- DL manuals
- CalAmp
- Modem
- GEMINI G3
- User Manual
CalAmp GEMINI G3 User Manual
Summary of GEMINI G3
Page 1
Gemini g3 mobile radio modem user manual 001-0001-401 rev a november 2013.
Page 2
Copyright notice ©2013 calamp. All rights reserved. Calamp reserves the right to modify the equipment, its specification or this manual without prior notice, in the interest of improving performance, reliability, or servicing. At the time of publication all data is correct for the op- eration of the...
Page 3
Revision history april 2012 rev 0 initial release under calamp branding, new pn 001-0001-401 changes from previous dataradio pn d12020131301, version 3.01, include all related acma specification information for uhf 403-512 mhz. November 2013 rev a add reference for preferred channel feature – rf fre...
Page 4
Table of contents 1. Product overview .................................................................................................................................... 6 1.1 g eneral d escription ........................................................................................................
Page 5
4.4 ip n etwork s ettings .................................................................................................................................... 24 4.4.1 ip network settings (with host) .......................................................................................................
Page 6
4.7.6 statistics ................................................................................................................................................. 67 4.7.6.1 statistics ► interfaces .........................................................................................................
Page 7
1. Product overview this document provides the information required for the installation, operation, and verification of the geminig3™ wireless radio modem. This document is designed for use by engineering design, installation, and maintenance personnel. 1.1 general description available in 700 mhz,...
Page 8
Configured as terminal servers. Using an in-car hub or switch makes adding other peripherals, such as a camera, possible. • sophisticated dsp-based modem design provides added system performance, fewer retries and more ef- fective throughput. • on-air data speeds and modulation types supported (depe...
Page 9
1.1.2 configuration the geminig3 product is factory-configured based on each customer network system requirements and finalized by calamp system engineering. Network-specific operating instructions should be prepared by the system administra- tors in conjunction with calamp system engineering. Instr...
Page 10
2. Installation 2.1 planning the installation 2.1.1 overview to ensure trouble-free, efficient installation, start by inspecting the vehicle to determine the optimum position for geminig3 unit and its antennas as well as the routing of all associated cabling and wiring. 2.1.2 location often, install...
Page 11
2.2.1 rf radiation warning recommended safety guidelines for the human exposure to radio frequency electromagnetic energy are contained in the canadian safety code 6 and the federal communications commission (fcc) bulletin 65. Proper installation of the transceiver antenna of geminig3 radiomodem as ...
Page 12
B) suppress transmissions whenever the blasting caps container is being loaded or unloaded into or from the vehicle. 2.2.5 installation in vehicles powered by liquefied gas. Geminig3 radiomodem installations in vehicles powered by liquefied petroleum gas with the lp-gas container in the trunk or oth...
Page 13
• use of drill bit stops is highly recommended. • after drilling, remove all metal shavings before installing screws. • do not overtighten self-tapping screws. 1. Once you have found a suitable mounting position for geminig3 radiomodem, hold the unit and the unat- tached mounting bracket in the prop...
Page 14
6. Securely mount geminig3 unit to the installed bracket using the four supplied metal shoulder screws as shown in figure 2 above. Push the screws through the rubber grommet and fasten securely to the unit. Do not over tighten. Figure 3 – rubber grommet and shoulder screw details 5. Drill any additi...
Page 15
The 22 feet (6.7 meters) long power cable consists of three wires attached to a packard electric “weather-pack” connector (dc power connector, see 2. Figure 4). Figure 4 - dc power connector the dc power connector has: • at position “a”, the smaller red switch-sense wire (commonly to ignition) • at ...
Page 16
Ensure tight and secure connections. 8. Fasten the fuse holder and leads. 9. Carefully route the “a” wire to where the connection will be made for switch sensing. • connect to “ignition” if you wish to have geminig3 unit turning on and off dependent on the vehi- cle’s ignition key. • connect to “acc...
