- DL manuals
- Cabletron Systems
- Switch
- Fast Network 10
- User Manual
Cabletron Systems Fast Network 10 User Manual
FAST NETWORK 10
USER GUIDE
X
2X
3X
4X
5X
6X
7X
8X
9X
10X
11X
12X
AUI 1
Link
2 3
1
4 5 6
7 8 9 10 11 12
A B
Usr
Segment Status
Select
TX
RX
Act
Col
Reset Ready
FN10-12
NMS Port
Pwr
X
2X
3X
4X
5X
6X
7X
8X
9X
10X
11X
12X
13X
14X
15X
16X
17X
18X
19X
20X
21X
22X
23X
24X
13 14 15 16 17 18
19 20 21 22 23 24
AUI 1
Link
Link
2 3
1
4 5 6
7 8 9 10 11 12
A B
Usr
Segment Status
Select
TX
RX
Act
Col
Reset Ready
NMS Port
Pwr
FN10-24
Summary of Fast Network 10
Page 1
Fast network 10 user guide x 2x 3x 4x 5x 6x 7x 8x 9x 10x 11x 12x aui 1 link 2 3 1 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 a b usr segment status select tx rx act col reset ready fn10-12 nms port pwr x 2x 3x 4x 5x 6x 7x 8x 9x 10x 11x 12x 13x 14x 15x 16x 17x 18x 19x 20x 21x 22x 23x 24x 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 2...
Page 3: Notice
Fast network 10 user guide i notice cabletron systems reserves the right to make changes in specifications and other information contained in this document without prior notice. The reader should in all cases consult cabletron systems to determine whether any such changes have been made. The hardwar...
Page 4
Ii fast network 10 user guide fcc notice this device complies with part 15 of the fcc rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause unde...
Page 5
Fast network 10 user guide iii cabletron systems, inc. Program license agreement important: before utilizing this product, carefully read this license agreement. This document is an agreement between you, the end user, and cabletron systems, inc. (“cabletron”) that sets forth your rights and obligat...
Page 6
Iv fast network 10 user guide united states government restricted rights the enclosed product (a) was developed solely at private expense; (b) contains “restricted computer software” submitted with restricted rights in accordance with section 52227-19 (a) through (d) of the commercial computer softw...
Page 7: Contents
Fastnet 10 user guide v contents chapter 1 introduction 1.1 about this manual....................................................................... 1-1 1.2 getting help................................................................................. 1-2 1.3 document conventions .......................
Page 8
Contents vi fastnet 10 user guide chapter 3 configuring your fn10 3.1 assigning ip addresses ...............................................................3-3 3.1.1 displaying ip addresses .................................................3-4 3.1.2 deleting an ip address................................
Page 9
Contents fastnet 10 user guide vii 4.5 using lcm to manage the fn10 ............................................... 4-15 4.5.1 disabling a port ............................................................ 4-15 4.5.2 enabling a port ............................................................. 4-16 4...
Page 10
Contents viii fastnet 10 user guide appendix a technical specifications a.1 fn10 specifications .................................................................... A-1 a.2 serial cable pin assignments..................................................... A-3 a.3 10base-t pin assignments ...............
Page 11: Chapter 1
Fast network 10 user guide page 1-1 chapter 1 introduction 1.1 about this manual this manual is for system administrators responsible for configuring, monitoring, and maintaining the fast network 10 (fn10). You should have a familiarity with networking concepts and principles. In addition, a basic u...
Page 12: Fn10 Filters
Chapter 1: introduction page 1-2 fast network 10 user guide • chapter 5, fn10 filters , describes fn10 filtering and provides specific examples of how filters can be used. It also provides instructions for adding, modifying, and deleting port filters using the local console manager (lcm). • chapter ...
Page 13: 1.3 Document Conventions
Document conventions fast network 10 user guide page 1-3 1.3 document conventions the following conventions are used throughout this document: lcm commands, prompts, and information displayed by the computer appear in courier typeface, for example: current number of learned addresses: 133 number of ...
Page 14: 1.4 Related Documentation
Chapter 1: introduction page 1-4 fast network 10 user guide 1.4 related documentation the following documentation may assist the user in using this product: • fast network 10 mib reference guide – contains enterprise mib information. • interconnections, bridges and routers, radia perlman, addison we...
Page 15
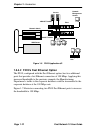
Overview fast network 10 user guide page 1-5 . Figure 1-1 fn10 front panels figure 1-2 fn10 rear panel with the optional fast ethernet ports the fn10: • provides dedicated bandwidth for each network connected to its ports. • provides full store and forward bridging functionality. • provides complete...
