D-Link AirPremier DWL-2210AP Manual
Summary of AirPremier DWL-2210AP
Page 1
Manual building networks for people d-link airpremier™ dwl-2210ap 802.11g wireless adaptive access point.
Page 2: Contents
22 contents package contents ................................................................................ 3 leds and connections ......................................................................... 4 overview .....................................................................................
Page 3: Contents of Package:
2 3 2 contents of package: d-link airpremier dwl-2210ap 802.11g wireless adaptive access point power over ethernet base unit power adapter-dc 48v, 0.4a power cord manual and warranty on cd quick installation guide ethernet cable internet explorer version 6.0 or netscape navigator version 6.0 and abo...
Page 4: Leds
44 leds connections pressing the reset button restores the dwl-2210ap to its original factory default settings. The lan port is auto-mdi/mdix. You can insert either a straight-through or a crossover ethernet cable in this port in order to connect the dwl-2210ap to the local network. Led stands for l...
Page 5
4 5 4 overview of the d-link dwl-2210ap the d-link dwl-2210ap provides continuous, high-speed access between your wireless and ethernet devices. It is an advanced, standards-based solution for wireless networking in small and medium-sized businesses. The d-link dwl-2210ap enables zero-administration...
Page 6: Features and Benefits
66 features and benefits “maximum wireless signal rate based on ieee standard 802.11a and 80211g specifications. Actual data throughput will vary. Network conditions and environmental factors, including volume of network traffic, building materials and construction, and network overhead lower actual da...
Page 7: Security Features
6 7 6 security features inhibit ssid broadcast ignore ssid broadcast weak iv avoidance wireless equivalent privacy ( wep ) wi-fi protected access ( wpa ) advanced encryption standard ( aes ) user based access control with local authentication server local user database and user life-cycle management...
Page 8: Networking
88 self-managed access points with automatic configuration synchronization the access points in a cluster periodically check that the cluster configuration is consistent, and check for the presence and availability of the other members of the cluster. The administrator can monitor this information thr...
Page 9: D-Link Dwl-2210Ap
8 9 8 before you plug in and boot a new access point , review the following sections for a quick check of required hardware components, software, client configurations, and compatibility issues. Make sure you have everything you need ready to go for a successful launch and test of your new (or extend...
Page 10: Default Settings:
10 10 default settings: option default settings related information system name dwl-2210ap “setting the dns name” in “setting the ethernet (wired) interface” user name admin the user name is read-only. It cannot be modified. Password admin “provide administrator password and wireless network name” in...
Page 11: Option
10 11 10 option default settings related information default settings (continued): connection type dynamic host configuration protocol ( dhcp ) if you do not have a dhcp server on the internal network and do not plan to use one, the first thing you must do after bringing up the access point is to chan...
Page 12: Option
12 12 default settings (continued): “broadcast ssid and security mode” in “configuring security” “controlling access by mac address filtering” “setting up guest access” what the access point does not provide the d-link dwl-2210ap is not designed to function as a gateway to the internet. To connect yo...
Page 13: Administrator’S Computer
12 13 12 administrator’s computer configuration and administration of the d-link dwl-2210ap is accomplished with the kickstart utility (which you run from the cd) and through a web-based user interface. The dwl-2210ap must be installed into a dhcp-enabled network in order to use the kickstart utility...
Page 14: Required Software
14 14 administrator’s computer (continued) required software or component description kickstart wizard on cd-rom cd-rom drive the administrator’s computer must have a cd-rom drive to run the kickstart wizard on the cd-rom. Security settings ensure that security is disabled on the wireless client use...
Page 15: Wireless Client Computers
14 15 14 wireless client computers the d-link dwl-2210ap provides wireless access to any client with a properly configured wi-fi client adapter for the 802.11b and 802.11g modes in which the access point is running. Multiple client operating systems are supported. Clients can be laptops or desktops, ...
Page 16: Required Software
16 16 client security settings security should be disabled on the client used to do initial configuration of the access point. If the security mode on the access point is set to anything other than plain text, wireless clients will need to set a profile to the authentication mode used by the access po...
Page 17: On The D-Link Dwl-2210Ap
16 17 16 understanding dynamic and static ip addressing on the d-link dwl-2210ap when installed in a dhcp network (dynamic ip addressing), the d-link dwl-2210aps are designed to auto-configure, with very little setup required for the first access point and no configuration required for additional acces...
Page 18: Dhcp Server
18 18 understanding dynamic and static ip addressing if you do not have a dhcp server on the internal network and do not plan to use one, the first thing you must do after bringing up the access point is change the connection type from dhcp to static ip. You can either assign a new static ip address ...
Page 19: Wireless Network
18 19 18 quick steps for the setup and launch of your wireless network setting up and deploying one or more d-link dwl-2210aps is in effect creating and launching a wireless network. The kickstart wizard (for dhcp-enabled networks) and corresponding basic settings administration web page simplify th...
Page 20: What’S Inside The Box?
20 20 step 2. Connect the access point to network and power • connect one end of an ethernet cable to the network port on the access point and the other end to the same hub where your pc is connected. The next step is to set up the network and power connections. 1. Do one of the following to create ...
Page 21
20 21 20 a note about setting up connections for a guest network the d-link dwl-2210ap offers an out-of-the-box guest interface that allows you to configure an access point for controlled guest access to the network. The same access point can function as a bridge for two different wireless networks: ...
Page 22: Points On A Dhcp Network
22 22 kickstart wizard is an easy-to-use utility for discovering and identifying new d-link dwl-2210aps in a network with a dchp server. Kickstart scans the network looking for access points, and displays id details on those it finds. • keep in mind that kickstart wizard recognizes and configures only...
Page 23
22 23 22 step 3. Run kickstart wizard (continued) 2. Wait for the search to complete, or until the kickstart wizard has found your new access points. If no access points are found, kickstart indicates this and presents some troubleshooting information about your lan and power connections. Once you h...
Page 24
24 24 step 3. Run kickstart wizard (continued) 4. Go to the access point administration web pages by taking the link provided on the kickstart page. Kickstart provides a link to the administration web pages via the ip address of the first access point of each model. (for more information about model ...
