- DL manuals
- Cabletron Systems
- Switch
- SmartSTACK 100
- User Manual
Cabletron Systems SmartSTACK 100 User Manual
Summary of SmartSTACK 100
Page 1
Smartstack 100 els100-16tx user guide pwr cpu reset com port status mode tx act fdx mon rx col 100 usr status els100-16tx epim100 epim100 10x 12x 14x 16x 9x 11x 13x 15x 2x 4x 6x 8x 1x 3x 5x 7x link status link status 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 9032405-01.
Page 3: Notice
I notice cabletron systems reserves the right to make changes in specifications and other information contained in this document without prior notice. The reader should in all cases consult cabletron systems to determine whether any such changes have been made. The hardware, firmware, or software de...
Page 4
Notice ii doc notice this digital apparatus does not exceed the class a limits for radio noise emissions from digital apparatus set out in the radio interference regulations of the canadian department of communications. Le présent appareil numérique n’émet pas de bruits radioélectriques dépassant le...
Page 5
Notice iii cabletron software program license 1. License. You have the right to use only the one (1) copy of the program provided in this package subject to the terms and conditions of this license agreement. You may not copy, reproduce or transmit any part of the program except as permitted by the ...
Page 6
Notice iv declaration of conformity application of council directive(s): 89/336/eec 73/23/eec manufacturer’s name: cabletron systems, inc. Manufacturer’s address: 35 industrial way po box 5005 rochester, nh 03867 european representative name: mr. J. Solari european representative address: cabletron ...
Page 7: Contents
V contents chapter 1 introduction 1.1 about this manual ........................................................................1-1 1.2 getting help.......................................................................................1-2 1.3 document conventions .......................................
Page 8: Your Els100-16Tx
Vi contents 3.10 displaying mirroring status ..............................................3-14 3.11 defining and deleting workgroups ..............................3-16 3.12 assigning a community name.............................................3-18 3.13 configuring broadcast/multicast storm protect...
Page 9: Appendix B Glossary
Contents vii 5.2 responses to failures at power-up......................................5-3 5.3 status and activity indicators ............................................5-3 5.4 troubleshooting............................................................................5-6 5.5 els100-16tx does not p...
Page 10
Viii contents.
Page 11: Chapter 1
1-1 chapter 1 introduction 1.1 about this manual this manual is for system administrators responsible for configuring, monitoring, and maintaining the smartstack 100 els100-16tx. You should have a familiarity with networking concepts and principles. In addition, a basic understanding of snmp is help...
Page 12: Els100-16Tx
1-2 introduction • chapter 5, els100-16tx diagnostics and troubleshooting , describes the smartstack 100 els100-16tx diagnostics and provides information on troubleshooting common problems. • appendix a, technical specifications , provides the smartstack 100 els100-16tx specifications and basic cabl...
Page 13: 1.3 Document Conventions
Introduction 1-3 • a description of any action(s) already taken to resolve the problem (e.G., changing mode switches, rebooting the unit, etc.) • the serial and revision numbers of all involved cabletron systems products in the network • a description of your network environment (layout, cable type,...
Page 14: 1.4 Related Documentation
1-4 introduction the following conventions are also used in this document: 1.4 related documentation the following documentation may assist the user in using this product: • getting started with the smartstack 100 els100-16tx - contains the basic information for using the smartstack 100 els100-16tx....
Page 15: 1.5 Overview
Introduction 1-5 1.5 overview the smartstack 100 els100-16tx is an intelligent ethernet-to- ethernet switch that is configured with 16 ieee 802.3 10/100base-t autosensing ethernet ports. The smartstack 100 els100-16tx provides the option of substituting rj45 ports 15 and 16 (either or both) with two...
Page 16
1-6 introduction • operates in either half duplex or full duplex modes on all ports. • implements the spanning tree protocol (802.1d). • configured with factory-set defaults for immediate plug-and- play capability (ip address is not configured at factory). In addition, the smartstack 100 els100-16tx...
Page 17
Introduction 1-7 the smartstack els100-16tx goes beyond switching basics incorporating unique management features, including, rmon statistics and broadcast/multicast storm protection, proactive alarms, and both in-band and out-of-band snmp management. The smartstack els100-16tx uses an asic-based sw...