Page 16: 1.5.1 Fn10 Architecture
Chapter 1: introduction page 1-6 fast network 10 user guide • implements the spanning tree protocol (802.1d). • configured with factory-set defaults for immediate plug-and-play capability. In addition, the fn10 offers features that can help you manage and maintain your network, such as: • configurat...
Page 17
Overview fast network 10 user guide page 1-7 media access control (mac) sub-layer of the data link layer. Figure 1-3 shows the osi reference model. Figure 1-3 osi reference model because the fn10 does not process any network layer information, it provides a high level of performance in terms of pack...
Page 18
Chapter 1: introduction page 1-8 fast network 10 user guide forwards the packet to the network segment associated with that destination address. However, if the packet’s source and destination address are on the same network segment, known as local traffic , the packet is automatically discarded (i....
Page 19
Overview fast network 10 user guide page 1-9 automatically reconfigured by the spanning tree protocol to create an alternate path to the lan. 1.5.2 fn10 bridge address table the fn10 creates and maintains a dynamic database of addresses called the bridge address table. The fn10 examines every packet...
Page 20: 1.5.3 Fn10 Filtering
Chapter 1: introduction page 1-10 fast network 10 user guide • a single port number of the lan on which the address resides • the age of the entry • various statistics counters • any filtering restrictions added by a network management station (nms) each static entry contains the same information as...
Page 21: 1.5.4.1 Fn10 Trunking
Overview fast network 10 user guide page 1-11 additional fn10 features, such as trunking, fast ethernet, and virtual workgroups allow you to optimize bandwidth and design a more efficient flow for your network traffic. 1.5.4.1 fn10 trunking the fn10 allows multiple trunk groups with up to eight port...
Page 22
Chapter 1: introduction page 1-12 fast network 10 user guide figure 1-6 fn10 application #2 1.5.4.2 fn10’s fast ethernet option the fn10, configured with the fast ethernet option, has two additional ports that provide a fast ethernet connection of 100 mbps. Applying this increased bandwidth to the p...
Page 23
Overview fast network 10 user guide page 1-13 figure 1-7 fn10 application #3 figure 1-8 illustrates how the fn10 can be used in a backbone network configuration using increased bandwidth of the optional fast ethernet configuration. Figure 1-8 fn10 application #4 fn10 / fe lan segment fn10 / fe 100 m...
Page 24: 1.5.4.3 Virtual Workgroups
Chapter 1: introduction page 1-14 fast network 10 user guide 1.5.4.3 virtual workgroups the fn10 allows you to define ports for logical groups of associated hosts (virtual workgroups) to provide a more efficient flow of traffic across your ethernet network. Virtual workgroups offer you the ability t...
Page 25: 1.6 Local Console Manager
Local console manager fast network 10 user guide page 1-15 figure 1-10 using the fn10 to create virtual workgroups to help optimize bandwidth a host from workgroup a can limit a broadcast to all hosts within workgroup a or b and prevent the broadcast from going across the network and adding to the a...
Page 26: In Chapter 5, Fn10 Filters.
Chapter 1: introduction page 1-16 fast network 10 user guide the following sections describe lcm command syntax and the basic lcm commands for logging in, logging out, and getting help. • lcm commands used for configuring the fn10 are described in chapter 3, configuring your fn10. • lcm commands use...
Page 27: 1.6.2 Basic Lcm Commands
Local console manager fast network 10 user guide page 1-17 • information that you need to enter with an lcm command is enclosed in square brackets [ ]. For example, you must enter a port number and an ip address to execute the ipaddr [port-number] [ip address] command: fn10 >ipaddr 6 192.138.217.40 ...
Page 28: 1.6.2.1 Help
Chapter 1: introduction page 1-18 fast network 10 user guide 1.6.2.1 help displays the menu of available commands. Help can also be displayed by typing a question mark (?). The output from the help command is displayed below. 1.6.2.2 erase entering erase to erase the current fn10 configuration sets ...
Page 29: 1.6.2.3 Exit
Local console manager fast network 10 user guide page 1-19 1.6.2.3 exit logs you out of lcm. (the exit command is functionally equivalent to the logout command.) 1.6.2.4 logout the logout command logs you out of lcm. (the logout command is functionally equivalent to the exit command.) 1.6.2.5 traplo...
Page 30
Chapter 1: introduction page 1-20 fast network 10 user guide.
Page 31: Chapter 2
Fast network 10 user guide page 2-1 chapter 2 unpacking and installing your fn10 carefully unpack the fn10 from the shipping carton and inspect it for possible damage. If any damage is evident, contact your supplier. The shipping carton contains the following: • the fn10 unit • one ac power cord • c...
