- DL manuals
- Cagiva
- Motorcycle
- Navigator
- Workshop Manual
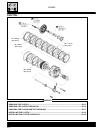
Cagiva Navigator Workshop Manual
Summary of Navigator
Page 1
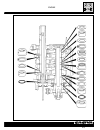
1 workshop manual navigator copyright by mvagusta motor cycles s.P.A. Via g. Macchi , 144 (schiranna) 21100 varese - italy 1st edition printed in italy print no. - 8a0095860
Page 2
2 introduction this publication is intended for cagiva workshops and is designed to help authorized personnel in service and repair operations. Familiarity with the specifications provided herein is a key factor in ensuring effective training of operators. To make the manual easy to understand, the ...
Page 3
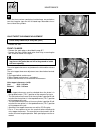
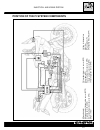
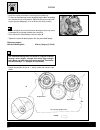
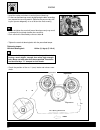
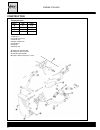
3 identification data the vehicle is identified by the following: - motorcycle serial number (1) on the right side of the head tube. - engine serial number (2) on the lower part of the right-hand crankcase half. - colour code on plate (3) inside the glove compartment under the saddle. - homologation...
Page 4
4 contents section page general information ..................................................................... A 5 maintenance ............................................................................................ B 9 injection - air intake system ..............................................
Page 5
A.1 general information a section.
Page 6
A.2 general information dimensions and weight .......................................................... A-3 engine unit ............................................................................. A-3 transmission unit ................................................................... A-3 frame ....
Page 7
A.3 general information dimensions and weights overall length .......................................................................... 2168 mm overall width ........................................................................... 790 mm overall height ..............................................
Page 8
A.4 general information frame type ........................................................................................... Rectangular and square box section tubular framework in highly resistant steel with box-type strengthening supports at the fork fulcrum attachment. Front suspension type ......
Page 9
B.1 maintenance b section.
Page 10
B.2 maintenance maintenance and tuning ......................................................... B-4 compression check ................................................................ B-23 oil pressure check ................................................................. B-24 technical data .........
Page 11
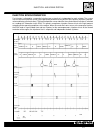
B.3 maintenance check ■ substitution ● first every every every every every 1000 km 1000 km 6000 km 12000 km 20000 km 24000 km engine oil check level ■ engine oil substitute ● ● engine oil filter substitute ● ● coolant check level ■ ■ coolant substitute every 2 years valve tappet clearance adjustment...
Page 12: Maintenance And Tuning
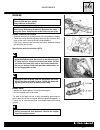
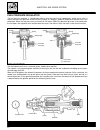
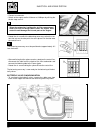
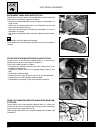
B.4 maintenance maintenance and tuning this section describes the servicing procedures for each part of pe- riodical maintenance. Fuel tank removal to complete this operation it is necessary to previously remove the seat. • remove the complete fuel tap assembly by unscrewing the three screws 1 indic...
Page 13
B.5 maintenance • remove the fairing by unscrewing the five screws 1. There is one front screw and four screws highlighted in the figure. • remove the front protection by unscrewing the two lower screws 2, as shown in the figure. • disconnect the indicator connectors. One is indicated in the figure ...
Page 14
B.6 maintenance • slacken and remove the two tank union clamps 1. One is situated at the front of the vehicle and the other at the back of the tank. • finally, remove the two fixing screws 2. Disconnect the overflow tube from the left fuel tank. Air filter check every 6000 km (or 6 months) substitut...
Page 15
B.7 maintenance spark plugs check every 6000 km (or 6 months) substitute every 12000 km (or 12 months) after the first 1000 km it is necessary to remove the spark plugs, clean them and check the distance between the electrodes (0.6÷0.7 mm). Removal of spark plug n° 1 (front) • remove the sump guard ...
Page 16
B.8 maintenance be careful to not damage the finning of the radiator. The radiator and engine can provocate serious burns when they are hot. Wait until the radiator and the engine are cool enough to be touched before carrying out this operation. Removal of spark plug n° 2 (rear) • remove the seat. •...
Page 17
B.9 maintenance heat grade code • check the heat grade code of the spark plug. The type “r” spark plug has a resistor on the central electrode to avoid radio disturbance. Carbon deposits • check the spark plugs for carbon deposits. If there are deposits, use the appropriate machine or a pointed tool...
Page 18
B.10 maintenance when the front and rear spark plug insulated caps are pushed on, turn the triangular signs on the insulated caps a towards the ex- haust side of the cylinders. Valve tappet clearance adjustment check every 24000 km (or every two years) • remove the seat. Front cylinder • remove the ...
Page 19
B.11 maintenance • remove the plug of the generator cover 1 and the timing cover inspection plug 2. • turn the engine camshaft to bring the piston of the n° 1 cylinder (front) to the top dead centre (t.D.C.) position of the compression cycle. Align the “f/t” line on the generator rotor with the timi...
Page 20
B.12 maintenance • unhook the rear brake fluid chamber by unscrewing the screw shown in the figure. • disconnect the electrical connector of the camshaft position sen- sor. • remove the sensor by unscrewing the two relative screws. • disassemble the fuel filter from its supports and disconnect it fr...
Page 21
B.13 maintenance • check the valve tappet clearance of the n° 2 cylinder (rear) using the same procedure used for the n° 1 cylinder (front) and adjust as necessary. Valve tappet clearance adjustment the valve tappet clearance adjustment is regulated by the substitu- tion of the valve stem pad with a...
Page 22
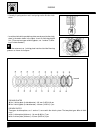
B.14 maintenance int ake v a l ve p ads selection t able no. (12892.41c00.Xxx) v a l ve p ad set (12800-41810) optional measured clearance (mm) suffix no. Actual pa d thickness (mm) specified clearance/no adjustment necessar y how t o use this t able: 1. Measure the clearance of the valve (cold engi...
Page 23
B.15 maintenance how t o use this t able: 1. Measure the clearance of the valve (cold engine). 2. Measure the thickness of the actual pad. 3. Make the vertical column (valve tappet clearance) and horizontal column (thickness) match. For example the valve tappet clearance is 0.23 mm the thickness of ...
Page 24
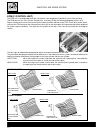
B.16 maintenance fuel tubing check every 6000 km (or 6 months). Substitute every 4 years. After removing the fuel tank, check to see if the feed tube 1 and return tubes 2 and 3 are damaged or show signs of leaking. Substi- tute the tubes if any defects are found. Engine oil and oil filter (engine oi...
Page 25
B.17 maintenance oil filter substitution • drain the engine oil following the same procedure described for the oil change. • remove the oil filter 1 utilising the appropriate wrench (special tool). • apply a light layer of engine oil to the gasket of the new filter be- fore assembly. • assemble the ...
Page 26
B.18 maintenance accelerator cable play check at 1000 km (or 1 month) every 6000 km (or 6 months). Adjust the accelerator cable play following these three phases. First phase: • slacken the locknut 1 of the accelerator return cable b and com- pletely screw in the screw adjuster 2. Second phase: • sl...
Page 27
B.19 maintenance clutch check every 6000 km (or 6 months). • remove the speed sensor 1. • remove the left hand footrest from the frame by unscrewing the two relative screws. • remove the engine pinion cover 2 by unscrewing the three rela- tive screws. • remove the exhaust protection 3. • screw in th...
Page 28
B.20 maintenance engine coolant change • after having removed the tank, remove the radiator cap 1, the expansion tank cap and the drain plugs 2 end 3. Drain the engine coolant. * do not remove the radiator cap when the engine is hot. Boiling liquid or steam can cause serious burns. * the engine cool...
Page 29
B.21 maintenance radiator tubes • remove the sump guard protection 5 by unscrewing the two screws 6 indicated in the figure. Push it aside in the direction of the arrow. Check to see if the radiator tubes are damaged, cracked or leak. If any defect is found, substitute the tubes immediately. Transmi...
Page 30
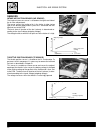
B.22 maintenance chain adjustment • slacken or tighten both chain screw adjusters 1 until the chain reaches a slack of 25-35 mm in the central position of the chain between the crown and pinion. The marks a on both screw adjust- ers must be in the same position of the scale to ensure the correct ali...
Page 31
B.23 maintenance brakes (brakes) check at 1000 km (or 1 month) every 6000 km (or 6 months) (brake and brake fluid tubing) check every 6000 km (or 6 months). Substitute the tubes every four years. Substitute the brake fluid every two years. Brake fluid level check • place the machine in a vertical po...
Page 32
B.24 maintenance • to change the rear brake pads, proceed as follows: • remove the two screws of the rear spray guard 3 rotate it as shown in the figure. Substitute the pads in pairs to guarantee maximum brak- ing performance.. Brake pedal height the rear brake pedal must have a travel of 10-15 mm b...
Page 33
B.25 maintenance bleeding the air from the braking system the air that is trapped in the braking system acts as a cushion, ab- sorbing the greater part of the pressure exerted by the brake pump. The performance of the brake pincer is therefore compromised. The presence of air in the system is indica...
Page 34
B.26 maintenance tyres check every 6000 km (or 6 months) condition of the tread badly worn tyres decrease the road holding and are therefore danger- ous. It is recommended that tyres be changed when the tread reaches the minimum level. Operating limit tread depth (front): 2.0 mm (rear): 2.0 mm tyre ...
Page 35: Compression Test
B.27 maintenance compression test the compression of a cylinder is an optimum indicator of the internal condition of the engine. The decision to overhaul the engine is often the result of a compression test. Amongst the periodical maintenance data to be found at the dealer are also the compression m...
Page 36: Oil Pressure Test
B.28 maintenance oil pressure test periodically check the oil pressure for an approximate evaluation of the condition of the moving parts of the engine. Oil pressure specification more than 300 kpa (3.0 kg/cm 2 ) at 3000 rpm, oil temperature 60°c. Less than 600 kpa (6.0 kg/cm 2 ) if the pressure of ...
Page 37: Technical Data
B.29 maintenance unit: mm technical data valve + guide unit: mm camshaft + cylinder head part standard limit valve diameter intake 40 ––––– exhaust 33 ––––– valve tappet clearance (cold) intake 0.10-0.20 ––––– exhaust 0.20-0.30 ––––– valve stem/guide play intake 0.010-0.037 ––––– exhaust 0.030-0.057...
Page 38
B.30 maintenance connecting rod + crankshaft part standard limit connecting rod big end - int. Diam. 22.010-22.018 22.040 connecting rod small end - lateral play 0.17-0.32 0.50 connecting rod small end – width 21.95-23.00 ––––––– gudgeon pin length 44.17-44.22 ––––––– small end oil play 0.032-0.056 ...
Page 39
B.31 maintenance oil pump part standard limit oil pump reduction ratio 1.301 (57/31 x 29/41) ––––– oil pressure (at 60°c.) more than 300 kpa (3.0 kg/cm 2 ) at 3000 rpm ––––– clutch part standard limit clutch lever play 10-15 ––––– clutch main plate thickness 2.92-3.08 ––––– clutch main plate teeth w...
Page 40
B.32 maintenance part standard limit transmission chain slack 25-35 ––––– gearlever travel 5 ––––– rear brake lever travel 10÷15 ––––– injector + fuel pump + fuel pressure adjuster part technical characteristics notes injector resistance 11-16 ohms at 20°c. Fuel pump flow approx. 1 litre per minute ...
Page 41
B.33 maintenance carburatore part technical characteristics minimum rpm - choke 2000 rpm at 20°-30° 3500-4000 at 90° minimum rpm – tickover 1300-1350 rpm accelerator cable play 2.0-4.0 mm electrical system part technical characteristics notes timing synchronisation 3° btdc at 1200 rpm firing order1·...
Page 42
B.34 maintenance wattage part technical characteristics headlight hi 60 lo 55 sidelight 5 stop/tail light 21/5 direction indicators 10 revcounter light 1.2 direction indicator warning light 2 main beam warning light 2 neutral warning light 2 fuel level warning light 2 number plate light 5 brakes + w...
Page 43
B.35 maintenance part standard limit axial deformation – wheel front –––––– 0.5 rear ––––– 0.5 wheel dimensions front 3.00“x18” ––––– rear 4.25 “x17” tyre dimensions front 110/80 -18” ––––– rear 150/70 -17” ––––– tread depth front ––––– 2.0 rear ––––– 2.0 suspension part standard limit fork travel 1...
Page 44
B.36 maintenance part technical characteristics notes fuel type the fuel must be 95 octane petrol or higher. It is recommended that lead free petrol be used. Fuel tank capacity 20 l engine oil type agip tec 4t 10w/40 sint 20005w/40 engine oil capacity oil change 3100 ml filter change 3300 ml overhau...
Page 45
C.1 injection - air intake system c section.
Page 46
C.2 injection - air intake system maintenance precautions ....................................................... C-3 fi system technical characteristics ........................................ C-9 intake air system technical characteristics ............................. C-21 fi system - position o...
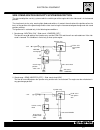
Page 47: Maintenance Precautions
C.3 injection - air intake system maintenance precautions observe the following when handling components of the fi system or when carrying out maintenance on the system. Connectors/couplings • when putting connectors together, make sure that the connectors are pushed fully home until a click is hear...
