- DL manuals
- Cambium
- Network Router
- PTP 670 Series
- User Manual
Cambium PTP 670 Series User Manual
Summary of PTP 670 Series
Page 1
F cambium ptp 670 series user guide system release 670-02-50
Page 2
Phn-4431_003v000 (september 2017) accuracy while reasonable efforts have been made to assure the accuracy of this document, cambium networks assumes no liability resulting from any inaccuracies or omissions in this document, or from use of the information obtained herein. Cambium reserves the right ...
Page 3: Contents
Page i contents about this user guide .................................................................................................................... 1 contacting cambium networks .............................................................................................. 1 purpose .............
Page 4
Contents page ii time division duplexing in ptp wireless topology ............................................................ 1-8 time division duplexing in hcmp wireless topology ...................................................... 1-10 link mode optimization .......................................
Page 5
Contents page iii critical security parameters ............................................................................................... 1-58 software upgrade ................................................................................................................ 1-59 capability upgrad...
Page 6
Contents page iv universal gps ...................................................................................................................... 2-46 network indoor unit (nidu) ...................................................................................................... 2-47 nidu descr...
Page 7
Contents page v calculating rf cable length (5.8 ghz fcc only) ............................................................... 3-30 configuration options for tdd synchronization ..................................................................... 3-31 using ptp-sync ...................................
Page 8
Contents page vi updates .................................................................................................................................. 4-5 maintenance .......................................................................................................................... 4-5 d...
Page 9
Contents page vii install the odu to top lpu drop cable .............................................................................. 5-14 install the main drop cable ................................................................................................. 5-16 install the bottom lpu to psu...
Page 10
Contents page viii logging into the web interface ............................................................................................ 6-6 using the menu options ....................................................................................................... 6-7 installation menu .......
Page 11
Contents page ix confirm snmp configuration (for snmpv1/2c) ............................................................. 6-102 security menu .......................................................................................................................... 6-103 preparation ....................
Page 12
Contents page x spectrum management settings ....................................................................................... 7-35 interpreting the receive spectrum plot .............................................................................. 7-37 barring channels .........................
Page 13
Contents page xi odu led blinks red ............................................................................................................. 8-16 gps led does not illuminate or blink on clustered units ................................................ 8-16 testing a tdm link .......................
Page 14: About This User Guide
Page 1 about this user guide this guide describes the planning, installation, configuration and operation of the cambium ptp 670 series of point-to-point wireless ethernet bridges. It is intended for use by the system designer, system installer and system administrator. For radio network design, ref...
Page 15: Purpose
About this user guide important regulatory information page 2 purpose cambium networks point-to-point (ptp) documents are intended to instruct and assist personnel in the operation, installation and maintenance of the cambium ptp equipment and ancillary devices. It is recommended that all personnel ...
Page 16: Radar Avoidance
About this user guide important regulatory information page 3 important regulatory information complying with rules for the country of operation the ptp 670 product operates in frequency bands between 4.8 ghz and 5.9 ghz. These bands are made available for licensed or unlicensed operation according ...
Page 17: Canada Specific Information
About this user guide important regulatory information page 4 the usa federal communications commission (fcc) requires manufacturers to implement special features to prevent interference to weather radar systems that operate in the band 5600 mhz to 5650 mhz. These features must be implemented in all...
Page 18: Eu Specific Information
About this user guide important regulatory information page 5 renseignements specifiques au canada attention le présent appareil est conforme aux cnr d'innovation, sciences et développement economique canada applicables aux appareils radio exempts de licence. L'exploitation est autorisée aux deux co...
Page 19: Application Firmware
About this user guide important regulatory information page 6 application firmware download the latest ptp 670 series firmware and install it in the outdoor units (odus) before deploying the ptp 670 equipment. Instructions for installing firmware are provided in upgrading software image on page 7-78...
Page 20: Lightning Protection
About this user guide important regulatory information page 7 lightning protection to protect outdoor radio installations from the impact of lightning strikes, the installer must be familiar with the normal procedures for site selection, bonding and grounding. Installation guidelines for the ptp 670...
Page 21: Problems And Warranty
About this user guide problems and warranty page 8 problems and warranty reporting problems if any problems are encountered when installing or operating this equipment, follow this procedure to investigate and report: 1 search this document and the software release notes of supported releases. 2 vis...
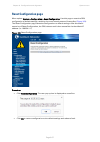
Page 22: Security Advice
About this user guide security advice page 9 security advice cambium networks systems and equipment provide security parameters that can be configured by the operator based on their particular operating environment. Cambium recommends setting and using these parameters following industry recognized ...
Page 23: Warnings
About this user guide warnings, cautions, and notes page 10 warnings, cautions, and notes the following describes how warnings and cautions are used in this document and in all documents of the cambium networks document set. Warnings warnings precede instructions that contain potentially hazardous s...
Page 24: Caring For The Environment
About this user guide caring for the environment page 11 caring for the environment the following information describes national or regional requirements for the disposal of cambium networks supplied equipment and for the approved disposal of surplus packaging. In eu countries the following informat...
Page 25: Chapter 1:
Page 1-1 chapter 1: product description this chapter provides a high level description of products in the ptp 670 series. It describes in general terms the function of the product, the main product variants and the main hardware components. The following topics are described in this chapter: • overv...
Page 26: Purpose
Chapter 1: product description overview of the ptp 670 series page 1-2 overview of the ptp 670 series this section introduces the key features, typical uses, product variants and components of the ptp 670 series. Purpose cambium ptp 670 series bridge products are designed for ethernet bridging over ...
Page 27: Frequency Bands
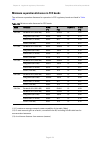
Chapter 1: product description overview of the ptp 670 series page 1-3 ptp 670 supports both synchronous ethernet and operation as an ieee 1588-2008 transparent clock. Table 1 gives a summary of the main ptp 670 characteristics. Table 1 main characteristics of the ptp 670 series characteristic value...
Page 28: Typical Bridge Deployment
Chapter 1: product description overview of the ptp 670 series page 1-4 note the supported frequency coverage may be further restricted in some country licenses to comply with the applicable regulations. Typical bridge deployment the ptp 670 is an “all outdoor” solution consisting of a wireless bridg...
Page 29: Hardware Overview
Chapter 1: product description overview of the ptp 670 series page 1-5 hardware overview the main hardware components of the ptp 670 are as follows: • outdoor unit (odu): the odu is a self-contained transceiver unit that houses both radio and networking electronics. The ptp 670 odu is supplied in tw...
Page 30
Chapter 1: product description overview of the ptp 670 series page 1-6 o a copper ethernet cat5e connection from the odu (aux port) to an auxiliary device. • lightning protection unit (lpu): lpus are installed in the psu and aux copper drop cables to provide transient voltage surge suppression. • gr...
Page 31: Wireless Operation
Chapter 1: product description wireless operation page 1-7 wireless operation this section describes how the ptp 670 wireless link is operated, including topology, modulation modes, power control and security. Wireless topology ptp 670 supports operation in two distinct topologies: • point to point ...
Page 32: Further Reading
Chapter 1: product description wireless operation page 1-8 the master odu includes an ethernet bridging function with address learning to forward ethernet data traffic via a wireless link to the appropriate slave, based on the destination address of the end-station reached through the slave. Traffic...
Page 33: Tdd Frame Parameters
Chapter 1: product description wireless operation page 1-9 3 the slave receives the burst from the master. 4 the slave processes the master-slave burst. 5 the slave transmits a burst to the master. 6 a delay occurs as the slave-master burst propagates over the link. 7 the master receives the burst f...
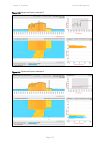
Page 34: Channel Selection
Chapter 1: product description wireless operation page 1-10 figure 2 tdd cycle channel selection the ptp 670 series links are capable of transmitting and receiving on the same channel or on different channels. In other words, the slave-master direction may use a different channel from the master-sla...
Page 35: Tdd Frame Parameters
Chapter 1: product description wireless operation page 1-11 the tdd cycle for a simple hcmp sector with two slave odus is illustrated in figure 3 . The steps in the cycle are as follows: 1 the tdd master transmits a burst to the first tdd slave. 2 a delay occurs as the master-slave burst propagates ...
Page 36: Channel Selection
Chapter 1: product description wireless operation page 1-12 figure 3 tdd cycle for hcmp channel selection in the hcmp topology, the odus in a sector all transmit and receive on a common channel. Further reading for information about… refer to… tdd synchronization in ptp and hcmp networks tdd synchro...
Page 37: Further Reading
Chapter 1: product description wireless operation page 1-13 ip link optimization in the ptp topology the ip link optimization mode provides the maximum possible link capacity. Ip mode is an appropriate choice where applications in the bridged networks provide some measure of reliable transmission, a...
Page 38: Hcmp Topology
Chapter 1: product description wireless operation page 1-14 • 2:1 – the capacity in the direction master to slave is twice that of the direction slave to master. The ptp 670 series achieves this by setting the burst duration of the master to twice that of the slave. • 1:2 – the capacity in the direc...
Page 39: Further Reading
Chapter 1: product description wireless operation page 1-15 the asymmetric options are available independent of tdd synchronization. The available link symmetry options in hcmp topology depend on channel bandwidth and the number of slaves, as shown in table 3 . Table 3 link symmetry options in hcmp ...
Page 40: Further Reading
Chapter 1: product description wireless operation page 1-16 further reading for information about… refer to… channel bandwidths per frequency band general wireless specifications on page 3-20 how to plan for channel bandwidth channel bandwidth on page 3-22 effect of channel bandwidth on link data th...
Page 41: Further Reading
Chapter 1: product description wireless operation page 1-17 spectrum management in fixed frequency mode the transmit and receive frequencies can be fixed in a ptp 670 wireless link. Once fixed frequency mode is configured, the spectrum management software will not attempt to move the wireless link t...
Page 42: Mimo
Chapter 1: product description wireless operation page 1-18 for information about… refer to… effect of modulation mode on system threshold, output power and link loss system threshold, output power and link loss on page 3-65 how to configure modulation modes interface configuration page on page 6-16...
Page 43: Further Reading
Chapter 1: product description wireless operation page 1-19 for information about… refer to… single and dual payload modulation modes system threshold, output power and link loss on page 3-65 tdm single payload lock feature tdm on page 7-15 dynamic spectrum optimization the ptp 670 series uses an in...
Page 44: Further Reading
Chapter 1: product description wireless operation page 1-20 • when operating on a channel, the spectrum management algorithm implements a radar detection function which looks for impulsive interference on the operating channel. If impulsive interference is detected, spectrum management will mark the...
Page 45: Hcmp Topology
Chapter 1: product description wireless operation page 1-21 hcmp topology in the hcmp wireless topology, ptp 670 always uses the group access method. The master and slave odus must all share the same group id. Note the configured access method provides effective protection against an accidental atte...
Page 46: Tls Rsa
Chapter 1: product description wireless operation page 1-22 tls rsa wireless encryption tls rsa can be used with the following access methods: • link access • group access access method is automatically configured to group access in the hcmp topology. Authentication using tls rsa tls rsa uses the bi...
Page 47: Further Reading
Chapter 1: product description wireless operation page 1-23 note authentication is the process of verifying the identity of the remote unit that is attempting to form a connection. Authorization is the check that takes place to confirm that a unit with the authenticated identity is permitted to conn...
Page 48: Further Reading
Chapter 1: product description wireless operation page 1-24 authentication and authorization in tls psk 128-bit or tls psk 256-bit occur as a single step, based on the secret pre-shared key. Both ends of the link must be configured for the same key size. Each unit will connect only to a remote unit ...
Page 49: Further Reading
Chapter 1: product description wireless operation page 1-25 • transmit power reduction in edge channels • frequency range • channel plan • hcmp and/or ptp topology the country of operation (and thus the supported regulatory bands) can be changed by generating a new license key at the license key gen...
Page 50: Using Frequency Planning
Chapter 1: product description wireless operation page 1-26 using frequency planning networks will benefit from the use of fixed channel allocations if (a) the network consists of multiple ptp links, and (b) rf interference predominantly arises from equipment in the same network. Frequency planning ...
Page 51: Ptp-Sync
Chapter 1: product description wireless operation page 1-27 • ptp-sync: one ptp-sync unit is connected in line in the drop cable between the ac+dc power injector 56v and each master odu, close to the ac+dc power injector 56v. The ptp sync hardware option can synchronize an isolated or standalone clu...
Page 52: Configuring The Tdd Frame
Chapter 1: product description wireless operation page 1-28 direct connection between two odus the direct connection option consists of one odu configured as a free-running synchronization source, with a 1 pps output on its aux port, and one odu configured to receive the 1 pps signal at its main psu...
Page 53
Chapter 1: product description wireless operation page 1-29 for information about… refer to… how to install the trimble gps receiver installing the trimble accutime gps receiver on page 5-29 how to enable tdd synchronization wireless configuration page on page 6-25 how to configure tdd synchronizati...
Page 54: Ethernet Bridging
Chapter 1: product description ethernet bridging page 1-30 ethernet bridging this section describes how the ptp 670 odu processes ethernet data, and how ethernet ports are allocated to the data service, second data service, management service and local management service. Ethernet ports the ptp 670 ...
Page 55: Further Reading
Chapter 1: product description ethernet bridging page 1-31 further reading for information about… refer to… a more detailed description of the data service data service on page 1-32. A more detailed description of the second data service second data service on page 1-34 . A more detailed description...
Page 56: Data Service
Chapter 1: product description ethernet bridging page 1-32 one to three ethernet ports may be allocated to the data service. If in band management is configured, management access shares the same set of ports. If out of band management is configured, up to two ports may be allocated to the managemen...
Page 57: Fragmentation
Chapter 1: product description ethernet bridging page 1-33 ethernet frames are classified by inspection of the ethernet priority code point in the outermost vlan tag, the differentiated services code point (dscp) in an ipv4 or ipv6 header including dscp in an ipv4 or ipv6 datagrams encapsulated in p...
Page 58: Further Reading
Chapter 1: product description ethernet bridging page 1-34 further reading for information about… refer to… factors to be considered when planning ptp 670 customer data networks data network planning on page 3-36 how to configure the ethernet service lan configuration page on page 6-43 how to config...
Page 59: Fragmentation
Chapter 1: product description ethernet bridging page 1-35 • multiple registration protocol (mrp) • generic attribute registration protocol (garp) the management service in the ptp 670 series does not generate or respond to any l2cp traffic. Quality of service for bridged ethernet traffic the ptp 67...
Page 60
Chapter 1: product description ethernet bridging page 1-36 for information about… refer to… how to configure ethernet quality of service qos configuration page on page 6-56 how to monitor ethernet performance system statistics on page 7-54 out-of-band management service transparent ethernet service ...
Page 61: Fragmentation
Chapter 1: product description ethernet bridging page 1-37 fragmentation ethernet frames in the ptp 670 series management service are always fragmented for transmission over the wireless link, even when the single queue for the management service has higher priority than all of the customer data que...
Page 62: Further Reading
Chapter 1: product description ethernet bridging page 1-38 during loopback operation, the same frame size restrictions that apply to management traffic are present, jumbo frames are not supported and the maximum frame size is restricted to 1536 bytes. Loopback is able to loop between ethernet ports ...
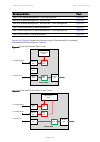
Page 63
Chapter 1: product description ethernet bridging page 1-39 figure 4 protocol layers between ethernet and wireless interfaces wireless port ethernet port ieee 802.3 media access method independent functions media access method dependent convergence functions media access method specific functions eth...
Page 64: Further Reading
Chapter 1: product description ethernet bridging page 1-40 figure 5 protocol layers between external interfaces and the management agent management agent management, wireless, data ports media access method specific functions http/snmp/smtp tcp/ip mac relay entity further reading for information abo...
Page 65: Further Reading
Chapter 1: product description ethernet bridging page 1-41 ptp 670 can be configured to relay a synchronous ethernet frequency reference across the wireless link, supporting operation as part of an itu-t g.781 synchronous digital hierarchy. A single ptp 670 link has at least two, and up to six, acti...
Page 66: Further Reading
Chapter 1: product description ethernet bridging page 1-42 ieee 1588-2008 transparent clock note ptp 670 does not support ieee 1588-2008 transparent clock in the hcmp topology. Ptp 670 is capable of operating as an ieee 1588-2008 transparent clock. When operational, ieee 1588-2008 event frames (sync...
Page 67: Tdm Bridging
Chapter 1: product description tdm bridging page 1-43 tdm bridging note ptp 670 does not support tdm bridging in the hcmp topology. This section describes how tdm traffic (e1 or t1) may be carried over ptp 670 links. If a nidu is installed at each link end, the ptp 670 link supports up to eight e1 c...
Page 68: Lowest Tdm Modulation Mode
Chapter 1: product description tdm bridging page 1-44 the nidu always connects to the odu using the main psu port of the odu. This constrains the flexible allocation of ports to services somewhat. Timing transfer for tdm circuits accurate timing transfer for tdm circuits in the ptp 670 series is bas...
Page 69: Ethernet Cables For Tdm
Chapter 1: product description tdm bridging page 1-45 ethernet cables for tdm the ethernet cables from the odu via the psu to the nidu must be capable of supporting operation at 1000base-t. If the odu port has negotiated a link at 100base-t, the nidu will not send or receive tdm data and will not br...
Page 70: System Management
Chapter 1: product description system management page 1-46 system management this section introduces the ptp 670 management system, including the web interface, installation, configuration, alerts and upgrades. Management agent ptp 670 equipment is managed through an embedded management agent. Manag...
Page 71: Network Management
Chapter 1: product description system management page 1-47 network management ipv4 and ipv6 interfaces the ptp 670 odu contains an embedded management agent with ipv4 and ipv6 interfaces. Network management communication is exclusively based on ip and associated higher layer transport and applicatio...
Page 72: Source Address Learning
Chapter 1: product description system management page 1-48 further examples of useful port allocation schemes are provided in chapter 3: system planning . Source address learning if local packet filtering is enabled, the ptp 670 learns the location of end stations from the source addresses in receiv...
Page 73: Icmp For Ipv6
Chapter 1: product description system management page 1-49 icmp for ipv6 ptp 670 supports icmpv6 as specified in rfc 4443. Ptp 670 does not support rfc 4884 (multi- part messages). Addressing the ptp 670 management agent is compatible with the ipv6 addressing architecture specified in rfc 4291. Ptp ...
Page 74: Further Reading
Chapter 1: product description system management page 1-50 further reading for information about… refer to… planning the ipv6 interface ip interface on page 3-50 how to enable ipv6 capability software license key page on page 6-13 how to configure ipv6 interface configuration page on page 6-16 lan c...
Page 75: Transport Layer Security
Chapter 1: product description system management page 1-51 transport layer security the https/tls interface provides the same set of web-pages as the http interface, but allows http traffic to be encrypted using transport layer security (tls). Ptp 670 uses aes encryption for https/tls. Operation of ...
Page 76: Password Complexity
Chapter 1: product description system management page 1-52 password complexity ptp 670 allows a network operator to enforce a configurable policy for password complexity. Password complexity configuration additionally allows a pre-determined best practice configuration to be set. Snmp control of pas...
Page 77: Further Reading
Chapter 1: product description system management page 1-53 further reading for information about… refer to… how to plan the use of radius planning for radius operation on page 3-63 how to configure radius. Radius configuration page on page 6-77 snmp the management agent supports fault and performanc...
Page 78: Further Reading
Chapter 1: product description system management page 1-54 if an sntp server connection is available, the clock can be set to synchronize with the server time at regular intervals. For secure applications, the ptp 670 can be configured to authenticate received ntp messages using an md5 signature. Fu...
Page 79
Chapter 1: product description system management page 1-55 access to critical security parameters the snmpv3 management interface does not provide access to critical security parameters (csps) of ptp 670. It is not possible to read or modify aes keys used to encrypt data transmitted at the wireless ...
Page 80
Chapter 1: product description system management page 1-56 the default user initial will have read/write access to the whole of the mib. This is described in further detail in view-based access control model on page 1-54 . The template users have no access to the mib in the default configuration. Us...
