- DL manuals
- Cabletron Systems
- Network Card
- TRMM-4
- User Manual
Cabletron Systems TRMM-4 User Manual
Summary of TRMM-4
Page 1
Trmm-4 token ring management module user’s guide booktitle2 optional.
Page 3: Trmm-4 Quick Reference
Qr-1 trmm-4 quick reference qr.1 switchblock sw1 settings switchblock sw1 with factory default settings switch function (default settings shown in bold ) 1 ring speed of fnb ring 1 for all port switching mims. On – 16 mbps ; off – 4 mbps 2 ring speed of fnb ring 2 for all port switching mims. On – 1...
Page 4: Qr.2
Trmm-4 quick reference qr-2 qr.2 led status descriptions note the trmm-4 does not control the ring speeds of single-ring mims. Led status meaning cpu off no power to module. Green testing and booting are nearly complete. Blinking green operational. Red module is resetting or has detected errors. Bli...
Page 5: Qr.3
Trmm-4 quick reference qr-3 qr.3 cpu - central processor unit the cpu led indicates the operational status of the trmm-4’s processor. During start-up, the cpu led indicates a variety of operational states, as shown below in the table. State(s) meaning off the module is not receiving power. Briefly t...
Page 6
Trmm-4 quick reference qr-4.
Page 7: Notice
I notice cabletron systems reserves the right to make changes in specifications and other information contained in this document without prior notice. The reader should in all cases consult cabletron systems to determine whether any such changes have been made. The hardware, firmware, or software de...
Page 8
Notice ii doc notice this digital apparatus does not exceed the class a limits for radio noise emissions from digital apparatus set out in the radio interference regulations of the canadian department of communications. Le présent appareil numérique n’émet pas de bruits radioélectriques dépassant le...
Page 9
Notice iii exclusion of warranty and disclaimer of liability 1. Exclusion of warranty. Except as may be specifically provided by cabletron in writing, cabletron makes no warranty, expressed or implied, concerning the program (including its documentation and media). Cabletron disclaims all warranties...
Page 10
Notice iv declaration of conformity application of council directive(s): 89/336/eec 73/23/eec manufacturer’s name: cabletron systems, inc. Manufacturer’s address: 35 industrial way po box 5005 rochester, nh 03867 european representative name: mr. J. Solari european representative address: cabletron ...
Page 11: Contents
V contents preface chapter 1 introduction 1.1 trmm-4 functional overview ..................................................... 1-2 1.1.1 port assignment ............................................................. 1-2 1.1.2 ring poll failure recovery ............................................. 1-...
Page 12
Contents vi chapter 2 installation 2.1 unpacking and handling the trmm-4 .......................................2-1 2.2 setting switches and jumpers ....................................................2-2 2.2.1 setting fnb ring speeds ...............................................2-3 2.2.2 forced n...
Page 13
Contents vii appendix a introduction to multiple-ring mmac functionality a.1 why use multiple rings? ............................................................A-1 a.2 the flexible network bus (fnb) .................................................A-1 a.2.1 new terminology ............................
Page 14
Contents viii.
Page 15: Preface
Ix preface welcome to the trmm-4 token ring management module user’s guide . This manual describes the trmm-4 management module capabilities and features, operating specifications and configuration, installation, and troubleshooting procedures. Users of the trmm-4 should have a basic working knowled...
Page 16: Using This Manual
Preface x using this manual prior to installing and operating the trmm-4, read through this manual completely. If you are not familiar with port switching and four-ring flexible network bus (fnb) applications, read appendix a. The manual is organized as follows: the quick reference card at the front...
Page 17: Local Area Networks
Preface xi related manuals and recommended reading the cabletron systems manuals listed below should be used to supplement procedures and other technical data provided in this manual. Procedures in related manuals are referenced where appropriate, but are not repeated. Trmm-4 local management user’s...
Page 18
Preface xii before calling the cabletron systems global call center, have the following information ready: • your cabletron systems service contract number • a description of the failure • a description of any action(s) already taken to resolve the problem (e.G., changing mode switches, rebooting th...
