Concurrent Technologies VP 110/01x VME Pentium III-M Single Manual - Table Of Tables
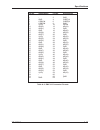
Table of Tables
Table 1-1
VME P2 Breakout Interfaces · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · 1-5
Table 5-1
VME Address Capture Read Register· · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · 5-4
Table 5-2
VME Address Modifier Codes · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · 5-5
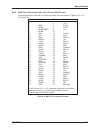
Table 5-2
VME Address Modifier Codes (Continued) · · · · · · · · · · · · · · 5-6
Table 8-1
I/O Address Map · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · 8-1
Table 9-1
Configurable PCI Bus Interrupts · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · 9-6
Table 9-2
PCI Device Numbers · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · 9-7
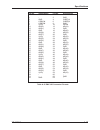
Table A-1
VME Interface Pin-outs · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · A-4
Table A-2
P2 Connector Pin-outs (64 PMC I/O Signals) · · · · · · · · · · · · · A-5
Table A-3
PMC I/O Connector (P0) Pin-outs · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · A-6
Table A-4
Keyboard and Mouse Header (LK1) Pin-outs · · · · · · · · · · · · · A-7
Table A-5
Serial Port Cable Connections · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · A-8
Table A-6
Serial Port Cable Connections · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · A-8
Table A-7
Ethernet RJ-45 Connector Pin-outs · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · A-9
Table A-8
On-Board Mass Storage Option Interface Pin-outs · · · · · · · · · · · A-10
Table A-9
PMC J11 Connector Pin-outs · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · A-11
Table A-10
PMC J12 Connector Pin-outs · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · A-12
Table A-11
PMC J13 Connector Pin-outs · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · A-13
Table A-12
PMC J14 Connector Pin-outs · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · A-14
Table A-13
PMC J21 Connector Pin-outs · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · A-15
Table A-14
PMC J22 Connector Pin-outs · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · A-16
Table A-15
PMC J23 Connector Pin-outs · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · A-17
Table A-16
PMC J24 Connector Pin-outs · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · A-18
Table A-17
30-way Debug Connector Pin-outs · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · A-19
Table A-18
Port 80 Connector Pin-outs · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · A-20
Table B-1
Breakout Modules List · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · B-1
Table B-2
Floppy 34-way IDC Header · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · B-5
Table B-3
EIDE 40-way IDC Header · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · B-5
Table B-4
USB Connector Pin-outs· · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · B-6
Table B-5
PMC I/O 1-32 IDC Header Pin-outs · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · B-6
Table B-6
PMC I/O 33-64 IDC Header Pin-outs · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · B-6
Table B-7
P5 68-way D-type Connector Pin-outs · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · B-7
xii
VP 110/01x
Summary of VP 110/01x VME Pentium III-M Single
Page 1
Technical reference manual for vp 110/01x vme pentium ® iii-m single board computer manual order code 550 0014 rev 02 august 2002 e-mail: info@gocct.Com http://www.Gocct.Com concurrent technologies inc 3840 packard road suite 130 ann arbor, mi 48108 usa tel: (734) 971 6309 fax: (734) 971 6350 concur...
Page 2
Notes information furnished by concurrent technologies is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, concurrent technologies assumes no responsibility for any errors contained in this document and makes no commitment to update or to keep current the information contained in this document. Concur...
Page 3
Glossary of terms bios · · · · · basic input output system bist · · · · · built in self test bsb· · · · · · back side bus cct· · · · · · concurrent technologies cpu · · · · · central processing unit crt· · · · · · cathode ray tube ddc · · · · · display data channel dib · · · · · · dual independent b...
Page 4
Notational conventions note notes provide general additional information. Warning warnings provide indication of board malfunction if they are not observed. Caution cautions provide indications of board or system damage if they are not observed. Iv vp 110/01x.
Page 5
Revision revision history date 01 initial release july 2002 02 added clarifications to several sections august 2002 vp 110/01x v.
Page 6: Table Of Contents
Table of contents 1. Introduction and overview · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · 1-1 1.1 general · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · 1-1 1.2 the vp 110/01x - main features· · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · 1-2 1.2.1 central processor · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · 1-2 1.2...
Page 7
4.3 rom disk · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · 4-3 4.4 ram disk · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · 4-4 5. Vme interface · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · 5-1 5.1 vme bus interface features · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · 5-1 5.2 vme byte swapping · · · ...
Page 8
10.2.1 slot numbering · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · 10-1 10.2.2 vsa console devices· · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · 10-1 10.2.3 starting the master test handler · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · 10-2 10.2.4 remote testing from the system controller · · · · · · · · · · · · · ...
Page 9
11.2.33 test 64: pc keyboard test· · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · 11-17 11.2.34 test 68: real time clock test· · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · 11-18 11.2.35 test 69: 82559er test · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · 11-19 11.2.35.1 sub-test 0 – default tests · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · ·...
Page 10
B.3.1 layout · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · b-2 b.3.2 pin-out tables · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · b-2 b.4 ad vp2/004-20 · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · b-3 b.4.1 layout · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · b-3 b.4.2 pin-out tables · ...
Page 11: Table Of Figures
Table of figures figure 1-1 overview · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · 1-1 figure 2-1 default jumper and switch settings · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · 2-3 figure 2-2 front panel indicators and controls · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · 2-4 figure 2-3 front panel reset and nmi switch · ...