Page 18: Port Trunking
1-8 introduction access control (mac) sub-layer of the data link layer. Figure 1-2 shows the osi reference model. Figure 1-2. Osi reference model port trunking another performance enhancing feature of the smartstack els100-16tx is port trunking. The smartstack els100-16tx allows two trunk groups of ...
Page 19: Store and Forward Switching
Introduction 1-9 ports allowing the switch port and an attached device to negotiate for full or half-duplex modes of operation. The smartstack 100 els100-16tx also supports auto-negotiation as defined by ieee 802.3u and will automatically set the port to the proper mode (10 mbps, half/full duplex or...
Page 20: Note:
1-10 introduction figure 1-3. Typical switching application by forwarding only packets addressed to devices on other network segments, the smartstack 100 els100-16tx reduces unnecessary traffic and thereby enhances the overall performance of the network. Note: if the packet address is not found in t...
Page 21: Table
Introduction 1-11 packets to the lan. If there is a cable break or a port failure, the network topology is automatically reconfigured by the spanning tree protocol to create an alternate path to the lan. 1.5.2 smartstack 100 els100-16tx bridge address table the smartstack 100 els100-16tx creates and...
Page 22: Applications
1-12 introduction each dynamic entry includes: • an ethernet mac address • a single port number of the lan on which the address resides • the age of the entry the smartstack 100 els100-16tx stores 8192 dynamic (learned) entries in its bridge address table. 1.5.3 smartstack 100 els100-16tx port mirro...
Page 23
Introduction 1-13 smartstack 100 els100-16tx trunking the smartstack 100 els100-16tx allows two trunk groups with up to eight ports each to be connected between the smartstack 100 els100-16tx and other devices in the fastnetwork and smartstack families. This capability provides a scalable dedicated ...
Page 24: Virtual Workgroups
1-14 introduction figure 1-4 illustrates the trunking of multiple smartstack 100 els100-16tx ports to increase the bandwidth. Figure 1-4. Smartstack 100 els100-16tx trunking with 100 mbps ports virtual workgroups the smartstack 100 els100-16tx allows you to define ports for logical groups of associa...
Page 25
Introduction 1-15 figure 1-5 shows two ethernet segments, a and b, that do not include a smartstack 100 els100-16tx. Figure 1-5. Multiple ethernet segments sharing 100 mbps bandwidth each host on segments a and b is limited to sharing a network bandwidth of 10 mbps. A b repeater traffic traffic.
Page 26
1-16 introduction figure 1-6 shows two ethernet segments that take advantage of the virtual workgroup feature of the smartstack 100 els100-16tx and the increased bandwidth applied to each a and b host. Figure 1-6. Using the smartstack 100 els100-16tx to create virtual workgroups to help optimize ban...
Page 27: 1.6 Local Console Manager
Introduction 1-17 as illustrated in the previous diagram, virtual workgroups allow you to associate multiple ports and define a workgroup. In reality, you are assigning workgroup ids to smartstack 100 els100-16tx ports. 1.6 local console manager the local console manager (lcm) is a command-line inte...
Page 28: Enter
1-18 introduction 1.6.1 command syntax conventions the following conventions apply as you use lcm commands: • press the enter key to execute a command after you type it in. • a port range is either a single port number, or a list of port numbers separated by commas or hyphens. For example, 3 is port...
Page 29: 1.6.2 Basic Lcm Commands
Introduction 1-19 1.6.2 basic lcm commands if you are going to manage the smartstack 100 els100-16tx using lcm, you first must connect the smartstack 100 els100-16tx to an ascii terminal or terminal emulator. See section 2.5, connecting the local console manager, for instructions. When you want to u...
Page 30
1-20 introduction els100-16 > help els100-16tx local console manager help or ? This menu status [port-range] to display unit or port status baud [baud-rate] to change the console baud rate exit or logout to logout erase to erase configuration information ident to display unit identification ipaddr [...
Page 31: Erase
Introduction 1-21 erase entering erase to erase the current smartstack 100 els100-16tx configuration returns all parameters to the default values. Exit or logout logs you out of lcm. (the exit command is functionally equivalent to the logout command.) traplog displays the traps messages captured by ...
Page 32
1-22 introduction.
Page 33: Chapter 2
2-1 chapter 2 unpacking and installing your els100-16tx carefully unpack the els100-16tx from the shipping carton and inspect it for possible damage. If any damage is evident, contact your supplier. The shipping carton contains the following: • the els100-16tx unit • one ac power cord • console cabl...
