- DL manuals
- D-Link
- Switch
- 1824i - Hub - EN
- User Manual
D-Link 1824i - Hub - EN User Manual
Summary of 1824i - Hub - EN
Page 1
10base-t stackable hubs intelligent series user’s guide rev. 02w (oct., 2004) 6snmpt....01 printed in taiwan recyclable.
Page 2: Fcc Warning
10base-t stackable hubs fcc warning this equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a class a digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the fcc rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a comme...
Page 3: Able of
10base-t stackable hubs t able of c ontents 0 a bout t his g uide .......................................................... Vi overview of the user's guide ................................................................... Vi 1 i ntroduction ...........................................................
Page 4
10base-t stackable hubs replacing the power supply...................................................................3-5 4 b uilding h ub s tacks ..................................................4-1 hub roles .............................................................................................
Page 5
10base-t stackable hubs hub stack configuration ......................................................................6-16 primary and backup master hubs..................................................................6-16 controlling hubs in the hub stack .............................................
Page 6: Bout
10base-t stackable hubs a bout t his g uide this user's guide discusses how to use intelligent 10base-t stackable managed hubs. This series includes: ♦ the 12/24-port stackable managed master hub, and ♦ the 12/24-port standard hub. In this user's guide, the intelligent series stackable hubs are freq...
Page 7
10base-t stackable hubs describes how to stack master and slave hubs into an integrated hub stack. ♦ chapter 5. Network connections describes how to connect workstations to the hub, and the hub to other hubs and network components on a local area network. ♦ chapter 6. Using the console interface des...
Page 9: Ntroduction
10base-t stackable hubs 1 1 i ntroduction the intelligent stackable managed hub series lets you build a 10mbps ethernet hub stack with full snmp manageability, convenient setup, and an unprecedented degree of flexibility. The series allows you to turn your network into the ideal connectivity solutio...
Page 10: Innovative Display
10base-t stackable hubs stackability and manageability a stack of intelligent hubs can be separated up to 100 meters apart and still keep their manageability. Up to 8 hubs can be daisy-chained together using utp or stp cable, with 7 client hubs sharing the master hub's snmp management agent, to prov...
Page 11: Highlights
10base-t stackable hubs highlights general highlights of the intelligent series ♦ complies with the ieee 802.3 10base-t, 10base2, 10base5, and 10base-fl standards. ♦ twelve or twenty-four independent rj-45 ports for category 3, 4, 5 twisted-pair wiring (either utp or stp) to nodes in a 10base-t- com...
Page 12
10base-t stackable hubs ♦ snmp-view network management program available for standard snmp-based management. ♦ fully configurable either in-band or out-of-band using any snmp- based network management system. ♦ flash eprom for software upgradeability (downloadable from tftp server. Initiate download...
Page 13
10base-t stackable hubs ♦ redundant backup management ◊ to maximize management uptime, two master hubs can be put in the same stack. If the first one goes down, the backup hub can automatically take over to provide uninterrupted traffic monitoring and network control. Introduction 1-5.
Page 15: Xternal
10base-t stackable hubs 2 2 e xternal f eatures and i ndicators this chapter introduces the controls and connectors on the front and rear panels of the hub, and explains the front panel display in detail. Figures 2-1, 2-2 and 2-3 show the layouts of the front panel, rear panel, and display of the st...
Page 16
10base-t stackable hubs aui connector daisy-chain port console port removable power supply expansion module port figure 2 -2 back panel layout the following components are found on the front and back panels of the hubs: ♦ ethernet ports used for connecting the hub to network devices using 10base-t s...
Page 17: Front Panel Indicators
10base-t stackable hubs ♦ aui port used when connecting the hub to a 10base5 "thick ethernet" backbone, or to other types of ethernet media. The recessed aui port accommodates most standard transceivers (also known as media access units or maus), allowing the transceiver to be safely and convenientl...
Page 18
10base-t stackable hubs the hub's front panel display features the following indicators: ♦ port status indicators each of the ports has an led status indicator for reporting its link and activity status, and showing whether or not it has been partitioned. The port status indicators always come on wh...
Page 19
10base-t stackable hubs ◊ manual partition the indicator of a port lights amber continually when the port is manually partitioned. Manually partitioning a port has the same effect as automatic partitioning, except that you must also manually re-enable it. You can choose to manually partition a port ...
Page 20
10base-t stackable hubs ♦ late col (manageable models only) the late col indicator lights when a collision is detected that happened after the 512th bit of a frame. Late collisions may be caused by overly long delays in the ethernet network, either due to cable that is too long or a repeater (hub) c...
