- DL manuals
- Canoga Perkins
- Modem
- 2240
- User Manual
Canoga Perkins 2240 User Manual
Summary of 2240
Page 1
Modems model 2240 fiber optic modem users manual.
Page 2: Caution!
2 canoga perkins caution! This product may contain a laser diode emitter operating at a wavelength of 1300 nm - 1600 nm. Use of optical instruments (for example: collimating optics) with this product may increase eye hazard. Use of controls or adjustments or performing procedures other than those sp...
Page 3: Notice!
2240 fiber optic modem 3 notice! Canoga perkins has prepared this manual for use by customers and canoga perkins person- nel as a guide for the proper installation, operation and/or maintenance of canoga perkins equipment. The drawings, specifications and information contained in this document are t...
Page 4
4 canoga perkins model 2240 fiber optic modem.
Page 5: Table of Contents
2240 fiber optic modem 5 table of contents 1. Description .................................................... 11 1.1 2240 modem ................................................................ 11 1.1.1 functions, leds and switches ............................................. 12 1.2 2201 rack chass...
Page 6
6 canoga perkins 3. Mode and rate selection ............................ 29 3.1 operating mode / data rate selection ..................... 29 3.2 external clock modes ................................................ 31 3.2.1 sampled external clock mode - mode 0 ............................... 31 3.2...
Page 7
2240 fiber optic modem 7 4.4.3 dsr jumper .......................................................................... 52 4.4.4 chassis_gnd jumper ....................................................... 52 4.4.5 sct switch ........................................................................... 54 ...
Page 8
8 canoga perkins 4.9.2 generic interface ................................................................... 81 4.9.3 external station ..................................................................... 82 4.9.4 internal ................................................................................
Page 9: List of Figures
2240 fiber optic modem 9 list of figures 1-1 model 2240 modem .......................................................................................... 11 1-2 model 2201 rack chassis ................................................................................. 13 1-3 model 2202 modem shelf .......
Page 10: List of Tables
10 canoga perkins list of tables 1-a control leads available ................................................................ 12 2-a link loss range ............................................................................ 22 3-a mode switch positions ................................................
Page 11: 1. Description
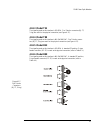
2240 fiber optic modem 11 1. Description 1.1 2240 modem the 2240 is a full-featured modem for full-duplex operation over fiber optic cable. The 2240 is available in standalone and rack-mount models. Figure 1-1. Model 2240 modem the 2240 modem operates at speeds from dc (0 bps) to 1.500 mbps in async...
Page 12
12 canoga perkins various configurations of the 2240 provide local and end-to-end modem controls including those listed in table 1-a. Table 1-a. Control leads available 1.1.1 functions, leds and switches the 2240 modem incorporates a loopback control switch, labeled "loop," located on the front pane...
Page 13: 1.2 2201 Rack Chassis
2240 fiber optic modem 13 1.2 2201 rack chassis the 2201 rack chassis (see figure 1-2) is designed to accommodate up to ten 2200 series modems, except for the mc1 and mc2 interfaces. For the model 2240 modem with mc1 and mc2 interfaces, only five modems may be installed in the rack chassis. The 2201...
Page 14: 1.5 Modem Operation
14 canoga perkins 1.4 2200r series redundant card this card allows a single electrical interface to be shared between two modems installed in a 2201 rack chassis. This model can be operated in three modes: remote control, manual control and automatic. In the remote control mode, two contact closure ...
Page 15
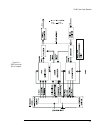
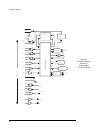
2240 fiber optic modem 15 figure 1-4. 2240 functional block diagram.
Page 16
16 canoga perkins the modem functions as a 10-channel multiplexer. The following discussion assumes an 8.19 mhz composite. Lower composite speeds result in proportionally lower submultiples. Clock and data are carried on a 4.096 mbps and 2.048 mbps channel, respectively. Each of the three control le...
Page 17
2240 fiber optic modem 17 the heart of the 2240 transmitter is a ten-channel multiplexer. This multiplexer takes the clock, data and control lead inputs from the interface, multiplexes them, then adds framing and supervisory information. This composite data is then converted into a manchester-coded ...
Page 18: 1.6 Loss Budget
18 canoga perkins 1.6 loss budget the maximum possible transmission distance is dependent on the overall power loss over the fiber optic link. This is called the link loss. The modem’s loss budget is determined by comparing the launch power at the modem with receiver sensitivity at the other end of ...