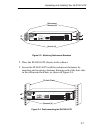
Page 34
2-2 unpacking and installing your els100-16tx figure 2-1. Els100-16tx front panel pwr cpu reset com port status mode tx act fdx mon rx col 100 usr status els100-16tx epim100 epim100 10x 12x 14x 16x 9x 11x 13x 15x 2x 4x 6x 8x 1x 3x 5x 7x link status link status 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 ...
Page 35
Unpacking and installing your els100-16tx 2-3 table 2-1. Meaning of els100-16tx leds led state meaning port status mode tx rx act col fdx 100 mon usr on on on on on off on off on blink on indicates port is transmitting a packet. Indicates port is receiving a packet. Indicates port is transmitting or...
Page 36: 2.2 Installing An Epim
2-4 unpacking and installing your els100-16tx table 2-2 describes the els100-16tx buttons. 2.2 installing an epim the els100-16tx provides two slots for a cabletron epim-100fx (ethernet port interface module). The els100-16tx is shipped without epims. To install an epim, follow the procedure below: ...
Page 37
Unpacking and installing your els100-16tx 2-5 figure 2-2. Installing an epim 10x 12x 14x 16x 9x 11x 13x 15x epim100 epim100 epim-100fx lnk epim-100fx lnk.
Page 38: Rack-Mounting An Els100-16Tx
2-6 unpacking and installing your els100-16tx 2.3 installing the els100-16tx rack-mounting an els100-16tx table 2-3 describes some general considerations you should be aware of before mounting an els100-16tx in a rack assembly. The els100-16tx can be rack-mounted in a standard 19-inch equipment cabi...
Page 39
Unpacking and installing your els100-16tx 2-7 . Figure 2-3. Attaching rackmount brackets 2. Place the els100-16tx chassis in the cabinet. 3. Secure the els100-16tx with the rackmount fasteners by inserting and securing a fastener through each of the four slots in the rackmount brackets, as shown in ...
Page 40: Sequence
2-8 unpacking and installing your els100-16tx 4. Once the els100-16tx is installed, plug the ac power cord into the ac power connector on the rear of the els100-16tx chassis. Plug the other end of the power cord into a three- prong grounded outlet. 2.4 checking the power-up diagnostics sequence befo...
Page 41
Unpacking and installing your els100-16tx 2-9 to connect the lcm: 1. Connect your ascii terminal or terminal emulator to the out- of-band management rs232c port on the front panel of the els100-16tx using the standard rj-45 twisted pair cable shipped with the unit. (only three wires are necessary: r...
Page 42: Caution:
2-10 unpacking and installing your els100-16tx 2.6.1 connecting utp cables before connecting a segment to the els100-16tx, check each end of the segment to verify wire crossover. Connect a twisted pair segment to the els100-16tx as follows: 1. Ensure that the device at the other end of the segment i...
Page 43
Unpacking and installing your els100-16tx 2-11 b. Verify that the rj45 connectors on the twisted pair segment have the proper pinouts (figure 2-6) and check the cable for continuity. Figure 2-6. Cable pinouts - (rj45) crossover cable c. Check that the twisted pair connection meets the db loss and ca...
Page 44: Caution:
2-12 unpacking and installing your els100-16tx fiber optic network connection 1. Remove the protective plastic covers from the fiber optic ports on the applicable port on the module and from the ends of the connectors. 2. Insert one end of the sc connector into the epim-100fx installed in the els100...
Page 45: Els100-16Tx
Unpacking and installing your els100-16tx 2-13 figure 2-7. Epim-100fx port 4. Verify that a link exists by checking that the port link led is solid green. If the link led is off, perform the following steps until it is on: a. Check that the power is turned on for the device at the other end of the l...
Page 46
2-14 unpacking and installing your els100-16tx.
Page 47: Chapter 3
3-1 chapter 3 configuring your els100-16tx the els100-16tx does not require any additional configuration to operate as a standard, transparent switch. However, if you want to use any of the els100-16tx advanced functions, you must first assign an ip (internet protocol) address to any of the ports on...
Page 48: 3.1 Assigning Ip Addresses
3-2 configuring your els100-16tx the following sections describe how to configure the optional parameters of the els100-16tx using lcm commands, including: • assigning ip addresses • enabling and disabling bridging • displaying bridging functions • enabling and disabling trunking • displaying trunki...