Page 32
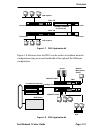
Chapter 2: unpacking and installing your fn10 page 2-2 fast network 10 user guide figure 2-1 fn10 12- and 24-port front panels figure 2-2 fn10 fast ethernet (fe) rear panel ethernet attachment unit interface (aui) port rj45 ethernet 10base-t status leds and buttons crossover ports x 2x 3x 4x 5x 6x 7...
Page 33
Fn10 panels fast network 10 user guide page 2-3 table 2-1 meaning of fn10 leds led meaning link (upper level of port leds) on – indicates the link is good. Off – indicates there is no link. Status (lower level of port leds) on/blinking – indicates you are monitoring the port for a selected segment s...
Page 34: 2.2 Installing The Fn10
Chapter 2: unpacking and installing your fn10 page 2-4 fast network 10 user guide table 2-2 describes the fn10 buttons. 2.2 installing the fn10 table-mounting an fn10 if the fn10 is to be table-mounted, make sure you install the four stick-on feet on the bottom of the unit, as shown in figure 2-3. I...
Page 35
Installing the fn10 fast network 10 user guide page 2-5 rack-mounting an fn10 the table below describes some general considerations you should be aware of before mounting a fn10 in a rack assembly. The fn10 can be rack-mounted in a standard 19-inch equipment cabinet. To mount the fn10 in a rack asse...
Page 36
Chapter 2: unpacking and installing your fn10 page 2-6 fast network 10 user guide 2. Place the fn10 chassis in the cabinet. 3. Secure the fn10 with the rack-mount fasteners by inserting and securing a fastener through each of the four slots in the rack-mount brackets, as shown in figure 2-4. Figure ...
Page 37
Connecting the local console manager fast network 10 user guide page 2-7 5. After several more seconds, the ready led will stay on, indicating that the power-up diagnostics sequence is complete. In addition, the port link leds will turn on for those ports with good links and the segment status leds ...
Page 38
Chapter 2: unpacking and installing your fn10 page 2-8 fast network 10 user guide 2.4 connecting the fn10 to the network installations vary depending on existing wiring, application objectives, and other considerations. Be sure to have your current network topology map available or contact your netw...
Page 39: Ethernet Module
Adding or replacing the optional fast ethernet module fast network 10 user guide page 2-9 2.4.1 connecting the aui interface the fn10 includes one ethernet attachment unit interface (aui) connector (port 1). To connect the aui to a thick coax network, you must use an aui drop cable and a tap-type tr...
Page 40
Chapter 2: unpacking and installing your fn10 page 2-10 fast network 10 user guide figure 2-5 removing the fn10 backplate 3. Insert the fe module assembly, making sure the edges of the board fit into the guides that allow the assembly to smoothly glide into place. Refer to figure 2-6. Figure 2-6 ins...
Page 41
Adding or replacing the optional fast ethernet module fast network 10 user guide page 2-11 figure 2-7 completed fe module installation 6. Reconnect the fn10 to the network, plug in the power cord, and power on the unit. 7. Configure the fe module using the lcm command line interface. Refer to chapte...
Page 42
Chapter 2: unpacking and installing your fn10 page 2-12 fast network 10 user guide.
Page 43: Chapter 3
Fast network 10 user guide page 3-1 chapter 3 configuring your fn10 the fn10 does not require any additional configuration to operate as a standard, transparent switch. However, if you want to use any of the fn10’s advanced functions, such as filtering, you must first assign an ip (internet protocol...
Page 44
Chapter 3: configuring your fn10 page 3-2 fast network 10 user guide • displaying trunking status • defining and deleting virtual workgroups • assigning a community name note you can use the lcm erase command to erase all configuration information on the next system reset. If you are using a network...
Page 45: 3.1 Assigning Ip Addresses
Assigning ip addresses fast network 10 user guide page 3-3 3.1 assigning ip addresses ip addresses for each port must be unique. Ip addresses are divided into classes based on what portion of the address is network or port information. The address classes are a, b, and c. • class a addresses are use...
Page 46
Chapter 3: configuring your fn10 page 3-4 fast network 10 user guide 3.1.1 displaying ip addresses to display ip addresses, subnet masks, and mac addresses of all ports on the fn10 you are configuring, at the lcm prompt: 1. Type ipaddr lcm displays the current ip address table, for example: 3.1.2 de...
Page 47: 3.2 Enabling Bridging
Enabling bridging fast network 10 user guide page 3-5 3.2 enabling bridging the lcm bridge command allows you to set bridging options for a single port or a range of ports. The options include: • off • on (the default with bpdu enabled) • no bpdu bpdu (bridge protocol data unit) is a data unit trans...
Page 48: 3.3 Disabling Bridging
Chapter 3: configuring your fn10 page 3-6 fast network 10 user guide 3.3 disabling bridging to turn off the bridging function for a port or port range, at the lcm prompt: 1. Type bridge [port-range] off for example, bridge 2 off would disable bridging on port 2. Lcm responds: 3.4 displaying bridging...
