- DL manuals
- Cabletron Systems
- Switch
- FAST NETWORK 100
- User Manual
Cabletron Systems FAST NETWORK 100 User Manual
1X
2X
3X
4X
5X
6X
7X
8X
2 3
1
4 5 6 7 8
Link
Status
Select
TX Act
Reset
Ready
FN100-8
NMS Port
Port
Status
Mode
100
Link
Status
1
TX RX
RX Col Usr
Pwr
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2 3
1
4 5 6 7 8
Link
Status
Select
TX Act
Reset
Ready
FN100-8FX
NMS Port
Port
Status
Mode
100
TX RX
TX RX
TX RX
TX RX
TX RX
TX RX
TX RX
TX RX
RX Col Usr
Pwr
1X
2X
3X
4X
5X
6X
7X
8X
9X
10X
11X
12X
13X
14X
15X
16X
13 14 15 16
Link
2 3
1
4 5 6 7 8
9 10 11 12
Status
Link
Status
Select
TX Act
Reset
Ready
FN100-16
NMS Port
Port
Status
Mode
100
Link
Status
Link
Status
1
9
TX
TX
RX
RX
RX Col Usr
Pwr
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
13 14 15 16
Link
2 3
1
4 5 6 7 8
9 10 11 12
Status
Link
Status
Select
TX Act
Reset
Ready
FN100-16FX
NMS Port
Port
Status
Mode
100
TX
TX
RX
RX
TX
TX
RX
RX
TX
TX
RX
RX
TX
TX
RX
RX
TX
TX
RX
RX
TX
TX
RX
RX
TX
TX
RX
RX
TX
TX
RX
RX
RX Col Usr
Pwr
FAST NETWORK 100
USER GUIDE
Summary of FAST NETWORK 100
Page 1
1x 2x 3x 4x 5x 6x 7x 8x 2 3 1 4 5 6 7 8 link status select tx act reset ready fn100-8 nms port port status mode 100 link status 1 tx rx rx col usr pwr 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 2 3 1 4 5 6 7 8 link status select tx act reset ready fn100-8fx nms port port status mode 100 tx rx tx rx tx rx tx rx tx rx tx rx tx ...
Page 3: Notice
Fast network 100 user guide i notice cabletron systems reserves the right to make changes in specifications and other information contained in this document without prior notice. The reader should in all cases consult cabletron systems to determine whether any such changes have been made. The hardwa...
Page 4
Notice ii fast network 100 user guide fcc notice this device complies with part 15 of the fcc rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may ca...
Page 5
Notice fast network 100 user guide iii cabletron systems, inc. Program license agreement important: before utilizing this product, carefully read this license agreement. This document is an agreement between you, the end user, and cabletron systems, inc. (“cabletron”) that sets forth your rights and...
Page 6
Notice iv fast network 100 user guide united states government restricted rights the enclosed product (a) was developed solely at private expense; (b) contains “restricted computer software” submitted with restricted rights in accordance with section 52227-19 (a) through (d) of the commercial comput...
Page 7: Contents
Fast network 100 user guide v contents chapter 1 introduction 1.1 getting help................................................................................. 1-2 1.2 document conventions ............................................................... 1-2 1.3 related documentation ....................
Page 8
Contents vi fast network 100 user guide 2.5 local console manager overview ...............................................2-6 2.6 command syntax conventions ...................................................2-6 2.6.1 basic lcm commands....................................................2-7 2.6.1.1 ...
Page 9
Contents fast network 100 user guide vii chapter 4 monitoring and managing the fn100 4.1 fn100 management tools .......................................................... 4-1 4.2 fn100 statistics .......................................................................... 4-2 4.2.1 gathering statistic...
Page 10
Contents viii fast network 100 user guide appendix a technical specifications a.1 fn100 specifications .................................................................. A-1 a.2 types/connectors ....................................................................... A-3 a.3 cable specifications .......
