- DL manuals
- Cabletron Systems
- Switch
- MMAC-Plus 9A000
- User Manual
Cabletron Systems MMAC-Plus 9A000 User Manual
Summary of MMAC-Plus 9A000
Page 1
Mmac-plus ™ 9a000, sfcs-200bx, sfcs-200wg and sfcs-1000 atm switch user’s guide.
Page 3: Notice
I notice notice cabletron systems reserves the right to make changes in specifications and other information contained in this document without prior notice. The reader should in all cases consult cabletron systems to determine whether any such changes have been made. The hardware, firmware, or soft...
Page 4: Fcc Notice
Ii notice fcc notice this device complies with part 15 of the fcc rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation. Not...
Page 5: Table of Contents
Iii table of contents preface technical support....................................................................................................... Vii typographical styles.................................................................................................. Vii important information ...
Page 6
Contents iv 3.2.4.2 sfcs-1000 ac power supply (model a).................................... 3-12 3.2.4.3 sfcs-1000 ac power supply (model b) .................................... 3-15 3.2.5 sfcs-1000 fan tray ................................................................................ 3-18 3.2.6 ...
Page 7
V contents chapter 6 software upgrade instructions 6.1 obtaining the software upgrade file via diskette ......................................... 6-2 6.2 performing the software upgrade .................................................................... 6-4 6.3 changing between multiple versions of...
Page 8
Contents vi appendix c hardware specifications c.1.1 sfcs-200wg ............................................................................................ C-2 c.1.2 sfcs-200bx .............................................................................................. C-3 c.1.3 sfcs-1000 ..........
Page 9
Vii preface this manual provides technical information needed to install and operate the cabletron tm 9a000 and securefast cell switch-200bx atm switches. It pro- vides information for the 9a000 and sfcs-200bx switches and the user- installable network modules offering both lan and wan interfaces. T...
Page 10
Viii preface cd /usr commands or file names that appear within the text of this manual will be represented in the following style: “...The fore_install program will install this distribution”. As in the following example, any messages that appear on your screen during software installation and netwo...
Page 11
Ix preface information contained in note statements has been found important enough to be called to the special attention of the operator and will be set off from the text as follows: note: cabletron systems strongly recommends that you disconnect the serial cable once you have configured the atm sw...
Page 12
X preface laser warning class 1 lasers are defined as products which do not permit human access to laser radiation in excess of the accessible limits of class 1 for applicable wave- lengths and durations. These lasers are safe under reasonably foreseeable conditions of operation. The following netwo...
Page 13
Xi preface safety agency compliance this preface provides safety precautions to follow when installing a cabletron systems, inc., product. Safety precautions for your protection, observe the following safety precautions when setting up your equipment: • follow all warnings and instructions marked on...
Page 14
Xii preface modifications to equipment do not make mechanical or electrical modifications to the equipment. Cabletron systems, inc., is not responsible for regulatory compliance of a modified product. Placement of a cabletron systems product caution to ensure reliable operation of your cabletron sys...
Page 15: Chapter 1
1-1 chapter 1 introduction the cabletron 9a000 and sfcs series atm switch brings atm connectivity to lan workgroup, lan backbone, and lan/wan internetworking applica- tions. Together with the cabletron series of atm computer interfaces, the 9a000 and sfcs series meet the networking demands of today’...
Page 16
1-2 introduction communication) to be switched to multiple destinations by fast atm switches such as the cabletron 9a000 and sfcs series (connecting up to 64 workstations with an aggregate capacity of 2.5 gbps or 96 workstations running at 100 mbps). Larger lans can be built by interconnecting multi...
Page 17
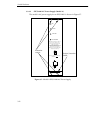
1-3 introduction figure 1.1 - 9a000 switch configuration.
Page 18
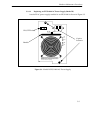
1-4 introduction figure 1.2 - sfcs-200bx switch configuration 1.2.1 front panel description the front panel of the 9a000 and sfcs series includes the following features: a power switch, two power supply leds, a reset button, an rs-232 serial port, an ethernet 10baset port, a next pushbutton, a selec...
Page 19
1-5 introduction 1.2.4 switch control processor the i960 switch control processor provides the distributed connection set-up for a network of atm switches. The switch control processor primarily pro- vides management access through snmp and is responsible for storing and updating all snmp management...
Page 20
1-6 introduction table 1.1 - system hardware and environmental specifications features sfcs series/9a000 switching fabric 2.5 gbps non-blocked traffic policing uni 3.1 dual leaky bucket support number of ports up to 24 ports switch transit delay connection setup time maximum port speed 622 mbps (oc-...
Page 21
1-7 introduction 1.2.7 standards compliance • itu i.361 atm layer • atm forum uni 3.0 1.2.8 safety compliance • us: ul 1950 • canada: csa 22.2 no. 950-m89 • europe: en 60950 1.2.9 emissions compliance • fcc part 15, class a • cispr 22, class a • vcci, class 1 1.2.10 electromagnetic compatibility (em...
Page 22
1-8 introduction.
Page 23: Chapter 2
2-1 chapter 2 installing the 9a000 this chapter contains the procedures for installing the 9a000. The installation of the sfcs series is covered in chapter 3. 2.1 installing the 9a000 to install the cabletron 9a000, follow the steps below: 1. Switch off the power supplies and remove all power from t...
Page 24
2-2 installing the 9a000 figure 2.1 - installing the 9a000 module 7 f l n k 8 f l n k f l n k 10 f l n k i n s 11 f l n k i n s 12 rx tx rx tx rx circuit card card guides metal back-panel jack for esd wrist strap warning: ensure that the circuit card is between the card guides. Lock down the top and...
Page 25
2-3 installing the 9a000 2.2 the reset switch the reset switch is located on the rightmost front panel, under the top plastic tab as shown in figure 2.2. It serves two functions: • pressing the reset switch twice within three seconds causes the pro- cessor (i960) to reset. • pressing and holding the...