Page 49: 3.5 Enabling Trunking
Enabling trunking fast network 10 user guide page 3-7 3.5 enabling trunking if your network configuration requires you to connect two or more fn10s together, but the applications you are running over the network require more than 10 mbps of bandwidth per connection, you can use the built-in trunking...
Page 50
Chapter 3: configuring your fn10 page 3-8 fast network 10 user guide trunk groups each set of connections between two fn10s is called a trunk group. You can create several trunk groups to interconnect your fn10s. Each fn10 can have up to four trunk groups. For example, if you have three fn10s (a, b,...
Page 51: 3.6 Disabling Trunking
Disabling trunking fast network 10 user guide page 3-9 to enable trunking for the example shown, you would: 1. Connect the desired ports of the fn10s together using 10base-t crossover cables. If fn10 a is handling only a small number of users, the a to b trunk group could have just two ports per fn1...
Page 52
Chapter 3: configuring your fn10 page 3-10 fast network 10 user guide 1. Type trunk off for example, trunk 2-4 off 3.7 displaying trunking status to check the status of your current trunking configuration, at the lcm prompt: 1. Type trunk the display could look like the following: the following cond...
Page 53
Displaying trunking status fast network 10 user guide page 3-11 to check the status for ports configured for trunking, at the lcm prompt: 1. Type status the display could look like the following: the following conditions can be displayed: • broken — trunking is enabled, but the port in non-operation...
Page 54
Chapter 3: configuring your fn10 page 3-12 fast network 10 user guide 3.8 defining and deleting workgroups the fn10 allows you to define logical groups of associated hosts (virtual workgroups) to provide a more efficient flow of traffic across your ethernet network. Virtual workgroups offer you the ...
Page 55
Defining and deleting workgroups fast network 10 user guide page 3-13 the lcm commands used to create the previous configuration are as follows: 1. To create workgroup a on ports 3, 4, 5, 13, and 16: fn10 > workgroup a 3-5,13,16 lcm responds with the following display: name: a ports: 3, 4, 5, 13, 16...
Page 56
Chapter 3: configuring your fn10 page 3-14 fast network 10 user guide 2. To create workgroup b: fn10 > workgroup b 7,11,16,24 ip 198.113.121.0 lcm responds with the following display: name: b ports: 7, 11, 16, 24 info: ip 198.113.121.0 255.255.255.0 in both cases, a specific netmask value was omitte...
Page 57
Assigning a community name fast network 10 user guide page 3-15 to delete a workgroup, at the lcm prompt: 1. Type workgroup name delete to create or modify the port list for a specific workgroup, at the lcm prompt: 1. Type workgroup name port-range to modify the network classification of a specific ...
Page 58
Chapter 3: configuring your fn10 page 3-16 fast network 10 user guide 3.10 configuring multicast storm protection the fn10 provides automatic protection against multicast storms. Multicast storms are excessive broadcasts to all ports, typically caused by a malfunctioning device. They can result in s...
Page 59: 3.11.1 System Contact
Modifying mib variables fast network 10 user guide page 3-17 3.11 modifying mib variables specific instructions for controlling fn10 operations, modifying parameters, and so on, depend on the nms you are using. This manual provides instructions for using lcm commands. However, lcm commands do not ex...
Page 60: 3.11.5 Aging Parameter
Chapter 3: configuring your fn10 page 3-18 fast network 10 user guide 3.11.4 authentication password the set password and get password variables (from the smc proprietary mib), must be initialized with the correct authentication passwords. All requests from any snmp manager contain a community name ...
Page 61: Chapter 4
Fast network 10 user guide page 4-1 chapter 4 monitoring and managing your fn10 monitoring the fn10 consists of collecting and analyzing statistics and system status information. Additional statistics gathered by the fn10 are the result of user-configurable filters. See chapter 5, fn10 filters, for ...
Page 62
Chapter 4: monitoring and managing your fn10 page 4-2 fast network 10 user guide • mac statistics • traffic analysis statistics • snmp statistics you can use this information to analyze your overall network performance and to make configuration changes as necessary. For example, ethernet port statis...
Page 63: 4.2.1 Pseudo Filters
Fn10 statistics fast network 10 user guide page 4-3 4.2.1 pseudo filters you can configure pseudo-filters to optimize your network design. Pseudo-filters generate statistics as if a filter had actually been applied without actually invoking the filter or impacting the network. See chapter 5, fast ne...
Page 64
Chapter 4: monitoring and managing your fn10 page 4-4 fast network 10 user guide • the number of times each filter was successfully invoked, and the source address of the packet for the last successful invocation of each of the combination filters. 4.2.4 ethernet port statistics for each ethernet po...