Page 19: 2. Installation and Setup
2240 fiber optic modem 19 2. Installation and setup 2.1 installation installation for the 2240 fiber optic modem includes unpacking the unit, and considerations for installing the standalone and rackmount models. 2.1.1 unpacking the unit each 2240 modem is shipped factory tested, and packed in prote...
Page 20
20 canoga perkins 2.1.3 rack-mount modem installation the 2201 rack chassis is designed for installation in a standard 19-inch wide equipment rack. Tabs are provided on each side of the unit, and are predrilled for standard spacing. Refer to the 2201 rack chassis user manual for more information on ...
Page 21
2240 fiber optic modem 21 2.1.5 2202 modem shelf installation the 2202 modem shelf is mounted in an equipment rack. Two 2200 series standalone modems may be installed in the 2202, side-by-side on the shelf. Refer to the 2202 modem shelf user manual for more information about installation. 2.1.6 cust...
Page 22: 2.2 Setup
22 canoga perkins 2.2 setup the setting up of the 2240 modem includes the two-section hi / lo optic power switch, internal control switches and the signal ground strap. The setup, as described in the following sections, provides the initial configurations for operation of the unit. 2.2.1 hi / lo opt...
Page 23
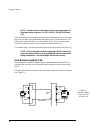
2240 fiber optic modem 23 2.2.2 internal control switches an 8-position dip switch located on the modem board provides access for internal control options (see figure 2-3). Switch positions 1 through 6 provide the follow- ing options: • carrier detect (cd) signal options (1 and 2) • clocking options...
Page 24
24 canoga perkins 2.2.2.1 carrier detect (cd) signal options there are two switches on the internal switch block which control the response of the cd signal on the standard data interfaces. These switches operate as a pair and only one switch should be set to on at any time. Factory setting = cd / d...
Page 25
2240 fiber optic modem 25 2.2.2.2 internal clock option switches there are two switches on the internal switch block which affect the operation of the clock circuits: • tbl / norm • clk / ext 2.2.2.2.1 tbl / norm switch the tbl / norm switch controls the data rate table as indicated in table 3-d. It...
Page 26
26 canoga perkins 2.2.3 signal ground strap the jumper selects whether chassis ground is connected directly to signal ground (chassis position) or signal ground is separated from chassis ground (float position). Note: float can be overridden by chassis ground jumpers on interface cards or by a jumpe...
Page 27
2240 fiber optic modem 27 2.2.5 extra clock jumper this two-pin jumper (w26, labeled xtclk), in conjunction with the enhanced interfaces (- 422, - 436 and - 430), allows the 2240 to accept both customer clocks for tail circuit applications. Refer to the rs-449, v.35 and rs-530 interface sections for...
Page 28
28 canoga perkins customer's t1 csu/dsu pll tx optics rt tt fifo control wr r fifo rd sd di do st x fifo control rd w sd rd do di optical rx rt fiber enhanced 2240 with extra clock note 1: x equals the extra clock input pins on the enhanced interfaces. "extra clock" jumper would have to be on at thi...
Page 29
2240 fiber optic modem 29 3. Mode and rate selection 3.1 operating mode / data rate selection the 2240 has eight clock operating modes: seven modes for synchronous data transmission and one asynchronous mode. Each synchronous mode is character- ized by one of three transmit clock types: external clo...
Page 30
30 canoga perkins table 3-a. Mode switch positions for many modes, the specific data rate must be selected. The data rate is selected by setting four switches on the front panel (positions 1-4). Refer to tables 3-b and 3-c for the data rate switch settings. Table 3-b. Locked external rates dip switc...
Page 31: 3.2 External Clock Modes
2240 fiber optic modem 31 3.2 external clock modes the external clock modes are used when it is necessary to have the dte provide the transmit clock or when the 2240 is used as a tail circuit connecting to a dce. In these modes, the dte or dce sends this clock to the modem on the terminal timing (tt...
Page 32
32 canoga perkins note: the pulse distortion is 37% of the bit period at a data rate of 1.544 mbps. When using this operating mode, it is important to con sider the effect of this large distortion on the connected equipment. Sampled external clock mode does not use the rate switches. 3.2.2 locked ex...
Page 33
2240 fiber optic modem 33 table 3-d. Group 4 internal clock rate divide ratio 3.3.1 standard internal clock rates (groups 1, 2 and 3) if the data rate appears in table 3-c, select the corresponding internal clock group with the mode switches (refer to table 3-a). Then set the rate switches to comple...