Page 25
24 25 24 viewing basic settings for access points when you first log in, the basic settings page for d-link dwl-2210ap administration is displayed. These are global settings for all access points that are members of the cluster and, if automatic configuration is specified, for any new access points tha...
Page 26
26 26 step 5. Configure “basic settings” provide a minimal set of configuration information by defining the basic settings for your wireless network. These settings are all available on the basic settings page of the administration web interface, and are categorized into steps 1-4 on the web page. For ...
Page 27: What’S Next?
26 27 26 what’s next? Next, make sure the access point is connected to the lan, bring up some wireless clients, and connect the clients to the network. Once you have tested the basics of your wireless network, you can enable more security and fine-tune by modifying advanced configuration features on t...
Page 28: Configuring Basic Settings
28 28 the basic configuration tasks are described in the following sections: • navigating to basic settings • review / describe the access point • provide administrator password and wireless network name • set configuration policy for new access points • update basic settings • summary of settings • b...
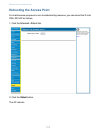
Page 29: Navigating to Basic Settings
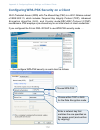
28 29 28 to configure initial settings, click basic settings . If you use kickstart wizard to link to the administration web pages, the basic settings page is displayed by default. Fill in the fields on the basic settings screen as described on the following page. Navigating to basic settings configuri...
Page 30: Field
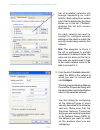
30 30 review / describe the access point field description ip address shows ip address assigned to this access point. This field is not editable because the ip address is already assigned (either via dhcp, or statically through the ethernet (wired) settings as described in “configuring guest interface...
Page 31: Field
30 31 30 field description administrator password enter a new administrator password. The characters you enter will be displayed as “ * ” characters to prevent others from seeing your password as you type. The administrator password must be an alphanumeric strings of up to 32 characters. Do not use ...
Page 32: Field
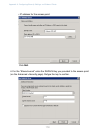
32 32 if you choose “are configured automatically”, then when a new access point is added to the network it automatically joins the existing cluster. The cluster configuration is copied to the new access point, and no manual configuration is required to deploy it. If you choose “are ignored”, new acces...
Page 33: Summary of Settings
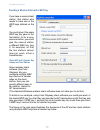
32 33 32 when you have reviewed the new configuration, click update to apply the settings and deploy the access points as a wireless network. Summary of settings when you update the basic settings, a summary of the new settings is shown along with information about next steps. At initial startup, no ...
Page 34: Icons
34 34 basic settings for a standalone access point the basic settings tab for a standalone access point indicates only that the current mode is standalone and provides a button for adding the access point to a cluster (group). If you click on any of the cluster tabs on the administration pages for a...
Page 35
34 35 34 the d-link dwl-2210ap is not designed for multiple, simultaneous configuration changes. If you have a network that includes multiple access points, and more than one administrator is logged on to the administration web pages and making changes to the configuration, all access points in the cl...
Page 36: Understanding Clustering
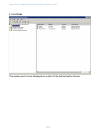
36 36 navigating to access points management to view or edit information on access points in a cluster, click the cluster > access points tab. Understanding clustering a key feature of the d-link dwl-2210ap is the ability to form a dynamic, configuration-aware group (called a cluster) with other d-li...
Page 37: Which Are Not?
36 37 36 which settings are shared as part of the cluster configuration and which are not? Most configuration settings defined via the d-link dwl-2210ap administration web • of the same radio and band configuration (all one-radio, single-band aps; the d-link dwl-2210ap is a one-radio, single-band ap) • ...
Page 38: Cluster Mode
38 38 • location descriptions • wds bridges • ethernet (wired) settings, including enabling or disabling guest access • guest interface configuration settings that are not shared must be configured individually on the administration pages for each access point. To get to the administration pages for a...
Page 39: Cluster Size and Membership
38 39 38 if a cluster configuration policy is in place, when a new access point is deployed, it attempts to rendezvous with an existing cluster. If it is unable to locate a cluster, then it establishes a new cluster on its own. If it locates a cluster but is rejected because the cluster is full, or t...
Page 40: Field
40 40 location description of where the access point is physically located. Mac address media access control ( mac ) address of the access point. A mac address is a permanent, unique hardware address for any device that represents an interface to the network. The mac address is assigned by the manuf...
Page 41
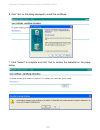
40 41 40 adding an access point to a cluster to add an access point that is currently in standalone mode back into a cluster, do the following. 1. Go to the administration web pages for the standalone access point. (see “navigating to an ap by using its ip address in a url” in this manual.) the admi...
Page 42: And Managing Standalone Aps
42 42 all clustered access points are shown on the cluster > access points page. To navigate to clustered access points, you can simply click on the ip address for a specific cluster member shown in the list. Navigating to an ap by using its ip address in a url you can also link to the administration...
Page 43: Managing User Accounts
42 43 42 the d-link dwl-2210ap includes user management capabilities for controlling client access to access points. User management and authentication must always be used in conjunction with the following two security modes, which require use of a radius server for user authentication and managemen...
Page 44: Points
44 44 navigating to user management for clustered access points to set up or modify user accounts, click the cluster > users tab. Viewing user accounts user accounts are shown at the top of the screen under “user accounts” user name, real name and status (enabled or disabled) are shown. You make mod...
Page 45: Fields
44 45 44 real name for information purposes, provide the user’s full name. There is a 256 character limit on real names. Password specify a password for this user. Passwords are alphanumeric strings of up to 256 characters. Do not use special characters or spaces. Field description fields descriptio...
Page 46: Enabling A User Account
46 46 this can come in handy in situations where users have an occasional need to access the network. For example, contractors who do work for your company on an intermittent but regular basis might need network access for 3 months at a time, then be off for 3 months, and back on for another assignm...
Page 47: Session Monitoring
46 47 46 session monitoring the d-link dwl-2210ap provides real-time session monitoring information including which clients are associated with a particular access point, data rates, transmit/receive statistics, signal strength, and idle time. The following session monitoring topics are covered here...
Page 48
48 48 field description understanding session monitoring information the sessions page shows information on client stations associated with access points in the cluster. Each client is identified by user name and user mac address, along with the ap (location) to which it is currently connected. To vi...