Page 65
Fn10 statistics fast network 10 user guide page 4-5 for each of the above categories, statistics on whether a packet was forwarded or filtered are available. In addition, if a packet was filtered, the following conditions are recorded: - if the packet is local traffic - if the port is not in the spa...
Page 66: 4.2.5 Mac Statistics
Chapter 4: monitoring and managing your fn10 page 4-6 fast network 10 user guide • the number of received packets with frame alignment errors. • the number of packet transmissions that were initially deferred due to the media being busy. • the number of packets not transmitted due to excessive colli...
Page 67: 4.2.7 Snmp Statistics
Fn10 statistics fast network 10 user guide page 4-7 4.2.6 traffic analysis statistics you can configure the fn10 to collect statistics on traffic between active ethernet ports, for example: • number of packets sent from station a to station b. Configure pseudo source-port filter with station a’s add...
Page 68
Chapter 4: monitoring and managing your fn10 page 4-8 fast network 10 user guide • the number of snmp pdus received by the fn10 which had an asn.1 parsing error while being decoded by the fn10. [ snmpinasnparseerrs ] • the total number of mib objects which have been successfully retrieved by the fn1...
Page 69: 4.3.1 Displaying Status
Using lcm to check fn10 status fast network 10 user guide page 4-9 • address display • ipaddr • ident these lcm commands are described in the sections that follow. 4.3.1 displaying status the status command displays the status of the fn10 and automatically pages through the status of all of the ethe...
Page 70
Chapter 4: monitoring and managing your fn10 page 4-10 fast network 10 user guide if you do not want to view the status of each ethernet port, use the ctrl-c keys to return to the lcm prompt. If you do not want to view the status of port 2, use the ctrl-c keys to return to the lcm prompt. You can vi...
Page 71
Using lcm to check fn10 status fast network 10 user guide page 4-11 4.3.2 displaying mac addresses the addresses display command displays all mac addresses in the fn10 bridge address table. The display includes: • the mac address • type of address, including: - dynamic (learned) - ethernet port (for...
Page 72
Chapter 4: monitoring and managing your fn10 page 4-12 fast network 10 user guide to display all mac addresses, at the lcm prompt: 1. Type addresses display any lcm responds with a list of all mac addresses, their associated ports, the type, age, and number of frames from and to that address. If you...
Page 73
Using lcm to check fn10 status fast network 10 user guide page 4-13 lcm would display: lcm allows you to display mac addresses in two formats: • little-endian (default) little-endian is a method of storing or transmitting data in which the least significant bit of each byte is presented first. This ...
Page 74: 4.4 Managing The Fn10
Chapter 4: monitoring and managing your fn10 page 4-14 fast network 10 user guide 4.3.3 displaying manufacturing information the ident command identifies fn10 manufacturing information, including the part number and any power-up test codes and diagnostic data. To display the manufacturing informatio...
Page 75: 4.5.1 Disabling A Port
Using lcm to manage the fn10 fast network 10 user guide page 4-15 4.5 using lcm to manage the fn10 the lcm commands that enable you to manage the fn10 include: • disable • enable • ipaddr • community • baud • reboot these lcm commands are described in the sections that follow. 4.5.1 disabling a port...
Page 76: 4.5.2 Enabling A Port
Chapter 4: monitoring and managing your fn10 page 4-16 fast network 10 user guide 4.5.2 enabling a port when you enable an ethernet port that has been disabled, whatever bridging functions you had previously configured for that port are re-enabled. To enable a port, or a range of ports, at the lcm p...
Page 77: Norip
Using lcm to manage the fn10 fast network 10 user guide page 4-17 the norip option allows you to turn off the routing information that builds the routing table. You would use this option when you are connecting network devices that do not support rip. 4.5.3 changing a subnet mask you can optionally ...
Page 78: 4.5.5 Setting The Baud Rate
Chapter 4: monitoring and managing your fn10 page 4-18 fast network 10 user guide 4.5.4 changing a community name a community name is similar to a password. You use the same steps to assign a new community name or to change an existing community name. This sets the mib variable sxadminanypass . You ...
Page 79
Using lcm to manage the fn10 fast network 10 user guide page 4-19 to display the current baud rate setting, at the lcm prompt: 1. Type baud lcm responds: to change the baud rate setting, at the lcm prompt: 1. Type baud for example, baud 9600 would set the baud rate to 9600. Lcm responds: 4.5.6 setti...
Page 80
Chapter 4: monitoring and managing your fn10 page 4-20 fast network 10 user guide.
Page 81: Chapter 5
Fast network 10 user guide page 5-1 chapter 5 fn10 filters one of the most significant features of the fn10 is its powerful user-configurable filtering capabilities. A filter is an instruction to the fn10 to screen data packets based on the criteria you define. Filtering is useful for gathering stat...