Page 49: Ipaddr
Configuring your els100-16tx 3-3 • class b addresses are used for medium sized networks. The first two bytes identify the network and the last two identify the node. The first byte of a class b address must be in the range 128–191. The address 128.150.50.10 identifies node 50.10 on network 128.150. ...
Page 50
3-4 configuring your els100-16tx 3.1.1 displaying ip addresses to display ip addresses, subnet masks, and mac addresses of all ports on the els100-16tx you are configuring, at the lcm prompt: 1. Type ipaddr lcm displays the current ip address table, for example: 3.1.2 deleting an ip address to delet...
Page 51: 3.2 Enabling Bridging
Configuring your els100-16tx 3-5 to change the subnet mask, at the lcm prompt: 1. Type ipaddr for example, ipaddr 6 192.138.217.40 255.255.240.0 would set the subnet mask for port 6 to 255.255.240.0. Lcm responds by redisplaying the current address table. 3.2 enabling bridging the lcm bridge command...
Page 53: 3.5 Enabling Trunking
Configuring your els100-16tx 3-7 you could also type bridge [port-range] to look at a specific range of ports. For example bridge 2-4 would display bridging functions for ports 2, 3, and 4. 3.5 enabling trunking if your network configuration requires you to connect two or more els100-16txs (or other...
Page 54: Trunk Groups
3-8 configuring your els100-16tx figure 3-1. Trunk connections trunk groups each set of connections between two els100-16txs is called a trunk group. You can create up to eight trunk groups, each with up to eight ports, to interconnect your els100-16txs. For example, if you have three els100-16txs (...
Page 55
Configuring your els100-16tx 3-9 figure 3-2. Trunk groups to enable trunking for the example shown, perform the following: 1. Connect the desired ports of the els100-16txs together using 100base-t crossover cables. If els100-16tx a is handling only a small number of users, the a to b trunk group cou...
Page 56: 3.6 Disabling Trunking
3-10 configuring your els100-16tx for els100-16tx b, at the lcm prompt: b. Type trunk 3-10,14-15 on for els100-16tx c, at the lcm prompt: c. Type trunk 3-10 on each els100-16tx determines which ports are part of which trunk group. After trunk group configuration, the els100- 16txs complete the stand...
Page 57: Note:
Configuring your els100-16tx 3-11 3.7 displaying trunking status to check the status of your current trunking configuration, at the lcm prompt: 1. Type trunk the display could look like the following: note: ip addresses are not required for trunking to function. To check the status for ports configu...
Page 58
3-12 configuring your els100-16tx the display could look like the following: the following conditions can be displayed: • broken — trunking is enabled, but the port in non-operational. • closed (or oneway) — trunking is enabled, and the trunking protocol is attempting to establish a trunk connection...
Page 59: 3.9 Disabling Mirroring
Configuring your els100-16tx 3-13 • perturbed — trunking is enabled, and a good trunk connection has been established. However, the forwarding of data packets is temporarily suspended to allow for a change in the membership of the trunk group. 3.8 enabling port mirroring the els100-16tx allows you t...
Page 60: Note:
3-14 configuring your els100-16tx 3.10 displaying mirroring status to check the status of your current mirroring configuration, at the lcm prompt: 1. Type mirror the display could look like the following: note: the mirror command will display the status of all ports, even if a specific port or range...
Page 61
Configuring your els100-16tx 3-15 to check the status for ports configured for mirroring: 1. Type status the display could look like the following: the following conditions can be displayed: • rx only — mirroring is enabled, but mirroring only packets received by the port. • tx only — mirroring is e...
Page 62
3-16 configuring your els100-16tx 3.11 defining and deleting workgroups the els100-16tx allows you to define logical groups of associated ports (virtual workgroups) to provide a more efficient flow of traffic across your ethernet network. Virtual workgroups offer you the ability to limit broadcasts ...
Page 63
Configuring your els100-16tx 3-17 the lcm commands used to create the previous configuration are as follows: 1. To create workgroup a on ports 3, 4, 5, 13, and 16: esl10-26 > workgroup a 3-5,13,16 lcm responds with the following display: name: a ports: 3, 4, 5, 13, 16 info: all 2. To create workgrou...