Page 81: Further Reading
Chapter 1: product description system management page 1-57 further reading for information about… refer to… how to plan for snmpv3 operation planning for snmpv3 operation on page 3-60 how to configure snmpv3 snmp pages (for snmpv3) on page 6-90 system logging (syslog) ptp 670 supports the standard s...
Page 82: Further Reading
Chapter 1: product description system management page 1-58 • at the wireless port to encrypt data transmitted over the wireless link. • at the snmp management interface in the snmpv3 mode. • at the https/tls management interface. Two levels of encryption are available to purchase: • 128-bit: this al...
Page 83: Further Reading
Chapter 1: product description system management page 1-59 further reading for information about… refer to… how to zeroize csps zeroize csps page on page 6-117 how to zeroize csps (recovery mode) zeroize critical security parameters on page 7-82 software upgrade the management agent supports applica...
Page 84: Capability Upgrades
Chapter 1: product description system management page 1-60 capability upgrades odus are shipped with a default license key factory-installed. The default license key enables a limited set of capabilities which depend upon the odu variant. Capability upgrades are purchased from cambium and supplied a...
Page 85: Recovery Mode Options
Chapter 1: product description system management page 1-61 note when recovery has been entered through a power on/off/on cycle, the odu will revert to normal operation if no web access has been made to the unit within 30 seconds. This prevents the unit remaining inadvertently in recovery following a...
Page 86: Chapter 2:
Page 2-1 chapter 2: system hardware this chapter describes the hardware components of a ptp 670 link. The following topics are described in this chapter: • outdoor unit (odu) on page 2-2 • power supply units (psu) on page 2-12 • antennas and antenna cabling on page 2-21 • ethernet cabling on page 2-...
Page 87: Outdoor Unit (Odu)
Chapter 2: system hardware outdoor unit (odu) page 2-2 outdoor unit (odu) odu description the odu is a self-contained transceiver unit that houses both radio and networking electronics. Two odus are required for a ptp link. Hardware platform variants ptp 670 odus are available in two different hardw...
Page 88: Ptp 670 Integrated Odu
Chapter 2: system hardware outdoor unit (odu) page 2-3 o 96 “4.8 ghz mexico” (4.8 to 5.9 ghz frequency variant only) for details of how to configure the odus to operate with other country licenses, refer to generating license keys on page 6-3 and software license key page on page 6-13 . The list of ...
Page 89: Capability Licensing
Chapter 2: system hardware outdoor unit (odu) page 2-4 capability licensing ptp 670 odus support the following capability upgrades (see odu capability upgrades on page 2-7 ): • sfp port operation • aes encryption • synchronous ethernet and 1588 transparent clock • tdm (e1 or t1) operation • high cap...
Page 90: Ptp 670 Connectorized Odu
Chapter 2: system hardware outdoor unit (odu) page 2-5 cambium description cambium part number ptp 670 integrated 23dbi end with ac+dc enhanced supply (row - u.S. Line cord) c050067h010a ptp 670 integrated 23dbi end with ac supply (row - eu line cord) c050067h015a ptp 670 integrated 23dbi end with a...
Page 91: Capability Licensing
Chapter 2: system hardware outdoor unit (odu) page 2-6 note to determine when to install external antennas and to calculate their impact on link performance and regulatory limits, see planning for connectorized units on page 3-29 . To select antennas, rf cables and connectors for connectorized units...
Page 92: Odu Capability Upgrades
Chapter 2: system hardware outdoor unit (odu) page 2-7 • one ac power injector 56v or one ac+dc enhanced power injector 56v psu. • one line cord, either us or eu as indicated. • one tilt bracket assembly ( figure 9 ). Table 7 odu kit part numbers for connectorized odus cambium description cambium pa...
Page 93: Odu Accessories
Chapter 2: system hardware outdoor unit (odu) page 2-8 odu accessories spare odu port blanking plugs are available from cambium networks ( table 9 ). Table 9 odu accessory part numbers cambium description cambium part number blanking plug pack (qty 10) n000065l036a odu mounting brackets the tilt bra...
Page 94: Odu Interfaces
Chapter 2: system hardware outdoor unit (odu) page 2-9 figure 10 odu mounting bracket (integrated) table 10 odu mounting bracket part numbers bracket odu variants bracket part number tilt bracket assembly ptp 670 integrated ptp 670 connectorized n000045l002a mounting bracket (integrated) ptp 670 int...
Page 95
Chapter 2: system hardware outdoor unit (odu) page 2-10 figure 11 odu rear interfaces table 11 odu rear interfaces port name connector interface description main psu rj45 poe input proprietary power over ethernet (poe). 100/1000base-t ethernet management and/or data. Aux rj45 100/1000base-t ethernet...
Page 96: Odu Specifications
Chapter 2: system hardware outdoor unit (odu) page 2-11 odu specifications the ptp 670 odu conforms to the specifications listed in table 12 . Table 12 odu specifications category specification dimensions integrated: 371 mm (14.6 in) x 371 mm (14.6 in) x 81 mm (3.2 in) connectorized: 204 mm (8.0 in)...
Page 97: Power Supply Units (Psu)
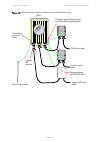
Chapter 2: system hardware power supply units (psu) page 2-12 power supply units (psu) psu description the psu is an indoor unit that is connected to the odu and network terminating equipment using cat5e cable with rj45 connectors. It is also plugged into an ac or dc power supply so that it can inje...
Page 98
Chapter 2: system hardware power supply units (psu) page 2-13 figure 13 ac power injector 56v figure 14 ac+dc power injector 56v.
Page 99
Chapter 2: system hardware power supply units (psu) page 2-14 figure 15 cmm5 power and sync injector figure 16 cmm5 controller.
Page 100: Further Reading
Chapter 2: system hardware power supply units (psu) page 2-15 figure 17 cmm5 240 watt ac/dc power supply warning always use an appropriately rated and approved ac supply cord-set in accordance with the regulations of the country of use. Caution the psu odu ports are designed to connect only to ptp 6...
Page 101
Chapter 2: system hardware power supply units (psu) page 2-16 cambium description cambium part number ac power injector 56v n000065l001c us line cord fig 8 n000065l003a uk line cord fig 8 n000065l004a eu line cord fig 8 n000065l005a australia line cord fig 8 n000065l006a cmm5 power and sync injector...
Page 102
Chapter 2: system hardware power supply units (psu) page 2-17 ac+dc enhanced power injector 56v interfaces the ac+dc enhanced power injector 56v interfaces are shown in figure 19 and described in table 15 . Figure 19 ac+dc enhanced power injector 56v interfaces table 15 ac+dc enhanced power injector...
Page 103
Chapter 2: system hardware power supply units (psu) page 2-18 interface function odu port rj45 socket for connecting cat5e cable to odu. Lan port rj45 socket for connecting cat5e cable to network. Dc power in (green) led dc power supply detection ac power in (green) led ac power supply detection eth...
Page 104: Psu Specifications
Chapter 2: system hardware power supply units (psu) page 2-19 psu specifications the ac power injector 56v conforms to the specifications listed in table 17. The ac+dc enhanced power injector 56v conforms to the specifications listed in table 18 . The cmm5 power and sync injector 56 v conforms to th...
Page 105
Chapter 2: system hardware power supply units (psu) page 2-20 category specification dc output current 1.7a efficiency better than 84% over current protection hiccup current limiting, trip point set between 120% to 150% of full load current hold up time at least 20 milliseconds power factor better t...
Page 106: Antenna Requirements
Chapter 2: system hardware antennas and antenna cabling page 2-21 antennas and antenna cabling antenna requirements each connectorized odu requires one external antenna (normally dual-polar), or if spatial diversity is required, each odu requires two antennas. These antennas are not supplied by camb...
Page 107: Antenna Accessories
Chapter 2: system hardware antennas and antenna cabling page 2-22 antenna accessories connectorized odus require the following additional components: • cable grounding kits: order one cable grounding kit for each grounding point on the antenna cables. Refer to lightning protection unit (lpu) and gro...
Page 108
Chapter 2: system hardware antennas and antenna cabling page 2-23 manufacturer antenna type nominal gain (dbi) cambium part number cambium 2-foot dual-pol parabolic, hpd2-4.7 26.8 rdh4518a mars ma-ws54-50r flat plate (dual-pol) 23.0 integrated mars ma-wa56-dp23g7cm flat plate (dual-pol) 23.0 integra...
Page 109
Chapter 2: system hardware antennas and antenna cabling page 2-24 manufacturer antenna type nominal gain (dbi) cambium part number mars ma-ws54-50r flat plate (dual-pol) 23.0 integrated mars ma-wa56-dp23g7cm flat plate (dual-pol) 23.0 integrated cambium 90 4.9 - 6 ghz, 90/120 deg sector antenna 18.0...
Page 110: Isedc Approved Antennas
Chapter 2: system hardware antennas and antenna cabling page 2-25 manufacturer antenna type nominal gain (dbi) cambium part number cambium 2ft 5ghz single-pol parabolic ptp antenna 29.1 n050067d012a cambium 2ft 5ghz dual-pol parabolic ptp antenna 28.8 n050067d002a mars ma-ws54-50r flat plate (dual-p...
Page 111
Chapter 2: system hardware antennas and antenna cabling page 2-26 • 4.9 ghz – 36.0 dbi par polarisation maximum. • 5.1 ghz – 34.5 dbi par polarisation maximum. • 5.2 ghz – 34.5 dbi par polarisation maximum. • 5.4 ghz – 34.5 dbi par polarisation maximum. • 5.8 ghz – 38.1 dbi par polarisation maximum....
Page 112
Chapter 2: system hardware antennas and antenna cabling page 2-27 table 27 antennas permitted for deployment in canada – 5.1 ghz manufacturer antenna type nominal gain (dbi) cambium part number andrew 4-foot dual-pol parabolic, px4f-52 34.5 rdg4453b cambium 4ft 5ghz single-pol parabolic ptp antenna ...
Page 113
Chapter 2: system hardware antennas and antenna cabling page 2-28 table 29 antennas permitted for deployment in canada – 5.4 ghz manufacturer antenna type nominal gain (dbi) cambium part number andrew 4-foot dual-pol parabolic, px4f-52 34.5 rdg4453b cambium 4ft 5ghz single-pol parabolic ptp antenna ...
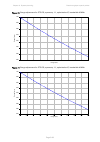
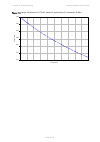
Page 114
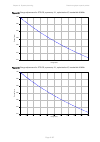
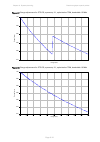
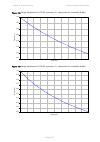
Chapter 2: system hardware antennas and antenna cabling page 2-29 manufacturer antenna type nominal gain (dbi) cambium part number kppa kppa-5.7-dpoma omni (dual-pol) 13.0
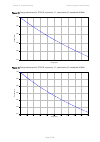
Page 115: Ethernet Cabling
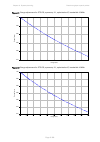
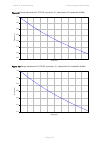
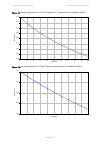
Chapter 2: system hardware ethernet cabling page 2-30 ethernet cabling ethernet standards and cable lengths all configurations require a copper ethernet connection from the odu (psu port) to the psu. Advanced configurations may also require one or both of the following: • a copper ethernet connectio...
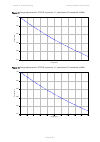
Page 116
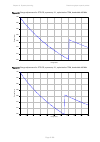
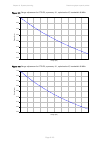
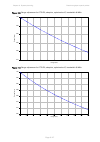
Chapter 2: system hardware ethernet cabling page 2-31 table 32 aux and copper sfp ethernet standards and cable length restrictions odu drop cable power over ethernet ethernet supported (*1) maximum cable length (*2) aux – auxiliary device poe to auxiliary device 100base-tx 1000base-t 100 m (330 ft) ...
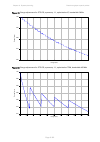
Page 117: Cable Grounding Kit
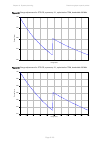
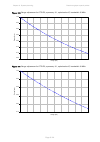
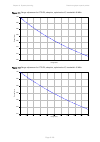
Chapter 2: system hardware ethernet cabling page 2-32 table 33 drop cable part numbers cambium description cambium part number 1000 ft reel outdoor copper clad cat5e wb3175 328 ft (100 m) reel outdoor copper clad cat5e wb3176 cable grounding kit copper drop cable shields must be bonded to the ground...
Page 118
Chapter 2: system hardware ethernet cabling page 2-33 lightning protection unit (lpu) and grounding kit lpus provide transient voltage surge suppression for ptp 670 installations. Each psu or aux drop cable requires two lpus, one near the odu and the other near the linked device, usually at the buil...
Page 119: Lpu For Gps Drop Cables
Chapter 2: system hardware ethernet cabling page 2-34 one lpu and grounding kit ( table 35 ) is required for the psu drop cable connection to the odu. If the odu is to be connected to an auxiliary device, one additional lpu and grounding kit is required for the aux drop cable. Order the kits from ca...
Page 120: Cable Hoisting Grip
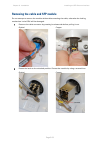
Chapter 2: system hardware ethernet cabling page 2-35 table 37 lpu and grounding kit part number – use with gps receiver drop cable only cambium description cambium part number lpu end kit ptp 250/300/500 wb2978 rj45 connectors and spare glands rj45 connectors are required for plugging cat5e cables ...
Page 121: Indoor Cat5E Cable
Chapter 2: system hardware ethernet cabling page 2-36 figure 25 cable hoisting grip indoor cat5e cable to connect the psu to network terminating equipment, use indoor cat5e cable. The odu network connection implements automatic mdi/mdi-x sensing and pair swapping, allowing connection to networking e...
Page 122
Chapter 2: system hardware ethernet cabling page 2-37 table 41 multi-mode optical sfp interface (part number c000065l009a) core/ cladding (microns) mode bandwidth at 850 nm (mhz/km) maximum length of optical interface insertion loss (db) 62.5/125 multi 160 220 m (720 ft) 2.38 62.5/125 multi 200 275 ...
Page 123
Chapter 2: system hardware ethernet cabling page 2-38 optical cable and connectors order an optical cable with lc connectors from a specialist fabricator, quoting the specification shown in figure 28 . It must be the correct length to connect the odu to the other device. Lc connectors should be supp...
Page 124: Ptp-Sync Unit
Chapter 2: system hardware ptp-sync unit page 2-39 ptp-sync unit ptp-sync unit description the ptp-sync unit is an optional component, used to synchronize the odu tdd frame with a network-wide reference. It measures the difference between the tdd frame timing and a 1 hz timing reference, and signals...
Page 125: Ptp-Sync Part Numbers
Chapter 2: system hardware ptp-sync unit page 2-40 figure 30 ptp-sync rack mounting adapter ptp-sync part numbers order ptp-sync kits and associated components from cambium networks ( table 42 ). Table 42 ptp-sync component part numbers cambium description cambium part number ptp-sync kit wb3665 cmu...
Page 126: Ptp-Sync Unit Interfaces
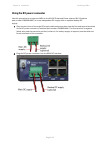
Chapter 2: system hardware ptp-sync unit page 2-41 ptp-sync unit interfaces the ptp-sync front panel is illustrated in figure 31. The annotated interfaces are described in table 43 and table 44 . Figure 31 ptp-sync front panel table 43 ptp-sync interface functions # description function 1 gps/sync i...
Page 127: Ptp-Sync Specifications
Chapter 2: system hardware ptp-sync unit page 2-42 ptp-sync specifications the ptp-sync unit conforms to the specifications listed in table 45 , table 46 and table 47 . Table 45 ptp-sync unit physical specifications category specification dimensions width excluding ears 174 mm (6.69 in) width includ...
Page 128
Chapter 2: system hardware ptp-sync unit page 2-43 category specification pulse width 1 μs to 500 ms polarity reference edge is when pin 3 (ppsa) is positive with respect to pin 6 (ppsb) table 49 ptp-sync unit timing specifications - 1pps in (sma) category specification signal type 1 hz signal pulse...
Page 129: Signal Polarities
Chapter 2: system hardware ptp-sync unit page 2-44 signal polarities a 1 pps timing datum is detected when gps_1ppsa goes positive relative to gps_1ppsb. A serial data start bit is detected when gps_rxda (or gps_txda) goes positive relative to gps_rxdb (or gps_txdb)..
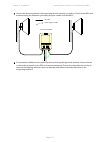
Page 130: Gps Receivers
Chapter 2: system hardware gps receivers page 2-45 gps receivers trimble acutime™ gg gps receiver for ptp-sync the gps receiver ( figure 32 ) is an optional timing reference source for ptp-sync. It provides a 1 hz signal, accurately synchronized in frequency and phase across the network. Figure 32 g...
Page 131: Gps Receiver Part Numbers
Chapter 2: system hardware gps receivers page 2-46 gps receiver part numbers order gps receivers and associated components from cambium networks ( table 51 ). Table 51 gps receiver component part numbers for use with ptp-sync cambium description cambium part number trimble acutime™gg gps receiver wb...
Page 132: Network Indoor Unit (Nidu)
Chapter 2: system hardware network indoor unit (nidu) page 2-47 network indoor unit (nidu) nidu description the nidu ( figure 34 ) is an optional component that adds up to eight tdm channels (e1 or t1) to a ptp 670 link. It multiplexes and demultiplexes e1, t1 and ethernet data over the wireless bri...
Page 133: Nidu Part Numbers
Chapter 2: system hardware network indoor unit (nidu) page 2-48 nidu part numbers order nidus and associated components from cambium networks ( table 53 ). Table 53 nidu component part numbers cambium description cambium part number network indoor unit (one per end) c000065l043 nidu - dc power conne...
Page 134: Nidu Specifications
Chapter 2: system hardware network indoor unit (nidu) page 2-49 nidu specifications the nidu conforms to the specifications listed in table 55 . Table 55 nidu specifications category specification dimensions width 172 mm (6.8 in) height 32 mm (1.3 in) depth 218 mm (8.6 in) weight 0.88 kg (1.95 lb) t...
Page 135
Chapter 2: system hardware network indoor unit (nidu) page 2-50 table 57 nidu odu port pinouts pin no. Connector pinout signal name (*) signal description pin 1 odu_phyn_pair1+ gigabit tx/rx pair 1 pin 2 odu_phyn_pair1- gigabit tx/rx pair 1 pin 3 odu_phyn_pair2+ gigabit tx/rx pair 2 pin 4 odu_phyn_p...
Page 136: Chapter 3:
Page 3-1 chapter 3: system planning this chapter provides information to help the user to plan a ptp 670 link. The following topics are described in this chapter: • typical deployment on page 3-2 contains diagrams illustrating typical ptp 670 site deployments. • site planning on page 3-11 describes ...
Page 137: Typical Deployment
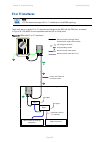
Chapter 3: system planning typical deployment page 3-2 typical deployment this section contains diagrams illustrating typical ptp 670 site deployments. Odu with poe interface to psu in the basic configuration, there is only one ethernet interface, a copper cat5e power over ethernet (poe) from the ps...
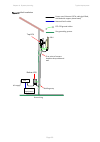
Page 138
Chapter 3: system planning typical deployment page 3-3 figure 37 wall installation odu psu network equipment ptp 670 ground cables site grounding system top lpu bottom lpu ground ring first point of contact between drop cable and wall building entry power over ethernet cat5e cable (gel-filled, shiel...
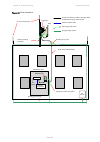
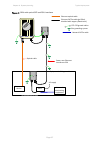
Page 139
Chapter 3: system planning typical deployment page 3-4 figure 38 roof installation air terminals (finials) tower grounding conductor building ground ring ac service equipment room top lpu odu ptp 670 ground cables network cat5e cable site grounding system ac supply psu network equipment bottom lpu b...
Page 140: E1 Or T1 Interfaces
Chapter 3: system planning typical deployment page 3-5 e1 or t1 interfaces note ptp 670 does not support e1 or t1 interfaces in the hcmp topology. There may be up to eight e1 or t1 channels connected to the odu via the psu port, as shown in figure 39 . The nidu is not compatible with the sfp or aux ...
