- DL manuals
- Cabletron Systems
- Switch
- 42T
- User Manual
Cabletron Systems 42T User Manual
Summary of 42T
Page 1
Micrommac-22t/24t/42t/44t stackable token ring intelligent hubs user’s guide.
Page 2: Notice
Iii notice cabletron systems reserves the right to make changes in specifications and other information contained in this document without prior notice. The reader should in all cases consult cabletron systems to determine whether any such changes have been made. The hardware, firmware, or software ...
Page 3: Fcc Notice
Notice iv fcc notice this device complies with part 15 of the fcc rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation. Not...
Page 4: License Agreement
Notice v cabletron systems, inc. Program license agreement important: before utilizing this product, carefully read this license agreement. This document is an agreement between you, the end user, and cabletron systems, inc. (“cabletron”) that sets forth your rights and obligations with respect to t...
Page 5: Rights
Notice vi 2. No liability for consequential damages. In no event shall cabletron or its suppliers be liable for any damages whatsoever (including, without limitation, damages for loss of business, profits, business interruption, loss of business information, special, incidental, consequential, or re...
Page 6: Contents
Vii contents chapter 1 introduction 1.1 contents overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1 1.2 micrommac-t overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2 1.3 micrommac-t features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3 1.4 stackable capabilities . . ....
Page 7: Chapter 4
Contents viii 3.5 resetting the micrommac-t . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-5 3.6 setting the ring speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-6 3.7 setting the nvram switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-7 3.8 connecting lobe port cabling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-8 3.9 i...
Page 8
Contents ix 5.2.4 saved system messages. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-6 5.3 viewing power up diagnostic tests . . . . . . . . . . 5-7.
Page 9: Chapter 1
1-1 chapter 1 introduction welcome to the cabletron systems micrommac-22t/-24t/-42t/ -44t stackable token ring intelligent hub user’s guide . This manual provides installation instructions, network requirements, reference information, and operating instructions for the micrommac-t (figure 1-1) famil...
Page 10: Local Management
Introduction 1-2 describes how to install a tpim and concludes with installation check-out instructions. Chapter 4, local management , explains how to set up and use a management terminal and a modem to access local management. Chapter 5, troubleshooting , explains how to monitor the operation perfo...
Page 11: Micrommac-22T
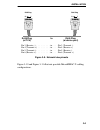
Introduction 1-3 figure 1-2. Typical micrommac-t configuration scenario all micrommac-ts are functionally and physically identical except for the number and type of their trunk connection unit (tcu) lobe ports. The following micrommac-t configurations are available: • micrommac-22t : twelve active r...
Page 12: Active Tcu Ports
Introduction 1-4 active tcu ports the active tcu ports regenerate, reshape, and filter the incoming signal, permitting utp lobe cable lengths of up to 120 meters and stp lobe cable lengths up to 150 meters at 16 mbps ring speed. The micrommac-22t and the micrommac-42t can be upgraded in the field us...
Page 13: Ring Speed Switch
Introduction 1-5 re-time all data. Cabletron offers a variety of tpims for ri/ro trunk connections as shown in table 1-1. Ring speed switch use the ring speed switch to select either 4 or 16 mbps ring speed. Flash eeprom the firmware image on the micrommac-t can be upgraded by flash eeprom downloads...
Page 14: Com Port Applications
Introduction 1-6 numerous management devices and serve as their management data representative. The network management station then has to query only one management device, the micrommac-t in dlm mode, to access management data for all management devices on the network. Consult your network manager ...
Page 15: Rmon Mib Support
Introduction 1-7 • token ring fnb (flexible network bus) • dot 5 logical and physical • ups (uninterruptible power supply) • device • dlm (distributed lan monitor) • pic mib (product information chip mib) • chassis mib rmon mib support the micrommac-t supports the rmon mib rfc 1271/1513 token ring e...
Page 16: 1.4 Stackable Capabilities
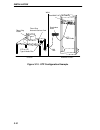
Introduction 1-8 1.4 stackable capabilities the micrommac-t can be stacked with up to four hubstack sth series non-intelligent hubs as shown in figure 1-3. Four connectors are available on the back panel of the micrommac-t for connecting sth 12/24 type non-intelligent hubs. The micrommac-t provides ...
