- DL manuals
- Cabletron Systems
- Network Hardware
- FDCMIM-04
- Installation Manual
Cabletron Systems FDCMIM-04 Installation Manual
Summary of FDCMIM-04
Page 1
Fdcmim-04/08/24/28/34/38/44/48 fddi concentrators installation guide cabletron systems, p.O. Box 5005, rochester, nh 03867-0505.
Page 2: Notice
Notice i notice cabletron systems reserves the right to make changes in specifications and other information contained in this document without prior notice. The reader should in all cases consult cabletron systems to determine whether any such changes have been made. The hardware, firmware, or soft...
Page 3: Fcc Notice
Fcc notice ii fcc notice this device complies with part 15 of the fcc rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation....
Page 4: Safety Information
Safety information iii safety information class 1 laser transceivers class 1 laser products the fdcmim-34 and fdcmim-38 connectors use class 1 laser transceivers. Read the following safety information before installing or operating the fdcmim-34 or fdcmim-38. The class 1 laser transceivers use an op...
Page 5: Safety Information
Safety information iv safety information class 1 laser transceivers laser radiation and connectors when the connector is in place, all laser radiation remains within the fiber. The maximum amount of radiant power exiting the fiber (under normal conditions) is -12.6dbm or 55x10 -6 watts. Removing the...
Page 6: Contents
Contents v contents chapter 1 introduction 1.1 using this manual .................................................................... 1-1 1.2 overview..................................................................................... 1-2 1.3 getting help ..............................................
Page 7: Chapter 1
Introduction page 1-1 chapter 1 introduction the fdcmim-04/08/24/28/34/38/44/48 are components of a modular dual attached concentrator. These components attach to an fddi dual ring through the cabletron systems fdmmim, fdmmim-04, fdmmim-24, or fdmmim-30. Note: throughout this manual, unless otherwis...
Page 8
Introduction page 1-2 figure 1-1. Fdcmim-04 / 24 / 34 / 44 fddi concentrator media interface modules 1.2 overview the fdcmim is a concentrator module that resides in an mmac network hub containing a flexible network bus (fnb). The fdcmim acts as a modular component in a dual attached concentrator. F...
Page 9
Introduction page 1-3 figure 1-2. Fdcmim-08 / 28 / 38 / 48 fddi concentrator media interface modules by using an fdmmim, fdmmim-04, fdmmim-24, or fdmmim-30 you can manage adjacent fdcmims through fdmmim local management, the out-of-band management facility resident on the fdmmim and fdmmim-04 module...
Page 10
Introduction page 1-4 1.3 getting help if you need additional support relating to the fdcmim, or if you have any questions, comments, or suggestions relating to this manual, contact cabletron systems technical support. Before calling, please have the following information ready: • the product type (...
Page 11: Chapter 2
Configuration and installation page 2-1 chapter 2 configuration and installation this chapter lists mmac configuration guidelines, explains how to configure the fdcmim in a hub that also holds ethernet or token ring mims, and then explains how to install the fdcmim as a stand- alone concentrator in ...
Page 12
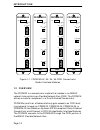
Configuration and installation page 2-2 to better explain how to configure your mmac, refer to the following examples. Figure 2-1 illustrates how the combined load of two fdcmims exceeds the available power of an mmac-3fnb. Figure 2-1. Fdcmims in an mmac-3fnb figure 2-2 represents an mmac-5fnb equip...
Page 13
Configuration and installation page 2-3 figure 2-3. Fdcmims in an mmac-m8fnb when unsure of a hub’s ability to support a planned mim configuration, check the appropriate manuals to determine the amount of power consumed by each mim (amps at 5 vdc), and then check your mmac power supply configuration...
Page 14
Configuration and installation page 2-4 2.3.1 fdcmims exclusively by mixing fdcmims, you can create a stand-alone fddi network of 4 to 56 nodes (7 fdcmim-x8s in an mmac-m8fnb = 56 master ports). Depending on mmac shunting capabilities, you may have to install your fdcmims in adjacent slots to ensure...
Page 15
Configuration and installation page 2-5 2.3.2 irm3 and ethernet mims with fdcmims this example uses the irm3, but the same guidelines apply if you are using an irm, irm2, or irbm. In figure 2-4, the mmac-5fnb has an irm3 in slot 1, tpmim-22s in slots 2 and 3, and fdcmims in slots 4 and 5. The fdcmim...