Page 11: Chapter 1
Fast network 100 user guide page 1-1 chapter 1 introduction this manual is for system administrators responsible for installing, configuring, monitoring, and maintaining the cabletron systems fast network 100 (fn100) switch. You should have a familiarity with networking concepts and principles. In a...
Page 12: Technical Specifications
Chapter 1: introduction page 1-2 fast network 100 user guide • appendix a, technical specifications , provides the fn100 specifications and basic 10base-t and 100base-tx cabling pin assignments. • appendix b, glossary , provides a glossary of terms both specific to the fn100 and common to the networ...
Page 13: 1.3 Related Documentation
Related documentation fast network 100 user guide page 1-3 1.3 related documentation you may need to refer to the following documentation: • fast network 100 mib reference guide – contains the enterprise mib. If you need internetworking reference material, you may find the following books helpful: •...
Page 14
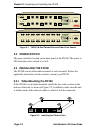
Chapter 1: introduction page 1-4 fast network 100 user guide (mm) fiber. The fn100 is available in the four configurations shown below. Figure 1-1 8 tx ports and 1 redundant fx (fiber optic) port (fn100-8) figure 1-2 16 tx ports and 2 redundant fx ports (fn100-16) figure 1-3 8 fx ports (fn100-8fx) f...
Page 15
Overview fast network 100 user guide page 1-5 the fn100 features the following: • supports 10base-t, 100base-tx, and 100base-fx standards. • supports ieee 802.3u auto-negotiation for 10base-t and 100base-tx connections. • provides full store and forward switching functionality. • supports trunking f...
Page 16: 1.4.1 Osi Compliance
Chapter 1: introduction page 1-6 fast network 100 user guide to dynamically arbitrate between 10 mbps and 100 mbps on each port, the fn100 employs ieee 802.3u auto-negotiation. Auto-negotiation allows each 10base-t/100base-tx port on the fn100 to self-configure to 100 mbps when the device on the oth...
Page 17: 1.5 Fn100 Architecture
Fn100 architecture fast network 100 user guide page 1-7 1.5 fn100 architecture the fn100 is based on an architecture that utilizes a high speed switch engine coupled with an amd 29200 risc processor for management functions. This architecture provides an efficient mix of optimal performance and inte...
Page 18
Chapter 1: introduction page 1-8 fast network 100 user guide 1.5.2 spanning tree algorithm the fn100 supports the ieee 802.1d spanning tree algorithm. The spanning tree algorithm converts multiple lans into a “spanning tree” of networks that prevents bridging loops. This standard defines a logical (...
Page 19
Fn100 architecture fast network 100 user guide page 1-9 the fn100 learns addresses from all packets, including data transmissions and “keep alive” packets (packets sent by an idle station to let other stations know it is present and functional). When devices are added to the network, removed from it...
Page 20: 1.6 Fn100 Applications
Chapter 1: introduction page 1-10 fast network 100 user guide 1.6 fn100 applications the fn100 provides the network designer with complete flexibility and has many applications including: • server farms • high-performance workgroups • backbones 1.6.1 server farms figure 1-6 using the fn100 to create...
Page 21
Fn100 applications fast network 100 user guide page 1-11 1.6.2 high-performance workgroups figure 1-7 creating high-performance workgroups as workstation performance continues to grow, fast ethernet switching is the perfect choice for addressing the new bandwidth requirement. Providing the most cost...
Page 22: 1.6.3 Backbones
Chapter 1: introduction page 1-12 fast network 100 user guide 1.6.3 backbones studies indicate that backbone congestion is the number one issue facing most networks. The fn100 reduces congestion by increasing the overall aggregate bandwidth between existing routers, switches or hubs. A fast ethernet...
Page 23
Fn100 configurations fast network 100 user guide page 1-13 1.7.1 trunking configurations if your network configuration requires you to connect two or more fn100 switches together, but the applications you are running over the network require more than 100 mbps of bandwidth per connection, you can us...