Page 21
10base-t stackable hubs connected together into a single ethernet “collision domain” through the daisy chain connectors on the back. Segmenting a hub places it in its own collision domain, while allowing it to be managed with the rest of the stack. External features and indicators 2-7.
Page 22
10base-t stackable hubs ♦ daisy-chain in/out the down arrow indicates that another hub in the stack is connected to the daisy-chain in port of the hub, and the up arrow indicates that another hub is connected to the daisy-chain out port. ♦ col ratio (manageable models only) the col ratio bar graph d...
Page 23: Etting
10base-t stackable hubs 3 3 s etting u p the h ub this chapter explains how to choose a place for your hub stack and how to set up your hubs. Power and environmental requirements the hubs feature an auto-selecting 100-240 v, 50-60 hz power supply unit, which works in most countries around the world....
Page 24: Power Connection
10base-t stackable hubs ♦ tandem blade ♦ grounding type attachment plug rated at 15 a, 250v when using a 230v power source outside of the u.S., use a cord with the following characteristics: ♦ 18 awg ♦ grounding attachment plug rated at 15a, 250v ♦ the cord should have the appropriate safety approva...
Page 25: Free-Standing Installation
10base-t stackable hubs free-standing installation if you are installing the hub as a free-standing unit, apply the four self- adhesive rubber feet to the bottom of the hub chassis. Make sure the bottom surface of the chassis is clean and dry. Stand the chassis up-on-end and attach one rubber foot a...
Page 26
10base-t stackable hubs installing the transceiver tray at the rear of the hub, there is an aui connector designed for connecting the hub to various types of ethernet media such as thick ethernet coaxial cable (10base5), thin ethernet coax (10base2), or fiber optic cabling (10base- fl). The aui conn...
Page 27: Replacing The Power Supply
10base-t stackable hubs replacing the power supply the hub comes with a removable power supply for easy replacement. In the unlikely event that the power supply fails or is damaged, follow the steps below to replace the power supply. 1. Disconnect the power cord from the ac outlet. 2. Disconnect the...
Page 29: Uilding
10base-t stackable hubs 4 4 b uilding h ub s tacks you can combine up to eight hubs in the intelligent series into a single manageable hub stack. Building a hub stack has two advantages: ♦ all of the hubs can be managed as a single unit using a network management system or the console interface. Up ...
Page 30: Position Within The Stack
10base-t stackable hubs can take on different roles depending on the type of hub it is and its position in the hub stack. Position within the stack hubs in the hub stack are connected using the daisy-chain ports located at the rear of the hub. Each hub has an in port and an out port. Hubs are daisy-...
Page 31: Slave Hub Roles
10base-t stackable hubs another master hub upstream. If it receives commands from a master hub, it becomes a standby master, controlled by the active master. If it does not receive any commands, or if the active master hub fails, it will become the active master. Note that even if there are more tha...
Page 32: Hub Id
10base-t stackable hubs when there is a working active master in the stack, then each slave hub in the stack will be a managed hub controlled by the active master hub, and will have its own hub id. Hub id hub id numbers, displayed on the front of the hub, are determined automatically by the master h...
Page 33: Segmenting Hubs
10base-t stackable hubs figure 4 -2 daisy-chaining hubs segmenting hubs the emergence of ethernet switching hub technology has made it more common to segment local area networks into smaller pieces to reduce congestion on each segment. This makes it easier to balance network loads, since a smaller n...
Page 34
10base-t stackable hubs figure 4 -3 all hubs connected to ethernet backbone figure 4 -3 shows an unsegmented stack of hubs. All hubs in the stack are in the same collision domain because they are connected together using the daisy-chain ports and they have not been segmented. Figure 4 -4 shows a sta...
Page 35
10base-t stackable hubs figure 4 -4 three separate collision domains when a hub is segmented from the rest of the stack, the segmented indicator on the front panel display will light. For information about segmenting hubs using the console interface, see chapter 6 in this user's guide. For informati...
Page 37: Etwork
10base-t stackable hubs 5 5 n etwork c onnections once you have set up your hubs and connected them into a stack, you are ready to connect network stations, and to connect your hub to the rest of your ethernet network. This chapter tells how to connect workstations to the hub, and the hub to the oth...
Page 38
10base-t stackable hubs plug the rj-45 connector at one end into the network station, and the other end into a free 10base-t port on the front of the hub. When both the hub and the device at the other end of the connection are turned on, and the cable is connected at both ends, then the link indicat...