Page 49: Sorting Session Information
48 49 48 signal indicates the strength of the radio frequency (rf) signal the client receives from the access point. The measure used for this is an ieee 802.1x value known as received signal strength indication (rssi), and will be a value between 0 and 100. Rssi is determined by a an ieee 802.1x me...
Page 50
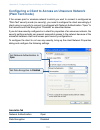
50 50 setting the ethernet (wired) interface the following sections describe how to configure “wired” address and related settings on the d-link dwl-2210ap: • navigating to ethernet • setting the dns name • configuring an internal lan and a guest network • using vlans for the guest network • configurin...
Page 51: Navigating to Ethernet
50 51 50 setting the ethernet (wired) interface navigating to ethernet to set the wired address for an access point, navigate to the advanced > ethernet tab, and update the fields as described in the following pages..
Page 52: Setting The Dns Name
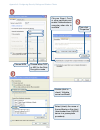
52 52 setting the dns name field description dns name enter the dns name for the access point in the text box. This is the host name. It may be provided by your isp or network administrator, or you can provide your own. The rules for system names are: • this name can be up to 20 characters long. • o...
Page 53
52 53 52 using vlans for the guest network if you enable guest access, two virtual lans ( vlan s) will be used: one for the internal network and one for the guest network. To use vlans, the lan port on the access point must be connected to a tagged port on a vlan capable switch and then you must defi...
Page 54
54 54 configuring internal interface ethernet settings to configure ethernet (wired) settings for the internal lan, fill in the fields as described below. Field description mac address shows the mac address for the internal interface for the ethernet port on this access point. This is a read-only field t...
Page 55: Updating Settings
54 55 54 configuring guest interface ethernet settings to configure ethernet settings for the “guest” interface, fill in the fields as described below. Field description mac address vlan id field description subnet mask enter the subnet mask in the text boxes. You must obtain this information from your ...
Page 56
56 56 setting the wireless interface wireless settings describe aspects of the local area network ( lan ) related specifically to the radio device in the access point ( 802.11 mode and channel ) and to the network interface to the access point ( mac address for access point and wireless network name,...
Page 57
56 57 56 setting the wireless interface navigating to wireless settings to set the wireless address for an access point, navigate to the advanced > wireless tab, and update the fields as described below. The following figure shows the wireless settings page for a two-radio ap. The administration web p...
Page 58
58 58 mac addresses (shown on two-radio ap only) mode the mode defines the physical layer ( phy ) standard being used by the radio. Select one of these modes: • ieee 802.11b • ieee 802.11g channel select the channel . The range of channels and the default is determined by the mode of the radio interf...
Page 59
58 59 58 configuring “internal” lan wireless settings the internal settings describe the mac address (read-only) and network name (also known as the ssid ) for the internal wireless lan (wlan) as described below. Field description field description mac address shows the mac address(es) for internal i...
Page 60: Updating Settings
60 60 configuring “guest” network wireless settings the guest settings describe the mac address (read-only) and wireless network name ( ssid ) for the guest network as described below. Configuring an access point with two different network names (ssids) allows you to leverage the guest interface featu...
Page 61
60 61 60 the network time protocol ( ntp ) is an internet standard protocol that synchronizes computer clock times on your network. Ntp servers transmit coordinated universal time (utc, also known as greenwich mean time) to their client systems. Ntp sends periodic time requests to servers, using the...
Page 62
62 62 enabling the network time protocol server navigating to time protocol settings to enable an ntp server, navigate to the advanced > time protocol tab, and update the fields as described below..
Page 63: Updating Settings
62 63 62 to configure your access point to use a network time protocol ( ntp ) server, first enable the use of ntp, and then select the ntp server you want to use. (to shut down ntp service on the network, disable ntp on the access point.) field description updating settings to apply your changes, cli...
Page 64: Configuring Security
64 64 configuring security the following sections describe how to configure security settings on the d-link dwl-2210ap: • understanding security issues on wireless networks • how do i know which security mode to use? • comparison of security modes for key management, authentication and encryption algo...
Page 65: And Encryption Algorithms
64 65 64 how do i know which security mode to use? In general, we recommend that on your internal network you use the most robust security mode that is feasible in your environment. When configuring security on the access point, you first must choose the security mode, then in some modes an authentica...
Page 66
66 66 following is a list of the security modes available on the d-link dwl-2210ap along with a description of the key management, authentication, and encryption algorithms used in each mode. We include some suggestions as to when one mode might be more appropriate than another. • when to use plain ...
Page 67
66 67 66 if you set the authentication algorithm to shared key, this protocol provides a rudimentary form of user authentication. However, if the authentication algorithm is set to “open system”, no authentication is performed. If the algorithm is set to “both”, only wep clients are authenticated. S...
Page 68
68 68 ieee 802.1x mode supports a variety of authentication methods, like cer tificates, kerberos, and public key authentication with a radius server. You have a choice of using the d-link dwl-2210ap embedded radius server or an external radius server. The embedded radius server supports protected e...
Page 69
68 69 68 keentication remote authentication dial-in user service ( radius ). You have a choice of using the d-link dwl-2210ap embedded radius server or an external radius server. The embedded radius server supports protected eap (peap) and mschap v2. Key management encryption algorithm user authenti...
Page 70
70 70 see also for information on how to configure wpa with radius security mode, see “wpa with radius” under “configuring security settings” in this manual. When to use wpa-psk wi-fi protected access ( wpa ) with pre-shared key ( psk ) is a wi-fi alliance subset of ieee 802.11i , which includes tempo...
Page 71
70 71 70 recommendations wpa w/psk not recommended for use with the d-link dwl-2210ap when wpa with radius is an option. We recommend that you use wpa with radius mode instead, unless you have interoperability issues that prevent you from using this mode. For example, some devices on your network ma...
Page 72
72 72 navigating to security settings to set the security mode, navigate to the advanced > security tab, and update the fields as described below. Configuring security settings the following configuration information explains how to configure security modes on the access point. Keep in mind that each wi...