Page 48
C.4 injection - air intake system fuses • always search for the cause of a blown fuse. Eliminate the cause and then substitute the fuse. • use only fuses of the correct amperage. • do not use wire or another substitute for a fuse. Ecm/various sensors • seeing that each component is a high precision ...
Page 49
C.5 injection - air intake system • do not remove the terminals of the battery whilst the engine is running. If a terminal is removed, this would cause an inverted electrical force that would seriously damage the ecm. • before measuring the voltage on any terminal of the electrical sys- tem, check t...
Page 50
C.6 injection - air intake system • disconnect the negative polarity cable from the battery. • check to see if the connectors/couplings and both ends of the circuit are not loose. Also check the snap-fit couplings for correct insertion. • check the tightness of the female terminals of the circuit by...
Page 51
C.7 injection - air intake system voltage test if the circuit tested has fewer volts than normal, the voltage test can also be used as a continuity test. • with all connectors/couplings connected and with voltage running through the circuit being tested, measure the voltage between each terminal and...
Page 52
C.8 injection - air intake system • disconnect the coupling in the circuit (coupling b) and measure the resistance between the terminals a and earth. If continuity is indicated signifies that there is a short circuit to earth between the terminals a and b of the circuit. Use of the tester • use batt...
Page 53
C.9 injection - air intake system fi system technical characteristics injection time (injection volume) the factor that determines the timing of the injection is the time of the basic injection. This is calculated on the basis of intake air pressure, the rpm of the engine, the opening of the throttl...
Page 54
C.10 injection - air intake system injection time adjustment (volume) various sensors allow injection time adjustments (volume) to be carried out on the basis of the following signals. Signal atmospheric pressure sensor signal engine coolant temperature sensor signal intake air temperature sensor si...
Page 55
C.11 injection - air intake system electric fuel pump the electric fuel pump, which is situated on the left hand side of the machine, is of the rotating lobe volumetric type. The pump motor has permanent magneto brushes. The pump has a non-return valve to avoid the emptying of the fuel system when t...
Page 56
C.12 injection - air intake system fuel pressure regulator the fuel pressure regulator is a diaphragm release valve that consists of a diaphragm, spring and a valve. It always maintains the pressure of the fuel to the injector at 2.9 kg/cm 2 (290 kpa) higher than the pressure in the carburettor. Whe...
Page 57
C.13 injection - air intake system tps fuel pump control system when the ignition switch is switched to on, the battery current reaches the fuel pump motor via the relay of the side stand and the also pump relay, that turns the motor. As the ecm possesses a timing function, the pump motor stops turn...
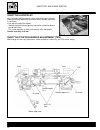
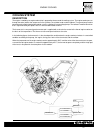
Page 58
C.14 injection - air intake system ecm (fi control unit) the ecm unit is situated underneath the seat and the seat compartment towards the rear of the machine. The ecm consists of a cpu (central control unit), a memory (rom) and incoming/outgoing sections (i/o). Signals sent by each sensor are recei...
Page 59
C.15 injection - air intake system injection synchronisation fuel injection is effected by a sequential injection type system that is independent for each cylinder. The system uses the crankshaft position sensor (signal generator) to determine the position of the pistons (injection synchroni- sation...
Page 60
C.16 injection - air intake system sensors intake air suction sensor (iap sensor) the intake air pressure sensor is situated on the right hand side of the air filter compartment. The sensor senses the suction of air in the intake air tube (spring type) of the butterfly body and this pressure is conv...
Page 61
Injection - air intake system c.17 injection - air intake system crankshaft position sensor (ckp sensor) the signal generating rotor is mounted on the extreme left of the engine crankshaft and the crankshaft position sensor (explorer coil) is situated inside the generator cover. The sensor generates...
Page 62
C.18 injection - air intake system intake air temperature sensor (iat sensor) the sensor of the intake air temperature is situated on the front part of the air filter compartment. The sensor reads the intake air temperature that is obtained and the sensor then converts the resistance of the thermist...
Page 63
Injection - air intake system c.19 injection - air intake system atmospheric pressure sensor (ap sensor) the sensor of the atmospheric pressure is situated underneath the ecm support. Remove the tool kit compartment as described in chapter b. Remove the ecm central processing unit and its support by...
Page 64
C.20 injection - air intake system intake air system technical characteristics whilst the machine is in motion, the frontal air pressure flows into the air filter compartment in such a way that it pressurises the intake air. This improves the intake air efficiency that subsequently permits a greater...
Page 65
C.21 injection - air intake system position of the fi system components a speedometer b engine coolant temperature sensor (ects) c ignition coils (ig coils) d c rankshaft position sensor (ckps) e rpm sensor f a tmospheric pressure sensor (aps) g fuel pump (fp) h camshaft position sensor (cmps) i int...
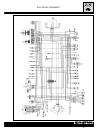
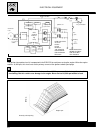
Page 66: Fi System Diagram
C.22 injection - air intake system fi system diagram switch clp fp tos relay fp ecm battery iats tps fi (#1) fi (#2) cmps ckps ects vd iaps aps fi (#1) fi (#2) fpr jet 2 nd air.
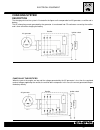
Page 67: Fi Electrical System Diagram
C.23 injection - air intake system fi electrical system diagram speedometer mode select or int ake air pressure sensor suction control va lv e solenoid side st and switch gearchange position switch st ar ter mot or fi: f uel inject o r tps: throttle position sensor ia ts: int ake air tempera t ure s...
Page 68: Auto-Diagnostic Function
C.24 injection - air intake system auto-diagnostic function an auto-diagnostic function is incorporated in the ecm. This function has two modes: the user mode and the dealer mode. The user can only utilise the lcd display and the led indicator. To check the functions of the fi system devices, it is ...
Page 69
C.25 injection - air intake system dealer mode the malfunction is memorised in the computer and it is possible to find it by connecting the coupling of the special tool to the coupling of the dealer mode. The malfunction code is visualised on the lcd display panel. Malfunction signifies that the ecm...
Page 70
C.26 injection - air intake system code malfunctioning component notes c00 none no component defective c11 camshaft position sensor (cmp sensor) c12 crankshaft position sensor (ckp sensor) explorer coil signal, generator signal c13 intake air pressure sensor (iap sensor) c14 throttle position sensor...
Page 71: Security Function
C.27 injection - air intake system security function the fi system is supplied with a security system that allows the switching on of the engine and the riding of the machine even when the ecm notes malfunctions. Item security intervention starting riding camshaft position when the signal of the cam...
Page 72: Fi Diagnostic System
C.28 injection - air intake system fi diagnostic system client’s claim analyses client’s note: note the details of the problem (defect, claim) and the description of the same. The use of this inspection form helps in the collection of information to carry out analyses and the appropriate diagnosis. ...
Page 73
C.29 injection - air intake system auto-diagnostic procedure • do not disconnect the ecm couplings, the battery cables, the ecm earth wiring from the engine or from the fuse before hav- ing checked that the malfunction code (auto-diagnostic code) has been memorised. The disconnection of these parts ...
Page 74
C.30 injection - air intake system malfunction codes and malfunctions malfunction related item related malfunction condition code check c00 no problem ––––––––––––––––––––––––– c11 camshaft position the signal does not reach the ecm for more than 2 seconds sensor after having received the starting s...
Page 75
C.31 injection - air intake system c25 ignition signal (#2 rear) c31 gearchange position signal c32 fuel injector signal #1 (front) c33 fuel injection signal (#2 rear) c41 fuel pump relay signal code c25 is indicated for the rear cylinder. The ignition coil, wiring/ coupling connections, battery fee...
Page 76
C.32 injection - air intake system “c11” cmp sensor circuit malfunction problem possible cause cmp sensor signal is missing for 2 seconds when the engine is turned. • metal particles or foreign bodies on the cmp sensor or on the end of the rotor. • cmp sensor circuit open or in short-circuit. • cmp ...
Page 77
C.33 injection - air intake system check • remove the sump guard as described in page b-7. • disassemble the left hand engine cover as described in page d-28. 1 turn the ignition switch to the off position. Check to see if the connector contacts of the ckp sensor are loose or ruined. If ok, measure ...
Page 78
C.34 injection - air intake system “c13” sensor circuit malfunction problem possible cause low voltage and pressure. High voltage and pressure. (0,5v sensor voltage outside the indicated range. Note: note that the atmospheric pressure varies accord- ing to weather conditions and the altitude. Take i...
Page 79
C.35 injection - air intake system 3 remove the iap sensor. Connect a suction pump with a dial to the suction passageway of the iap sensor. Connect three batteries of 1.5v in series (check that the total voltage is 4.5-5.0v) and connect the – terminal to the earth terminal and the + terminal to the ...
Page 80
C.36 injection - air intake system tp “c14” sensor circuit malfunction problem high or low voltage signal difference between the actual opening of the throttle and the opening calculated by the ecm that is more than specified (0,2v ≤ sensor voltage 4,8v) outside of the specified range. Possible caus...
Page 81
C.37 injection - air intake system 3 connect the tp sensor connector. Turn the ignition switch to the on position. Measure the outgoing voltage of the tp sensor on the connector (between the grey/orange lead and the black/ brown lead) whilst turning the handgrip of the throttle. Tp sensor outgoing v...
Page 82
C.38 injection - air intake system ect “c15” sensor circuit malfunction problems high temperature of the engine coolant (low voltage – low resistance) low temperature of the engine coolant (high voltage – high resistance) possible cause • brown/violet lead circuit in short-circuit to earth. • black/...
Page 83
C.39 injection - air intake system “c21” iat sensor circuit malfunction problem high temperature – air intake (low voltage – low resist- ance) low temperature – air intake (high voltage – high re- sistance) possible cause • yellow/brown lead circuit in short-circuit to earth. • black/brown lead circ...
Page 84
C.40 injection - air intake system “c22” ap sensor circuit malfunction problem possible cause low pressure and high voltage. High pressure and high voltage. (0,25v ≤ voltage sensor 4,85v) outside the indicated range. Note: note that the atmospheric pressure varies accord- ing to the weather conditio...
Page 85
C.41 injection - air intake system 3 remove the ap sensor. Connect a suction pump with a dial to the suction passageway of the ap sensor. Connect three 1.5v batteries in series (check that the total volts is 4.5-5.0v). Connect the – terminal to the earth terminal and + terminal to the vcc terminal. ...
Page 86
C.42 injection - air intake system “c23” to sensor circuit malfunction problem possible cause missing to sensor signal for several seconds after the ignition switch has been turned on. Voltage signal or high. (sensor voltage 4,85 v) outside the indicated range. • to sensor circuit open or in short-c...
Page 87
C.43 injection - air intake system “c24” or “c25” ignition system malfunction (see page g24) “c31” gearchange sensor circuit malfunction problem possible cause gearchange position switch voltage not present low switch voltage (switch voltage > 0,6 v) outside the indicated range. • gearchange positio...
Page 88
C.44 injection - air intake system “c32” or “c33” fuel injection malfunction problem possible cause injector current not present. • injector circuit open or in short-circuit. • injector malfunction. • ecm malfunction. Check • remove the seat. • remove the fuel tank as described in chapter b. • remov...
Page 89
C.45 injection - air intake system “c41” fp relay circuit malfunction problem possible cause relay signal at the fuel pump not present. • fuel pump relay circuit open or in short-circuit. • fuel pump relay malfunction. • ecm malfunction. Check • remove the seat. 1 turn the ignition switch to the off...
Page 90
C.46 injection - air intake system fuel pressure check • remove the seat. • remove the fuel tank as described in chapter b. • place a cloth underneath the fuel pressure control plug 1. Slacken it slowly and collect the remaining fuel by utilising a suitable con- tainer. • remove the fuel pressure co...
Page 91
C.47 injection - air intake system fuel pump relay check the fuel pump relay is situated underneath the seat compartment and can be individuated by the orange, red, brown and violet leads. Firstly, check the isolation of the terminals 1 and 2 with a portable tester. Therefore, apply 12 volts to the ...
Page 92
C.48 injection - air intake system intake filter after having removed the left hand fuel tank, remove the central union indicated in the figure as follows: • slacken the locking ring nut 1. • unscrew the union 2 complete with filter. • blow and clean with compressed air. Carry out the reassembly in ...
Page 93
Injection - air intake system c.49 injection - air intake system air filter removal • remove the seat. • remove the fuel tank as described in chapter b. • remove the iap sensor 1 from the filter and the suction extin- guisher 2 from the left hand side of the machine. • remove the iat air intake temp...
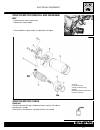
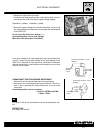
Page 94: Butterfly Body
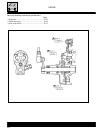
C.50 injection - air intake system butterfly body construction 1 fuel pressure control plug 2 fuel tube union nut 3 sealing washer 4 incoming fuel tube union 5 fuel pressure adjuster 6 fuel feed tubing 7 throttle lever connection rod 15 injector 16 dust protector 17 o-ring 18 seal 19 throttle stop s...
Page 95
Injection - air intake system c.51 injection - air intake system butterfly body removal • remove the air filter and other relative parts as described in page c-49. • disconnect the suction tube from the three way union. • remove the left hand and right hand plastic protective covers of the fuel pump...