Page 26
2-4 installing the 9a000
Page 27: Chapter 3
3-1 chapter 3 switch hardware cabletron systems offers a full line of atm products that work together to provide a complete atm network solution. The cabletron sfcs-200wg atm switch provide high-performance atm connectivity for lan workgroup and desktop applications. The sfcs-200bx atm switch and th...
Page 28
3-2 switch hardware 3.1 switch hardware configurations the sfcs-200wg, as shown in figure 3.1, is a self-contained atm switch that provides an ethernet connection for network management access. The sfcs-200wg atm switch hardware consists of a single switch board with an i960 scp, network modules, an...
Page 29
3-3 switch hardware figure 3.2 - sfcs-200bx switch configuration the sfcs-1000, as shown in figure 3.3, is a self-contained atm switch that provides an ethernet connection for network management access. The hard- ware for the sfcs-1000 consists of up to four switch boards, each with an i960 scp; net...
Page 30
3-4 switch hardware figure 3.3 - sfcs-1000 switch configuration ac volt. In 110 ac volt. In c a b d tx1 rx1 tx2 rx2 tx3 rx3 tx4 rx4 tx2 rx2 tx4 rx4 tx3 rx3 rx1 tx1 rx2 tx2 rx3 tx3 rx4 tx4 tx1 rx1 tx2 rx2 tx4 rx4 tx3 rx3 tx1 rx1 c a b d tx1 rx1 tx2 rx2 tx3 rx3 tx4 rx4 tx2 rx2 tx4 rx4 tx3 rx3 rx1 tx1 ...
Page 31
3-5 switch hardware 3.2 switch hardware components 3.2.1 switch board the switch board (also referred to as the “switch fabric”) contains the vpi/ vci lookup tables and routing circuitry to ensure that a cell received from an input port is correctly switched to one or more output ports. The sfcs- 20...
Page 32
3-6 switch hardware 3.2.2.1 i960 switch control processor the front panel of an i960 scp for the sfcs-200wg, sfcs-200bx, and the sfcs-1000 includes the following features: a reset button, an rs-232 serial port, an ethernet 10baset port, a next pushbutton, a select pushbutton, a display led, and a po...
Page 33
3-7 switch hardware table 1.1 describes the rs-232 serial port pinouts that are illustrated in figure 3.5. 3.2.2.1.3 ethernet 10baset port the ethernet 10baset port on the front panel of the scp has a standard rj45 connector. There is a transmit led to the left of this port and a receive led to the ...
Page 34
3-8 switch hardware 3.2.2.1.4 ctl port a control port inside the scp, referred to in the switch software as the ctl port, is a logical (not physical) location where cells that are directed to the scp itself are sent. The ctl port has two roles, serving as both a host and a switch board controller. A...
Page 35
3-9 switch hardware 3.2.2.1.8 power led the power led that is located to the right of the display led on the front panel of the scp reflects the current state of power to the scp. Table 1.4 lists the states of the power led and their meanings. A power switch is located on the upper right-hand corner...
Page 36
3-10 switch hardware for example, according to this notation, the fourth port on a network module in slot b of switch board #2 is port 2b4. Figure 3.6 illustrates how the ports of various network modules, located in switch board #4 of an sfcs-1000, for example, would be numbered. Figure 3.6 - networ...
Page 37
3-11 switch hardware 3.2.4 power supply modules the sfcs-200bx and the sfcs-1000 each come with two removable power supply modules. In the event of a single power supply failure, the power sup- ply indicator led(s) on the front panel of the supplies will indicate the failed supply. The failed power ...
Page 38
3-12 switch hardware 3.2.4.2 sfcs-1000 ac power supply (model a) the model a ac power supply for an sfcs-1000 is shown in figure 3.7. Figure 3.7 - model a sfcs-1000 ac power supply ac caution: this unit has more than one power cord. To reduce the risk of electric shock, disconnect two power supply c...
Page 39
3-13 switch hardware 3.2.4.2.1 power supply leds there are four leds on the front panel of the model a sfcs-1000 ac power supply which indicate the status of the power supply. The leds and their functions are described in the following table: table 3.5 - sfcs-1000 power supply led descriptions 3.2.4...
Page 40
3-14 switch hardware if a model a power supply goes into shutdown, it will remain shut down until the power switch is turned off and turned on again (power cycle). The power switch must remain off long enough for the shutdown led to extinguish (this allows the capacitors to discharge). Warning! A re...
Page 41
3-15 switch hardware 3.2.4.3 sfcs-1000 ac power supply (model b) the model b ac power supply for an sfcs-1000 is shown in figure 3.8. Figure 3.8 - model b sfcs-1000 ac power supply caution: this unit has more than one power cord. To reduce the risk of electric shock, disconnect two power supply cord...
Page 42
3-16 switch hardware 3.2.4.3.1 power supply leds there are four leds on the front panel of the model b sfcs-1000 ac power supply which indicate the status of the power supply. The leds and their functions are described in the following table: table 3.6 - sfcs-1000 power supply led descriptions 3.2.4...
Page 43
3-17 switch hardware if a model b power supply goes into shutdown, it remains turned off until the fault condition is rectified. At that point, the power supply restarts itself, except in the case of an overvoltage condition. To recover from a shutdown caused by an overvoltage state, the ac line inp...
Page 44
3-18 switch hardware 3.2.5 sfcs-1000 fan tray the sfcs-1000 comes with a removable fan tray. The speed of each fan is monitored by circuitry in the cec, and is available via snmp. In this manner, the failure of any fan can be detected immediately. The fan tray is hot-swap- pable, and the entire tray...
Page 45
3-19 switch hardware 3.2.7 sfcs-1000 common equipment card (cec) the cec provided with the sfcs-1000 performs several functions. Because each scp contains an ethernet port, a major function of the cec is to provide a single, unified ethernet port connection for all of the scps. The cec is also respo...
Page 46
3-20 switch hardware the alarm relay contacts are normally closed when there is no power to the switch. The user can attach alarm circuits to these contacts to trigger an exter- nal alarm in the case of an alarm condition on the switch. The user can define al1 and al2 as major and minor alarm indica...
