times, 8 times, or 16 times. The next two...
Page 114
Standard features 106 basler scout light only include values of 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, and so on. This absence of some gray values is commonly referred to as "missing codes". If the pixel values being output by the camera’s sensor are high enough to set bit 11 to 1, we recommend not using shift by 1. If yo...
Page 115: 9.3.2
Standard features basler scout light 107 shift by 4 when the camera is set to shift by 4, the output from the camera will include bit 7 through bit 0 from the adc along with 4 zeros as lsbs. The result of shifting 4 times is that the output of the camera is effectively multiplied by 16. When the cam...
Page 116
Standard features 108 basler scout light if the pixel values being output by the camera’s sensor are high enough to set bit 11 to 1, we recommend not using shift by 1. If you do nonetheless, all bits ouput from the camera will automatically be set to 1. Therefore, you should only use the shift by 1 ...
Page 117: 9.3.3
Standard features basler scout light 109 automatically be set to 1. Therefore, you should only use the multiply by 4 setting when your pixel readings with an 8 bit pixel format selected and with digital shift disabled are all less than 16. 9.3.3 precautions when using digital shift there are several...
Page 118
Standard features 110 basler scout light // enable digital shift by 2 camera.Digitalshift.Setvalue( 2 ); for detailed information about using the pylon api, refer to the basler pylon programmer’s guide and api reference. You can also use the basler pylon viewer application to easily set the paramete...
Page 119: 9.4
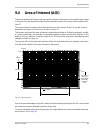
Standard features basler scout light 111 9.4 area of interest (aoi) the area of interest (aoi) feature lets you specify a portion of the sensor array and after each image is acquired, only the pixel information from the specified portion of the array is transmitted to the host pc. The area of intere...
Page 120
Standard features 112 basler scout light setting the aoi the aoi is set by default to use the full resolution of the camera’s sensor. You can change the size and the position of the aoi by changing the value of the camera’s x offset, y offset, width, and height parameters. The value of the x offset ...
Page 121
Standard features basler scout light 113 you can set the x offset, y offset, width, and height parameter values from within your application software by using the pylon api. The following code snippets illustrate using the api to get the maximum allowed settings and the increments for the width and ...
Page 122: 9.4.1
Standard features 114 basler scout light 9.4.1 changing aoi parameters "on-the-fly" making aoi parameter changes “on-the-fly” means making the parameter changes while the camera is capturing images continuously. On-the-fly changes are only allowed for the parameters that determine the position of th...
Page 123: 9.5
Standard features basler scout light 115 9.5 reverse x the reverse x feature is a horizontal mirror image feature. When the reverse x feature is enabled, the pixel values for each line in a captured image will be swapped end-for-end about the line’s cen- ter. This means that for each line, the value...
Page 124
Standard features 116 basler scout light setting reverse x you can enable or disable the reverse x feature by setting the reversex parameter value. You can set the parameter value from within your application software by using the pylon api. The following code snippet illustrates using the api to se...
Page 125: 9.6
Standard features basler scout light 117 9.6 disable parameter limits for each camera parameter, the allowed range of parameter values normally is limited. The factory limits are designed to ensure optimum camera operation and, in particular, good image quality. For special camera uses, however, it ...
Page 126: 9.7
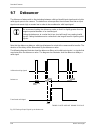
Standard features 118 basler scout light 9.7 debouncer the debouncer feature aids in discriminating between valid and invalid input signals and only lets valid signals pass to the camera. The debouncer value specifies the minimum time that an input signal must remain high or remain low in order to b...
Page 127
Standard features basler scout light 119 setting the debouncer the debouncer value is determined by the value of the line debouncer time abs parameter value. The parameter is set in microseconds and can be set in a range from 0 to approximately 1 s. To set the debouncer: use the line selector to sel...
Page 128: 9.8
Standard features 120 basler scout light 9.8 trigger delay the trigger delay feature lets you specify a delay (in microseconds) that will be applied between the receipt of a hardware trigger and it becoming effective. The trigger delay may be specified in the range from 0 to 10000000l µs (equivalent...
Page 129: 9.9
Standard features basler scout light 121 9.9 acquisition status when controlling image acquisition with a software trigger you can use the acquisition staus feature to detemine when the camera is ready to be triggered for an image acquisition. Using this feature, you can avoid triggering the camera ...