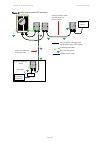
Page 141
Chapter 3: system planning typical deployment page 3-6 sfp and aux ethernet interfaces there may be one or two additional ethernet interfaces connected to the odu: one to the sfp port (copper or optical) and one to the aux port, as shown in the following diagrams: • odu with copper sfp and psu inter...
Page 142
Chapter 3: system planning typical deployment page 3-7 figure 41 odu with optical sfp and psu interfaces equipment building or cabinet . Psu network terminating equipment ac supply xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx sfp aux psu optical cable connected device ethernet optical cable power over ethernet interface to psu ...
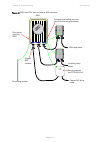
Page 143
Chapter 3: system planning typical deployment page 3-8 figure 42 odu with aux and psu interfaces auxiliary device ethernet interface (with optional power) to auxiliary device equipment building or cabinet . Psu network terminating equipment ac supply xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx sfp aux psu power over ethernet i...
Page 144: Gps Receiver Interfaces
Chapter 3: system planning typical deployment page 3-9 gps receiver interfaces if a gps receiver is deployed for ptp-sync, it may be mounted on the wall of the equipment building ( figure 43 ) (preferred option), or on a metal tower or mast ( figure 44 ). Figure 43 gps receiver wall installation psu...
Page 145
Chapter 3: system planning typical deployment page 3-10 figure 44 gps receiver tower or mast installation ptp 670 ground cables power over ethernet cat5e cable (gel- filled, shielded with copper-plated steel) network cat5e cable site grounding system tower ground bar ground ring equipment building o...
Page 146: Site Planning
Chapter 3: system planning site planning page 3-11 site planning this section describes factors to be considered when planning the proposed link end sites, including grounding, lightning protection and equipment location for the odu, psu, ptp-sync unit (if installed) and gps receivers (if installed)...
Page 147: Site Grounding System
Chapter 3: system planning site planning page 3-12 figure 45 rolling sphere method to determine the lightning protection zones zone a: in this zone a direct lightning strike is possible. Do not mount equipment in this zone. Zone b: in this zone, direct emd (lightning) effects are still possible, but...
Page 148
Chapter 3: system planning site planning page 3-13 odu and external antenna location find a location for the odu (and external antenna for connectorized units) that meets the following requirements: • the equipment is high enough to achieve the best radio path. • people can be kept a safe distance a...
Page 149: Odu Wind Loading
Chapter 3: system planning site planning page 3-14 odu wind loading ensure that the odu and the structure on which it is mounted are capable of withstanding the prevalent wind speeds at a proposed ptp 670 site. Wind speed statistics should be available from national meteorological offices. The odu a...
Page 150: Psu Dc Power Supply
Chapter 3: system planning site planning page 3-15 psu dc power supply if using the dc input on the ac+dc power injector 56v, ensure that the dc power supply meets the following requirements: • the voltage and polarity must be correct and must be applied to the correct psu terminals. • the power sou...
Page 151: Nidu Location
Chapter 3: system planning site planning page 3-16 • it must have an un-interrupted view of at least half of the sky. For a receiver mounted on a wall there must be no other significant obstructions in the view of the sky. • it must be mounted at least 1 m (3 ft), preferably 2 m (6 ft), away from ot...
Page 152: Drop Cable Grounding Points
Chapter 3: system planning site planning page 3-17 drop cable grounding points to estimate how many grounding kits are required for each drop cable, refer to the site installation diagrams ( figure 36 , figure 37 and figure 38 ) and use the following criteria: • the drop cable shield must be grounde...
Page 153
Chapter 3: system planning site planning page 3-18 figure 46 odu with psu, aux and copper sfp interfaces odu sfp aux psu copper sfp drop cable auxiliary drop cable psu drop cable common grounding point for top lpus and surge protector grounding point for odu grounding system copper sfp module surge ...
Page 154
Chapter 3: system planning site planning page 3-19 figure 47 odu with psu, aux and optical sfp interfaces figure 48 bottom lpu and surge protector.
Page 155: Radio Spectrum Planning
Chapter 3: system planning radio spectrum planning page 3-20 radio spectrum planning this section describes how to plan ptp 670 links to conform to the regulatory restrictions that apply in the country of operation. Caution it is the responsibility of the user to ensure that the ptp product is opera...
Page 156: Regulatory Limits
Chapter 3: system planning radio spectrum planning page 3-21 table 62 ptp 670 wireless specifications (per frequency band), 4.8 ghz to 5.9 ghz variant item 4.8 ghz 4.9 ghz 5.1 ghz 5.2 ghz 5.4 ghz 5.8 ghz rf band (mhz) 4800–4900 4900–4990 5150–5250 5250–5350 5470–5725 5725–5875 channel bandwidth (mhz...
Page 157: Conforming to The Limits
Chapter 3: system planning radio spectrum planning page 3-22 conforming to the limits ensure the link is configured to conform to local regulatory requirements by installing license keys for the correct country. When using connectorized odus with external antennas, ensure that the antenna gain and f...
Page 158
Chapter 3: system planning radio spectrum planning page 3-23 • dynamic spectrum optimization (dso): in this mode, the unit monitors the spectrum looking for the channel with the lowest level of interference. Statistical techniques are used to select the most appropriate transmit and receive channels...
Page 159: Link Planning
Chapter 3: system planning link planning page 3-24 link planning this section describes factors to be taken into account when planning links, such as range, obstacles path loss and throughput. Linkplanner is recommended. Linkplanner the cambium linkplanner software and user guide may be downloaded f...
Page 160: Path Loss
Chapter 3: system planning link planning page 3-25 • with higher gain connectorized antennas, ensure the predicted receiver signal level (from linkplanner) is below -53 dbm (for 5.2 ghz or 5.4 ghz) or below -58 dbm (for 5.8 ghz). Linkplanner for synchronized networks tdd synchronization should be pl...
Page 161
Chapter 3: system planning link planning page 3-26 calculating data rate capacity the data capacity of a ptp or hcmp link is defined as the maximum end-to-end ethernet throughput (including ethernet headers) that it can support, assumed ethernet frames of 1518 octets. Data capacity is determined by ...
Page 162
Chapter 3: system planning link planning page 3-27 calculation example for ptp topology suppose that the link characteristics are: • link symmetry = 1:1 • link mode optimization = tdm • modulation mode = 64qam 0.92 dual • channel bandwidth = 10 mhz • link range = 60 km the calculation procedure for ...
Page 163
Chapter 3: system planning link planning page 3-28 note the capacity of a link in the hcmp topology depends on the maximum link range configured in the odu, but does not depend on the range of the individual link. The number of slaves is the maximum number that can be supported by the master, and no...
Page 164: Ptp Topology
Chapter 3: system planning planning for connectorized units page 3-29 planning for connectorized units this section describes factors to be taken into account when planning to use connectorized odus with external antennas in ptp 670 links. When to install connectorized units ptp topology the majorit...
Page 165
Chapter 3: system planning planning for connectorized units page 3-30 note enter the antenna gain and cable loss into the installation wizard, if the country selected has an eirp limit, the corresponding maximum transmit power will be calculated automatically by the unit. Note under innovation, scie...
Page 166: Using Ptp-Sync
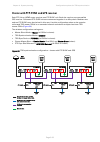
Chapter 3: system planning configuration options for tdd synchronization page 3-31 configuration options for tdd synchronization this section describes the different configuration options that may be used for implementing tdd synchronization in the ptp 670 series. Schematic diagrams are included. Us...
Page 167
Chapter 3: system planning configuration options for tdd synchronization page 3-32 single ptp link or hcmp sector configuration with ptp-sync each ptp link or hcmp sector requires one ptp-sync unit connected to the master odu and one compatible gps receiver. Use this configuration where a site conta...
Page 168
Chapter 3: system planning configuration options for tdd synchronization page 3-33 cluster with ptp-sync and gps receiver each ptp link or hcmp sector requires one ptp-sync unit. Each site requires one compatible gps receiver. Collocated ptp-sync units are connected together in a daisy-chain. Betwee...
Page 169
Chapter 3: system planning configuration options for tdd synchronization page 3-34 cluster with ptp-sync and no gps receiver each ptp link or hcmp sector requires one ptp-sync unit. Ptp-sync units are connected together in a daisy-chain. Between two and ten ptp-syncs may be chained in this way. One ...
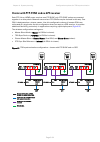
Page 170: Using Cmm5
Chapter 3: system planning configuration options for tdd synchronization page 3-35 using cmm5 each odu must be connected to the cmm5 power and sync injector. The cmm5 power and sync injector must be connected directly or indirectly to a ugps receiver. The wireless configuration settings are: • maste...
Page 171: Data Network Planning
Chapter 3: system planning data network planning page 3-36 data network planning this section describes factors to be considered when planning ptp 670 data networks. Ethernet interfaces the ptp 670 ethernet ports conform to the specifications listed in table 71 . Table 65 ptp 670 ethernet bridging s...
Page 172: Port Allocation Rules
Chapter 3: system planning data network planning page 3-37 01-80-c2-00-00-30 to 01-80-c2-00-00-3f ieee 802.1ag, connectivity fault management (cfm) 01-19-a7-00-00-00 to 01-19-a7-00-00-ff ring automatic protection switching (r-aps) 00-e0-2b-00-00-04 ethernet automatic protection switching (eaps) tabl...
Page 173
Chapter 3: system planning data network planning page 3-38 service combination figure data + out-of-band management + local management figure 58 data with in-band management + second data figure 59 data with in-band management + second data + local management figure 60 data + second data with in-ban...
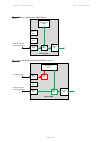
Page 174
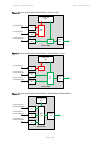
Chapter 3: system planning data network planning page 3-39 figure 54 ports and services: data/in-band figure 55 ports and services: data/in-band + local ptp 670 odu management agent wireless port ethernet port ethernet port ethernet port mac relay customer data and in-band management ptp 670 odu man...
Page 175
Chapter 3: system planning data network planning page 3-40 figure 56 ports and services: data/in-band + local + local figure 57 ports and services: data + out-of-band ptp 670 odu management agent wireless port ethernet port ethernet port ethernet port mac relay customer data and in-band management l...
Page 176
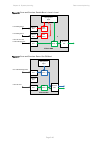
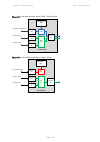
Chapter 3: system planning data network planning page 3-41 figure 58 ports and services: data + out-of-band + local figure 59 ports and services: data/in-band + second data ptp 670 odu management agent ethernet port ethernet port ethernet port mac relay local management mac relay customer data ether...
Page 177
Chapter 3: system planning data network planning page 3-42 figure 60 ports and services: data/in-band + second data + local figure 61 ports and services: data + second data/in-band ptp 670 odu management agent ethernet port ethernet port ethernet port mac relay local management mac relay second data...
Page 178
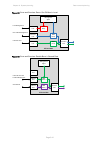
Chapter 3: system planning data network planning page 3-43 figure 62 ports and services: data + second data/in-band + local figure 63 ports and services: data + second data + local use a compatible combination of services at both ends of the link ptp 670 allows twelve different combinations of servi...
Page 179
Chapter 3: system planning data network planning page 3-44 table 69 combinations of services with optional local management service combination data + local management + [local management] data + in-band management + [local management] + [local management] data + out-of-band management + [local mana...
Page 180
Chapter 3: system planning data network planning page 3-45 figure 64 example of independent mapping of services to ports additional port allocation rules the three ethernet ports are generally interchangeable, except for some specific additional rules listed below: • if the tdm interface (e1 or t1) ...
Page 181: Port Allocation Rules
Chapter 3: system planning data network planning page 3-46 ethernet port allocation for hcmp topology port allocation rules decide how the three odu ethernet ports will be allocated to the data service, management service and local management service based on the following rules: • map the data serv...
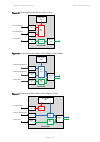
Page 182
Chapter 3: system planning data network planning page 3-47 figure 65 ports and services: data + local + local figure 66 ports and services: data + out-of-band + out-of-band figure 67 ports and services: data + out-of-band + local ptp 670 odu management agent wireless port ethernet port ethernet port...
Page 183
Chapter 3: system planning data network planning page 3-48 figure 68 ports and services: data + data + out-of-band figure 69 ports and services: data + data + local ptp 670 odu management agent wireless port ethernet port ethernet port ethernet port mac relay customer data out-of-band management mac...
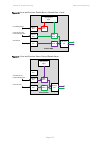
Page 184
Chapter 3: system planning data network planning page 3-49 figure 70 ports and services: data/in-band + local + local figure 71 ports and services: data/in-band + data/in-band + local figure 72 ports and services: data/in-band + data/in-band + data/in-band ptp 670 odu management agent wireless port ...
Page 185: Vlan Membership
Chapter 3: system planning data network planning page 3-50 use a compatible combination of services at both ends of the link ptp 670 supports flexible allocation of ports to services, and this allocation may be different at the two ends of the link. However, the management service configuration must...
Page 186: Layer 2 Control Protocols
Chapter 3: system planning data network planning page 3-51 find out the correct subnet mask (ipv4) or prefix length (ipv6) and gateway ip address for this network segment and vlan. Ensure that the design of the data network permits bidirectional routing of ip datagrams between network management sys...
Page 187: Ip/mpls Priority Scheme
Chapter 3: system planning data network planning page 3-52 ip/mpls priority scheme ip priority is determined by the dscp value encoded in the tos field in ipv4 and traffic class in ipv6. Ptp 670 can locate the dscp value in ip headers encapsulated within vlan tags and/or ppp and pppoe headers. The d...
Page 188: Tdm Network Planning
Chapter 3: system planning tdm network planning page 3-53 tdm network planning this section describes factors to be considered when planning ptp 670 tdm networks. Caution if the odu port has negotiated a link at 100base-t, the nidu will not send or receive tdm data, and will not bridge customer data...
Page 189: Network Management Planning
Chapter 3: system planning network management planning page 3-54 network management planning this section describes how to plan for ptp 670 links to be managed remotely using snmp. Planning for snmp operation the supported notifications are as follows: • cold start • wireless link up/down • channel ...
Page 190: Enabling Snmp
Chapter 3: system planning network management planning page 3-55 enabling snmp enable the snmp interface for use by configuring the following attributes in the snmp configuration page: • snmp state (default disabled) • snmp version (default snmpv1/2c) • snmp port number (default 161).
Page 191: Security Planning
Chapter 3: system planning security planning page 3-56 security planning this section describes how to plan for ptp 670 links to operate in secure mode. Planning for sntp operation note ptp 670 does not have a battery-powered clock, so the set time is lost each time the odu is powered down. To avoid...
Page 192: Aes License
Chapter 3: system planning security planning page 3-57 table 72 security wizard attributes item description quantity required key of keys an encryption key generated using a cryptographic key generator. The key length is dictated by the installed license key. License keys with aes-128 will require a...
Page 193: Tls-Rsa
Chapter 3: system planning security planning page 3-58 tls-rsa determine tls minimum security level. This is the smallest key size that will be allowed in a link between master and slave. For example, if the master has tls minimum security level of 128-bit aes and the slave has no aes license then t...
Page 194: Tls-Psk
Chapter 3: system planning security planning page 3-59 item description quntity required root ca public certificate the self-signed public key certificate for the root ca that signed the device certificate in the remote odu. The root ca must form a certificate chain with the device certificate witho...
Page 195: Snmp Security Mode
Chapter 3: system planning security planning page 3-60 planning for protocols and ports detemine the protocols that will be enabled at the management agent, and the port numbers to be used. Table 76 protocol and port settings item description quantity required port numbers for http, https and telnet...
Page 196
Chapter 3: system planning security planning page 3-61 • ipv6 address if snmp engine id will be based on a text string, identify the text string required by the network management system. This is often based on some identifier that survives replacement of the ptp hardware. Identify the user names an...
Page 197: Vacm Default Configuration
Chapter 3: system planning security planning page 3-62 identify up to two snmp users that will be configured to receive notifications (traps). Identify the internet address (ipv4 or ipv6) and udp port number of the associated snmp manager. Snmpv3 default configuration (mib-based) when snmpv3 mib-bas...
Page 198
Chapter 3: system planning security planning page 3-63 table 79 default vacm view trees object entry 1 entry 2 viewname internet restricted subtree 1.3.6.1 1.3.6.1 mask “” “” type included included storagetype nonvolatile nonvolatile table 80 default data fill for access table object entry 1 entry 2...
Page 199: Radius Attributes
Chapter 3: system planning security planning page 3-64 • ms-chapv2 ensure that the authentication method selected in ptp 670 is supported by the radius server. Radius attributes if the standard radius attribute session-timeout (type 27) is present in a radius response, ptp 670 sets a maximum session...
Page 200
Chapter 3: system planning system threshold, output power and link loss page 3-65 system threshold, output power and link loss use the following tables to look up the system threshold (dbm), output power (dbm) and maximum link loss (db) per channel bandwidth and modulation mode: frequency variant ba...
Page 201
Chapter 3: system planning system threshold, output power and link loss page 3-66 4.8 ghz to 5.9 ghz frequency variant table 82 4.8 ghz ip mode: system threshold per channel bandwidth and output power (dbm) modulation mode 5 mhz 10 mhz 15 mhz 20 mhz 30 mhz 40 mhz 45 mhz p (all bands) bpsk 0.63 singl...
Page 202
Chapter 3: system planning system threshold, output power and link loss page 3-67 table 84 4.8 ghz tdm mode: system threshold per channel bandwidth and output power (dbm) modulation mode 5 mhz 10 mhz 15 mhz 20 mhz 30 mhz 40 mhz 45 mhz p (all bands) bpsk 0.63 single -93.5 -92.0 -90.2 -89.0 -87.2 -86....
Page 203
Chapter 3: system planning system threshold, output power and link loss page 3-68 table 86 4.9 ghz ip mode: system threshold per channel bandwidth and output power (p) (dbm) modulation mode 5 mhz 10 mhz 15 mhz 20 mhz 30 mhz 40 mhz 45 mhz p (all bands) bpsk 0.63 single -93.6 -92.1 -90.3 -89.1 -87.3 -...
Page 204
Chapter 3: system planning system threshold, output power and link loss page 3-69 table 88 4.9 ghz tdm mode: system threshold per channel bandwidth and output power (dbm) modulation mode 5 mhz 10 mhz 15 mhz 20 mhz 30 mhz 40 mhz 45 mhz p (all bands) bpsk 0.63 single -93.6 -92.1 -90.3 -89.1 -87.3 -86....
Page 205
Chapter 3: system planning system threshold, output power and link loss page 3-70 table 90 5.1/5.2 ghz ip mode: system threshold per channel bandwidth and output power (dbm) modulation mode 5 mhz 10 mhz 15 mhz 20 mhz 30 mhz 40 mhz 45 mhz p (all bands) bpsk 0.63 single -93.6 -92.1 -90.3 -89.1 -87.3 -...
Page 206
Chapter 3: system planning system threshold, output power and link loss page 3-71 table 92 5.1/5.2 ghz tdm mode: system threshold per channel bandwidth and output power (dbm) modulation mode 5 mhz 10 mhz 15 mhz 20 mhz 30 mhz 40 mhz 45 mhz p (all bands) bpsk 0.63 single -93.6 -92.1 -90.3 -89.1 -87.3 ...
Page 207
Chapter 3: system planning system threshold, output power and link loss page 3-72 table 94 5.4 ghz ip mode: system threshold per channel bandwidth and output power (dbm) modulation mode 5 mhz 10 mhz 15 mhz 20 mhz 30 mhz 40 mhz 45 mhz p (all bands) bpsk 0.63 single -93.6 -91.6 -89.8 -88.6 -86.8 -85.6...
Page 208
Chapter 3: system planning system threshold, output power and link loss page 3-73 table 96 5.4 ghz tdm mode: system threshold per channel bandwidth and output power (dbm) modulation mode 5 mhz 10 mhz 15 mhz 20 mhz 30 mhz 40 mhz 45 mhz p (all bands) bpsk 0.63 single -93.6 -91.6 -89.8 -88.6 -86.8 -85....