Page 12: Table Of Tables
Table of tables table 1-1 vme p2 breakout interfaces · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · 1-5 table 5-1 vme address capture read register· · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · 5-4 table 5-2 vme address modifier codes · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · · 5-5 table 5-2 vme address modifier codes (continued) · ...
Page 13: Introduction And Overview
Introduction and overview 1.1 general this manual is a guide and reference handbook for engineers and system integrators who wish to use the concurrent technologies’ vp 110/01x ultra high-performance pentium iii processor-m (pentium iii-m) single board computer. The board has been designed for high-...
Page 14
1.2 the vp 110/01x - main features the vp 110/01x is a member of the concurrent technologies range of single-board computers for the vme bus architecture. It has been designed as a powerful single board computer based upon the pentium iii processor-m (pentium iii-m) incorporating the following featu...
Page 15
1.2.4 sdram the on-board sdram operates at 133mhz and features ecc data protection. The board is fitted with 512 mbytes of soldered-on sdram. A 144-pin sodimm socket is provided for memory expansion. This accepts a standard pc133 sdram module having a capacity up to 512 mbytes. Hence a maximum of 1 ...
Page 16
1.2.14 floppy disk a floppy disk interface is provided by the super i/o controller for up to two floppy drives and is connected via the p2 connector. 1.2.15 serial communication the vp 110/01x has one rs232 serial data communication channel, accessible via a front panel mounted rj45 connector. This ...
Page 17
1.3 additional board options two on-board mass storage options are available, namely; l a 2.5” eide hard disk drive of at least 10 gbyte capacity. L a compactflash carrier that supports the ibm ® microdrive ™ . Only one of these mass storage options may be fitted at a time. Refer to the vp 110/01x d...
Page 18
This page has been left intentionally blank 1-6 vp 110/01x introduction and overview.
Page 19: Hardware Installation
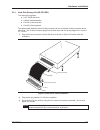
Hardware installation 2.1 general this chapter contains general information on unpacking and inspecting the vp 110/01x after shipment, and information on how to configure board options and install the board into a vme chassis. Caution it is strongly advised that, when handling the vp 110/01x and its...
Page 20
2.2 unpacking and inspection immediately after the board is delivered to the user’s premises the user should carry out a thorough inspection of the package for any damage caused by negligent handling in transit. Caution if the packaging is badly damaged or water-stained the user must insist on the c...
Page 21
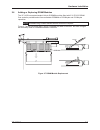
2.3 default jumper settings vp 110/01x 2-3 hardware installation lk3 sram backup power lk2 flash program lk5 cmos clear lk4 pmc v(i/o) 5v normal enabled battery section 2.8 section 2.7 section 7.4 section 7.3 vga console mode mode - bios user switch - ‘1’ watchdog - disabled 1 2 3 4 section 2.4.6 1 ...
Page 22
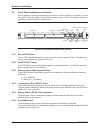
2.4 front panel indicators and controls when installing or removing the board for the first time, or when checking it’s operation, it can be very useful to note the behavior of the leds on the front panel. Figure 2-2 shows the location of the leds, and their purpose is outlined below. 2.4.1 run led ...
Page 23
Selecting the reset jumper position will cause the board to be reset when the front panel switch is operated. If the board is in the system controller slot, it will also assert rst# on the vme backplane and hence reset the other boards in the chassis. If the board is operating in any other slot, it ...
Page 24
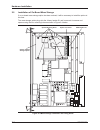
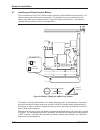
2.5 installation of on-board mass storage if an on-board mass storage option has been ordered, it will be necessary to install the option at this time. The mass storage option plugs into the 44-way header s1 and is secured via screws and spacers using the four mounting holes as shown in figure 2-4 b...
Page 25
2.5.1 hard disk storage kit (ad cp1/dr1) the option kit comprises: l a 2.5” eide disk drive. L a ribbon cable assembly. L four m3 x 10mm screws. L four m3 x 5mm spacers. The ribbon cable assembly has a 50-way connector at one end and a 44-way connector at the other end. The 50-way connector plugs in...
Page 26
2.5.2 compactflash storage kit (ad 200/001) the option kit comprises: l a compactflash carrier module. L four m3 panhead screws. 1) the m3 panhead screws may be loosely screwed into the end of the pillars, if so unscrew them. Note do not unscrew the countersunk screws attaching the pillars to the ci...
Page 27
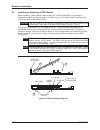
2.6 adding or replacing dram modules the vp 110/01x accepts standard 144-pin sodimm modules fitted with 3.3v pc133 dram. One socket is provided and will accommodate sodimms of 256 mbytes and 512 mbytes capacities. Note sodimms using 256mbit drams with 8k refresh are required. Figure 2-7 shows shows ...
Page 28
2.7 installing and replacing the battery the on-board real-time clock, cmos memory and non-volatile sram are powered by a 3.3v lithium battery when the board is powered off. It is advisable, though not essential, for the battery to be fitted prior to using the board. Figure 2-8 shows how to do this....
Page 29
Caution when replacing the battery, proper anti-static precautions must be observed. Warning dispose of battery properly. Do not burn. If the battery is disconnected with out any other power, the date and time settings will need to be initialized and sram data will be lost. If the bios setup screens...
Page 30
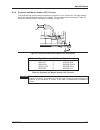
2.8 installing or removing a pmc module before installing a pmc module, check that the vp 110/01x board pmc v(i/o) voltage is configured to match the requirements of the pmc module. If two pmc modules are fitted, their v(i/o) requirements must be the same. Caution if the vp 110/01x is not correctly ...