Page 130: 9.10 Test Images
Standard features 122 basler scout light 9.10 test images all cameras include the ability to generate test images. Test images are used to check the camera’s basic functionality and its ability to transmit an image to the host pc. Test images can be used for service purposes and for failure diagnost...
Page 131
Standard features basler scout light 123 test image 1 - fixed diagonal gray gradient (8 bit) the 8 bit fixed diagonal gray gradient test image is best suited for use when the camera is set for monochrome 8 bit output. The test image consists of fixed diagonal gray gradients ranging from 0 to 255. If...
Page 132
Standard features 124 basler scout light test image 3 - moving diagonal gray gradient (12 bit) the 12 bit moving diagonal gray gradient test image is similar to test image 2, but it is a 12 bit pattern. The image moves by one pixel from right to left whenever a new image acquisition is initiated. Th...
Page 133
Standard features basler scout light 125 9.11 device information parameters each camera includes a set of "device information" parameters. These parameters provide some basic information about the camera. The device information parameters include: device vendor name (read only) - contains the name o...
Page 134
Standard features 126 basler scout light for detailed information about using the pylon api, refer to the basler pylon programmer’s guide and api reference. You can also use the basler pylon viewer application to easily read the parameters and to read or write the device id. For more information abo...
Page 135: 9.12 Configuration Sets
Standard features basler scout light 127 9.12 configuration sets a configuration set is a group of values that contains all of the parameter settings needed to control the camera. There are three basic types of configuration sets: the active configuration set, the default configuration set, and user...
Page 136: 9.12.1 Saving User Sets
Standard features 128 basler scout light settings from the current active set to a reserved area in the camera’s non-volatile memory. A configuration set saved in the non-volatile memory is not lost when the camera is reset or switched off. There are three reserved areas in the camera’s non-volatile...
Page 137
Standard features basler scout light 129 9.12.2 selecting a factory setup as the default set when the camera is delivered, the standard factory setup will be selected as the default configuration set. You can, however, select either one of the two factory setups to serve as the default set. To selec...
Page 138: Into The Active Set
Standard features 130 basler scout light 9.12.3 loading a saved set or the default set into the active set if you have saved a configuration set into the camera’s non-volatile memory, you can load the saved set from the camera’s non-volatile memory into the camera’s active set. When you do this, the...
Page 139
Standard features basler scout light 131 9.12.4 selecting the startup set you can select the default configuration set (i.E., whichever was selected as the default configuration set, either the standard factory setup or the high gain factory setup) or one of the user configuration sets stored in the...
Page 140
Standard features 132 basler scout light.
Page 141: Single Bus and Managing
Using multiple cameras on a single bus and managing bandwidth basler scout light 133 10 using multiple cameras on a single bus and managing bandwidth this section includes information about using multiple cameras on a single ieee 1394 bus. 10.1 using multiple cameras where all devices are 1394b most...
Page 142
Using multiple cameras on a single bus and managing bandwidth 134 basler scout light that we could have made the packet sizes smaller and thus the total byte load per cycle would be less than the maximum allowed. It is ok to make the total byte load smaller than the maximum, but not larger. Fig. 35:...
Page 143: And 1394B Devices Are Mixed
Using multiple cameras on a single bus and managing bandwidth basler scout light 135 10.2 using multiple cameras where 1394a and 1394b devices are mixed the descriptions in the previous section assume that all of the devices on the bus are ieee 1394b devices. If the bus has mixed ieee 1394a devices ...
Page 144
Using multiple cameras on a single bus and managing bandwidth 136 basler scout light fig. 36: examples of mixed device types so what does all of this mean when we are trying to share bandwidth between devices operating at different speeds on the same bus? Some examples will provide the best explanat...
Page 145
Using multiple cameras on a single bus and managing bandwidth basler scout light 137 you may be asking why we multiply the percentage for camera 1 by 4096 and the percentage for camera 2 by 8192. The reason is: during the part of the bus cycle when the packet for camera 1 is transmitted, the bus wil...
Page 146
Using multiple cameras on a single bus and managing bandwidth 138 basler scout light 10.2.1 recommended packet size when you change the value of the packet size setting on a camera, there is something that you must keep in mind. If you lower the packet size setting, the camera takes longer to transm...
Page 147: 11.1 Tech Support Resources
Troubleshooting and support basler scout light 139 11 troubleshooting and support this section outlines the resources available to you if you need help working with your camera. It also provides some basic troubleshooting information that you can use to solve problems. 11.1 tech support resources th...