Page 17
2.5.2 planning referring to figure 5, the geminig3 radiomodem commonly uses three separate antennas: • “t” - main transceiver - constraints are the limit of 50 cm (see section 2.5 above) and omni-directional factors • “r” - auxiliary receiver – constraints are the receiver spacing of at least 5/8 λ ...
Page 18
• much less preferred, but permissible for receiver antenna: left or right rear fenders, just in back of rear window • least preferred, but permissible for receiver antenna: left or right front fenders, ahead of windshield proximity to other vehicle-mounted antennas may cause mutual interference esp...
Page 19
You are now ready to check for normal operation and to run the geminig3 web interface program for testing or trouble-shooting 2.7 checking out normal operation check that the vehicle ignition is on. 1. Check for proper operation of the geminig3 leds as per table 2 on page 20. 2. Using the geminig3 w...
Page 20
3. Operating description 3.1 front & rear panels the front panel includes: • one female antenna connector for the auxiliary receiver • one sma type female connector for the gps receiver • three led indicators • two de-9f rs232 ports • one ethernet 10/100baset port • one usb port (future use) the rea...
Page 21
Table 2 - g3 leds indications g3 leds indications power-on sequence (leds are paired) pwr / pgm rx / tx indication o ff off off geminig3 off b o o t 1 solid red off boot in progress blinking red on black (3 short red) off ram or self test error blinking red on black (long / short reds) off unable to...
Page 22
Note: blinking refers to the leds turning on and off based on time (such as number of times per second) . Flashing refers to the leds turning on and off in response to an event occurring (such as packets) 3.2 dte port interface for all three ports, we recommend the use of a shielded 9-wire cable wit...
Page 23
4. Operation & configuration instructions and examples given in this manual are based on e-dba operating software version at the time of writing this document and may not apply to earlier or later software versions. Screen captures used through- out this document may vary from actual screens. 4.1 br...
Page 24
4.2 lan setup check that dc power is applied to the geminig3 radiomodem. On a pc running ms-windows with an existing lan connection, connect to the rj-45 input of the geminig3 unit. 1. Click start settings control panel network and dial-up connection 2. Click on the relevant local area connection 3....
Page 25
• netmask: 255.0.0.0 • tcp proxy enabled notes: xx:yy:zz refer to lower three bytes of ethernet mac address 4.4 ip network settings for advanced ip settings, web interface screen captures, and descriptions, see section 4.5 below. 4.4.1 ip network settings (with host) below illustrates geminig3 radio...
Page 26
Referring to below illustrates geminig3 radiomodem settings. In setup (advanced) lan (ip), set addresses and ip netmask of both base and mobile(s). Figure 9 - ip network settings (with router) add default gateway to the pc enable ripv2 on bsc3 and on router 4.5 login screen on your internet browser ...
Page 27
For subsequent access to the geminig3 unit, use the user name and password that you will have configured. Notes: user name field can be left blank. It only serves to identify the person gaining access. Password is common and affects all user name entries. 4.6 web interface the geminig3 user interfac...
Page 28
When making an entry into a dialog box, click on apply when satisfied to temporarily apply the value(s) en- tered to the relevant parameter(s). If not satisfied, click on cancel button to restore to the value(s) present be- fore a change was made. Note: cancel command only affects the dialog boxes o...
Page 29
4.7 ip settings 4.7.1 unit status displays values that identify the unit and show its basic operating condition. 4.7.1.1 unit status figure 12- unit identification and status item description banner displays geminig3 software revision information retrieved from the connected unit. Have this informat...
Page 30
Status displays “initializing” at startup, “registered” in normal operation and “roaming” while attempting to register to another base station. Unit status normally displays “ok” in the message area. Displays various warnings or messages in the event of hardware failure, if indications persist, have...
Page 31
4.7.1.2 radio info provides pertinent radio information retrieved from the connected geminig3 unit. Have this information handy if contacting calamp support. Figure 13 - maintenance - radio personality item description model number identifies the model of radio module installed serial number unique ...
Page 32
4.7.2 setup (basic) 4.7.2.1 setup (basic) ► general setup used to set two basic operating fields on the connected unit. Figure 14 - general setup item description station name station name identifier – enter string up to forty characters in length system id factory default id is zero. To prevent col...
