- DL manuals
- Campbell
- Modem
- RF500M
- Instruction Manual
Campbell RF500M Instruction Manual - Components
Section 2. Radiotelemetry Network
Components
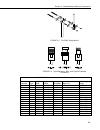
2.1 RF500M Modem
The RF500M is an interface between the computer and the radio when used at
a base station, and an interface between the radio and the datalogger at a field
station. In a repeater station, the RF500M is an interface between two other
communication stations. The RF500M is an RF modem. LoggerNet will refer
to the RF500M as an RFBase-TD or RFRemote-PB.
2.1.1 Physical Description
There are three ports for interfacing external devices on the front of the
RF500M. The port labeled Transceiver connects to the radio (RF310 series,
RF300 series, or DataRadio DL-3400), the port labeled CS I/O connects to
either the datalogger or to the PC as an RF Base, and the port labeled RS-232
connects to an RS-232 radio or the PC as an RF Base.
FIGURE 2-1. RF500M Modem
2-1
Summary of RF500M
Page 1
Rf500m radio modem revision: 8/10 c o p y r i g h t © 2 0 0 8 - 2 0 1 0 c a m p b e l l s c i e n t i f i c , i n c ..
Page 2: Warranty and Assistance
Warranty and assistance the rf500m radio modem is warranted by campbell scientific, inc. To be free from defects in materials and workmanship under normal use and service for twelve (12) months from date of shipment unless specified otherwise. Batteries have no warranty. Campbell scientific, inc.'s ...
Page 3: Rf500M Table of Contents
Rf500m table of contents pdf viewers note: these page numbers refer to the printed version of this document. Use the adobe acrobat® bookmarks tab for links to specific sections. 1. General radiotelemetry network ...............................1 1.1 introduction .........................................
Page 4
Rf500m table of contents ii 4. Operation of the radiotelemetry network ............. 4-1 4.1 monitoring and collecting data with loggernet .................................... 1 4.1.1 basic concepts ............................................................................... 1 4.1.2 using the log...
Page 5: Network
Section 1. General radiotelemetry network 1.1 introduction data retrieval from a remote site can be difficult. One method to accomplish data collection from isolated sites is through a radio telemetry (rf telemetry) network. Dataloggers can be accessed by rf telemetry, which requires no physical con...
Page 6: 1.3 Base Station
Section 1. General radiotelemetry network 1-2 1.3 base station purpose: a base station utilizes a computer to collect data from the field station(s). Normally, all communication to the field stations originate at the base station. Data retrieval, remote programming, and system analysis can all be do...
Page 7: Components
Section 2. Radiotelemetry network components 2.1 rf500m modem the rf500m is an interface between the computer and the radio when used at a base station, and an interface between the radio and the datalogger at a field station. In a repeater station, the rf500m is an interface between two other commu...
Page 8
Section 2. Radiotelemetry network components the light located between the transceiver port and the rs-232 port is used primarily to indicate when the radio is transmitting and receiving by blinking red and green. The light located between the rs-232 and cs i/o ports is used primarily to indicate wh...
Page 9
Section 2. Radiotelemetry network components the lights can also be used to verify the appropriate power up sequence of the rf500m. View the indicator lights while applying power with the power adapter or connecting the datalogger to the rf500m cs i/o port with an sc12 cable. The sequence of the lig...
Page 10
Section 2. Radiotelemetry network components depending on the radio being used, the appropriate internal jumper must be selected on the rf500m circuit board. There is a set of six jumpers in series located just under the campbell scientific, inc. Name and circuit board version number etched on the b...
Page 11: 2.3 Antennas and Cables
Section 2. Radiotelemetry network components figure 2-3. Rf500m radio jumper expanded view 2.2.3 digital radio description the rf500m is compatible with digital rs-232 radios such as the dataradio integra radio. The digital radios are connected to the rf500m modem with a serial cable between rs-232 ...
Page 12
Section 2. Radiotelemetry network components an omnidirectional antenna will transmit/ receive in a full 360 degree circle. Generally, an omnidirectional antenna will be a straight cylindrical rod which is to be mounted vertically at the top of a tripod. A unidirectional antenna is designed to trans...
Page 13
Section 2. Radiotelemetry network components figure 2-5. The pd46 clamp mount figure 2-6. Type-nm (male), bnc, and type-nf (female) connectors table 2-2. Common antennas and characteristics antenna type vhf or uhf cable gain(db) pipe o.D. Mounting type ba1010 omni vhf coax nm-l unity 3/4" - 2 1/8" u...
Page 14: Supplies
Section 2. Radiotelemetry network components 2-8 2.4 tripods, towers, enclosures, and power supplies there are several methods of mounting and housing sensors and other equipment for a station. 2.4.1 tripods and towers for mounting for the different mounting requirements, campbell scientific offers ...
Page 15: Section 3. Assembling The
Section 3. Assembling the radiotelemetry network this section provides a logical order for rf network assembly and deployment. Details of specific components in the system are described in section 2 “radiotelemetry network components.” section 2 is cross-referenced throughout this assembly section. ...