Page 31
Vp 110/01x 2-13 hardware installation lk4 pmc v(i/o) or 3.3v key 5v v(i/o) key 3.3v v(i/o) key or 5v keys 5v = 3.3v = figure 2-10 pmc v(i/o) jumper.
Page 32
2.9 installing the board in a vme backplane before the board is installed in a vme chassis, check the following points: for backplanes that do not have p0 fitted:- l if you have a variant of the vp 110/01x fitted with a p0 connector, then check to see that no strengthening bars or other tall objects...
Page 33: Software Installation
Software installation in most cases, installing operating system software on the vp 110/01x board follows the same sequence as installing on a pc. However, there are some additional points to note. The sections below summarize the special actions required for a few common operating systems. All but ...
Page 34
3.2 bootloading from cd-rom operating systems which install on the target hardware will generally install from cd-rom, or may require both a cd-rom and floppy disk. Bootloading from floppy disk requires no special steps other than to connect the drive using an appropriate cable. To bootload from cd-...
Page 35
3.3 installing windows nt ® 4.0 to install windows nt from cd-rom, set up the board initially using the steps outlined in sections 3.1 and 3.2 above, ensuring that all the necessary drives are connected. Then follow the procedure below. 1) obtain the ethernet driver from the intel web site, starting...
Page 36
3.4 installing windows ® 2000 to install windows 2000 from cd-rom, set up the board initially using the steps outlined in sections 3.1 and 3.2 above, ensuring that all the necessary drives are connected. Then follow the procedure below. 1) obtain the ethernet driver from the intel web site, starting...
Page 37
3.5 installing redhat ® linux ® 7.2 to install redhat linux 7.2 from cd-rom, set up the board initially using the steps outlined in sections 3.1 and 3.2 above, ensuring that all the necessary drives are connected. Then follow the procedure below. 1) follow the standard redhat installation instructio...
Page 38
3.6 using vxworks 5.4 with tornado 2 applications using this operating system are not developed on the target hardware. Concurrent technologies can supply on request a separate board support package (bsp) for this board and many others. Read the “readme” file provided with this package for details o...
Page 39: Mass Storage Interfaces
Vp 110/01x 4-1 mass storage interfaces the vp 110/01x board has three interfaces which can be used to attach mass storage devices: l a floppy disk interface is accessible via the vme p2 connector. L a primary eide (ata100) interface is accessible via the vme p2 connector. L a secondary eide (ata100)...
Page 42
4.4 ram disk the bios can optionally provide a ram disk, which uses the battery-backed sram to store user code and data in a robust, but easily accessible format that is also writeable without the need to erase and program flash memory. Drive b: may be configured as a ram disk via the bios setup scr...
Page 43: Vme Interface
Vme interface the vp 110/01x board is fitted with a tundra universe ii pci-to-vme bus bridge device together with additional support logic. This hardware implements a flexible interface to and from the vme bus with the following key characteristics. 5.1 vme bus interface features the vp 110/01x can ...
Page 44
5.2 vme byte swapping the vp 110/01x provides hardware that performs fast byte swapping for aligned d16, d32 and d64 vme transfers. Byte swapping can be enabled separately for master and slave transfers under software control, using status & control register 0 (see section 9.1 for further details). ...
Page 45
5.3 vme bus error interrupt the vp 110/01x contains hardware to detect bus errors for vme bus cycles in which the universe is the bus master. The hardware is controlled by status and control register 1 (see section 8.3). The bus error interrupt is connected to the universe lint0 interrupt, so softwa...
Page 47
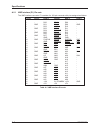
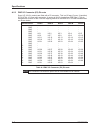
Am05 am04 am03 am02 am01 am00 hex access type 0 0 0 0 0 0 00 a64 64-bit mblt 0 0 0 0 0 1 01 a64 single transfer 0 0 0 0 1 0 02 rfu 0 0 0 0 1 1 03 a64 blt 0 0 0 1 0 0 04 a64 lock command (lck) 0 0 0 1 0 1 05 a32 lock command (lck) 0 0 0 1 1 0 06 rfu 0 0 0 1 1 1 07 rfu 0 0 1 0 0 0 08 a32 non-privilege...
Page 48
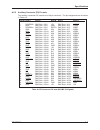
Am05 am04 am03 am02 am01 am00 hex access type 1 0 1 0 0 1 29 a16 non-privileged 1 0 1 0 0 0 2a rfu 1 0 1 0 0 1 2b rfu 1 0 1 1 1 0 2c a16 lock command (lck) 1 0 1 1 1 1 2d a16 supervisory 1 0 1 1 1 0 2e rfu 1 0 1 1 1 1 2f control/status register 1 1 0 0 0 0 30 rfu 1 1 0 0 0 1 31 rfu 1 1 0 0 1 0 32 a2...
Page 49: Other Interfaces
Other interfaces many additional standard interfaces are provided on the vp 110/01x board. These interfaces consist primarily of those found in a regular desktop or mobile pc, and are outlined below. 6.1 serial port a single rs232 serial interface is provided, and connects via the front panel the fr...
Page 50
6.2 keyboard and mouse ports a single 8-way x 0.1 inch, board mounted header provides connections for a pc keyboard and a ps/2 mouse. The pin-out of the front panel connector is detailed in section a.5.4. Power for the keyboard and mouse interfaces is protected by a 0.75a self-resetting current limi...