Page 39: Cascading Hub Stacks
10base-t stackable hubs cascading hub stacks if you need to expand your network beyond an eight-port stack, or you need to connect your hub to other parts of your network, you can cascade it using several different network media, including 10base-t twisted-pair cabling, 10base2 thin coaxial cabling,...
Page 40
10base-t stackable hubs this means you can cascade to another hub using an ordinary straight- through twisted-pair cable. Figure 5 -2 uplink switch setting when using this method, set the port 1 uplink switch to mdi, connect one end of the straight-through cable port 1 of the hub, and connect the ot...
Page 41: Using Thin Coaxial Cabling
10base-t stackable hubs using thin coaxial cabling with the addition of a 10base2 transceiver connected to the aui port at the rear of the hub (as described in chapter 3), you can cascade the hub to other hubs or stations using thin coaxial cabling. This method of cascading hubs gives additional fle...
Page 42: Multilevel Cascading
10base-t stackable hubs when connecting a transceiver to the hub, the transceiver's sqe (heartbeat) function should be disabled. Multilevel cascading hubs can be cascaded in multiple levels, provided no path between stations on the network goes through more than four repeaters. For example, a backbo...
Page 43: Sing The
10base-t stackable hubs 6 6 u sing the c onsole i nterface your intelligent stackable ethernet hub supports a console management interface that allows you to set up and control your hub, either with an ordinary terminal (or terminal emulator), or over the network using the tcp/ip telnet protocol. Yo...
Page 44: Console Usage Conventions
10base-t stackable hubs ♦ 8 data bits ♦ no parity ♦ one stop bit you can also access the same functions over a telnet interface. Once you have set an ip address for your hub, you can use a telnet program (in a vt- 100 compatible terminal mode) to access and control the hub. All of the screens are fo...
Page 45: Logging In
10base-t stackable hubs logging in to the hub console the intelligent series master hubs support user-based security that can allow you to prevent unauthorized users from accessing the hub or changing its settings. This means that before you can access the functions of the hub, you will need to firs...
Page 46
10base-t stackable hubs 3. With the cursor on the ok selection, press enter. The main menu screen will be displayed. Note: when the hub is shipped from the factory, the default user name is snmp-t and the default password is also snmp-t. You will need to use this user name and password when you firs...
Page 47: Changing Your Password
10base-t stackable hubs changing your password to change your user password: 1. Choose user account change from the main menu. 2. Choose change password . Figure 6 -3 change password 1. Type in your user name and press enter. 2. Type in your old password and press enter. 3. Type in the new password ...
Page 48: Setting Up The Master Hub
10base-t stackable hubs this method can also be used by a super user to change another user’s password. Setting up the master hub this section describes the settings you will need to change to allow you to be able to manage the hub from an snmp-based network management system such as snmp-view, or t...
Page 49
10base-t stackable hubs ♦ default gateway: ip address that determines where frames with a destination outside the current subnet should be sent. This is usually the address of a router or a host acting as an ip gateway. If your network is not part of an internetwork, or you do not want the hub to be...
Page 50: Settings
10base-t stackable hubs out-of-band management and console settings you can use the out-of-band/console setting menu to choose whether to use the hub’s rs-232c serial port for console management or for out-of-band tcp/ip communications using slip, and to set the bit rate used for slip communications...
Page 51: Software Updates
10base-t stackable hubs figure 6 -5 out-of-band/console setting menu software updates the hub is capable of obtaining its boot-time configuration information, as well as updated versions of its internal firmware, using tftp (the trivial file transfer protocol) and bootp (the bootstrap protocol). You...
Page 52
10base-t stackable hubs ♦ boot server ip address the ip address of the tftp server where the configuration file is located. This entry is used only if the s/w update control is enabled and your boot protocol is tftp only ; if you are using bootp-tftp mode, or if send bootp request on power up is ena...
Page 53: Snmp Information
10base-t stackable hubs snmp information the system configuration menu screen shows various pieces of information about your hub, and allows you to set the system name, system location, and system contact. These settings can be retrieved from the hub using snmp requests, allowing these settings to b...
Page 54: Snmp Traps
10base-t stackable hubs the system configuration menu also contains the console/telnet display timeout parameter, which determines how long the console may sit idle before the user is “logged out.” snmp traps the hub sends out snmp traps to network management stations whenever certain exceptional ev...
Page 55
10base-t stackable hubs ♦ status: determines whether this trap entry is valid or invalid. You can delete an entry by changing its status to invalid. Snmp security (community names) snmp (version 1) implements a rudimentary form of security by requiring that each request include a community name. A c...