Page 209
Chapter 3: system planning system threshold, output power and link loss page 3-74 table 98 5.8 ghz ip mode: system threshold per channel bandwidth and output power (dbm) modulation mode 5 mhz 10 mhz 15 mhz 20 mhz 30 mhz 40 mhz 45 mhz p (all bands) bpsk 0.63 single -93.1 -91.1 -89.3 -88.1 -86.3 -85.1...
Page 210
Chapter 3: system planning system threshold, output power and link loss page 3-75 table 100 5.8 ghz tdm mode: system threshold per channel bandwidth and output power (dbm) modulation mode 5 mhz 10 mhz 15 mhz 20 mhz 30 mhz 40 mhz 45 mhz p (all bands) bpsk 0.63 single -93.1 -91.1 -89.3 -88.1 -86.3 -85...
Page 211
Chapter 3: system planning system threshold, output power and link loss page 3-76 4.9 ghz to 6.05 ghz frequency variant table 102 4.9 ghz ip mode: system threshold per channel bandwidth and output power (dbm) modulation mode 5 mhz 10 mhz 15 mhz 20 mhz p (all bands) bpsk 0.63 single -96.6 -95.1 -93.3...
Page 212
Chapter 3: system planning system threshold, output power and link loss page 3-77 table 104 4.9 ghz tdm mode: system threshold per channel bandwidth and output power (dbm) modulation mode 5 mhz 10 mhz 15 mhz 20 mhz p (all bands) bpsk 0.63 single -96.6 -95.1 -93.3 -92.0 27 qpsk 0.63 single -90.4 -88....
Page 213
Chapter 3: system planning system threshold, output power and link loss page 3-78 table 106 5.1/5.2 ghz ip mode: system threshold per channel bandwidth and output power (dbm) modulation mode 5 mhz 10 mhz 15 mhz 20 mhz 30 mhz 40 mhz 45 mhz p (all bands) bpsk 0.63 single -95.8 -94.3 -92.5 -91.3 -89.5 ...
Page 214
Chapter 3: system planning system threshold, output power and link loss page 3-79 table 108 5.1/5.2 ghz tdm mode: system threshold per channel bandwidth and output power (dbm) modulation mode 5 mhz 10 mhz 15 mhz 20 mhz 30 mhz 40 mhz 45 mhz p (all bands) bpsk 0.63 single -95.8 -94.3 -92.5 -91.3 -89.5...
Page 215
Chapter 3: system planning system threshold, output power and link loss page 3-80 table 110 5.4 ghz ip mode: system threshold per channel bandwidth and output power (dbm) modulation mode 5 mhz 10 mhz 15 mhz 20 mhz 30 mhz 40 mhz 45 mhz p (all bands) bpsk 0.63 single -96.6 -94.6 -92.8 -91.5 -89.8 -88....
Page 216
Chapter 3: system planning system threshold, output power and link loss page 3-81 table 112 5.4 ghz tdm mode: system threshold per channel bandwidth and output power (dbm) modulation mode 5 mhz 10 mhz 15 mhz 20 mhz 30 mhz 40 mhz 45 mhz p (all bands) bpsk 0.63 single -96.6 -94.6 -92.8 -91.5 -89.8 -88...
Page 217
Chapter 3: system planning system threshold, output power and link loss page 3-82 table 114 5.8 ghz ip mode: system threshold per channel bandwidth and output power (dbm) modulation mode 5 mhz 10 mhz 15 mhz 20 mhz 30 mhz 40 mhz 45 mhz p (all bands) bpsk 0.63 single -96.8 -94.8 -93.0 -91.8 -90.0 -88....
Page 218
Chapter 3: system planning system threshold, output power and link loss page 3-83 table 116 5.8 ghz tdm mode: system threshold per channel bandwidth and output power (dbm) modulation mode 5 mhz 10 mhz 15 mhz 20 mhz 30 mhz 40 mhz 45 mhz p (all bands) bpsk 0.63 single -96.8 -94.8 -93.0 -91.8 -90.0 -88...
Page 219
Chapter 3: system planning system threshold, output power and link loss page 3-84 table 118 5.9 ghz ip mode: system threshold per channel bandwidth and output power (dbm) modulation mode 5 mhz 10 mhz 15 mhz 20 mhz 30 mhz 40 mhz 45 mhz p (all bands) bpsk 0.63 single -95.8 -94.3 -92.5 -91.3 -89.5 -88....
Page 220
Chapter 3: system planning system threshold, output power and link loss page 3-85 table 120 5.9 ghz tdm mode: system threshold per channel bandwidth and output power (dbm) modulation mode 5 mhz 10 mhz 15 mhz 20 mhz 30 mhz 40 mhz 45 mhz p (all bands) bpsk 0.63 single -95.8 -94.3 -92.5 -91.3 -89.5 -88...
Page 221
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-86 data throughput capacity tables data capacity in ptp topology use the following tables to look up the data throughput rates (mbits/s) that are achieved when two ptp 670 odus are linked and the link distance (range) is 0 km: link sy...
Page 222
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-87 link symmetry link optimization bandwidth 15 mhz 10 mhz 5 mhz 1:1 ip figure 77 figure 78 figure 79 tdm figure 84 figure 85 figure 86 2:1 ip figure 91 figure 92 - tdm figure 97 figure 98 - 3:1 ip figure 103 figure 104 - 5:1 ip - - -...
Page 223
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-88 table 122 throughput at zero link range (mbit/s), symmetry 1:1, optimization ip modulation mode 45 mhz (tx/rx/aggregate) 40 mhz (tx/rx/aggregate) 256qam 0.81 dual 225.85 225.85 451.70 206.11 206.11 412.22 64qam 0.92 dual 190.29 190...
Page 224
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-89 modulation mode 15 mhz (tx/rx/aggregate) 10 mhz (tx/rx/aggregate) 256qam 0.81 dual 75.29 75.29 150.58 50.04 50.04 100.09 64qam 0.92 dual 63.43 63.43 126.87 42.16 42.16 84.33 64qam 0.75 dual 51.84 51.84 103.67 34.46 34.46 68.91 16qa...
Page 225
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-90 table 123 throughput at zero link range (mbit/s), symmetry 1:1, optimization tdm modulation mode 45 mhz (tx/rx/aggregate) 40 mhz (tx/rx/aggregate) 256qam 0.81 dual 198.59 198.59 397.18 184.89 184.89 369.78 64qam 0.92 dual 167.32 16...
Page 226
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-91 modulation mode 15 mhz (tx/rx/aggregate) 10 mhz (tx/rx/aggregate) 256qam 0.81 dual 72.69 72.69 145.38 49.03 49.03 98.05 64qam 0.92 dual 61.24 61.24 122.49 41.30 41.30 82.61 64qam 0.75 dual 50.05 50.05 100.09 33.75 33.75 67.51 16qam...
Page 227
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-92 table 124 throughput at zero link range (mbit/s), symmetry 2:1, optimization ip modulation mode 45 mhz (tx/rx/aggregate) 40 mhz (tx/rx/aggregate) 256qam 0.81 dual 299.34 149.67 449.01 273.32 136.66 409.98 64qam 0.92 dual 252.20 126...
Page 228
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-93 modulation mode 15 mhz (tx/rx/aggregate) 10 mhz (tx/rx/aggregate) 256qam 0.81 dual 100.39 50.19 150.58 66.27 33.13 99.40 64qam 0.92 dual 84.58 42.29 126.87 55.83 27.91 83.75 64qam 0.75 dual 69.12 34.56 103.67 45.63 22.81 68.44 16qa...
Page 229
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-94 modulation mode 30 mhz (tx/rx/aggregate) 20 mhz (tx/rx/aggregate) 256qam 0.81 dual 192.39 96.19 288.58 130.32 65.16 195.48 64qam 0.92 dual 162.09 81.04 243.13 109.80 54.90 164.70 64qam 0.75 dual 132.46 66.23 198.69 89.73 44.86 134....
Page 230
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-95 table 126 throughput at zero link range (mbit/s), symmetry 3:1, optimization ip modulation mode 45 mhz (tx/rx/aggregate) 40 mhz (tx/rx/aggregate) 256qam 0.81 dual 336.76 112.25 449.01 307.48 102.49 409.98 64qam 0.92 dual 283.73 94....
Page 231
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-96 modulation mode 15 mhz (tx/rx/aggregate) 10 mhz (tx/rx/aggregate) 256qam 0.81 dual 111.94 37.31 149.25 75.07 25.02 100.09 64qam 0.92 dual 94.31 31.43 125.74 63.25 21.08 84.33 64qam 0.75 dual 77.07 25.69 102.76 51.68 17.23 68.91 16q...
Page 232
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-97 modulation mode 30 mhz (tx/rx/aggregate) 256qam 0.81 dual 247.78 49.56 297.34 64qam 0.92 dual 208.76 41.75 250.52 64qam 0.75 dual 170.60 34.12 204.72 16qam 0.87 dual 132.72 26.54 159.26 16qam 0.63 dual 95.41 19.08 114.49 256qam 0.8...
Page 233
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-98 modulation mode 30 mhz (tx/rx/aggregate) 20 mhz (tx/rx/aggregate) 256qam 0.81 dual 262.16 37.45 299.61 159.17 39.79 198.96 64qam 0.92 dual 220.88 31.55 252.43 134.11 33.53 167.63 64qam 0.75 dual 180.50 25.78 206.28 109.59 27.40 136...
Page 234
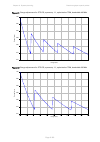
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-99 figure 73 range adjustment for ptp 670, symmetry 1:1, optimization ip, bandwidth 45 mhz figure 74 range adjustment for ptp 670, symmetry 1:1, optimization ip, bandwidth 40 mhz 0.86 0.88 0.90 0.92 0.94 0.96 0.98 1.00 0 20 40 60 80 1...
Page 235
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-100 figure 75 range adjustment for ptp 670, symmetry 1:1, optimization ip, bandwidth 30 mhz figure 76 range adjustment for ptp 670, symmetry 1:1, optimization ip, bandwidth 20 mhz 0.75 0.80 0.85 0.90 0.95 1.00 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 14...
Page 236
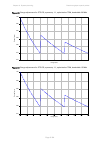
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-101 figure 77 range adjustment for ptp 670, symmetry 1:1, optimization ip, bandwidth 15 mhz figure 78 range adjustment for ptp 670, symmetry 1:1, optimization ip, bandwidth 10 mhz 0.75 0.80 0.85 0.90 0.95 1.00 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 14...
Page 237
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-102 figure 79 range adjustment for ptp 670, symmetry 1:1, optimization ip, bandwidth 5 mhz figure 80 range adjustment for ptp 670, symmetry 1:1, optimization tdm, bandwidth 45 mhz 0.60 0.70 0.80 0.90 1.00 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160...
Page 238
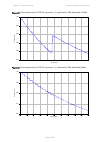
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-103 figure 81 range adjustment for ptp 670, symmetry 1:1, optimization tdm, bandwidth 40 mhz figure 82 range adjustment for ptp 670, symmetry 1:1, optimization tdm, bandwidth 30 mhz 0.70 0.75 0.80 0.85 0.90 0.95 1.00 0 20 40 60 80 100...
Page 239
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-104 figure 83 range adjustment for ptp 670, symmetry 1:1, optimization tdm, bandwidth 20 mhz figure 84 range adjustment for ptp 670, symmetry 1:1, optimization tdm, bandwidth 15 mhz 0.70 0.75 0.80 0.85 0.90 0.95 1.00 0 20 40 60 80 100...
Page 240
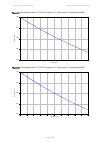
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-105 figure 85 range adjustment for ptp 670, symmetry 1:1, optimization tdm, bandwidth 10 mhz figure 86 range adjustment for ptp 670, symmetry 1:1, optimization tdm, bandwidth 5 mhz 0.75 0.80 0.85 0.90 0.95 1.00 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 1...
Page 241
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-106 figure 87 range adjustment for ptp 670, symmetry 2:1, optimization ip, bandwidth 45 mhz figure 88 range adjustment for ptp 670, symmetry 2:1, optimization ip, bandwidth 40 mhz 0.80 0.85 0.90 0.95 1.00 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160...
Page 242
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-107 figure 89 range adjustment for ptp 670, symmetry 2:1, optimization ip, bandwidth 30 mhz figure 90 range adjustment for ptp 670, symmetry 2:1, optimization ip, bandwidth 20 mhz 0.70 0.75 0.80 0.85 0.90 0.95 1.00 0 20 40 60 80 100 1...
Page 243
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-108 figure 91 range adjustment for ptp 670, symmetry 2:1, optimization ip, bandwidth 15 mhz figure 92 range adjustment for ptp 670, symmetry 2:1, optimization ip, bandwidth 10 mhz 0.75 0.80 0.85 0.90 0.95 1.00 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 14...
Page 244
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-109 figure 93 range adjustment for ptp 670, symmetry 2:1, optimization tdm, bandwidth 45 mhz figure 94 range adjustment for ptp 670, symmetry 2:1, optimization tdm, bandwidth 40 mhz 0.65 0.70 0.75 0.80 0.85 0.90 0.95 1.00 0 20 40 60 8...
Page 245
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-110 figure 95 range adjustment for ptp 670, symmetry 2:1, optimization tdm, bandwidth 30 mhz figure 96 range adjustment for ptp 670, symmetry 2:1, optimization tdm, bandwidth 20 mhz 0.60 0.70 0.80 0.90 1.00 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 1...
Page 246
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-111 figure 97 range adjustment for ptp 670, symmetry 2:1, optimization tdm, bandwidth 15 mhz figure 98 range adjustment for ptp 670, symmetry 2:1, optimization tdm, bandwidth 10 mhz 0.75 0.80 0.85 0.90 0.95 1.00 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 ...
Page 247
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-112 figure 99 range adjustment for ptp 670, symmetry 3:1, optimization ip, bandwidth 45 mhz figure 100 range adjustment for ptp 670, symmetry 3:1, optimization ip, bandwidth 40 mhz 0.65 0.70 0.75 0.80 0.85 0.90 0.95 1.00 0 20 40 60 80...
Page 248
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-113 figure 101 range adjustment for ptp 670, symmetry 3:1, optimization ip, bandwidth 30 mhz figure 102 range adjustment for ptp 670, symmetry 3:1, optimization ip, bandwidth 20 mhz 0.65 0.70 0.75 0.80 0.85 0.90 0.95 1.00 0 20 40 60 8...
Page 249
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-114 figure 103 range adjustment for ptp 670, symmetry 3:1, optimization ip, bandwidth 15 mhz figure 104 range adjustment for ptp 670, symmetry 3:1, optimization ip, bandwidth 10 mhz 0.65 0.70 0.75 0.80 0.85 0.90 0.95 1.00 0 20 40 60 8...
Page 250
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-115 figure 105 range adjustment for ptp 670, symmetry 5:1, optimization ip, bandwidth 45 mhz figure 106 range adjustment for ptp 670, symmetry 5:1, optimization ip, bandwidth 40 mhz 0.65 0.70 0.75 0.80 0.85 0.90 0.95 1.00 0 20 40 60 8...
Page 251
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-116 figure 107 range adjustment for ptp 670, symmetry 5:1, optimization ip, bandwidth 30 mhz figure 108 range adjustment for ptp 670, adaptive, optimization ip, bandwidth 45 mhz 0.60 0.65 0.70 0.75 0.80 0.85 0.90 0.95 1.00 0 20 40 60 ...
Page 252
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-117 figure 109 range adjustment for ptp 670, adaptive, optimization ip, bandwidth 40 mhz figure 110 range adjustment for ptp 670, adaptive, optimization ip, bandwidth 30 mhz 0.75 0.80 0.85 0.90 0.95 1.00 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 ...
Page 253
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-118 figure 111 range adjustment for ptp 670, adaptive, optimization ip, bandwidth 20 mhz figure 112 range adjustment for ptp 670, adaptive, optimization ip, bandwidth 15 mhz 0.65 0.70 0.75 0.80 0.85 0.90 0.95 1.00 0 20 40 60 80 100 12...
Page 254
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-119 figure 113 range adjustment for ptp 670, adaptive, optimization ip, bandwidth 10 mhz 0.70 0.75 0.80 0.85 0.90 0.95 1.00 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 r an g e fa cto r range (km).
Page 255
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-120 data capacity in hcmp topology use the tables in this section to look up the tdd frame duration as a function of bandwidth, number of slaves and link symmetry. Then look up one-way capacity (mbit/s) achieved in each time slot of a...
Page 256
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-121 table 130 hcmp frame duration, 40 mhz channel bandwidth, without tdd sync number of slaves link symmetry maximum range frame duration two 1:1 5.0 km to 7.9 km 1370 μs 8.0 km to 15.9 km 1439 μs 16.0 km to 27.9 km 1504 μs 28.0 km to...
Page 257
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-122 number of slaves link symmetry maximum range frame duration five 1:1 5.0 km to 7.9 km 3311 μs 8.0 km to 31.8 km 3460 μs 31.9 km to 40.0 km 3610 μs 1:2 and 2:1 5.0 km to 23.9 km 5000 μs 24.0 km to 40.0 km 5236 μs six 1:1 5.0 km to ...
Page 258
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-123 table 131 hcmp frame duration, 40 mhz channel bandwidth, with tdd sync number of slaves link symmetry maximum range frame duration two 1:1 5.0 km to 7.9 km 1370 μs 8.0 km to 40.0 km 2000 μs 1:2 and 2:1 5.0 km to 40.0 km 2283 μs 1:...
Page 259
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-124 table 132 throughput (mbit/s) per time slot in hcmp topology, 20 mhz channel bandwidth frame duration modulation mode 2747 μs 2882 μs 3012 μs 4000 μs 4184 μs 4367 μs 256qam 0.81 dual 40.22 38.34 36.68 27.62 26.41 25.30 64qam 0.92 ...
Page 260
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-125 table 133 throughput (mbit/s) per time slot in hcmp topology, 40 mhz channel bandwidth frame duration modulation mode 1370 μs 1439 μs 1504 μs 1575 μs 1623 μs 2000 μs 256qam 0.81 dual 80.65 76.78 73.46 70.15 68.07 55.24 64qam 0.92 ...
Page 261
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-126 frame duration modulation mode 3145 μs 3311 μs 3460 μs 3610 μs 4000 μs 4184 μs 256qam 0.81 dual 35.13 33.37 31.93 30.61 27.62 26.41 64qam 0.92 dual 29.60 28.11 26.90 25.79 23.27 22.25 64qam 0.75 dual 24.19 22.97 21.99 21.07 19.02 ...
Page 262: Tdm Traffic Load
Chapter 3: system planning data throughput capacity tables page 3-127 tdm traffic load encapsulated data the nidu supports separate management and tdm data protocol interfaces. The management interface is between the nidu and a directly-connected odu. The tdm data interface is between peer nidus. Th...
Page 263: Chapter 4:
Page 4-1 chapter 4: legal and regulatory information this chapter provides end user license agreements and regulatory notifications. Caution intentional or unintentional changes or modifications to the equipment must not be made unless under the express consent of the party responsible for complianc...
Page 264: Definitions
Chapter 4: legal and regulatory information cambium networks end user license agreement page 4-2 cambium networks end user license agreement definitions in this agreement, the word “software” refers to the set of instructions for computers, in executable form and in any media, (which may include dis...
Page 265: Conditions Of Use
Chapter 4: legal and regulatory information cambium networks end user license agreement page 4-3 conditions of use any use of the software and documentation outside of the conditions set forth in this agreement is strictly prohibited and will be deemed a breach of this agreement. 1. Only you, your e...
Page 266: Title and Restrictions
Chapter 4: legal and regulatory information cambium networks end user license agreement page 4-4 title and restrictions if you transfer possession of any copy of the software and documentation to another party outside of the terms of this agreement, your license is automatically terminated. Title an...
Page 267: Transfer
Chapter 4: legal and regulatory information cambium networks end user license agreement page 4-5 right to use cambium’s name except as required in “conditions of use”, you will not, during the term of this agreement or thereafter, use any trademark of cambium networks, or any word or symbol likely t...