Page 19: Chapter 1
1-1 chapter 1 introduction the trmm-4 management module (see figure 1-1 ) can manage four token rings simultaneously and control all token ring mims within a multi media access center (mmac). Also, it can assign ports to different rings on port switching mims. The trmm-4 is 802.5 and ibm compliant. ...
Page 20: 1.1.1 Port Assignment
Introduction 1-2 1.1 trmm-4 functional overview the trmm-4 offers the following features for the monitoring and control of token ring lans: • complete compatibility with all token ring mims. • ability to assign ports to different rings on port switching mims. • full rmon statistical/error network mo...
Page 21: 1.1.3 Network Management
Introduction 1-3 1.1.2 ring poll failure recovery the cabletron systems ring poll failure recovery process automatically removes any station that fails to correctly participate in the ring poll process. This feature ensures that other stations are not prevented from inserting into the ring by an unr...
Page 22
Introduction 1-4 1.1.4 dividing stations among rings the trmm-4 is a port assigning management module. As described in appendix a, it provides the support needed by port switching mims to execute port switching. This feature enables you to segment and manage multiple token rings in the mmac. Figure ...
Page 23
Introduction 1-5 figure 1-3 sample port/station assignments to the fnb rings (configuration b) refer also to the trmm-4 local management user’s guide for details on the execution of port assignment within an mmac through the local management application. 1.1.5 segmenting the fnb for additional rings...
Page 24: Disabling
Introduction 1-6 all single ring mims can wrap their connection (on either side) to the fnb which makes it possible to segment the fnb; port switching mims (e.G., the trxmim) do not. See the trmm-4 local management user’s guide for details and procedures. Figure 1-4 bird’s-eye model of fnb segmentin...
Page 25: 1.1.7 Network Interfaces
Introduction 1-7 ring bypassing with port switching mims (e.G., the trxmim), bypassing may also be performed on a per ring basis. For example, a mim’s ring 3 channel may be bypassed (i.E., isolated) from the fnb while the mim’s ring 1, ring 2, and ring 4 channels remain connected to their respective...
Page 26: 1.1.10 Rmon Functionality
Introduction 1-8 1.1.10 rmon functionality the trmm-4 performs rmon (remote monitoring mib) statistical monitoring on all interfaced lans. See appendix d, for a listing of supported mibs. 1.1.11 snmp traps the trmm-4 operates as a ring error monitor (rem), collecting data on the network, monitoring ...
Page 27: 1.1.16 Ups Monitoring
Introduction 1-9 1.1.15 tftp download of flash image the firmware in the trmm-4, sometimes referred to as the flash image, is the module’s operating system file. Using the local management flash download screen, this file may be replaced or upgraded; a new image may be downloaded by tftp (trivial fi...
Page 28: 1.2.2 Telnet
Introduction 1-10 lm when configured for lm (default configuration), com ports provide access directly to the local management application for any actual or emulated dec vt100 terminal configured according to appendix c. Each com port automatically detects the baud rate of the connecting terminal an...
Page 29: 1.3 Front Panel Features
Introduction 1-11 1.3 front panel features the front panel contains lanview leds and a reset button. 1.3.1 lanview leds the lanview led system comprises several leds, located on the front panel of the trmm-4. Operating as a visual diagnostic and status monitoring system, the leds light, blink, and f...
Page 30
Introduction 1-12.
Page 31: Chapter 2
2-1 chapter 2 installation this chapter discusses the following topics: • unpacking the trmm-4 • setting switches and jumpers on the trmm-4 • management module overrides • installing the trmm-4 into an mmac • resetting the trmm-4 • configuring the trmm-4 using the local management application • choo...
Page 32
Installation 2-2 save the box and packaging materials for possible future repackaging and shipment. 2. Put on the grounding wrist strap. Remove the trmm-4 from the protective bag and place it on top of the bag in a dry, static-free, dust-free area. 3. Inspect the contents for any signs of damage. No...