Page 47
3-21 switch hardware 3.2.7.3 cec status leds this subsection discusses the meaning of the status leds on the cec of the sfcs-1000 switch. The leds have been designed to provide information per- taining to the state of the switch at a glance. Figure 3.11 - cec status leds there are eight status leds ...
Page 48
3-22 switch hardware 3.2.7.3.2 power supply leds there are two power supply leds on the front panel of the cec, one for each power supply. The leds for the two power supplies should be illuminated yellow, indicating that the cec is on and that the power supply correspond- ing to that led is function...
Page 49
3-23 switch hardware table 3.8 - cec receive (rx) led description table 3.9 - cec link integrity (li) led description table 3.10 - cec collision (col) led description table 3.11 - cec polarity (pol) led description led color meaning green the ethernet port is receiving traffic normally. Off the ethe...
Page 50
3-24 switch hardware.
Page 51: Chapter 4
4-1 chapter 4 switch setup this chapter describes how to handle and set up a cabletron atm switch prior to its operation. 4.1 introduction before installing a cabletron atm switch, there are several important factors that must be taken into consideration, depending on the type of installation site. ...
Page 52
4-2 switch setup 4.2.1 inventorying the unit a complete inventory of the cabletron atm switch package should be per- formed before any power is supplied to the unit. The cabletron atm switch package should contain the following: • cabletron atm switch • cabletron atm switch user’s manual (this manua...
Page 53
4-3 switch setup 4.3 electrical considerations the following items should be considered when setting up the switch: caution consideration should be given to the connec- tion of the equipment to the supply circuit and the effect that the overloading of circuits could have on overcurrent protection an...
Page 54
4-4 switch setup 4.4 rack-mounting an sfcs-200bx the sfcs-200bx is designed to be installed either as a stand-alone unit placed on the desktop, or as a rack-mounted unit using the included rack-mount kit (refer to section 4.2.1). The following items should be addressed when rack- mounting this switc...
Page 55
4-5 switch setup 4.4.2 installing the rack-mount brackets to install the rack-mount brackets and cable relief strain rail, use the follow- ing procedure: 1. Carefully place the sfcs-200bx unit upside down on a clean, flat, sturdy work surface with the front of the unit still facing front. 2. Using a...
Page 56
4-6 switch setup note: the sfcs-200bx is an operational atm switch at this point if used with other cabletron switches or with atm interface cards. However, if other vendor equipment is connected, you may have to complete an ini- tial user configuration. Note: if you wish to have remote access to th...
Page 57
4-7 switch setup 4.5 rack-mounting an sfcs-200wg the sfcs-200wg is designed to be installed either as a stand-alone unit placed on the desktop, or as a rack-mounted unit using the optional rack- mount kit (refer to section 4.2.1), which may be purchased separately. The fol- lowing items should be ad...
Page 58
4-8 switch setup 4.5.2 installing the rack-mount brackets to install the rack-mount brackets and cable relief strain rail, use the follow- ing procedure: 1. Carefully place the sfcs-200wg unit upside down on a clean, flat, sturdy work surface with the front of the unit still facing front. 2. Using a...
Page 59
4-9 switch setup note: the sfcs-200wg is an operational atm switch at this point if used with other cabletron switches or with atm interface cards. However, if other vendor equipment is connected, you may have to complete an ini- tial user configuration. Note: if you wish to have remote access to th...
Page 60
4-10 switch setup 4.6 rack-mounting an sfcs-1000 the sfcs-1000 switch is designed to be rack-mounted. The following items should be addressed when rack-mounting this switch: warning! When rack-mounting equipment, make sure that a hazardous condition is not created due to uneven weight distribution. ...
Page 61
4-11 switch setup 4.6.1 installing the sfcs-1000 to install the sfcs-1000 in the equipment rack, use the following procedure: 1. Choose a rack position for the sfcs-1000. Warning! Because of the unit’s weight, two people should lift the unit to place it in the equipment rack. 2. Place the sfcs-1000 ...
Page 62
4-12 switch setup 4.7 installing the serial cable connect the serial cable (supplied with the switch) from the switch’s serial port to any tty-type device (such as a terminal, or the serial port of a worksta- tion or pc running a terminal emulation program). Note: the switch’s tty port comes configu...
Page 63
4-13 switch setup 4.8 modem configuration all cabletron atm switches support modem access. This may be useful if a switch is installed in a remote location where direct, physical access to the switch is not possible or practical. Keep the following in mind when using a modem to access a cabletron at...
Page 64
4-14 switch setup 4.9 configuring ip addresses the recommended configuration for a cabletron atm switch is to assign an ip address to its network interfaces. This allows you to communicate with the switch from any workstation connected to your atm lan. Ip addresses must be assigned to the network in...
Page 65
4-15 switch setup 4.10 ami security the administrative password on your cabletron atm switch may be changed to provide password-protected access to ami. Cabletron systems recom- mends that you do this to prevent unauthorized users from accessing your cabletron atm switch. This option is available in...
Page 66
4-16 switch setup 4.12 verifying the installation to verify that your switch is up and running, log in to ami and open a session on the switch. Enter the following parameters at the localhost::> prompt to show the configuration of all of the ports on an individual switch fabric: configuration port s...
Page 67: Chapter 5
5-1 chapter 5 hardware maintenance procedures this chapter discusses various hardware maintenance procedures for the cabletron atm switches. Items discussed include the following: • network module replacement • power supply replacement • fan tray replacement • switch control processor replacement • ...
Page 68
5-2 hardware maintenance procedures 5.1.2 multicast mode when hot-inserting or hot-swapping a network module, the mode in which the switch is running must also be considered. A cabletron 200 series switch can operate in one of two multicast modes: extended mode or non-extended mode. • extended mode ...
Page 69
5-3 hardware maintenance procedures 5.1.3 hot-swapping network modules when removing or replacing network modules, use the following procedure: warning! To reduce risk to the user and to prevent dam- age to equipment, it is recommended that you use the included grounding strap when han- dling this o...