Page 33
4.7.2.3 setup (basic) ► serial ports setup the geminig3 serial ports can be logically connected to local and remote services to aid in configuration and troubleshooting, or they can be connected to a remote host application or even to the serial port of a remote unit. Figure 16 - setup (basic) – ser...
Page 34
Remote ip address default remote ip address is the loopback interface address, 127.0.0.1 and can be changed dynamically without a unit reset remote ip port for socket connection modes (tcp active, udp), set to any value between 1 and 65535. Default local port value is 23 and can be changed dynamical...
Page 35
4.7.3 setup (advanced) 4.7.3.1 setup (advanced) ► lan (ip) figure 17 - advanced ip configuration - lan (ip) complements the setting of ip characteristics beyond those set in setup (basic) basic ip configuration. Item description mtu ethernet interface mtu - default 1500. – for optimal performance, s...
Page 36
4.7.3.2 setup (advanced) ► rf (ip) at the time of manufacture, each paragon4 base station and gemini g3 radiomodem is provided with a unique mac address for its ethernet and rf interfaces. These addresses cannot be changed. The rf interface is also provided with a unique factory rf ip address. If th...
Page 37
4.7.3.3 setup (advanced) ► rf (freq.) ► radio table set up each gemini g3 unit is provided with 32 internally stored over-the-air programmable channels. Use the table below to set up rx and tx frequencies for each channel. 1 figure 19 - radio table set up note: exercise caution when entering rf freq...
Page 38
Item description enable if checked, the channel is accessible when the mobile needs to roam to a new base station. There may also be an icon appearing next to the checkbox to indicate if the chan- nel is currently in use or is a preferred neighboring channel: channel currently in use preferred neigh...
Page 39
4.7.3.4 setup (advanced) ► roaming setup figure 20 - roaming setup item description …roam across…cycles when a base becomes congested and indicates that some mobiles should try to roam to another base, this value spreads the activity so that mobiles do not roam at the same time. Set this value large...
Page 40
4.7.3.5 setup (advanced) ► ip services item description server dhcp server disabled, enabled (default). The dynamic host configuration pro- tocol provides a framework for passing configuration information e.G.: ip address to hosts (i.E. Pc/rtu) on a tcp/ip network. Gateway gateway address handed out...
Page 41
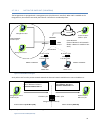
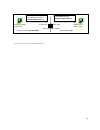
4.7.3.6 nat overview the purpose of the “network address translation” (nat) protocol is to hide a private ip network from a public network. The mechanism serves both as a firewall function and to save ip address space. Figure 22 - basic nat operations the source address of packets transiting from th...
Page 42
4.7.3.6.1 nat on the base unit (paragon4) the paragon4 unit is equipped with a management port (the ethernet 2 interface). When nat is enabled on the paragon4 unit, the network covered by the ethernet 2 interface is considered private. Figure 23 - nat enabled on paragon4 an ip packet sent from the p...
Page 43
An ip packet sent from the private network towards the rf network will have its source ip address replaced by the rf ip address of the paragon4 radiomodem. 4.7.3.6.2 nat on the mobile unit (geminig3) when nat is enabled on a geminig3 unit, the network covered by the ethernet interface is considered ...
Page 44
Figure 27 - geminig3 - private to public network (rf) packet (1) source address 173.30.1.2 destination address 200.1.1.1 packet (1) source address 10.0.1.2 destination address 200.1.1.1 173.30.1.1/2 10.0.1.2/24 geminig3 (nat enabled) management host 1 173.30.1.2/24 mobile host 1 200.1.1.1/24 private...
Page 45
4.7.3.7 snmp overview snmp (simple network management protocol) is used by network management systems to manage and monitor network-attached devices. Snmp is based on the manager/agent model consisting of a manager, an agent, a data- base of management information, managed objects, and the network p...
