- DL manuals
- Cabletron Systems
- Switch
- Cabletron BRIM-F6
- User Manual
Cabletron Systems Cabletron BRIM-F6 User Manual
Summary of Cabletron BRIM-F6
Page 1
Brim-f6 user’s guide brim-f book page 1 monday, january 29, 1996 9:26 am.
Page 3: Contents
Brim-f6 user’s guide i contents chapter 1 introduction ......................................................... 1-1 1.1 using this manual ....................................................................... 1-2 1.2 getting help........................................................................
Page 5: Chapter 1
Brim-f6 user’s guide page 1-1 chapter 1 introduction welcome to the cabletron systems brim-f6 user’s guide . This manual describes features, explains installation procedures, and provides specifications for the brim-f6 — cabletron systems fddi bridge/ router interface module (brim). The brim-f6 resi...
Page 6: 1.1
Chapter 1: introduction page 1-2 brim-f6 user’s guide 1.1 using this manual read through this manual completely to familiarize yourself with its content and to gain an understanding of the features and capabilities of the brim-f6. In addition to having a general working knowledge of ethernet and iee...
Page 7: 1.3
Brim-f6 overview brim-f6 user’s guide page 1-3 1.3 brim-f6 overview the brim-f6 is an fddi bridge router interface module (brim) developed for use in cabletron’s mmac-fnb and micrommac. The brim-f6 can be used to provide a high-speed uplink from lower speed networks such as ethernet to a 100 mbps fd...
Page 8: 1.5
Chapter 1: introduction page 1-4 brim-f6 user’s guide lanview diagnostic leds the brim-f6’s front panel leds help you diagnose bridge, port, and network status. 1.5 related documentation use the following documentation to supplement the procedures, and other technical data in this manual. This manua...
Page 9: Chapter 2
Brim-f6 user’s guide page 2-1 chapter 2 installation this chapter contains instructions for unpacking the brim-f6, installing fpims, and installing the brim-f6 into cabletron devices that support brim technology. Note : the brim-f6 is not shipped with the fpims installed. You must order the correct ...
Page 10: 2.2
Chapter 2: installation page 2-2 brim-f6 user’s guide 2.2 installing the fpims to install an fpim into the brim-f6: 1. Remove the screws securing the fpim coverplate and the coverplate. See figure 2-1. 2. Insert the connector pins of the fpim into the connector on the brim-f6. See figure 2-2. Figure...
Page 11: 2.3
Installing the brim-f6 brim-f6 user’s guide page 2-3 figure 2-2. Installing fpims 2.3 installing the brim-f6 this section contains procedures on how to install a brim-f6 to upgrade or change the capabilities of a device’s motherboard. Note: cabletron provides disposable wrist straps and faceplate an...
Page 12: 2.3.1
Chapter 2: installation page 2-4 brim-f6 user’s guide 2.3.1 installing a brim-f6 into a mim to install a brim-f6 in a media interface module (mim) that supports brim technology (e.G., emm-e6): note : we recommend that you power down your hub even though cabletron mims have “hot swap” capabilities. 1...
Page 13
Installing the brim-f6 brim-f6 user’s guide page 2-5 figure 2-3. Installing the brim-f6 the brim-f6 requires a special 24 pin ribbon connector in addition to the standard 96 pin brim connector. This ribbon connector allows the brim-f6 to use in-line filtering functionality. Brim-f6 xmt pwr rcv sts f...
Page 14: Caution:
Chapter 2: installation page 2-6 brim-f6 user’s guide to install the brim-f6 ribbon cable: 1. Insert one ribbon cable connector into the ribbon cable jack on the brim. (see figure 2-4.) figure 2-4. Installing the brim-f6 ribbon cable caution: the ribbon cable connector only fits into the ribbon cabl...
Page 15: 2.3.2
Installing the brim-f6 brim-f6 user’s guide page 2-7 3. Insert the remaining ribbon cable connector into the ribbon cable jack on the mim. 4. Press down on the connector until the clips on the jack snap into a vertical locked position. After returning the mim to the chassis, returning power to your ...
Page 16: Note:
Chapter 2: installation page 2-8 brim-f6 user’s guide 9. Press down firmly on the back of the brim until the pins slide all the way into the connector holes. Note: make sure that the standoffs align with the standoff screw holes. 10. Reinstall the coverplate/faceplate screws and standoff screws. Not...