Page 96
C.52 injection - air intake system • disconnect the throttle cables 1 and the choke cables 2 by loosen- ing the relative locknuts. After having disconnected the throttle cables, do not com- pletely open and completely close the butterfly valve. This could damage the valve and the body of the carbure...
Page 97
C.53 injection - air intake system • extract the expansion tank from the right hand side of the ma- chine. This creates space in which the butterfly body can be re- moved more easily. • loosen the two fasteners on the collectors. • unscrew the screws 3 and free the choke adjuster support plate. • un...
Page 98
C.54 injection - air intake system 1 3 2 5 4 disassembling the carburettor • disconnect the suction tubes of the carburettor assembly. • remove the tp sensor 1. • remove the choke adjuster assembly 2. Remove the throttle cable guide 3. • remove the fuel feed tubing 1 by removing the nuts. • remove t...
Page 99
C.55 injection - air intake system • remove the injector seals 6. • remove the fuel feed tubing support 7 by removing the screws. • remove the n° 1 throttle lever 1 and the n° 2 throttle lever 2. Re- move the connection rod 3 by unscrewing the nuts. • remove the spring stop 4, the spring 5 and the f...
Page 100
C.56 injection - air intake system • remove the carburettor air screw cap. • slowly rotate the air screw in a clockwise direction and count the number of turns necessary to gently screw in the air screw into its seat. Note the number of turns so that the screw can be replaced correctly after cleanin...
Page 101
Injection - air intake system c.57 injection - air intake system cleaning the carburettor when cleaning carburettors, certain chemical products (es- pecially liquids for immersing and cleaning carburettors) are extremely corrosive and therefore must be handled with great care. Always follow the manu...
Page 102
C.58 injection - air intake system carburettor reassembly • after cleaning the carburettor, replace the air screw in its original position by screwing in until it lightly rests on its seat. Then un- screw the number of turns noted during the removal. Air screw standard adjustment: approx. 1-1/2 turn...
Page 103
Injection - air intake system c.59 injection - air intake system • completely close the butterfly valve 1 on the rear carburettor and on the front carburettor. • before replacing the n° 2 throttle lever, check the insertion of the ferrule 3, the washer 4 and the spring 5. • replace the n° 2 throttle...
Page 104
C.60 injection - air intake system • correctly replace the suction tube clamp a. • replace the fuel feed tubing support 1. • tighten the connecting plate screws and the screws of the fuel feed tubing support. • apply a thin layer of engine oil to the new injector seals 2 and replace them. Substitute...
Page 105
C.61 injection - air intake system • replace the incoming fuel tube joint 1 at the correct angle on the feed tubing. • tighten the joint nut of the incoming fuel tube to the specified torque. Torque pressure tube joint nut: 23 nm (2.3 kg-m) replace and renew the sealing washers on both sides of the ...
Page 106
C.62 injection - air intake system • connect the suction tubes 1 of the three-way sensor 2 and the fuel pressure adjuster 3 as shown in the figure. Carburettor installation • install the carburettor assembly and tighten the screws of the bands on the side of the air intake collectors. During reassem...
Page 107
C.63 injection - air intake system • replace the support plate of the tickover adjustment using the mounting screw. Torque pressure mounting nut: 23 nm (2.3 kg-m) • replace the complete t-shaped coil support. • connect the injector couplings 2 and 3. • connect the connector of the tp sensor 4. • con...
Page 108
C.64 injection - air intake system • replace the expansion tank in the reverse order of removal. Carry out the bleeding of air of the cooling system as described in chapter b. • assemble the engine support frames 3 and the relative screws, 4, 5, 6 and 7. Tighten these screws to the following torque ...
Page 109
C.65 injection - air intake system fuel injector check the fuel injector must be checked without removing it from the car- burettor. See page c-49 for details. Fuel injector removal • lift up and sustain the fuel tank with a suitable support. • remove the air filter compartment. • disconnect the neg...
Page 110
C.66 injection - air intake system choke adjustment the choke is a cold start system that mechanically opens the butter- fly valve by utilising a cam. The cam is made to rotate by the cable and it pushes the butterfly valve rod attachment. The butterfly valve therefore opens allowing the engine to t...
Page 111
C.67 injection - air intake system carburettor synchronisation check and adjust the butterfly valve synchronisation of the front and rear cylinders. Calibration accessory • remove the right hand fuel tank. • switch on the engine and let it run for several minutes to warm up. • switch off the engine ...
Page 112
C.68 injection - air intake system • connect a revcounter. • switch on the engine and let it tickover at 1300 rpm by utilising the throttle stop screw 1. When the carburettor is without the air filter compartment, make sure that no foreign bodies enter the engine. Such material could damage the inte...
Page 113
C.69 injection - air intake system • connect a revcounter and switch on the engine. • utilising the throttle stop screw, turn the engine over at 1300 rpm. • check the suction of the two cylinders and balance the two butter- fly valves. The balancing accessory must be positioned approximately 30° fro...
Page 114
C.70 injection - air intake system throttle lever play after synchronising the butterfly valves and adjusting the tickover, check that the play a between the throttle lever 1 and the stop screw 2 is 0.25 mm. If not, adjust the play a as follows. • slacken the locknut 3 and tighten or loosen the scre...
Page 115
C.71 injection - air intake system throttle cable adjustment fine adjustments can be carried out by using the screw adjuster on the throttle handgrip (see chapter b). Major adjustments • remove the fuel tank as described in pages b-4 and b-6. • remove the air filter compartment. (see page c-51.) • s...
Page 116: Sensors
C.72 injection - air intake system sensors iap sensor check the air intake air pressure sensor is situated on the right hand side of the air filter compartment. Iap sensor removal/reassembly • remove the right hand fuel tank. • remove the fixing screws of the iap sensor 1 and disconnect the coupling...
Page 117
C.73 injection - air intake system iat sensor check the air intake air temperature sensor is situated on the front part of the air filter compartment. Iat sensor removal/reassembly • remove the fuel tank. • disconnect the iat sensor coupling 1 and remove the iat sensor from the air filter compartmen...
Page 118
C.74 injection - air intake system.
Page 119
D.1 engine d section.
Page 120
D.2 engine camshaft/cylinder head .................................................. D-81 cylinder/piston ..............................................................D-105 clutch ............................................................................ D-114 water pump/clutch cover ...............
Page 121: Ing The Engine
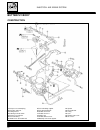
D.3 engine engine components that can be removed without remov- ing the engine the parts listed below can be removed and reinstalled without removing the engine from the chassis. Refer to the pages shown next to each item for information on the removing and installing procedures. Gear change lever a...
Page 122: Gine
D.4 engine • remove radiator cap 3 and coolant drain plugs 4, 5 and 6, and then drain the coolant. * to avoid severe burns caused by the hot liquid or steam, do not open the radiator cap when the engine is hot. * the coolant is harmful if swallowed or through contact with the eyes or the skin. Shoul...
Page 123
D.5 engine • remove the air filter and its various components (see page c.51) • remove the engine support frames 1 and 2 as described in page c.54. • remove the engine coolant expansion tank as described in page c.55. • remove the connector from the temperature sensor that is situ- ated on the cooli...
Page 124
D.6 engine • disconnect the connectors of the engine coolant temperature hous- ing 1 and the cooling fan connector 2 and the hoses 6. They are all found on the right hand side of the machine. Take care when reassembling the electrical wiring and the rubber bands. It is important to replace the wirin...
Page 125
D.7 engine • remove the two fixing screws, the front cylinder exhaust tube as indicated in the figure. • remove the exhaust tube. • after removing the screws as indicated in the figure, remove the rear cylinder exhaust tube. • remove the left hand footrest assembly 1 together with the gearchange lev...
Page 126
D.8 engine • slacken off the rear wheel spindle nut 8. • slacken the left and right hand chain adjusters 9 and then com- pletely slacken the transmission chain. • remove the speed sensor rotor 6 by unscrewing the screw 7. • remove the two mounting bolts 1 and the washer of the clutch disengagement m...
Page 127
D.9 engine • remove the nut 1 and the engine pinion washer. • remove the engine pinion 2. • remove the oil radiator 3 by unscrewing the mounting bolts 4 and the junction bolts of the oil tubes. • remove the transmission chain from the crown wheel. 2 1 3 4.
Page 128
D.10 engine • disconnect the electrical leads of the starter motor 1 and the oil pressure sensor 2. • remove the insulated covers from the spark plugs. Take care when reassembling the electrical wiring and the rubber bands. It is important to replace the wiring exactly as it was before disassembly. ...
Page 129
D.11 engine • remove the right hand footrest by unscrewing the two fixings as shown in the figure. Removing the right hand footrest assists the removal of the engine from the frame. • remove the return spring of the rear brake pedal. • remove the rear brake pedal by unscrewing the fixings indicated ...
Page 130
D.12 engine • gradually lower the power plant. When removing the engine from the frame, take care not to damage either..
Page 131
D.13 engine installation of the engine into the frame install the engine in the reverse order of removal. Proceed carefully taking care to correctly position the tubing and wiring. • before proceeding with the installation of the engine into the frame, support the frame with a jack or an adequate su...
Page 132
D.14 engine • reinstall the secondary air tubes on the cylinders tightening the screws to the specified torque. Torque pressure secondary air tube fixing 8.6/9.8 n.M (0.9/1.0 kg-m) utilise new washers when refitting the tubes onto the cylinders. • when inserting the insulated covers onto the spark p...
Page 133
D.15 engine item n·m kg-m description a 45÷50 4,5÷5,0 front fix. Screw-left hand side of the eng./frame b 45÷50 4,5÷5,0 front fix. Screw-right hand side of the eng./frame c 45÷50 4,5÷5,0 central fixing screw engine/2 support frames d 45÷50 4,5÷5,0 upper rear fix. Screw engine/frame bracket e 45÷50 4...
Page 134
D.16 engine • fit the clutch push rod grease the clutch push rod before installing it. Specific product: agip grease 30 • loosen counternut 7 and completely unscrew adjusting screw 8. • install the oil-cooler and tighten oil line union bolts 1 with the pre- scribed torque. Tightening torque: oil lin...
Page 135
D.17 engine • turn in or out adjuster 8 under the sheath to obtain 10-15 mm (0.3937-0.5905 in) of play a at the end of the clutch lever. Clutch lever play: 10-15 mm (0.3937-0.5905 in) • fit the cable on the generator cover and momentarily place throw- out lever 1 on the push rod. • pull the cable an...
Page 136
D.18 engine • reassemble the left hand footrest tightening the two bolts to the specified torque. Torque pressure footrest fixing bolts 23.5/25.4 n.M (2.4/2.6 kg-m) • reassemble the gearchange lever onto the gear lever shaft mak- ing sure that the previously marked countersigns are in line with each...
Page 137
D.19 engine • reassemble the various components following the reverse order of removal of the engine from the frame. Reassemble the left and right hand engine support frames, supporting the engine so that the various fixing holes can be aligned correctly. Tighten the various fixings to the specified...
Page 138: The Engine
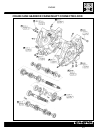
D.20 engine disassembling and reassembling the engine disassembling the engine identify the position of each removed component (intake pipe, camshaft, cylinder head, piston, connecting rod, etc.) and sort the parts into groups so that each component can be reinstalled in its original position. • rem...
Page 139
Engine d.21 engine front in ex no. 1 (front) cylinder head • remove camshaft bearings 4 after unscrewing the bolts. The camshaft journal bearings should be marked “front in.” and “front ex.”. Be sure to loosen the camshaft journal bearing bolts evenly by shifting the spanner diagonally. • turn the c...
Page 140
D.22 engine • remove oil cooler mounting bracket 13 after removing the cylin- der head nuts (m6). • remove the two camshafts, intake 1 and exhaust 2. • remove c-rings 3. • remove dowel pins 4. Take care not to drop c-rings 3 and dowel pins 4 into the crankcase. • remove front timing chain tension ad...
Page 141
D.23 engine • remove cylinder head nut (m8) 1, and loosen cylinder nuts 2. • remove the cylinder head bolts (m10) with the related washers. • remove the cylinder head assembly. Loosen the cylinder head bolts gradually by following a crosswise pattern. Take care not to damage the cylinder while remov...
Page 142
D.24 engine • remove camshaft bearings 3 after removing the related bolts. The camshaft journal bearings should be marked “rear in.” and “rear ex.”. Be sure to loosen the camshaft bearing bolts evenly by shift- ing the spanner diagonally. • place a clean rag over the cylinder base to prevent the pis...
Page 143
D.25 engine • remove no. 2 valve motion idler gear/sprocket 7 after removing shaft 8 with copper washer 9 and thrust washer 10. Take care not to drop thrust washer 10 into the crankcase. • remove the two camshafts, intake 1 and exhaust 2. • remove c-rings 3. • remove dowel pins 4. Take care not to d...
Page 144
D.26 engine • remove cylinder head bolts (m6) 1 and timing chain stretcher fas- tening bolt 2. • remove timing chain stretcher 3. • remove the cylinder head bolts (m10) with the related washers. • remove the cylinder head assembly. Loosen the cylinder head bolts gradually by following a crosswise pa...