Page 268: Disclaimer
Chapter 4: legal and regulatory information cambium networks end user license agreement page 4-6 disclaimer cambium networks disclaims all warranties of any kind, whether express, implied, statutory, or in any communication with you. Cambium networks specifically disclaims any warranty including the...
Page 269: Term Of License
Chapter 4: legal and regulatory information cambium networks end user license agreement page 4-7 term of license your right to use the software will continue in perpetuity unless terminated as follows. Your right to use the software will terminate immediately without notice upon a breach of this agr...
Page 270: Trademarks
Chapter 4: legal and regulatory information cambium networks end user license agreement page 4-8 trademarks java technology and/or j2me : java and all other java-based marks are trademarks or registered trademarks of sun microsystems, inc. In the u.S. And other countries. Unix : unix is a registe...
Page 271
Chapter 4: legal and regulatory information cambium networks end user license agreement page 4-9 this software is provided by the copyright holders and contributors “as is” and any express or implied warranties, including, but not limited to, the implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for...
Page 272
Chapter 4: legal and regulatory information cambium networks end user license agreement page 4-10 • redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the distributio...
Page 273: Openssl
Chapter 4: legal and regulatory information cambium networks end user license agreement page 4-11 • redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. • redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice,...
Page 274
Chapter 4: legal and regulatory information cambium networks end user license agreement page 4-12 redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met: 1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above cop...
Page 275: Zlib
Chapter 4: legal and regulatory information cambium networks end user license agreement page 4-13 if this package is used in a product, eric young should be given attribution as the author of the parts of the library used. This can be in the form of a textual message at program startup or in documen...
Page 276: Libpng
Chapter 4: legal and regulatory information cambium networks end user license agreement page 4-14 mark adler madler@alumni.Caltech.Edu libpng libpng versions 1.2.6, august 15, 2004, through 1.2.35, february 14, 2009, are copyright © 2004, 2006-2008 glenn randers-pehrson, and are distributed accordin...
Page 277: Bzip2
Chapter 4: legal and regulatory information cambium networks end user license agreement page 4-15 tim wegner the png reference library is supplied “as is”. The contributing authors and group 42, inc. Disclaim all warranties, expressed or implied, including, without limitation, the warranties of merc...
Page 278: Usb Library Functions
Chapter 4: legal and regulatory information cambium networks end user license agreement page 4-16 this software is provided by the author “as is” and any express or implied warranties, including, but not limited to, the implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose are d...
Page 279
Chapter 4: legal and regulatory information cambium networks end user license agreement page 4-17 "derivative works" shall mean any work, whether in source or object form, that is based on (or derived from) the work and for which the editorial revisions, annotations, elaborations, or other modificat...
Page 280
Chapter 4: legal and regulatory information cambium networks end user license agreement page 4-18 (c) you must retain, in the source form of any derivative works that you distribute, all copyright, patent, trademark, and attribution notices from the source form of the work, excluding those notices t...
Page 281: D3 Js Library
Chapter 4: legal and regulatory information cambium networks end user license agreement page 4-19 9. Accepting warranty or additional liability. While redistributing the work or derivative works thereof, you may choose to offer, and charge a fee for, acceptance of support, warranty, indemnity, or ot...
Page 282
Chapter 4: legal and regulatory information compliance with safety standards page 4-20 compliance with safety standards this section lists the safety specifications against which the ptp 670 has been tested and certified. It also describes how to keep rf exposure within safe limits. Electrical safet...
Page 283
Chapter 4: legal and regulatory information compliance with safety standards page 4-21 human exposure to radio frequency energy relevant standards (usa and ec) applicable when working with rf equipment are: • ansi ieee c95.1-1991, ieee standard for safety levels with respect to human exposure to rad...
Page 284: Calculated Distances
Chapter 4: legal and regulatory information compliance with safety standards page 4-22 calculation of power density the following calculation is based on the ansi ieee c95.1-1991 method, as that provides a worst case analysis. Details of the assessment to en50383:2002 can be provided, if required. P...
Page 285: Gains And Power Densities
Chapter 4: legal and regulatory information compliance with safety standards page 4-23 table 138 minimum safe distances for ptp 670 at maximum transmitter power antenna p (w) (*1) g (*2) s (w/m 2 ) d (m) (*3) parabolic 6 ft (38.1 dbi) 0.635 5248.1 10 5.15 parabolic 4 ft (35.3 dbi) 0.635 3388.4 10 3....
Page 286
Chapter 4: legal and regulatory information compliance with safety standards page 4-24 minimum separation distances in fcc bands the minimum separation distances for operation in fcc regulatory bands are listed in table 139 . Table 139 minimum safe distances for fcc bands band antenna p (w) (*1) g (...
Page 287
Chapter 4: legal and regulatory information compliance with safety standards page 4-25 minimum separation distances in isedc bands the minimum separation distances for operation in isedc regulatory bands are listed in table 140. Table 140 minimum safe distances for isedc bands band antenna p (w) (*1...
Page 288
Chapter 4: legal and regulatory information compliance with radio regulations page 4-26 compliance with radio regulations this section describes how the ptp 670 complies with the radio regulations that are in force in various countries. Caution where necessary, the end user is responsible for obtain...
Page 289: Type Approvals
Chapter 4: legal and regulatory information compliance with radio regulations page 4-27 type approvals the system has been tested against various local technical regulations and found to comply. Table 141 to table 145 list the radio specification type approvals that have been granted for ptp 670 pro...
Page 290: Fcc Compliance
Chapter 4: legal and regulatory information compliance with radio regulations page 4-28 fcc compliance the ptp 670 complies with the regulations that are in force in the usa. Caution if this equipment does cause interference to radio or television reception, refer to radio and television interferenc...
Page 291: 4.9 Ghz Fcc Notification
Chapter 4: legal and regulatory information compliance with radio regulations page 4-29 figure 115 fcc certifications on atex/hazloc odu product labels 4.9 ghz fcc notification the system has been approved under fcc part 90 for public safety agency usage. The installer or operator is responsible for...
Page 292: Selection Of Antennas
Chapter 4: legal and regulatory information compliance with radio regulations page 4-30 channel bandwidth channel frequency maximum conducted power above 5838.0 mhz 24 dbm 10 mhz below 5737.0 mhz 25 dbm above 5837.0 mhz 25 dbm 15 mhz below 5740.0 mhz 25 dbm above 5835.0 mhz 25 dbm 20 mhz below 5742....
Page 293
Chapter 4: legal and regulatory information compliance with radio regulations page 4-31 table 148 isedc ids product id ptp 670 (4.9 to 6.05 ghz) integrated 23 dbi odu (ic) ptp 670 (4.9 to 6.05 ghz) connectorized odu (ic) ptp 670 (4.9 to 5.9 ghz) atex/hazloc integrated 23 dbi odu (ic) ptp 670 (4.9 to...
Page 294
Chapter 4: legal and regulatory information compliance with radio regulations page 4-32 4.9 ghz isedc notification the system has been approved under isedc rss-111 for public safety agency usage. The installer or operator is responsible for obtaining the appropriate site licenses before installing o...
Page 295
Chapter 4: legal and regulatory information compliance with radio regulations page 4-33 pour la version du produit avec antenne externe et afin de réduire le risque d'interférence avec d'autres utilisateurs, le type d'antenne et son gain doivent être choisis afin que la puissance isotrope rayonnée é...
Page 296
Chapter 4: legal and regulatory information compliance with radio regulations page 4-34 le ptp 670 prend en compte le gain de l'antenne et les pertes des câbles de connexion configurés par l'installateur professionnel via l'interface graphique pour limiter la pire pour assurer la conformité à la rég...
Page 297: Selection Of Antennas
Chapter 4: legal and regulatory information compliance with radio regulations page 4-35 réduction de puissance aux bords de la bande 5.8 ghz la puissance isotrope rayonnée équivalente (pire) est limitée dans les canaux en bord de la bandes lorsque le ptp 670 est configuré pour utiliser la band 5,8 g...
Page 298: Chapter 5:
Page 5-1 chapter 5: installation this chapter describes how to install and test the hardware for a ptp 670 link. It contains the following topics: • safety on page 5-2 contains important safety guidelines that must be observed by personnel installing or operating ptp 670 equipment. • odu variants an...
Page 299: Safety
Chapter 5: installation safety page 5-2 safety warning to prevent loss of life or physical injury, observe the following safety guidelines. In no event shall cambium networks be liable for any injury or damage caused during the installation of the cambium ptp 670. Ensure that only qualified personne...
Page 300: Dc Supply
Chapter 5: installation safety page 5-3 dc supply to power the odu from a dc supply, use the ac+dc enhanced power injector 56v (cambium part number c000065l002c) or cmm5. Ensure that the dc power supply meets the requirements specified in psu dc power supply on page 3-15 . Powering down before servi...
Page 301: Siting Odus And Antennas
Chapter 5: installation safety page 5-4 minimum separation distances ensure that personnel are not exposed to unsafe levels of rf energy. The units start to radiate rf energy as soon as they are powered up. Never work in front of the antenna when the odu is powered. Install the odus so as to provide...
Page 302
Chapter 5: installation safety page 5-5 warning do not install the odu in a location where the ambient temperature could exceed 40°c unless this is a restricted access location as defined by en 60950-1. Alerte l’unité externe ne doit pas être installée dans un endroit où la température ambiante est ...
Page 303: Mounting Bracket Options
Chapter 5: installation odu variants and mounting bracket options page 5-6 odu variants and mounting bracket options mounting bracket options the ptp 670 series supports three mounting bracket options. Select the optimum mounting bracket arrangement based on the pole diameter and the odu variant: ta...
Page 304: Mount The Odu On The Mast
Chapter 5: installation installing the odu and top lpu page 5-7 installing the odu and top lpu to install the odu and top lpu, use the following procedures: • attach ground cables to the odu on page 5-7 • mount the odu on the mast on page 5-7 • mount the top lpu on page 5-10 • interconnect and groun...
Page 305
Chapter 5: installation installing the odu and top lpu page 5-8 3 thread two of the nuts to the long bolts and tighten against the bracket body using a 13 mm spanner. Fit the bracket strap and thread the remaining nuts onto the long bolts. 4 fix the assembled bracket body to the pole, adjust the azi...
Page 306
Chapter 5: installation installing the odu and top lpu page 5-9 2 feed the band clamps through the slots in the bracket body. Secure the bracket body to the pole using band clamps (not supplied by cambium), ensuring that the arrow in the body is pointing upwards. Adjust the azimuth angle, and tighte...
Page 307: Mount The Top Lpu
Chapter 5: installation installing the odu and top lpu page 5-10 1 fix the mounting plate to the back of the odu using the four bolts, and spring and plain washers provided. Ensure that the spring washer is between the bolt head and the plain washer tighten the bolts to a torque setting of 5.0 nm (3...
Page 308
Chapter 5: installation installing the odu and top lpu page 5-11 locking nut washer m6 lug washer nut toothed washer m6 lug to odu 2 select a tower or building grounding point within 0.3 meters (1 ft) of the odu bracket. Remove paint from the surface and apply anti-oxidant compound. Fasten the odu g...
Page 309
Chapter 5: installation install external antennas for a connectorized odu page 5-12 install external antennas for a connectorized odu to mount and connect an external antenna, proceed as follows: 1 mount the antenna(s) according to manufacturer’s instructions. When using separate antennas to achieve...
Page 310
Chapter 5: installation install external antennas for a connectorized odu page 5-13 7 ground the antenna cables to the supporting structure within 0.3 meters (1 foot) of the odu and antennas using the cambium grounding kit (part number 01010419001): 8 fix the antenna cables to the supporting structu...
Page 311
Chapter 5: installation installing the copper cat5e ethernet interface page 5-14 installing the copper cat5e ethernet interface to install the copper cat5e ethernet interface, use the following procedures: • install the odu to top lpu drop cable on page 5-14 • install the main drop cable on page 5-1...
Page 312
Chapter 5: installation installing the copper cat5e ethernet interface page 5-15 2 fit the parts into the body and lightly screw on the gland nut (do not tighten it): connect the drop cable to the odu (psu port) and lpu 1 (a) plug the rj45 connector into the socket in the unit, ensuring that it snap...
Page 313: Install The Main Drop Cable
Chapter 5: installation installing the copper cat5e ethernet interface page 5-16 disconnect the drop cable from the lpu or odu use this procedure if it is necessary to remove an emc strain relief cable gland and rj45 connector from the odu (as illustrated) or lpu. 1 (a) remove the gland nut. Wiggle ...
Page 314
Chapter 5: installation installing the copper cat5e ethernet interface page 5-17 terminate with rj45 connectors and glands caution check that the crimp tool matches the rj45 connector, otherwise the cable or connector may be damaged. 1 thread the cable gland (with black cap) onto the main drop cable...
Page 315
Chapter 5: installation installing the copper cat5e ethernet interface page 5-18 pin color (supplied cable) color (conventional) pins on plug face 1 light orange white/orange 2 orange orange 3 light green white/green 4 blue blue 5 light blue white/blue 6 green green 7 light brown white/brown 8 brown...
Page 316: Ground The Main Drop Cable
Chapter 5: installation installing the copper cat5e ethernet interface page 5-19 ground the main drop cable at all required grounding points, connect the screen of the main drop cable to the metal of the supporting structure using the cable grounding kit (cambium part number 01010419001). Install th...
Page 317
Chapter 5: installation installing the copper cat5e ethernet interface page 5-20 install the lpu to psu drop cable use this procedure to terminate the bottom lpu to psu drop cable with rj45 connectors at both ends, and with a cable gland at the lpu end. Warning the metal screen of the drop cable is ...
Page 318
Chapter 5: installation installing the copper cat5e ethernet interface page 5-21 test resistance in the drop cable connect the bottom end of the copper cat5e drop cable to a suitable drop cable tester and test that the resistances between pins are within the correct limits, as specified in the table...
Page 319: Installing The Psu
Chapter 5: installation installing the psu page 5-22 installing the psu install one of the following types of psu (as specified in the installation plan): • ac power injector 56v (cambium part number n000065l001c). Refer to installing the ac power injector 56v on page 5-22 . • ac+dc enhanced power i...
Page 320
Chapter 5: installation installing the psu page 5-23 (a) (b) installing the ac+dc enhanced power injector 56v follow this procedure to install the ac+dc enhanced power injector 56v (cambium part number c000065l002c): 1 mount the ac+dc power injector 56v by screwing it to a vertical or horizontal sur...
Page 321: Installing The Cmm5
Chapter 5: installation installing the psu page 5-24 (a) (b) and (c) installing the cmm5 installation instructions for the cmm5 are provided in pmp synchronization solutions user guide available from the cambium web site..
Page 322: Installing A Ptp-Sync Unit
Chapter 5: installation installing a ptp-sync unit page 5-25 installing a ptp-sync unit to install a ptp-sync unit (for tdd synchronization), use the following procedures: • mounting the ptp-sync unit on page 5-25 • connecting up the ptp-sync unit on page 5-26 • powering up the ptp-sync installation...
Page 323
Chapter 5: installation installing a ptp-sync unit page 5-26 figure 119 ptp-sync mounted on a wall connecting up the ptp-sync unit use this procedure to connect the ptp-sync to the ac+dc power injector 56v, odu, gps receiver (if fitted), and lpu (if fitted). 1 disconnect the power supply from the ac...
Page 324
Chapter 5: installation installing a ptp-sync unit page 5-27 3 to link clustered ptp-sync units, connect the sync out port of the first ptp-sync to the gps/sync in port of the second ptp-sync in the chain. Repeat for subsequent ptp-sync units in the chain. 4 connect the cable from the psu to the pid...
Page 325
Chapter 5: installation installing a ptp-sync unit page 5-28 6 use a grounding cable to connect the ground stud of the ptp-sync to the master ground bar of the building, or to the rack ground bar. Powering up the ptp-sync installation use this procedure to power up the ptp-sync installation. Caution...
Page 326: Mounting The Gps Receiver
Chapter 5: installation installing the trimble accutime gps receiver page 5-29 installing the trimble accutime gps receiver to install a gps receiver as the timing reference source for ptp-sync, use the following procedures: • mounting the gps receiver on page 5-29 • preparing the gps drop cable on ...
Page 327
Chapter 5: installation installing the trimble accutime gps receiver page 5-30 4 fit a suitable gps connector to the top end of the drop cable: • if a gps adapter cable kit is available, attach the plug housing and an rj45 plug to the top end of the main gps drop cable, as described in assembling an...
Page 328
Chapter 5: installation installing the trimble accutime gps receiver page 5-31 3 install the rj45 crimp plug. Start with tails over-length to assist insertion into load bar, then trim them to 5 mm (t). Connect the rj45 pins to the following conductors (superior essex bbdge colors): 4 assemble plug h...
Page 329
Chapter 5: installation installing the trimble accutime gps receiver page 5-32 assembling a 12 way circular connector use this procedure to connect the gps drop cable to a 12 way circular connector. This procedure is only performed when a gps adapter cable kit is not available. Note this procedure r...
Page 330
Chapter 5: installation installing the trimble accutime gps receiver page 5-33 figure 120 inserting rj45 pins into the 12 way circular connector 1 prepare the drop cable end as follows: • bare back the cable outer and copper screen to 50mm. • bare back the cable inner to 17mm. • un-twist the cable p...
Page 331
Chapter 5: installation installing the trimble accutime gps receiver page 5-34 2 fit the plug outer, associated boot, and boot insert. 3 connect the socket contacts using either of the following techniques: • crimp: crimp the socket contacts onto each of the conductors using the correct crimp tool a...
Page 332
Chapter 5: installation installing the trimble accutime gps receiver page 5-35 note if a contact is pushed in to the point where the locking mechanism engages before all of the contacts have been inserted it will limit the amount of room available to fit the remaining contacts, requiring harder bend...
Page 333
Chapter 5: installation installing the trimble accutime gps receiver page 5-36 connecting the gps drop cable use this procedure to connect the gps drop cable to the gps unit and supporting structure. 1 if a gps adapter cable is available, use it to connect the main gps drop cable to the gps unit: 2 ...
Page 334
Chapter 5: installation installing the trimble accutime gps receiver page 5-37 figure 121 grounding and weatherproofing requirements for gps adapter cable follow the procedure described in creating a drop cable grounding point on page 5-56 , but observe the following differences: • there is no need ...
Page 335
Chapter 5: installation installing the trimble accutime gps receiver page 5-38 figure 123 wrapping pvc tape around the gps adapter cable joint figure 124 grounding and weatherproofing example for gps adapter cable installing and connecting the gps lpu install and ground the gps drop cable lpu at the...
Page 336: Installing A Nidu
Chapter 5: installation installing a nidu page 5-39 installing a nidu to install a nidu (for tdm), use the following procedures: • mounting the nidu on page 5-39 • connecting the nidu to the psu, lan and tdm cables on page 5-40 • connecting the nidu to a dc power supply on page 5-42 mounting the nid...
Page 337
Chapter 5: installation installing a nidu page 5-40 connecting the nidu to the psu, lan and tdm cables caution always connect the nidu to the main psu port of the odu via the psu. The tdm service will not operate if the nidu is connected to the aux or sfp port of the odu. Caution if the odu port has...
Page 338
Chapter 5: installation installing a nidu page 5-41 4 connect up to eight indoor cat5e cables (with rj48 connectors) from the nidu (e1/t1 ports) to the local tdm transceivers: 5 use an m5 nut and washer to connect the grounding cable lug to the nidu ground bolt. Connect the other end of the groundin...
Page 339
Chapter 5: installation installing a nidu page 5-42 connecting the nidu to a dc power supply caution do not power up the nidu until site installation is complete, otherwise equipment may be damaged. Main and backup dc supplies the nidu requires a 40 v – 60 v dc power supply. The nidu dc interface pr...
Page 340
Chapter 5: installation installing a nidu page 5-43 using the dc power connector use this procedure to connect the nidu to the ac+dc enhanced power injector 56v (cambium part number c000065l002c) or to an independent dc supply with an optional backup dc supply: 1 strip the two wires of the main dc s...