Page 24
Chapter 1: introduction page 1-14 fast network 100 user guide 1.7.1.1 trunking configuration examples the fn100 allows multiple trunk groups with up to eight ports each to be connected between the fn100 and other network devices. This capability provides a scalable dedicated bandwidth of up to 800 m...
Page 25
Fn100 configurations fast network 100 user guide page 1-15 figure 1-11 fn100 trunking configuration example #2 1.7.2 virtual switch configurations the fn100 can be configured as a collection of virtual switches. Virtual switches provide increased bandwidth, enhanced security, and other advantages ga...
Page 26
Chapter 1: introduction page 1-16 fast network 100 user guide 1.7.2.1 virtual switch configuration examples figure 1-12 shows a 16-port fn100 configured as two virtual switches, each attached to a separate non-cabletron systems device. Figure 1-12 fn100 virtual switch configuration example #1 figure...
Page 27: 1.7.3 Workgroups
Fn100 configurations fast network 100 user guide page 1-17 1.7.3 workgroups the fn100 allows you to define ports for logical groups of associated hosts to create workgroups. Workgroups provide an efficient flow of traffic across an ethernet network by enabling you to limit broadcasts to logical doma...
Page 28
Chapter 1: introduction page 1-18 fast network 100 user guide.
Page 29: Chapter 2
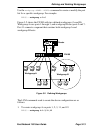
Fast network 100 user guide page 2-1 chapter 2 unpacking and installing the fn100 carefully unpack the fn100 from the shipping carton and inspect it for possible damage. If any damage is evident, contact cabletron systems. The shipping carton contains: • the fn100 device • console cable kit • one ac...
Page 30: 2.2 Power Switch
Chapter 2: unpacking and installing the fn100 page 2-2 fast network 100 user guide . Figure 2-1 fn100 16-port twisted pair and fiber front panels 2.2 power switch the power switch is located on the back panel of the fn100. The power is on when the rocker switch is set to 1. 2.3 installing the fn100 ...
Page 31
Installing the fn100 fast network 100 user guide page 2-3 2.3.2 rack-mounting the fn100 the table below describes some general considerations you should be aware of before mounting the fn100 in a rack assembly. The fn100 can be rack-mounted in a standard 19-inch equipment cabinet (eia rs310c). To mo...
Page 32
Chapter 2: unpacking and installing the fn100 page 2-4 fast network 100 user guide 3. Secure the fn100 with the rack-mount fasteners by inserting and securing a fastener through each of the four slots in the rack-mount brackets, as shown in figure 2-3. Figure 2-3 rack-mounting the fn100 4. Once the ...
Page 33
Connecting the local console manager fast network 100 user guide page 2-5 5. After several more seconds, the ready led will stay on, indicating that the power-up diagnostics sequence is complete. In addition, the port link leds will turn on for those ports with good links and the segment status leds...
Page 34
Chapter 2: unpacking and installing the fn100 page 2-6 fast network 100 user guide 2.5 local console manager overview the local console manager (lcm) is a command-line interface built into the fn100 that enables you to monitor, manage, and configure the fn100 through the out-of-band rs232c connectio...
Page 35: 2.6.1 Basic Lcm Commands
Command syntax conventions fast network 100 user guide page 2-7 • a previous command can be repeated by typing !! . • mac addresses are displayed in little-endian ethernet bit order, with each octet separated by a colon. For example: fn100 > address 00:40:27:04:1a:0f • information that you need to e...
Page 36: 2.6.1.1 Help
Chapter 2: unpacking and installing the fn100 page 2-8 fast network 100 user guide 2.6.1.1 help use the help command to display the menu of available commands. Help can also be displayed by typing a question mark ( ? ). The output from the help command is displayed below. Fn100 > help fast network 1...