Page 73: Plaintext
72 73 72 broadcast ssid select the broadcast ssid setting by clicking the “allow” or “prohibit” radio button. By default, the access point broadcasts (allows) the service set identifier (ssid) in its beacon frames. You can suppress (prohibit) this broadcast to discourage stations from automatically d...
Page 74: Static Wep
74 74 static wep wired equivalent privacy ( wep ) is a data encryption protocol for 802.11 wireless networks. All wireless stations and access points on the network are configured with a static 64-bit (40-bit secret key + 24-bit initialization vector (iv)) or 128-bit (104-bit secret key + 24-bit iv) ...
Page 75
74 75 74 field description transfer key index select a key index from the drop-down menu. Key indexes 1 through 4 are available. The default is 1. The transfer key index indicates which wep key the access point will use to encrypt the data it transmits. Key length specify the length of the key by cl...
Page 76
76 76 authentication algorithm the authentication algorithm defines the method used to determine whether a client station is allowed to associate with an access point when static wep is the security mode. Specify the authentication algorithm you want to use by choosing one of the following from the d...
Page 77
76 77 76 rules to remember for static wep all client stations must have the wireless lan (wlan) security set to wep and all clients must have one of the wep keys specified on the ap in order to decode ap-to-station data transmissions. The ap must have all keys used by clients for station-to-ap transm...
Page 78
78 78 providing a wireless client with a wep key if you have a second client station, that station also needs to have one of the wep keys defined on the ap. You could give it the same wep key you gave to the first station. Or for a more secure solution, you could give the second station a different we...
Page 79: Ieee 802.1X
78 79 78 example of using multiple wep keys and transfer key index on client stations ieee 802.1x ieee 802.1x is the standard defining port-based authentication and infrastructure for doing key management. Extensible authentication protocol ( eap ) messages sent over an ieee 802.11 wireless network u...
Page 80
80 80 if you selected “ieee 802.1x” security mode, provide the following: field description configuring security click “enable radius accounting” if you want to track and measure the resources a particular user has consumed such system time, amount of data transmitted and received, and so on. Radius ...
Page 81: Wpa With Radius
80 81 80 wpa with radius wi-fi protected access ( wpa ) with remote authentication dial-in user service ( radius ) is a wi-fi alliance subset of ieee 802.11i , which includes temporal key integrity protocol ( tkip ), counter mode/ cbc-mac protocol ( ccmp ), and advanced encryption standard ( aes ) m...
Page 82
82 82 select the cipher you want to use from the drop-down menu: • tkip • ccmp ( aes ) • both temporal key integrity protocol ( tkip ) is the default. Tkip provides a more secure encryption solution than wep keys. The tkip process more frequently changes the encryption key used and better ensures th...
Page 83
82 83 82 authentication server select one of the following from the drop-down menu: • built-in - to use the authentication server provided with the d- link dwl-2210ap. If you choose this option, you do not have to provide the radius ip and radius key; they are automatically provided. • external - to...
Page 84: Wpa-Psk
84 84 wpa-psk wi-fi protected access ( wpa ) with pre-shared key ( psk ) is a wi-fi alliance subset of ieee 802.11i , which includes temporal key integrity protocol ( tkip ), advanced encryption algorithm ( aes ), and counter mode/cbc-mac protocol ( ccmp ) mechanisms. Psk employs a pre-shared key. T...
Page 85: Configuring Radio Settings
84 85 84 configuring radio settings the following sections describe how to configure radio settings on the d-link dwl- 2210ap: • understanding radio settings • configuring radio settings • updating settings understanding radio settings radio settings directly control the behavior of the radio device in...
Page 86: Navigating to Radio Settings
86 86 navigating to radio settings to specify radio settings, navigate to advanced > radio tab, and update the fields as described below. Configuring radio settings.
Page 87: Configuring Radio Settings
86 87 86 field description status (on/off) specify whether you want the radio on or off by clicking on or off. Mode the mode defines the physical layer ( phy ) standard being used by the radio. Select one of these modes: • ieee 802.11b • ieee 802.11g channel the channel defines the portion of the radi...
Page 88
88 88 fragmentation threshold specify a number between 256 and 2,346 to set the frame size threshold in bytes. The fragmentation threshold is a way of limiting the size of packets (frames) transmitted over the network. If a packet exceeds the fragmentation threshold set here, the fragmentation funct...
Page 89: Updating Settings
88 89 88 transmit power provide a percentage value to set the transmit power for this access point. The default is to have the access point transmit using 100 percent of its power. Recommendations: •for most cases, we recommend keeping the default and having the transmit power set to 100 percent. Th...
Page 90
90 90 controlling access by mac address filtering a media access control ( mac ) address is a hardware address that uniquely identifies each node of a network. All ieee 802 network devices share a common 48-bit mac address format, usually displayed as a string of 12 hexadecimal digits separated by co...
Page 91
90 91 90 controlling access by mac address filtering navigating to mac filtering settings to enable filtering by mac address, navigate to the advanced > mac filtering tab, and update the fields as described below..
Page 92: Using Mac Filtering
92 92 using mac filtering field description filter to set the mac address filter , click one of the following radio buttons: • allow only stations in the list • allow any station unless in list stations list to add a mac address to stations list, enter its 48-bit mac address into the lower text boxe...
Page 93: Load Balancing
92 93 92 load balancing • understanding load balancing • identifying the imbalance: overworked or under-utilized access points • specifying limits for utilization and client associations • load balancing and qos • navigating to load balancing settings • configuring load balancing • updating settings ...
Page 94: Load Balancing and Qos
94 94 specifying limits for utilization and client associations you can correct for imbalances in network ap utilization by enabling load balancing and setting limits on utilization rates and number of client associations allowed per access point. Load balancing and qos load balancing also plays a p...
Page 95: Configuring Load Balancing
94 95 94 load balancing to enable load balancing on this access point, click enable. To disable load balancing on this access point, click disable. Utilization for no new associations utilization rate limits relate to wireless bandwidth utilization. Provide a bandwidth utilization rate percentage li...
Page 96: Updating Settings
96 96 specify the number of client stations you want as a “stations threshold” for disassociation. If the number of client stations associated with the ap at any one time is equal to or less than the number you specify here, no stations will be disassociated regardless of the “utilization for disass...