Page 46
Ample, object titled “snmp” has a unique oid: 1.3.6.1.2.1.11. The mib associates each oid with a label (e.G. “snmp”) and various other parameters. When an snmp manager wants to obtain information on an object, it will assemble a specific message (e.G. Get packet) that includes the oid of the object ...
Page 47
• gcu3statistics • gcu3diagnostics • gcu3locationdata • gcu3radiochannel • gcu3traps these eight branches expand into additional branches and leaves. Again, all gcu3.Mib objects can be accessed through a mib browser. Figure 30 – gcu3.Mib tree note: although each mobile is equipped with an snmp agent...
Page 48
4.7.3.8 setup (advanced) ► ip addressing for a more detailed description of the broadcast and multicast features of the geminig3 radiomodem, please refer to paragraph 4.7.3.8.0 below. Figure 31 - advanced ip configuration – ip adressing modes item description broadcast directed broadcast disabled, e...
Page 49
Multicast white list when the "multicast forwarding" mode is enabled and no multicast groups are specified in the "multicast white list", all multicast packets re- ceived on the rf interface are passed to the "lan". When "multicast forwarding" mode is enabled and some multicast groups are specified ...
Page 50
4.7.3.8.1 ip broadcast/multicast overview when an ip packet needs to reach more than one unit, the destination address can be set to either a broad- cast address or a multicast address. Figure 32 - broadcast window detail 4.7.3.8.2 broadcasts there are two types of ip broadcast addresses: • directed...
Page 51
• if directed broadcast packets can be forwarded (directed broadcast is enabled): forwards the packet according to the routing table. • if directed broadcast packets cannot be forwarded (directed broadcast is disabled): silently discards the packet. Note: occasionally, the unit cannot determine that...
Page 52
Example (directed broadcast forwarding disabled) figure 34 - example of directed broadcast forwarding disabled in this example figure 34, directed broadcast forwarding is enabled on the base unit and disabled on the mo- bile (1) unit. If sender sends a packet to destination address 172.30.1.255, the...
Page 53
Sends a copy of the packet out to all the interfaces with the exception of the interface where the packet was received. • if limited broadcast packets cannot be forwarded (limited broadcast is disabled): silently discards the packet. Example (limited broadcast forwarding enabled) figure 35 - example...
Page 54
Example (limited broadcast forwarding disabled) figure 36 - example of limited broadcast forwarding disabled in this example figure 36, limited broadcast forwarding is enabled on the base unit, disabled on the mobile (1) unit and enabled on the mobile (2) unit. If sender sends a packet to destinatio...
Page 55
4.7.3.9 multicast ip multicast addresses are in the range 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255. These addresses are used to represent logical groups of units that may or may not reside on the same networks. Multicast is used when “one-to-many” communication is required. For instance, a radio station might o...
Page 56
Figure 38 - reception of multicast packets (second step) in the e-dba environment, an outside sender-host might be interested in sending multicast packets to any one of the following groups: • “all base” group (not currently supported) • “all mobile” group (dmp-ip only) • various “mobile host” group...
Page 57
Figure 39 - typical e-dba multicast groups the following setup example would allow the “sender” unit to communicate with different multicast groups. The settings for mobile and base are shown in figure 40 below. Also represented in figure 41, it would enable the sender unit to reach all entities of ...
Page 58
Figure 40 - multicast window details (on the mobile on the left and on the base on the right) multicast (enabled/disabled) enables or disables the registration of the multicast groups by the base must be enabled on both base and mobiles base address indicates the “all base” multicast group (not curr...
Page 59
4.7.3.10 setup (advanced) ► ip optimization & tuning figure 42 - advanced ip configuration - ip optimization & tuning - oip item description rf ack disabled, enabled (default) oip retries number of oip retries. Default = 2 4.7.3.11 setup (advanced) ► time source to facilitate tracking of events in a...
Page 60
Item description source selection time source ♦ gps – no on-air penalty, very accurate ♦ airlink – light on-air penalty, least accurate ♦ sntp – medium on-air penalty, medium accuracy place a check mark against each of the available time sources to be used on your network. The preference order is gp...
