- DL manuals
- Cabletron Systems
- Network Card
- EMME
- User Manual
Cabletron Systems EMME User Manual
Summary of EMME
Page 1
Emme (ethernet management module with ethernet) user’s guide bok stbya stbyb rcva rcvb rcvc rcvd emme sn reset on pwr on pwr a u i 1 a u i 2 err stybc stbyd clna clnb clnc clnd.
Page 2: Notice
Emme user’s guide i notice cabletron systems reserves the right to make changes in specifications and other information contained in this document without prior notice. The reader should in all cases consult cabletron systems to determine whether any such changes have been made. The hardware, firmwa...
Page 3
Notice ii emme user’s guide fcc notice this device complies with part 15 of the fcc rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesi...
Page 4
Notice emme user’s guide iii cabletron systems, inc. Program license agreement important: before utilizing this product, carefully read this license agreement. This document is an agreement between you, the end user, and cabletron systems, inc. (“cabletron”) that sets forth your rights and obligatio...
Page 5
Notice iv emme user’s guide united states government restricted rights the enclosed product (a) was developed solely at private expense; (b) contains “restricted computer software” submitted with restricted rights in accordance with section 52227-19 (a) through (d) of the commercial computer softwar...
Page 6: Table of Contents
Emme user's guide v table of contents chapter 1 introduction 1.1 using this manual ................................................................ 1-1 1.2 ethernet management module overview.................. 1-2 1.2.1 multi media access center with flexible network bus ... 1-4 1.2.2 repeater inter...
Page 7
Table of contents vi emme user's guide chapter 2 network planning and configuration 2.1 network requirements.....................................................2-1 2.2 emme in the multi media access center......................2-1 2.3 repeater media interface modules .............................2-...
Page 8
Emme user's guide vii table of contents 5.8 the system level screen ............................................... 5-13 5.8.1 system level screen fields ......................................... 5-13 5.8.2 setting the system date ............................................... 5-15 5.8.3 setting th...
Page 9
Table of contents viii emme user's guide appendix a image file download using oids a.1 setting up a unix workstation as a tftp server... A-2 a.2 standard local download ............................................. A-3 appendix b emme oids b.1 spanning tree protocol ....................................
Page 10: Chapter 1
Emme user’s guide page 1-1 chapter 1 introduction welcome to the cabletron systems ethernet management module (emme) user’s guide . This manual provides the technical user with a description of the emme and the information needed to install and operate it in a cabletron systems multi media access ce...
Page 11: Mib Navigator
Chapter 1 : introduction page 1-2 emme user’s guide chapter 6, mib navigator , describes mib navigator’s management and control. The mib navigator manages emme-related management information bases. Chapter 7, troubleshooting , details the remote lanview leds incorporated into the emme that enable yo...
Page 12
Ethernet management module overview emme user’s guide page 1-3 the emme operates in conjunction with cabletron systems’ repeater interface controller (ric) media interface modules (mims) by using the mmac’s fnb ethernet channels b and c. The emme is snmp compliant and can be controlled and monitored...
Page 13: Bus
Chapter 1 : introduction page 1-4 emme user’s guide 1.2.1 multi media access center with flexible network bus the multi media access center with flexible network bus (mmac-fnb) provides the platform for the operation of the emme. The mmac backplane provides three ethernet buses designated as etherne...
Page 14: Modules
Ethernet management module overview emme user’s guide page 1-5 table 1-1 provides a list of the mmac-fnb chassis where shunting capabilities are set at the factory. 1.2.2 repeater interface controller media interface modules cabletron systems’ multichannel family of media interface modules (mims) in...
Page 15: Tpmim, Fomim, and Thnmim
Chapter 1 : introduction page 1-6 emme user’s guide 1.2.3 ethernet channels a, b, c, and d the emme supports up to four ethernet channels, provides management for the four channels, and bridging between the ports. The four emme ethernet channels access the same shared memory so that bridging between...
Page 16: Fddi and Token Ring Modules
Ethernet management module overview emme user’s guide page 1-7 fddi and token ring modules - the emme recognizes the following fddi and token ring modules, but the emme management does not provide control or statistics. • crm-3t • snacmim • trmim-32a • trmim-34a • trrmim-f2t • trrmim-f3t with trmmim...