Page 37
Connecting the fn100 to the network fast network 100 user guide page 2-9 2.7 connecting the fn100 to the network installations vary depending on existing wiring, application objectives, and other considerations. Be sure to have your current network topology map available or contact your network admi...
Page 38: 2.7.3 Wiring Considerations
Chapter 2: unpacking and installing the fn100 page 2-10 fast network 100 user guide 2.7.3 wiring considerations each port on the fn100 has built-in internal crossovers. If the network device you are connecting to the fn100 has an internal crossover design, use an internal crossover cable. If the dev...
Page 39: Chapter 3
Fast network 100 user guide page 3-1 chapter 3 configuring the fn100 the fn100 does not require any additional configuration to operate as a standard, transparent switch. However, if you want to use any of the fn100 advanced functions, such as workgroups, you must first assign an ip (internet protoc...
Page 40: 3.1 Assigning Ip Addresses
Chapter 3: configuring the fn100 page 3-2 fast network 100 user guide • assigning a community name 3.1 assigning ip addresses ip addresses for each port must be unique. Ip addresses are divided into classes based on what portion of the address is network or port information. The address classes are ...
Page 41
Assigning ip addresses fast network 100 user guide page 3-3 3.1.1 displaying ip addresses use the ipaddr command to display ip addresses, subnet masks, and mac addresses of all ports on the fn100 you are configuring. Lcm displays the current ip address table, for example: fn100 > ipaddr port ip addr...
Page 42: 3.2 Setting Port Speed
Chapter 3: configuring the fn100 page 3-4 fast network 100 user guide 3.2 setting port speed use the lcm speed command to select a bandwidth of 10 mbps or 100 mbps for each port. The options include: • auto - (default) allows the fn100 to auto-detect the maximum bandwidth available for the port(s) b...
Page 43: 3.3 Enabling Bridging
Enabling bridging fast network 100 user guide page 3-5 3.3 enabling bridging use the lcm bridge command to set bridging options for a single port or a range of ports. The options include: • off • on (the default with bpdu enabled) • nobpdu bpdu (bridge protocol data unit) is a data unit transmitted ...
Page 44: 3.6 Trunking
Chapter 3: configuring the fn100 page 3-6 fast network 100 user guide fn100 > bridge lcm responds with a list of all ports and the bridging function that is enabled. Port 1 sw1 bridging: transparent bridging port 2 sw1 bridging: transparent bridging port 3 sw1 bridging: transparent bridging port 4 s...
Page 45: In The B to C Trunk Group.
Trunking fast network 100 user guide page 3-7 figure 3-1 trunk groups to enable trunking for the example shown above, you would: 1. Connect the desired ports of the fn100 switches together using crossover cables. If switch a is handling only a small number of users, the a to b trunk group could have...
Page 46: 3.7 Disabling Trunking
Chapter 3: configuring the fn100 page 3-8 fast network 100 user guide standard 802.1d spanning tree state changes, treating each trunk group as a single 802.1d spanning tree port. 802.1d spanning tree takes about thirty seconds to resolve which fn100 ports are to become forwarding ports. As ports wi...
Page 47
Displaying trunking status fast network 100 user guide page 3-9 the following conditions can be displayed: • closed (or oneway) — trunking is enabled, and the trunking protocol is attempting to establish a trunk connection. • heldown — trunking is enabled, but the trunk connection was rejected. Afte...
Page 48: Sw1 - Virtual Switch 1
Chapter 3: configuring the fn100 page 3-10 fast network 100 user guide the following conditions can be displayed in the trunking state field: • broken — trunking is enabled, but the port in non-operational. • closed (or oneway) — trunking is enabled, and the trunking protocol is attempting to establ...
Page 49
Defining and deleting virtual switches fast network 100 user guide page 3-11 3.9.1 displaying virtual switch information use the vswitch command to display all of the virtual switch configurations defined by the fn100. Fn100 > vswitch lcm responds: virtual switch: sw1: 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8 sw2: 9,10,11,1...