Page 17: Chapter 3
Brim-f6 user’s guide page 3-1 chapter 3 using lanview lanview is a visual diagnostic and status monitoring system developed by cabletron systems. Lanview leds (see figure 3-1) help you troubleshoot bridge, port, and network problems. The following sections describe brim-f6 leds. Figure 3-1. Brim-f6 ...
Page 18
Chapter 3: using lanview page 3-2 brim-f6 user’s guide twr (twisted ring) when on, this red led indicates an undesirable cable connection. Twr illuminates when you connect a to a, or b to b, instead of a to b, or b to a. The brim-f6 supports undesirable configurations, but alerts you to them. (appen...
Page 19: Chapter 4
Brim-f6 user’s guide page 4-1 chapter 4 specifications this chapter lists the operating specifications for the brim-f6. Cabletron systems reserves the right to change these specifications at any time, without notice. 4.1 fiber optic interface depending on the fpim, interfaces have the following char...
Page 20
Chapter 4: specifications page 4-2 brim-f6 user’s guide single mode specifications multimode receiver (signal detect) assert power: -33.0 dbm typical -31.0 dbm maximum assert time: 10 µ sec typical 100 µ sec maximum deassert power: -36.0 dbm typical -45.0 dbm minimum deassert time: 10 µ sec typical ...
Page 21
Single mode specifications brim-f6 user’s guide page 4-3 single mode receiver optical wavelength: 1330 nm typical optical input: (avg. Sensitivity) -31.0 dbm minimum -14.0 dbm maximum output rise time: 3 nsec maximum output fall time: 3 nsec maximum supply current: 115 mamps maximum single mode rece...
Page 22
Chapter 4: specifications page 4-4 brim-f6 user’s guide unshielded twisted pair specifications unshielded twisted pair transmitter amplitude 1.080 vpk maximum 0.920 vpk minimum rise time 2 nsec minimum 4 nsec maximum fall time 2 nsec minimum 4 nsec maximum rise/fall variation 0.5 nsec maximum oversh...
Page 23: 4.2
Shielded twisted pair transmitter specifications brim-f6 user’s guide page 4-5 shielded twisted pair transmitter specifications 4.2 cable specifications the fddi physical layer medium dependent (pmd), twisted pair physical layer medium dependent (tp-pmd), and single mode fiber physical layer medium ...
Page 24
Chapter 4: specifications page 4-6 brim-f6 user’s guide multimode fiber: core diameter: 62.5 µ m nominal cladding diameter: 128.0 µ m maximum 122.0 µ m minimum cable attenuation: ≤ 2.5 db/km typical single mode fiber: core diameter: 8.7 µ m +/- 0.5 µ m cladding diameter: 127.0 µ m maximum cable atte...
Page 25: 4.3
Twisted pair cable length brim-f6 user’s guide page 4-7 maximum total cable length: 100 km (62 miles) — dual ring 200 km (124 miles) — wrapped maximum twisted pair cable length between adjacent nodes: 100 m (328.1 feet) 4.3 twisted pair pinout configuration this section provides the rj-45 pinout con...
Page 26: 4.4
Chapter 4: specifications page 4-8 brim-f6 user’s guide 4.4 environment storage temperature: -40 ° c minimum 85 ° c maximum operating temperature: 5 ° c minimum 40 ° c maximum operating humidity: 5% to 95% non-condensing 4.5 safety this unit meets the safety requirements of ul 1950, csa c22.2 no. 95...
Page 27: Appendix A
Brim-f6 user’s guide page a-1 appendix a basic fddi networks this appendix covers basic fiber distributed data interface (fddi) network concepts relating to fddi network design and installation. Ansi standard x3t9.5 provides greater detail on fddi access methods. Reference this standard whenever you...
Page 28
Appendix a: basic fddi networks page a-2 brim-f6 user’s guide when a station has a frame waiting to transmit, the station captures the token at the next opportunity, transmits the data frame, and then reissues the token. (a token holding timer (tht) controls the maximum length of time that any stati...