Page 97: Understanding Qos
96 97 96 the following sections describe how to configure quality of service queues on the d-link dwl-2210ap: • understanding qos • qos and load balancing • 802.11e and wme standards support • qos queues and parameters to coordinate traffic flow • navigating to qos settings • configuring qos queues • u...
Page 98
98 98 as with all ieee 802.11 working group standards, the goal is to provide a standard way of implementing qos features so that components from different companies are interoperable. The d-link dwl-2210ap provides qos based on the wireless multimedia enhancement ( wme ) specification, which is an i...
Page 99
98 99 98 packets in a higher priority queue will be transmitted before packets in a lower priority queue. Interactive data in the queue labeled “data 2” is always sent first, best effort data in “data 1” is sent next, and bulk data in “data 0” is sent last. Each lower priority queue (class of traffic)...
Page 100
100 100 each frame includes a source and destination mac address, a control field with protocol version, frame type, frame sequence number, frame body (with the actual information to be transmitted) and frame check sequence for error detection. The 802.11 standard defines various frame types for manag...
Page 101
100 101 100 the random backoff used by the access point is a configurable parameter. To describe the random delay, a “minimum contention window” (mincw) and a “maximum contention window” (maxcw) is defined. Packet bursting for better performance the d-link dwl-2210ap includes 802.11e based packet burs...
Page 102: Navigating to Qos Settings
102 102 navigating to qos settings configuring qos queues configuring quality of service ( qos ) on the d-link dwl-2210ap consists of setting parameters on existing queues for different types of wireless traffic, and effectively specifying minimum and maximum wait times (via contention windows) for tra...
Page 103
102 103 102 queue queues are defined for different types of data transmitted from ap-to-station: data 0 (bulk) lowest priority queue, high throughput. Bulk data that requires maximum throughput and is not time-sensitive is sent to this queue (ftp data, for example). For information purposes, the hexa...
Page 104: Updating Settings
104 104 min. Contention window this parameter is input to the algorithm that determines the initial random backoff wait time (“window”) for retry of a transmission. The value specified here in the minimum contention window is the upper limit (in milliseconds) of a range from which the initial random ...
Page 105: System (Wds)
104 105 104 configuring the wireless distribution system (wds) the d-link dwl-2210ap lets you connect multiple access points using a wireless distribution system ( wds ). Wds allows access points to communicate with one another wirelessly in a standardized way. This capability is critical in providin...
Page 106
106 106 configuring the wireless distribution system (wds) you can bridge the conference room and west wing access points with a wds link to create a single network for clients in both areas. Using wds to extend the network beyond the wired coverage area an ess can extend the reach of the network int...
Page 107
106 107 106 backup links and unwanted loops in wds bridges another use for wds bridging, the creation of backup links, is not supported in this release of the d-link dwl-2210ap. The topic is included here to emphasize that you should not try to use wds in this way; backup links will result in unwant...
Page 108: Navigating To Wds Settings
108 108 navigating to wds settings to specify the details of traffic exchange from this access point to others, navigate to the advanced > wds tab, and update the fields as described below. The following figure shows the wds settings page for the two-radio ap. The administration web page for the one-ra...
Page 109: Configuring Wds Settings
108 109 108 configuring wds settings the following notes summarize some critical guidelines regarding wds configuration. Please read all the notes before proceeding with wds configuration. To configure wds on this access point, describe each ap intended to receive handoffs and send information to this a...
Page 110
110 110 local address indicates the media access control ( mac ) addresses for this access point. A mac address is a permanent, unique hardware address for any device that represents an interface to the network. The mac address is assigned by the manufacturer. You cannot change the mac address. It i...
Page 111
110 111 110 field description key type if wep is enabled, specify the wep key type: • ascii • hex characters required indicates the number of characters required in the wep key. The number of characters required updates automatically based on how you set key length and key type. Wep key enter a stri...
Page 112: Updating Settings
112 112 configuring the wireless distribution system (wds) • navigate to the wds tab on myap2 administration web pages. (myap2’s mac address will show as the “local address”.) • configure a wds interface for data exchange with myap1, starting with the mac address for myap1. • navigate to the radio set...
Page 113: Setting Up Guest Access
112 113 112 setting up guest access out-of-the-box guest interface features allow you to configure the d-link dwl-2210ap for controlled guest access to an isolated network. You can configure the same access point to broadcast and function as two different wireless networks: a secure “internal” lan and...
Page 114
114 114 setting up guest access 2. Set up the guest welcome screen for the guest captive portal as described in the section below, “configuring the welcome screen (captive portal)” in this manual. Configuring internal and guest vlans to configure internal and guest networks on virtual lans, do the foll...
Page 115
114 115 114 setting up guest access configuring the welcome screen (captive portal) you can set up or modify the welcome screen guest clients see when they open a web browser or try to browse the web. To set up the captive portal, do the following. 1. Navigate to the advanced > guest login tab. 2. Ch...
Page 116: Deployment Example
116 116 setting up guest access deployment example in the figure below, the dotted red lines indicate dedicated guest connections. All access points and all connections (including guests) are administered from the same d-link dwl-2210ap administration web pages..
Page 117: Maintenance and Monitoring
116 117 116 maintenance and monitoring the maintenance and monitoring tasks described here all pertain to viewing and modifying settings on specific access points; not on a cluster configuration that is automatically shared by multiple access points. Therefore, it is important to ensure that you are a...
Page 118: Interfaces
118 118 maintenance and monitoring interfaces to monitor wired lan and wireless lan ( wlan ) settings, navigate to status > interfaces on the access point you want to monitor. This page displays the current settings of the d-link dwl-2210ap. It displays the ethernet (wired) settings and the wireless...
Page 119: Wireless Settings
118 119 118 maintenance and monitoring wireless settings event log to view transmit/receive statistics for a particular access point, navigate to status > events on the administration web pages for the access point you want to monitor. This page lists the most recent events generated by this access ...
Page 120: Statistics
120 120 maintenance and monitoring statistics to view transmit/receive statistics for a particular access point, navigate to status > statistics on the administration web pages for the access point you want to monitor. The following figure shows the transmit / receive page for a two-radio ap. The adm...