Page 33
Installation 2-3 switchblock 1 (sw1), shown in figure 2-1 , contains switches that: • set the speed of fnb rings • clear nvram • clear snmp community names passwords • initiate a forced network download 2.2.1 setting fnb ring speeds switches 1, 2, 3, and 4 set the ring speeds for the fnb rings (see ...
Page 34: 2.2.3 Clearing Nvram
Installation 2-4 2.2.3 clearing nvram the hub’s configuration is stored in the nvram of the management module. To clear nvram and erases the configuration of the hub (except for the system time and system date), move switch 7 to the opposite position. This is a toggle switch therefore on/off are irr...
Page 35: 2.4 Installing The Trmm-4
Installation 2-5 any later attempt to use the switches and jumper of a mim to set its configuration will be overridden until the management module’s nvram is cleared or a different type of mim is installed. 2.4 installing the trmm-4 the following guidelines are helpful in configuring the system at i...
Page 36
Installation 2-6 put on the anti-static wrist strap included in the shipment and install the trmm-4 into the mmac as follows: 1. Remove the blank protective panel from the slot 1 (see figure 2-3 ). Figure 2-3 removing the protective panel of slot 1 2. Slide the trmm-4 into the mmac chassis (see figu...
Page 37
Installation 2-7 figure 2-4 inserting the trmm-4 into the mmac 3. Secure the trmm-4 to the mmac by tightening the knobs on the trmm-4. Failure to tighten down the knobs may result in a faulty connection to the mmac backplane. Trmm-4 leds light in accordance with the existing configuration. 2.5 reset...
Page 38: Trmm-4
Installation 2-8 figure 2-5 reset button on front panel 2.6 configuring the trmm-4 using lm this section provides a quick reference for lm configurations to complete the installation. Detailed instructions are provided in the trmm-4 local management user’s guide. 2.6.1 establishing the terminal conn...
Page 39
Installation 2-9 figure 2-6 connecting the terminal cable to the trmm-4 4. Press the return key on the terminal to enable the com port to self-adjust to the baud rate. The local management password screen appears. 5. Press the return key to enter the main menu screen. (the default password is no ent...
Page 40: 2.7.1 Auto Configuration
Installation 2-10 3. Select the setup menu screen. 4. Enter the system level screen. 5. Select the host ip address field and type the appropriate ip address. Press the enter key to accept the entry. 6. Select save at the bottom of the screen and press the enter key. The trmm-4 does a warm reboot tha...
Page 41: Press Y
Installation 2-11 figure 2-7 configuration screen 2.7.2 collapsed backbone configuration the collapsed backbone configuration isolates all mim rings from the fnb. An external device such as a switch or router is required for these rings to communicate. To implement a collapsed backbone: 1. Install a...
Page 42: Press Y.
Installation 2-12 4. Press y. The “ hub reconfiguration selected : all mims will bypass the fnb rings. Is this correct? Y/[n] ” message appears . 5. Press y. The “ configuring as collapsed backbone ” message appears. 2.7.3 split hub configuration the split hub configuration allows you to segment the...
Page 43: 2.8 Connecting A Ups
Installation 2-13 2.8 connecting a ups the trmm-4 can be used to monitor a ups. It must be connected to the ups using a special db9-to-rj45 cable assembly available from cabletron sales. See table c-5 for details about pinouts for the cable. 2.9 power-on diagnostics during the start-up sequence, the...
Page 44
Installation 2-14.
Page 45: Chapter 3
3-1 chapter 3 monitoring and troubleshooting this chapter describes how to verify proper configuration and operation of the trmm-4 using the lanview led system. It also provides a checklist to help isolate problems typically encountered during installation. 3.1 lanview leds lanview leds are a built-...
Page 46
Monitoring and troubleshooting 3-2 table 3-1 lanview led status descriptions led status meaning cpu off no power to module. Green testing and booting are nearly complete. Blinking green operational. Red module is resetting or has detected an error. Blinking red module has failed self-tests. Lwrp off...