Page 17: 1.2.4 Local Management
Chapter 1 : introduction page 1-8 emme user’s guide 1.2.4 local management built into the front panel of the emme are two rj45 ports. The console port allows access to local management by locally connecting a dec vt 320 terminal, or a pc using vt320 emulation software. Refer to chapter 5, local mana...
Page 18
Ethernet management module overview emme user’s guide page 1-9 eavesdrop prevention delivers a modified data portion (filled with a random pattern of binary ones and zeros) of the ethernet packet to all ports except the port specified in the original packet’s destination mac address field. Effective...
Page 19: 1.3
Chapter 1: introduction page 1-10 emme user’s guide 1.3 repeater functionality the emme’s repeater functionality ensures that any problem segments connected to any port on the mmac-fnb will not affect any other segments connected to the mmac-fnb. For example, if 32 consecutive collisions are detecte...
Page 20: 1.5
More about bridges emme user’s guide page 1-11 1.5 more about bridges a bridge is a device that can be added to a network to allow expansion beyond the limitations of ieee 802.3. If an ethernet network has a repeater hop (count) of four repeaters or a propagation delay near the 51.2-microsecond maxi...
Page 21
Chapter 1: introduction page 1-12 emme user’s guide the bridge is considered a node on the network and performs store and forward functions for packets on each network. This contrasts with a repeater which repeats the signal bit by bit from one side of the network to the other. The bridge actually r...
Page 22: 1.6
Routing functionality emme user’s guide page 1-13 1.5.2 spanning tree algorithm the spanning tree algorithm (sta) is used by bridges to detect data loops (duplicate data paths). The bridges will then automatically break the loop and use the now blocked path as a backup in case the primary path fails...
Page 23
Chapter 1: introduction page 1-14 emme user’s guide the routing services software provides the following additional funtionality: • security via access lists • directed user datagram protocol (udp) broadcast forwarding • support for multiple frame types: - internet protocol (ip) and decnet - etherne...
Page 24: 1.7
Community names emme user’s guide page 1-15 1.7 community names when using local or remote management tools to access the emme, it is important that the network manager has the ability to maintain network security. Community names provide some network security by serving as passwords to the device a...
Page 25: 1.9
Chapter 1: introduction page 1-16 emme user’s guide 1.8.1 management information base (mibs) the mibs are a database which are resident on the network device (i.E., emme). Objects in the information base are uniquely identified by administratively assigned identifiers (called object identifiers or o...
Page 26: 1.9.1 Network Id
Ip addressing emme user’s guide page 1-17 table 1-4. Class c 1.9.1 network id the internet assigned numbers authority (iana) assigns the network id and uniquely identifies a network on the global internet. On private internal networks, unofficial ip addresses can be used allowing the network address...
Page 27: 1.9.4 Subnet Masks
Chapter 1: introduction page 1-18 emme user’s guide 1.9.4 subnet masks the purpose of the subnet mask is to indicate the part of the host id that is being used as a subnet address. By default no part of the host id is used, and therefore, the default or “natural mask” masks just the octets that comp...
Page 28: 1.10 Default Gateway
Default gateway emme user’s guide page 1-19 1.10 default gateway the default gateway is the ip address of the network or host to which all packets addressed to unknown network or host are sent. The default gateway should be a perimeter or border device that connects the network with the rest of the ...
Page 29: 1.14 Emme Upgrades
Chapter 1: introduction page 1-20 emme user’s guide for example, you can gather a large amount of statistical information about the emme, including the quantities of the following. For further specific information, refer to the applicable network management package user’s manual. 1.13 uninterruptibl...
Page 30
Emme upgrades emme user’s guide page 1-21 to determine the upgrade required for a specific emme, the emme board revision level must be known. The revision level can be found using one of the following: • local management, where it is shown on the password screen • mib navigator, described in chapter...
Page 31: 1.15 Getting Help
Chapter 1: introduction page 1-22 emme user’s guide 1.15 getting help for additional support related to the emme or for any questions, comments, or suggestions related to this manual, contact cabletron systems technical support by any of the following methods. Mail: cabletron systems, inc. P.O. Box ...
Page 32: Chapter 2
Emme user’s guide page 2-1 chapter 2 network planning and configuration before you attempt to install the cabletron systems emme, review the requirements outlined in this chapter. Also, refer to the operating specifications and environmental requirements that are listed. All conditions, guidelines, ...