Page 341
Chapter 5: installation installing a nidu page 5-44 3 connect the main dc supply cable to its power source. If this supply is from the ac+dc enhanced power injector 56v, the dc out first terminal is negative (black wire) and the second is positive (red wire): 4 connect the backup dc supply cable to ...
Page 342
Chapter 5: installation installing an sfp ethernet interface page 5-45 installing an sfp ethernet interface in more advanced configurations, there may be an optical or copper cat5e ethernet interface connected to the sfp port of the odu. Refer to typical deployment on page 3-2 for diagrams of these ...
Page 343
Chapter 5: installation installing an sfp ethernet interface page 5-46 figure 128 odu with copper cat5e connections to all three ethernet ports odu sfp aux psu copper sfp drop cable auxiliary drop cable psu drop cable common grounding point for top lpus and surge protector grounding point for odu gr...
Page 344: Fitting The Long Cable Gland
Chapter 5: installation installing an sfp ethernet interface page 5-47 fitting the long cable gland optical sfp interface: disassemble the long cable gland and thread its components over the lc connector at the odu end as shown below. Copper cat5e sfp interface: disassemble the long cable gland and ...
Page 345: Inserting The Sfp Module
Chapter 5: installation installing an sfp ethernet interface page 5-48 4 fit the parts into the body and lightly screw on the gland nut (do not tighten it): optical copper inserting the sfp module to insert the sfp module into the odu, proceed as follows: 1 remove the blanking plug from the sfp port...
Page 346
Chapter 5: installation installing an sfp ethernet interface page 5-49 2 insert the sfp module into the sfp receptacle with the label up: optical copper 3 push the module home until it clicks into place: optical copper.
Page 347: Connecting The Cable
Chapter 5: installation installing an sfp ethernet interface page 5-50 4 rotate the latch to the locked position: optical copper connecting the cable caution the fiber optic cable assembly is very delicate. To avoid damage, handle it with extreme care. Ensure that the fiber optic cable does not twis...
Page 348: Fitting The Gland
Chapter 5: installation installing an sfp ethernet interface page 5-51 optical copper fitting the gland 1 fit the gland body to the sfp port and tighten it to a torque of 5.5 nm (4.3 lb ft) 2 fit the gland nut and tighten until the rubber seal closes on the cable. Do not over-tighten the gland nut, ...
Page 349
Chapter 5: installation installing an sfp ethernet interface page 5-52 correct incorrect.
Page 350
Chapter 5: installation installing an sfp ethernet interface page 5-53 removing the cable and sfp module do not attempt to remove the module without disconnecting the cable, otherwise the locking mechanism in the odu will be damaged. 1 remove the cable connector by pressing its release tab before pu...
Page 351
Chapter 5: installation installing an aux ethernet interface page 5-54 installing an aux ethernet interface in more advanced configurations, there may be a copper cat5e ethernet interface connected to the aux port of the odu. Refer to typical deployment on page 3-2 for a diagram of this configuratio...
Page 352: Stripping Drop Cable
Chapter 5: installation supplemental installation information page 5-55 supplemental installation information this section contains detailed installation procedures that are not included in the above topics, such as how to strip cables, create grounding points and weatherproof connectors. Stripping ...
Page 353
Chapter 5: installation supplemental installation information page 5-56 creating a drop cable grounding point use this procedure to connect the screen of the main drop cable to the metal of the supporting structure using the cable grounding kit (cambium part number 01010419001). To identify suitable...
Page 354
Chapter 5: installation supplemental installation information page 5-57 4 tighten the cable ties with pliers. Cut the surplus from the cable ties. 5 cut a 38mm (1.5 inches) section of self-amalgamating tape and wrap it completely around the joint between the drop and ground cables. 6 use the remaind...
Page 355
Chapter 5: installation supplemental installation information page 5-58 7 wrap a layer of pvc tape from bottom to top, starting from 25 mm (1 inch) below and finishing 25 mm (1 inch) above the edge of the self-amalgamating tape, over lapping at half width. 8 repeat with a further four layers of pvc ...
Page 356
Chapter 5: installation supplemental installation information page 5-59 weatherproofing an n type connector use this procedure to weatherproof the n type connectors fitted to the connectorized odu and external antenna (if recommended by the antenna manufacturer). 1 ensure the connection is tight. A ...
Page 357
Chapter 5: installation supplemental installation information page 5-60 4 cut a 125mm (5 inches) length of rubber tape (self-amalgamating): 5 expand the width of the tape by stretching it so that it will wrap completely around the connector and cable: 6 press the tape edges together so that there ar...
Page 358
Chapter 5: installation supplemental installation information page 5-61 8 repeat with a further four layers of 19 mm (0.75 inch) pvc tape, always overlapping at half width. Wrap the layers in alternate directions: • second layer: top to bottom. • third layer: bottom to top. • fourth layer: top to bo...
Page 359: Replacing Psu Fuses
Chapter 5: installation supplemental installation information page 5-62 replacing psu fuses the ac+dc enhanced power injector 56v contains two replaceable fuses. These fuses protect the positive and negative grounded dc input voltages. If an incorrect power supply (that is, not in the range 37v to 6...
Page 360: Chapter 6:
Page 6-1 chapter 6: configuration and alignment this chapter describes how to use the web interface to configure the ptp 670 link. It also describes how to align antennas. This chapter contains the following topics: • preparing for configuration and alignment on page 6-2 • connecting to the unit on ...
Page 361: Safety Precautions
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment preparing for configuration and alignment page 6-2 preparing for configuration and alignment this section describes the checks to be performed before proceeding with unit configuration and antenna alignment. Safety precautions all national and local safety stan...
Page 362: Generating License Keys
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment preparing for configuration and alignment page 6-3 generating license keys to obtain license keys for capabilities that are not factory-installed, proceed as follows: 1 identify and purchase the required entitlement for additional capabilities by referring to o...
Page 363: Connecting to The Unit
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment connecting to the unit page 6-4 connecting to the unit this section describes how to connect the unit to a management pc and power it up. Configuring the management pc use this procedure to configure the local management pc to communicate with the ptp 670. Proc...
Page 364
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment connecting to the unit page 6-5 4 enter an ip address that is valid for the 169.254.X.X network, avoiding 169.254.0.0 and 169.254.1.1. A good example is 169.254.1.3: 5 enter a subnet mask of 255.255.0.0. Leave the default gateway blank. Connecting to the pc and...
Page 365: Using The Web Interface
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment using the web interface page 6-6 using the web interface this section describes how to log into the ptp 670 web interface and use its menus. Logging into the web interface use this procedure to log into the web interface as a system administrator. Procedure: 1 ...
Page 366: Using The Menu Options
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment using the web interface page 6-7 using the menu options use the menu navigation bar in the left panel to navigate to each web page. Some of the menu options are only displayed for specific system configurations. Use table 152 to locate information about using e...
Page 367
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment using the web interface page 6-8 main menu menu option web page information software upgrade software upgrade page on page 6-68 reboot reboot wireless unit page on page 7-18 installation installation menu on page 6-9 graphical install graphical install page on ...
Page 368: Installation Menu
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment installation menu page 6-9 installation menu this section describes how to use the installation wizard to complete the essential system configuration tasks that must be performed on a new link. Caution if the system designer has provided a list of channels to b...
Page 369: Disarm Installation Page
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment installation menu page 6-10 disarm installation page menu option: installation ( figure 129 ). This page is displayed only when unit is armed. Note the installation agent cannot be armed (or disarmed) when the odu operates as a master in the hcmp topology. Figu...
Page 370
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment installation menu page 6-11 figure 130 current installation summary page (ptp topology) click continue to installation wizard..
Page 371
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment installation menu page 6-12 figure 131 current installation summary page (hcmp topology).
Page 372: Software License Key Page
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment installation menu page 6-13 click continue to installation wizard. Software license key page menu option: installation. Use this page to configure the unit with a new license key and to review the capabilities of an installed license key. The appearance of this...
Page 373
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment installation menu page 6-14 figure 133 software license key page (tdm, ipv6 and other capabilities).
Page 374
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment installation menu page 6-15 procedures: to enter a new license key, proceed as follows: • to clear the existing license key (if present), click clear. • to format the new license key: copy it from the cambium notification email, paste it into the license key bo...
Page 375: Interface Configuration Page
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment installation menu page 6-16 interface configuration page menu option: installation. Use this page to update the ip interface attributes. The appearance of this page varies depending upon which capabilities have been enabled by license key. For example, figure 1...
Page 376
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment installation menu page 6-17 figure 135 interface configuration page (ipv6, aux, sfp, second data service and oob support) figure 136 interface configuration page (hcmp wireless topology).
Page 377
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment installation menu page 6-18 figure 137 interface configuration page (tdm support) table 153 interface configuration attributes attribute meaning ip version the internet protocols to be supported by this odu: ipv4: ipv4 protocols only. Ipv4 attributes are displa...
Page 378
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment installation menu page 6-19 attribute meaning gateway ip address the ipv4 address of a computer on the current network that acts as an ipv4 gateway. A gateway acts as an entrance and exit to frames from and to other networks. Ipv6 address the ipv6 internet prot...
Page 379
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment installation menu page 6-20 attribute meaning data service the port selection for the data service in the ptp wireless topology: main psu port: the data service is connected to the main psu port aux port: the data service is connected to the aux port sfp port: ...
Page 380
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment installation menu page 6-21 attribute meaning second data service the port allocation for the second data service in the ptp topology: none: the second data service is disabled. Main psu port: the second data service is connected to the main psu port aux port: ...
Page 381
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment installation menu page 6-22 configuring port allocations with tdm when tdm is enabled, the data service is mapped to the main psu port with no other options presented to the user. Mapping of the second data service, management service and local management servi...
Page 382
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment installation menu page 6-23 configuring port allocations in ptp wireless topology the interface configuration page controls the allocation of the main psu port, aux port and sfp port to the data service, second data service, management service and local managem...
Page 383
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment installation menu page 6-24 the ptp 670 must always be manageable through one of three ports. Therefore it is not possible to disable the management service unless at least one port is allocated to the local management service. For more details, see ethernet po...
Page 384: Wireless Configuration Page
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment installation menu page 6-25 wireless configuration page menu option: installation ( figure 138 and figure 139 ). This page is part of the installation wizard. Use it to update the wireless attributes. Figure 138 wireless configuration page (ptp topology).
Page 385
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment installation menu page 6-26 figure 139 wireless configuration page (hcmp topology) figure 140 wireless configuration page (connectorized antenna type, hcmp topology) procedure: • update the attributes ( table 155 ). • to save any changes and continue with the i...
Page 386
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment installation menu page 6-27 caution the lower center frequency attribute must be configured to the same value for both the master and slave, otherwise the wireless link will fail to establish. The only way to recover from this situation is to modify the lower c...
Page 387
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment installation menu page 6-28 attribute meaning max receive modulation mode the maximum mode the unit will use as its adaptive modulation. By default the max receive modulation mode is the highest mode available. For minimum error rates, set the maximum modulatio...
Page 388
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment installation menu page 6-29 attribute meaning link symmetry only displayed when wireless topology is set to point to point and master slave mode is set to master. Adaptive: allows link symmetry to vary dynamically in response to offered traffic load. This is no...
Page 389
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment installation menu page 6-30 attribute meaning lower center frequency the center frequency (mhz) of the lowest channel that may be used by this link. Not displayed when spectrum management control is set to fixed frequency. Use this attribute to slide the availa...
Page 390
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment installation menu page 6-31 attribute meaning maximum transmit power the maximum power (dbm) at which the unit will transmit, configurable in steps of 1 db. Its maximum value is controlled by the combination of the selected regulatory band, bandwidth and (for c...
Page 391: Tdd Frame Page
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment installation menu page 6-32 attribute meaning ranging mode this can only be modified if the unit is operating in the ptp topology, and installation mode is arm with tones or arm without tones. Auto..: during alignment, the wireless units use algorithms to calcu...
Page 392
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment installation menu page 6-33 figure 141 tdd frame page table 156 tdd frame attributes attribute meaning hcmp maximum link range this determines the maximum range between the hcmp master and any of the hcmp slave. The same value must be used on the hcmp master an...
Page 393
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment installation menu page 6-34 for more information on the available options, refer to configuration options for tdd synchronization on page 3-31 . Procedure: • update the attributes ( table 157 and table 158 ) • click next. Figure 142 tdd synchronization page, pt...
Page 394
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment installation menu page 6-35 figure 143 tdd synchronization page, cmm5 or direct connection, ptp topology figure 144 tdd synchronization page, ptp-sync, hcmp topology.
Page 395
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment installation menu page 6-36 figure 145 tdd synchronization page, cmm5 or direct connection, hcmp topology figure 146 tdd synchronization page, hcmp slave note for units operating in the ptp topology, obtain the data required to populate this page using the link...
Page 396
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment installation menu page 6-37 attribute meaning slave receive to transmit gap only displayed in ptp topology. The duration of the gap between receive and transmit at the slave odu. Table 158 tdd synchronization attributes at a tdd master odu attribute meaning tdd...
Page 397
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment installation menu page 6-38 confirm installation configuration page menu option: installation ( figure 147 ). Use this page to review and confirm the updated wireless configuration of the unit. Figure 147 confirm installation configuration page (top and bottom ...
Page 398: System Menu
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment system menu page 6-39 system menu this section describes how to configure the ip and ethernet interfaces of the ptp 670 unit. System configuration page menu option: system > configuration ( figure 148 ). Use this page to enable aes encryption and to review and ...
Page 399
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment system menu page 6-40 figure 149 system configuration page, tls rsa encryption algorithm caution configuring link encryption over an operational link will necessitate a service outage. Therefore, the configuration process should be scheduled during a period of ...
Page 400
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment system menu page 6-41 attribute meaning site name user defined name for the site, with additional notes (if required). Latitude the latitude of the odu, measured in decimal degrees. This attribute has no internal function. Longitude the longitude of the odu, me...
Page 401
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment system menu page 6-42 attribute meaning antenna gain only displayed for a connectorized odu. Gain of the external antenna. Cable loss only displayed for a connectorized odu. Loss in the odu-antenna rf cable. If there is a significant difference in length of the...
Page 402: Lan Configuration Page
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment system menu page 6-43 attribute meaning encryption algorithm values are: none, tls rsa, tls psk 128-bit or tls psk 256-bit. Use the same setting at both link ends. Tls psk 128-bit and tls psk 256-bit are only displayed when an aes encryption license key has bee...
Page 403
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment system menu page 6-44 caution before configuring a vlan for management interfaces, ensure that the vlan is accessible, otherwise the unit will be inaccessible after the next reboot. Caution before configuring in-band management, ensure that the master and slave...
Page 404
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment system menu page 6-45 figure 150 lan configuration page (ptp topology, aux and oob support).
Page 405
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment system menu page 6-46 figure 151 lan configuration page (ptp topology, tdm support).
Page 406
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment system menu page 6-47 figure 152 lan configuration page (ptp topology, sfp support).
Page 407
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment system menu page 6-48 figure 153 lan configuration page (sync e and ieee 1588 support).
Page 408
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment system menu page 6-49 figure 154 lan configuration page (hcmp topology).
Page 409
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment system menu page 6-50 procedure: 1 review and update the attributes: ip interface ( table 160 ); main psu or aux port ( table 161 ); bridging ( table 163 ). 2 to save changes, click submit updated system configuration. The system may reboot. 3 if main psu port ...
Page 410
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment system menu page 6-51 attribute meaning local management service defined in table 153 for more help, see ethernet port allocation for ptp topology on page 3-37 . Ethernet loopback mode sets a temporary loopback between the selected ports. The loopback is disabl...
Page 411
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment system menu page 6-52 table 161 main psu port, nidu lan port and aux port attributes attribute meaning auto negotiation disabled: configuration of the ethernet interface is forced. Enabled: configuration of the ethernet interface is automatically negotiated (de...
Page 412
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment system menu page 6-53 attribute meaning forced configuration only displayed when sfp port auto negotiation is set to disabled and sfp port is connected with copper module. This forces the speed and duplex setting of the ethernet interface. Over-the-air throughp...
Page 413
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment system menu page 6-54 table 164 synchronous ethernet attributes attribute meaning sync e tracking disabled: the synchronous ethernet feature is disabled. Synchronization status messages received at the main psu port will be discarded. Enabled: the synchronous e...
Page 414
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment system menu page 6-55 attribute meaning main psu port ssm tx disabled: ssms are not transmitted from the main psu port. Disabling ssms may be useful in a test environment. Enabled: ssms are transmitted from the main psu port (normal operation) aux port ssm tx d...
Page 415: Qos Configuration Page
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment system menu page 6-56 qos configuration page menu option: system > configuration > qos configuration ( figure 155 or figure 156 or figure 157 ). Use this page to control the quality of service configuration. Classification may be based on fields in the ethernet...
Page 416
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment system menu page 6-57 figure 156 qos configuration page (ip/mpls).
Page 417
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment system menu page 6-58 figure 157 qos configuration page showing out-of-band management procedures: • review and update the attributes ( table 166 , table 167 and table 168 ). • to use ieee 802.1q classification rules, click reset default priority mappings. • to...
Page 418: Sfp Configuration Page
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment system menu page 6-59 table 166 qos configuration attributes – data service attribute meaning bridge mrp cfm r-aps eaps pppoe discovery the classification of each layer 2 control protocol (l2cp) to an egress queue at the wireless port. Data priority scheme ethe...
Page 419
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment system menu page 6-60 figure 158 sfp configuration page (optical sfp module) figure 159 sfp configuration page (copper sfp module) procedure (only applies when copper sfp module is installed): • update the attributes o when optical sfp module is installed (tabl...
Page 420
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment system menu page 6-61 table 169 sfp configuration (optical module) attributes attribute meaning sfp port auto negotiation disabled: configuration of the ethernet interface is forced. This is to be used as a last resort only if auto-negotiation fails. Enabled: c...
Page 421: Tdm Configuration Page
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment system menu page 6-62 tdm configuration page note the tdm service is not supported in the hcmp topology. Menu option: system > configuration > tdm configuration ( figure 160 ). Use this page to control how the unit handles e1 or t1 channels over the wireless br...
Page 422: Authorization Control Page
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment system menu page 6-63 table 171 tdm configuration attributes attribute meaning tdm interface control display only. Defined in table 154 . Tdm local mac address display only. Mac address of the local nidu. Tdm remote mac address display only. Mac address of the ...
Page 423
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment system menu page 6-64 authorization control does not require an aes license. Procedure: • select whitelist or blacklist • update the mac addresses • to save changes, click submit configuration. Figure 161 authorization control page save and restore configuratio...
Page 424
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment system menu page 6-65 figure 162 save & restore configuration page save the system configuration in the following situations: • after a new unit has been fully configured as described in this chapter. • after any change has been made to the configuration. • bef...
Page 425
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment system menu page 6-66 note the stored configuration must be restored in a unit configured for the same topology for example, if a unit configured as hcmp needs to be restored to a ptp configuration, the following steps must be taken: • first, go through the ins...
Page 426: Reset Configuration Page
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment system menu page 6-67 reset configuration page menu option: system > configuration > reset configuration. Use this page to reset the odu configuration to default settings, retaining the most recently entered license key ( figure 163 ). The reset configuration p...
Page 427: Further Reading
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment system menu page 6-68 further reading for information about… refer to… erase configuration use this option to erase the entire configuration of the unit. Refer to resetting all configuration data on page 7-81 . Software upgrade page menu option: system > softwa...
Page 428
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment system menu page 6-69 • if the support web page contains a later software version than that installed on the ptp 670 unit, perform the procedure below. Procedure: 1 save the system configuration; see save and restore configuration page on page 6-64 . 2 on the c...
Page 429: Management Menu
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment management menu page 6-70 management menu this section describes how to configure web-based management of the ptp 670 unit. Web-based management page menu option: management > web ( figure 165 ). Use this page to configure web-based management of the unit. Figu...