Page 82
Chapter 5: fn10 filters page 5-2 fast network 10 user guide • multicast traffic from any station (mac layer address). Multicast packets are those destined for more than one address. Each source address can be assigned one of the following restrictions: • filter all packets from this source address. ...
Page 83: 5.1.1 Source Address Filter
Bridge address table filters fast network 10 user guide page 5-3 with the bridge address table entry shown in table 5-1, you can use any of the following types of bridge address table filtering: • source address • source address multicast • destination address 5.1.1 source address filter the source ...
Page 84: 5.2 Port Filters
Chapter 5: fn10 filters page 5-4 fast network 10 user guide 5.1.3 destination address filter a destination address filter can be used to discard all traffic destined to a specific mac address. This type of filter is configured by setting a static address entry for the mac address and specifying {nul...
Page 85: 5.2.1 Configurable Fields
Port filters fast network 10 user guide page 5-5 likewise, you can assign an exit port one of the following restrictions: • only allow a certain number of multicast packets every “n” seconds and then stop transmitting. • filter a packet destined for this port that matches all of the fields in the po...
Page 86: 5.2.1.1 Pseudo Filtering
Chapter 5: fn10 filters page 5-6 fast network 10 user guide for the fields defined as true, false, or not applicable (na) in the following sections: • true – means all traffic that matches the field will be filtered. • false – means all traffic that does not match the field selection will be filtere...
Page 87
Port filters fast network 10 user guide page 5-7 for example, if you had the configuration shown below, the and operator assigned to port 2 would apply to the next instance of port 2, not necessarily the next sequential filter number in the port filter table index. The port filter configuration fiel...
Page 88
Chapter 5: fn10 filters page 5-8 fast network 10 user guide source range start the starting mac address for the source range of mac addresses. If you are filtering on a single source address, enter that address here. Source range end ending mac address for the source range of mac addresses. If you a...
Page 89
Port filters fast network 10 user guide page 5-9 field origin either type, ip, mac, or sr (see field offset description). The origin is the field from which the offset count starts. Type field offset the decimal offset of the portion of the packet to be examined. If the origin is type, the field off...
Page 90
Chapter 5: fn10 filters page 5-10 fast network 10 user guide when adding or modifying a filter, you must enter both a source range start value and a source range end value. For example: source range: [na] (inrange/outrange/na)>inrange source range start: [00:00:00:00:00:00] >08:00:20:00:00:00 source...
Page 91
Using filters for security purposes fast network 10 user guide page 5-11 figure 5-1 using filters to restrict access to an adjoining network segment fn10 engineering subnet lan 2 accounting subnet lan 3 manufacturing subnet lan 1 concentrator concentrator.
Page 92
Chapter 5: fn10 filters page 5-12 fast network 10 user guide the company wants to allow engineering and accounting workstations to access resources on the manufacturing subnet (lan 1), but wants to prevent users on the engineering subnet (lan 2) from accessing resources on the accounting subnet (lan...
Page 93
Using filters for security purposes fast network 10 user guide page 5-13 example 2: blocking access to specific stations in this example, a company uses a fn10 to connect two lans (see figure 5-2). Three workstations on lan 2 (the accounting subnet) contain sensitive data (workstations f, g, and h)....
Page 94
Chapter 5: fn10 filters page 5-14 fast network 10 user guide this information is used to configure the filter as follows: • filter identifier – port number of the port attached to lan 2 as a destination. • filter fields – destination address f-h (range, match) source lan = 1 (match). Note that a mat...
Page 95
Using filters for security purposes fast network 10 user guide page 5-15 example 3: restricting access to authorized users the example shown in figure 5-3 is very similar to the previous example. The difference is that access to workstations f, g, and h will not be denied to all lan 1 users. Instead...
Page 96: Performance
Chapter 5: fn10 filters page 5-16 fast network 10 user guide note that the fn10 is not storing information designed to identify restricted devices or authorized or unauthorized users. Instead, it is using address information (which it does store) to act on filters that have been configured to meet t...
Page 97
Using filters to enhance network performance fast network 10 user guide page 5-17 example 4: using a firewall filter to control multicasts to optimize network performance, you can configure filters to reduce multicasts (packets broadcast to multiple destinations). In addition, you can prevent multic...
Page 98
Chapter 5: fn10 filters page 5-18 fast network 10 user guide this filter is configured as follows: • filter identifier – port number of the port attached to lan 2 as a destination (i.E., exit) • filter identifier – port number of the port attached to lan 3 as a destination (i.E., exit) • filter fiel...
Page 99
Configuring a port filter fast network 10 user guide page 5-19 5.5 configuring a port filter to configure a port filter, use the local console manager (lcm). The lcm prompts you through the fields for each port filter you want to configure. If you are adding a port filter to be used in conjunction w...