Page 50
Chapter 3: configuring the fn100 page 3-12 fast network 100 user guide lcm responds: virtual switch: sw1: 2,3,4,5,6,8 use the vswitch remove command to remove ports from an existing virtual switch configuration. For example: fn100 > vswitch sw1 remove 2-4 lcm responds: virtual switch: sw1: 5,6,8 3.1...
Page 51
Defining and deleting workgroups fast network 100 user guide page 3-13 use the workgroup command to create or modify the port list for a specific workgroup. For example: fn100 > workgroup a 2-6 figure 3-2 shows the fn100 with two defined workgroups (a and b). Workgroup a uses ports 1 through 3, and ...
Page 52
Chapter 3: configuring the fn100 page 3-14 fast network 100 user guide lcm responds: name: a ports: 1, 2, 3, 11, 12 type: all 2. To create workgroup b on ports 5, 7, 15: fn100 > workgroup b 5,7,15 lcm responds: name: b ports: 5, 7, 15 type: all port 11 has been assigned to a segment that includes ho...
Page 54
Chapter 3: configuring the fn100 page 3-16 fast network 100 user guide use the community command to assign a community name. At the lcm prompt: 1. Type community 2. Enter the old community name. If one has not been assigned, you do not need to enter anything. Lcm prompts you for the new community na...
Page 55: 3.14.1 System Contact
Modifying mib variables fast network 100 user guide page 3-17 the two management information base (mib) variables for configuring multicast storm protection are: • sfiftxstormcnt – specifies the maximum number of multicasts that can be broadcast within the given time. • sfitxstormtime – specifies th...
Page 56: 3.14.2 System Name
Chapter 3: configuring the fn100 page 3-18 fast network 100 user guide 3.14.2 system name the system name is a name assigned to the fn100 by the network administrator. By convention, the system name is the fully qualified domain name. (this name then becomes the lcm prompt.) sysname - {system 5} dis...
Page 57: 3.14.4.2 Get Password
Modifying mib variables fast network 100 user guide page 3-19 3.14.4.2 get password the get password variable ( sfadmingetpass ) must be set to the value of the community name used by the snmp manager for performing get operations. A zero length password means that any community name is acceptable. ...
Page 58
Chapter 3: configuring the fn100 page 3-20 fast network 100 user guide.
Page 59: Chapter 4
Fast network 100 user guide page 4-1 chapter 4 monitoring and managing the fn100 monitoring the fn100 consists of collecting and analyzing statistics and system status information. You can use the select button on the front panel of the fn100 to monitor segment status on any of the ethernet ports. S...
Page 60: 4.2.1 Gathering Statistics
Chapter 4: monitoring and managing the fn100 page 4-2 fast network 100 user guide example, ethernet port statistics help you identify network devices that require high bandwidth, and therefore should be connected through a dedicated, rather than a shared, network connection. In addition, ethernet po...
Page 61
Fn100 statistics fast network 100 user guide page 4-3 4.2.3 ethernet port statistics ethernet statistics help you analyze network activity and utilization, and in some cases, indicate faulty equipment or cabling. For each ethernet port connection on the fn100, the following statistics are available:...
Page 62: 4.2.4 Snmp Statistics
Chapter 4: monitoring and managing the fn100 page 4-4 fast network 100 user guide • the number of packets not transmitted to the lan. The packets are broken down into the following categories: - not sent due to congestion - not sent due to multicast storm protection • the number of received frame ch...
Page 63
Using lcm to check fn100 status fast network 100 user guide page 4-5 • the number of snmp pdus received with an authentication failure. [ snmpinbadcommunityuses ] • the number of snmp pdus received with an asn.1 parsing error while being decoded. [ snmpinasnparseerrs ] • the total number of mib obje...