Page 61
4.7.3.12 setup (advanced) ► ethernet (phy) figure 44 - advanced ip configuration - ethernet (phy) item description phy bitrate auto negotiate force to 100 mbps force to 10 mbps (default) phy duplex displays factory configured mode of operation: half duplex 60
Page 62
4.7.4 gps all geminig3 radiomodems shipped from the calamp factory are fitted with a 12-channel high efficiency gps receiver, equipped with waas feature for better location precision ( gps "strings" are collected from embedded gps receiver in the geminig3 mobile radiomodems. The strings are converte...
Page 63
Ground speed (km/h) shows travel speed (in km/h) from gps-equipped geminig3 mobiles. 4.7.4.2 gps ► delivery options figure 46 - gps - delivery options (initial screen on left - screen with 2 udp hosts on right) 62.
Page 64
Item description local port read-only field – indicates port configured for the ipsd. Note: ipsd should be enabled in setup (advanced)-> ip services format field provides a drop-down box for selecting the appropriate gps report format for the local ipsd. The possible choices are: format definition m...
Page 65
4.7.4.3 gps ► aavl the “autonomous automatic vehicle location” (aavl) feature adds the ability for gps-equipped geminig3 models to initiate "here i am" position message transmissions. Aavl allows the system designer to specify the maximum distance or the time interval between position reports: if th...
Page 66
4.7.5 security 4.7.5.1 password and encryption control the setup web pages, the cli (command line interface) and the ftp server all require a password to prevent unauthorized users from changing a unit’s configuration. At the time of manufacture, the password is set to “administrator” (all uppercase...
Page 67
Encryption key all units in a network must have the same key. Read only - displayed in pairs separated with spaces 66.
Page 68
4.7.6 statistics 4.7.6.1 statistics ► interfaces note: figure 49 - statistics - interfaces all definitions given below use the following convention: • rx (or input) = data received from a lower network layer • tx (or output) = data transmitted to a lower network layer item description the lan (ether...
Page 69
Packets not correct number of e-dba packets received over-the-air with errors that could not be cor- rected . These packets were discarded. Note: for transport (tcp/udp) and network (ip) interface layers statistics refer to mib 1213. 4.7.7 maintenance 4.7.7.1 maintenance ► ping test to aid in troubl...
Page 70
4.7.7.2 maintenance ► config control figure 51 - maintenance - unit configuration control (initial screen) important note: record all original geminig3 radiomodem factory settings for possible future use. Item description active configuration description active configuration description field – avai...
Page 71
Factory settings restore factory settings: restores all settings to default factory configura- tion. Upon performing the firmware upgrade, should you decide to restore to factory settings instead of to “merge with bundled settings”, simply select the “restore factory settings” option button right af...
Page 72
4.7.7.3 maintenance ► package control figure 52 - maintenance – package validation item description package control used for verifying the field upgrade of the geminig3 mobile radiomodem firmware. The firmware transfer procedure outlined in section 5.5.1 instructs to “click on maintenance / package ...
Page 73
4.7.7.4 maintenance ► rf tests figure 53 - control - rf tests 72.
Page 74
Rf tests: item description r ssi rssi table main raw = raw dbm value from main radio receiver main cal = calibrated dbm value from main receiver dsp diversity raw = diversity raw dbm value from diversity radio diversity cal = calibrated dbm value from diversity receiver dsp range -120 to –40 dbm thr...
Page 75
Test tone: select the desired test tone, press the “execute” button to transmit a test signal on the channel selected for 20 seconds or until the “cancel current test” button is pressed. The functions of all the other buttons are inoperative during test transmissions. Te s t tone s modulated test tr...
Page 76
4.7.8 feature options “feature options” are used to implement customer’s option(s) selected at the time of radiomodem purchase (fac- tory-installation ) or as add-on (field-installation) . Software options must match the sales/work order entries. Figure 54 – feature option icon further option inform...