Page 51
6.3 ethernet controllers the vp 110/01x supports two 10/100mbits ethernet interfaces via two rj45 connectors on the front panel. The interfaces are provided by two intel 82559er devices. These interfaces are pre-configured in the factory with unique ieee addresses which are identified by two labels ...
Page 52
6.4 real-time clock a conventional pc real-time clock is included on this board. This is year 2000 compliant and can be powered by an additional lithium battery when main power to the board is removed. See section 2.7 for more details of how to fit or replace the battery. The clock device also provi...
Page 53
6.5 universal serial bus (usb) a single usb 1.0 interface is provided on this board, and is accessed via the vme p2 connector or a breakout module. This channel can operate at 1.5mbits/s or 12mbits/s. Other interfaces vp 110/01x 6-5.
Page 54
6.6 power on self test led/speaker the power on self test (post) led is connected to the pc speaker port. The led will light when the speaker port is driven. The vp 110/01x is not fitted with an audio/speaker output. 6-6 vp 110/01x other interfaces.
Page 55: Memory
Memory the board supports several combinations of the following memory: l sdram l bios/vsa flash eprom l strataflash eprom l battery backed sram the specific memory provision is determined by suffixes to the part number. Vp 110/01x 7-1 ffffffffh fff80000h fff00000h ffe00000h ffc00000h 00100000h 000a...
Page 56
7.1 sdram the vp 110/01x board supports a large amount of ecc sdram. 512 mbytes is soldered onto the board, and a single 144-pin sodimm site allows an additional 256 mbytes or 512 mbytes to be fitted either at the factory or in the field, giving a maximum size of 1 gbyte. Section 2.6 describes how t...
Page 57
7.2 flash eprom the vp 110/01x has two flash eprom parts: the first is installed in a socket and is programmed at the factory with pc bios firmware. This eprom will not normally be reprogrammed by the user, but concurrent technologies has programming software which allows bios updates to be carried ...
Page 58
7.3 application flash eprom the board is fitted with between 16 and 64 mbytes of intel strataflash eprom which is free for use by application software. The memory is connected to the csb5 x-bus interface and is accessible in protected mode via a paged 512 kbyte window (refer to figure 7-1). This win...
Page 59
7.4 battery backed sram the board can be fitted with 512k to 2 mbytes of static ram. This sram is non volatile as data can be automatically retained via the on-board battery when the board is not powered. The memory is connected to the csb5 x-bus interface and is accessible via a paged 512 kbyte win...
Page 60
This page has been left intentionally blank 7-6 vp 110/01x memory.
Page 61
Additional local i/o functions the vp 110/01x supports a variety of i/o functions whose addresses are summarized in table 8-1. I/o address range description 0000-000fh master dma controller (csb5 lpc host) 0020-0021h master interrupt controller (csb5) 002e-002fh configuration index & data registers ...
Page 62
There are 13 byte wide status and control registers. They are accessed at the following i/o addresses: l 210h for status & control register 0; l 211h for status & control register 2; l 212h for status & control register 1; l 213h for vme address capture data & control registers; (refer to note) l 21...
Page 66
8.4 watchdog timer the vp 110/01x board includes a hardware watchdog timer which can be used by the operating software to monitor the normal operation of the system. The timer is enabled by a board switch (see figure 8-1) and controlled by software. Once enabled it must be restarted at regular inter...
Page 68
8.4.2 watchdog configuration the watchdog circuitry contains features to safeguard against accidental use through faulty or unintended software actions. To enable the watchdog the following sequence of events needs to be performed. 1) read the watchdog register. Check the status of the watchdog enab...
Page 69
8.4.4 programming the watchdog the following functions show how to use the watchdog facility available through the status and control registers. It is worth noting that the software enable bit in the watchdog status and control register does not read back the value last written; it is the output fro...
Page 74
8.8 long duration timer/periodic interrupt timer the long duration timer (ldt) consists of a 32-bit free running counter with a 32-bit holding register and a status & control register. The counter bytes are laid out in little-endian format to permit multi-byte read/write operations. The status & con...
Page 77
8.8.6 programming the ldt/pit the following code fragments illustrate how the system software, by using the on-board hardware, can create accurate time delays and measure elapsed times, accurate to 1 µ s, irrespective of the cpu’s operating frequency. The ldt and pit control registers and operationa...
Page 78
It is possible to implement delays of 5ms, 2ms, 1ms, 500 µ s, 200 µ s and 100 µ s by utilizing other pit modes. The pit can generate an interrupt whenever the pit rolls over. The system programmer must initialize the interrupt vector, enable pic interrupts, etc. The following code fragment shows the...
Page 80
8.9 port 80 a header has been provided for monitoring data written to i/o port 80. The pc bios writes status bytes to port 80 that indicate a boot progress status and/or highlight any faults found. Data written to this port can be monitored using a logic state analyzer (lsa) or seven segment hexadec...
Page 81: Pc Bios
Pc bios the vp 110/01x board is fitted with pc bios firmware that performs many of the functions of a standard desktop pc. It also includes additional features specifically tailored for the vme bus environment. In addition to the core bios firmware, the board is fitted with bios extensions for remot...
Page 82
This switch. A vt100-compatible serial terminal or emulator program should be used. By default the serial line is programmed to operate at 9600 baud with 8 data bits, 1 stop bit and no parity (8n1). There is no flow control. For fast terminals, the baud rate can be increased via the serial console b...