Page 16
Section 3. Assembling the radiotelemetry network to configure the rf500m, apply power to the modem, wait for the power-up sequence lights to cycle and then turn off, connect the pc to the rf500m rs- 232 port with a null modem cable, open device configuration utility, highlight the rf500m option in t...
Page 17
Section 3. Assembling the radiotelemetry network 4. Baud rate – set the baud rate for the rs-232 interface. 5. Sleep-mode enabled – determine if sleep mode functionality will be enabled for rf300 series radios. In all other cases, this setting will be ignored. Once the rf500m has been configured, it...
Page 18: 3.3 Loggernet Setup
Section 3. Assembling the radiotelemetry network following is the order in which a general rf field station should be installed. A repeater station is installed in the same order. 1. Tripod or tower 2. Enclosure and datalogger 3. Antenna - orient correctly; remember direction and polarization 4. Sol...
Page 19: Attempts
Section 3. Assembling the radiotelemetry network remote” then highlight the rf remote to test. Click “start test” and wait for the test results. After a successful rf link test, the next step is to attempt communication with the datalogger over the rf link. From the troubleshooter client choose the ...
Page 20
Section 3. Assembling the radiotelemetry network 3-6.
Page 21: Radiotelemetry Network
Section 4. Operation of the radiotelemetry network all field stations can be accessed and monitored from the central base site. Regular visits to the field sites are required to ensure that all sensors are in place, enclosures are dry, solar panel is clean, and that the tripod and antenna are secure...
Page 22
Section 4. Operation of the radiotelemetry network remotes by using the same method but highlight the rfbase-td and select rfremote-pb. The last device to add is a datalogger. Use the add button or right click on the rfremote-pb and add the appropriate datalogger. If a mistake is made, highlight the...
Page 23
Section 4. Operation of the radiotelemetry network figure 4-2. Loggernet setup screen - schedule tab 4.1.4 general communication – loggernet connect screen general communications include: collect data, send and retrieve programs, monitor measurements in real time, graph real time data, etc. The logg...
Page 24
Section 4. Operation of the radiotelemetry network figure 4-3. Loggernet connect screen 4.2 datalogger initiated communications the datalogger can send collected data to loggernet using the senddata instruction in the datalogger. This method of data collection is referred to as one way data. With sc...
Page 25
Section 4. Operation of the radiotelemetry network when programming a pakbus datalogger, the senddata instruction must be included in the datalogger to enable one way data. When the datalogger executes this instruction and a new record exists in the specified table, the datalogger sends the record o...
Page 26
Section 4. Operation of the radiotelemetry network 4-6 if the rf remote is storing more data in its buffer than can be sent in the defined time window of the polling event, the rf remote requests more time to send the remaining data. After all rf remotes have had a chance to respond during their def...
Page 27: Radiotelemetry
Appendix a. Fundamentals of radiotelemetry a.1 radio waves radiotelemetry is the process of transferring information (data) in the form of radio waves. The data is transferred on a carrier wave, which normally has a sinusoidal form. Therefore, the carrier wave can be described entirely by the freque...
Page 28: A.2 Antennas
Appendix a. Fundamentals of radiotelemetry filtering efficient, and to isolate the radio waves from the common low frequency man-made noise. The main forms of modulation are amplitude, frequency, and pulse modulation. Frequency modulation (fm) is used by campbell scientific. A.2 antennas an antenna ...
Page 29: A.4 Transceiver
Appendix a. Fundamentals of radiotelemetry sequences, sets data to be transferred into data blocks, creates signatures of data blocks, modulates the radio's carrier wave, and stores information on communication quality. The user at the computer is responsible for naming the desired communication pat...
Page 30
Appendix a. Fundamentals of radiotelemetry a-4.
Page 31
Appendix b. Power calculations there must be enough transmission power in any rf link to complete communication. The sources of power are the radio and the antennas. Conversely, power is lost both through the cables (coax loss) and over the distance of communication (path loss). The power of the sig...
Page 32
Appendix b. Power calculations b-2 power conversion conversion of watts to dbm can be done with the following formula. Dbm = 10 * log((watts)/0.001).
Page 33: Glossary
Glossary antenna - device for radiating and receiving radio signals. Attenuation - the reduction of an electrical signal without appreciable distortion. Base station - the destination for accumulated data; where data is received via radio from one or more field stations. Baud rate - a unit of data t...
Page 34
Glossary b radio frequency - the number of cycles per second with which the carrier wave travels, usually specified in megahertz. Radiotelemetry - process of transmitting data by radio communication. Radiotelemetry link - a temporary communication path within a network. Radiotelemetry network - a gr...
Page 36
Campbell scientific companies campbell scientific, inc. (csi) 815 west 1800 north logan, utah 84321 united states www.Campbellsci.Com • info@campbellsci.Com campbell scientific africa pty. Ltd. (csaf) po box 2450 somerset west 7129 south africa www.Csafrica.Co.Za • cleroux@csafrica.Co.Za campbell sc...