Page 17: Note
Introduction 1-9 figure 1-3. Typical stackable configuration note : token ring hubstack interface cables, which are used to connect between the micrommac-t and stacked sth hubs, are not included with the micrommac-t. 1.5 bridging/routing capabilities a slot on the back panel of the unit provides ins...
Page 18: 1.5.1 Sna/wan Integration
Introduction 1-10 . 1.5.1 sna/wan integration the microsnac add-on daughterboard provides two ports, both of which can be used to provide conversion from sna/sdlc or bsc links to llc2. The microsnac can operate in a converter mode or as a wan concentrator. 1.6 remote management capabilities the micr...
Page 19: 1.8 Recommended Reading
Introduction 1-11 module. This feature complements the remote snmp management and allows for quick hub configuration changes or checks. 1.8 recommended reading the following publications provide more information on token ring network implementation. Local area networks, token ring access method , ie...
Page 20: Chapter 2
2-1 chapter 2 requirements/specifications read this chapter prior to installing the micrommac-t. It contains operating specifications and requirements for power and cabling. To obtain satisfactory performance from this equipment, networks must meet the requirements and conditions specified in this c...
Page 21: Warning
Requirements/specifications 2-2 2.1.1 utp cable specifications the micrommac-22t and micrommac-24t lobe ports and the tpim-t2 support voice grade unshielded twisted pair (utp) cable, as described in specifications for eia/tia tsb 568 and ibm type 3 cable. Utp consists of four pairs of 24 awg solid w...
Page 22: Maximum Lobe Lengths
Requirements/specifications 2-3 maximum lobe lengths lobe length is the physical length of the cable connecting a station to its tcu port at the micrommac-t. Table 2-2 lists the maximum lobe cable length for ring speeds of 4 and 16 mbps. The values listed refer to total lengths made up of utp cable ...
Page 23: Attenuation and Impedance
Requirements/specifications 2-4 2.1.2 stp cable specifications micrommacs 42t and 44t and tpims t1 and t4 support ibm type 1, 2, 6, and 9 stp cabling as described below: • ibm type 1: two stp lengths of 22 awg solid wire for data. Used for the longest cable runs within building walls of buildings. •...
Page 24: Maximum Trunk Lengths
Requirements/specifications 2-5 cable length for ring speeds of 4 and 16 mbps. The cable lengths listed in table 2-4 refer to total lengths made up of stp cable only . Maximum trunk lengths the maximum trunk cable length between the micrommac-t and other active devices is equal to the maximum drive ...
Page 25: Mixed Cable Types
Requirements/specifications 2-6 mixed cable types if multiple cable types exist in network, compensations must be made for the different cable attenuations. Type 6 and type 9 cables can run only 2/3 the distance of type 1. Therefore 10 meters of type 1 ≈ 6.6 meters of types 6 and 9. 2.1.3 multimode ...
Page 26: Fiber Optic Budget
Requirements/specifications 2-7 fiber optic budget the fiber optic delay budget, which determines the fiber optic cable’s maximum length, should be calculated and taken into consideration in the network design stage. Fiber optic delay budget is determined by summing the optical signal loss due to fi...
Page 27: Fiber Optic Budget
Requirements/specifications 2-8 fiber optic budget the fiber optic delay budget, which determines the fiber optic cable’s maximum length, should be calculated and taken into consideration in the network design stage. Fiber optic delay budget is determined by summing the optical signal loss due to fi...
Page 28
Requirements/specifications 2-9 other considerations in addition to complying with the preceding cable specifications, the following recommendations should be followed to minimize errors and obtain optimum performance from the network: • utp cabling should be free of splices, stubs, or bridged taps....
Page 29: Local Management
Requirements/specifications 2-10 local management both com 1 and com 2 ports are factory-configured to support local management access by an actual or emulated digital equipment corporation vt 100™ terminal. Booting/diagnostics terminal display of power up booting/diagnostic tests available only whe...
Page 30: Tpim-T2
Requirements/specifications 2-11 figure 2-3. Tpim-t1 pinouts tpim-t2 tpim-t2 provides an rj45 connector that supports utp cabling. Figure 2-4 shows pinouts for ring out and ring in applications. Figure 2-4. Tpim-t2 pinouts tpim-t4 tpim-t4 is an rj45 connector that supports stp cabling. Figure 2-5 sh...