Page 56: Adding and Deleting Users
10base-t stackable hubs adding and deleting users access to the console, whether using the console port or via telnet, is controlled using a user name and password. Up to three of these user names can be defined. One user, named snmp, is defined by default; this user name can be removed if desired. ...
Page 57
10base-t stackable hubs figure 6 -11 create new user 1. Choose save and press enter to let the user addition take effect. 2. Choose exit to leave the create new user menu. To delete a user, 1. Choose user account change from the main menu. 2. Choose delete users from the user account change menu. 3....
Page 58: Hub Stack Configuration
10base-t stackable hubs figure 6 -12 delete user 1. Choose save and press enter to let the user addition take effect. 2. Choose exit to leave the delete users menu. Hub stack configuration several important hub parameters useful in the day-to-day management of the hub can be viewed and controlled us...
Page 59
10base-t stackable hubs figure 6 -13 primary/backup master menu controlling hubs in the hub stack the group configuration menu screen, found within the network monitoring menu, displays information about each of the hubs in the stack, and allows you to make the hub id indicator flash. The items disp...
Page 60
10base-t stackable hubs ♦ group port capacity: shows the total number of controllable ports (includes the utp ports, aui ports, an internal management port, etc.) ♦ group hardware revision: shows the design version of the hub hardware. ♦ group status: shows whether the hub is up or down. ♦ group las...
Page 61: Controlling Individual Ports
10base-t stackable hubs you can use the prev group and next group commands to switch to another hub, or you can enter the hub’s group id number directly into the group id field. Controlling individual ports the port state menu, accessible from the network monitoring menu, allows you to view the stat...
Page 62: Segmenting Hubs
10base-t stackable hubs ♦ auto partition: displays on if the port has been automatically partitioned off from the rest of the network due to excessive errors, and off if the port is operating normally. ♦ admin state: this toggle determines whether the port should be enabled or disabled (manually par...
Page 63: Monitoring The Hub Stack
10base-t stackable hubs to segment an individual hub from the rest of the stack: 1. Enter the port state menu screen, accessible from the network monitoring menu. 2. Select the group id of the hub you wish to segment. 3. Select port 25 for the 24-port hub models, or port 13 for the 12-port hub model...
Page 64
10base-t stackable hubs choose which to view through the statistics menu, accessible from the network monitoring menu. Figure 6 -16 network monitoring menu the statistics shown are the same for each of these selections. The statistics displayed are: ♦ too long frame: counts frames longer than the 15...
Page 65
10base-t stackable hubs are too long, and you have either exceeded the repeater count or cable length specified in the ethernet standard. ♦ runt frame: counts frames shorter than the 64-byte (octet) minimum defined by the ethernet standard. These are usually caused by collisions. ♦ collision: counts...
Page 66
10base-t stackable hubs ♦ broadcast frame: counts valid frames that are broadcast to all stations on the network. ♦ 64 octs, 65-127 octs, 128-255 octs, 256-511 octs, 512-1023 octs, 1024-1518 octs: counts frames of various length ranges, both valid and invalid. ♦ readable oct: counts the total number...
Page 67
10base-t stackable hubs displaying node tracking information the node tracking information screen, accessible from the network monitoring menu, displays the source and destination addresses of packets recently received on a given port. Ethernet (mac) addresses are displayed for all packets, and ip a...
Page 68: Resetting The Hub
10base-t stackable hubs resetting the hub you can use the console interface to reset the hub stack, either doing a system reset (which restarts the hub and is identical to powering the hub off and back on again) or a factory reset (which sets all of the hub’s parameters to what they were when the hu...
Page 69: Factory Reset
10base-t stackable hubs factory reset before performing a factory reset, be absolutely certain that this is what you want to do. Once the reset is done, all of the hub’s settings stored in nvram (including tcp/ip parameters, snmp parameters, the enabled/disabled settings of ports, security settings,...
Page 71: Pecifications
10base-t stackable hubs a a s pecifications interface snmpt12 snmpt12i snmpt24 snmpt24i ieee 802.3 10base-t twisted-pair ports 12 12 24 24 ieee 802.3 10base5 aui port 1 1 1 1 rs-232 port no 1 no 1 daisy chain port 2 2 2 2 display indicators snmpt12 snmpt12i snmpt24 snmpt24i for each tp port: link y ...