Page 33: 2.3
Chapter 2: network planning and configuration page 2-2 emme user’s guide 2.3 repeater media interface modules repeater media interface modules (rmims) also called ricmims for repeater interface control mims, shown in figure 2-1, are based on repeater interface technology that enables each of the mod...
Page 34
Repeater media interface modules emme user’s guide page 2-3 • tpxmim-33/-34 - these mims are equipped with 50 pin champ connectors and one user configurable epim. The tpxmim-33 has one 50 pin champ connector and the -34 has two. Figure 2-1. Sample repeater mims rcv pok cln sn tprmim-36 10base-t ethe...
Page 35
Chapter 2: network planning and configuration page 2-4 emme user’s guide 2.3.1 ethernet port interface modules for an additional connection to the ethernet network, the tprmim-20/ 22, tprmim-33/36, and cxrmim utilize the cabletron systems ethernet port interface modules (epims), figure 2-2, that all...
Page 36: 2.4
Sample network configurations emme user’s guide page 2-5 to support the additional functionality of the lanview secure products, the epims used in products that support lanview secure must be at or above the revision levels listed in table 2-1. The epim revision level is located on the epim module a...
Page 37
Chapter 2: network planning and configuration page 2-6 emme user’s guide 2.4.1 three networks with a single mmac-fnb one of the basic applications of the emme is for configuring three separate networks with one mmac-fnb. This provides you with the advantages of having three separate networks in one ...
Page 38
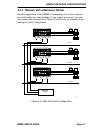
Sample network configurations emme user’s guide page 2-7 2.4.2 network with a multi-port router another application of the emme is configuring two or three separate networks within the same building. Using a multi-port router, you can interconnect the three networks figure 2-4 illustrates an example...
Page 39: Segment
Chapter 2: network planning and configuration page 2-8 emme user’s guide 2.4.3 configuring additional users to a separate segment before the emme was available, adding users to a separately repeated segment required investing in a great deal of additional equipment. The example in figure 2-5 has one...
Page 40
Sample network configurations emme user’s guide page 2-9 figure 2-5. Adding new users current technology current technology new technology new technology - two additional 24-port ric mims - an additional mmac - an additional irm2 - two additional 24-port mims - an external bridge bridge irm3 tpmim-2...
Page 41
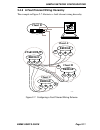
Chapter 2: network planning and configuration page 2-10 emme user’s guide 2.4.4 multiple routed sub-networks the example in figure 2-6 illustrates how you can use the emme to configure up to seven individual networks in a single mmac-fnb. This can be done by connecting each mim in the mmac-fnb to a ...
Page 42: Bridge
Sample network configurations emme user’s guide page 2-11 2.4.5 a fault tolerant wiring hierarchy the example in figure 2-7 illustrates a fault tolerant wiring hierarchy. Figure 2-7. Configuring a fault tolerant wiring scheme d c b a a b c bridge star hub a b c bridge closet b a b c bridge closet c ...
Page 43
Chapter 2: network planning and configuration page 2-12 emme user’s guide closets a, b, and c each contain an mmac-fnb with an emme, mims and ric mims operating on ethernet channels a, b, and c. Within each closet, each ethernet channel is separately repeated, and each is dedicated to a specific set...
Page 44: Chapter 3
Emme user’s guide page 3-1 chapter 3 installing the emme this chapter contains unpacking information and installation instructions for the cabletron systems emme into a cabletron systems mmac-fnb. Additional instructions are provided on setting the mode switches and for connecting segments to the em...
Page 45: 3.2
Chapter 3: installing the emme page 3-2 emme user’s guide 3.2 setting the emme mode switches the bank of dip switches located at the top right of the emme (shown in figure 3-1) should be set to their default positions when the module is shipped. Check these switches to ensure that they are in the co...
Page 46
Setting the emme mode switches emme user’s guide page 3-3 switches should be positioned as follows: • switch 1 - nmi (non-maskable interrupt). This switch must be in the on position. Cabletron systems use only. • switch 2 - stestdis (system test disable). This switch must be in the off position. Cab...
Page 47
Chapter 3: installing the emme page 3-4 emme user’s guide for more information on configuring a station as a bootp server refer to the spectrum element manager for windows user’s manual. • switch 7 - nvram (non-volatile ram reset). The emme uses nvram to store user entered parameters such as ip addr...
Page 48: 3.3
Installing the emme emme user’s guide page 3-5 3.3 installing the emme no special skills or tools are required to install the emme into an mmac-fnb. Use the following guidelines when installing the emme. • the emme must be installed in slot 1 of the mmac-fnb. (identified as the irm slot in the older...