Page 145
Engine d.27 • place a clean rag over the cylinder base to prevent the piston pin circlip from falling into the crankcase. Pull up the timing chains, or they may get caught between the crankcase and the valve gear driving sprocket when the crankshaft is turned. • remove the piston pin circlip. • extr...
Page 146
D.28 engine • remove bushings 9 from the crankcase and the generator cover. • remove generator cover 1. • remove dowel pin 2 and gasket 3. • remove starting torque limiter 4 and washers 5. • remove starting idler gear 6, spacer 7, and shaft 8. 1 2 3 5 4 6 8 9 7.
Page 147
D.29 engine • while holding the generator rotor with a 36 mm (1.417 in) span- ner, remove the bolts fastening the clutch springs and then the spring following a crosswise pattern. • remove water pump casing 1 with the o-ring. • remove dowel pin 2. • remove impeller 3. • remove clutch bell housing co...
Page 148
D.30 engine • unlock clutch drum nut 8. • while holding the clutch drum with the special tool, remove clutch drum nut 8. • remove pressure plate 1. • remove push rod 2, bearing 3 and thrust washer 4. • remove clutch push rod 5. Should push rod 5 be difficult to extract, use a magnet or an iron wire....
Page 149
D.31 engine • remove thrust washer 5. • remove primary driving gear assembly 6. • remove washer 1. • remove clutch drum 2 together with driving cam 3 and driven cam 4. • remove driving cam 3 and driven cam 4 from clutch drum 2. These three parts must be replaced as a set. 3 4 2 1 4 3 2 6 5.
Page 150
D.32 engine • remove neutral switch 9 and cable guide 10 after removing the related screws. • remove needle roller bearing 1, collar 2, and thrust washer 3. • remove oil pump driven gear 4 after removing the circlip. • remove pin 5 and washer 6. Take care not to drop the circlip, pin 5 or washer 6 i...
Page 151
D.33 engine • insert a bar of suitable size into the holes of the primary driving gears to align the teeth of the scissors gears. • remove no. 1 valve motion idler gear/sprocket 4 and timing chain 5. • remove key 6. • remove neutral switch contact 1 and the related spring 2. • while holding the gene...
Page 152
D.34 engine • while holding the generator rotor with a 36 mm (1.417 in) span- ner, remove its bolt and washer. • while holding the generator rotor with a 36 mm (1.417 in) span- ner, remove primary driving gear nut 1. This nut has a left-hand thread. Turning it anticlockwise may cause damage. • remov...
Page 153
D.35 engine • remove dowel pins 8 and gasket 9. • after removing the generator rotor bolt, fit the special tool in the hub and remove generator rotor assembly 1 by rotating the spe- cial tool while holding the rotor with a 36 mm (1.417 in) spanner. Specific tool: 800096684 rotor extractor • remove k...
Page 154
D.36 engine • remove oil seal retainer 8 and oil pressure switch 9. Specific tool: 800096659 oil filter spanner • pull out gear shaft/arm 1 with washers 2. • remove gear preselector plate 3. • remove gear preselector stop 4 with the related spring and washer. • remove gear arm stop bolt 5. • remove ...
Page 155
D.37 engine • remove gear change fork shafts 4 and gear change forks 5. • remove gear preselector 6. • remove driving shaft assembly 7 and countershaft assembly 8. • remove the crankcase bolts. • separate the crankcase into two parts, left and right, using the specially designed tool. Specific tool:...
Page 156
D.38 engine • remove the oil jet from the left crankcase half. • remove o-ring 1, oil pump 2 and plate 3. Refer to page d-170 for details of how to inspect the oil pump. • remove reed valve 4. • remove piston cooling oil nozzles 5 from the left and right crank- case halves. • remove the oil seals us...
Page 157
D.39 engine replace the removed bearings with new ones. • remove bearing 7. Refer to pages d-163 to d-167 for directions on how to remove and install the crankshaft bearings. • remove the bearing setscrews. • remove bearings 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 using the special tools. Specific tools: 800096676: bea...
Page 158
D.40 engine • fit the bearing retainers. Apply a small quantity of specific product to the bearing setscrews and then tighten with the prescribed torque. Specific product: loc-tite 243 tightening torque: bearing setscrew 8 n.M (0,8 kg-m) (5.84 lb·ft) assembling the engine the engine is reassembled b...
Page 159
D.41 engine • fit new o-rings to the cooling oil nozzle of each piston. To prevent oil leakage, always use new o-rings. • fit oil seals 1 and 2 in the crankcase using the specially designed tools. • grease the oil seal lips. Specific tools: 800096873: bearing installer (for1) 800096657: bearing inst...
Page 160
D.42 engine • install gear change forks 5, 6 and 7, gear change fork shafts 8 and 9, and gear preselector 10. • fit thrust shim 1 to the crankshaft. * grooved side a of thrust shim 1 must face the crankshaft web side. * the thrust shim is selected according to the crankshaft thrust clear- ance (refe...
Page 161
D.43 engine • clean the mating surfaces of the left and right crankcase halves. • apply specific product to the mating surface of the left crankcase half (see page d-44). Specific product: rhodorseal 5552 the rhodorseal 5552 sealant is used as follows: * remove all traces of moisture, dust and other...
Page 162
D.44 engine • when fastening the left and right crankcase halves, tighten each bolt gradually to equalize the pressure. Tighten all fastening bolts with the specified torques. Tightening torques: crankcase bolts (m8) 22 n.M (2,2 kg-m) (16.06 lb·ft) (m6) 11 n.M (1,1 kg-m) (8.03 lb·ft) when assembling...
Page 163
Engine d.45 engine • fit a new o-ring in engine sprocket spacer 1. Use a new o-ring to prevent oil leakage. • fit engine sprocket spacer 1 to the driving shaft. * grooved side a of the engine sprocket spacer must face the crank- case side. * grease the lips of the oil seal and the o-ring. Specific p...
Page 164
D.46 engine • fit gear shaft/arm 7 and washer 8 as shown in the figure. • apply a small quantity of specific product to gear arm stop bolt 1 and then tighten with the specified torque. Specific product: loc-tite 270 tightening torque: gear arm stop bolt 23 n.M (2,3 kg-m) (16.79 lb·ft) • fit gear pre...
Page 165
D.47 engine • degrease the tapered portion of the generator rotor assembly and the crankshaft. Remove the oil and grease with a nonflammable solvent and then dry the surfaces completely. • fit dowel pins 1 and gasket 2. Use a new gasket to prevent oil leakage. • fit the gearbox cover. Fit the new se...
Page 166
D.48 engine • fit thrust washer 5 to the crankshaft. Bevelled side a of thrust washer 5 must face the crankcase side. • fully insert key 1 into its slot on the crankshaft. • fit generator rotor assembly 2 and driven starting gear 3 to the crankshaft. • apply specific product to rotor bolt 4 and then...
Page 167
D.49 engine • insert a bar of suitable size into the holes of the primary driving gears to align the teeth of the scissors gears. • fit timing chain 3 and no. 1 valve motion idler gear/sprocket 4. Align punched marks b on the no. 1 valve motion idler gear/sprocket and the primary driving gear to fac...
Page 168
D.50 engine • install neutral switch assembly 5 and cable guide 6 as shown in the figure. Apply a small quantity of specific product to the neutral switch screw and the cable guide screw. Specific product: loc-tite 243 • insert key 1 as shown in the figure. • fit no. 1 valve motion idler gear/sprock...
Page 169
D.51 engine • fit washer 3, pin 4, oil pump driven gear 5, and circlip 6 to the oil pump shaft. Projection b of oil pump driven gear 5 must face the crankcase side. • fit the thrust washer on the countershaft. Bevelled side c of the thrust washer must face the crankcase side. • install oil sump filt...
Page 170
D.52 engine when fitting the clutch spring support bolts, apply specific product and tighten with the specified torque. Specific product: loc-tite 270 tightening torque: clutch spring bolt 11n.M (1,1 kg-m) (8.03 lb·ft) • fit needle roller bearing 1 and collar 2 to the countershaft and lubricate them...
Page 171
D.53 engine • tighten clutch drum nut 5 with the specified torque using the spe- cially designed tool. Tightening torque: clutch drum nut 100 n·m (10,0 kg-m) (73 lb·ft) specific tool: 800096675 - clutch hub sleeve support • fit clutch driving cam 1 on clutch drum 2. Align “i” mark a on the clutch dr...
Page 172
D.54 engine driving plates a no. 1 driving plate (inside diameter): 101 mm (3.976 in) 9 pcs b no. 2 driving plate (inside diameter): 108 mm (4.252 in) 1 pcs driven plates two types of driven plates, no. 1 and no. 2, are used in the clutch system. The two plate types differ in thick- ness. A no. 1 dr...
Page 173
Engine d.55 engine • grease the oil seal rim on the clutch cover. Specific product: agip grease 30 • fit clutch push rod 1 in the countershaft. • fit clutch push rod 2, bearing 3 and thrust washer 4 to the countershaft. • place pressure plate 5 on the clutch drum. • while holding the generator rotor...
Page 174
D.56 engine • fit the clutch cover. • to avoid damaging the oil seal lip, cover the edge of the no. 1 valve motion idler gear shaft with a vinyl film or tape a before fitting the clutch cover. • to prevent damage to the oil seal lip, fit the clutch cover squarely. • remove vinyl film or tape a after...
Page 175
Engine d.57 engine • fit the sealing washer and the washer on impeller fastening bolt 1. Sealing washer metal side e and washer convex side f must face the head of the impeller fastening bolt. • fit impeller 2 and its fastening bolt 1 to the shaft. • tighten impeller fastening bolt 1 with the specif...
Page 176
D.58 engine • firmly tighten the clutch bell housing cover bolts, the water pump casing bolts, and the clutch cover bolts. • fit starting idler gear 1, spacer 2 and shaft 3. Apply engine oil and specific product to shaft 3. Specific product: molikote • fit bushings 4 into the crankcase and the gener...
Page 177
D.59 engine • fit the generator cover and firmly tighten its bolts. Fit the sealing washer on generator cover bolt a as shown in the figure. To prevent oil leakage, use a new sealing washer. • fit a new o-ring to the starter motor. To prevent oil leakage, use a new o-ring. • grease the o-ring. Speci...
Page 178
D.60 engine • the first element of the scraper ring to be inserted into the groove is spacer 1. After fitting the spacer, insert the two side rings 2. The spacer and the side rings do not have an upper or lower side and can be fitted either way. • position the end gaps of the three piston rings as s...
Page 179
D.61 engine • apply engine oil to the new o-rings. • install front and rear oil jets 1 as shown in the figure. To prevent oil leakage, use new oil rings. • apply a film of specific product to the mating surfaces of the left and right crankcase halves as shown in the figure. When replacing stud bolt ...
Page 180
D.62 engine • hold the piston rings in position and insert the pistons into the front and rear cylinders. When installing the cylinders, keep the timing chains taut. Make sure the timing chains are not caught between the driving sprocket and the crankcase when the crankcase is turned. • temporarily ...
Page 181
D.63 engine • place the rear cylinder head on the cylinder. When installing the cylinder head, keep the timing chain taut. • using a torque spanner, tighten the cylinder head bolts (m10) to the specified torque in two steps and following a sequential cross- wise pattern. Tightening torque: cylinder ...
Page 182
D.64 engine • place the front cylinder head on the cylinder. When installing the cylinder head, keep the timing chain taut. • using a torque spanner, tighten the cylinder head bolts (m10) to the specified torque in two steps and following a sequential cross- wise pattern. Tightening torque: cylinder...
Page 183
D.65 engine • pull up the timing chains and fit the timing chain stretchers in each cylinder head. 1 no. 1 (front) cylinder head 2 no. 2 (rear) cylinder head * when fitting a timing chain stretcher, insert the end of its support a into the guide cast in the cylinder. * when fitting the no. 1 (front)...
Page 186
D.68 engine • tighten the shaft of the no. 2 valve motion idler gear/sprocket with the specified torque. Tightening torque: no. 2 valve motion idler gear/sprocket shaft 40 nm (4,0 kg-m) (29.2 lb·ft) no. 1 (front) timing chain tension adjuster • fit the front timing chain tension adjuster by followin...
Page 187
Engine d.69 • fully compress timing chain tension adjuster rod 1 after releasing ratchet 2. • from this position, unscrew adjuster bolt 1 until adjuster rod 2 locks. The timing chain tension adjuster is now ready for installation. Unscrew adjuster bolt 3 while compressing the adjuster rod. • fit a n...
Page 188
D.70 engine • install the timing chain tension adjuster as shown in the figure and tighten the fastening bolts with the specified torque. Tightening torque: timing chain tension adjuster fastening bolt 10 n·m (1,0 kg-m) (7.3 lb·ft) • release the adjuster by screwing in bolt 1. A click may be heard w...
Page 189
D.71 engine no. 2 (rear) timing chain tension adjuster • fit the rear timing chain tension adjuster by following these steps: • remove the no. 2 (rear) timing chain tension adjuster. • fit a new gasket 1. To prevent oil leakage, use a new gasket. • fully compress the timing chain tension adjuster ro...
Page 191
Engine d.73 the camshafts are identified by letters and differ in shape. 1 for the no. 1 (front) exhaust camshaft 2 for the no. 1 (front) intake camshaft 3 for the no. 2 (rear) intake camshaft 4 for the no. 2 (rear) exhaust camshaft immediately before placing the camshafts in the cylinder head, ap- ...