Page 64
3-18 configuring your els100-16tx to display information about a specific workgroup, at the lcm prompt: 1. Type workgroup name to create or modify a workgroup, at the lcm prompt: 1. Type workgroup name port-range info to delete a workgroup, at the lcm prompt: 1. Type workgroup name delete to create ...
Page 65: Protection
Configuring your els100-16tx 3-19 5. Lcm prompts you to verify the new community name by retyping it. 6. Retype the new community name. 3.13 configuring broadcast/multicast storm protection the els100-16tx provides automatic protection against broadcast/multicast storms. Multicast storms are excessi...
Page 66: 3.15 System Contact
3-20 configuring your els100-16tx the two management information base (mib) variables for configuring multicast storm protection are: • kxiftxstormcnt – specifies the maximum number of multicasts that can be broadcast within the given time. • kxitxstormtime – specifies the period of time that the ma...
Page 67: 3.16 System Name
Configuring your els100-16tx 3-21 3.16 system name the system name is a name assigned to the els100-16tx by the network administrator. By convention, the system name is the fully qualified domain name. (this name then becomes the lcm prompt.) sysname - {system 5} displaystring (size (0..255)) 3.16.1...
Page 68: Set Community Name
3-22 configuring your els100-16tx set community name the set community name variable ( kxadminanypass ) and get community name variable ( kxadmingetpass ) must be set to the value of the community name used by the snmp manager for performing either set or get operations. A zero length community name...
Page 69: Chapter 4
4-1 chapter 4 monitoring and managing your els100-16tx monitoring the els100-16tx consists of collecting and analyzing statistics and system status information. You can use the select button on the front panel of the els100- 16tx to monitor segment status on any of the ethernet ports. Refer to secti...
Page 70: 4.2.1 Gathering Statistics
4-2 monitoring and managing your els100-16tx els100-16tx statistics are divided into four groups: • system statistics • ethernet port statistics • traffic analysis statistics • snmp statistics you can use this information to analyze your overall network performance and to make configuration changes ...
Page 71: Note:
Monitoring and managing your els100-16tx 4-3 • the number of spanning tree topology changes that have occurred since the els100-16tx was last reset. • the time since a topology change was last initiated. • the physical location of the els100-16tx. • the name and address of the contact person for the...
Page 72: 4.3.1 Displaying Status
4-4 monitoring and managing your els100-16tx 4.3 using lcm to check els100-16tx status the lcm commands that enable you to quickly check on the status of the els100-16tx include: • status • address display • ipaddr • ident these lcm commands are described in the sections that follow. 4.3.1 displayin...
Page 73
Monitoring and managing your els100-16tx 4-5 if you do not want to view the status of each ethernet port, use the ctrl-c keys to return to the lcm prompt. Software currently running: version xx.Xx.Xx software, tue 08/23/94 15:0 next bootstrap (1st bank): version xx.Xx.Xx software tue 08/23/94 15:03:...
Page 74
4-6 monitoring and managing your els100-16tx if you do not want to view the status of port 2, use the ctrl-c keys to return to the lcm prompt. You can view the status for multiple of ports by typing status and indicating the range of port numbers, for example status 2-6 . 4.3.2 displaying mac addres...
Page 75
Monitoring and managing your els100-16tx 4-7 to display all mac addresses, at the lcm prompt: 1. Type addresses display any lcm responds with a list of all mac addresses, their associated ports, the type, age, and number of frames from and to that address. If you do not specify any , only the learne...
Page 76
4-8 monitoring and managing your els100-16tx lcm would display: the ipaddr command displays the ip addresses, subnet masks, and mac addresses of all els100-16tx ports. At the lcm prompt: 1. Type ipaddr lcm displays the current ip address table, for example. 4.3.3 displaying manufacturing information...
Page 77
Monitoring and managing your els100-16tx 4-9 4.4 managing the els100-16tx managing the els100-16tx consists of: • disabling and enabling ethernet ports • changing a subnet mask • changing a community name • setting the baud rate of your terminal connection • setting a reboot time you can use the loc...
Page 78: 4.5.1 Disabling A Port
4-10 monitoring and managing your els100-16tx 4.5.1 disabling a port there can be times when you need to disable a specific ethernet port, for example, after you have determined that there is faulty equipment. Disabling a port effectively stops all bridging functions for that port. Disabled ports do...