Page 49
Chapter 3: installing the emme page 3-6 emme user’s guide figure 3-2. Installing the emme 4. After the system boot procedure, the leds should be in the following conditions: • bok led flashing, indicating that the emme is operating properly. • stby (a, b, c, d) leds on or off, depending on the port’...
Page 50: 3.4
Connecting the emme to the network emme user’s guide page 3-7 3.4 connecting the emme to the network this section provides procedures for connecting the emme to the network via the aui 1 or aui 2 port. When the emme is first powered up, the aui 1 port acts as the bridge port and the aui 2 port is of...
Page 51: Chapter 4
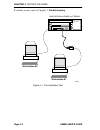
Emme user’s guide page 4-1 chapter 4 testing the emme this chapter contains emme testing procedures for before and after making network connections. 4.1 pre-installation test before installing the emme in a live network, test the module in a controlled situation to insure that it is repeating bridgi...
Page 52
Chapter 4: testing the emme page 4-2 emme user’s guide if a failure occurs, refer to chapter 7, troubleshooting. Figure 4-1. Pre-installation test emme mmac-3fnb tpt t tprmim-33 workstation #2 workstation #1 mmac3/fnb with emme and tprmim 051443.
Page 53: 4.2
Installation check-out emme user’s guide page 4-3 4.2 installation check-out after the emme is connected to the network, verify that packets can be passed over the network segments via the emme. Again you can use two workstations set up as file server and client. Keep the server workstation stationa...
Page 54: Chapter 5
Emme user’s guide page 5-1 chapter 5 local management this chapter describes how to access and use local management for the emme. To access local management, you need to attach a management terminal to the emme’s console port or establish a telnet connection from a station connected to the network. ...
Page 55: 5.1
Chapter 5: local management page 5-2 emme user’s guide 5.1 management terminal configuration to access local management, you need either a vt320 terminal or pc running vt terminal emulation software. The following instructions explain how to configure a terminal to communicate with local management....
Page 56
Management terminal configuration emme user’s guide page 5-3 5.1.1 cable configuration for the management terminal this section outlines the proper cable configurations to connect a management terminal to the console port of the emme. For information on the appropriate pinouts, refer to appendix c. ...
Page 57: 5.2
Chapter 5: local management page 5-4 emme user’s guide 5.1.2 cable configuration for the ups to configure a cable from the uninterruptible power supply (ups) to the emme perform the following steps: 1. Plug a straight-through twisted pair, rs232, cable into the emme rj45 modem port. 2. Plug the othe...
Page 58: 5.3
Local management keyboard conventions emme user’s guide page 5-5 5.3 local management keyboard conventions all key names appear in this manual as capital letters. For example, the enter key appears as enter, the escape key appears as esc, and the backspace key appears as backspace. Table 5-2 explain...
Page 59
Chapter 5: local management page 5-6 emme user’s guide shift + [+] keys this key combination increments values in a local management increment field. For example, “press shift + [+]” means to hold down the shift key while pressing the plus sign key. [–] key this key decreases values from a local man...
Page 60: 5.4
Accessing local management emme user’s guide page 5-7 5.4 accessing local management verify that your terminal has been properly connected to the emme before proceeding. To access local management, perform the following steps: 1. Power on the terminal. The emme password screen, figure 5-1, appears. ...
Page 61
Chapter 5: local management page 5-8 emme user’s guide 2. Enter your password and press enter. The default super-user access password is “public” or press enter. • if an invalid password is entered the terminal beeps and the cursor returns to the beginning of the password entry field. • entering a v...
Page 62: 5.5
Navigating local management screens emme user’s guide page 5-9 5.5 navigating local management screens emme local management consists of a series of menu screens. You navigate through local management by selecting items from the menu screens. Emme local management consists of the following menu scre...
Page 63
Chapter 5: local management page 5-10 emme user’s guide 5.5.2 exiting local management screens to exit any of the local management screens, perform the following steps: 1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the return command at the bottom of the local management screen. 2. Press enter. The previous sc...
Page 64: 5.6
The main menu screen emme user’s guide page 5-11 5.6 the main menu screen the main menu screen is the starting point from which all the local management screens are accessed. Figure 5-3 shows the main menu screen. Figure 5-3. The main menu the main menu screen displays the following menu items: • se...