Page 192
D.74 engine • install the intake and exhaust camshaft journal bearings. • fix the camshaft bearings evenly by tightening the bolts according to a sequential crosswise pattern. (equalize the pressure by shift- ing the spanner diagonally so as to fasten the shafts evenly.) * failure to tighten the cam...
Page 194
D.76 engine • install the intake and exhaust camshaft journal bearings. • fix the camshaft bearings evenly by tightening the bolts according to a sequential crosswise pattern. (equalize the pressure by shift- ing the spanner diagonally so as to fasten the shafts evenly.) * failure to tighten the cam...
Page 196
D.78 engine • pour engine oil into each of the front and rear cylinder head pock- ets. Be sure to check the tappet clearance (refer to pages b-7 to b-11.) • install camshaft position sensor 1 and tighten the fastening bolts with the specified torque. Tightening torque: camshaft position sensor faste...
Page 197
Engine d.79 engine • place the cylinder head covers on the cylinder heads. • fit a gasket to each cylinder head cover bolt. To prevent oil leakage, use new gaskets. • after applying engine oil to the gaskets, tighten the cylinder head cover bolts with the specified torque. Tightening torque: cylinde...
Page 198
D.80 engine • firmly tighten the cooling system union bolts. • install the thermostat casing with the coolant lines and firmly tighten the fastening screws. Turn the heads of the fastening screws to the left. • fit crankcase breather pipe 1. • fit the spark plugs on each cylinder head and tighten th...
Page 199: Camshaft/cylinder Head
D.81 engine camshaft/cylinder head.
Page 200
D.82 engine contents description of the valve gear system .................................................................................... D-83 removing the camshafts ............................................................................................................... D-88 checking and...
Page 201
D.83 engine description of the valve gear system the navigator 1000 valve gear system consists of the crankshaft, the primary driving gear, the no. 1 valve motion idler gear/sprocket, the no. 1 valve motion idler gear/sprocket shaft, the timing chains, the no. 2 valve motion idler gears/sprockets an...
Page 202
D.84 engine the two top dead centres, one on the compression stroke and the other on the exhaust stroke, can be identified by the position of the punched mark on the no. 1 valve motion idler gear/sprocket relative to the punched mark on the primary driving gear. They can also be distinguished by the...
Page 203
D.85 engine when reassembling the engine, position the no. 1 and no. 2 valve motion idler gears/sprockets at their top dead centres. Improper assembly - such as the positioning of the no. 2 valve motion idler gear/sprocket at the top dead centre of the compression stroke and the no. 1 valve motion i...
Page 204: Ve Timing Diagram
D.86 engine v a l ve timing diagram front front cylinder tdc of compression stroke.
Page 205: Ve Timing Chart
D.87 engine v a l ve timing chart front pow . Ex. In com in. Ex. Pow . Com. In. Position position position front cylinder front cylinder head rear cylinder rear cylinder head v a lve timing inspection hole primary driving gear and no. 1 valve motion idler gear/sprocket * refer to figure on page 3a-2...
Page 206: Removing The Camshafts
D.88 engine removing the camshafts no. 1 (front) camshafts to remove the no. 1 (front) camshafts, remove the following parts in the order given below. Refer to the pages indicated for details on how to perform each step. • the intake camshaft. • the exhaust camshaft (see page d-22) remove: • the rad...
Page 207
D.89 engine no. 2 (rear) camshafts to remove the no. 2 (rear) camshafts, remove the following parts in the order given below. Refer to the pages indicated for details on how to perform each step. • the intake camshaft. • the exhaust camshaft (see page d-25). Remove: • the saddle. • the spark plug (p...
Page 208: Head
D.90 engine camshafts if abnormal engine noise, vibration or lack of power output is no- ticed, all camshafts should be checked for signs of runout and wear of the cams and journals. Any of these conditions may occur if the camshafts have become worn or distorted beyond the service limit. The camsha...
Page 209
D.91 engine camshaft journal wear to determine whether a camshaft journal is worn beyond the service limit, measure the oil clearance with the camshaft in place. Measure plastigauge 1 in its widest portion to determine the oil clearance, which should be as follows: service limit camshaft journal oil...
Page 210
D.92 engine camshaft runout measure the runout with a comparator. Replace the camshaft if the runout exceeds the specified limit. Service limit camshaft runout (in. & ex.): 0,1 mm (0.0039 in) specific tools: comparator (1/100 mm, 10 mm) (0.039/3.937 in, 0.3937 in) magnetic stand 800096650: v-blocks ...
Page 211
D.93 engine cylinder head • remove the tappets and shims 1 either manually or using a mag- net. • utilizzando gli attrezzi speciali, comprimere le molle della valvola e rimuovere i due semiconi 2 dallo stelo della valvola. Specific tools: 800096664: valve spring compression tool 800096665: valve spr...
Page 212
D.94 engine • remove oil seals 1 and spring seats 2 do not reuse the oil seals. Cylinder head distortion decoke the combustion chambers. Check the gasketed surface of the cylinder head for distortion using a straightedge and a thickness gauge. Take measurements at the positions shown in the figure. ...
Page 213
D.95 engine valve stem deflection lift the valve about 10 mm (0.3937 in) over the valve seat. Position the comparator as shown in the figure and measure the valve stem deflection in the two directions, perpendicular to each other, x and y. If the deflection exceeds the specified limit (see below), d...
Page 214
D.96 engine • lubricate the hole in the cylinder head and the stem hole of each valve guide and then insert the guide into the hole using the valve guide installer and its attachment. Specific tools: 800096671 - valve guide remover/installer 800096672 - valve guide installer attachment failure to oi...
Page 215
D.97 engine the valve seating area must be inspected after each cut. Specific tools: 96768 - valve seat cutter (n-626) 800096667 - valve seat working guide (n-140-5.5) 800096666 - valve seat working set • insert the guide with a slight rotation. Seat the guide snugly. Fit the 45° cutter, the attachm...
Page 216
D.98 engine • clean and fit the cylinder head and valve components. Fill the intake and exhaust ports with petrol and check that there are no leaks. If any leaks are found, check for burrs or other factors that prevent the valve seat and the seating surface from sealing prop- erly. Handle petrol wit...
Page 217
D.99 engine no. 2 valve motion idler gear/sprocket thrust clearance install no. 2 valve motion idler gear/sprocket 1, its shaft 2, copper washer 3 and thrust washer 4 on each cylinder head as shown in the figure. Tighten shaft 2 with the specified torque. Using a thick- ness gauge, measure the thrus...
Page 218
D.100 engine cylinder head assembly • fit the valve spring seats. • oil all the oil seals and fit them using the valve guide installer. Specific tool: 800096671 - valve guide remover/installer never reuse used oil seals. • insert the valves after lubricating their stems completely and evenly with go...
Page 219
D.101 engine • fit the tappet biscuit and pad in their original positions. * apply engine oil to the tappet biscuit and pad before fitting them. * be sure to insert the tappet pad so that the surface stamped with a figure faces the tappet. Intake pipe • grease the o-ring when installing the intake p...
Page 220
D.102 engine installing the camshafts no. 1 (front) camshaft installation is obtained by following the disassembling procedure in reverse order. Refer to the pages indicated for details on how to perform each step. Fit: • the camshafts. • the dowel pins • the c-rings (see pages d-72 -73). • the cams...
Page 221
D.103 engine • the spark plug. • the radiator (see page h-8). No. 2 (rear) camshaft install the components listed below in the order indicated. When fitting the components, follow the fitting procedures described in the pages indicated. Fit: • the camshafts. • the dowel pins. • the c-rings (see page...
Page 222
D.104 engine • the generator cover plug. • the tappet timing inspection plug (see page d-79). • the cylinder head cover (see pages d-78 -79). • the spark plug..
Page 223: Cylinder/piston
D.105 engine cylinder/piston contents removing the cylinder and the piston .................................................................................. D-106 checking the cylinder and the piston .................................................................................. D-108 installing...
Page 224
D.106 engine no. 1 (front) cylinder and piston the components listed below must be removed in the order indi- cated before removing the no. 1 (front) cylinder and piston. Refer to the pages indicated for details on how to perform each step. Remove: • the cylinder head (see pages d-21 -23). • the tim...
Page 225
D.107 engine no. 2 (rear) cylinder and piston the components listed below must be removed in the order indi- cated before removing the no. 2 (rear) cylinder and piston. Refer to the pages indicated for details on how to perform each step. Remove: • the cylinder head (see page d-26). • the timing cha...
Page 226
D.108 engine checking the cylinder and the piston cylinder block distortion check the gasketed surface of the cylinder block for distortion using a straightedge and a thickness gauge. Take measurements at the positions shown in the figure. If the maximum reading at any posi- tion exceeds the specifi...
Page 227
D.109 engine piston/cylinder clearance after completing the previously described measurement, if the clear- ance between the piston and the cylinder exceeds the specified limit, replace both the cylinder and the piston. Service limit piston/cylinder clearance: 0,12 mm (0.0047 in) piston ring/piston ...
Page 228
D.110 engine piston ring free end gap and piston ring end gap before fitting the piston rings, measure the free end gap of each ring using a vernier caliper. Then fit the ring in the cylinder and measure the end gap of the ring using a thickness gauge. If the end gap is excessive, replace the ring. ...
Page 229
D.111 engine installing the piston and the cylinder install the piston rings in the following order: scraper, 2nd ring, 1st ring. The sections of the 1st and 2nd rings differ in shape. • be sure to fit the 1st ring so that its convex side faces upwards. • the 2nd ring is marked “rn” on one side. Whe...
Page 230
D.112 engine no. 1 (front) piston and cylinder installation is obtained by following the removing procedure in re- verse order. Refer to the pages indicated for details on how to perform each step. Fit: • the piston pin. • the piston. • the oil jet. • the dowel pins. • the gasket (see pages d-61, d-...
Page 231
D.113 engine no. 2 (rear) piston and cylinder installation is obtained by following the removing procedure in re- verse order. Refer to the pages indicated for details on how to perform each step. Fit: • the piston pin. • the piston. • the oil jet. • the dowel pins. • the gasket (see page d-59). • t...
Page 232: Clutch
D.114 engine contents removing the clutch ..................................................................................................................... D-115 removing the clutch throw-out ............................................................................................. D-116 chec...
Page 233
D.115 engine removing the clutch after draining the engine oil, remove the following components in the order indicated. Refer to the pages indicated for details on how to perform each step. Drain: • the engine oil. Remove: • the clutch bell housing cover (see page d-29). • the clutch springs. • the ...
Page 234
D.116 engine • the clutch drum. • the clutch driving cam. • the clutch driven cam (see pages d-30 and d-31). • the thrust washer. • the primary driven gear assembly (see page d-37). • the needle roller bearing. • the collar. • the thrust washer (see page d-32). Removing the clutch throw-out remove t...
Page 235
D.117 engine • the throw-out assembly (see page d-8.) • the clutch push rod (see page d-8.) checking the clutch and the throw- out clutch driving plates wipe the oil from the driving plates with a clean rag. Measure the thickness of the clutch driving plates using a vernier caliper. If any plate is ...
Page 236
D.118 engine measuring distortion clutch driven plates wipe the oil from the driven plates with a clean rag. Measure the distortion of the driven plates using a thickness gauge and a surface plate. Replace any driven plates that are distorted beyond the specified limit. Service limit driven plate di...
Page 237
D.119 engine installing the clutch to install the clutch, use the removing procedure in reverse order. Refer to the pages indicated for details on how to perform each step. Fit: • the thrust washer. • the collar. • the needle roller bearing (see page d-52). • the primary driven gear assembly. • the ...
Page 238
D.120 engine • the clutch plates. • the clutch push rod (see pages d-54 and d-55). • the clutch push rod. • the bearing. • the washer (see page d-55). • the pressure plate. • the clutch springs (see page d-55). • the clutch bell housing cover (see page d-56). Adjust the following according to specif...
Page 239
D.121 engine location of thicker (2.0 mm) driven plate.
Page 240
D.122 engine installing the clutch throw-out to fit the clutch throw-out, use the removing procedure in reverse order. Refer to the pages indicated for details on how to perform each step. Fit: • the clutch push rod (see page d-18). • the throw-out assembly. • the engine sprocket cover. • the gearch...
Page 241: Water Pump/clutch Cover
D.123 engine water pump/clutch cover contents removing the water pump and the clutch cover ............................................................. D-124 checking and servicing the water pump and the clutch cover ................................ D-125 installing the water pump and the clutch co...
Page 242
D.124 engine after draining the engine oil and the coolant, remove the parts listed below in the order indicated. • this operation must be carried out with the engine installed in the frame. Refer to the pages indicated for details on how to perform each step. Drain: • the engine oil (see page b-16....
Page 243
D.125 engine checking and servicing the water pump and the clutch cover checking the mechanical seal and the sealing washer before removing the water pump and draining the coolant, check for coolant leakages from the clutch cover drain hole. If coolant is leak- ing, remove the clutch cover and visua...
Page 244
D.126 engine • remove the mechanical seal using a tubular spanner or a similar tool. Replace the removed mechanical seal with a new one. If no coolant or oil leakage from the drain hole is found, there is no need to remove the mechanical seal and the oil seal. Installing the oil seal and the mechani...