Page 83
9.2 the pc bios startup sequence when the board starts up without operator intervention, it will run a basic power-on self-test (post) sequence, including ecc dram initialization and a dram test. The full dram test will be omitted on subsequent restarts if the bios configuration settings have not be...
Page 84
9.3 boot device selection the order in which the pc bios searches for a bootable medium is pre-configured but may be altered by the operator using the boot setup menu. When the order is changed using this menu it will be retained in non-volatile memory so that the order is maintained after a restart...
Page 85
9.4 pci bus resource management the local bus structure of the vp 110/01x is quite complex, and is based around two independent pci busses. In some cases the user may need to understand this structure and in particular how the pc bios firmware allocates addresses and interrupt signals to the availab...
Page 86
Table 9-1 lists the configurable interrupts for this board. The actual allocation of pci bus interrupts to available interrupt controller inputs will depend on both the default “plug-and-play” settings programmed by the pc bios, and the way in which the user has overridden them using the setup scree...
Page 87
9.4.2 pci device ids each pci bus, and each device on an individual pci bus, has a unique id. For the vp 110/01x, the bus and device ids are listed in table 9-2. The serverworks chipset includes two pci bus bridges to interface to the 64-bit and 32-bit on-board pci busses, and these bridges are iden...
Page 88
This page has been left intentionally blank 9-8 vp 110/01x pc bios.
Page 89
Vme system architecture test handler 10.1 introduction the vme system architecture (vsa) test handler firmware provides an environment where interactive testing may be performed on one or more concurrent technologies’ vme cpu boards. The level of testing provided by vsa is more comprehensive than th...
Page 90
10.2.3 starting the master test handler vsa mode is selected by setting the mode switch to the vsa position as indicated in figure 9-1. The board will enter vsa mode before the bios starts displaying sign-on text, so the first console output will be the vsa user attention prompt. When vsa starts, it...
Page 91
10.2.6 bist execution bist execution is started using the test command. While a test is executing, no further commands may be entered. It is possible to specify more than one bist for execution using the “;” separator, for example: t14;t15;t20,4 execute test 14, test 15 and test 20. Test 20 has a co...
Page 92
10.3 mth command reference this section details all of the commands available from the mth (master test handler) prompt. Commands are divided into general and utility sections. The list below shows the commands in uppercase letters only, but lowercase letters may also be used. Where numbers are ente...
Page 93
Sum [no short command] prints the pass and fail counts for all bists available on the default slot. Sum # [no short command] # - test number, in the range 0-255 prints the pass and fail count, for the bist indicated, on the default slot. Test # [short command t] # - test number, in the range 0-255 s...
Page 94
10.3.3 utility commands iro, irr, icr, icw these commands are reserved for factory testing. They report and modify the state of the vsa board communication data structures. Inb port_address read a byte from the specified i/o address inw port_address read a word from the specified i/o address ind por...
Page 95: Vsa Mode Diagnostics
Vsa mode diagnostics this chapter describes the board’s initialization into vsa mode and the tests that can be run from vsa mode. For details of the vsa command line interface, refer to chapter 10. Some of these tests are described to be run when the board is fitted with additional test hardware at ...
Page 96
11.2 bist descriptions the following is a list of the tests that are available in the firmware set installed on this board, together with an overview of the function of each test. A description of each possible error condition, with its code, is given for each test. 11.2.1 test 1: test initializatio...
Page 97
11.2.4 test 6: interconnect image check this bist reads and verifies the vendor id and the board name from the header record of the local interconnect template. The interconnect template is a data structure used by vsa to communicate between boards. Error codes: 0300h - image check failed 11.2.5 tes...
Page 98
11.2.8 test 12: local ram fixed pattern test this bist performs a short test on local ram. The range of memory to be tested depends upon the test handler from which the bist was invoked. When the test is executed from the power-up test handler, it is necessary to limit execution time; therefore the ...
Page 99
11.2.11 test 20: universe nmi test this bist checks the ability of the universe to generate a nmi to the processor using the software generated interrupt via lint1. Error codes: 0406h - no interrupt generated or spurious interrupt 11.2.12 test 22: ram data and address bus test this bist checks rams ...
Page 100
11.2.14 test 25: local ram dual address test this bist checks for dual addressing in the ram. The range of memory to be tested depends upon the test handler from which the bist was invoked. When the test is executed from the slave test handler, e.G. During soak testing, the test range is limited to ...
Page 101
11.2.16 test 28: scc interrupt test this bist checks that the serial channel on the board is capable of generating an interrupt. A null character is transmitted on the channel to generate a transmit interrupt from that channel. If the interrupt occurs, checks are made to ensure that there is a trans...
Page 102
11.2.20 test 34: universe pci config utility this pseudo test configures a universe pci slave image register for off-board vme accesses. The following parameters are required: slave to program (default = 3), lower address (default = 90000000h), upper address (default = 91000000h), translation offset...
Page 103
11.2.23 test 37: bus error detection test this bist checks the operation of the vme bus error detection facilities available on the vp 100/01x board. This bist is composed of a series of sub-tests. The sub-test number is selected by a bist parameter; when run without parameters, all sub-tests are pe...
Page 104
11.2.24 test 39: watchdog test this bist checks the watchdog facilities available on the vp 110/01x board. The bist is composed of a series of sub-tests. The sub-test number is selected by a bist parameter; when run without parameters, a default series of sub-tests is performed. The available sub-te...