Page 121
120 121 120 maintenance and monitoring this page provides some basic information about the current access point and a real-time display of the transmit and receive statistics for this access point as described in the following table. All transmit and receive statistics shown are totals since the acc...
Page 122: Associated Wireless Clients
122 122 maintenance and monitoring associated wireless clients to view the client stations associated with a particular access point, navigate to status > associations on the administration web pages for the access point you want to monitor. The associated stations are displayed along with informati...
Page 123: Rebooting The Access Point
122 123 122 maintenance and monitoring rebooting the access point for maintenance purposes or as a troubleshooting measure, you can reboot the d-link dwl-2210ap as follows. 1. Click the advanced > reboot tab. 2. Click the reboot button. The ap reboots..
Page 124: Resetting The Configuration
124 124 maintenance and monitoring resetting the configuration if you are experiencing extreme problems with the d-link dwl-2210ap and have tried all other troubleshooting measures, use the reset configuration function. This will restore factory defaults and clear all settings, including settings such...
Page 125: Upgrading The Firmware
124 125 124 maintenance and monitoring upgrading the firmware as new versions of the d-link dwl-2210ap firmware become available, you can upgrade the firmware on your devices to take advantages of new features and enhancements. To upgrade the firmware on a particular access point: 1. Navigate to advanc...
Page 126: Update
126 126 maintenance and monitoring verifying the firmware upgrade to verify that the firmware upgrade completed successfully, check the firmware version shown on the advanced > upgrade tab (and also on the basic settings tab). If the upgrade was successful, the updated version name or number will be i...
Page 127: Neighbors
126 127 126 neighbors the status page for “neighboring access points” provides real-time statistics for all access points within range of the access point on which you are viewing the administration web pages. To view information about other access points on the wireless network, navigate to status ...
Page 128
128 128 maintenance and monitoring mac address shows the mac address of the neighboring access point. A mac address is a hardware address that uniquely identifies each node of a network. Beacon interval shows the beacon interval being used by this access point. Beacon frames are transmitted by an acc...
Page 129
128 129 128 maintenance and monitoring field description band this indicates the ieee 802.11 mode being used on this access point. (for example, ieee 802.11b and ieee 802.11g .) the number shown indicates the mode according to the following map: • 2.4 indicates ieee 802.11b mode or ieee 802.11g mode...
Page 130: On Wireless Clients
130 130 appendix a. Configuring security settings on wireless clients typically, users will configure security on their wireless clients for access to many different networks (access points). The list of “available networks” will change depending on the location of the client and which aps are online ...
Page 131: Authentication Server
130 131 130 • configuring an external radius server to recognize the d-link dwl-2210ap • obtaining a tls-eap certificate for a client network infrastructure and choosing between built-in or external authentication server network security configurations including public key infrastructures (pki), remote...
Page 132: Security Settings
132 132 make sure the wireless client software is up-to-date before starting out, please keep in mind that service packs, patches, and new releases of drivers and other supporting technologies for wireless clients are being generated at a fast pace. A common problem encountered in client security se...
Page 133
132 133 132 list of available networks will change depending on client location. Each network (or access point) that is detected by the client shows up in this list. (“refresh” updates the list with current information.) for each network you want to connect to, configure security settings on the cli...
Page 134: (Plain Text Mode)
134 134 appendix a: configuring security settings on wireless clients configuring a client to access an unsecure network (plain text mode) if the access point or wireless network to which you want to connect is configured as “plain text” security mode (no security), you need to configure the client acco...
Page 135
134 135 134 appendix a: configuring security settings on wireless clients configuring static wep security on a client static wired equivalent privacy (wep) encrypts data moving across a wireless network based on a static (non-changing) key. The encryption algorithm is a “stream” cipher called rc4. The...
Page 136
136 136 appendix a: configuring security settings on wireless clients disable this option (click to uncheck the box). Disable auto key option . . . Then configure wep security on each client as follows. Choose wep as the data encryption mode enter a network key that matches the wep key on the access p...
Page 137
136 137 136 appendix a: configuring security settings on wireless clients click ok on the wireless network properties dialog to close it and save your changes. Connecting to the wireless network with a static wep client static wep clients should now be able to associate and authenticate with the acce...
Page 138
138 138 appendix a: configuring security settings on wireless clients configuring ieee 802.1x security on a client ieee 802.1x is the standard defining port-based authentication and infrastructure for doing key management. Extensible authentication protocol (eap) messages sent over an ieee 802.11 wirel...
Page 139
138 139 138 appendix a: configuring security settings on wireless clients choose wep data encryption mode enable auto key option choose protected eap (peap) disable (click to uncheck) “validate server certificate” choose “secured password (eap- mschap v2)” . . . Then click “configure” choose open . . ....
Page 140
140 140 1. Configure the following settings on the association tab on the network properties dialog. Appendix a: configuring security settings on wireless clients 4. Click configure to bring up the eap mschap v2 properties dialog. On this dialog, disable (click to uncheck) the option to “automatically ...
Page 141
140 141 140 appendix a: configuring security settings on wireless clients ieee 802.1x client using eap/tls certificate extensible authentication protocol (eap) transport layer security (tls), or eap-tls, is an authentication protocol that supports the use of smart cards and certificates. You have the o...
Page 142
142 142 appendix a: configuring security settings on wireless clients if you configured the d-link dwl-2210ap to use ieee 802.1x security mode with an external radius server . . . . . . Then configure ieee 802.1x security with certificate authentication on each client as follows. Choose wep data encrypt...
Page 143
142 143 142 appendix a: configuring security settings on wireless clients 1. Configure the following settings on the association tab on the network properties dialog. Enable (click to check) this option. Choose smart card or other certificate. Authentication tab enable ieee 802.1x authentication for th...
Page 144
144 144 appendix a: configuring security settings on wireless clients 3. Click properties to bring up the smart card or other certificate properties dialog and enable the “validate server certificate” option. Click ok on all dialogs to close and save your changes. 4. To complete the client configuration...
Page 145
144 145 144 appendix a: configuring security settings on wireless clients configuring wpa with radius security on a client wi-fi protected access (wpa) with remote authentication dial-in user service (radius) is a wi-fi alliance subset of ieee 802.11i, which includes temporal key integrity protocol (t...