Page 65: 5.7
Chapter 5: local management page 5-12 emme user’s guide 5.7 setup menu screen the setup menu provides access to local management screens that are used to configure or alter the configuration of the emme. Examples of functions accessible through the setup menu include configuring ip addresses and sub...
Page 66: 5.8
The system level screen emme user’s guide page 5-13 5.8 the system level screen figure 5-5 shows the emme system level screen. This screen allows you to configure the following parameters: • system date and system time • ip addresses, subnet masks, and default gateway • default interface • console a...
Page 67
Chapter 5: local management page 5-14 emme user’s guide channel - shows the channel, or bus, through which packets with that ip address are passing. Channel a is the original ethernet bus channel. Channels b & c are the flexible network bus channels. Channel d is the external ethernet network access...
Page 68
The system level screen emme user’s guide page 5-15 5.8.2 setting the system date to set the system date, perform the following steps: 1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the system date field. 2. Enter the date in a mm/dd/yy format. 3. Press enter to set the system calender to the date in the input ...
Page 69
Chapter 5: local management page 5-16 emme user’s guide 4. Use the arrow keys to highlight the save command at the bottom of the screen and press enter. If the time entered was a valid format, the event message line at the top of the screen displays “saved ok.” if the entry was not valid, local mana...
Page 70
The system level screen emme user’s guide page 5-17 5.8.5 setting the subnet mask if the management workstation that will be receiving snmp traps from the snmp agent of the managed device is located on a separate subnet, the subnet mask for the managed device must be changed from its default. To cha...
Page 71
Chapter 5: local management page 5-18 emme user’s guide 3. Press enter. If the subnet mask entered was a valid format, the cursor returns to the beginning of the subnet mask field. If the entry was not valid, the event message line displays “permissible range: 1...4.” local management does not alter...
Page 72
The system level screen emme user’s guide page 5-19 5.8.8 configuring console and modem ports the emme console and modem ports support the following applications: • local management connections • american power conversion (apc) uninterruptible power supply (ups) connections • telnet connections to a...
Page 73
Chapter 5: local management page 5-20 emme user’s guide 2. Press spacebar or backspace to cycle through the available settings until the operation you require appears. Table 5-3 lists the available settings and their corresponding applications. 3. Press enter to accept the application. If the slip a...
Page 74: 5.9
Snmp community names screen emme user’s guide page 5-21 5.9 snmp community names screen figure 5-6 shows the snmp community names screen. The network manager may control local management access by establishing three (3) passwords. Each password controls varying levels of access to emme local managem...
Page 75
Chapter 5: local management page 5-22 emme user’s guide 5.9.1 setting snmp community names to set a community name, perform the following steps: 1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the community name you want to change. 2. Type the new community name and press enter. The old community name text will ...
Page 76: 5.10 Snmp Traps Screen
Snmp traps screen emme user’s guide page 5-23 5.10 snmp traps screen figure 5-7 shows the snmp traps screen. Configuring the snmp traps screen allows the emme to send snmp traps to multiple network management stations. The following sections explain snmp trap screen information fields as well as pro...
Page 77
Chapter 5: local management page 5-24 emme user’s guide 5.10.2 setting snmp trap destinations to set snmp trap destinations using local management requires three distinct operations: the configuration of a destination address for the traps to be sent to, the assignment of a community name for that i...
Page 78: 5.11 Status Menu
Status menu emme user’s guide page 5-25 5.11 status menu figure 5-8 shows the status menu screen. The status menu screen provides access to the component status screen. Figure 5-8. The status menu screen flash image version: xx.Xx.Xx status menu component status 051451 emme local management return e...
Page 79
Chapter 5: local management page 5-26 emme user’s guide 5.12 the component status screen figure 5-9 shows the component status screen. The component status screen monitors the status of the mib components of the emme. Figure 5-9. The component status screen 5.12.1 component status screen fields the ...
Page 80
The device statistics screen emme user’s guide page 5-27 5.13 the device statistics screen figure 5-10 shows the device statistics screen. The device statistics screen displays error, collision, and traffic statistics for the entire network, a selected slot, or a selected port. This screen also prov...
Page 81
Chapter 5: local management page 5-28 emme user’s guide collisions - displays the number of collisions received. Oow collisions - displays the number of out of window (oow) collisions. Oow collisions are usually caused by the network being too long where the round trip propagation delay is greater t...