Page 245
D.127 engine installing the water pump and the clutch cover installation is obtained by following the removing procedure in re- verse order. Refer to the pages indicated for details on how to perform each step. Fit: • the gasket. • the dowel pin (see page d-55). • clutch cover 4 (see pages d-55 and ...
Page 246
D.128 engine • the water pump casing (see pages d-57 and d-58). • the water hose. Adjust the following according to specifications: page * engine coolant .............................................. B-19 * engine oil ...................................................... B-16 mechanical sealing ri...
Page 247: Sprocket Shaft
D.129 engine contents primary driving gear/no. 1 valve motion idler gear/ sprocket shaft removing the primary driving gear and the no. 1 valve motion idler gear/sprocket shaft .................................................................. D-130 checking the primary driving gear/no. 1 valve motio...
Page 248
D.130 engine removing the primary driving gear and the no. 1 valve motion idler gear/ sprocket shaft the above items can be removed while supporting the engine as- sembly with a suitable jack. For further details, refer to the section on engine removal. Engine removal .............................. ...
Page 249
D.131 engine • the generator cover (see page d-28). • the no. 1 valve motion idler gear/sprocket. • the timing chain (see page d-33). • the primary driving gear (see page d-34). • the generator rotor (see pages d-34 and d-35). • the no. 1 valve motion idler gear/sprocket shaft. • the timing chain (s...
Page 250
D.132 engine checking the primary driving gear/no. 1 valve motion sprocket and the pri- mary driving gear/no. 1 valve motion idler gear/sprocket shaft check visually check the wear of the gear and sprocket teeth. If the teeth are worn, replace the gear and the sprocket with new parts. Checking and s...
Page 251
D.133 engine • carefully fit the circlip with the specially designed pliers. Specific tool: 800096765 - snap ring pliers * never reuse a removed circlip. After removing the circlip from the gear, discard it and fit a new circlip. * when fitting a new circlip, take care not to part its ends more than...
Page 252
D.134 engine starting system/generator/crankshaft position sensor contents removing the starting torque limiter, the generator and the crankshaft position sensor ................................................................................... D-135 checking and servicing the starting torque limit...
Page 253
D.135 engine removing the starting torque limiter, the generator and the crankshaft position sensor the following components must be removed in the order indicated so that the starter torque limiter, the generator and the crankshaft position sensor can be removed. • this operation can be carried out...
Page 254
D.136 engine • the dowel pin. • the gasket (see page d-28). • the starting torque limiter (see page d-28). • the starting idler gear. • the shaft. • the spacer. • the bushings (see page d-28). • the generator rotor assembly (see pages d-34 and d-35). • the starting driven gear (see page d-35)..
Page 255
D.137 engine checking and servicing the starting torque limiter, the generator and the crankshaft position sensor checking the starting torque limiter do not attempt to disassemble the starting torque limiter. The starting torque limiter is only available as an assembly. • check the slipping torque ...
Page 256
D.138 engine checking the generator stator and the crank- shaft position sensor refer to section g. Servicing the generator stator and the crank- shaft position sensor when replacing the generator stator or the crankshaft position sen- sor, apply specific product to generator stator fastening bolts ...
Page 257
D.139 engine • when fitting one-way coupling 2 into guide 1, position one-way coupling flanged side a so that it faces starter coupling housing 3. • when fitting starter coupling housing 3 on the generator rotor, align hole b in the starter coupling housing with projection c on the generator rotor. ...
Page 258
D.140 engine installing the starting torque limiter, the generator and the crankshaft position sensor installation is obtained by following the removing procedure in re- verse order. Refer to the pages indicated for details on how to perform each step. Fit: • the starting driven gear. • the generato...
Page 259
D.141 engine • the gasket. • the dowel pin (see page d-58). • the generator cover (see page d-59). • the clutch throw-out assembly (see pages d-16 and d-17). • the engine sprocket cover. • the silencer protection by tightening the two fixings. • reassemble the left hand footrest and gearchange lever...
Page 260
D.142 engine removing the starter motor after previously removing the sump guard as described in page xx, disconnect the starter motor lead and remove the starter motor by unscrewing the two mounting bolts. • detach the oil cooler from its supports and push it downwards. Checking and servicing the s...
Page 261: Gear Preselector
D.143 engine gear preselector contents removing the gear preselector assembly ......................................................................... D-144 checking and servicing the gear preselector assembly ............................................ D-146 installing the gear preselector assemb...
Page 262
D.144 engine after draining the oil from the engine, remove the components listed below in the order indicated. Refer to the pages indicated for details on how to perform each step. Remove: • the engine pinion cover and the silencer protection (see page d- 7 and d-8). • the left hand footrest and ge...
Page 263
D.145 engine • remove the gear covering by unscrewing the five relative fixings (see page d-35.) • the dowel pins. • the gasket (see page d-35). • the gear shaft/arm (see page d-36). • the gear preselector plate. • the gear preselector stop. • the gear arm stop bolt (see page d-36)..
Page 264
D.146 engine checking and servicing the gear preselector assembly removing the gear shaft/arm • remove the following parts from gear shaft/arm assembly 1: 2 washer 6 plate return spring 3 circlip 7 washer 4 gear shaft return spring 8 circlip 5 gear preselector plate 9 washer specific tool: 800096765...
Page 265
D.147 engine checking the oil seal check if the gear shaft oil seal is damaged or if its lip is worn. If any defects are found, replace the oil seal with a new one. Replacing the oil seal • remove the gear shaft oil seal from the gearbox cover. • fit a new oil seal. Always replace removed oil seals ...
Page 266
D.148 engine installing the gear preselector assembly installation is obtained by following the removing procedure in reverse order. Refer to the pages indicated for details on how to perform each step. Fit: • the gear arm stop bolt. • the gear preselector stop. • the gear preselector plate (see pag...
Page 267
D.149 engine • the engine sprocket (see page d-16.) • the speed sensor rotor (see page d-16) • the clutch throw-out assembly (see page d-17). • the engine sprocket cover. • the left hand footrest and gearchange lever assembly (see page d-18).
Page 268
D.150 engine adjust the following according to specifications: page * engine oil .............................................................. B-13 * clutch lever play .................................................... B-15 * drive chain slack ................................................... B...
Page 269
D.151 engine crankcase/gearbox/crankshaft/connecting rod.
Page 270
D.152 engine removing the transmission, the crankshaft and the connecting rod .................. D-153 checking and servicing the transmission ........................................................................... D-153 checking the connecting rod and the crankshaft ...............................
Page 271
D.153 engine removing the transmission, the crank- shaft and the connecting rod the crankcase must be separated to allow the transmission, the crankshaft and the connecting rod to be serviced. Access to these engine parts is obtained by removing and disassembling the en- gine. Refer to the sections ...
Page 272
D.154 engine standard gear change fork thickness: 4,8-4,9 mm (0.1906-0.1929 in) removal countershaft • remove o-ring 1, 2nd driving gear 2, and 6th driving gear 3. Replace the removed o-ring with a new one. • remove 6th driving gear bushing 4, washer 5, and 3rd/4th driving gears 6. • remove the circ...
Page 273
D.155 engine driving shaft • remove 1st driven gear 1 and washer 2. • remove 1st driven gear bushing 3, washer 4, and 5th driven shaft 5. • remove the circlip using the specially designed tool. Specific tool: 800096765 - snap ring pliers • remove 4th driven gear 6 and its bushing 7. • remove washer ...
Page 274
D.156 engine • remove 3rd driven gear bushing 1. • remove 6th driven gear 2 after removing the circlip. Specific tool: 800096765 - snap ring pliers • remove the circlip using the specially designed tool. Specific tool: 800096765 - snap ring pliers • remove 2nd drive gear 3, its bushing 4, and washer...
Page 275
D.157 engine * never reuse a removed circlip. After removing the circlip from the shaft, discard it and fit a new circlip. * when fitting a new circlip, take care not to part its ends more than is required to fit it on the shaft. * after fitting a circlip, always check that it is fully and se- curel...
Page 276
D.158 engine 1st driven gear 5th driven gear 4th driven gear 3rd driven gear 6th driven gear 2nd driven gear driving shaft 1st driven gear 5th driven gear 4th driven gear 3rd driven gear 6th driven gear 2nd driven gear driving shaft countershaft/1st driving gear 5th driving gear 3rd/4th driving gear...
Page 277
D.159 engine.
Page 278
D.160 engine checking the connecting rod and the crankshaft connecting rod small end i.D. Measure the small end inside diameter with a bore gauge. Specific tools: comparator (1/1000 mm, 1 mm, 0.00004-0.03937 in) bore gauge (18-35 mm, 0.708-1.389 in) service limit small end i.D.: 22,040 mm (0.8677 in...
Page 279
D.161 engine selecting the connecting rod-crankpin bearings • position some plastigauge axially on the crankpin, avoiding the oil hole, in the top dead centre or low dead centre position as shown in the figure. • tighten the bearing cap bolts in two steps to the prescribed torque. When fitting the b...
Page 280
D.162 engine connecting rod i.D. Specification code b i.D. Specification 1 48.000-48.008 mm (1.8897-1.8904 in) 2 48.008-48.016 mm (1.8901-1.8904 in) connecting rod o.D. Specification code c o.D. Specification 1 44.992-45.000 mm (1.7713-1.7716 in) 2 44.984-44.992 mm (1.7710-1.7713 in) 3 44.976-47.984...
Page 281
D.163 engine • apply engine oil and specific product to the crankpin and bearing surface. Specific product: molikote • when fitting the connecting rods to the crankshaft, ensure that connecting rod inside diameter codes a face the cylinder intake valves and that oil holes b face inwards. • tighten t...
Page 282
D.164 engine selecting the crankshaft bearings select the specified bearings by referring to crankcase hole i.D. Code. The crankcase hole i.D. Codes a, “a”, “b” or “c”, are stamped on the inside of each crankcase half. Bearing selection table a bearing thickness colour (part no.) thickness green 122...
Page 283
D.165 engine • gradually remove the bearing using the special tool and a hand press. Removed bearings must be replaced with new ones. We recommend using a hand press to remove the crankshaft bear- ings. However, the crankshaft bearings can also be removed with the following special tools. Special to...
Page 284
D.166 engine before fitting the bearing, slightly shave the sharp edge in- side the bevel with an oilstone and then wash the crank- case hole with engine oil. • insert the bearings installed in the special tool into the crankcase half as shown in the figure. • ensure that bearing projection a faces ...
Page 285
D.167 engine we recommend using a hand press to remove the crankshaft bear- ings. However, the crankshaft bearings can also be removed with the following special tools. Special tools: 800096678 - bearing installer set 800096677 - final drive bearing separating/assembling tool • after installing the ...
Page 286
D.168 engine • using a thickness meter, measure the thrust clearance at some points between the crankcase and the thrust washer. Standard crankshaft thrust clearance: 0,050-0,100 mm (0.00197-0.00394 in) specific tool: thickness gauge if the thrust clearance exceeds the specified range, adjust it by ...
Page 287: Engine Lubrication System
D.169 engine engine lubrication system contents oil pump ............................................................................................................................................... D-170 oil sump filter/oil pressure regulator .........................................................
Page 288
D.170 engine oil pump removal to service the oil pump one must first separate the crankcase. It is also necessary to remove and disassemble the engine. For fur- ther information, refer to the sections on engine removal and disas- sembly. * engine removal ................... Refer to page d-4. * engi...
Page 289
D.171 engine assembly and installation wash the oil pump with clean engine oil before reassembly. • insert the rotor shaft into the inner rotor. Align driving pin 1 with slot a in the inner rotor. • install the outer and inner rotors in the oil pump body. Punched mark b on the outer rotor must face ...
Page 290
D.172 engine oil sump filter/oil pressure regulator removal after draining the engine oil and the coolant, remove the compo- nents listed below in the order indicated refer to the pages indicated for details on how to perform each step. Drain: • the engine oil (see page b-16.) • the engine coolant (...
Page 291
D.173 engine • the oil sump filter. • the oil pressure regulator. Checking the oil pressure regulator check the operation of the oil pressure regulator by pushing the piston with a suitable bar. If the piston does not work, replace the oil pressure regulator with a new one. Cleaning the oil sump fil...
Page 292
D.174 engine installing the oil sump filter installation is obtained by following the removing procedure in re- verse order. Refer to the pages indicated for details on how to perform each step. Fit: • the oil pressure regulator (see page d-51). • the oil sump filter (see page d-51). • the gasket. •...
Page 293
D.175 engine • the impeller (see page d-56). • the impeller fastening bolt (see page d-57). • the dowel pin. • the water pump casing (see pages d-57 and d-58). • the water hose. Adjust the following according to specifications: page * engine coolant .....................................................
Page 294
D.176 engine checking the oil pressure switch refer to section g. Checking the oil cooler pipes check if the oil cooler pipes show any signs of damage or leakage. If any defects are found, replace the oil cooler pipes with new ones. Checking and cleaning the oil cooler using a compressed air jet, re...
Page 295
D.177 engine oil filter refer to page b-17. Oil pressure refer to page b-28. Piston cooling oil jet/oil nozzle removal the oil jet (for the transmission) can be removed after draining the oil from the engine. The piston cooling oil nozzles and the oil jets (for each cylinder head) can be removed aft...