Page 34
34 canoga perkins table 3-e. Standard oscillator and divide factors.
Page 35
2240 fiber optic modem 35 3.4 slave clock mode - mode 5 the slave clock mode is used to provide a clock to the dte which is identical to the clock received from the other modem. In this mode, the clock signal received from the other end of the link is sent to the dte on both receive timing (rt) and ...
Page 36
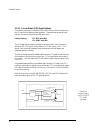
36 canoga perkins figure 3-2. Typical tail circuit implementation note: if the customer's dce does not support tt (or equivalent) lead, a buffered interface may be needed to realign the data or the extra clock function may be used (refer to section 4.9). Canoga perkins offers a wide selection of buf...
Page 37
2240 fiber optic modem 37 3.6 consideration of propagation delays whenever the modem is sending a transmit clock to the dte, it is important to understand the effect of the time required for that clock to propagate from the modem to the dte. Clock-to-data phasing is particularly important in any syn...
Page 38
38 canoga perkins 3.7 internal clock option switches there are two switches on the internal switch block which affect the operation of the clock circuits: tbl / norm and clk / ext (see figures 2-3 and 3-4 for the locations of these switches). 3.7.1 tbl / norm switch the tbl / norm switch controls th...
Page 39
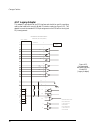
2240 fiber optic modem 39 in te rn al o pt io n sw itc h es fa c to ry se t o ff o n o ff o ff o n o ff o ff o n o ff o n c d /d c d c d /s yn c a lm /c h an a lm /l o c al m /r em al m /in v c lk /e xt tb l/ n o rm in te rn al o pt io n sw itc h es re la y o pt io n ju m pe r c o n ta c t po w er j...
Page 40
40 canoga perkins this page is intentionally left blank..
Page 41: 4. Data Interfaces
2240 fiber optic modem 41 4. Data interfaces 4.1 data interfaces overview a variety of interfaces are available for the 2240 modem (see following listing). Rs-423 / 232 ccitt v.35 rs-449 transparent t1 / e1 rs-449 / rs-423 (mc1) ccitt v.35 / rs-423 (mc2) rs-530 programmable rs-530 twinax 422 ttl / b...
Page 42
42 canoga perkins 4.2 rs-423 / 232d model 432 note: the maximum data rate for this interface, 153.6 kbps, is limited by the interface driver slew rate. This interface is electrically compatible with eia rs-423a. It will also operate with rs-232d systems when adhering to the more limiting rs-232d spe...
Page 43
2240 fiber optic modem 43 data set ready (dsr) and test mode (tm) are local status leads and follow the functions described in rs-232d. Dsr typically indicates that the modem is ready to handle transmit data. During loopbacks, the behavior of this signal is dependent on the position of the dsr jumpe...
Page 44
44 canoga perkins 4.2.1 rts_bias jumper the rts_bias jumper controls the state that rts floats to when there is no signal driving the rts pin. The off position forces this signal to the off (negated) state when the interface cable is disconnected. The on position forces it to the on (asserted) state...
Page 45: 4.3 Rs-449 / 422 Model 422
2240 fiber optic modem 45 4.2.4 dsr jumper the dsr jumper controls the behavior of the dsr signal. The eia position causes the dsr to turn off in certain test conditions when the transmit data is blocked and has no end-to-end or loopback path. This condition exists when the far-end 2240 modem has a ...
Page 46
46 canoga perkins table 4-b. Rs-449 pinouts * the extra clock is an enhancement added to -422 interfaces. Any -422 interface card outfitted with this capability can be identified via the lack of the w16 / w15 bal_ctrl jumper. The w16 / w15 jumper was never described in the manual, so do not try to f...
Page 47
2240 fiber optic modem 47 the sd, rd, st, rt and tt pins carry the primary data and clock signals (conforming to the rs-449 and rs-422 standards). In addition, an extra clock signal input (conforming to rs-422) is provided to make the 2240/-422 combina- tion more "dte-like" in tail circuit applicati...
Page 48
48 canoga perkins local loopback (ll) and remote loopback (rl) are loopback control leads and perform the same functions as the 2240 front panel loop switch loc and rem positions. Ll and rl are interface signal inputs which can be used to activate the loc or rem loop functions. These signals can con...