Page 64: 4.3.1 Displaying Status
Chapter 4: monitoring and managing the fn100 page 4-6 fast network 100 user guide • address display • ipaddr • ident these lcm commands are described in the sections that follow. 4.3.1 displaying status use the status command to display the status of the fn100 and automatically page through the stat...
Page 65
Using lcm to check fn100 status fast network 100 user guide page 4-7 port rx packets tx packets collisions erred packets 1 179539521 215252 1492 0 2 179529809 83296 981 0 3 179525816 83296 904 0 4 179524026 83289 928 0 5 179585909 172032 1258 0 6 179515393 82167 1029 2 7 0 0 0 0 8 0 0 0 0 . . . 16.
Page 66
Chapter 4: monitoring and managing the fn100 page 4-8 fast network 100 user guide you can continue to press the return key to display status information for each individual port. Port 1 status bridging: transparent bridging enabled/disabled: enabled, rip listening spanning tree: forwarding trunking ...
Page 67
Using lcm to check fn100 status fast network 100 user guide page 4-9 - bpdu (the mac address to which all bpdus are directed) - reserved (the address reserved by 802.1d, but not yet assigned) - all lans (the addresses reserved by 802.1d for network management) • port number • virtual switch number t...
Page 68
Chapter 4: monitoring and managing the fn100 page 4-10 fast network 100 user guide use the address display command to display a range of addresses using a net mask. This is helpful when determining the status associated with stations containing the same make of ethernet network interface cards. For ...
Page 69: Addresses.
Using lcm to check fn100 status fast network 100 user guide page 4-11 lcm displays the current ip address table, for example: port ip address address mask mac address 1 198.113.121.149 255.255.255.0 00:40:27:07:b6:f6 2 0.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 00:40:27:07:b6:f7 3 0.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 00:40:27:07:b6:f8 4 0.0.0...
Page 70: 4.4.1 Disabling A Port
Chapter 4: monitoring and managing the fn100 page 4-12 fast network 100 user guide 4.4 using lcm to manage the fn100 you can use the local console manager (lcm), any cabletron systems nms, or a standard snmp-based nms to manage the fn100. For more information, see section 4.1, fn100 management tools...
Page 71: 4.4.2 Enabling A Port
Using lcm to manage the fn100 fast network 100 user guide page 4-13 4.4.2 enabling a port when you enable an ethernet port that has been disabled, whatever bridging functions you had previously configured for that port are re-enabled. Use the enable command to enable a port, or a range of ports. For...
Page 72: Addresses.
Chapter 4: monitoring and managing the fn100 page 4-14 fast network 100 user guide 4.4.3 changing a subnet mask you can optionally set the subnet mask for a port. A subnet mask is a 32-bit address mask used in ip to specify a particular subnet. If the subnet mask is omitted, the fn100 automatically ...
Page 73: 4.4.5 Setting The Baud Rate
Using lcm to manage the fn100 fast network 100 user guide page 4-15 3. Enter the new community name. Lcm prompts you to verify the new community name by retyping it. 4. Retype the new community name. 4.4.5 setting the baud rate you can set the baud rate for your lcm console connection. The options f...
Page 74
Chapter 4: monitoring and managing the fn100 page 4-16 fast network 100 user guide 4.4.6 setting a reboot time use the reboot command to enter the number of seconds the fn100 waits before rebooting. For example, to set the reboot time interval to 60 seconds: fn100 > reboot 60 lcm responds: system wi...
Page 75: Chapter 5
Fast network 100 user guide page 5-1 chapter 5 fn100 diagnostics and troubleshooting the fn100 incorporates several built-in diagnostic and testing capabilities which are convenient to use and cause minimal or no disruption to the operational network. These capabilities are effective for isolating p...
Page 76
Chapter 5: fn100 diagnostics and troubleshooting page 5-2 fast network 100 user guide 5. After several more seconds, the ready led will stay on, indicating that the power-up diagnostics sequence is complete. In addition, the port link leds will turn on for those ports with good links and the segment...