Page 82
The device statistics screen emme user’s guide page 5-29 network - this command lets you select the network you want to monitor. The choices range from a to d, depending on the configuration of your network and the options available from this configuration. For example, if you do not have a device r...
Page 83: 5.13.4 Enabling Ports
Chapter 5: local management page 5-30 emme user’s guide 5.13.4 enabling ports the enable port command lets you enable the port selected in the port command. You must first use the port command to select the desired port. To set the port enable command, perform the following steps: 1. Use the arrow k...
Page 84: Chapter 6
Emme user’s guide page 6-1 chapter 6 mib navigator this chapter describes the mib navigator utility. Mib navigator is a feature of emme local management. 6.1 managing device mibs the mib navigator allows access to a command set from which you can configure and manage the emme. The mib navigator enab...
Page 85: 6.2
Chapter 6: mib navigator page 6-2 emme user’s guide 6.2 accessing the mib navigator mib navigator is a feature of local management. Refer to chapter 5 of this manual for instructions about accessing local management. To access the mib navigator screen, perform the following steps: 1. Use the arrow k...
Page 86: 6.3
Mib navigator command set overview emme user’s guide page 6-3 6.3 mib navigator command set overview there are three categories of commands in the command set. • navigation commands - allow the user to access and manage the mib for the device running the mib navigator. Some of these commands also pr...
Page 87: Syntax:
Chapter 6: mib navigator page 6-4 emme user’s guide mib navigator command conventions are as follows: • to abort the output or interrupt a process the escape character is ^c (where ^ equals the control key). • a slash (/) proceeding an oid issues that command from the root directory regardless of wh...
Page 88: 6.3.2 Navigation Commands
Mib navigator command set overview emme user’s guide page 6-5 6.3.2 navigation commands navigation commands allow you to move from mib object to mib object within the mib tree. Branch: syntax: branch [path] description: the branch command displays all of the leaves in the mib tree below a specified ...
Page 89: Syntax:
Chapter 6: mib navigator page 6-6 emme user’s guide ctron: syntax: ctron description: the ctron command allows you to change directories to the cabletron mib (1.3.6.1.4.1.52) without keying in the entire path. Options: not applicable example: help: syntax: help description: the help command can prov...
Page 90: Syntax:
Mib navigator command set overview emme user’s guide page 6-7 mib2: syntax: mib2 description: the mib2 command allows you to move directly to the mib ii subtree (1.3.6.1.2.1) without entering the entire path. Options: not applicable example: next: syntax: next [path] description: the next command en...
Page 91: Syntax:
Chapter 6: mib navigator page 6-8 emme user’s guide pwd: syntax: pwd description: the pwd command displays the full path name for the directory in which you are currently working. The directory will be displayed in ascii format. Options: not applicable example: set: syntax: set description: the set ...
Page 92: Options:
Mib navigator command set overview emme user’s guide page 6-9 options: not applicable example: su: syntax: su [community name] description: the su command enables you to change your community name to allow for different access to the mib. The community name that you enter allows you either read only...
Page 93: Syntax:
Chapter 6: mib navigator page 6-10 emme user’s guide tree: syntax: tree description: the tree command provides a display of the entire mib for the device. Leaves and associated values are displayed in columns. Options: not applicable example: whoami: syntax: whoami description: the whoami command di...
Page 94: 6.3.3 Built-In Commands
Mib navigator command set overview emme user’s guide page 6-11 6.3.3 built-in commands the built-in commands listed in this section activate functions on the lm managed device or devices being accessed through mib navigation. Arp: syntax: arp description: the arp command provides access to the arp (...
Page 95: Example:
Chapter 6: mib navigator page 6-12 emme user’s guide example: defroute: syntax: defroute [interface number] [ip address] description: the defroute command allows you to set the default ip route to a managed device through the specified interface. Options: not applicable example: mibnav-> arp -a # in...
Page 96: Syntax:
Mib navigator command set overview emme user’s guide page 6-13 netstat: syntax: netstat [option] description: the netstat command provides a display of general network statistics for the managed device. The netstat command must be used with one of the two display options. Options: -i displays status...
Page 97: Syntax:
Chapter 6: mib navigator page 6-14 emme user’s guide ping: syntax: ping [ip address] description: the ping command generates an outbound ping request to check the status (alive/not alive) of a device at a specified ip address. Options: not applicable example: snmpbranch: syntax: snmpbranch [ip addre...