Page 105
11.2.25 test 40: ldt and pit test this bist checks the operation of the ldt (long duration timer) and the pit (periodic interrupt timer) facilities available on the vp 110/01x board. This bist is composed of a series of sub-tests. The sub-test number is selected by a bist parameter; when run without...
Page 106
11.2.28 test 41: strataflash test this bist checks the programmability of each strataflash device on the board. Each sub-test first identifies the device and reports the part number, then an erase/program/verify test is performed for all sectors in the strataflash. The original contents of the devic...
Page 107
11.2.29 test 42: non-volatile ram test this bist checks the operation of the non-volatile sram on the vp 110/01x board. The bist is composed of a series of sub-tests. The sub-test number is selected by a bist parameter; when run without parameters, a default series of sub-tests is performed. The ava...
Page 108
11.2.30 test 56: ide controller test this bist checks the operation of the embedded ide controller that forms part of the csb5 south bridge. This test consists of a number of sub-tests, which can be selected via a command line parameter. If the bist is invoked without parameters, only those tests th...
Page 109
11.2.31 test 58: ide fixture test this bist checks the operation of the on-board ide controller by means of an external test fixture. This fixture is identified as “tf0169”. There are no sub-commands or parameters relevant to this test. This fixture tests the following features of the ide interface:...
Page 110
11.2.32 test 63: ps/2 mouse test this bist tests the ps/2 port and ps/2 mouse (if connected). The ps/2 port test includes opening the auxiliary port on keyboard controller, sending an echo to the auxiliary port and testing the auxiliary bus. The ps/2 mouse test resets the mouse, reads the device ide...
Page 111
11.2.33 test 64: pc keyboard test this bist performs checks on the keyboard controller, the test also determines whether a keyboard is present. First, the keyboard controller’s output buffer is flushed and a ‘keyboard present’ test is performed. The keyboard controller is then enabled and initialize...
Page 112
11.2.34 test 68: real time clock test this bist tests the pc compatible, real time clock. The bist provides a number of sub-tests, which are selected by a command parameter. If no parameter is supplied the current time and date is displayed, the interrupt signal is tested and the non-destructive nvr...
Page 113
11.2.35 test 69: 82559er test this bist tests the operation of both 82559er ethernet controllers on the baseboard. The bist is split into a series of sub-tests. By default, only the device checks and internal loopback tests are performed, however the other sub-tests can be selected from the mth comm...
Page 114
11.2.36 test 70: maxim 1617 thermal sensor test this bist checks the operation of the maxim 1617 thermal sensor. This test consists of a number of sub-tests, which can be selected via a command line parameter. If the bist is invoked without parameters, only basic diagnostics and cpu over-heat are ch...
Page 115
11.2.36.4 change update frequency this option allows the user to change the update frequency of the maxim 1617 thermal sensor. All possible options are listed below: value update frequency (hz) 0 0.0625 1 0.125 2 0.25 3 0.5 4 1 5 2 6 4 7 8 alarms will only trigger when an update occurs. Should there...
Page 116
11.2.36.5 full readout this option reads and displays the data currently available from the maxim 1617 thermal sensor. The display is in the following format. !Alert mask : 1 s/w standby : 0 conv. Rate : 0.0625hz chip busy : 0 cpu open : 0 cpu short : ? Cpu vcc : ? Temp. Amb. : xxx^c temp. Cpu : xxx...
Page 117
11.2.37 test 71: 82559er interface test this bist verifies the operation of the external ethernet interface of both 82559er controllers, when communicating with a second ethernet equipped board. The test will only run in conjunction with a concurrent technologies soak test master. The test exchanges...
Page 118
11.2.40 test 101: display memory utility this bist allows any area of the target board’s local memory to be examined and displayed by the test master. This utility requires command-line parameters to function correctly, so it should only be run in an interactive manner by a local or remote test mast...
Page 119
11.2.43 test 104: i/o write utility this bist allows modification of any i/o register on the target board. This utility requires command-line parameters to function correctly, so it should only be run in an interactive manner by a local or remote test master. The parameters are: 16-bit i/o address (...
Page 120
11.2.46 test 107: cache control utility this bist allows the status of dram and eprom caching on the target board to be interrogated or configured. If the utility is invoked without parameters, the default action is to display the state of dram and eprom caching. The available options are: 1) disabl...
Page 121
11.2.48 test 121: pci read utility this bist allows pci configuration registers to be examined on the target board. This utility requires command-line parameters to function correctly, so it should only be run in an interactive manner by a local or remote test master. The parameters are: device numb...
Page 122
This page has been left intentionally blank 11-28 vp 110/01x vsa mode diagnostics.
Page 123: Specifications
Specifications a.1 functional specification processor: • 800mhz or 1.2ghz pentium iii-m with 32 kbyte level 1 cache. Level 2 cache: • 512 kbytes on-die ram operating at core frequency. Memory: • 512 kbytes flash eprom for pc bios using socketed 28sf040 device. • 512 kbytes flash eprom for factory te...
Page 124
A.2 environmental specification a.2.1 temperature range operating . . . . . . . . 0 to +55ºc @ 400lfm air flow storage . . . . . . . . . -40 to +70ºc note if the on-board hard disk drive option is fitted, the operating temperature range will be restricted to +5 to +55ºc and the storage temperature r...
Page 125
A.5 connectors specifications vp 110/01x a-3 j9 j15 j16 j3 j6 s1 j21 j23 j11 j13 j14 j1 p2 p0 p1 j12 j24 j22 figure a-1 connector layout ethernet ch1 pmc site 2 pmc site 1 ethernet ch0 com1 external reset ground figure a-2 front panel connectors.