Page 70
5-4 hardware maintenance procedures 5.2 power supply module replacement the power supplies in the sfcs-200bx and the sfcs-1000 are hot-swappable, meaning that they can be removed/replaced without having to shut down the switch. Warning! Do not attempt to replace a power supply module without reading...
Page 71
5-5 hardware maintenance procedures warning! Failure to perform step 2 can result in serious injury to the user or damage to the equipment. 2. Turn off the power switch on the front of the defective power supply. 3. Unplug and remove the power cord from the rear of the unit that corresponds to the f...
Page 72
5-6 hardware maintenance procedures 5.2.2 sfcs-1000 power supply module replacement 5.2.2.1 replacing an sfcs-1000 ac power supply (model a) a model a ac power supply module for an sfcs-1000 is shown in figure 3.2. Figure 5.2 - model a sfcs-1000 ac power supply ac caution: this unit has more than on...
Page 73
5-7 hardware maintenance procedures the procedure for hot-swapping a model a sfcs-1000 ac power supply is as follows: warning! A replacement dc power supply should never be placed in an sfcs-1000 that already contains an ac power supply, and vice-versa. If these instructions are not heeded, there is...
Page 74
5-8 hardware maintenance procedures warning! Failure to perform steps 6 or 7 can result in serious injury to the user or damage to the equipment. 6. Ensure that the power switch on the new power supply is turned off before inserting it into the enclosure. 7. Ensure that the fuses on the new unit are...
Page 75
5-9 hardware maintenance procedures 5.2.2.2 replacing an sfcs-1000 ac power supply (model b) a model b ac power supply module for an sfcs-1000 is shown in figure 3.3. Figure 5.3 - model b sfcs-1000 ac power supply caution: this unit has more than one power cord. To reduce the risk of electric shock,...
Page 76
5-10 hardware maintenance procedures the procedure for replacing a model b sfcs-1000 ac power supply module is as follows: warning! A replacement dc power supply should never be placed in an sfcs-1000 that already contains an ac power supply, and vice-versa. If these instructions are not heeded, the...
Page 77
5-11 hardware maintenance procedures 5. Pull forward on the power supply’s handle (located below the power switch and ac plug) to remove it from the chassis. 6. Set the failed supply aside and prepare to install the new one. Warning! Failure to perform steps 7 or 8 can result in serious injury to th...
Page 78
5-12 hardware maintenance procedures 5.3 sfcs-1000 fan tray replacement the sfcs-1000 has a removable fan tray with large fans that cool the switch hardware and power supply modules. Located at the base of the upright unit, the fan tray is removable from the front of the unit and is hot-swappable, m...
Page 79
5-13 hardware maintenance procedures 5.4 switch control processor replacement the following procedure explains how to remove an i960 switch control processor (scp) from a switch fabric and install a new scp. Warning! It is highly recommended that you use the included grounding strap when handling th...
Page 80
5-14 hardware maintenance procedures caution take care to properly align the scp in the card guides in the following step. 4. Insert the new scp into the switch fabric by sliding it into the card guides. 5. Push firmly to seat the scp so that its faceplate is flush with the front panel of the switch...
Page 81
5-15 hardware maintenance procedures 5.5 switch board replacement the switch boards in the sfcs-1000 are hot-swappable, meaning that they can be removed and replaced with the chassis under power. The proper pro- cedure for hot-swapping a switch board is as follows: warning! It is highly recommended ...
Page 82
5-16 hardware maintenance procedures note: to ensure that the switch will work with the previously established network configuration, the relative position of the network modules must not change when you transfer them to the new fabric. For example, an oc-3c network module that is removed from slot ...
Page 83
5-17 hardware maintenance procedures caution make sure the replacement board is properly aligned in the slot in the next step. 6. Carefully slide the replacement board into the chassis using enough force to ensure that the connectors on the board mate with the connectors in the chassis. 7. Be sure t...
Page 84
5-18 hardware maintenance procedures.
Page 85: Chapter 6
6-1 chapter 6 software upgrade instructions this chapter details the steps necessary to upgrade the software on your cabletron atm switch. Some instructions in this chapter are only necessary under certain conditions—check the following before you proceed: • if, after performing the upgrade, you wis...
Page 86
6-2 software upgrade instructions 6.1 obtaining the software upgrade file via diskette using the cabletron systems distribution diskettes, the upgrade software must be installed on a workstation attached (via ethernet or atm) to the scp being upgraded. The first disk contains a part of the distribut...
Page 87
6-3 software upgrade instructions execute the fore_extract script with the following command: ./fore_extract once again, device> is the block device name of the floppy drive. You will be asked to insert the remaining disks in sequence. If these steps are per- formed correctly, something similar to t...
Page 88
6-4 software upgrade instructions 6.2 performing the software upgrade to perform the software upgrade, you will use the operation upgrade com- mand in ami. The underlying file transfer mechanism used by this command is tftp. If tftp is to run properly between two machines, the file(s) being transfer...
Page 89
6-5 software upgrade instructions note: if you obtained the upgrade file via ftp, full path to remotefile is the name of the uncompressed file. If you obtained the file from diskette, full path to remotefile is the path name printed during extraction. For example, if you used ftp, you would enter so...
Page 90
6-6 software upgrade instructions to use the new version of software that you have just loaded, type y and press or simply press to reboot. Reboot the switch[y]? Y once the scp reboots, you will be closed out of all active sessions on the scp. You will need to log in to ami again if you want to begi...
Page 91
6-7 software upgrade instructions 6.3 changing between multiple versions of software it is possible to select between multiple versions of installed software at any time (not just during an upgrade procedure). You can display all the versions that are installed by typing the following: localhost::op...
Page 92
6-8 software upgrade instructions at this point, the switch is still running ft330.35 , but current is pointing to ft340.11 . To make the change complete, enter the following: localhost::operation> reboot are you sure you want to reboot this switch [n]? Y when the scp reboots, it will look to see wh...