Page 100
Chapter 5: fn10 filters page 5-20 fast network 10 user guide complete the following steps to configure a port filter. To accept a default value, press the enter key. At the lcm prompt: 1. Type filters add 2. Enter the port number. 1 is the default. If the filter is for port 1, you do not need to ent...
Page 101
Configuring a port filter fast network 10 user guide page 5-21 9. Select whether the filter will use a destination range of mac addresses. Na is the default; meaning the filter will not use a destination range. You do not need to enter anything unless you are using a destination range. (if you are n...
Page 102
Chapter 5: fn10 filters page 5-22 fast network 10 user guide 18. Enter the field value. 19. Enter the field mask. 20. Select the operator. Or is the default. You do not need to enter anything if the filter will use the or operator. If you want the filter to use the and operator, type and . 21. Enter...
Page 103: Considerations
Filtering and performance considerations fast network 10 user guide page 5-23 5.5.2 deleting a port filter to delete a port filter, at the lcm prompt: 1. Type filters delete lcm prompts you for the filter index. 2. Enter the filter number. Lcm responds filter deleted. 5.6 filtering and performance c...
Page 104
Chapter 5: fn10 filters page 5-24 fast network 10 user guide.
Page 105: Chapter 6
Fast network 10 user guide page 6-1 chapter 6 fn10 diagnostics and troubleshooting the fn10 incorporates several built-in diagnostic and testing capabilities which are convenient to use and cause minimal or no disruption to the operational network. These capabilities are effective for isolating prob...
Page 106: 6.1.1 Power-Up Led Sequence
Chapter 6: fn10 diagnostics and troubleshooting page 6-2 fast network 10 user guide 6.1.1 power-up led sequence when you power-up the fn10, the following occurs: 1. All leds, except for the port link leds, turn on for one second. 2. The power (pwr) led remains on. 3. The ready led starts flashing. 4...
Page 107
Responses to failures at power-up fast network 10 user guide page 6-3 6.1.3 software checksum comparison when the fn10 reboots, its operational software is verified by a checksum comparison before it is loaded. If the software fails the checksum test due to an interrupted new software distribution p...
Page 108: 6.3.1 Loopback Tests
Chapter 6: fn10 diagnostics and troubleshooting page 6-4 fast network 10 user guide 6.3.1 loopback tests built-in local and remote loopback tests can be used to test individual ports while the fn10 is operational. When in local loopback mode, a port is disconnected from the network. The fn10 generat...
Page 109
Status and activity indicators fast network 10 user guide page 6-5 figure 6-1 fn10 front panel leds x 2x 3x 4x 5x 6x 7x 8x 9x 10x 11x 12x 13x 14x 15x 16x 17x 18x 19x 20x 21x 22x 23x 24x 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 aui 1 link link 2 3 1 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 a b usr segment status select tx rx...
Page 110
Chapter 6: fn10 diagnostics and troubleshooting page 6-6 fast network 10 user guide table 6-2 describes the fn10 buttons. Table 6-1 meaning of fn10 leds led meaning link (upper level of port leds) on – indicates the link is good. Off – indicates there is no link. Status (lower level of port leds) on...
Page 111: 6.5 Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting fast network 10 user guide page 6-7 6.5 troubleshooting this section lists several situations that could happen while using the fn10, and suggests appropriate action. Because every situation is potentially unique, the corrective actions suggested here should be considered as guidelin...
Page 112: 6.5.3 Fn10 Has Rebooted
Chapter 6: fn10 diagnostics and troubleshooting page 6-8 fast network 10 user guide 6.5.3 fn10 has rebooted • use the lcm ident command to check the fn10 diagnostic codes, and call your authorized cabletron systems representative. 6.5.4 fn10 does not respond to nms • check the port status using lcm....
Page 113: Appendix A
Fast network 10 user guide page a-1 appendix a technical specifications a.1 fn10 specifications physical height 1.75 in (4.45 cm) (1 u) width 17 in (43.18 cm) depth 15.75 in (40 cm) weight 9 lb (4.1 kg) installation options tabletop or rack-mount electrical input voltage auto-ranging from 100-120, 2...
Page 114
Appendix a: technical specifications page a-2 fast network 10 user guide bridging technologies • ieee 802.1 part d • ieee802.2 (logical link control) • ieee 802.3 (csma/cd, 10base-t) • transparent bridging with spanning tree • ethernet version 2 • eia rs232c (dte-to-dce interface specification) • ei...
Page 115
Serial cable pin assignments fast network 10 user guide page a-3 a.2 serial cable pin assignments for a pc running a windows terminal connected to the rs232c network management port on the front panel of the fn10, the following serial cable pin assignments are required to manage the fn10 using the l...