Page 49
2240 fiber optic modem 49 4.3.4 dm jumper the dm jumper controls the behavior of the dm signal. The eia position turns dm off when the far-end 2240 modem has a local loopback active. The test position causes dm to turn off whenever any loopback is active at one or both modems. Factory setting = eia ...
Page 50
50 canoga perkins 4.4 rs-530 interface model 430 note: the -430 interface supersedes the previous -r30 interface for 2240 applications. The -430 interface is a superset of the -r30. If exact compatibility with the older -r30 is desired, the dcd jumper can be moved from the factory strapped ctrl sett...
Page 51
2240 fiber optic modem 51 table 4-c. Rs-530 signals and pin assignments two end-to-end control leads are provided as part of this interface. An input to rts (request to send) is transmitted to the dcd (data carrier detect) output at the other end of the link (refer to sections 4.4.1, "rts-bias jumpe...
Page 52
52 canoga perkins 4.4.1 rts_bias jumper the rts_bias jumper controls the state that rts floats to when there is no signal driving the rts pin. The off position forces this signal to the off (negated) state when the interface cable is disconnected. The on position forces it to on (asserted). Factory ...
Page 53
2240 fiber optic modem 53 4.4.5 sct switch this slide switch selects whether the sct leads are outputs (out position) or inputs (in position). The out position makes the 2240 "pure-dce" and rd data is shifted out in sync with the 2240-supplied scr clock. The in position makes the sct leads inputs an...
Page 54
54 canoga perkins 4.4.8 cts (a) jumper this jumper selects the electrical characteristic of the cts (a) lead. In the norm position, the cts (a) is a normal rs-422 balanced driver, as per rs-530. The kg position is intended for interfacing to cryptography equipment. If you are not interested in kg ap...
Page 55
2240 fiber optic modem 55 4.5 ccitt v.35 (iso 2593-1993) model 436 this interface complies with ccitt standard v.35 and iso 2593-1993. Electrical characteristics comply with v.35 for clock and data signals and rs-232 levels for control signals. This interface uses the physical connector type and pin...
Page 56
56 canoga perkins table 4-e. Ccitt v.35 pinouts function pin ccitt direction (a/b) circuit number shield a 101 - signal ground b 102 - request to send (aka rts) c 105 to modem clear to send (aka cts) d 106 from modem data set ready (aka dsr) e 107 from modem data channel receive line f 109 from mode...
Page 57
2240 fiber optic modem 57 table 4-f. Pinout differences (-435 vs. -436) note: the previous v.35 interface, model -435, did not conform to the iso 2593 pinout and was the predecessor to the -436 interface. The signals listed in table 4-f have different pinouts on the -435 versus the -436. The -435 al...
Page 58
58 canoga perkins local loopback (ll) and remote loopback (rl) are loopback control leads and perform the same functions as the 2240 front panel loop switch, loc and rem positions. Ll and rl are interface signal inputs which can be used to activate the loc or rem loop functions. These signals can co...
Page 59
2240 fiber optic modem 59 4.5.4 dsr jumper the dsr jumper controls the behavior of the dsr signal. The ccitt turns dsr off when the far-end 2240 modem has a local loopback active. The test position causes dsr to turn off (negate) whenever any loopback is active at one or both modems. Factory setting...
Page 60
60 canoga perkins 4.6 multi-channel interfaces 4.6.1 rs-449 / rs-423 model mc1 this interface includes two physical connectors. The rs-449 / 422 uses a 37-pin, female d-type connector and the rs-423 uses a 25-pin, female d-type connector. A typical application for this interface is to transport data...
Page 61
2240 fiber optic modem 61 4.6.1.1 rs-449 / dc-37 interface this interface complies with eia standard rs-449. Electrical characteristics comply with rs-422 for clock and data signals and rs-423 for control signals. The interface uses the physical connector type and pinouts specified in rs-449 (refer ...
Page 62
62 canoga perkins the sd, rd, st, rt and tt pins carry the primary data and clock signals (conforming to the rs-449 and rs-422 standards). In addition, an extra clock signal input (conforming to rs-422) is provided to make the 2240 / -422 combi- nation more "dte-like" in tail circuit applications at...
Page 63
2240 fiber optic modem 63 4.6.1.1.1 rs_bias jumper the rs_bias jumper controls the state that rs floats to when there is no signal driv- ing the rs pin. The off position forces this signal to the off (negated) state when the interface cable is disconnected. The on position forces it to on (asserted)...