Page 93
6-9 software upgrade instructions 6.4 using bootp to download software to the switch note: section 6.5 needs to be performed only if your scp fails to boot from its flash. 6.4.1 overview each scp on a cabletron switch comes with its hardware address (ethernet mac address) burned in from the factory,...
Page 94
6-10 software upgrade instructions before any of the above changes can take effect, inetd must re-read the config- uration file. Note: if you need to set up a tftpboot server, as described in section 6.5.4, the following pro- cess is not necessary at this time. Instead, make inetd re-read its config...
Page 95
6-11 software upgrade instructions note: make sure the last line added to bootptab ends in a colon (:) and not a backslash (\). Otherwise, that line will merge with the next entry, causing your switch to cycle in its attempts to find a bootp server. The variables in the previous example are defined ...
Page 96
6-12 software upgrade instructions 6.4.4 setting up a tftpboot server to set up a tftpboot server, on a sunos 4.1.X system, perform the following steps: note: this procedure only has to be done the first time that the switch is turned on and each scp is upgraded. The next time that the soft- ware is...
Page 97: Appendix A
A-1 appendix a troubleshooting the troubleshooting tests detailed in this appendix will clearly indicate and identify the most common problems in establishing atm networks. There- fore, before calling cabletron systems’ technical support, perform these tests to correct or at least pinpoint the probl...
Page 98
A-2 troubleshooting figure a.1 - adapter hardware troubleshooting flowchart y y call cabletron. N is fiber bad? Change fiber. Y n n n self-test y firmware download y call cabletron. Y call cabletron. Test the looptest y n software as in figure a.3. Run atmstat -d. Passed? Passed? Tried reseating the...
Page 99
A-3 troubleshooting a.1.1 run looptest to determine if an interface is functioning properly, run the looptest utility on a host that has been disconnected and isolated from the network. Note: before running looptest , the receive and transmit connectors on the backplate of the card must be connected...
Page 100
A-4 troubleshooting a.1.2 check self-test (automatically performed) during a system boot, the atm adapter automatically performs a self-test of the hardware, running a low-level diagnostic which checks memory read/write capability. Upon completion of the self-test, a message is printed to the consol...
Page 101
A-5 troubleshooting a.1.4 hardware detected by driver to determine if the driver software on the host has detected the presence of an atm adapter board, issue the following command once the host system has come up completely: netstat -i if the driver has located the atm board, the screen output show...
Page 102
A-6 troubleshooting a.1.5 check firmware to check whether or not the firmware is running correctly, issue the following command: atmstat fa0 1 in this command, the last parameter “1”, causes the command to be repeated at one-second intervals. If the firmware is running correctly, the response will s...
Page 103
A-7 troubleshooting a.1.6 check physical link to see the carrier state of the board, issue the following command: atmstat -d fa0 the -d option displays device statistics in the following format: device statistics: buffer allocation failures type 1 type 2 small large small large receive queue full ca...
Page 104
A-8 troubleshooting a.2 testing network connectivity using pvcs the network connectivity tests require that two atm adapters be connected to an atm switch fabric with pvcs (as shown in figure a.2). The carrier lights should be extinguished on the adapters and on the switch fabric, indi- cating that ...
Page 105
A-9 troubleshooting figure a.3 - networking connectivity using pvcs call cabletron. V erify outgoing a tm arp cache entry? Run atmarp -a. N y create an outgoing a t m arp cache entry . Run atmarp -s. Run atmstat f a0 on remote end when continuously pinging. Run ping ip . No cells recei v ed by remot...
Page 106
A-10 troubleshooting this test sequence requires that the switch fabric be configured with a valid pvc and the endstations to have the proper ip configuration and atm arp cache entries. The tests in figure a.3 assume that there is no ip connectivity between the two endstations. The lack of an ip con...
Page 107
A-11 troubleshooting a.2.1 verifying the outgoing atm arp entry to verify the outgoing atm arp cache entry for the endstation originating the ping, enter the following command on the host: atmarp -a the following is an example of a typical atm arp cache display: outgoing connections: fa0: ws2-atm (1...
Page 108
A-12 troubleshooting a.2.2 atmstat to determine a particular failure state, enter the following command on the remote workstation while continuously pinging: atmstat fa0 1 phy/atm/aal statistics: output input errors atm aal* atm aal* 4b5b 4b5b atm aal* aal* cells cs-pdus cells cs-pdus framing hdr-cr...
Page 109
A-13 troubleshooting a.2.2.1 no cells received by remote end if no cells are received by the remote end (the input atm cells field displays zero), then run the following command on the local machine to verify that cells are going out to the atm interface: atmstat fa0 1 if there are no cells going ou...
Page 110
A-14 troubleshooting a.2.2.4 cells and no errors received by remote and transmitting no cells if the remote workstation is receiving cells with no errors, but is not transmit- ting any cells, then either the outgoing ip address on the remote end is incor- rect or the ip encapsulation does not match ...
Page 111
A-15 troubleshooting a.3 collecting additional information once basic adapter installation and network connectivity have been tested, this section explains how to obtain all of the additional information that you need to have ready before calling cabletron systems technical support. This information...
Page 112
A-16 troubleshooting note: the assumed adapter name in the examples is fa0 . On your particular system, the adapter may have a different designation. To check the name of your adapter, use the command: netstat -in. Uname -a irix beluga 5.3 11091812 ip22 mips ifconfig fa0 fa0: flags=863 inet 198.29.3...
Page 113
A-17 troubleshooting netstat -in name mtu network address ipkts ierrs opkts oerrs coll ec0 1500 192.88.243 192.88.243.171 1173050 39926 509363 0 107115 fa0 9188 198.29.38 198.29.38.206 0 0 0 0 0 qaa0 9180 198.29.22 198.29.22.206 0 0 0 0 0 qaa1*9180 none none 0 0 0 0 0 qaa2*9180 none none 0 0 0 0 0 q...
Page 114
A-18 troubleshooting a.3.3 switch information on the host, at a command line, type the following commands and note the responses: • atmstat fa0 command • netstat -ai command • asxmon command • cport command log in to the atm management interface (ami) and open a session on the switch fabric to check...