Page 98: Syntax:
Mib navigator command set overview emme user’s guide page 6-15 snmpget: syntax: snmpget [ip address] [community name] [oid] description: the snmpget command enables you to query another snmp device to obtain a value for a specified object. This command requires the appropriate community string and o...
Page 99: Options:
Chapter 6: mib navigator page 6-16 emme user’s guide options: not applicable example: snmptree: syntax: snmptree [ip address] [community name] description: the snmptree command provides a display of all objects in the device and their corresponding values. Options: not applicable example: mibnav-> s...
Page 100: Syntax:
Mib navigator command set overview emme user’s guide page 6-17 traceroute: syntax: traceroute [ip address] description: the traceroute command generates a traceroute request to a specified ip address and provides a display of all next-hop routers in the path to the device. If the device is not reach...
Page 101: Chapter 7
Emme user’s guide page 7-1 chapter 7 troubleshooting this chapter includes information to help you troubleshoot your emme should a problem occur. Described are the emme’s lanview leds, a troubleshooting checklist, and information to have available if you call cabletron technical support. 7.1 interpr...
Page 102
Chapter 7: troubleshooting page 7-2 emme user’s guide table 7-1 describes the leds and the associated troubleshooting actions. Figure 7-2. Lanview leds led color description error condition/ recommended action bok (board ok) green when flashing, indicates that the board is operating properly. If off...
Page 103
Interpreting the lanview leds emme user’s guide page 7-3 rcv a,b,c,d (receive) yellow light flashes to indicate that a segment is receiving a packet. If none of the receive lights are flashing, the emme is not receiving packets on any of the segments. Check that each module is firmly installed in th...
Page 104: 7.2
Chapter 7: troubleshooting page 7-4 emme user’s guide 7.2 troubleshooting checklist if your emme is not operating properly, refer to table 7-2 for a checklist describing some of the problems that may occur with the emme installed in an mmac, possible causes for the problem, and suggestions for resol...
Page 105
Troubleshooting checklist emme user’s guide page 7-5 a port on a mim managed by the emme cannot access the network, while other ports on the same mim are able to. The port is either off or segmented. Port cable is defective. Enable the port via local or remote management. Try connecting the port wit...
Page 106: 7.3
Chapter 7: troubleshooting page 7-6 emme user’s guide 7.3 using the reset button the emme incorporates a recessed reset button, located above the leds. See figure 7-1. This reset button initializes the emme processor. This will not initialize nvram, the non-volatile random access memory where your n...
Page 107: Appendix A
Emme user’s guide page a-1 appendix a image file download using oids this appendix provides instructions for setting up a tftp server and to download an image file to the emme by setting specific mib oid strings. To set oid strings, you can use the snmp tools screen described in chapter 5 or mib nav...
Page 108: A.1
Appendix a: image file download using oids page a-2 emme user’s guide a.1 setting up a unix workstation as a tftp server due to variations between unix systems and individual configurations, this section provides only guidelines for configuring a unix workstation to perform an image file download. T...
Page 109: A.2
Standard local download emme user’s guide page a--3 4. Store the hex image file in the /tftpboot directory as emme.Hex. 5. Edit the /etc/inetd.Conf file by removing anything prior to the tftpboot daemon (e.G., the # sign) that comments-out the line. 6. Kill the inetd process (e.G., unix% kill -hup ‘...
Page 110
Appendix a: image file download using oids page a-4 emme user’s guide when performing the steps in table a-1, keep the following in mind: • you must follow the steps in order. • enter the ip address of the tftp server in standard dotted decimal notation (e.G., 132.177.118.24). • enter the full path ...
Page 111: Appendix B
Emme user’s guide page b-1 appendix b emme oids this appendix contains a selected number of oid strings that are most frequently needed. The oids are implemented by using either the snmp tools procedures detailed in chapter 5 or the mib navigator procedures located in chapter 6. Note that the oids c...
Page 112: B.2
Appendix b: emme oids page b-2 emme user’s guide b.2 port group security the next seven oids are used for port, group security features. Rptrsrcaddrmgmtportlock description: setting this object to lock activates the network port security lock. Setting a value of portmismatch (3) is invalid. A read o...
Page 113
Port group security emme user’s guide page b-3 rptrportsecuritylockstatus description: defines the lock status for this particular port entry. Object identifier: 1.3.6.1.4.1.52.4.1.1.1.4.3.9.1.1.3 data type: integer values: 1 = unlock 2 = lock access policy: read-write rptrportsecuritylockaddaddress...