Page 64
64 canoga perkins 4.6.1.1.4 ch_gnd jumper the jumper selects whether chassis ground is connected directly to signal ground (short position) or through a 100 ohm resistor (100_ohm position). 4.6.1.1.5 unbal_ref jumper rs-449 specifies that unbalanced inputs to a dce are to be referenced to the sc (se...
Page 65
2240 fiber optic modem 65 there are six end-to-end control lead pairs. They are listed with the input signal listed first. Td to rd std to srd dtr to ri srts to sdcd dsrs to scts rts to dcd table 4-i. Rs-423 pinouts for model mc1 pin rs-232 direction number pin name (abbrev) (full name) 1 pg protect...
Page 66
66 canoga perkins 4.6.2 v.35 / rs-423 model mc2 this interface includes two physical connectors. The ccitt v.35 uses a 34-pin, female winchester connector and the rs-423 uses a 25-pin, female d-type connector. A typical application for this interface is to transport data and dialer information from ...
Page 67
2240 fiber optic modem 67 4.6.2.1 ccitt v.35 / mrc 34 interface this interface complies with ccitt standard v.35 and iso 2593-1993. Electri- cal characteristics comply with v.35 for clock and data signals and rs-232 levels for control signals. This interface uses the physical connector type and pino...
Page 68
68 canoga perkins table 4-k. Ccitt v.35 pinouts for mc2 function pin ccitt direction (a/b) circuit number shield a 101 - signal ground b 102 - request to send (aka rts) c 105 to modem clear to send (aka cts) d 106 from modem data set ready e 107 from modem data channel receive line f 109 from modem ...
Page 69
2240 fiber optic modem 69 the previous v.35 interface model mc2 / 435, did not conform to the iso 2593 pinout and was the predecessor to the mc2 / 436 interface. The mc2 / 436 went into production during mid-summer 1996. The signals listed in table 4-l have different pinouts on the mc2 / 435 versus ...
Page 70
70 canoga perkins 4.6.2.1.2 dcd jumper the dcd jumper determines the source of the dcd output. In the ctrl posi- tion, the dcd output functions as the output for the rts input at the far end. In the cd jumper position and with local rts on, cts will turn on either when the modem’s fiber optic receiv...
Page 71: 4.7 T1 / E1 Interfaces
2240 fiber optic modem 71 4.6.2.2 rs-423 / db-25 interface note: the maximum data rate for this interface is 9.6 kbps. This interface is electrically compatible with eia rs-423a. It will also operate with asynchronous rs-232d systems. This interface uses the physical connector type and pinouts speci...
Page 72
72 canoga perkins table 4-m. Configuration switch settings there are three different types of interface connectors, and each is identified by the number at the end of the interface code of the order number (refer to table 4- n). The connectors are female da-15 (4b1); four-position terminal block (4b...
Page 73
2240 fiber optic modem 73 this interface performs jitter attenuation of the transmit line input signal. It is also designed to propagate an all "1's" ami stream if the end-to-end line is interrupted at any point. When using any of the transparent bipolar interfaces, the 2240 modem rate and mode fron...
Page 74
74 canoga perkins t1 2240 (mode 7) 2240 (mode 5 slave) v.35 rx tx data clk tx data clk rx 4b1 436 figure 4-2. Transparent bipolar interface connectors figure 4-3. Example of link between bipolar and clocked interface.
Page 75
2240 fiber optic modem 75 4.8 ttl / bnc interface model -bn this model uses bnc (bayonet) connectors for the physical interface. The electrical signal characteristics are unbalanced ttl levels, with only the clock and data circuits supported. Four bnc connectors are supplied for connection to a dte ...
Page 76
76 canoga perkins 4.9 programmable buffered interface / model p53 signal full name direction txd transmit data to modem rxd receive data from modem scr serial clock receive from modem sct serial clock transmit from modem scte external clock transmit to modem table 4-o. Bnc supported signals the mode...
Page 77
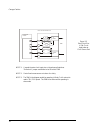
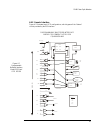
2240 fiber optic modem 77 a wire wrap header (j3) provides the means to interconnect these resources together with the standard modem transmit and receive circuits to perform the intended function. Figure 4-5 illustrates how the resources are tied into the j3 header. Specific applications are satisf...