Page 115
A-19 troubleshooting asxmon asx-200 switch up 3:35, 17 ports (9 active), software 2.3.5, hardware 1.1 port name uptime vps/max vcs/max kb/s free max total mb b1 198.29.22.34 2:57 1/1 5/5 0 0 140000 847 b2 198.29.22.18 3:35 1/1 3/3 0 0 140000 141 c1 198.29.22.27 3:35 1/1 4/4 0 0 140000 83035 c2 198.2...
Page 116
A-20 troubleshooting the following commands are run by logging in to ami and opening a session on the switch fabric. Enter the following parameters at the prompt for the type of network modules that are installed in your switch fabric: configuration spans show port vpi state type cdvt action remotea...
Page 117
A-21 troubleshooting configuration uni30 show port vpi state ilmi uniside type opertype remoteaddress 1c1 0 down down network auto privateuni 1c2 0 down down network auto privateuni 1c3 0 down down network auto privateuni 1c4 0 down up network auto privateuni 169.144.64.108 1d2 0 down down network a...
Page 118
A-22 troubleshooting configuration port ds1 show port carrier status mode framing loopback clocksource linelength idlecells 1c1 no 0x60 hcs esf none internal lt110 unassigned 1c2 no 0x60 hcs esf none internal lt110 unassigned configuration port sonet show port width carrier status line mode loopback...
Page 119: Appendix B
B-1 appendix b scp diagnostics the tests provided in this section are very specific diagnostics that are only to be run if you have determined that there is a problem with your scp. The diagnostics for the sfcs-200wg, sfcs-200bx, and sfcs-1000 are described first. B.1 sfcs-200wg, sfcs-200bx, sfcs-10...
Page 120
B-2 scp diagnostics b.1.1 accessing the monitor mode to access the monitor mode on an i960 scp to run these tests, perform the fol- lowing steps: 1. Soft boot the scp by pressing the reset button on the front panel of the scp. Because the reset button was designed to avoid acci- dental resets, you w...
Page 121
B-3 scp diagnostics do [offset] - download using xmodem ps [address] - single step through program, skipping procedure calls st [address] - single step through program go [address] - go from start, or continue from breakpoint fr address#times - display one or more real (32 bit) floating point number...
Page 122
B-4 scp diagnostics b.1.2 running the hardware tests this last portion from the displayed list is the group of hardware tests that the user can run on the scp: test-clock - test real time clock test-dram - test dram test-dc - test dram chip # in bank test-ethernet - test ethernet test-flash - test f...
Page 123
B-5 scp diagnostics b.1.2.3 dram chip test this test checks the functionality of a dram chip. It takes about two seconds to run. =>test-dc a dram chip: ok b.1.2.4 ethernet test this test checks the functionality of the ethernet chip. It takes about two sec- onds to run. => test-ethernet ethernet: ok...
Page 124
B-6 scp diagnostics . . Erase chip pattern 1 erase chip pattern 2 erase chip pattern 3 flash: ok b.1.2.6 flash chip test this test checks the functionality of an individual flash chip. It takes about one and a half minutes to run. Note: it is recommended that you back up your cdb before running this...
Page 125
B-7 scp diagnostics b.1.2.7 serial port test this test checks the serial port’s functionality. It takes about two seconds to run. => test-serial serial: ok b.1.2.8 sram test this test checks the sram’s functionality. It takes about two seconds to run. Note: it is recommended that you back up your cd...
Page 126
B-8 scp diagnostics b.1.2.11 complete hardware test this series of tests checks the functionality of all of the hardware devices, in the scp including the flash chips and sram. It takes about six minutes to run. Note: it is recommended that you back up your cdb before running this test. The chips ar...
Page 127: Appendix C
C-1 appendix c hardware specifications this appendix provides information about the hardware for all of cabletron systems’ atm products. Information provided includes fiber-optic and utp cabling specifications; pinout specifications; and hardware and general oper- ating specifications. The products ...
Page 128
C-2 hardware specifications c.1.1 sfcs-200wg the sfcs-200wg atm switch has the following specifications: features specification switching fabric 2.5 gbps, non-blocking number of ports 12 to 24 ports traffic policing upc, dual leaky bucket support switch transit delay connection setup time control pr...
Page 129
C-3 hardware specifications c.1.2 sfcs-200bx the sfcs-200bx atm switch has the following specifications: features specification switching fabric 2.5 gbps, non-blocking number of ports 2 to 24 ports traffic policing upc, dual leaky bucket support switch transit delay connection setup time control pro...
Page 130
C-4 hardware specifications c.1.3 sfcs-1000 the sfcs-1000 atm switch has the following specifications: features specification switching fabric 10 gbps, non-blocking number of ports 2 to 96 ports traffic policing upc, dual leaky bucket support switch transit delay connection setup time control proces...
Page 131
C-5 hardware specifications c.2 atm network modules the lan and wan network modules are the physical atm port interface cards that provide lan/wan connectivity to other atm switches, atm- compatible desktop computers and servers, hubs, routers, multiplexers, and carrier atm services. Currently, netw...
Page 132
C-6 hardware specifications c.2.2 155 mbps oc-3c/stm-1 mm module the following specifications apply to network modules nm-4/155mmscc and nm-4/155mmstc: description specification port capacity four sonet/sdh ports per module data rate 155.52 mbps output buffer 13,312 cell capacity media multimode fib...
Page 133
C-7 hardware specifications c.2.3 155 mbps sts-3c/stm-1 utp module the following specifications apply to network modules nm-4/155utp5ec and nm-4/155utp5c: description specification port capacity four sonet/sdh ports per module data rate 155.52 mbps output buffer 2,560 or 13,312 cell capacity media c...
Page 134
C-8 hardware specifications c.2.3.1 155 mbps utp pinout specifications 155 mbps utp network modules have a standard rj-45 female connector and use rj-45 network equipment pinouts as illustrated in the table below: c.2.3.2 connecting switches with 155 mbps utp network modules when connecting switches...