Page 31: Tpim-F2
Requirements/specifications 2-12 figure 2-5. Tpim-t4 pinouts tpim-f2 tpim-f2, shown in figure 2-6, provides an st connector that supports multimode fiber optic cabling. Figure 2-6. Tpim-f2 note: transmitter power and receive sensitivity levels, shown in table 2-8, are peak power levels after optical...
Page 32: Tpim-F3
Requirements/specifications 2-13 . Tpim-f3 tpim-f3, shown in figure 2-7, is an st connector that supports single mode fiber optic cabling. Figure 2-7. The tpim-f3 table 2-8. Tpim-f2 specifications. Parameter typical value worst case worst case budget typical budget receive sensitivity -30.5 dbm -28....
Page 33
Requirements/specifications 2-14 note: transmitter power decreases as temperatures rise and increases as temperatures fall. Use the output power coefficient to calculate increased or decreased power output for an operating environment. For example, the typical power output at 25 ° c is -16.4 dbm. Fo...
Page 34: 2.5 General Specifications
Requirements/specifications 2-15 to the average power measurement to correctly compare the average power values measured to the values listed above (i.E., -33.5 dbm average + 3 db = -30.5 dbm peak). 2.5 general specifications cabletron systems reserves the right to change the following operating spe...
Page 35: 2.5.3 Safety
Requirements/specifications 2-16 non-operating temperature: -30 ° to +90 ° c operating humidity: 5 to 95% (non-condensing) 2.5.3 safety this unit meets the safety requirements of ul 1950, csa c22.2 no. 950 and en 60950; the emi requirements of fcc class a and en 55022 class a; and the emc requiremen...
Page 36: Chapter 3
3-1 chapter 3 installation this chapter outlines micrommac-t installation and network connection procedures. Be sure that the network meets the guidelines and requirements outlined in chapter 2, requirements/specifications, before installing the micrommac-t. 3.1 unpacking the micrommac-t unpack the ...
Page 37
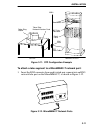
Installation 3-2 figure 3-1. Attaching the strain relief bracket 3.3 installing the micrommac-t the micrommac-t can be rack-mounted, wall-mounted, or placed on any horizontal surface. Refer to the following subsections for the appropriate installation instructions. When installing the micrommac-t in...
Page 38
Installation 3-3 2. Using the four cover screws removed in step 1, attach the rack-mounting brackets to each end of the micrommac-t. Figure 3-2. Installing of rack-mount brackets 3. With the mounting brackets installed, position the micrommac-t between the vertical frame members of the 19-inch rack ...
Page 39
Installation 3-4 figure 3-4. Wall-mounting the micrommac-t 2. Select a wall location within seven feet of a power outlet for the micrommac-t. Warning: when drilling pilot holes, any electrical wiring inside the wall may present a potential shock hazard. Select a wall location accordingly. 3. Positio...
Page 40
Installation 3-5 3.3.3 free-standing installation for a free-standing shelf or table top installation, locate the micrommac-t, as shown in figure 3-5, within 7 feet of its power source on an unrestricted free surface area 21 inches wide, 18 inches deep, and 6 inches high. Figure 3-5. Free-standing i...
Page 41: To Reset The Micrommac-T:
Installation 3-6 to reset the micrommac-t: insert a small pointed-tip object (e.G., ballpoint pen) into the recessed reset button hole, press the button once, and then release. Figure 3-6. The reset button 3.6 setting the ring speed the ring speed switch is located on the front face of the micrommac...
Page 42
Installation 3-7 figure 3-7. The ring speed switch 3.7 setting the nvram switch figure 3-8 shows the location of the nvram reset switch. It can be reached by a inserting a small screwdriver through the side vent. Nvram (non-volatile random access memory) stores user-entered parameters such as ip add...
Page 43
Installation 3-8 2. Press the micrommac-t’s reset button. Once the module is reset, use the factory-default settings or enter new parameters. The micrommac-t stores these settings in nvram during normal operation and during power down until the reset switch is toggled again. Note: clearing and reset...