Page 79: Norip Option
Monitoring and managing your els100-16tx 4-11 for example, enable 7-9 would enable ports 7, 8, and 9. Lcm responds: norip option the routing information protocol (rip) is one of the protocols that allows the els100-16tx to build an accurate, current routing table. This table includes the networks it...
Page 80: Note:
4-12 monitoring and managing your els100-16tx lcm displays the current ip address table, for example: to change the subnet mask, at the lcm prompt: 1. Type ipaddr for example, ipaddr 6 192.138.217.40 255.255.240.0 would set the subnet mask for port 6 to 255.255.240.0. Lcm responds by redisplaying th...
Page 81: Note:
Monitoring and managing your els100-16tx 4-13 3. Enter the new community name. Lcm prompts you to verify the new community name by retyping it. 4. Retype the new community name. 4.5.5 setting the baud rate you can set the baud rate for your lcm console connection. The options for baud rate include: ...
Page 82
4-14 monitoring and managing your els100-16tx to change the baud rate setting, at the lcm prompt: 1. Type baud for example, baud 9600 would set the baud rate to 9600. Lcm responds: 4.5.6 setting a reboot time you can enter the number of seconds the els100-16tx waits before rebooting. At the lcm prom...
Page 83: Chapter 5
5-1 chapter 5 els100-16tx diagnostics and troubleshooting the els100-16tx incorporates built-in diagnostic and testing capabilities which are convenient to use and cause minimal or no disruption to the rest of the operational network. These capabilities are effective for isolating problems within th...
Page 84: Note:
5-2 els100-16tx diagnostics and troubleshooting 5.1.2 specific power-up tests the power-up diagnostic tests performed on the els100-16tx include: • rom checksum test • instruction/data memory test • flash checksum test • nvram checksum test 5.1.3 software checksum comparison when the els100-16tx reb...
Page 85
Els100-16tx diagnostics and troubleshooting 5-3 5.1.4 power-up diagnostics results after completion of the power-up diagnostic sequence, both the power (pwr) and cpu leds located on the front panel of the els100-16tx should be on. 5.2 responses to failures at power-up how the els100-16tx responds to...
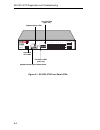
Page 86
5-4 els100-16tx diagnostics and troubleshooting figure 5-1. Els100-16tx front panel leds pwr cpu reset com port status mode tx act fdx mon rx col 100 usr status els100-16tx epim100 epim100 10x 12x 14x 16x 9x 11x 13x 15x 2x 4x 6x 8x 1x 3x 5x 7x link status link status 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 1 3 5 7 9 11...
Page 87
Els100-16tx diagnostics and troubleshooting 5-5 table 5-1. Meaning of els100-16tx leds led state meaning port status mode tx rx act col fdx 100 mon usr on on on on on off on off on blink on indicates port is transmitting a packet. Indicates port is receiving a packet. Indicates port is transmitting ...
Page 88: 5.4 Troubleshooting
5-6 els100-16tx diagnostics and troubleshooting table 5-2 describes the els100-16tx buttons. 5.4 troubleshooting this section lists several situations that could happen while using the els100-16tx, and suggests appropriate action. Because every situation is potentially unique, the corrective actions...
Page 89
Els100-16tx diagnostics and troubleshooting 5-7 5.5.1 connectivity problems • check for led abnormalities. • check port status using lcm. • check for loose port connections. • check to see if the number of carrier losses is increasing using lcm. This indicates that the connection is suspect. • check...
Page 90
5-8 els100-16tx diagnostics and troubleshooting.
Page 91: Appendix A
A-1 appendix a technical specifications a.1 els100-16tx specifications physical height 2.55 in (6.48 cm) width 17 in (43.18 cm) depth 15.5 in (39.4 cm) weight 9 lb (4.1 kg) electrical input voltage auto-ranging from 100–120, 200–240 vac frequency 50/60 hz ac power consumption 80 watts connector port...
Page 92: Diagnostic Leds
A-2 technical specifications diagnostic leds individual port link status individual port segment status segment status, specifying one of the following: - transmit activity - receive activity - both transmit and receive activity - collision - 100 (mbps) - duplex - mon (monitor) - user-defined cpu po...