Page 72
10base-t stackable hubs 240vac, 20w max, 50/60 hz 240vac, 50w max, 50/60 hz 240vac, 20w max, 50/60 hz 240vac, 50w max, 50/60 hz weight 2.4kg 2.7kg 2.5kg 2.8kg dimensions 441mm × 44.4mm × 217mm operating temperature 0 to 50 °c emi fcc class a, ce, vcci level 1 network management snmpt12 snmpt12i snmp...
Page 73: Ower
10base-t stackable hubs b b p ower -o n s elf t est when the master hub is powered on, it does a power-on self test (post) to verify that all of its components are working properly. As it performs its tests, the test progress is displayed on the terminal console, provided the hub is in console mode....
Page 74
10base-t stackable hubs will halt, the hub id “a” indicator will flash, and the last frame lit in the series will show what test failed. The parts of the power-on self test, and the indicator associated with each part, are as follows: 1. Prom test (port 1 frame) tests the integrity of the hub’s inte...
Page 75
10base-t stackable hubs when the power-on self-test is completed, the hub begins its boot sequence. If you are using out-of-band software downloading, the hub waits for 5 seconds to give you an opportunity to stop the boot process by pressing control-c (and blinks the port 3 and port 4 frames), befo...
Page 76
10base-t stackable hubs duplicate ip address detected ◊ f invalid ip address or subnet mask 1. Tftp download (port 3 frame/port 9 frame) the hub uses the tftp protocol to load its boot configuration file, and optionally the run-time image. This step is omitted if the hub is configured to not use tft...
Page 77
10base-t stackable hubs ordinary memory in preparation for use. This is the last step in the boot process. Error codes in this step include: ◊ 1 local flash download error (flash memory checksum error) ◊ 2 local flash download error (run time image error) power-on self test b-5.
Page 79: Oot
10base-t stackable hubs c c b oot c onfiguration f ile the master hubs in the series support a powerful configuration file which allows many of the hub stack’s configuration parameters to be stored on a centralized server. When the master hub starts up, it can be configured to read its configuration...
Page 80
10base-t stackable hubs contact information for the person responsible for administering the hub. The string can be up to 64 characters long. ♦ syslocation string takes string as the system location, corresponding to the snmp mib ii variable syslocation. This field is used to indicate the physical l...
Page 81
10base-t stackable hubs enables or disables authentication failure traps for invalid snmp community names. The argument may be enable or disable . ♦ clear-snmp-comm-table clears the hub’s snmp community name table. ♦ snmp-community community permissions adds community to the hub’s list of snmp commu...
Page 83: Ables and
10base-t stackable hubs cables and connectors d-1 d d c ables and c onnectors ports 2 through 24 are mdi-x 10base-t ethernet ports. Port 1 is a 10base-t ethernet port, with a sliding switch that enables a connection to a network station (in the mdi-x setting) or to a repeater, bridge, or hub (in the...
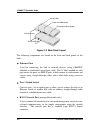
Page 84: Crossover Cable
10base-t stackable hubs d-2 cables and connectors 2 rd- (receive) td- (transmit) 3 td+ (transmit) rd+ (receive) 4 not used 5 not used 6 td- (transmit) rd- (receive) 7 not used 8 not used td+ rd+ 1 1 3 3 6 6 rd+ td+ td- rd- rd- td- 2 2 workstation (mdi) hub (mdi-x) figure d-2 straight-through cable c...
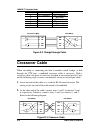
Page 85: Daisy-Chain Cable
10base-t stackable hubs cables and connectors d-3 daisy-chain cable the hubs use ordinary category 5 twisted-pair cable with rj-45 connectors on each end for stacking. All four pairs of the eight-wire cable are used. A 30cm daisy-chain cable is included with the hub; this information is included in ...
Page 86
10base-t stackable hubs d-4 cables and connectors terminal/pc serial port (dte, db-9) console port (dce, db-9) - (9) rxd (2) txd (3) dtr (4) sg (5) dsr (6) rts (7) cts (8) dcd (1) - (9) rxd (2) txd (3) dtr (4) sg (5) dsr (6) rts (7) cts (8) dcd (1) figure d-4 local connection to 9-pin serial port te...
Page 87
10base-t stackable hubs cables and connectors d-5 modem (dce, db-25) console port (dce, db-9) - (9) rxd (2) txd (3) dtr (4) sg (5) dsr (6) rts (7) cts (8) dcd (1) rxd (3) txd (2) dtr (20) sg (7) dsr (6) rts (4) cts (5) dcd (8) figure d-7 remote (modem) connection to 25-pin serial port.