Page 44
Installation 3-9 rj45 plug to rj45 plug (at tcu) (at device port) pin 3 (receive -) . . . . . . . . . To. . . . Pin 3 (transmit -) pin 4 (transmit +) . . . . . . . . To. . . . Pin 4 (receive +) pin 5 (transmit -). . . . . . . . . To. . . . Pin 5 (receive -) pin 6 (receive +) . . . . . . . . . To. . ...
Page 45
Installation 3-10 figure 3-10. Utp configuration example punchdown block wiring closet office token ring station token ring network interface card wall jack utp lobe cable wall micrommac-24t trmf stp to utp type 3 media filter ro token ring hub with lanview® supporting 100 ohm stp cable micrommac-24...
Page 46
Installation 3-11 figure 3-11. Stp configuration example to attach a lobe segment to a micrommac-t network port: 1. Insert the rj45 connector from each twisted pair segment into an rj45 network lobe port on the micrommac-t, as shown in figure 3-12. Figure 3-12. Micrommac-t network ports patch panel ...
Page 47
Installation 3-12 2. The associatedport statusled lights green when the station boots up. If the led doesn’t light, perform the following steps: a. Check that the device at the other end of the twisted pair segment has power, and that the network interface driver is initialized. B. Verify the rj45 c...
Page 48
Installation 3-13 3.9.1 setting phantom and ri/ro switches the phantom switch (shown in figure 3-13) enables the port to “autowrap” if a trunk cable fails or is removed. The phantom switch should be set to the appropriate setting before tpim installation. When attaching a cabletron hub to the tpim, ...
Page 49: 3.9.2 Tpim Installation
Installation 3-14 figure 3-13. The phantom and ri/ro switches 3.9.2 tpim installation to install a tpim, perform the following steps: caution: observe all static precautions while handling tpims. 3. Remove the mounting screw from the faceplate of the ri/ro port on the micrommac-t. 4. If replacing a ...
Page 50
Installation 3-15 figure 3-14. Installing a tpim 3.9.3 connecting stp segments use tpim-t1 to connect stp segments. Before connecting a segment to the tpim-t1, confirm proper pinouts at each end of the segment. To connect a tpim-t1 to a twisted pair segment: 1. Insert the db9 connector on the segmen...
Page 51
Installation 3-16 figure 3-15. The tpim-t1 2. Check that the lnk led on the tpim lights green. If the led is red or is not lighted, perform each of the following steps: a. Check that the device at the other end of the segment has power. B. Verify that the db9 connector is pinned properly. C. Check t...
Page 52
Installation 3-17 figure 3-16. The tpim-t2/-t4 2. Check that the lnk led on the tpim lights green. If the led lights red or is not lit, perform each of the following steps: a. Check that the device at the other end of the segment has power. B. Verify that the rj45 is pinned properly. C. Check that t...
Page 53: Transmit Port (Labeled Tx).
Installation 3-18 • the physical communication link consists of two strands of fiber optic cabling. The transmit strand (tx) at one end connects to the receive (rx) port at the other end and vice versa. • cabletron systems labels its fiber optic cable to indicate which fiber is receive and which is ...
Page 54
Installation 3-19 a. Check that the device at the other end of the link has power. B. Verify that the fiber strands are properly “crossed-over” between the ports on the module and on the fiber optic device at the other end of the fiber optic link segment. C. Verify that the fiber connection meets th...
Page 55: Chapter 4
4-1 chapter 4 local management this chapter explains how to set up a management terminal and a modem to access micrommac-t’s local management (lm). It also explains how to use local management tools to manage the micrommac-t, its components, and its attached segments (i.E., brims, microsnac). Use lo...
Page 56
Local management 4-2 cabletron supplies an rj45 cable kit with the micrommac-t. This kit includes a utp console cable with rj45 connectors on each end. It also provides adapters for db9 or db25 connections. Refer to the rj45 cable kit instruction sheet for adapter pinouts and additional instructions...
Page 57
Local management 4-3 when you have finished attaching and setting up the terminal, you can access local management. 4.1.3 modem cable configuration and setup to access local management from a modem, use an rs-232 cable available from cabletron systems. This cable connects the modem to the table 4-1....