Page 146
146 146 appendix a: configuring security settings on wireless clients if you configured the d-link dwl-2210ap to use wpa with radius security mode and to use either the built-in authentication server or an external radius server that uses eap/peap . . . First set up user accounts on the access point (...
Page 147
146 147 146 appendix a: configuring security settings on wireless clients choose either tkip or aes for the data encryption mode choose protected eap (peap) disable (click to uncheck) “validate server certificate” choose “secured password (eap- mschap v2)” . . . Then click “configure” choose wpa . . . ...
Page 148
148 148 appendix a: configuring security settings on wireless clients 2. Configure this setting on the authentication tab. 3. Click properties to bring up the protected eap properties dialog and configure the following settings. 4. Click configure to bring up the eap mschap v2 properties dialog. On this...
Page 149
148 149 148 wpa with radius client using eap-tls certificate extensible authentication protocol (eap) transport layer security (tls), or eap-tls, is an authentication protocol that supports the use of smart cards and certificates. You have the option of using eap-tls with both wpa with radius and ieee...
Page 150
150 150 appendix a: configuring security settings on wireless clients choose wpa choose either tkip or aes for the data encryption mode choose smart card or other certificate and enable “authenticate as computer when info is available” then click “properties” enable (click to check) “validate server c...
Page 151
150 151 150 appendix a: configuring security settings on wireless clients smart card or other certificate properties dialog validate server certificate enable this option (click to check the box). Certificates in the certificate list shown, select the certificate for this client. 1. Configure the following...
Page 152
152 152 appendix a: configuring security settings on wireless clients configuring wpa-psk security on a client wi-fi protected access (wpa) with pre-shared key (psk) is a wi-fi alliance subset of ieee 802.11i, which includes temporal key integrity protocol (tkip), advanced encryption algorithm ( aes )...
Page 153
152 153 152 association tab network authentication wpa-psk data encryption tkip or aes depending on how this option is configured on the access point. Note: when the cipher suite on the access point is set to “both”, then tkip clients with a valid tkip key and aes clients with a valid ccmp (aes) key ...
Page 154: The D-Link Dwl-2210Ap
154 154 configuring an external radius server to recognize the d-link dwl-2210ap an external remote authentication dial-in user server (radius) server running on the network can support of eap-tls smart card/certificate distribution to clients in a public key infrastructure (pki) as well as eap-peap u...
Page 155
154 155 154 appendix a: configuring security settings on wireless clients the radius server is identified by its ip address and udp port numbers for the different services it provides. On the current release of the d-link dwl-2210ap, the radius server user datagram protocol (udp) ports used by the acc...
Page 156
156 156 appendix a: configuring security settings on wireless clients 4. For the “shared secret” enter the radius key you provided to the access point (on the advanced >security page). Retype the key to confirm. • ip address for the access point. Click next..
Page 157
156 157 156 appendix a: configuring security settings on wireless clients 5. Click finish. The access point is now displayed as a client of the authentication server. • ip address for the access point..
Page 158
158 158 appendix a: configuring security settings on wireless clients obtaining a tls-eap certificate for a client i f you want to use ieee 802.1x mode with eap-tls certificates for authentication and authorization of clients, you must have an external radius server and a public key authority infrastru...
Page 159
158 159 158 appendix a: configuring security settings on wireless clients the welcome screen for the certificate server is displayed in the browser. 3. Click “request a certificate” to get the login prompt for the radius server. 4. Provide a valid user name and password to access the radius server. The...
Page 160
160 160 appendix a: configuring security settings on wireless clients 6. Click “yes” on the dialog displayed to install the certificate. 7. Click “submit” to complete and click “yes” to confirm the submittal on the popup dialog..
Page 161
160 161 160 appendix a: configuring security settings on wireless clients 8. Click “install this certificate” to install the newly issued certificate on your client station. (also, click “yes” on the popup windows to confirm the install and to add the certificate to the root store.).
Page 162: Appendix B. Troubleshooting
162 162 appendix b. Troubleshooting this section provides information about how to solve common problems you might encounter in the course of updating network configurations on networks served by multiple, clustered access points. Cluster recovery in cases where the access points in a cluster become ...
Page 163: Table 1:
162 163 162 appendix b: troubleshooting the stop clustering page for this access point is displayed. Click the stop clustering button. Repeat this “stop clustering” step for every access point in the cluster. Table 1: do not proceed to the next step of resetting any access points until you have stop...
Page 164: Table 2:
164 164 appendix b: troubleshooting on the administration ui left-hand tabs, click advanced > reset to bring up the reset page. Click reset to restore the factory defaults on the access point. (this will clear all of your previous settings, including updated passwords.) repeat this “reset” step for ...
Page 165
164 165 164 appendix b: troubleshooting at this point you should see all previous cluster members displayed in the list. Before proceeding to the last step, verify that the cluster has reformed by making sure all are access points are listed. 4. Review all configuration settings and make modifications...
Page 166: Glossary
166 166 glossary 802 ieee 802 ( ieee std. 802-2001 ) is a family of standards for peer-to-peer communication over a lan . These technologies use a shared-medium, with information broadcast for all stations to receive. The basic communications capabilities provided are packet-based. The basic unit of...
Page 167
166 167 166 glossary 802.11b ieee 802.11b ( ieee std. 802.11b-1999 ) is an enhancement of the initial 802.11 phy to include 5.5 mbps and 11 mbps data rates. It uses direct sequence spread spectrum (dsss) or frequency hopping spread spectrum (fhss) in the 2.4 ghz ism band as well as complementary cod...
Page 168
168 168 glossary when one access point is connected to a wired network and supports a set of wireless stations, it is referred to as a basic service set ( bss ). An extended service set ( ess ) is created by combining two or more bsss. Ad hoc mode ad hoc mode is a wireless networking framework in wh...
Page 169
168 169 168 glossary broadcast a broadcast sends the same message at the same time to everyone. In wireless networks, broadcast usually refers to an interaction in which the access point sends data traffic in the form of ieee 802.1x frame s to all client stations on the network. Some wireless securit...