Page 16
Configuration and installation page 2-6 figure 2-4. Mmac-5fnb with fddi and ethernet mims figure 2-5. Mmac data bus structure fail power ok sn mmac - 5psm off on fddi fdcmim-04 sn lnk pst lnk pst lnk pst lnk pst 1 2 3 4 pwr fnb fddi fdcmim-04 sn lnk pst lnk pst lnk pst lnk pst 1 2 3 4 pwr fnb fail p...
Page 17
Configuration and installation page 2-7 even though rmims can place ethernet traffic on the bus that normally handles fddi traffic, fddi mims can still reside in the same hub with rmims. Rmims determine whether or not the mim that resides in the next higher numbered mmac slot is an ethernet mim. If ...
Page 18
Configuration and installation page 2-8 2.4 twisted pair pinout configuration this section provides the rj-45 pinout configuration for unshielded twisted pair (utp) and shielded twisted pair (stp) physical layer medium dependent (pmd) ports. Note: when connecting two twisted pair ports together (e.G...
Page 19
Configuration and installation page 2-9 2.5 installing the fdcmim the fdcmim has “hot swap” capabilities. This means you can insert and remove the module without first turning off the mmac. Occasionally, depending on the mmac configuration, other mims in the hub may go into a reset condition when yo...
Page 20
Configuration and installation page 2-10 6. Once the module seats in the backplane, tighten the two knurled knobs. This step is important. If you do not tighten the knurled knobs, vibration can cause the module to lose contact with the backplane and disrupt your network. 7. Return power to the mmac....
Page 21: Chapter 3
Using lanview page 3-1 chapter 3 using lanview lanview is a visual diagnostic and status monitoring system developed by cabletron systems. Lanview leds can help you troubleshoot network problems such as open segments or fdcmim power problems. The following sections describe fdcmim leds. 3.1 fdcmim s...
Page 22
Using lanview page 3-2 fnb (continued) red or flashing red the fdcmim has failed. Led off the fdcmim does not connect to any other mim through the mmac bus. The single fdcmim comprises a stand-alone network. 3.2 port status leds each fdcmim port has two leds — pst and lnk. These leds show the port s...
Page 23
Using lanview page 3-3 lnk (media link ok) when on, this green led indicates that a connection exists between the fdcmim and the node at the other end of the port cable segment. To ensure you maintain the link, the port generates an idle signal when not transmitting data. When off, this led indicate...
Page 24: Chapter 4
Specifications page 4-1 chapter 4 specifications this chapter lists the operating specifications for the fdcmim series modules. Cabletron systems reserves the right to change these specifications at any time, without notice. Fiber optic interface depending on the fdcmim, interfaces have the followin...
Page 25
Specifications page 4-2 multimode receiver (signal detect) assert power: -33.0 dbm typical -31.0 dbm maximum assert time: 10 µ sec typical 100 µ sec maximum deassert power: -36.0 dbm typical -45.0 dbm minimum deassert time: 10 µ sec typical 350 µ sec maximum hysteresis: 1.5 db unshielded twisted pai...
Page 26
Specifications page 4-3 shielded twisted pair transmitter amplitude: 1.325 vpk maximum 1.125 vpk minimum rise time: 2 nsec minimum 4 nsec maximum fall time: 2 nsec minimum 4 nsec maximum rise/fall variation: 0.5 nsec maximum overshoot: 5% maximum droop (14 symbols): 3% maximum shielded twisted pair ...
Page 27
Specifications page 4-4 single mode receiver optical wavelength: 1330 nm typical optical input: -31.0 dbm minimum -14.0 dbm maximum optical rise time: 5 nsec maximum optical fall time: 5 nsec maximum supply current: 115 mamps maximum single mode receiver (signal detect) assert power: -33.0 dbm typic...
Page 28
Specifications page 4-5 cable types the fddi physical layer medium dependent (pmd), twisted pair physical layer medium dependent (tp-pmd), and single mode fiber physical medium dependent (smf-pmd) ansi standards define cable requirements as follows: multimode fiber: core diameter: 62.5 µ m nominal c...
Page 29
Specifications page 4-6 twisted pair cable length the tp-pmd fddi standard specifies the following: maximum total cable length: 100 km (62 miles) — dual ring 200 km (124 miles) — wrapped maximum twisted pair cable length between adjacent nodes: 100 m (328.1 feet) single mode fiber optic cable length...
Page 30
Specifications page 4-7 use the following power consumption numbers when determining if a particular mmac has enough power to support your configuration. Fdcmim-04 (sn 0568): 6.8 amp at 5 vdc fdcmim-04 (all others): 4.1 amp at 5 vdc fdcmim-08 (sn 0569): 11.8 amp at 5 vdc fdcmim-08 (all others): 7.0 ...