Page 47: 3.1.2 Lwrp - Left Wrap
Monitoring and troubleshooting 3-3 3.1.1 cpu - central processor unit the cpu led indicates the operational status of the trmm-4’s processor. When the module first receives power or is reset, it begins a boot sequence and some self-tests. Booting takes several minutes, the time depends on the number...
Page 48: 3.1.4 Xmt - Transmit
Monitoring and troubleshooting 3-4 3.1.3 16 mb - ring speed 16 mbps the 16 mb led indicates the ring speed. Amber indicates that the interface ring speed is set to 16 mbps. Off indicates that the interface ring speed is set to 4 mbps. 3.1.4 xmt - transmit the xmt led indicates the transmitting statu...
Page 49
Monitoring and troubleshooting 3-5 3.2.1 failure to access local management if you cannot connect to local management, check the following: • ensure that the terminal is set to the correct settings as described in the trmm-4 local management user’s guide. • try accessing the lm of another management...
Page 50: 3.2.4 Checking The Hub
Monitoring and troubleshooting 3-6 3.2.3 failure to manage rings if the trmm-4 is not gathering statistical data on an interface, try the following: • use each nsrt led to verify the management interfaces are inserted and participating in the ring. • if the problem is with fnb ring 1, verify that th...
Page 51
Monitoring and troubleshooting 3-7 • check that the trmm-4 and all mims are securely installed in and fastened to the mmac. If necessary, correctly re-insert the trmm-4 and each mim and then tighten the knobs. • be sure that the token ring stations and the mmac are operating in accordance with their...
Page 52
Monitoring and troubleshooting 3-8.
Page 53: Appendix A
A-1 appendix a introduction to multiple-ring mmac functionality this appendix explains the closely related concepts of port switching and the four-ring flexible network bus (fnb). It also compares port switching mims with single ring mims. The appendix concludes with a sample configuration. A.1 why ...
Page 54: Mims
Introduction to multiple-ring mmac functionality a-2 a.3 comparing port switching and single ring mims the fnb serves as a single token ring (fnb ring 1) for topologies comprised of mims that do not support port switching (such as a trmim-24a and trrmim-2at). Each mim in the mmac may attach to adjac...
Page 55
Introduction to multiple-ring mmac functionality a-3 figure a-2. Four vertically stacked rings figure a-3. Comparative view of single ring and multi-ring connectivity port switching mims fnb ring 1 fnb ring 2 fnb ring 3 fnb ring 4 trmm-4 trxmim-54a trxmim-54a trxmim-54a trxmim-54a trxmim-54a tdrmim-...
Page 56: Modules
Introduction to multiple-ring mmac functionality a-4 a.3.1 single ring versus port assignment management modules a single ring management module can only manage one ring. A mid-slot management module must be installed to manage each additional ring. The use of mid-slot management modules reduces the...
Page 57: A.4.2 Auxiliary Rings
Introduction to multiple-ring mmac functionality a-5 a.4.2 auxiliary rings each port switching mim has two auxiliary rings. These rings never communicate with fnb rings, unless through an external device such as a switch or router. A station on an auxiliary ring can only communicate with stations at...
Page 58
Introduction to multiple-ring mmac functionality a-6 figure a-4. Mmac configured with multiple rings err 16 mb act sn byp mgmt ring 4 16 mb 16 mb 16 mb 16 mb 16 mb ring 2 ring 1 ring 3 aux 2 aux 1 1 x 3 x 5 x 7 x 9 x 11 x 13 x 15 x 17 x 19 x 21 x 23 x 2 x 4 x 6 x 8 x 12 x 10 x 14 x 16 x 18 x 20 x 22...
Page 59: Appendix B
B-1 appendix b beaconing protection and recovery the cabletron systems automatic beacon recovery process (abrp) is an effective beaconing protection and recovery system. It automatically identifies and partitions malfunctioning ring segments and re-enables the trunk and lobe ports associated with th...
Page 60
Beaconing protection and recovery b-2 after the abrp completes the troubleshooting and corrective processes required to isolate a problematic ring segment, it transmits traps to the network management station (nms) that identify the beacon type, the problem’s origin and duration, and ports/modules t...