Page 126
A.5.1 vme interface (p1) pin-outs the vme interface connector p1 consists of a 160-pin connector with pins assigned as follows: pin no. Row z row a row b row c row d 1 - d00 bbsy d08 - 2 gnd d01 bclr d09 gnd 3 - d02 acfail d10 - 4 gnd d03 bg0in d11 - 5 - d04 bg0out d12 - 6 gnd d05 bg1in d13 - 7 - d0...
Page 127
A.5.2 auxiliary connector (p2) pin-outs the auxiliary connection p2 consists of a 160-pin connector. The pin assignments are as shown in table a-2. Pin no. Row z row a row b row c row d 1 drvden0 pmc slot 1 i/o 2 +5v pmc slot 1 i/o 1 iderst 2 gnd pmc slot 1 i/o 4 gnd pmc slot 1 i/o 3 ided8 3 drvden1...
Page 128
A.5.3 pmc i/o connector (p0) pin-outs some vp 110/01x variants are fitted with a p0 connector. This is a 95-way (5-row x 19-position) iec 61076-4-101 2mm pitch connector. It carries all 64 i/o signals from pmc site 2. The pin assignments conform to the p4v0-64 mapping defined in the ansi/vita 35-200...
Page 129
A.5.4 keyboard and mouse header (lk1) pin-outs the keyboard and mouse interface signals are routed to a 2 row x 4-way 0.1 inch pitch header, which is located behind the serial port connector. The pin assignments are shown in table a-4. Connector location and pin orientation is detailed in figure a-3...
Page 130
A.5.5 serial interface (j9) pin-outs the com1 rs232 serial interfaces use 8-way rj45 connectors with the following pinouts. Pin no. Signal name direction 1 rts - request to send output from board 2 dtr - data terminal ready output from board 3 gnd - 4 tx - tx data output from board 5 rx - rx data in...
Page 131
A.5.6 ethernet interface (j15 and j16) pin-outs the ethernet interfaces use 8-way rj45 connectors with the following pin-out: pin no. Signal name 1 transmit (+) 2 transmit (-) 3 receive (+) 4 not used 5 not used 6 receive (-) 7 not used 8 not used table a-7 ethernet rj-45 connector pin-outs note eth...
Page 132
A.5.7 on-board mass storage option connector (s1) pin-outs pin no. Signal name pin no. Signal name 1 ide_rst 2 gnd 3 sdd7 4 sdd8 5 sdd6 6 sdd9 7 sdd5 8 sdd10 9 sdd4 10 sdd11 11 sdd3 12 sdd12 13 sdd2 14 sdd13 15 sdd1 16 sdd14 17 sdd0 18 sdd15 19 gnd 20 +3.3 21 sdreq 22 gnd 23 sdiow 24 gnd 25 sdior 26...
Page 133
A.5.8 pmc site 1 connectors (j11, j12, j13 and j14) pin-outs signal assignments on the pmc connectors for pmc site 1 are shown in tables a-9, a-10, a-11 and a12. Pin no. Signal name pin no. Signal name 1 - 2 -12v 3 gnd 4 intb# 5 intc# 6 intd# 7 busmode#1 8 +5v 9 inta# 10 - 11 gnd 12 +3.3v†† 13 clk 1...
Page 134
Pin no. Signal name pin no. Signal name 1 +12v 2 - 3 - 4 - 5 - 6 gnd 7 gnd 8 - 9 - 10 - 11 +3.3v†† 12 +3.3v 13 rst# 14 gnd 15 +3.3v 16 gnd 17 - 18 gnd 19 ad(30) 20 ad(29) 21 gnd 22 ad(26) 23 ad(24) 24 +3.3v 25 idsel 26 ad(23) 27 +3.3v 28 ad(20) 29 ad(18) 30 gnd 31 ad(16) 32 c/be(2)# 33 gnd 34 idsel ...
Page 135
Pin no. Signal name pin no. Signal name 1 - 2 gnd 3 gnd 4 c/be(7)# 5 c/be(6)# 6 c/be(5)# 7 c/be(4)# 8 gnd 9 v(i/o) 10 par64 11 ad(63) 12 ad(62) 13 ad(61) 14 gnd 15 gnd 16 ad(60) 17 ad(59) 18 ad(58) 19 ad(57) 20 gnd 21 v(i/o) 22 ad(56) 23 ad(55) 24 ad(54) 25 ad(53) 26 gnd 27 gnd 28 ad(52) 29 ad(51) 3...
Page 136
Pin no. Signal name pin no. Signal name 1 i/o 1 2 i/o 2 3 i/o 3 4 i/o 4 5 i/o 5 6 i/o 6 7 i/o 7 8 i/o 8 9 i/o 9 10 i/o 10 11 i/o 11 12 i/o 12 13 i/o 13 14 i/o 14 15 i/o 15 16 i/o 16 17 i/o 17 18 i/o 18 19 i/o 19 20 i/o 20 21 i/o 21 22 i/o 22 23 i/o 23 24 i/o 24 25 i/o 25 26 i/o 26 27 i/o 27 28 i/o 2...
Page 137
A.5.9 pmc site 2 connectors (j21, j22, j23 and j24) pin-outs signal assignments on the pmc connectors for pmc site 2 are shown in tables a-13, a-14, a-15 and a-16. Pin no. Signal name pin no. Signal name 1 - 2 -12v 3 gnd 4 intc# 5 intd# 6 inta# 7 busmode#1 8 +5v 9 intb# 10 - 11 gnd 12 +3.3v†† 13 clk...