Page 77
Responses to failures at power up fast network 100 user guide page 5-3 5.1.4 power-up diagnostics results after completion of the power-up diagnostic sequence, both the power (pwr) and ready leds located on the front panel of the fn100 should be on. 5.2 responses to failures at power up how the fn10...
Page 78
Chapter 5: fn100 diagnostics and troubleshooting page 5-4 fast network 100 user guide table 5-2 describes how to interpret fn100 port leds table 5-1 interpreting system leds led meaning port status mode you can select a single status condition to monitor for all ports by pressing the select button o...
Page 79: 5.4 Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting fast network 100 user guide page 5-5 table 5-3 describes the fn100 button functions. 5.4 troubleshooting this section lists several situations that could happen while using the fn100, and suggests appropriate action. Because every situation is potentially unique, the corrective actio...
Page 80: 5.4.2 Power Supply Fuse
Chapter 5: fn100 diagnostics and troubleshooting page 5-6 fast network 100 user guide 5.4.2 power supply fuse the power supply contains a 3.15 ampere 250 v slow-blow fuse located immediately above the three-prong power input connector on the back of the fn100. If you think this fuse may have blown, ...
Page 81: 5.4.4 Fn100 Has Rebooted
Troubleshooting fast network 100 user guide page 5-7 5.4.4 fn100 has rebooted • use the lcm ident command to check the fn100 diagnostic codes, and call cabletron systems technical support. 5.4.5 fn100 does not respond to nms • check the port status using lcm. • check to see if the spanning tree topo...
Page 82
Chapter 5: fn100 diagnostics and troubleshooting page 5-8 fast network 100 user guide.
Page 83: Appendix A
Fast network 100 user guide page a-1 appendix a technical specifications a.1 fn100 specifications physical height 3.5 in. (8.89 cm) width 17 in. (43.18 cm) depth 17.5 in. (44.45 cm) weight 10 lb. (4.54 kg) installation options tabletop or rack-mount electrical input voltage auto-ranging 100-120 vac,...
Page 84
Appendix a: technical specifications page a-2 fast network 100 user guide standards • ieee 802.1 part d (spanning tree) • ieee802.2 (logical link control) • ieee 802.3 (csma/cd, 10base-t), 802.3u • 10base-t, 100base-tx, 100base-fx • transparent bridging with spanning tree • ethernet version 2 • eia ...
Page 85: A.2 Types/connectors
Types/connectors fast network 100 user guide page a-3 a.2 types/connectors depending on the type of fn100 you’re using, you’ll need to use specific cables, as described in the ieee 802.3u specification, shown in the table below: a.3 cable specifications a.3.1 10base-t cable specifications table a-1 ...
Page 86
Appendix a: technical specifications page a-4 fast network 100 user guide a.3.2 100base-tx cable specifications a.3.3 100base-fx cable specifications table a-3 100base-tx twisted-pair cable specifications 100base-tx twisted-pair cable specifications type category 5 balanced utp number of pairs 2 max...
Page 87: Crossover Wiring.
Management cable pin assignments fast network 100 user guide page a-5 a.4 management cable pin assignments for a pc running a windows terminal connected to the rs232c network management port on the front panel of the fn100, the following serial cable pin assignments are required to manage the fn100 ...
Page 88: A.5.1 Connectors
Appendix a: technical specifications page a-6 fast network 100 user guide a.5.1 connectors refer to the diagram below and note how the pins are numbered. Be sure to hold the connectors in the same orientation when connecting the wires to the pins. Figure a-1 connector pin numbers each twisted-pair c...
Page 89: A.6 Straight-Through Wiring
Straight-through wiring fast network 100 user guide page a-7 a.6 straight-through wiring if you are connecting the fn100 to a device that has a straight-through design, the two pairs of wires must be straight-through, as shown in table a-7. A.7 crossover wiring if you are connecting the fn100 to a d...
Page 90
Appendix a: technical specifications page a-8 fast network 100 user guide.