Page 77
5. Maintenance, trouble-shooting and testing the checks described below should be done at annual intervals or whenever deterioration in performance is not- ed. 5.1 equipment required • 13.8 vdc (nominal) car battery, or 13.8 vdc/20a regulated power supply (in the case the unit is not installed in a ...
Page 78
Table 5 - test checklist test checklist step action expected results at 25 ° c measure with if not? Geminig3 units are set and characterized at the factory to optimize performances. It is not recommended to try to readjust the units. 1 power-up led sequence as per table 2 - g3 leds indications for s...
Page 79
5 tx deviation (in khz) in “test tone” section of the page select m odulated – press execute carrier will be modulated with a 1 khz tone. Refer to 5.3.1for tx deviation details. Tolerance is +5%, -10% for all bit rates service monitor set to read devia- tion (if filter set to mid or 30 khz position)...
Page 80
57.6 ± 3.37 half channel (uhf) 12.5khz bandwidth 16.0 ± 1.7 24.0 ± 2.0 32.0 ± 2.1 wide channel (700mhz) 50khz bandwidth 64.0 ± 5.3 96.0 ± 6.2 128.0 ± 6.5 full channel (800mhz) 25khz bandwidth 32.0 ± 2.4 48.0 ± 2.7 64.0 ± 2.9 43.2 ± 3.3 npspac channel (usa - 800mhz) 16.0 ± 2.4 24.0 ± 2.7 32.0 ± 2.9 5...
Page 81
5.4 troubleshooting tools 5.4.1 network connectivity • ping (dos/windows) the ping command determines whether a specific ip address is accessible. It works by sending a packet to the specified address and waiting for a reply. It is useful for troubleshooting “end-to-end” reachability, network connec...
Page 82
The address resolution protocol (arp) is used with the ip protocol for mapping a 32-bit internet pro- tocol address to a mac address that is recognized in the local network specified in rfc 826. Once recognized the server or networking device returns a response containing the required address. Avail...
Page 83
Warning: be aware that base and mobile’s firmware archives are often distributed at the same time. Files intended for the geminig3 radiomodem are labeled in the form geminig3_edba_vx.X_rx.Xx.Zip . Be careful not to transfer firmware into the wrong unit! 2. Using an ftp program of your choice, establ...
Page 84
5. Verify the integrity of the newly transferred files. A) connect to the mobile’s ip address using an internet browser such as ie (5.0 or later) or mozilla. B) enter the user name and password (in the usual manner) and allow the welcome page to load. C) in the left pane, click on unit status . The ...
Page 85
6. Specifications general uhf 700mhz 800 mhz frequency range (mhz) fcc 403 - 512 rx/tx 1 ic 406 - 470 rx/tx acma 450-512 rx/tx fcc (part 90) 796 - 803 tx 766 - 773 rx fcc (part 27) 792 - 794 tx 762-764 rx fcc 809 - 824 tx 854 - 869 rx ic 806 - 821 tx 851 - 866 rx fcc part 90 i.C. Rss-119 fcc part 90...
Page 86
Forward error correction hypercode addressability native tcp/ip encryption aes 128-bit protocols dataradio e-dba with oob aavl support ethernet ieee 802.3 (icmp, igmp, tcp, udp) ip fragmentation address resolution protocol (arp) ip directed broadcast, ip limited broadcast, ip multicast relay dhcp cl...
Page 87
Geminig3-adb model rx sensitivity (for 1% packet error rate (per) with parallel decode at carrier frequency) 700 mhz 50 khz channel 800 mhz 25 khz channel 800 mhz npspac channel -93 dbm @ 128 kbps -99 dbm @ 96 kbps -104 dbm @ 64 kbps -94 dbm @ 64 kbps -100 dbm @ 48 kbps -104 dbm @ 43.2 kbps -108 dbm...
Page 88
800 eotgpdb 773195643a emission designators bit rate baud rate modulation uhf (fcc/ic mask) 700 mhz (fcc/ic mask) 800 mhz (fcc mask) 800 mhz - npspac (fcc mask) 128000 32000 srrc16fsk - 28k0f1d - - *96000 32000 srrc8fsk - 28k0f1d - - *64000 32000 srrc4fsk - 28k0f1d - - 64000 16000 srrc16fsk 16k4f1d(...