Page 58: To Access Local Management:
Local management 4-4 micrommac-t’s com 2 port. Figure 4-2 shows the pinout for a cable with an rj45 connector at the micrommac-t end of the cable. Figure 4-2. Modem cable pinouts 4.2 accessing local management to access local management: 1. Turn on the display terminal and then press the return key....
Page 59
Local management 4-5 figure 4-3. Micrommac-t local management screen 2. Enter the password (the factory default password is the return key) and then press the return key. If your password is invalid, the cursor returns to the beginning of the password field; otherwise, the main menu screen appears. ...
Page 60: 4.3 Using Local Management
Local management 4-6 4.2.2 accessing local management from a modem 1. Turn on the modem. The modem must be set for auto answer and data carrier detect must be active. Refer to your modem’s user manual for operating instructions. 2. Call the modem. The micrommac-t local management screen appears when...
Page 61: 2. Press The Return Key.
Local management 4-7 figure 4-4. Local management menu screens hierarchy note: local management automatically disconnects after 15 minutes of keyboard inactivity. To prevent disconnection, press any key during periods of inactivity. If you are disconnected, just press return to re-access the lm pass...
Page 62: 2. Press The Return Key.
Local management 4-8 (or other procedures where they are described) when working with lm screens: 1. Use the tab key or arrow keys to highlight the parameter(s). 2. Use the spacebar to toggle through settings for fields offering selections; type settings over fields that you can edit or type over. 3...
Page 63: Setting The System Date
Local management 4-9 4.3.2 the system level screen the system level screen (figure 4-5) displays and lets you set the following parameters: • ip address, • subnet mask • system date • system time • default gateway • beacon recovery • com port applications it also displays the physical mac device add...
Page 64: Return Key.
Local management 4-10 1. Highlight thesystem date field. 2. Type the date into the field in a mm/dd/yy format and then press the return key. 3. If the format is invalid, the message “invalid date” appears. Re-type the date using the correct format. 4. If the format is correct, highlight the save com...
Page 65: 3. Press The Return Key.
Local management 4-11 3. Press the return key. The new value appears in the ip address field. 4. If the ip address is correct, highlight the save command and then press the return key. The “saved” message appears on the screen indicating that your changes have been saved to memory. The micrommac-t w...
Page 66: Setting The Default Gateway
Local management 4-12 the “saved” message appears on the screen indicating that your changes have been saved to memory. The micrommac-t will then do a soft reset. Setting the default gateway the default gateway is the ip address of the network connection (e.G., external router) used in forwarding ma...
Page 67: Setting Is 21.
Local management 4-13 abrp locates the problem and corrects it, the micrommac-t generates traps to provide the network’s designated remote management station with information regarding the incident, including: • the beaconing device’s address • the address of the beaconing device’s nearest active up...
Page 68
Local management 4-14 2. Toggle between enabled and disabled to make your selection. 3. Highlight the save command and then press the return key. The “save” message appears on the screen indicating that your selection was saved to memory and the new value of the field takes effect. To set the number...
Page 69
Local management 4-15 serve two purposes: they act as passwords to local management (lm) and control snmp management access to the micrommac-t. You control micrommac-t access by establishing access policy privileges at three increasingly higher levels of security: • read-only: the user can view any ...
Page 70: Community Name
Local management 4-16 community name this field displays designated user names. Access policy this field displays the access privileges accorded to each community name. Editing the community name field 1. Highlight the community namefield. 2. Type in the password, up to 32 characters in length, into...
Page 71: Trap Destination
Local management 4-17 figure 4-7. Snmp traps screen the following sections discuss the fields on the snmp traps screen and provide instructions for using them. Trap destination this field shows the ip address of the workstation that receives traps from the micrommac-t. Trap community name this field...
Page 72: 3. Press The Return Key.
Local management 4-18 3. Press the return key. If the format is invalid, the “invalid ip format” message appears. Re-type the trap destination ip address using the correct format. 4. Highlight the trap community name field. 5. Enter the community name of the device to receive traps and then press th...
Page 73
Local management 4-19 figure 4-8. Ring security screen only stations on the ring’s allowed list can enter the ring. The micrommac-t retains this allowed list and automatically re-enables ring security whenever you power up or reset the unit. You can select from two modes of ring security: • alarm on...