Page 148
Troubleshooting and support 140 basler scout light 11.3 troubleshooting with the camera led if the camera boots up successfully, the led on the back of the camera will light and will remain green continuously. If an error condition is detected, the led will begin to flash. The number of flashes indi...
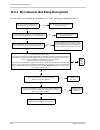
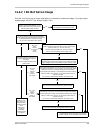
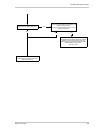
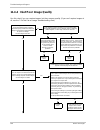
Page 149: 11.4 Troubleshooting Charts
Troubleshooting and support basler scout light 141 11.4 troubleshooting charts the following pages contain several troubleshooting charts that can help you find the cause of problems users sometimes encounter. The charts assume that you are familiar with the camera’s features and settings. If you ar...
Page 150
Troubleshooting and support 142 basler scout light 11.4.1 my camera is not being recognized use this chart if your camera is connected to a pc, but is not being recognized by the pc. Correct the power source no yes no does your pc have a windows xp or a windows 2000 operating system? Go to the “i do...
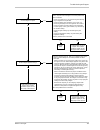
Page 151
Troubleshooting and support basler scout light 143 11.4.2 i do not get an image use this chart if you get no image at all when you attempt to capture an image. If you get a poor quality image, use the "poor image quality" chart. No go to the “my camera is not being recognized” troubleshooting chart....
Page 152
Troubleshooting and support 144 basler scout light 11.4.3 i can not get the full frame rate use this troubleshooting chart if you are attempting to run the camera at its maximum stated frame rate and you are not able to do so. No yes when the packet size setting is set low, it increases the number o...
Page 153
Troubleshooting and support basler scout light 145 is there more than one camera attached to the ieee 1394 bus? No leave one camera attached to the bus and detach all of the others. Can the attached camera now run at a higher frame rate? Yes the ieee bus does not have sufficient bandwidth to transmi...
Page 154
Troubleshooting and support 146 basler scout light 11.4.4 i get poor image quality use this chart if you can capture images, but they are poor quality. (if you can’t capture images at all, use the "i do not get an image" troubleshooting chart.) yes no no no yes yes no yes yes no no yes make sure tha...
Page 155
Troubleshooting and support basler scout light 147 no are the images too light? Yes take the following actions. After you complete each action, capture several images to see if the problem has been corrected: check your light source. Try decreasing the intensity of your light source if possible. Che...
Page 156: Technical Support
Troubleshooting and support 148 basler scout light 11.5 before contacting basler technical support to help you as quickly and efficiently as possible when you have a problem with a basler camera, it is important that you collect several pieces of information before you contact basler technical suppo...
Page 157
Troubleshooting and support basler scout light 149 7 how often did/does the problem occur? Once. Every time. Regularly when: occasionally when: 8 how severe is the problem? Camera can still be used. Camera can be used after i take this action: camera can no longer be used. 9 did your application eve...
Page 158
Troubleshooting and support 150 basler scout light.
Page 159
Revision history basler scout light 151 revision history doc. Id number date changes aw00075301000 25 nov 2008 initial release of this document. Aw00075302000 17 june 2009 updated sensor name "micron mt9v022" to "aptina mt9v022" in section 1.2 on page 2 . Updated minimum allowed exposure times in se...
Page 160
Revision history 152 basler scout light.
Page 161
Feedback basler scout light 153 feedback your feedback will help us improve our documentation. Please click the link below to access an online feedback form. Your input is greatly appreciated. Http://www.Baslerweb.Com/umfrage/survey.Html.
Page 162
Feedback 154 basler scout light.
Page 163
Index basler scout light 155 index a acquisition frame rate and aoi size ................................65 , 70 maximum allowed .......................65 , 70 acquisition frame rate abs parameter .................................................... 38 , 42 , 49 acquisition mode parameter .............
Page 164
Index 156 basler scout light f factory setup ......................................... 127 high gain factory setup .................... 127 standard factory setup .................... 127 frame rate controlling with a hardware trigger .... 44 controlling with a software trigger ..... 42 maximum allo...
Page 165
Index basler scout light 157 r recommended packet size parameter ...138 resulting frame rate abs parameter .............................................. 65 , 69 , 70 , 73 return material authorization ..................139 reverse x ...............................................115 rma number .......
Page 166
Index 158 basler scout light.