Page 430
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment management menu page 6-71 procedure: • review and update the attributes ( table 172 ). • to save changes, click submit updated configuration. Table 172 web-based management attributes attribute meaning https access enabled only displayed when https is configure...
Page 431: Local User Accounts Page
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment management menu page 6-72 attribute meaning cross site request forgery protection enabled: the system is protected against cross-site request forgery attacks at the web-based interface. Local user accounts page menu option: management > web > local user account...
Page 432
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment management menu page 6-73 figure 167 local user accounts page (identity based user accounts enabled).
Page 433
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment management menu page 6-74 procedure: • choose whether to set identity based user accounts to disabled or enabled. • review and update the local user account management attributes ( table 173 ). • if identity based user accounts is set to enabled: o review and u...
Page 434
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment management menu page 6-75 table 174 password complexity configuration attributes attribute meaning best practice minimum password length the minimum number of characters required in passwords. 10 password can contain user name no: passwords must not contain the...
Page 435
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment management menu page 6-76 attribute meaning best practice special characters user defined set of special characters used in password construction. The only characters permitted in a password are: (a-z), (a-z), (0-9) and any of the special characters entered her...
Page 436: Radius Configuration Page
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment management menu page 6-77 radius configuration page menu option: management > web > radius configuration ( figure 168 ). Use this page to configure radius authentication. Radius authentication is only available when ptp 670 is configured for identity-based user...
Page 437: Webpage Properties Page
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment management menu page 6-78 table 176 radius authentication attributes attribute meaning radius client enabled enabled: ptp 670 users may be authenticated via the radius servers. Disabled: radius authentication is not used. This may only be selected if at least o...
Page 438
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment management menu page 6-79 figure 169 webpage properties page procedure: • update the attributes ( table 177 ). • click apply properties. Table 177 webpage properties attributes attribute meaning web properties view summary and status pages without login: • if t...
Page 439
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment management menu page 6-80 attribute meaning transmitter channels control disabled: hides the transmitter channels attribute. Enabled: shows the transmitter channels attribute ( wireless configuration page on page 6-25 , and system configuration page on page 6-3...
Page 440: Email Configuration Page
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment management menu page 6-81 variable meaning $ipv6linklocaladdress ipv6 auto configured link local address of the odu. This cannot be updated, but it can be viewed in the lan configuration page ( table 160 ). $sysname sys name for this snmp managed node, as set i...
Page 441
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment management menu page 6-82 • click reboot wireless unit and click ok. The reboot progress message is displayed. On completion, the unit restarts. Table 179 email configuration attributes attribute meaning smtp email alert controls the activation of the smtp clie...
Page 442: Diagnostic Alarms Page
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment management menu page 6-83 diagnostic alarms page menu option: management > diagnostic alarms ( figure 171 ). Use this page to select which diagnostic alarms will be notified to the system administrator. Figure 171 diagnostic alarms page procedure: • tick the re...
Page 443: Time Configuration Page
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment management menu page 6-84 time configuration page menu option: management > time ( figure 172 and figure 173 ). Use this page to set the real- time clock of the ptp 670. Setting the real-time clock manually use this procedure to keep time without connecting to ...
Page 444
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment management menu page 6-85 procedure: • set the sntp state attribute to enabled ( figure 173 ). • review and update the sntp clock attributes ( table 181 ). • click submit updated configuration..
Page 445
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment management menu page 6-86 figure 173 time configuration page (sntp enabled).
Page 446
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment management menu page 6-87 table 181 sntp clock attributes attribute meaning sntp state enabled: the odu will obtain accurate date and time updates from a networked time server. Sntp primary server specifies the primary sntp server, determining the order in whic...
Page 447: Syslog Configuration Page
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment management menu page 6-88 attribute meaning daylight saving disabled: daylight saving adjustments will not be applied to the time. Enabled: daylight saving adjustments will be applied to the time, according to local rules. To set the clock to utc time, set dayl...
Page 448
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment management menu page 6-89 procedure: • update the attributes ( table 182 ). • click submit updated configuration. Table 182 syslog configuration attributes attribute meaning syslog state when system logging is enabled, log entries are added to the internal log ...
Page 449: Snmp Pages (For Snmpv3)
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment snmp pages (for snmpv3) page 6-90 snmp pages (for snmpv3) this section describes how to configure simple network management protocol version 3 (snmpv3) traps using the snmp wizard. Current snmp summary (for snmpv3) menu option: management > snmp ( figure 175 )....
Page 450
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment snmp pages (for snmpv3) page 6-91 step 1: snmp configuration (for snmpv3) menu option: management > snmp. Part of the snmp wizard ( figure 176 ). Use this page to enable snmp, select snmpv3 and configure access to the snmp server. Figure 176 step 1: snmp config...
Page 451
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment snmp pages (for snmpv3) page 6-92 table 183 step 1: snmp configuration attributes (for snmpv3) attribute meaning snmp minimum privilege level minimum security level which is permitted to administer snmp security settings. Only displayed when identity based user...
Page 452
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment snmp pages (for snmpv3) page 6-93 step 2: snmp mib-ii system objects (for snmpv3) menu option: management > snmp. Part of the snmp wizard ( figure 177 ). Use this page to enter details of the snmp managed node. Figure 177 step 2: snmp mib-ii system objects page...
Page 453
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment snmp pages (for snmpv3) page 6-94 step 3: snmp user policy configuration (for snmpv3) menu option: management > snmp. Part of the snmp wizard ( figure 178 ). This page is only displayed when snmp security mode is set to web-based in the step 1: snmp configurati...
Page 454
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment snmp pages (for snmpv3) page 6-95 attribute meaning privacy protocol the privacy protocol to be used to access the ptp 670 via snmp. This is disabled when security level is set to no auth no priv or auth no priv. Des: data encryption standard (des) symmetric en...
Page 455
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment snmp pages (for snmpv3) page 6-96 table 186 step 4: snmp user accounts configuration attributes (for snmpv3) attribute meaning name name to be used by the snmp user to access the system. Role selects which of the two web-based security profiles are applied to t...
Page 456
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment snmp pages (for snmpv3) page 6-97 figure 180 step 5: snmp trap configuration page (for snmpv3) procedure: • update the attributes ( table 187 ). • click next..
Page 457
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment snmp pages (for snmpv3) page 6-98 table 187 step 5: snmp trap configuration attributes (for snmpv3) attribute meaning snmp enabled traps select the events that will generate snmp traps. Snmp trap receiver 1 and snmp trap receiver 2: snmp trap receiver enabled d...
Page 458: Snmp Pages (For Snmpv1/2C)
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment snmp pages (for snmpv1/2c) page 6-99 snmp pages (for snmpv1/2c) this section describes how to configure simple network management protocol version 1 or 2c (snmpv1 or snmpv2c) traps using the snmp wizard. Current snmp summary (for snmpv1/2c) menu option: managem...
Page 459
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment snmp pages (for snmpv1/2c) page 6-100 procedure: • set snmp state to enabled. • set snmp version to v1/2c. The page is redisplayed with snmpv1/2c attributes. • update the attributes ( table 188 ). • click next. Table 188 step 1: snmp configuration attributes (f...
Page 460
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment snmp pages (for snmpv1/2c) page 6-101 step 3: snmp trap configuration (for snmpv1/2c) menu option: management > snmp. Part of the snmp wizard ( figure 183 ). Figure 183 step 3: snmp trap configuration page (for snmpv1/2c) procedure: • update the attributes ( ta...
Page 461
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment snmp pages (for snmpv1/2c) page 6-102 table 189 step 3: snmp trap configuration attributes (for snmpv1/2c) attribute meaning snmp trap version select the snmp protocol version to use for snmp traps: v1 or v2c. Snmp enabled traps select the events that will gene...
Page 462: Security Menu
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment security menu page 6-103 security menu this section describes how to configure security options using the security wizard. Caution ensure that the operator’s security requirements are configured before connecting the ptp 670 to the network. Otherwise, security ...
Page 463: Security Options
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment security menu page 6-104 figure 185 security configuration wizard page to continue with the security wizard, click continue to security wizard. Security options menu option: security. Part of the security wizard ( figure 186 ). Select optional security features...
Page 464: Key Of Keys
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment security menu page 6-105 set the remaining options to no to disable the associated feature, or set to yes to enable the associated feature. Enabled features are configured in the remaining pages of the security wizard. Figure 186 security options page key of ke...
Page 465: Entropy
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment security menu page 6-106 figure 188 key of keys page with configured value caution erasing or changing the key of keys resets all csps. Procedure: • if the keys of keys has already been configured, check the sha-1 thumbprint, otherwise • enter and confirm the g...
Page 466: Enter User Security Banner
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment security menu page 6-107 figure 190 entropy page with configured value procedure: • if valid entropy input exists, then an sha-1 thumbprint of the input is displayed. If this input is correct, then take no action. Otherwise, enter the generated input in the ent...
Page 467
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment security menu page 6-108 figure 191 enter user security banner page procedure: • update the user defined security banner (optional). • set the acknowledgement to no or yes. • click next. Enter login information settings menu option: security. Part of the securi...
Page 468: Enter Https Configuration
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment security menu page 6-109 figure 192 enter login information settings page procedure: • set display login information to no or yes. • click next. Enter https configuration menu option: security. Part of the security wizard ( figure 193 and figure 194 ). Use this...
Page 469
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment security menu page 6-110 figure 194 configured https configuration page caution if the certificates expire, your web browser will display security warnings. Always investigate the cause of security warnings, and rectify errors in the content or expiry of certif...
Page 470
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment security menu page 6-111 figure 195 wireless link encryption settings, tls-rsa figure 196 wireless link encryption settings, user-supplied device certificates.
Page 471
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment security menu page 6-112 figure 197 wireless link encryption settings, authorization control figure 198 wireless link encryption settings, tls-psk.
Page 472: Http And Telnet Options
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment security menu page 6-113 figure 199 wireless link encryption settings, tls-psk procedure: • select the applicable value in the encryption algorithm field. • for tls-rsa, select factory or user device certificates. • for user device certificates, install private...
Page 473
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment security menu page 6-114 figure 200 http and telnet settings page caution if https, http, telnet and snmp are all disabled, management access will be impossible until the unit is placed in recovery mode. Note if http, telnet and snmp are all disabled, the secur...
Page 474
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment security menu page 6-115 attribute meaning snmp control of http and telnet disabled: neither http nor telnet can be controlled remotely via snmp. Enabled: both http and telnet can be controlled remotely via snmp. Snmp control of passwords enabled: passwords for...
Page 475
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment security menu page 6-116 figure 201 confirm security configuration page procedure: • review all changes that have been made in the security wizard. • to ensure that the changes take effect, click commit security configuration and reboot. The unit reboots and th...
Page 476: Zeroize Csps Page
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment security menu page 6-117 note if the key of keys is entered or modified in the security wizard, user accounts are reset when commit security configuration and reboot is clicked. It is then necessary to reconfigure them. Zeroize csps page menu option: security >...
Page 477: Aligning Antennas
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment aligning antennas page 6-118 aligning antennas this section describes how to align the antennas for master and slave odus in the ptp topology, and slave odus in the hcmp topology, using the web interface to assist with alignment, and checking wireless performan...
Page 478: Aligning Antennas
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment aligning antennas page 6-119 aligning antennas use this procedure to align linked antennas (master and slave), whether integrated or connectorized. The goal of antenna alignment is to find the center of the main beam. This is done by adjusting the antennas whil...
Page 479
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment aligning antennas page 6-120 5 when the antennas have been aligned on the center of the beam, verify that the receive level is within the predicted range (from the installation report). If this is not the case, go back to step 2. The current value of receive le...
Page 480: Odu Installation Tones
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment aligning antennas page 6-121 odu installation tones this is the first of two methods that may be used to monitor receive signal level during antenna alignment. The odu emits audible tones during installation to assist with alignment. The pitch of the alignment ...
Page 481
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment aligning antennas page 6-122 during alignment, the installation tones should exhibit the following behavior: • band scan: when first started up and from time to time, the master unit will carry out a band scan to determine which channels are not in use. During ...
Page 482: Graphical Install Page
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment aligning antennas page 6-123 graphical install page menu option: installation > graphical install ( figure 203 ). This is the second of two methods that may be used to monitor receive signal level during antenna alignment. Figure 203 graphical install page proc...
Page 483: Disarming The Units
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment aligning antennas page 6-124 disarming the units when antenna alignment is complete, use this procedure to disarm both units in the link in order to: • turn off the audible alignment aid. • enable adaptive modulation. • fully enable spectrum management features...
Page 484
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment aligning antennas page 6-125 comparing actual to predicted performance for at least one hour of operation after disarming, use this procedure to monitor the link to check that it is achieving predicted levels of performance. Linkplanner provides the prediction ...
Page 485: Other Configuration Tasks
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment other configuration tasks page 6-126 other configuration tasks this section describes other configuration tasks. Connecting to the network use this procedure to complete and test network connections. Procedure: 1 if a management pc is connected directly to the ...
Page 486
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment other configuration tasks page 6-127 upgrading software using tftp use this procedure to upgrade software remotely using trivial ftp (tftp) triggered by snmp. Procedure: 1 check that the tftp client is enabled. Refer to web-based management page on page 6-70 . ...
Page 487
Chapter 6: configuration and alignment other configuration tasks page 6-128 table 193 monitoring tftp attributes attribute meaning tftpsoftwareupgradestatus this is the current status of the tftp software upgrade process. Values: idle(0) uploadinprogress(1) uploadsuccessfulprogrammingflash(2) upgrad...
Page 488: Chapter 7:
Page 7-1 chapter 7: operation this chapter provides instructions for operators of the ptp 670 wireless ethernet bridge. The following topics are described in this chapter: • system summary and status on page 7-2 • rebooting and logging out on page 7-18 • alarms, alerts and messages on page 7-20 • sp...
Page 489: System Summary And Status
Chapter 7: operation system summary and status page 7-2 system summary and status this section describes how to use the summary and status pages to monitor the status of the ethernet ports and wireless link. System summary page menu option: home ( figure 206 ). This page contains a high level summar...
Page 490: System Status Page
Chapter 7: operation system summary and status page 7-3 attribute meaning elapsed time indicator the time (hh:mm:ss) that has elapsed since the last system reboot. The system can reboot for several reasons, for example, commanded reboot from the system reboot webpage, or a power cycle of the equipme...
Page 491
Chapter 7: operation system summary and status page 7-4 note link symmetry is configured at the master odu only. The appropriate matching link symmetry is set at the slave odu automatically. For example, if link symmetry is configured as 2 to 1 at the master odu, then the slave odu will be set autom...
Page 492: Hcmp Topology
Chapter 7: operation system summary and status page 7-5 hcmp topology menu option: status ( figure 209 to figure 211 ). This page provides a detailed view of the operation of the ptp 670 link from both the wireless and network perspectives. Figure 209 system status page (master, hcmp topology, wirel...
Page 493
Chapter 7: operation system summary and status page 7-6 figure 210 system status page (master, hcmp topology, wireless interface set to “all wireless interfaces”).
Page 494: Equipment
Chapter 7: operation system summary and status page 7-7 figure 211 system status page (slave, hcmp topology) in the hcmp topology, one ptp 670 series unit is the master and up to eight ptp 670 series units are configured as slaves. The roles of the units in this relationship are displayed in the pag...
Page 495: Ethernet / Internet
Chapter 7: operation system summary and status page 7-8 attribute meaning site name the site name is allocated by the system administrator and can be used as a generic scratch pad to describe the location of the equipment or any other equipment related notes. The site name attribute is limited to a ...
Page 496: Wireless
Chapter 7: operation system summary and status page 7-9 attribute meaning aux port speed and duplex the negotiated speed and duplex setting of the ethernet link to the aux port. The speed setting is specified in mbps. Sfp port status the current status of the ethernet link to the sfp port: • green “...
Page 497
Chapter 7: operation system summary and status page 7-10 attribute meaning receive power the maximum, mean, minimum and latest measurements of receive power (dbm). See system histograms on page 7-54 . Vector error the maximum, mean, minimum and latest measurements of vector error (db). See system hi...
Page 498
Chapter 7: operation system summary and status page 7-11 attribute meaning receive modulation mode the modulation mode currently being used on the receive channel. Link symmetry a ratio that expresses the division between transmit and receive time in the tdd frame. The first number in the ratio repr...
Page 499: Synchronous Ethernet
Chapter 7: operation system summary and status page 7-12 synchronous ethernet note synchronous ethernet is available in the ptp topology. The synchronous ethernet section of the system status page contains the attributes described in table 199 . Table 199 system status attributes – synchronous ether...
Page 500: Tdd Synchronization
Chapter 7: operation system summary and status page 7-13 tdd synchronization the tdd synchronization section of the system status page contains the attributes described in table 201 . Table 201 system status attributes – tdd synchronization attribute meaning tdd synchronization status the status of ...
Page 501
Chapter 7: operation system summary and status page 7-14 value meaning holdover the odu is a cluster slave and the 1 pps reference has been lost at the input to an upstream ptp-sync unit. The odu is locked to an upstream odu that is in the holdover (no gps sync in) state. The odu is transmitting. If...
Page 502: Tdm
Chapter 7: operation system summary and status page 7-15 value meaning holdover the odu is transmitting. If the reference input is not restored, the holdover state will terminate automatically after a period set by tdd holdover duration. Not synchronized the holdover period has expired. If the odu i...
Page 503
Chapter 7: operation system summary and status page 7-16 table 205 system status attributes – tdm attribute meaning tdm interface control the type of tdm interface that is activated (none, e1 or t1). This is set on the interface configuration page. Tdm interface status the current status of the ethe...
Page 504
Chapter 7: operation system summary and status page 7-17 value meaning remote timing tdm data is being received at the tdm port on the local and remote nidus. The modulation mode of the link is too low to support bridging of tdm data in either direction. The transmit clocks at the tdm ports on local...
Page 505: Rebooting and Logging Out
Chapter 7: operation rebooting and logging out page 7-18 rebooting and logging out this section describes how to reboot the unit and log out of the web interface. Login information page menu option: management > web > login information ( figure 212 ). Use this page to show recent successful and unsu...
Page 506: Change Password Page
Chapter 7: operation rebooting and logging out page 7-19 o click ok. The reboot progress message is displayed. On completion, the unit restarts. Figure 214 reboot confirmation pop up change password page menu option: change password ( figure 215 ). Use this page to change a personal password. Figure...
Page 507: Alarms
Chapter 7: operation alarms, alerts and messages page 7-20 alarms, alerts and messages this section describes how to use alarms, alerts and syslog messages to monitor the status of a ptp 670 link. Alarms whenever system alarms are active, a yellow warning triangle is displayed on the navigation bar....
Page 508
Chapter 7: operation alarms, alerts and messages page 7-21 table 207 system alarms alarm meaning aux port configuration mismatch ethernet fragments (runt packets) have been detected when the aux port is in full duplex. This indicates an auto- negotiation or forced configuration mismatch. Aux port di...
Page 509
Chapter 7: operation alarms, alerts and messages page 7-22 alarm meaning incompatible master and slave the master and slave ends of the wireless link are different hardware products, or have different software versions. It is very unusual to detect this because incompatible units will normally fail ...
Page 510
Chapter 7: operation alarms, alerts and messages page 7-23 alarm meaning sfp error a non-ok value indicates that the sfp link is down. There are two possible causes: • either: the fiber link has been installed but disabled (because the license key does not include sfp support), • or: the sfp link co...
Page 511: Email Alerts
Chapter 7: operation alarms, alerts and messages page 7-24 alarm meaning unit out of calibration the unit is out of calibration and must be returned to the factory using the rma process for re-calibration. Wireless link disabled warning the wireless link has been administratively disabled via the sn...
Page 512: Syslog Page
Chapter 7: operation alarms, alerts and messages page 7-25 syslog page menu option: management > syslog ( figure 217 ). Use this page to view the local log of event messages. Figure 217 syslog local log note for more information about system logging, refer to: • system logging (syslog) on page 1-57 ...