Page 74: Station Address
Local management 4-20 in alarm/remove mode, the micrommac-t sends a “remove mac frame command” to new stations attempting to enter the ring. A trap sent to the nms informs it of the action taken. If the remove mac frame command fails to remove the new station after three attempts, a trap to the nms ...
Page 75: Save/execute
Local management 4-21 it sends a trap to the nms informing it that the station could not be removed. The station must then be physically removed from the ring. Save/execute use this field to save changes made to ring security in the micrommac-t’s nvram. You must use the save/execute command for your...
Page 76: Key.
Local management 4-22 2. Highlight the save/execute command and then press the return key. Viewing the revised allowed list 1. Highlight the return command and then press the return key. The setup menu screen appears. 2. Highlight ring security and then press the return key. The ring security screen...
Page 77: Device Statistics
Local management 4-23 4.3.6 the device statistics screen the device statistics screen (figure 4-9) displays ring information, isolating errors, and non-isolating errors. Figure 4-9. Device statistics screen the following sections discuss the fields on the device statistics screen and provide instruc...
Page 78: 2. Press The Return Key.
Local management 4-24 • total: this mode automatically displays statistics describing network performance since the last power-up. Selecting the device statistics counter mode 1. Highlight the current modeat the bottom of the screen and toggle to a counter mode selection. 2. Press the return key. Th...
Page 79: Kbytes Received
Local management 4-25 kbytes received this field displays the sum in kilobytes of frames received by the micrommac-t. Errors received this field displays the isolating and non-isolating errors (described below) detected on the ring. Beacon states this field displays the beacon conditions detected on...
Page 80: Ac Errors
Local management 4-26 occurs when stations enter or leave the ring with the absence of phantom current. This error can also indicate a problem with the receiver of the reporting node, or the transmitter of its naun, or the cabling and hub hardware between them. Ac errors this field displays the tota...
Page 81: Ring Number
Local management 4-27 • closed -- indicates that the management station has closed the adapter • normal -- indicates the ring is running with no problems, and tokens are being detected by the management station • purge -- indicates that the active monitor has issued a ring purge command. Communicati...
Page 82: Frame Copied Errors
Local management 4-28 frame copied errors this field displays the total number of frame copied errors. These errors occur when a station finds a frame with its address as the destination, but finds the address recognized indicator bits not set to zero. This indicates a possible duplicate address. Rc...
Page 83: Mode
Local management 4-29 • operational (figure 4-10) -- lets you monitor the operational status of the token ring network • administrative (figure 4-11) -- lets you manage access to the token ring network • ring out enable (figure 4-12) -- lets you enable all ports the following sections describe gener...
Page 85: O For Operational, Or
Local management 4-31 2. Toggle to a screen mode selection, or press a for administrative, o for operational, or r for ring out enable, and then press the return key. The selected screen mode appears. Setting the refresh field 1. Highlight the refresh3sec field. 2. Use the spacebar to toggle through...
Page 86: States: Enb Or Byp.
Local management 4-32 • enb (enabled): the port is enabled and allows an attached station to enter the ring. • byp (bypassed): the port is disabled and the station is not on the ring. • lnk (linked): the port is disabled and an attached station is trying (sending phantom current) to access the ring ...
Page 87
Local management 4-33 using the administrative mode screen in addition to displaying the operational status of ring ports, the administrative mode screen provides you with two methods for controlling access to them: • bypassing ports. • enabling and disabling ports. When you bypass a module, or devi...
Page 88: Return Key.
Local management 4-34 2. Toggle between on and off, make your selection, and then press the return key. Enabled ports provide access for other stations into the token ring network; disabled ports cannot provide access to the ring until they have been enabled. To enable all ports for all modules: 1. ...
Page 89: Return Key.
Local management 4-35 figure 4-12. Chassis status view (ring out enable) screen to switch to and from stn and ro: 1. Highlight the port-status field showing stn or ro. 2. Toggle between stn and ro, make selection and then press the return key. You can now connect the ro enabled ports to multi-statio...