Page 61: Appendix C
C-1 appendix c specifications and setup requirements c.1 trmm-4 specifications ports: 4 fnb (rings 1, 2, 3, 4) 2 rs232c com ports (rj45) cpu: 33 mhz intel i960 risc-based microprocessor cpu memory: 8 mb dynamic ram (expandable to 12 mb) buffering memory: 4 mb dram (expandable to 12 mb) operating sys...
Page 62: C.3 Com Port Pinouts
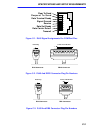
Specifications and setup requirements c-2 c.3 com port pinouts the com ports (female rj45) support rs232c connections. Figure c-1 shows the pin signals for each com port. Figure c-2 and figure c-3 show the connector numbers for db25 and db9 plugs. The maximum cable length from the com port to any de...
Page 63
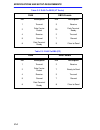
Specifications and setup requirements c-3 figure c-1. Rj45 signal assignments for com port pins figure c-2. Rj45 and db25 connector plug pin numbers figure c-3. Rj45 and db9 connector plug pin numbers 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 transmit receive data terminal ready data carrier detect data set ready r e q u e s...
Page 64
Specifications and setup requirements c-4 table c-2 rj45-to-db25 (vt series) rj45 db25 female pin description pin description 1 transmit 3 receive 2 data carrier detect 20 data terminal ready 4 receive 2 transmit 5 ground 7 ground 6 data terminal ready 5 clear to send table c-3 rj45-to-db9 (pc) rj45...
Page 65: C.5 Regulatory Compliance
Specifications and setup requirements c-5 c.4 environmental requirements operating temperature: 5 ° c to 40 ° c (41 ° f to 104 ° f) storage temperature: -30 ° c to 73 ° c (-22 ° f to 164 ° f) operating relative humidity: 5% to 90% (non-condensing) c.5 regulatory compliance the trmm-4 meets the follo...
Page 66: C.6 Year 2000 Compliance
Specifications and setup requirements c-6 electromagnetic compatibility (emc) fcc part 15, en 55022, csa c108.8, vcci v-3, en 50082-1, and 89/336/eec c.6 year 2000 compliance the trmm-4 is year 2000 compliant..
Page 67: Appendix D
D-1 appendix d supported mib groups the trmm-4 provides access to the following management information bases and their respective functionality: standard mibs • mib-2 (rfc 1231) • ieee rmon mib (rfc 1271) • rmon extensions for token ring (rfc 1513) cabletron enterprise mibs • download • mib-ii exten...
Page 68
Supported mib groups d-2 - history group – records frame-traffic and network-performance statistics for a specific time period. - alarm group – compares threshold parameters to event counters to determine if event thresholds have been crossed. - events group – controls the generation and disposition...
Page 69
Supported mib groups d-3 rmon mib groups rmon mib groups are shown in table d-1 . . Table d-1 rmon mib rfc 1271/1513 support group subgroup statistics rmon 1 token ring ml stats table token ring p stats table history rmon 2 history control table token ring ml history table token ring p history table...
Page 70
Supported mib groups d-4.
Page 71: Index
Ix-1 index a access using spectrum family 1-9, 1-10 access using telnet 1-10 assigning a host ip address 2-9 automatic beacon recovery process (abrp) described b-1 to b-2 setting via local management 1-8 automatic configuration at power up 1-7 b beaconing, protection and recovery b-1 to b-2 c com po...
Page 72
Index ix-2 m mib groups supported d-1, d-3 mib navigator access to mib libraries 1-8 using local management 1-8 mims management module overrides 2-4 port switching 1-6, a-4 single-ring a-4 module bypassing 1-6 n network beacon recovery b-1 to b-2 ring poll failure recovery 1-3 nvram clear switch 7 2...
Page 73
Index ix-3 u ups connection 2-13 v vt100 series terminal setup requirements for access to lm c-1, c-2 w wrist strap, anti-static 2-1.
Page 74
Index ix-4.