Page 135
C-9 hardware specifications c.2.4 622 mbps oc-12c/stm-4c mm module the following specifications apply to network module nm-1/622mmscc and nm-1/622mmstc: description specification port capacity one sonet/sdh port per module data rate 622.08 mbps output buffer 13,312 cell capacity media multimode fibe...
Page 136
C-10 hardware specifications c.2.5 25 mbps tp25 module the following specifications apply to network module nm-6/25utpec: description specification port capacity six tp25 ports per module data rate 25.6 mbps output buffer 2,560 cell capacity media cat. 3, 4, or 5 unshielded twisted pair (utp) max. L...
Page 137
C-11 hardware specifications c.2.5.1 connecting switches with tp25 network modules the tp25 network modules have a standard rj45 connector that uses pins 1, 2, 7 and 8. When connecting switches using tp25 network modules, you will need to use a utp crossover cable with the following specification: •...
Page 138
C-12 hardware specifications c.2.5.3 connecting adapters with token ring pinouts to cabletron switches like switches, some adapters use different pin assignments than those men- tioned before. Connecting one of these adapters to a cabletron switch would require the connections to be mapped as follow...
Page 139
C-13 hardware specifications c.2.6 34 mbps e3 module the following specifications apply to network modules nm-2/e3c and nm-4/e3c: description specification port capacity two or four e3 ports per module data rate 34.368 mbps output buffer 13,312 cell capacity media coaxial max. Line length ~450 ft co...
Page 140
C-14 hardware specifications c.2.7 45 mbps ds3 module the following specifications apply to network modules nm-2/ds3c and nm-4/ds3c: description specification port capacity two or four ds3 ports per module data rate 44.736 mbps output buffer 13,312 cell capacity media coaxial max. Line length ~450 f...
Page 141
C-15 hardware specifications c.2.8 155 mbps oc-3c/stm-1 sm module the following specifications apply to network modules nm-4/155smsrc and nm-4/155smlrc: description specification port capacity four sonet/sdh ports per module data rate 155.52 mbps output buffer 13,312 cell capacity media short or lon...
Page 142
C-16 hardware specifications c.2.9 155 mbps oc-3c/stm-1 3mm/1sm module the 155 mbps oc-3c/stm-1 3mm/1sm network module contains one sonet/sdh single mode port (port 4) and three sonet/sdh multimode ports (ports 1, 2, and 3) per module. The following specifications apply to port 4 on network modules ...
Page 143
C-17 hardware specifications the following specifications apply to ports 1, 2, and 3 on network modules nm-4/155sr3scc and nm-4/155lr3scc: description specification data rate 155.52 mbps output buffer 13,312 cell capacity media multimode fiber max. Line length ~2 km connectors sc line encoding non-r...
Page 144
C-18 hardware specifications c.2.10 622 mbps oc-12c/stm-4c sm module the following specifications apply to network module nm-1/622smirc: description specification port capacity one sonet/sdh port per module data rate 622.08 mbps output buffer 13,312 cell capacity media single mode fiber max. Line le...
Page 145
C-19 hardware specifications c.3 atm adapters the family of atm adapters provides a flexible atm interface for the commu- nications needs of today’s high-speed workstations and personal computers. C.3.1 adapter cabling specifications c.3.1.1 fiber-optic cable specifications the table below lists the...
Page 146
C-20 hardware specifications c.3.1.2 utp cable specifications the table below lists the recommended cable specifications for all cabletron atm adapters that use utp cabling to ensure optimal adapter and switch performance. C.3.1.3 utp pinouts all atm adapters that can be connected using copper cabli...
Page 147
C-21 hardware specifications c.3.2 esa-200pc technical specifications the esa-200pc atm adapter provides atm connectivity to eisa-based pcs and servers, and has the following specifications: hardware architecture on-board 25 mhz i960 risc processor aal support special-purpose hardware for aal5 and a...
Page 148
C-22 hardware specifications c.3.3 pca-200pc technical specifications the pca-200pc atm adapter provides atm connectivity to pci-based pcs and servers, and has the following specifications: hardware architecture on-board 25 mhz i960 risc processor aal support special-purpose hardware for aal5 and aa...
Page 149
C-23 hardware specifications c.3.4 pca-200mac technical specifications the pca-200mac atm adapter provides atm connectivity to pci-based apple power macintoshes, and has the following specifications: hardware architecture on-board 25 mhz i960 risc processor aal support special-purpose hardware for a...
Page 150
C-24 hardware specifications c.3.5 nba-200 technical specifications the nba-200 atm adapter provides atm connectivity to 68040-based mac- intosh workstations and servers with full-size nubus slots, and has the fol- lowing specifications: hardware architecture on-board 25 mhz i960 cell processor with...
Page 151
C-25 hardware specifications c.3.6 gia-200 technical specifications the gia-200 atm adapter provides atm connectivity to silicon graphics indy and indigo (r3k, r4k, and challenge s supported) workstations, and has the following specifications: hardware architecture on-board 25 mhz i960 cell processo...
Page 152
C-26 hardware specifications c.3.7 hpa-200 technical specifications the hpa-200 atm adapter provides atm connectivity to the following machines: hp9000/715, hp9000/720, hp9000/725, hp9000/730, hp9000/735, hp9000/750, hp9000/755, and has the following specifications: hardware architecture on-board 25...
Page 153
C-27 hardware specifications c.3.8 mca-200 technical specifications the mca-200 atm adapter provides atm connectivity to microchannel- based workstations, pcs, and servers, and has the following specifications: hardware architecture on-board 25 mhz i960 cell processor with micro channel bus mas- ter...
Page 154
C-28 hardware specifications c.3.9 sba-200 technical specifications the sba-200 atm adapter provides atm connectivity to sun microsystems’ sparc 1, 1+, 2, 10, 20, 630 mp, 670 mp, 690 mp, sparc 5, sparcstation ipc, ipx, lx, sparcclassic, sparcserver 1000, and sparccenter 2000, and has the following s...