Page 90
Local management 4-36 figure 4-13. Component status view screen 4.3.9 the mib navigator screen the mib navigator screen (figure 4-14) provides the mib navigator prompt where you can issue commands for navigating and modifying the management information base (mib) structure. Mibs are the databases of...
Page 91
Local management 4-37 figure 4-14. Mib navigator screen the following sections define mib commands and describe how to get help on using them. To access a list of mib commands: type “help” or “?” at the mib prompt and then press the return key. The mib navigator screen appears showing the mib naviga...
Page 92: Navigational Commands
Local management 4-38 navigational commands navigational commands allow you to access and manage mib objects for the device. Mib commands are described as follows: branch this command displays the object leaves of a specified directory tree. Cd this command changes directories within a mib sub-tree....
Page 93: Next
Local management 4-39 next this command shows the next leaf in a path. Pwd this command displays the full path name of the directory in which you are working. Set this command lets you set the value of a managed object. Su this command lets you change your community name. Tree this command displays ...
Page 94: Ping
Local management 4-40 ping this command let you generate an outbound ping request. Snmp branch this command lets you query another snmp device. Snmpget this command lets you query another snmp device to obtain a value for an object. Snmpset this command lets set the values of object in other devices...
Page 95: Download Method Field
Local management 4-41 figure 4-15. The flash download screen the following sections discuss the fields on the flash download screen and provide instructions for using them. Download method field use the download method field to select either the runtime or the bootprom download method. The reboot af...
Page 96: Flash Image Server Ip
Local management 4-42 the reboot after download field appears by default when the runtime method is used. If yes is selected, the micrommac-t will automatically reset after the image is downloaded into flash to load the new image into the active system file. You can choose to use the bootprom method...
Page 97: Chapter 5
5-1 chapter 5 troubleshooting this chapter describes and explains how to use lanview leds and the liquid crystal display (lcd) to troubleshoot physical layer network problems. The chapter concludes with an overview of the power up diagnostic test. 5.1 using lanview leds lanview leds (located on the ...
Page 98: 5.2 Using The Lcd Display
Troubleshooting 5-2 5.2 using the lcd display the micrommac-t is equipped with an lcd and a lcd display button as shown in figure 5-1. Figure 5-1. Lcd display the lcd is a diagnostic tool for viewing the following important status information about the micrommac-t: • power up diagnostics • revision ...
Page 99
Troubleshooting 5-3 5.2.1 static system messages static system messages (table 5-2) display micrommac-t configuration information. To view them, press and release the display button (figure 5-1). Press the display button to scroll through each message. If the display button is not pressed again with...
Page 100: 5.2.2 Alarm Messages
Troubleshooting 5-4 5.2.2 alarm messages alarm messages (table 5-3) describe events that occur within the micrommac-t. To view the alarm messages queue, press the display button (figure 5-1) and hold for five seconds. Press the display button to scroll through each message. If the display button is ...
Page 101
Troubleshooting 5-5 5.2.3 unsaved initialization messages unsaved intialization messages appear on the lcd as the event occurs, but are not saved in a buffer for future recall. Table 5-4 lists unsaved failure or error messages (if failure or error messages appear, call your cabletron technical suppo...
Page 102
Troubleshooting 5-6 5.2.4 saved system messages saved system message are device-related start-up or boot strap messages, bootp/tftp host, or start-up error messages as shown in table 5-6. To access the saved system messages queue, enter the saved alarm messages queue. While in the alarm messages que...
Page 103: Responding to Error Messages
Troubleshooting 5-7 5.3 viewing power up diagnostic tests the micrommac-t runs from bootprom comprehensive booting and diagnostic tests of the device whenever it has been started or reset. You can view a chronicle of the tests and any error condition messages they produce by connecting your terminal...
Page 104: Delete Key.
Troubleshooting 5-8 • retry • loop choosing continue, or c, lets you proceed with the remainder of the diagnostic test. Choosing retry, or r , lets you repeat the test that produced the error message. Choosing loop, or l , lets you continuously repeat the test that produced the error message until y...
Page 105
Power supply cord the main cord used with this equipment must be a 2 conductor plus ground type with minimum 0.75 mm square conductors and must incorporate a standard iec appliance coupler on one end and a mains plug on the other end which is suitable for the use and application of the product and t...