Page 29
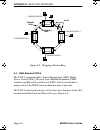
Reliability brim-f6 user’s guide page a-3 figure a-1. Typical fddi physical installation a.3 reliability fddi networks employ a ring topology and are inherently vulnerable to the frailties of each ring segment and failures of individual stations. The ring of trees topology reduces the risk of a sing...
Page 30
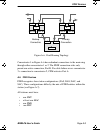
Appendix a: basic fddi networks page a-4 brim-f6 user’s guide figure a-2. Wrapping a broken ring a.4 ansi standard x3t9.5 the x3t9.5 standard includes: station management (smt), media access control (mac), physical layer medium dependent (pmd) standards and physical layer protocol (phy). Each sectio...
Page 31
Ansi standard x3t9.5 brim-f6 user’s guide page a-5 figure a-3. Fddi structure and the osi network model the pmd standard establishes the physical characteristics of the network connection, including the fiber optic transmitter power levels, receiver sensitivity, the fiber optic cable type, the type ...
Page 32
Appendix a: basic fddi networks page a-6 brim-f6 user’s guide other functions of the phy include generation of a 125 mhz transmit clock, synchronization of the receive clock with an upstream transmitter, encoding and decoding for media control symbols, and in some applications, buffering for the inc...
Page 33
Ansi standard x3t9.5 brim-f6 user’s guide page a-7 smt (station management) manages the fddi station. It controls internal fddi station processes and protocol compliance and provides an interface for human intervention. Internal smt management functions consist of three major categories: smt frame s...
Page 34
Appendix a: basic fddi networks page a-8 brim-f6 user’s guide connection management (cmt) controls physical layer insertion and removal of stations. Cmt has three main components: • entity coordination management (ecm) controls bypass switches and coordinates trace (recovery) functions. • configurat...
Page 35
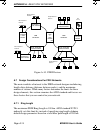
Fddi devices brim-f6 user’s guide page a-9 figure a-6. Dual homing topology concentrator 3 in figure a-6 has redundant connections to the main ring through either concentrator 1 or 2. The fddi connection rules only permit one active connection, port b. If a cable failure severs concentrator 3’s conn...
Page 36
Appendix a: basic fddi networks page a-10 brim-f6 user’s guide each physical ring connection requires: • one pmd • one phy. A sas consists of: • one smt • one mac • one pmd • one phy. A das consists of: • two pmds • two phys. Figure a-7. Valid station configurations phy pmd single attached concentra...
Page 37
Fddi devices brim-f6 user’s guide page a-11 fddi devices physically attach to the ring using fixed shroud duplex (fsd) media interface connectors. The x3t9.5 physical layer, pmd standard defines four connector types (see figure a-7). These connectors provide proper trunk fiber alignment for each of ...
Page 38
Appendix a: basic fddi networks page a-12 brim-f6 user’s guide optical bypass switches, concentrators, and bridges exist throughout fddi networks. These devices allow creation of ring topologies that meet the specific needs of different network applications. Repeaters, often found in other network t...
Page 39
Fddi devices brim-f6 user’s guide page a-13 figure a-9. Optical bypass switch a concentrator is a hub. It provides connections to the dual ring for single attached stations and controls their access to the ring. The network can optically bypass each main ring connection if the attached station becom...
Page 40
Appendix a: basic fddi networks page a-14 brim-f6 user’s guide figure a-10. Fddi devices a.7 design considerations for fddi networks the main variables of interest to the fddi network designer include ring length, drive distance (distance between nodes), and the maximum number of stations. While man...
Page 41
Design considerations for fddi networks brim-f6 user’s guide page a-15 to translate fiber path to ring length, remember that fddi networks contain two counter-rotating rings. Under normal conditions (no failed segment), the ring length remains the same as the fiber path length. However, if a wrap oc...
Page 42
Appendix a: basic fddi networks page a-16 brim-f6 user’s guide the attenuation of the typical multimode fiber optic cable used in fddi networks is 2.5 db/km or 5 db for the 2 km maximum node separation. When installing optical bypass switches, each switch could add 2.5 db to the attenuation. With an...
Page 43
Design considerations for fddi networks brim-f6 user’s guide page a-17 figure a-11. Physical device connections das 2 dac 2 sac sas sas sas sas sas 16 physical connections 2 2 2 1 + 1 2 2 2 2 brim-f book page 17 monday, january 29, 1996 9:26 am.