Page 78
78 canoga perkins figure 4-5. Available strapping options for programmable buffered interface kg swing jumpers internal clock from modem rx data tx clock tx data modem alarm from fiber to fiber delay line inverter fifo data out data in shift out shift i n wi re wra p he ad er j 3 w19 w20 8 sg fg cts...
Page 79
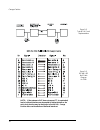
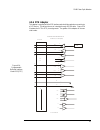
2240 fiber optic modem 79 table 4-p. Delay times for programmable buffered interface figure 4-6. Board layout for programmable buffered interface w8 w9 w7 w14 w13 w12 -6v +/-6v +6v 100 ohm chassis gnd w2 w1 short j3 rstbias off on kg norm w18 w17 w6 w5 w19 w20 test gnd dsr w16 w15 dl1 sw1 w10 w11 in...
Page 80
80 canoga perkins table 4-r. Strap configurations for rlsd (cd) output the w1 / w2 strap connects chassis ground to signal ground (w2 position), connects chassis ground through 100 ohms to signal ground (w1 position), or isolates chassis ground from signal ground (jumper out). The w5, w6 and w7 jump...
Page 81
2240 fiber optic modem 81 4.9.2 generic interface figure 4-7 illustrates basic dce configurations, which bypass all the "feature" circuits provided by the p53 interface. Figure 4-7. Programmable buffered interface, model p53, basic dce rs-530 kg swing jumpers internal clock from modem rx data tx clo...
Page 82
82 canoga perkins 4.9.3 external station the external station is used when an external station clock is providing timing (see figures 4-8 and 4-9). When connecting kg or kiv encryptors together on the black side, using an external timing device you should install the external station clock strapped ...
Page 83
2240 fiber optic modem 83 4.9.4 internal the internal function is used when network equipment is set for eternal timing (see figures 4-10 and 4-11). When connecting kg or kiv encryptors together on the black side, you should install the internal strapped header in the j3 position. In this applica- t...
Page 84
84 canoga perkins 4.9.5 external the external function is used when network equipment is set for network or inter- nal timing (see figures 4-12 and 4-13). When connecting kg or kiv encryptors on the red side to a dte device, you should install the external strapped header in the j3 position. In this...
Page 85
2240 fiber optic modem 85 4.9.6 dte adapter this adapter is supplied with the p53 interface and should be used when connecting to a dce device. This allows the use of a straight-through rs-530 cable. Figure 4-14 illustrates the dce to dte pin assignments. The gender of this adapter on the user side ...
Page 86
86 canoga perkins 4.9.7 legacy adapter this adapter is provided with the p53 interface and should be used if preexisting cabling was installed for use with model p2 interface cards (see figure 4-15). This adapter converts the standard rs-530 pin assignment on the p53 back to the original p2 pin assi...
Page 87: 114C
2240 fiber optic modem 87 4.10 high-speed rs-422 / mil-std 188- 114c interfaces there are three high-speed rs-422 interface models (tw, t22 and d22) and three high-speed mil-std 188-114c interface models (tw8, t88 and d88) available. All can operate up to 20 mbps (2240 limited to 2.048 mbps). All su...
Page 88
88 canoga perkins sct should be selected if the modem is set for internal or slave clock mode. Scte should be selected if the modem is set for external clock mode. Note: the sct output cannot be returned on the scte leads to eliminate propagation delay problems with this interface. Table 4-t. Model ...
Page 89
2240 fiber optic modem 89 table 4-u. Jumper strap options jumper description factory configuration id tw tw8 t22 t88 d22 d88 w3 / w4* w3 = vco disabled w4 w4 w4 w4 w4 w4 w4 = vco enabled w5 / w6** w6 = normal sct w6 w6 w6 w6 w6 w6 w5 = inverted sct w5 / w6 w7 = shield connected to w7 w7 w7 w7 w7 w7 ...
Page 90
90 canoga perkins 4.10.2 model tw8 the signaling used on this interface is mil-std 188-114c. Four twinax connec- tors (bj-77, 3-lug) are used for the physical connection (see figure 4-16). A switch is provided to select whether the fourth twinax (sct / scte) is to be used as an output (sct) or as an...
Page 91
2240 fiber optic modem 91 4.10.3 model t22 the signaling used on this interface is rs-422a. Five twinax connectors (bj-77, 3-lug) are used for the physical connection (see figure 4-17). 4.10.4 model t88 the signaling used on this interface is mil-std 188-114c. Five twinax connec- tors (bj-77, 3-lug)...