Page 116: A.4 Straight-Through Wiring
Appendix a: technical specifications page a-4 fast network 10 user guide a.4 straight-through wiring if the twisted-pair link segment is to join two ports on a switch, and only one of the ports has an internal crossover, the two pairs of wires must be straight-through, as shown in table a-2. A. The ...
Page 117: A.5 Crossover Wiring
Crossover wiring fast network 10 user guide page a-5 a.5 crossover wiring two fn10s can communicate only if the transmitter on one unit is connected to the receiver on the other unit. This reversal, or crossover function, can be implemented either in the wiring or in the device itself. When connecti...
Page 118
Appendix a: technical specifications page a-6 fast network 10 user guide.
Page 119: Appendix B
Appendix b: glossary fast network 10 user guide page b-1 appendix b glossary address a set of characters that uniquely identifies a station, peripheral device, node, or other unit in a network. Address table a database of device addresses and their associated ports maintained by a switch or bridge f...
Page 120
Appendix b: glossary page b-2 fast network 10 user guide aui (attachment unit interface) a standard connector type used for ethernet connections. Backbone the major, central transmission path for a network. A backbone usually handles high-volume, high-density traffic. Typically a backbone connects v...
Page 121
Appendix b: glossary fast network 10 user guide page b-3 concentrator a device that provides attachment points for stations that are not connected to the fn10. The concentrator is connected directly to the network; the stations connect to the concentrator. Congestion a condition where a portion of t...
Page 122
Appendix b: glossary page b-4 fast network 10 user guide eia (electronic industries association) organization that sets standards for electrical interfaces (connectors). Encapsulation a method for moving messages across networks that use different types of protocols. The message is encapsulated (rat...
Page 123
Appendix b: glossary fast network 10 user guide page b-5 full wire speed refers to packet forwarding at the maximum rate at which data can be transmitted on a given lan. Icmp (internet control message protocol) an auxiliary protocol of ip used to convey advice and error messages about events in the ...
Page 124
Appendix b: glossary page b-6 fast network 10 user guide internetworking the linking of one or more networks to facilitate communication across networks. Interoperability the ability of equipment from multiple vendors to exchange information using standardized protocols. Ip (internet protocol) ip is...
Page 125
Appendix b: glossary fast network 10 user guide page b-7 local traffic traffic within a given network segment. Mac (media access control) the data link layer sublayer responsible for scheduling, transmitting, and receiving data on a shared medium local area network. Mask specified a subset of a larg...
Page 126
Appendix b: glossary page b-8 fast network 10 user guide packet a group of bits including data and control elements arranged in a specific format that are transmitted and switched as a composite whole. Control elements include a source address, destination address, frame control and status indicator...
Page 127
Appendix b: glossary fast network 10 user guide page b-9 rarp (reverse address resolution protocol) a protocol that binds mac addresses to specific ip addresses. Risc (reduced instruction set computing) a data processing technology in which functions are performed using the least possible number of ...
Page 128
Appendix b: glossary page b-10 fast network 10 user guide synchronous transmission a transmission technique in which an uninterrupted block of data is transmitted, using no redundant information such as stop and start bits to identify the beginning and end of a unit of data. Tcp/ip (transmission con...
Page 129: Index
Fast network 10 user guide index-1 index numerics 10base-t pin assignments a-3 5 - 4 - 3 rule a-5 802.1d spanning tree 3-9 a adding filters 5-20 ip addresses 3-3 address table dynamic entry 1-10 size a-2 address table filters about 5-2 destination address 5-4 source address 5-3 source address multic...
Page 130
Index index-2 fast network 10 user guide overview 6-1 power-up 2-6, 6-1 disabling bridging functions 3-6 ports 4-15 trunking 3-9 displaying baud rate 4-19 bridge functions 3-6 fn10 status 4-9 ip addresses 3-4, 4-13, 4-17 mac addresses 4-12 manufacturing information 4-14 document conventions 1-3 dyna...
Page 131
Index fast network 10 user guide index-3 bridge 3-5 community 3-15, 4-18 disable 4-15 enable 4-16 erase 3-2 exit 1-19 ident 4-14 ipaddr 3-4, 4-13 logout 1-19 reboot 4-19 status 4-9 trunk 3-9 led sequence power-up 6-2 linking filters 5-6 little-endian 4-13 llc type 1 test packets 6-4 local console ma...
Page 132
Index index-4 fast network 10 user guide snmp statistics 4-2, 4-7 source range 5-7 spanning tree algorithm 1-8 specifications electrical a-1 physical a-1 static entry bridge address table 1-10 statistics ethernet port 4-4 gathering 4-3 mac 4-6 overview 4-2 snmp 4-7 system 4-3 traffic analysis 4-7 st...