Page 516: Spectrum Management
Chapter 7: operation spectrum management page 7-29 spectrum management this section describes how to use the spectrum management pages to monitor the radio spectrum usage of the ptp 670 link. Spectrum expert and spectrum management pages there are two alternative web pages providing access the spect...
Page 517: Spectrum Expert Page
Chapter 7: operation spectrum management page 7-30 note when configured to use the spectrum expert page, the ptp 670 is capable of automatically detecting whether the browser accessing the unit supports the required features. If it does not, the spectrum management page will be returned instead of t...
Page 518: Standard Display Mode
Chapter 7: operation spectrum management page 7-31 standard display mode figure 219 spectrum expert page – standard display mode.
Page 519: Extended Display Mode
Chapter 7: operation spectrum management page 7-32 extended display mode figure 220 spectrum expert page – extended display mode note figure 219 shows the default layout for a unit configured as a master. On a unit configured as slave, some of the controls at the bottom of the page are not available...
Page 520: Full Layout
Chapter 7: operation spectrum management page 7-33 figure 221 spectrum expert page with receive spectrum and timeseries for the local unit full layout the page layout may be extended further to give access to more information on either or both the local and the peer interference spectra. For the loc...
Page 521: Spectrum Management Page
Chapter 7: operation spectrum management page 7-34 figure 223 spectrum expert page showing the receive spectrum, timeseries, interference waterfall and histogram for the local unit spectrum management page menu option: system > spectrum management note that this page is only shown when the spectrum ...
Page 522
Chapter 7: operation spectrum management page 7-35 figure 224 spectrum management page (master unit) figure 224 shows the spectrum management page layout for a unit configured as a master. On a unit configured as slave, some of the controls at the bottom of the page are not available. Spectrum manag...
Page 523
Chapter 7: operation spectrum management page 7-36 note before attempting to improve the performance of the spectrum management algorithm by changing the default configuration, consult the cambium point-to-point distributor or one of the system field support engineers. Procedure: • review the config...
Page 524: X Axis And Y Axis
Chapter 7: operation spectrum management page 7-37 attribute meaning hopping period the spectrum management algorithm evaluates the metrics every “hopping period” seconds (180 seconds by default) looking for a channel with lower levels of interference. If a better channel is located, spectrum manage...
Page 525: Channel States
Chapter 7: operation spectrum management page 7-38 channel states the active channel (channel 9 in figure 219 ) is always marked using hatched green and white lines on the spectrum management page or solid green on the spectrum expert page. The width of the hatching is directly proportional the chan...
Page 526
Chapter 7: operation spectrum management page 7-39 metric description how represented mean of means the arithmetic mean of the measured means during a quantization period. The mean of means is a coarse measure of signal interference and gives an indication of the average interference level measured ...
Page 527
Chapter 7: operation spectrum management page 7-40 figure 225 spectrum expert page for fixed frequency – standard display mode figure 226 spectrum expert page for fixed frequency – extended display mode.
Page 528
Chapter 7: operation spectrum management page 7-41 channel barring is disabled in fixed frequency mode; it is not required as dynamic channel hopping is prohibited in this mode. The only controls available to the master are the spectrum expert display mode and interference threshold attributes. They...
Page 529
Chapter 7: operation spectrum management page 7-42 figure 228 spectrum expert page with radar avoidance – extended display when operating with rttt (road transport and traffic telematics) avoidance enabled or other regulatory restrictions on channel usage, all channels marked with a “no entry” symbo...
Page 530: Barring Channels
Chapter 7: operation spectrum management page 7-43 color state and color meaning dark grey barred the system administrator has barred this channel from use. Because the low signal levels encountered when a unit is powered up in a laboratory environment prior to installation (which makes the grey of ...
Page 531
Chapter 7: operation spectrum management page 7-44 figure 229 selecting channels for barring figure 230 channel barring confirmation.
Page 532
Chapter 7: operation spectrum management page 7-45 figure 231 barred channels selecting a channel and a time period the timeseries plot uses measurements for the selected channel. The histogram plot uses measurements for the selected channel and the selected measurement period. To select a channel, ...
Page 533
Chapter 7: operation spectrum management page 7-46 figure 232 selecting a channel on the receive spectrum to freeze the selection of channel and time period, click on the cursor position. The frequency and time period are now fixed until a new combination is selected by clicking in a different locat...
Page 534
Chapter 7: operation spectrum management page 7-47 figure 233 spectrum expert, timeseries plot table 214 interference represented in the time series plot color meaning red peak of means interference measurement black 99.9% percentile of means interference measurement blue mean of means interference ...
Page 535
Chapter 7: operation spectrum management page 7-48 figure 234 spectrum expert, interference waterfall plot setting the interference threshold the interference threshold may be set using the sliding control located directly below the interference waterfall plot. This is an alternative to the method d...
Page 536
Chapter 7: operation spectrum management page 7-49 viewing the channel states to display the channel states, tick the show channel state control right below the interference waterfall plot. Figure 236 shows an example of the interference waterfall when the channel states are displayed. The colors us...
Page 537: Spectrum Expert Example
Chapter 7: operation spectrum management page 7-50 spectrum expert example in this example from a real-world link, shown in figure 238 , the channel at 5740 mhz has been selected for analysis. The spectrum display is based in the most recent 20 minute period. The height of the colored bar in the sel...
Page 538
Chapter 7: operation spectrum management page 7-51 figure 239 spectrum expert, example 2 the interference observed in figure 239 for the channel at 5740 mhz during the recent two hour period is not compatible with satisfactory operation a ptp 670 link. The situation is, if anything, even worse in th...
Page 539
Chapter 7: operation spectrum management page 7-52 figure 240 spectrum expert, example 3 figure 241 spectrum expert, example 4.
Page 540: Managing Security
Chapter 7: operation managing security page 7-53 managing security this section describes the procedure for zeroising critical security parameters. Other security configuration procedures are described in security menu on page 6-103 . Zeroizing critical security parameters use this procedure to zero...
Page 541: System Statistics
Chapter 7: operation system statistics page 7-54 system statistics this section describes how to use the system statistics pages to manage the performance of the ptp 670 link, use the following web pages: system statistics page menu option: system > statistics. Use this page to check system statisti...
Page 542
Chapter 7: operation system statistics page 7-55 figure 243 system histograms section of the system statistics page (hcmp topology, wireless interface selector set to “all wireless interfaces”) the element arrays represent the following: • max: the maximum value measured over the last hour. • mean: ...
Page 543
Chapter 7: operation system statistics page 7-56 table 215 system histogram attributes in the system statistics page attribute meaning transmit power the transmit power histogram, calculated over a one hour period. Receive power the receive power histogram, calculated over a one hour period. Vector ...
Page 544
Chapter 7: operation system statistics page 7-57 system counters (ptp topology) the system counters section of the system statistics page ( figure 244 ) contains data port counters ( table 216 ), management agent counters ( table 218 ) and wireless port counters and performance information ( table 2...
Page 545
Chapter 7: operation system statistics page 7-58 table 217 second data port counters attribute meaning tx frames the total number of good frames the bridge has sent for transmission through the port selected for second data service rx frames the total number of good frames the bridge has received th...
Page 546: Other Attributes
Chapter 7: operation system statistics page 7-59 attribute meaning receive modulation mode detail the receive modulation mode in use. For a list of values and their meanings, see table 198 . Wireless link availability wireless link availability calculated since the last system counters reset. Ethern...
Page 547: Ptp Topology
Chapter 7: operation system statistics page 7-60 wireless port counters page ptp topology menu option: system > statistics > wireless port counters ( figure 246 ). Use this page to check the ethernet performance of the wireless bridge. Figure 246 wireless port counters page (ptp topology) note if th...
Page 548: Hcmp Topology
Chapter 7: operation system statistics page 7-61 table 221 wireless port counters attributes attribute meaning tx/rx frames number of frames transmitted and received over the wireless bridge. Rx frames with crc error number of received frames with crc errors. Tx/rx frames q0…q7 number of transmitted...
Page 549
Chapter 7: operation system statistics page 7-62 figure 248 wireless port counters page (master, hcmp topology, wireless interface selector set to all wireless links).
Page 550
Chapter 7: operation system statistics page 7-63 figure 249 wireless port counters page (slave, hcmp topology) procedure: • only on a device configured as in hcmp topology as a master, select one interface using the wireless interface selector. Note the remote mac address indicates the mac address o...
Page 551
Chapter 7: operation system statistics page 7-64 figure 250 main port counters page (when main port is bridging traffic).
Page 552
Chapter 7: operation system statistics page 7-65 procedure: • review the attributes ( table 223 ). • to change the refresh period, update the counter page refresh period attribute and click submit page refresh period. • to reset all counters to zero, click reset system counters. Table 223 main port ...
Page 553
Chapter 7: operation system statistics page 7-66 aux port counters page (ptp topology only) menu option: system > statistics > aux port counters ( figure 251 ). Use this page to check the ethernet performance of the aux port. Figure 251 aux port counters page (when aux port is is allocated to the lo...
Page 554
Chapter 7: operation system statistics page 7-67 figure 252 sfp port counters page (when sfp port is allocated to the local management service) procedure: • update the attributes ( table 225 ). • to change the refresh period, update the counter page refresh period attribute and click submit page ref...
Page 555
Chapter 7: operation system statistics page 7-68 figure 253 ethernet port counters page (hcmp topology) procedure: • review the attributes (table 226). • to change the refresh period, update the counter page refresh period attribute and click submit page refresh period. • to reset all counters to ze...
Page 556
Chapter 7: operation system statistics page 7-69 attribute meaning rx frames with error total number of received frames with crc errors. Tx/rx broadcasts total number of good transmitted and received broadcast packets. Rx frames undersize total number of frames received that are less than 64 bytes. ...
Page 557: Synce Status Page
Chapter 7: operation system statistics page 7-70 synce status page menu option: system > statistics > synce status use this page to monitor the state of the synchronous ethernet function. Note when tdm is enabled ( tdm configuration page on page 6-62 ), the following restrictions are automatically a...
Page 558
Chapter 7: operation system statistics page 7-71 table 228 sync e status attributes attribute meaning sync e tracking state the state of the synchronous ethernet state machine. See table 229 for further details. Main psu port accepted ql rx the “accepted” ql received by the main psu port. This shoul...
Page 559
Chapter 7: operation system statistics page 7-72 attribute meaning sfp port accepted ql rx the “accepted” ql received by the sfp port. This should be the same as sfp port ql rx, unless: • an “overwrite” has been configured • the system is starting up or recovering from an exception the odu synchroni...
Page 560: Diagnostics Plotter Page
Chapter 7: operation system statistics page 7-73 value meaning locked remote, holdover acquired the tracking loop has locked to a synchronisation signal form the remote odu and has acquired holdover history. In normal operation, with the synchronous ethernet feature enabled and a valid timing source...
Page 561
Chapter 7: operation system statistics page 7-74 figure 257 diagnostic plotter page (hcmp topology) procedure: • only on a device configured as in hcmp topology as a master, set the wireless interface selector to the wireless interface the diagnostic data needs to be displayed for. Note the remote m...
Page 562
Chapter 7: operation system statistics page 7-75 generate downloadable diagnostics page menu option: system > diagnostics plotter > csv download ( figure 258 ). Use this page to download diagnostics data to a csv file. Figure 258 generate downloadable diagnostics page procedure: • select a diagnosti...
Page 563: Recovery Mode
Chapter 7: operation recovery mode page 7-76 recovery mode this section describes how to recover a ptp 670 unit from configuration errors or software image corruption. Entering recovery mode use this procedure to enter recovery mode manually. Note the unit may enter recovery mode automatically, in r...
Page 564
Chapter 7: operation recovery mode page 7-77 figure 259 recovery options page table 231 recovery options attributes attribute meaning software version the software version of the recovery operating system permanently installed during manufacture. Recovery reason the reason the unit is operating in r...
Page 565: Upgrading Software Image
Chapter 7: operation recovery mode page 7-78 table 232 recovery options buttons button purpose upgrade software image use this option to restore a working software version when software corruption is suspected, or when an incorrect software image has been loaded. Refer to upgrading software image on...
Page 566
Chapter 7: operation recovery mode page 7-79 5 click reboot wireless unit. When the “ are you sure? ” message is displayed, click ok. 6 the unit will now reboot and restart in normal operational mode, and the link should recover. If the unit or link fails to recover, refer to testing link end hardwa...
Page 567
Chapter 7: operation recovery mode page 7-80 • sfp port auto neg advertisement • sfp port auto mdix • local packet filtering • nidu lan port auto negotiation • nidu lan port auto neg advertisement • nidu lan port auto mdix • snmp access control • access control • ip address label procedure: 1 click ...
Page 568
Chapter 7: operation recovery mode page 7-81 4 click reboot. When the “ are you sure you want to reboot this unit? ” message is displayed, click ok. 5 the unit will now reboot. The unit should now start up in normal mode but with the ip and ethernet configuration reset to factory defaults. If the un...
Page 569
Chapter 7: operation recovery mode page 7-82 3 click reboot. When the confirmation message is displayed, click ok. 4 the unit reboots and starts up in normal mode but with all configuration reset to default values. If the unit fails to start up, refer to testing link end hardware on page 8-7 and and...
Page 570: Rebooting The Unit
Chapter 7: operation recovery mode page 7-83 procedure: 1 click zeroize critical security parameters. The confirmation pop up box is displayed: 2 click ok. The zeroize csps confirmation page is displayed: 3 click reboot. When the “ are you sure you want to reboot this unit? ” message is displayed, c...
Page 571
Chapter 7: operation recovery mode page 7-84 • when the “ are you sure you want to reboot this unit? ” message is displayed, click ok. The unit will now reboot. The unit should now start up in normal operational mode. If the unit fails to start up, refer to testing link end hardware on page 8- 7..
Page 572: Chapter 8:
Page 8-1 chapter 8: troubleshooting this chapter contains procedures for identifying and correcting faults in a ptp 670 link. These procedures can be performed either on a newly installed link, or on an operational link if communication is lost, or after a lightning strike. The following topics are ...
Page 573: Cable Diagnostics
Chapter 8: troubleshooting cable diagnostics page 8-2 cable diagnostics this section describes how to diagnose cable faults. The cable diagnostics feature may be used to test ethernet cables connected to the main psu port and the aux port. The feature uses time domain reflectometry (tdr) technology ...
Page 574: Cable Diagnostics Test
Chapter 8: troubleshooting cable diagnostics page 8-3 scenarios actions if packet error rate is greater than 1 in 1 million, perform cable diagnostics test . If number of lost packets are less than two ( test ping packet loss , perform cable diagnostics test . Otherwise check the odu’s parameter con...
Page 575
Chapter 8: troubleshooting cable diagnostics page 8-4 table 233 pin to pair mapping of a cable (t568b termination) pin pair wire color (supplied cable) color (conventional) pins on plug face 1 2 1 light orange white/orange 2 2 2 orange orange 3 3 1 light green white/green 4 1 2 blue blue 5 1 1 light...
Page 576
Chapter 8: troubleshooting cable diagnostics page 8-5 note the local management port connection will be lost when the local management port is under test. However the management port will be accessible when the other ports are under test. 4 on completion of the test, the web page is refreshed automa...
Page 577
Chapter 8: troubleshooting cable diagnostics page 8-6 attribute meaning there are four twisted pairs in each cat5 cable. The cable diagnostics test is performed on each pair of the cable. Results ok: reported when the test is passed for a respective cable pair. Open circuit: reported when the impeda...
Page 578: Testing Link End Hardware
Chapter 8: troubleshooting testing link end hardware page 8-7 testing link end hardware this section describes how to test the link end hardware when it fails on startup or during operation. Before testing link end hardware, confirm that all outdoor drop cables, that is those that connect the odu to...
Page 579: Power Led Is Blinking
Chapter 8: troubleshooting testing link end hardware page 8-8 • if the power led does not illuminate, confirm that the mains power supply is working, for example, check the plug and fuse (if fitted). If the power supply is working, report a suspected psu fault to cambium networks. • if the power led...
Page 580
Chapter 8: troubleshooting testing link end hardware page 8-9 ethernet led blinks ten times then stays off meaning: there is no ethernet traffic between the psu and odu. Action: the fault may be in the lan or odu cable: • confirm that ethernet traffic is connected to the ac+dc injector lan port, con...
Page 581: Ethernet Packet Test
Chapter 8: troubleshooting testing link end hardware page 8-10 ethernet packet test follow the ethernet packet test flowchart ( figure 260 ) and procedures below. Figure 260 ethernet packet test flowchart.
Page 582: Test Ping Packet Loss
Chapter 8: troubleshooting testing link end hardware page 8-11 test ethernet packet errors reported by odu log into the unit and click administration, statistics, detailed counters. Click reset system counters at the bottom of the page and wait until the ethernet rx packets counter has reached 1 mil...
Page 583
Chapter 8: troubleshooting testing link end hardware page 8-12 5 send 1000 ping packets of length 1500 bytes. The process will take 1000 seconds, which is approximately 17 minutes. If the computer is running a windows operating system, this is achieved by typing (for an ipv6 address, use the ping6 c...
Page 584: Testing The Radio Link
Chapter 8: troubleshooting testing the radio link page 8-13 testing the radio link this section describes how to test the link when there is no radio communication, when it is unreliable, when the data throughput rate is too low, or when a unit is causing radio or tv interference. It may be necessar...
Page 585
Chapter 8: troubleshooting testing the radio link page 8-14 radio and television interference if a ptp 670 unit is interfering with radio or television reception (this can be determined by turning the equipment off and on), attempt the following corrective actions: • realign or relocate the antenna....
Page 586: Testing Ptp-Sync
Chapter 8: troubleshooting testing ptp-sync page 8-15 testing ptp-sync this section describes how to test the ptp-sync unit and its connections when the ptp-sync leds do not illuminate correctly, or when a synchronization fault is suspected. Checking the ptp-sync leds if a fault is suspected in the ...
Page 587: Status Led Is On Steady
Chapter 8: troubleshooting testing ptp-sync page 8-16 status led is on steady meaning: there is power but no satellite lock. This probably indicates that a 1 pps synchronization pulse is not detected by the ptp-sync unit. Action: depending on system configuration, take one of the following actions: ...
Page 588
Chapter 8: troubleshooting testing ptp-sync page 8-17 table 236 clustered ptp-sync units - gps leds fault-finding cluster timing source gps led on master gps led on slave(s) diagnosis gps receiver providing nmea data blink blink ok off any fault in gps unit or gps cable blink off fault in daisy chai...
Page 589: Testing A Tdm Link
Chapter 8: troubleshooting testing a tdm link page 8-18 testing a tdm link this section describes how to check the nidu leds and how to perform a tdm loopback test. Checking the nidu leds if a fault is suspected in the nidu, check the nidu led states and use table 237 to choose the correct test proc...
Page 590
Chapter 8: troubleshooting testing a tdm link page 8-19 performing a tdm loopback test the loopback test allows a tdm data stream to be looped back at the copper or wireless interface. A typical t1 or e1 installation test includes a copper loopback on the local unit followed by a wireless loopback o...
Page 591: Glossary
Page i glossary term definition aes advanced encryption standard ansi american national standards institution arp address resolution protocol atpc automatic transmit power control aux auxiliary bbdr broadband disaster relief bpsk binary phase shift keying bw bandwidth cfm connection fault management...
Page 592
Glossary page ii term definition ge gigabit ethernet gui graphical user interface http hypertext transfer protocol ib in-band ic industry canada icmp internet control message protocol icnirp international commission on non-ionizing radiation protection ieee institute of electrical and electronic eng...
Page 593
Glossary page iii term definition ns neighbor solicitation ntp network time protocol nud neighbor un-reachability detection odu outdoor unit ofdm orthogonal frequency division multiplex oob out-of-band pc ibm compatible personal computer pidu powered indoor unit poe power over ethernet psu power sup...
Page 594
Glossary page iv term definition tdd time division duplexing tdm time division multiplexing tdwr terminal doppler weather radar tgb tower ground bus bar tls transport layer security unii unlicensed national information infrastructure url universal resource location usm user-based security model utc ...