Page 93: Address Table Size
Technical specifications a-3 address table size 8,192 dynamic entries management support • mib ii, 802.1d, 802.3, and cabletron enterprise mib • cabletron systems local console manager (lcm) • any snmp-based network management system regulatory compliance safety ul 1950, csa c22.2 no. 950, en 60950,...
Page 94: Connectors
A-4 technical specifications table a-2. Db9 pin assignments a.3 100base-t pin assignments an ethernet twisted-pair link segment requires two pairs of wires. Each wire pair is identified by solid and striped colored wires. For example, one wire in the pair might be red and the other wire, red with wh...
Page 95: A.5 Crossover Wiring
Technical specifications a-5 a. The “+” and “-” signs are used to represent the polarity of the two wires that make up each wire pair. A.4 straight-through wiring if the twisted-pair link segment is to join two ports on a switch, and only one of the ports has an internal crossover, the two pairs of ...
Page 96: A.6 The 5 - 4 - 3 Rule
A-6 technical specifications a.6 the 5 - 4 - 3 rule between any two nodes (i.E., pcs or other stations) on the network, there can be: • up to five segments in series • up to four repeaters or multi-port hubs • up to three populated segments (that is, segments attached to two or more pcs). The remain...
Page 97
Technical specifications a-7 figure a-2. Epim-100fx specifications for the epim-100fx are listed in table a-6. The transmitter power levels and receive sensitivity levels listed are peak power levels after optical overshoot. A peak power meter must be used to correctly compare the values given above...
Page 98
A-8 technical specifications.
Page 99: Appendix B
B-1 appendix b glossary address a set of characters that uniquely identifies a station, peripheral device, node, or other unit in a network. Address table a database of device addresses and their associated ports maintained by a switch or bridge for use in making data packet forwarding and filtering...
Page 100: Backbone
B-2 glossary backbone the major, central transmission path for a network. A backbone usually handles high-volume, high-density traffic. Typically a backbone connects various lans into an integrated network. Bandwidth a measure of the amount of traffic a given medium can handle at one time: the commu...
Page 101: Congestion
Glossary b-3 congestion a condition where a portion of the network is overloaded with more data than can be transmitted in the desired time period. Csma/cd (carrier-sense multiple access with collision detection) a channel access (contention) method that requires each station to wait for an idle cha...
Page 102: Encapsulation
B-4 glossary encapsulation a method for moving messages across networks that use different types of protocols. The message is encapsulated (rather than translated), so it can move across a network that otherwise could not understand its protocol. Encapsulating bridges and switches generally use prop...
Page 103: Ieee 802.2
Glossary b-5 icmp (internet control message protocol) an auxiliary protocol of ip used to convey advice and error messages about events in the ip layer. Ieee (institute of electrical and electronic engineers) international professional society which issues networking and other standards. The ieee cr...
Page 104: Internetworking
B-6 glossary internetworking the linking of one or more networks to facilitate communication across networks. Interoperability the ability of equipment from multiple vendors to exchange information using standardized protocols. Ip (internet protocol) ip is the basic datagram protocol used at the net...
Page 105: Mac (Media Access Control)
Glossary b-7 mac (media access control) the data link layer sublayer responsible for scheduling, transmitting, and receiving data on a shared medium local area network. Mask specified a subset of a larger set of data to be included for comparison and analysis. For example, in switch filtering, a mas...
Page 106: Packet
B-8 glossary osi (open systems interconnection) refers to the osi reference model, a logical structure for network operations. Osi is the internationally accepted framework of standards for internetwork communication. Packet a group of bits including data and control elements arranged in a specific ...
Page 107: Protocol
Glossary b-9 protocol a set of rules used by computers and related devices to communicate with each other. Protocol suite a group of protocols related to a common framework. Rarp (reverse address resolution protocol) a protocol that binds mac addresses to specific ip addresses. Risc (reduced instruc...
Page 108: Switch
B-10 glossary switch an intelligent, protocol independent device used to connect similar or dissimilar lans. Symbol the smallest signaling element used by the mac sublayer. Each symbol corresponds to a specific sequence of code bits to be transmitted by the physical layer. Synchronous transmission a...
Page 109: Upstream
Glossary b-11 upstream refers to the relative position of a station in a network to another station in the same network. A station is upstream from its neighbor if it receives data before its neighbor receives the data. Wan (wide area network) a communication network that spans a large geographic ar...
Page 110
B-12 glossary.