Page 138
Pin no. Signal name pin no. Signal name 1 +12v 2 - 3 - 4 - 5 - 6 gnd 7 gnd 8 - 9 - 10 - 11 +3.3v†† 12 +3.3v 13 rst# 14 gnd 15 +3.3v 16 gnd 17 - 18 gnd 19 ad(30) 20 ad(29) 21 gnd 22 ad(26) 23 ad(24) 24 +3.3v 25 idselc 26 ad(23) 27 +3.3v 28 ad(20) 29 ad(18) 30 gnd 31 ad(16) 32 c/be(2)# 33 gnd 34 idsel...
Page 139
Pin no. Signal name pin no. Signal name 1 - 2 gnd 3 gnd 4 c/be(7)# 5 c/be(6)# 6 c/be(5)# 7 c/be(4)# 8 gnd 9 v(i/o) 10 par64 11 ad(63) 12 ad(62) 13 ad(61) 14 gnd 15 gnd 16 ad(60) 17 ad(59) 18 ad(58) 19 ad(57) 20 gnd 21 v(i/o) 22 ad(56) 23 ad(55) 24 ad(54) 25 ad(53) 26 gnd 27 gnd 28 ad(52) 29 ad(51) 3...
Page 140
Pin no. Signal name pin no. Signal name 1 i/o 1 2 i/o 2 3 i/o 3 4 i/o 4 5 i/o 5 6 i/o 6 7 i/o 7 8 i/o 8 9 i/o 9 10 i/o 10 11 i/o 11 12 i/o 12 13 i/o 13 14 i/o 14 15 i/o 15 16 i/o 16 17 i/o 17 18 i/o 18 19 i/o 19 20 i/o 20 21 i/o 21 22 i/o 22 23 i/o 23 24 i/o 24 25 i/o 25 26 i/o 26 27 i/o 27 28 i/o 2...
Page 141
A.5.10 processor debug port (j1) pin-outs the processor debug port, which is supported by a number of emulator devices, is accessible via an intel specified 30-way receptacle connector with the following pin-out. Pin no. Signal name 1 gnd 2 cpu reset 3 gnd 4 debug reset 5 gnd 6 cpu tck 7 cpu tdi 8 c...
Page 142
A.5.11 port 80 (j3) pin-outs pin no. Signal name 1 gnd 2 not connected 3 port 80 select 4 not connected 5 d3 6 d7 7 d2 8 d6 9 d1 10 d5 11 d0 12 d4 13 +5 volts 14 gnd table a-18 port 80 connector pin-outs a-20 vp 110/01x specifications 1 3 5 2 4 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 figure a-6 port 80 connector.
Page 143: Breakout Modules
Breakout modules b.1 introduction this section details all the available breakout modules available for use with the vp 110/01x. Each breakout module provides a means of connecting interface cables to the rear i/o of the vp 110/01x. An overview of each breakout module is given with a reference to a ...
Page 144
B.3 ad vp2/004-10 the ad vp2/004-10 product is a 3-row p2 breakout board designed for use with the vp 110/01x-1x vme board. It provides two idc connectors for the pmc i/o signals on p2, and also makes all these signals available via a single 68-way high-density d-type socket. This breakout requires ...
Page 145
B.4 ad vp2/004-20 the ad vp2/004-20 product is a 5-row p2 breakout board designed for use with the vp 110/01x-3x vme board. It provides two idc connectors for the pmc i/o signals on p2, and also makes all these signals available via a single 68-way high density d-type socket. It also provides idc co...
Page 146
B.5 ad vp2/005-00 the ad vp2/005-00 product is a p0 and 5-row p2 breakout board designed for use with the vp 110/01x-2x vme board. It provides idc connectors for the pmc i/o signals on p0 and p2 and standard pc connectors for the eide, floppy disk and usb interfaces on p2. B.5.1 layout figure b-3 sh...
Page 147
B.6 header/connector configuration tables the headers and connectors are designed to enable use of standard p.C. Interface cables wherever possible. Detailed below are the pin-outs of the headers and connectors used on the breakout modules. Pin no. Signal name pin no. Signal name 1 gnd 2 drvden0 3 g...
Page 148
Pin no. Signal name 1 +5v 2 data (-) 3 data(+) 4 gnd table b-4 usb connector pin-outs pin no. Signal name pin no. Signal name 1 i/o 1 2 i/o 2 3 i/o 3 4 i/o 4 5 i/o 5 6 i/o 6 7 i/o 7 8 i/o 8 9 i/o 9 10 i/o 10 11 i/o 11 12 i/o 12 13 i/o 13 14 i/o 14 15 i/o 15 16 i/o 16 17 i/o 17 18 i/o 18 19 i/o 19 20...
Page 149
Pin no. Signal name pin no. Signal name 1 i/o 1 35 i/o 2 2 i/o 3 36 i/o 4 3 i/o 5 37 i/o 6 4 i/o 7 38 i/o 8 5 i/o 9 39 i/o 10 6 i/o 11 40 i/o 12 7 i/o 13 41 i/o 14 8 i/o 15 42 i/o 16 9 i/o 17 43 i/o 18 10 i/o 19 44 i/o 20 11 i/o 21 45 i/o 22 12 i/o 23 46 i/o 24 13 i/o 25 47 i/o 26 14 i/o 27 48 i/o 2...
Page 150
This page has been left intentionally blank b-8 vp 110/01x breakout modules.