Page 89
Appendix 1 – "officer requires assistance" alarm function overview the dte port interface pin 9 (aux) on dev-2 is used for the “officer requires assistance” alarm function. Intended audience this appendix is designed for use by system integrators. Physical connection this auxiliary input may be acti...
Page 90
Operation when using gemini g3 product running firmware version 2.1 or later, activating the “officer requires assis- tance” alarm input starts emergency communications: • on systems using dmp-transition facilities, the modem sends a dmp “x” or “y” message through to the msc2 to the host pc. • the a...
Page 91
Appendix 2 – "gps data collection" instructions the extract in this appendix is taken from technical instruction sheet 043 (tis043), dated may 03, 2006. Overview the instructions in tis043 are intended for application programmers and provide details on how to collect gps data in vis networks using g...
Page 92
Appendix 3 – e-dba throughput/latency measurements methods the contents of this appendix are also available in technical instruction sheet 044 (tis044), dated march 01, 2006. Overview the instructions in tis044, intended for end-users, discuss the effectiveness of tcp/ip troubleshooting tools in e- ...
Page 93
Ping example c:\>ping -w 5000 172.23.10.2 pinging 172.23.10.2 with 32 bytes of data: reply from 172.23.10.2: bytes=32 time=641ms ttl=59 reply from 172.23.10.2: bytes=32 time=703ms ttl=59 reply from 172.23.10.2: bytes=32 time=593ms ttl=59 reply from 172.23.10.2: bytes=32 time=641ms ttl=59 ping statis...
Page 94
Conclusion although some standard tools such as the ones outlined above can be used to get a rough idea of an e-dba sys- tem's performance, the best metric will always be to test the system in conditions that reproduce as closely as possible its real-life usage. For example, by using applications si...
Page 95
Appendix 4 – time synchronisation, and web browser cache - instructions the contents of this appendix are also available in technical instruction sheet 051 (tis051), dated november 10, 2006. Overview the instructions in tis051, intended for maintenance technicians and for end-users, address a built-...
Page 96
If using mozilla firefox v1.5.0.4, select “tools” in the menu bar and select the “clear private data” option. Alter- nately, you can use the keystroke combination of “ctrl+shift+delete”. Adjust the above methods according to your browser or to its version number. Appendix 5 – ethernet configuration ...
Page 97
Appendix 6 – definitions item definition aavl autonomous automatic vehicle location. Feature that involves using gps (global posi- tioning system) signals from the mobile unit by the host pc. Access point c ommunication hub for users to connect to a lan. Adb agile dual-band. Gemini g3 model that all...
Page 98
Feature key method used to implement customer’s option(s) selected at the time of radiomodem purchase (factory-installation) or as add-on (field-installation). Ethernet ieee standard network protocol that specifies how data is placed on and retrieved from a common transmission medium. Firewall a con...
Page 99
Palette synchronization patterns used to identify the speed and coding of packets transmitted over-the-air in e-dba. Paragon4 ip-based data radio base station used in mobile networks and designed specifically to fit the needs of vehicular applications. Runs up to 128 kb/s parallel decode patented te...
Page 100
Telnet a user command and tcp/ip protocol used for accessing remote pcs. Tftp trivial file transfer protocol - a version of the protocol that has no directory or pass- word capability. Depends on udp and is used on local network. Topology the physical layout of a network. Transparent a transparent u...
Page 101
Appendix 7 – service and support product warranty, rma and contact information calamp guarantees that every gemini will be free from physical defects in material and workmanship for one (1) year from the date of purchase when used within the limits set forth in the specifications section of this man...
Page 102
Appendix 8 – warranty statement calamp warrants to the original purchaser for use ("buyer") that data telemetry products ("products") are free from defects in material and workmanship and will conform to published technical specifications for a period of, except as noted below, one (1) year from the...