Page 170
170 170 glossary csma/ca carrier sense multiple access with collision avoidance (csma/ca) is a low-level network arbitration/contention protocol. A station listens to the media and attempts to transmit a packet when the channel is quiet. When it detects that the channel is idle, the station transmit...
Page 171
170 171 170 glossary dom the document object model (dom) is an interface that allows programs and scripts to dynamically access and update the content, structure, and style of documents. The dom allows you to model the objects in an html or xml document (text, links, images, tables), defining the att...
Page 172
172 172 glossary legacy ieee 802.11b devices cannot detect the erp-ofdm signals used by ieee 802.11g stations, and this can result in collisions between data frames from ieee 802.11b and ieee 802.11g stations. If there is a mix of 802.11b and 802.11g nodes on the same channel, the ieee 802.11g stati...
Page 173
172 173 172 glossary ibss an independent basic service set (ibss) is an ad hoc mode wireless networking framework in which stations communicate directly with each other. Ieee the institute of electrical and electronic engineers (ieee) is an international standards body that develops and establishes ...
Page 174
174 174 glossary • the broadcast address consists of a host number that is all ones (for example, 192.168.2.255). There are a finite number of ip addresses that can exist. Therefore, a local area network typically uses one of the iana -designated address ranges for use in private networks. These addr...
Page 175
174 175 174 connects multiple computers and other network devices such as storage and printers. Ethernet is the most common technology implementing a lan. Wireless ethernet ( 802.11 ) is another very popular lan technology (also see wlan ). Ldap the lightweight directory access protocol (ldap) is a ...
Page 176
176 176 glossary multicast a multicast sends the same message to a select group of recipients. Sending an e-mail message to a mailing list is an example of multicasting. In wireless networks, multicast usually refers to an interaction in which the access point sends data traffic in the form of ieee 8...
Page 177
176 177 176 glossary • layer 3, the network layer, defines the how to determine the best path for information traversing the network. Packet s and logical ip address es operate on the network layer. • layer 4, the transport layer, defines connection oriented protocols such as tcp and udp . • layer 5, ...
Page 178
178 178 glossary ppp the point-to-point protocol is a standard for transmitting network layer datagrams ( ip packets) over serial point-to-point links. Ppp is designed to operate both over asynchronous connections and bit-oriented synchronous systems. Pppoe point-to-point protocol over ethernet (ppp...
Page 179
178 179 178 glossary router a router is a network device which forwards packets between networks. It is connected to at least two networks, commonly between two local area networks ( lan s) or between a lan and a wide-area network ( wan ), for example, the internet. Routers are located at gateways—p...
Page 180
180 180 glossary snmp consists of managed devices and their agents, and a management system. The agents store data about their devices in management information bases (mibs) and return this data to the snmp management system when requested. Ssid the service set identifier (ssid) is a thirty-two chara...
Page 181
180 181 180 tcp the transmission control protocol (tcp) is built on top of internet protocol ( ip ). It adds reliable communication (guarantees delivery of data), flow-control, multiplexing (more than one simultaneous connection), and connection-oriented transmission (requires the receiver of a packe...
Page 182
182 182 glossary url a uniform resource locator (url) is a standard for specifying the location of objects on the internet, such as a file or a newsgroup. Urls are used extensively in html documents to specify the target of a hyperlink which is often another html document (possibly stored on another ...
Page 183
182 183 182 glossary wins the windows internet naming service (wins) is a server process for resolving windows-based computer names to ip addresses. It provides information that allows these systems to browse remote networks using the network neighborhood. Wireless networking framework there are two...
Page 184: Technical Specifications
184 184 standards • ieee 802.11b • ieee 802.11g • ieee 802.3 • ieee 802.3af • ieee 802.3u • ieee 802.3x device management • web-based – internet explorer v6 or later; netscape navigator v6 or later; or other java-enabled browsers. • telnet • kickstart data rate* for 802.11g: • 108, 54, 48, 36, 24, 1...
Page 185
184 185 184 wireless operating range* 802.11g (full power with 5dbi gain diversity dipole antenna) indoors: • 98ft (30m) @ 54mbps • 108ft (33m) @ 48mbps • 121ft (37m) @ 36mbps • 151ft (46m) @ 24mbps • 203ft (62m) @ 18mbps • 223ft (68m) @ 12mbps • 256ft (78m) @ 9mbps • 302ft (92m) @ 6mbps outdoors: •...
Page 186
186 186 technical specifications (continued) transmit output power for 802.11b: • 63mw (18dbm) • 40mw (16dbm) • 32mw (15dbm) • 23mw (13dbm) • 10mw (10dbm) • 6mw (7dbm) • 1mw (0dbm) for 802.11g: • 63mw (18dbm) • 40mw (16dbm) • 32mw (15dbm) • 6mw (7dbm) • 1mw (0dbm) receiver sensitivity for 802.11b: • ...
Page 187
186 187 186 technical specifications (continued) leds • power • 10m/100m • wlan temperature • operating: 32ºf to 104ºf (0ºc to 40ºc) • storing: -4ºf to 149ºf (-20ºc to 65ºc) humidity • operating: 10%~90% (non-condensing) • storing: 5%~95% (non-condensing) certifications • fcc part 15 • ul dimensions •...
Page 188
188 188 you can find software updates and user documentation on the d-link website. D-link provides free technical support for customers within the united states and within canada for the duration of the warranty period on this product. U.S. And canadian customers can contact d-link technical support...
Page 189
188 189 188 subject to the terms and conditions set forth herein, d-link systems, inc. (“d-link”) provides this limited warranty for its product only to the person or entity that originally purchased the product from: • d-link or its authorized reseller or distributor and • products purchased and de...
Page 190
190 190 • the original product owner must obtain a return material authorization (“rma”) number from the authorized d-link service office and, if requested, provide written proof of purchase of the product (such as a copy of the dated purchase invoice for the product) before the warranty service is p...
Page 191
190 191 190 governing law: this limited warranty shall be governed by the laws of the state of california. Some states do not allow exclusion or limitation of incidental or consequential damages, or limitations on how long an implied warranty lasts, so the foregoing limitations and exclusions may no...
Page 192: Registration
192 192 (5/12/05) registration register your d-link product online at http://support.Dlink.Com/register/.
Page 193
192 193 192.