Page 92
92 canoga perkins table 4-v. Models d22 and d88 connector pin assignments *.
Page 93
2240 fiber optic modem 93 4.11 interface reconfiguration figure 4-18 illustrates how the interface circuit board fits into the larger main modem board opening. A header-type connector is provided to connect the two circuit boards together. The interface board may be removed by loosening the two reta...
Page 94
94 canoga perkins 4.12 standalone reconfiguration to access the circuit board on a standalone unit, the enclosure cover must first be removed by loosening the six screws on the sides of the unit. Next, unplug the power supply connector from the pc board, and remove the two screws holding the rear pa...
Page 95: 5. Troubleshooting
2240 fiber optic modem 95 5. Troubleshooting 5.1 diagnostic procedures the following procedures are intended for use in the event of a system failure, not during the initial installation of a 2240 optical link. For initial installation checkout, refer to section 1.7 of this manual. Also, refer to se...
Page 96
96 canoga perkins note: interface control of the loopback tests is only supported on the following modular interfaces: rs-423 / rs-232c, rs-449, rs-530 and v.35. When activated, the local loopback test will cause all data transmission from the near end (local) user device to be looped back toward th...
Page 97: 6. Diagnostic Procedures
2240 fiber optic modem 97 6. Diagnostic procedures 6.1 2240 / 2201 diagnostic procedures the following diagnostic procedures should be followed to test the 2240 system, troubleshoot a defective link or detect a defective fiber optic cable, connector, modem or power supply. Note: refer to the 2201 ra...
Page 98
98 canoga perkins 6.2 loopback test diagnostic procedure step symptom possible cause(s) action 1 no sync indication. Defective fiber optic continue to the modem(s), cable(s) to the next step. Or connectors. If the modems are con- figured for a tail circuit (one is externally locked and the other is ...
Page 99
2240 fiber optic modem 99 step symptom possible cause(s) action 3 cable loss exceeds defective repair or modem loss budget. F/o cable replace defective cable 4 cable loss exceeds defective fiber repolish or modem loss budget. Optic connectors replace defective connector 5 set the remote loopback swi...
Page 100
100 canoga perkins table 6-a. Link loss range 6.3 fiber optic diagnostic procedure if the loopback test is successful, and the modems still do not function, check the fiber optic parameters as outlined below. There also may be a data rate incompat- ibility. If this check out of the electrical and op...
Page 101: 7. Specifications
2240 fiber optic modem 101 7. Specifications 7.1 optical interface composite error rate: 1 in 10 10 or better fiber optic cable compatibility: 50 and 62.5 micron multimode or 8 to 10 micron single mode fiber transmitter: led (850nm) laser diode (1310nm or 1550nm) hi / lo optical power switch: reduce...
Page 102: 7.2 System Electrical
102 canoga perkins 7.2 system electrical interface connector: interface connector type rs-232c / 423 / 530 female db-25 programmable rs-530 (p53) female db-25 rs-422 (422) female dc-37 ccitt v.35 (v.36) female 34-pin winchester ttl / bnc four female bnc coaxial rs-422, mil-std 188-114c four or five ...
Page 103
2240 fiber optic modem 103 power requirement: standalone 115 vac +10% @ 0.22 amps 115/230 vac + 10% switchable @ 0.11 amps ,47 to 63 hz -48vdc; 0.5 amps (max) rack mount pc card 18 vac +10% @ 1.1 amps per board 50 to 64 hz 7.3 indicators and controls indicators (6): tx/rx data activity; local / remo...
Page 104
104 canoga perkins 7.5 2240 fiber optic modem configurations 2240-s-xxx-xx-xx-x s = standalone 2240-r-xxx-xx-xx-0 r = rackmount power options 0 - n/a 1 - 115v-ac wall plug 2 - 115/230v in-line 3 - 48vdc (call canoga perkins for additional dc options) crystal options 00 - no crystal the 2240 fiber op...
Page 105: Appendix A
2240 fiber optic modem 105 appendix a limited warranty a.1 products canoga perkins warrants that, at the time of sale, its products will be free from defects in material and workmanship, and if properly installed and used will substantially conform to canoga perkins' published specifications. Subjec...
Page 106
106 canoga perkins perkins' maximum liability shall not exceed and customer's rem- edy is limited to either (i) repair or replacement of the defective part of product, or at canoga perkins' option (ii) return of the product and refund of the purchase price, and such remedy shall be customer's entire...