Page 114
Appendix b: emme oids page b-4 emme user’s guide rptrportsecuritydisableonviolation description: designates whether port is disabled if source address is violated. A source address violation occurs when a address is detected which is not in the source address list for this port. If this port is disa...
Page 115: B.3
Network and channel level traps emme user’s guide page b-5 b.3 network and channel level traps the next three oids control traps enable and disable at the network level or channel level. Rptrhwtrapssetlink description: enables and disables link traps for this network (i.E., channel a, b, or c). Obje...
Page 116: B.4
Appendix b: emme oids page b-6 emme user’s guide b.4 board level traps the next three oids are for traps enable and disable at the board level. Rptrportgrphwtrapsetlink description: enables and disables link traps for the specified port group at the board level. Object identifier: 1.3.6.1.4.1.52.4.1...
Page 117: B.5
Port level traps emme user’s guide page b-7 b.5 port level traps the next three oids are for traps enable and disable at the port level. Rptrporthwtrapsetlink description: enables and disables link traps for this port. Object identifier: 1.3.6.1.4.1.52.4.1.1.1.4.3.8.1.1.1.3.Slot.Port data type: inte...
Page 118: B.6
Appendix b: emme oids page b-8 emme user’s guide b.6 bridging the following oid is used to enable and disable the interface for the bridging function. Dot1dstpportenable description: the enabled/disabled status of the port. Object identifier: 1.3.6.1.2.1.17.2.15.1.4 data type: integer values: 1 = en...
Page 119: B.8
Channel selection emme user’s guide page b-9 b.8 channel selection the following two oids are needed to select channel assignments (a, b, or c) for all boards or individual ports. These oids are needed for products supporting multichannel connectivity. Fnbconnect description: denotes the connection ...
Page 120: Appendix C
Emme user’s guide page c-1 appendix c emme specifications the operating specifications for the cabletron systems emme are provided in this appendix. Cabletron systems reserves the right to change these specifications at any time without notice. C.1 bridging functionality shared sonic memory: 4 mb in...
Page 121: C.2
Appendix c: emme specifications page c-2 emme user’s guide c.2 repeater functionality delay times (port x in to port x out) start of packet: 1,450 ns max. Collision to jam: 1,550 ns max. Preamble input: minimum of 40 bits to a max. Of 64 bits required. Preamble output: 64 bits min. (last 2 bits are ...
Page 122: C.4
Modem port emme user’s guide page c-3 c.4 modem port type: standard rj45 port modem port pinout pin 1: transmit data (from modem port) pin 2: data carrier detect (to modem port) pin 3 not used pin 4: receive data (to modem port) pin 5: signal ground pin 6: data terminal ready (from modem port) pin 7...
Page 123: C.6
Appendix c: emme specifications page c-4 emme user’s guide c.6 environmental requirements operating temperature: +5 ° to +40 ° c (+41 ° to +104 ° f) non-operating temperature: -30 ° to +90 ° c (-22 ° to +194 ° f) operating humidity: 5% to 95% (non-condensing) c.7 flash eprom the flash eprom memory e...
Page 124: Index
Index-1 index a aui cable connection 3-7 aui port pin-outs c-3 b bpdu 1-13 bridge 1-11 bridging description 1-10 functionality c-1 c command set 6-3 community name 1-15 configuration screen baud rate field 5-14 channel field 5-14 default gateway field 5-14 default interface field 5-14 i/f field 5-13...
Page 125
Index index-2 epims epim-a 2-4 epim-c 2-4 epim-f1 2-4 epim-f2 2-4 epim-f3 2-4 epim-t 2-4 epim-x 2-4 eprom flash c-4 ethernet description 1-2 ports 1-6 f figure 7-1 7-1 filter 1-12 g get 1-15 getting help 1-22 h host id 1-17 i image file download a-1 ip address 1-16 l lanview 7-2 lanview leds bok 7-2...
Page 126
Index index-3 mode switches baud rate default switch 3-3 cadic switch 3-3 forced download switch 3-3 location 3-2 mimrev switch 3-3 nmi switch 3-3 nvram switch 3-4 password default switch 3-4 reset factory defaults 3-4 setting 3-2 stestdis switch 3-3 modem port pin-outs c-3 n natural mask 1-18 netwo...