Page 296
D.178 engine engine lubrication chart no. 2 (rear) cylinder no. 1 (front) cylinder ex. Camshaft journals and cams in. Camshaft journals and cams in. Camshaft journals and cams ex. Camshaft journals and cams tappets tappets timing idler gear bushing timing idler gear bushing timing chain and sprocket...
Page 297
D.179 engine engine lubrication system.
Page 298
D.180 engine.
Page 299
E.1 suspensions and wheels e section.
Page 300
E.2 suspensions and wheels front wheel ............................................................................ E-3 front suspension .................................................................... E-6 rear wheel ............................................................................. E...
Page 301: Front Wheel
E.3 suspensions and wheels front wheel light alloy wheel rim with traditional spokes .......................................................... 3.00” x 18” six spoke alloy wheel rim ....................................................................................... 3.00” x 18” tubeless tyre dime...
Page 302
E.4 suspensions and wheels the removed bearings must be substituted. When re-assembling the new ensure that the bearing seat is clean and free of grooves and scratches. Lubricate the seat then hammer the bearing into place utilising an appropriate metal tube that is the same diameter as the external...
Page 303
E.5 suspensions and wheels bent wheel spindle check the distortion of the axis of the wheel spindle using “v” supports and a comparator. Maximum axis distortion .............................................. ≤ 0,25 [mm] wheel assembly replace the wheel, the wheel spindle and spacer on the right hand...
Page 304: Front Suspension
E.6 suspensions and wheels front suspension the front suspension consists of conventional advanced pivot telescopic hydraulic forks. Fork leg diameter ................................................................................................... Ø 43 [mm] front wheel travel .......................
Page 305
Suspensions and wheels e.7 suspensions and wheels • unscrew the four mudguard fixing screws 1. Remove the mudguard. • slacken the two fixing clamp screws 2 that fix the fork tubes to the steering head. • slacken the four fixing clamp screws 3 at the base of the steering. As a preventive measure, it ...
Page 306
E.8 suspensions and wheels • empty the used oil from the tube. Slide out the support spacer, moving the tube around so that it is removed more easily. Dispose of the oil in the correct way. • remove the screw 1 placed at the base of each stem and slide out the cartridge 2. During this operation, pro...
Page 307
E.9 suspensions and wheels • to substitute fork oil seals, proceed as follows: it is advisable to protect the edge of the sliding section with a special ring cap 1, when extracting the sealing ring. Using a wide screwdriver, exert pressure under the sealing ring and at the same time, rotate the slid...
Page 308
E.10 suspensions and wheels • assemble the bush onto the stem. • insert the stem inside the sheath. • using the special tool, assemble in the following sequence, the bush, spacer and the oil seal as shown in the figure. • assemble the stop ring and the dust seal. • insert the assembled parts into th...
Page 309
E.11 suspensions and wheels * always keep the oil level above the upper extremity of the cartridge to avoid the possibility of air entering into the cartridge during this operation. * make sure that all air is bled from the system. • keep the fork in a vertical position and regulate the oil level to...
Page 310
E.12 suspensions and wheels fork assembly – reassembly • proceed with the reassembly of the fork assembly in the reverse order of removal. • position the fork tubes to 33.5 mm, as indicated in the figure. • tighten the four screws at the base of the steering and the two screws at the steering head t...
Page 311
E.13 suspensions and wheels steering removal carry out the following procedure to remove the steering assembly from the frame: • remove the fuel tank as described in page b-4. • remove the front wheel, the mudguard and the fork legs as previously described. Handlebar removal • to remove the handleba...
Page 312
E.14 suspensions and wheels 7 8 9 10 • if the handlebars have to be substituted, it will be necessary to remove the left hand and right hand counterweights by unscrewing the two screws 7. • to reassemble the handlebar assembly, follow the instructions for removal in reverse order. If the handlebars ...
Page 313
E.15 suspensions and wheels • remove the screw from the steering spindle 1. • slacken the screws 2 on the steering head fixing to the fork tubes. • remove the connector of the ignition switch assembly. Lift up the steering head and remove it. • remove the screw of the front brake tubing support. • u...
Page 314
E.16 suspensions and wheels • accurately clean the various seats, the external part of the steering tube and the internal part of the steering head housing. • assemble the new bearing on the steering tube by using a tube of the correct diameter placed against the external ring of the bearing. See th...
Page 315: Rear Wheel
E.17 suspensions and wheels rear wheel light alloy wheel rim with traditional spokes (with flexible joints) ............................. 4.25”x17” six spoke alloy wheel rim (with flexible joints) ......................................................... 4.25”x17” tubeless tyre dimensions .............
Page 316
E.18 suspensions and wheels rear wheel overhaul proceed as follows for the wheel bearing and flange substitution, the wheel rim check and the wheel spindle for deformation check. • check the bearings and the flexible joints for wear. If necessary, substitute them. When reassembling the rear wheel, i...
Page 317
E.19 suspensions and wheels substitution of the chain • open the chain using the appropriate tool on the chain removal link that can be seen from the inside of the fork. It has two rollers closed in a different way from the other links. See figure. To reassemble, carry out the phases of assembly in ...
Page 318: Rear Suspension
E.20 suspensions and wheels rear shock absorber removal if the rear shock absorber is leaking liquid or damaged, substitute it as follows: • remove the under seat compartment, the right and left hand side covers situated under the seat as described in the maintenance chapter. • place a support under...
Page 319
E.21 suspensions and wheels pre-load spring adjustment after reinstalling the rear shock absorber, adjust the length as indicated in the figure: • slacken the upper ring nut 1. • screw or unscrew the ring nut 2 until the standard length is reached. Standard length: 180 [mm]. The shock absorber conta...
Page 320
E.22 suspensions and wheels • remove the oil seals. Using a drift of the correct diameter, knock out the roller bearing from its seat, exerting pressure on the external diameter of the bearing. Carry out the substitution of the bearings and reassemble in the reverse order of removal. Check the condi...
Page 321
E.23 suspensions and wheels reassembly - compensator assembly • reassemble the compensator assembly and the connection rod in the reverse order of removal. Tighten the nuts to the specified torque. Torque pressure-connection rod/frame39.2/44.1 n·m (4.0/4.5 kg·m) torque pressure-compensator/frame 39....
Page 322
E.24 suspensions and wheels • check the various components on the fork (bearings, oil seals, chain guide and the fork itself). If excessive play is found between the bush 1 and the relative bearings 2 or the fork axis 3 and the relative bushes, substitute them. First, remove the oil seals and then t...
Page 323: Frame
E.25 suspensions and wheels frame rectangular and square section tube framework in highly resistant steel. Frame substitution if it is necessary to substitute or realign the frame, all components must be removed. Follow the procedures for removal of the various components as described in the various...
Page 324
F.1 brakes f section.
Page 325
F.2 brakes brakes .................................................................................... F-3 brake discs ............................................................................. F-4 brake pad wear check ............................................................ F-4 brake fluid s...
Page 326
F.3 brakes front brake type ....................................................... Fixed twin discs Ø 296 mm. Double piston pincers. Rear brake type .......................................................................................... Fixed single disc Ø 240 mm..
Page 327: Brake Pad Wear Check
F.4 brakes brake pad wear check check the brake pads for wear every 6000 km. The thickness must not be less than the wear check grooves cut into the sur- face of the pad and must not be absolutely less than 1.5 mm. Disc brake checking the disc is important. It must be perfectly clean without rust, o...
Page 328
F.5 brakes to check the pads, the following components must be removed: front brake: • remove the blocking screw 1; • unscrew the plug underneath; • extract the pad. Rear brake: • remove the two screws of the spray guard 2 and remove it; • remove the rear brake pincer from its attachment by unscrewi...
Page 329: Brake Fluid Substitution
F.6 brakes brake fluid substitution • place the machine on a level surface and straighten the handle- bars. • remove the cap of the brake fluid chamber and the diaphragm by removing the cap stop 1. • suck out as much of the old liquid as possible. • remove the rubber cap 2 on the air bleed valve nip...
Page 330: Ing System
F.7 brakes bleeding the air from the brak- ing system the air that is trapped in the braking system acts as a cushion, absorbing the greater part of the pressure exerted by the brake pump. The performance of the brake pincer is therefore compro- mised. The presence of air in the system is indicated ...
Page 331
F.8 brakes front brake pincer assembly removal if there are signs of leakage or traces of oil on the pincer body, it must be substituted. • drain the brake fluid as previously described and illustrated. • remove the brake tube from the pincer by unscrewing the joint bolt 1. Collect the brake fluid t...
Page 332: Rear Brake Pincer Removal
F.9 brakes rear brake pincer removal • remove the spray guard fixing screws. Never use brake fluid left over from a previous change of fluid or brake fluid that has been stored for a long period of time. If the brake system leaks fluid, riding security is compro- mised. Leaking fluid can also damage...
Page 333: Moval
F.10 brakes front brake pump assembly re- moval • drain the brake fluid as described in page f-6. • disconnect the front brake switch leads. • place a cloth underneath the brake pump joint bolt to collect the last drops of fluid left in the system. Remove the joint bolt 1 and disconnect the brake tu...
Page 334
F.11 brakes brake pump reassembly reassemble the brake pump in the reverse order of removal. • when reassembling the brake switch, align the projection of the switch with the hole of the pump. • when reassembling the brake pump onto the handlebars, tighten the upper fixing bolt first. Torque pressur...
Page 335: Rear Brake Pump Removal
F.12 brakes rear brake pump removal • drain the brake fluid from the rear brake system as described in page b-7. • remove the right hand passenger footrest by unscrewing the two screws 1 as shown in the figure. • remove the screws 3 and the relative nut. • remove the two screws 5 indicated in the fi...
Page 336
F.13 brakes brake pump reassembly install the brake pump assembly in the reverse order of removal. Pay attention to the following points: specified product: agip brake 4 brake fluid. • tighten each bolt to the specified torque. Torque pressure: brake tube joint bolt: 23 n.M (2.3 kg-m) brake pump mou...
Page 337
F.14 brakes.
Page 338
G.1 electrical equipment + - g section.
Page 339
G.2 electrical equipment + - precautionary maintenance advice ........................................ G-5 battery .................................................................................... G-6 charging system .................................................................... G-7 starter...
Page 340
G.3 electrical equipment + -.
Page 341
G.4 electrical equipment + - electrical wiring system diagram: 1. Injection cpu 2. Atmospheric pressure sensor 3. Air intake air pressure sensor 4. Oil pressure 5. Leaning angle sensor 6. Air intake air temperature sensor 7. Fuel probe 8. Butterfly sensor 9. Vehicle security 10. Rear stop switch 11....
Page 342
G.5 electrical equipment + - precautionary maintenance advice connectors • when connecting a connector, make sure that a click is heard. • check to see if the connector is dirty, corroded or if its cover is broken. Connectors • block connectors – release the block before disconnecting it and push it...
Page 343: Battery
G.6 electrical equipment + - battery - the battery is sealed and does not need any maintenance whatsoever. Bear in mind that the battery electro- lyte contains sulphuric acid. Should there be a leakage of acid from the battery, avoid contact with the eyes, skin and clothing. If the acid should come ...
Page 344: Charging System
G.7 electrical equipment + - charging system description the charging circuit of the system is illustrated in the figure and is composed of an ac generator, a rectifier and a battery. The ac alternating current generated by the generator is transformed into cc continuous current by the rectifier and...
Page 345
G.8 electrical equipment + - when the engine rpm increase, the voltage generated by the ac generator also increases. The voltage between the battery terminals also increases in proportion. When it reaches the regulated voltage of the ci (integrated circuit) and the ci is then in an “on” position, a ...
Page 346
G.9 electrical equipment + - diagnostics the battery discharges rapidly check the accessories that consume too much energy. Not installed check the battery current leakage. (see page g-10) there are no leakages check the voltage charge between the terminals of the battery. (see page g-10) incorrect ...
Page 347
G.10 electrical equipment + - check battery current leakage test • remove the seat and the under seat compartment. • turn the ignition switch to the “off” position. • disconnect the negative cable - of the battery. • connect a multi-tester between the - negative terminal and the – negative cable of ...
Page 348
G.11 electrical equipment + - generator winding resistance test • remove the left side support cover. • disconnect the coupling from the generator. Measure the resistance between the three leads of connector 1. Check that the stator nucleus is isolated. If the resistance does not conform to the spec...
Page 349
G.12 electrical equipment + - starter system and side stand/ignition security system starter system description the starter system is represented by the diagram below. It is comprised of a starter motor, clutch lever position switch, starter relay, starter button, engine kill button, right hand comm...
Page 350
G.13 electrical equipment + - side stand/ignition security system description the side stand/ignition security system avoids the switching on of the engine whilst the side stand is in the lowered position. The circuit consists of a relay, warning light, diode and switches. It controls the activation...
Page 351
G.14 electrical equipment + - diagnostics the starter motor does not turn. With the gears in neutral, turn the ig- nition switch to the “on” position with the engine kill switch on “run”. Listen for the click of the starter relay when the starter button is pressed. Pull in the clutch lever when the ...
Page 352
G.15 electrical equipment + - starter motor removal and disassem- bly • disconnect the starter motor lead. • remove the starter motor. • disassemble the starter motor as indicated in the figure. Starter motor check brushes check the brushes for signs of abnormal wear, cracks or if the brush attachme...