Page 155
C-29 hardware specifications c.3.10 esa-200 technical specifications the esa-200 atm adapter provides atm connectivity to eisa-based work- stations, pcs, and servers, and has the following specifications: hardware architecture on-board 25 mhz i960 cell processor aal support special purpose, on-board...
Page 156
C-30 hardware specifications c.3.11 vma-200 technical specifications the vma-200 atm adapter provides atm connectivity to crimson, onyx, challenge xl, challenge l, and power challenge machines, and has the fol- lowing specifications: hardware architecture on-board 25 mhz i960 cell processor aal supp...
Page 157
C-31 hardware specifications.
Page 158
C-32 hardware specifications.
Page 159
G-1 glossary 802.1d spanning tree bridging - the ieee standard for bridging; a mac layer standard for transparently connecting two or more lans (often called subnetworks) that are running the same protocols and cabling. This arrange- ment creates an extended network, in which any two workstations on...
Page 160
G-2 glossary work module hardware and software, ip connectivity, and snmp network management. Ansi (american national standards institute) - a private organization that coordinates the setting and approval of some u.S. Standards. It also repre- sents the united states to the international standards ...
Page 161
G-3 glossary atm peer-to-peer connection - a virtual channel connection (vcc) or a vir- tual path connection (vpc) directly established, such as workstation-to-work- station. This setup is not commonly used in networks. Atm traffic descriptor - a generic list of parameters that can be used to cap- t...
Page 162
G-4 glossary a common protocol. Bridges can usually be made to filter certain packets (to forward only certain traffic). Broadband - a service or system requiring transmission channels capable of supporting rates greater than the integrated services digital network (isdn) primary rate. Broadband acc...
Page 163
G-5 glossary cell header - atm layer protocol control information. Cell transfer delay - the transit delay of an atm cell successfully passed between two designated boundaries. Clp (cell loss priority) - the last bit of byte four in an atm cell header; indi- cates the eligibility of the cell for dis...
Page 164
G-6 glossary dip switch (dual in-line package) - a device that has two parallel rows of contacts that let the user switch electrical current through a pair of those con- tacts to on or off. They are used to reconfigure components and peripherals. Domain name server - a computer that converts names t...
Page 165
G-7 glossary eprom - erasable programmable read only memory (see prom.) es (end system) - a system in which an atm connection is terminated or ini- tiated. An originating end system initiates the atm connection, and a termi- nating end system terminates the atm connection. Oam cells may be generated...
Page 166
G-8 glossary ft-pnni (forethought pnni) - a fore systems routing and signalling pro- tocol that uses private atm (nsap) addresses; a precursor to atm forum pnni (see pnni). Ftp (file transfer protocol) - a tcp/ip protocol that lets a user on one com- puter access, and transfer data to and from, anot...
Page 167
G-9 glossary icmp (internet control message protocol) - the protocol that handles errors and control messages at the ip layer. Icmp is actually a part of the ip protocol layer. It can generate error messages, test packets, and informational mes- sages related to ip. Ieee (institute of electrical and...
Page 168
G-10 glossary in a class a network, the first of the numbers is the network number, the last three numbers are the local host address. In a class b network, the first two numbers are the network, the last two are the local host address. In a class c network, the first three numbers are the network a...
Page 169
G-11 glossary isdn (integrated services digital network) - an emerging technology that is beginning to be offered by the telephone carriers of the world. Isdn com- bines voice and digital network services into a single medium or wire. Iso (international standards organization) - a voluntary, non tre...
Page 170
G-12 glossary lecs (lan emulation configuration server) - the lecs is responsible for the initial configuration of lecs. It provides information about available elans that a lec may join, together with the addresses of the les and bus associated with each elan. Leq - a fore program that provides inf...
Page 171
G-13 glossary microchannel - a proprietary 16- or 32-bit bus developed by ibm for its ps/2 computers’ internal expansion cards; also offered by others. Mtu (maximum transmission unit) - the largest unit of data that can be sent over a type of physical medium. Multi-homed - a device that has both an ...
Page 172
G-14 glossary osi (open systems interconnection) - the 7-layer suite of protocols designed by iso committees to be the international standard computer net- work architecture. Ospf (open shortest path first) protocol - a routing algorithm for ip that incorporates least-cost, equal-cost, and load bala...
Page 173
G-15 glossary physical layer (phy) connection - an association established by the phy between two or more atm-entities. A phy connection consists of the concat- enation of phy links in order to provide an end-to-end transfer capability to phy saps. Pmd (physical medium dependent) - a sublayer concer...
Page 174
G-16 glossary proxy - the process in which one system acts for another system to answer protocol requests. Proxy agent - an agent that queries on behalf of the manager, used to monitor objects that are not directly manageable. Psn (packet switched network) - a network designed to carry data in the f...
Page 175
G-17 glossary sar (segmentation and reassembly) - the sar accepts pdus from the cs and divides them into very small segments (44 bytes long). If the cs-pdu is less than 44 bytes, it is padded to 44 with zeroes. A two-byte header and trailer are added to this basic segment. The header identifies the ...
Page 176
G-18 glossary snap - subnetwork access protocol snmp (simple network management protocol) - the internet standard pro- tocol for managing nodes on an ip network. Snmpd - an smnp agent for a given adapter card. Sonet (synchronous optical network) - a new and growing body of stan- dards that defines a...
Page 177
G-19 glossary switched connection - a connection established via signalling. Symmetric connection - a connection with the same bandwidth value speci- fied for both directions. Synchronous - signals that are sourced from the same timing reference and hence are identical in frequency. Systems network ...
Page 178
G-20 glossary trap - a program interrupt mechanism that automatically updates the state of the network to remote network management hosts. The snmp agent on the switch supports these snmp traps. Ubr (unspecified bit rate) - a type of traffic that is not considered time-criti- cal (e.G., arp messages...
Page 179
G-21 glossary vines (virtual network software) - banyan’s network operating system based on unix and its protocols. Virtual channel switch - a network element that connects vcls. It termi- nates vpcs and translates vci values. The virtual channel switch is directed by control plane functions and rel...
Page 180
G-22 glossary.