Page 91: Appendix B
Fast network 100 user guide page b-1 appendix b glossary address a set of characters that uniquely identifies a station, peripheral device, node, or other unit in a network. Address table a database of device addresses and their associated ports maintained by a switch or bridge for use in making dat...
Page 92
Appendix b: glossary page b-2 fast network 100 user guide backbone the major, central transmission path for a network. A backbone usually handles high-volume, high-density traffic. Typically a backbone connects various lans into an integrated network. Bandwidth a measure of the amount of traffic a g...
Page 93
Appendix b: glossary fast network 100 user guide page b-3 concentrator a device that provides attachment points for stations that are not connected to the fn100. The concentrator is connected directly to the network; the stations connect to the concentrator. Congestion a condition where a portion of...
Page 94
Appendix b: glossary page b-4 fast network 100 user guide eia (electronic industries association) organization that sets standards for electrical interfaces (connectors). Encapsulation a method for moving messages across networks that use different types of protocols. The message is encapsulated (ra...
Page 95
Appendix b: glossary fast network 100 user guide page b-5 full wire speed refers to packet forwarding at the maximum rate at which data can be transmitted on a given lan. Icmp (internet control message protocol) an auxiliary protocol of ip used to convey advice and error messages about events in the...
Page 96
Appendix b: glossary page b-6 fast network 100 user guide internetworking the linking of one or more networks to facilitate communication across networks. Interoperability the ability of equipment from multiple vendors to exchange information using standardized protocols. Ip (internet protocol) ip i...
Page 97
Appendix b: glossary fast network 100 user guide page b-7 local traffic traffic within a given network segment. Mac (media access control) the data link layer sublayer responsible for scheduling, transmitting, and receiving data on a shared medium local area network. Mask specified a subset of a lar...
Page 98
Appendix b: glossary page b-8 fast network 100 user guide packet a group of bits including data and control elements arranged in a specific format that are transmitted and switched as a composite whole. Control elements include a source address, destination address, frame control and status indicato...
Page 99
Appendix b: glossary fast network 100 user guide page b-9 rarp (reverse address resolution protocol) a protocol that binds mac addresses to specific ip addresses. Risc (reduced instruction set computing) a data processing technology in which functions are performed using the least possible number of...
Page 100
Appendix b: glossary page b-10 fast network 100 user guide synchronous transmission a transmission technique in which an uninterrupted block of data is transmitted, using no redundant information such as stop and start bits to identify the beginning and end of a unit of data. Tcp/ip (transmission co...
Page 101: Index
Fast network 100 user guide index-1 index numerics 100base-fx cabling specifications a-4 100base-tx cabling pin assignments a-5 specifications a-4 10base-t cabling pin assignments a-5 specifications a-3 802.1d spanning tree 3-8 a address table dynamic entry 1-10 size a-2 addresses adding ip addresse...
Page 102
Index index-2 fast network 100 user guide e enable command 4-13 environmental specifications a-1 erasing configuration 2-8, 3-2 ethernet port statistics 4-3 exit command 2-8 f filtering hardware 3-14 software 3-14 fn100 bridge address table 1-9 buttons 5-5 connecting to network 2-9 diagnostics 5-1 m...
Page 103
Index fast network 100 user guide index-3 local console manager. See lcm 2-6, 4-1 localfilter command 3-14 logout command 2-8 m mac addresses, displaying 4-9 management cable pin assignments a-5 management support a-2 management tools 4-1 manufacturing information displaying 4-11 mib variables aging...
Page 104
Index index-4 fast network 100 user guide physical a-1 standards a-2 speed command 3-4 standards a-2 statistics ethernet port 4-3 gathering 4-2 overview 4-2 snmp 4-5 system 4-3 status command 4-6 status leds 5-4 straight-through wiring 2-10, a-7 pin assignments a-7 subnet mask, ip changing 4-14 syst...