Page 353
G.16 electrical equipment + - commutator check to see if the connector is discoloured, abnormally worn or if the height a is insufficient. Substitute the rotor if the commutator is abnormally worn. If the sur- face is discoloured, brighten it with emery paper and clean it with a dry cloth. If the in...
Page 354
G.17 electrical equipment + - • apply a small quantity of loctite 243 to the bolts of the starter motor housing. Starter relay check • disconnect the – negative cable of the battery 1. Apply 12 volts to the terminals a and b and check the continuity. Circuit tester dial indication: continuity test (...
Page 355
G.18 electrical equipment + - • check to see if the winding of the relay is open or to earth. Check the resistance. The winding is in good condition if the resistance is as indicated. Starter relay resistance standard: 3-6 Ω testing the parts of the side stand/ig- nition security system if the secur...
Page 356
G.19 electrical equipment + - gearchange position switch the lead connector of the gearchange position switch is situated underneath the right hand cover of the machine. • disconnect the lead of the gearchange position switch and check the continuity between the blue lead and earth with gears in neu...
Page 357
G.20 electrical equipment + - injection relay and fuel pump relay the injection relay and the fuel pump relay are situated in the com- partment underneath the ecm cpu. • remove the injection relay or the fuel pump relay. The injection relay and the fuel pump relay are the same but can be distinguish...
Page 358: Ignition System
G.21 electrical equipment + - ignition system description the ecm cpu controls the ignition system. It is a normal transistorised digital ignition system that determines precise ignition timing according to the rpm of the engine, the gearchange position and the throttle position. The system consists...
Page 359
G.22 electrical equipment + - the ignition interruption circuit is incorporated in the ecm cpu to avoid over-revving the engine. When the engine reaches 10,200 rpm, this circuit cuts out the primary current of the ignition to both spark plugs. The engine could function without load at more than 10,2...
Page 360
G.23 electrical equipment + - diagnostics worn or non-firing spark plugs check to see if the connectors of the ignition system are connected cor- rectly. Correct check the battery voltage between the incoming lead (b/r and b) on the ecm cpu with ignition switch turned to the “on” position. Correct t...
Page 361
G.24 electrical equipment + - test peak voltage of the primary winding of the igni- tion coil • remove the insulated covers of the two spark plugs as described in pages b-7 and b-8. • connect two new spark plugs to the insulated covers and then connect them to earth. Check that the connectors and th...
Page 362
G.25 electrical equipment + - test the peak voltage of the n° 2 ignition coil primary winding follow- ing the same procedure used for the n° 1 ignition coil. N° 2 ignition coil: gr/bk terminal – earth (probe +) (probe -) do not disconnect the lead of the ignition coil primary winding. — circuit test...
Page 363
G.26 electrical equipment + - ignition coil resistance primary winding: 3-5 Ω (pole (+) -(pole (+) secondary winding: 20-28 k Ω (spark plug cover – pole +) crankshaft position sensor (multi-tester check) • remove the seat. • remove the under seat compartment tray. • disconnect the connector 1 from t...
Page 364
G.27 electrical equipment + - • remove the right hand frame cover • disconnect the lead coupling of the crankshaft position sensor 1 and connect the multi-tester with the peak voltage adaptor. Green/blue (+ probe) – violet/blue (- probe) • measure the peak voltage of the crankshaft position sensor u...
Page 365: Instruments
G.28 electrical equipment + - ca gi va instruments removal • remove the nose fairing and the instrument panel as described in chapter b. • raise up the instrument panel, freeing it from the anti-vibration mountings. • disconnect the lead coupling. When connecting or disconnecting the instrument pane...
Page 366
G.29 electrical equipment + - check using a circuit tester, check the continuity between the indicated terminals in the following diagram. If the measurement of the conti- nuity is not correct, remove and check the bulb. If the bulb is blown, replace with a new bulb and recheck the conti- nuity. If ...
Page 367
G.30 electrical equipment + - engine coolant temperature sensor and indica- tor check the lcd 1 (liquid crystal display) and led 2 (light emission di- ode) in the revcounter dial supply the information about the engine coolant temperature. The checking procedure for this system is de- scribed as fol...
Page 368
G.31 electrical equipment + - the following table indicates the relation of resistance between the led and the lcd. Resistance led lcd off “– – –” on approx. 0,811 k Ω off “50”°c on approx. 0,088 k Ω on “130”°c flashes with jumper lead on “hi” flashes if one or all of the indications are abnormal, s...
Page 369
G.32 electrical equipment + - speedometer check if the speedometer, kilometre counter or the partial kilometre coun- ter do not function in the correct way, check the speedometer sen- sor and the coupling connections. If the sensor and the connections are ok, substitute the speedom- eter. Speedomete...
Page 370: Lights
G.33 electrical equipment + - lights headlight halogen lamp substitution remove the instrument assembly from its rubber supports. • remove the nose fairing and the windshield (see chapter b) by unscrewing the six fixing screws. • remove the protective rubber cover 1 of the halogen lamp. • remove the...
Page 371
G.34 electrical equipment + - instrument panel bulb substitution to gain access to the various warning light bulbs and the bulbs that illuminate the instruments, operate as follows: • remove the windshield and the nose fairing by unscrewing the six fixing screws. • extract the instrument panel from ...
Page 372
G.35 electrical equipment + - headlight beam adjustment periodically check the headlight beam for adjustment. Carry out the adjustment as follows: • place the machine 10 metres from a vertical wall. • ensure that the ground is level and that the headlight beam axis is perpendicular to the wall. • th...
Page 373: Starter Relay
G.36 electrical equipment + - injection relay the lateral injection relay is situated underneath the ecm cpu. Fuel pump relay the fuel pump relay is situated underneath the ecm cpu. Starter relay the starter relay is situated underneath the rear cover of the parcel carrier. Direction indicator relay...
Page 374: Switches
G.37 electrical equipment + - o/w y/g • press o y g/r r on off lock o/bi gr o/r y/w off • on lg lbl b l press r y/w w y hi lo o/r y • press o/b o/w off run b/bl b/r off on b/bi b/w • press b b off on b/y b/y off on on (engine off) off (engine on) switches check the continuity of each switch using a ...
Page 375
G.38 electrical equipment + -.
Page 376
H.1 engine cooling h section.
Page 377
H.2 engine cooling cooling system ....................................................................... H-3 engine coolant ....................................................................... H-5 radiator and engine coolant tubes ........................................ H-6 cooling fan ...........
Page 378: Cooling System
H.3 engine cooling cooling system description the engine is cooled by an engine coolant that is pumped by force around the cooling system. The engine coolant passes through the water jackets that are present in the cylinders, the cylinder heads and the radiator. The type of pump used to pump the eng...
Page 379
H.4 engine cooling construction part n·m kg-m a 6 0,6 b 8 0,8 c 6 0,6 d 18 1,8 1. Cooling fan 2. Thermostat housing 3. Radiator cap 4. Engine coolant tank 5. Thermostat 6. Radiator 7. Water pump a. Cooling fan mounting bolt b. Cooling fan thermal switch c. Radiator mounting bolt d. Engine coolant te...
Page 380: Engine Coolant
H.5 engine cooling engine coolant the cooling circuit is filled with a 50/50 mixture of distilled water and ethyl-glycol antifreeze in the factory. This 50/50 mixture supplies an optimum protection against corrosion and the temperature. It also protects the system against freezing to –31°c. If the m...
Page 381: Tubes
H.6 engine cooling engine coolant - radiator and tubes removal • drain the engine coolant as described in chapter b. • remove the radiator following the procedure outlined in pages c- 54 and c-55. * do not open the cap of the radiator when the engine is hot. Boiling liquid or vapours can cause serio...
Page 382
H.7 engine cooling radiator cap check check the release pressure of the radiator cap utilising the appropri- ate tester as follows: • apply the cap to the tester as indicated and slowly create a pres- sure by activating the tester. Make sure to interrupt the pressure at 110 ±15 kpa (1.1 ±0.15 kg/cm ...
Page 383
H.8 engine cooling radiator check and cleaning dirt and foreign bodies embedded in the radiator must be removed. Compressed air is advisable for this type of cleaning. Bent or notched fins can be straightened with a little screwdriver. If it is necessary to substitute the radiator, release it from t...
Page 384: Cooling Fan
H.9 engine cooling cooling fan removal • remove the radiator. • remove the cooling fan by unscrewing the three screws indicated in the figure. Check • remove the coupling of the cooling fan lead. Check the charging current of the fan motor with an ampmeter as shown in the figure. A voltmeter is used...
Page 385: Cooling Fan Thermal Switch
H.10 engine cooling cooling fan thermal switch the cooling fan, positioned behind the radiator, is fixed to the radiator by three bolts. A thermal switch automatically controls the fan motor. This switch remains open when the temperature of the engine coolant is low. It closes when the temperature o...
Page 386
H.11 engine cooling test as shown in the figure, check that the thermal switch enters into the closing phase on reaching the specified temperature of 105°c. Connect the thermal switch to a tester and immerse it in a pan of oil. Place the pan onto the lighted gas and heat the oil to slowly in- crease...
Page 387: Sor
H.12 engine cooling engine coolant temperature sen- sor removal • drain the engine coolant as described in page d-20. * do not open the cap of the radiator when the engine is hot. Boiling liquid or vapours can cause serious burns. * the engine coolant is dangerous if swallowed or if it comes into co...
Page 388: Thermostat
H.13 engine cooling assembly • tighten the engine coolant temperature sensor to the torque speci- fied. Torque pressure: engine coolant temperature sensor 18 n.M (1.8 kg-m) be careful when handling the engine coolant temperature sensor. It could be damaged if dropped. • after installing the engine c...
Page 389: Water Pump
H.14 engine cooling check check the pad of the thermostat for cracks. Check the functioning of the thermostat as follows: • pass a piece of string through the flange as indicated in the figure. • immerse the thermostat in a heat-resistant glass of water as indi- cated in the figure. Check that the t...
Page 390
I.1 specific tooling i section.
Page 391
I.2 specific tooling.
Page 392
I.3 specific tooling 1 800096765 1 pincers for elastic rings 2 800096766 1 pincers for elastic rings 3 800096650 1 “v” blocks 4 800096651 1 feeler gauges 4 800096872 1 feeler gauges 5 800096767 1 tester 6 800096653 1 gasket separator 7 800096654 1 load bearing separator/assembler 8 800096655 1 beari...
Page 393
I.4 specific tooling.
Page 394
L.1 torque pressures l section.
Page 395: Torque Pressures
L.2 torque pressures torque pressures engine application n·m kg-m cylinder head valve cover bolt 14 1.4 spark plug 11 1.1 camshaft seat support bolt 10 1.0 timing chain tension adjuster bolt (f) 23 2.3 [r] 7 0.7 timing chain tension adjuster mounting bolt 10 1.0 intermediate gear shaft/n° 2 timing s...
Page 396
L.3 torque pressures application n·m kg-m engine mounting blocking bolt 115 11.5 engine mounting bolt 23 2.3 engine thrust bearing adjuster (m12) 93 9.3 (m10) 55 5.5 engine thrust bearing adjuster locknut 10 1.0 camshaft position sensor mounting bolt 45 4.5 cooling fan thermal switch 8 0.8 engine co...
Page 397
L.4 torque pressures front suspension application n·m kg-m application n·m kg-m steering head to fork leg fixing 23/25 2.3/2.5 steering base to fork leg fixing 23/25 2.3/2.5 steering pin fixing ring torque controlled u-clamp/steering head fixing 23/25 2.3/2.5 steering pin fixing 60/65 6.0/6.5 front ...
Page 398
L.5 torque pressures fairing and mudguards application n·m kg-m front mudguard fixing 5/7 0.5/0.7 underneath seat side cover fixing 9/10 0.9/1.0 front mudguard fixings central 9/10 0.9/1.0 rear mudguard fixings 9/10 0.9/1.0 atmospheric pressure sensor fixing 4/5 0.4/0.5 fuse box fixing 4/5 0.4/0.5 s...
Page 399
L.6 torque pressures application n·m kg-m front brake disc fixing 22/24 2.2/2.4 front wheel spindle fixing 95/100 9.5/10 rear brake disc fixing 33/35 3.3/3.5 crown sprocket fixing 50/52 5.0/5.2 rear wheel spindle fixing 95/100 9.5/10 wheels and brakes application n·m kg-m exhaust tube and silencer b...
Page 400
M.1 index m section.
Page 401
M.2 index general description .................................................... A-1 instrument panel .................................................................... A-4 dimensions and weight .......................................................... A-3 electrical system .......................
Page 402
M.3 index auto-diagnostic function ......................................................... C-24 security function ..................................................................... C-27 fuses ..................................................................................... C-4 throttle leve...
Page 403
M.4 index camshaft installation .............................................................. D-102 crankshaft/connecting rod/gearbox installation ..................... D-168 clutch disengagement device installation .............................. D-122 clutch installation .............................
Page 404
M.5 index brakes ................................................................................. F-1 brake pump check ................................................................. F-11 brake pump check ................................................................. F-15 brake pad wear check ...
Page 405
M.6 index.
Page 406
M.7 index.
Page 407
M.8 index.